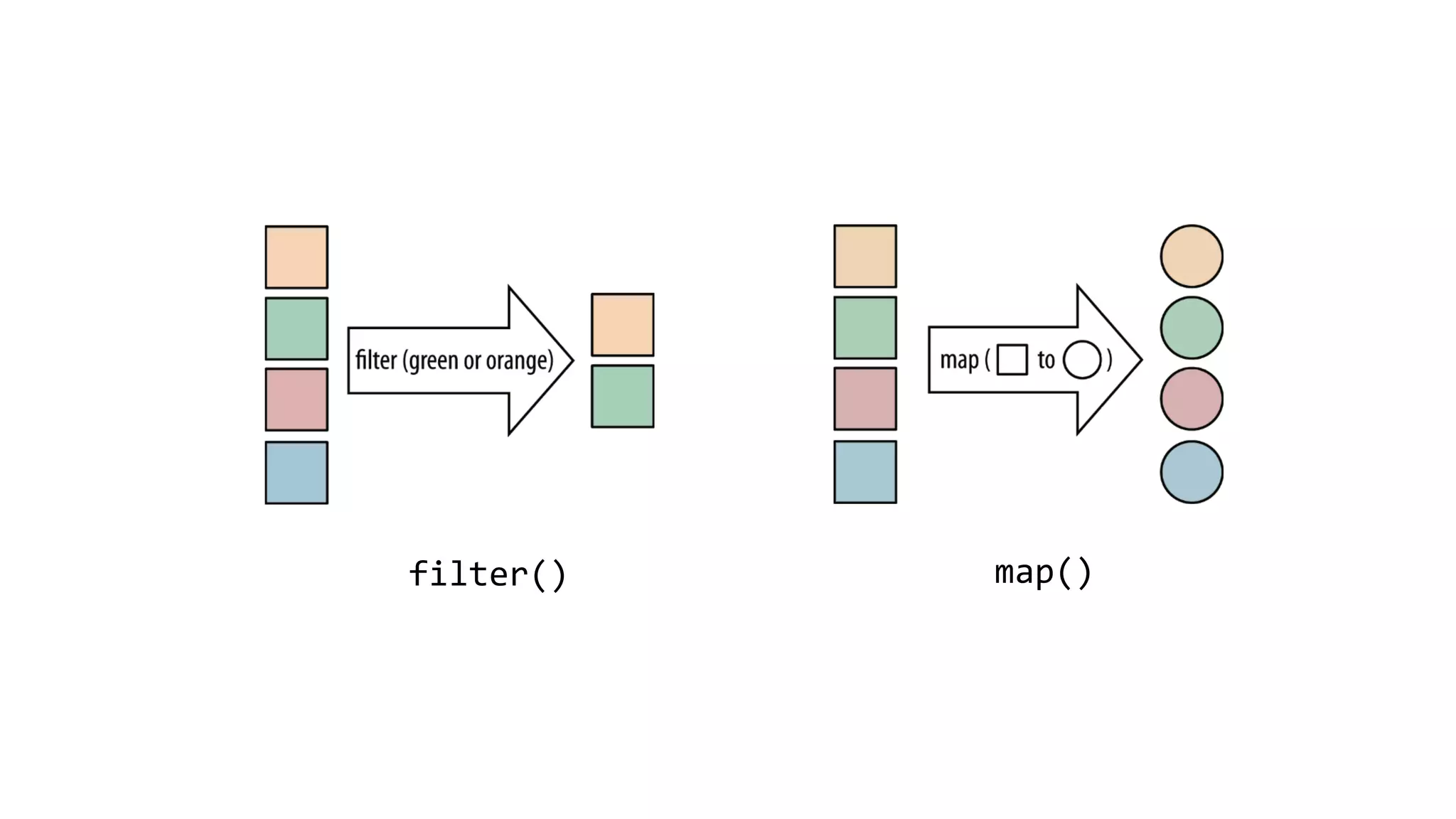
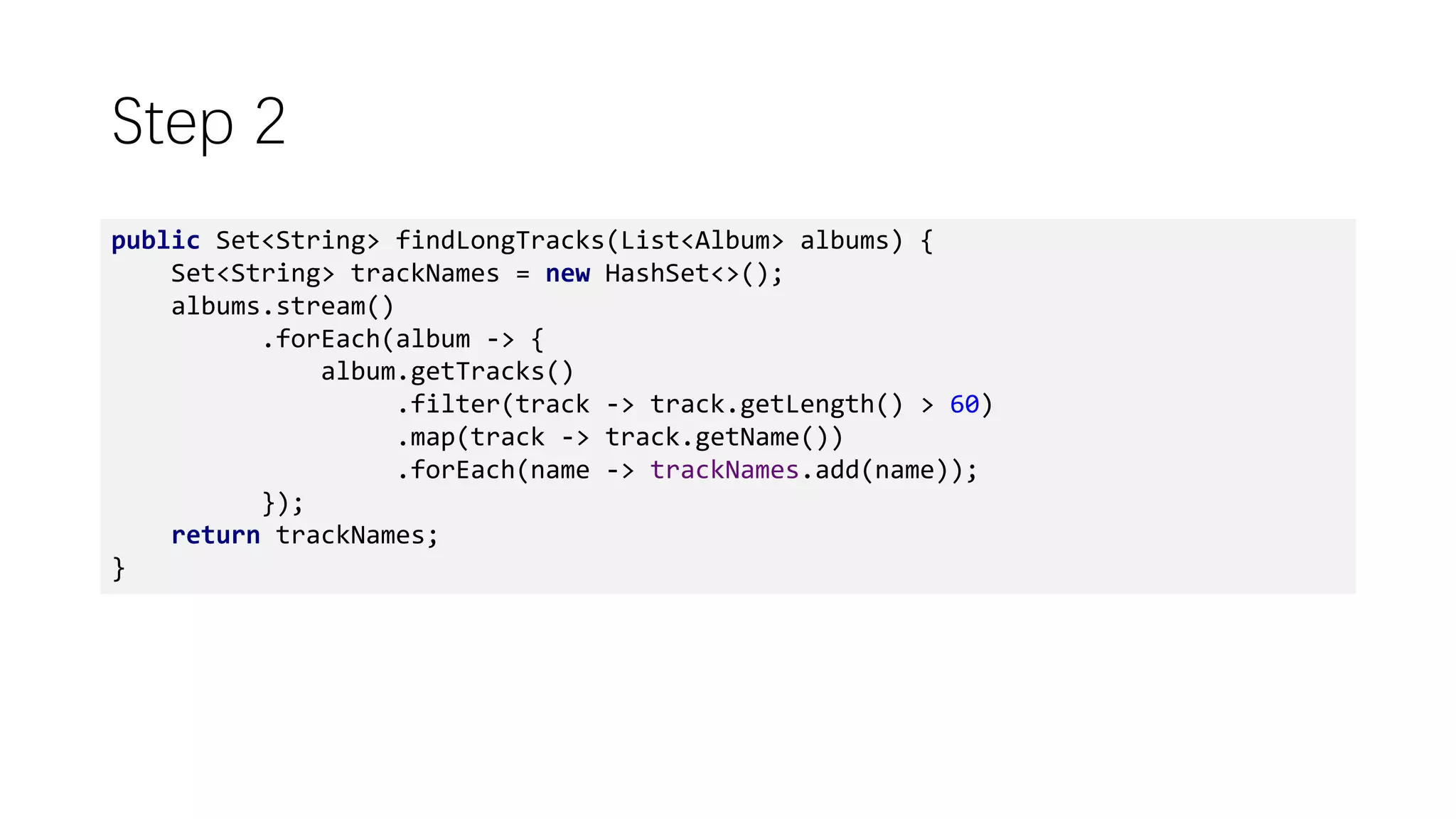
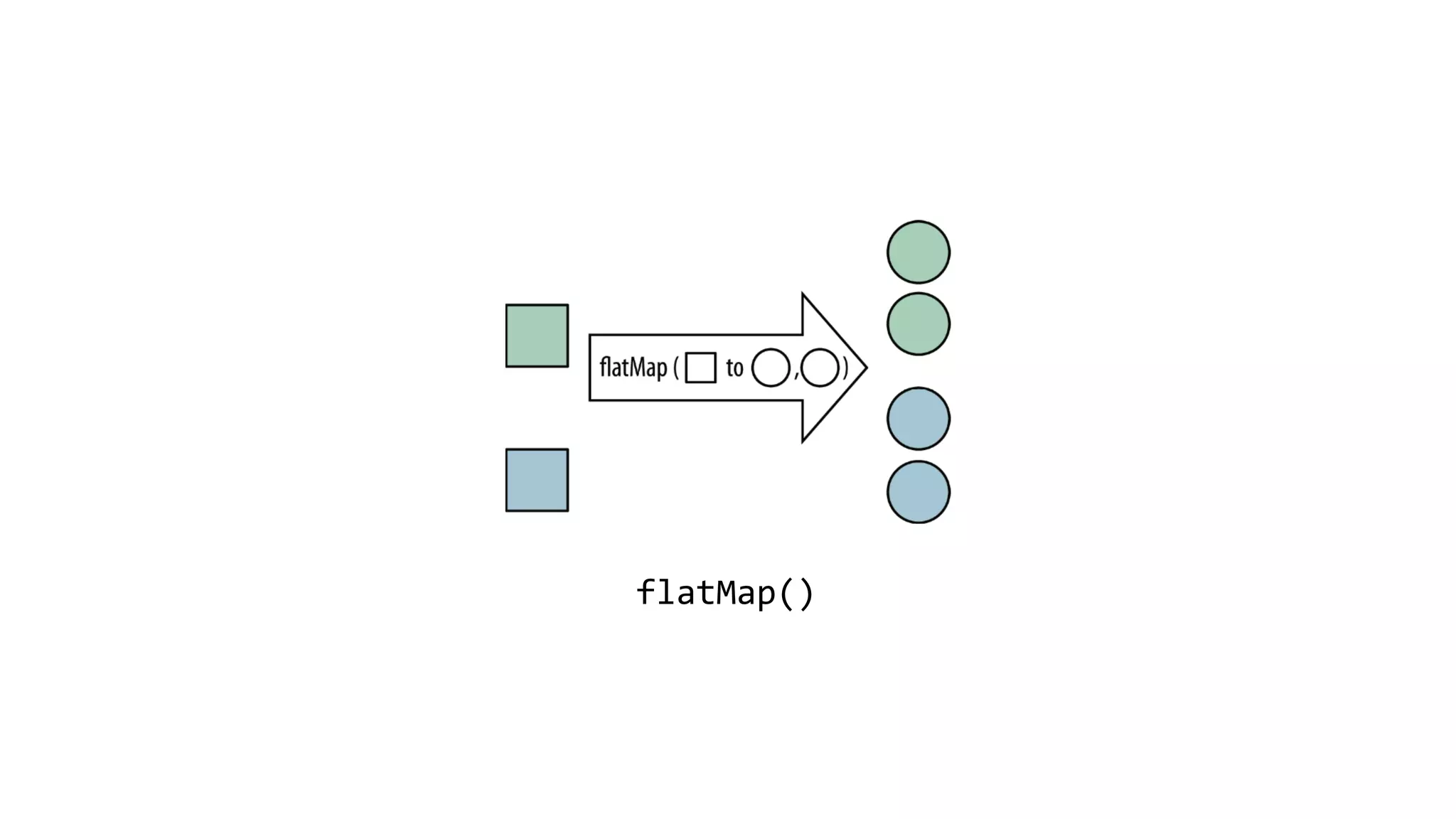
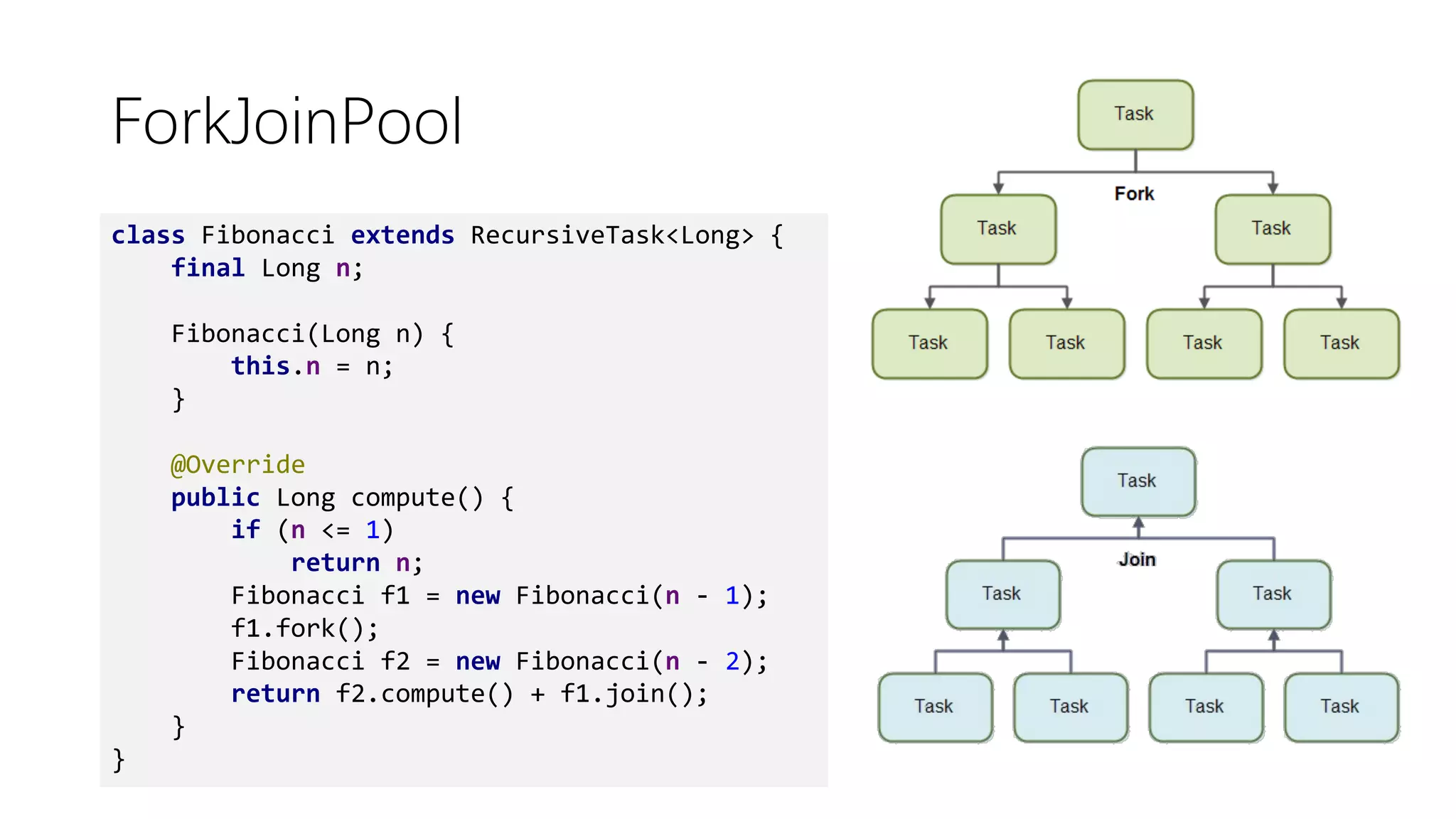
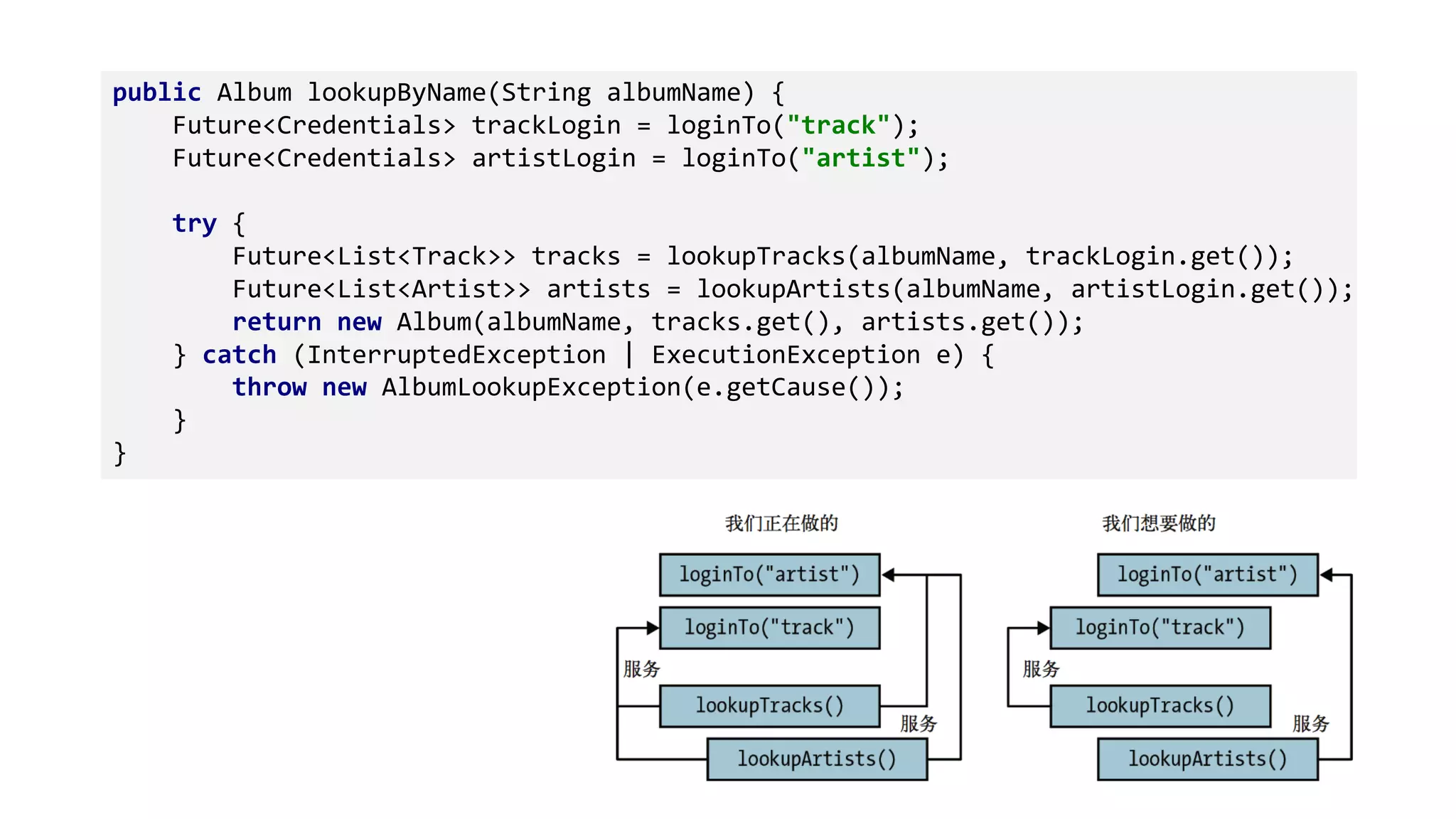
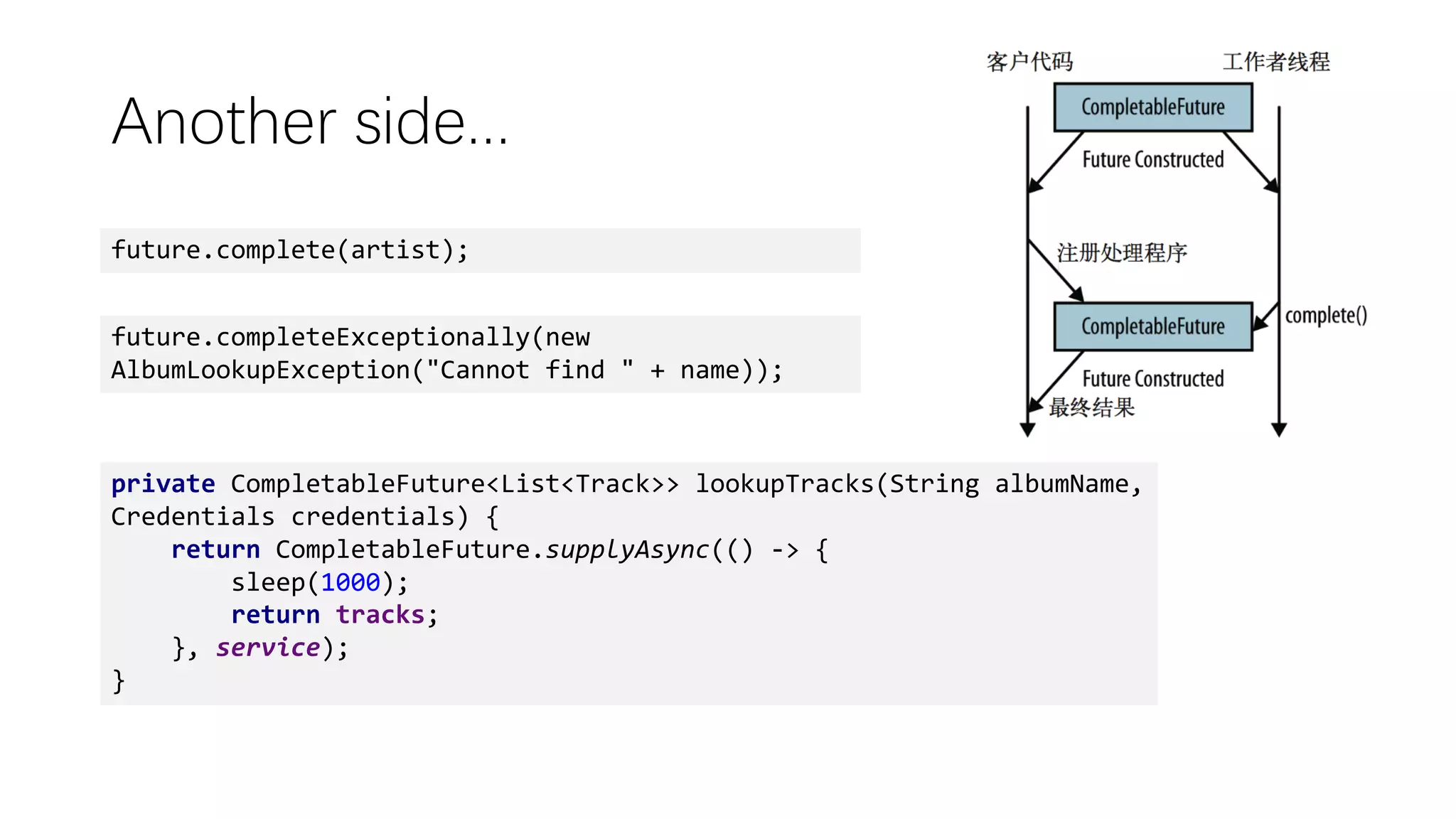
This document discusses functional programming concepts in Java 8 such as lambda expressions, streams, parallelization, and asynchronization. It covers lambda expressions as a syntactic sugar for anonymous classes, closures that capture variables from enclosing scopes, and functional interfaces. It also covers stream operations like map, filter, flatMap, and collect, parallelization using stream.parallel(), and asynchronization using CompletableFuture and RxJava. It reminds readers about functional programming concepts like pure functions, currying, and the Y-combinator.