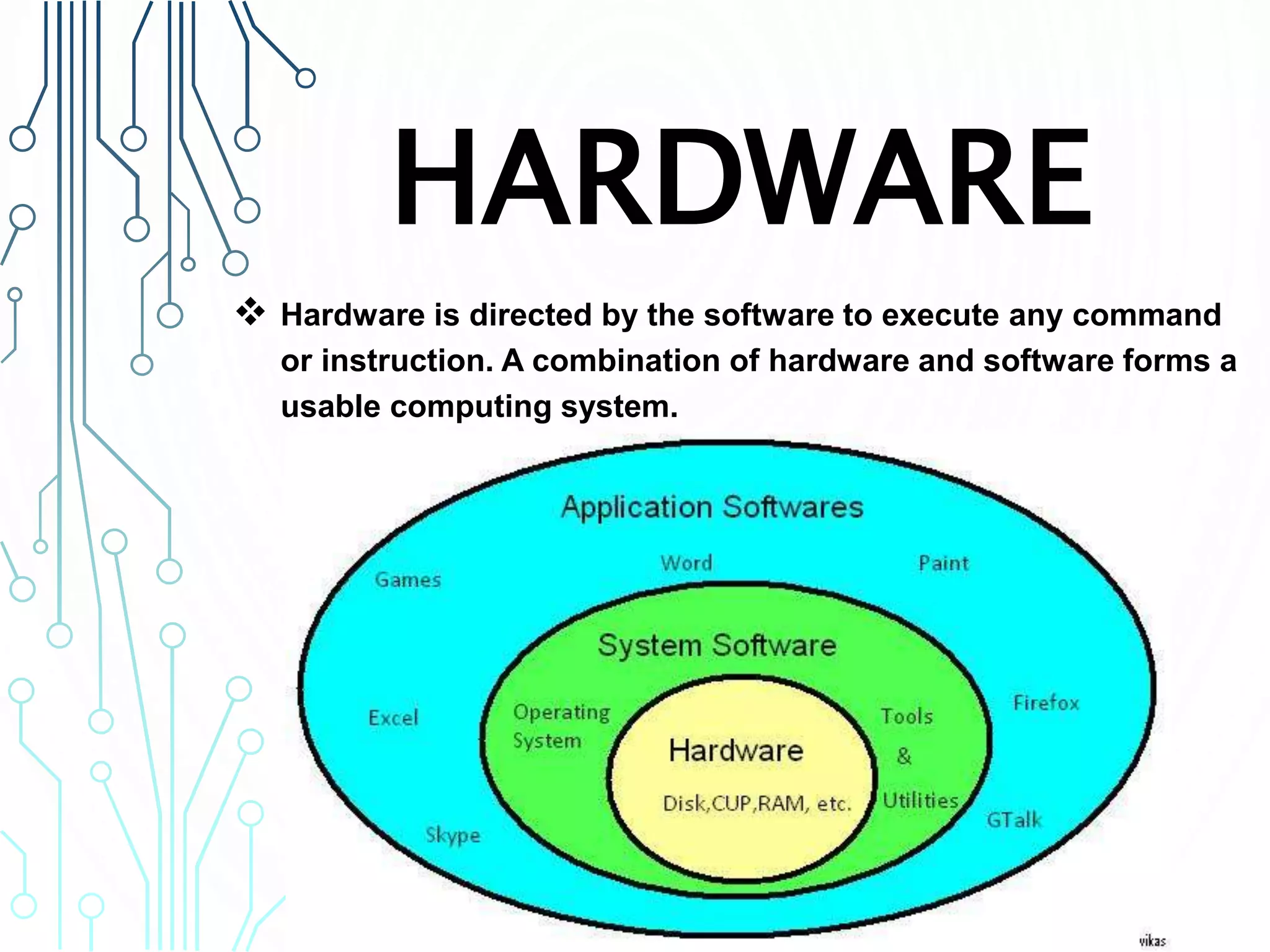
This document provides an overview of computer software and hardware. It defines software as collections of instructions that enable users to interact with computers and perform tasks. It distinguishes between application software, which performs specific functions, and system software, which operates hardware and provides platforms for applications. Examples of system software include operating systems, device drivers, and utilities. The document also defines computer hardware as the physical components of a computer like processors, storage, memory, and input/output devices. It provides examples of common hardware components such as motherboards, expansion cards, power supplies, and input/output peripherals.