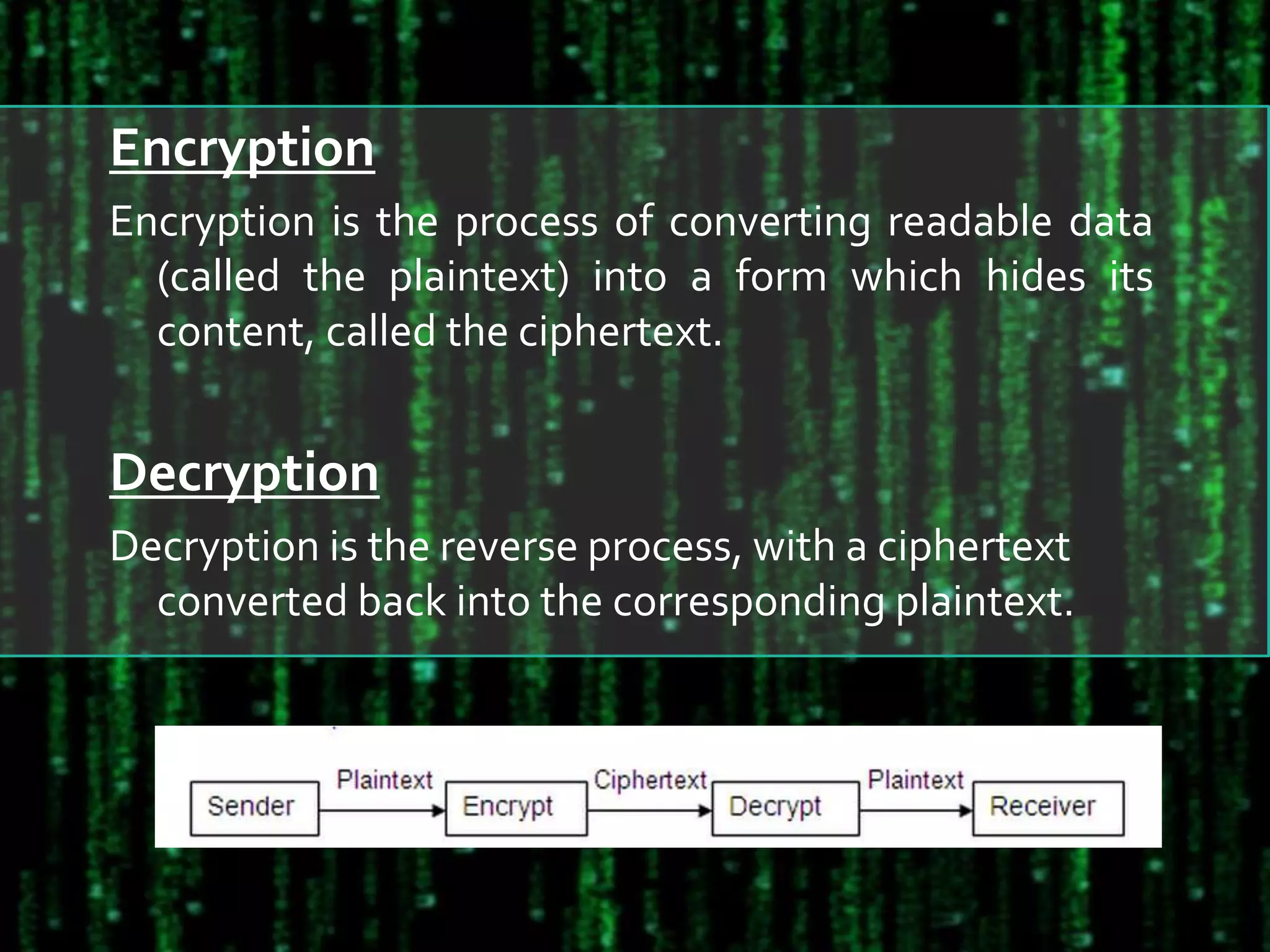
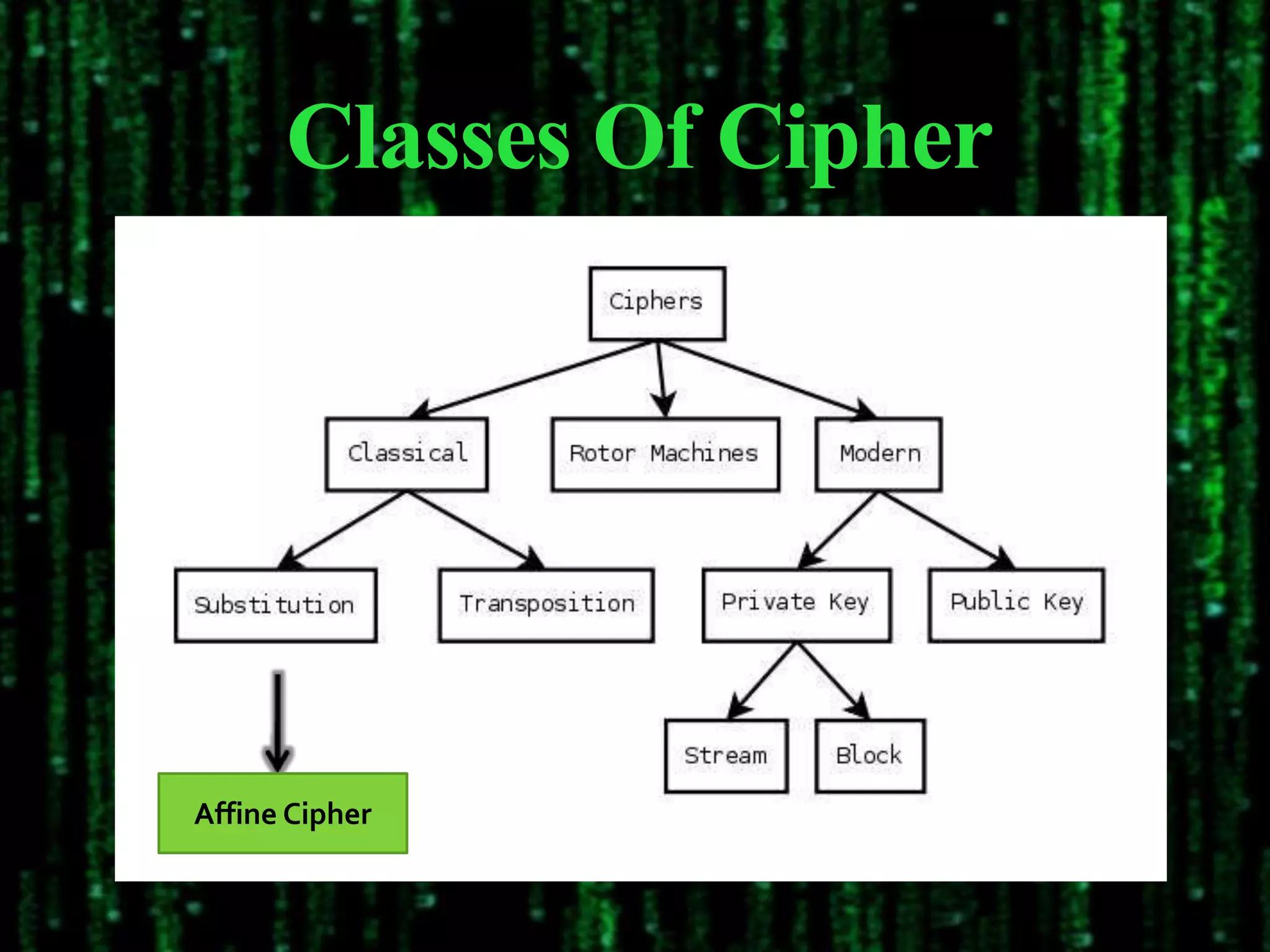
The document discusses the design and implementation of an encryption/decryption scheme for Devanagari script using the affine cipher, a mathematical function that maps letters to numeric values. It outlines the encryption and decryption processes, key calculation methods, and provides algorithms for implementation along with time and space complexity analysis. The conclusion emphasizes the uniqueness of the affine cipher's key determination based on character unicodes.