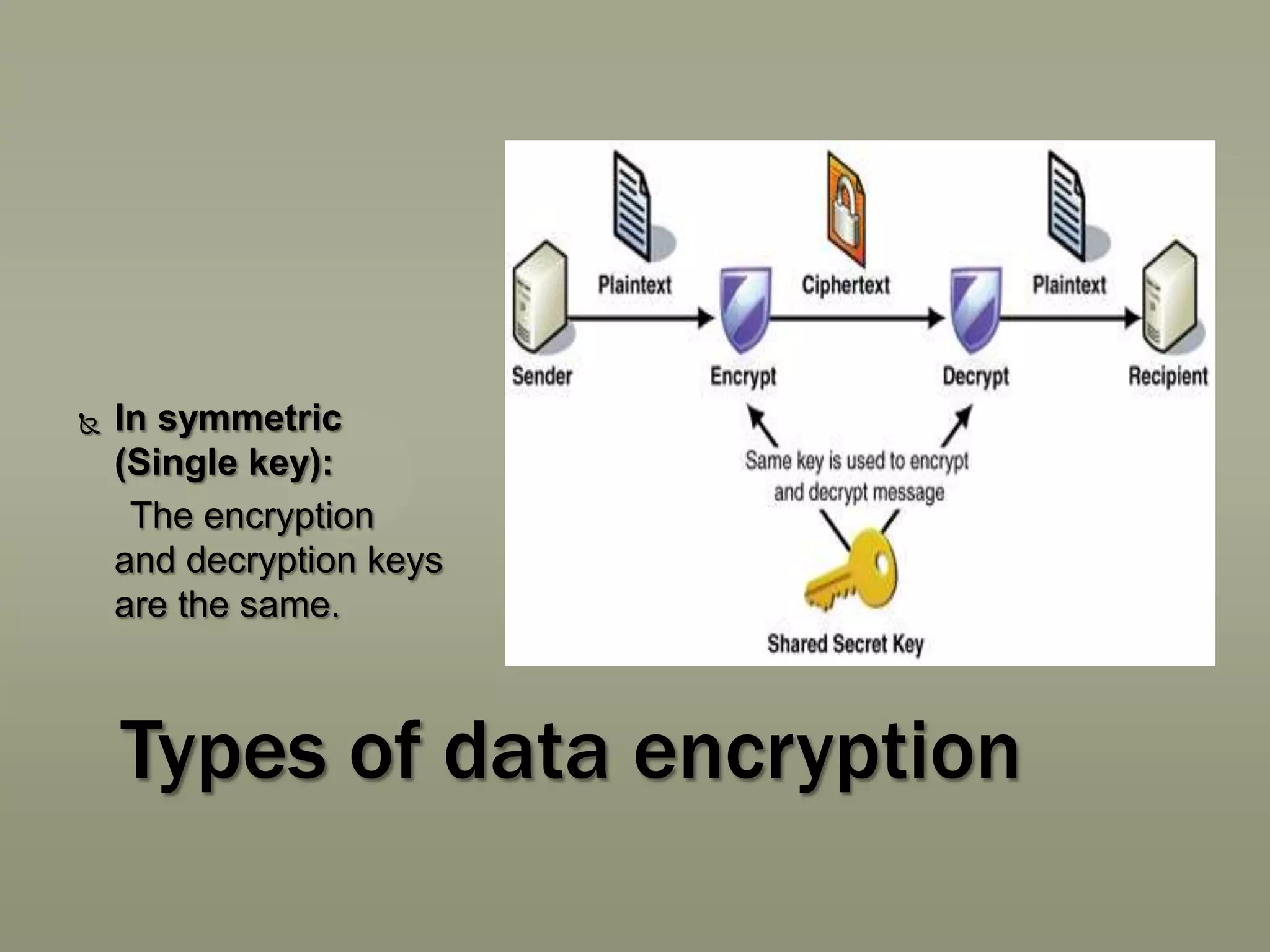
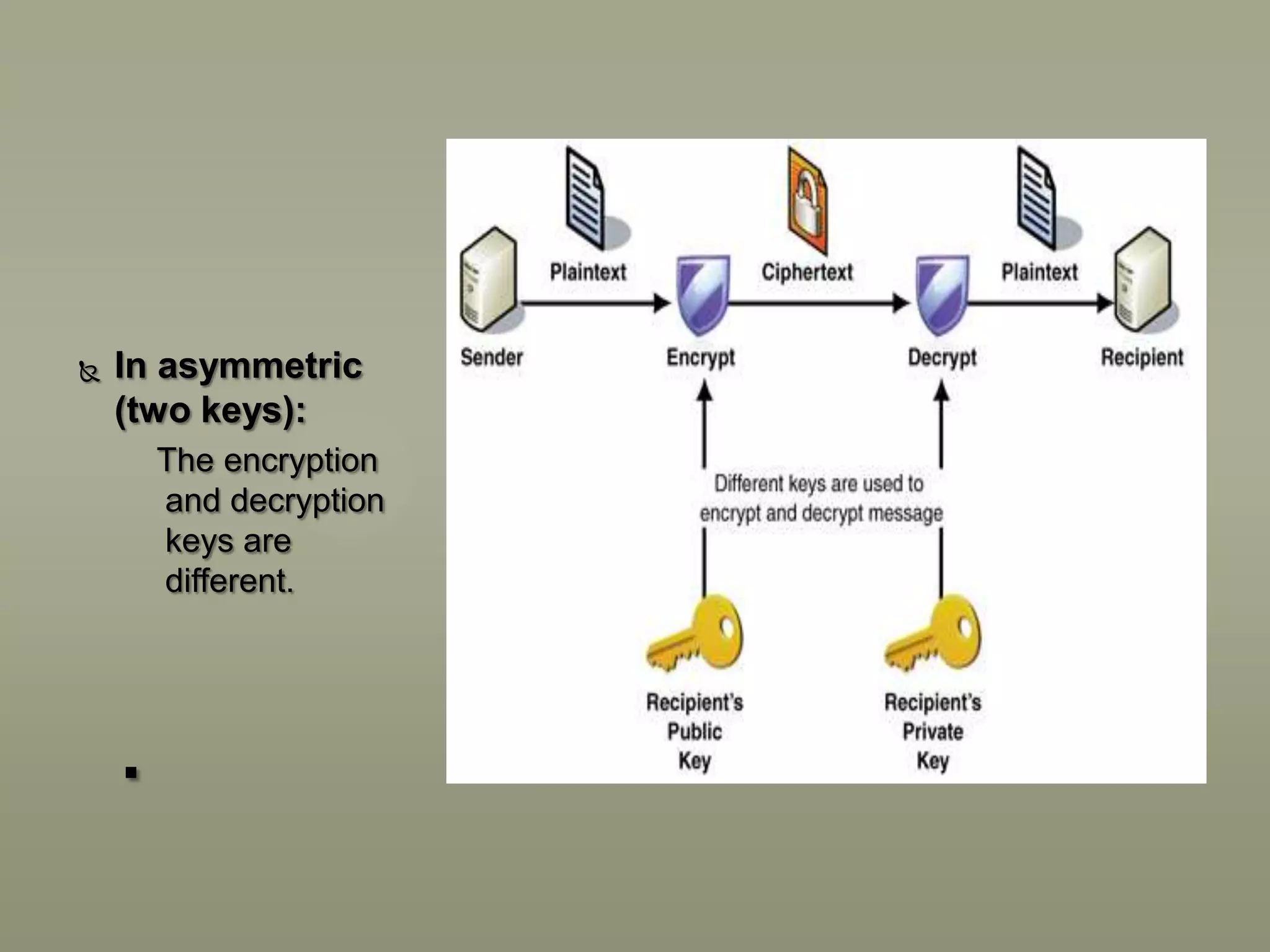
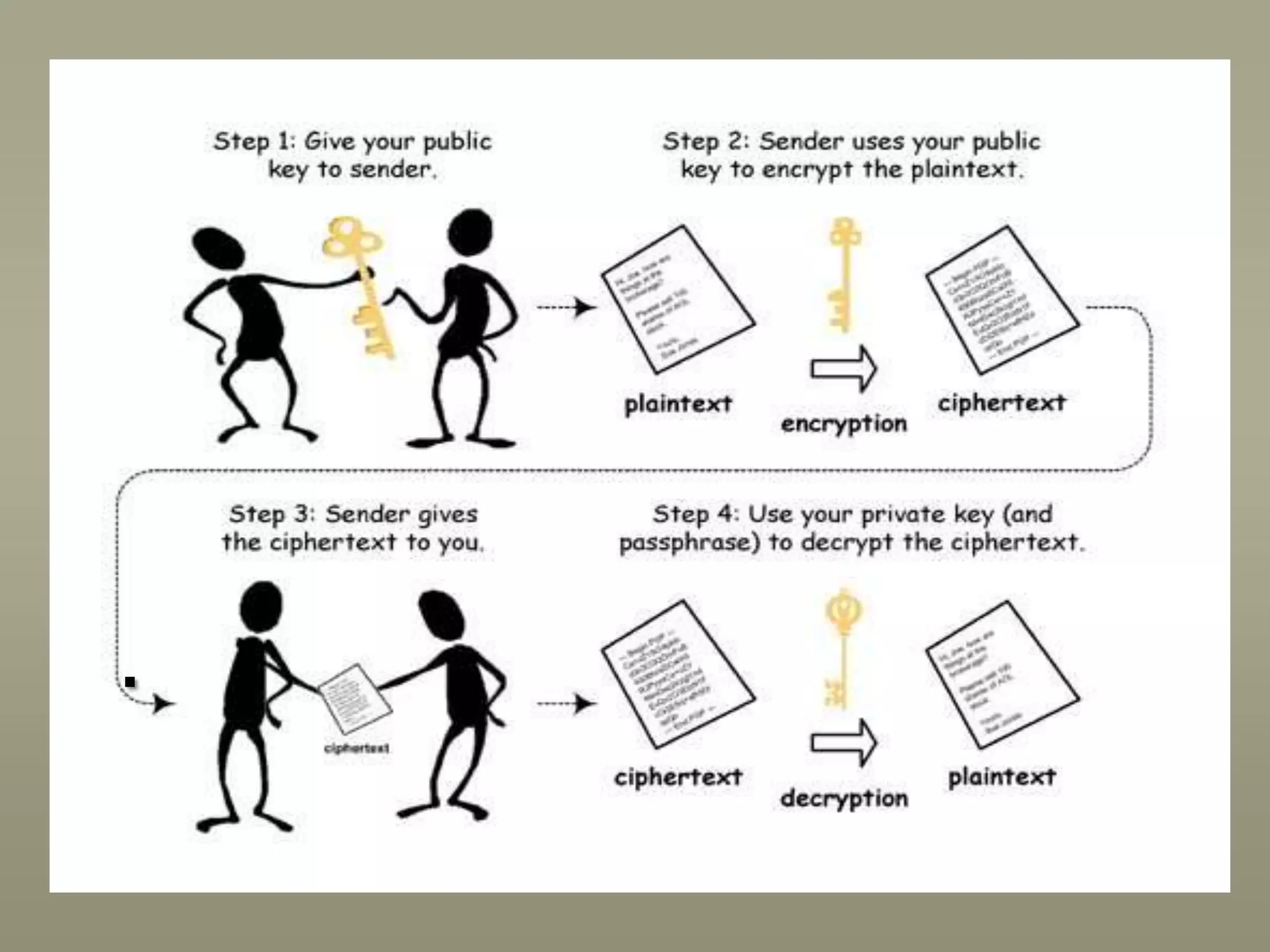
This presentation discusses various aspects of data encryption. It defines data encryption as mathematical calculations and algorithms that transform plain text into ciphertext. It then covers the main types of encryption, distinguishing between symmetric encryption which uses the same key for encryption and decryption, and asymmetric encryption which uses different public and private keys. The presentation also explains some common encryption methods like the Data Encryption Standard and public key cryptosystems.