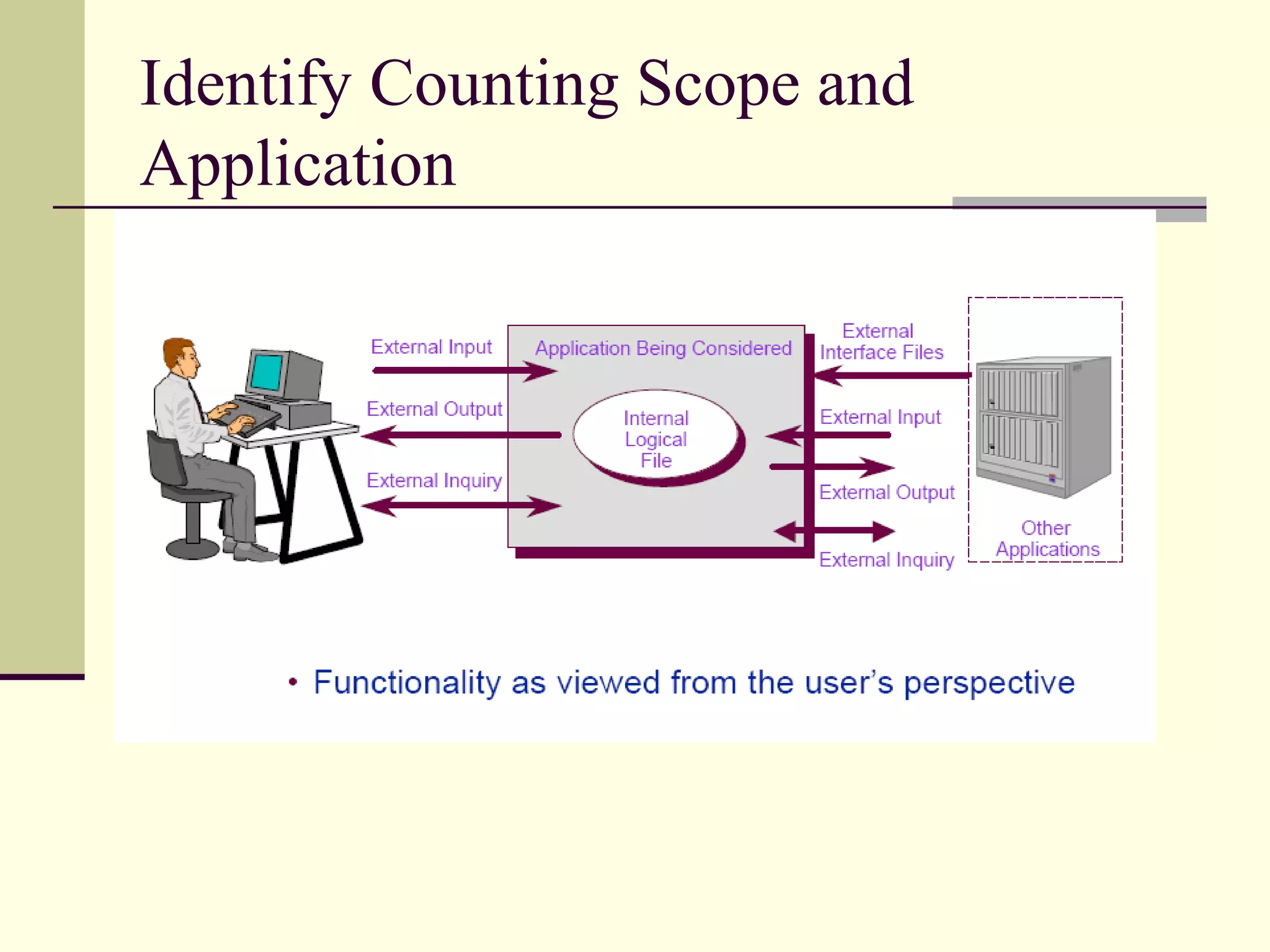
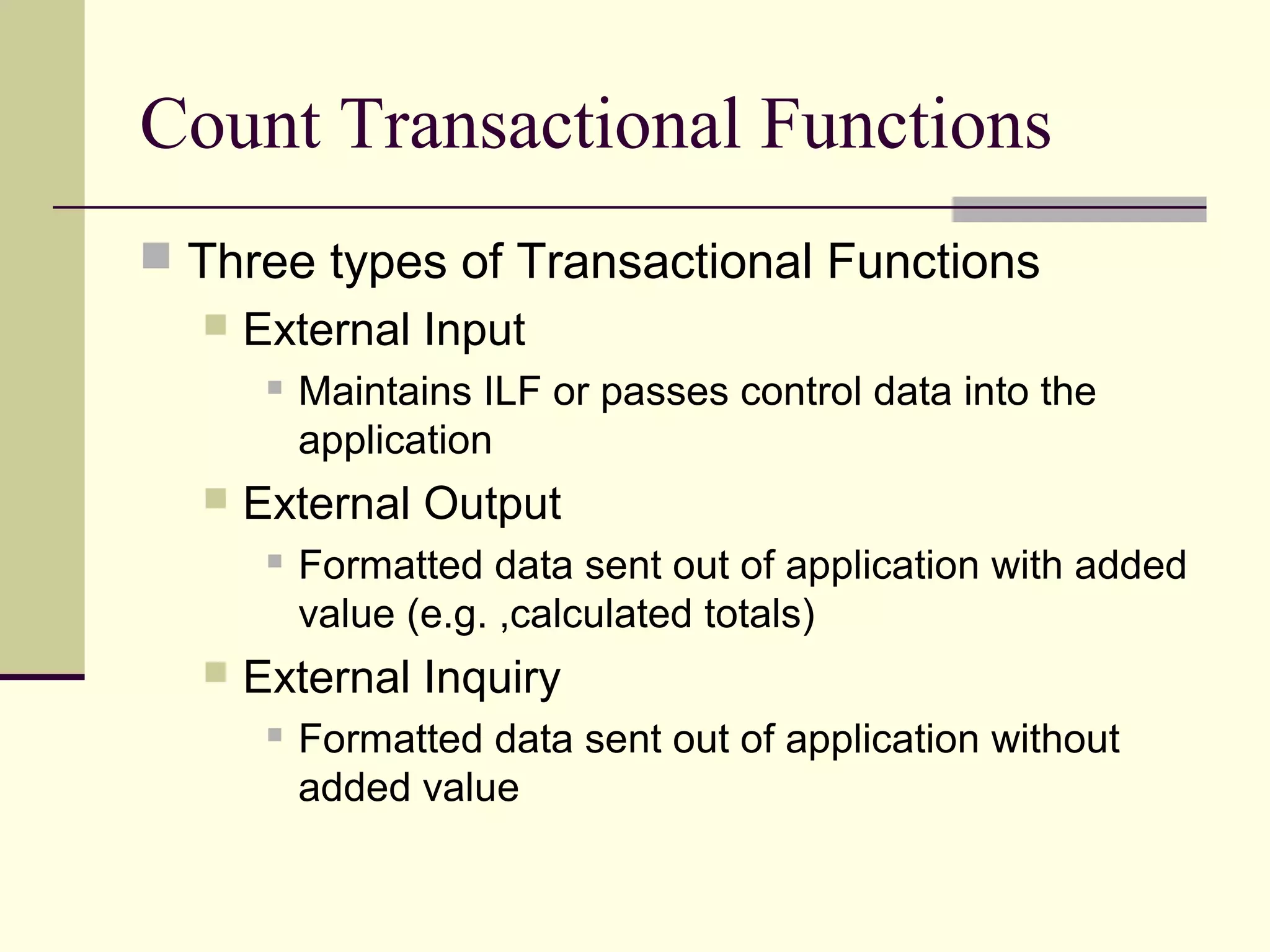
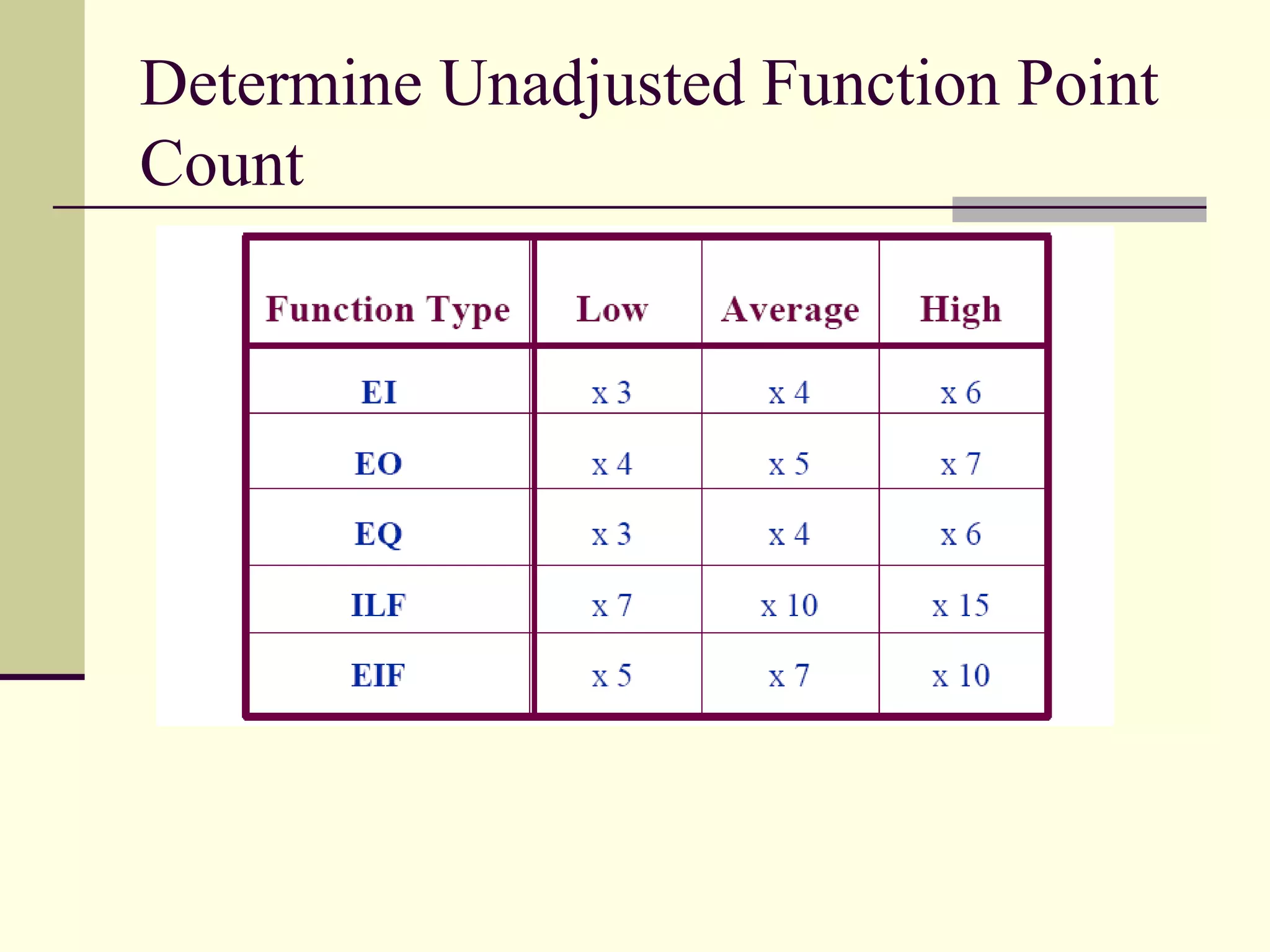
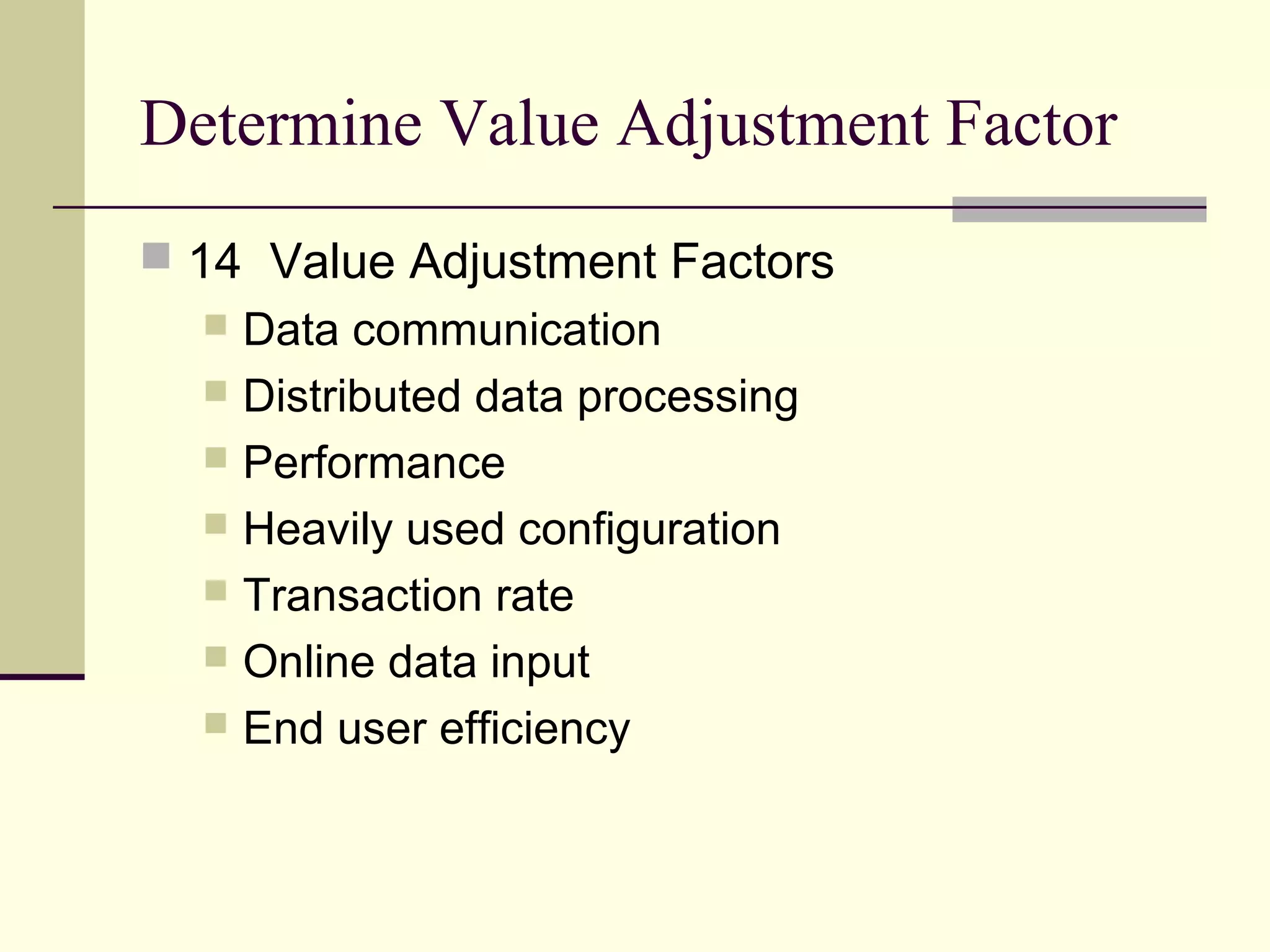
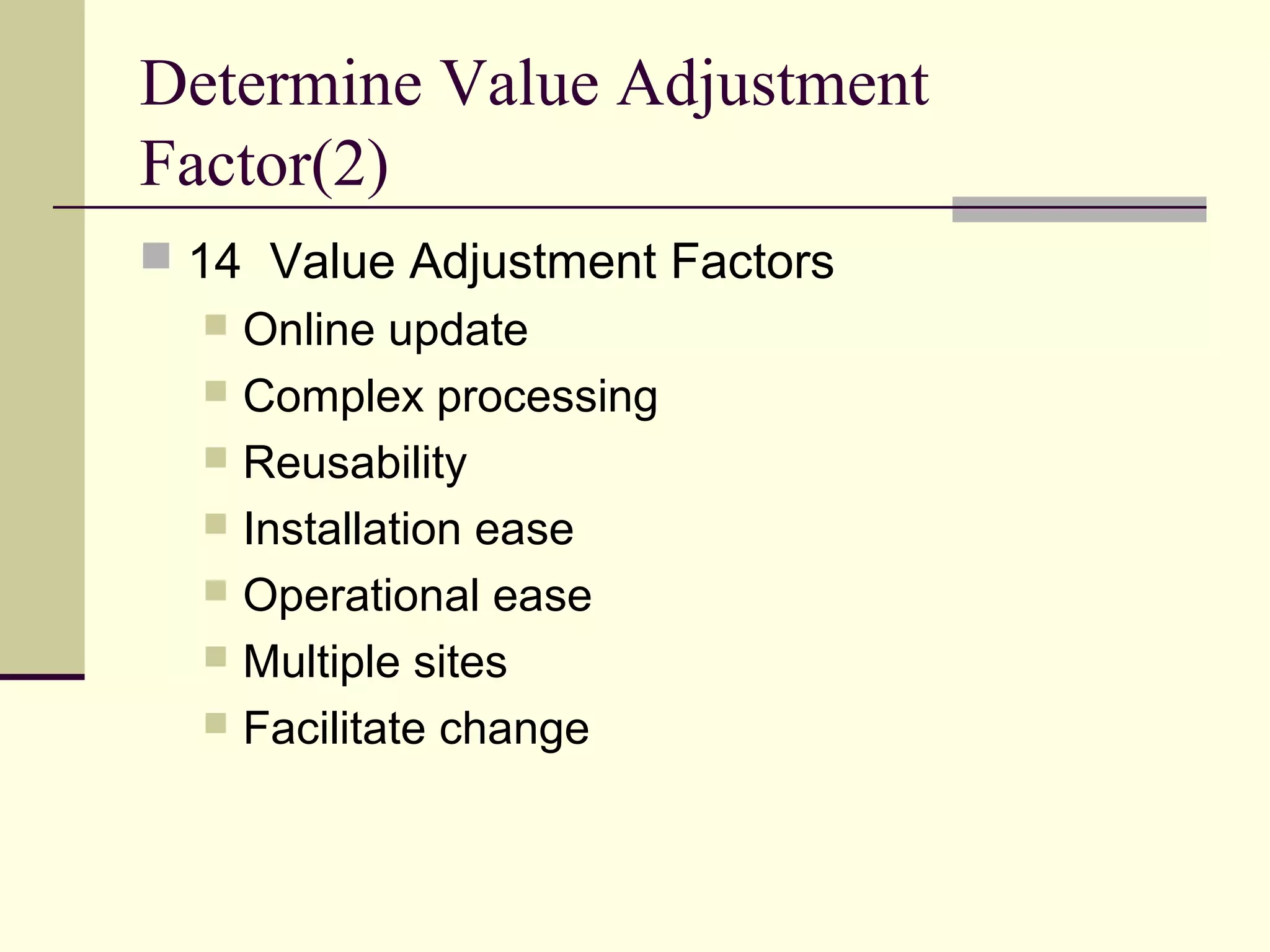
Function point analysis is a method of estimating the size of a software application based on the number and complexity of inputs, outputs, inquiries, internal logical files, and external interface files. The document outlines the process for counting function points, which involves identifying the different types of components, determining the unadjusted function point count, assessing value adjustment factors, and calculating the adjusted function point count. Function point analysis provides a standardized, technology-independent way to measure and estimate software size that allows for more accurate comparisons of projects.