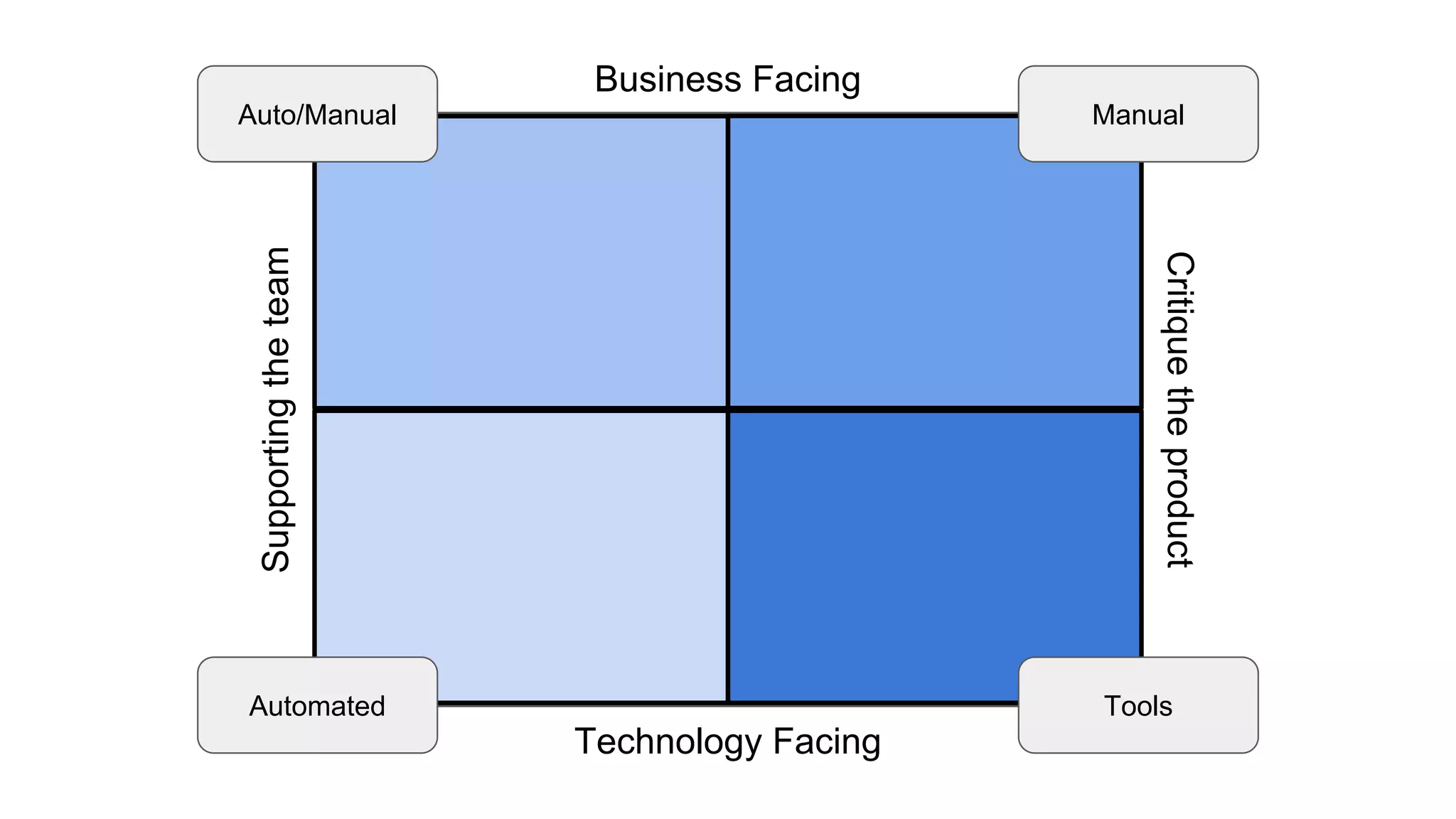
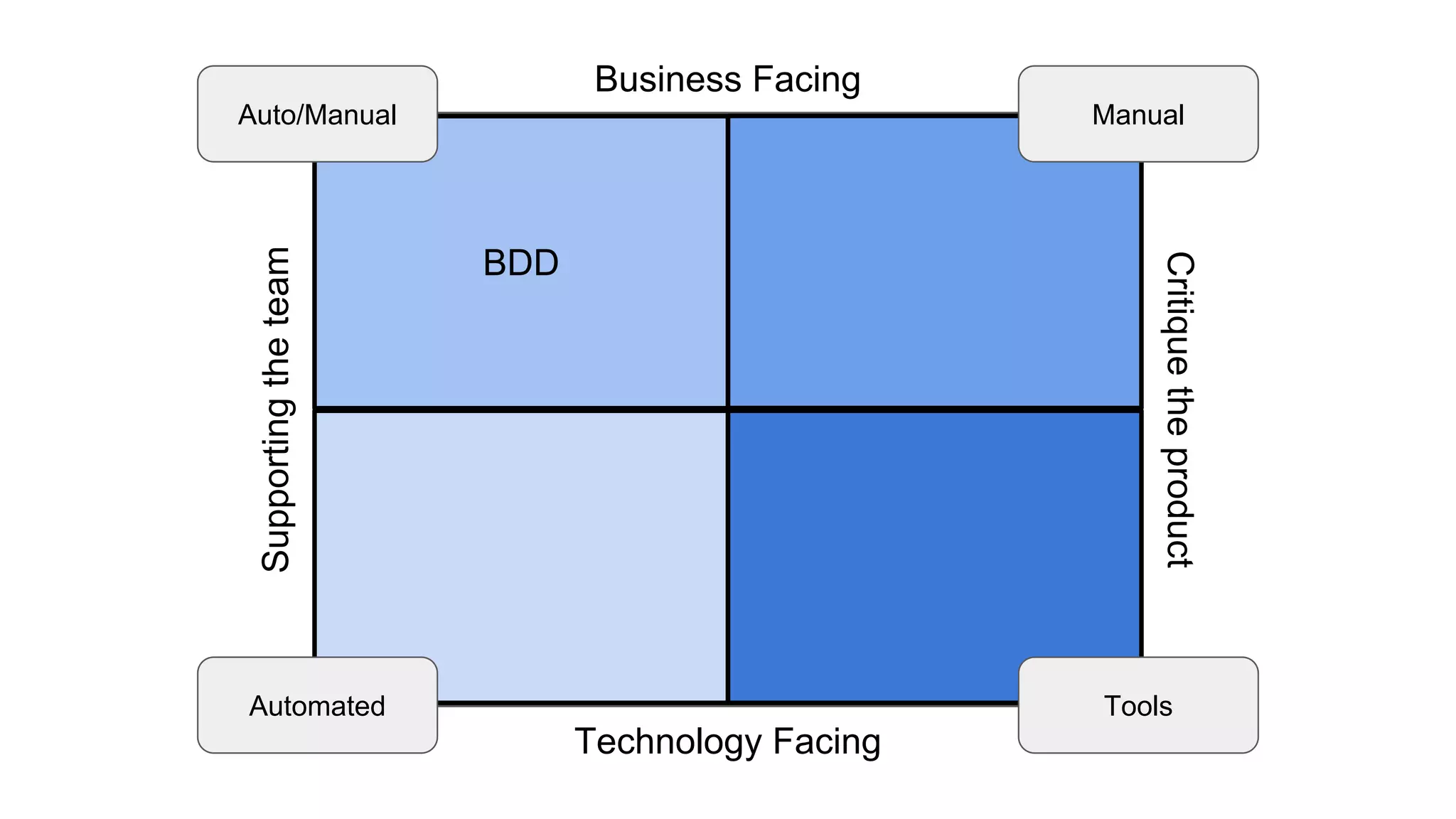
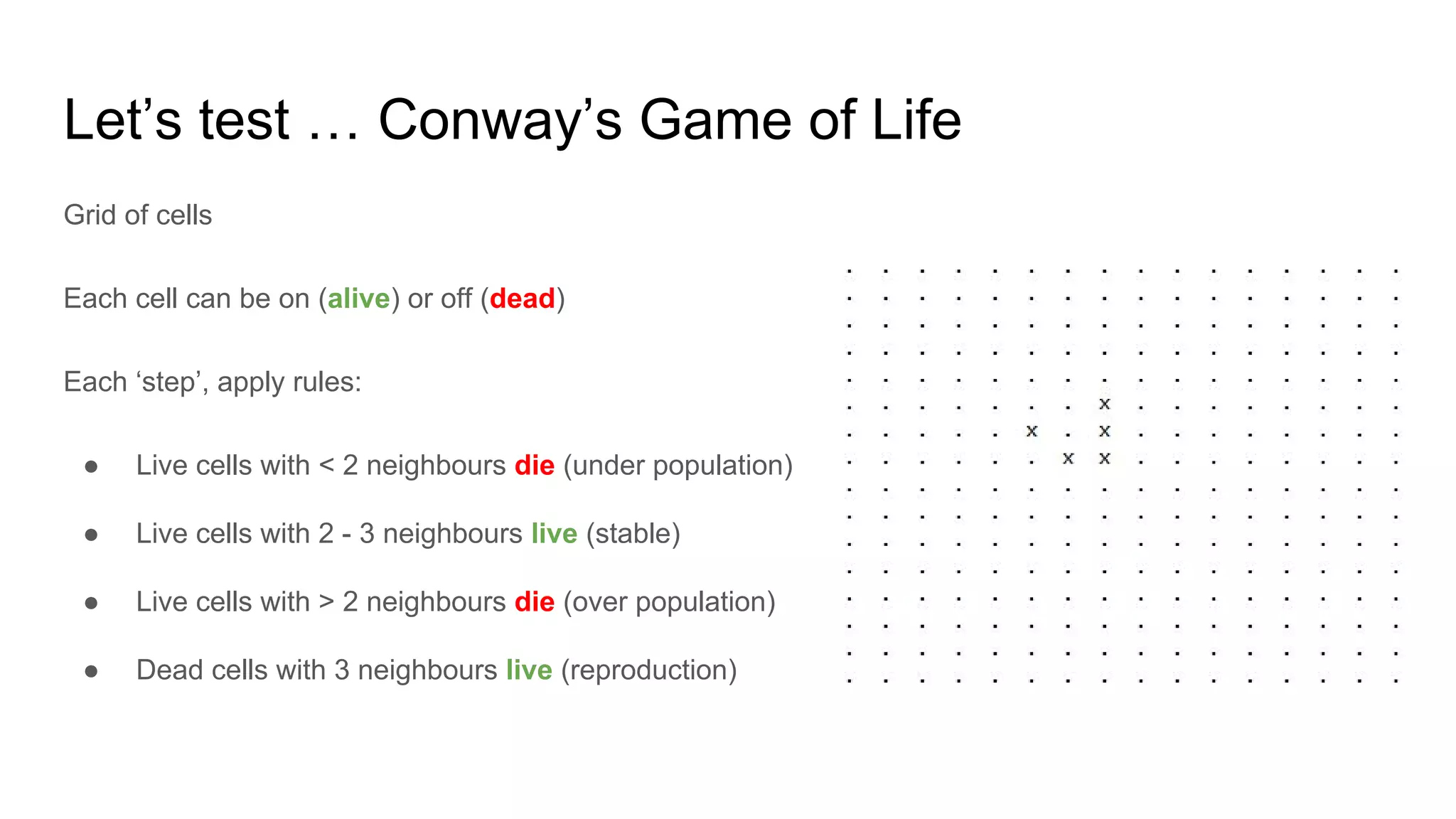
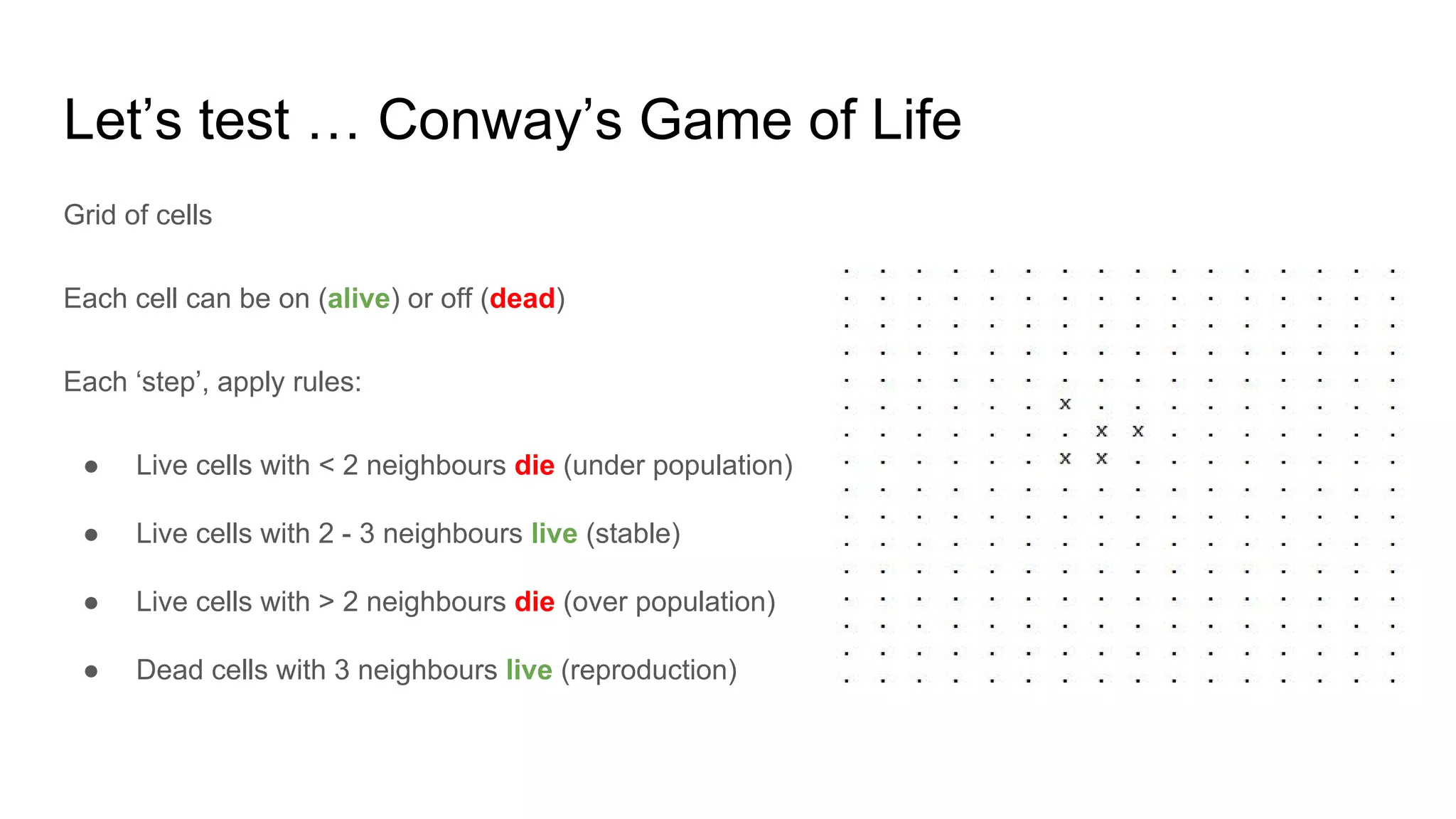
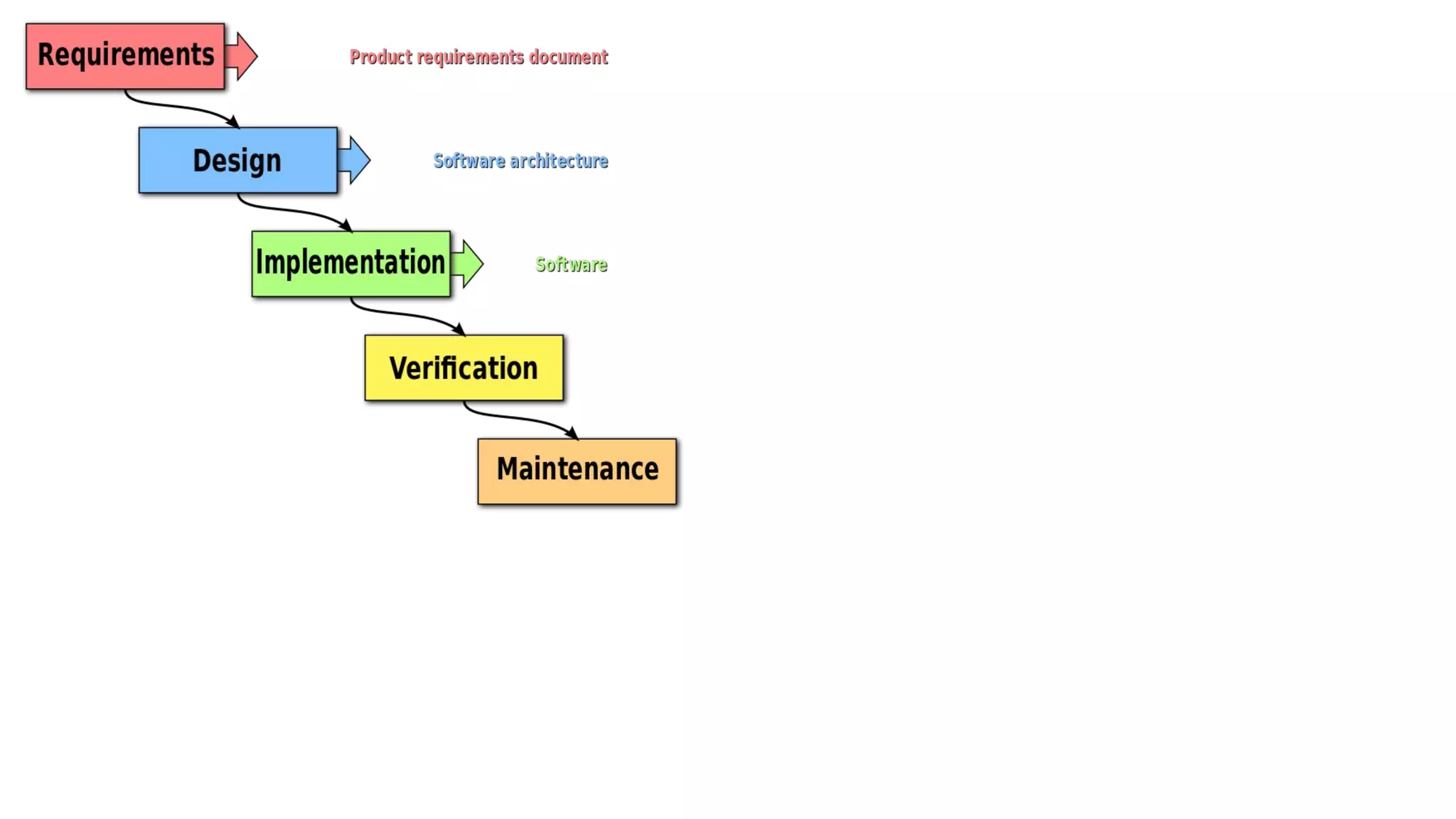
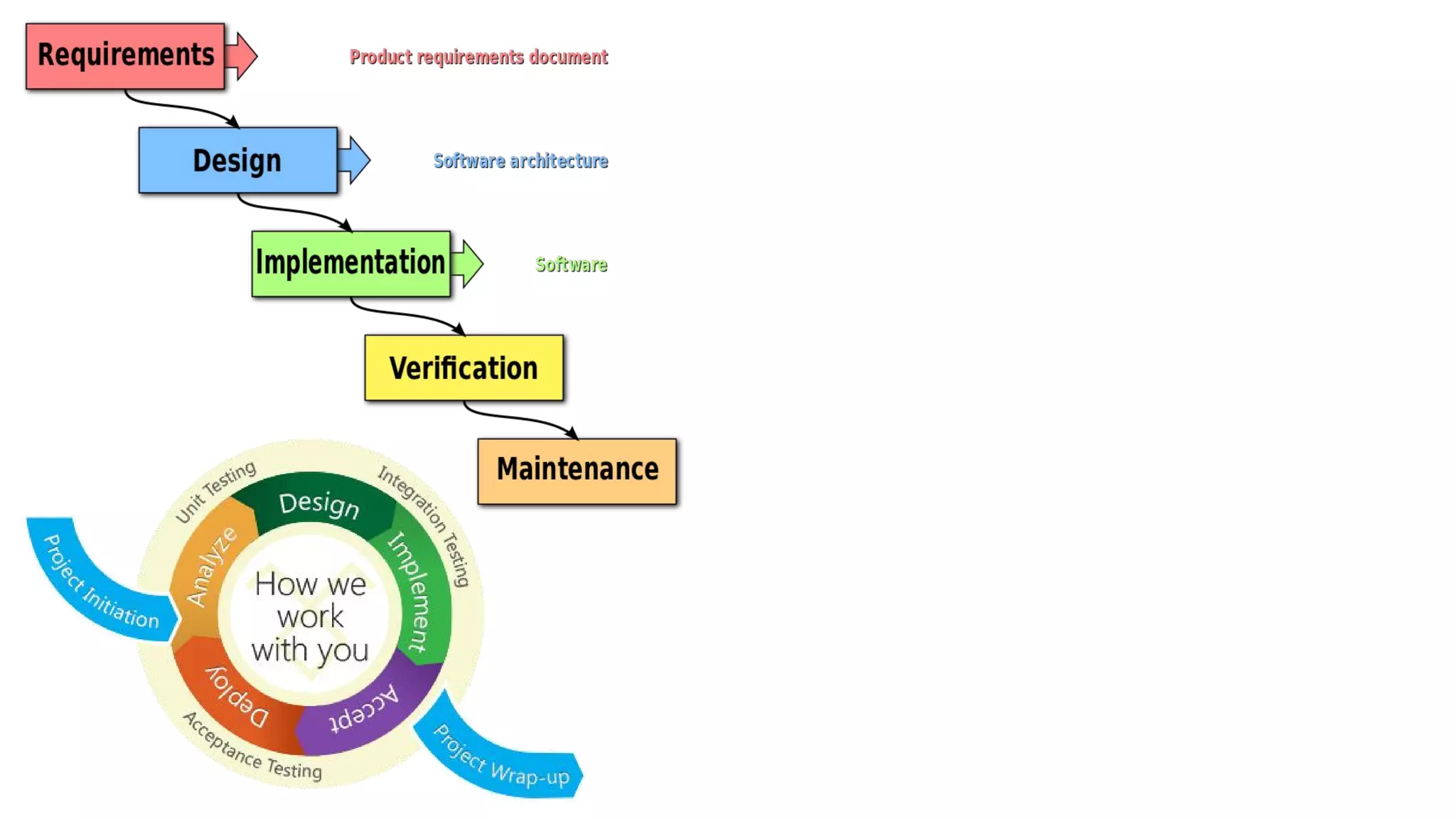
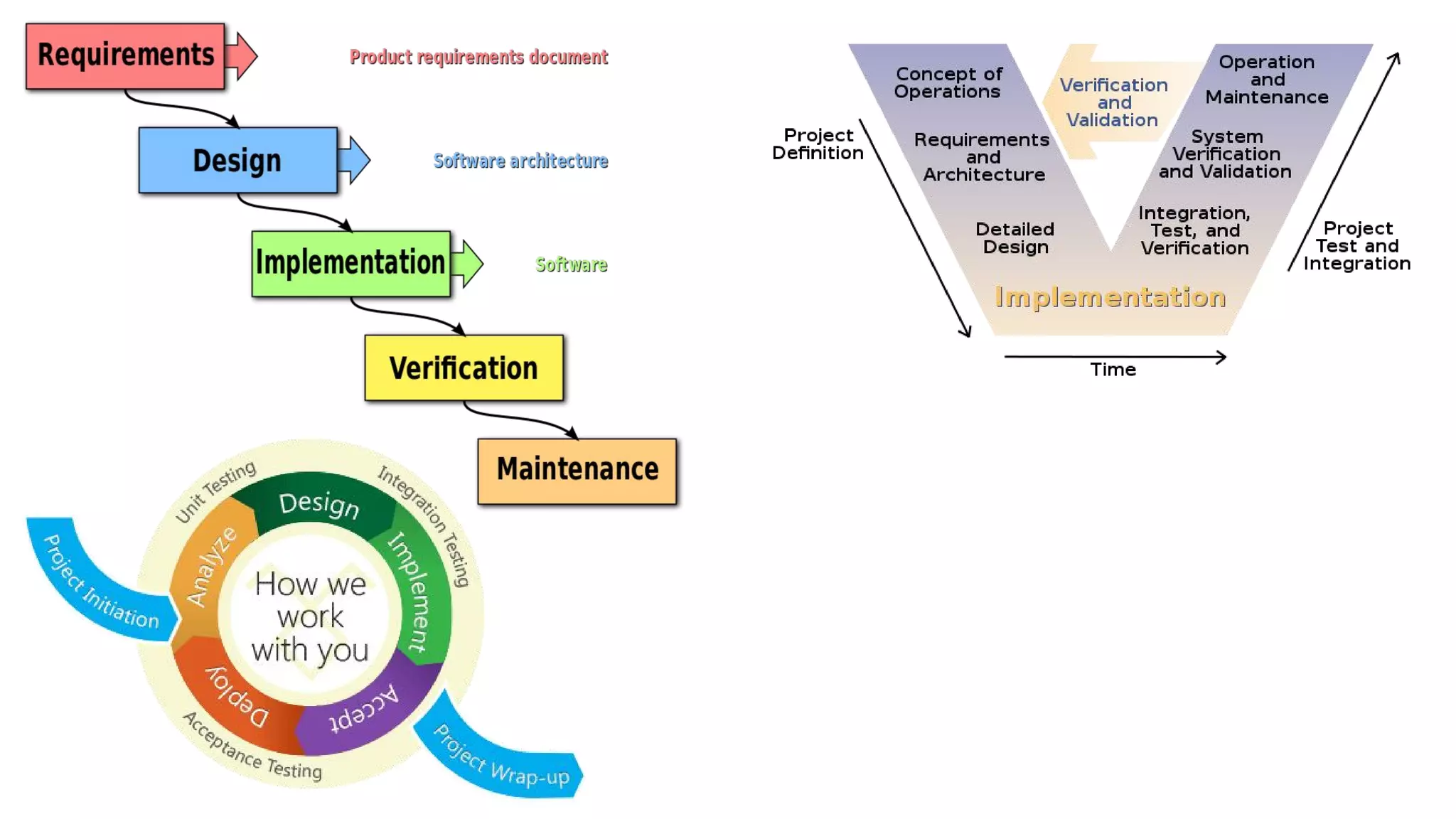
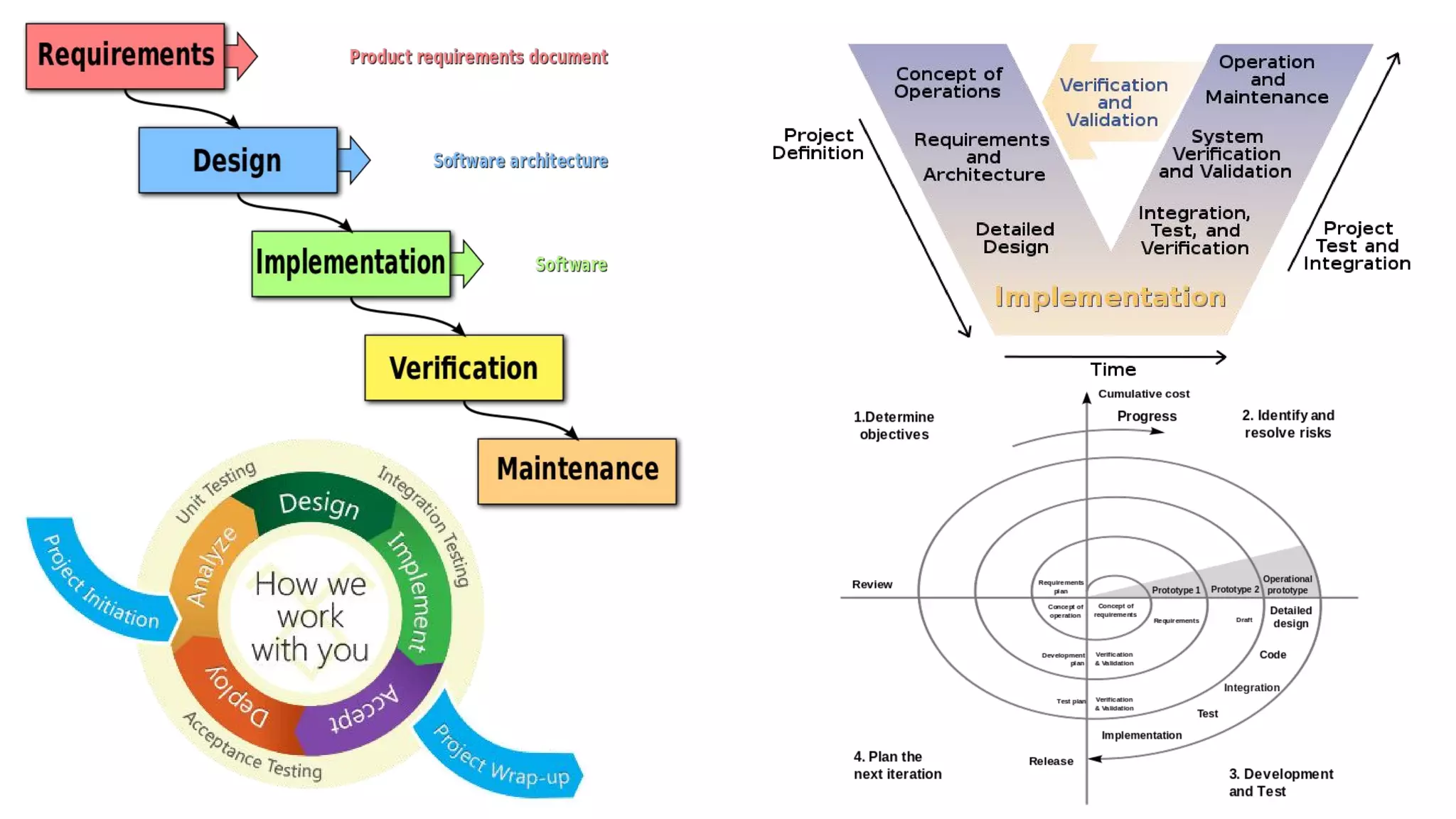
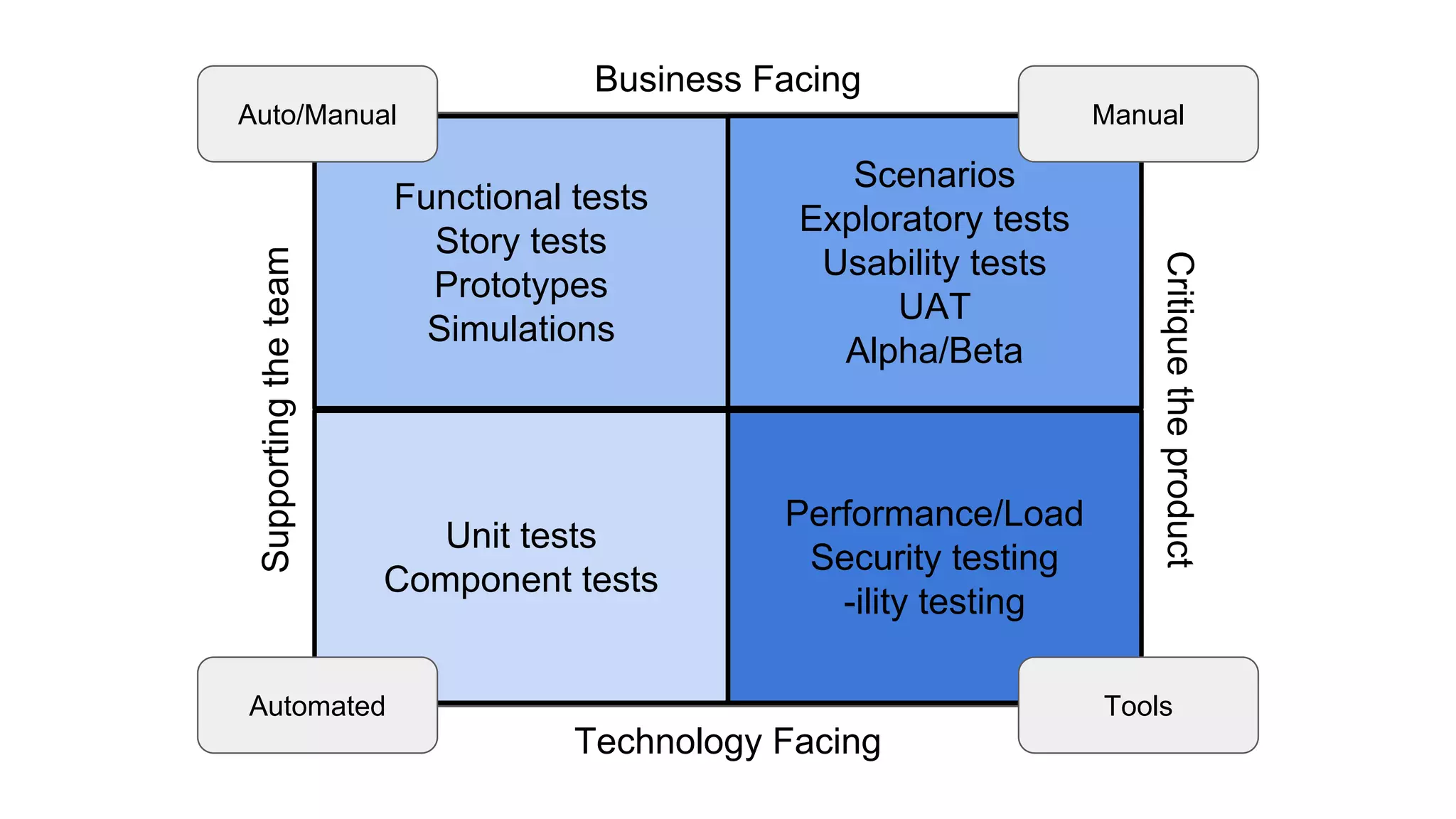
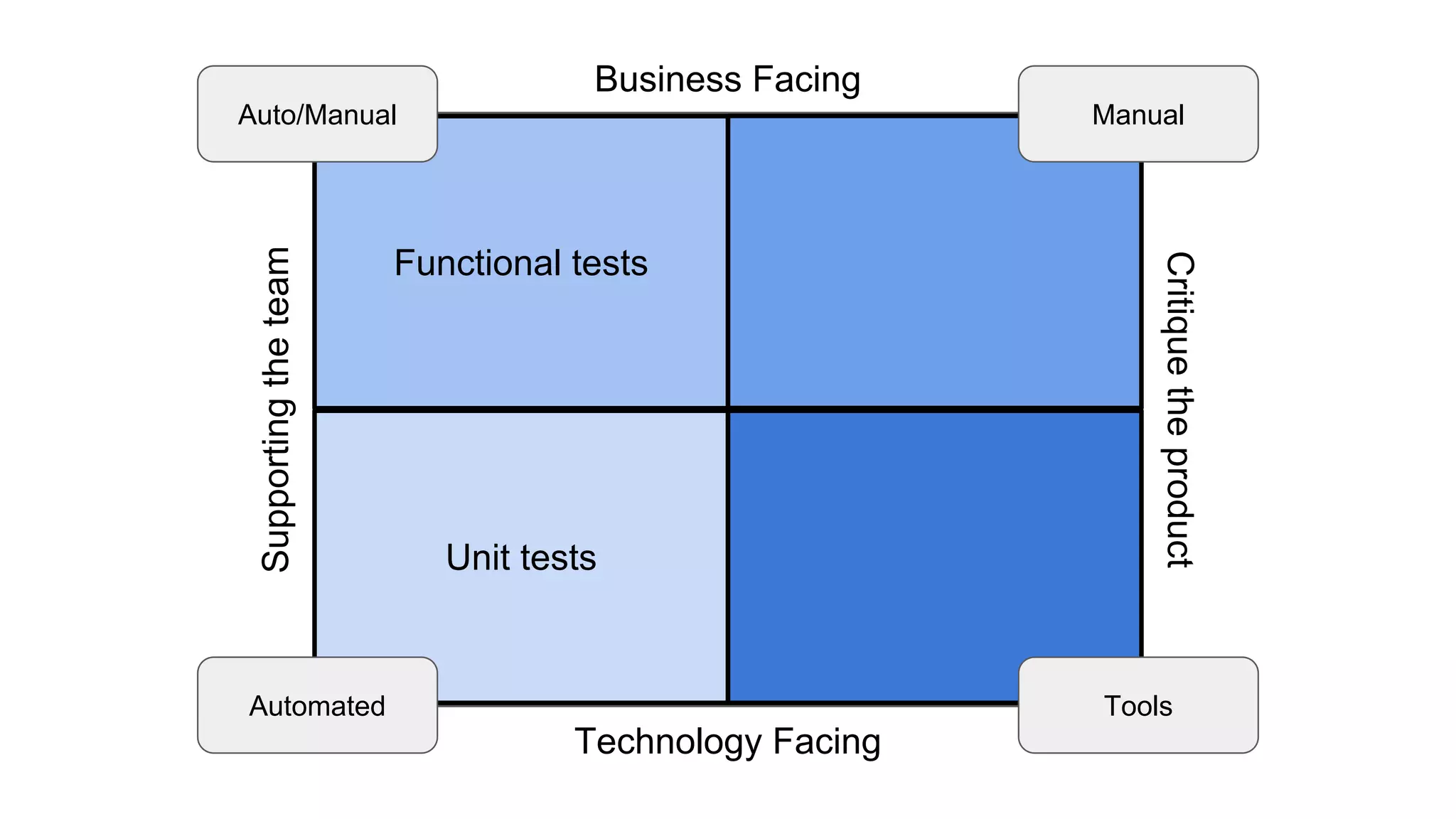
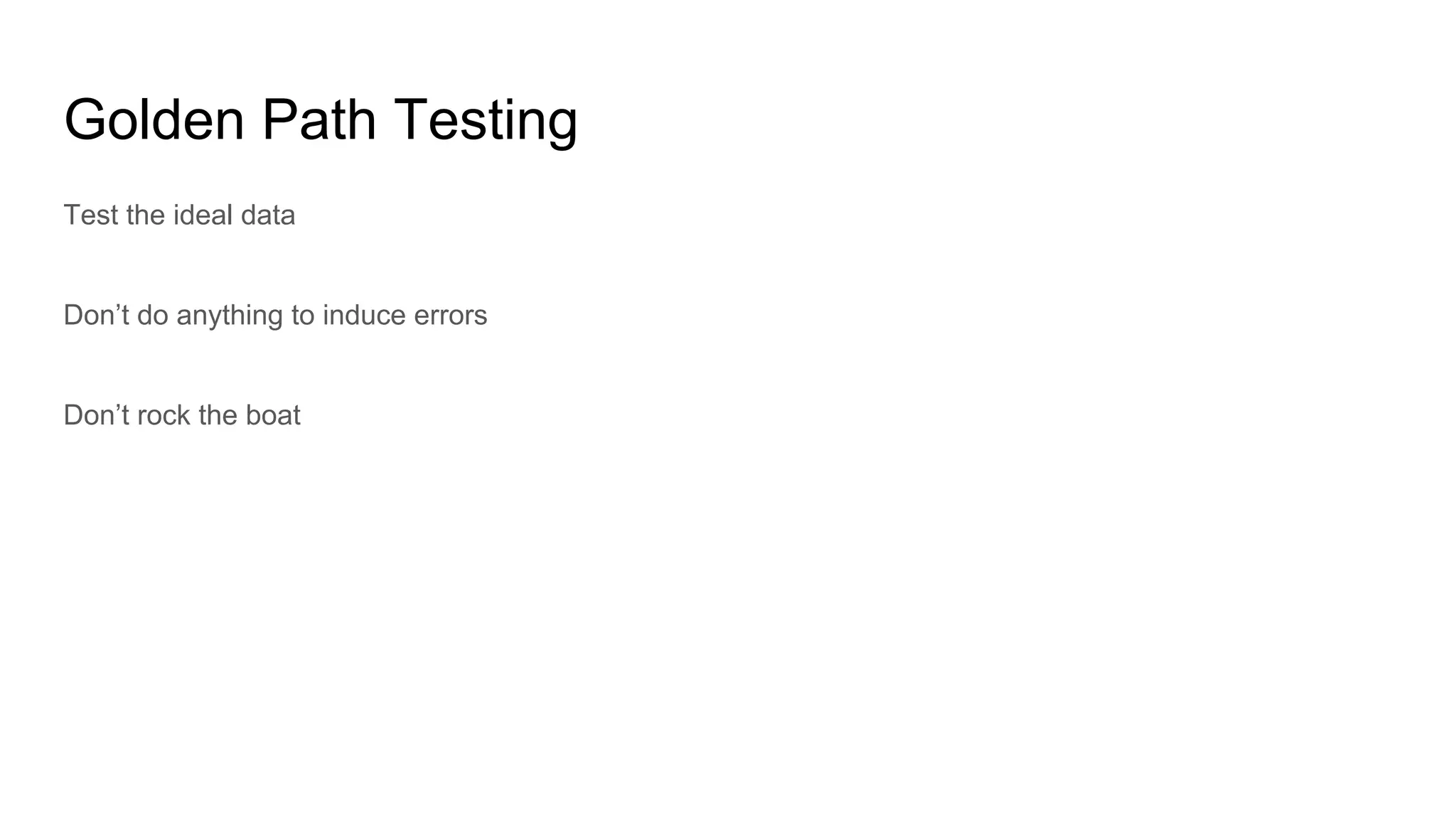
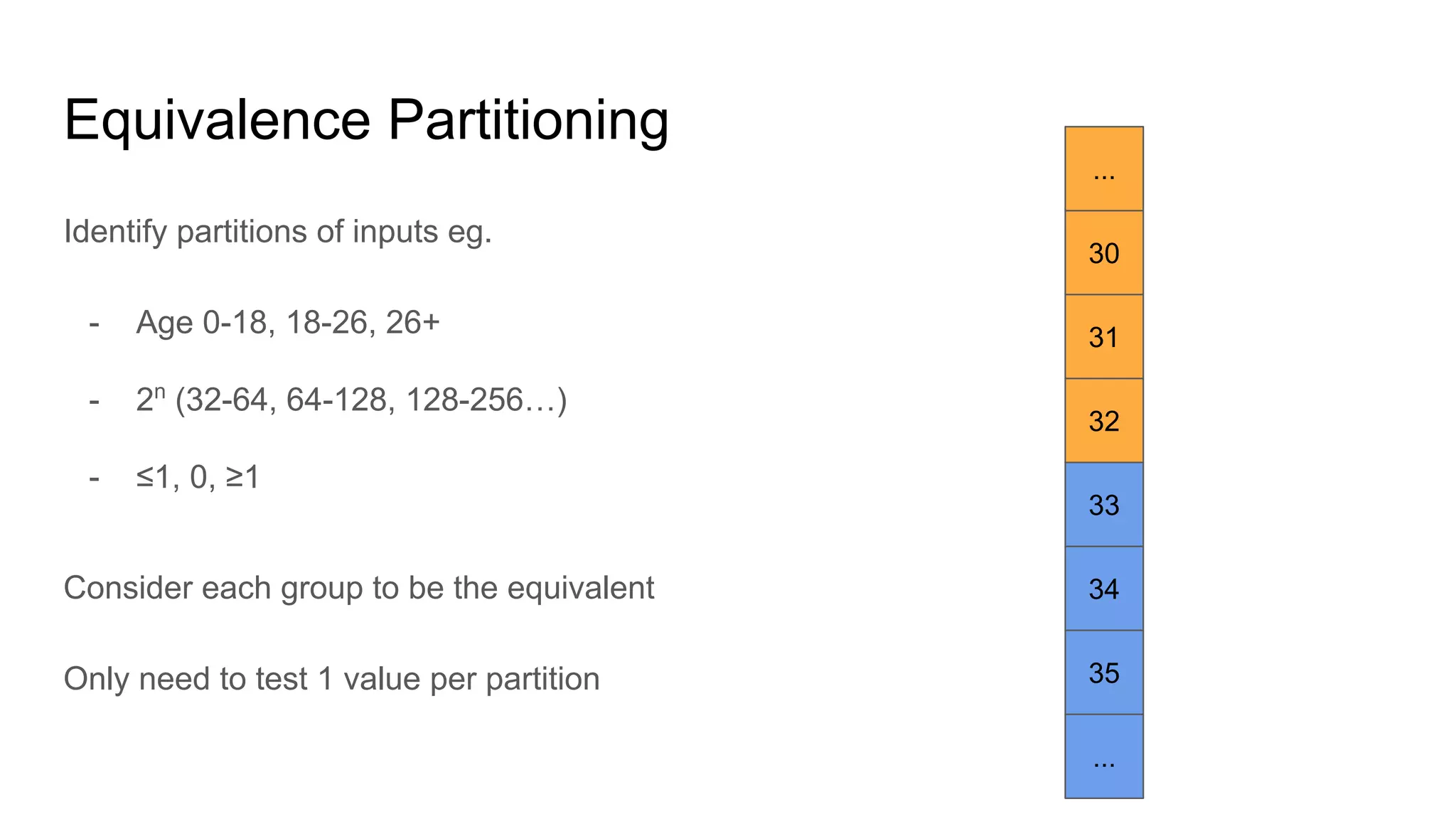
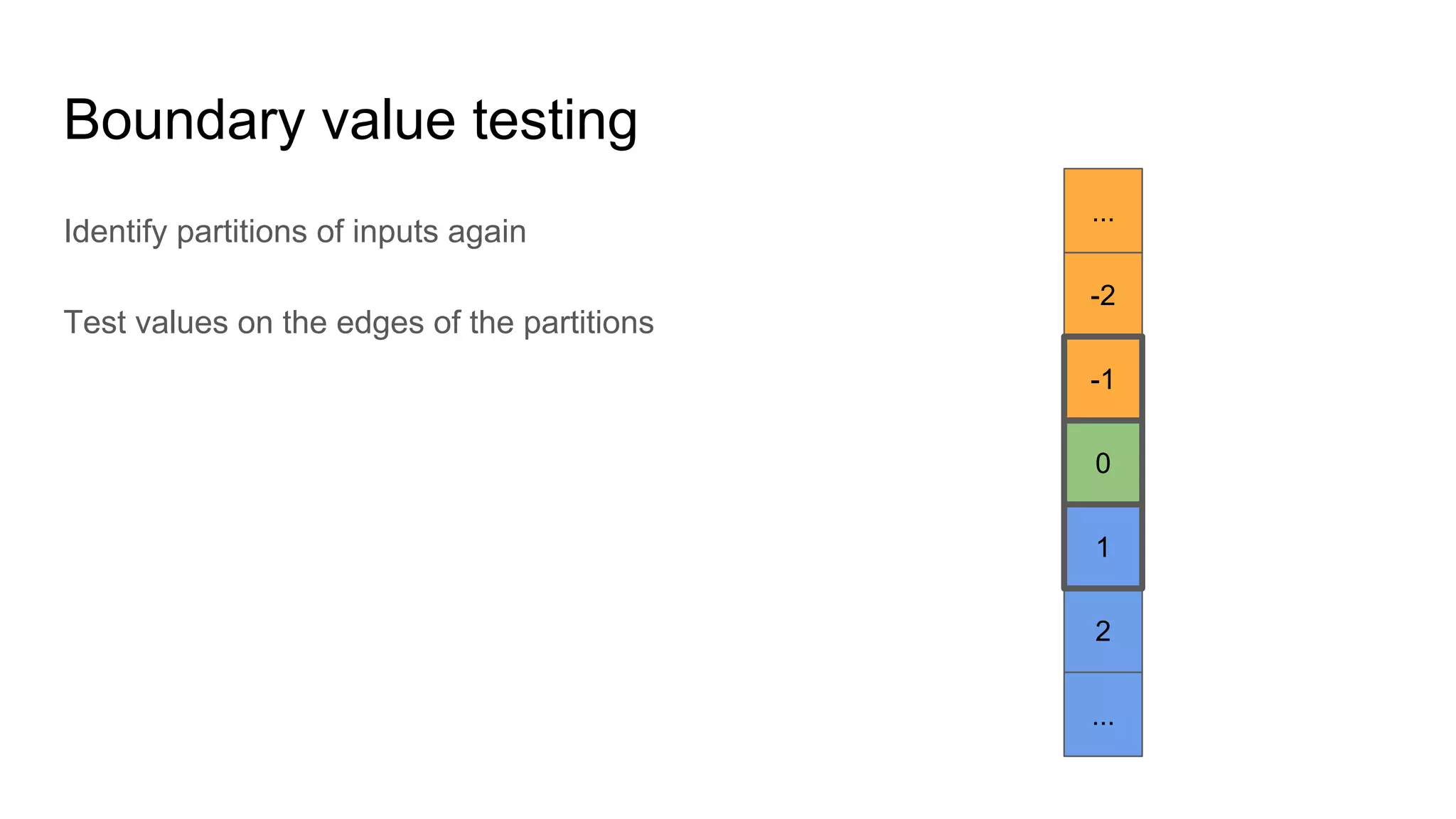
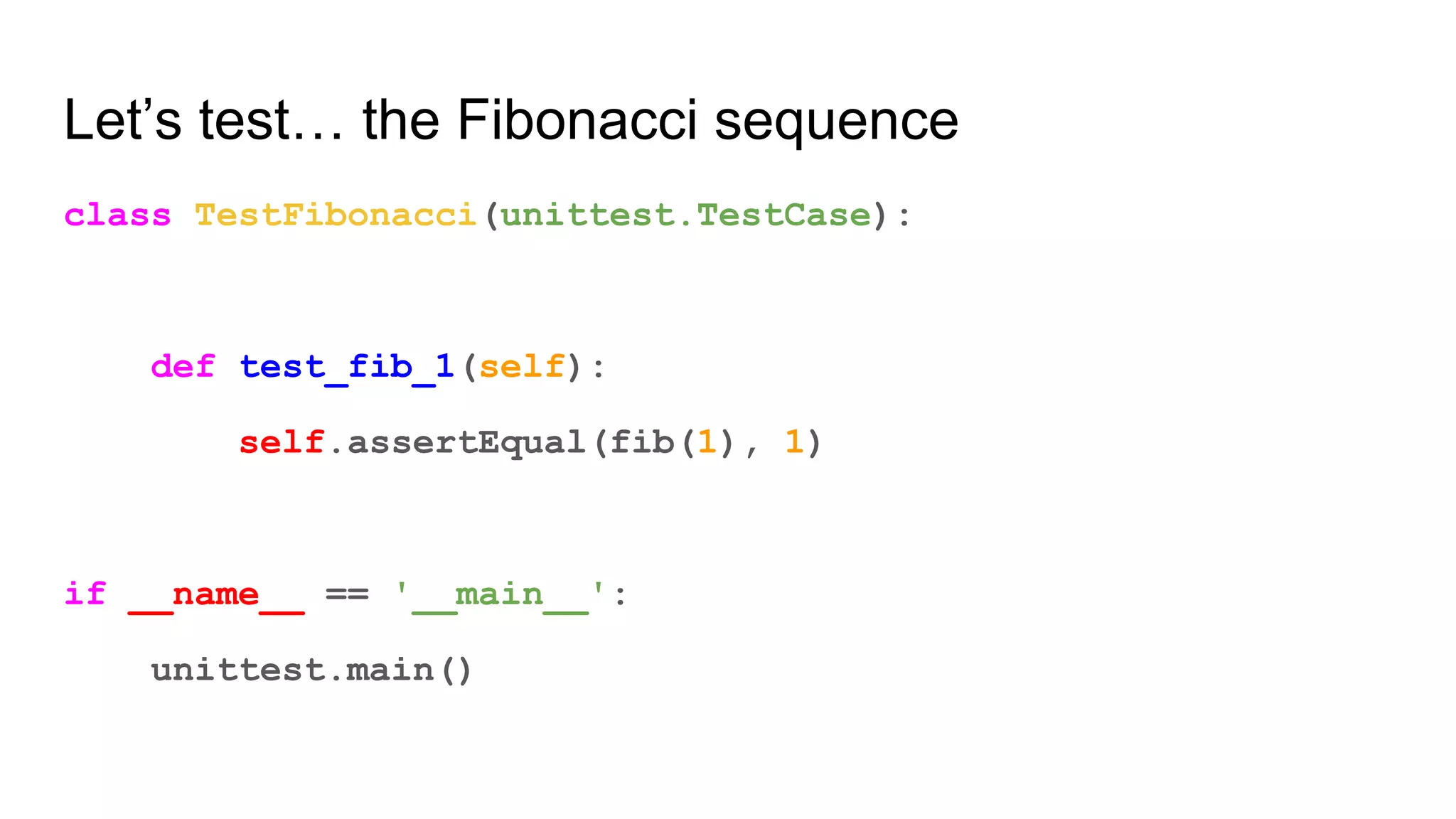
This document provides an overview of software testing concepts. It discusses different types of testing like unit testing, functional testing, error path testing, boundary value testing, and equivalence partitioning. It also covers test strategies like golden path testing, black box testing, and white box testing. The purpose of a tester is explained as quantifying risk to make decisions that improve confidence and quality.






















































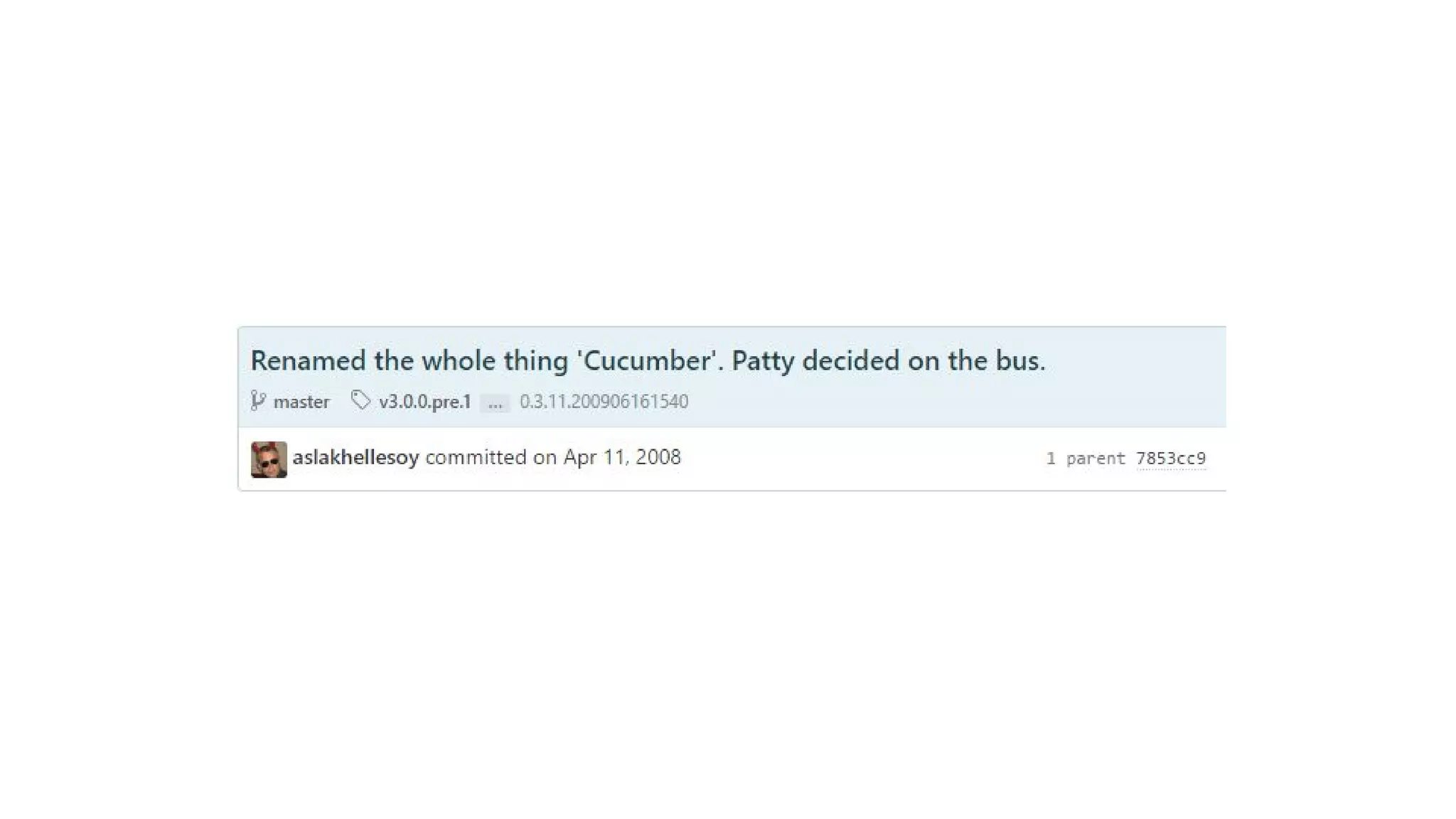
![Automated testing
#!/bin/bash
out=`python script.py`
if [ $out = 1 ]; then
echo "test passed"
else
echo "test failed"
fi
Same principle, but repeatable
Useful for regression testing
Requires tooling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrtestingpart1-170208231129/75/DSR-Testing-Part-1-81-2048.jpg)


















































![As a [user]
I want [feature]
so that [benefit]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrtestingpart1-170208231129/75/DSR-Testing-Part-1-143-2048.jpg)

![Given [some initial context]
When [an event occurs]
Then [ensure some outcomes]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrtestingpart1-170208231129/75/DSR-Testing-Part-1-145-2048.jpg)
















![Should you use BDD?
More tooling, organisational requirements
Might not be applicable in all cases
Pick and choose!
describe('Array', function() {
describe('#indexOf()', function() {
it('should return -1 when value is not present', function() {
assert.equal(-1, [1,2,3].indexOf(4));
});
});
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsrtestingpart1-170208231129/75/DSR-Testing-Part-1-165-2048.jpg)