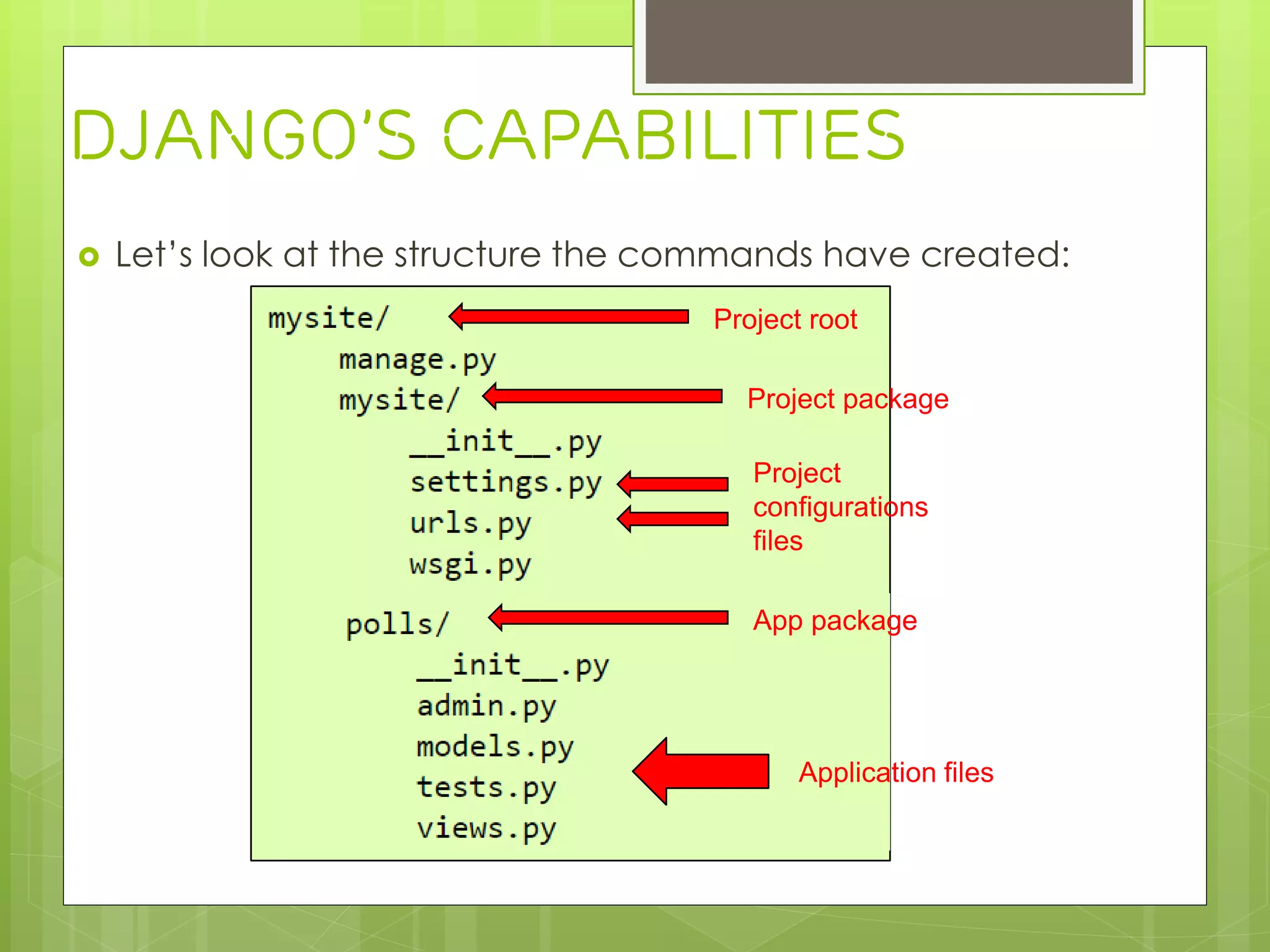
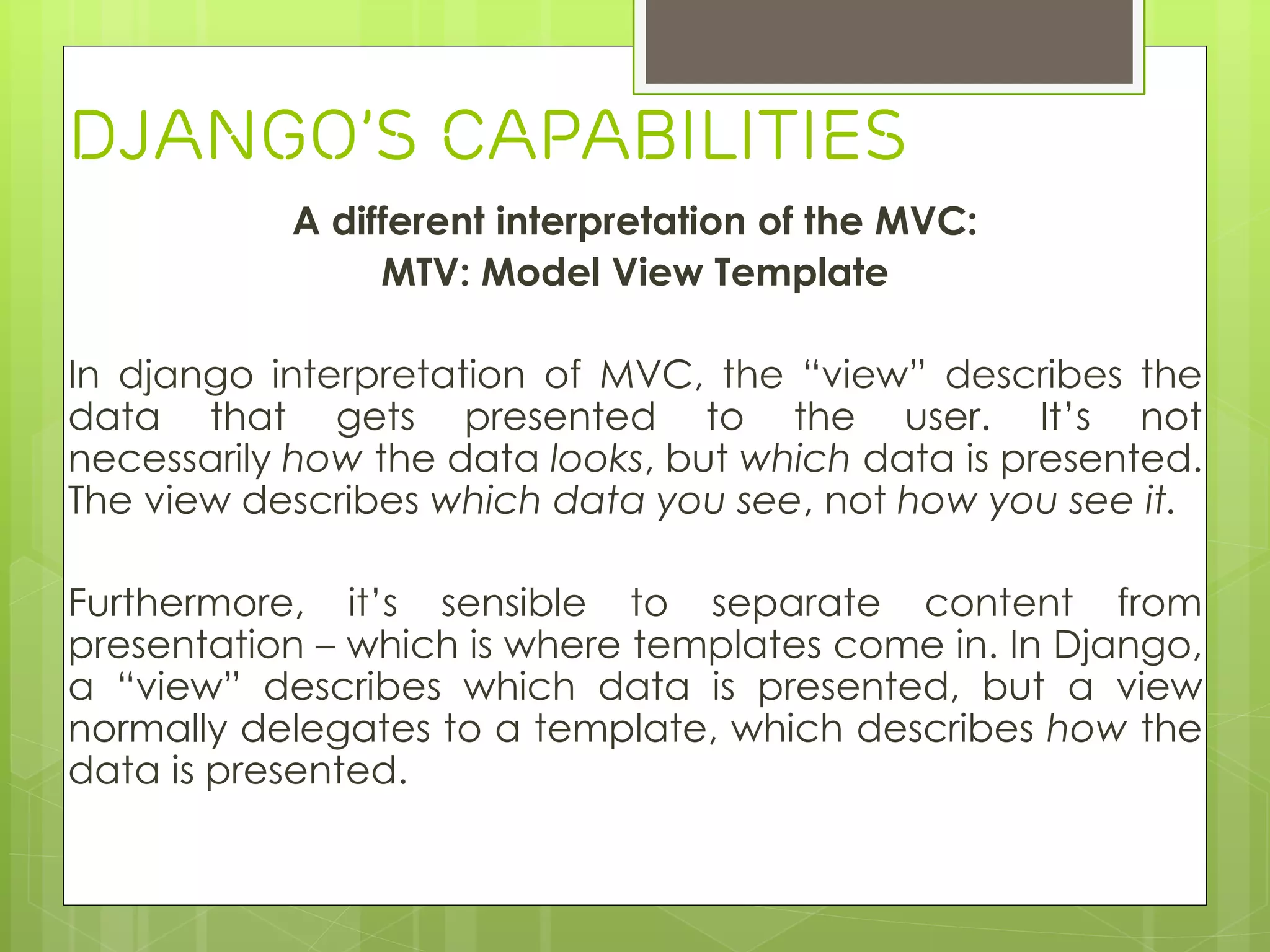
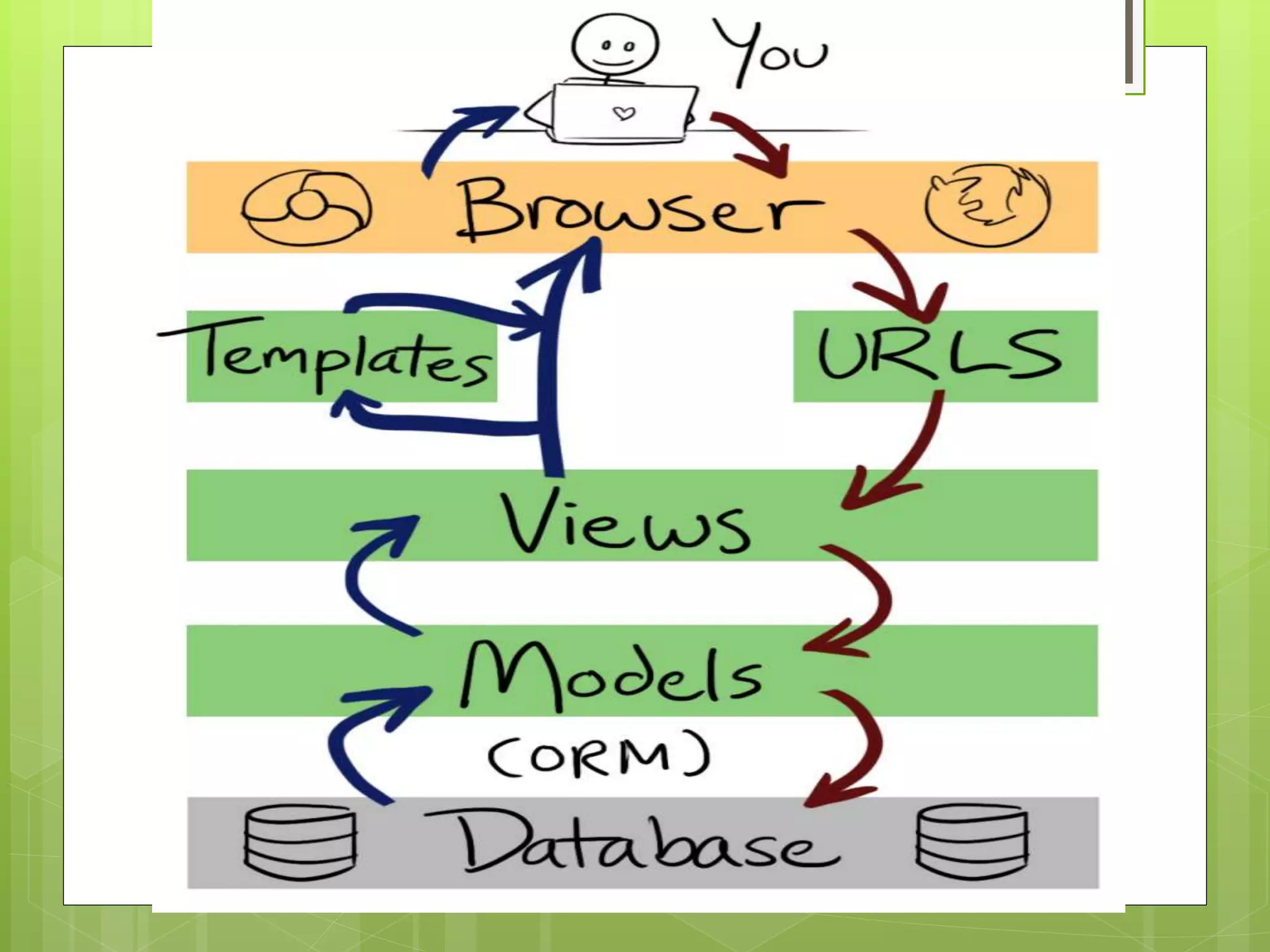
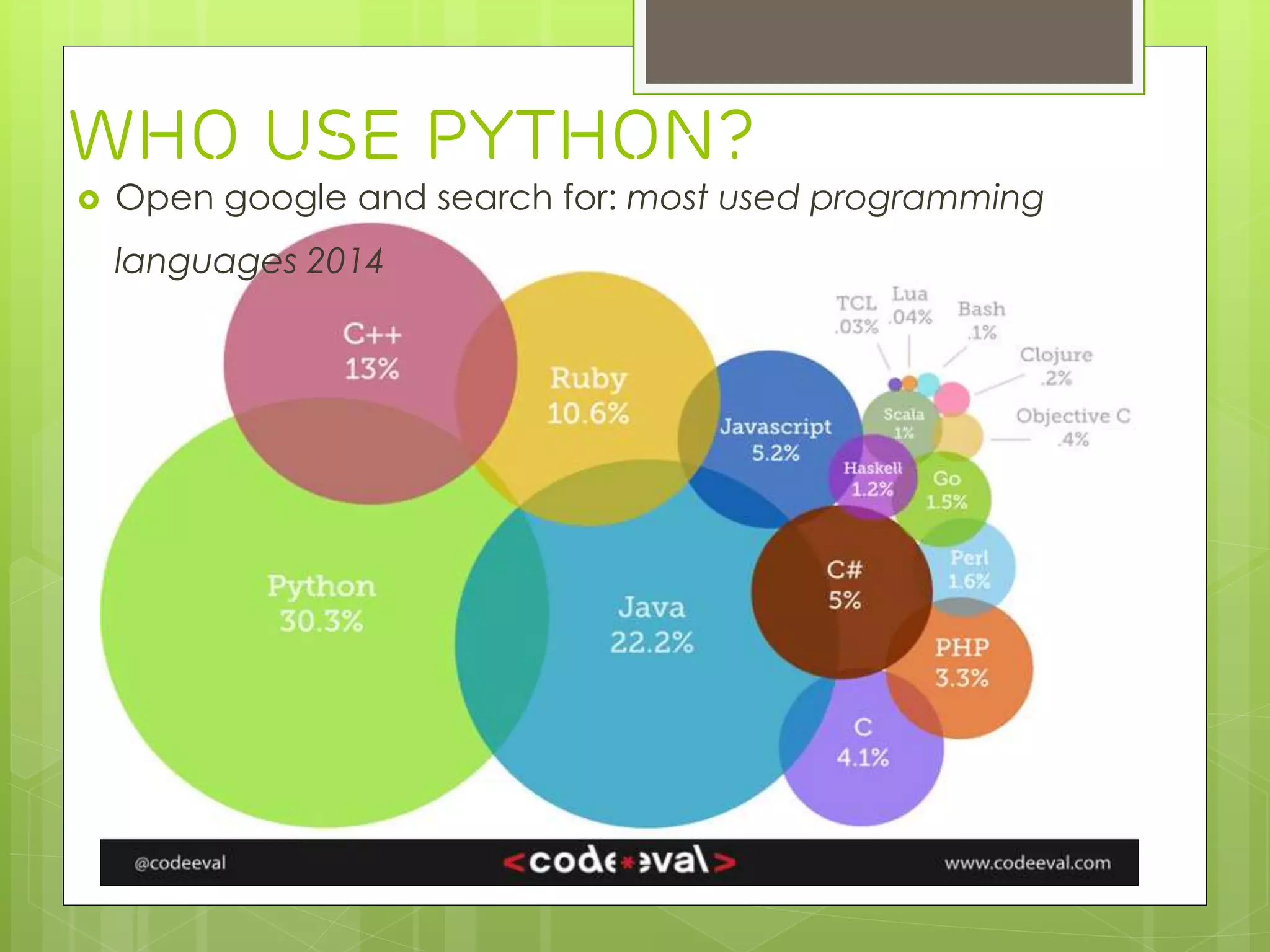
› Django is a Python-based web framework that allows for rapid development of web applications. It handles common tasks like database abstraction, forms, sessions, site maps, and administration interfaces out of the box. Django emphasizes reusability and modularity through reusable apps and a MTV (model-template-view) pattern that encourages DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) principles. Popular sites like Instagram and Pinterest use Django for its flexibility and productivity.









![ List:
Declared using “[ ]”
Access using index
Mutable
Tuple:
Declared using “( )”
Access using index
Immutable
Dictionary:
Declared using “ { } “
Access using keyword
Data Structure:
What is python ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoframeworkoverviewfornon-pythondevelopers-150130054034-conversion-gate02/75/Django-Framework-Overview-forNon-Python-Developers-13-2048.jpg)