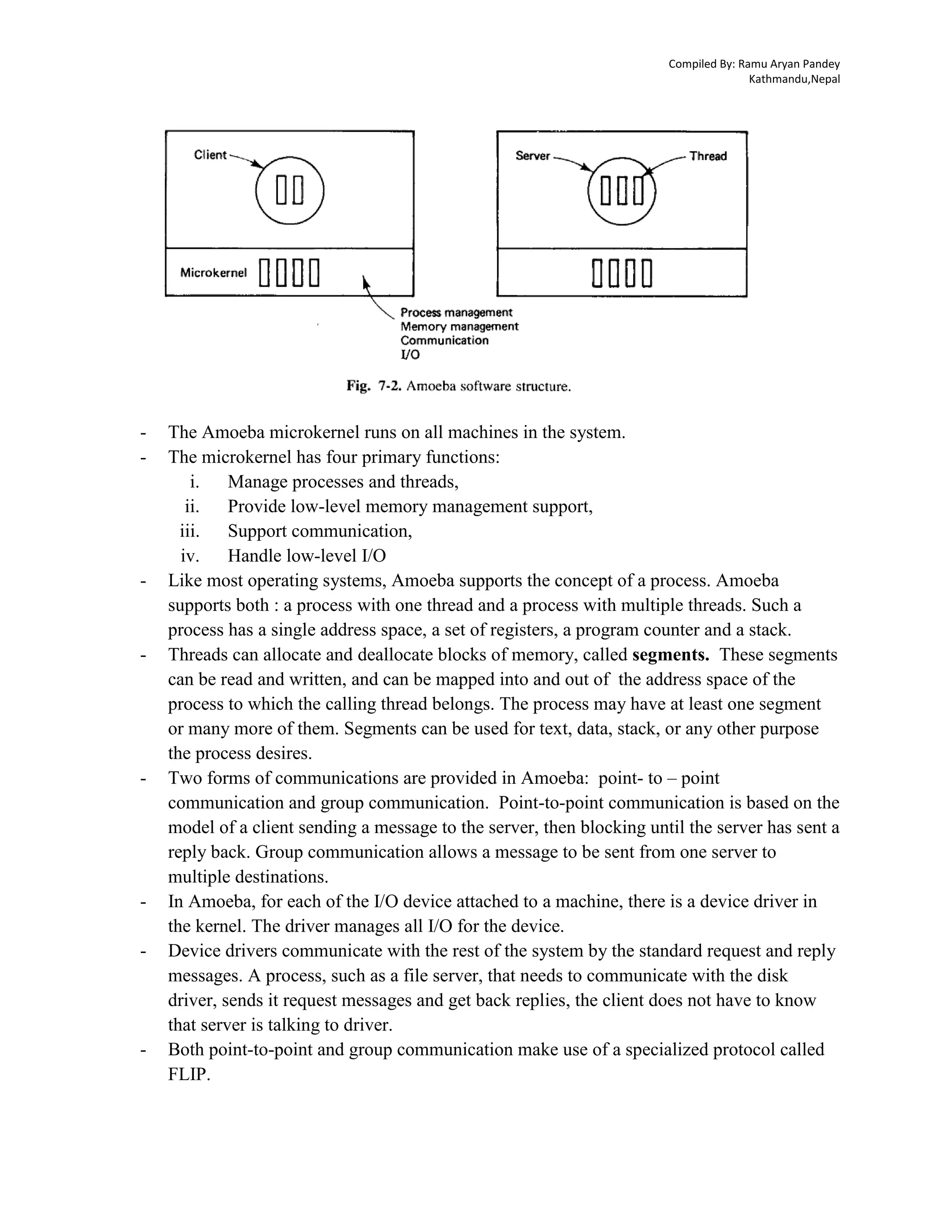
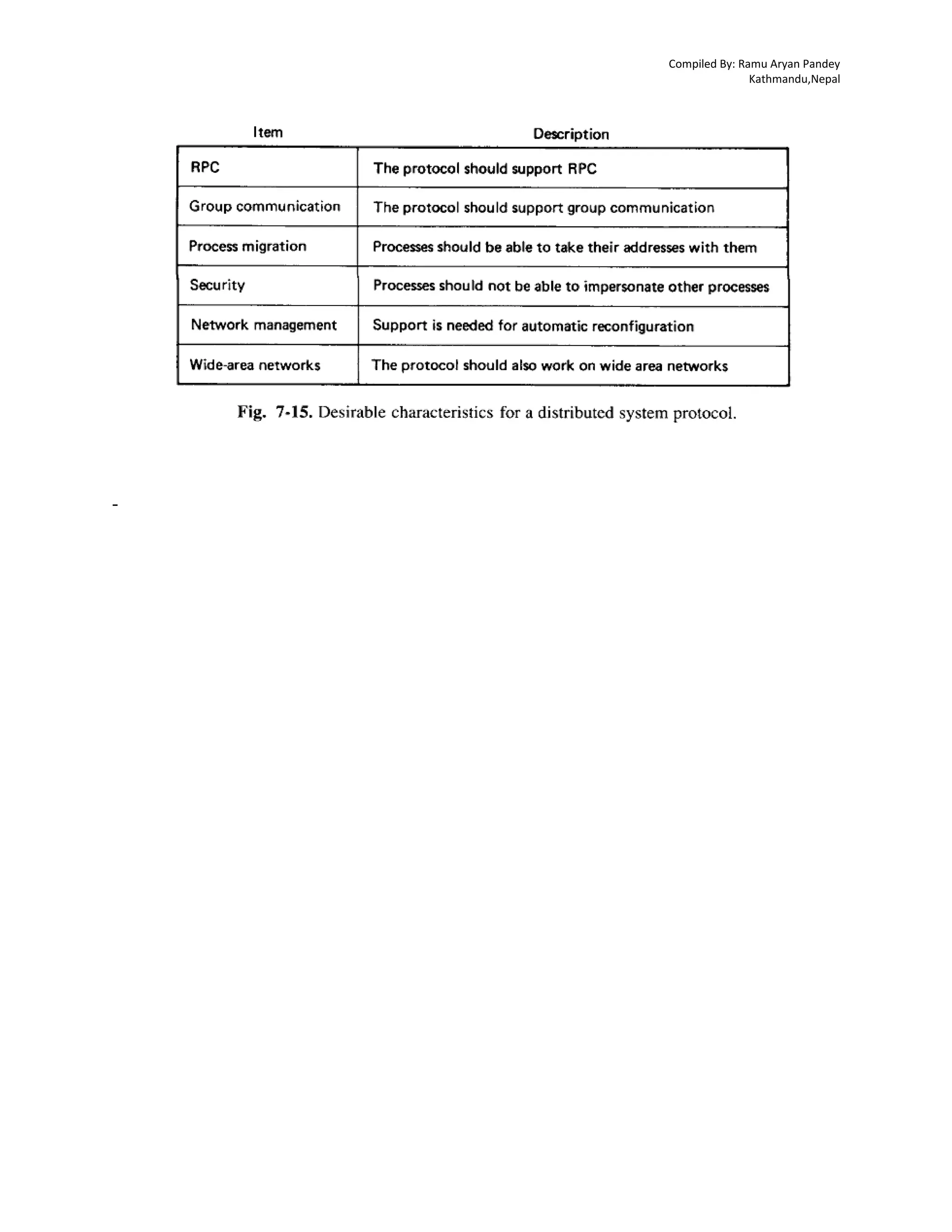
Amoeba is a distributed operating system designed to make multiple CPUs and I/O devices function as a single unit, primarily developed at Vrije Universiteit in Amsterdam since 1981. Its architecture enables location transparency and efficient resource management by dynamically assigning tasks across various processors without user awareness, thus simplifying user interaction to resemble traditional timesharing systems. Additionally, the Amoeba system relies on a microkernel and a robust client-server model for process management, communication, and object handling, which facilitates flexibility and adaptability across diverse computing environments.