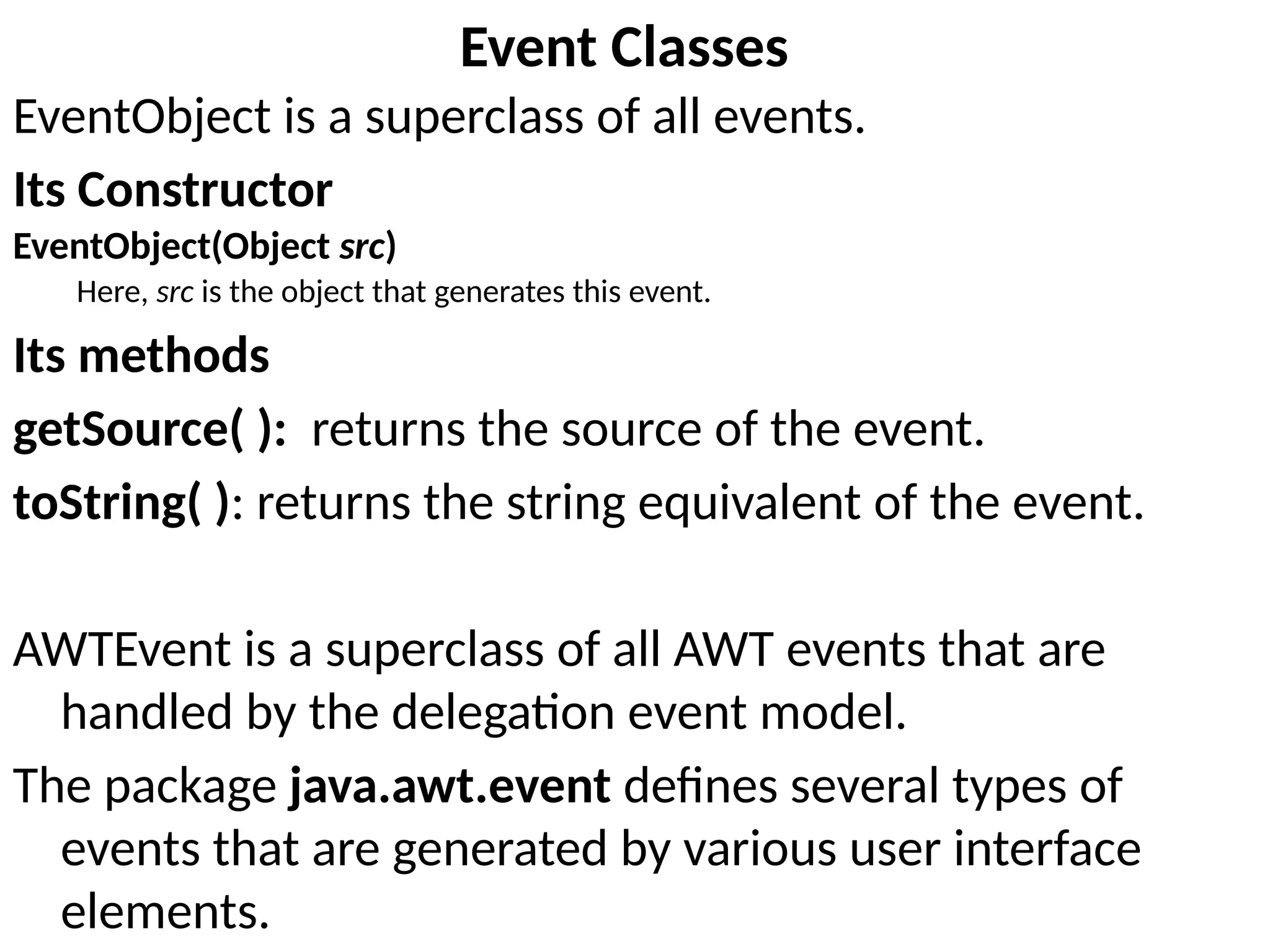
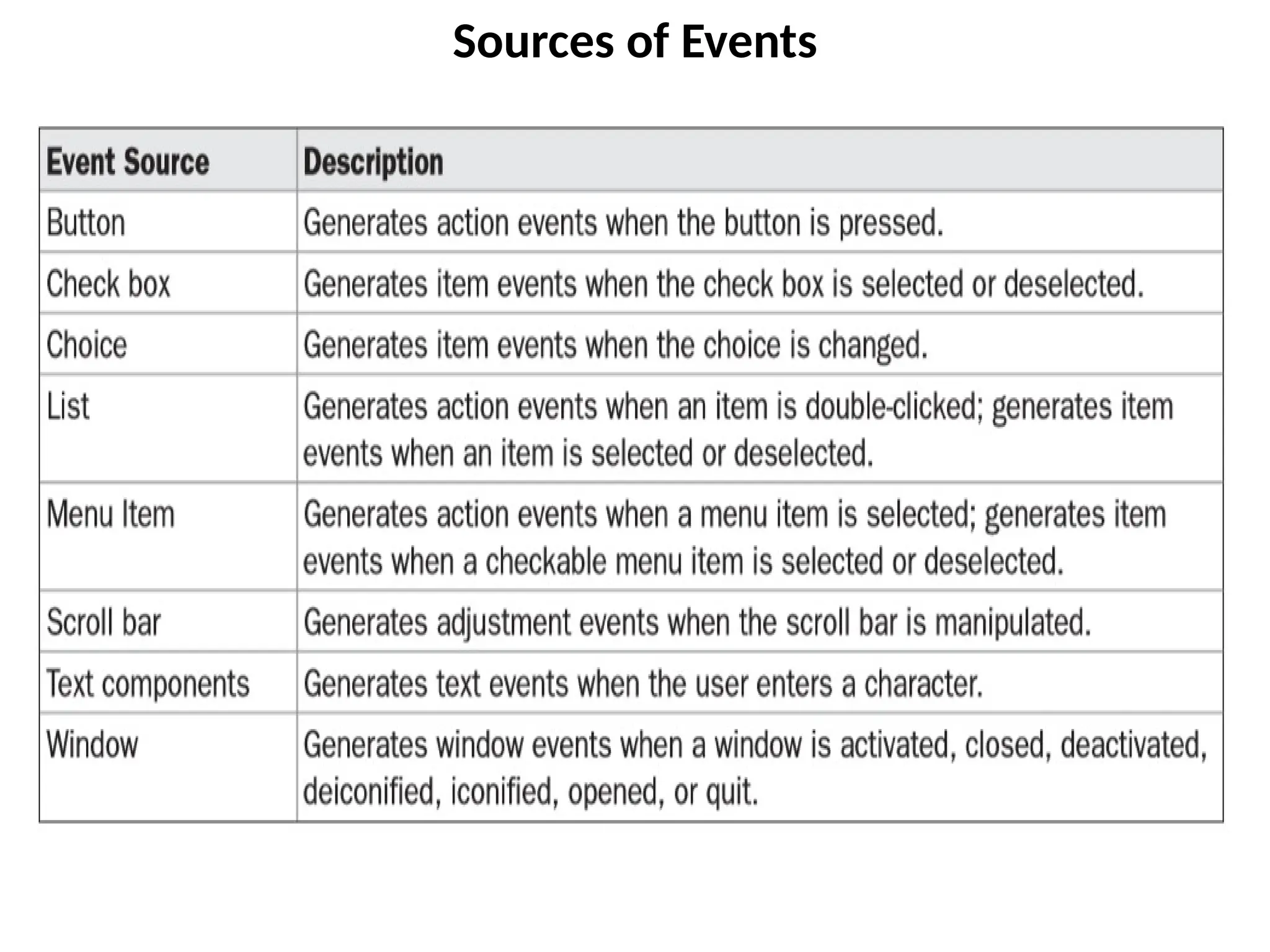
The document outlines the Java event handling mechanism, detailing how events in graphical user interfaces are generated, processed, and handled through a delegation event model. It describes various event classes and listener interfaces, including mouse and keyboard events, and provides code examples illustrating the implementation of mouse and key event handling. Additionally, it explains the use of adapter classes to simplify listener implementation.









![Handling Mouse events
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class Mouseevents extends Frame implements MouseListener,
MouseMotionListener
{
String msg="";
int x=0,y=0;
Mouseevents()
{
addMouseListener(this );
addMouseMotionListener(this);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mouseevents e=new Mouseevents();
e.setSize(400,400);
e.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
e.setVisible(true);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventhandling-250212075930-c01e15a9/75/EventHandling-in-object-oriented-programming-12-2048.jpg)



![public void keyTyped(KeyEvent event)
{
input.setText("Key Typed");
}
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent event)
{
output.setText("Key Pressed");
}
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent event)
{
output.setText("Key Released");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
KeyEventExample k=new KeyEventExample();
k.setSize(500,500);
k.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
k.setVisible(true);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventhandling-250212075930-c01e15a9/75/EventHandling-in-object-oriented-programming-16-2048.jpg)

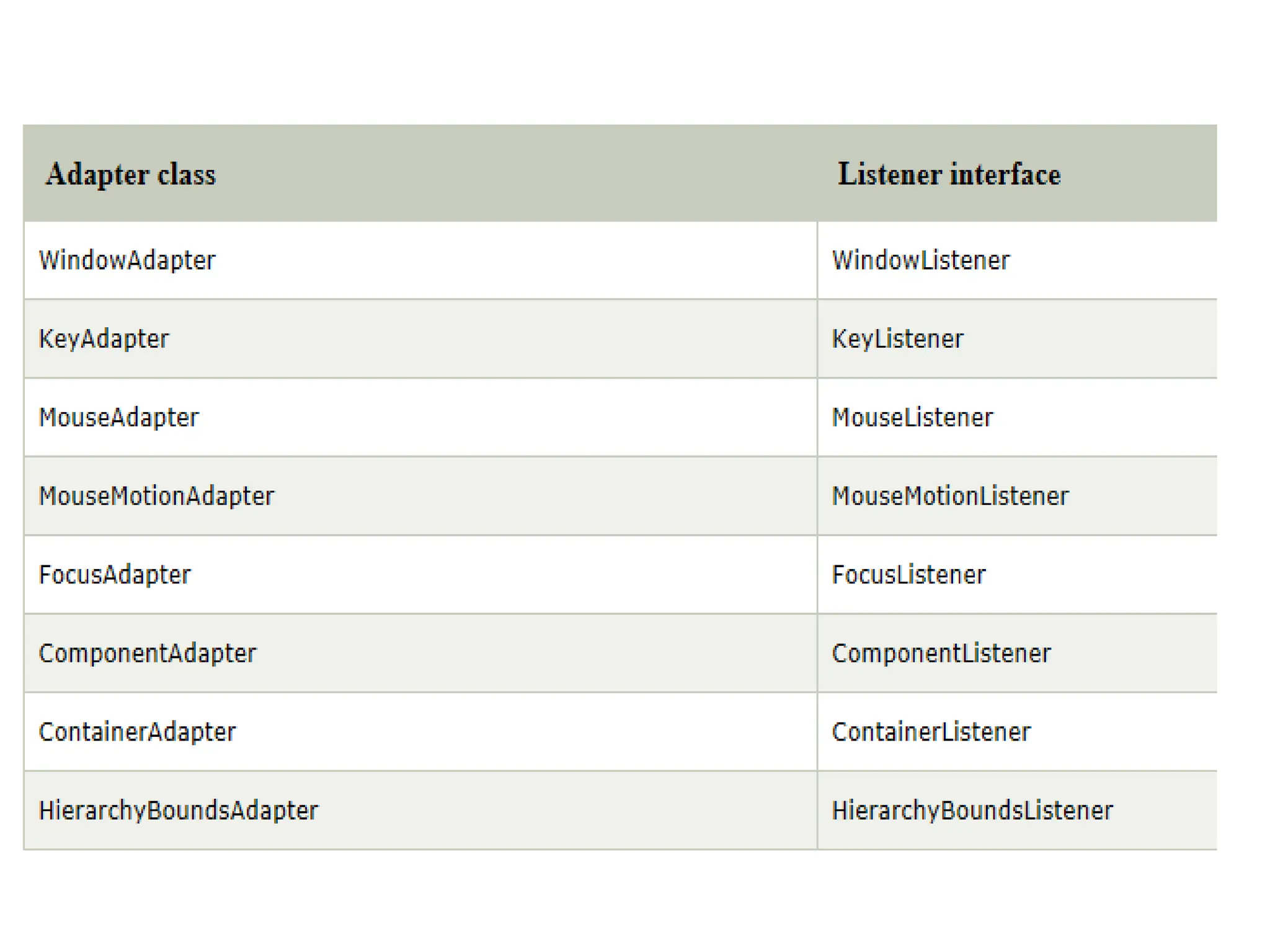
![WindowAdapter
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class AdapterExample{
Frame f;
AdapterExample(){
f=new Frame("Window Adapter");
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
f.dispose();
}
});
f.setSize(400,400);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new AdapterExample();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventhandling-250212075930-c01e15a9/75/EventHandling-in-object-oriented-programming-19-2048.jpg)
![MouseAdapter
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class MouseAdapterExample extends MouseAdapter{
Frame f;
MouseAdapterExample(){
f=new Frame("Mouse Adapter");
f.addMouseListener(this);
f.setSize(300,300);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
Graphics g=f.getGraphics();
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.fillOval(e.getX(),e.getY(),30,30);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MouseAdapterExample();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventhandling-250212075930-c01e15a9/75/EventHandling-in-object-oriented-programming-20-2048.jpg)
![MouseMotionAdapter
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class MouseMotionAdapterExample extends MouseMotionAdapter{
Frame f;
MouseMotionAdapterExample(){
f=new Frame("Mouse Motion Adapter");
f.addMouseMotionListener(this);
f.setSize(300,300);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) {
Graphics g=f.getGraphics();
g.setColor(Color.ORANGE);
g.fillOval(e.getX(),e.getY(),20,20);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MouseMotionAdapterExample();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventhandling-250212075930-c01e15a9/75/EventHandling-in-object-oriented-programming-21-2048.jpg)
![KeyAdapter
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class KeyAdapterExample extends KeyAdapter{
Label l;
TextArea area;
Frame f;
KeyAdapterExample(){
f=new Frame("Key Adapter");
l=new Label();
l.setBounds(20,50,200,20);
area=new TextArea();
area.setBounds(20,80,300, 300);
area.addKeyListener(this);
f.add(l);f.add(area);
f.setSize(400,400);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
String text=area.getText();
String words[]=text.split("s");
l.setText("Words: "+words.length+" Characters:"+text.length());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new KeyAdapterExample();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eventhandling-250212075930-c01e15a9/75/EventHandling-in-object-oriented-programming-22-2048.jpg)