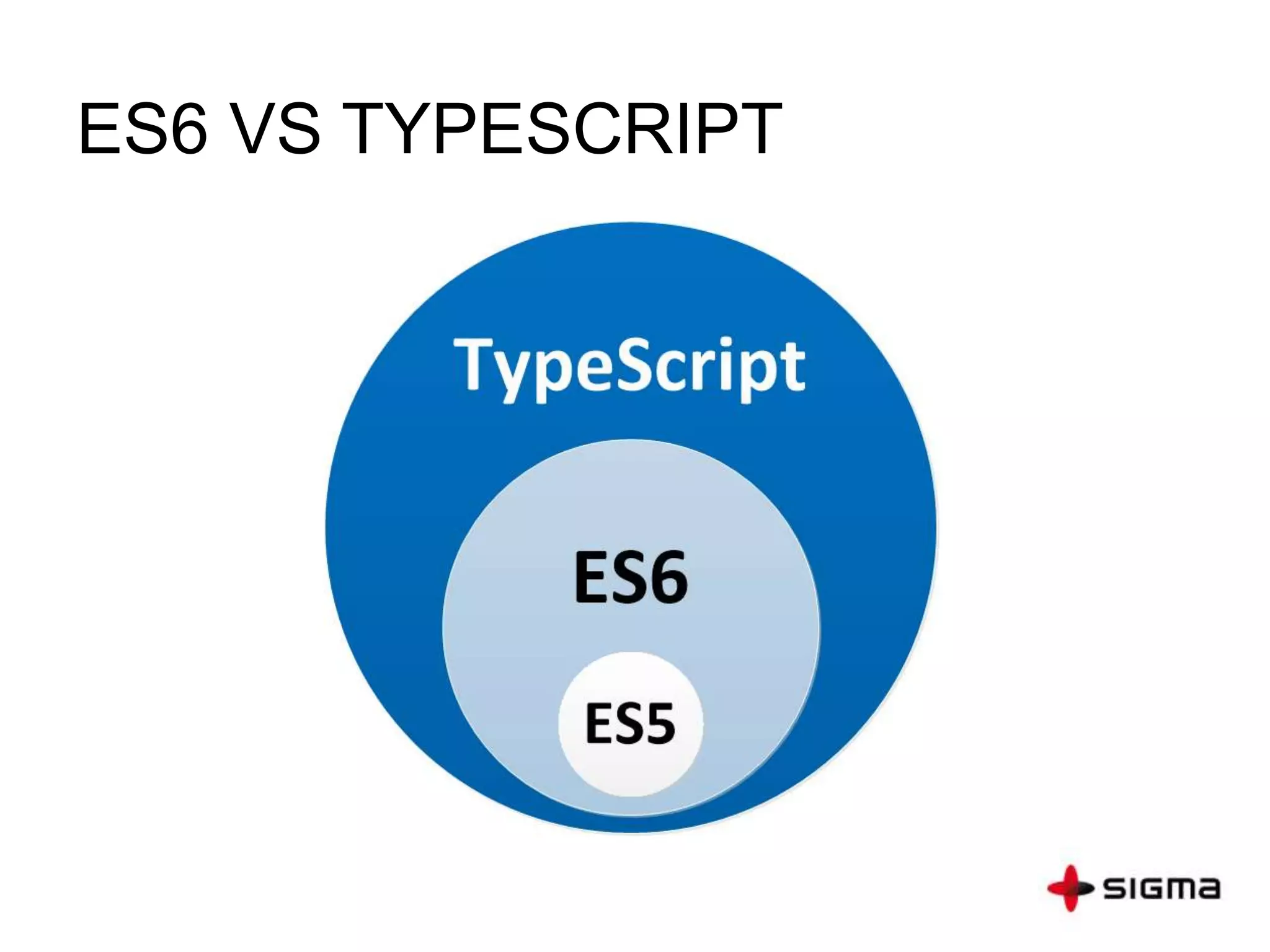
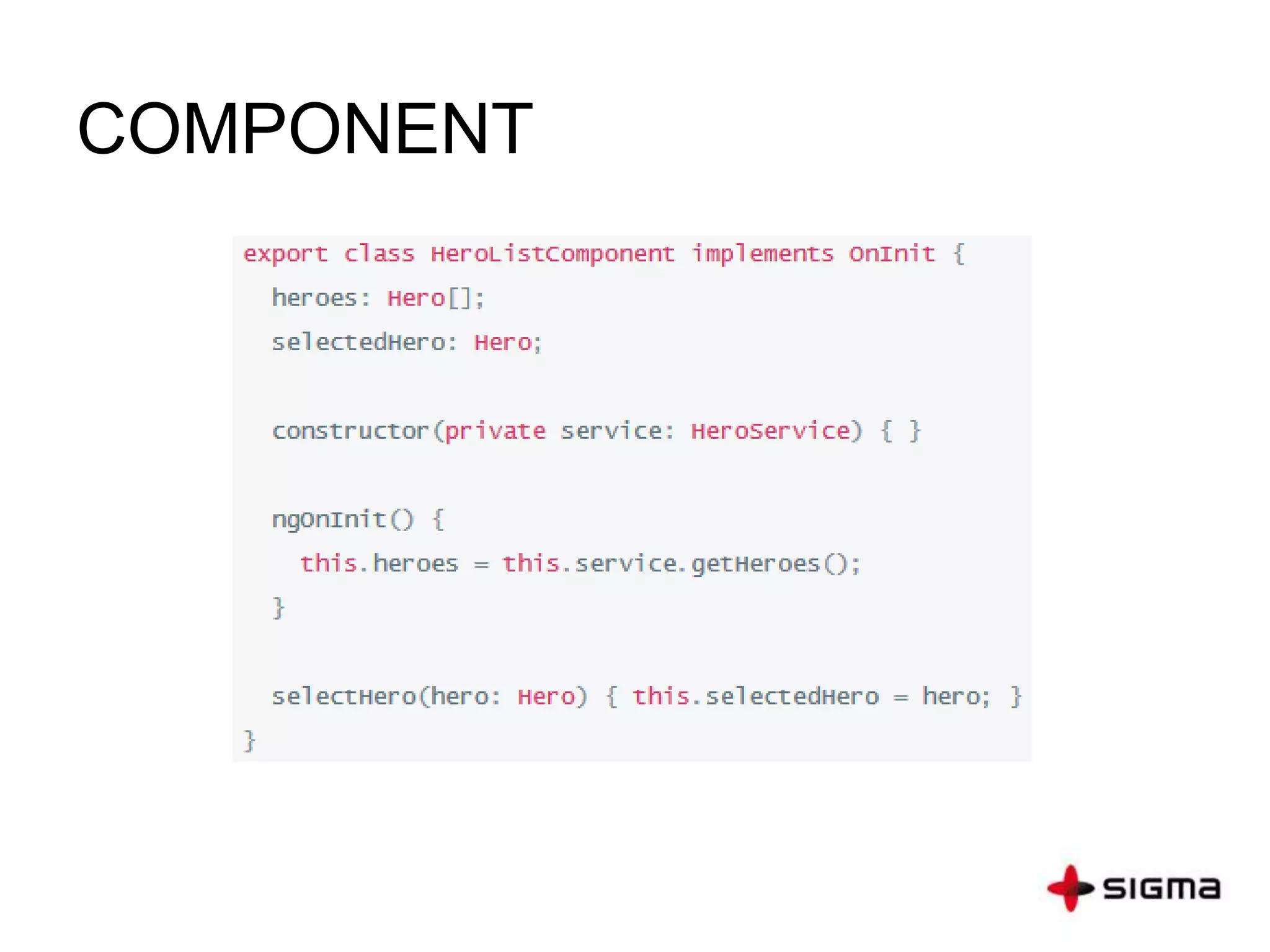
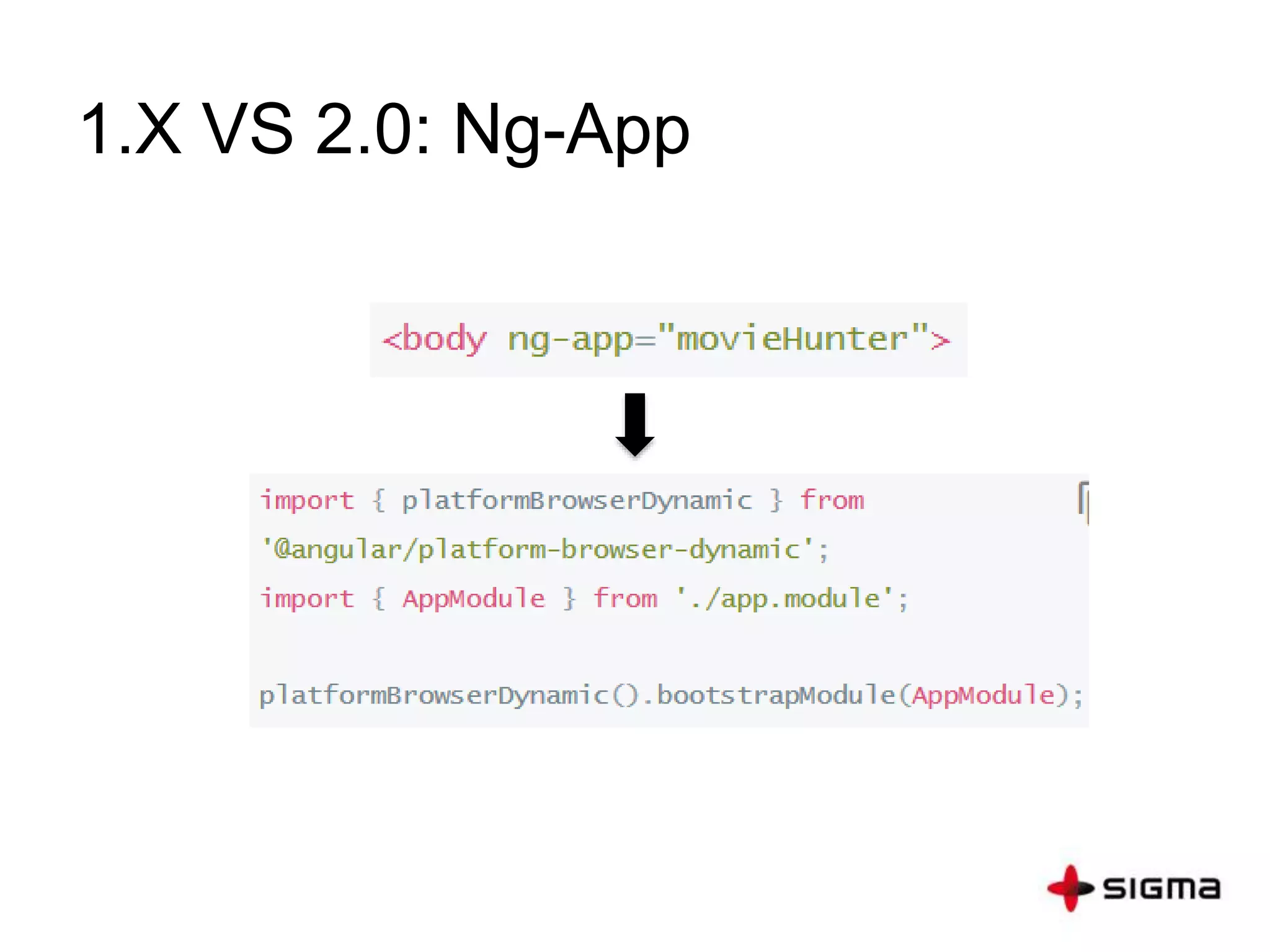
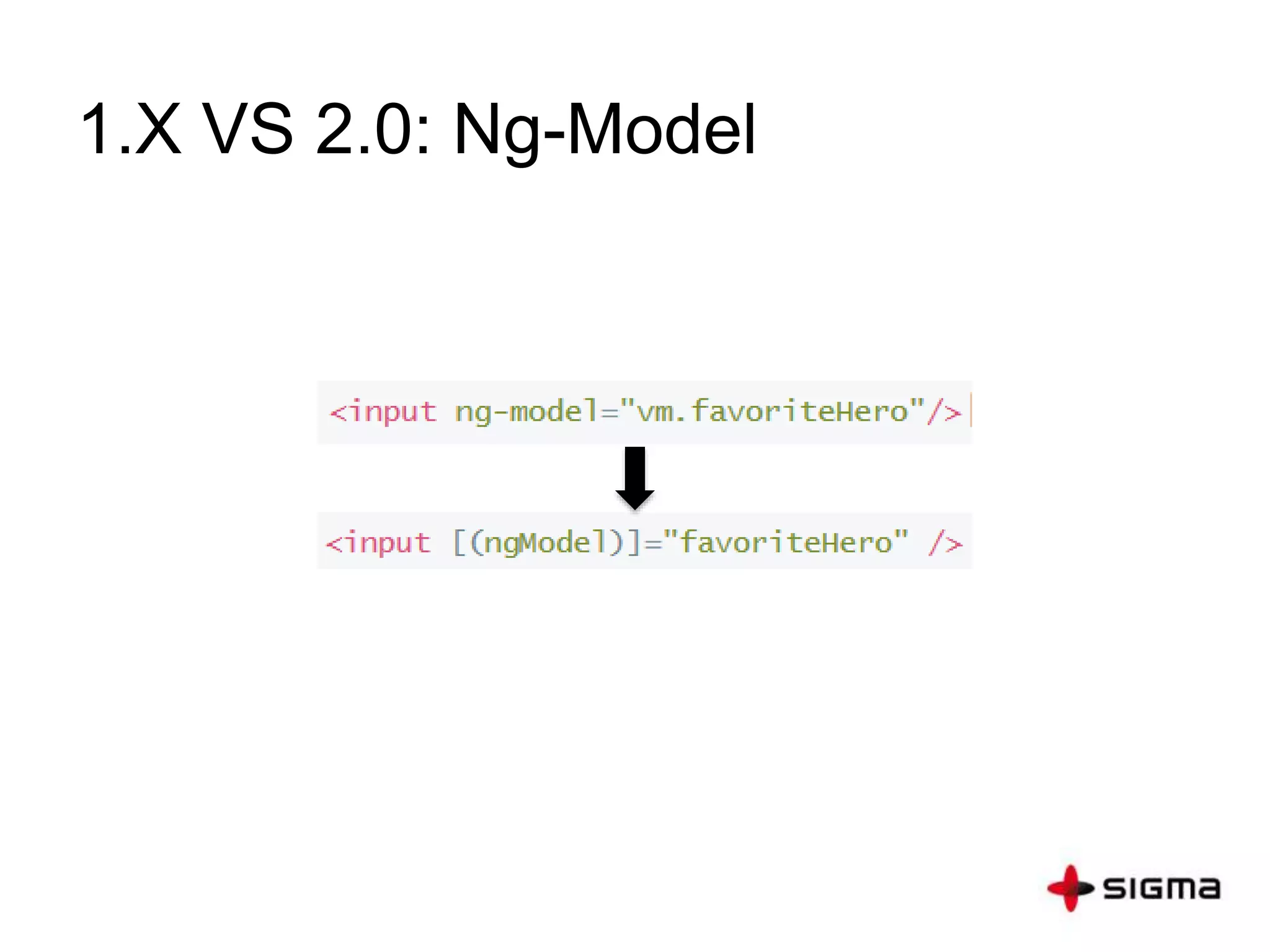
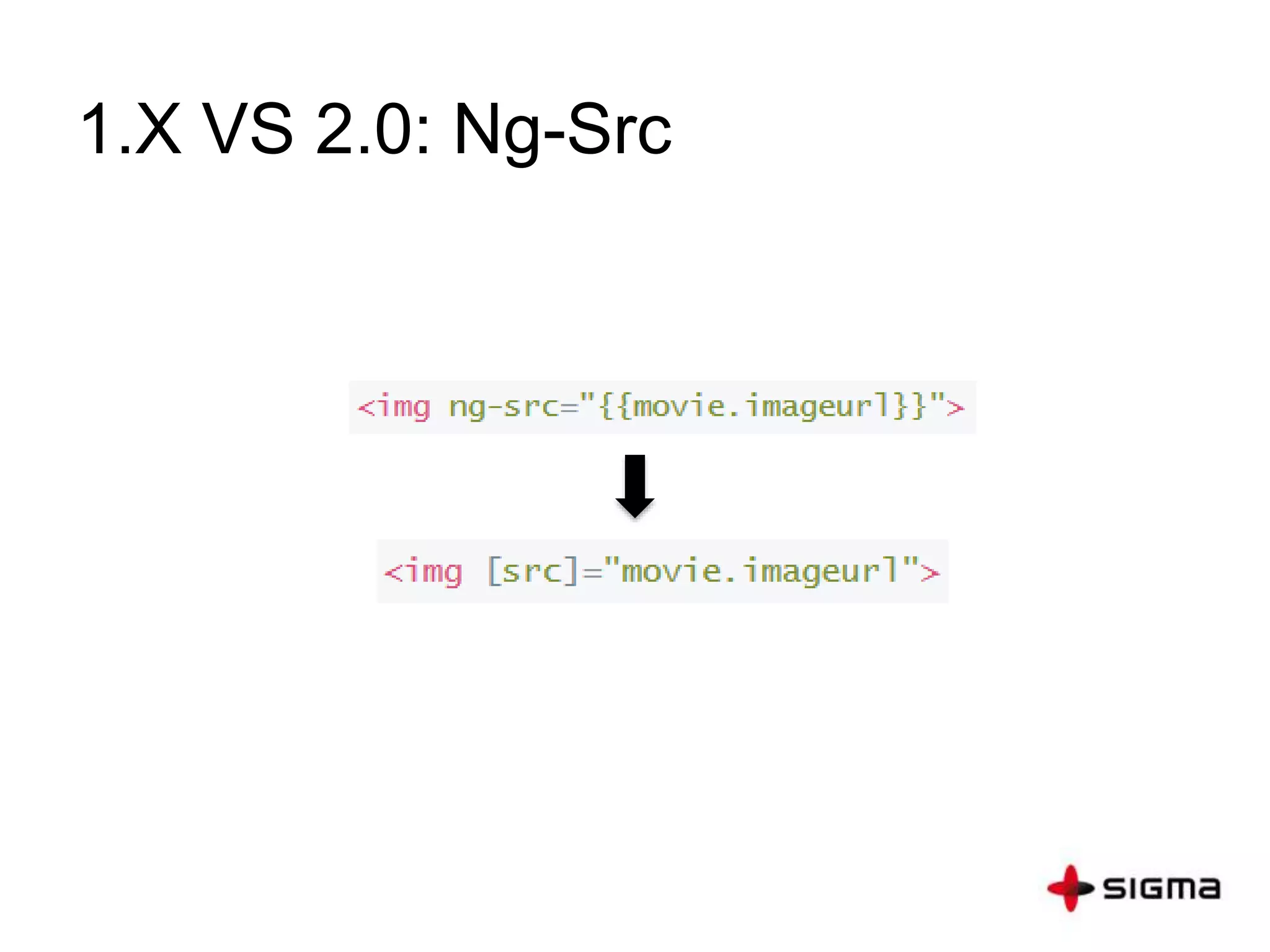
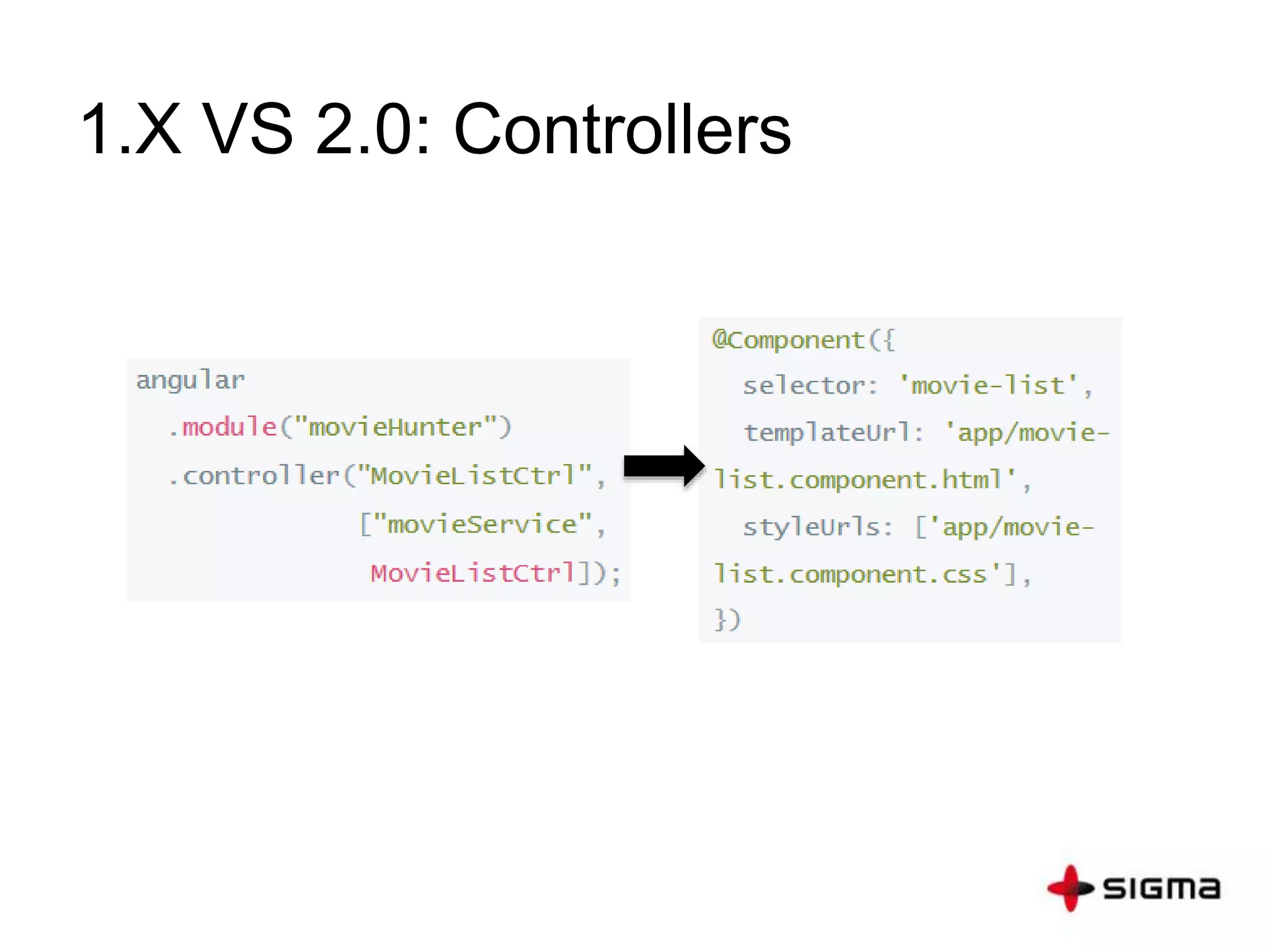
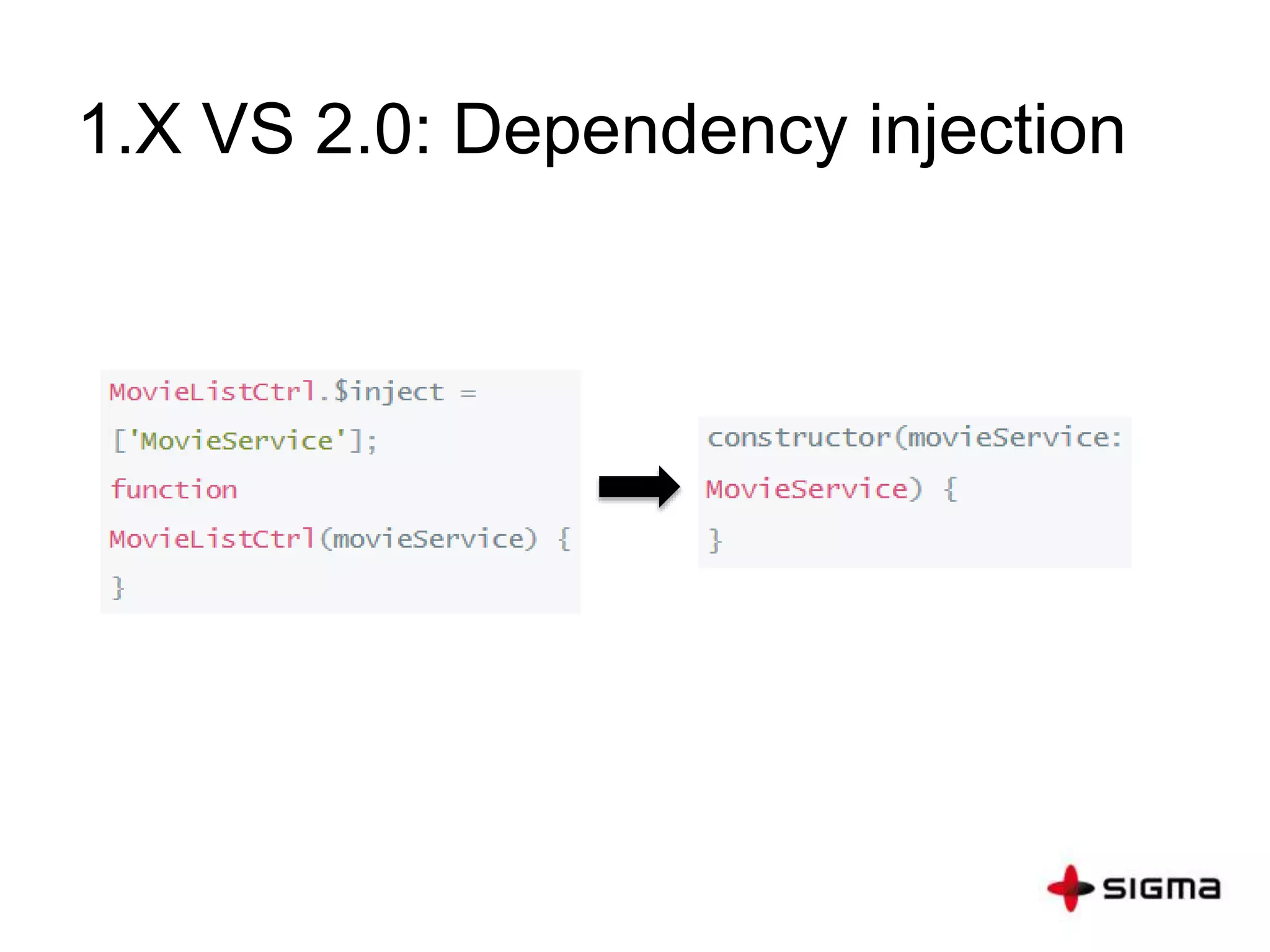
This document provides a comprehensive overview of Angular 2.0, detailing new features such as component-based architecture, simplified directives, and dependency injection. It outlines a six-step process for building an Angular 2 application and compares key differences between Angular 1.x and 2.0. Additionally, it covers essential concepts like components, modules, templates, data binding, and services, along with references for further learning.