The document provides an overview of functional programming, highlighting key concepts such as pure functions, higher-order functions, recursion, immutability, and lazy evaluation, particularly in the context of Python. It outlines the benefits and techniques of functional programming, including the use of lambda expressions and currying. The author, Haim Michael, emphasizes the importance of these principles for writing expressive and maintainable code.








![© 2008 Haim Michael 20151026
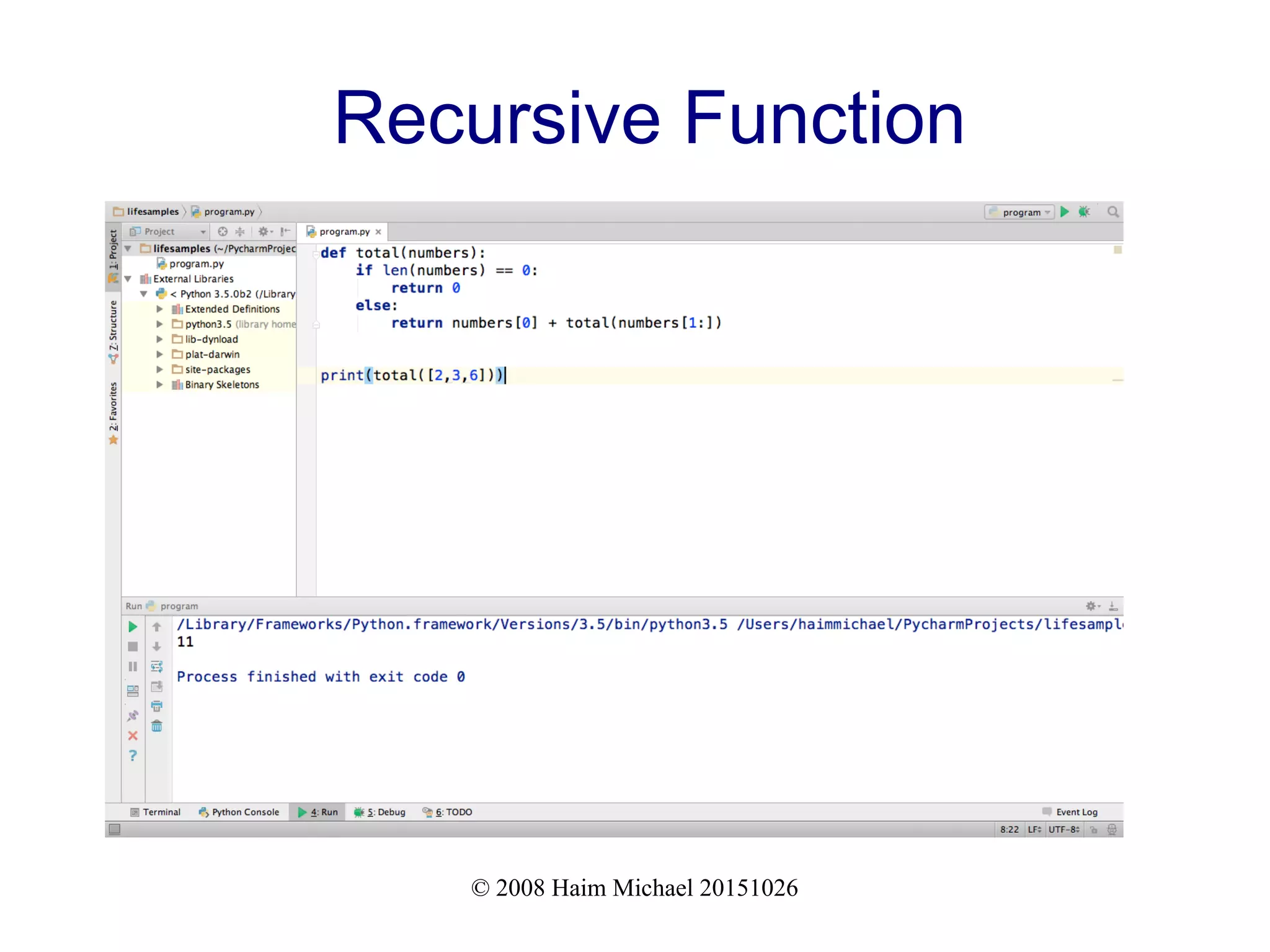
Recursive Function
def total(numbers):
if len(numbers) == 0:
return 0
else:
return numbers[0] + total(numbers[1:])
print(total([2,5,7]))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionalprogramminginpython20181114-181114194217/75/Functional-Programming-in-Python-9-2048.jpg)


![© 2008 Haim Michael 20151026
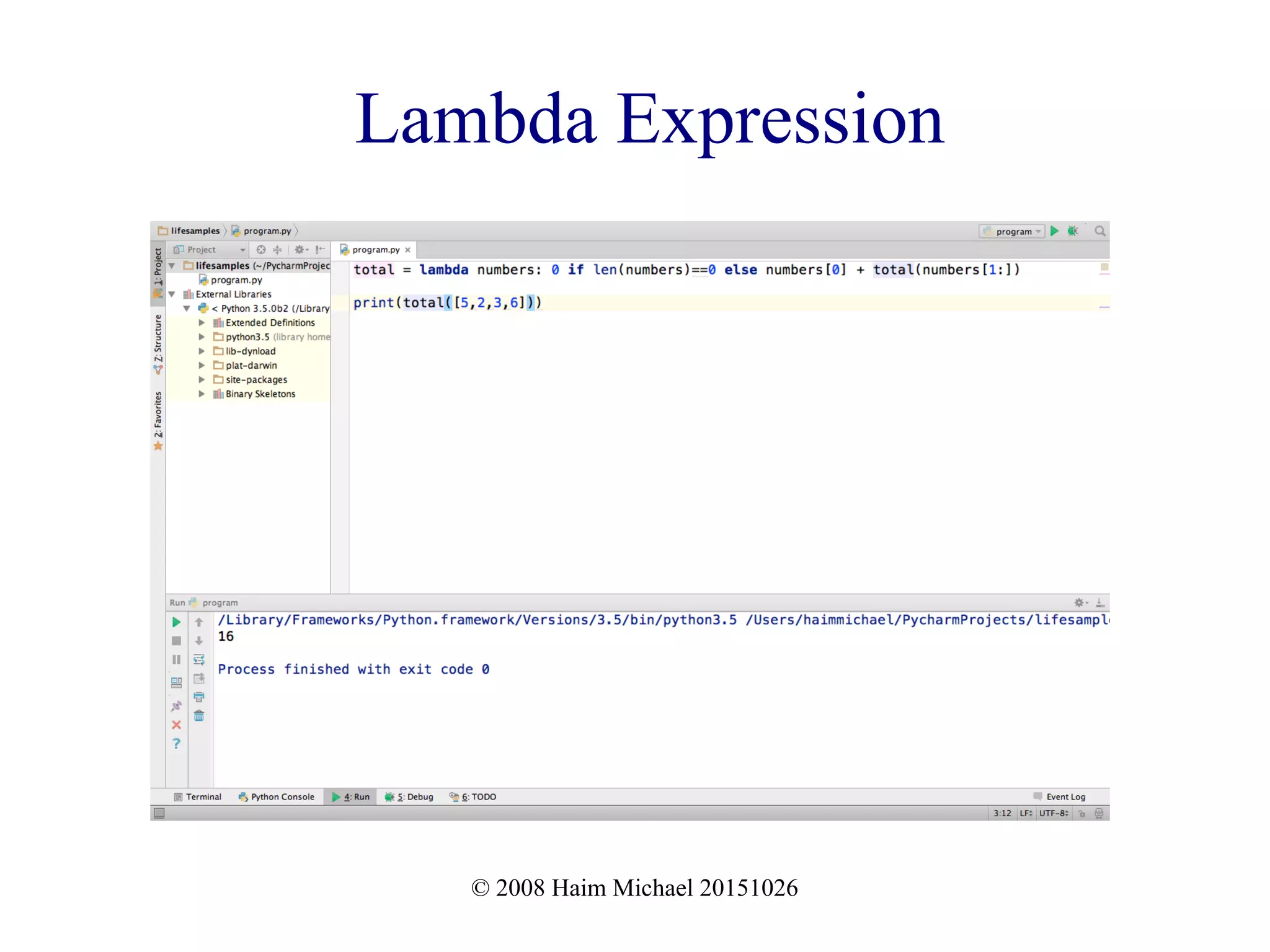
Lambda Expression
Using lambda expressions we can define a recursive
function that feels much more as an expression than a
function we define using the def keyword.
total = lambda numbers: 0 if len(numbers)==0 else numbers[0] +
total(numbers[1:])
print(total([5,2,3,6]))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionalprogramminginpython20181114-181114194217/75/Functional-Programming-in-Python-13-2048.jpg)

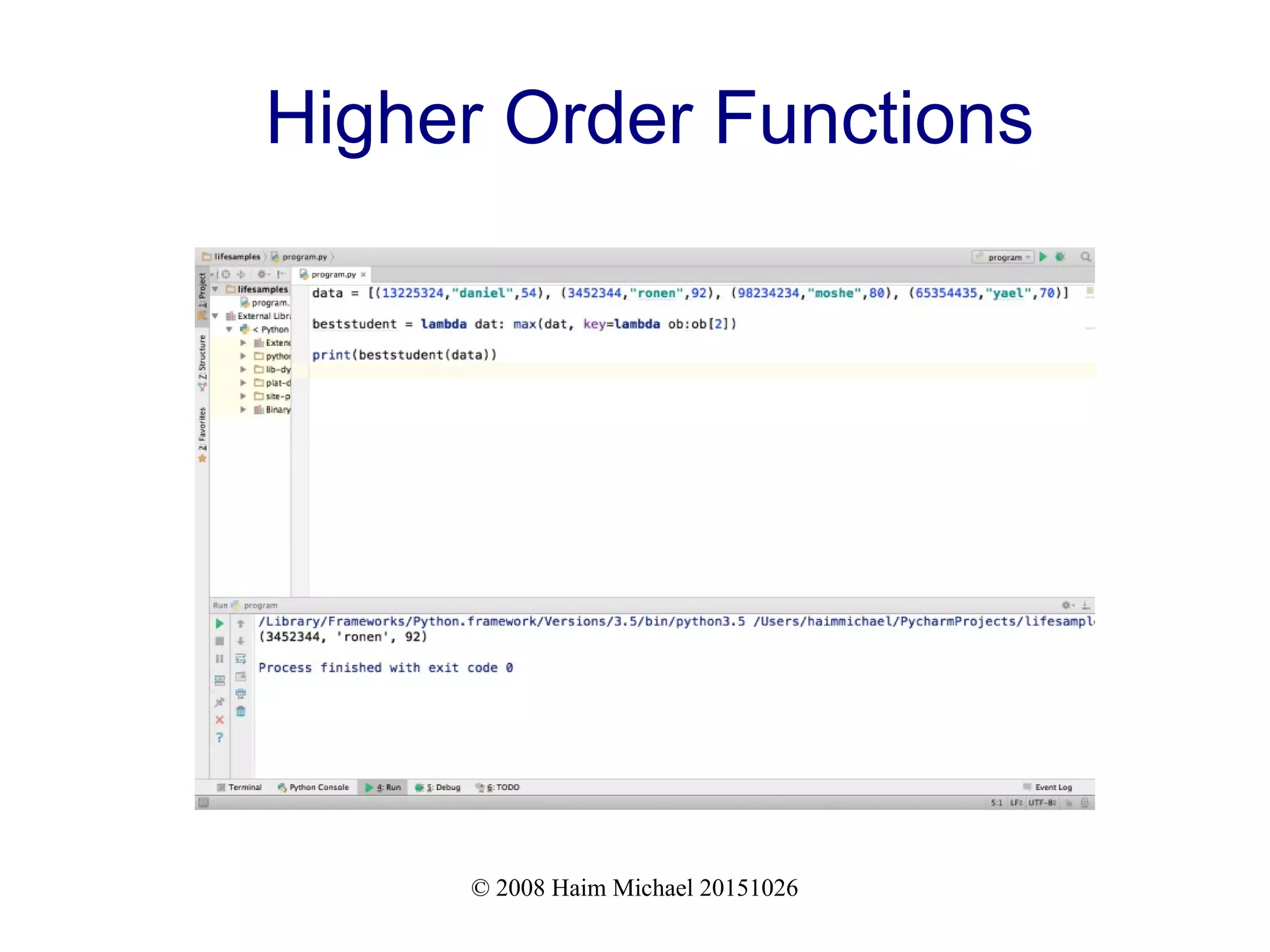
![© 2008 Haim Michael 20151026
Higher Order Functions
data = [(13225324,"daniel",54), (3452344,"ronen",92),
(98234234,"moshe",80), (65354435,"yael",70)]
beststudent = lambda dat: max(dat, key=lambda ob:ob[2])
print(beststudent(data))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionalprogramminginpython20181114-181114194217/75/Functional-Programming-in-Python-16-2048.jpg)