Downloaded 303 times





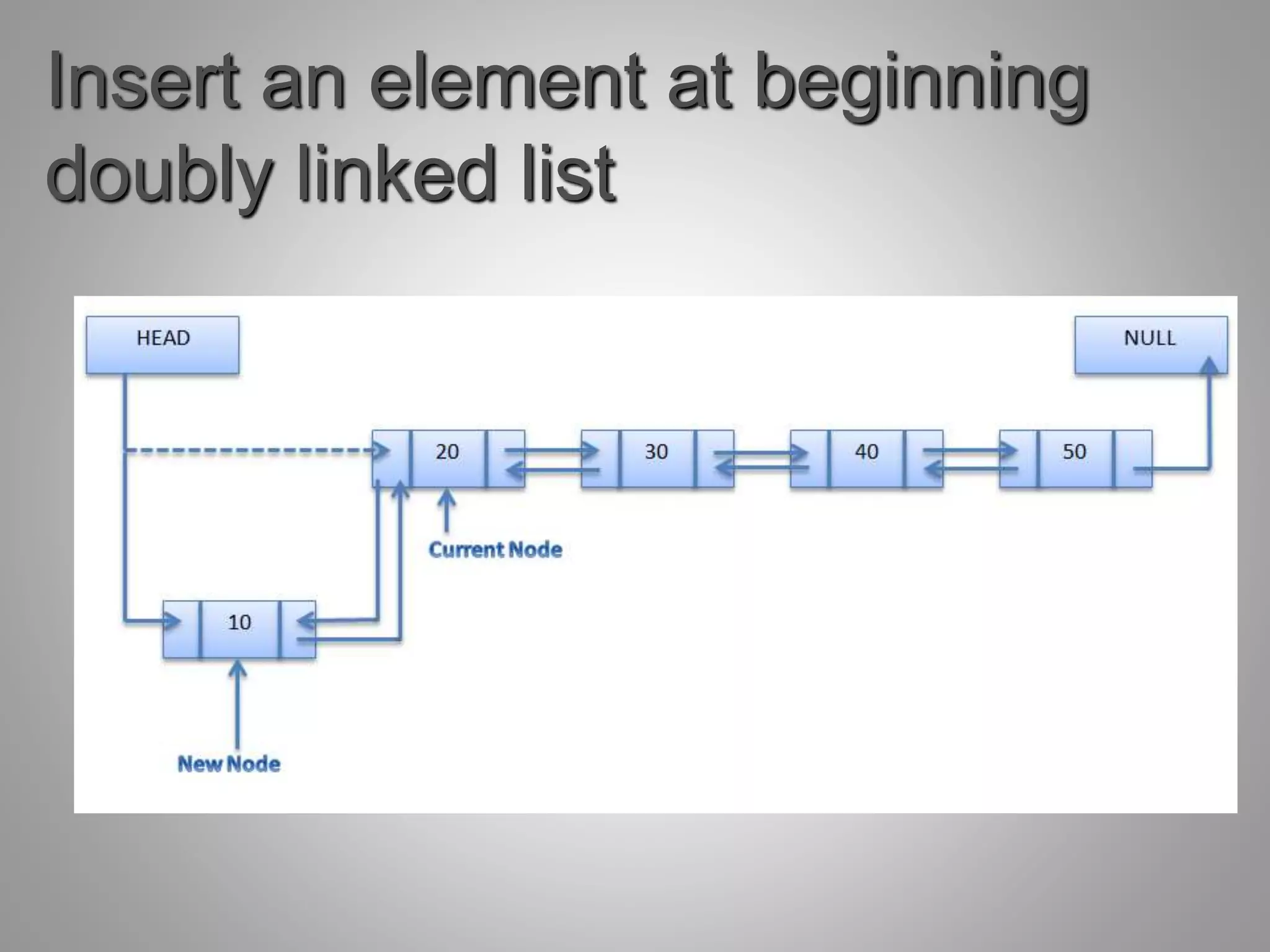
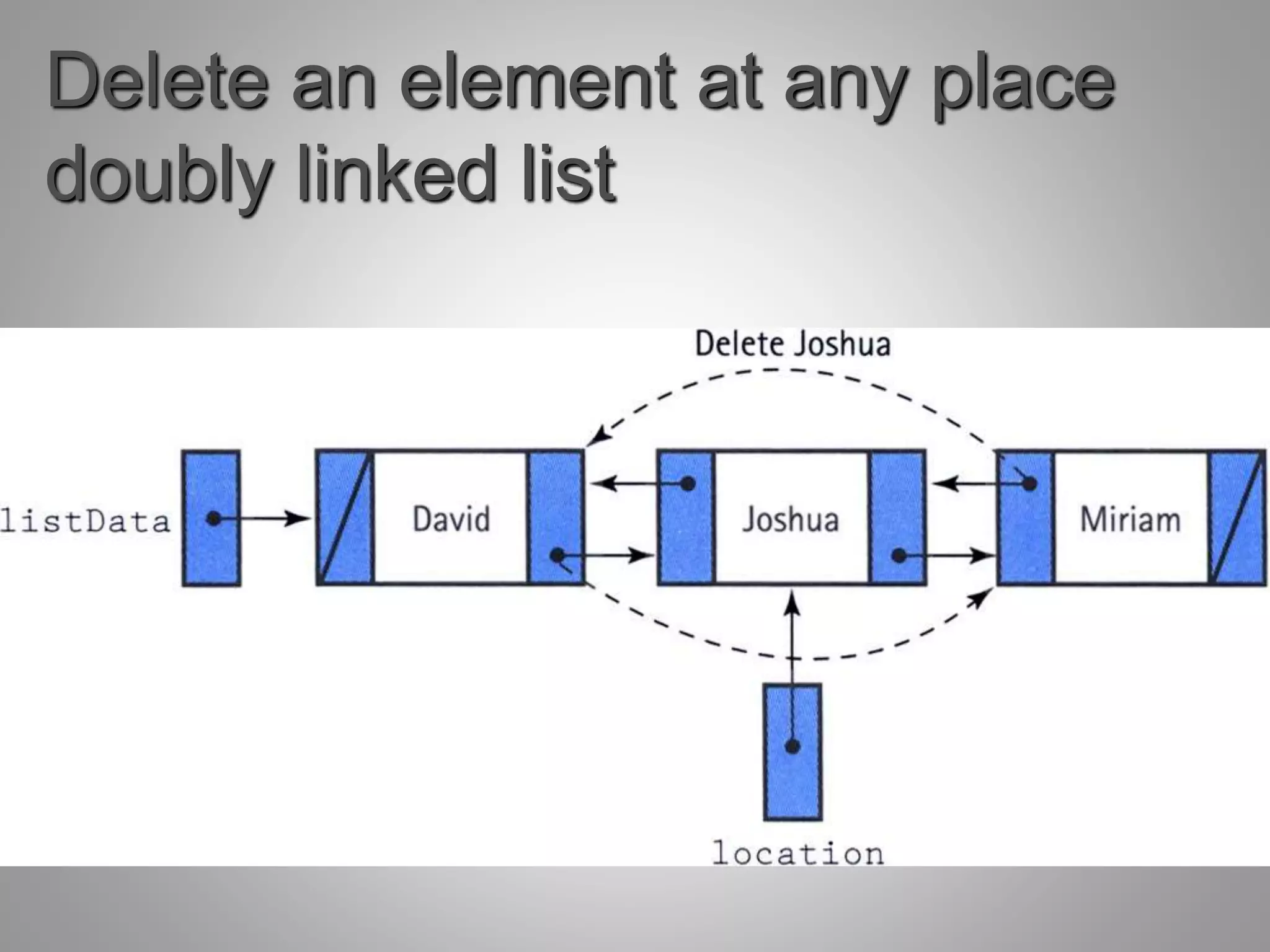


Each node in a doubly linked list contains two pointers - one pointing to the next node and one pointing to the previous node. This allows traversal in both directions through the list. A doubly linked list supports common operations like insertion and deletion at both ends of the list as well as anywhere in the list by updating the relevant pointer fields of the nodes. While requiring more space per node, doubly linked lists allow easy traversal backwards through the list and reversing of the list.









Introduction to doubly linked lists and node structure with two pointers: previous and next. It allows bidirectional traversal.
Key operations such as creating a list, inserting elements (at beginning, end, or any position), and deleting elements.
Benefits include bidirectional traversal and easy reversibility; drawbacks are increased space for pointers and slower insert/delete operations compared to linear lists.