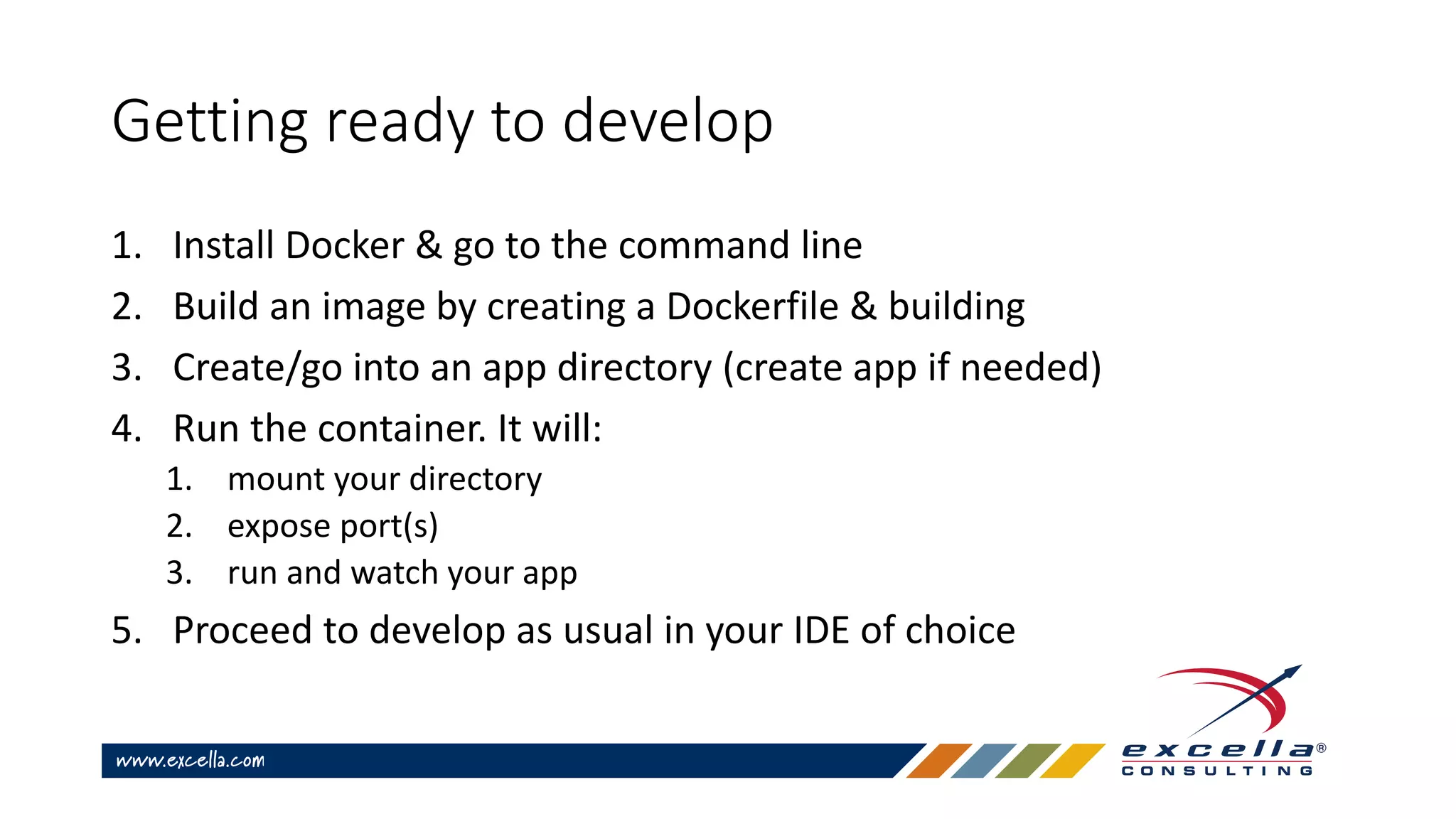
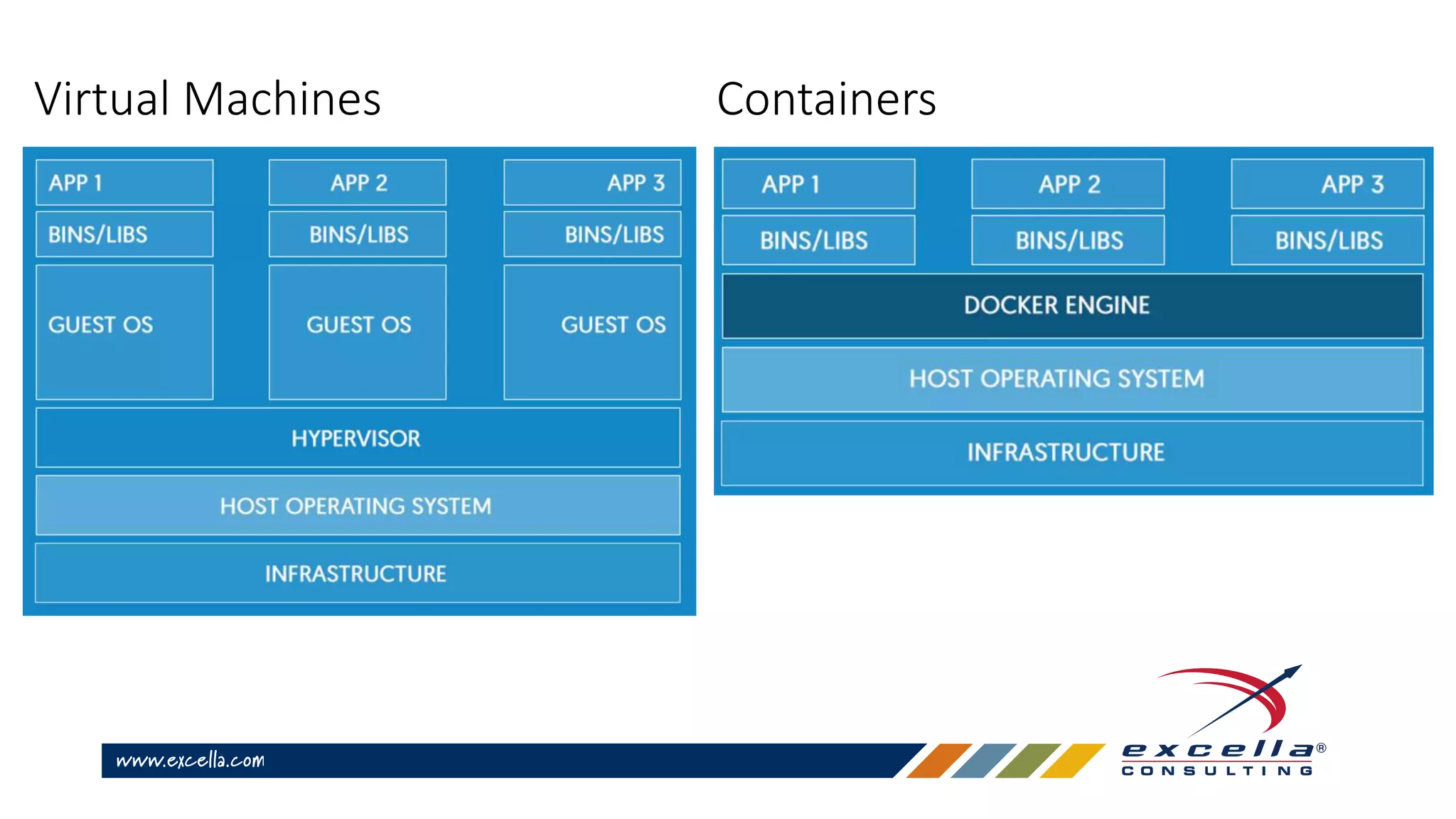
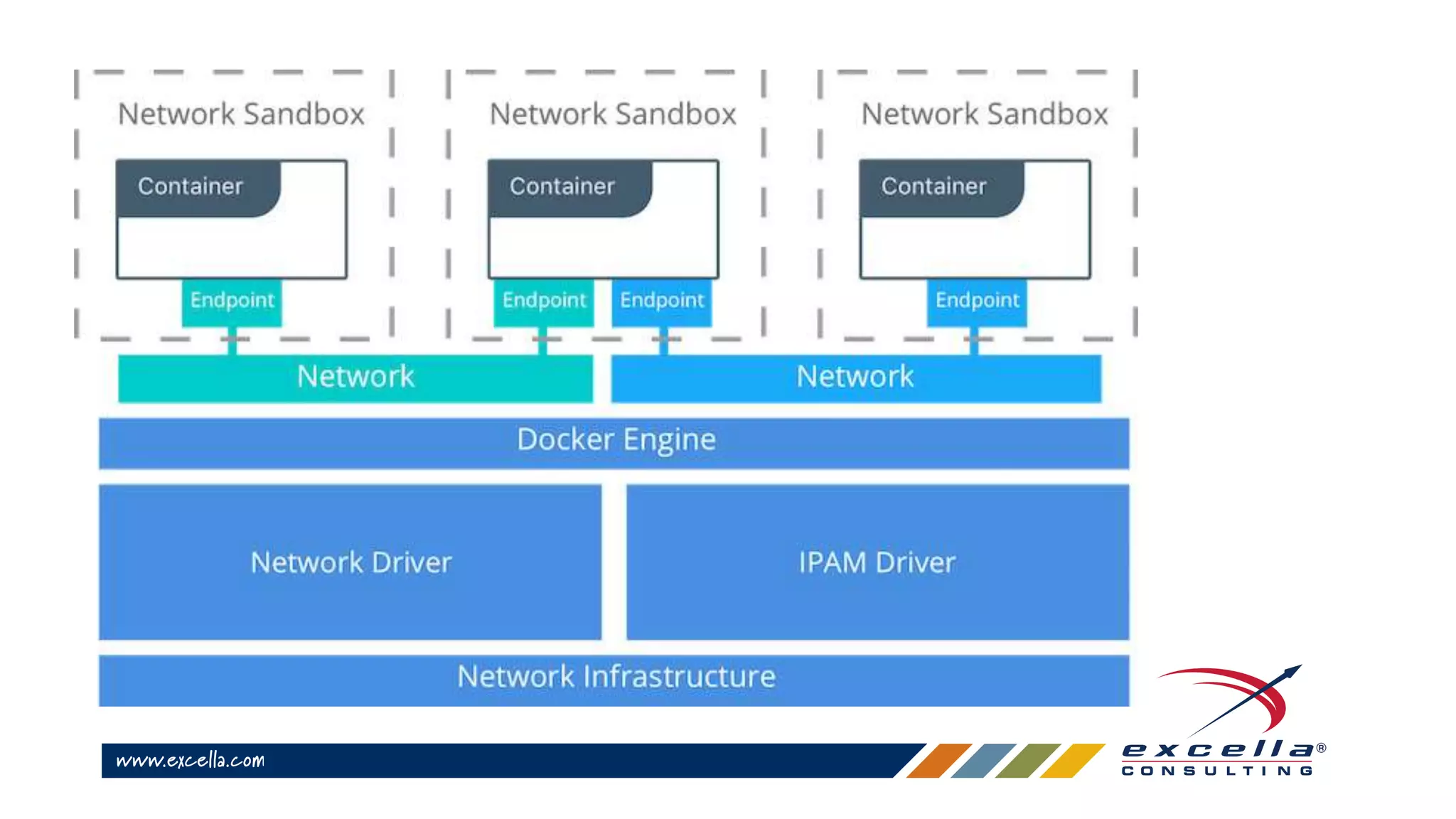
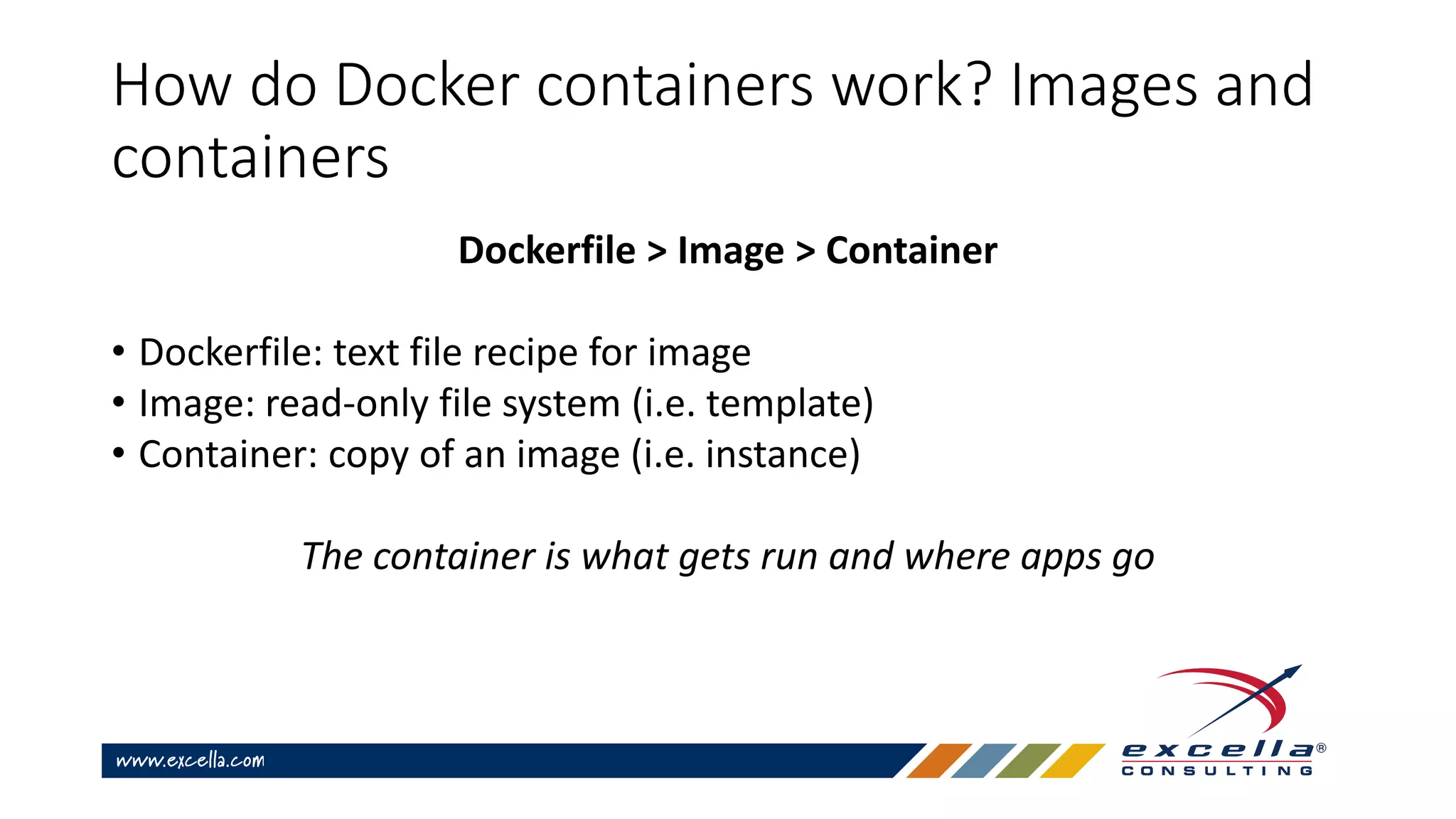
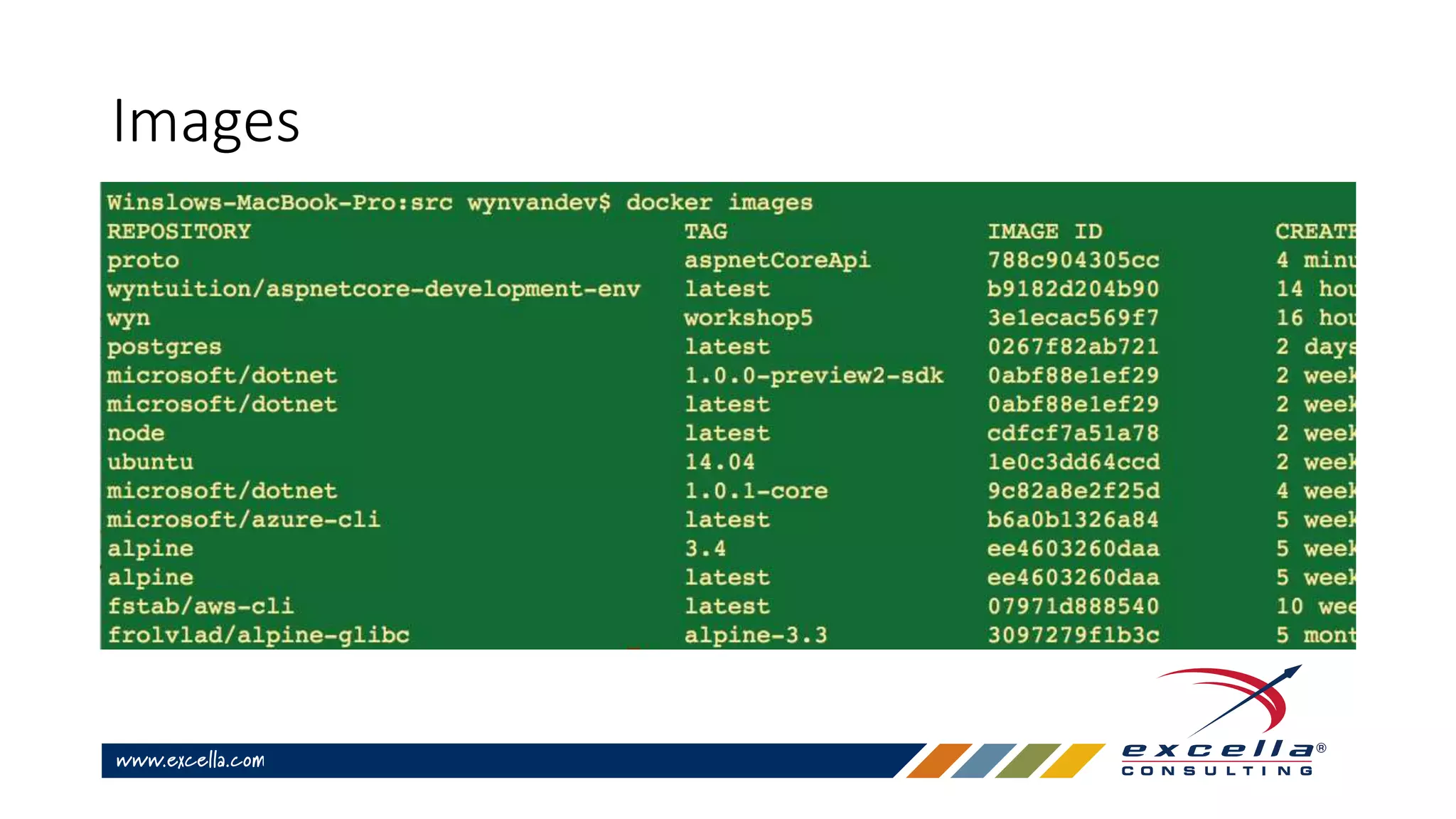
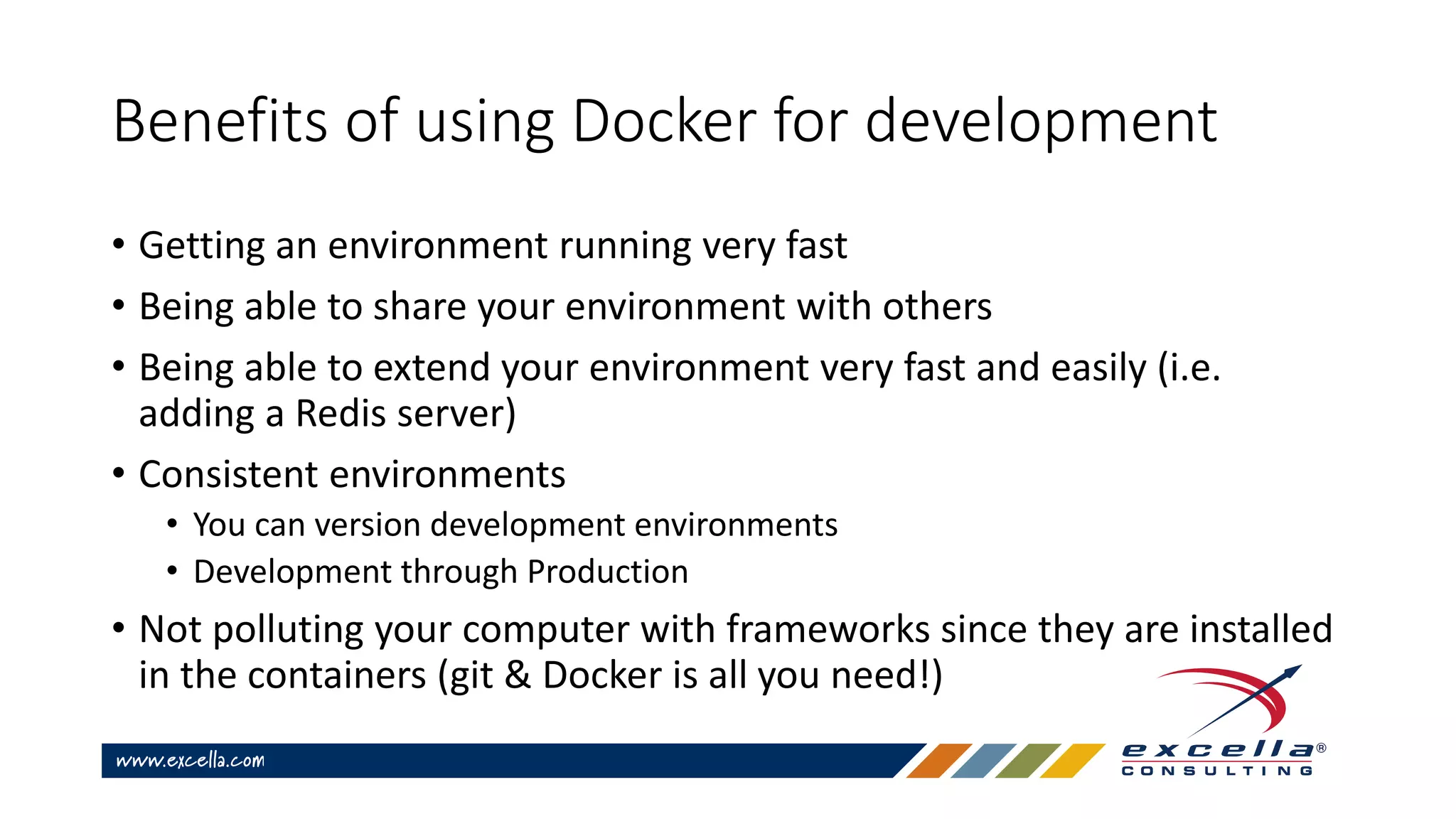
This document provides an overview of Docker containers and developer workflows using Docker. It defines containers and images, and explains how Docker abstracts machine-specific settings to allow containers to run on different machines. Popular Docker images are listed, and benefits of using Docker for development are outlined. Common Docker commands are also described.












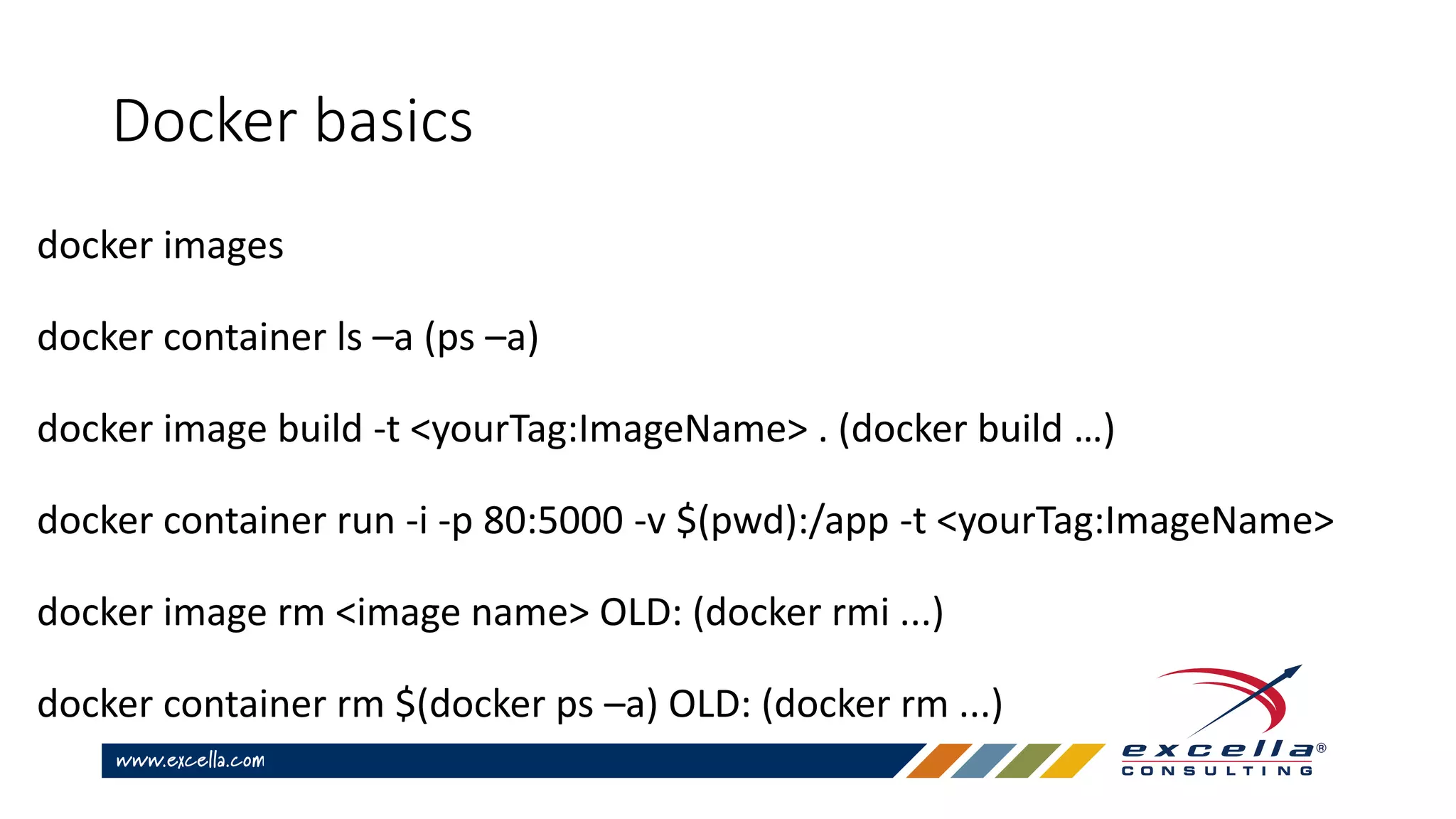



![Other common commands
docker logs <container_name> [--tail 10]
docker exec -it <container_name> sh
docker volume … (ls, inspect, etc)
docker network … (ls, inspect, etc)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developerworkflowwithdocker-180516125905/75/Developer-workflow-with-docker-30-2048.jpg)