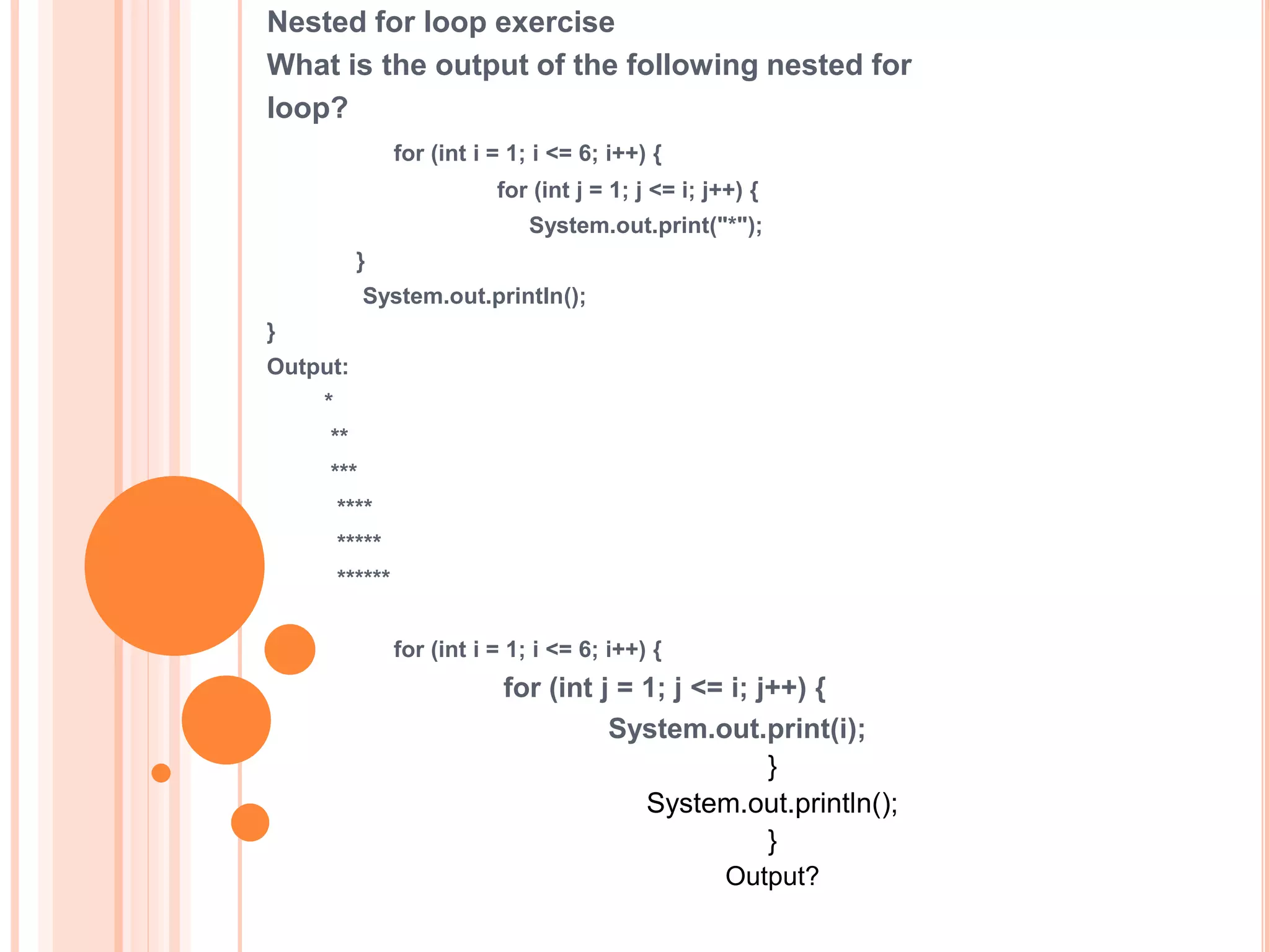
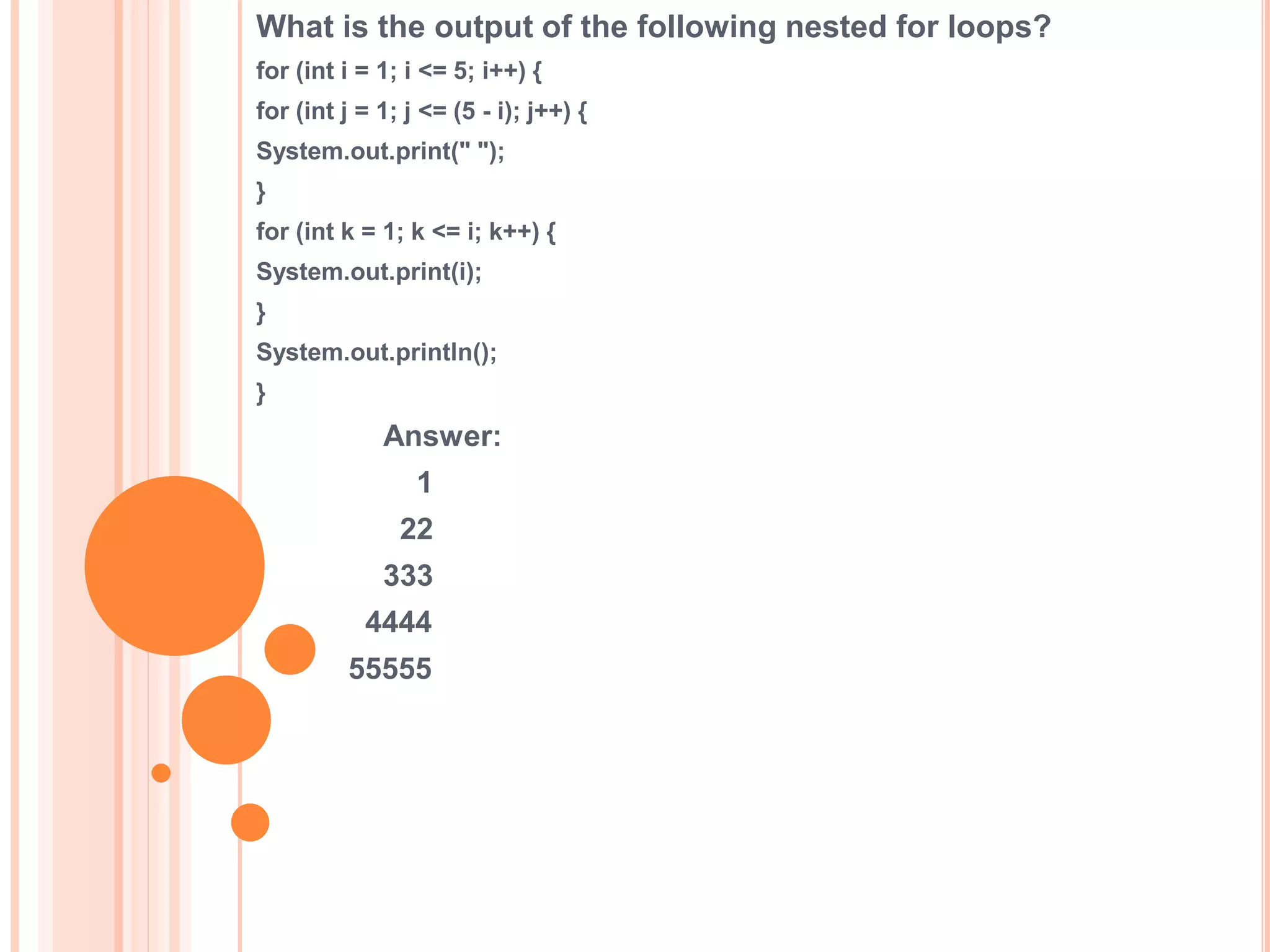
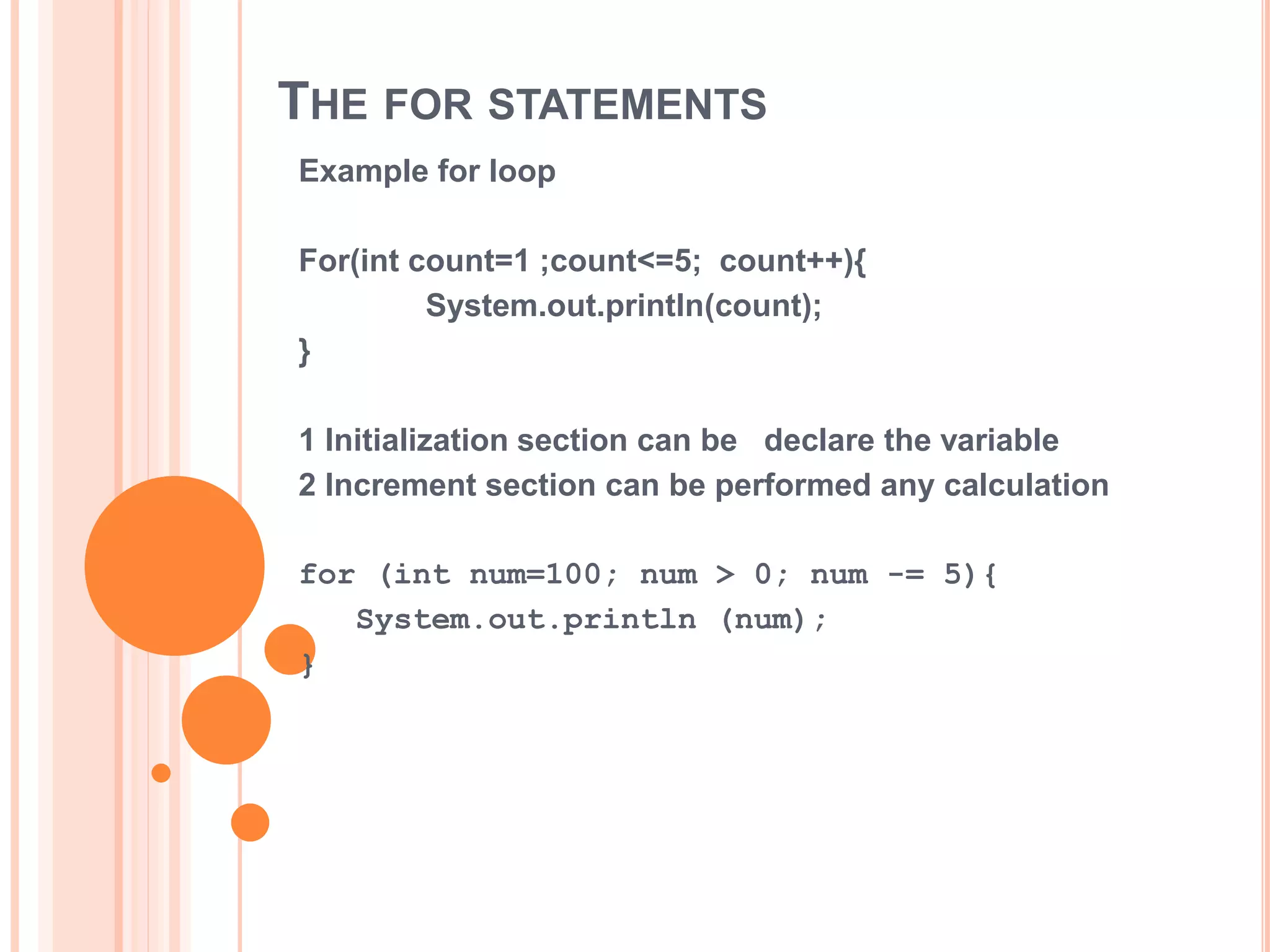
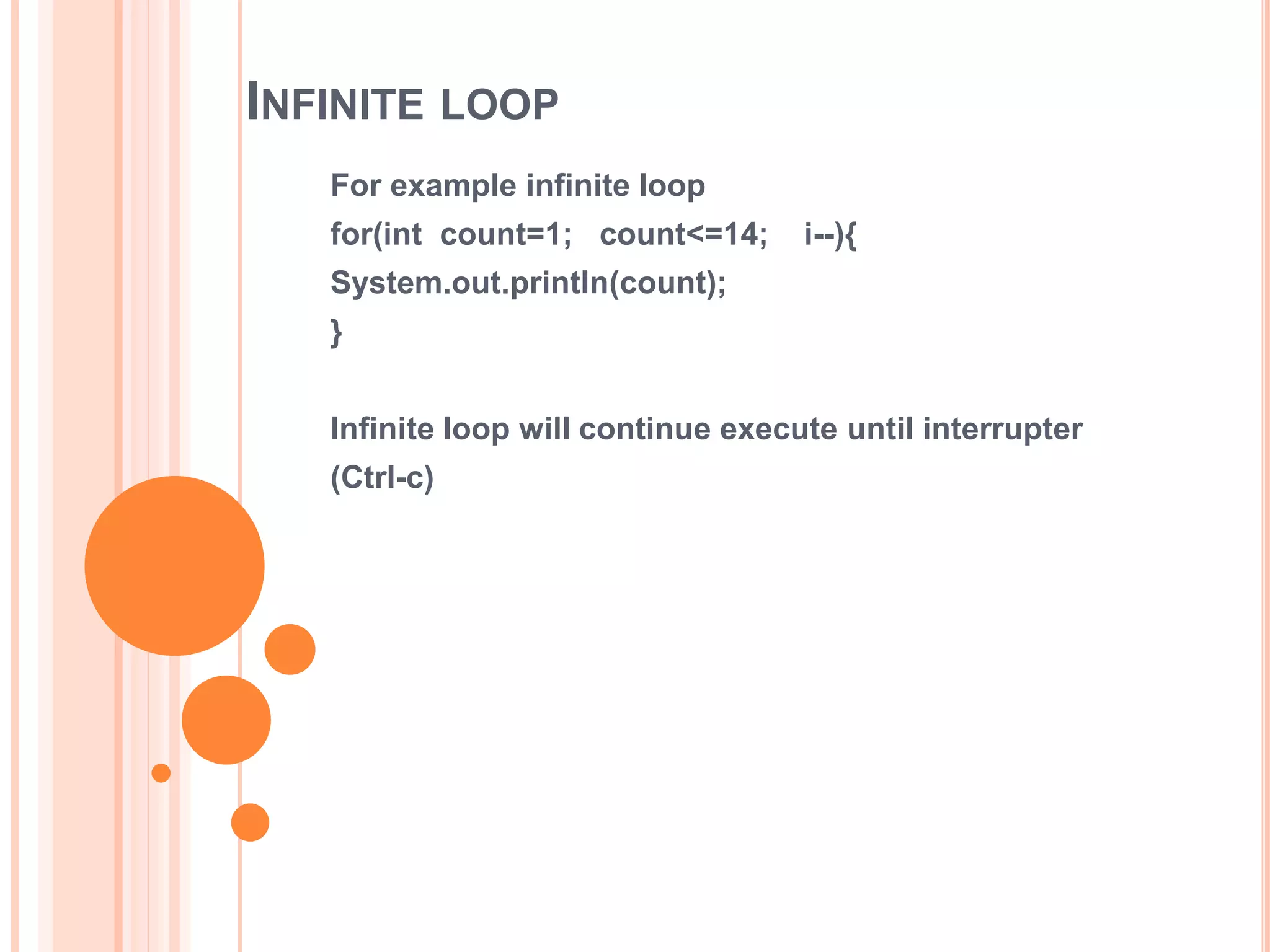
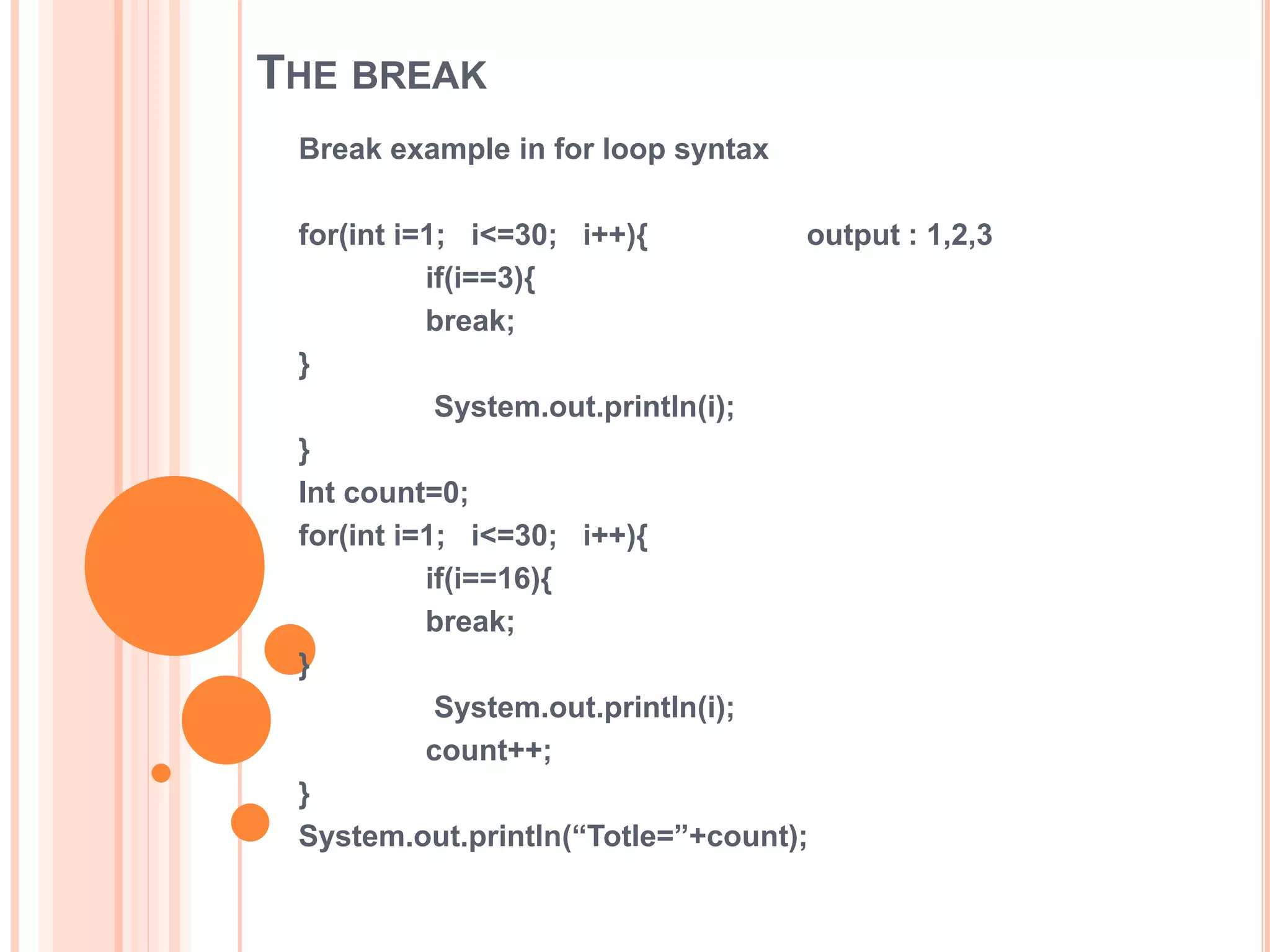
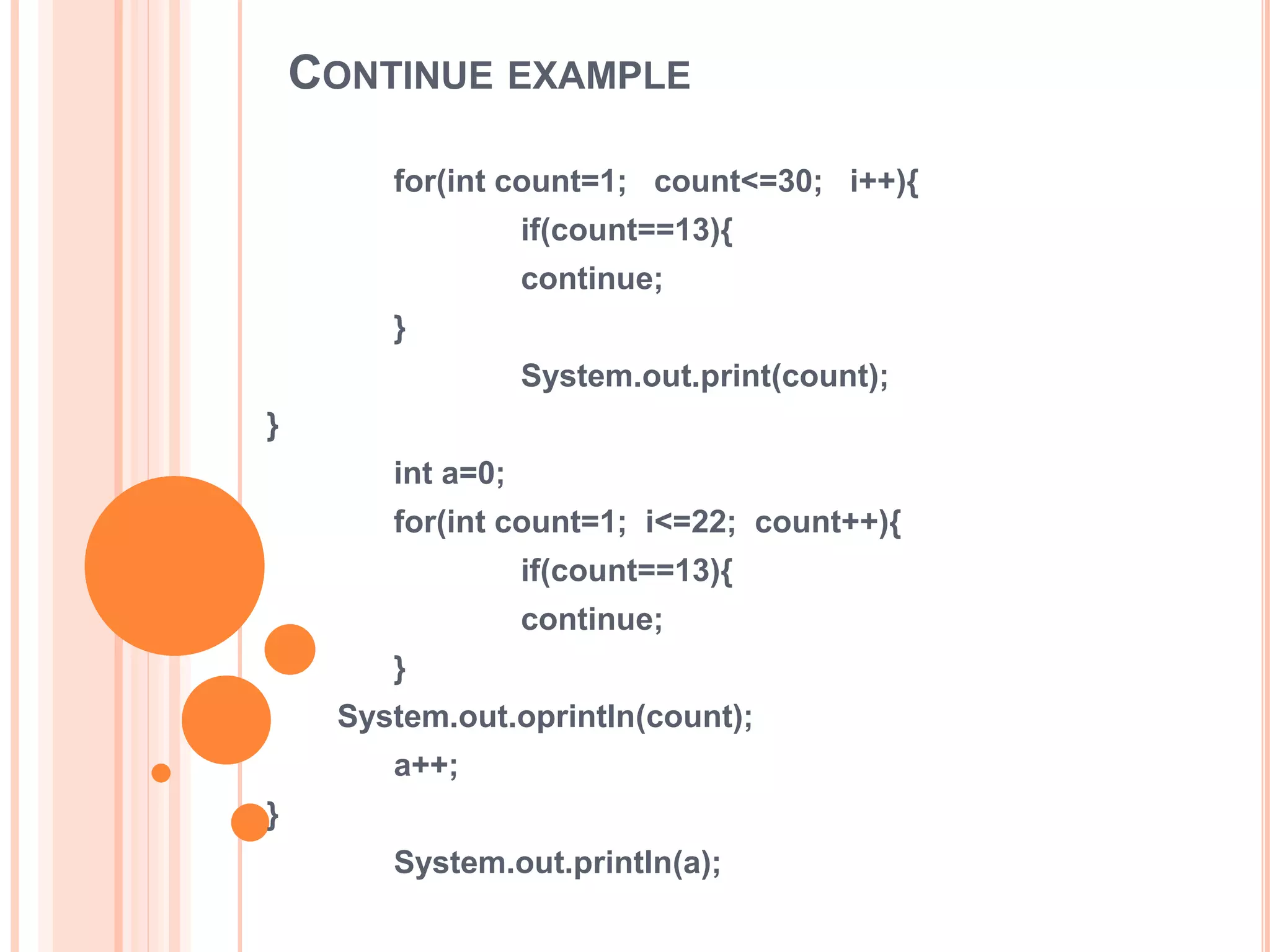
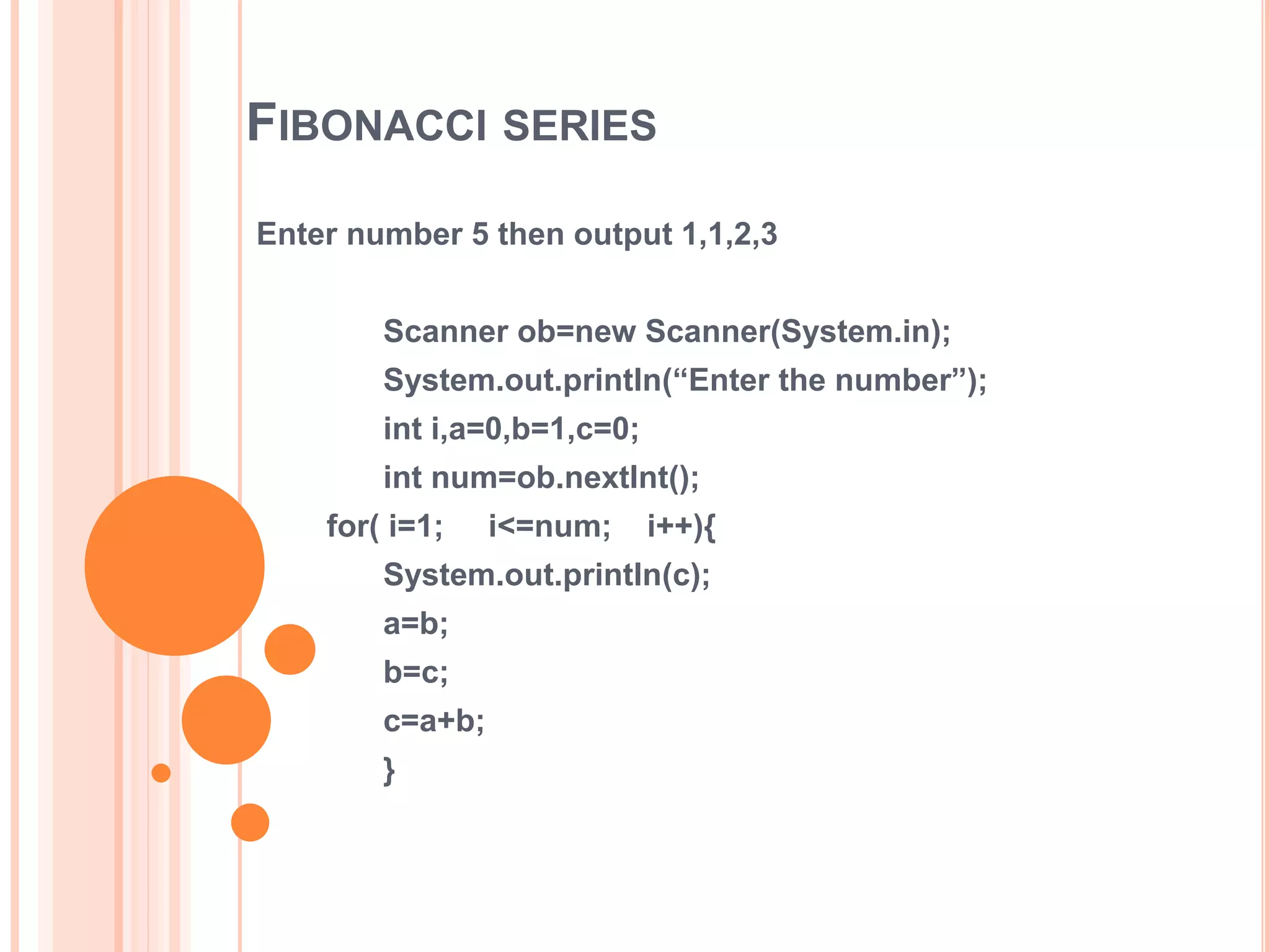
The document discusses for loops in Java including their syntax, examples of using for loops to print numbers, infinite loops, breaking and continuing loops, and nested for loops. It provides examples of using for loops to generate Fibonacci sequences, factorials, prime numbers, and nested patterns.






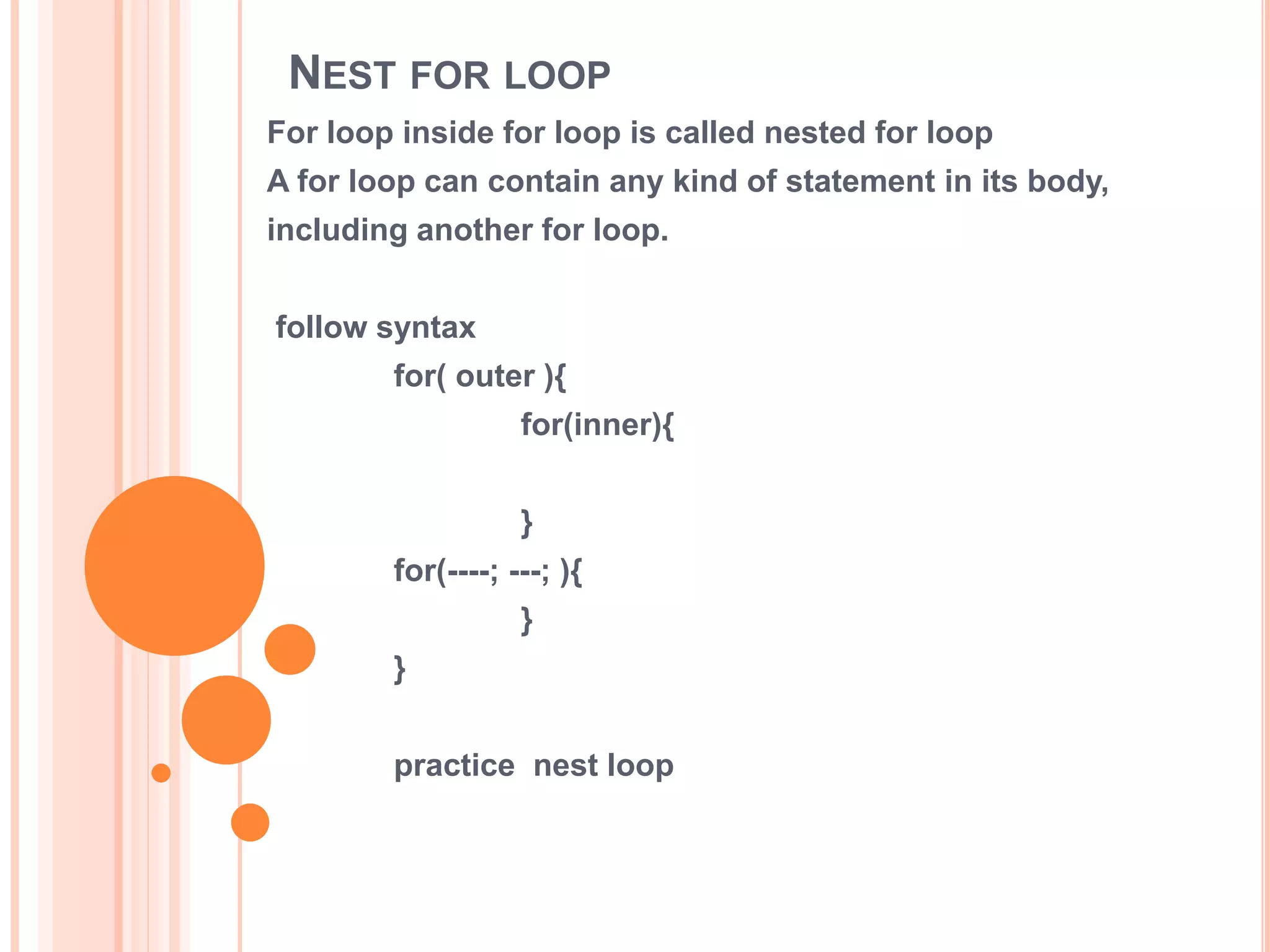
![PATRICE NEST LOOP SAME EXAMPLE
class Test{
public static void main(String arg[]){
for(int i=1 ; i=4; i++ ){
f(int j=1; j<=4; j++ ){
}// inner loop close
System.out.println(j);
}// outer loop close;
}
}
another example
for(int i=2 i<5; i++ ){
for(int j=i; j<=5; j++){
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaforloop-161027171840/75/for-loop-in-java-13-2048.jpg)