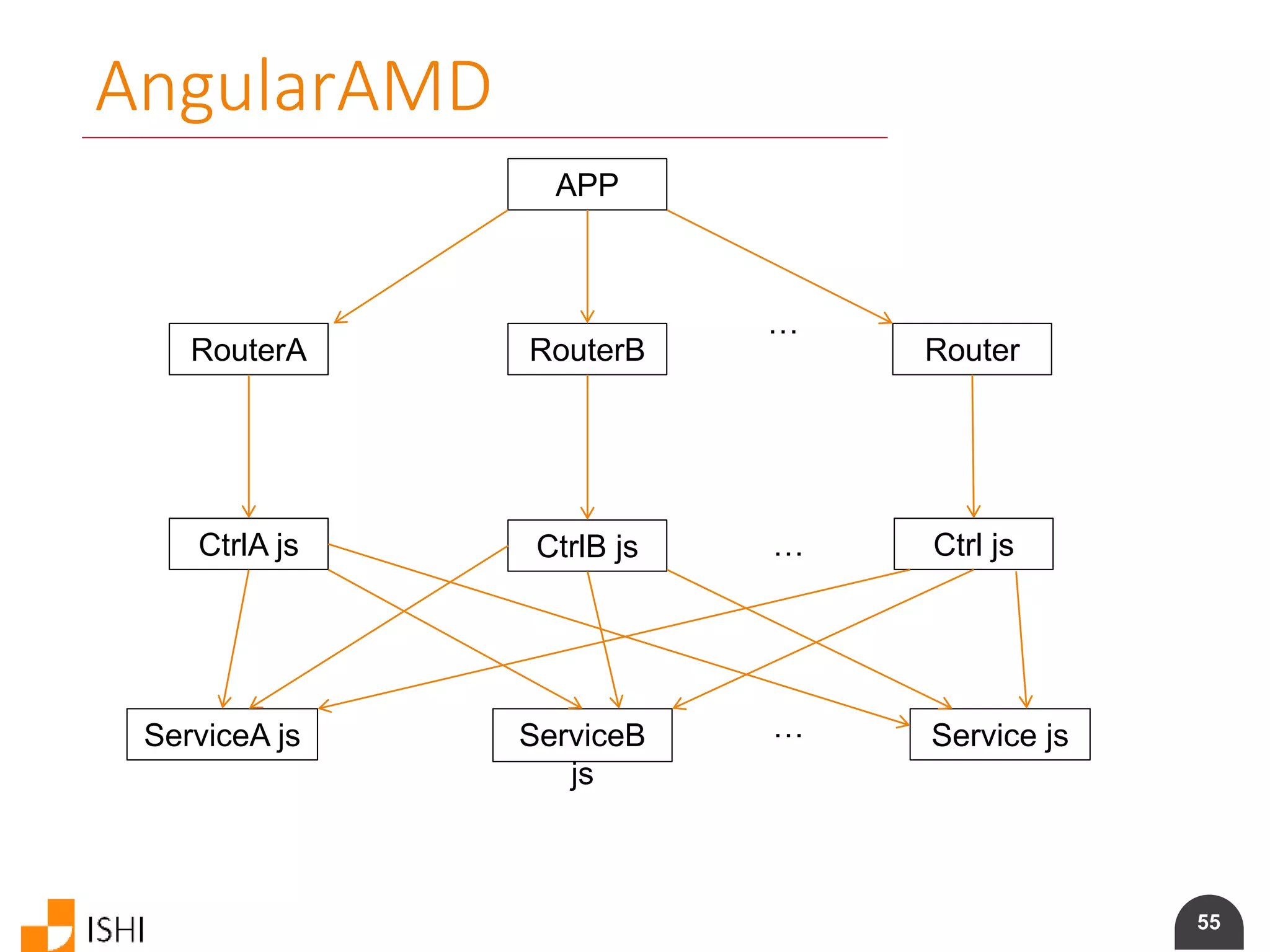
The document provides an overview of ECMAScript 6 (ES6) and Asynchronous Module Definition (AMD). It discusses features of ES6 like constants, block scoping, arrow functions, classes, and generators. It also covers using AMD modules with AngularJS and demonstrates importing and exporting modules. The presentation aims to introduce developers to ES6 and show how to use AMD modules with AngularJS applications.







![9
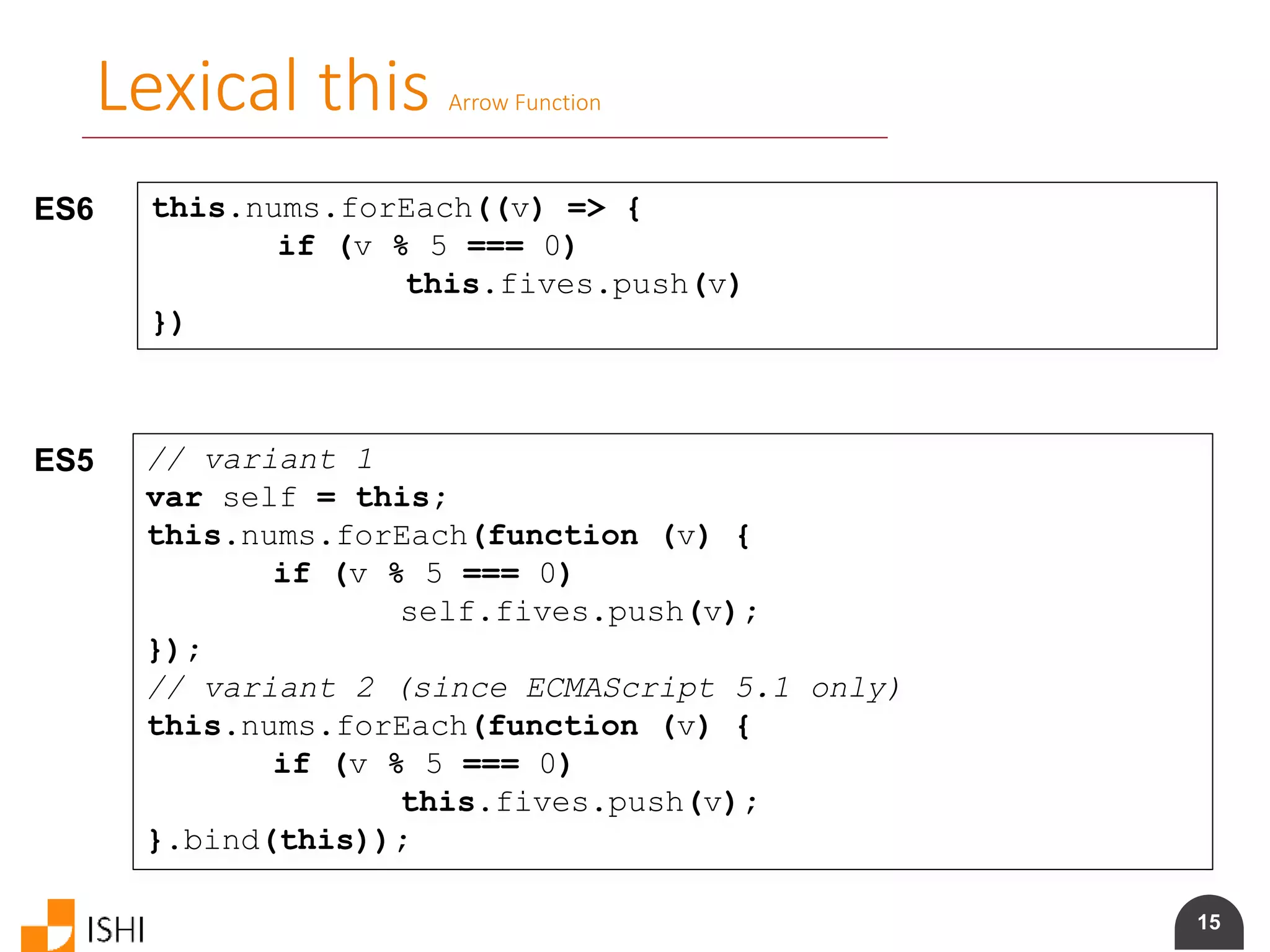
Blocked-scoped variables without hoisting
ES6 for (let i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
let x = a[i]
…
}
for (let i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
let y = b[i]
…
}
ES5 var i, x, y;
for (i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
x = a[i];
…
}
for (i = 0; i < b.length; i++){
y = b[i];
…
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-9-2048.jpg)
![10
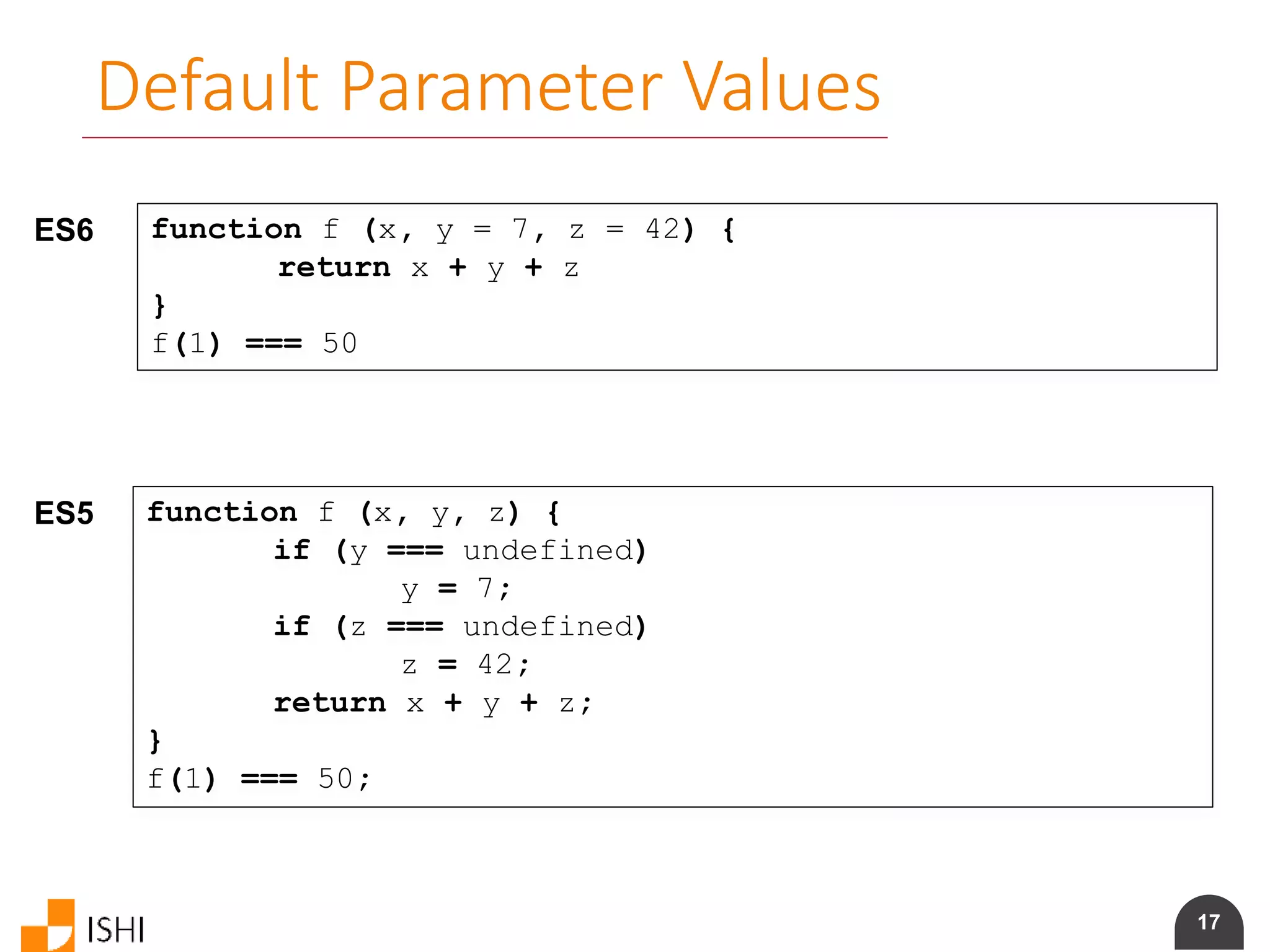
Blocked-scoped variables with hoisting
ES6 let callbacks = []
for (let i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
callbacks[i] = function () {
return i * 2
}
}
callbacks[0]() === 0
callbacks[1]() === 2
ES5 var callbacks = [];
for (var i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
(function (i) {
callbacks[i] = function() {
return i * 2;
};
})(i);
}
callbacks[0]() === 0;
callbacks[1]() === 2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-10-2048.jpg)




![19
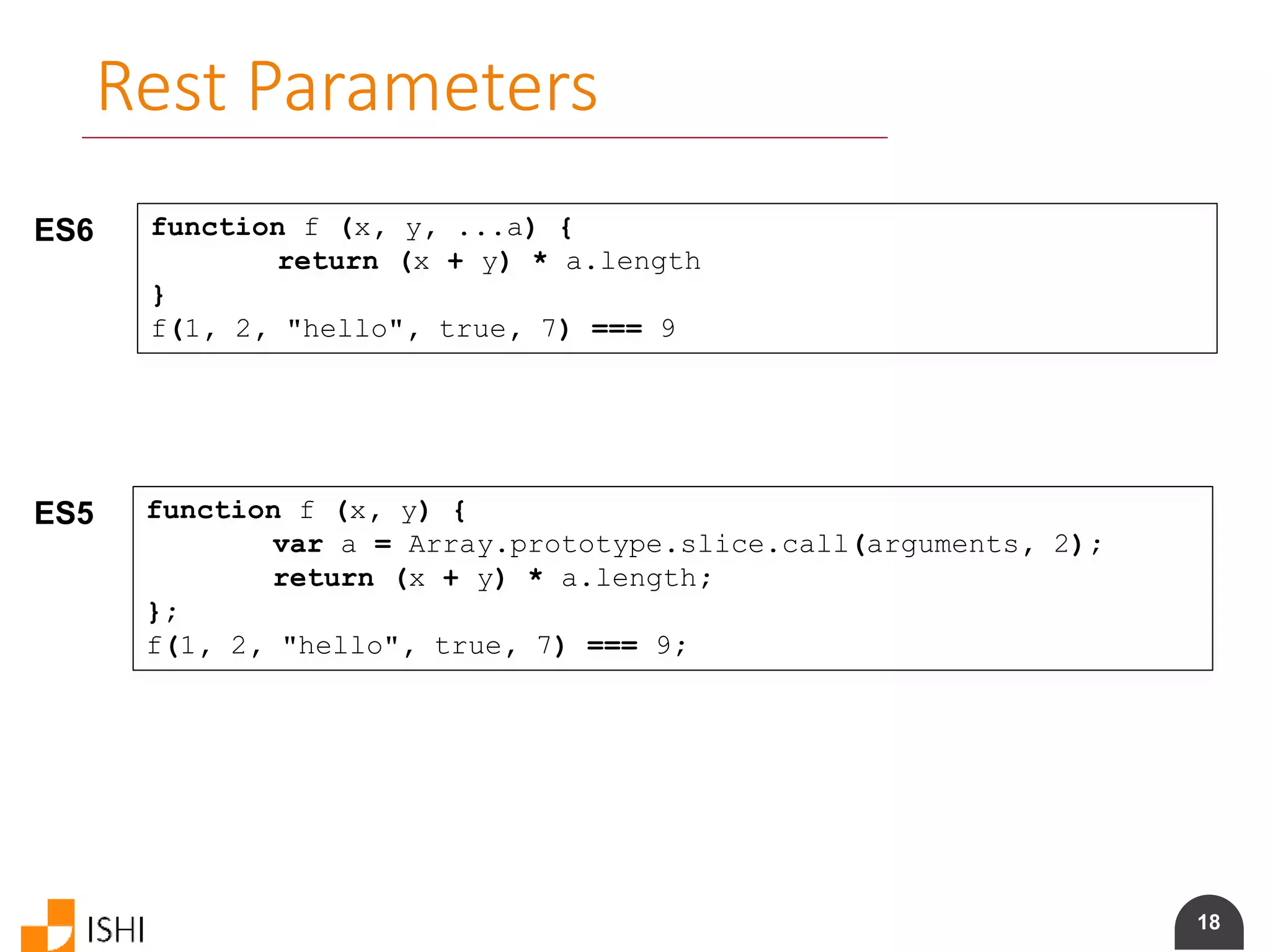
Spread Parameters
ES6 var params = [ "hello", true, 7 ]
var other = [ 1, 2, ...params ] // [ 1, 2, "hello", true, 7 ]
f(1, 2, ...params) === 9
var str = "foo"
var chars = [ … str ] // [ "f", "o", "o" ]
ES5 var params = [ "hello", true, 7 ];
var other = [ 1, 2 ].concat(params); // [ 1, 2, "hello", true, 7 ]
f.apply(window, other) === 9;
var str = "foo";
var chars = str.split(""); // [ "f", "o", "o" ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-19-2048.jpg)

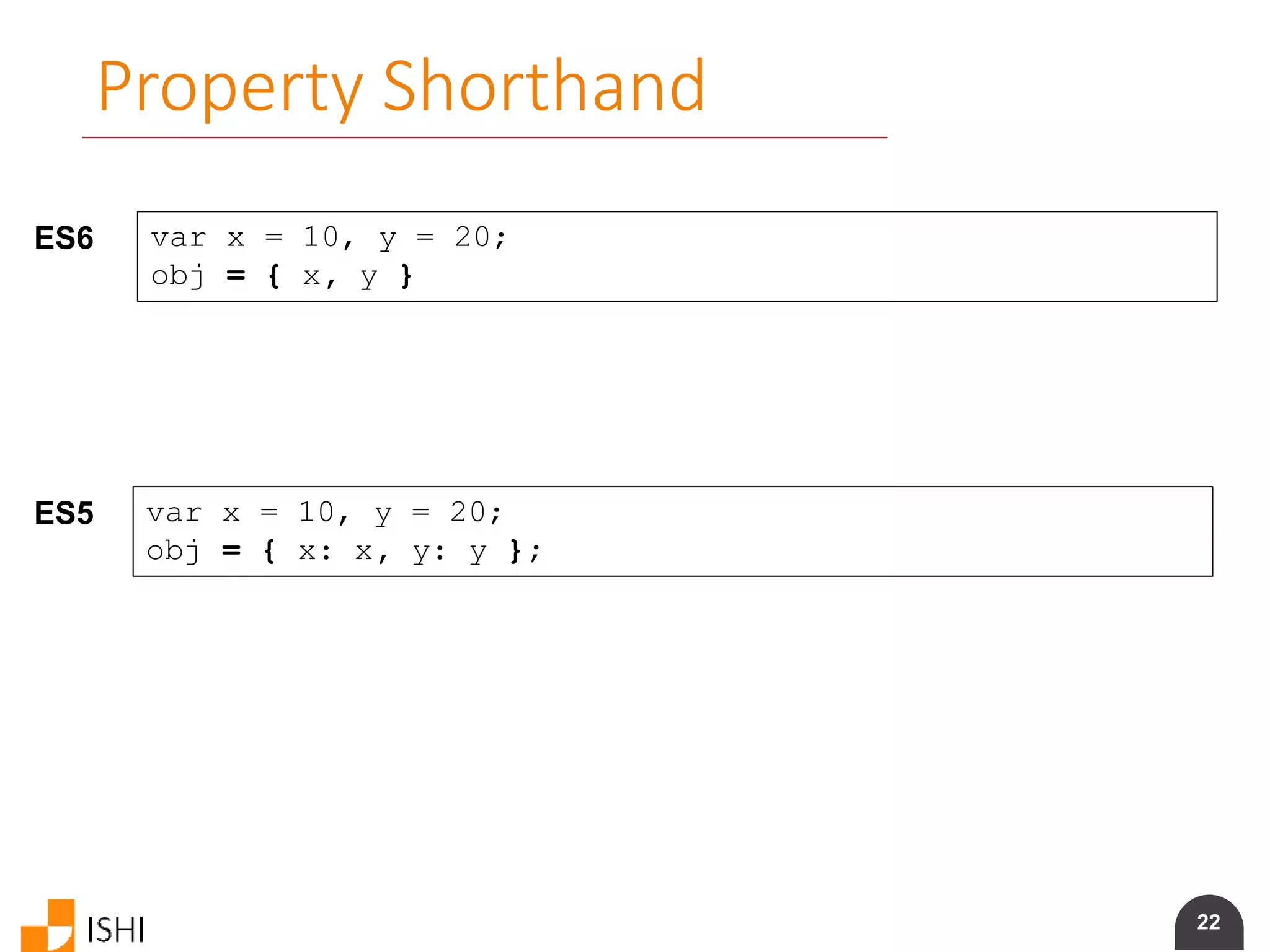
![23
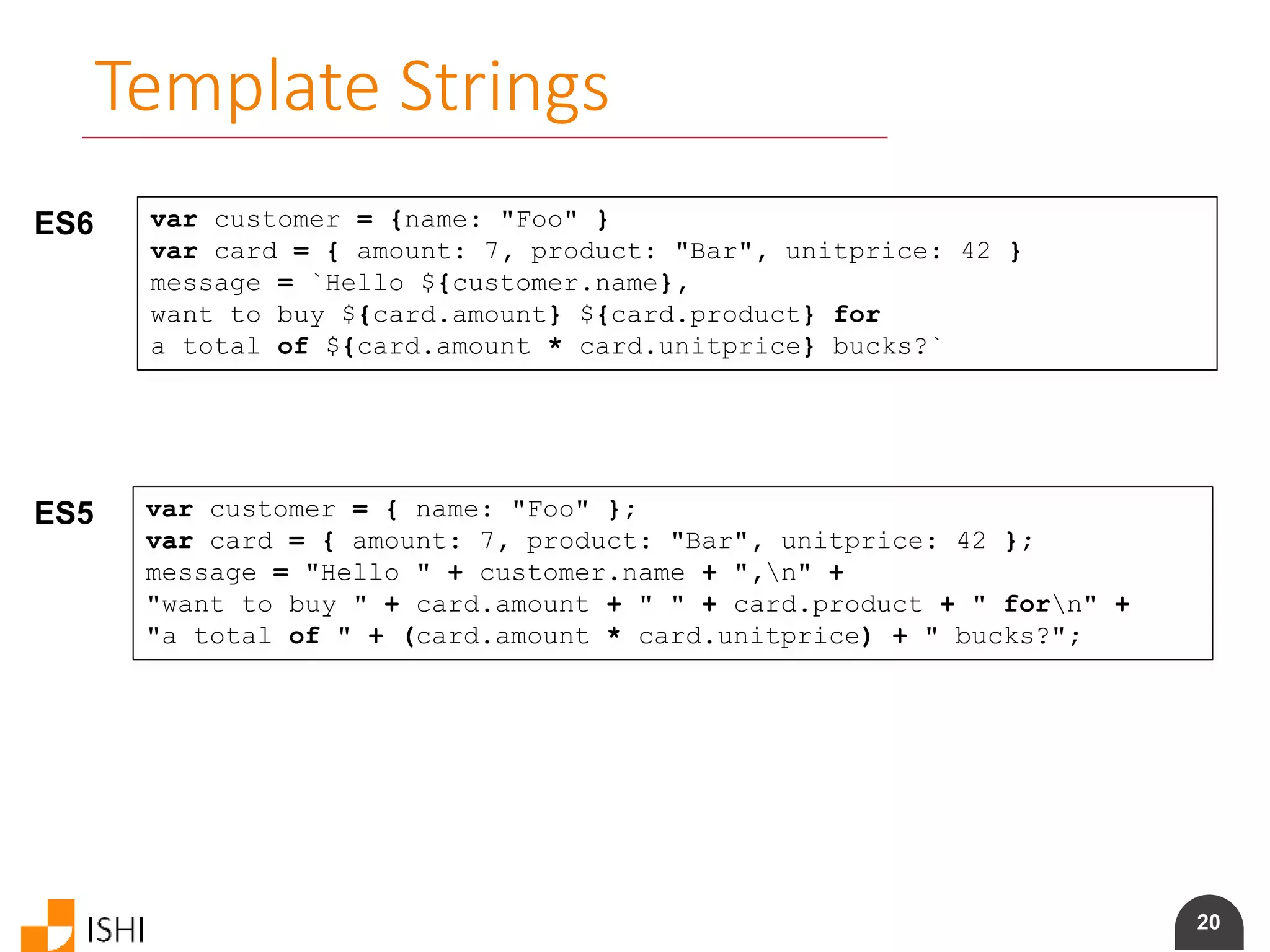
Computed Property Names
ES6 obj = {
foo: "bar",
[ "prop_" + foo() ]: 42
}
ES5 obj = {
foo: "bar"
};
obj[ "prop_" + foo() ] = 42;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-23-2048.jpg)
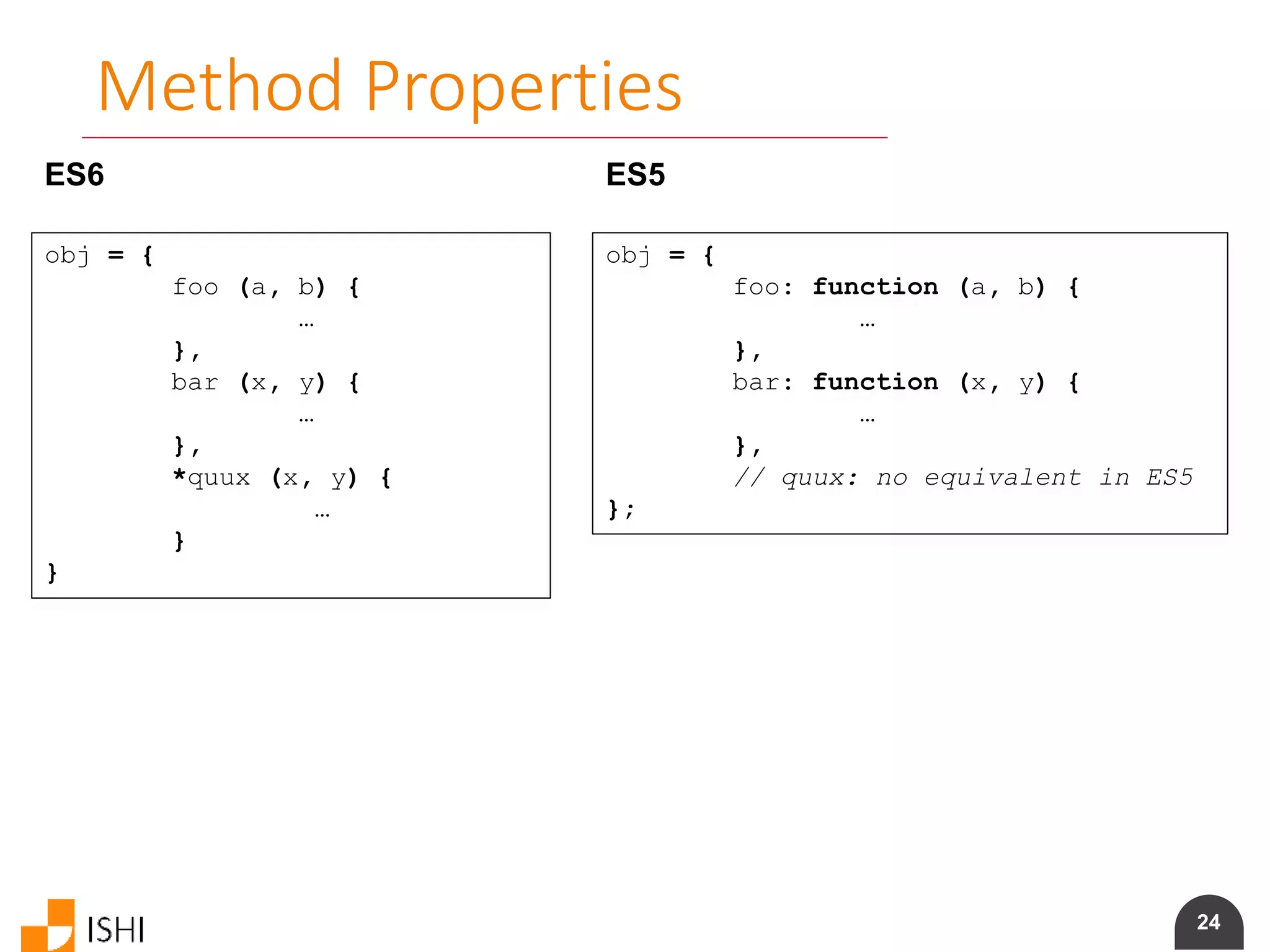

![26
Array Matching
ES6 var list = [ 1, 2, 3 ]
var [ a, , b ] = list
[ b, a ] = [ a, b ]
ES5 var list = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
var a = list[0], b = list[2];
var tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-26-2048.jpg)
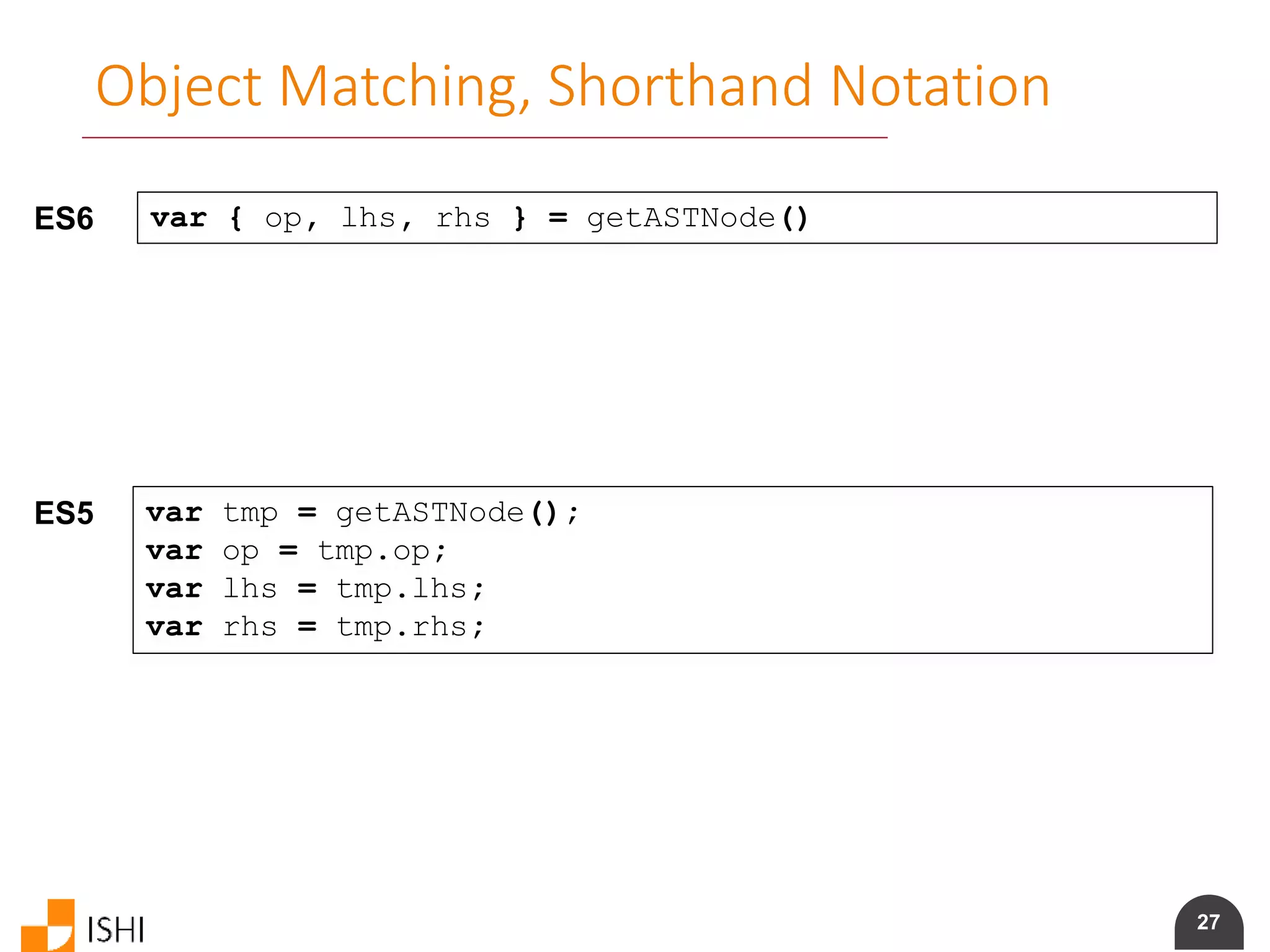

![29
Parameter Context Matching
ES6
function f ([ name, val ]) {
console.log(name, val)
}
function g ({ name: n, val: v }) {
console.log(n, v)
}
function h ({ name, val }) {
console.log(name, val)
}
f([ "bar", 42 ])
g({ name: "foo", val: 7 })
h({ name: "bar", val: 42 })
ES5
function f (arg) {
var name = arg[0];
var val = arg[1];
console.log(name, val);
};
function g (arg) {
var n = arg.name;
var v = arg.val;
console.log(n, v);
};
function h (arg) {
var name = arg.name;
var val = arg.val;
console.log(name, val);
};
f([ "bar", 42 ]);
g({ name: "foo", val: 7 });
h({ name: "bar", val: 42 });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-29-2048.jpg)

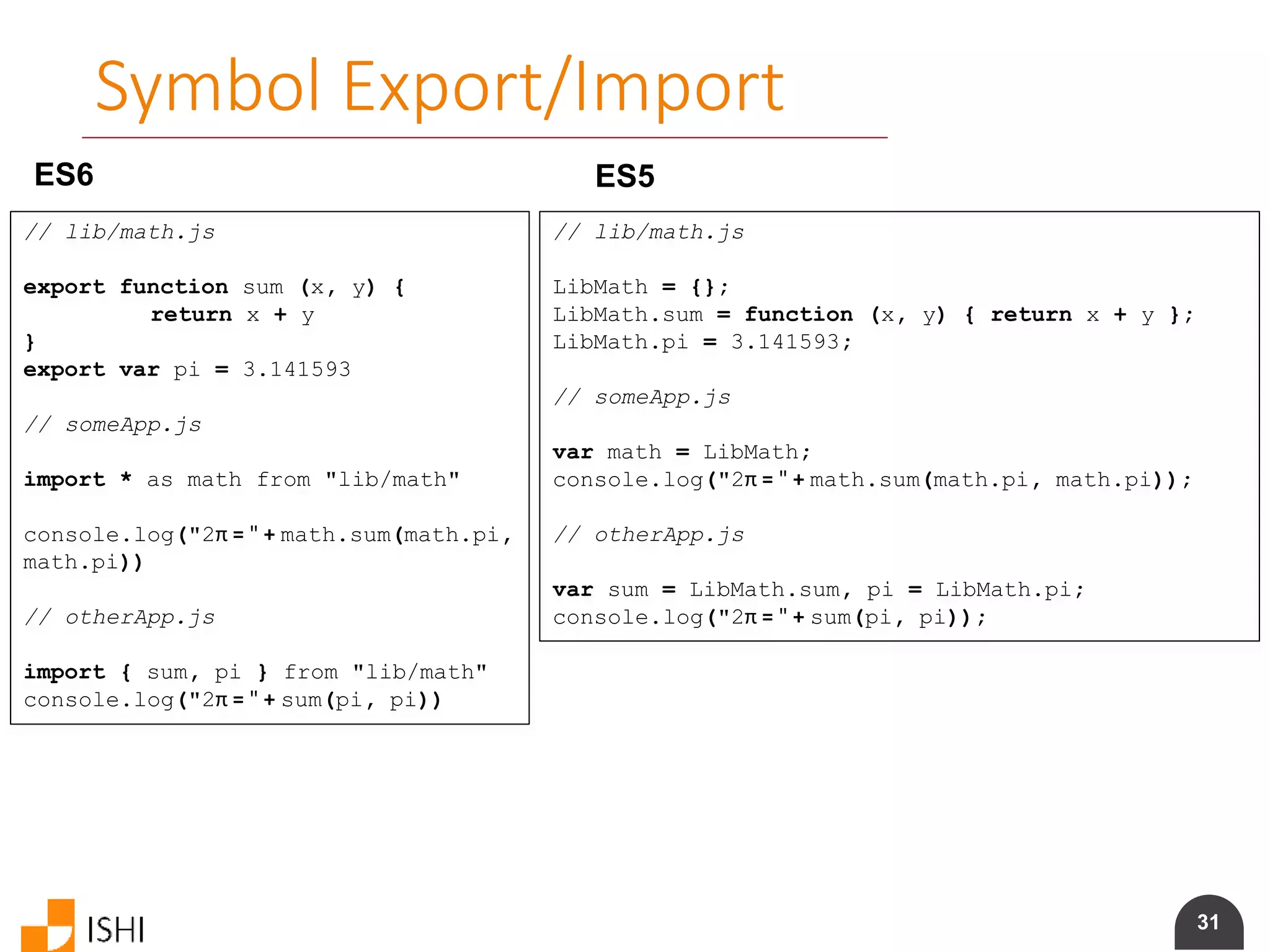




![43
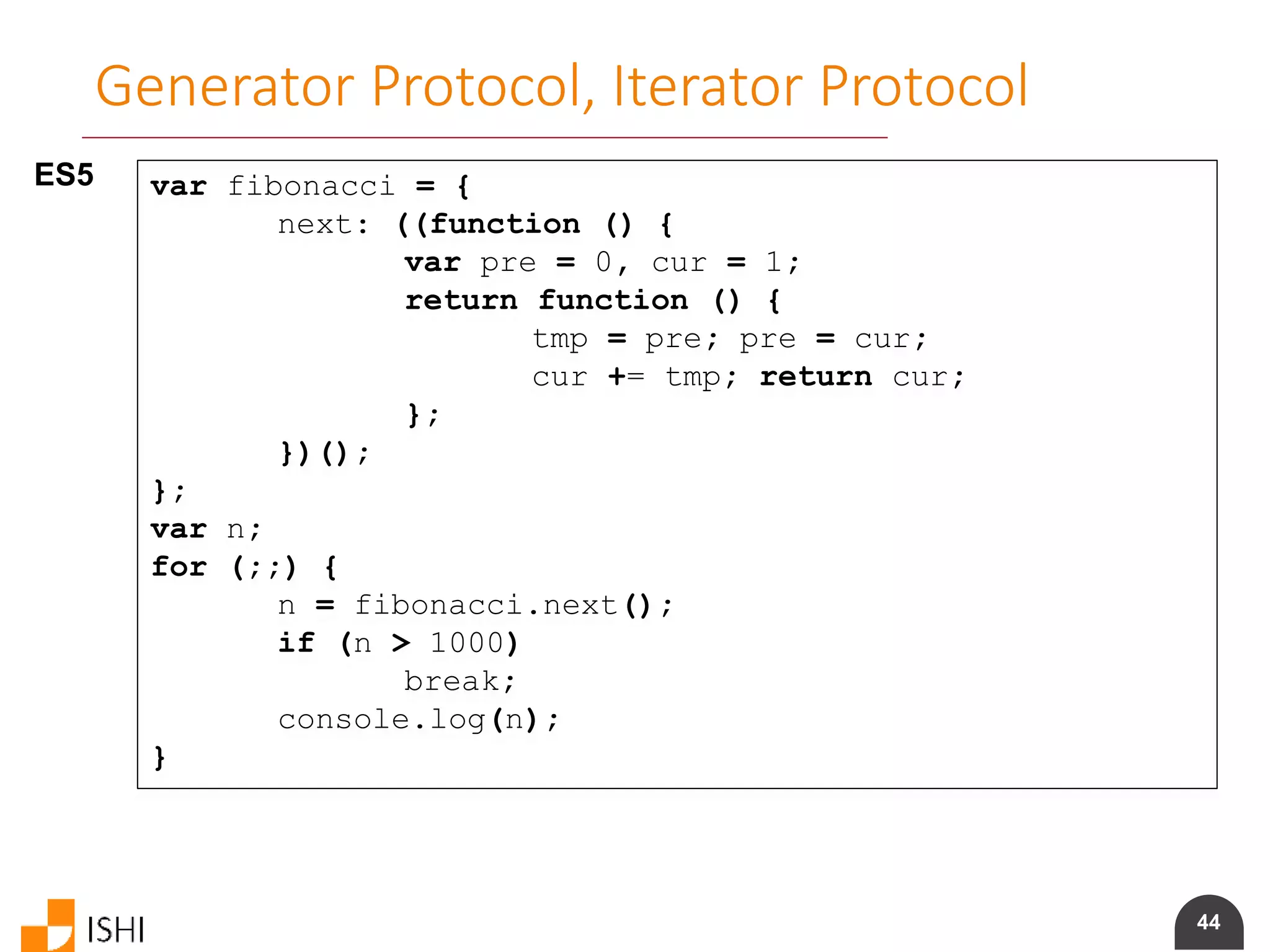
Generator Protocol, Iterator Protocol
ES6 let fibonacci = {
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
let pre = 0, cur = 1
for (;;) {
[ pre, cur ] = [ cur, pre + cur ]
yield cur
}
}
}
for (let n of fibonacci) {
if (n > 1000)
break
console.log(n)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-43-2048.jpg)
![45
Generator Function, Direct Use
ES6 function* range (start, end, step) {
while (start < end) {
yield start
start += step
}
}
for (let i of range(0, 10, 2)) {
console.log(i) // 0, 2, 4, 6, 8
}
ES5
function range (start, end, step) {
var list = [];
while (start < end) {
list.push(start);
start += step;
}
return list;
}
var r = range(0, 10, 2);
for (var i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
console.log(r[i]); // 0, 2, 4, 6, 8
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-45-2048.jpg)
![46
Generator Matching
ES6 let fibonacci = function* (numbers) {
let pre = 0, cur = 1
while (numbers-- > 0) {
[ pre, cur ] = [ cur, pre + cur ]
yield cur
}
}
for (let n of fibonacci(1000))
console.log(n)
let numbers = [ ...fibonacci(1000) ]
let [ n1, n2, n3, ...others ] = fibonacci(1000)
ES5 // no equivalent in ES5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-46-2048.jpg)

![48
Set Data-Structure
ES6 let s = new Set()
s.add("hello").add("goodbye").add("hello")
s.size === 2
s.has("hello") === true
for (let key of s.values()) // insertion order
console.log(key)
ES5
var s = {};
s["hello"] = true;
s["goodbye"] = true;
s["hello"] = true;
Object.keys(s).length === 2;
s["hello"] === true;
for (var key in s) // arbitrary order
if (s.hasOwnProperty(key))
console.log(s[key]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-48-2048.jpg)
![49
Map Data-Structure
ES6 let m = new Map()
m.set("hello", 42)
m.set(s, 34)
m.get(s) === 34
m.size === 2
for (let [ key, val ] of m.entries())
console.log(key + " = " + val)
ES5
var m = {};
m["hello"] = 42;
// no equivalent in ES5
// no equivalent in ES5
Object.keys(m).length === 2;
for (key in m) {
if (m.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
var val = m[key];
console.log(key + " = " + val);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-49-2048.jpg)


![52
Promise Combination
ES6 function fetchAsync (url, timeout, onData, onError) {
…
}
let fetchPromised = (url, timeout) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetchAsync(url, timeout, resolve, reject)
})
}
Promise.all([
fetchPromised("http://backend/foo.txt", 500),
fetchPromised("http://backend/bar.txt", 500),
fetchPromised("http://backend/baz.txt", 500)
]).then((data) => {
let [ foo, bar, baz ] = data
console.log(`success: foo=${foo} bar=${bar} baz=${baz}`)
}, (err) => {
console.log(`error: ${err}`)
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/es6angularamd-150726064820-lva1-app6891/75/ES6-and-AngularAMD-52-2048.jpg)