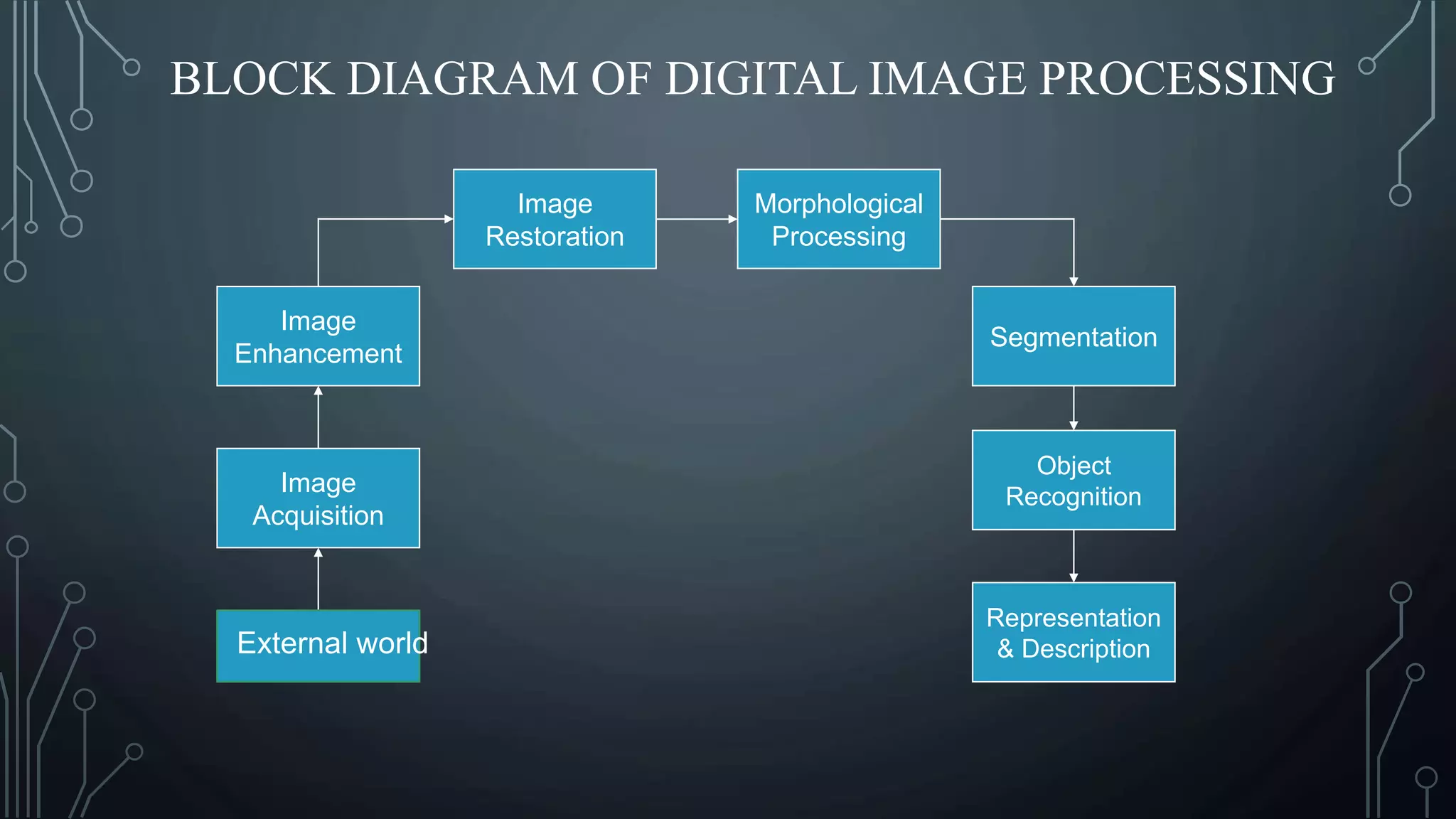
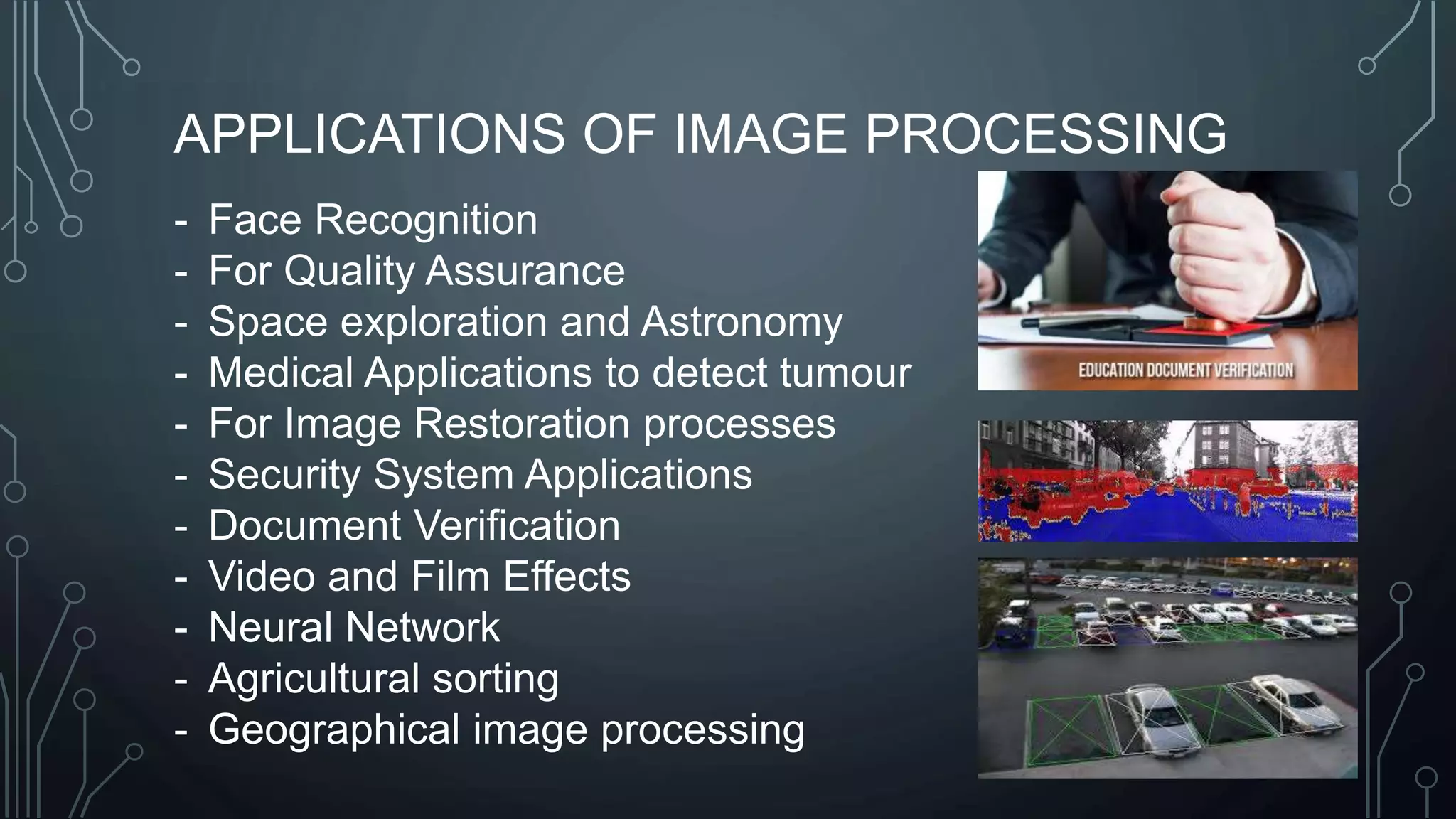
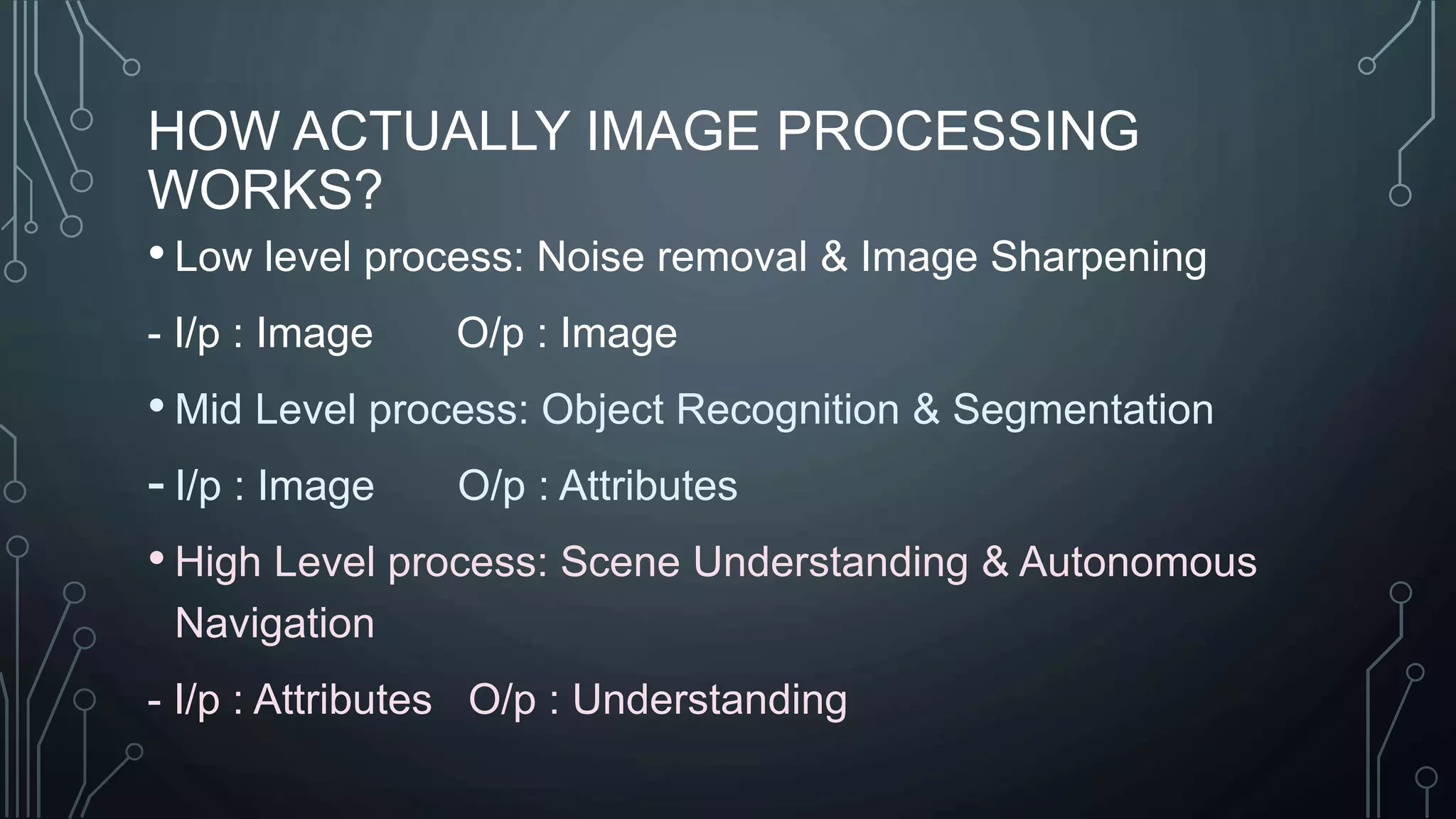
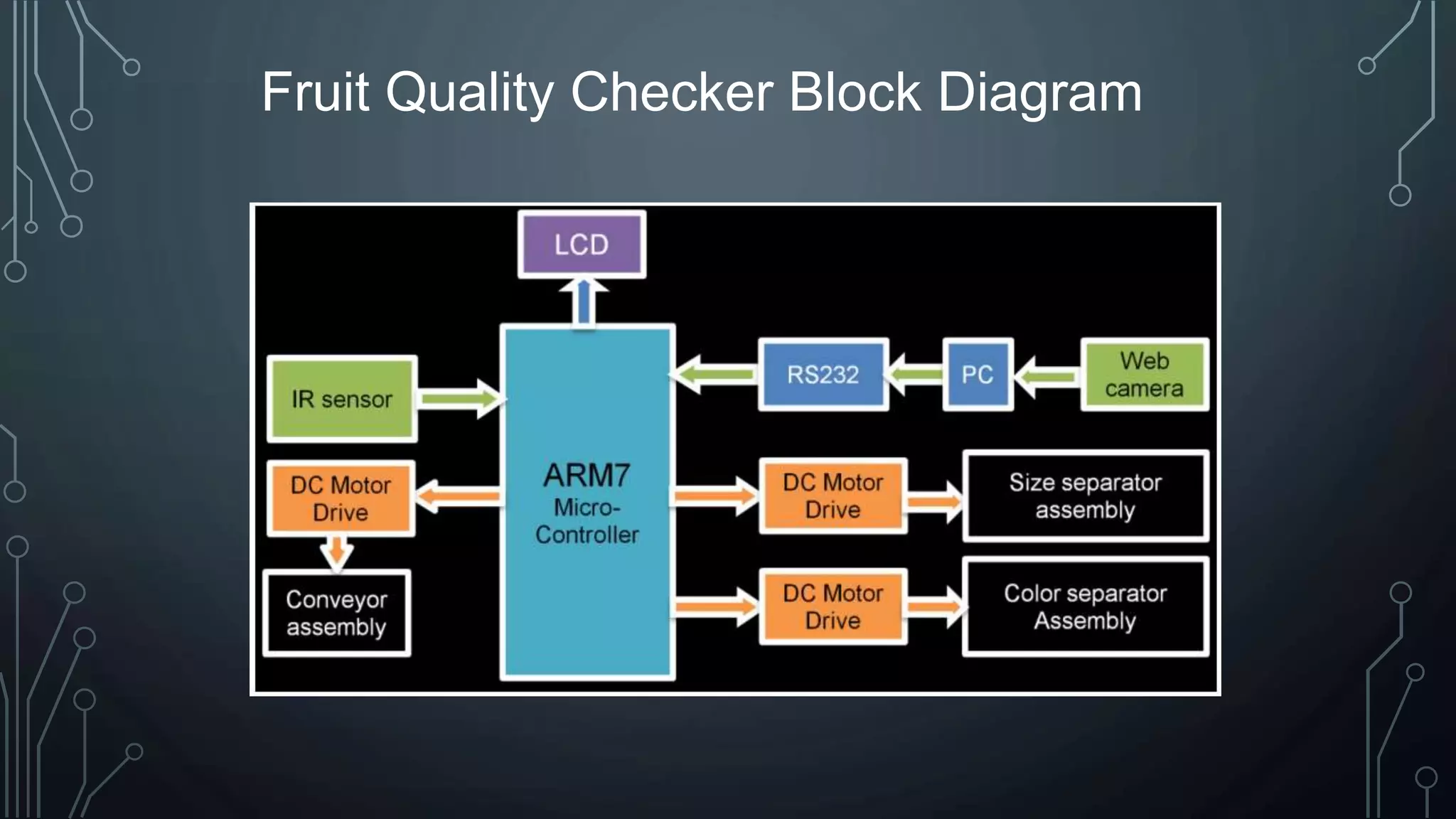
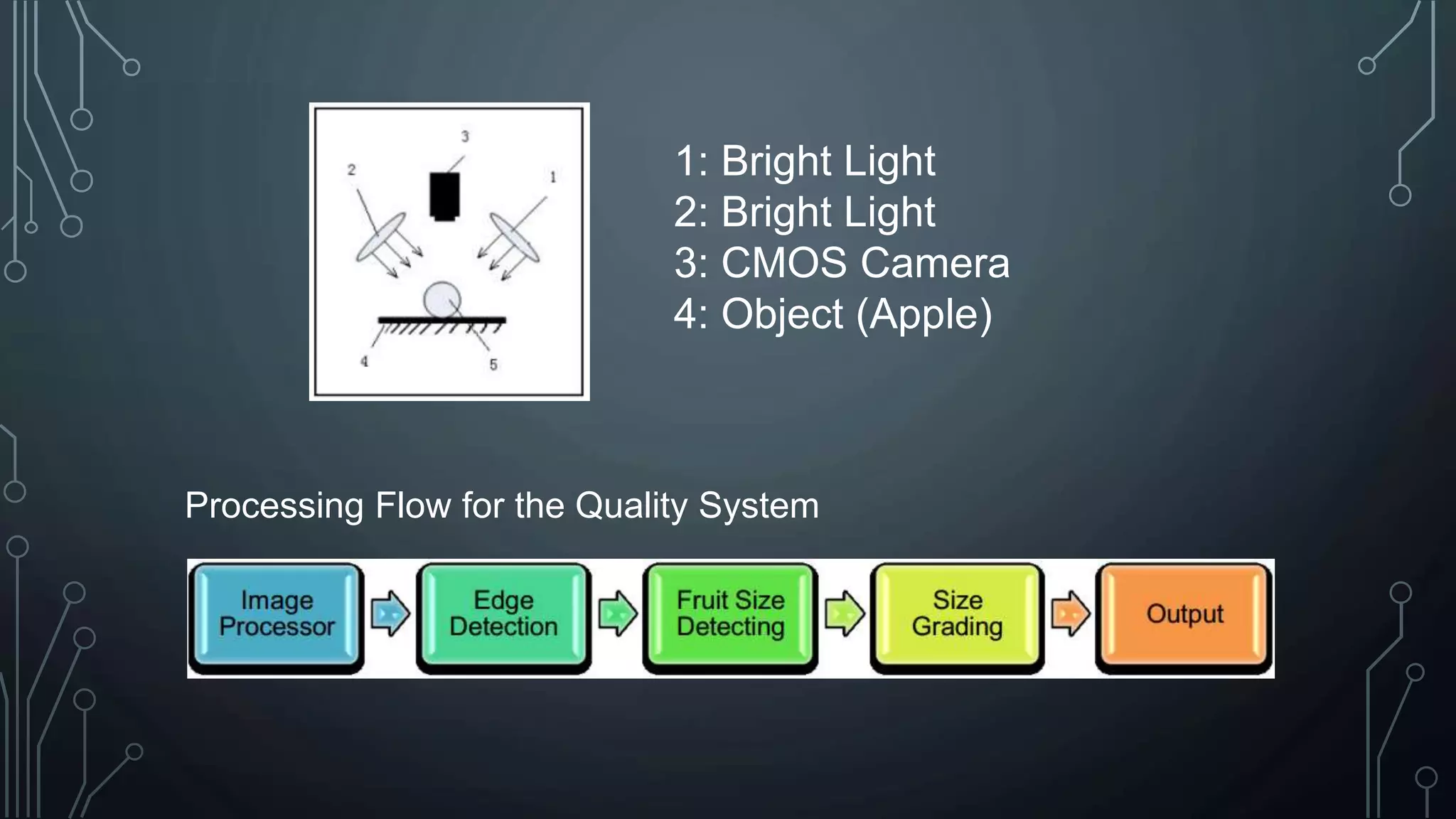
The document discusses digital image processing utilizing MATLAB with Arduino, highlighting key concepts such as digital images, processing methods, classification, and algorithms for applications like fruit sorting and face detection. It outlines various processes including image acquisition, enhancement, morphological processing, and object recognition. Additionally, it covers practical applications in multiple fields such as medical imaging, security systems, and agricultural sorting.











![BIBLIOGRAPHY
• Gonzalez and Woods, Digital Image Processing. Pearson Education Inc.
• Rudra Pratap, Getting Started With MATLAB, Oxford University.
• http://ivpl.eecs.northwestern.edu/research
• Image processing with Aggelos K. Katsaggelos [M.S., Ph.D. degrees in electrical
engineering from the Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalimageprocessingusingmatlabwitharduino1-180907210958/75/Digital-Image-Processing-using-MatLAB-with-Arduino-27-2048.jpg)