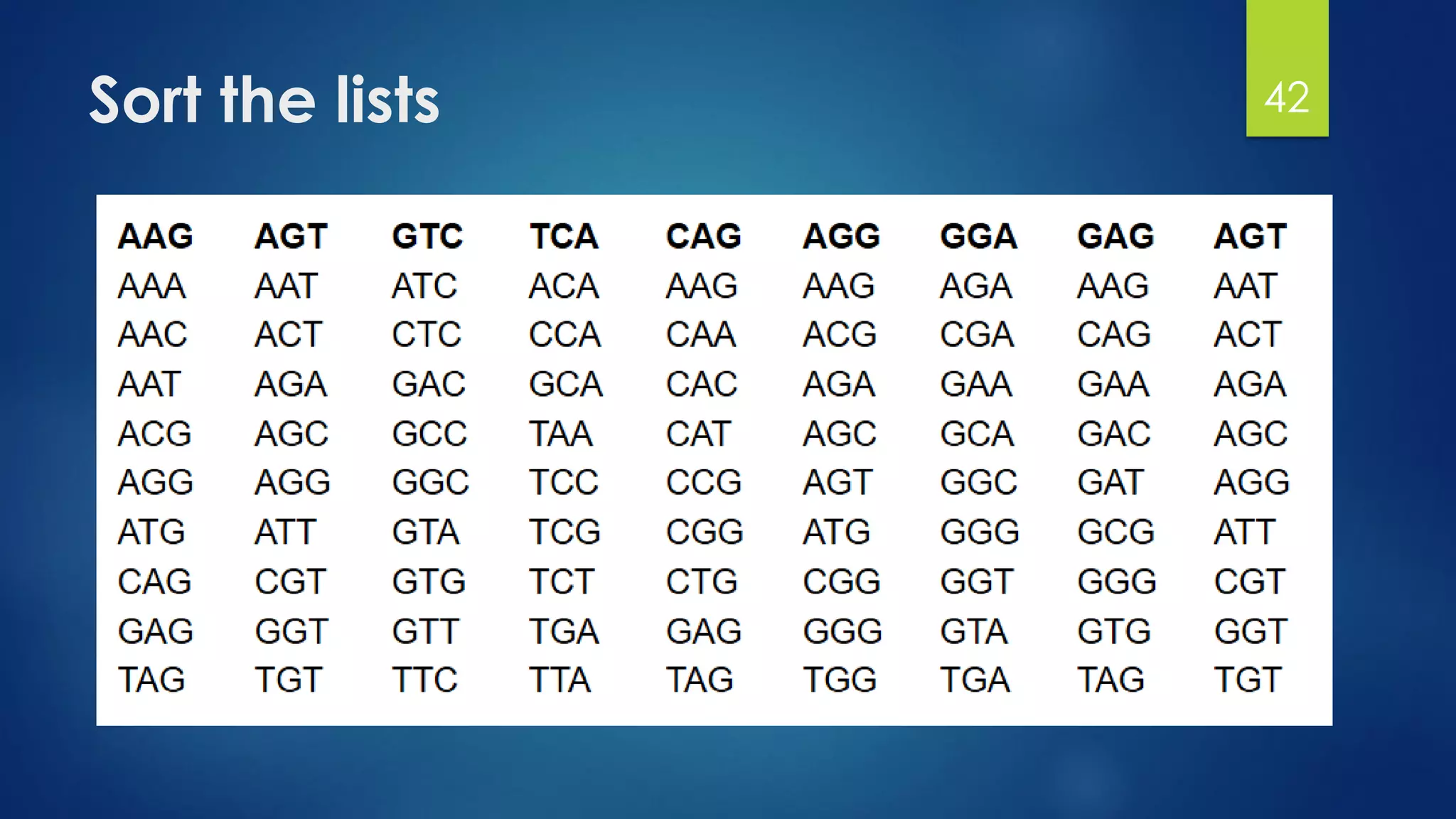
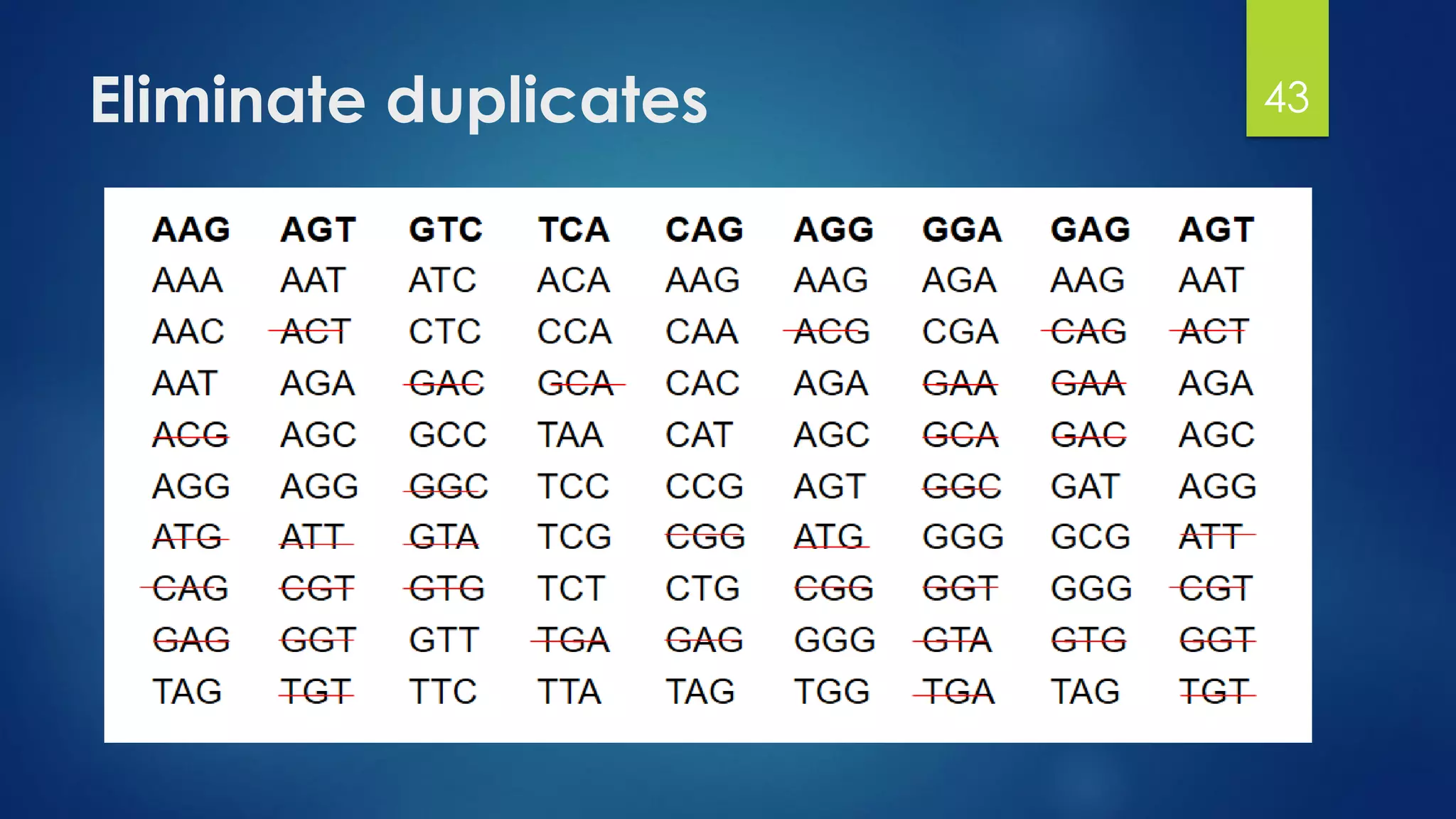
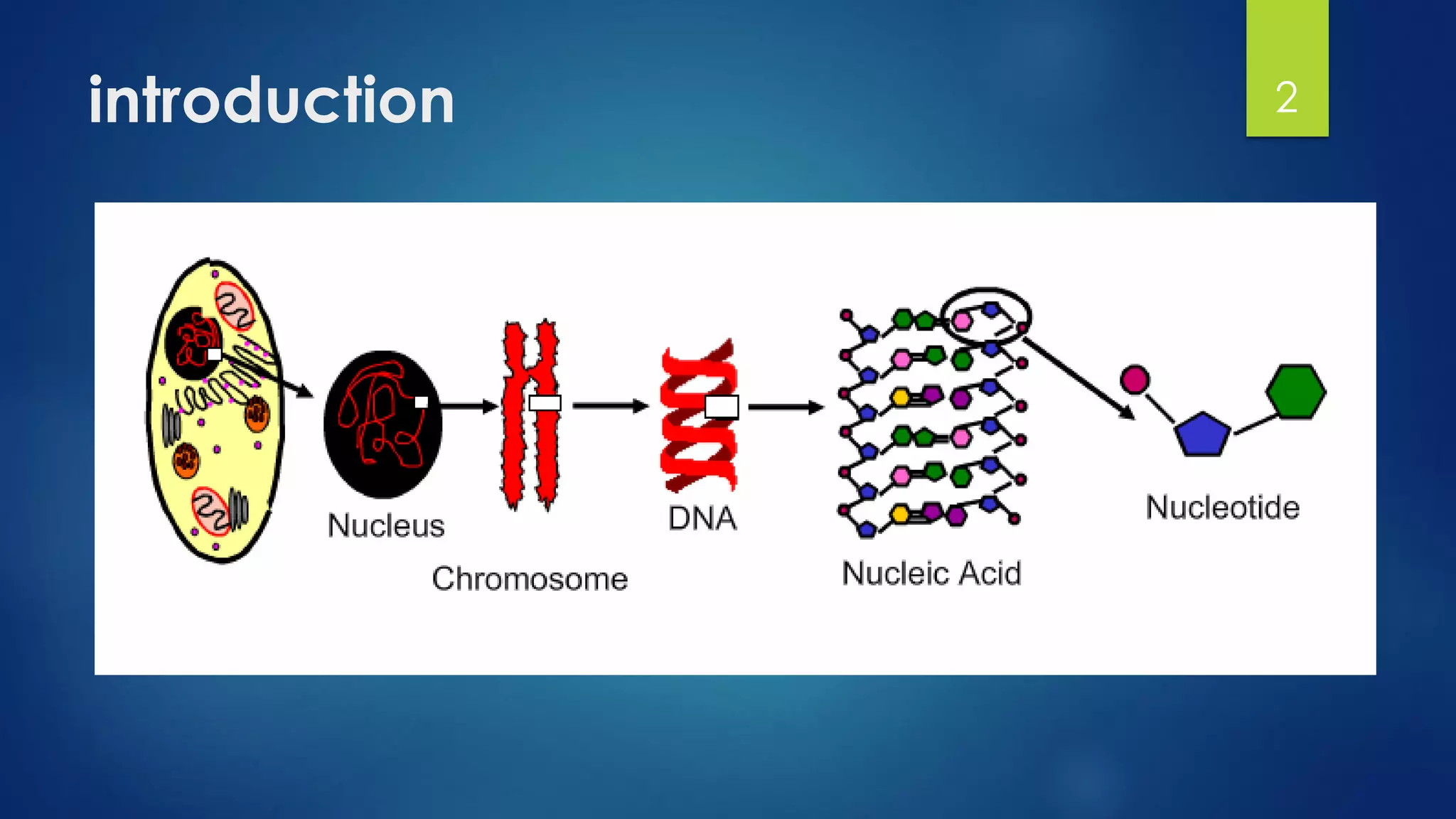
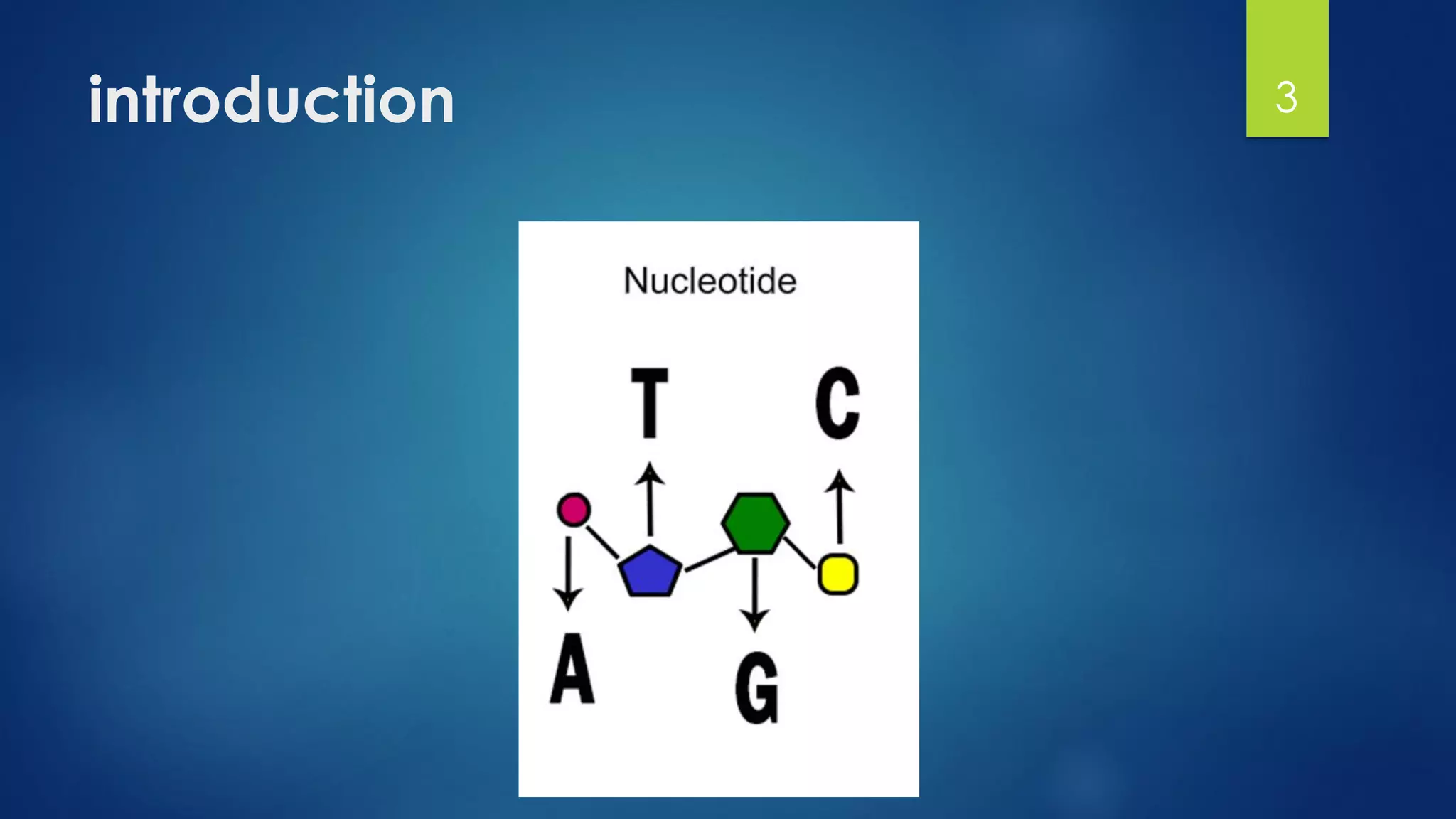
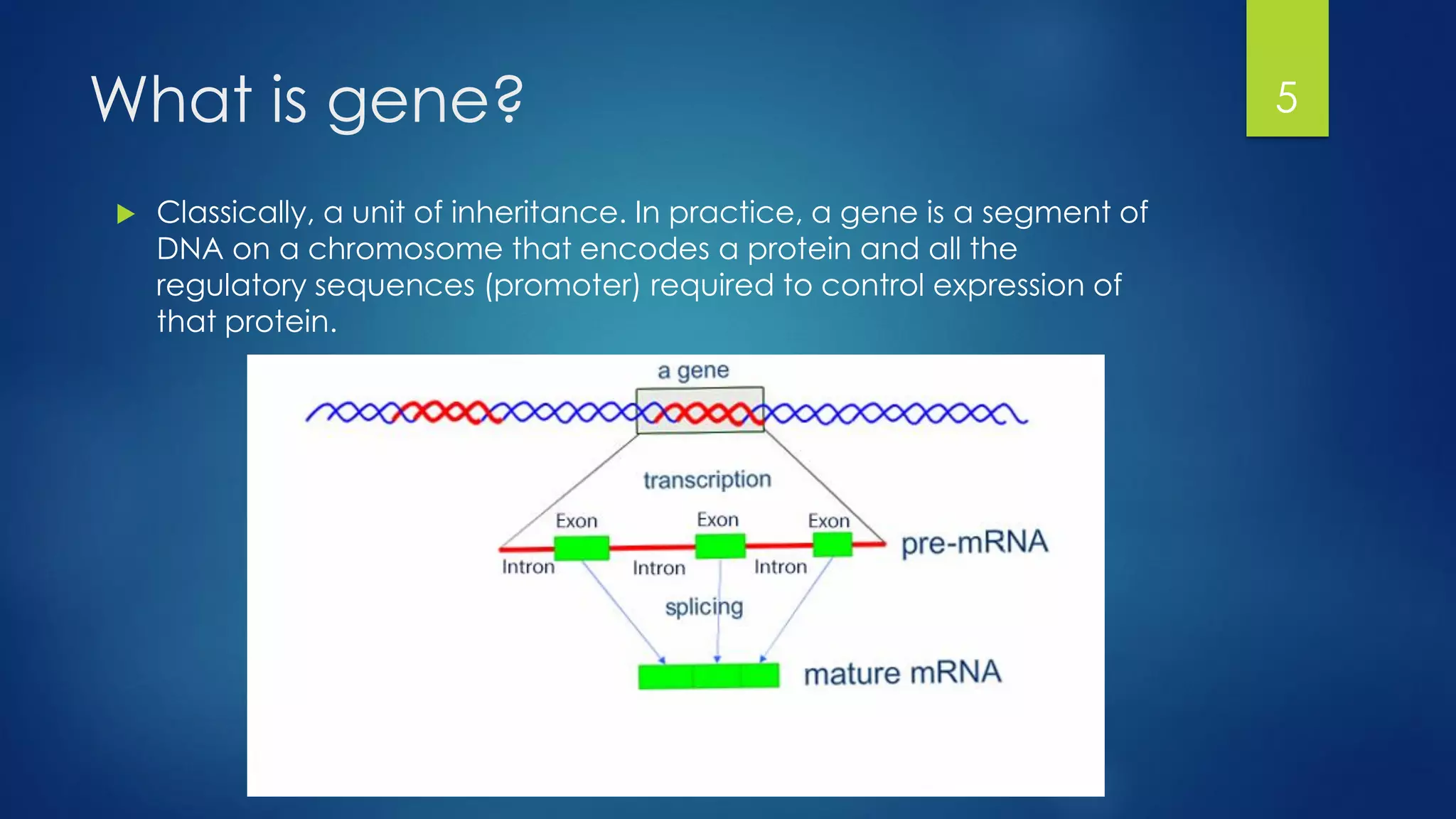
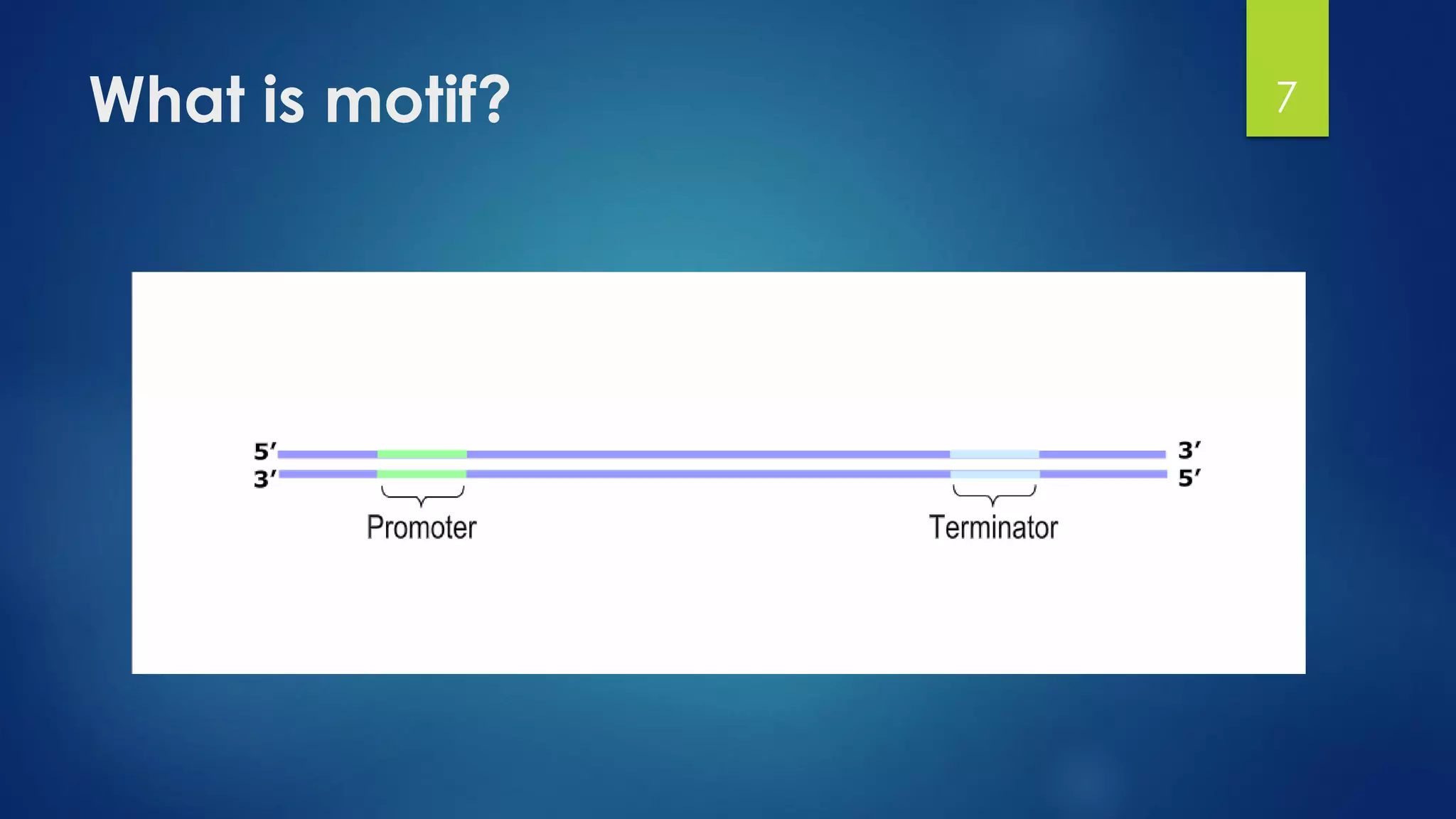
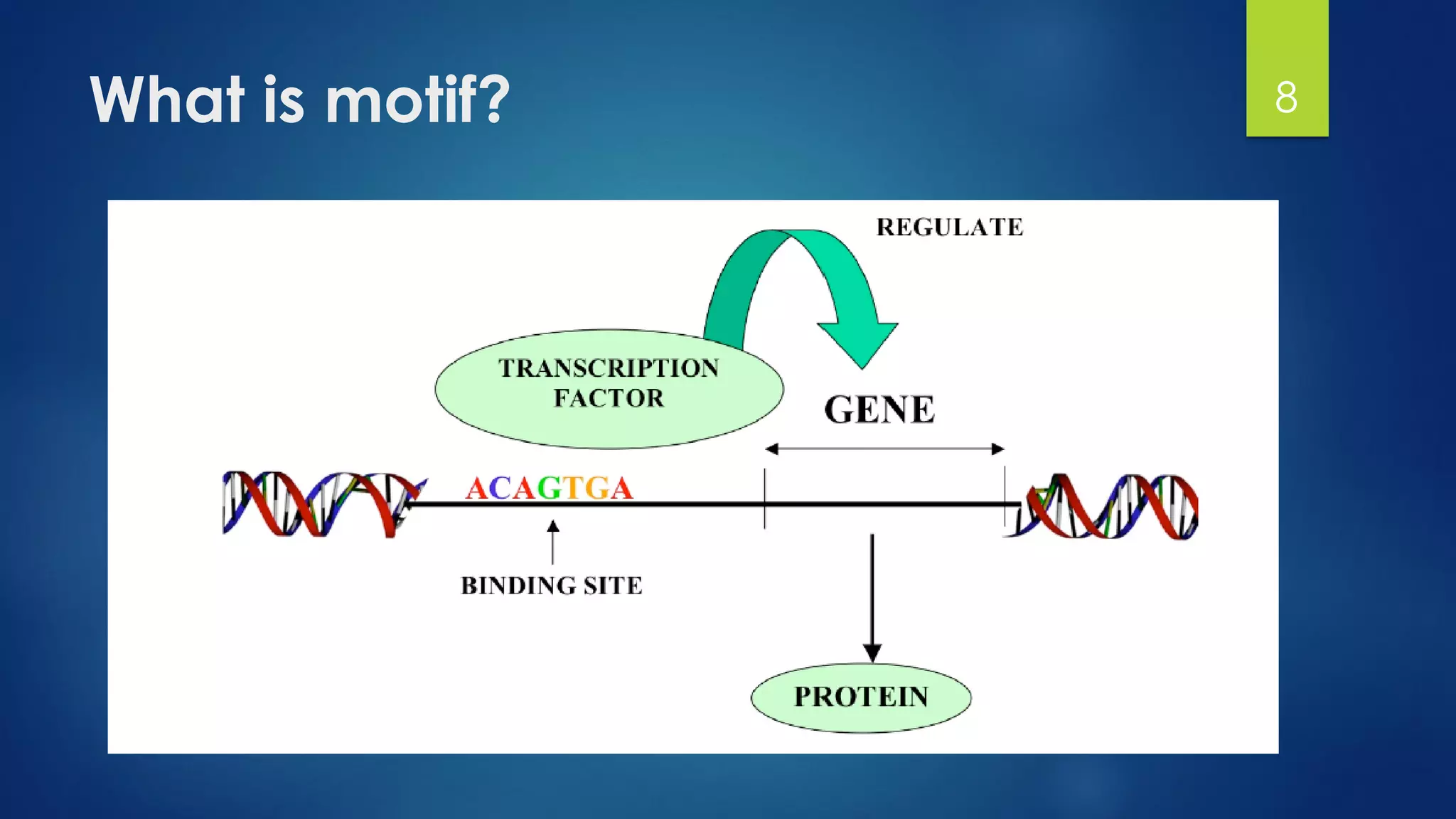
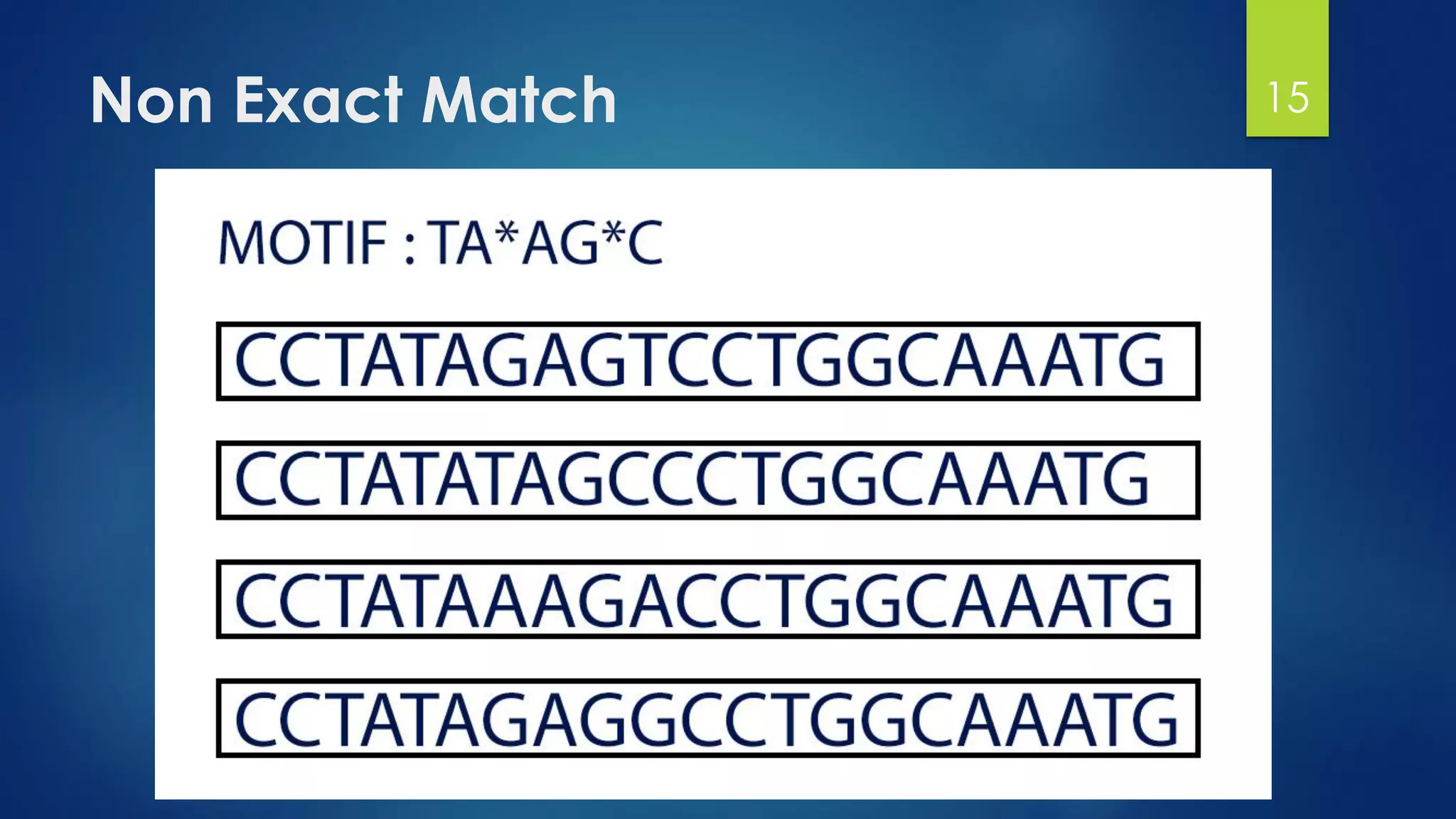
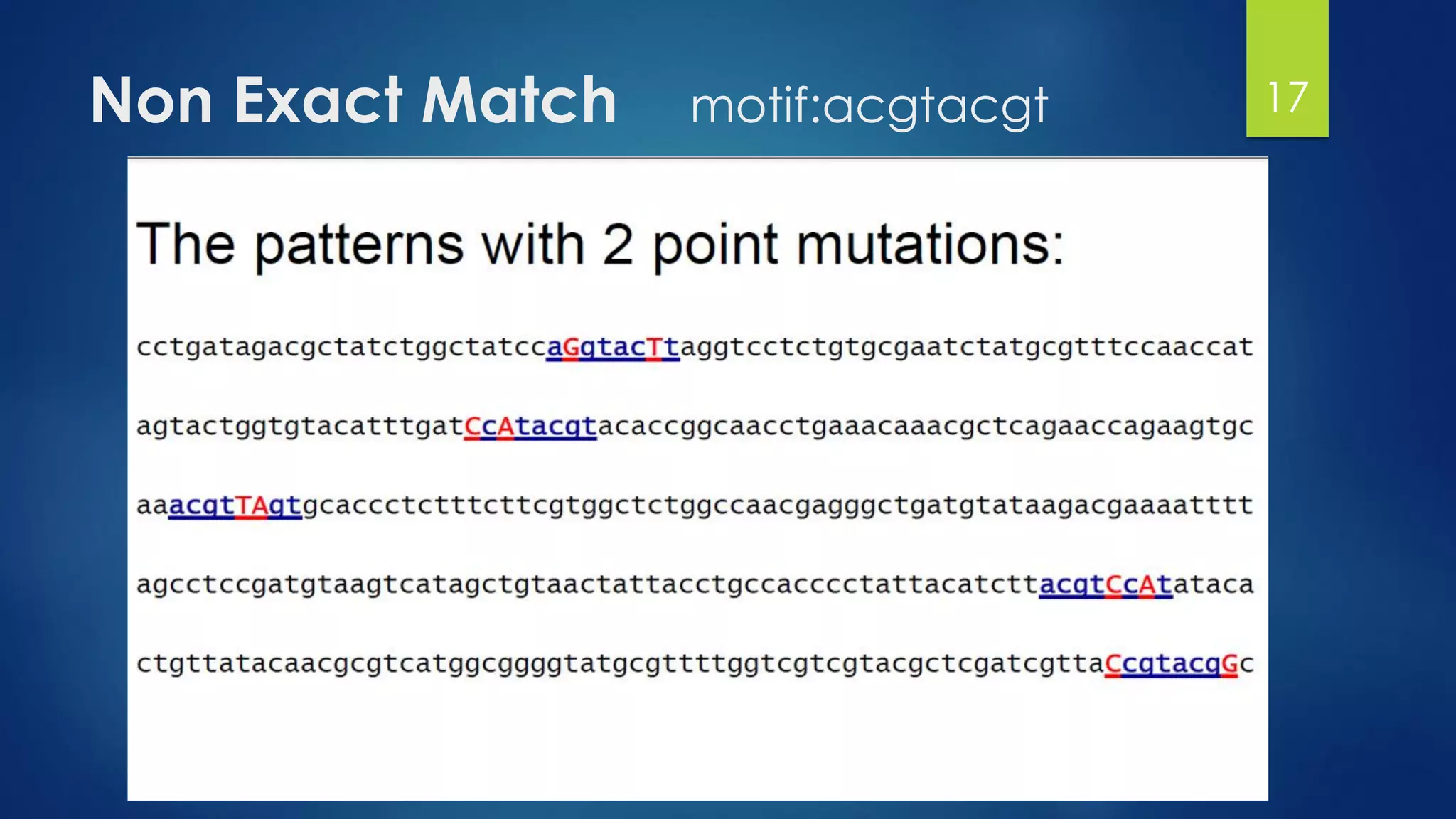
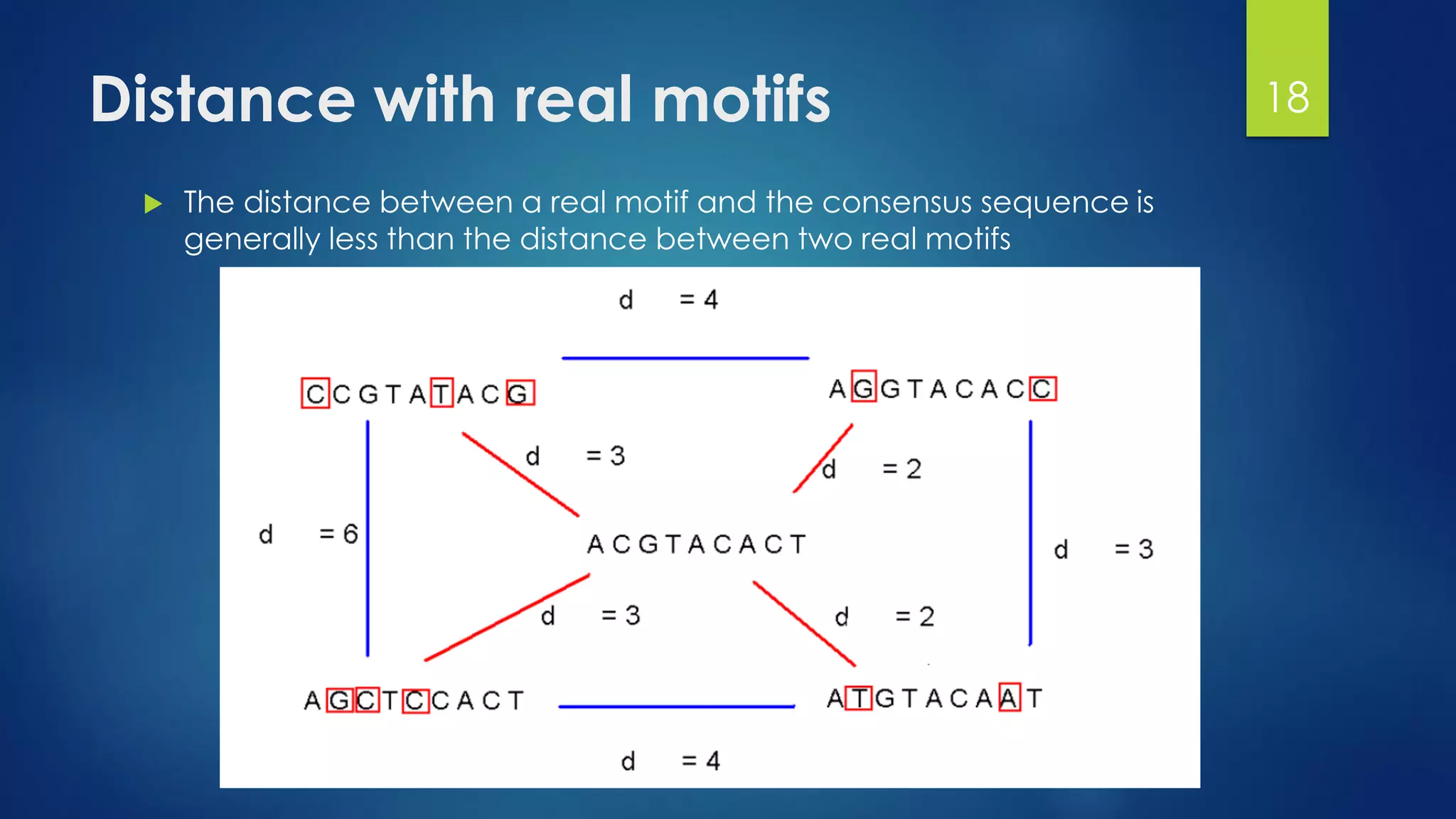
This document discusses gene motifs and algorithms for finding motifs in DNA sequences. It defines a gene as a segment of DNA that encodes a protein, and a motif as a conserved element in a protein sequence alignment that correlates with a function. It describes exact and non-exact matching algorithms for finding motifs, including brute force searching all possible motif positions and planted motif search (PMS) algorithms. PMS works by generating all possible short subsequences (l-mers) from each input sequence and finding the common motif.














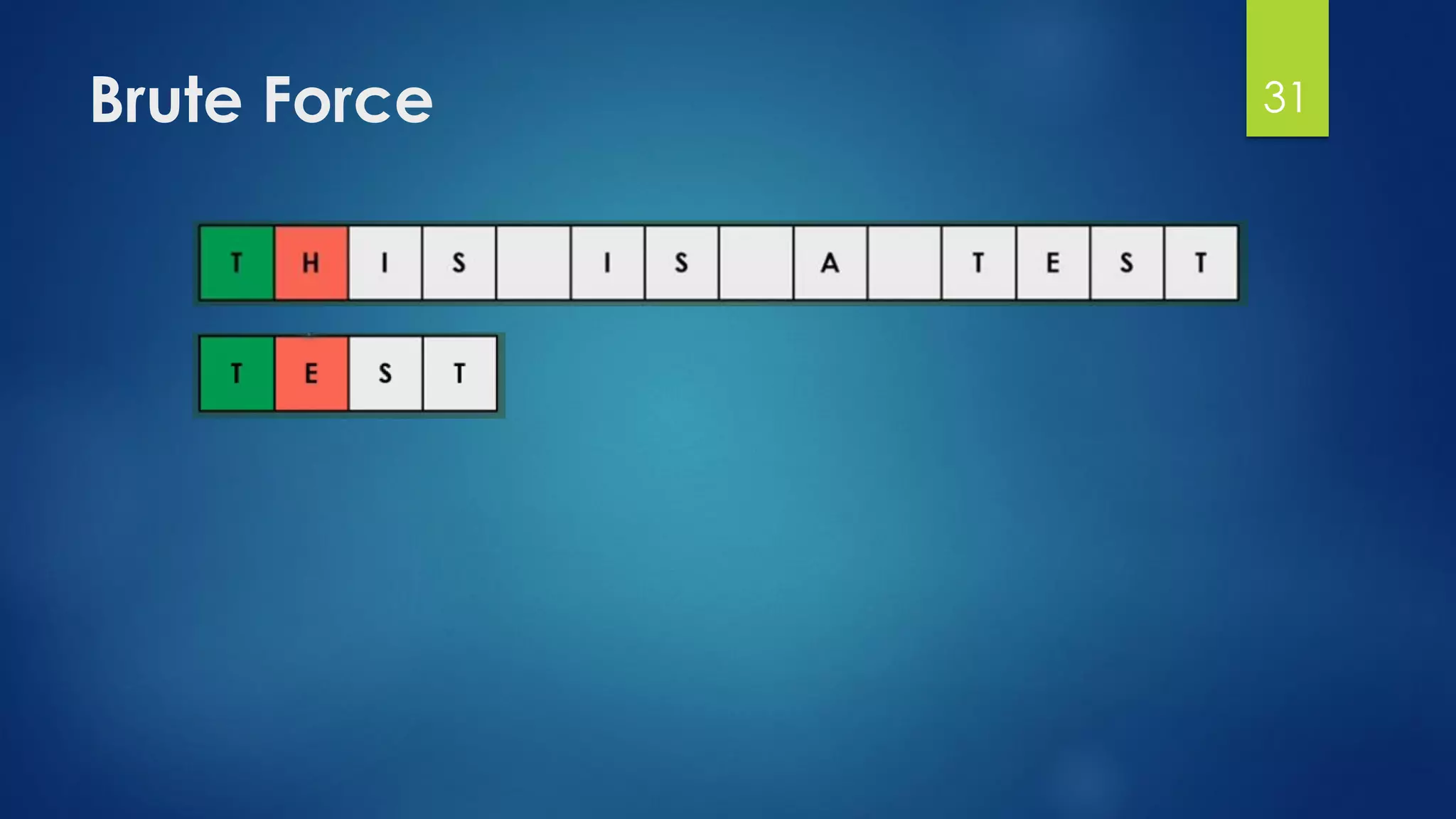
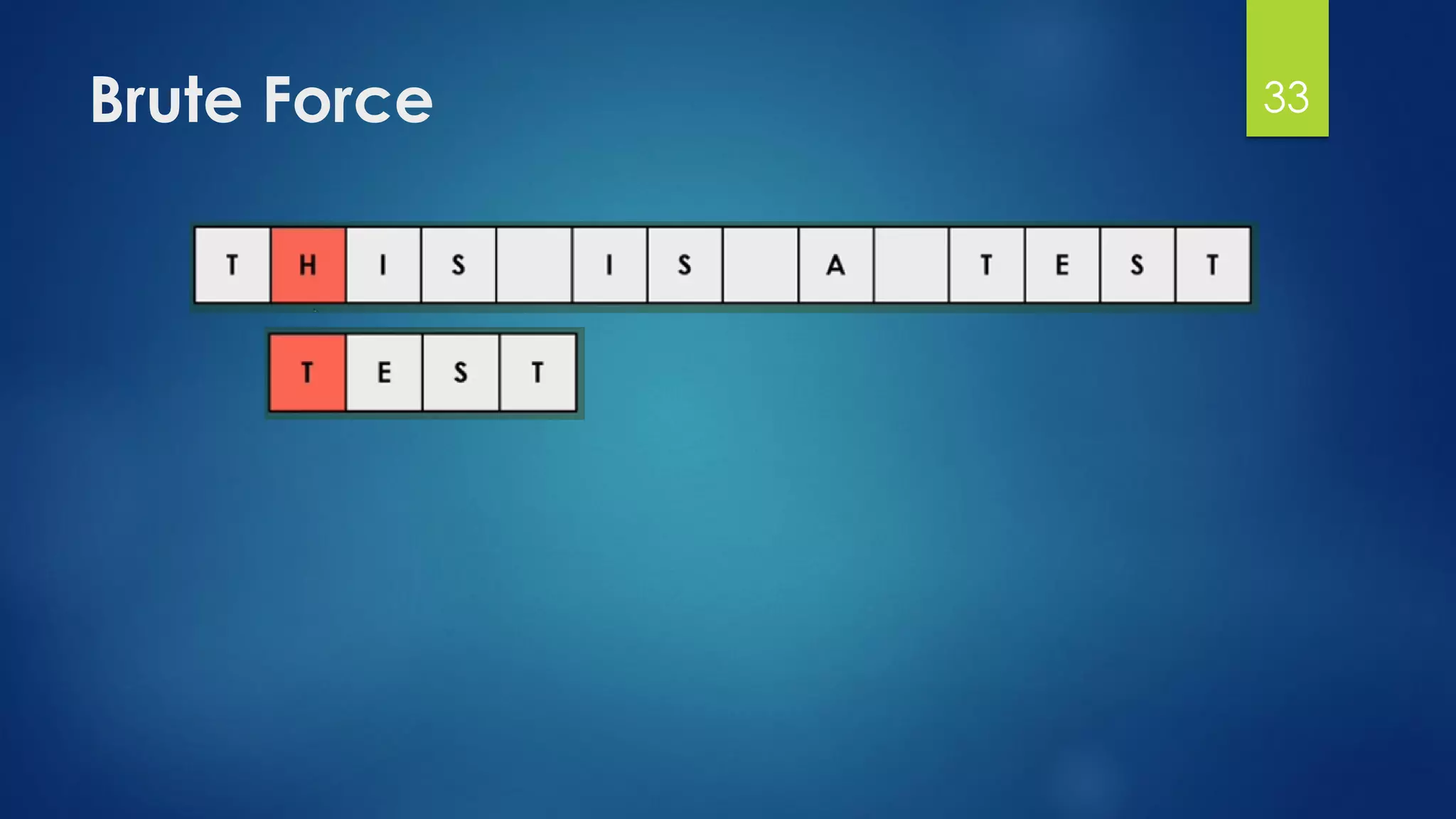
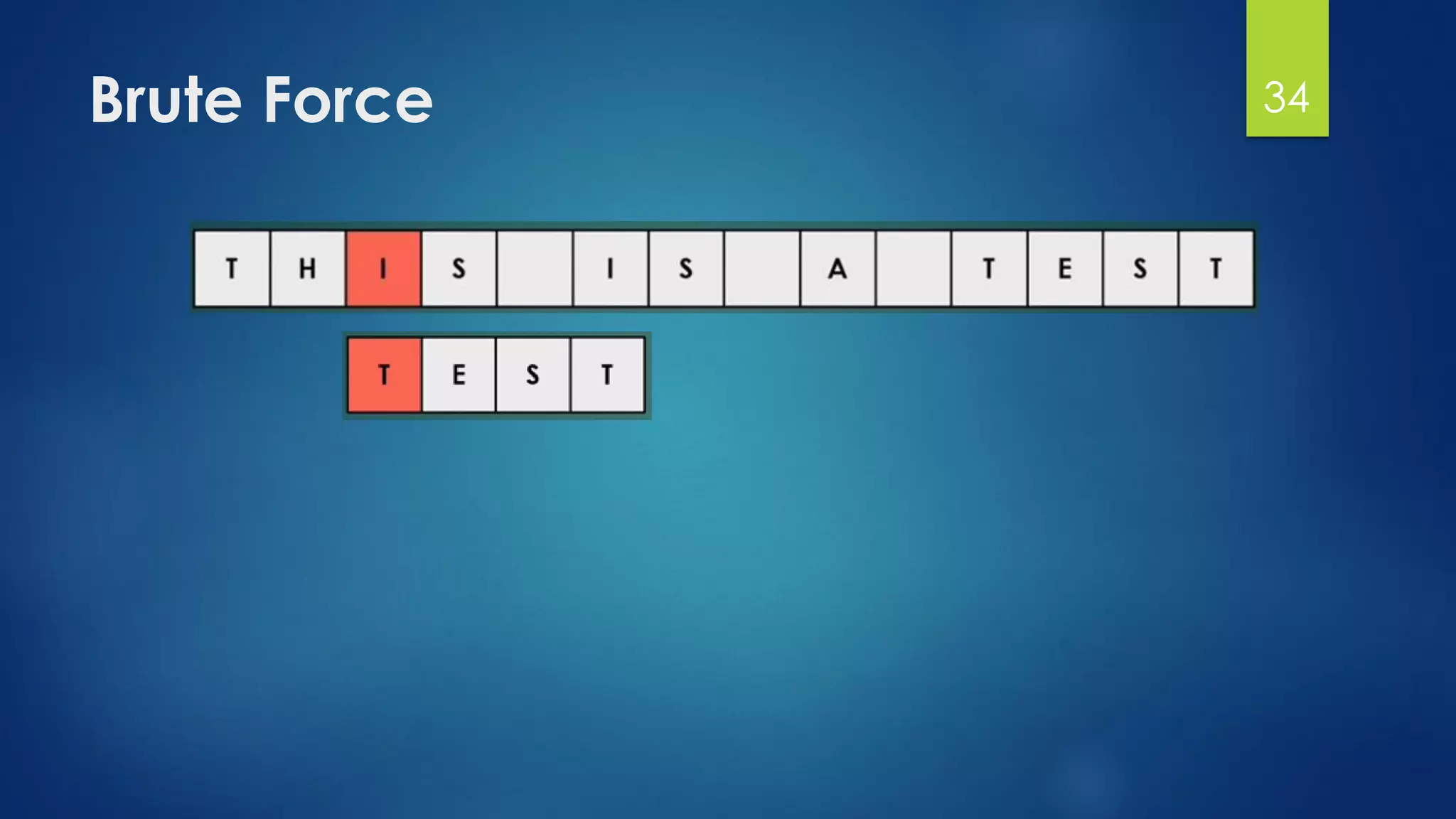
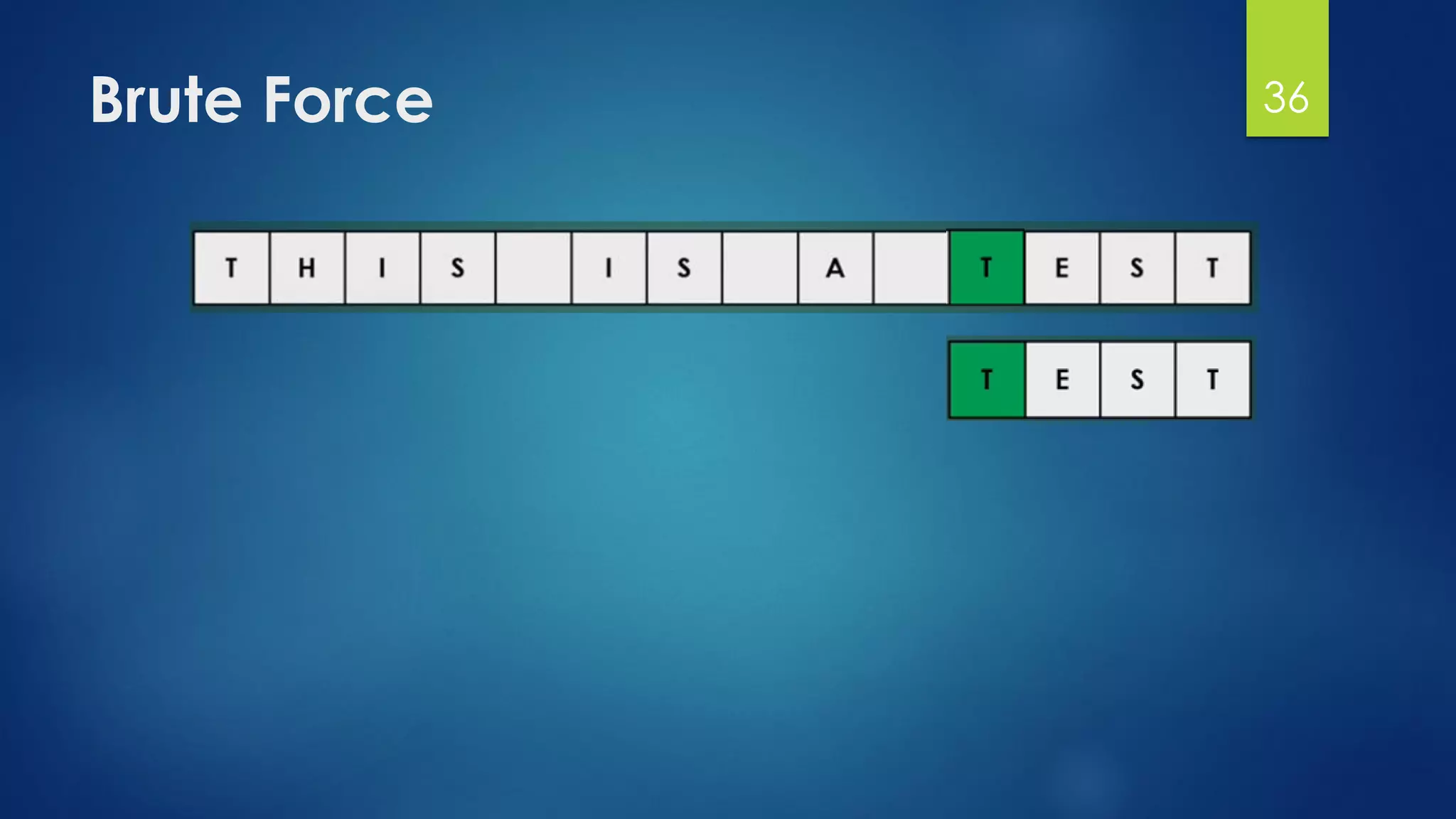
![Brute Force Finding Motif Solution
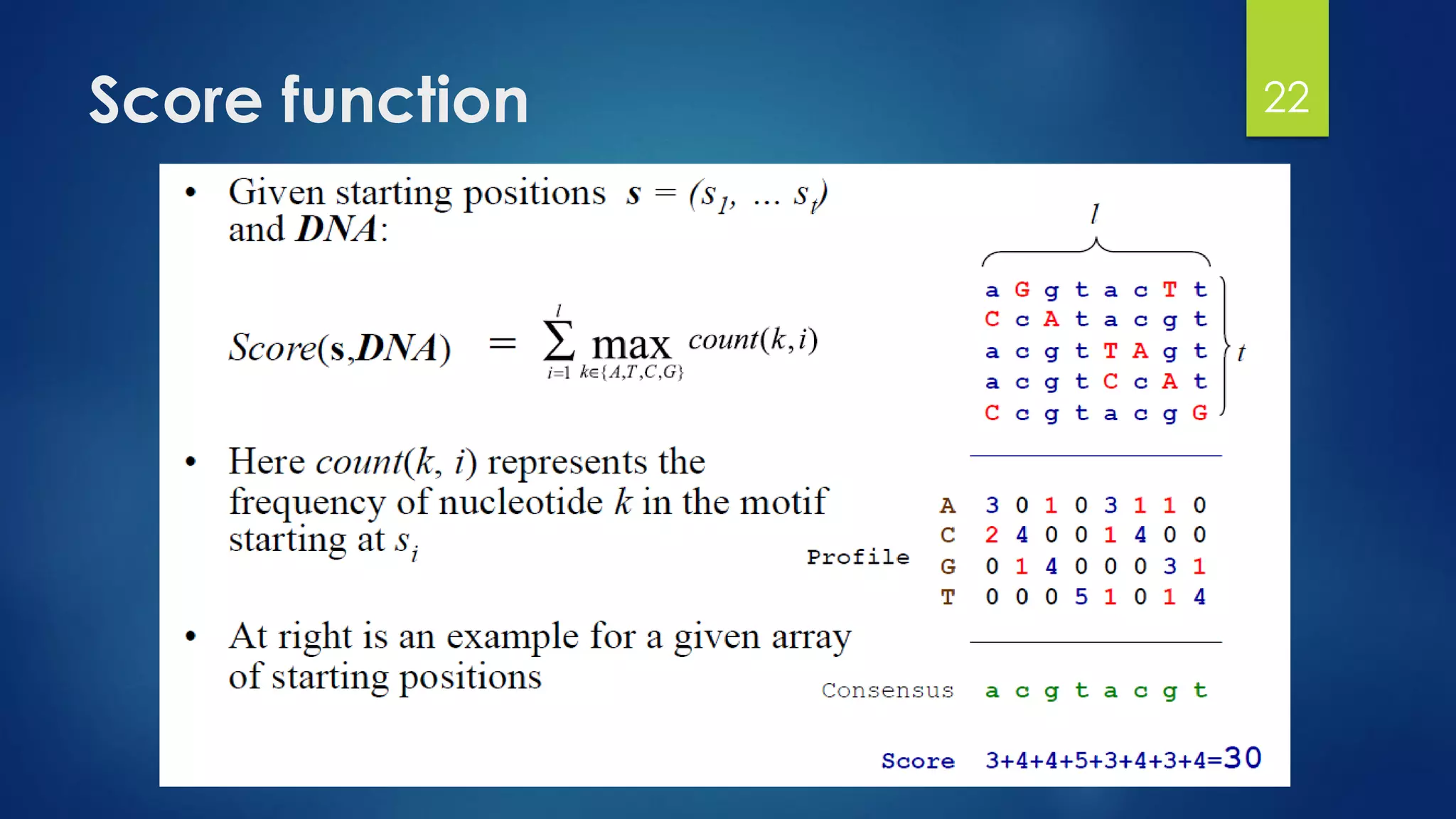
Compute the scores for each possible combination of
starting positions s
The best score will determine the best profile and the
consensus pattern in DNA
The goal is to maximize Score(s,DNA) by varying the
starting positions si, where:
si = [1, …, n-l+1]
i = [1, …, t]
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/findingmotif-171225104847/75/Finding-motif-25-2048.jpg)