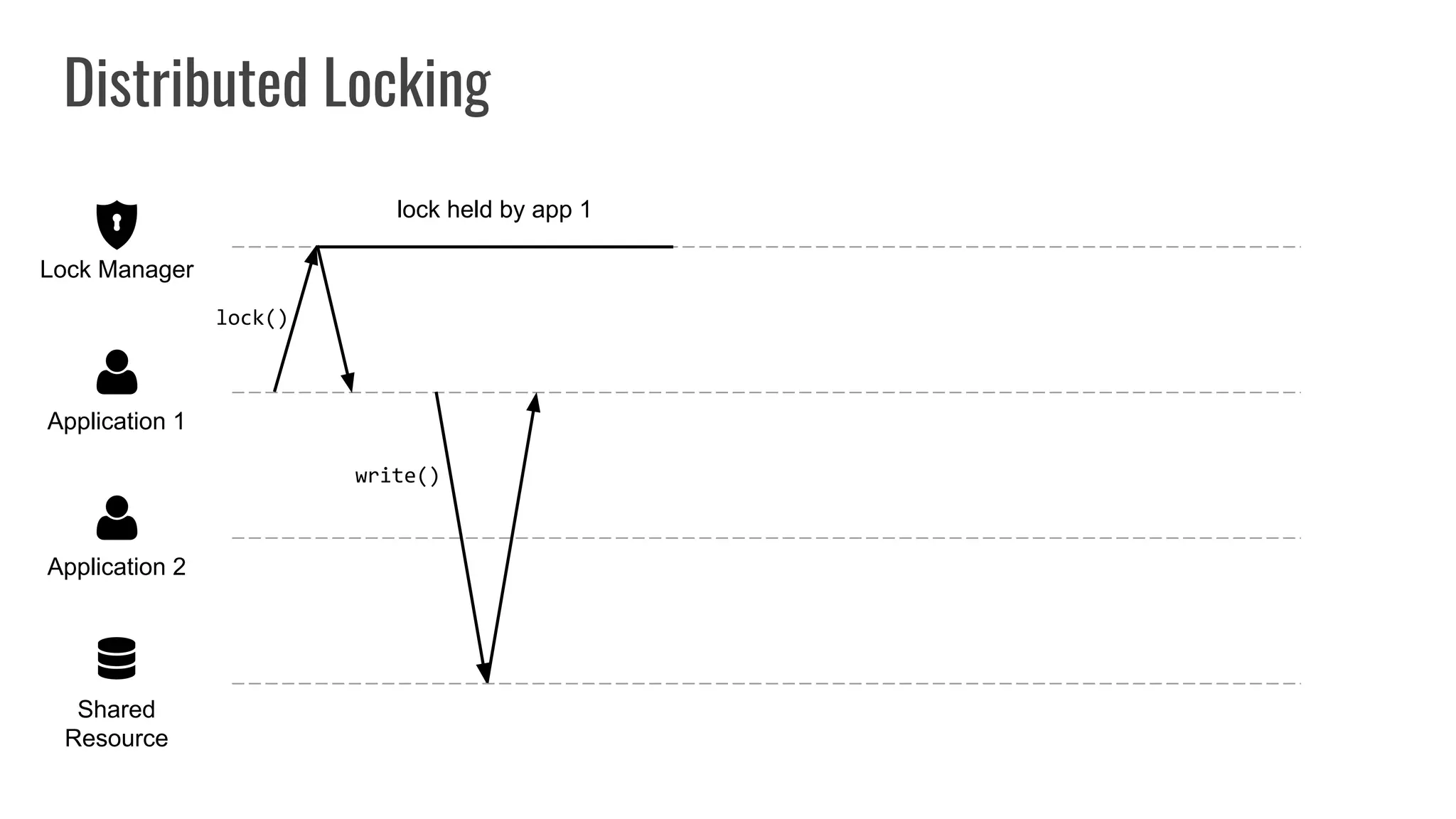
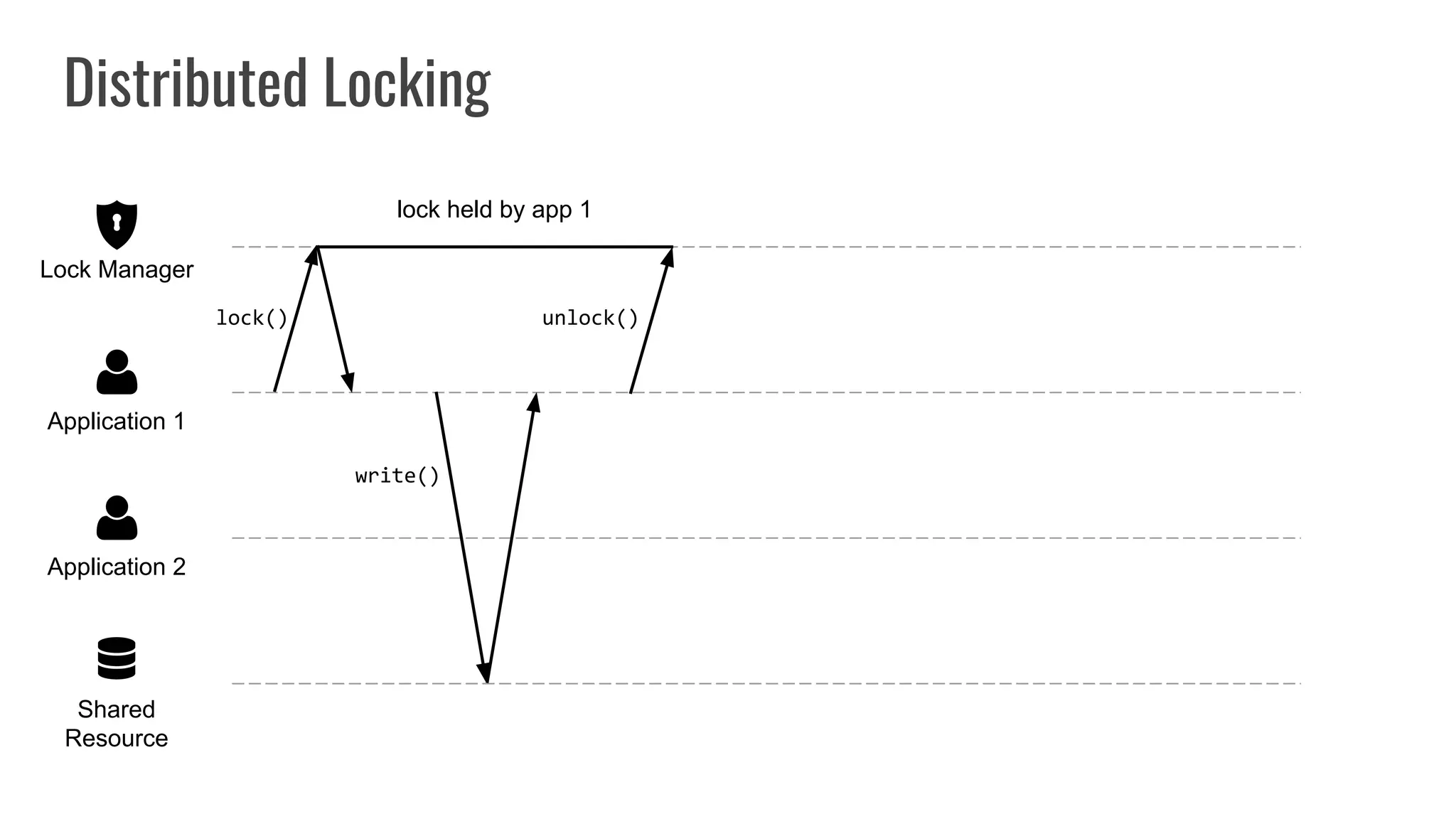
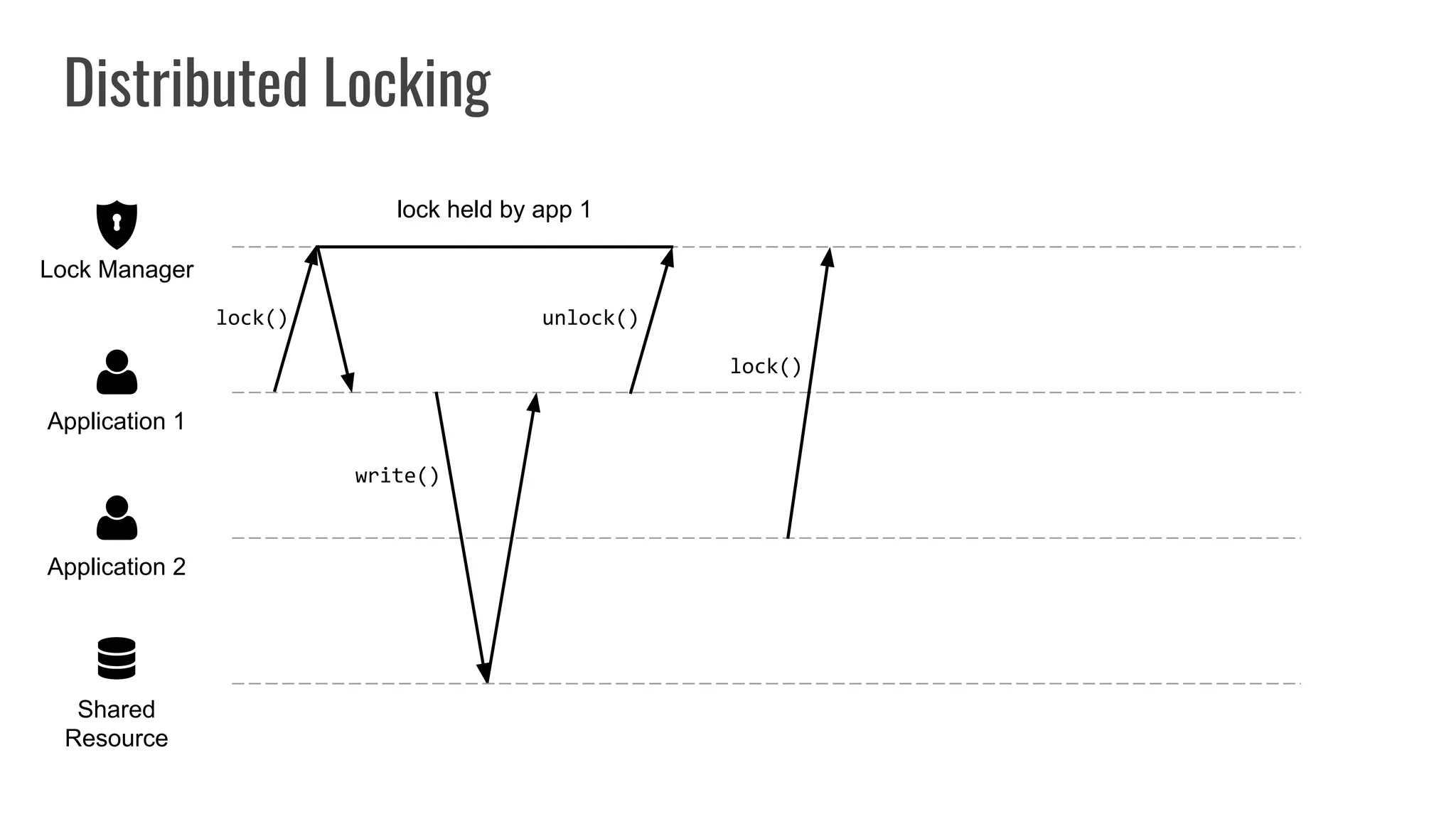
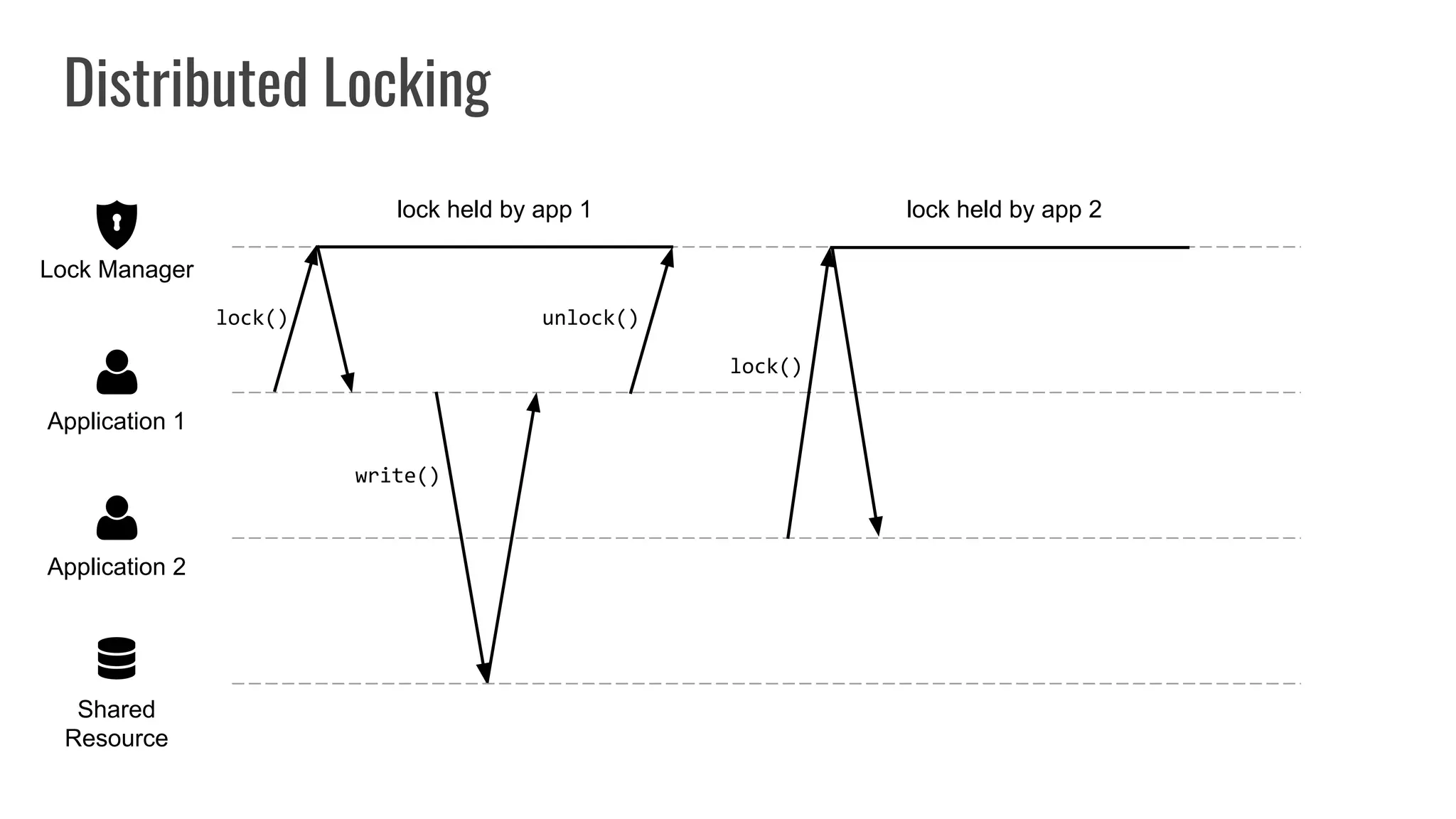
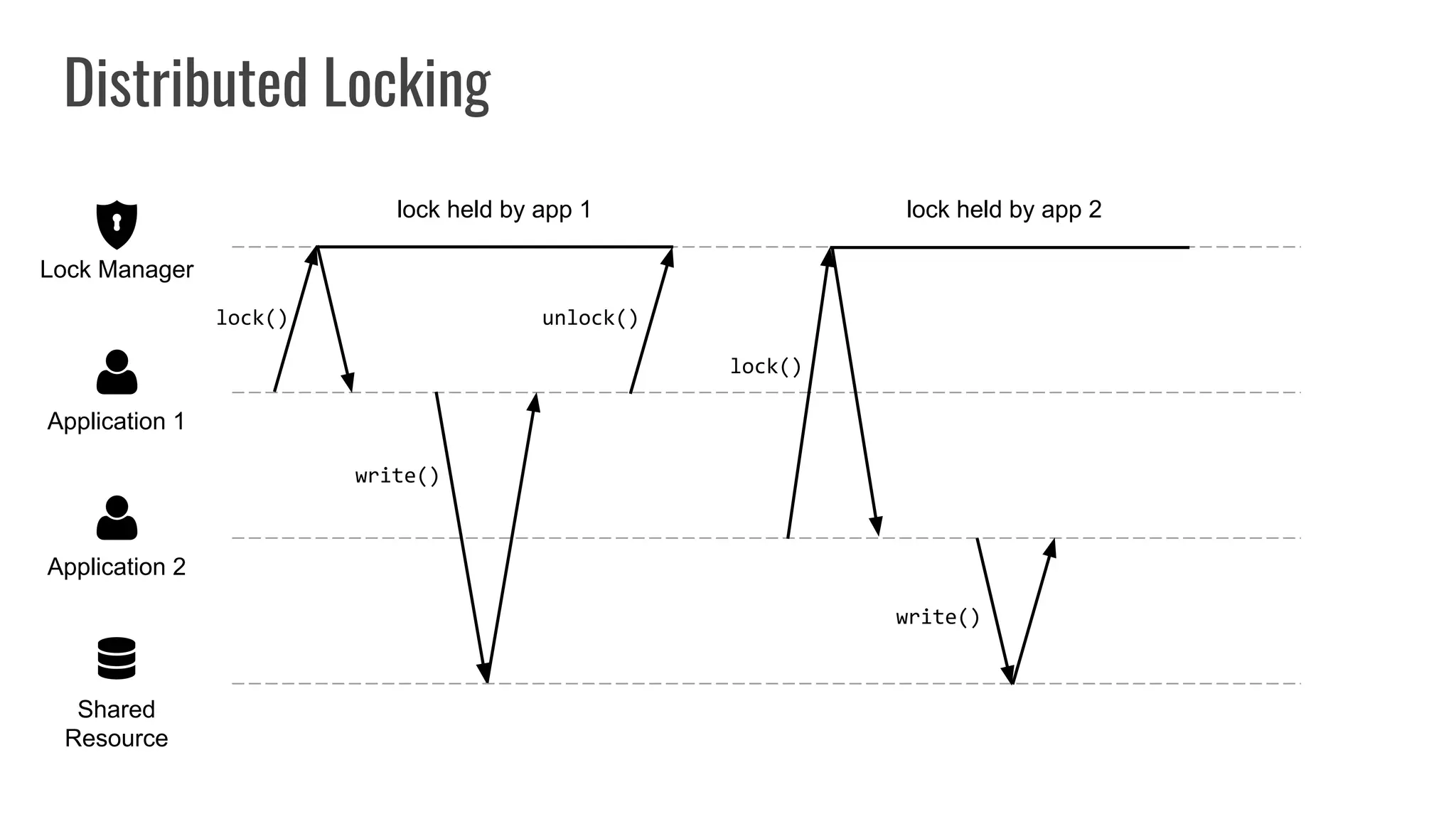
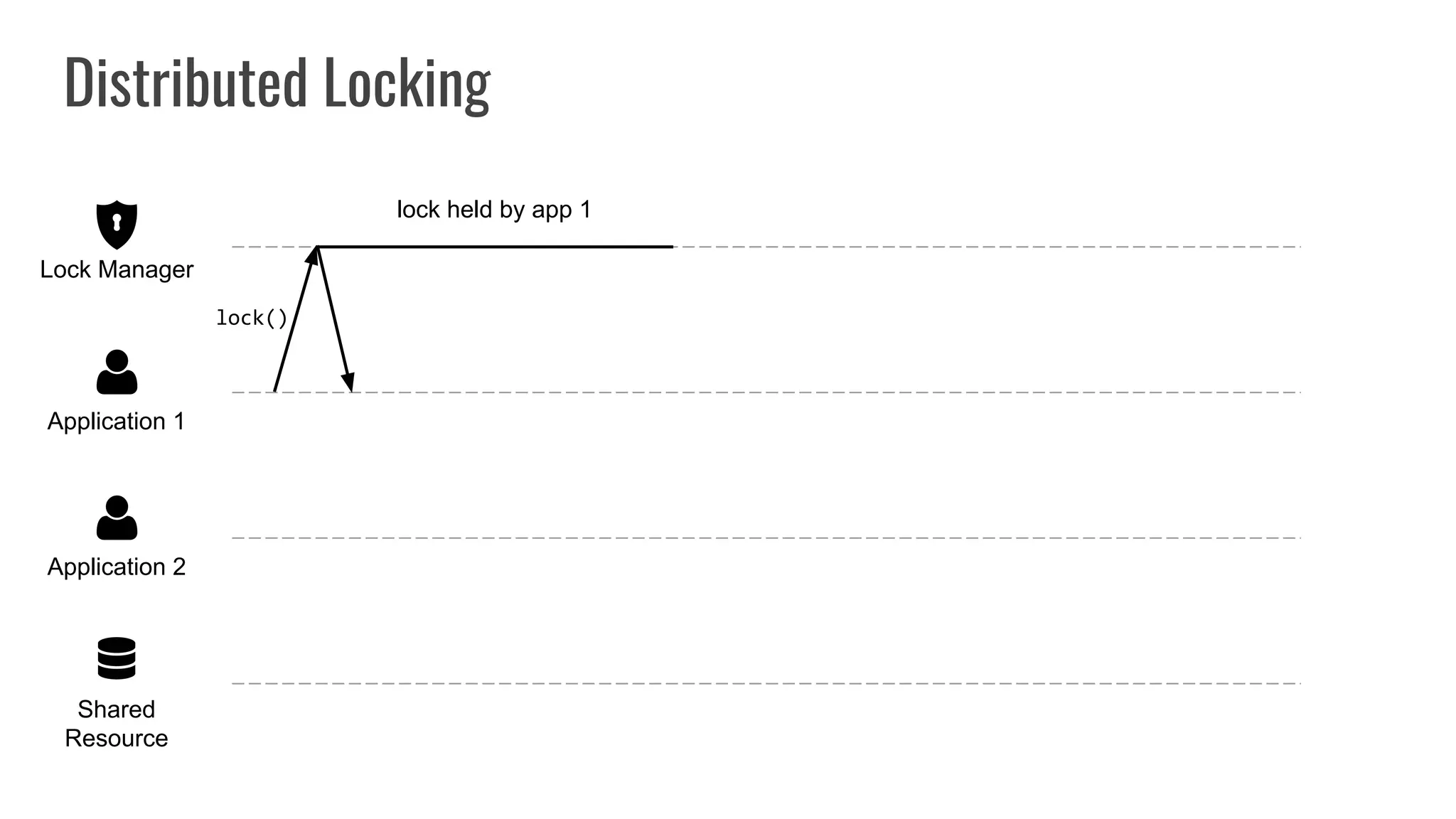
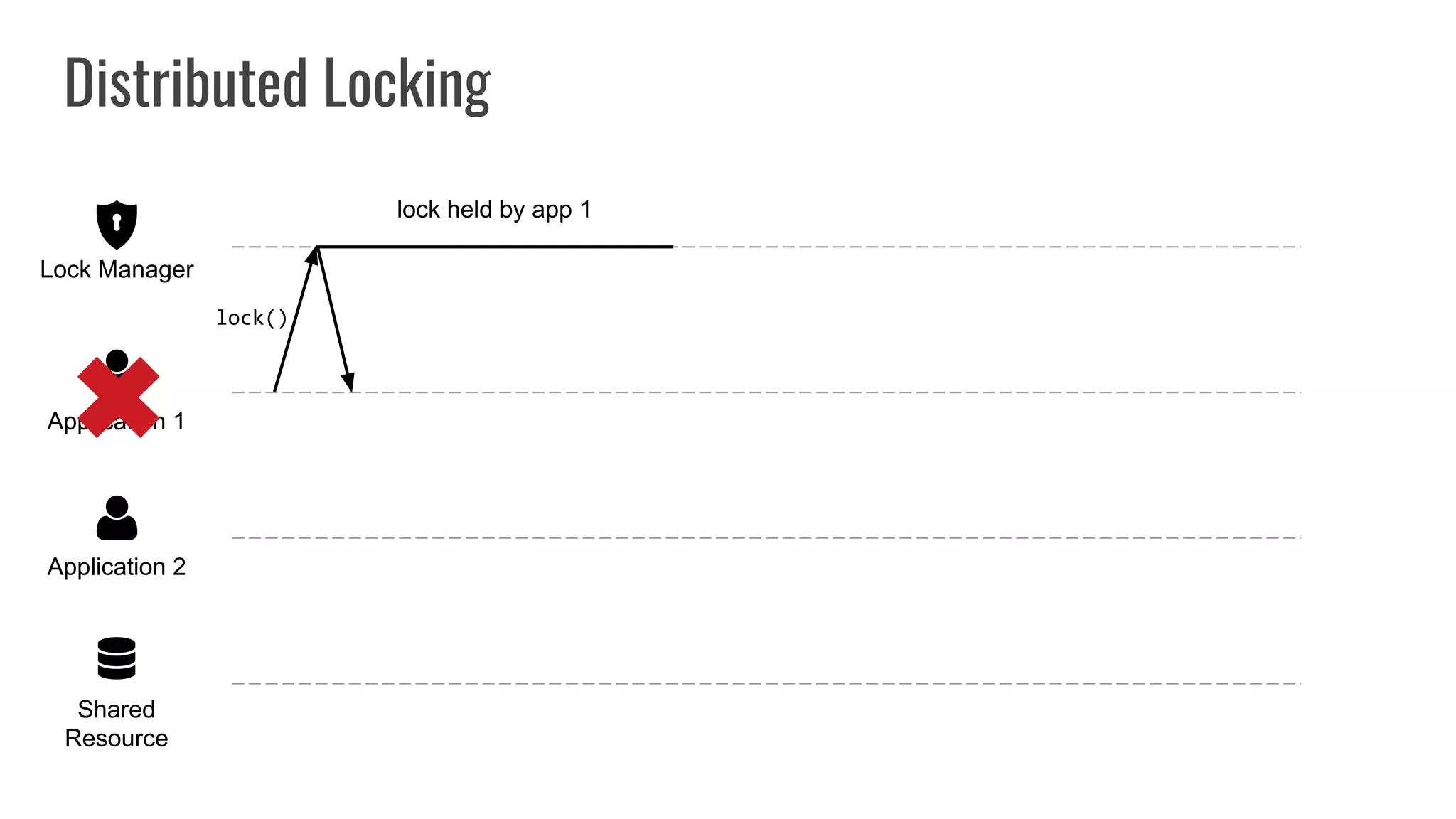
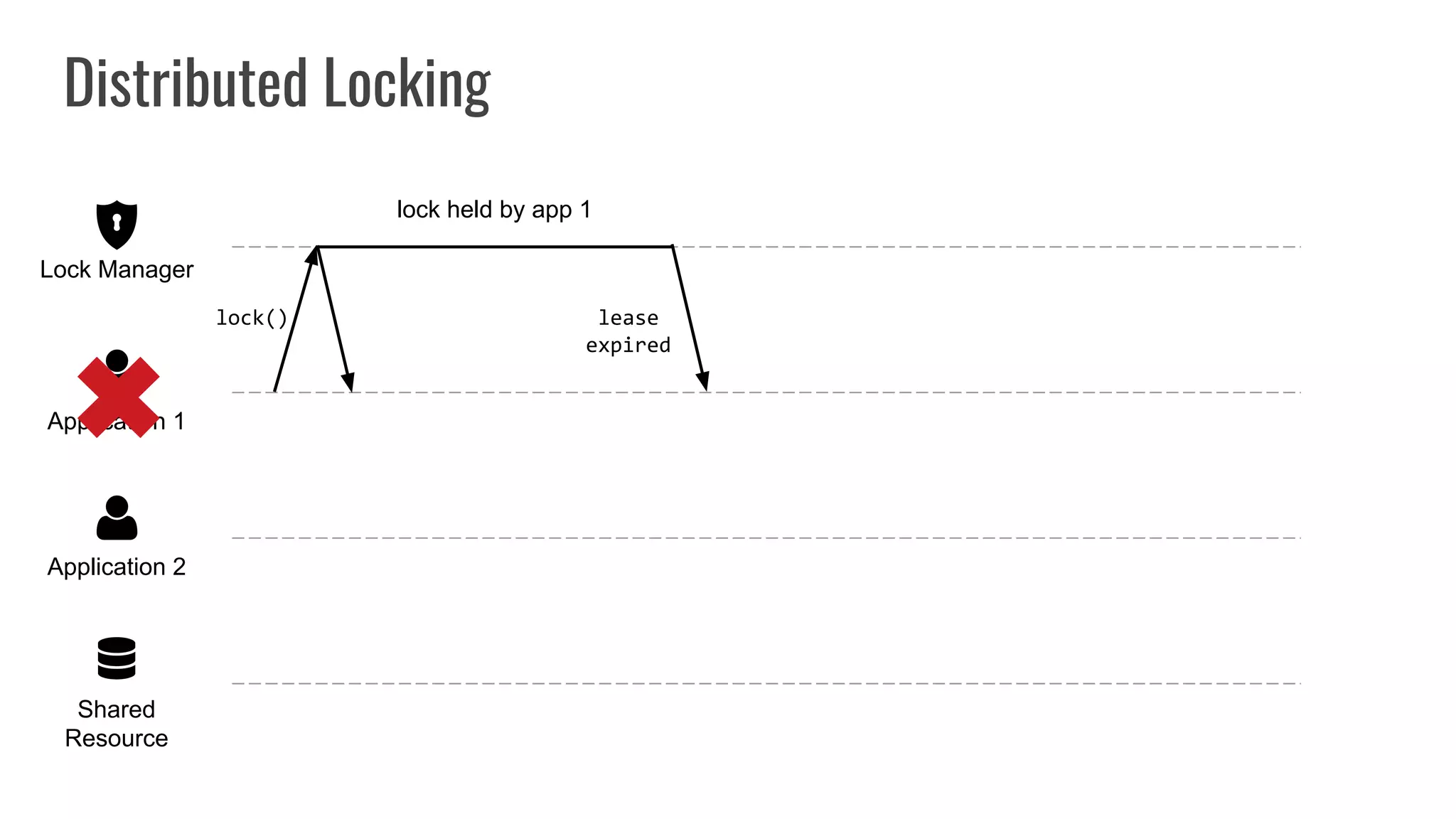
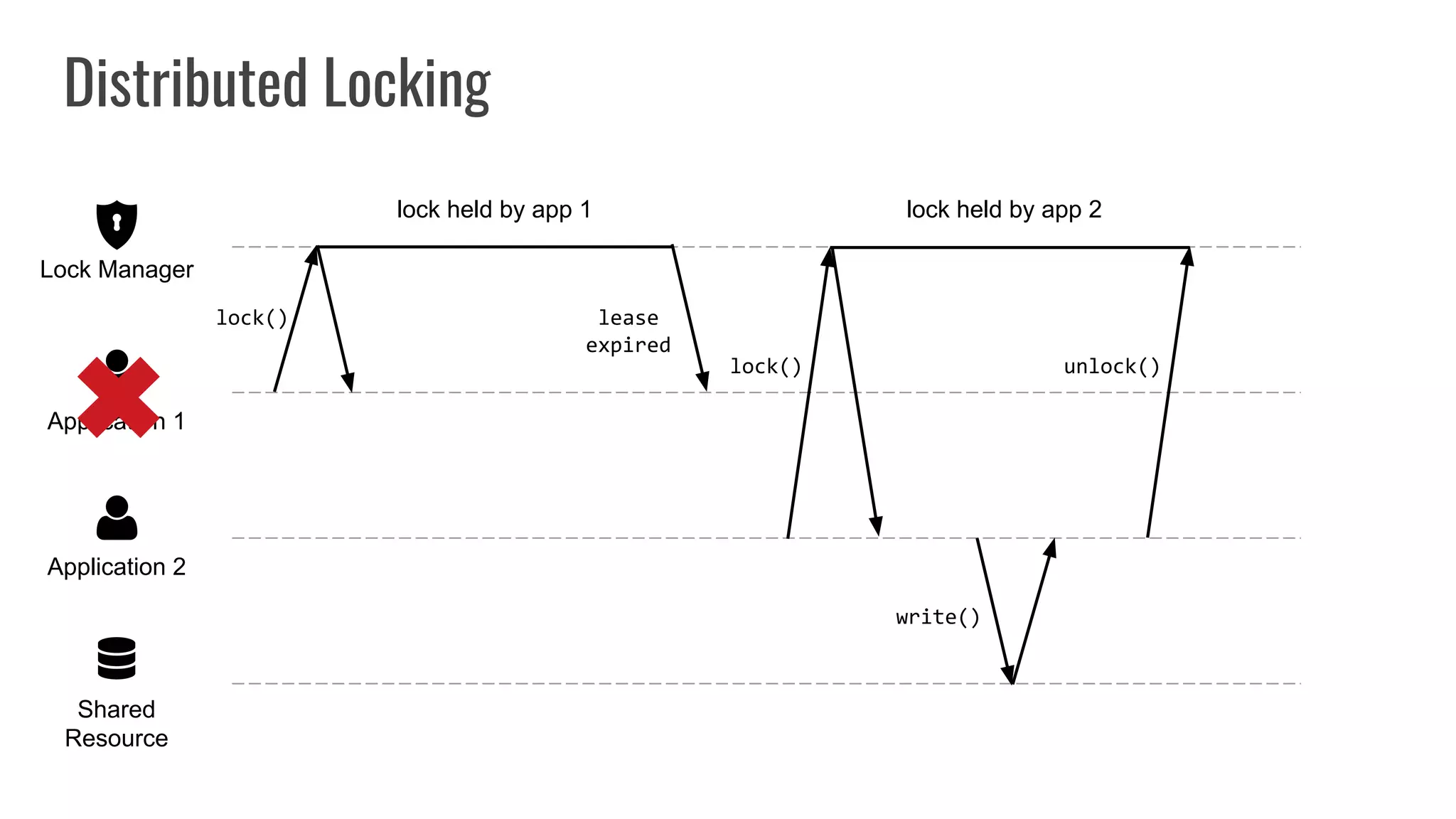
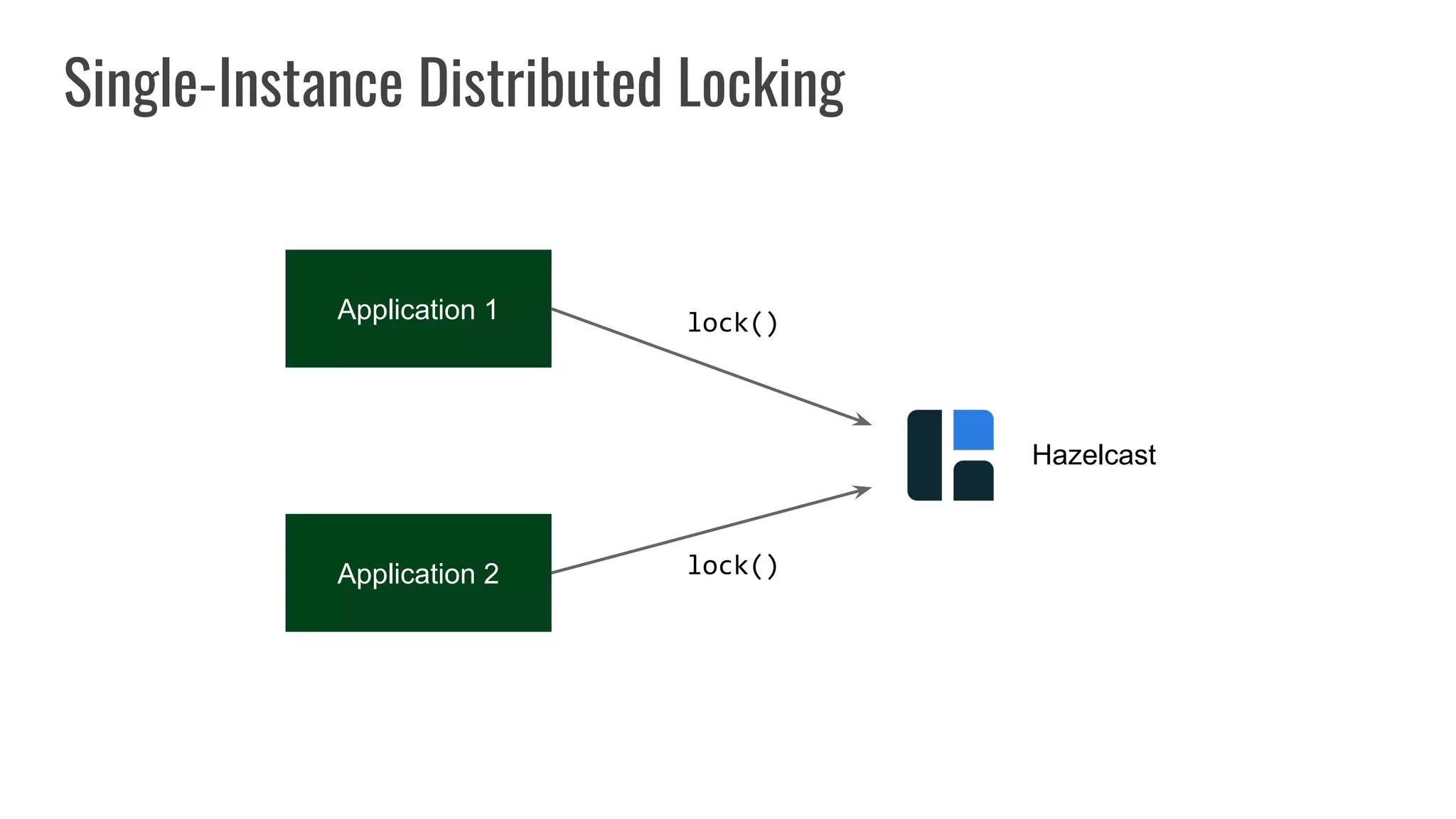
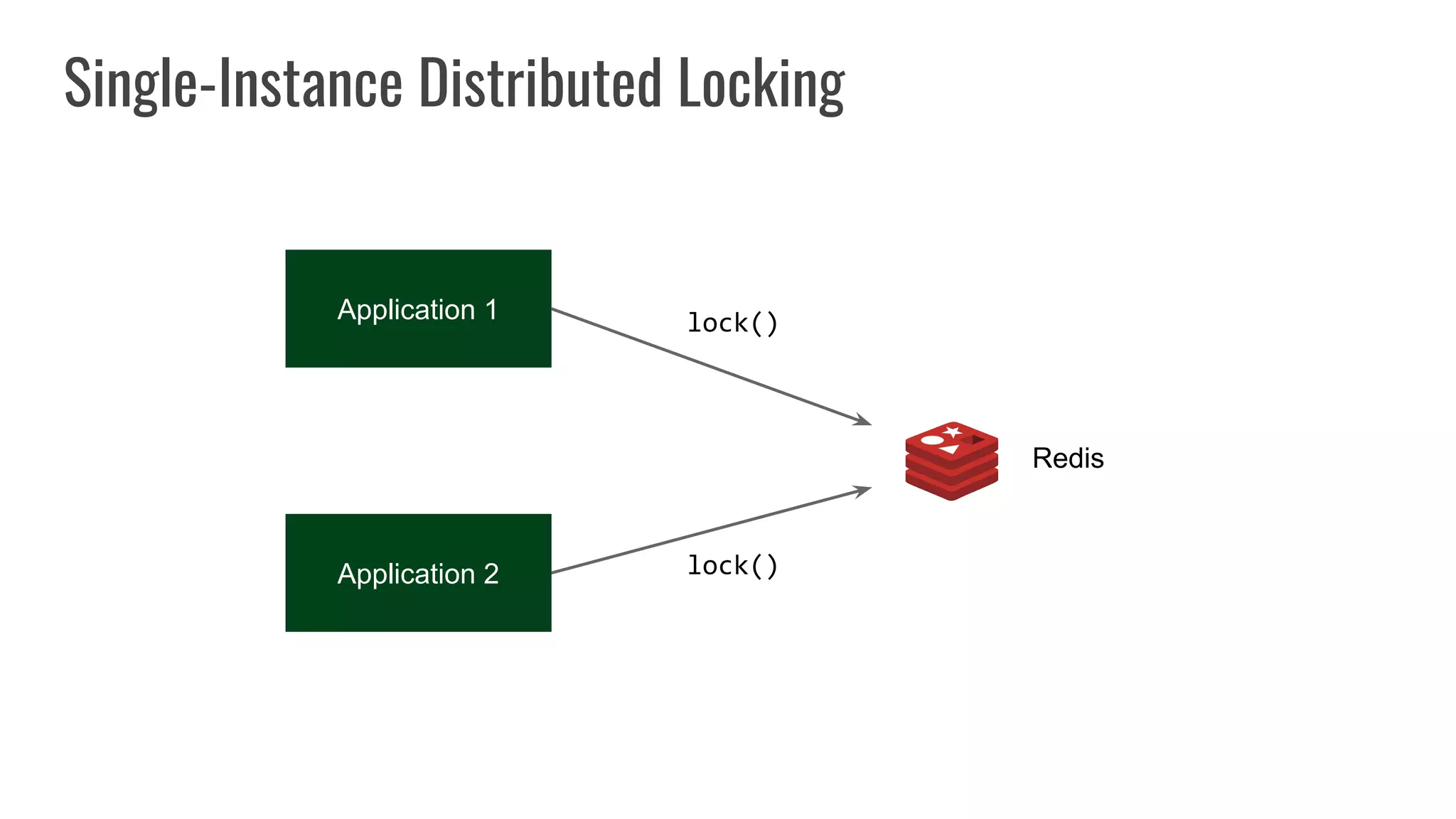
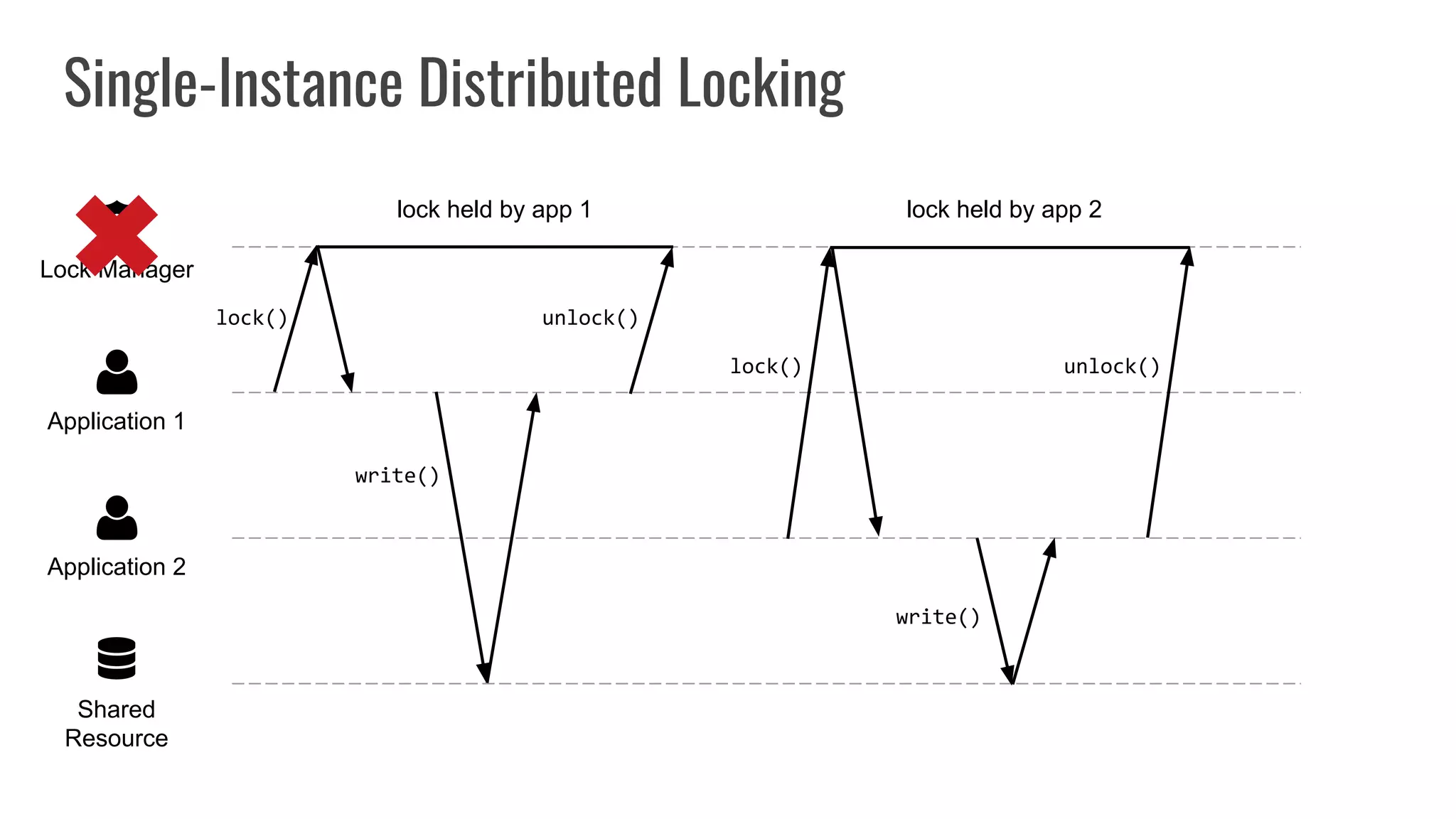
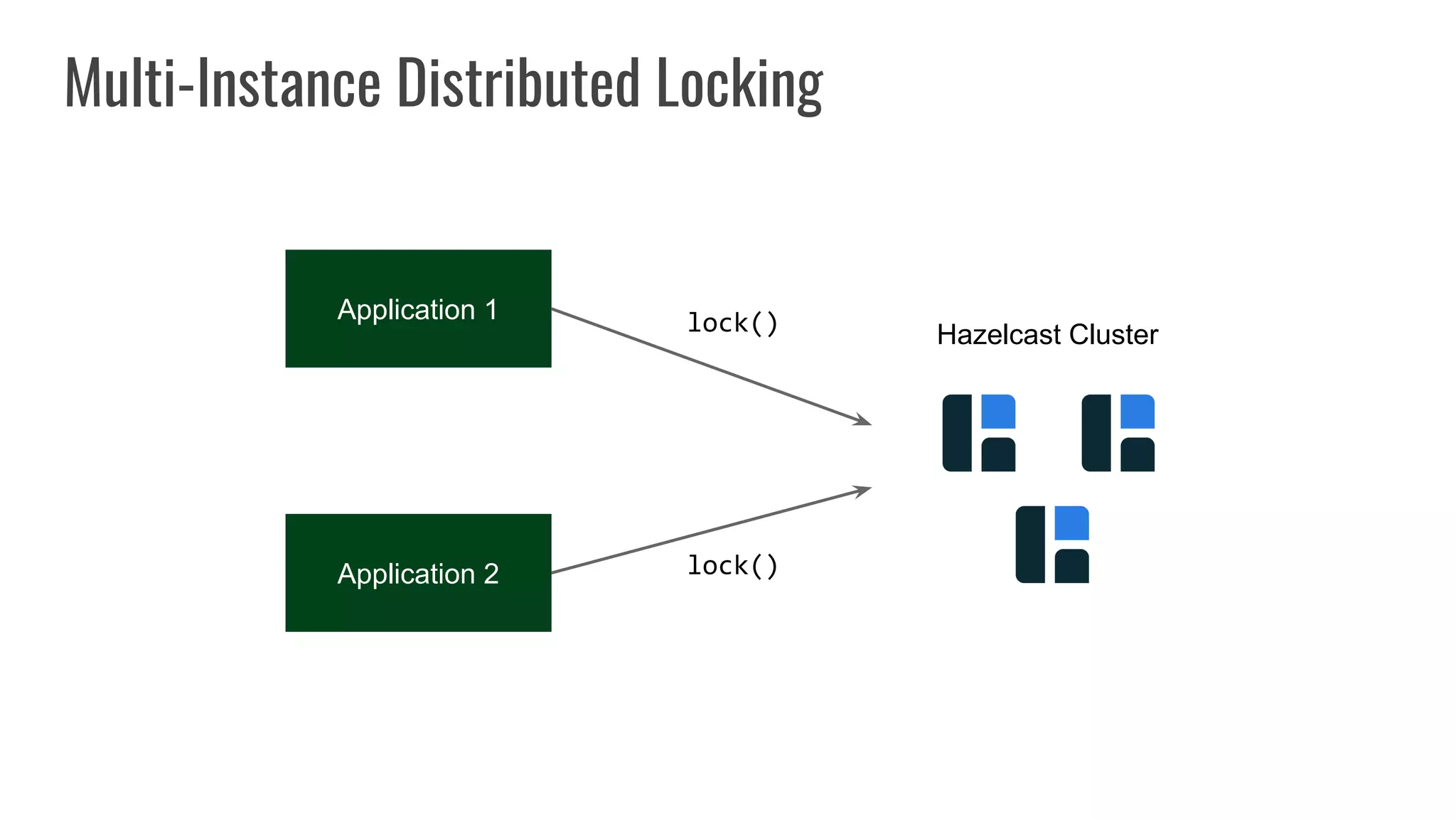
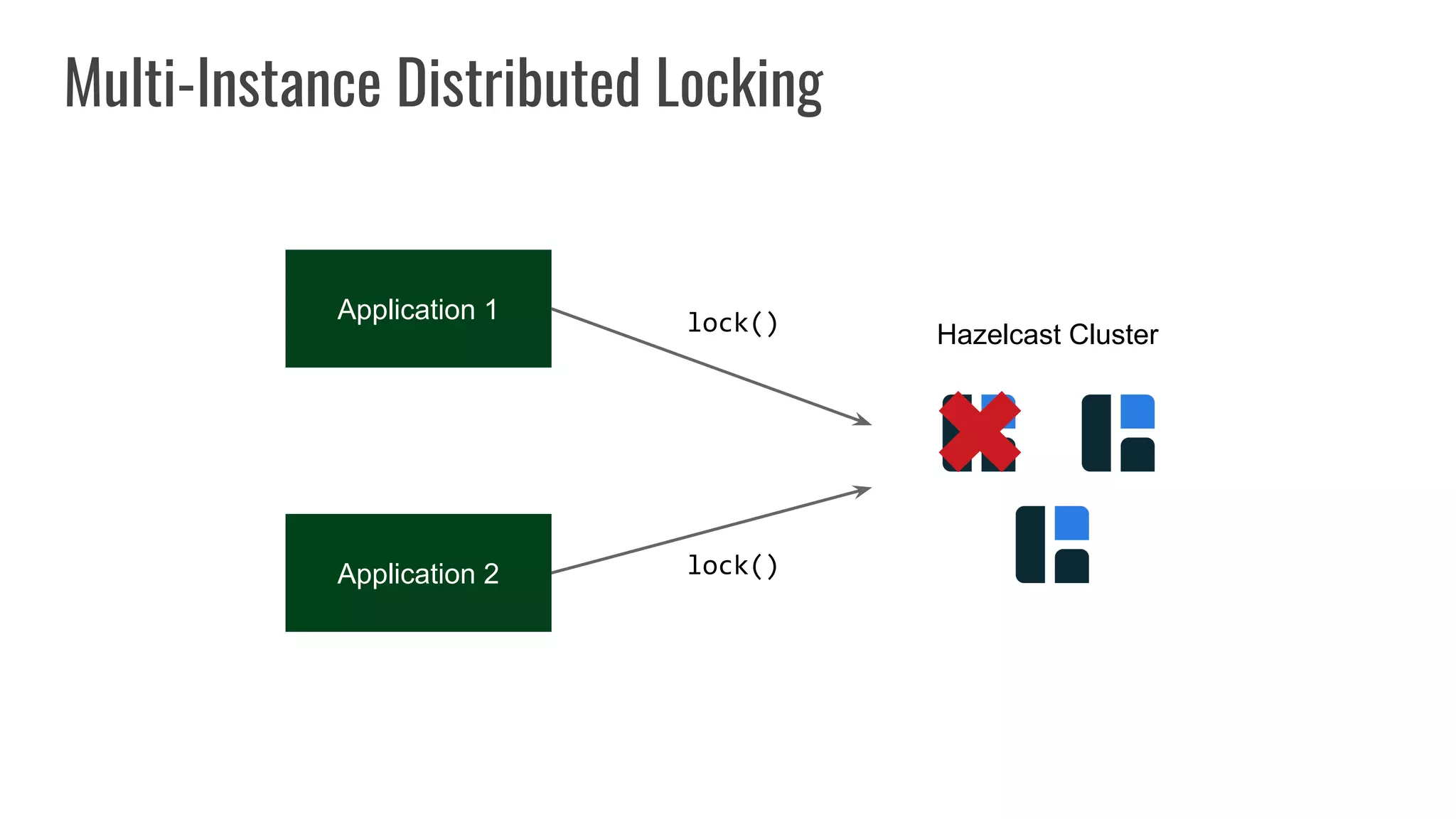
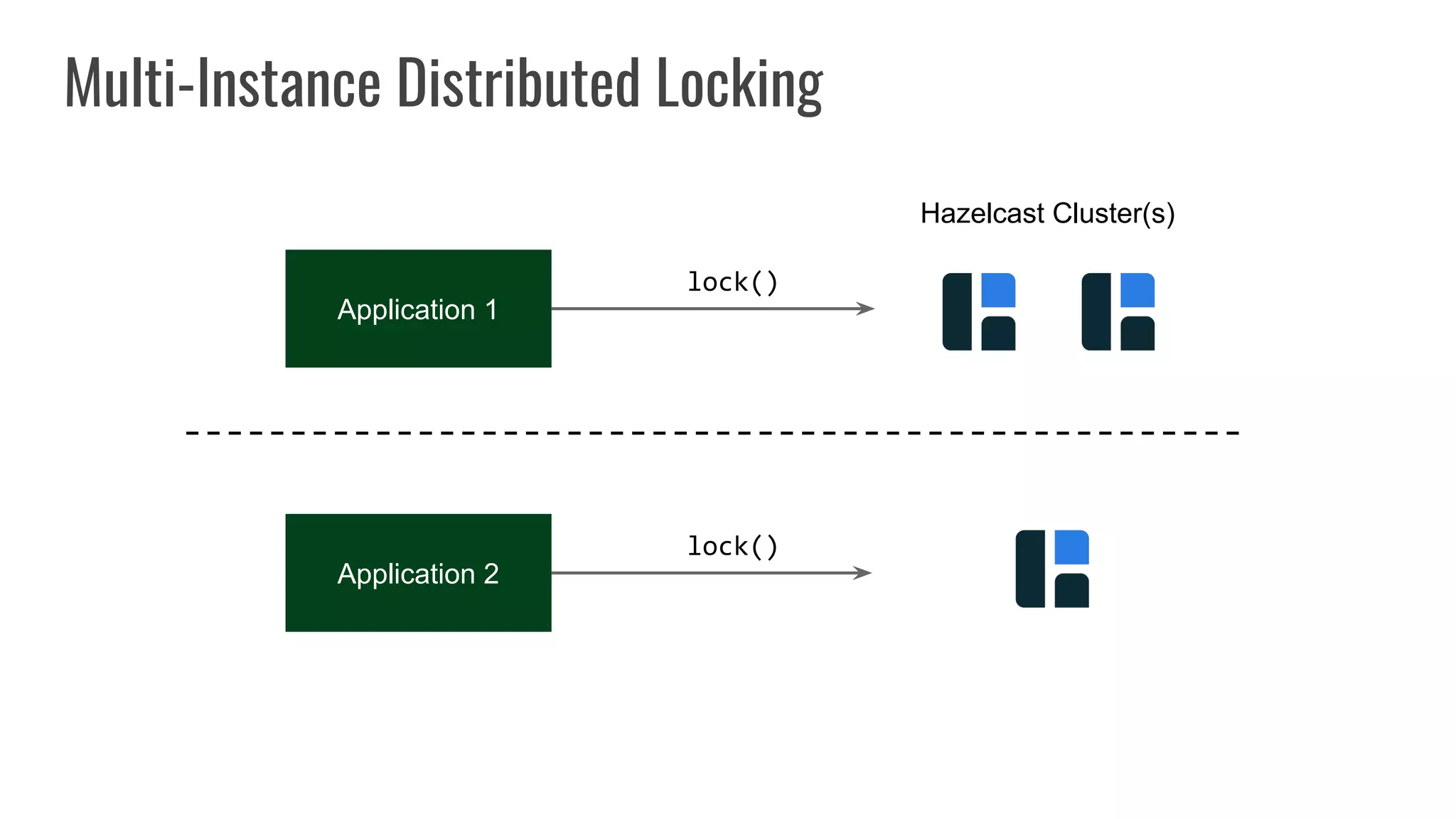
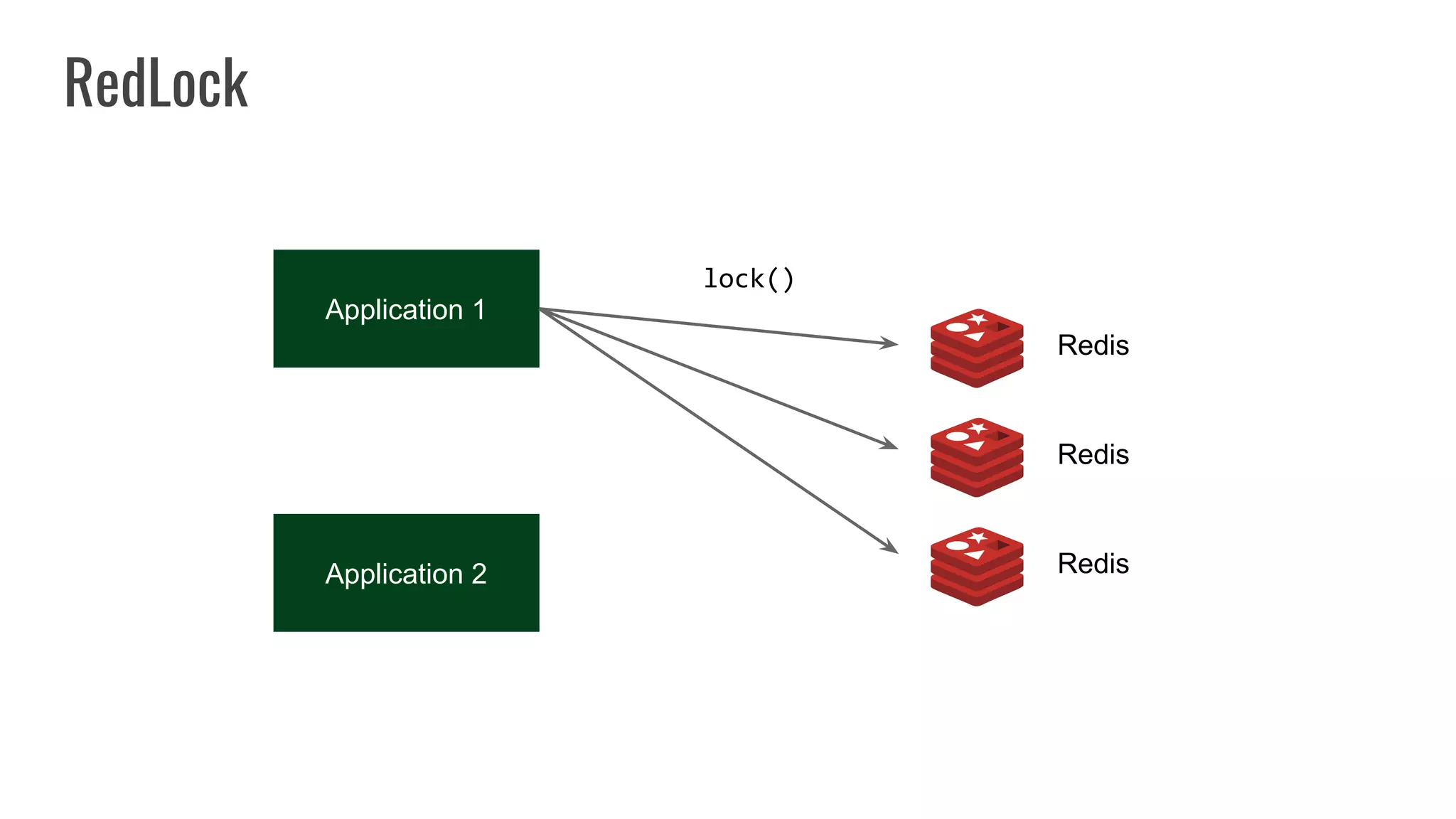
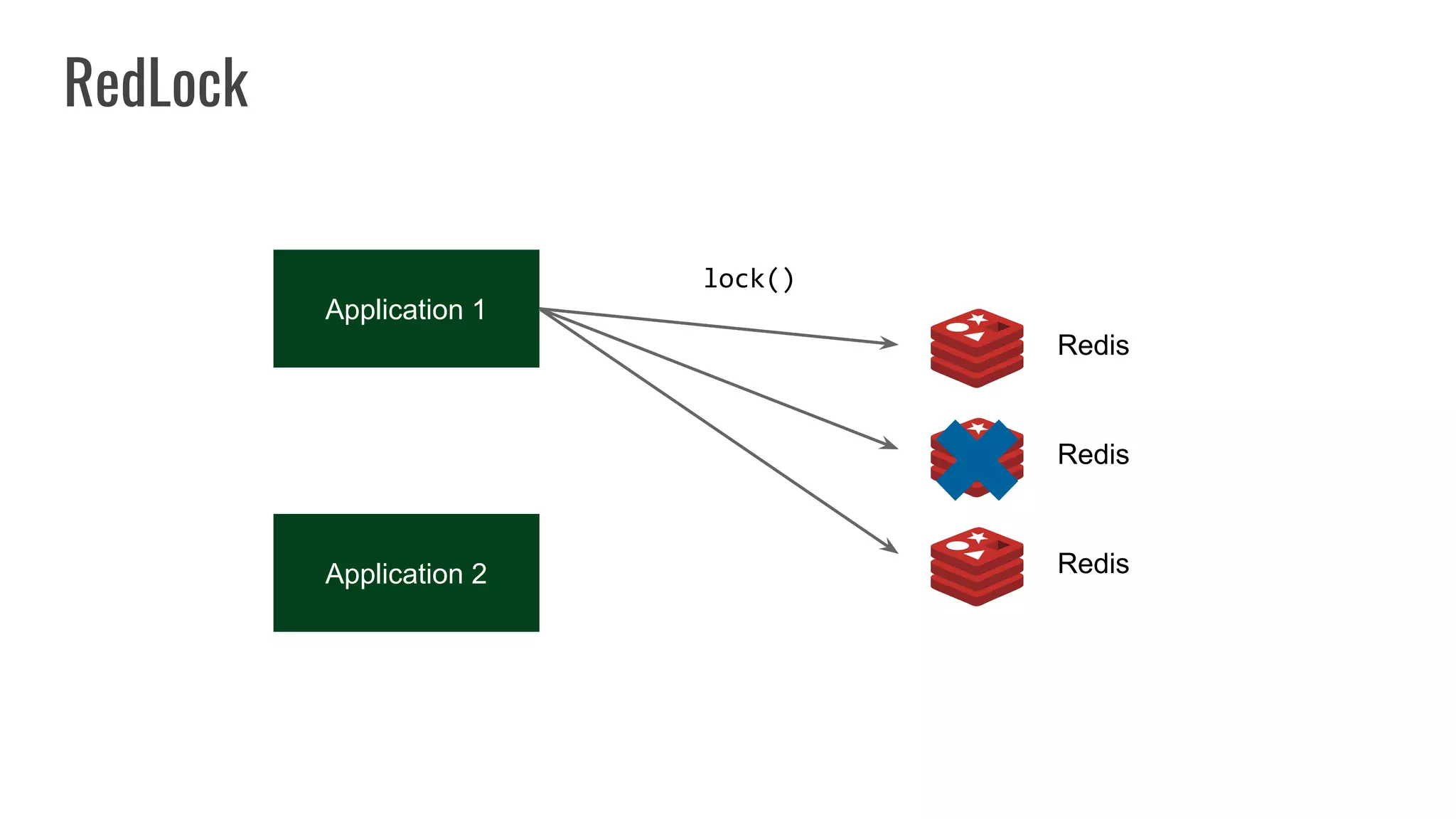
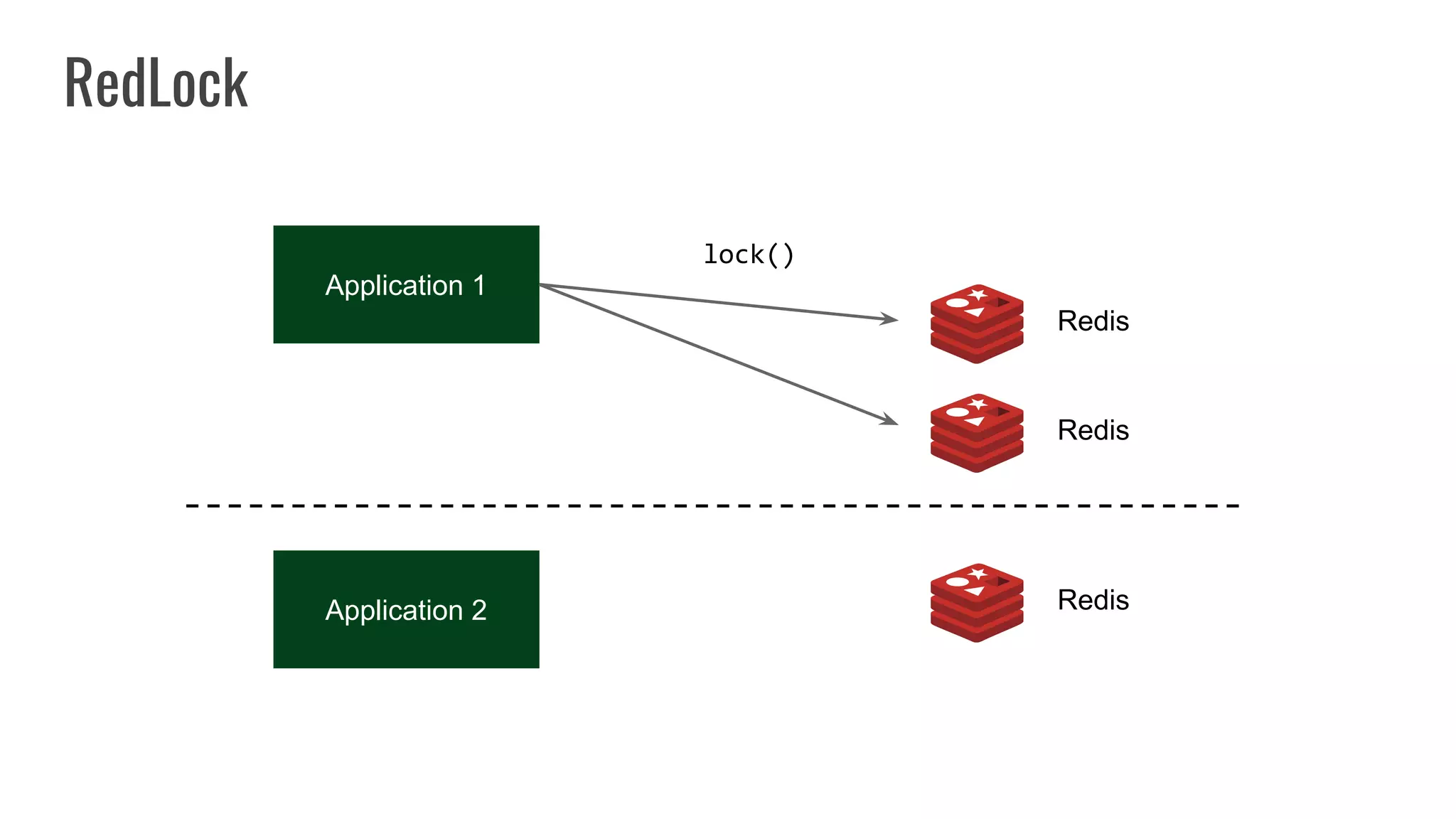
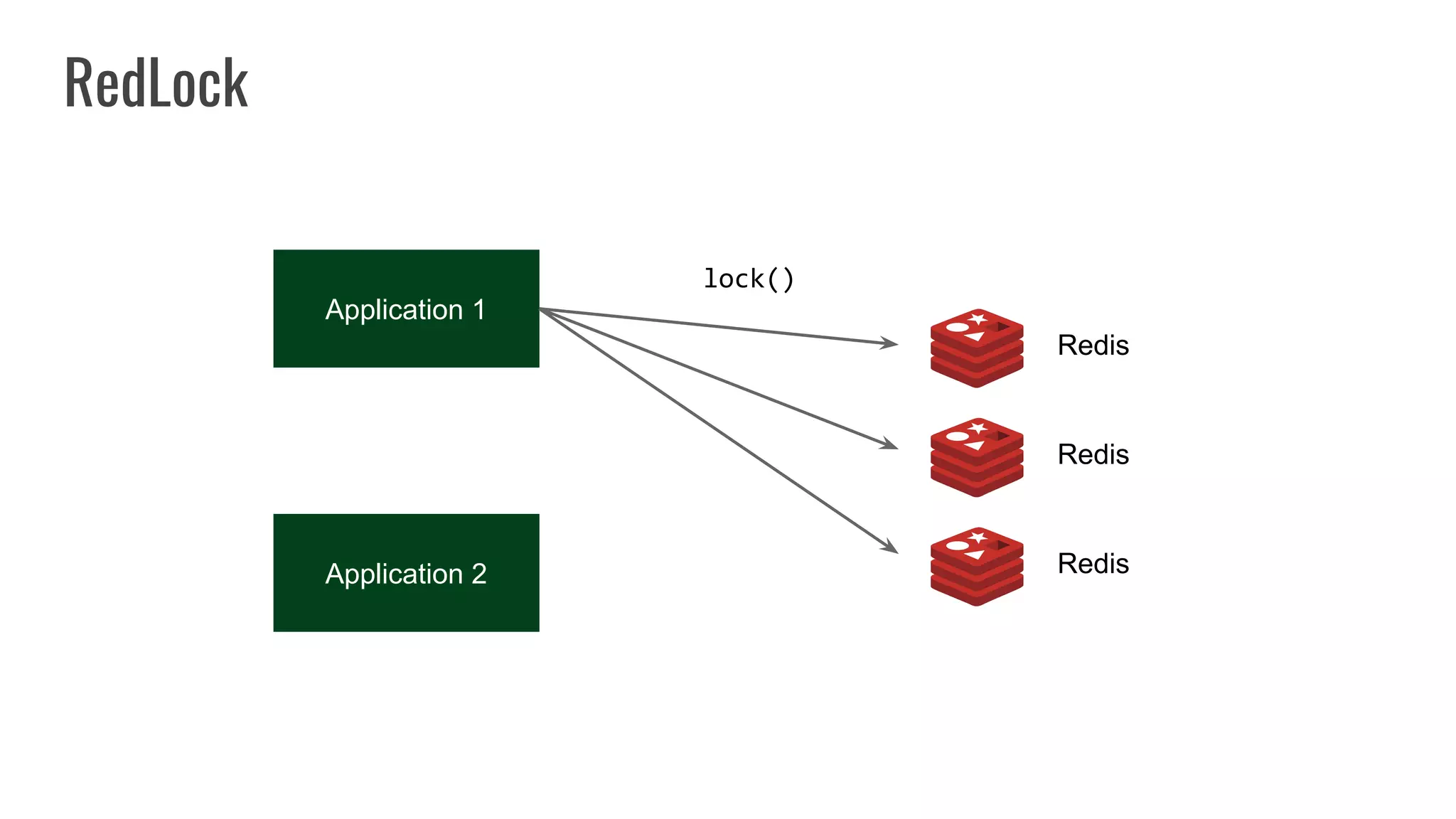
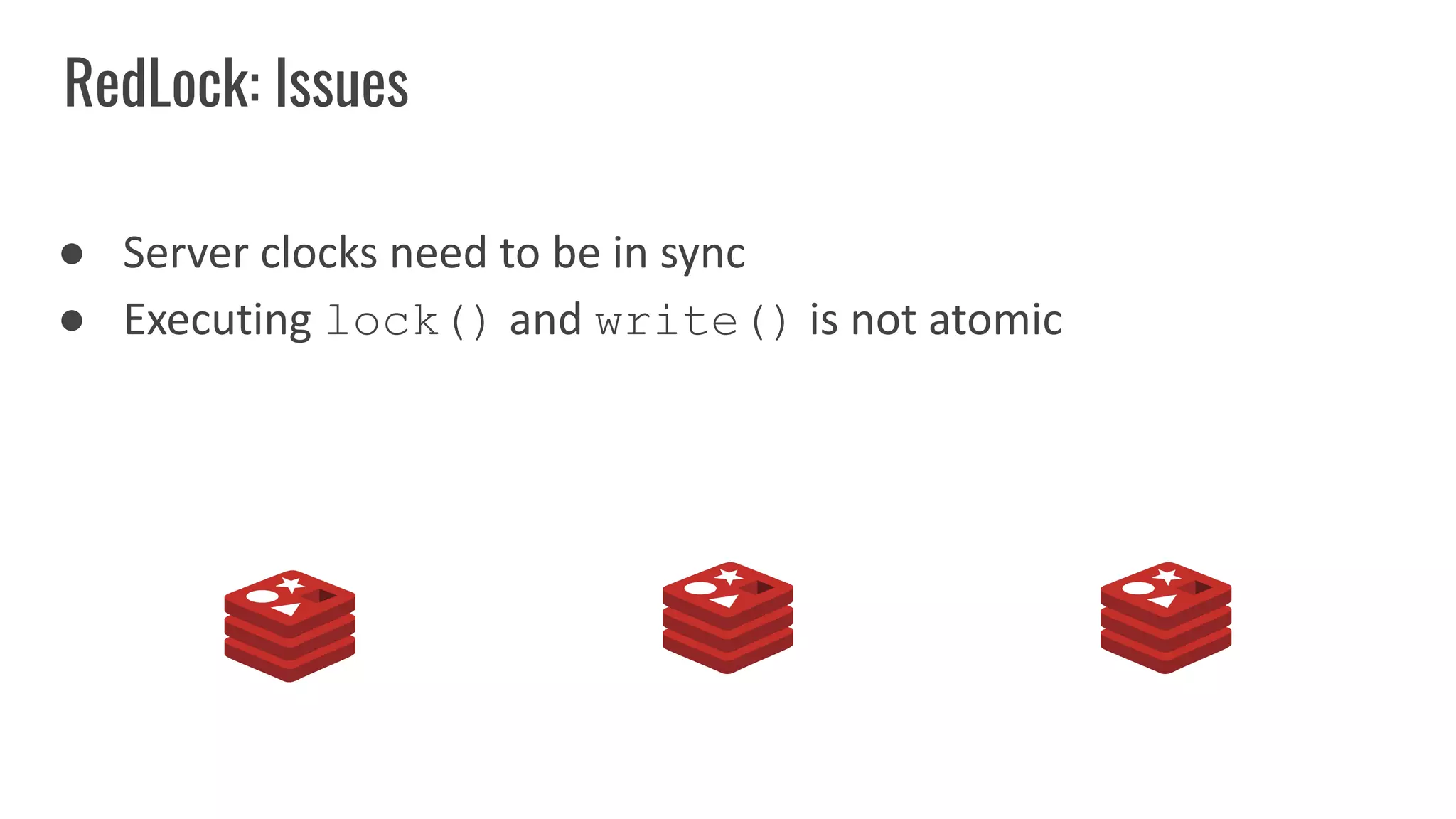
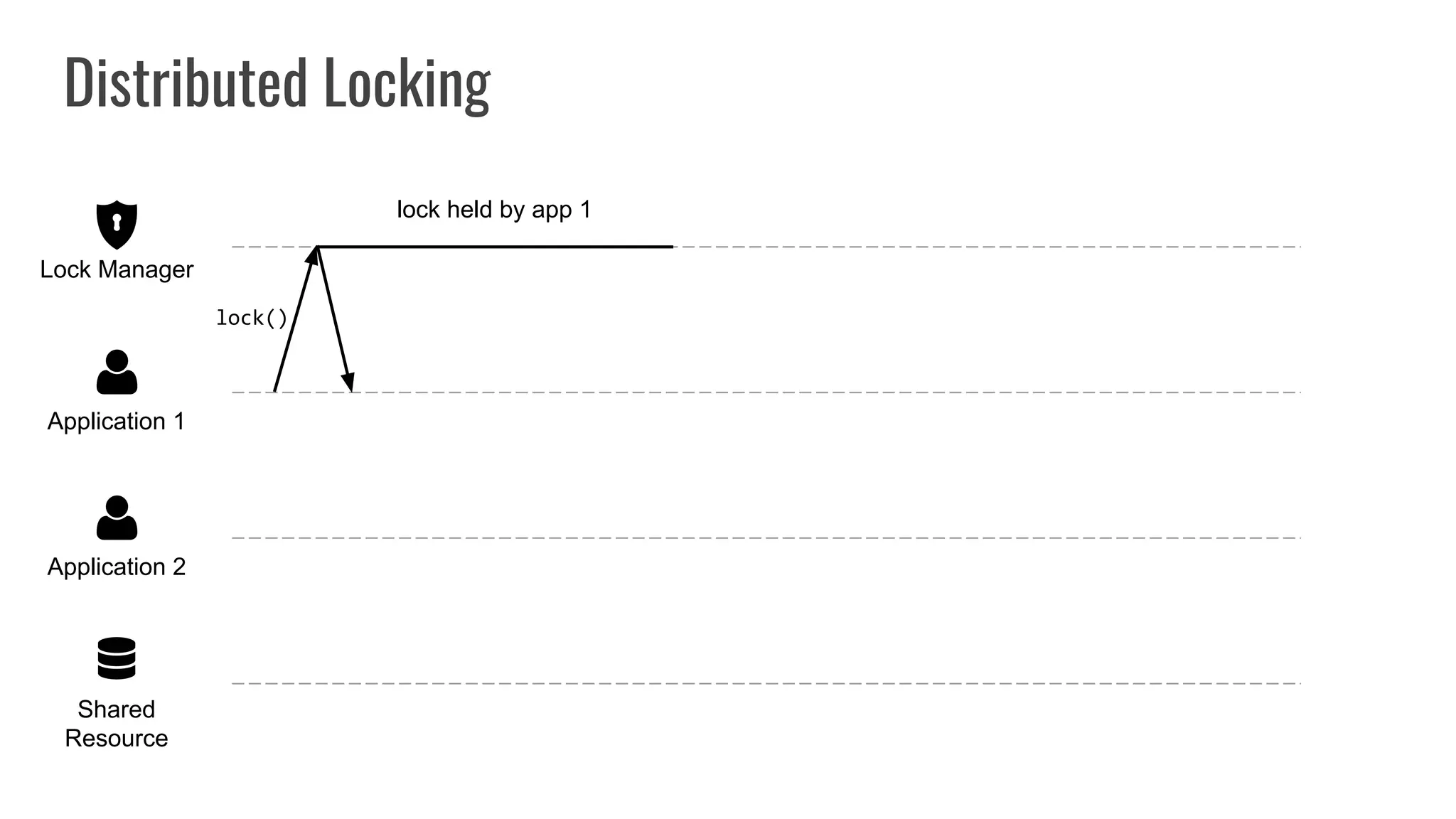
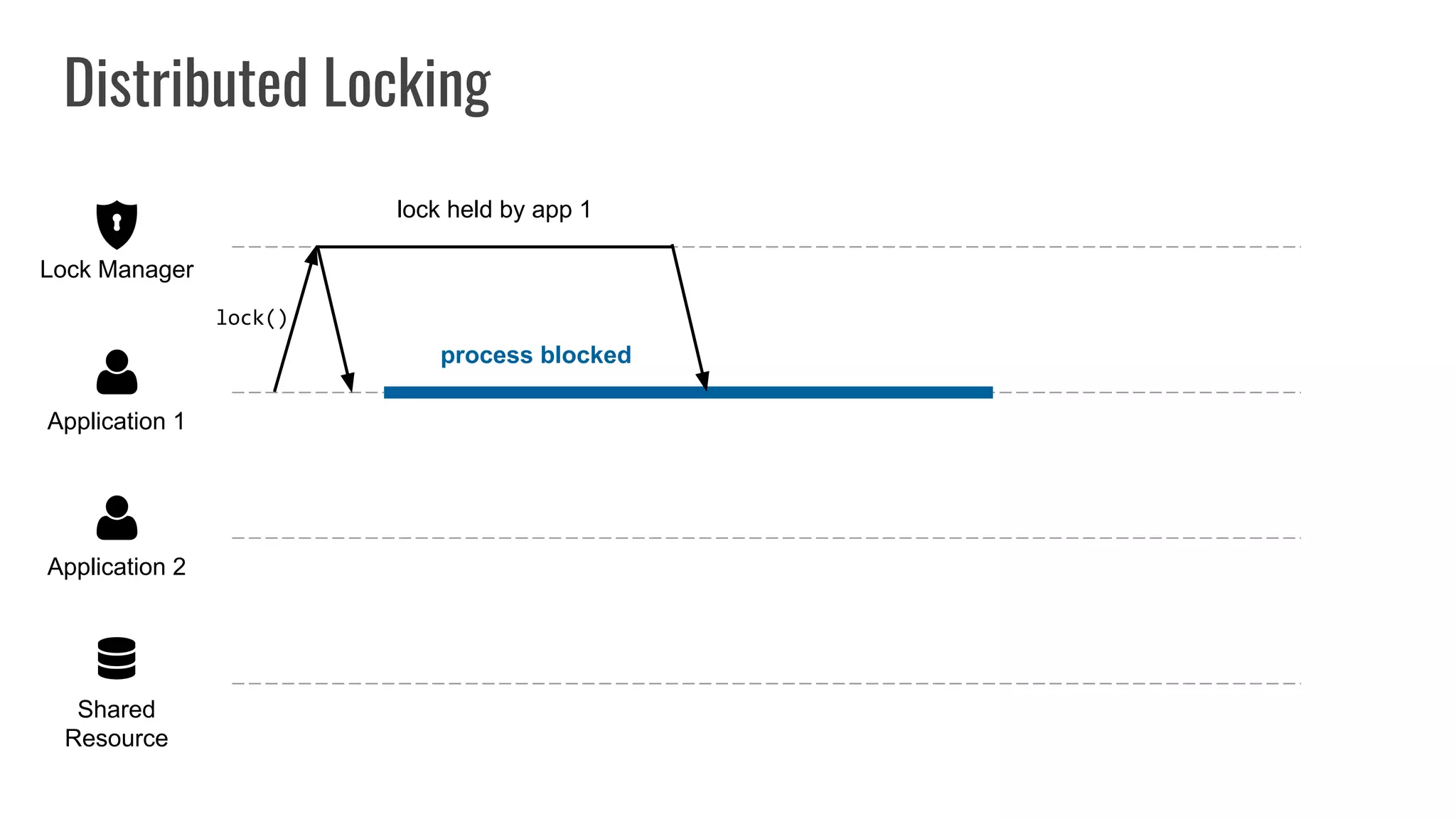
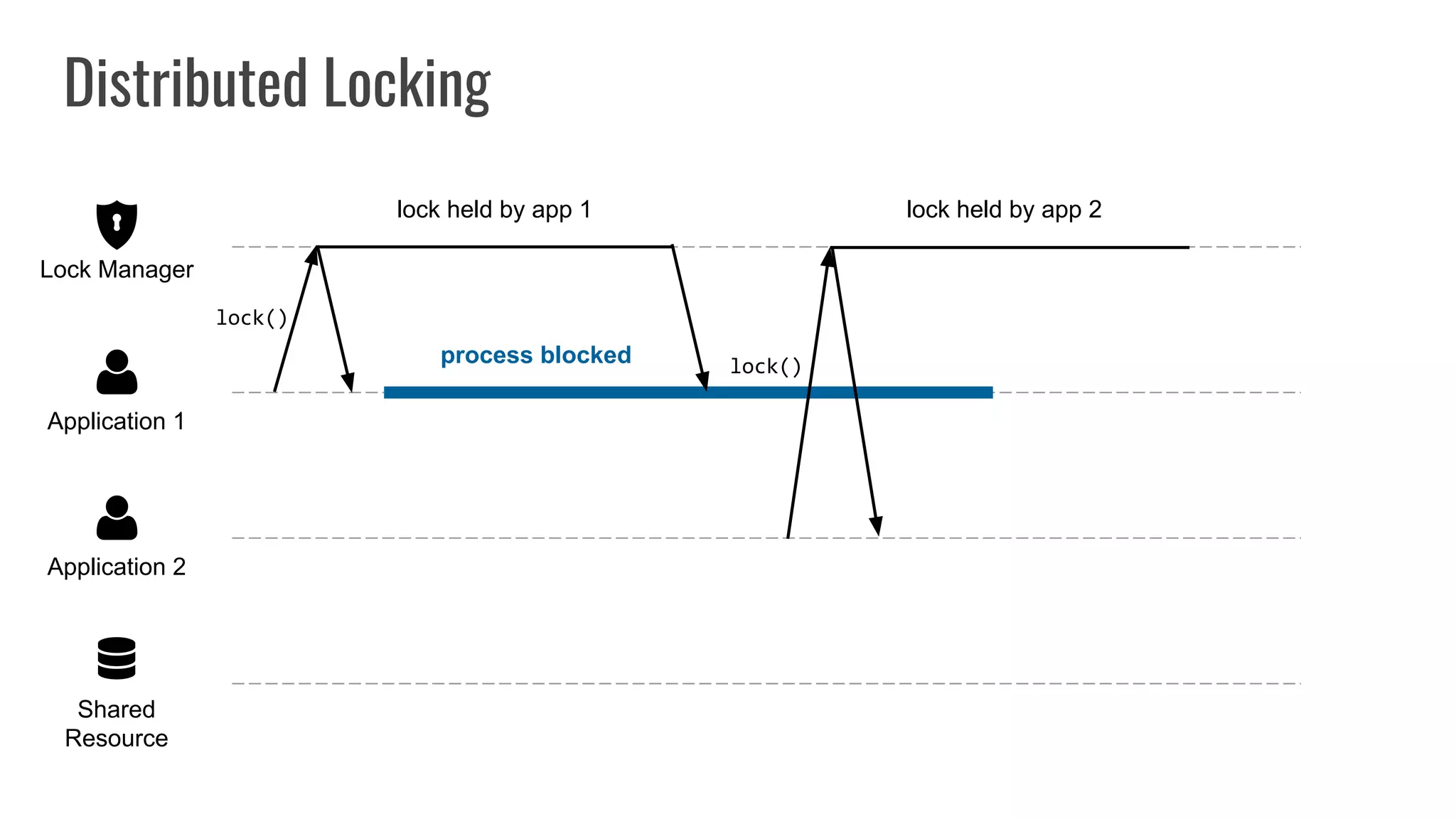
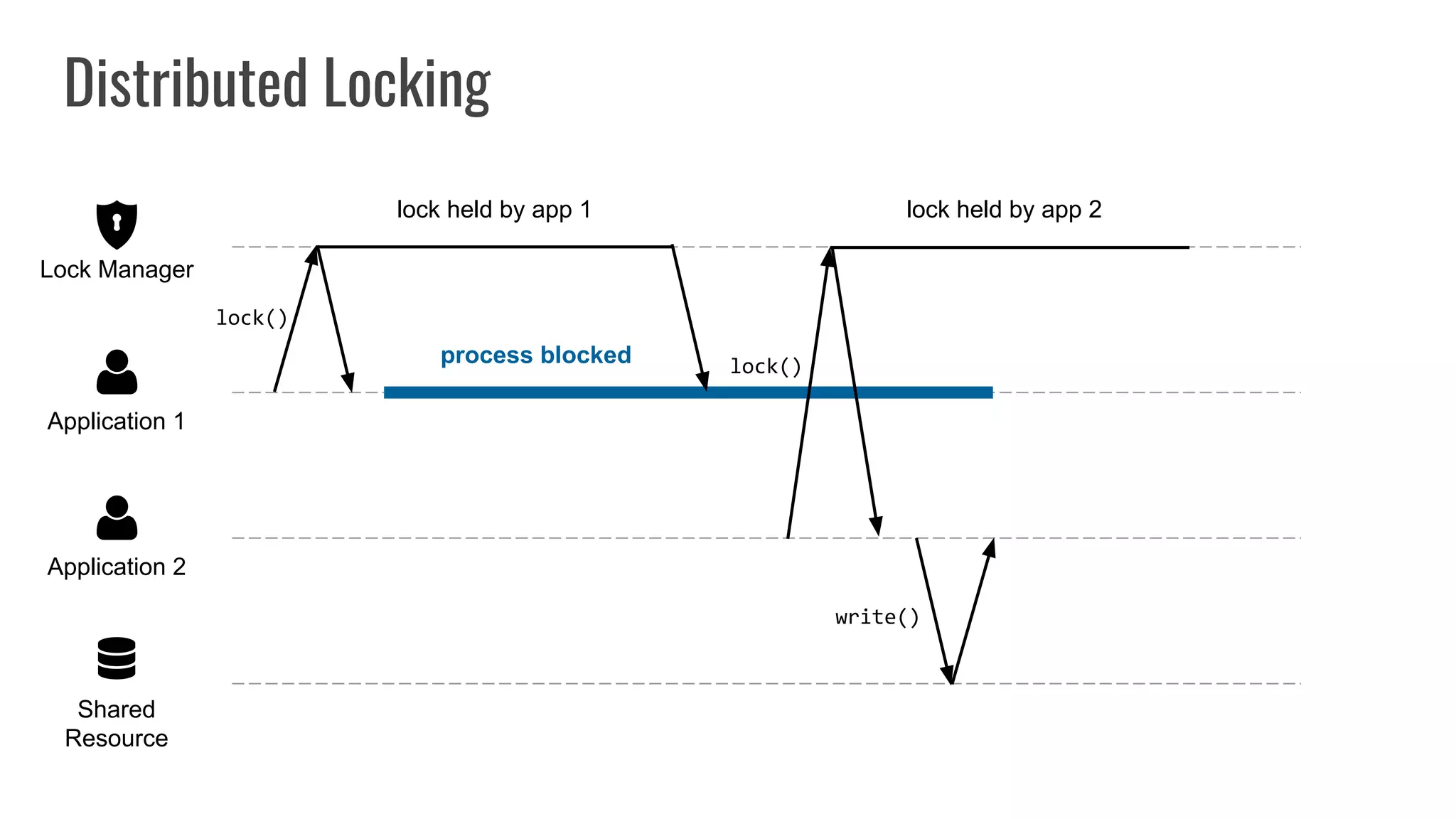
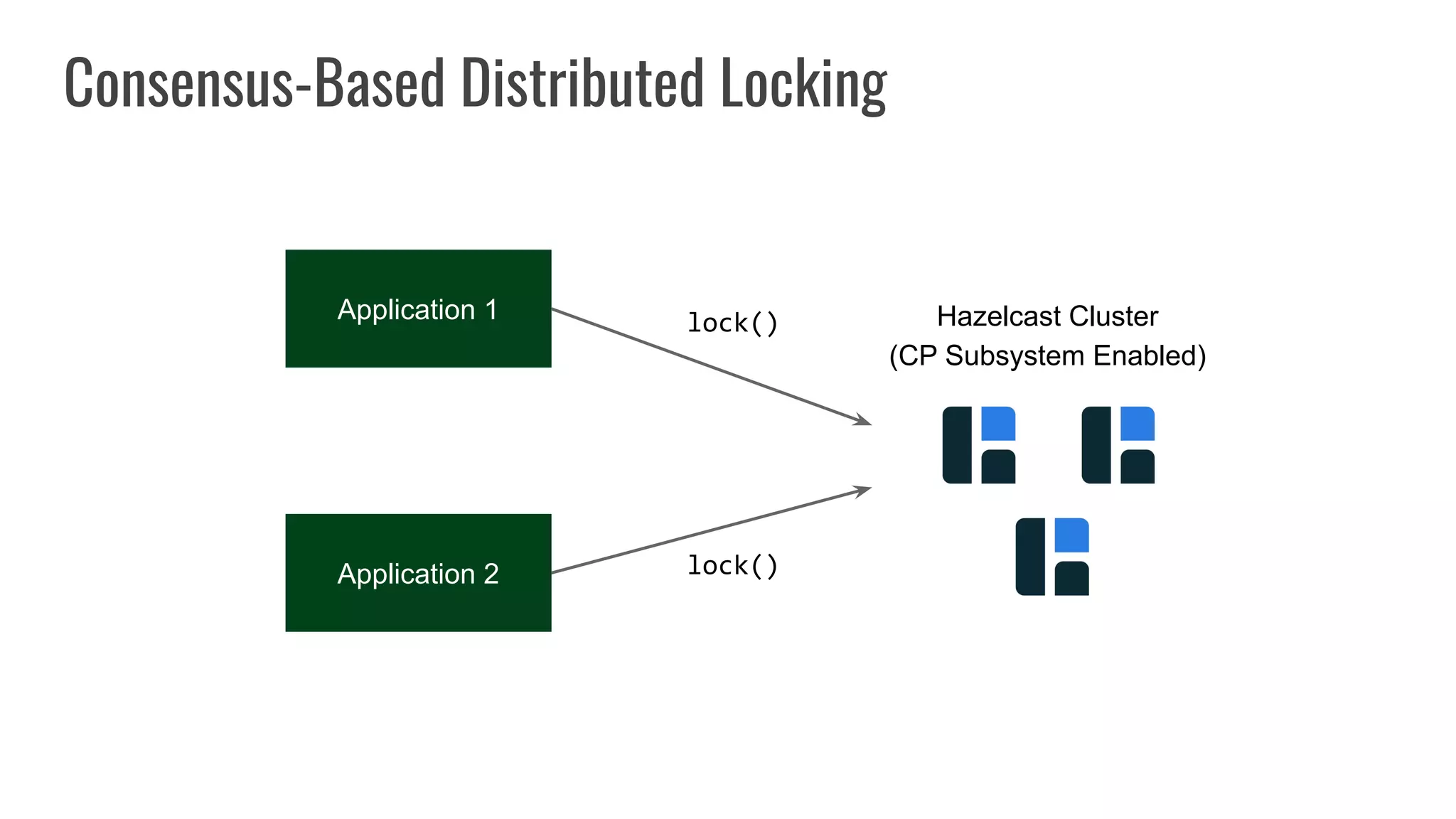
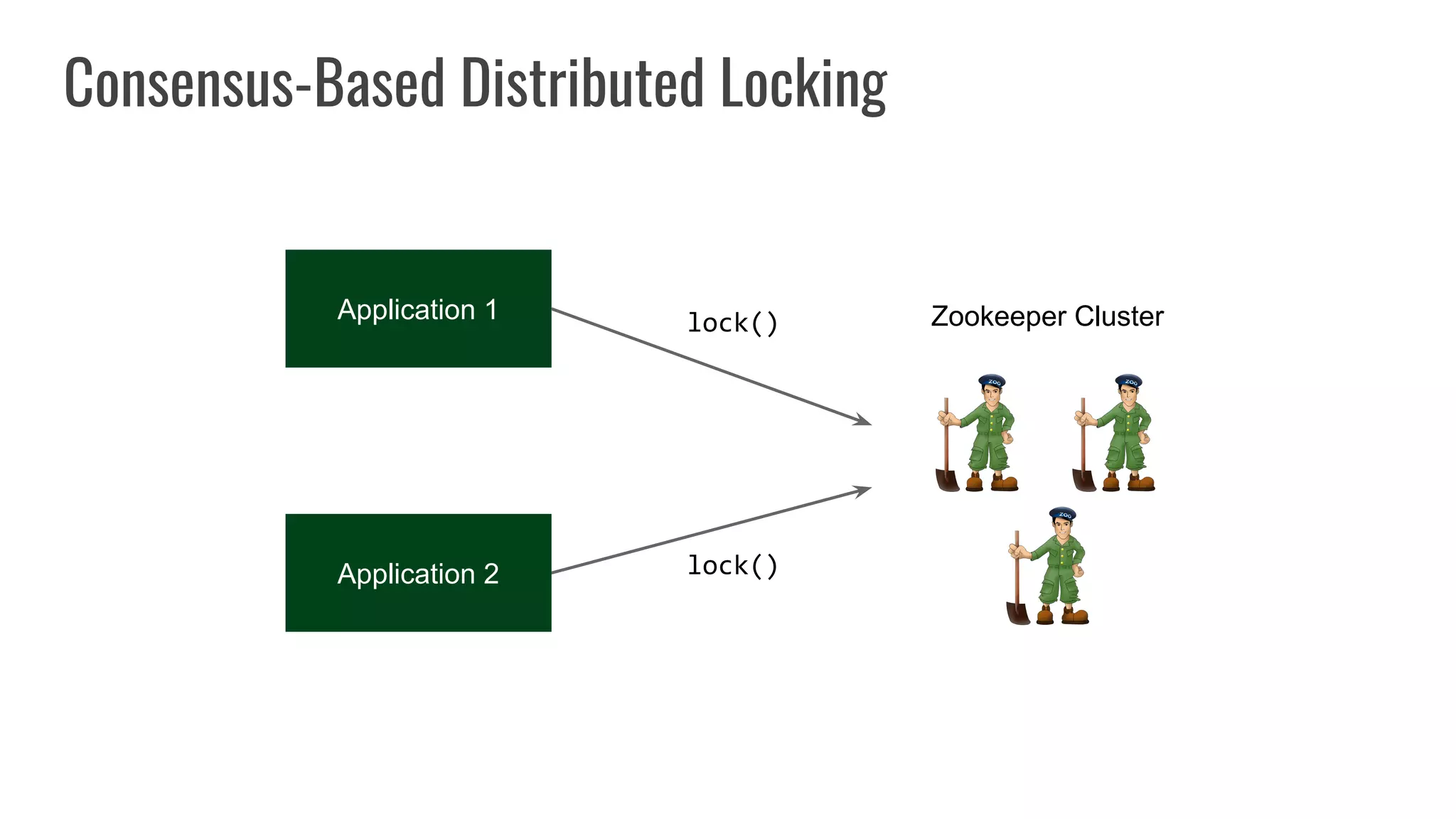
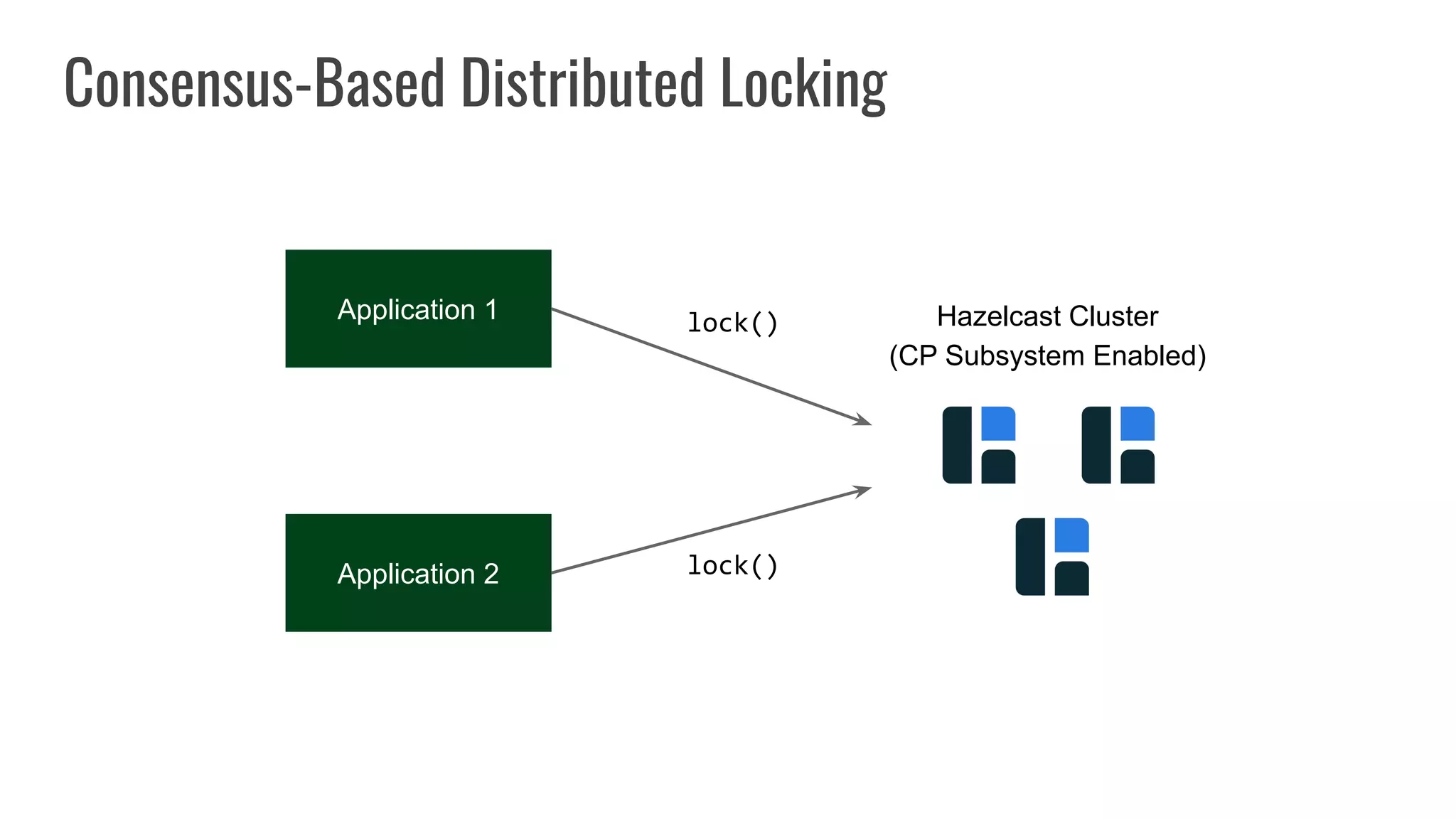
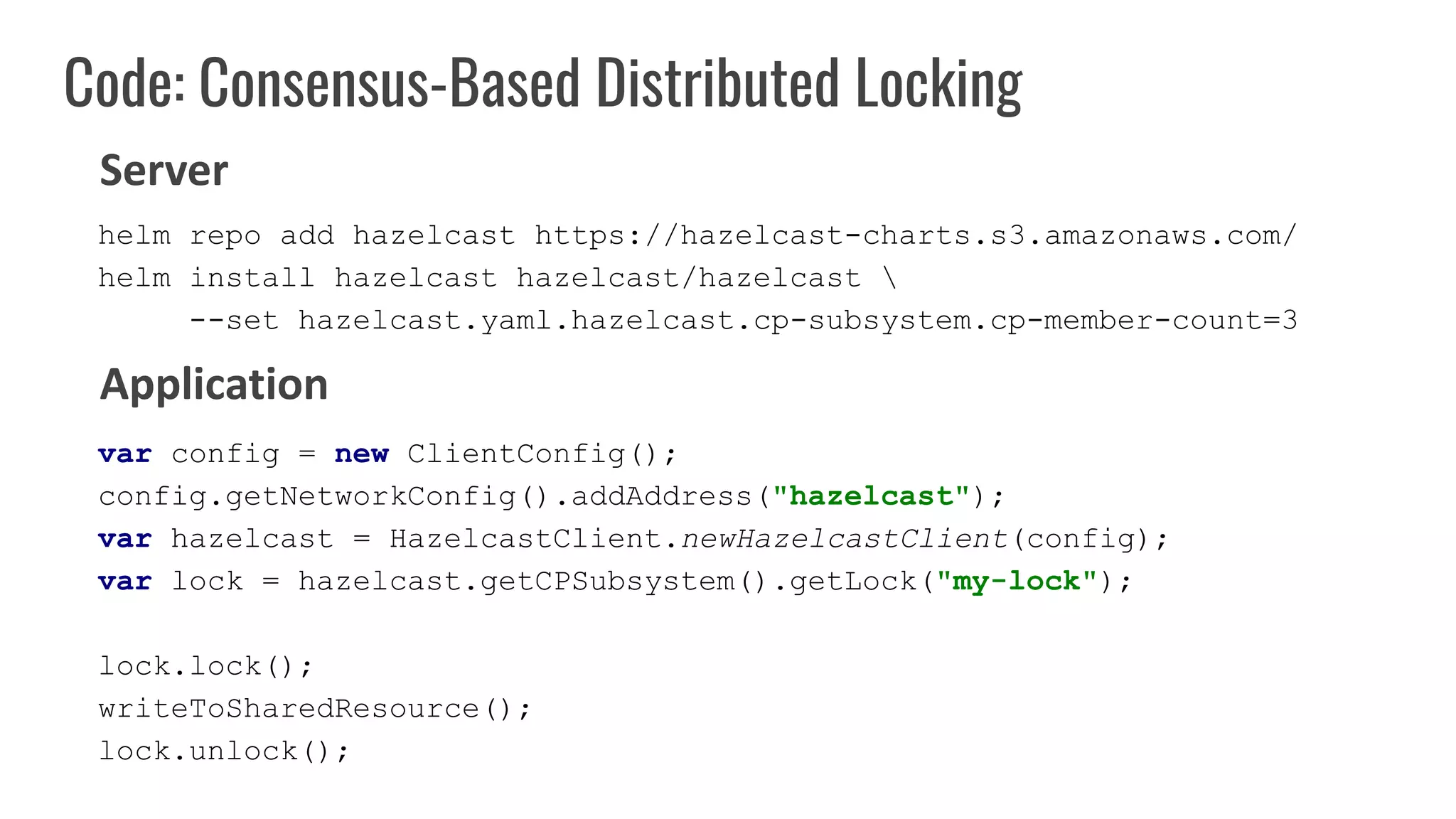
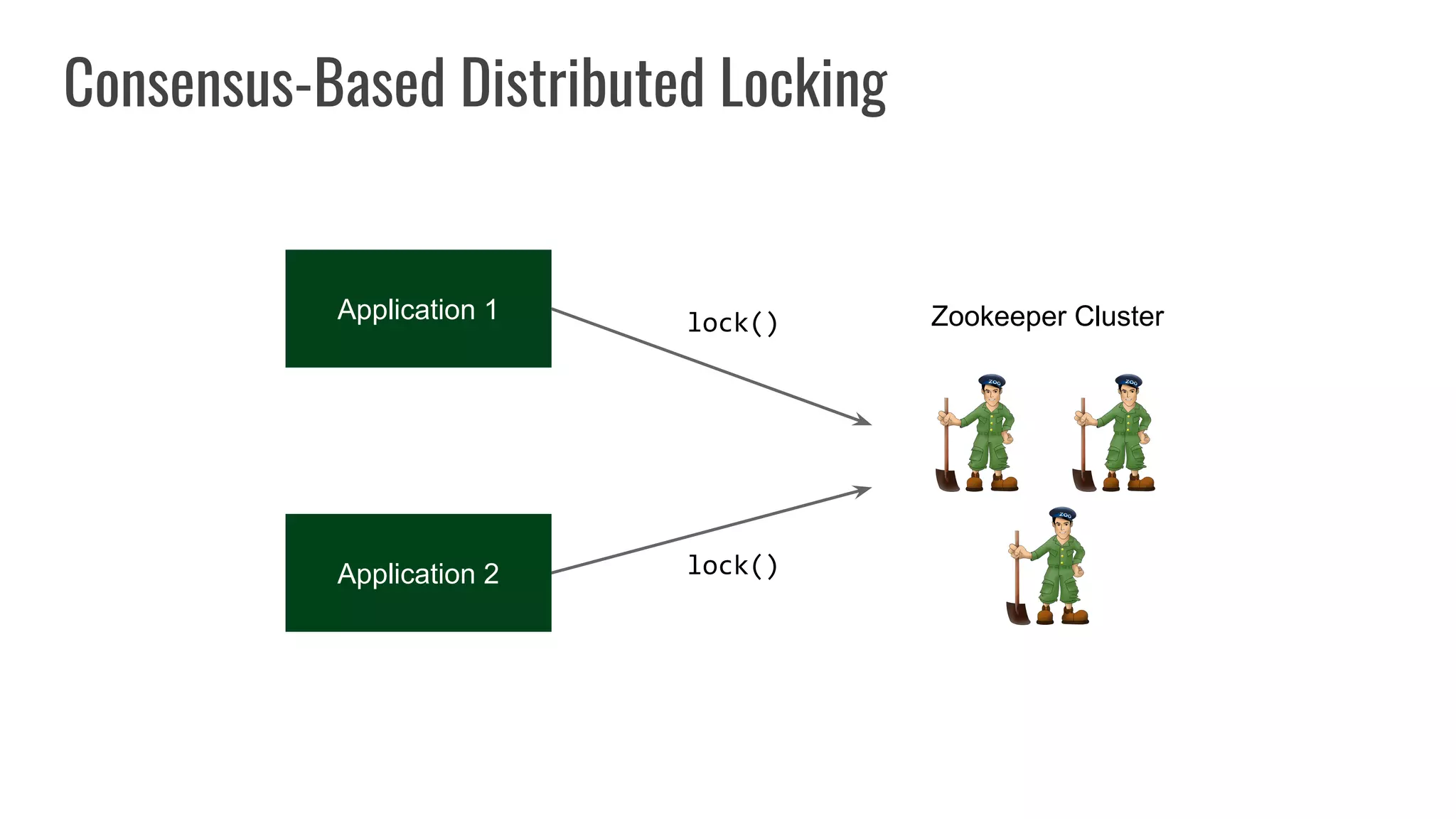
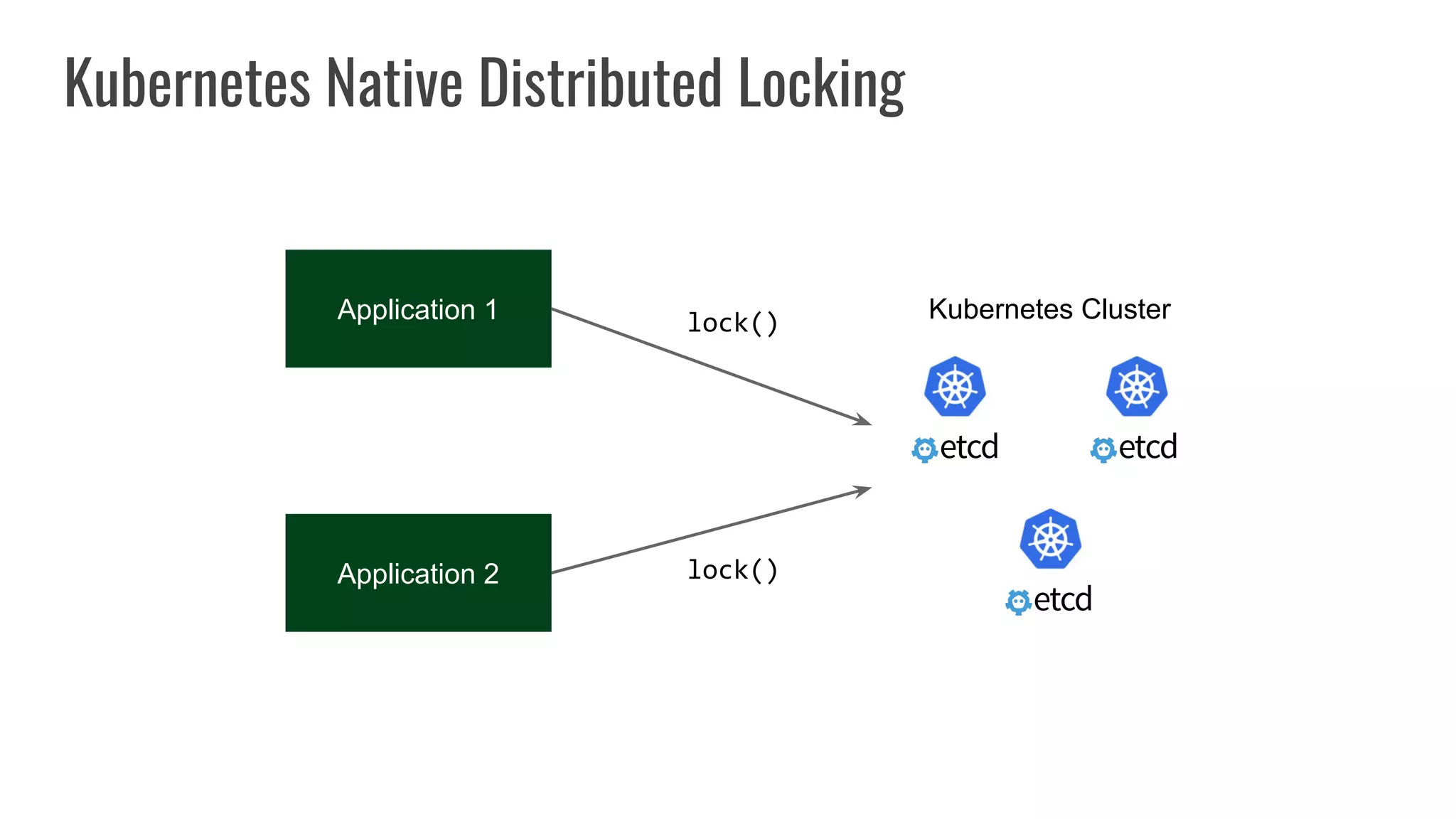
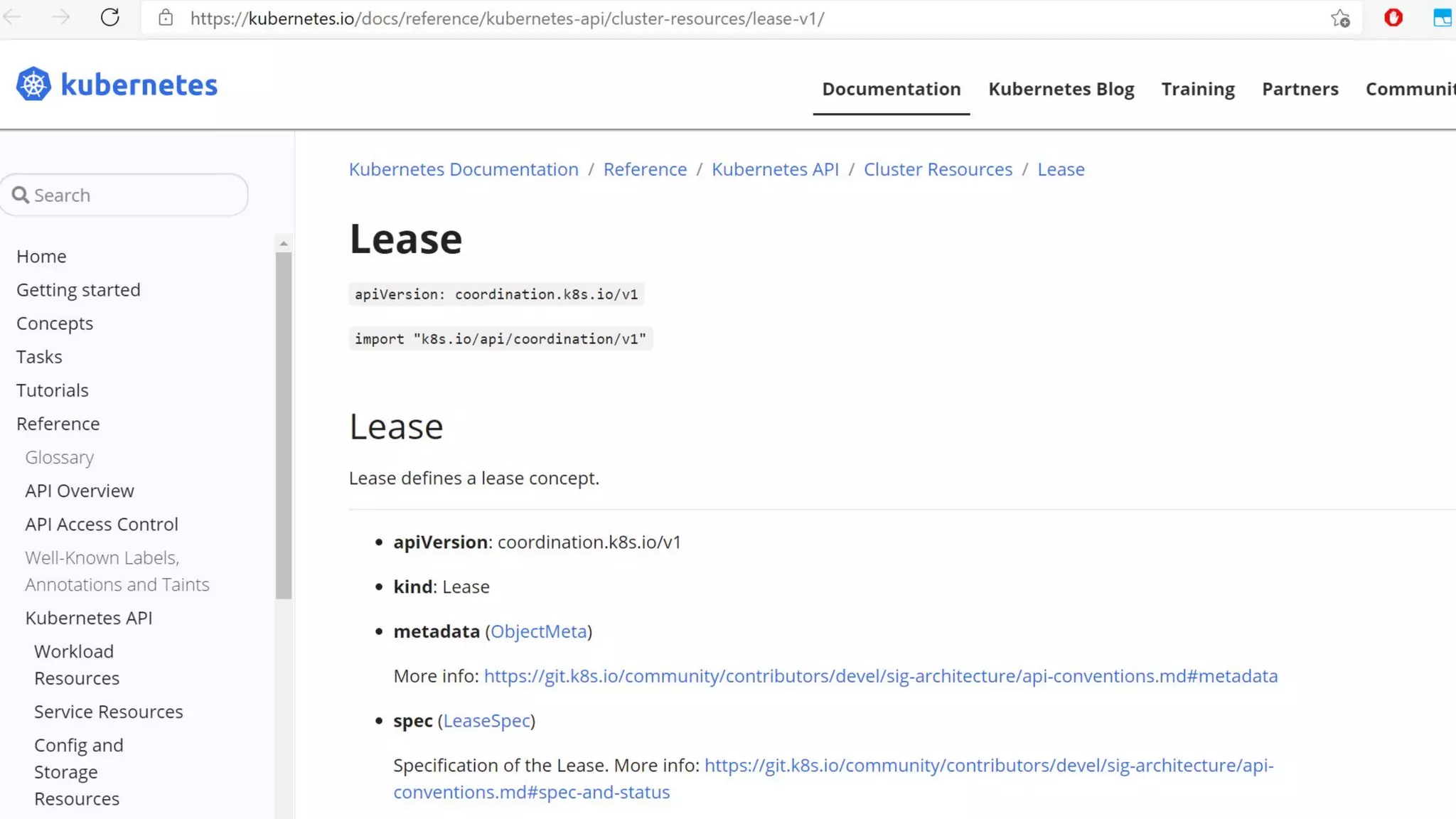
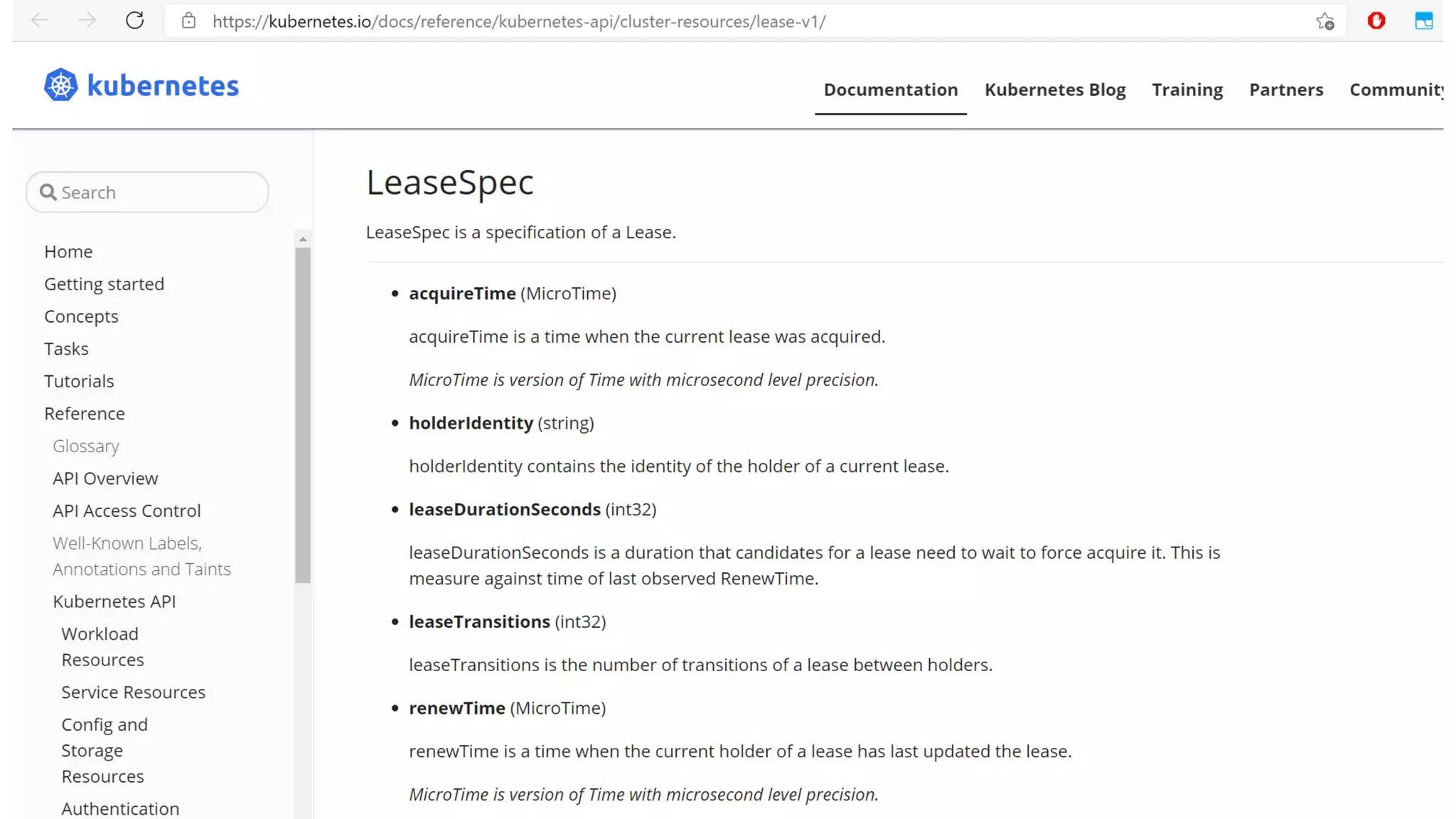
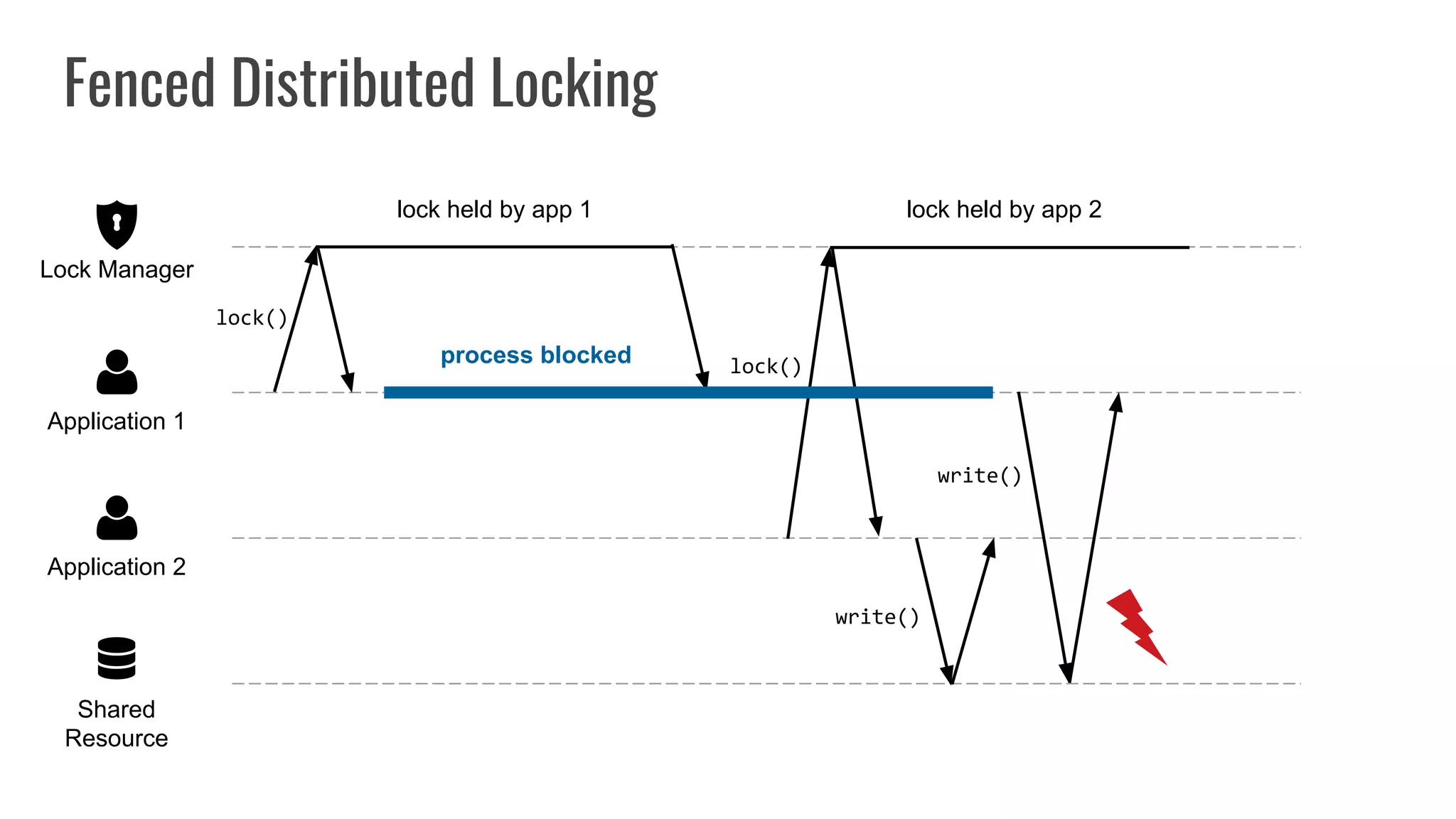
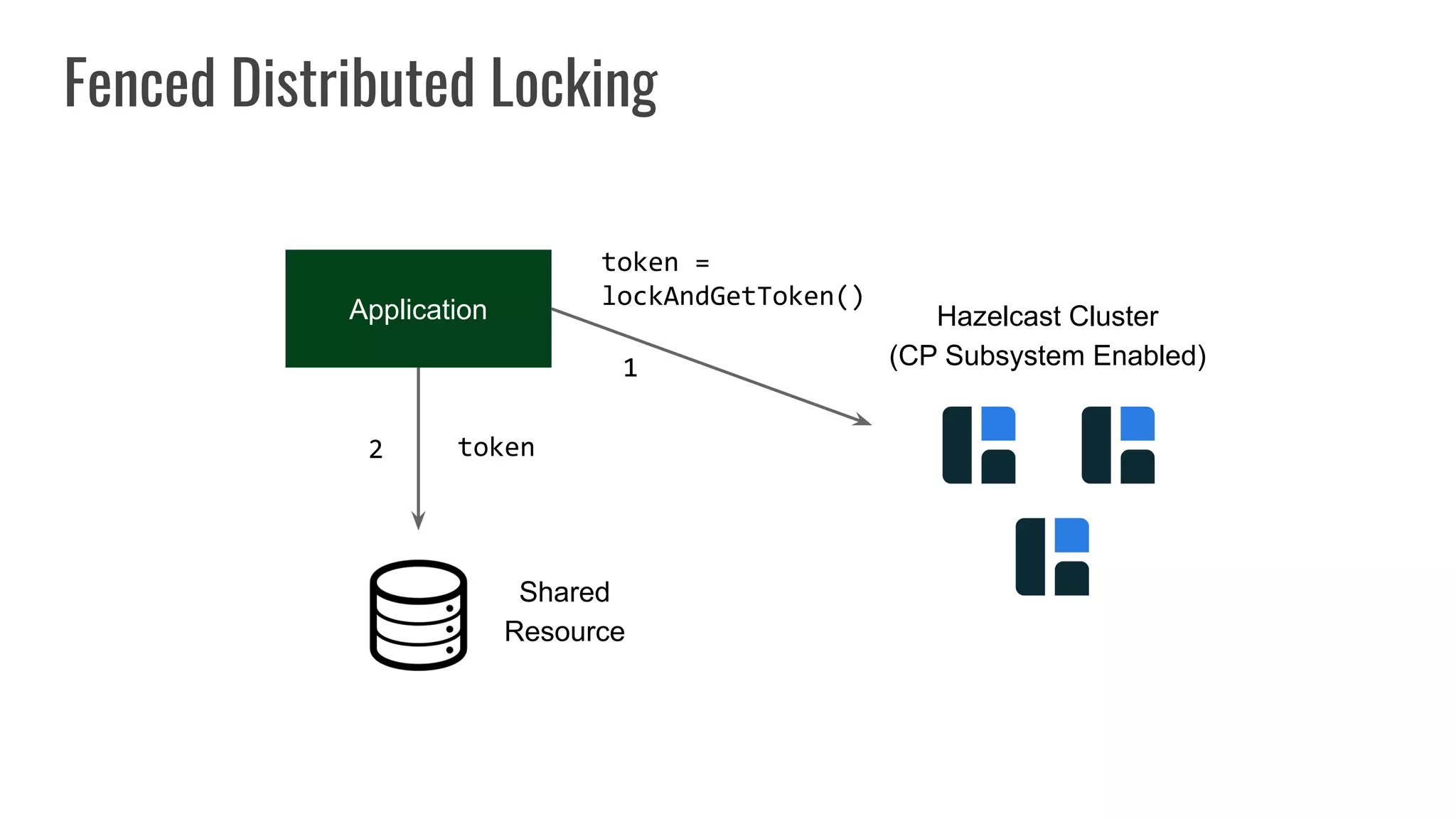
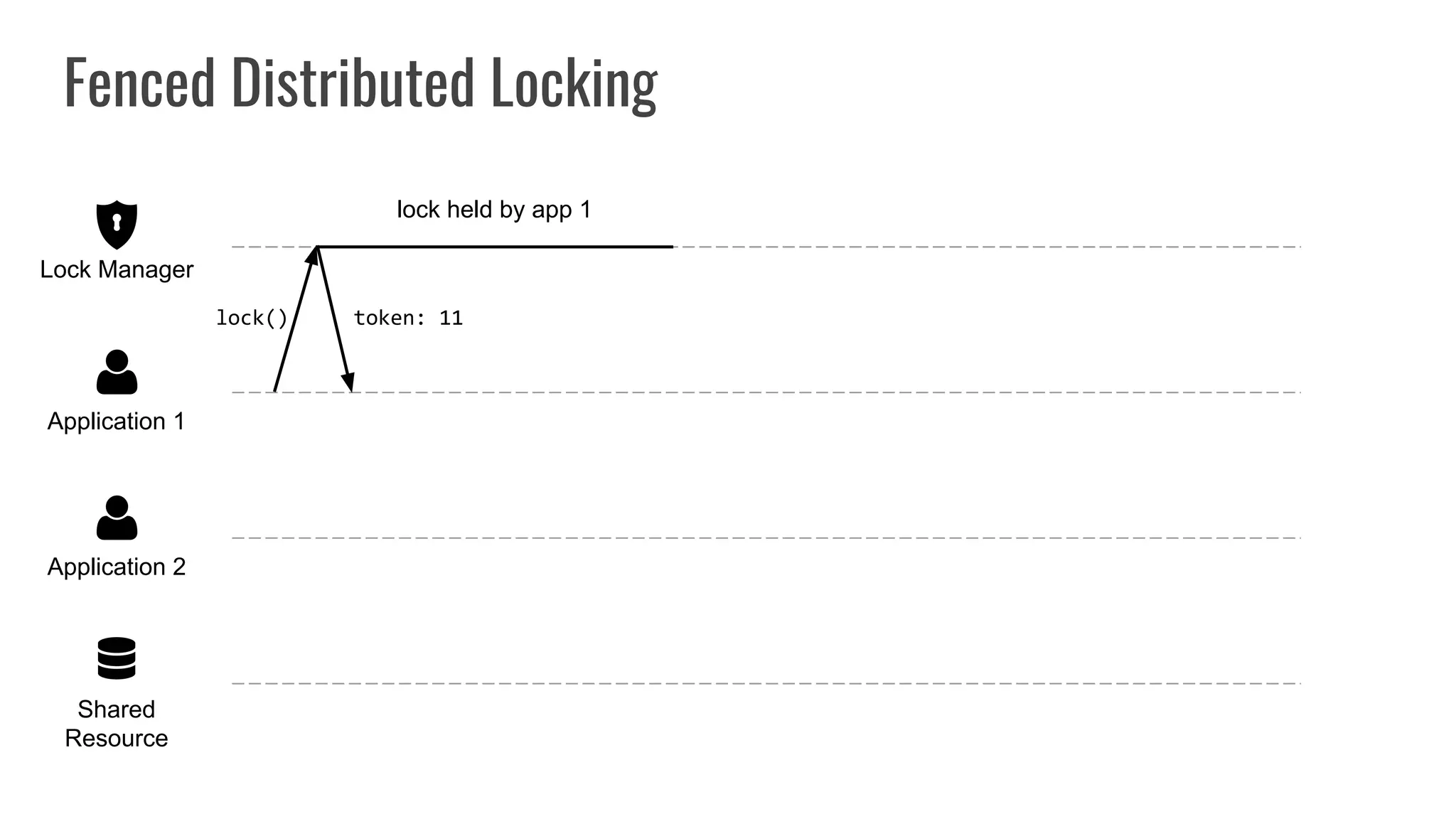
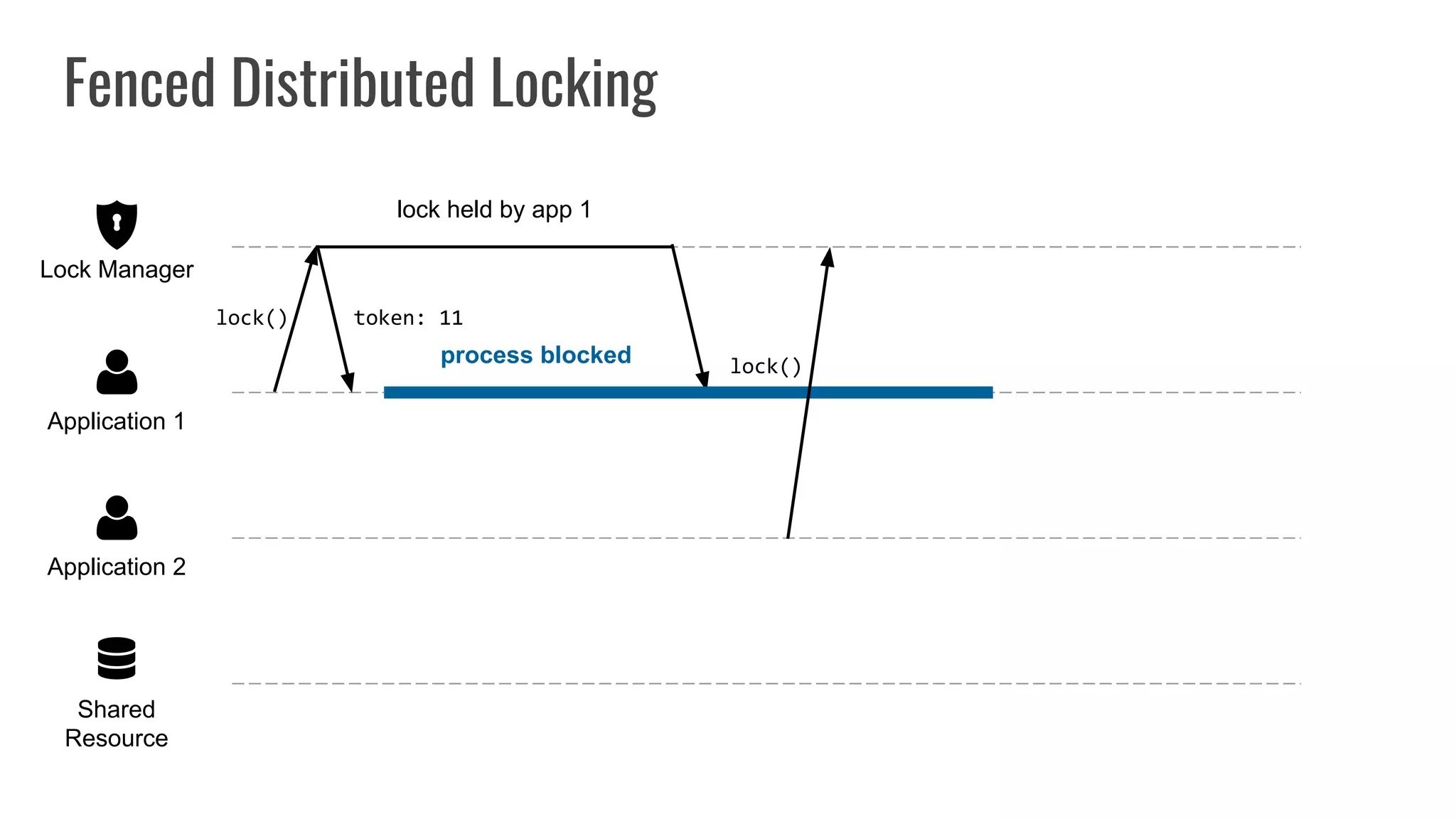
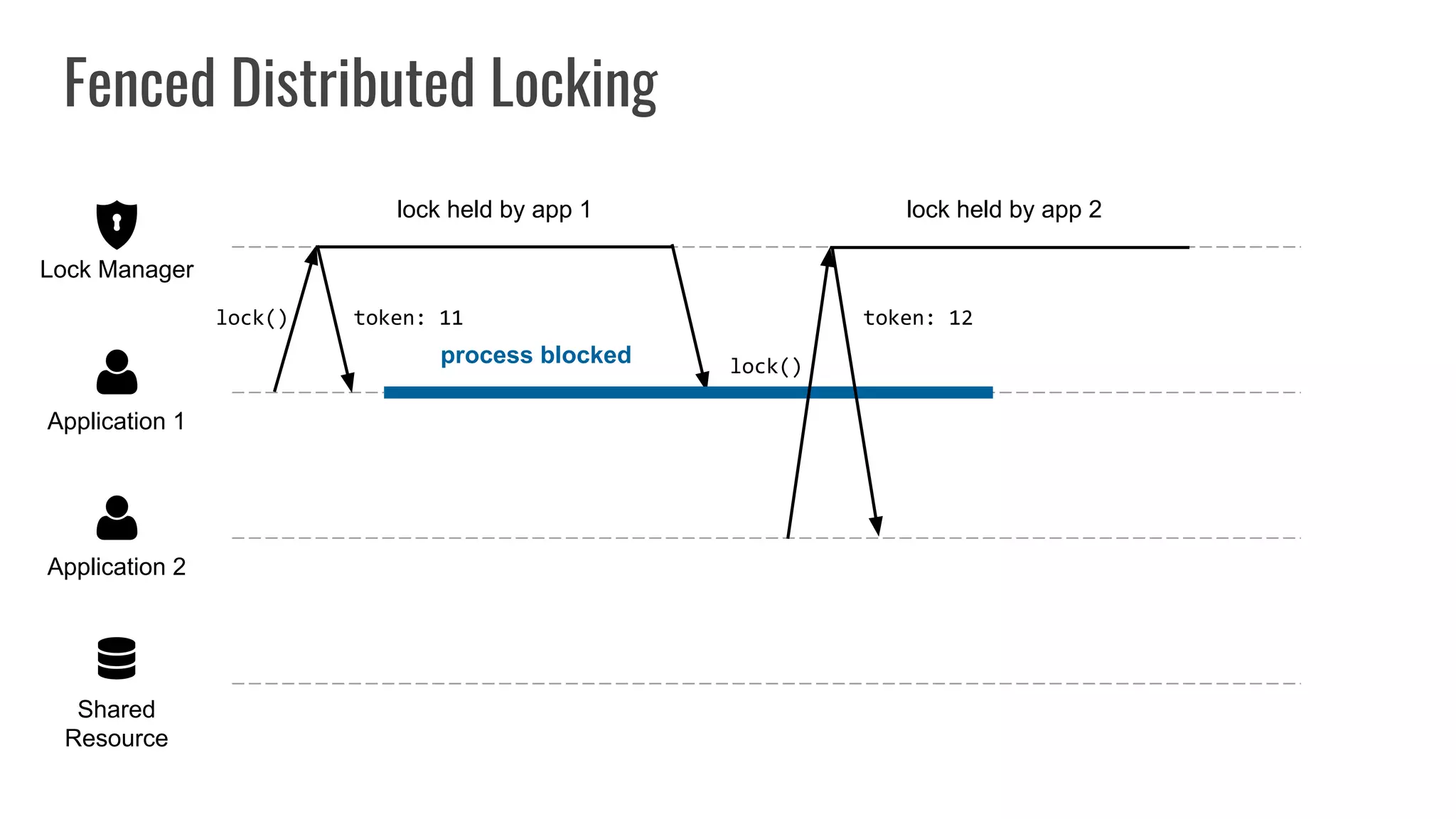
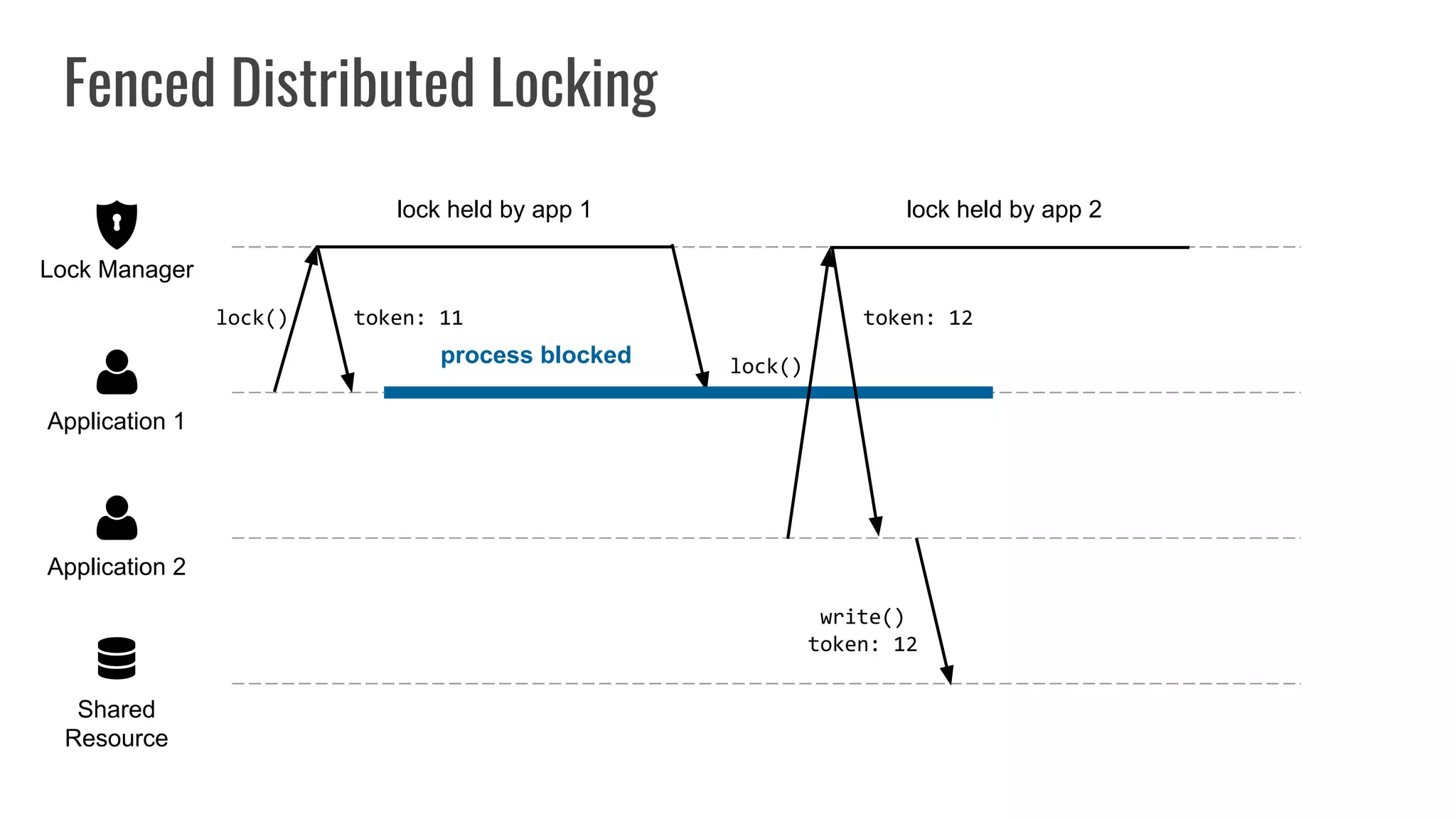
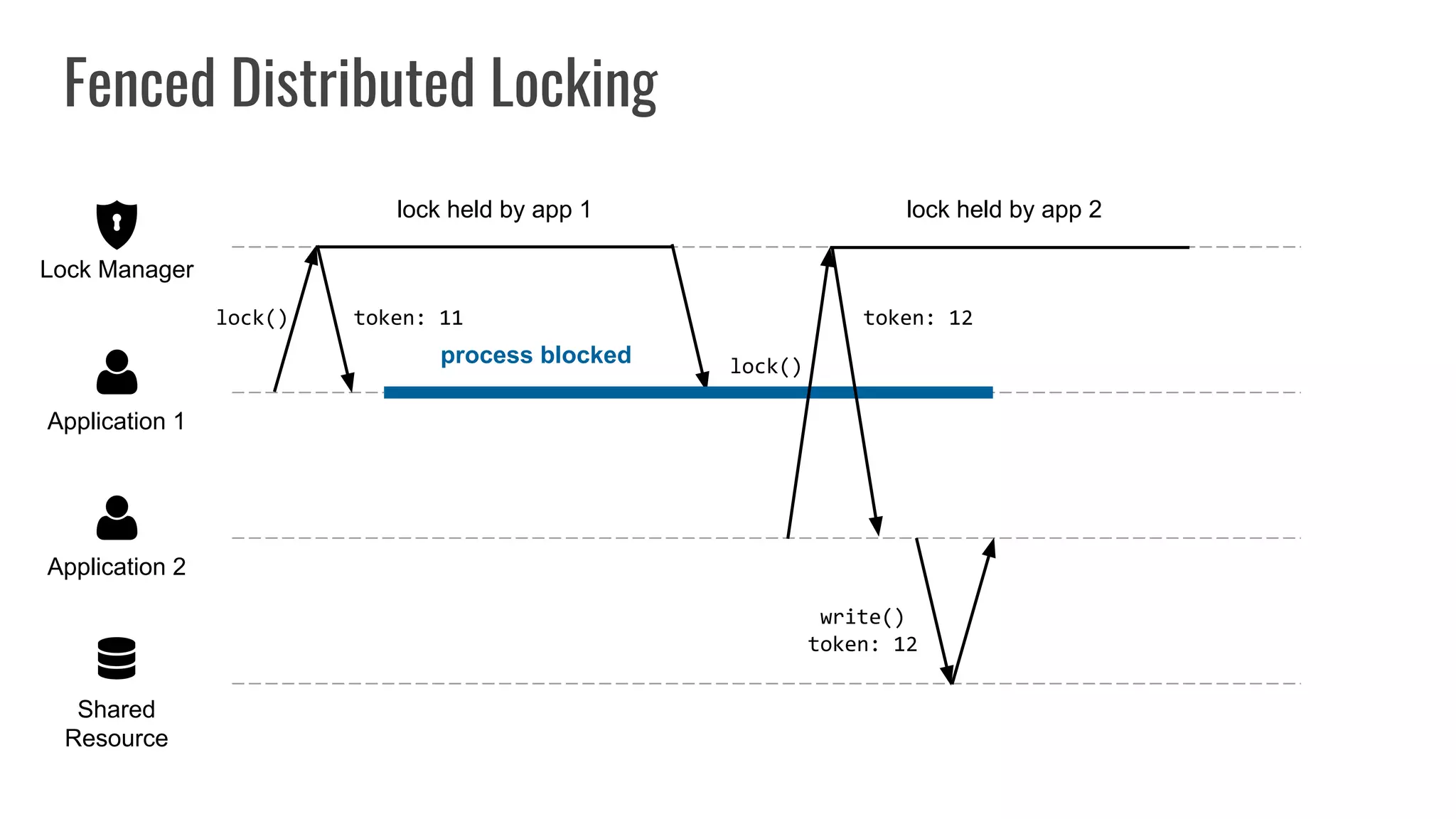
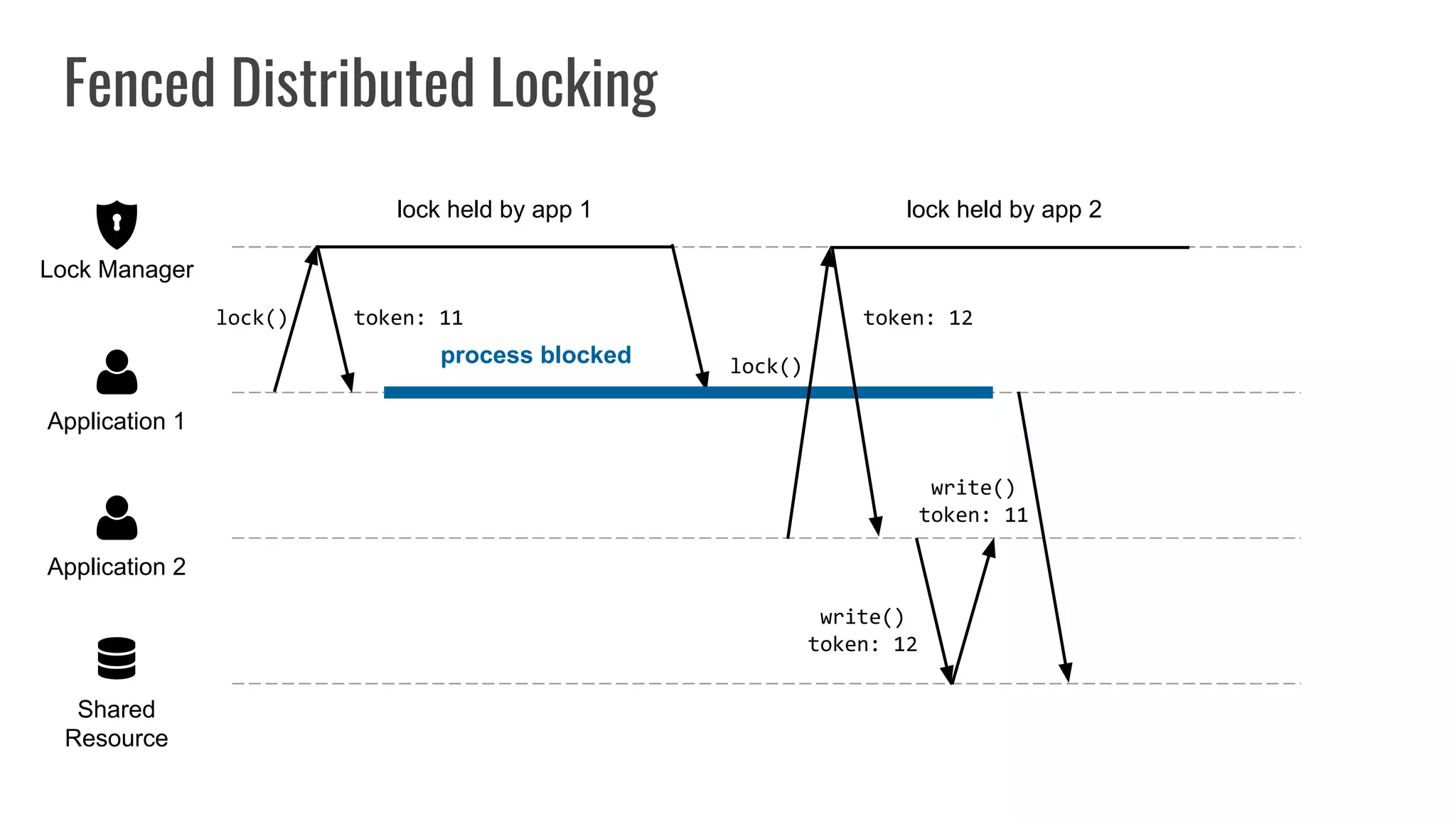
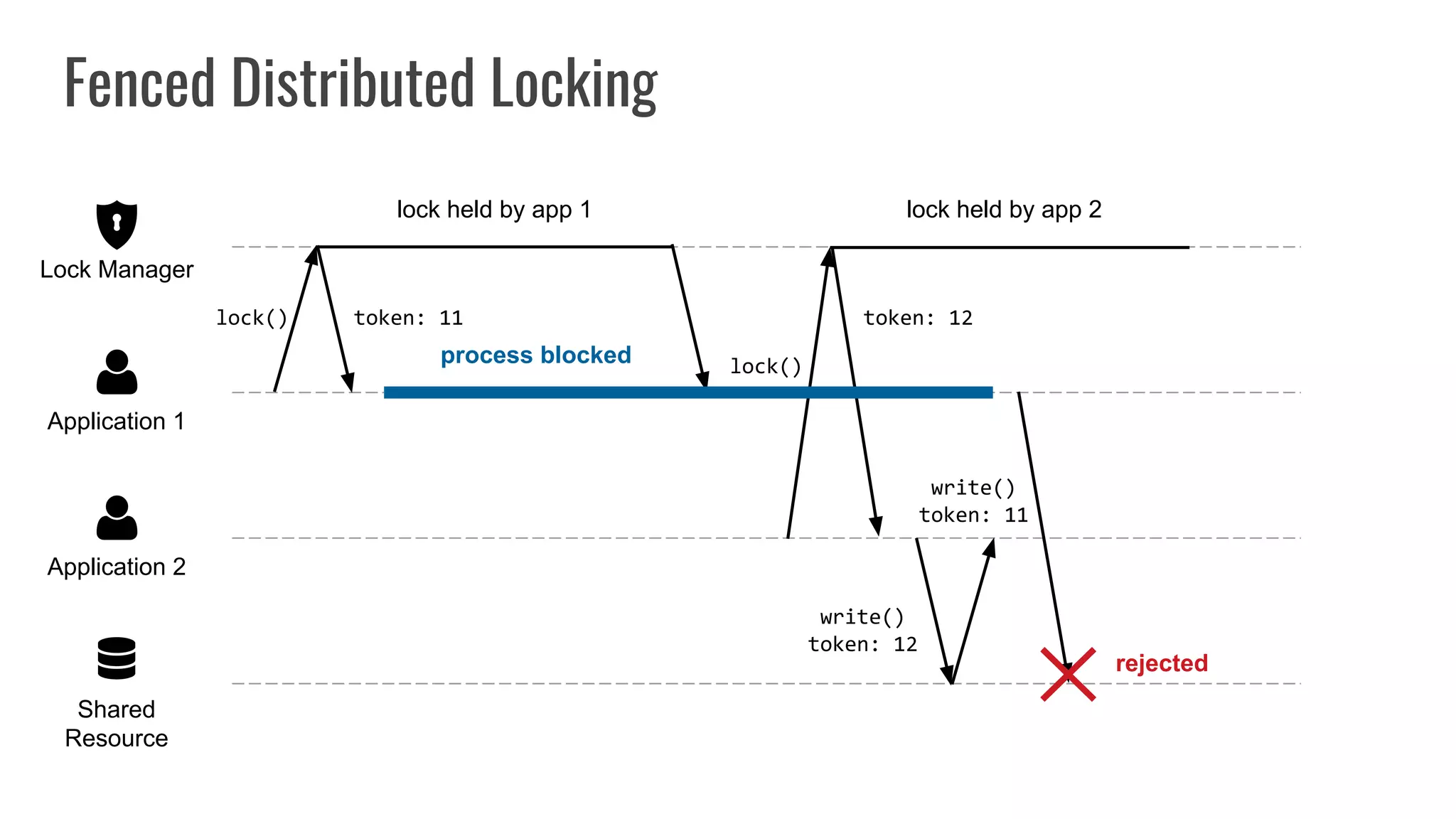
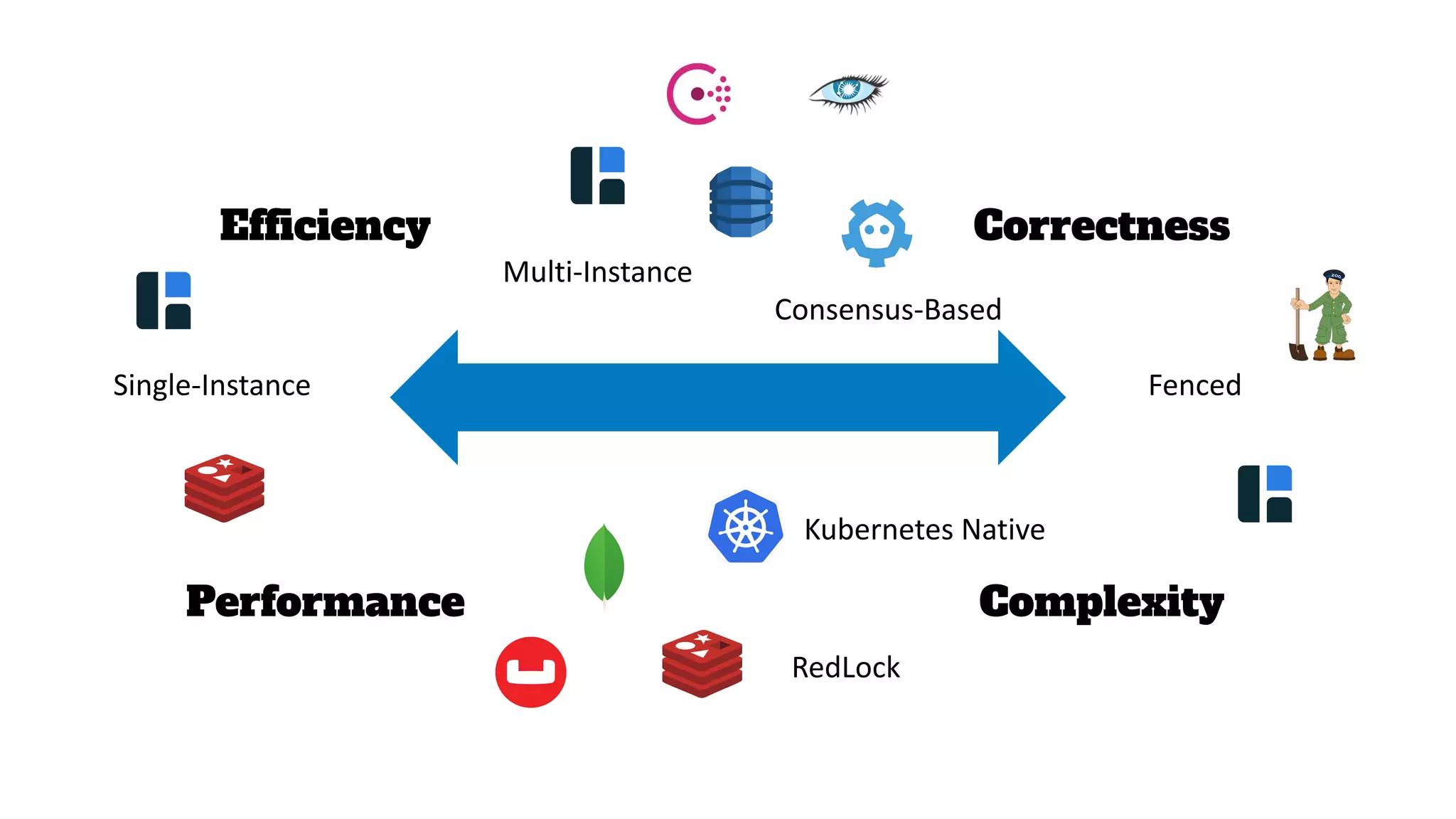
The document discusses different approaches to distributed locking in Kubernetes. It begins with an introduction to distributed locking and reasons for using it. It then covers several approaches: single-instance locking using a centralized lock manager like Hazelcast; multi-instance locking across a cluster; RedLock using multiple Redis instances; consensus-based locking; Kubernetes native locking libraries; and fenced locking which uses tokens to prevent lost updates. The document provides code examples for several approaches and discusses tradeoffs around efficiency, correctness, complexity and performance for each.