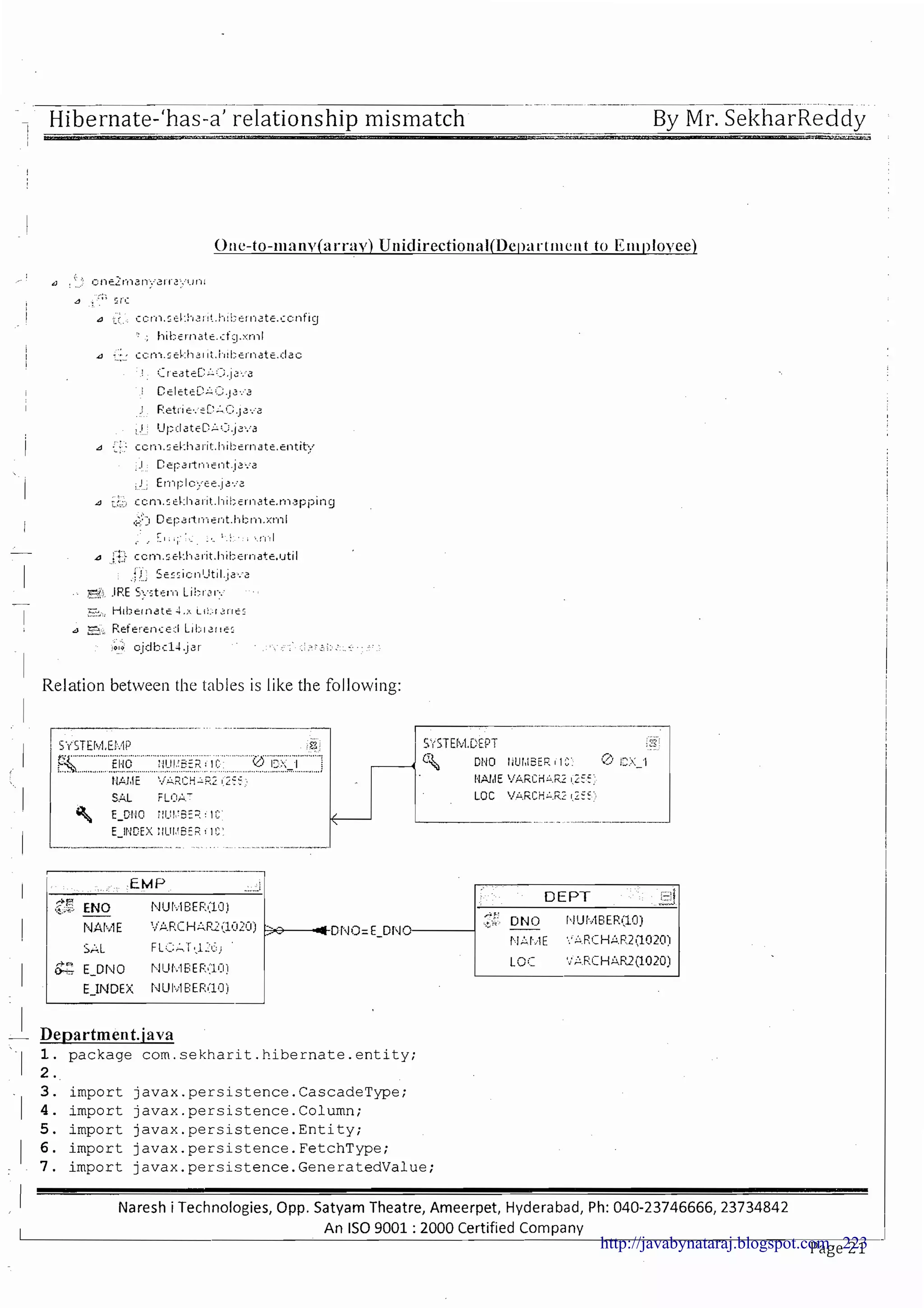
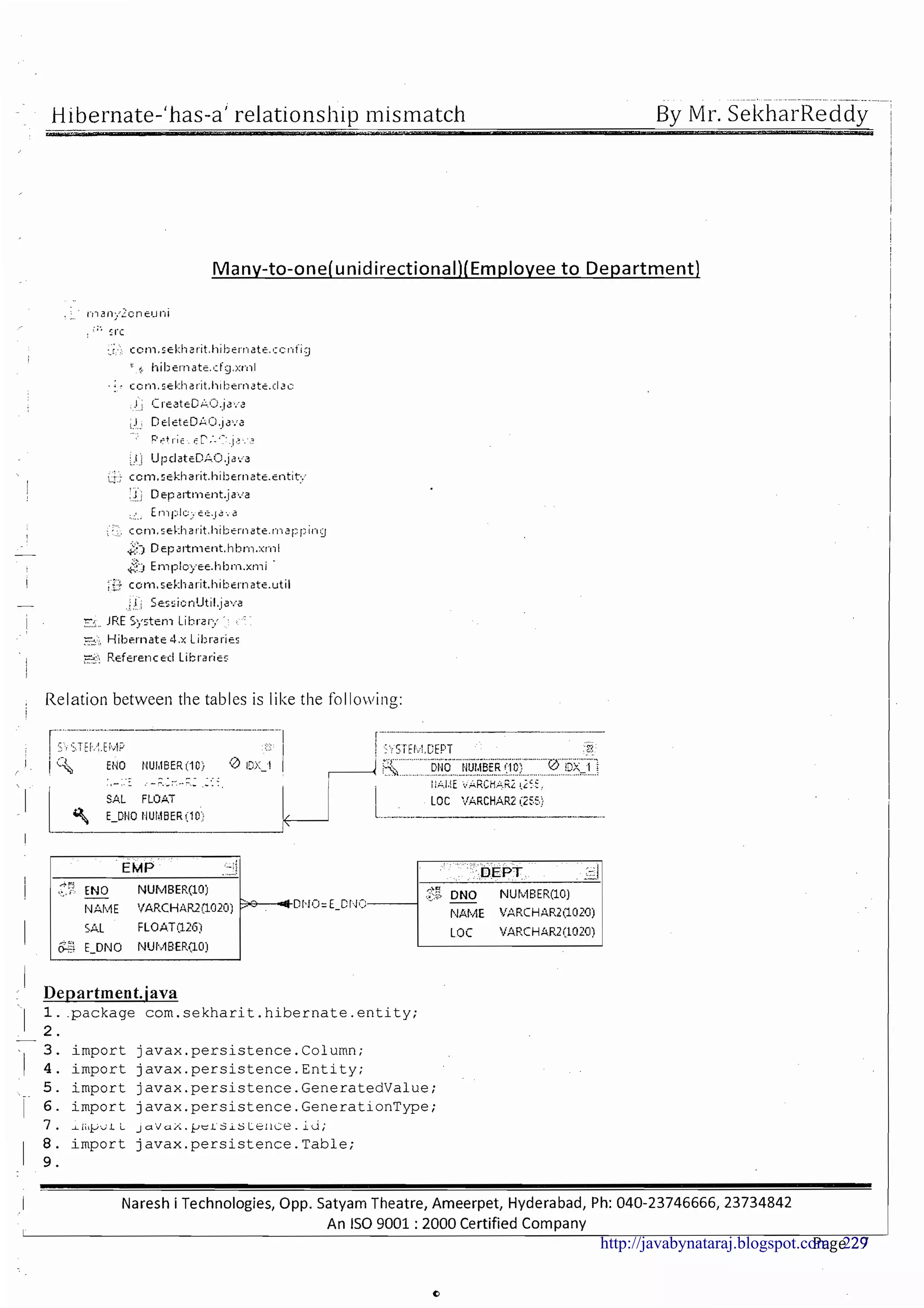
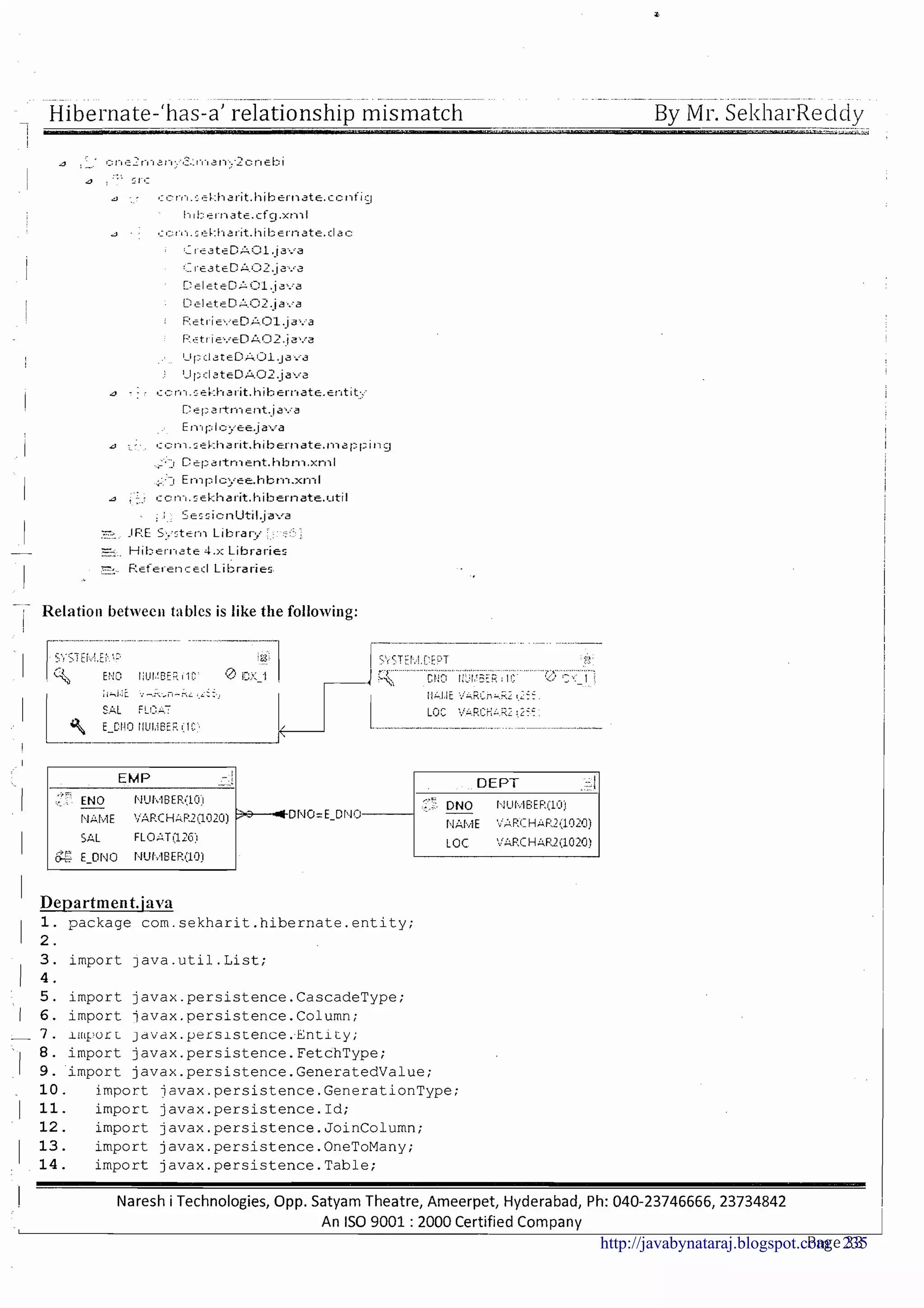
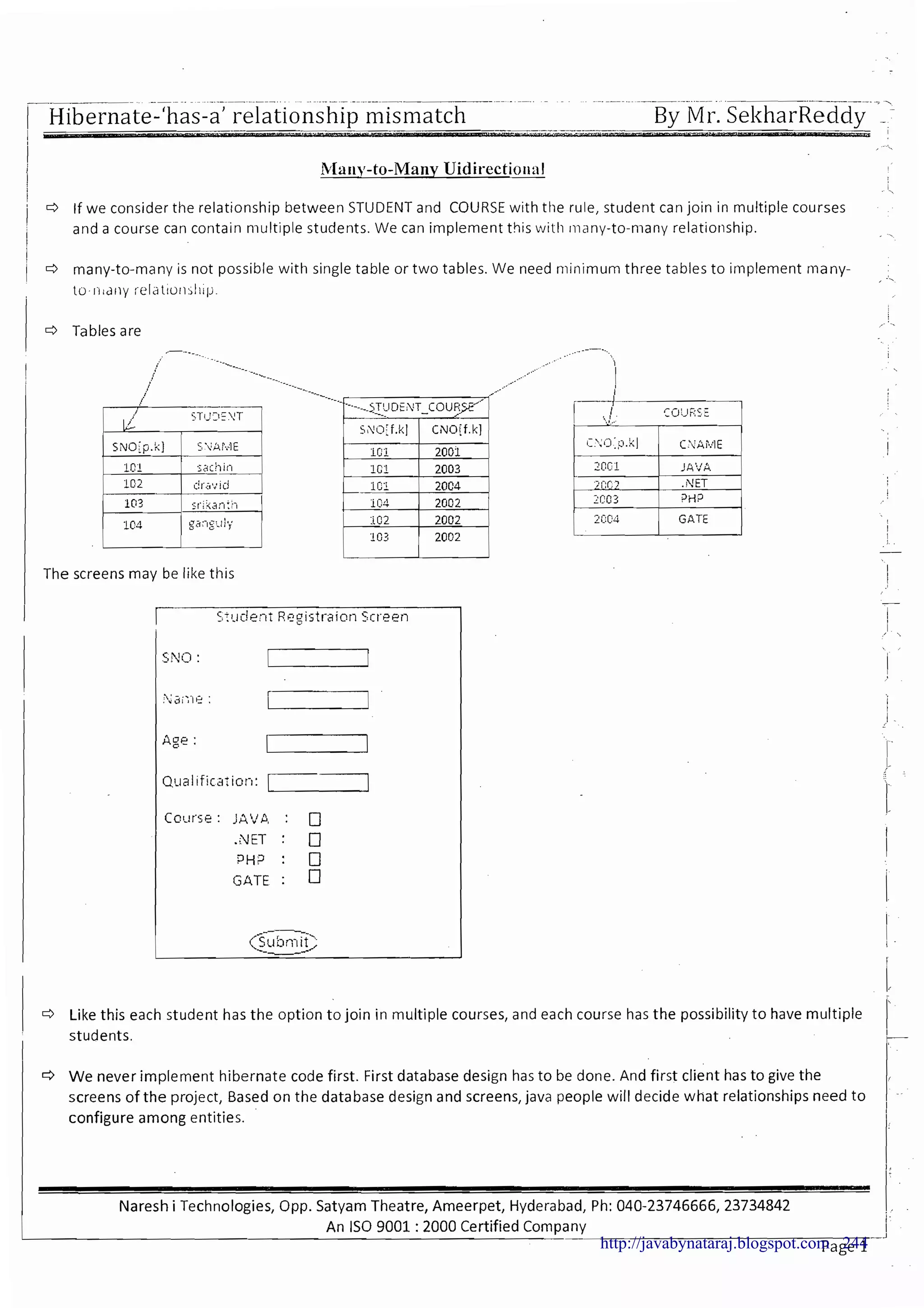
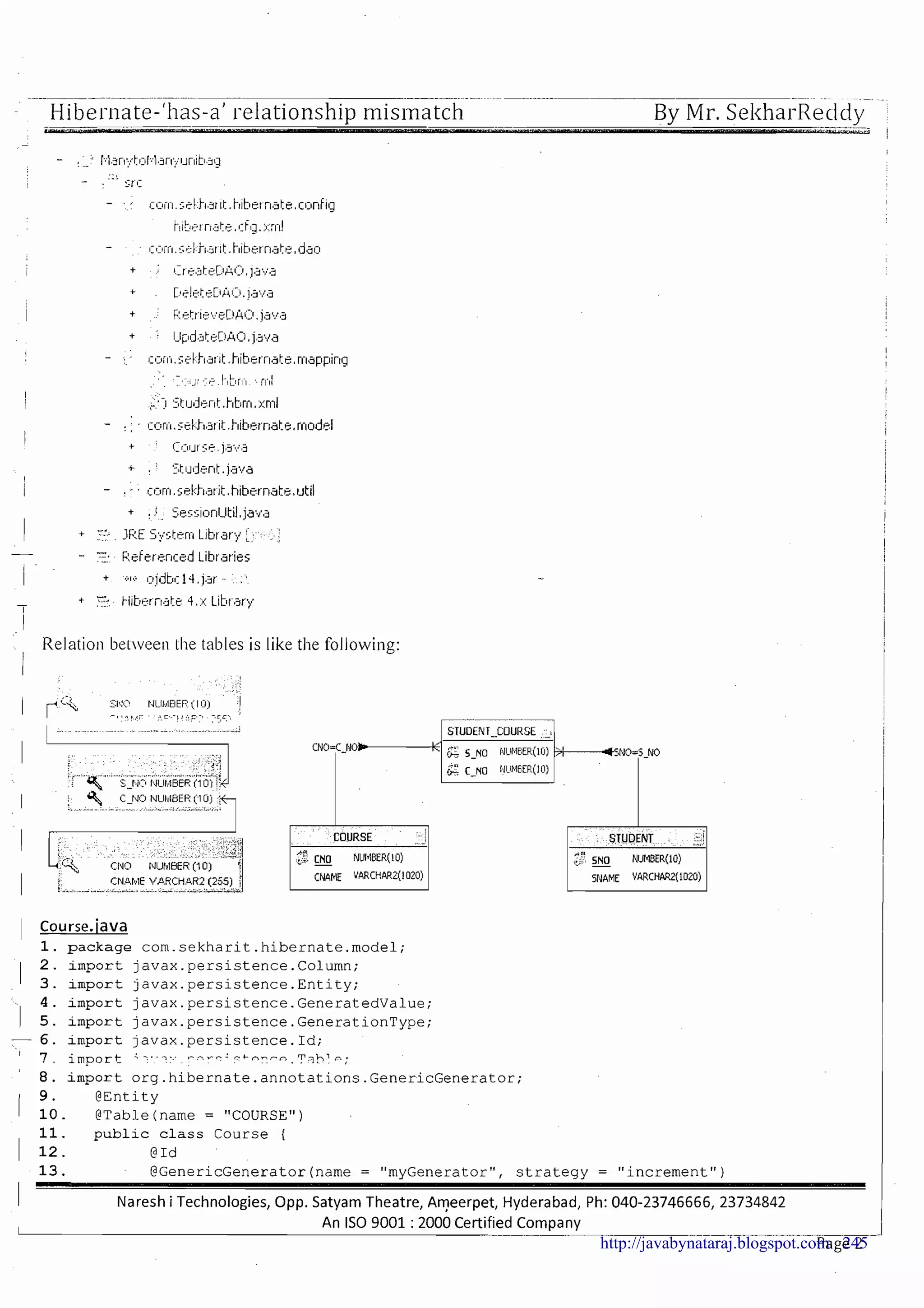
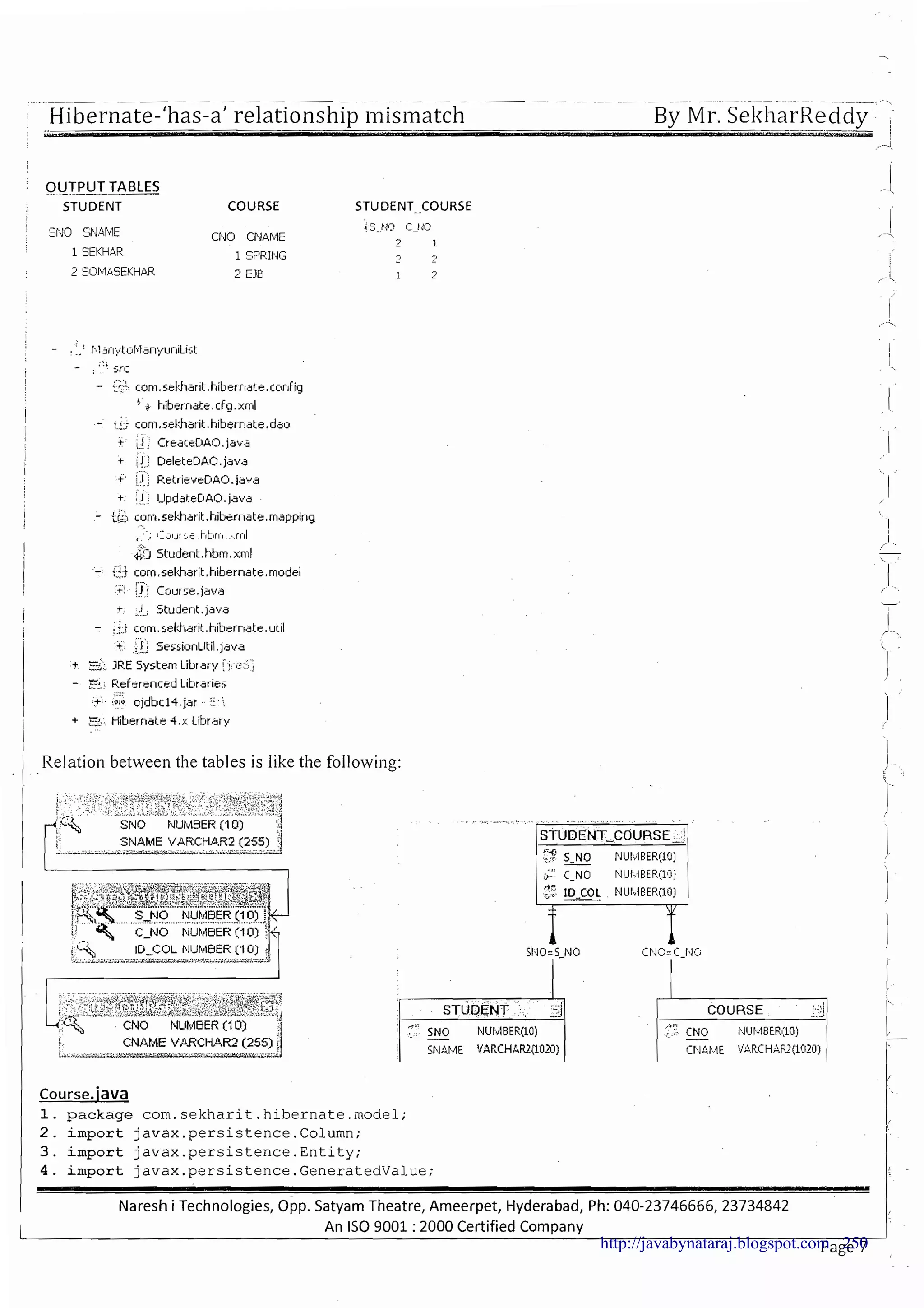
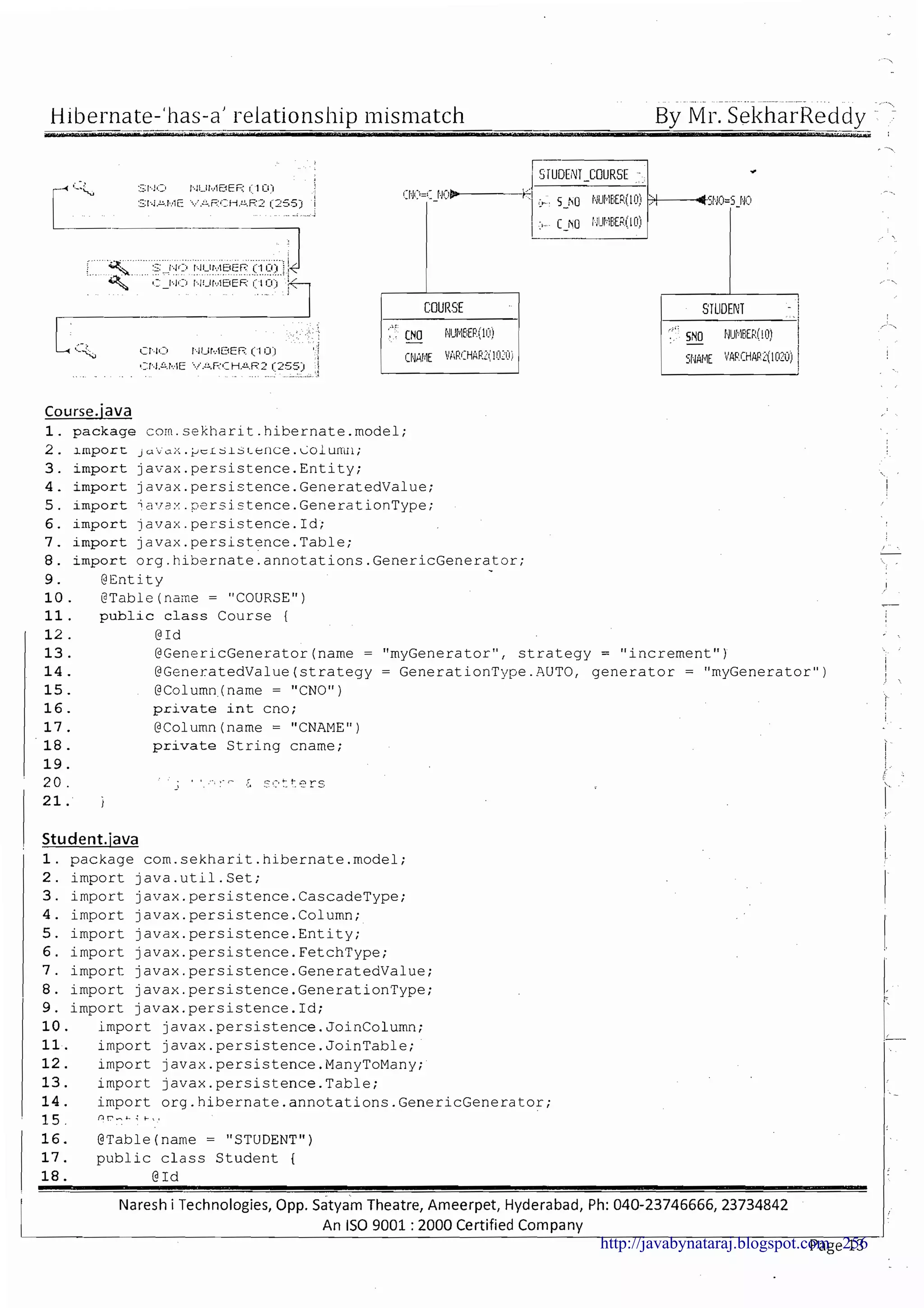
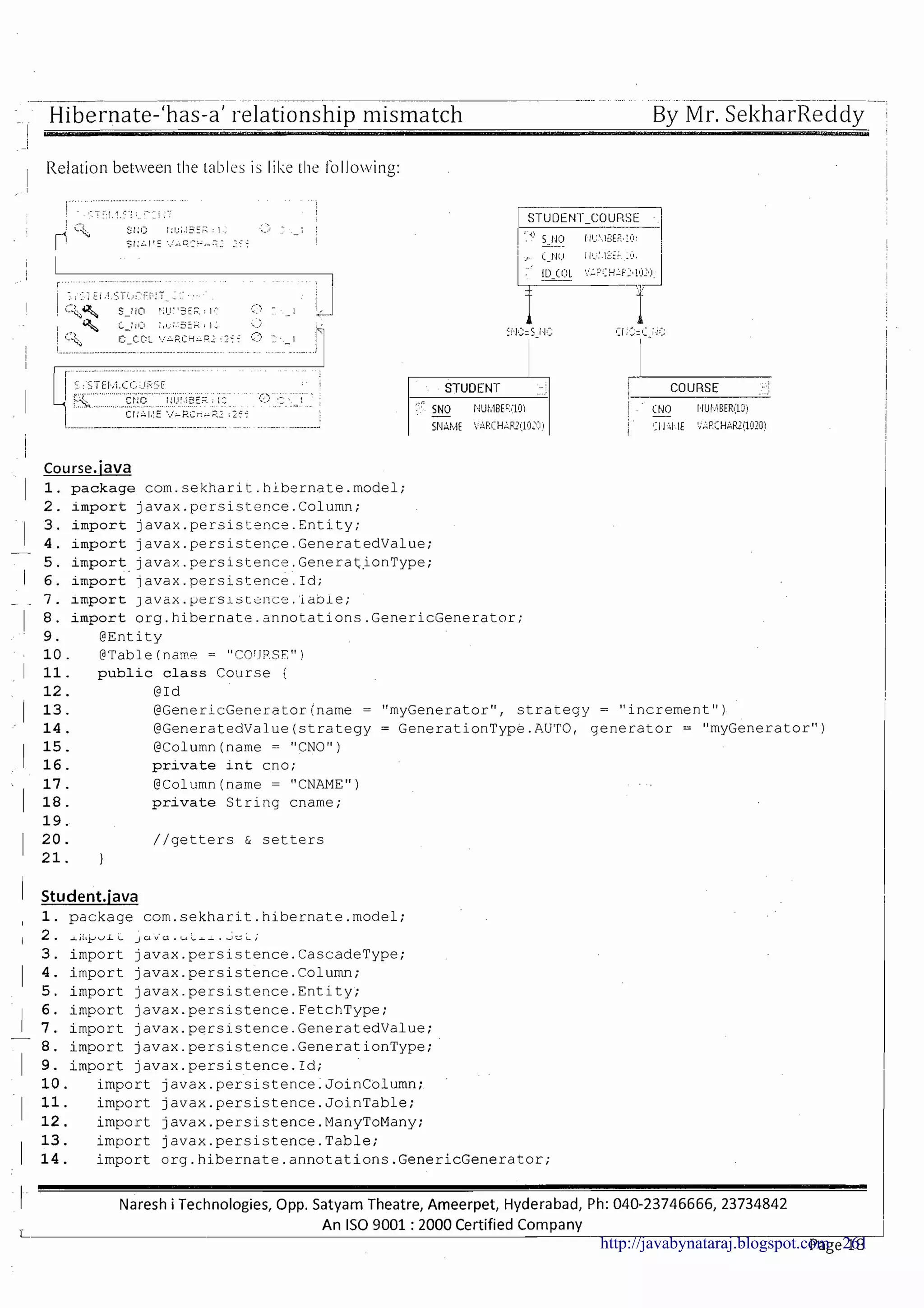
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Hibernate and its role in developing enterprise applications, addressing concepts such as the architecture of enterprise applications, various application layers, and the ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) approach. It discusses traditional persistence methods, their limitations, and how Hibernate serves as an alternative, offering advantages like portability, automatic SQL generation, and support for various features like caching and lazy loading. Additionally, it covers the configuration and mapping files necessary for setting up a Hibernate application.

![. , -.-- . . . - - - L--.-. i
--
O Receiving request from Controller Layer
1
P Contacting the Data Access Layer to get the database data
3 Implementing the business logic
3 Return the control/processed-data to Controller Layer
PersistentIData-Access Laver:
i Receiving the request from business Layer
I P Contacting database to get the database data
O Return the accessed data to business Layer
I
Data Laver:
1 > It is a database.
- ' Q) What are the different logics available in Enterprise Application? I
I Presentation Logic: Logic used to present the output/input. I
I
Application/Controlling Logic: Logic used t o control the flow of application. II-
1
/
Business Logic: Programmatical implementation of business rules is nothing but business logic. jI
Data Access Logic: Logic used t o contact the Database.
-
I
Q) What are the Sun Microsystems technologies and frameworks in enterprise application development?
Controller Layer
'IServlets
I / JSF
. ' I
Presentation Layer
JSP
Business Layer
t
EJB2 session beans
EJB3 session beans
WIDB(Message Driven
Beans)
' WEB-SERVICES
Data Access Layer
JDBC
Ejb2 entity beans
Ejb3 entitys[JPA ] (java
persistence API)
I Q) What are the non-Sun Microsystems technologies and frameworks in enterprise application
1 development?
1 1 Controller Layer
struts
Spring Web MVC
' I Wicket--
Tapestry
'I Flash
I I 1 ,
1 Objective of Hibernate: Developing Data access layer of an Enterprise application
1
I Naresh iTechnologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666,23734842
II
Presentation Layer
HTML
Velocity
Freemarker
Flex
~ u s i n e kLa-yer
Spring AOP
Spring JEE
WEB-SERVICES
L--.
An IS0 9001:2000 Certified Company-..- -- --..-.-- --- - -- -. .--
Page 2 -
1
Data Access Layer
Hibernate
lbatis
Toplink
JDO
Spring DAO
Spring ORM
http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-3-2048.jpg)












![-.-- -.-- - - - -. - -- .-- - . -. .- --- -. -
Hibernate-CRUD Application B Mr.Sel<harRecldy--
Session session = null;
Tramaction transaction = null;
try I
session = SessionUtil.getSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Account account = (Account) session.get(Account.class, accno);
session.delete(account);
transaction.commit();
} catch (HibernateExceptione) {
transaction.rolIback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
SessionUtil.closeSession(session);
1
i AccountService.iava
1. package com.seltharit.hibernate.service;
I 3. import java.util.Date;
5. import corn.sekharit.hibernate.bean.Account;
I 6. import corn.sel~harit.hibernate.dao.AccountDA0;
1 7.
/ 8. public class Accountservice {
9. public static void main(String[] args) { -
I
10. AccountDAO dao = new AccountDAO();
11.
12. // Retrieve Account
13. Account rAccount = dao.get(90001);
14. Svstern.out,println("Account details ....");
Systern.out.println("Accno : " + rAccount.getAccno());
1 ::: System.out.println("Name : " + rAccount.getName());
17. System.out.println("8alance : " + rAccount.getBalance());
18. Systern.out.println("CreationDate: " + rAccount.getCreationDate());
1 19.
20. // Create Account
21. Account cAccount = new Account();
22. cAccount.setAccno(90005);
23. c~ccount.set~ame("sekhar");
24. cAccount.setBalance(6899);
25. cAccount.setCreationDate(new Date());
1 26. dao.insert(cAccount);
1 27. System.out.println("Account created successfully");
28.
29. // Update Account
I 30. Account uAccount = new Account();
31. uAccount.setAccno(90003);
32. uAccount.setName("sekhareddy");
Naresh i Technologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666,23734842
An IS0 9001 :2000 Certified Company
---
Page 6http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-18-2048.jpg)
![I--, Hibernate-CRUD Application--- -- ---.. . . . . . -- . . . . . .
By Mi-.Sel;ha~-Reddy
!
33. uAccount.setBalance(4500);
34. uAccount.setCreationDate(new Date());
35. dao.update(uAccount);
36. System.out.println("Account updated successfully");
37.
38. // Delete Account
39. dao.delete(90002);
40. System.out.println("Account is deleted successfully");
41.
42. }
43. }
After Execution ACCOUNT TABLE :
,-*. .?
;;.,-.c c- 1.10 Il.,li.lE E:AL CREhT 101I-UT
t I:i.:a>, ?:-eddy 69541.03 5: 29,'21:1!::
9l:ll:lOj ~e;tllll-edjj' 45i10 j!Z?jLI:l]z
!21:11:105 5el:hal- 6Sgg 529jiC112
1 Q.) Rewrite the above application, using annotations instead of mapping file?
d . . *' cctn.rtkb~arit.hih~rnatr.utiI
:.i. .: Ser-~ian!JtiI,~a~.~a
. ., .
r-:.:,.-J. JRE S y . ~ t i i i ~L i b r a y ,...;;a::,:. . ,
- -Hitxrnate 3.3 Annctation': F,t Entit!. I:;lanagel......
i , . Hitlel-nate3.3 Cnre Libraries
LI ~ i jRefer~ticedLihrariel:
080 c<clbclJ,jar
lib
3 . . ,.
1 hibernate.cfg.xml
. .
: 1. <?xml version='l.O' encoding='UTF-8'?>
1 2. <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
3 .-- "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//ENn
4. "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.O.dtd"~
I 5 .
6. <hibernate-configuration>
8. <session-factory>
9. <property.... />
............
! Naresh i Technologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666,23734842
An IS0 9001 : 2000 Certified Company
Page Ihttp://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-19-2048.jpg)






![~ pppp-.- ..... . .
Hibernate-AI-chitecturalElements .......................8 _nl..x&r ... -~.. , . . I
~ r . ~ e k l ~ a i - ~ e c l d y--. -
-
o @GeneratedValue
o @Temporal
/- All the above annotations we are taking from java.persistence package. Actually this paclcage is not
the part of hibernate API. This paclcage is from .IPA(Java Persistence API).
> These annotations also given by hibernate. But we don't prefer to use hibernate given annotations.
We prefer t o use .lPA annotations. Reason for this is, Hibernate is a specific API, where as ]PA is a
specification.
If we use JPA annotations we have to flexibility to change the implementation vendor without
changing application code.
i > .IPA is an APl(from SUN), its not the implementation. There are multiple implementations are there
for ]PA. Some of famous implementation of ]PA are Open.lPA, Hibernate, Toplink Essentials, Eclipselinlc
...etc.
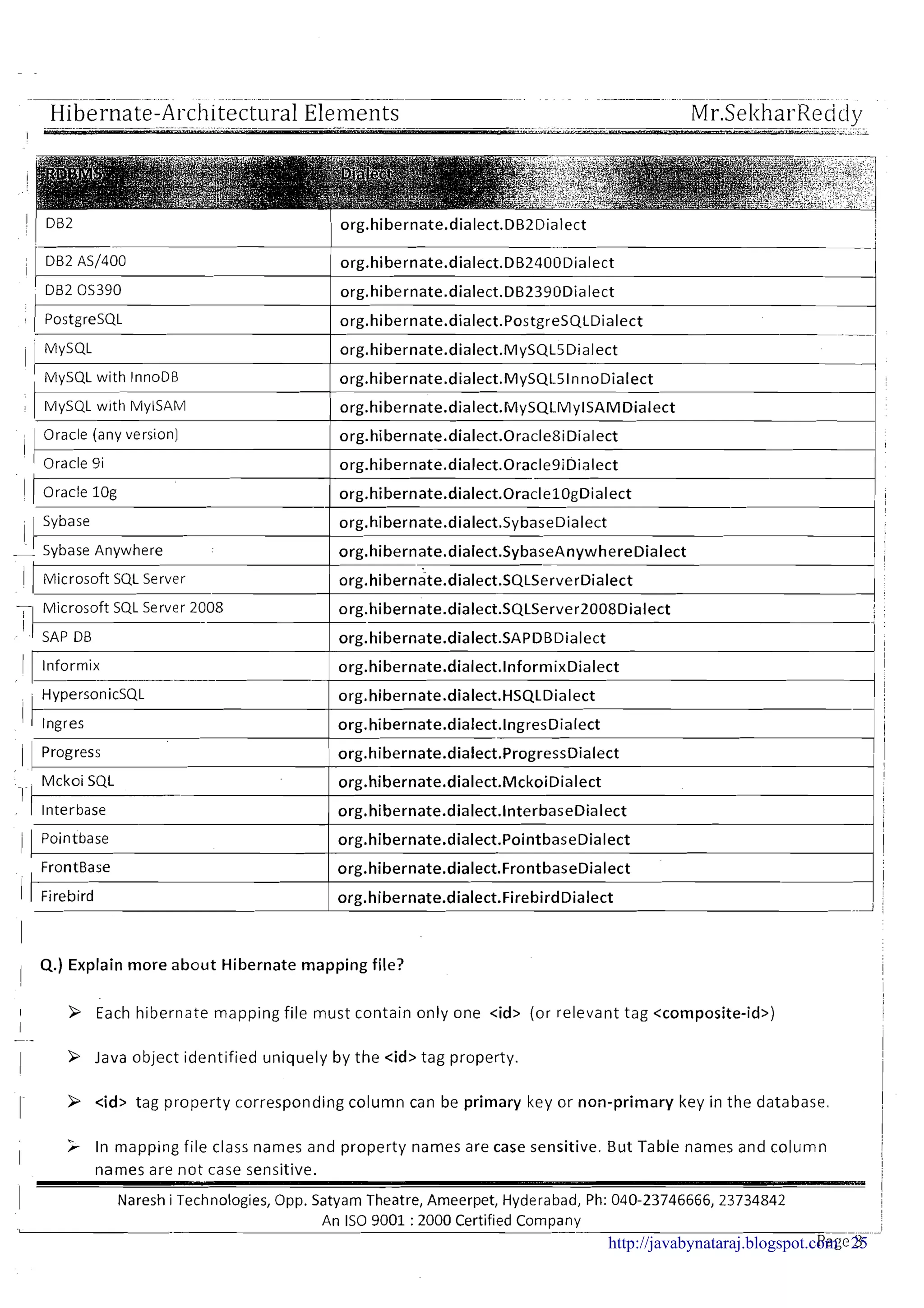
' 4.)What is Configuration object?
> Object Oriented representation of hibernate configuration file along with mapping file is known as
-
Configuration object
- 3 By default Hibernate reads configuration file with name "hibernate.cfg.xml" which is located in1
"classes" folder
I
9 If we want t o change the file name or if we want change the location of "hibernate.cfg.xml" then we
need to pass user given configuration file name (along with path) t o "configure()" method of
1 Configuration class
1 P Configuration object Stores the configuration file data in different variables. Finally all these
variables are grouped and create one high level hibernate object called SessionFactory object.
I
P So Configuration object only meant for creating SessionFactory object
I
> If we want we can provide the configuration information programmatically, without writing
I configuration file.(But it will become Hard coding, so not advisable)
1 Programmatic configuration
I Adding mapping files to configuration object programmatically
-- Configuration cfg = new Configuration()
1 .addResource("ltem.hbm.xml")
.addResource("Bid.hbm.xml");
I
- . -
Adding Entities(anrl0tated persistent classes) t o configuration object programmatically
I
Nareshi Technologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666,23734842
An IS0 9001 :2000 Certified CompanyI . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 5http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-27-2048.jpg)



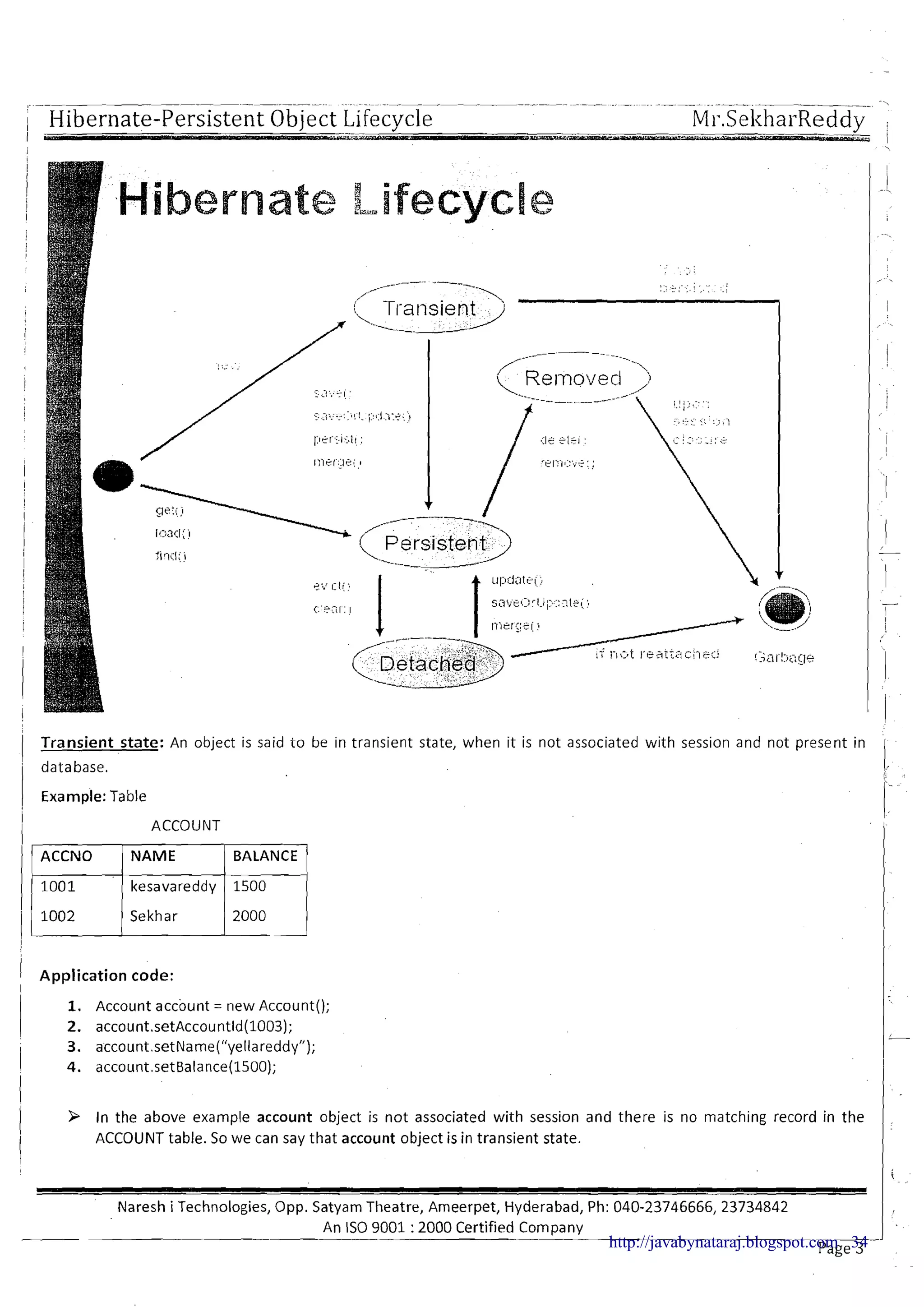
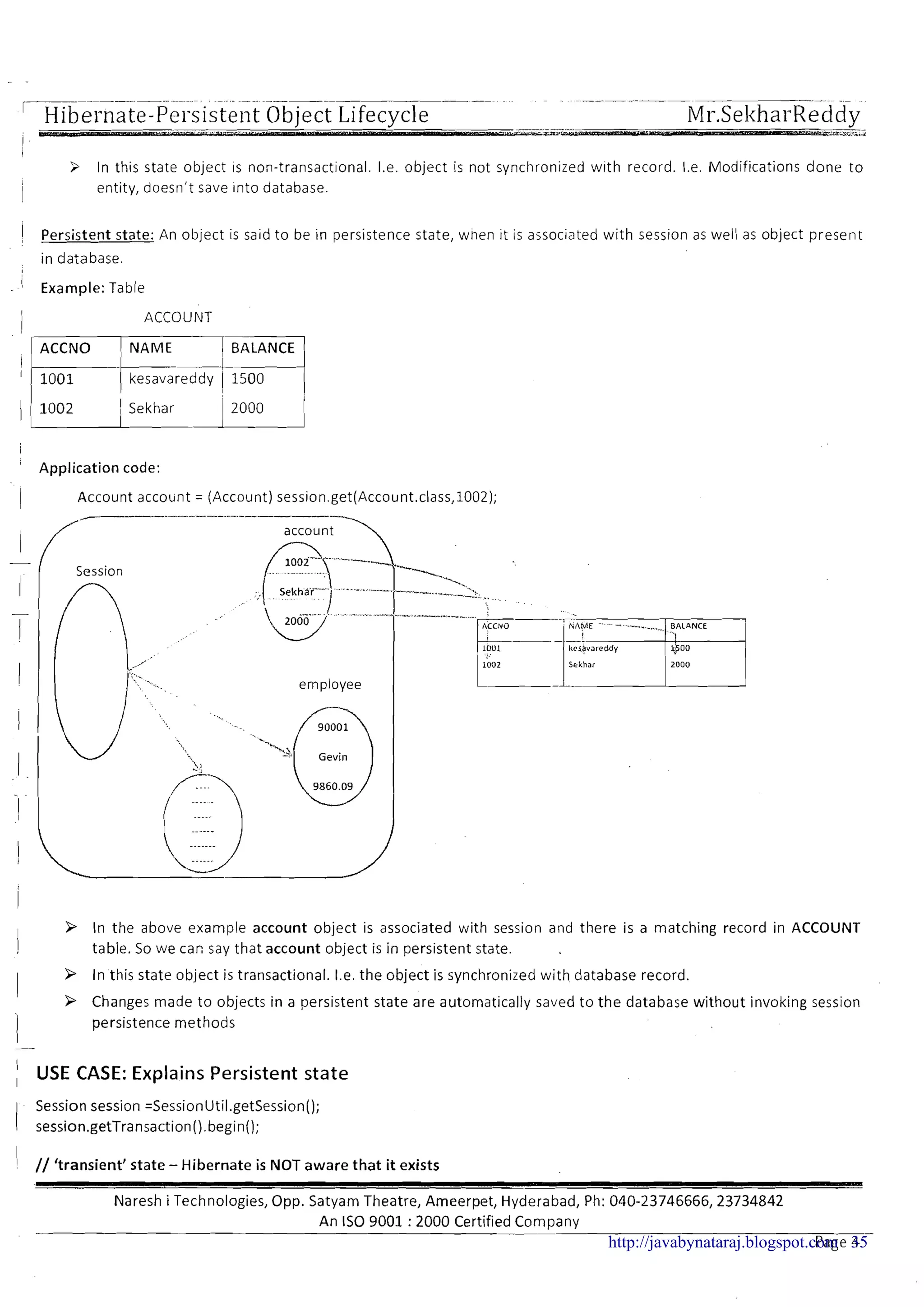
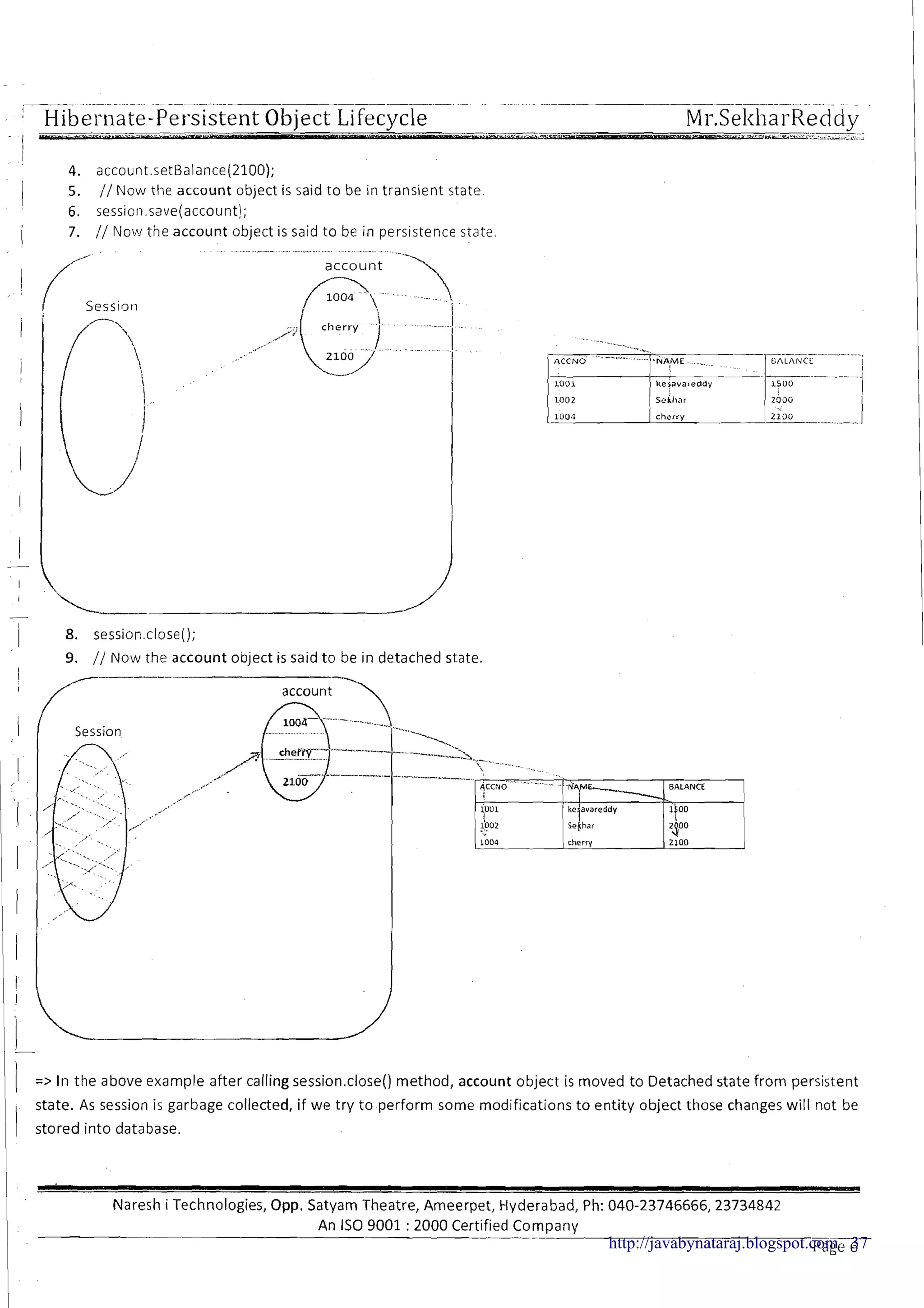
![; Hibernate-Persiste~~tObject Lifecycle. . ." Mr.SekharReddy -I - - - , -
1 ,,
I
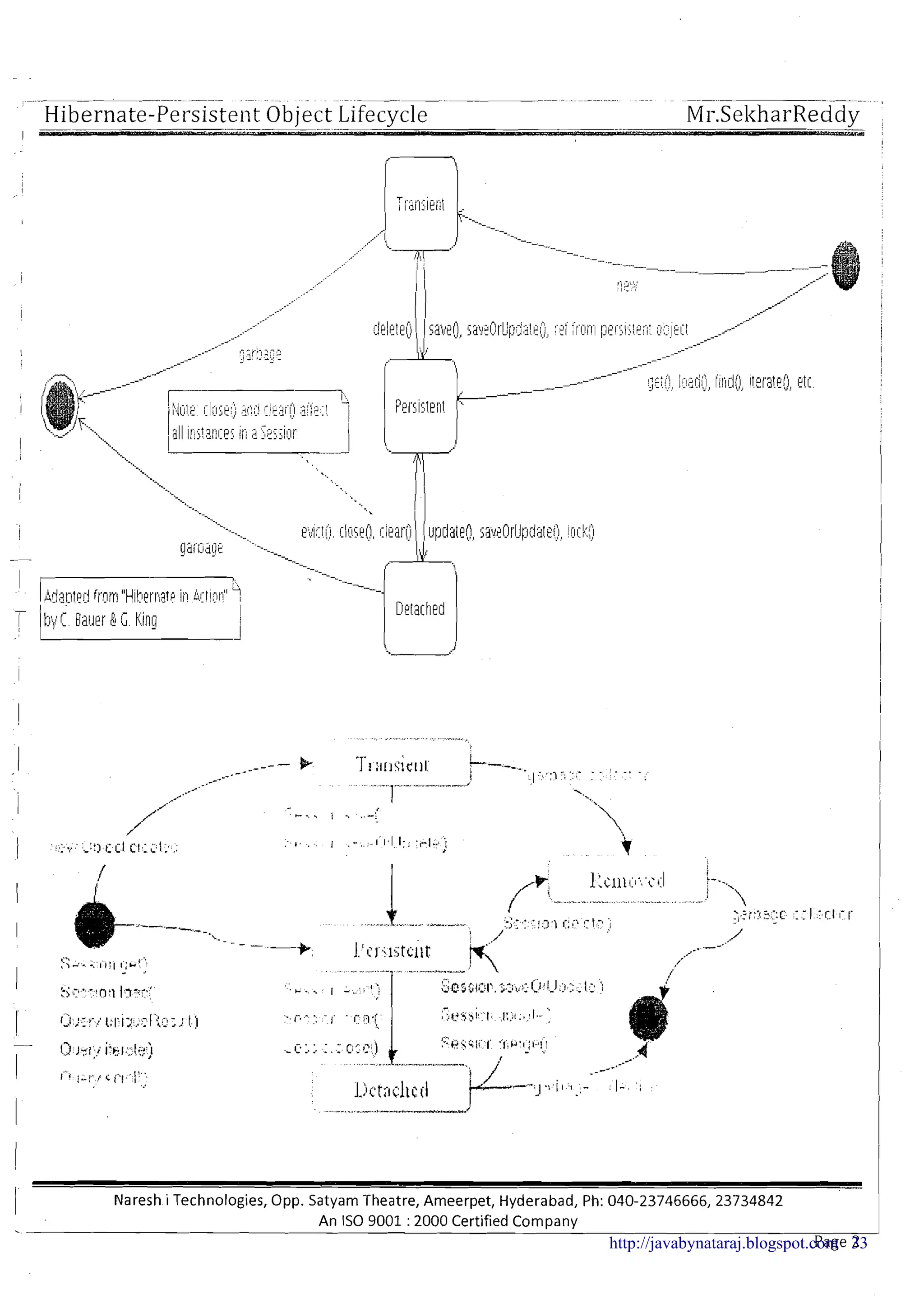
Persistent Object life cycle
1 Persistent Object has three life cycle states
1. Transient state
! 2. Persistent state
I
3. Detached stateI
I (-"]new - -.-.-instance
: 'L-
Transient State
--A -- --
I Session.get()
I j Session.load() Session.save() ; Session.delete()
Session.iterate()
! Session.saveOrUpdate() i
Session.uniqueResult() Sc.ssion.persist()
arb age collection
I
1.
B Session.scroll()1 : : Session.merge()
i
f
i
1 I
: Session.evict() Session.update()1
! Session.saveOrUpdate()
i : Session.clear() i
t Session.merge() ~arbage'collection
i : Session.close()
1 Session.lock()
I j Session.replicate() ,,(. '
! /.',.
i ; :
Detached State ,
/
Persistent state
Note:
Life cycleobject description
Transient state
Object associate with session
NO
IIDetached state
I I
-
3 Object is associated with session means object reference is available to the session object
Object present in the database
YES
N0
9 Object present in the database means object identifier value is available in database primary key column (Non
identifier column values are not matter)
YES
YES
Note: We can find the different diagrams for the persistent object life cycle as follows
Naresh i Technologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666,23734842
An IS0 9001 : 2000 Certified Company
Page 1http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-32-2048.jpg)













![Hibernate-Session Methods- -- ---- --MI-.SeltharReddy--
l
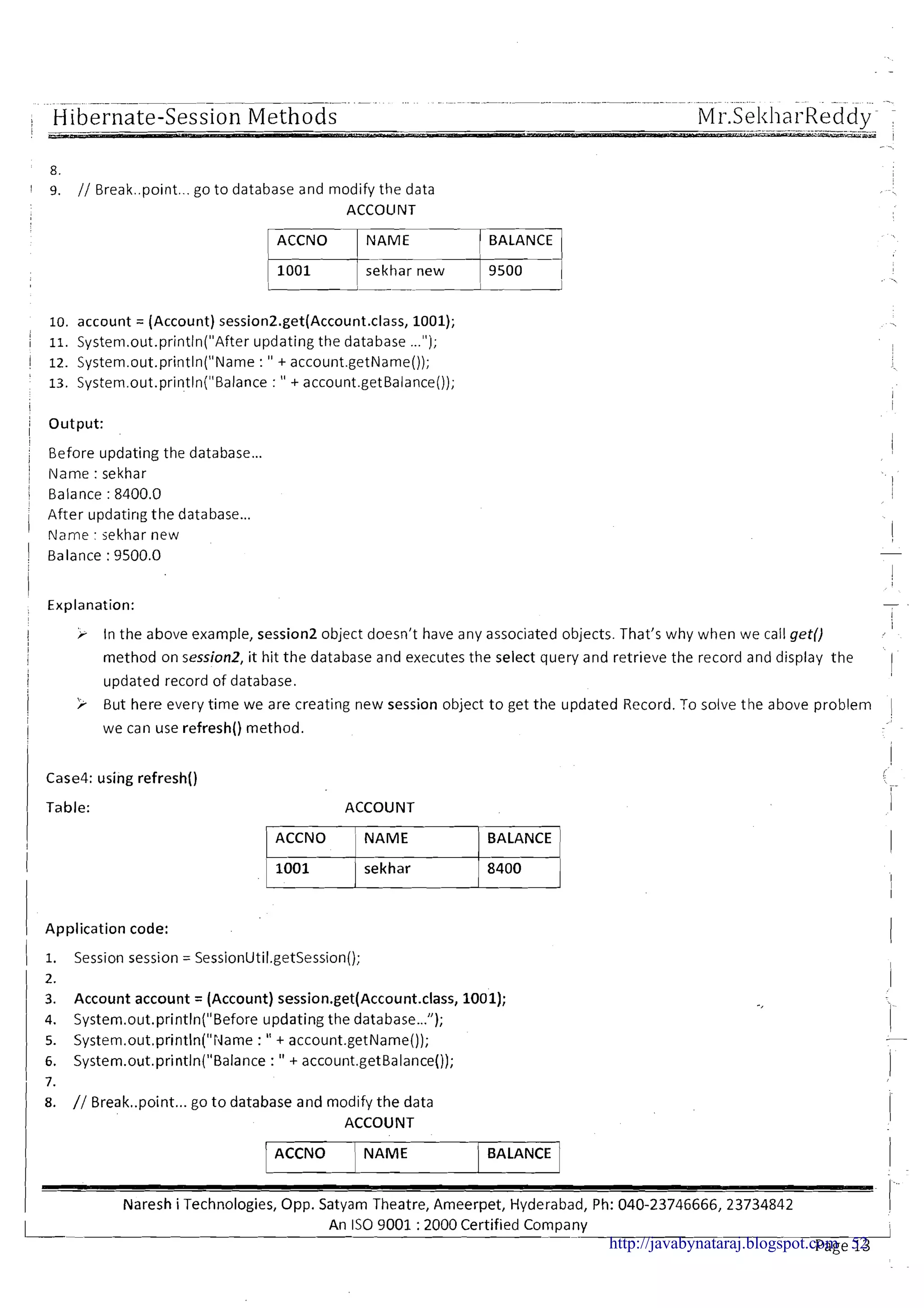
8.
9. // Break..point...go to database and mod~fythe data
10. ACCOUNT
m]NAME
I
1 BALANCE 1
/-tsekhar new
1
9500
/ 11. account = (Account) session.get(Account.class, 1001);
12. System.out.println("After updating the database ...");
'
13. Systcm.out.println("Name : " + account.getName());
14. System.out.println("Balance : " + account getBalance0);
I
15.
16. session.getTransaction().cornmit();
I 17.
18. session.close();
- Output:
II
Before updating the database ...
Name : sekhar
-1
Balance : 8400.0
After updating the database...
I Name : sekhar
Balance : 8400.0
/ Explanation:
> When we call the get() on session object(second time), it will check whether the object is available in session or
not. If the object is available in session, it will not hit the database.
> In above example with Accno 1001already account object is already available in session object. That's why even
we call get() method on session object 2ndtime, it will not hit the database. That's why it didn't display the
updated record data of database, instead it displayed previous data only.
Case 3: creating multiple sessions.
Table: ACCOUNT
1 ACCNO 1 NAME 1 BALANCE 1
) 1001 I sekhar 1 8400 1I I I I
Application code:
1. Session session1 = SessionUtil.getSession();
2. Session session2 = SessionUtil.getSession();
3.
4. Account account = (Account) sessionl.get(Account.c~ass,1001);
5. System.out.println("Before updating the database...");
6. Systern.out.println("Name : " + account.getName());
7. Systern.out.println("Balance :" + account.getBalance());
Naresh iTechnologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666,23734842
An IS0 9001 : 2000 Certified Company
http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-51-2048.jpg)
![Hibernate-Session Methods ---- -- ---- - - - ..,
Mr-SekharReddy
' -2
v-1sekhar new 1 9500 I
9. session.refresh(account);
I
lo. System.out,println("After updating the database ...");
11. System.out.println("Name : " + account getName());
12. System.out.println("Balance : " + account getBalance0);
! Output: I
I Before updating the database... I
I Name : sekhar
Balance : 8400.0
' After updating the database ..
, Name :sekhar new
1 Balance : 9500.0
I
' Explanation:
I > In the above example when we call refresh(), Hibernate compares database data and object data. If it finds any 1
- difference it will again execute select query and update the object data.
-
i public Obiect mergejobiect obiect) throws HibernateException;
Consider the following example,
Table: ACCOUNT
Application Code:
ACCNO
1001
1. session.getTransaction().begin();
2.
3. Account accountl=(Account)session.get(Account.class, 1001);
4.
5. Account account2= new Account();
6. account2.setAccountld(1001);
7. account2.setName("cherry");
8. account2.setBalance(6500);
9.
10. session.update(account2);
11.
12. session.getTransaction~).commit();
, Output: org.hibernate.NonUnique0bjectException: a different object with the same identifier value was already
NAME
sekhar
1 associated with the session: [com.sekharit.hibernate.entity.Account#lOOl]
I
BALANCE
8400
1 Naresh iTechnologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23745666,23734842
I-
An IS0 9001 :2000 Certified Company---- -. -- .-
Page 14http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-53-2048.jpg)


![, ..__ .- .. ---.--~-- -.--.~,
' Hibernate-Session MethodsI -
Mr.SekharReddy .-
.L -, : I
I
,-,
11 5.
1 6. Account account2= new Account(); - ..
1 7. account2.setAccountld(1001);
i 8. account2.setNarne("kesavareddy"); . ~
9, account2.setBalance(6500);
i
I 10. /--.
, 11. session.merge(account2];
12.
I . .
i 13. session.getTransaction().commit();
j 14. session.close();
1 After execution: ACCOUNT
ACCNO BALANCE
yellareddy
I I
,In the above example, Before llthline; accountl is in Persistent state, and account2 in detached state.I . - ,
-
. ,
/ > In the above example, when we call merge() method it will check, weather there i i any object associated with
the session with same identifier(1001). -
> In our example, accountl#1001 object is already associated with session, So merge() method now, Copy the I
< - .
state of accoun2#1001 object state into accountl#1001 object. After llthline also, account1 is in Persistent ,
j
state, and account2 in detached state.
1 3 When the transaction is committed, As acountl#lOOl(Persistent-state)data is modified, so it will hit the update
I
!
query, t o update session data with database.
Q) What is the difference between merge and update? i
i
update () :When the session does not contain an persistent instance with the same identifier, and if it is sure use update I
for the data persistence in hibernate.
i
I
merge (): Irrespective of the state of a session, if there is a need t o save the modifications at any given time, use
I
merge(). !
, public Serialiiable getldentifieriobiect object) throws HibernateException; I
To know the object identifier value at the runtime, we need to call getldentifierfobject object)
I
Application code: 1
I Account account = (Account)session.get(Account.class,1001);
I Serializable id = session.getldentifier (account);
System.out.println("Identifier of Account is :"+ id); '1
1Transaction methods:
I
Naresh i Technologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666,23734842 1
An I S 0 9001 :2000 Certified Company
--- I-
Page 17-http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-56-2048.jpg)




![~..~.~...................................... . . ~~ --...-- ~
- ~
Hibernate-Multi Database Communication 7By Mr. SekharReddy I
1. package com.neo.hibernate.dao;
2 .
3. import crg.hibernate.Session;
4. lrilport org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
5. import org.hibernate.cfg .C ~ n figuration;
6.
7. import com.neo.hibernate.util.Conn~ctionUti1;
8. import com.neo.hibernate.vo.Account;
9.
10. public class PracticeDao {
11. public static void main(String[] args) {
12.
13. Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
14. configuration.configure("com/neo/hibernate/config/hibernate.cfg.xml");
15. SessionFactcry factory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(j;
16. / / Oracle
17. Sesslon oracleSession =
18. factory.openSession(ConnectionUtil.getOracleConnecti~n());
19. Account oracleAccount = (Account)
20. oracleSession.get(Account.class, 1001);
21. System.out.println("0racle Account table details . . . . ") ;
22. System.out.println("Accno : "+oracleAccount.getAccno());
23. System.out.println("Name : "+oracleAccount.getName());
24. System.out.println("Ba1ance : "+oracleAccount.getBalance()) ;
25. //Mysql
26. Session mysqlSession =
27. factory.openSession(ConnectionUtil.getMysqlConnection()) ;
28. Account mysqlAccount= (Account)mysqlSession.get(Account.class, 1001);
29. System.out.println("Mysq1 Account table details . . . . " );
30. System.out.println("Accno : "-1-mysqlAccount.getAccno()) ;
31. System.out.println ("Name : "+mysqlAccount.getName ( ) ) ;
32. System.out.println("Balance : "+mysqlAccount.getBalance());
33.
34. 1
35. )
36.
ConnectionUtil.iava
1. package com.neo.hibernate.ut11;
2.
3. import java .sql .Connection;
4. import java.sql.DriverManager;
5. lmport java.sql.SQLException;
6.
7. public class ConnectionUtil {
8. static {
9 . try {
10. Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver~');
11. Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
12. 1 catch (Exception e) {
13. e.printStackTrace0;
14. 1
15.
I Naresh i Technologies, Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Ph: 040-23746666, 23734842 iAn IS0 9001 :2000 Certified Company I
1.-
Page 3http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-61-2048.jpg)



![.~.~ - - ~ -. ~ ~.. ~ ~ ~~ .~
,~ Hibernate-Multi Database Colnmunication By Mr. SeltharReddy
, 21. System.out .prlntln("Name : "tmysqlAccount.aetl.!a:ne( ) ) ;
, 22. System.out.pr~1ltln("5alance: "tmysqlAccount.qer.Balance()) ;
23. 1
2 4 . 1
I SessionUtil.java
- 1. package corr,.neo.hibernate.util;
2.
1 3. import 01-9.hibernate.S-ssion;
4. import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
1 5. import org.hibernate.cfg .Configuration;i
6. import org .ja:<en.Eunction .ConcatFunction;
1 7.
8. public class SessionUtil {
9.
1 10. private static SessionFactory oraclFactory;
11. private static SessionFactory mysqlFactory;
1 12.I stacic (
13. n r ? c l Factory = new Configuration i : . ranfigure (
. I ;;: "com/neo/hibernate/config/~racle.hibernate.cfg.xml")
-- .buildSessionFactory();
' 1 16. mysqlFactory = new configuration().configure(
, I 17. "corn/neo/hibernate/config/~nys~ql.hibernate.cfg.xml")
- 18. .buildSessionFactory(!;
1 19. 1
20.
I ;;: public static Session getOracleSession() [
return oraclFactory.openSession();
23. 1
1 24.
25. public static Session getMysqlSession() {
1 26. return mysqlFactory.openSession();
27. 1
28. public static void main(String[] args) {
1 29. System.out.println(getMysqlSession()) ;
30. 1
' 3 1 , !
1 Account.hbm.xrnl
1. <?xml version="l.0" encoding="UTF-8Ir?>
1 2. <!DOCTYPE hibernate-rnapplng PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/HlbernateMapping DTD 3.O//ENU
I "http://h~bernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mappng-3.0td">
3.
4. <hibernate-mapping>
5. <class name="corn.neo.hibernate.vo.Account" table="ACCOUNT">
I 6 -
<id name="accno" column="ACNO"></id>
- 7. <property narne="name"></property>
8. <property name="balance" column="BAL1'></property>
1 9. </class>
I
10. </hibernate-mapping>
I I
I Naresh I l.echnolog~es,Opp. Satyam Theatre, Ameerpet, ~ ~ d e r a b a d ,Ph: 040-23746666, 23734842 I
An I S 0 9001 :2000 Certified Company I
I __I
Page 7http://javabynataraj.blogspot.com 65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hibernatecompletenotesbysekharsirjavabynataraj-150509192348-lva1-app6892/75/Hibernate-complete-notes_by_sekhar_sir_javabynatara_j-65-2048.jpg)