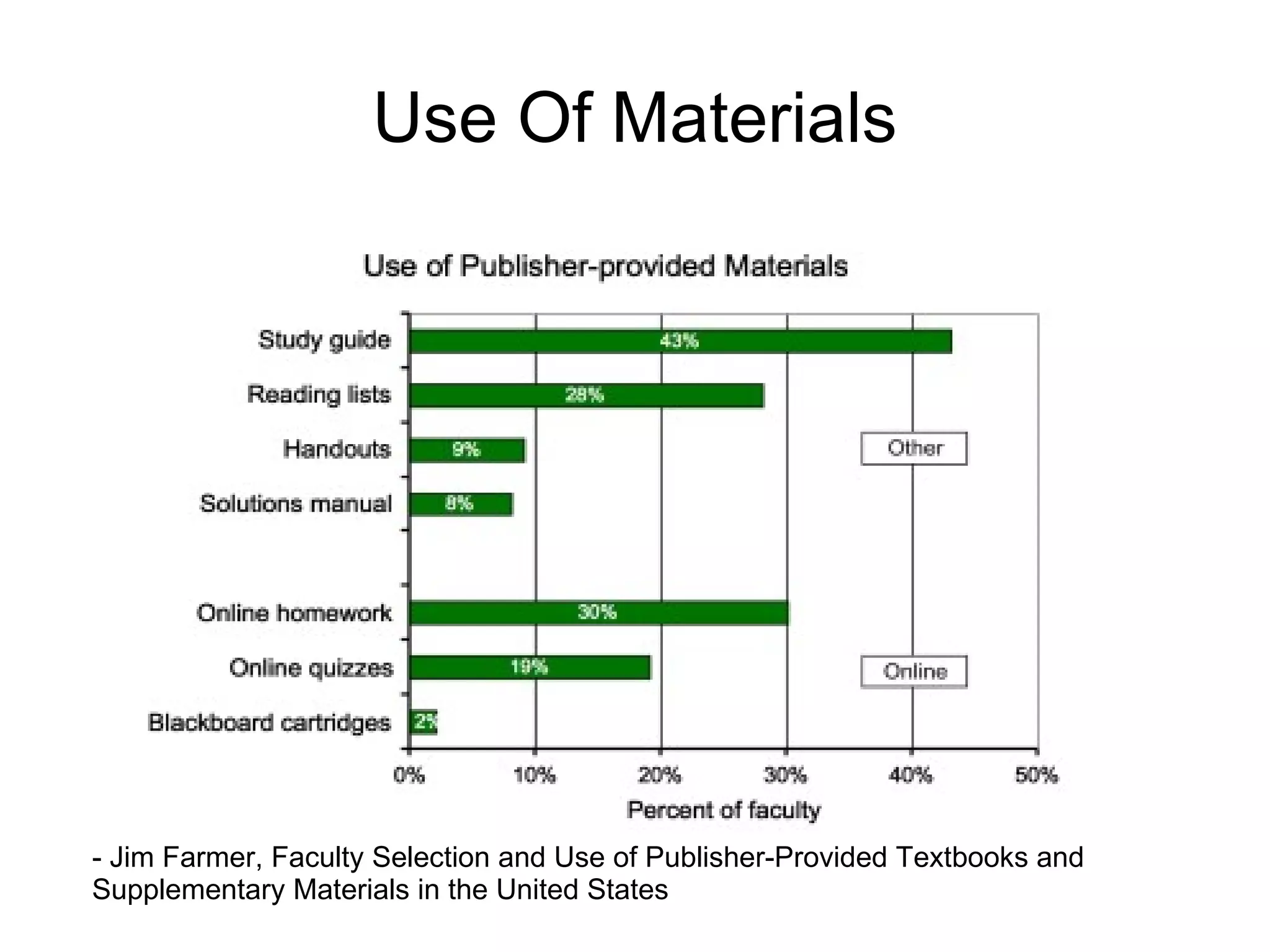
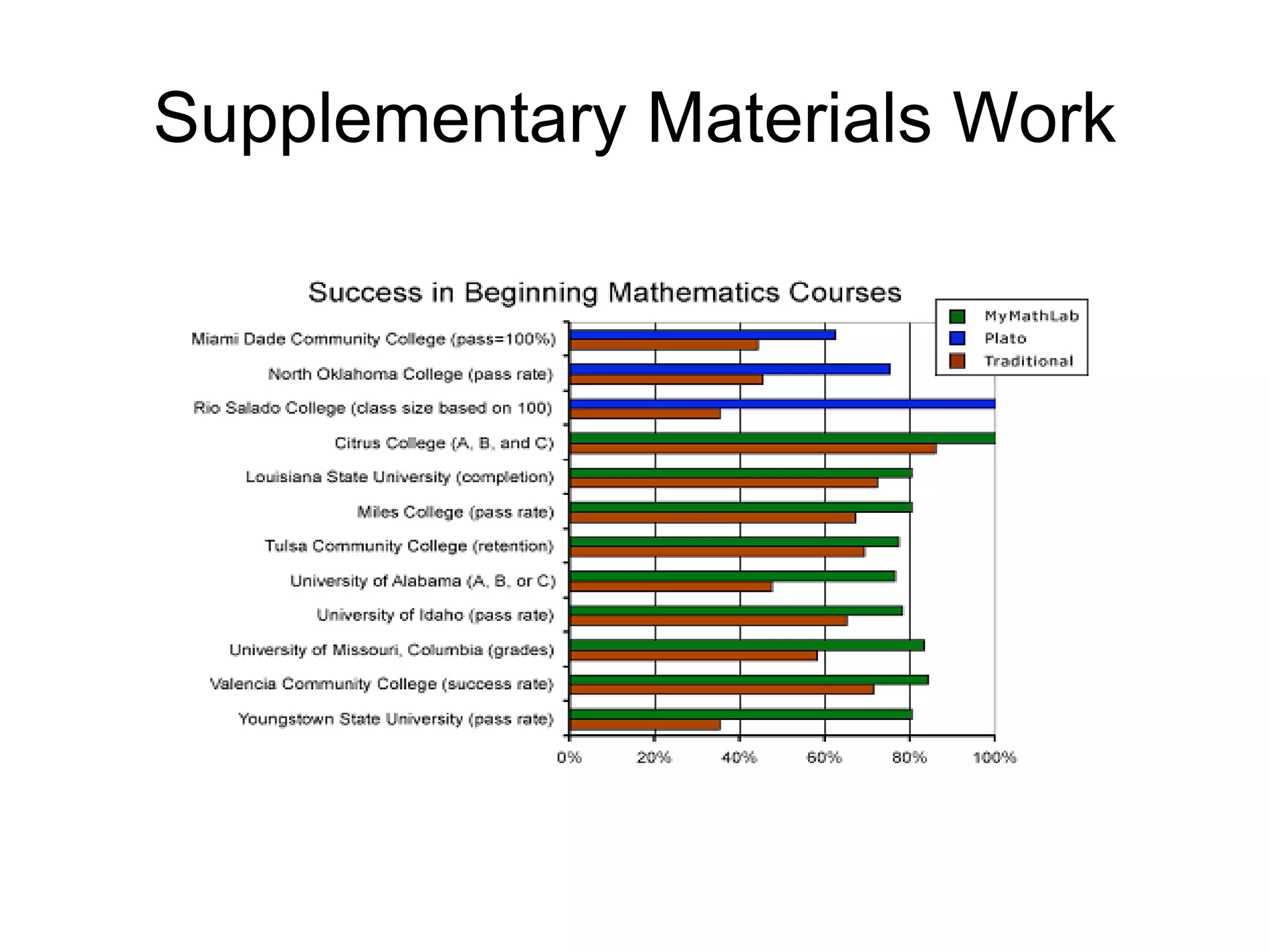
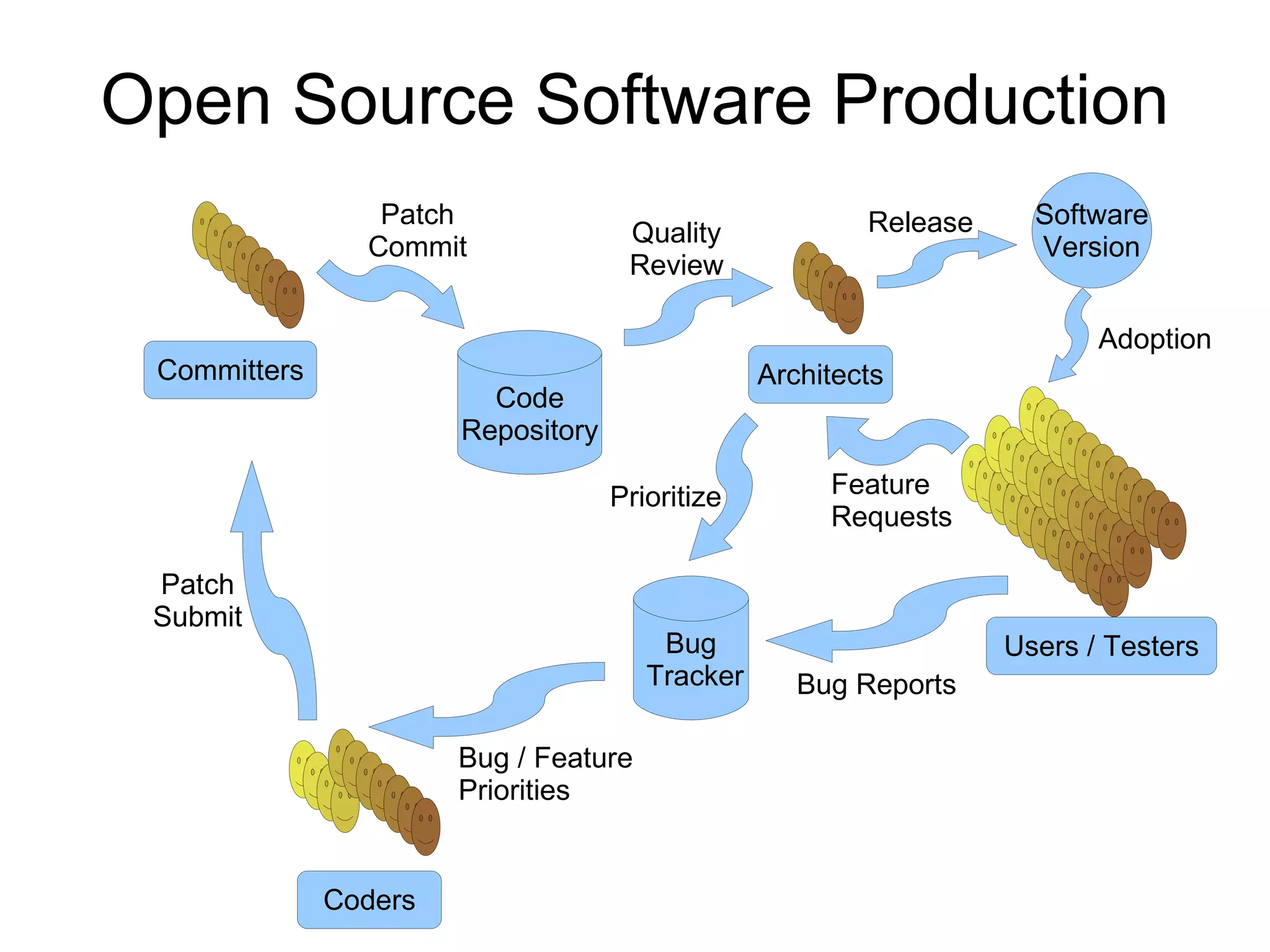
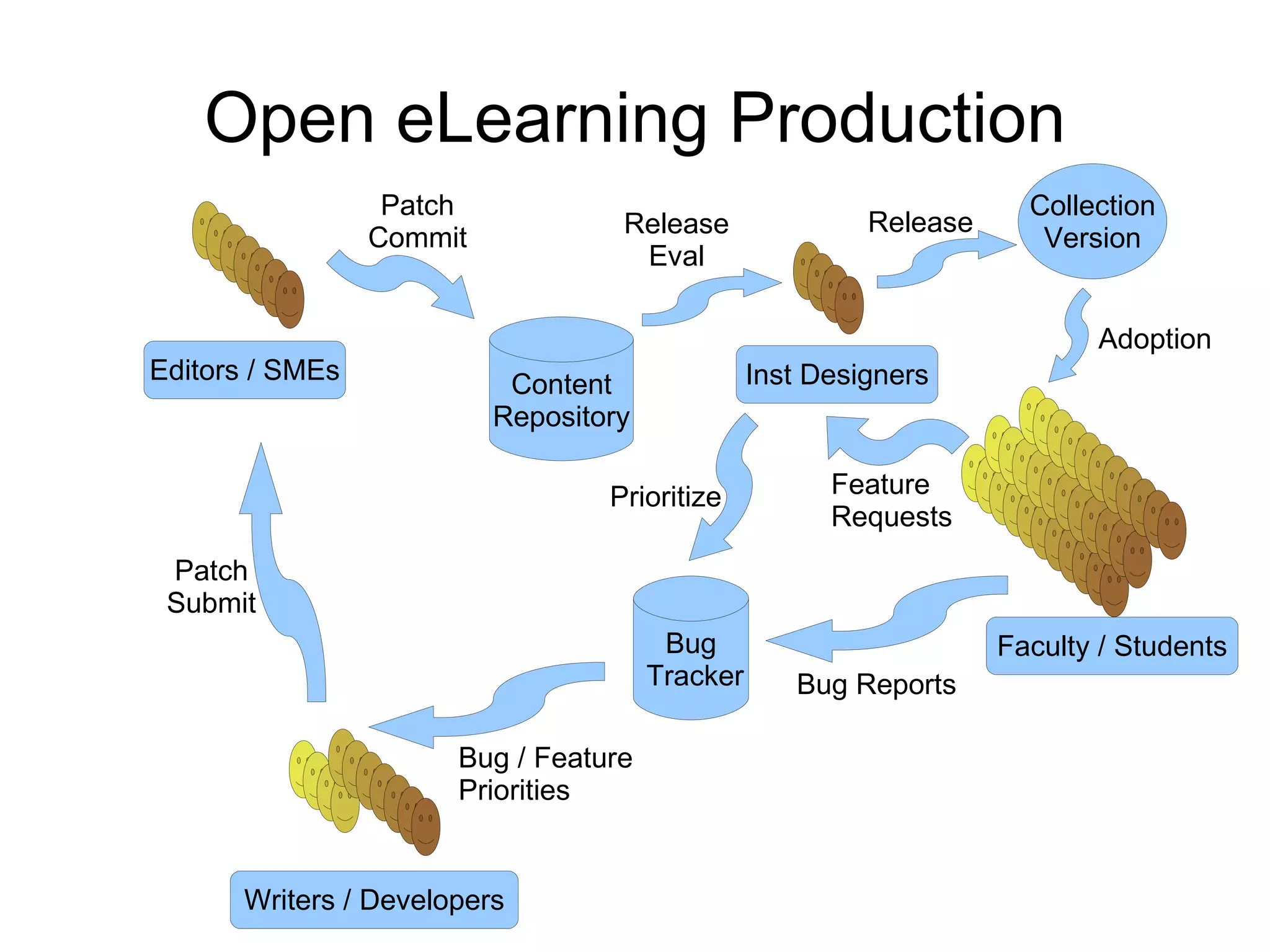
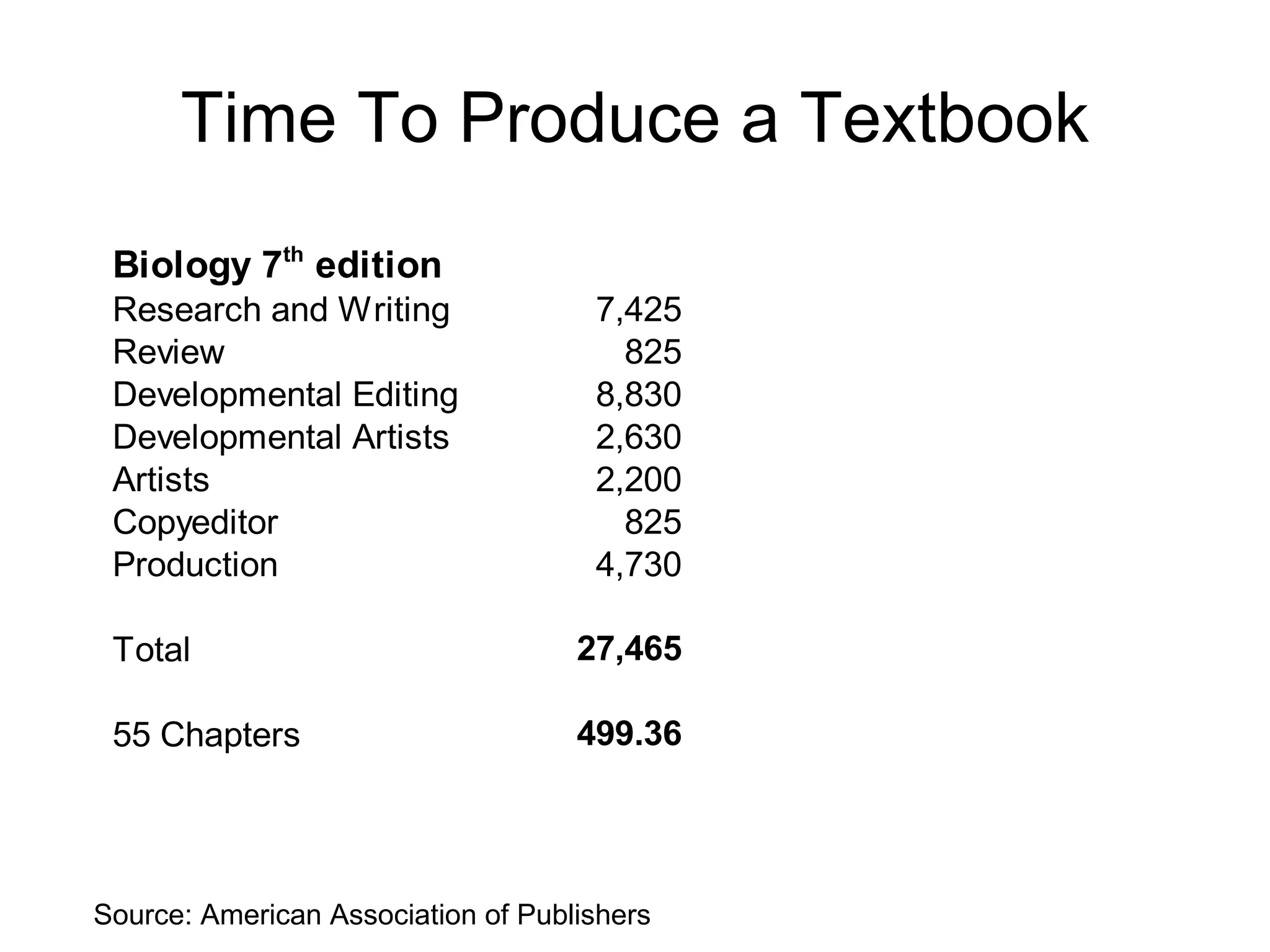
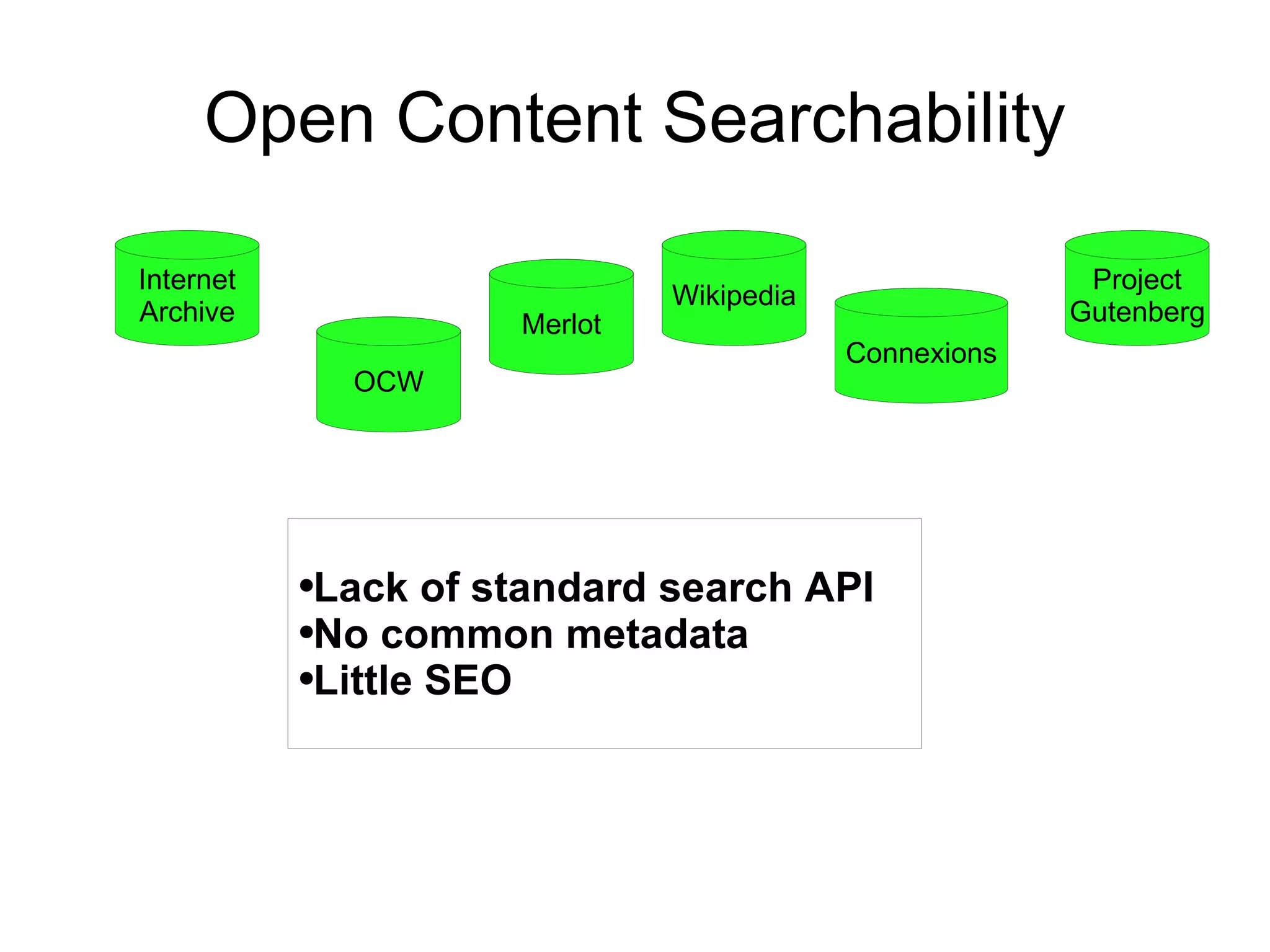
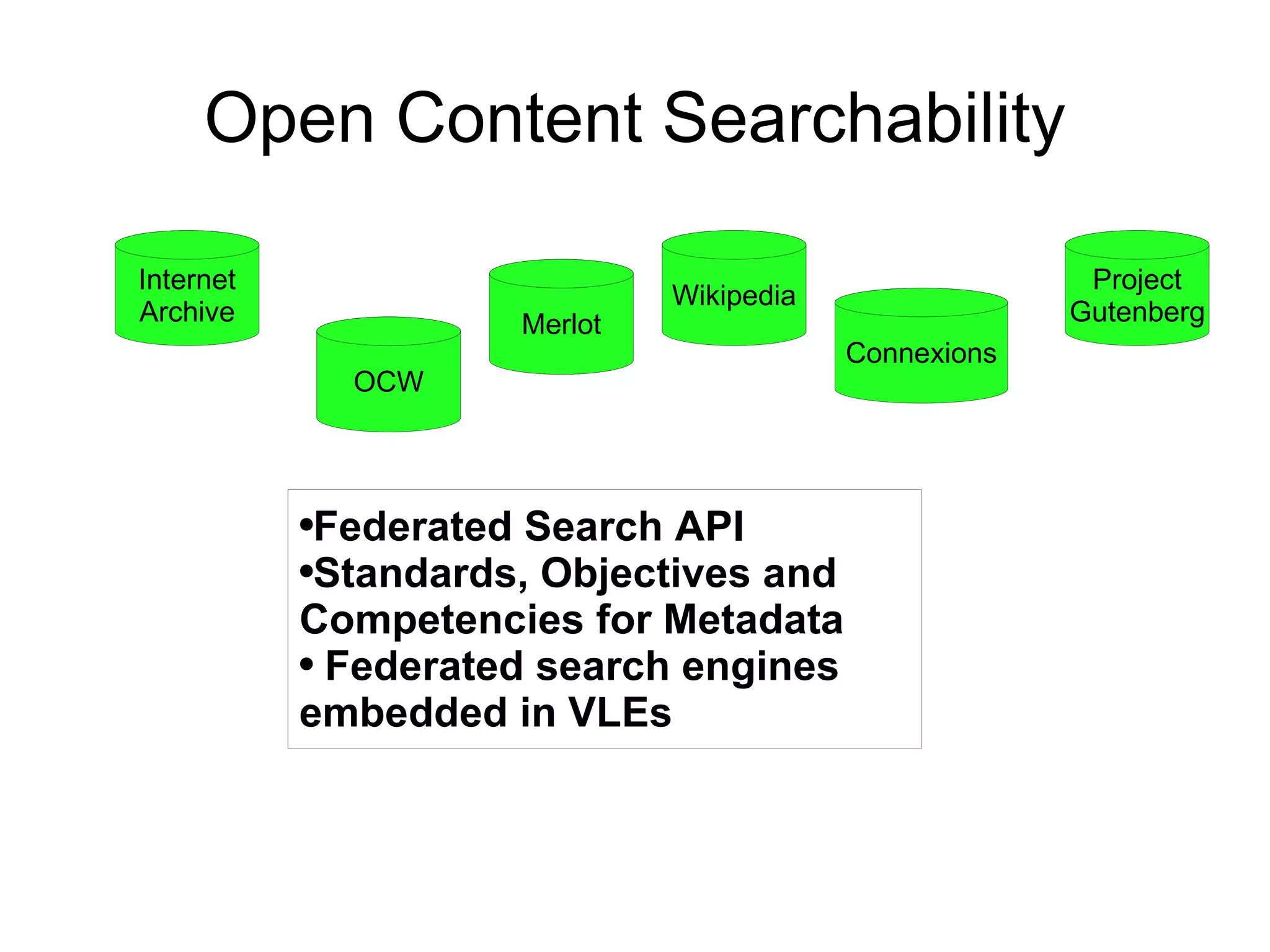
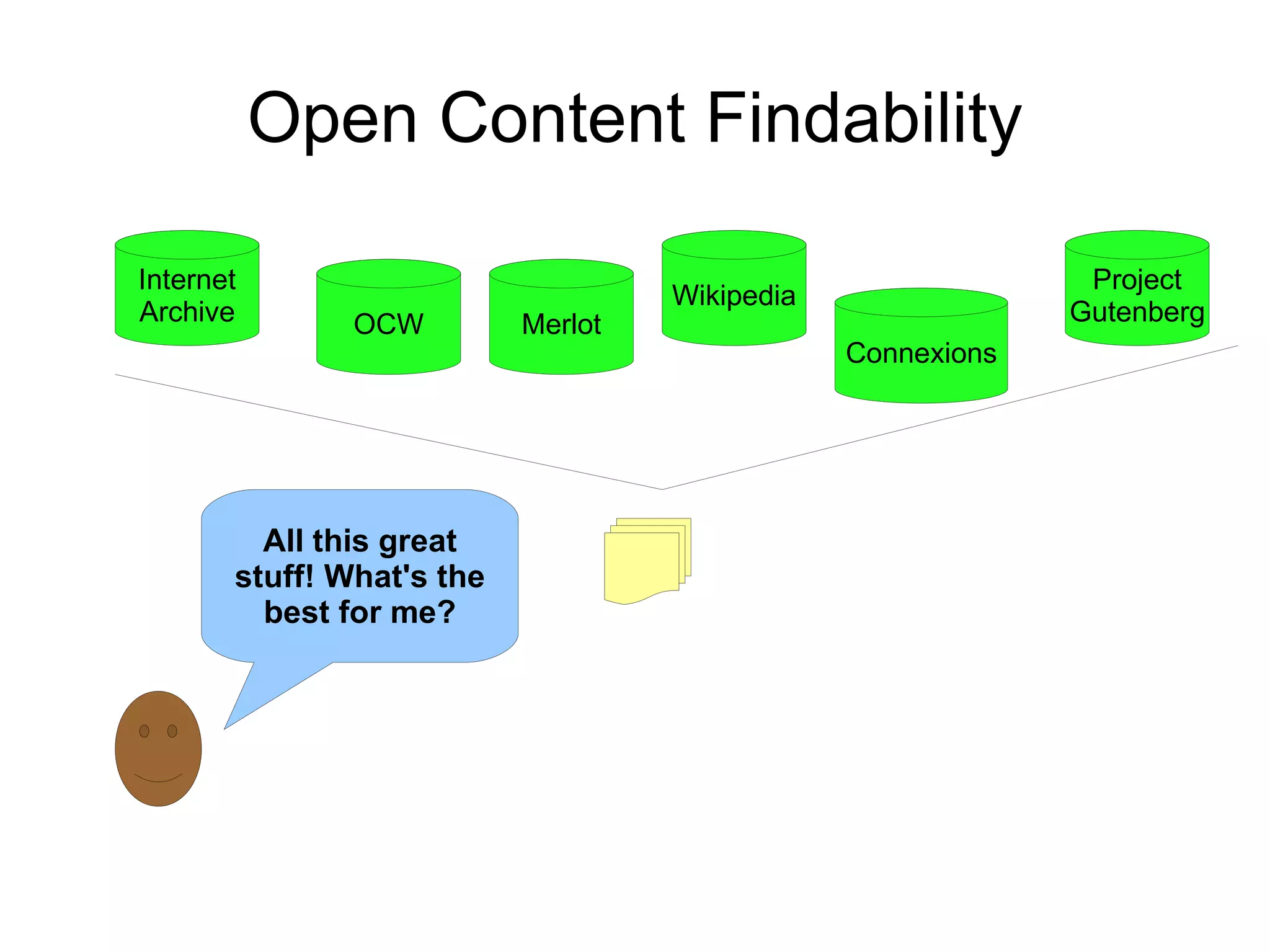
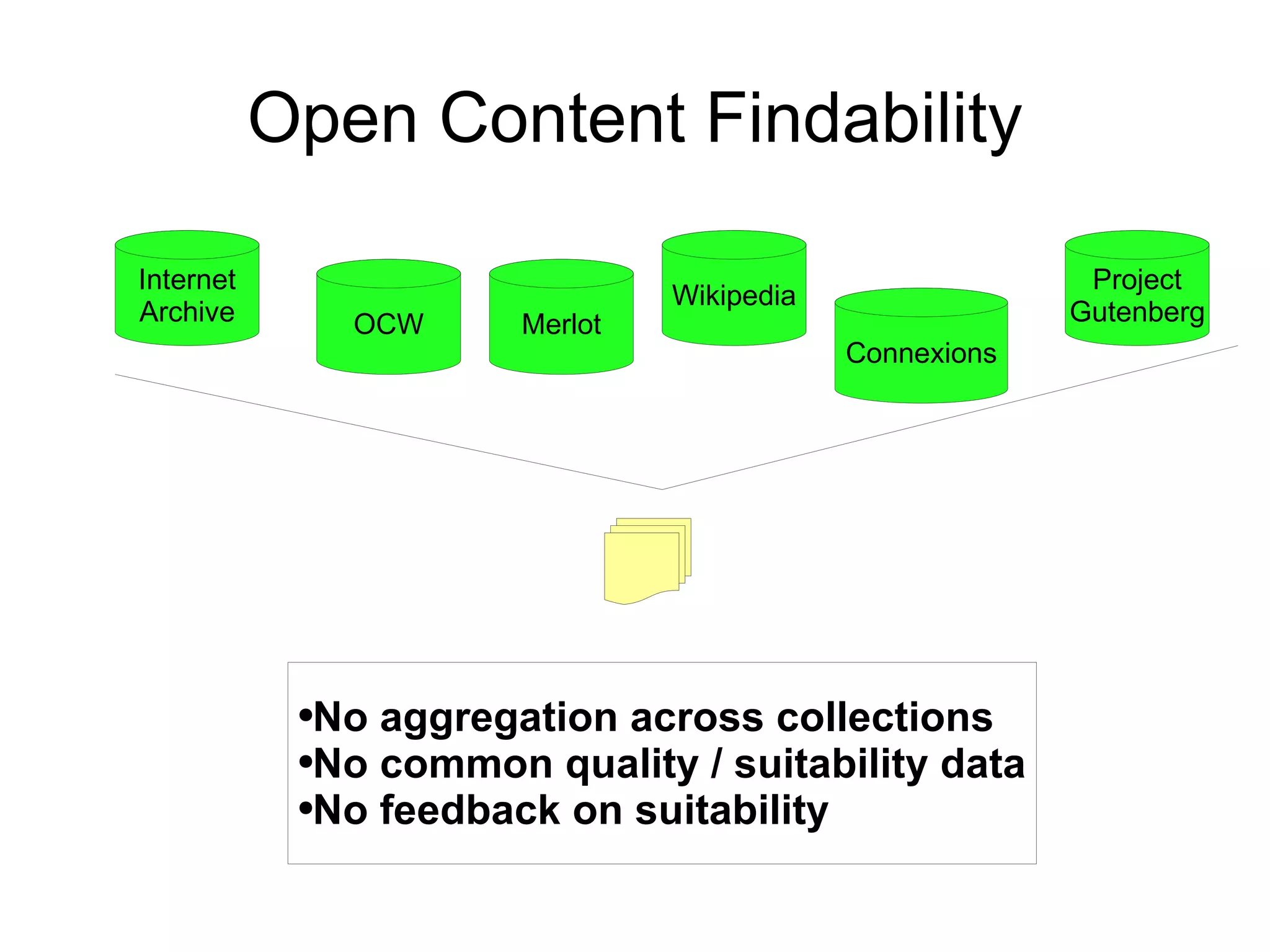
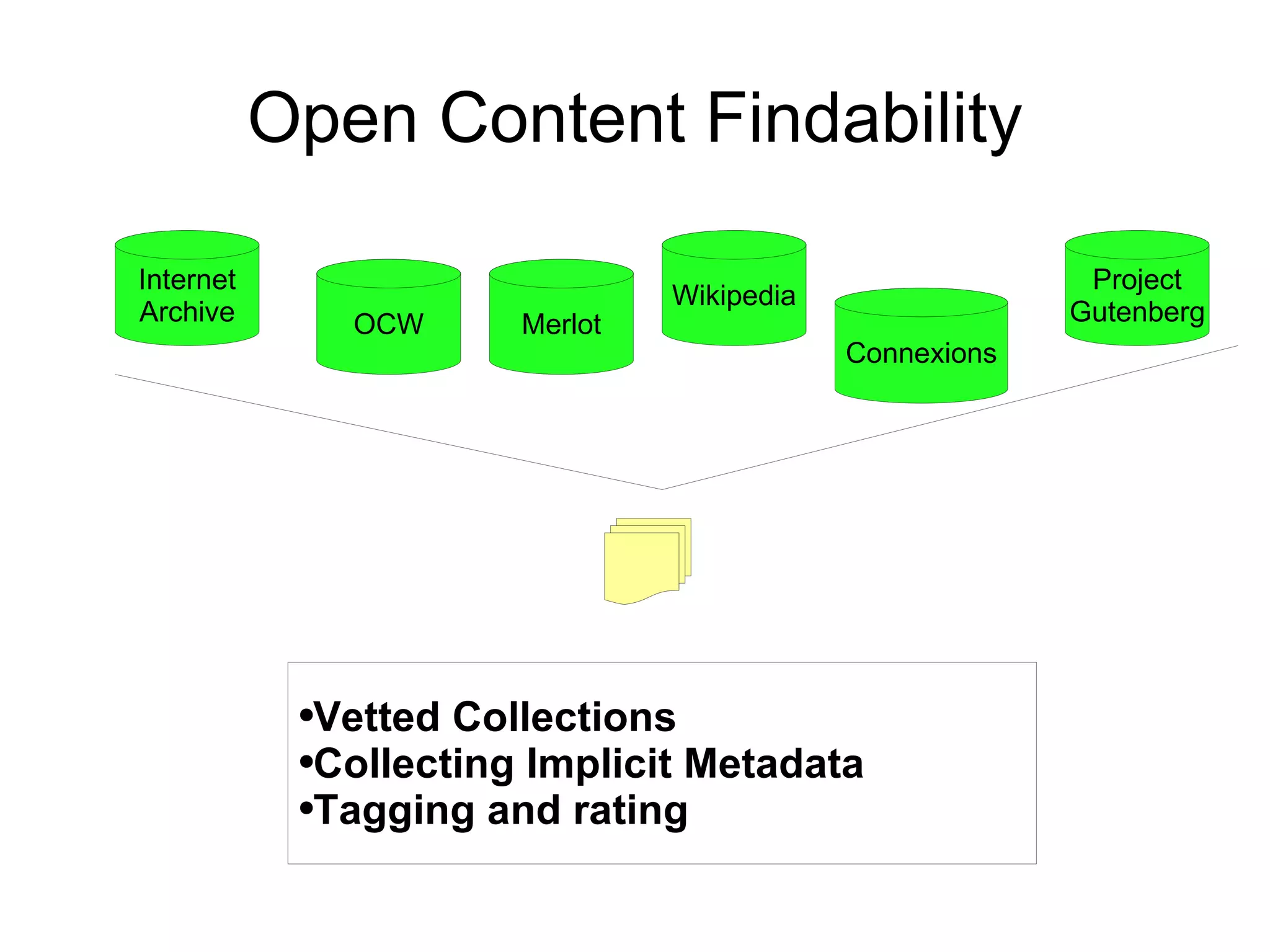
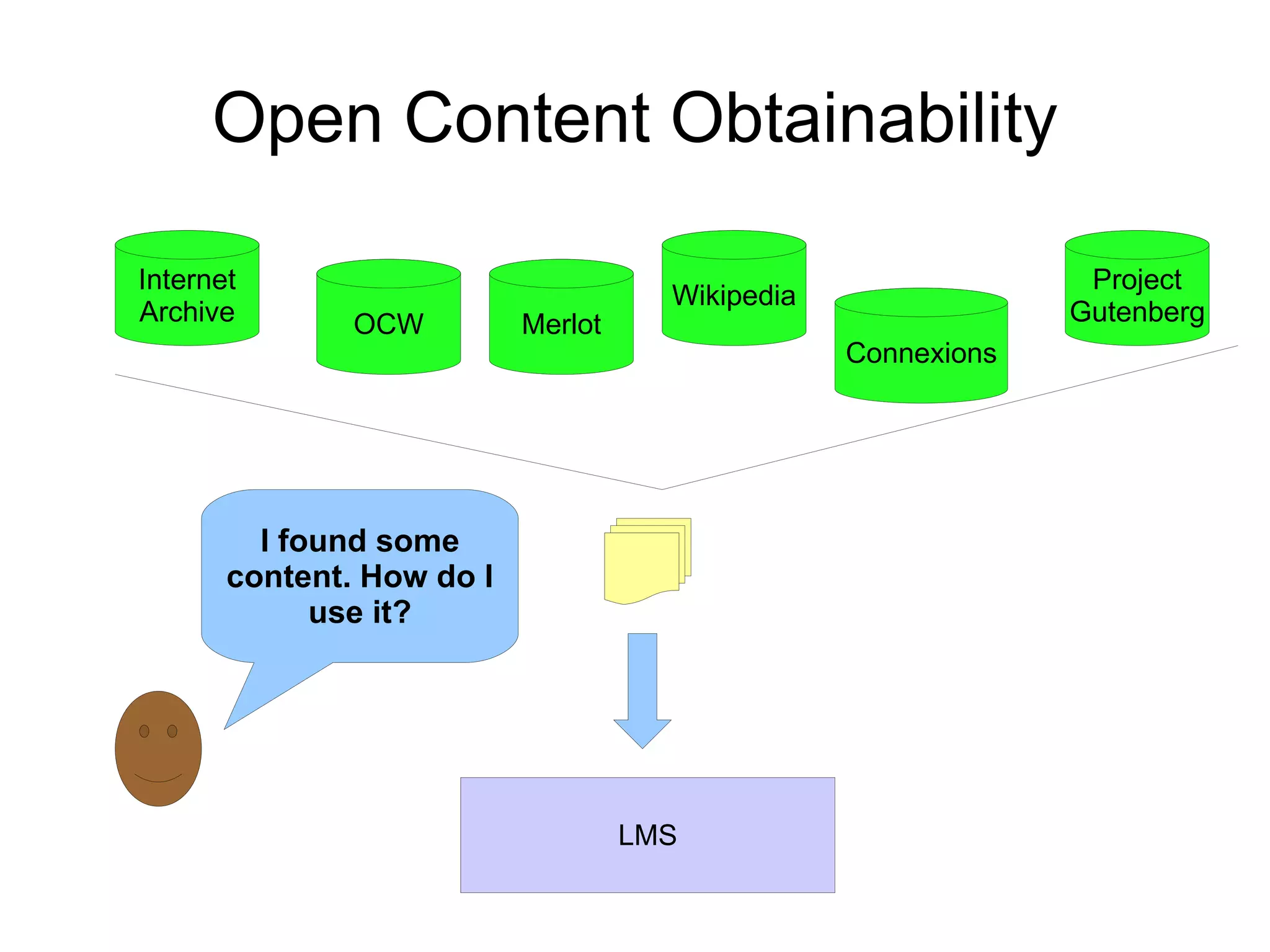
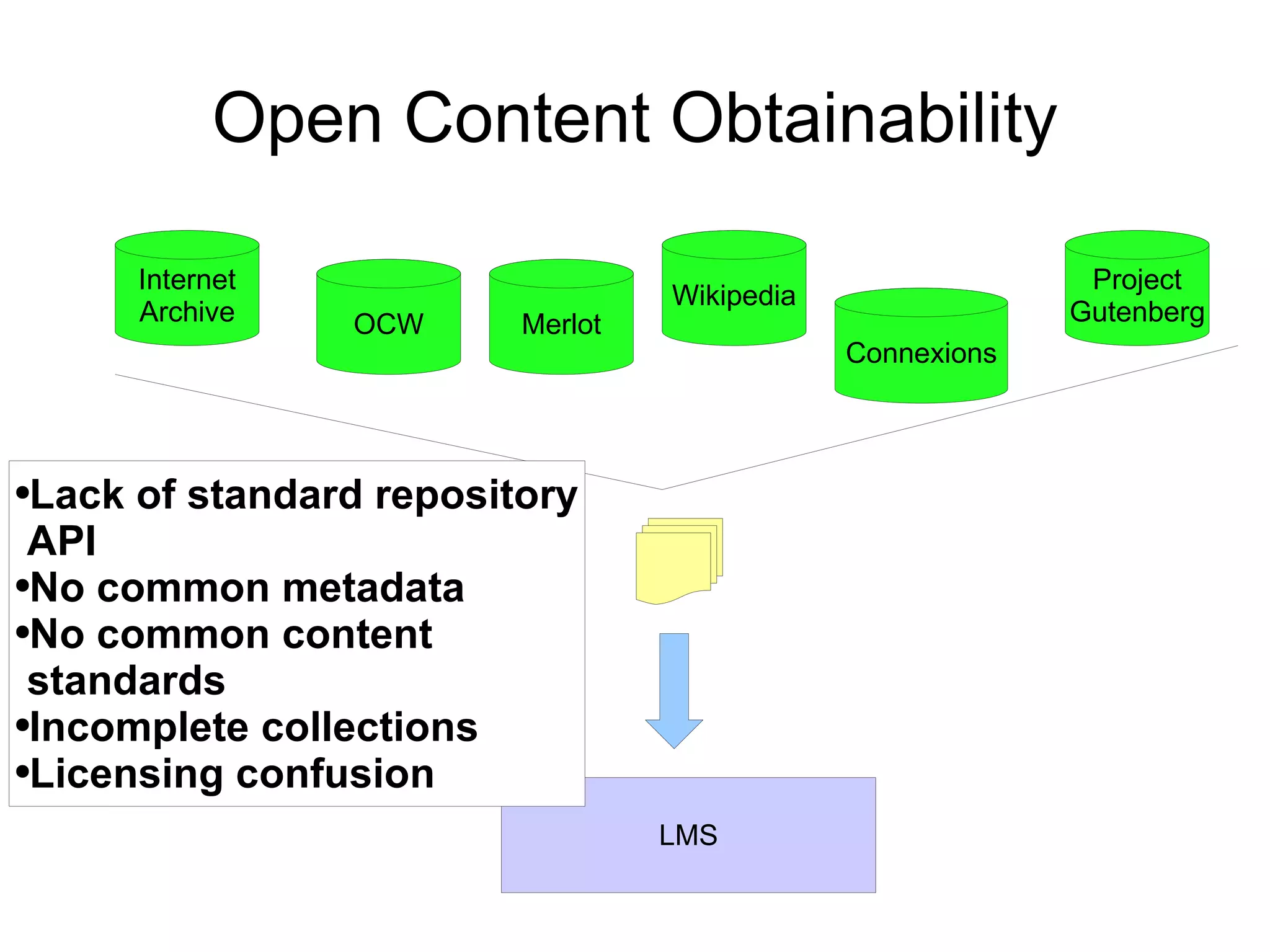
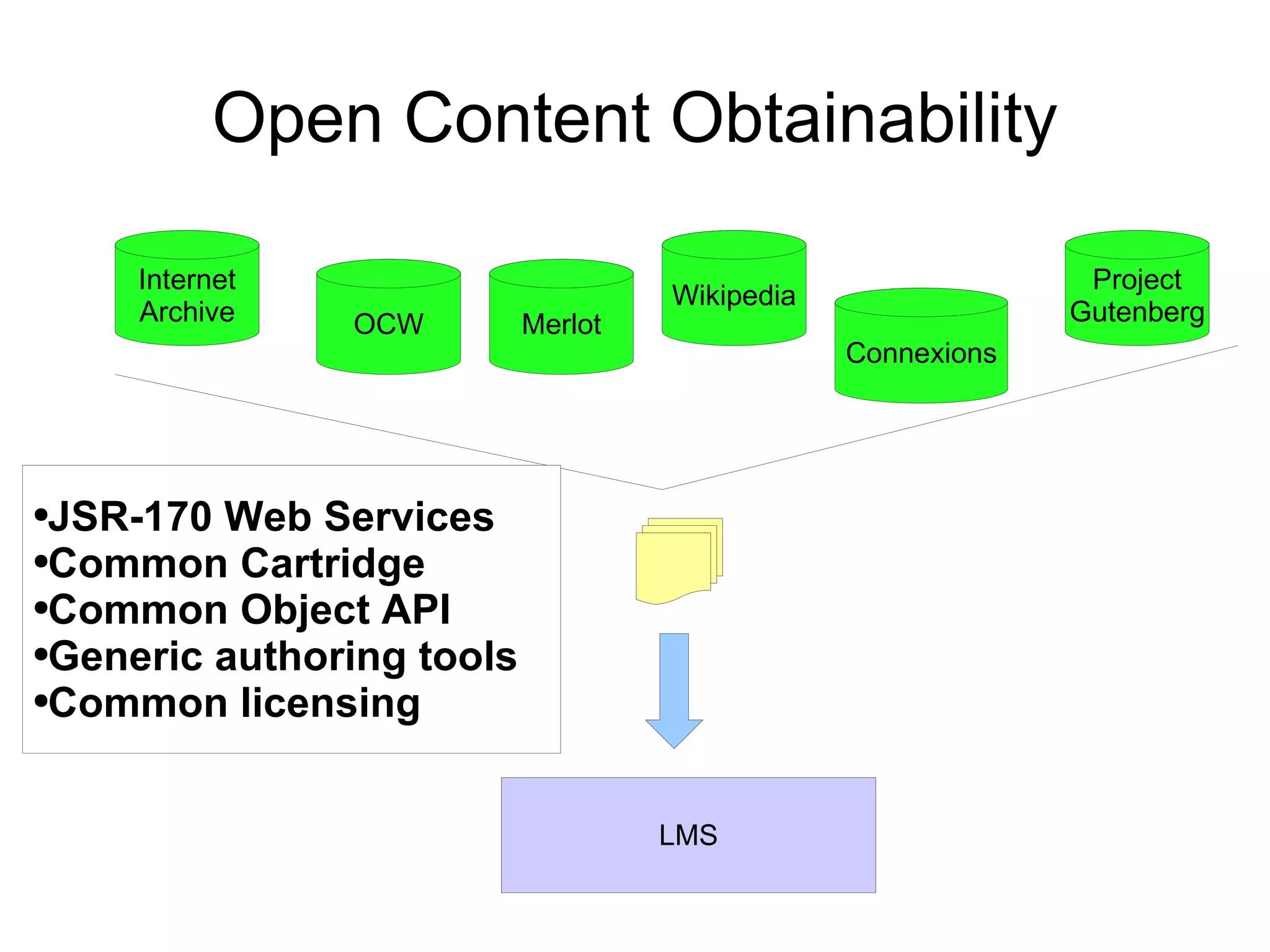
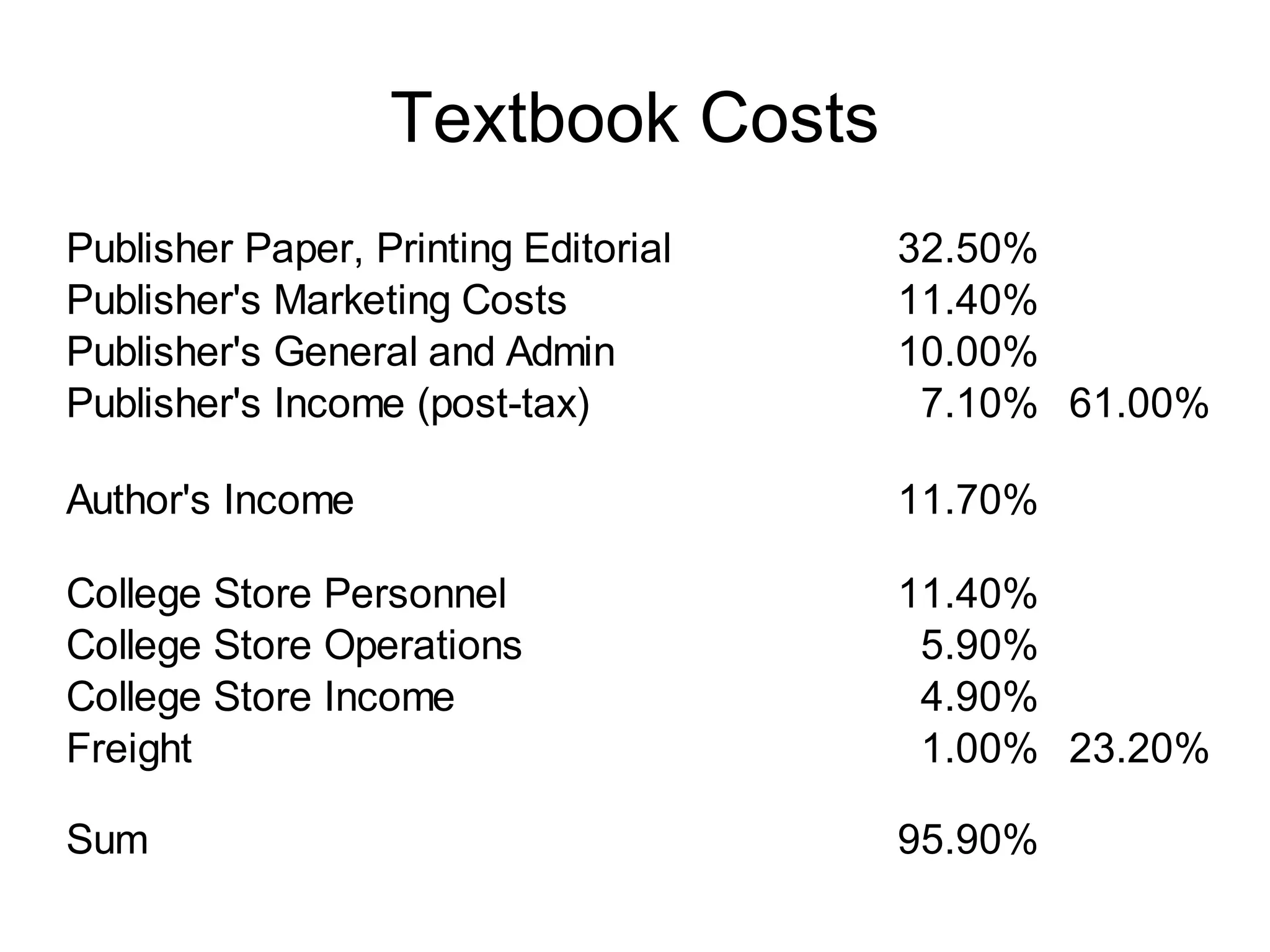
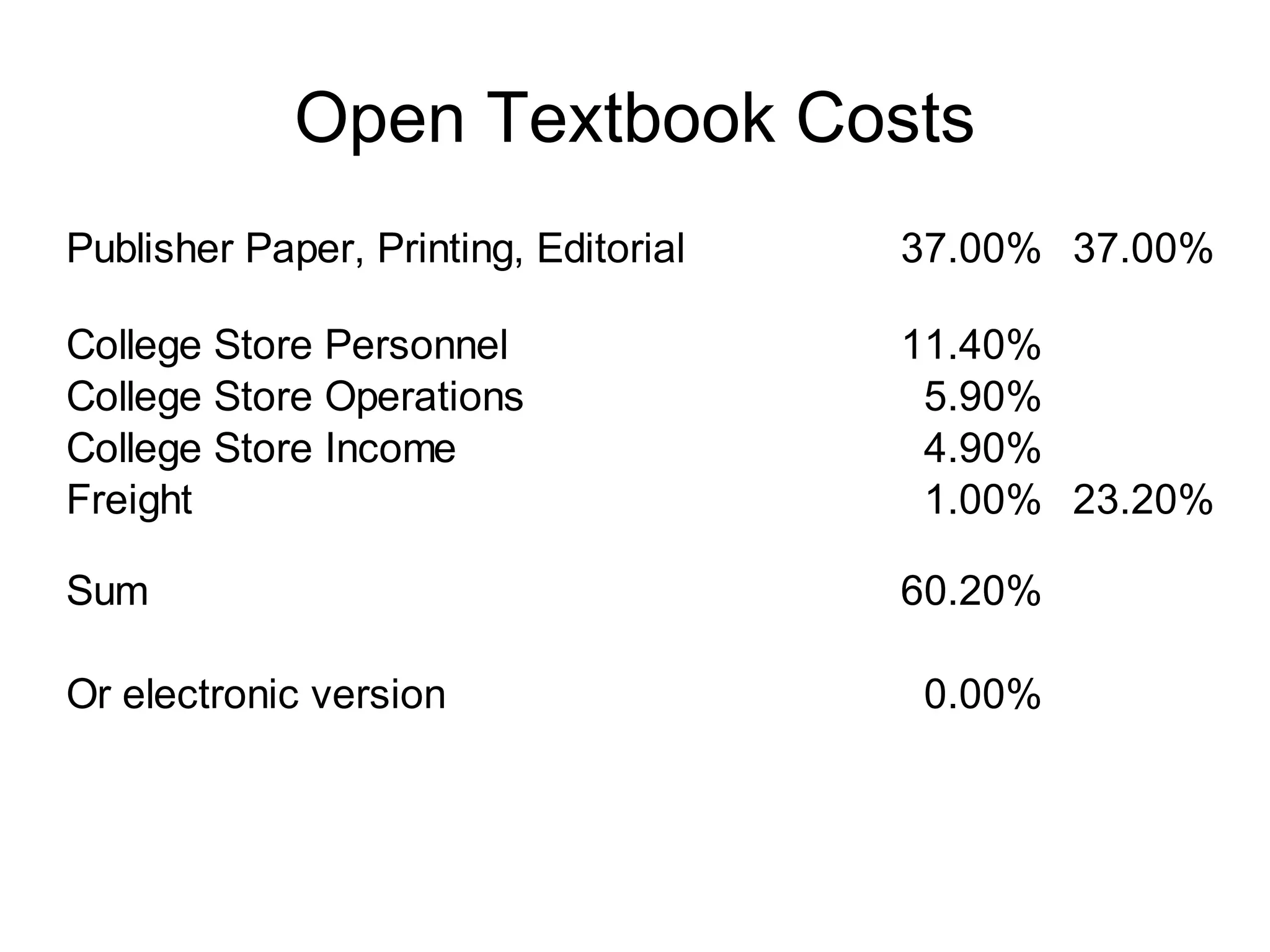
The document discusses the high cost of textbooks and supplementary materials for students and proposes open education as an alternative. It analyzes different models for openly developing and sharing educational content, including open courseware repositories and wikis. It advocates for the creation of open learning communities to collaboratively develop open educational resources using common standards and licensing to make the content more searchable, findable, and usable across different platforms.
![Open Source + Open Content = Jason Cole Cognition and Instruction Associates [email_address] Open Education](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developing-open-content-like-open-software-3423/75/Developing-Open-Content-Like-Open-Software-1-2048.jpg)