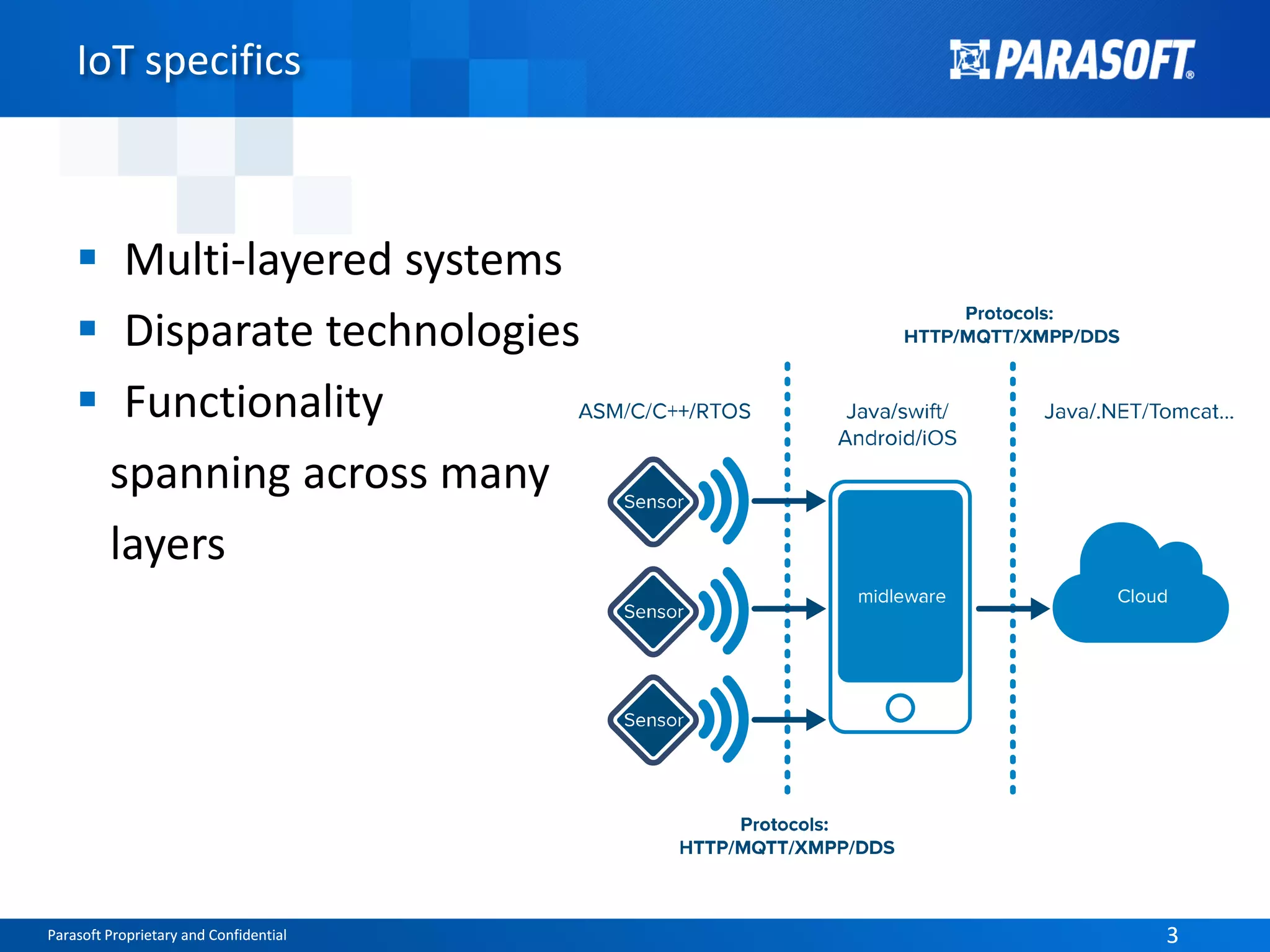
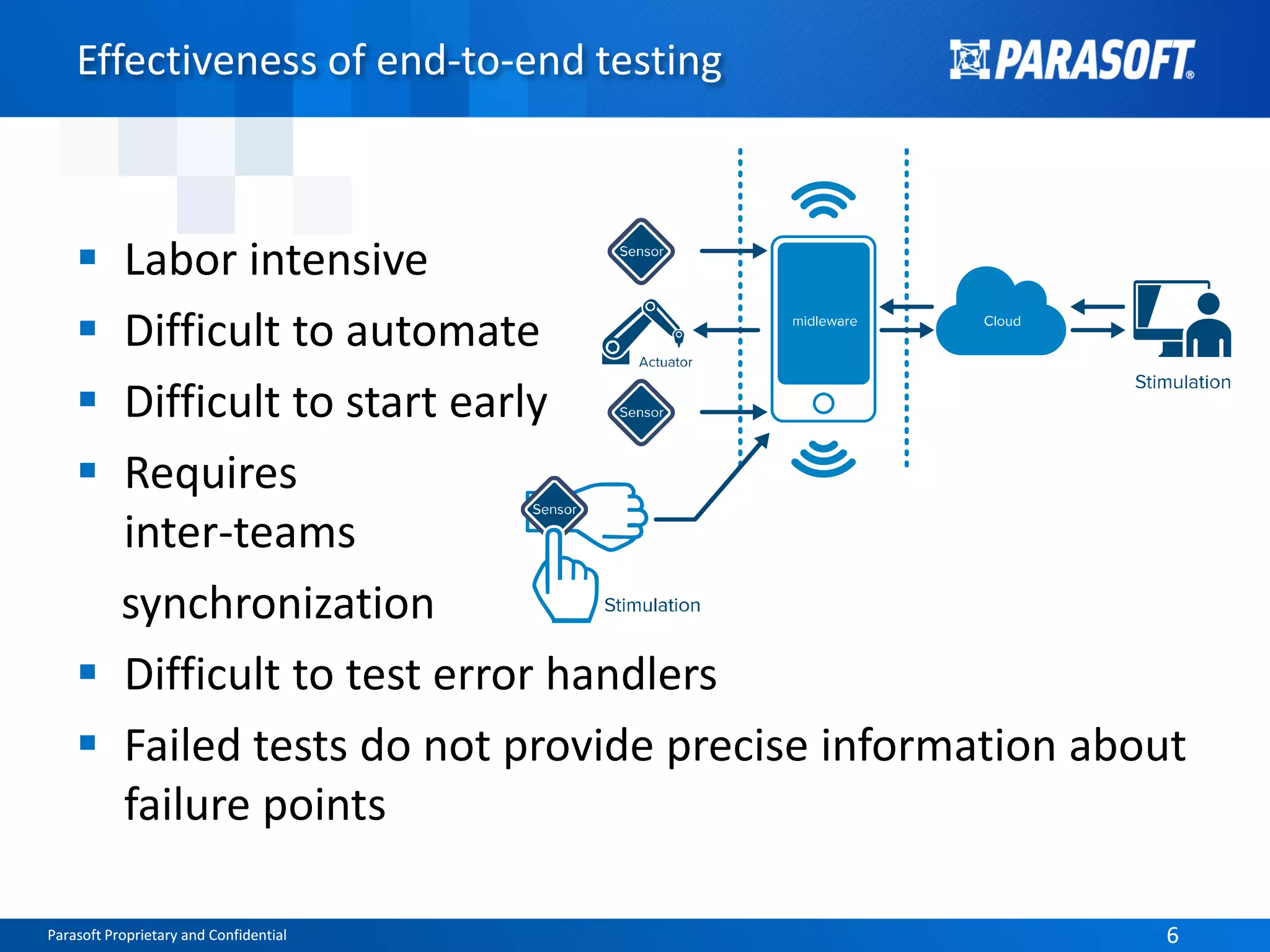
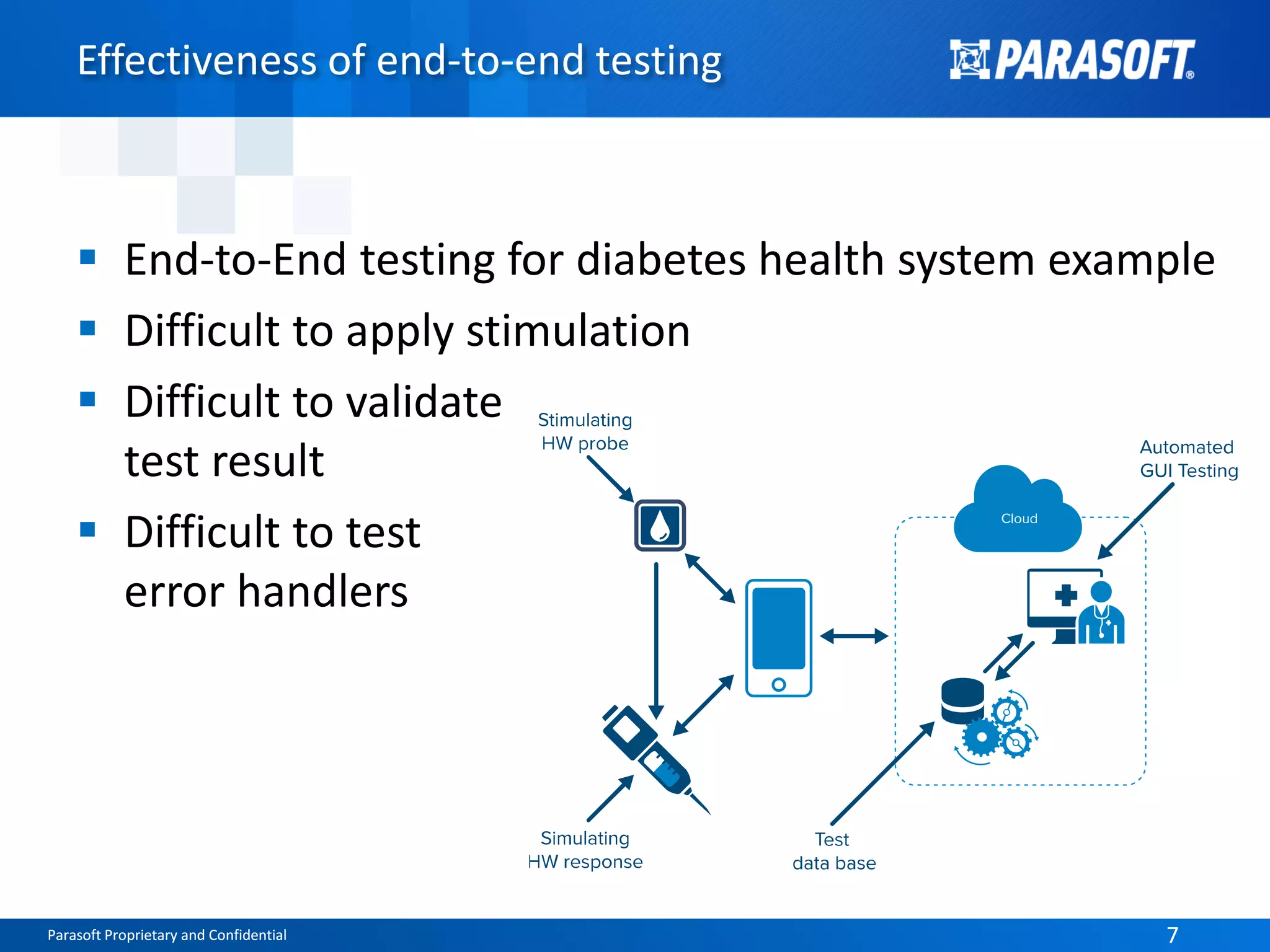
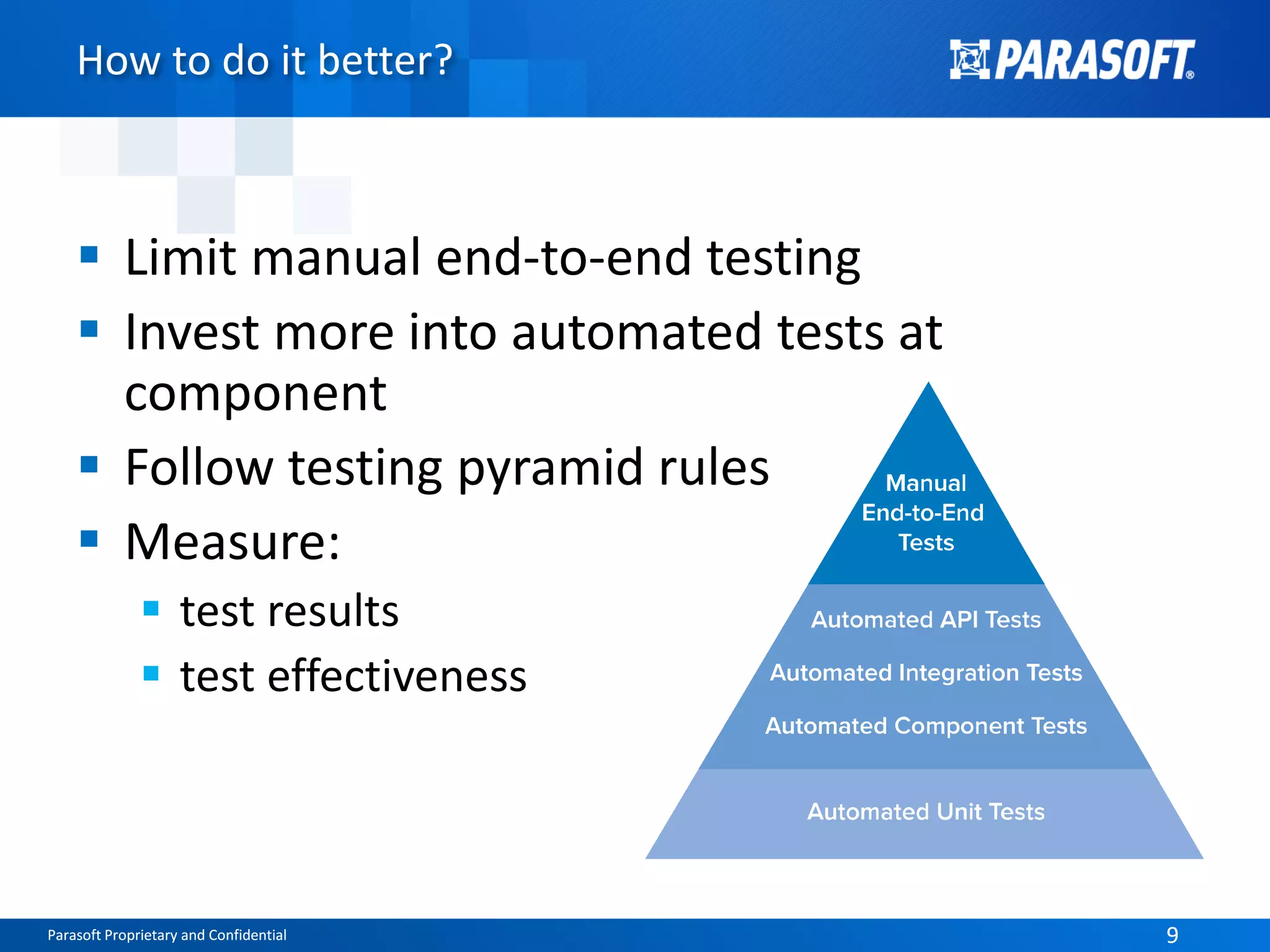
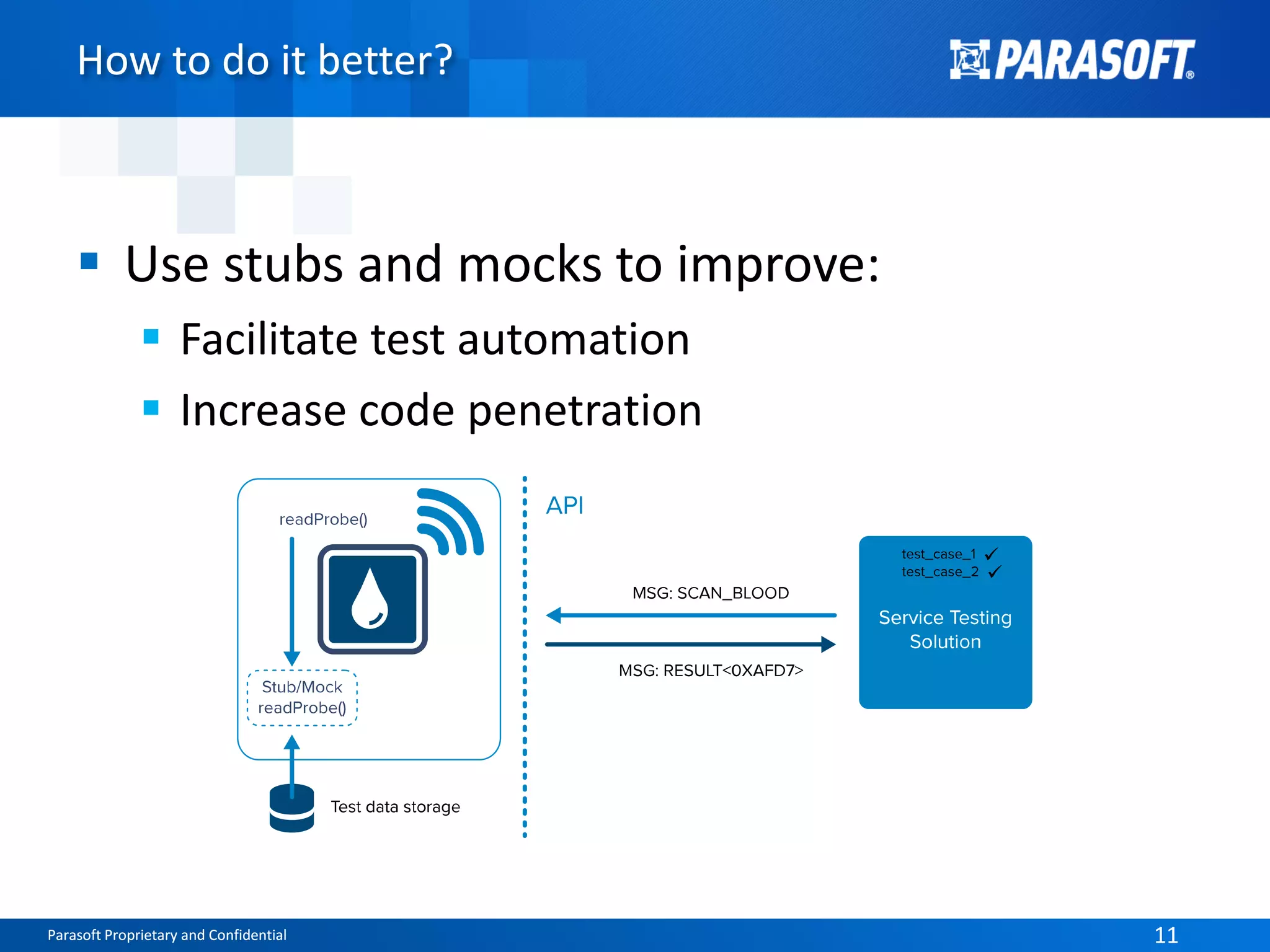
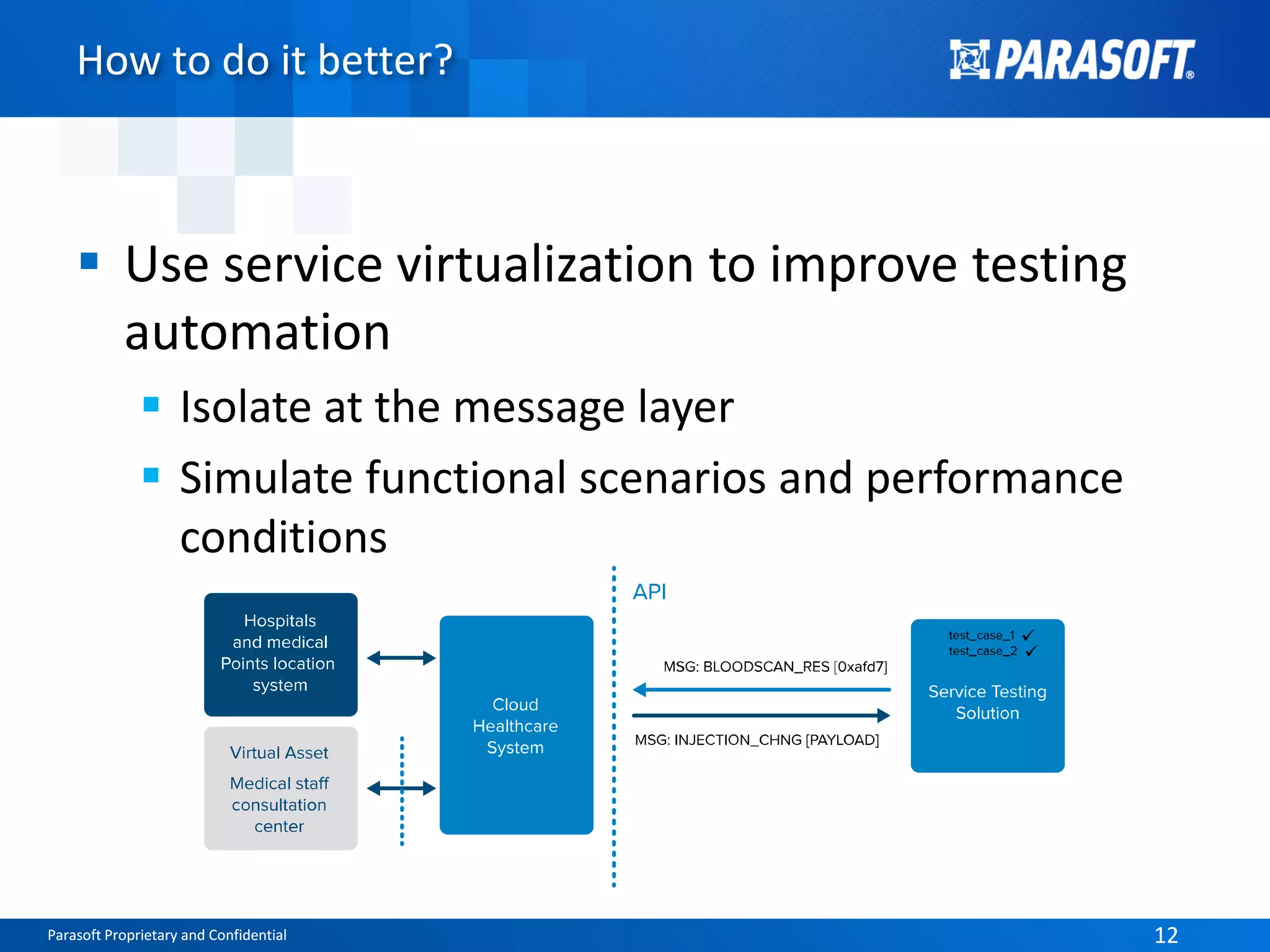
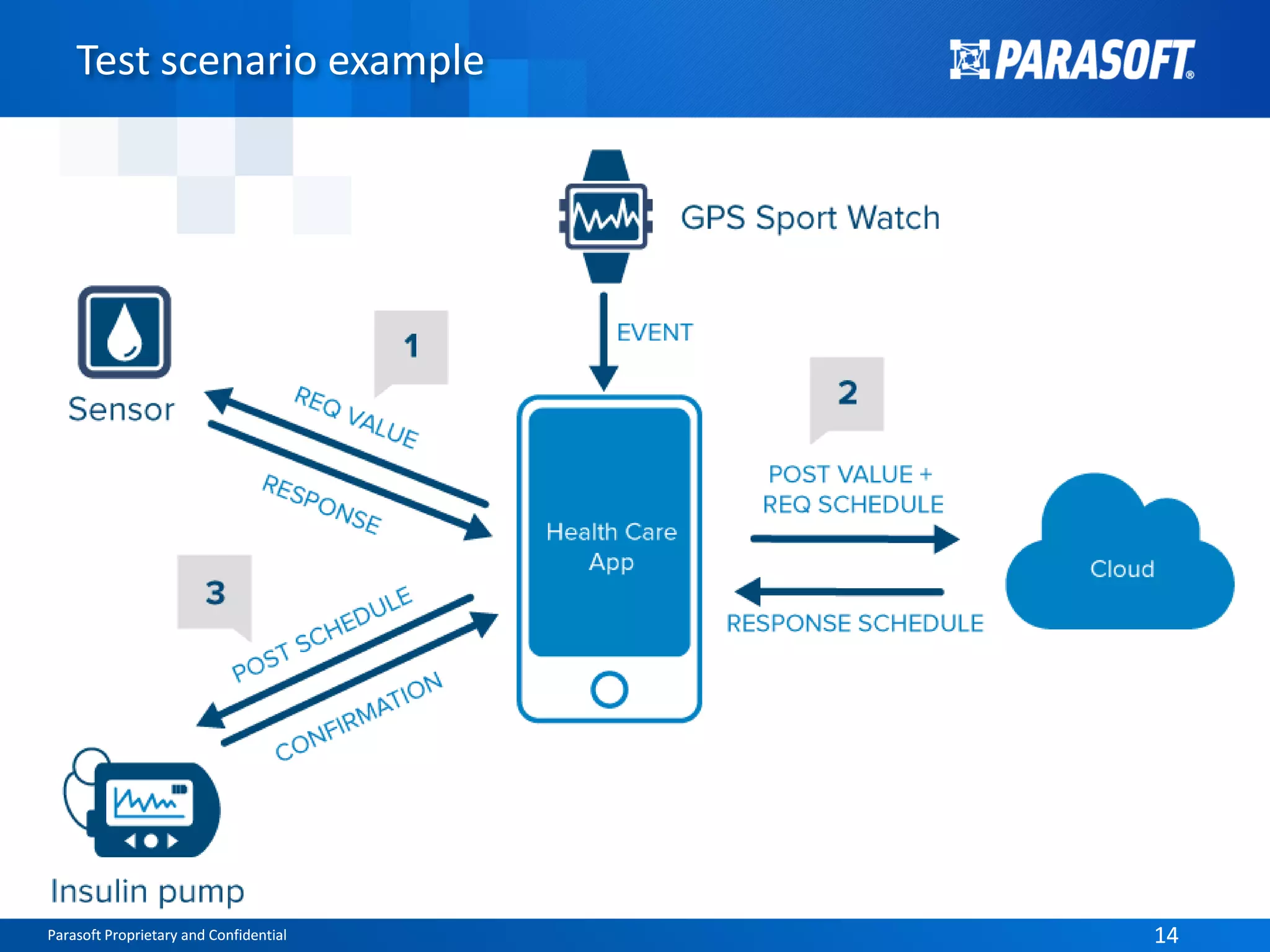
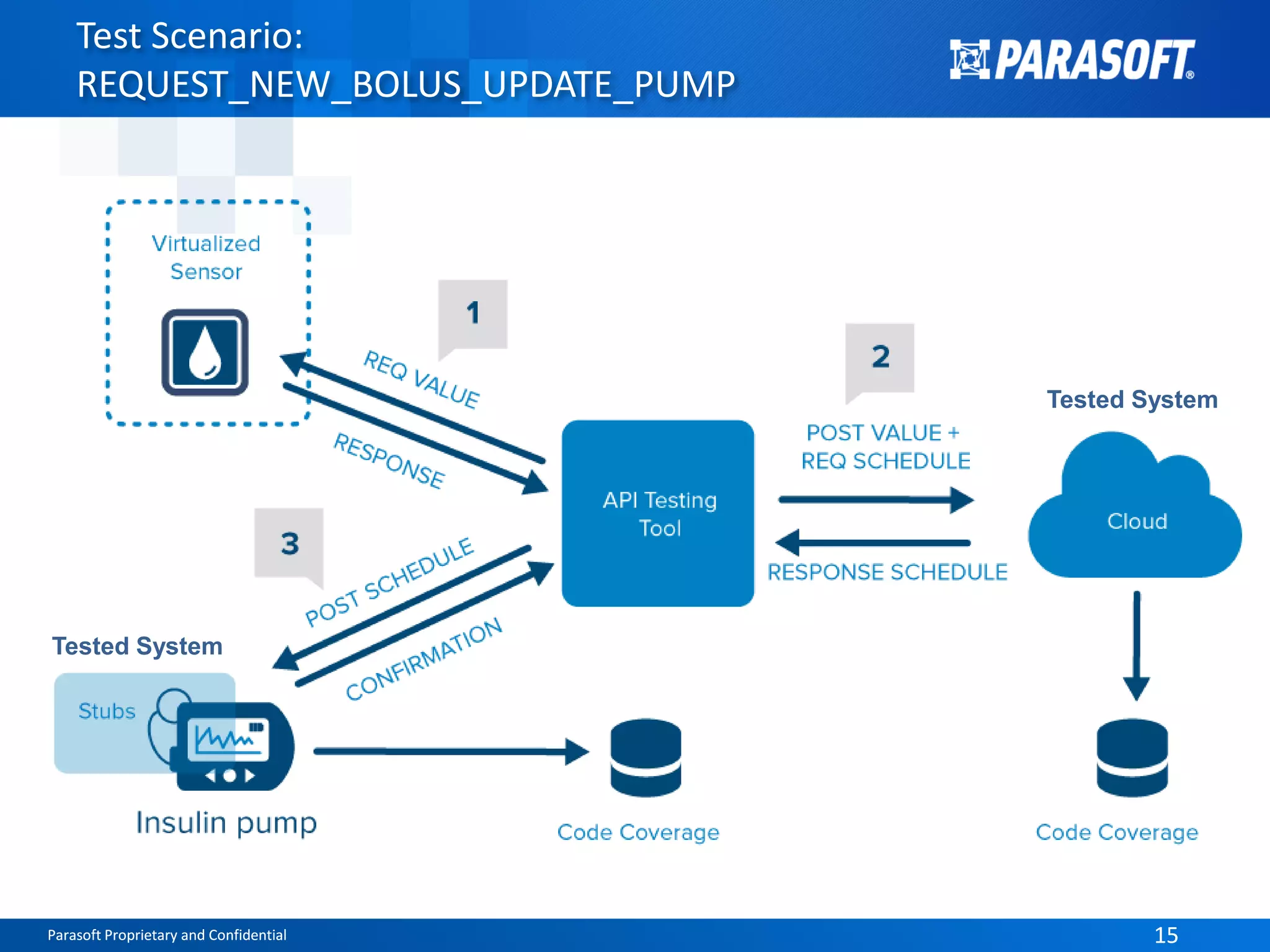
The document discusses the complexities and challenges of end-to-end testing in IoT systems, highlighting issues such as disparate technologies, limited testing strategies, and difficulties in automation. It suggests improving testing effectiveness through prioritization of automated tests, the use of service virtualization, and measuring test results comprehensively. The overarching theme emphasizes the need for reliable quality processes that enable organizations to assess modules and their interactions effectively.