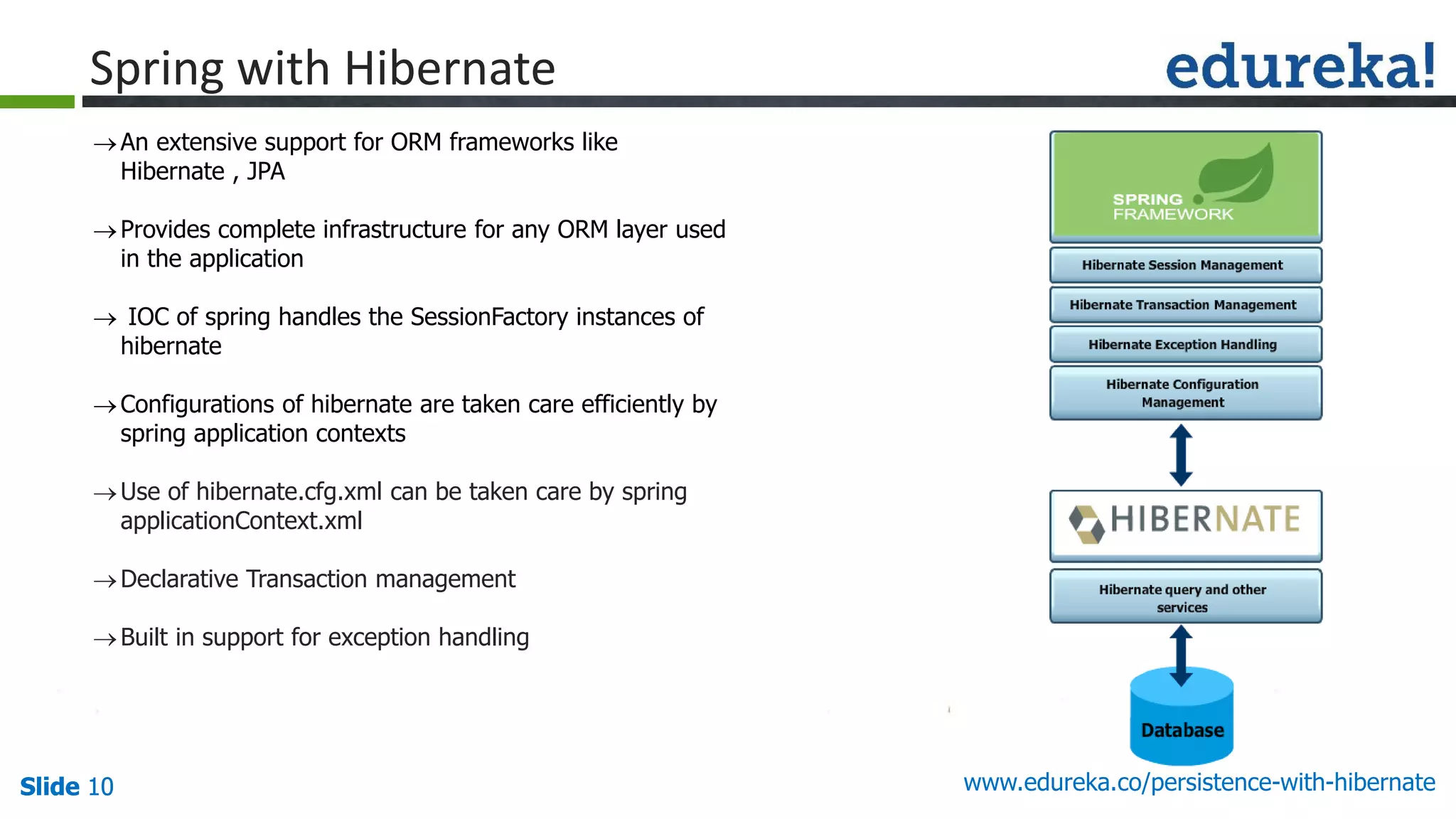
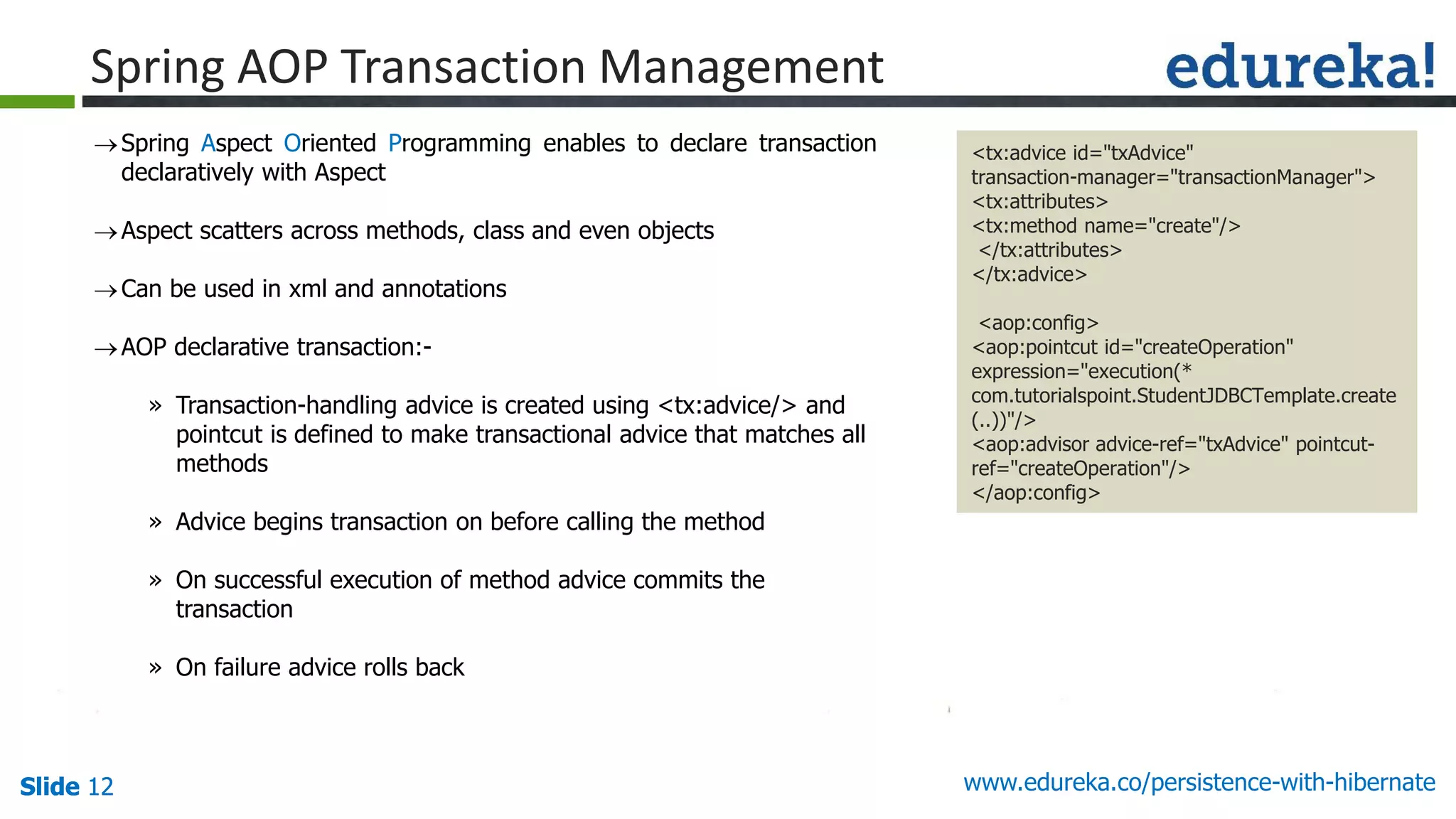
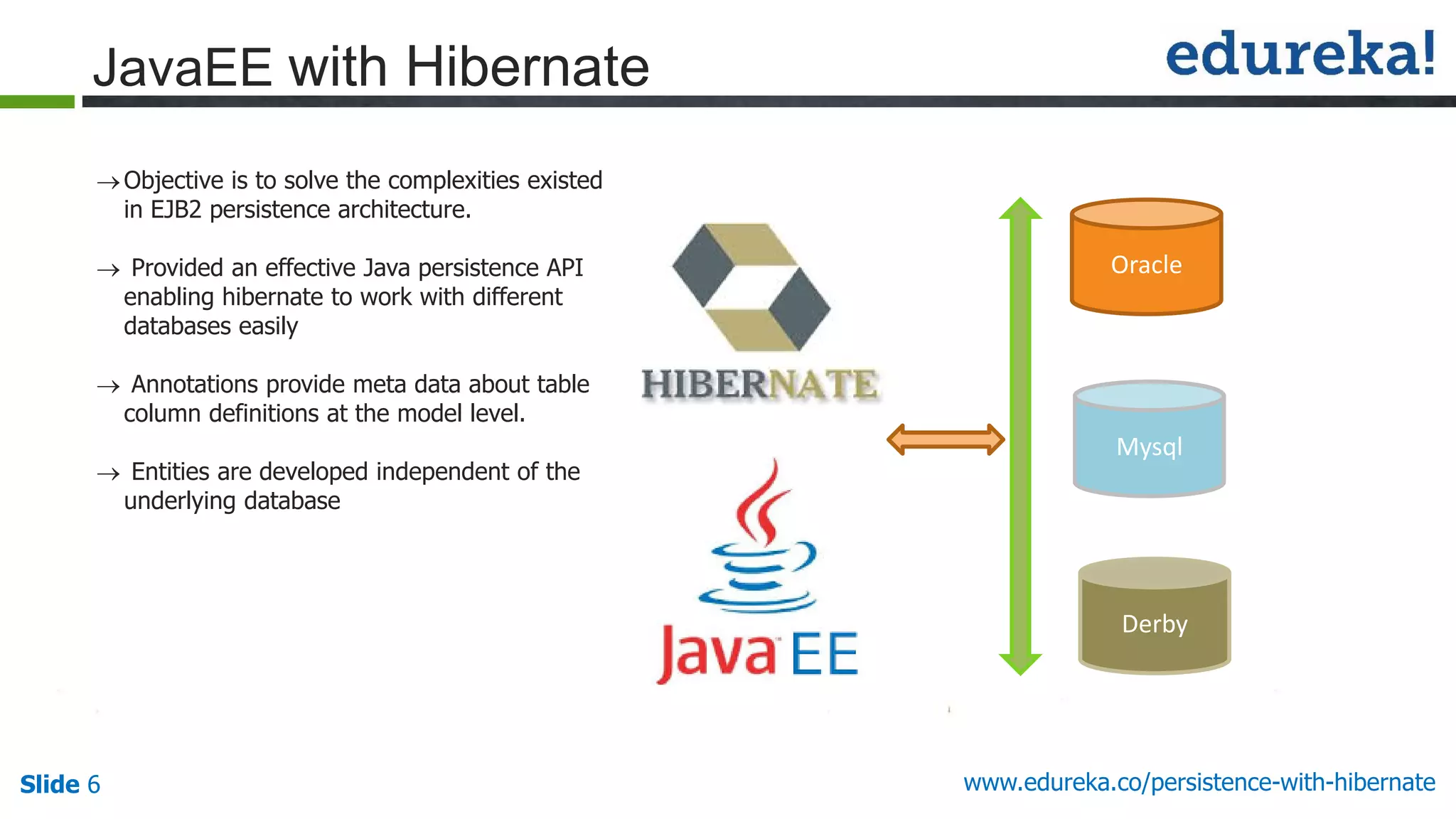
The document outlines the 'Persistence with Hibernate' course offered by Edureka, covering themes such as Java EE, Hibernate, Spring integration, transaction management, and NoSQL databases. The curriculum includes modules on object-relational mapping (ORM), persistence techniques, query languages, and search capabilities with Hibernate and Lucene. Additional support includes live online classes, course recordings, and a verifiable certificate upon completion.


![Slide 7 www.edureka.co/persistence-with-hibernate
Provides a simple API for storing and retrieving Java objects directly to and from the database
Non-intrusive: No need to follow specific rules or design patterns
Transparent: Your object model is unaware
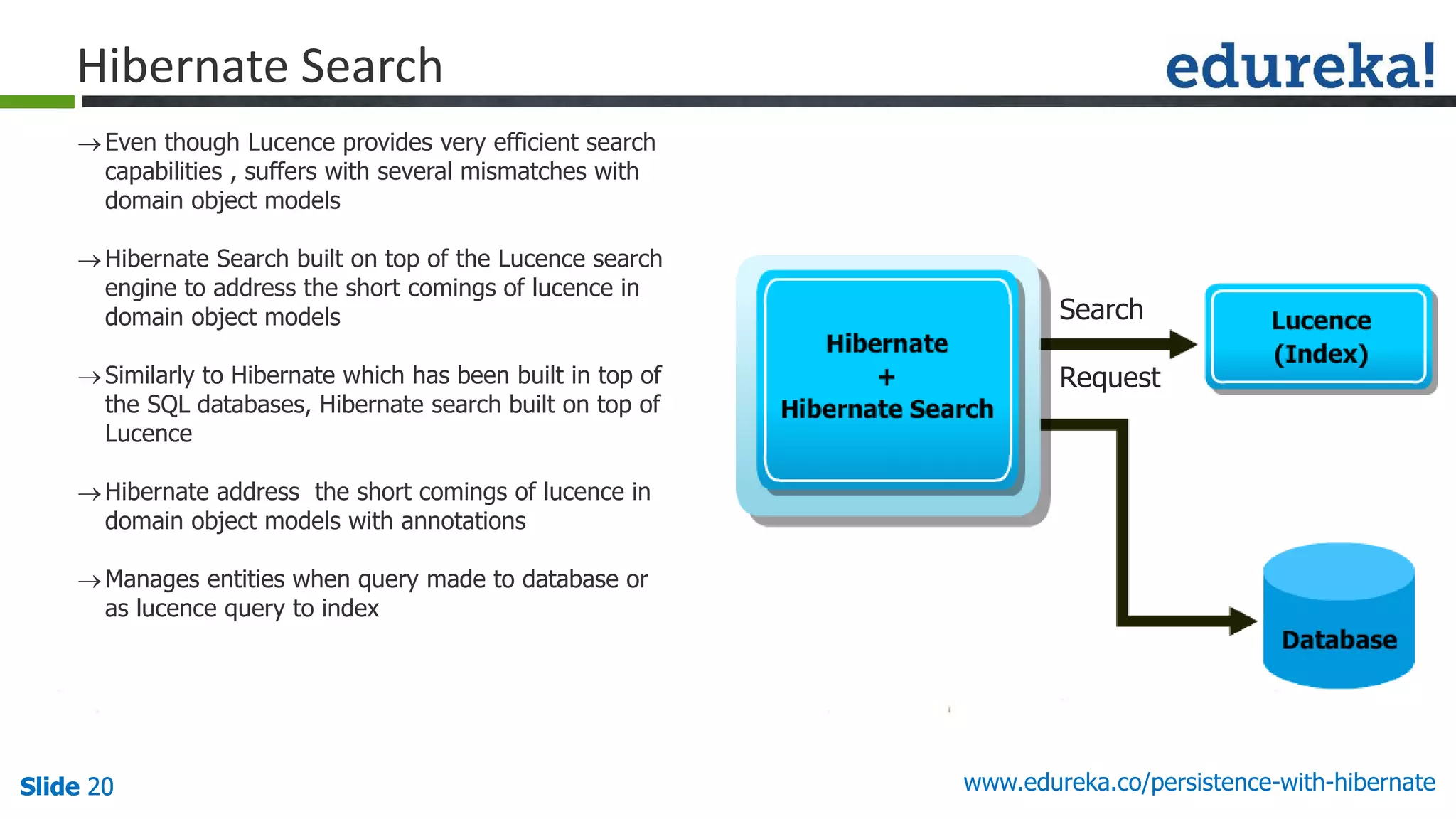
Persistence using Hibernate
JavaObject
int id;
String name;
String getName()
int getId()
void setName(String)
SQL Table
id [int] primary key,
name [varchar(50)],
Magic Happens Here
(O/R Mapper – i.e. Hibernate)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatewebinar9june-150610122056-lva1-app6891/75/Effective-Persistence-Using-ORM-With-Hibernate-7-2048.jpg)