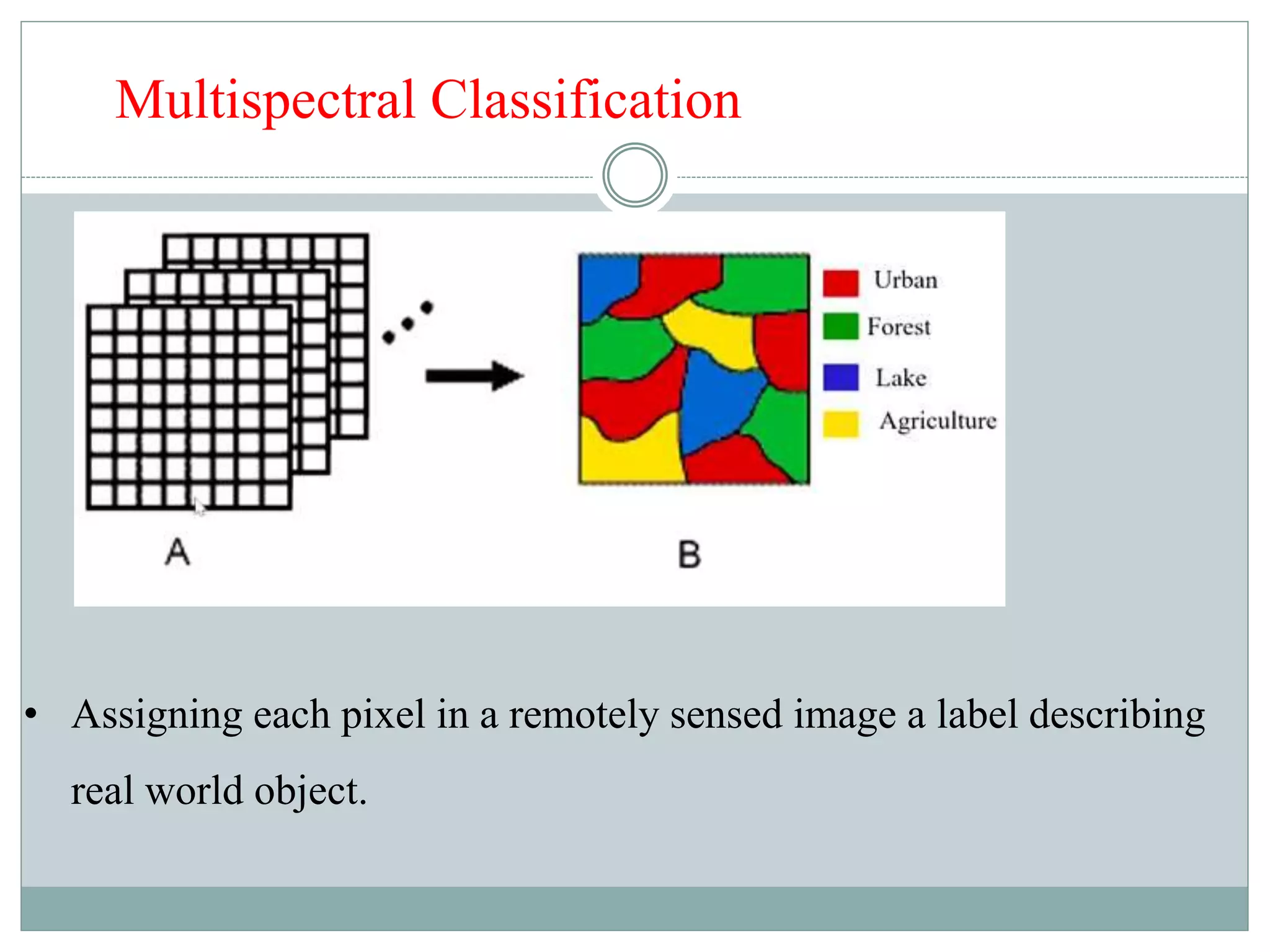
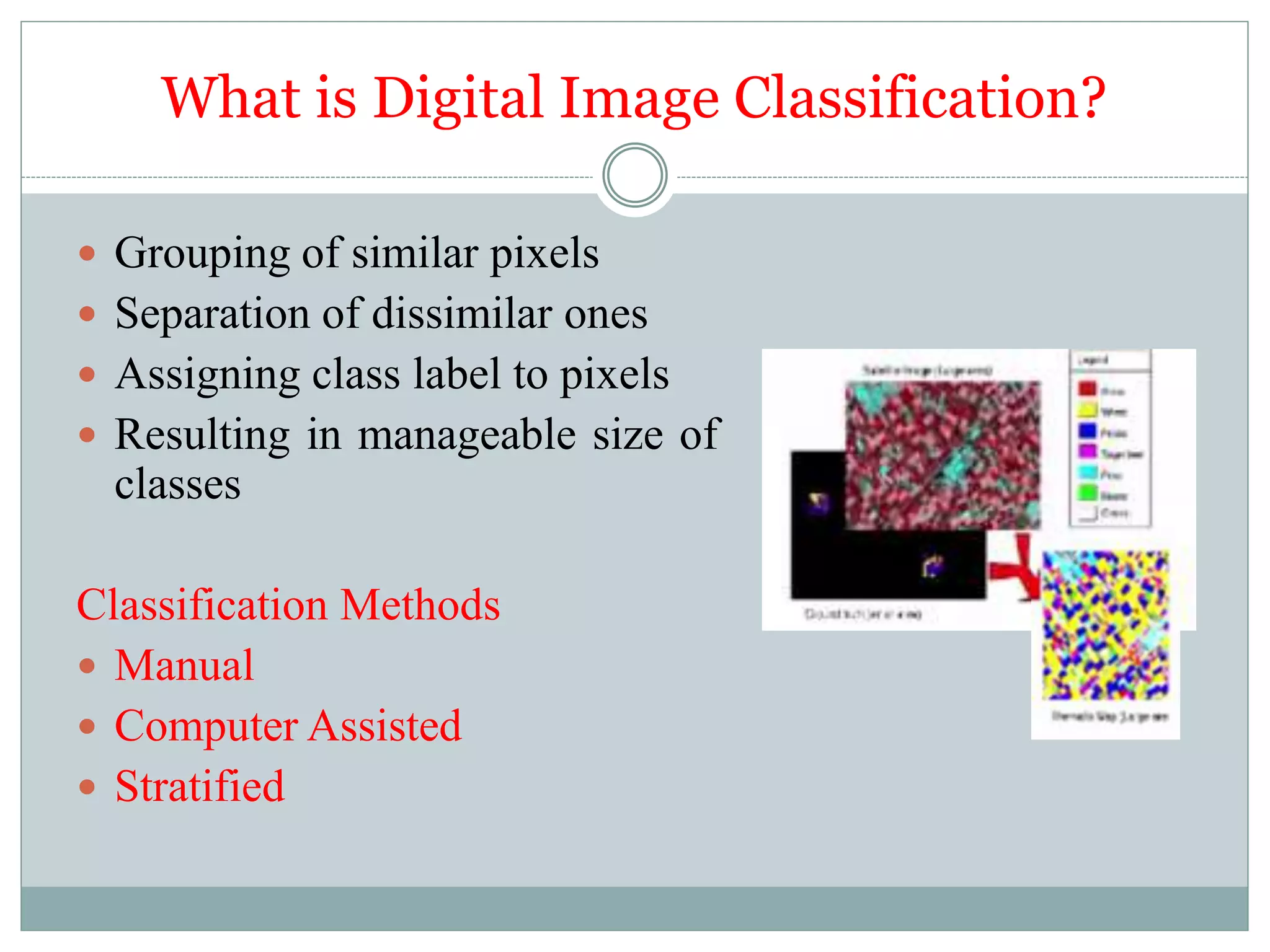
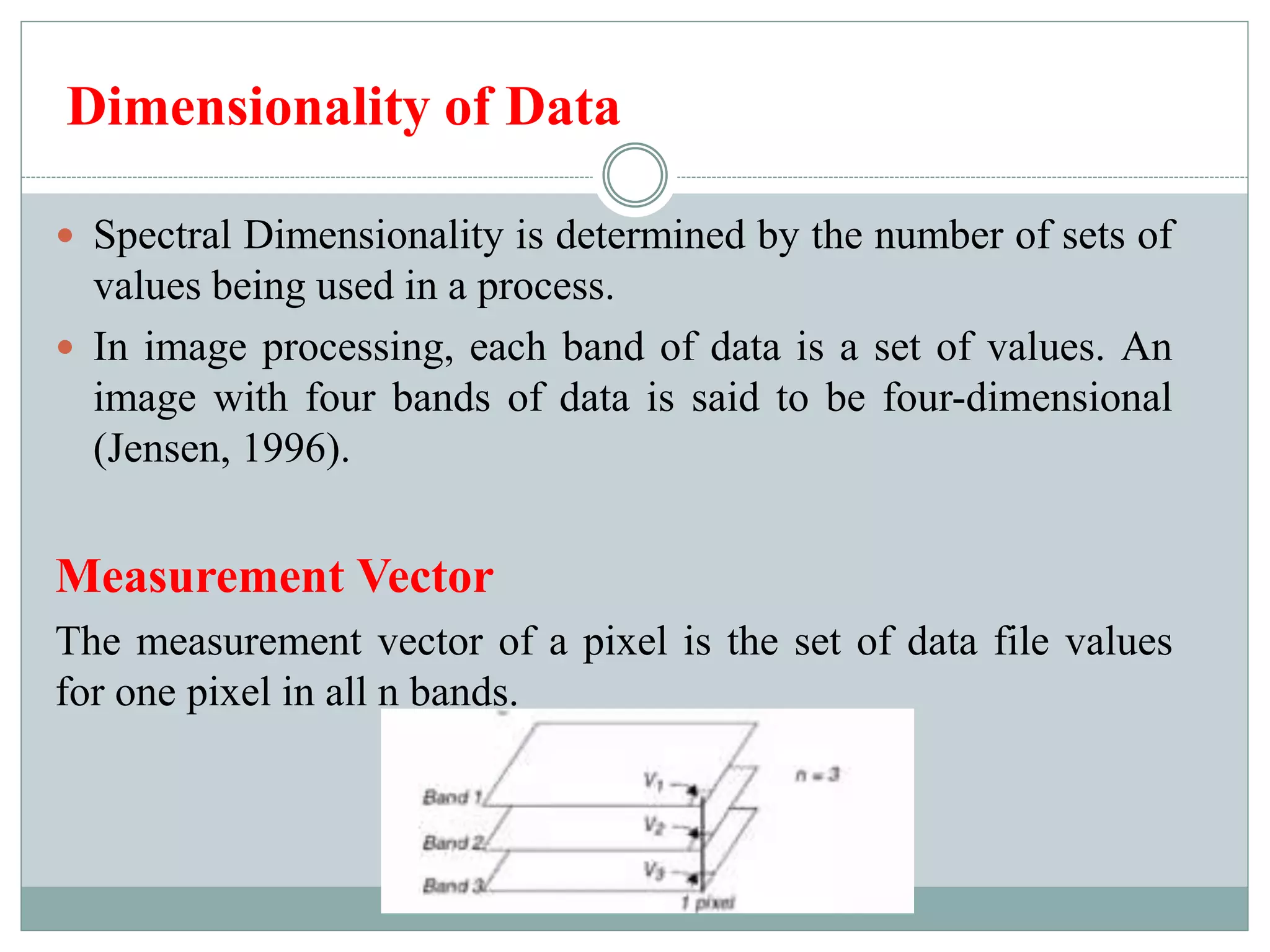
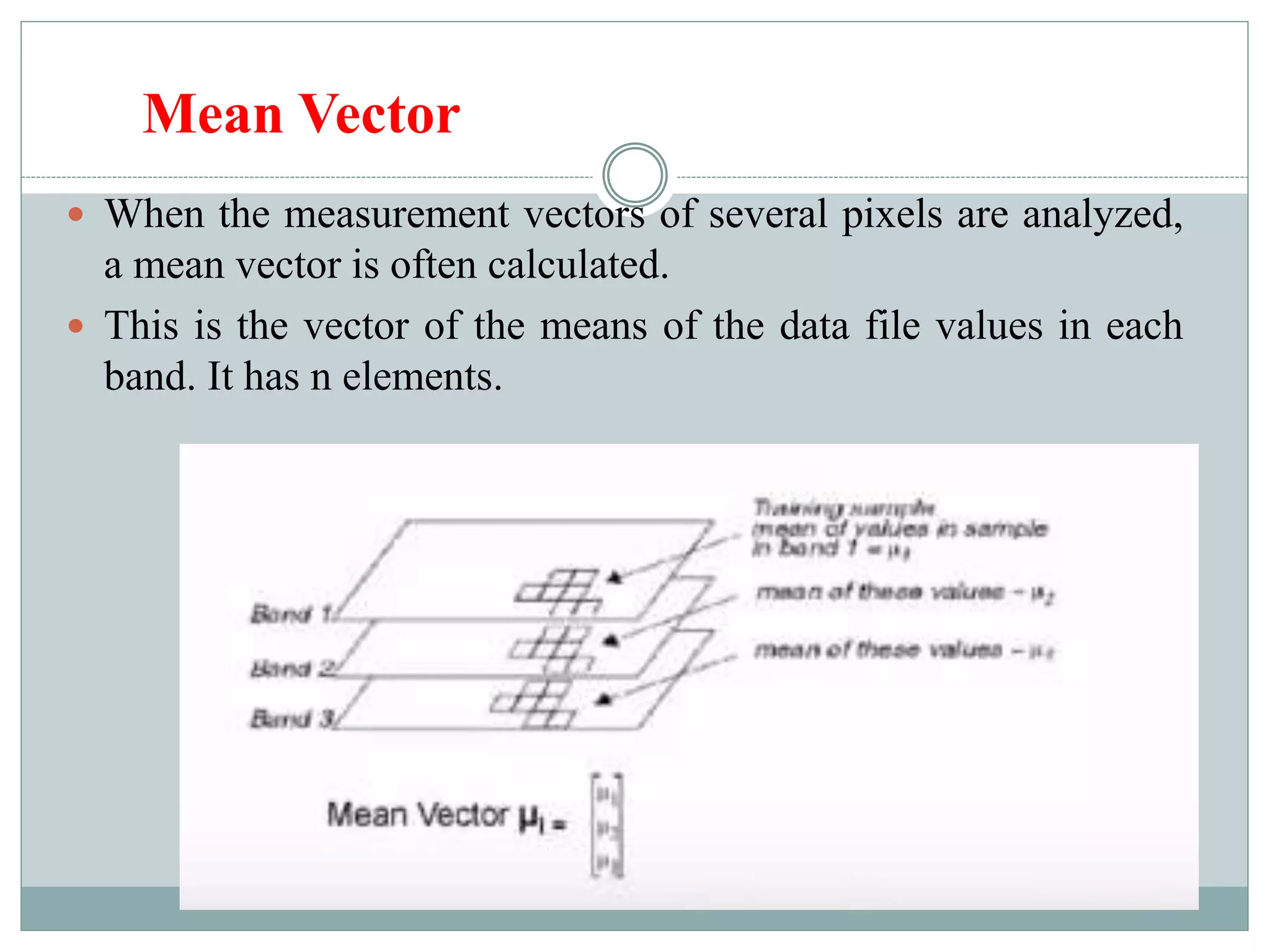
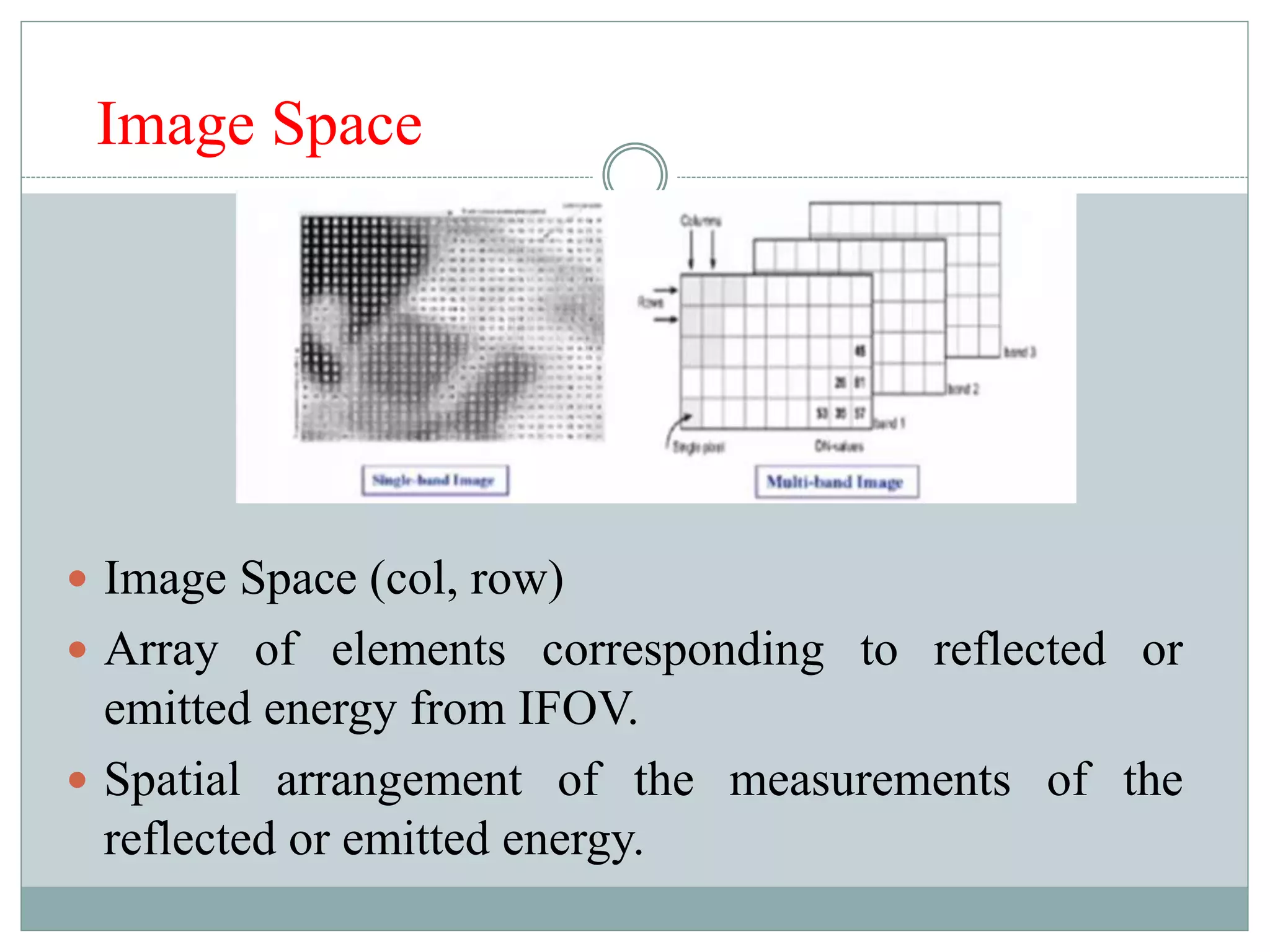
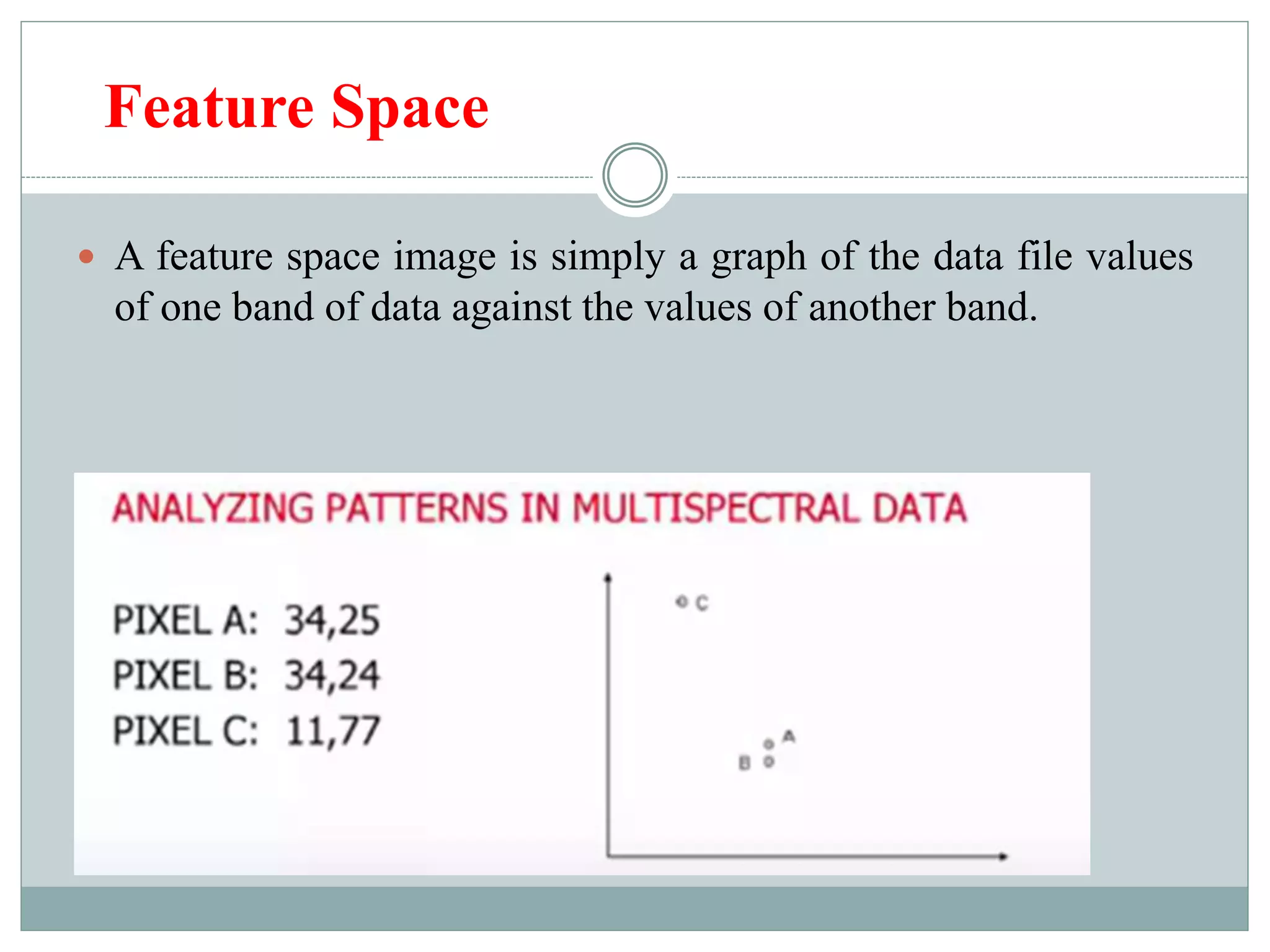
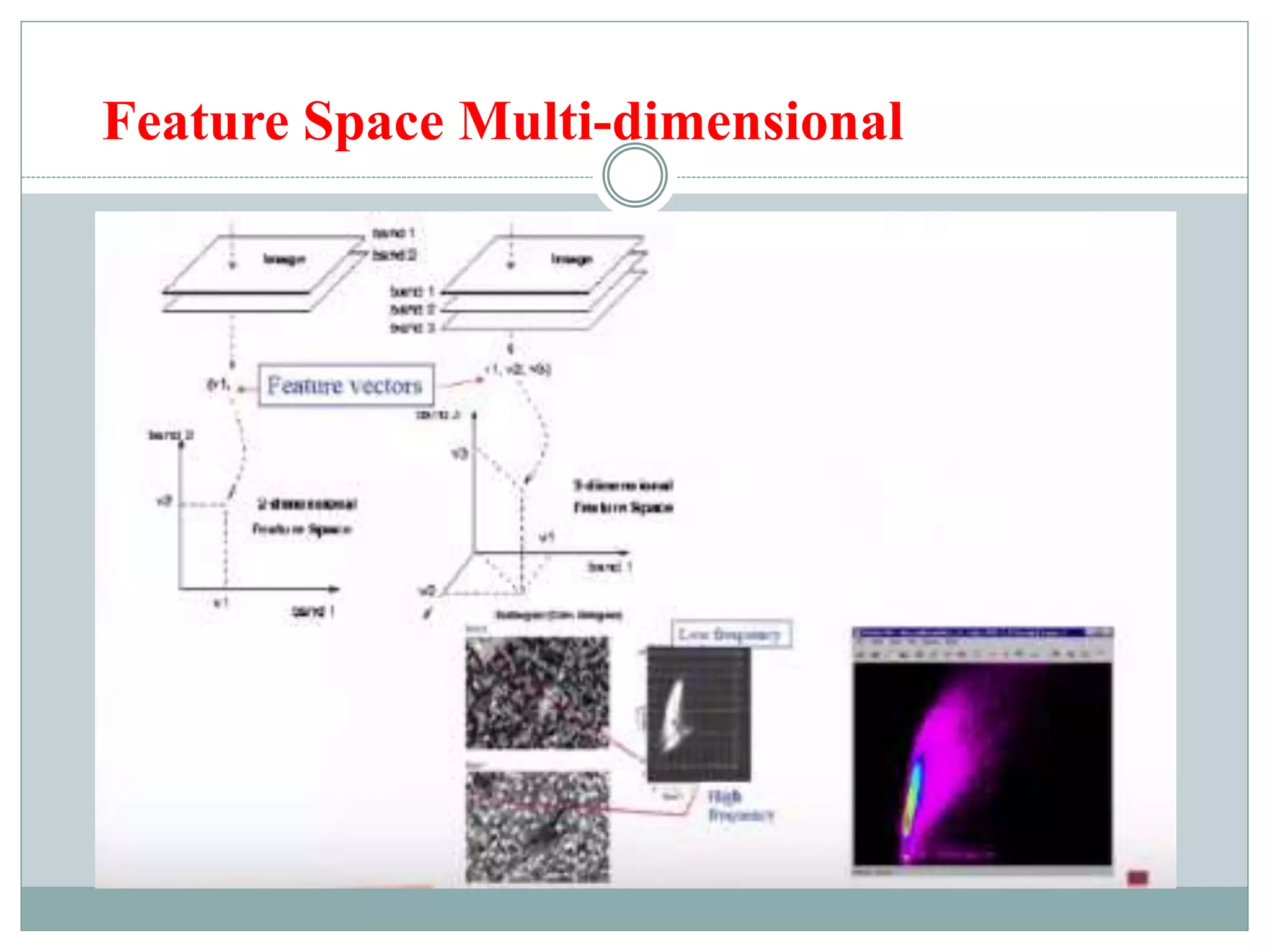
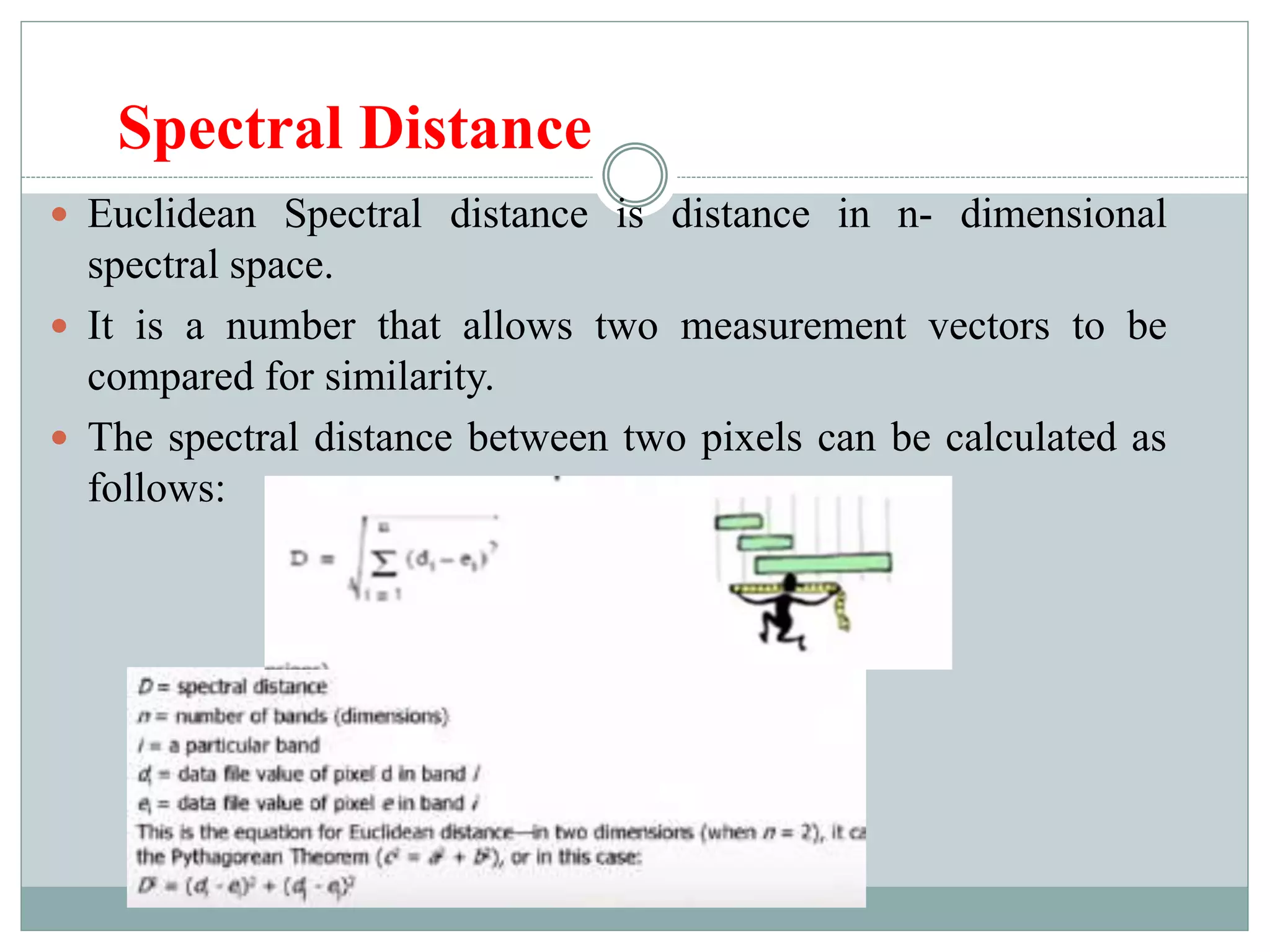
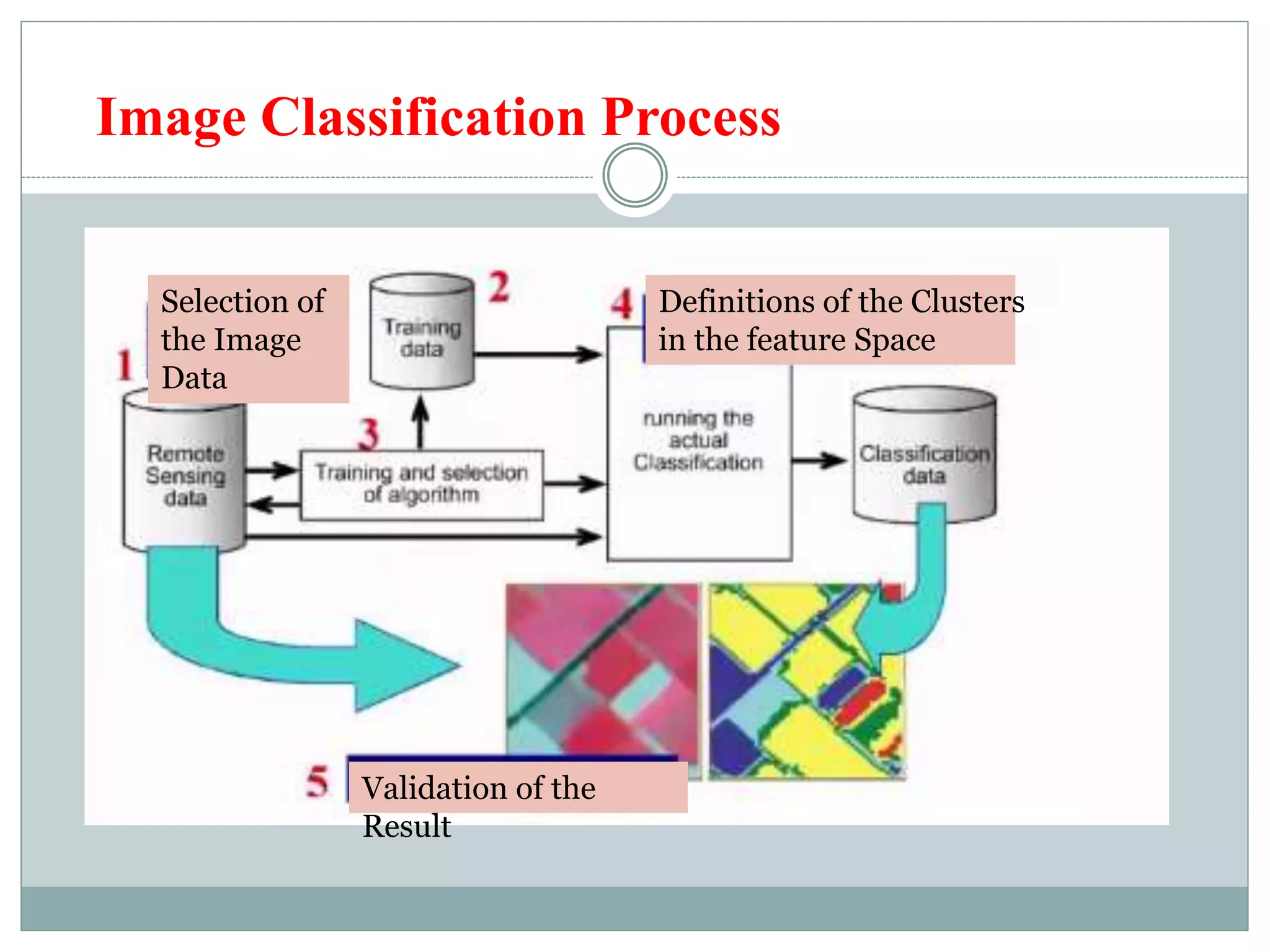
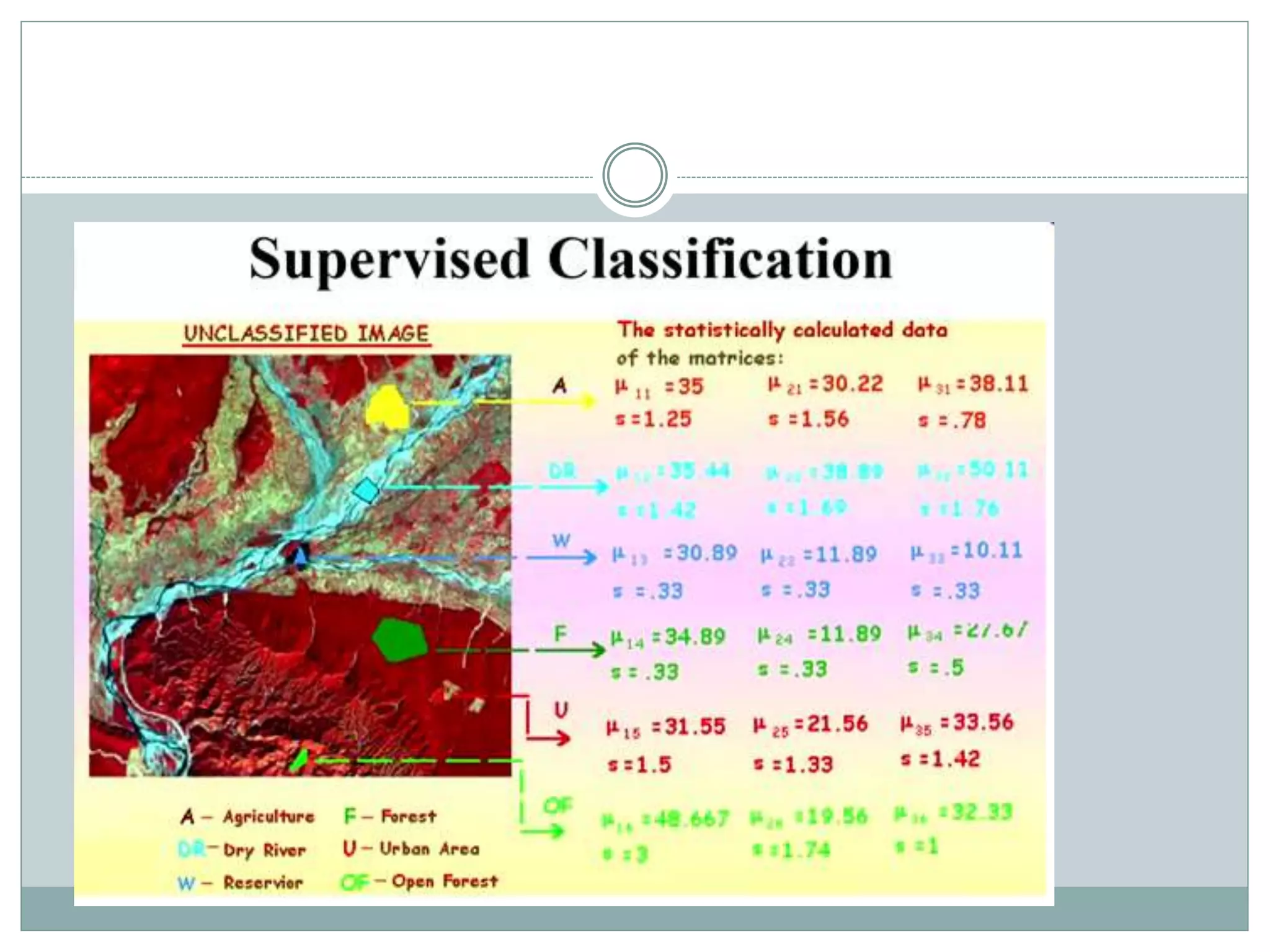
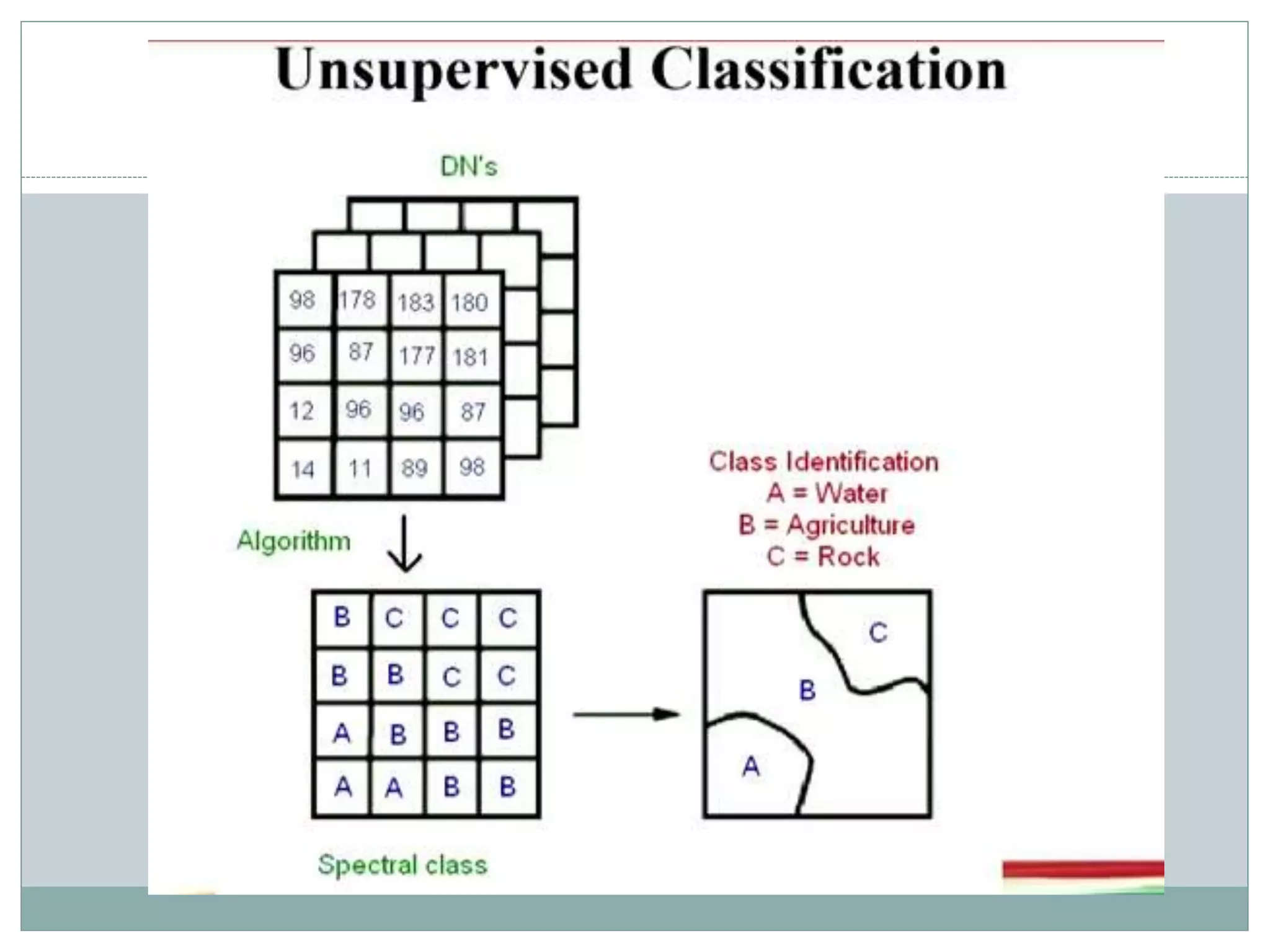
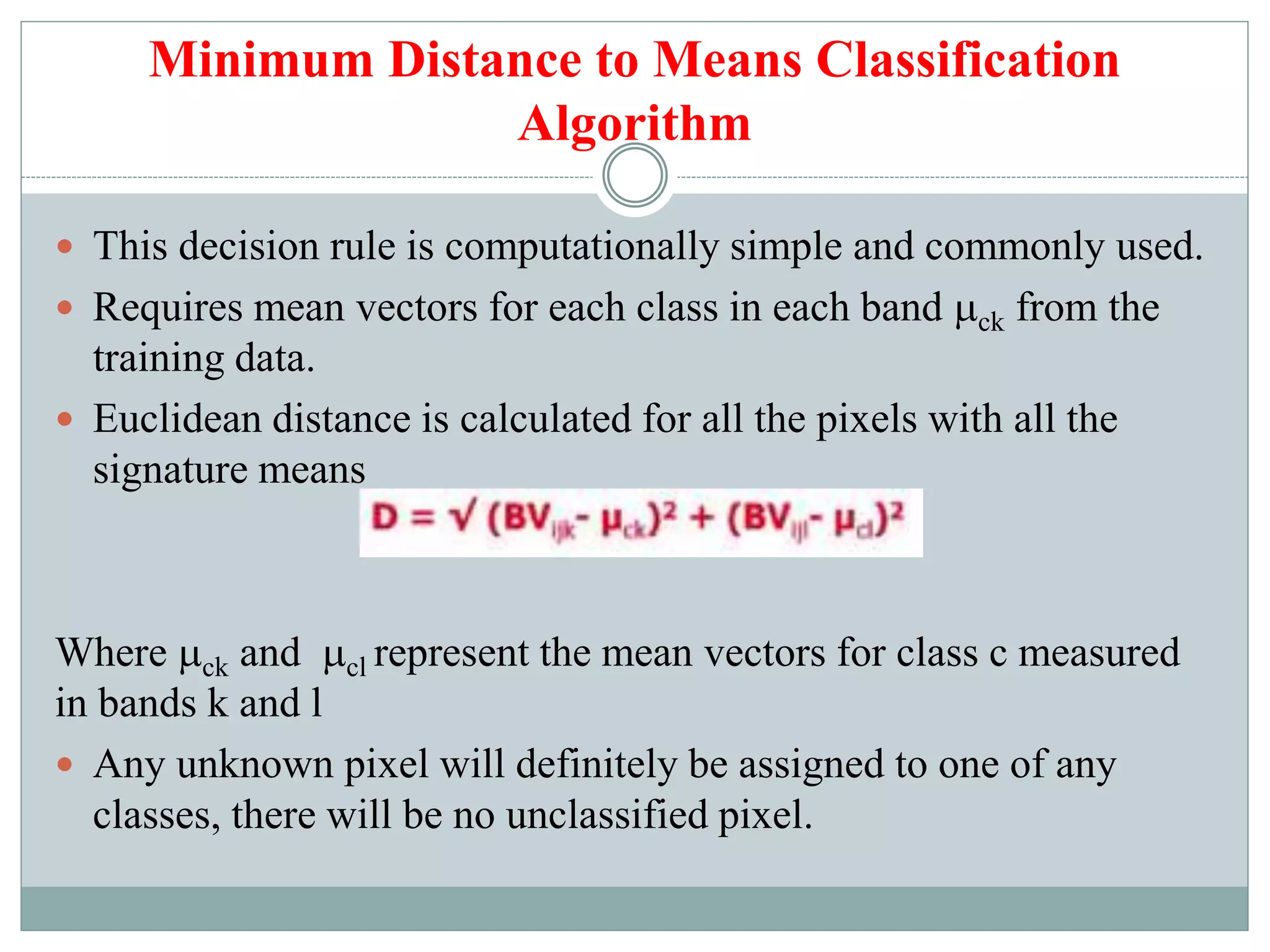
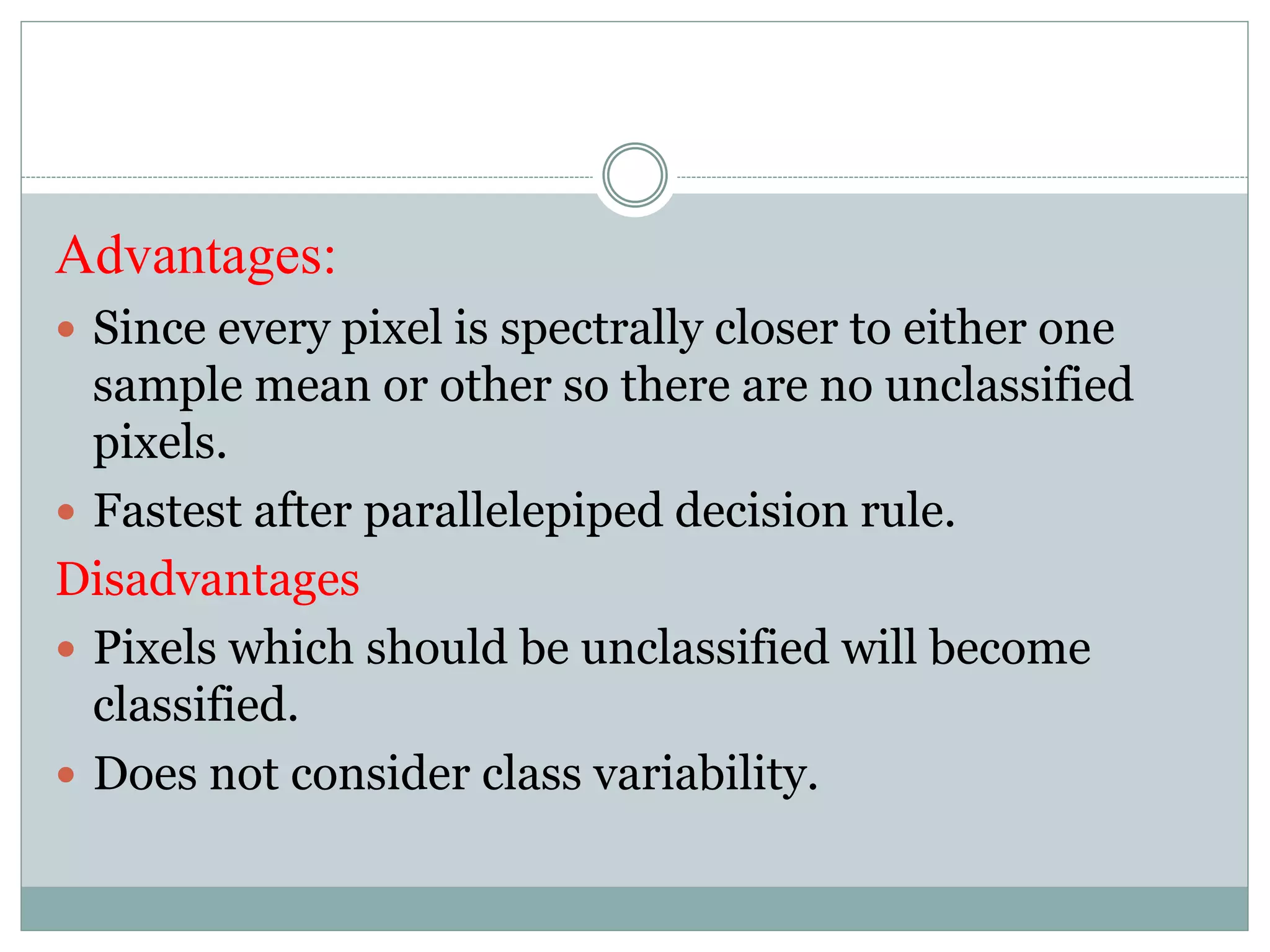
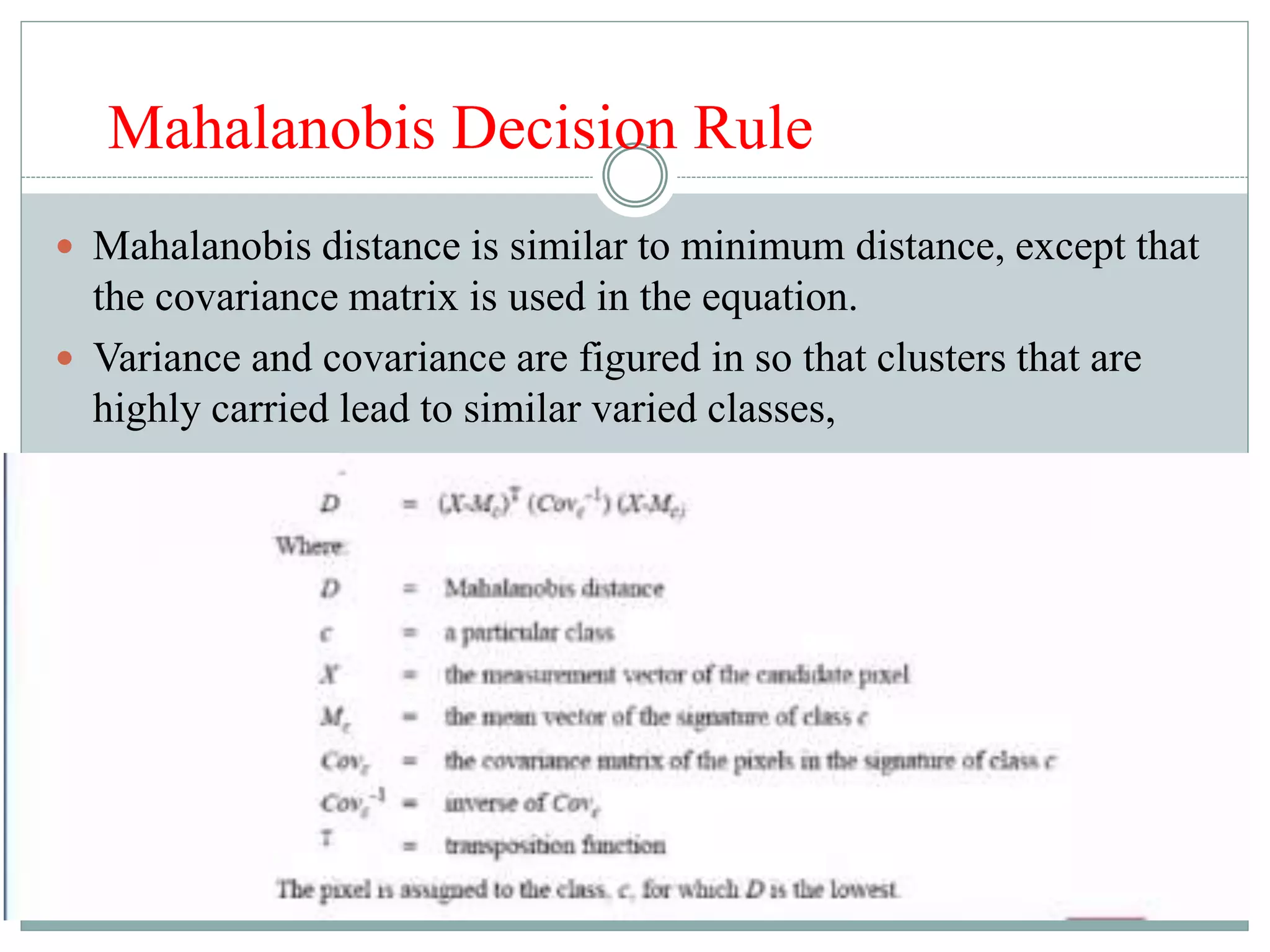
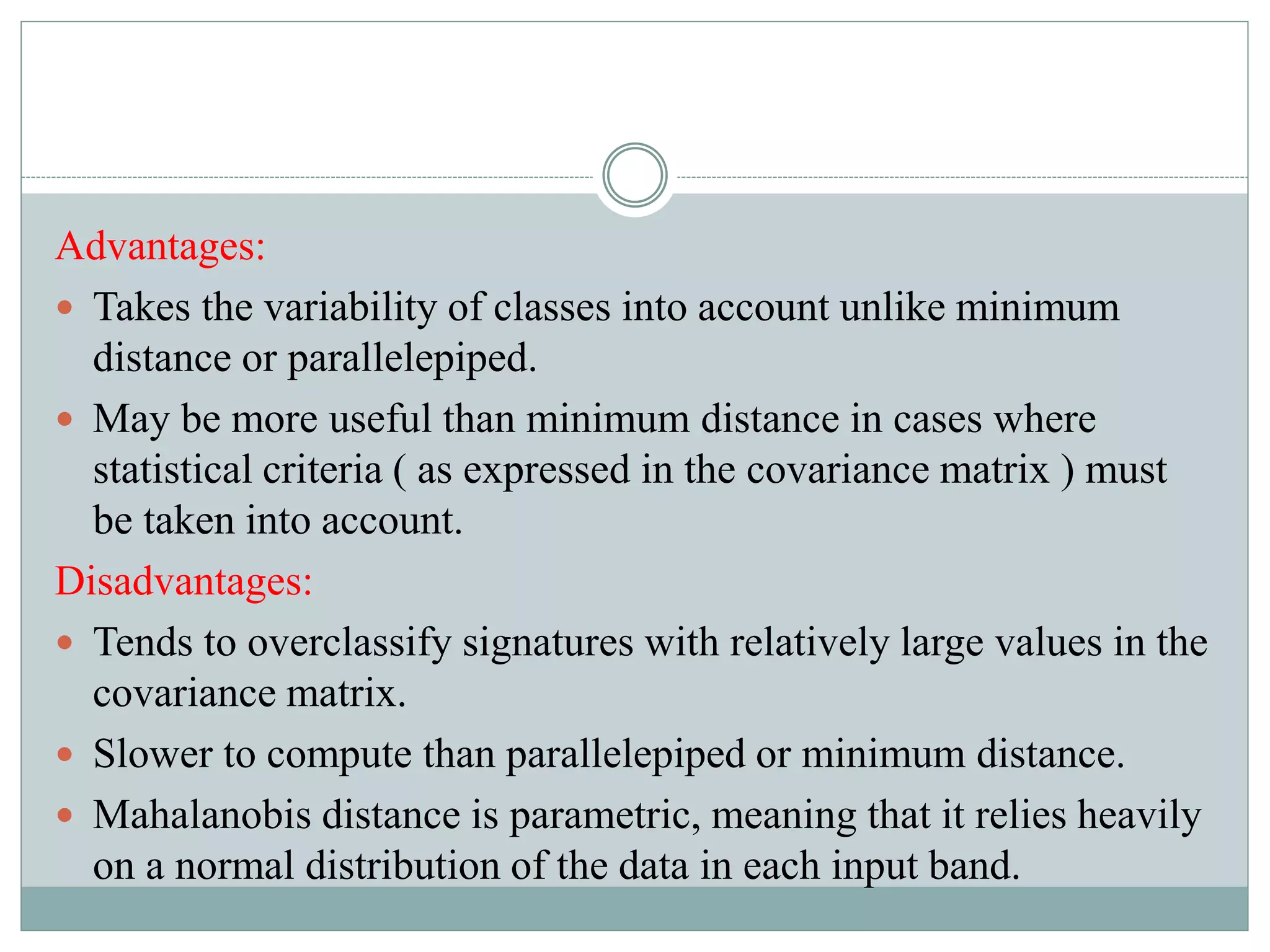
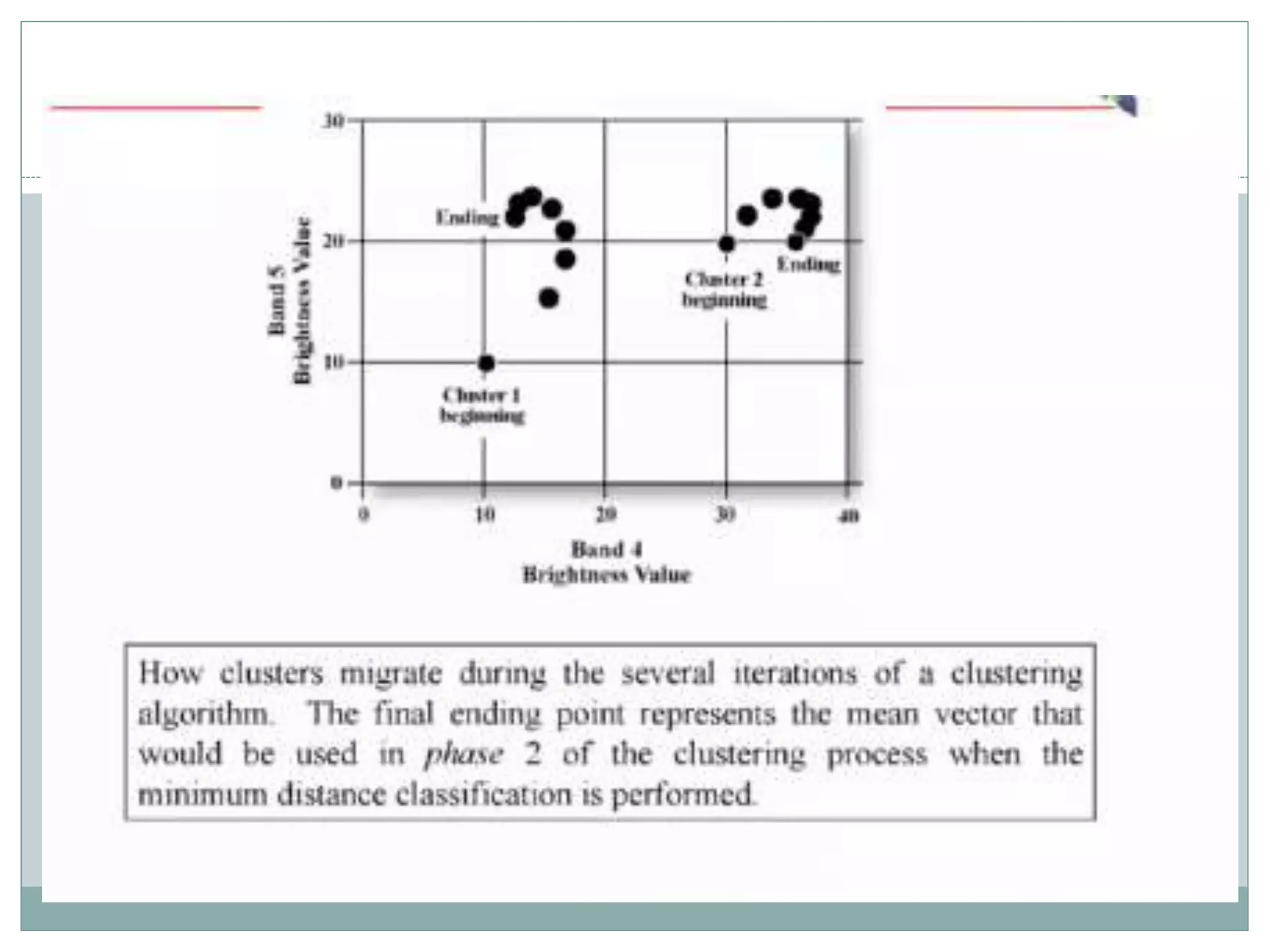
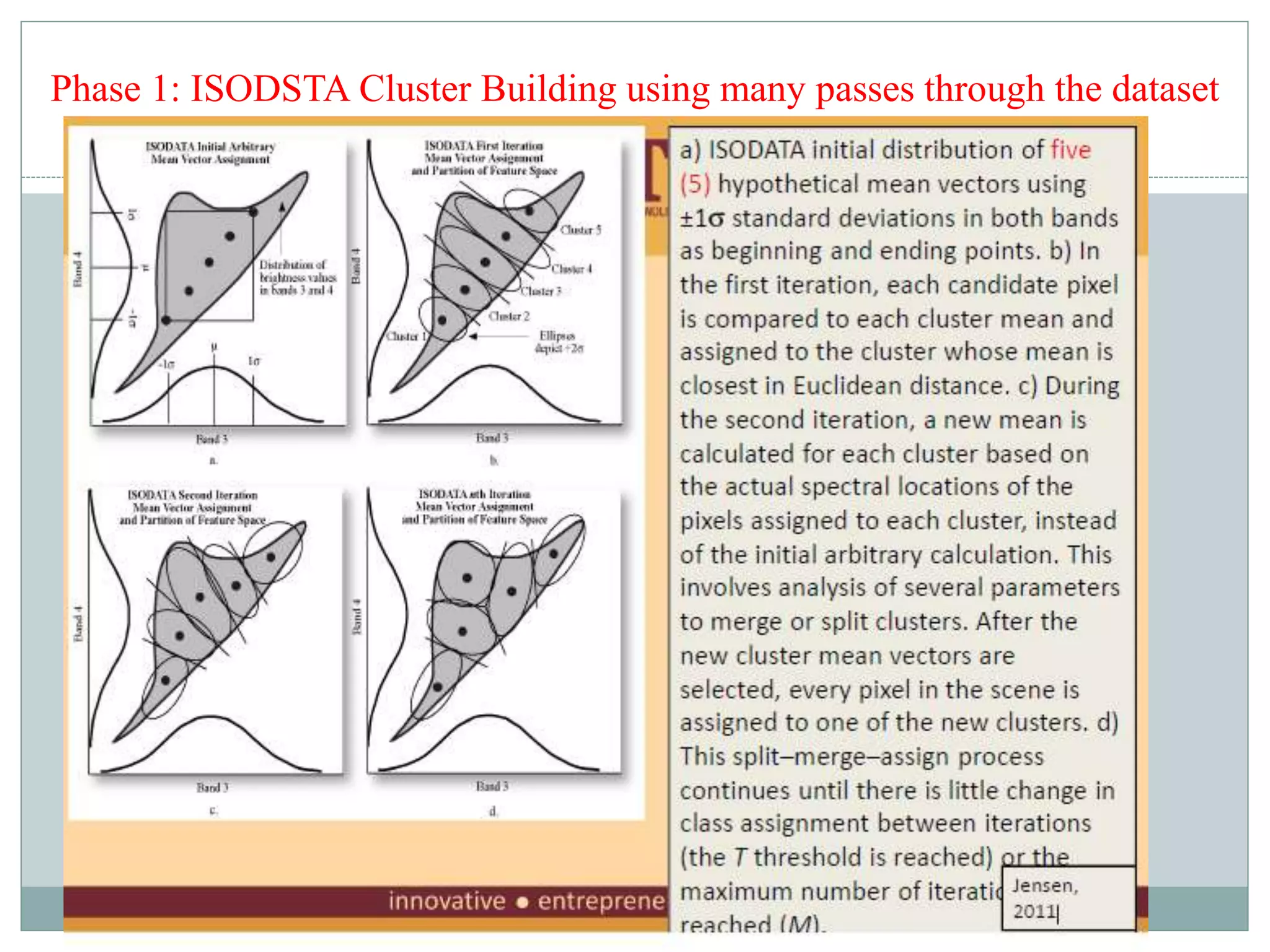
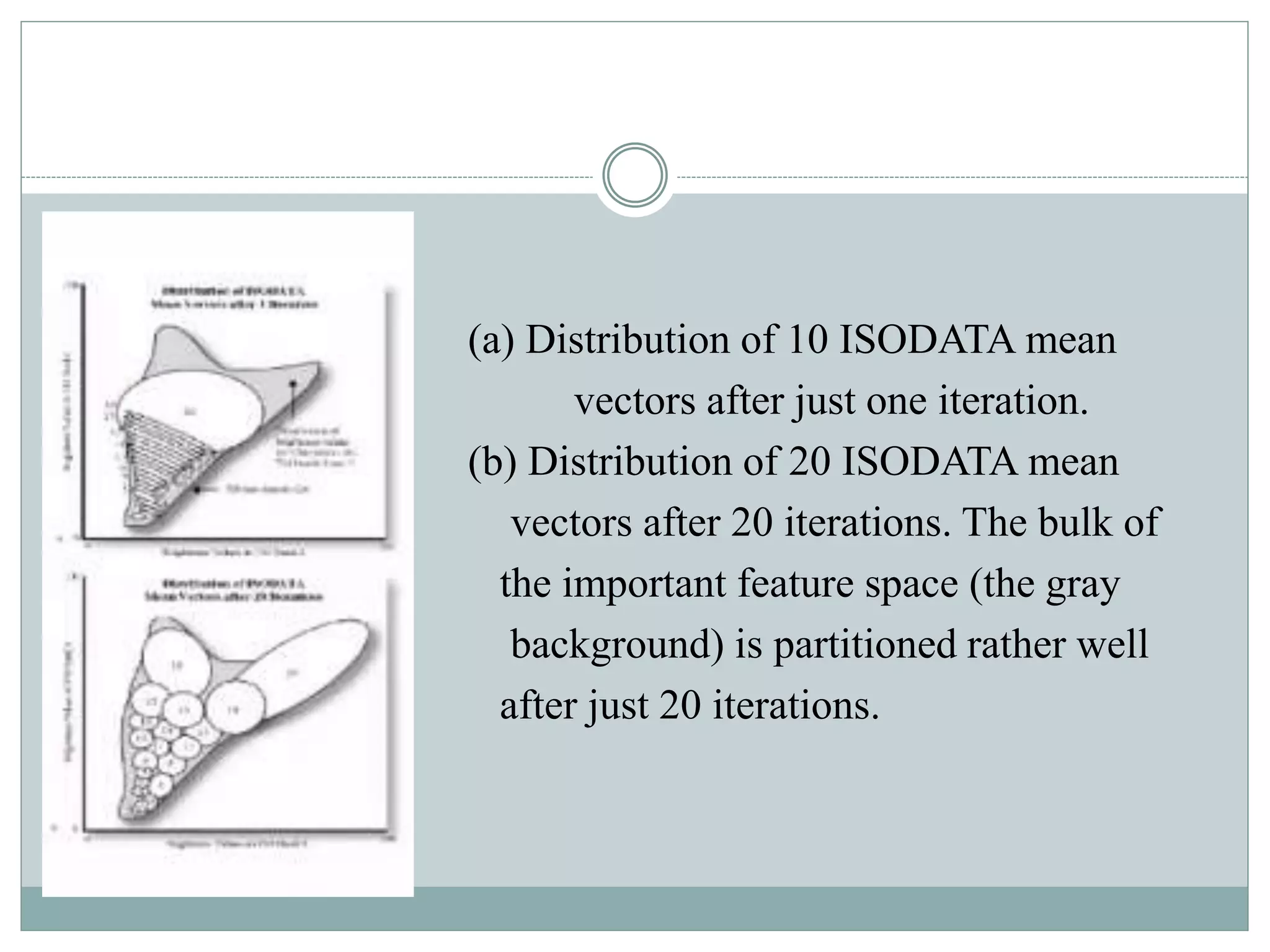
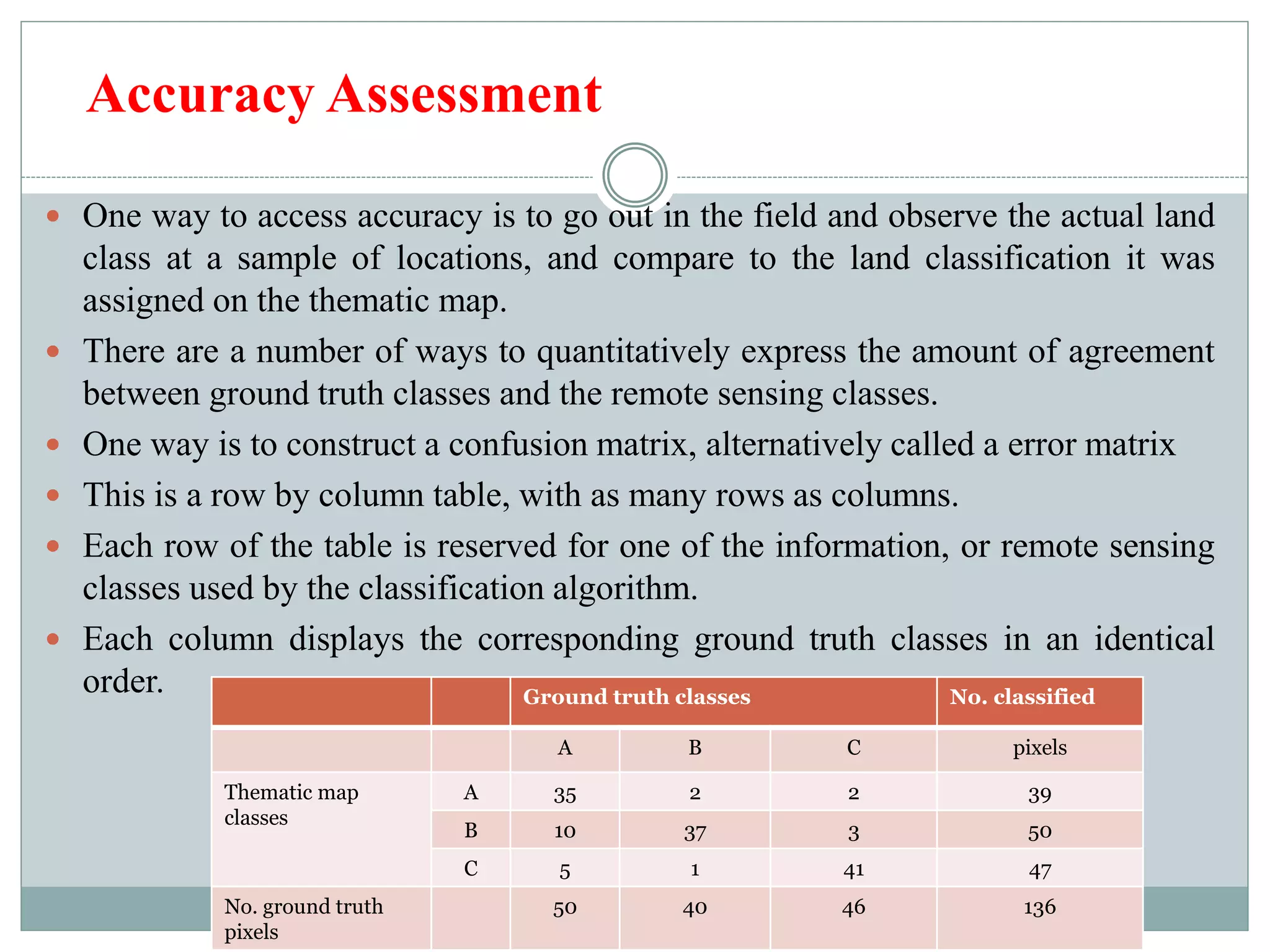
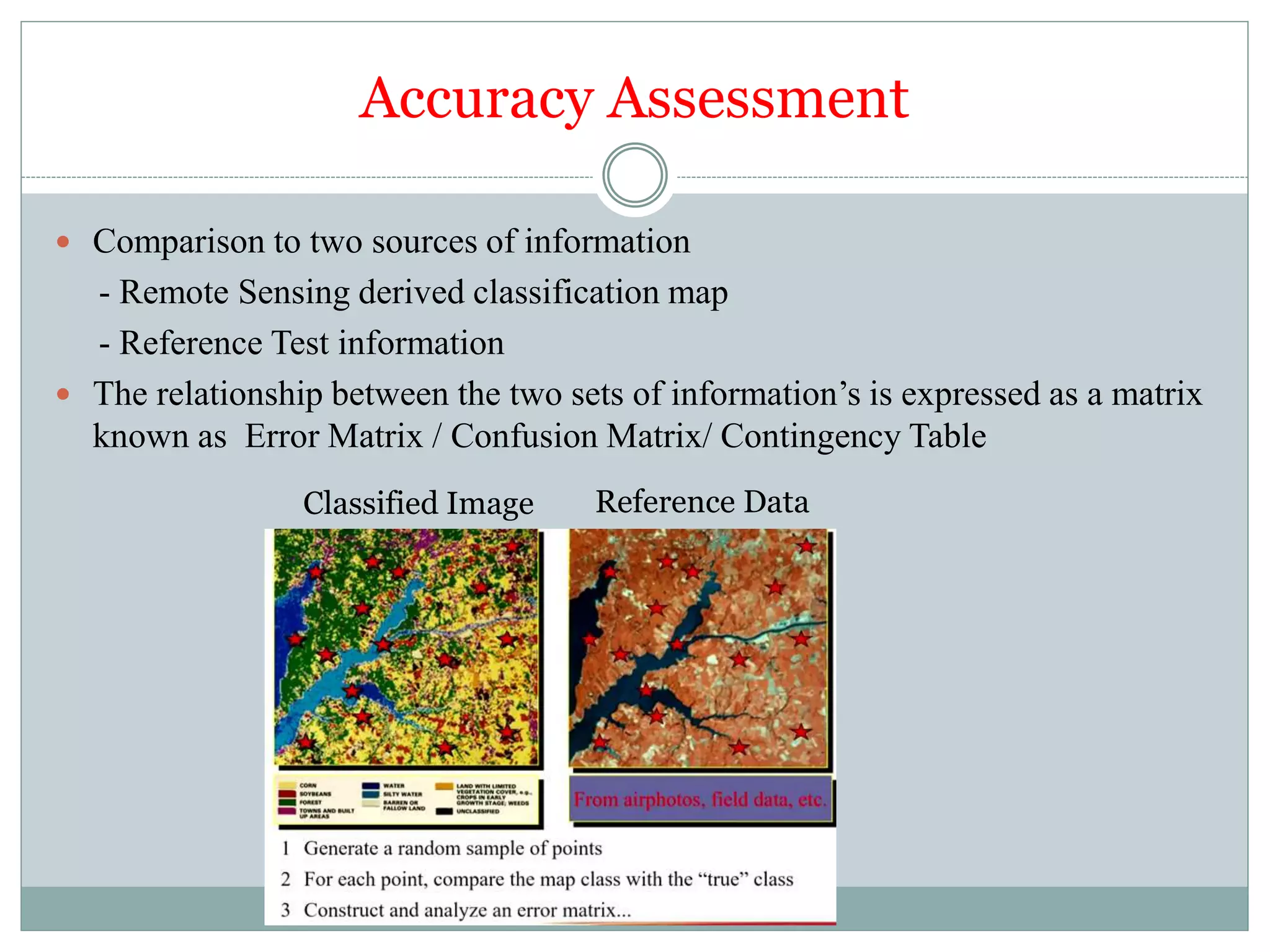
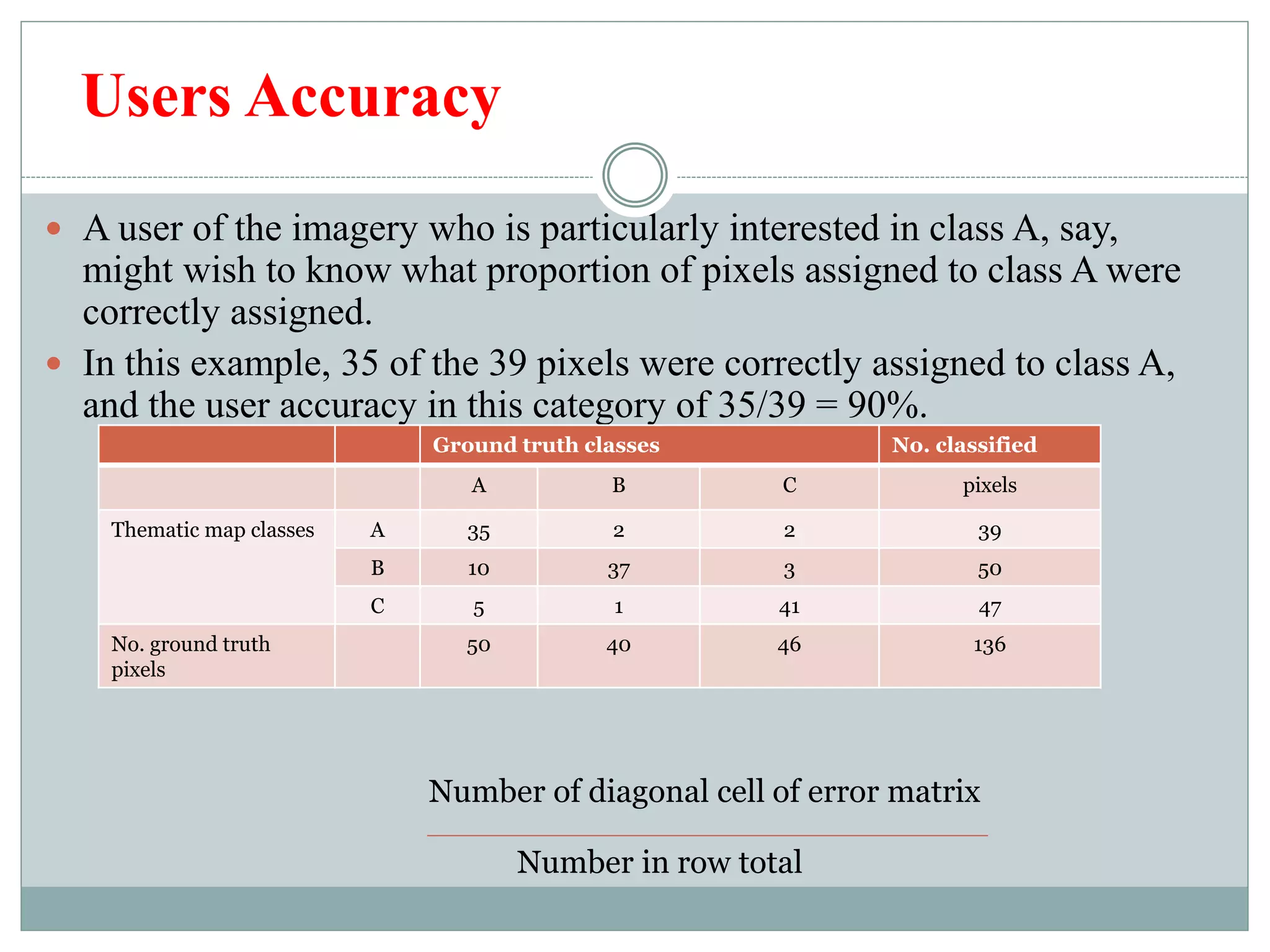
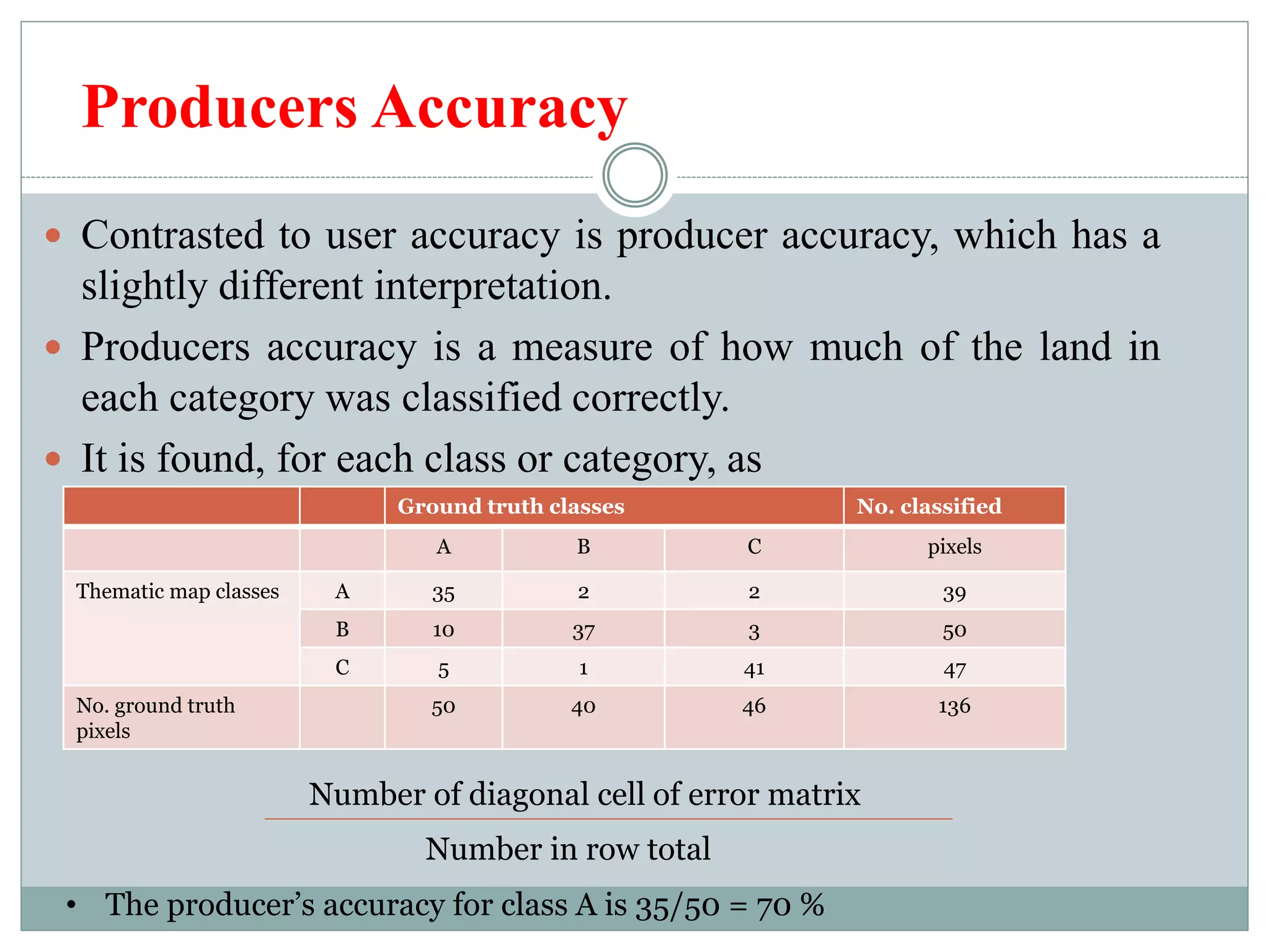
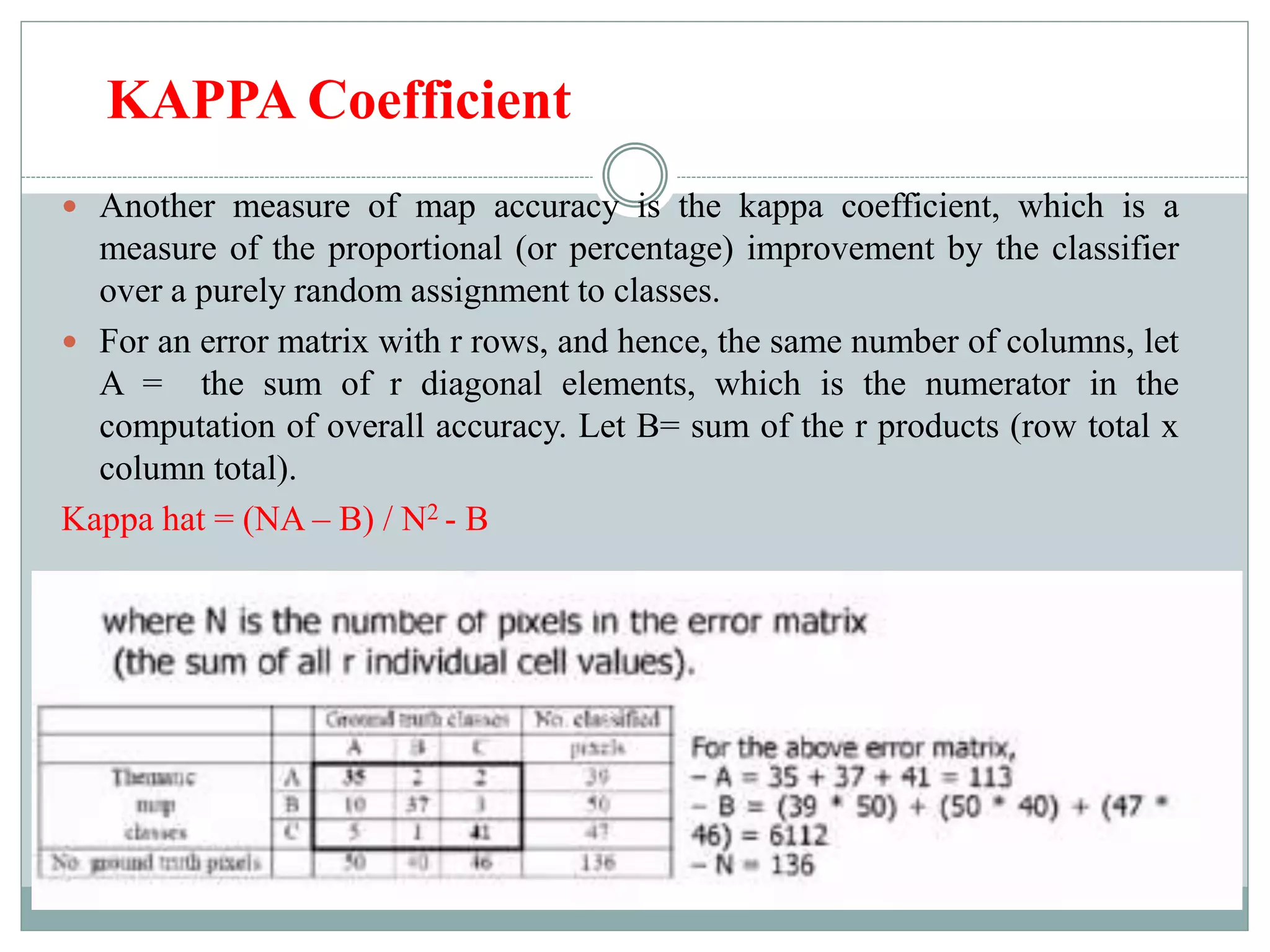
Digital image classification involves sorting pixels into discrete classes based on their spectral values. It can be performed using supervised or unsupervised approaches. Supervised classification involves using training data to define classes, while unsupervised classification uses algorithms to automatically group similar pixels. Accuracy assessment involves comparing the classification to reference data to determine accuracy through an error matrix.