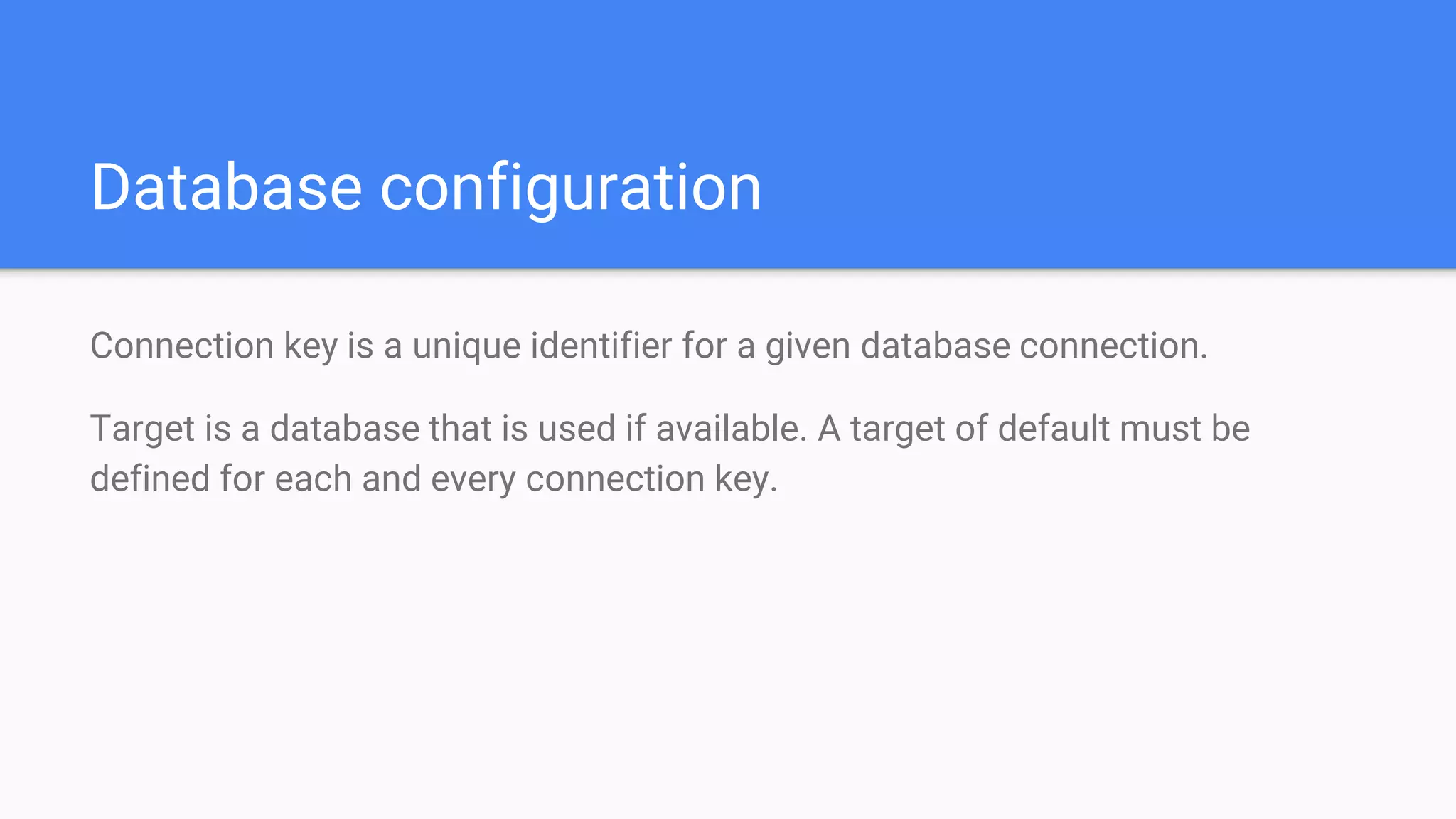
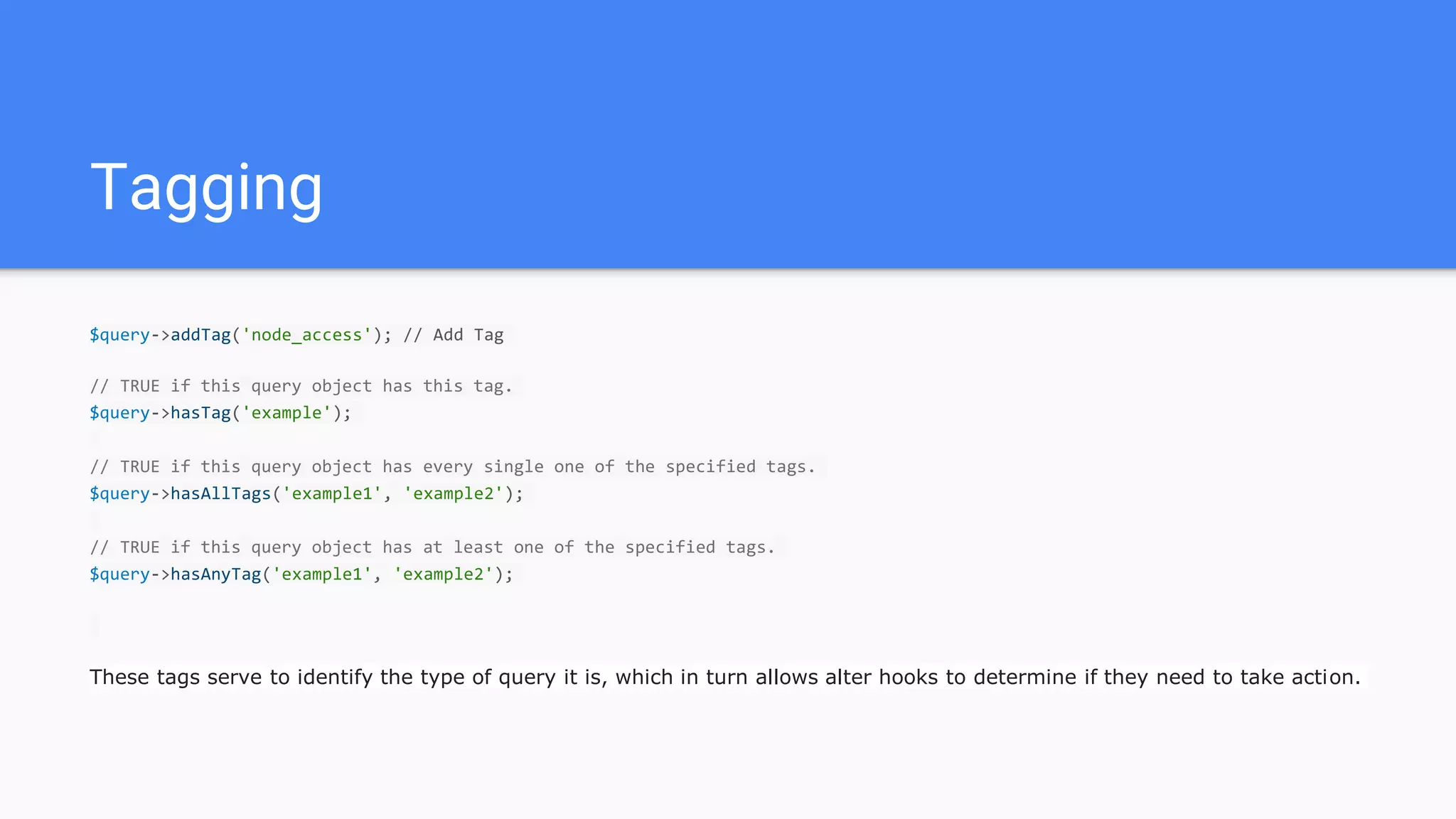
The document provides an overview of the Drupal 8 database API. It discusses concepts like database connections, configuration, and query types (static, dynamic, insert, update, delete). It explains how to perform queries, work with result sets, add conditions/tags, and use transactions. Key points are that the API is built on PDO, drivers are required for each database, and dynamic queries should be used for operations like insert/update while static can be used for select.



![Connection syntax
$databases['default']['default'] = array(
'driver' => 'mysql',
'database' => 'drupaldb',
'username' => 'username',
'password' => 'secret',
'host' => 'localhost',
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8databaseapi-170707055406/75/Drupal-8-database-api-5-2048.jpg)
![For a master/slave configuration
$databases['default']['default'] = array(
'driver' => 'mysql',
'database' => 'drupaldb1',
'username' => 'username',
'password' => 'secret',
'host' => 'dbserver1',
);
$databases['default']['slave'][] = array(
'driver' => 'mysql',
'database' => 'drupaldb2',
'username' => 'username',
'password' => 'secret',
'host' => 'dbserver2',
);
$databases['default']['slave'][] = array(
'driver' => 'mysql',
'database' => 'drupaldb3',
'username' => 'username',
'password' => 'secret',
'host' => 'dbserver3',
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8databaseapi-170707055406/75/Drupal-8-database-api-6-2048.jpg)
![For connecting mysql as well as sqlite
$databases['default']['default'] = array(
'driver' => 'mysql',
'database' => 'drupaldb1',
'username' => 'username',
'password' => 'secret',
'host' => 'dbserver1',
);
$databases['extra']['default'] = array(
'driver' => 'sqlite',
'database' => 'files/extradb.sqlite',
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8databaseapi-170707055406/75/Drupal-8-database-api-7-2048.jpg)
![How to specify pdo options
$databases['default']['default'] = array(
'driver' => 'mysql',
'database' => 'drupaldb',
'username' => 'username',
'password' => 'secret',
'host' => 'dbserver1',
'pdo' => array(ATTR_TIMEOUT => 2.0),
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8databaseapi-170707055406/75/Drupal-8-database-api-8-2048.jpg)
![Static queries
Only select queries can be static.
For example:
$result = db_query("SELECT nid, title FROM {node}");
$result = db_query("SELECT nid, title FROM {node} WHERE created > :created", array(
':created' => REQUEST_TIME - 3600,
));
$result = db_query("SELECT * FROM {node} WHERE nid IN (:nids[])", array(':nids[]' => array(13, 42, 144)));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8databaseapi-170707055406/75/Drupal-8-database-api-9-2048.jpg)
![Passing options and using the results
$result = db_query("SELECT nid, title FROM {node}", array(), array(
'target' => 'slave',
'fetch' => PDO::FETCH_ASSOC, // Passing Option
));
if ($result) {
while ($row = $result->fetchAssoc()) {
// Do something with:
// $row['nid']
// $row['title']
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8databaseapi-170707055406/75/Drupal-8-database-api-10-2048.jpg)





![Result Sets
$record = $result->fetch(); // Use the default fetch mode.
$record = $result->fetchObject(); // Fetch as a stdClass object.
$record = $result->fetchAssoc(); // Fetch as an associative array.
$record = $result->fetchField($column_index);
$number_of_rows = $result->rowCount();
// Retrieve all records into an indexed array of stdClass objects.
$result->fetchAll();
// Retrieve all records into an associative array keyed by the field in the result specified.
$result->fetchAllAssoc($field);
// Retrieve a 2-column result set as an associative array of field 0 => field 1
$result->fetchAllKeyed();
// You can also specify which two fields to use by specifying the column numbers for each field
$result->fetchAllKeyed(0,2); // would be field 0 => field 2
$result->fetchAllKeyed(1,0); // would be field 1 => field 0
// If you need an array where keys and values contain the same field (e.g. for creating a 'checkboxes' form element), the following is
a perfectly valid method:
$result->fetchAllKeyed(0,0); // would be field 0 => field 0, e.g. [article] => [article]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8databaseapi-170707055406/75/Drupal-8-database-api-17-2048.jpg)






