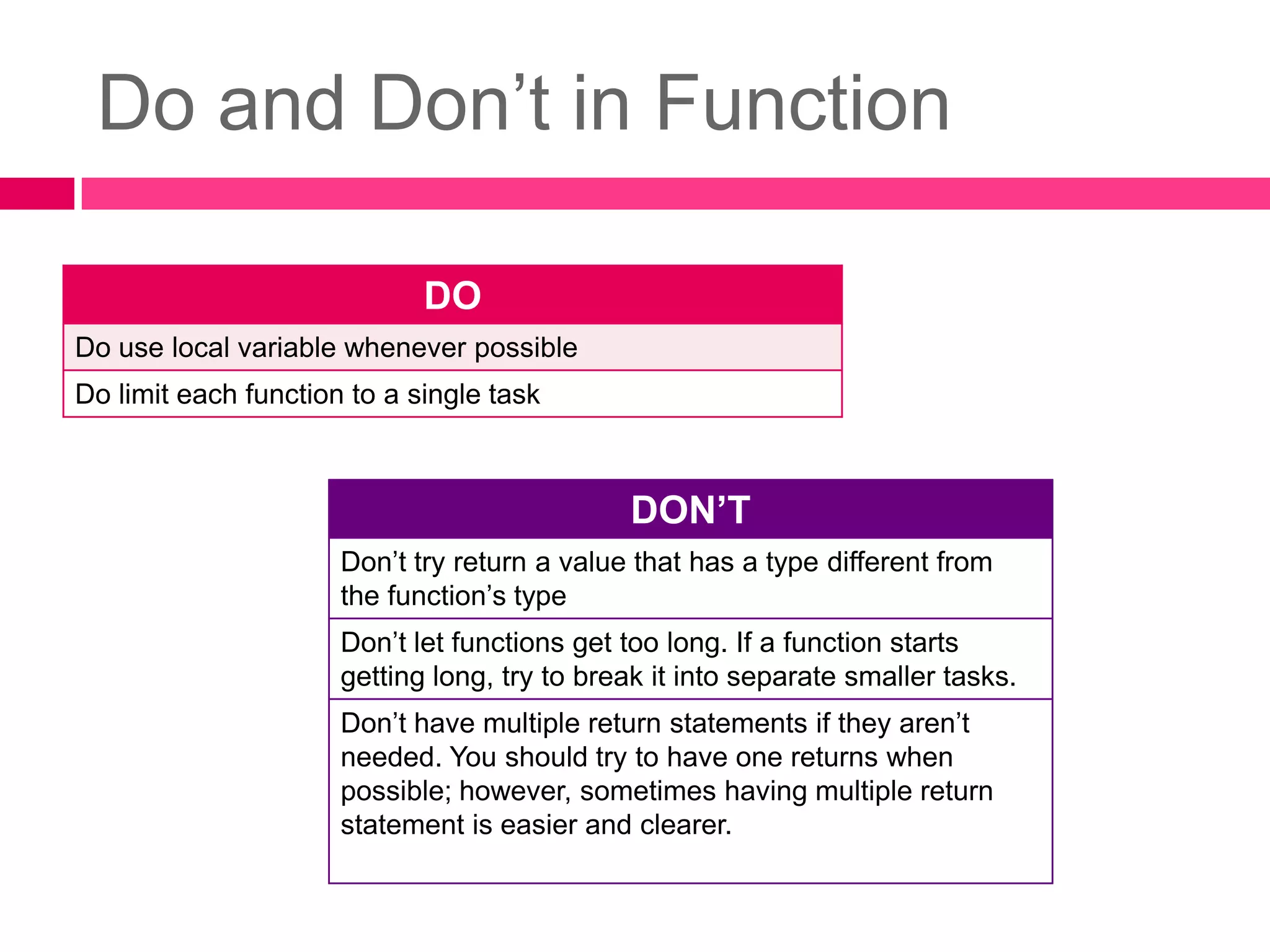
1. A function is a section of code that performs a specific task and makes programming simpler by splitting problems into sub-problems.
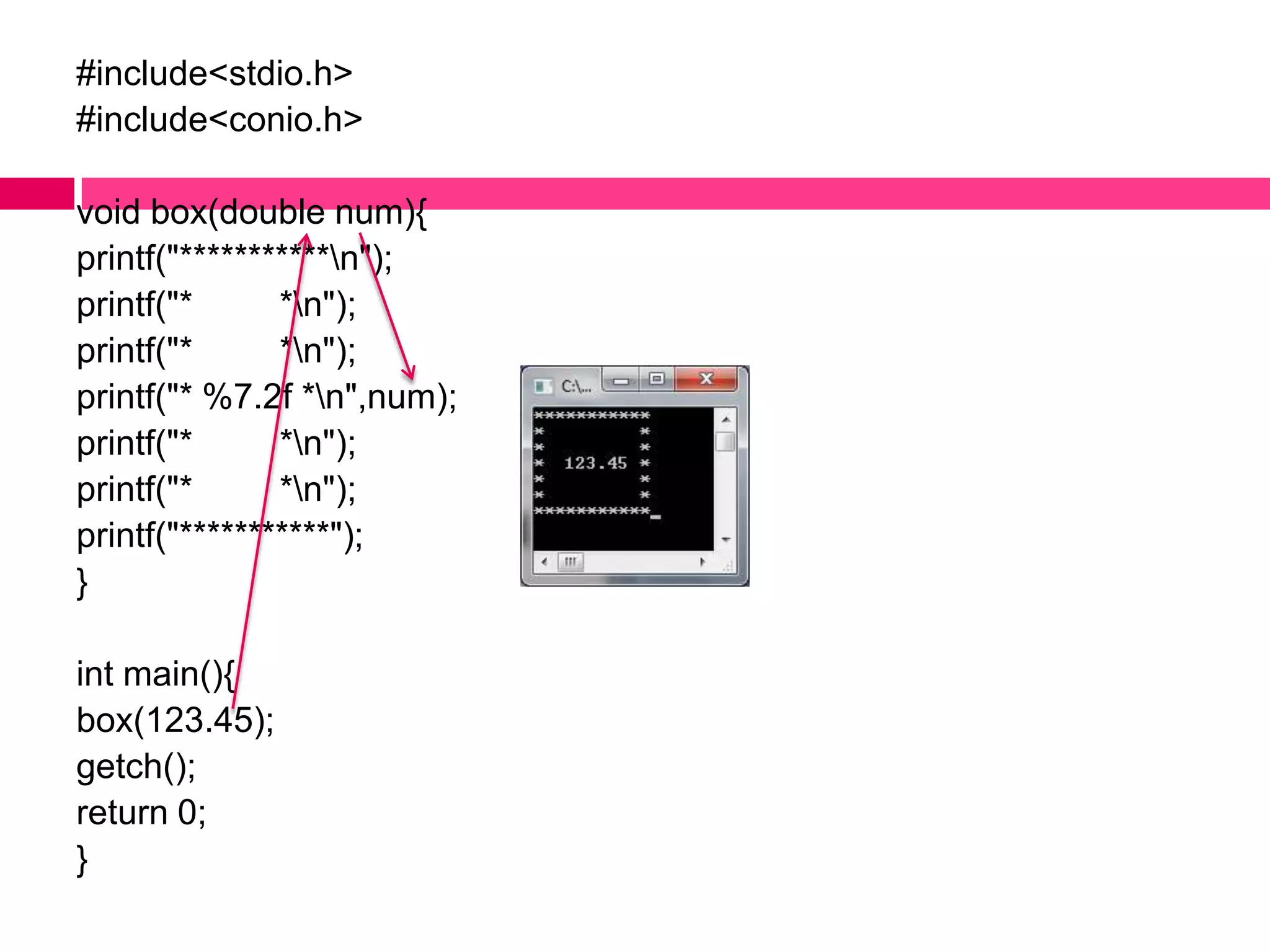
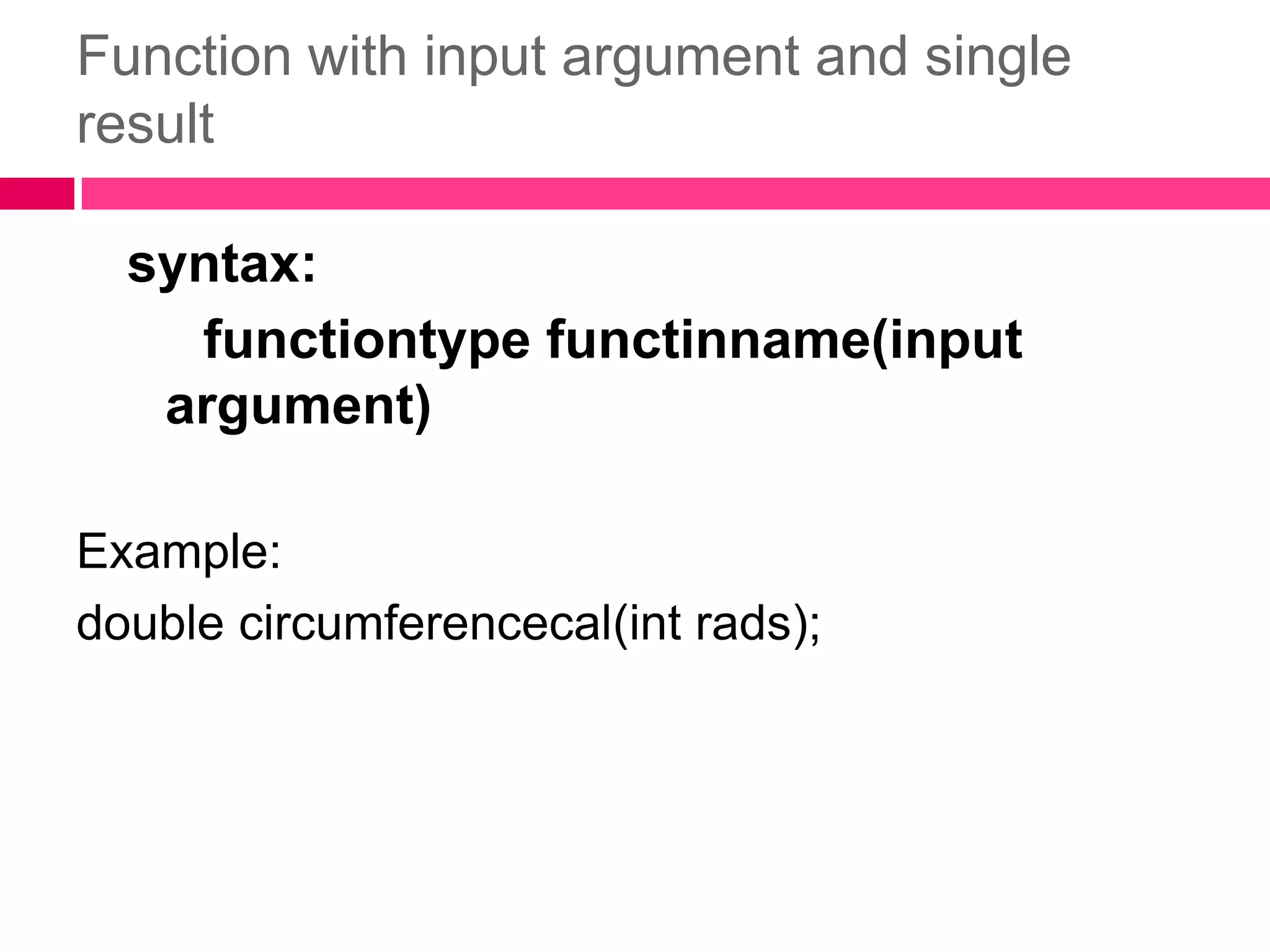
2. There are different types of functions including void functions without arguments, void functions with input arguments, and functions that return a single result.
3. Functions allow code to be reused by calling the function from the main program or from other functions. Functions can take input arguments and return values to provide modularity and simplify programming.