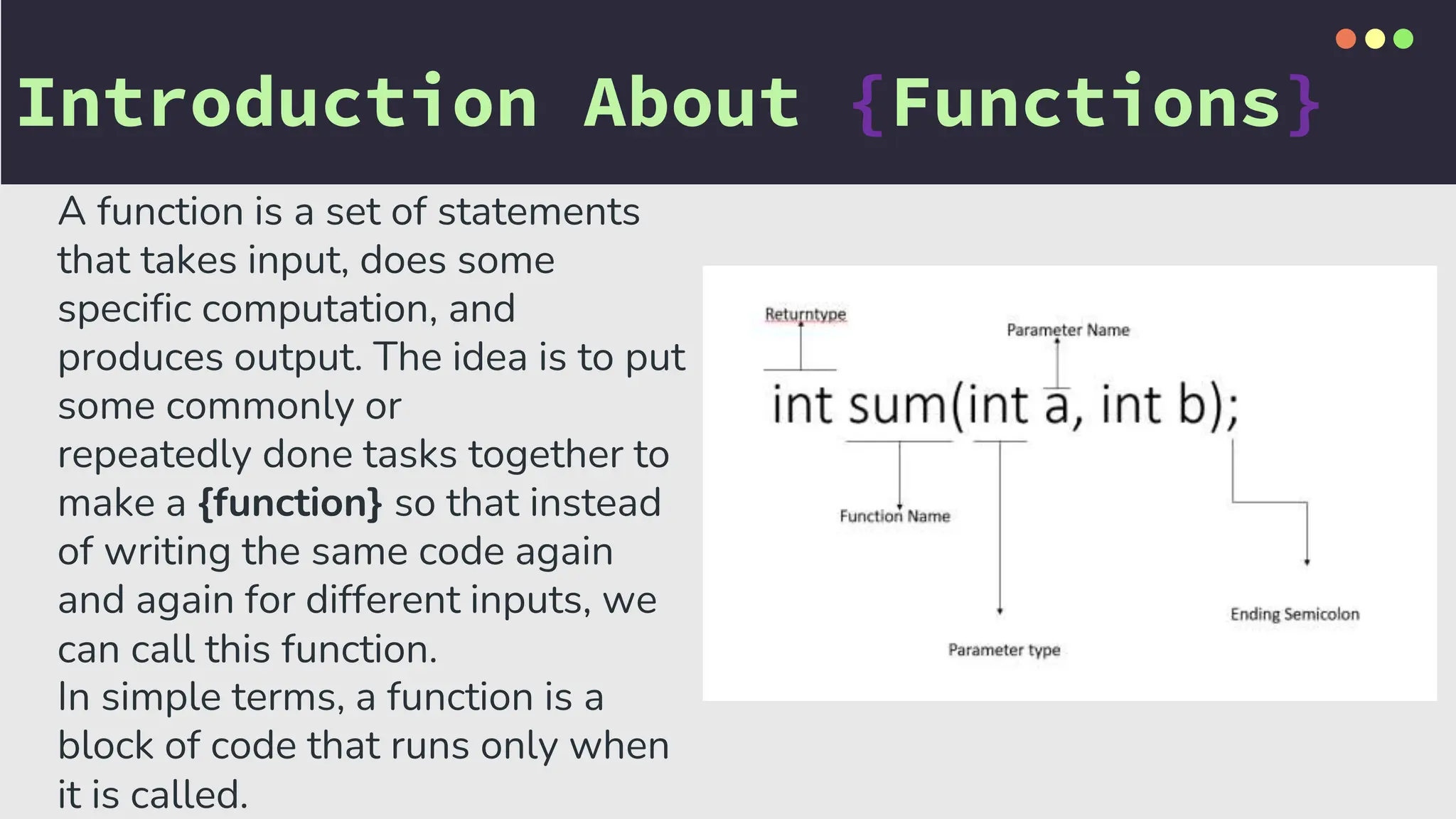
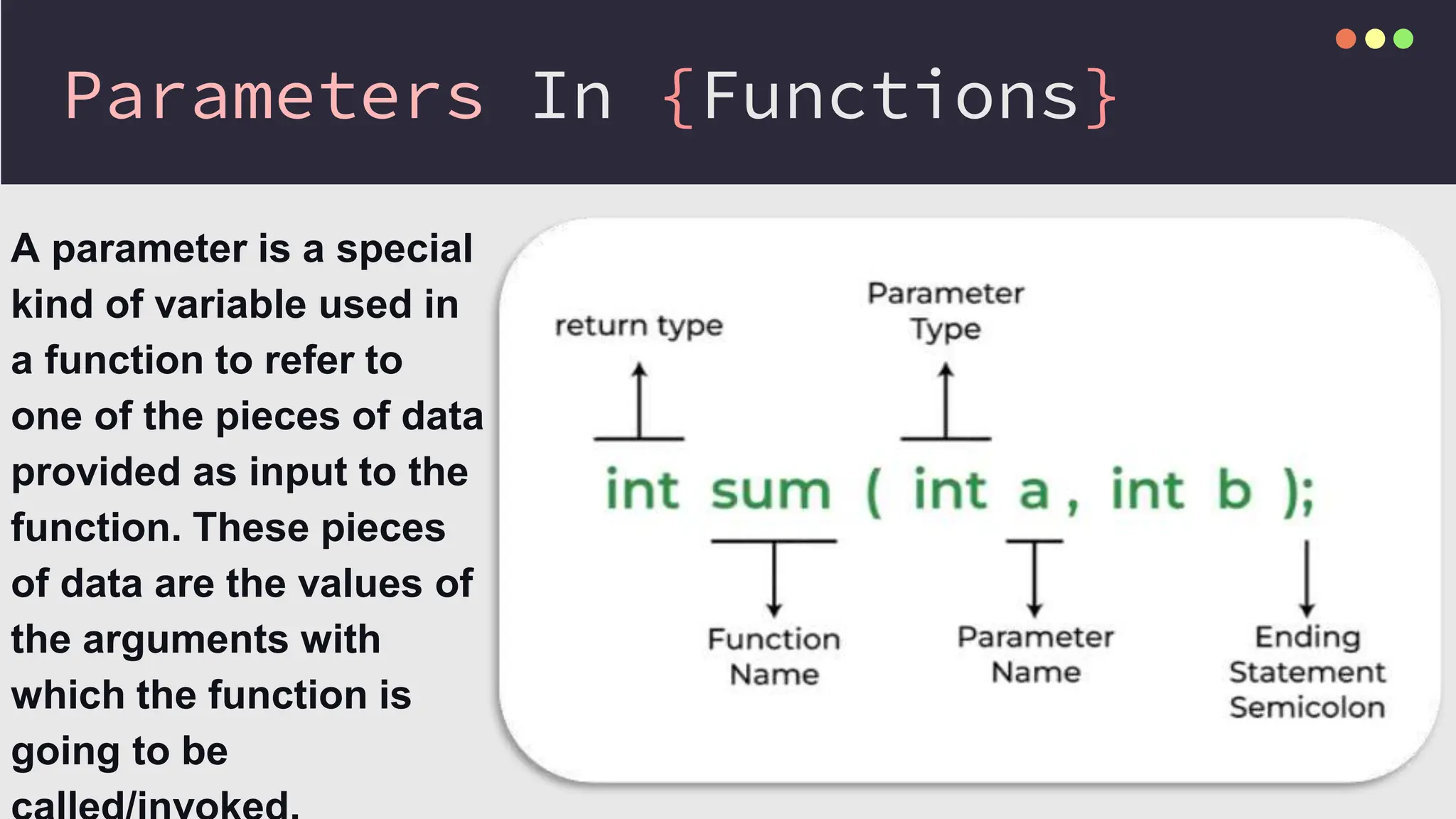
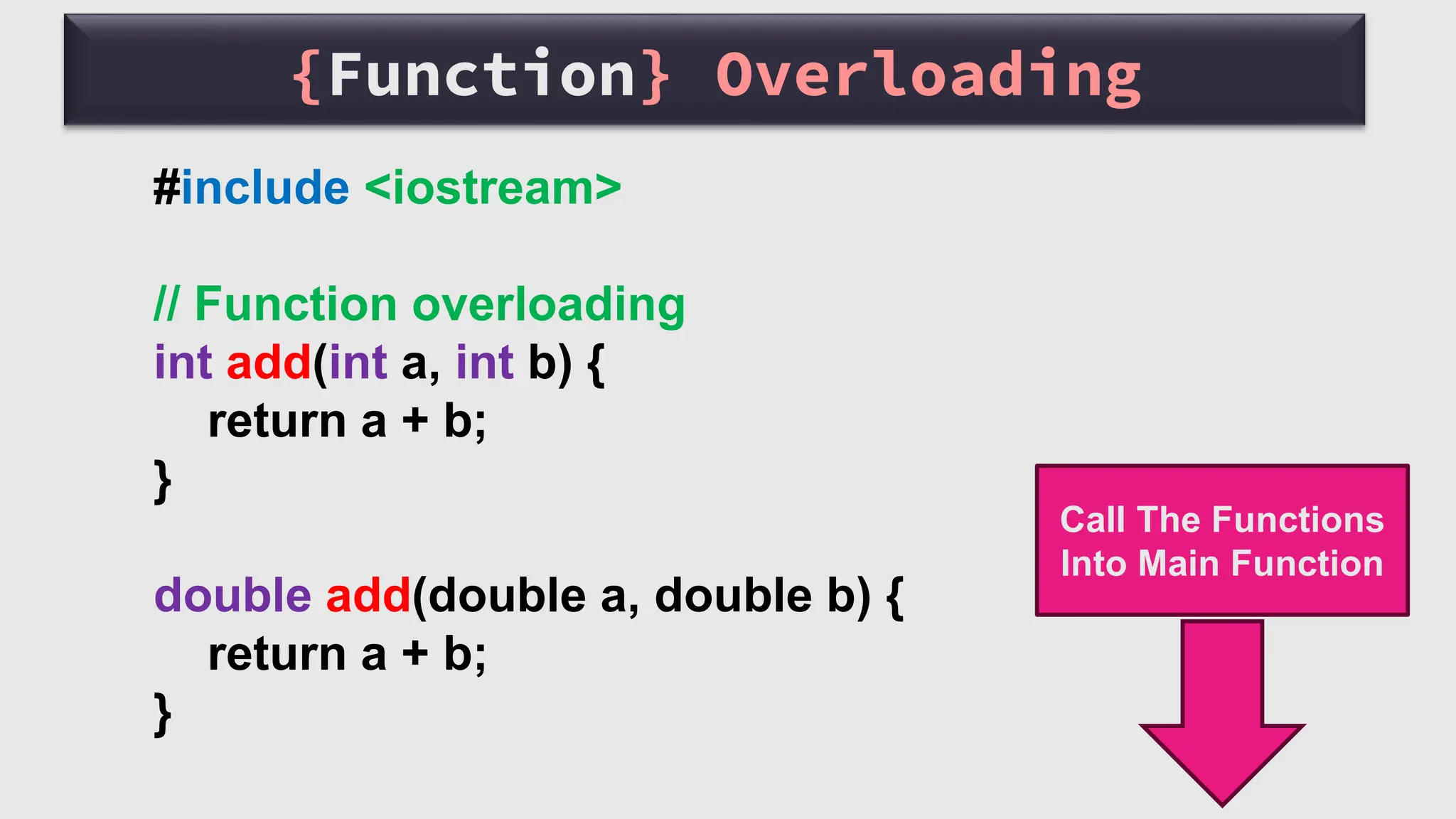
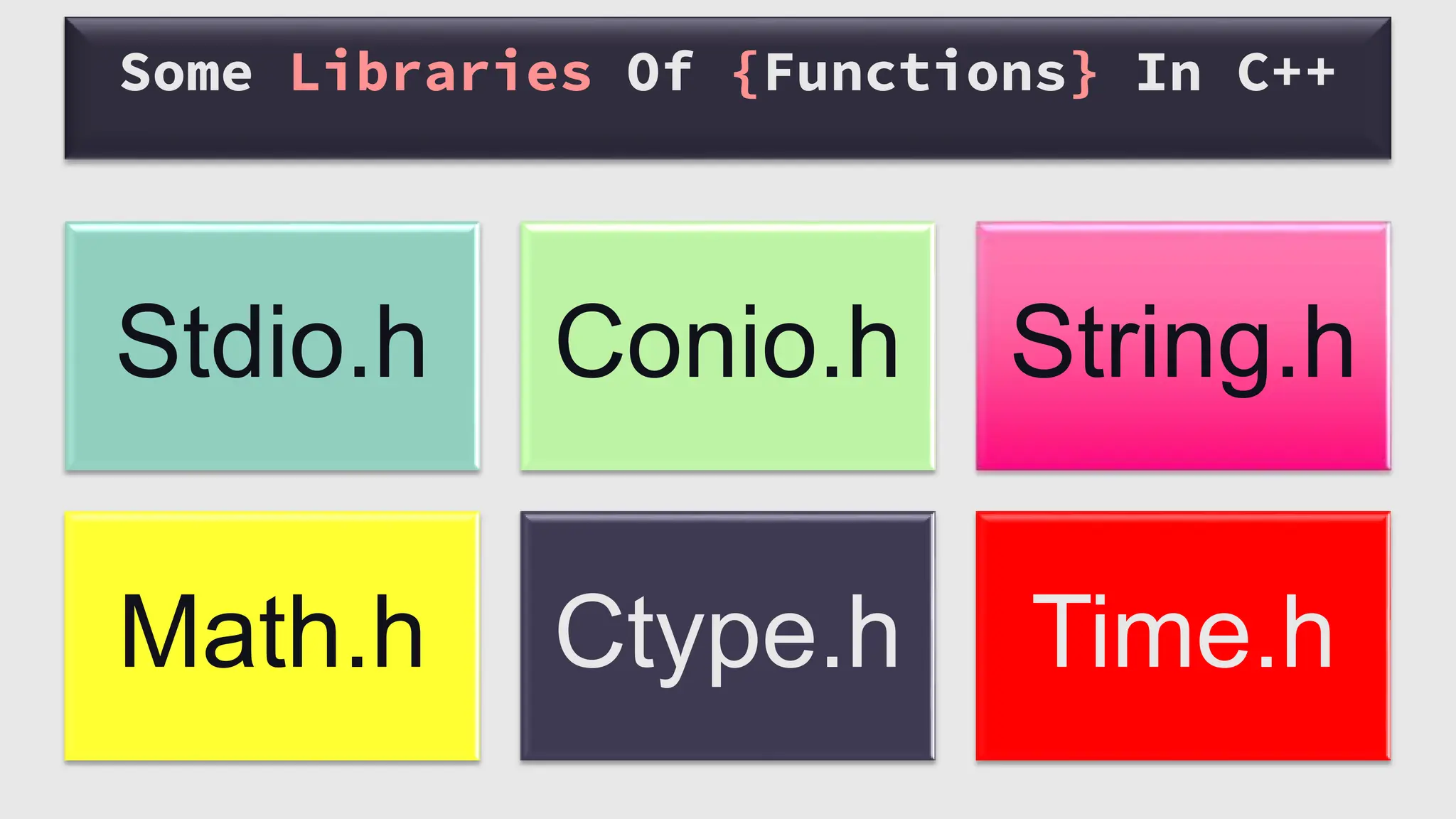
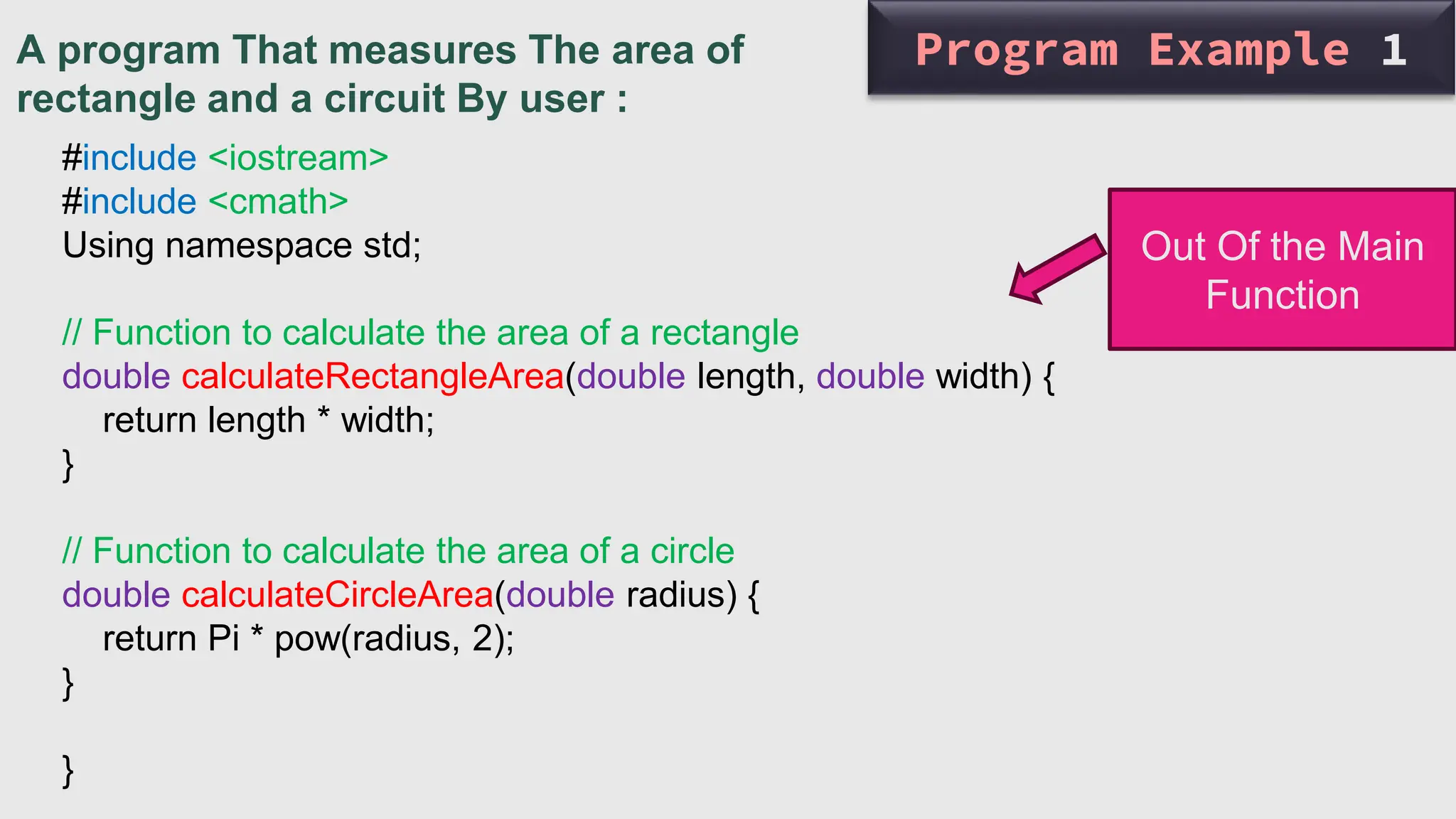
The document provides an overview of functions in C++, including topics such as declaration, definition, parameters, default arguments, and function overloading. It includes practical examples demonstrating how to implement functions for calculating areas of geometric shapes and working with strings. Key libraries related to functions in C++ are also listed.






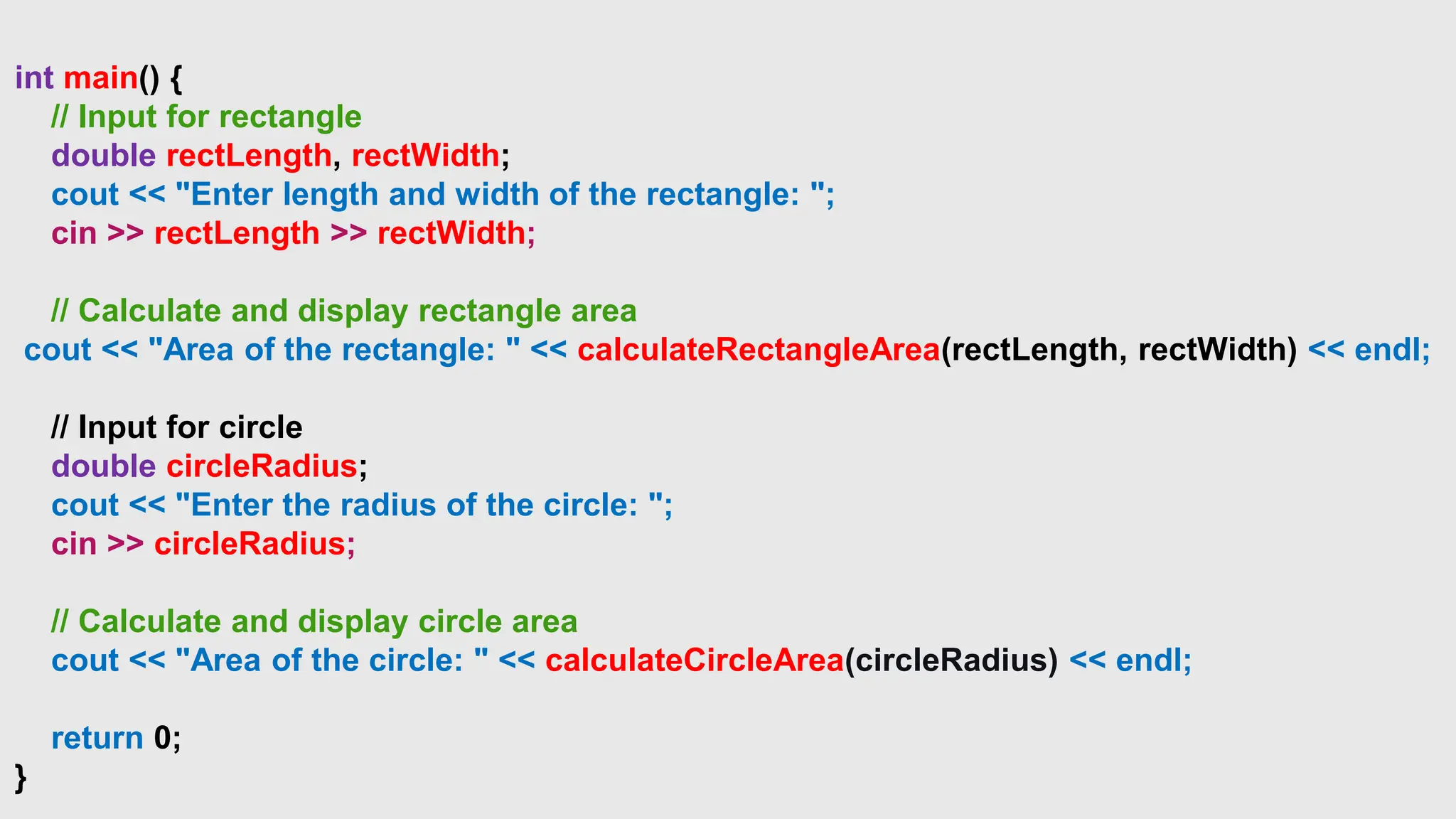

![// Access individual characters in the string
cout << "First character: " << greeting[0] << endl;
cout << "Last character: " << greeting.back() << endl;
// Check if the string is empty
if (greeting.empty()) {
cout << "The string is empty." << endl;
} else {
cout << "The string is not empty." << endl;
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionsic-240421201831-93a290b1/75/Functions-in-C-programming-language-pptx-17-2048.jpg)

