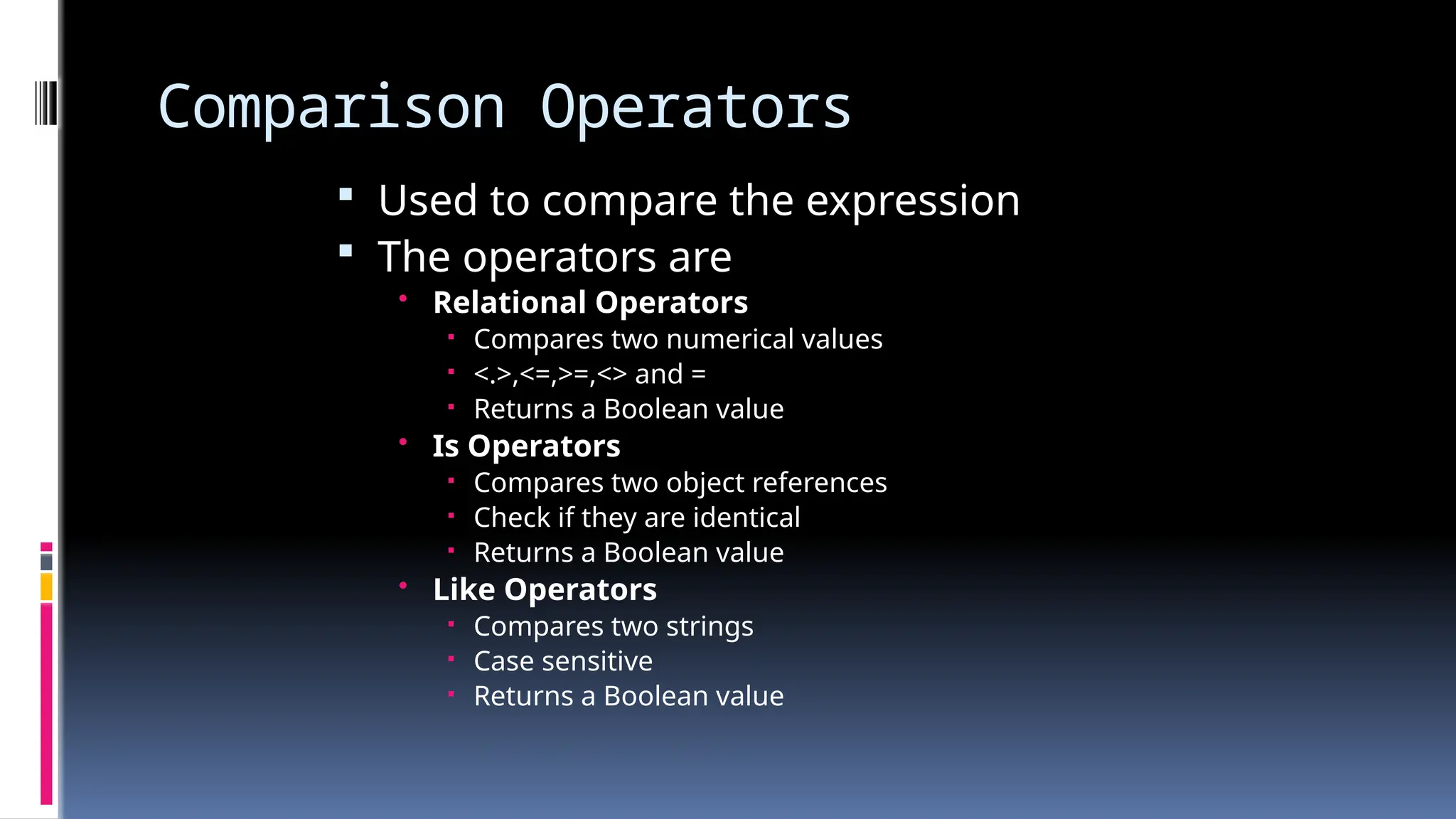
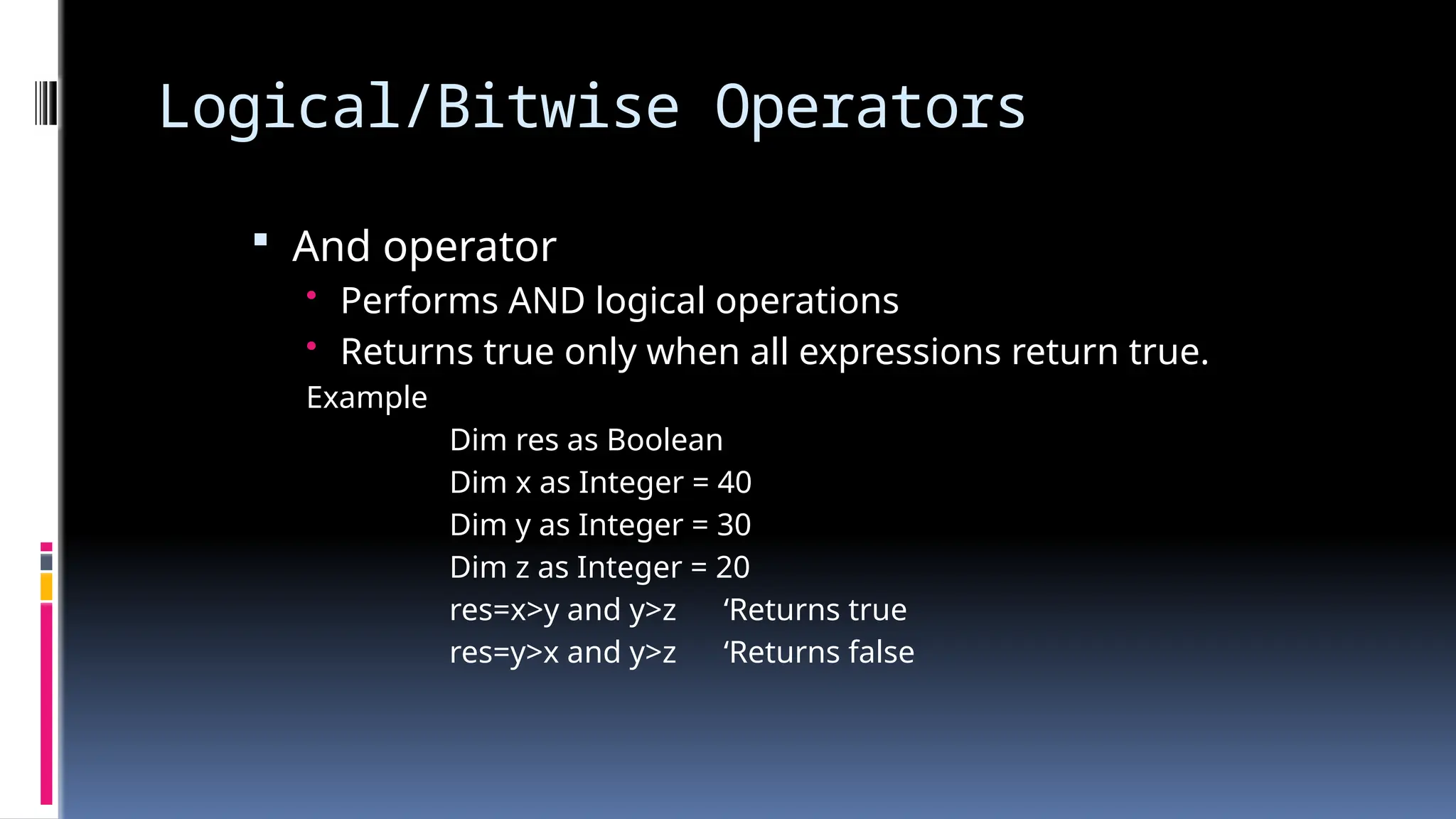
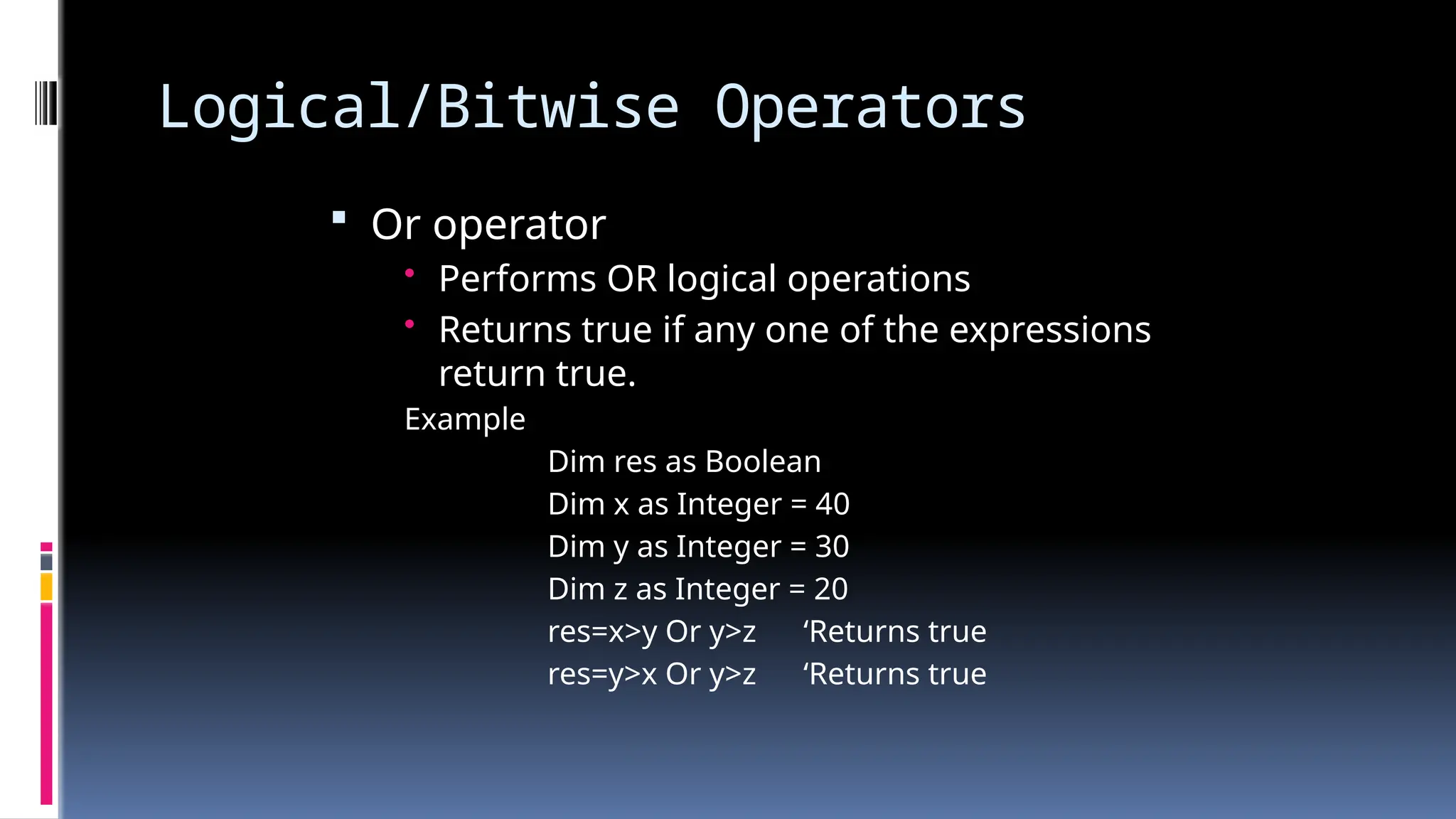
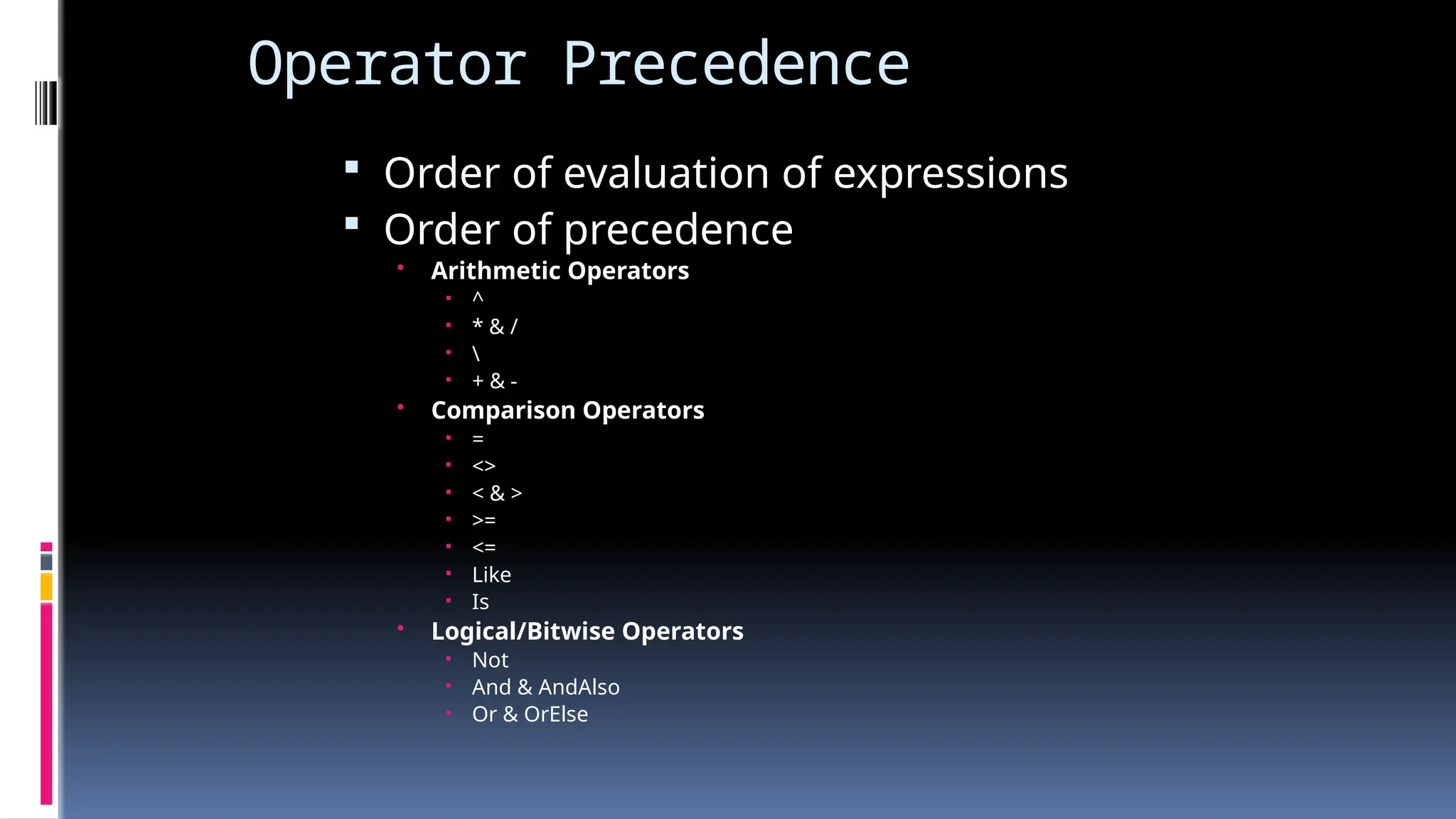
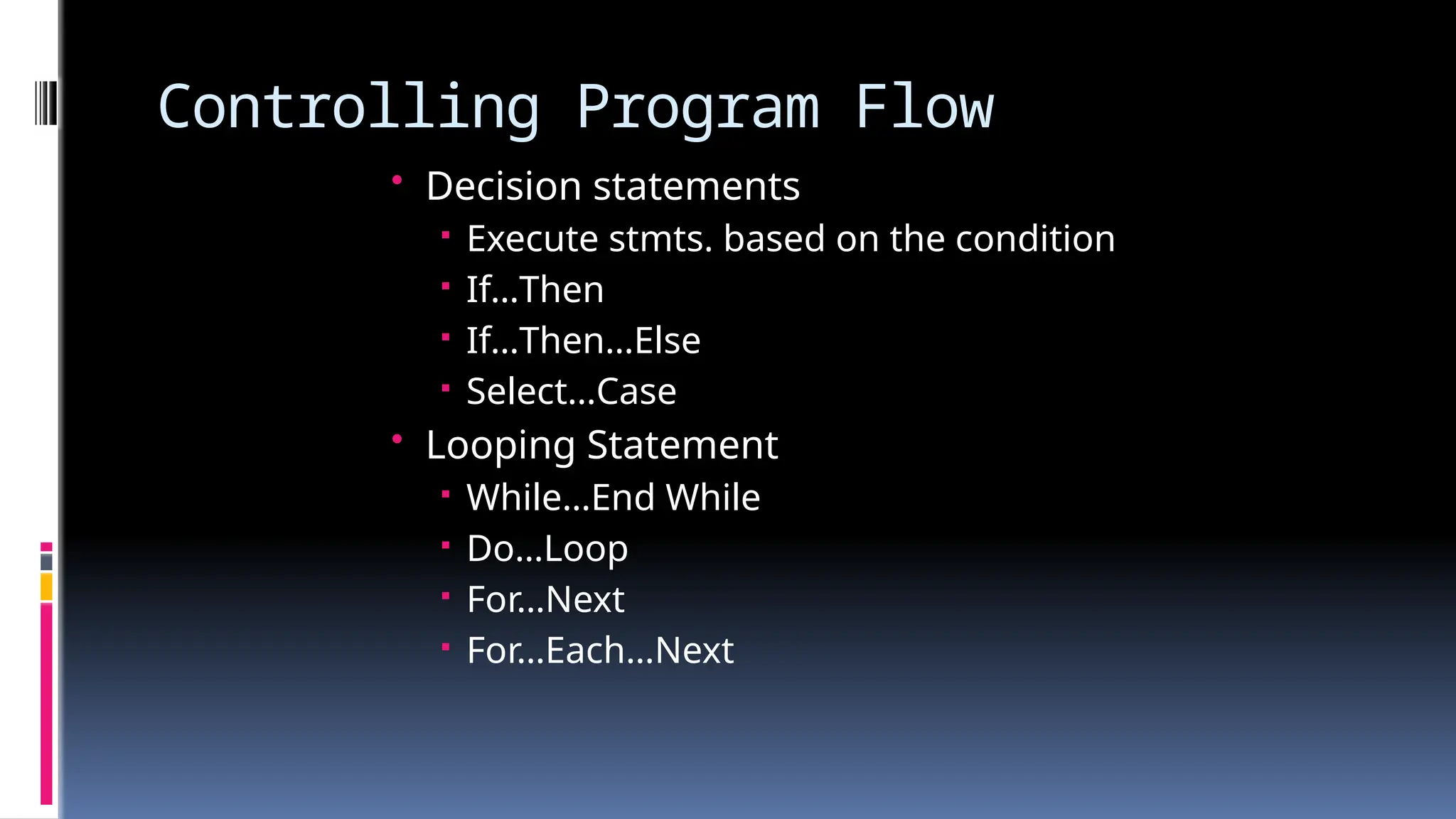
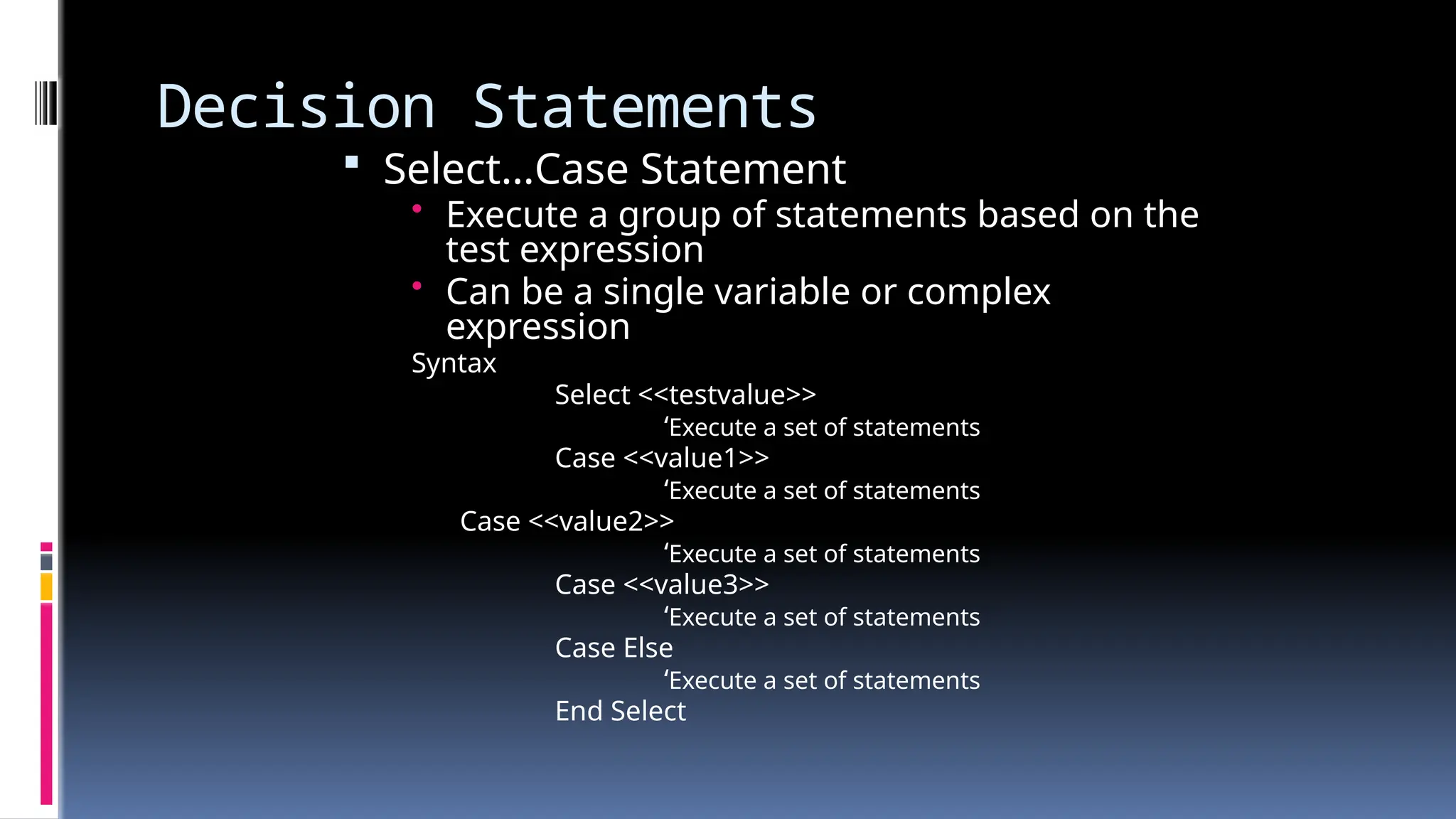
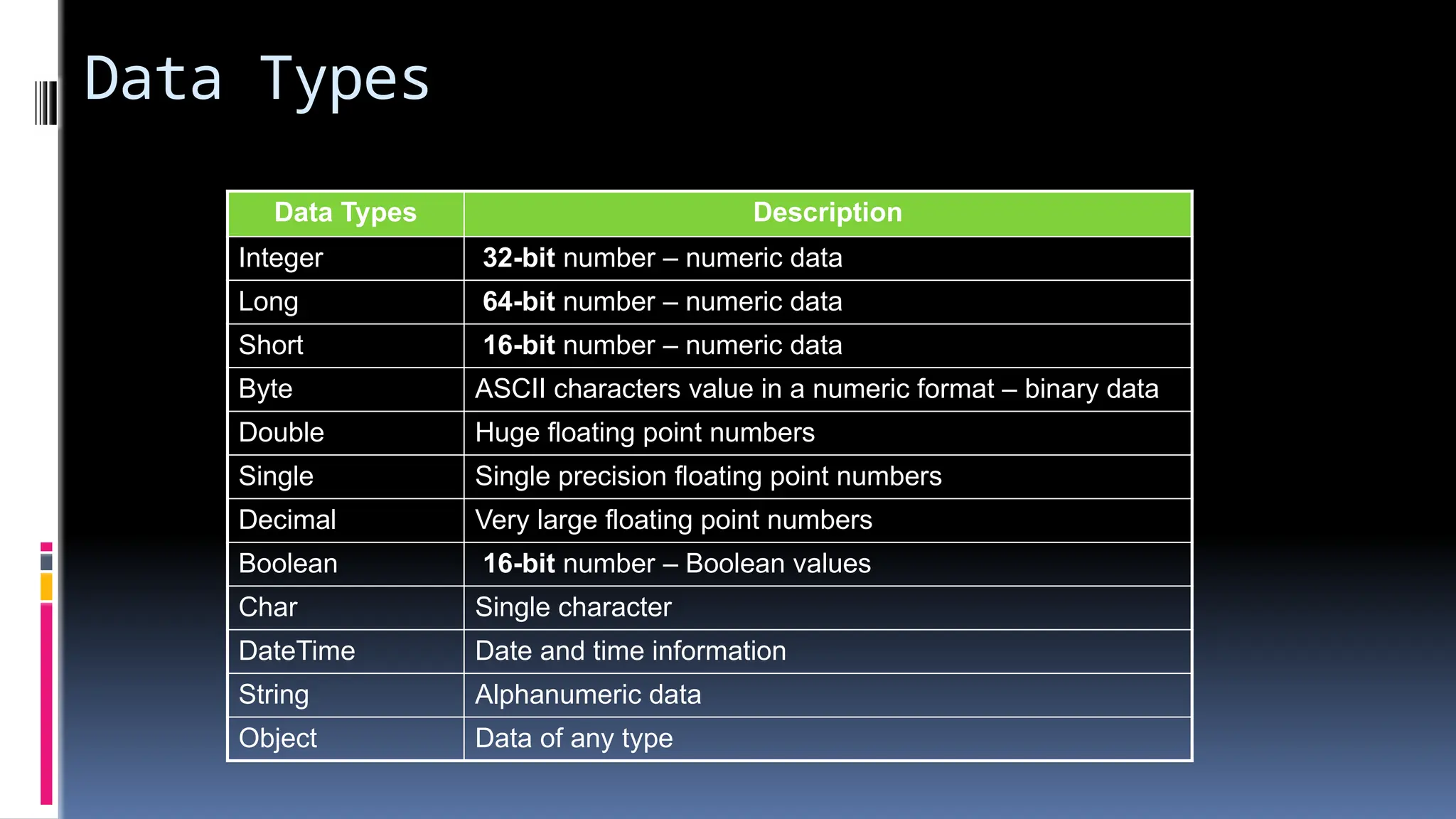
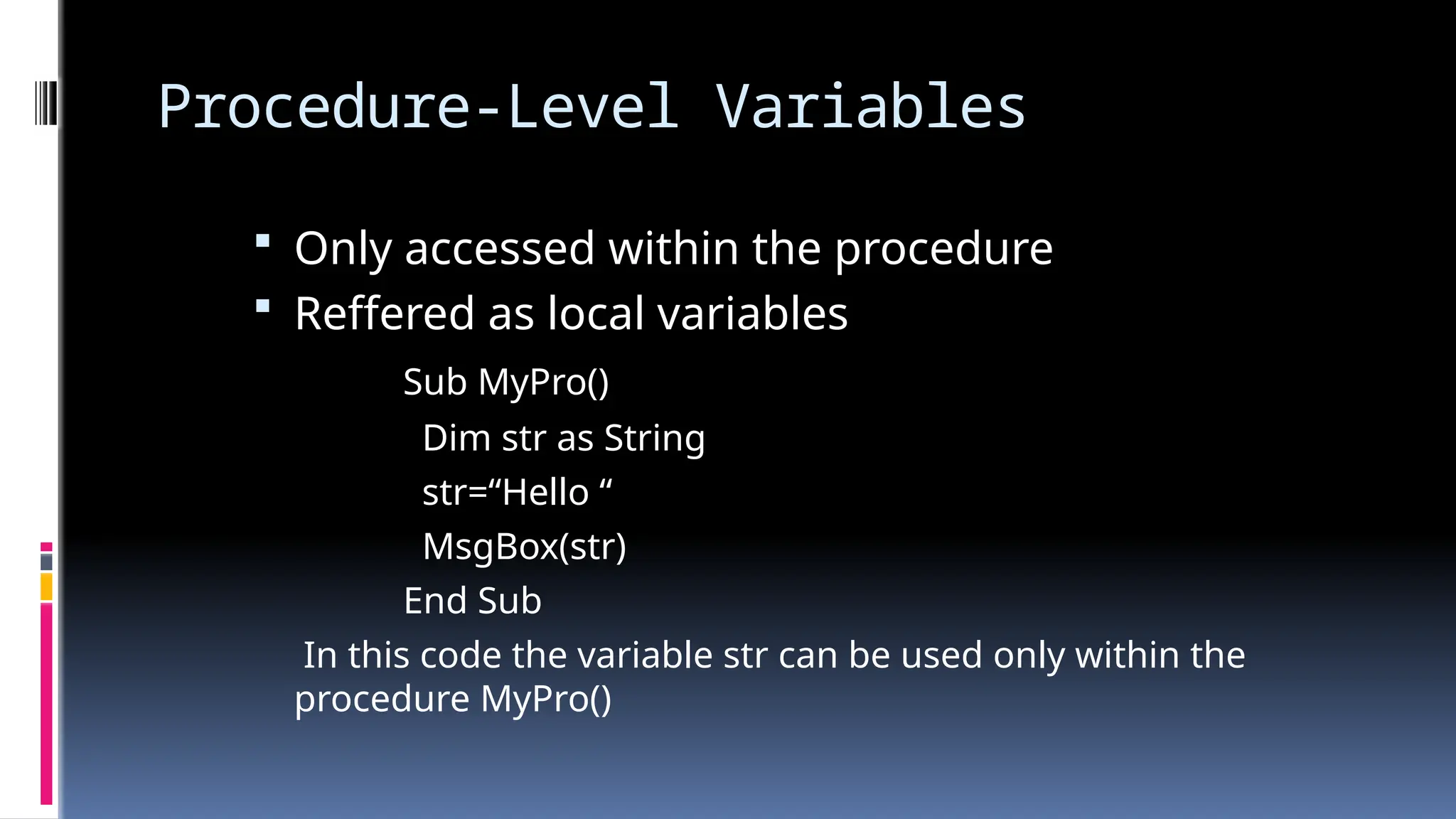
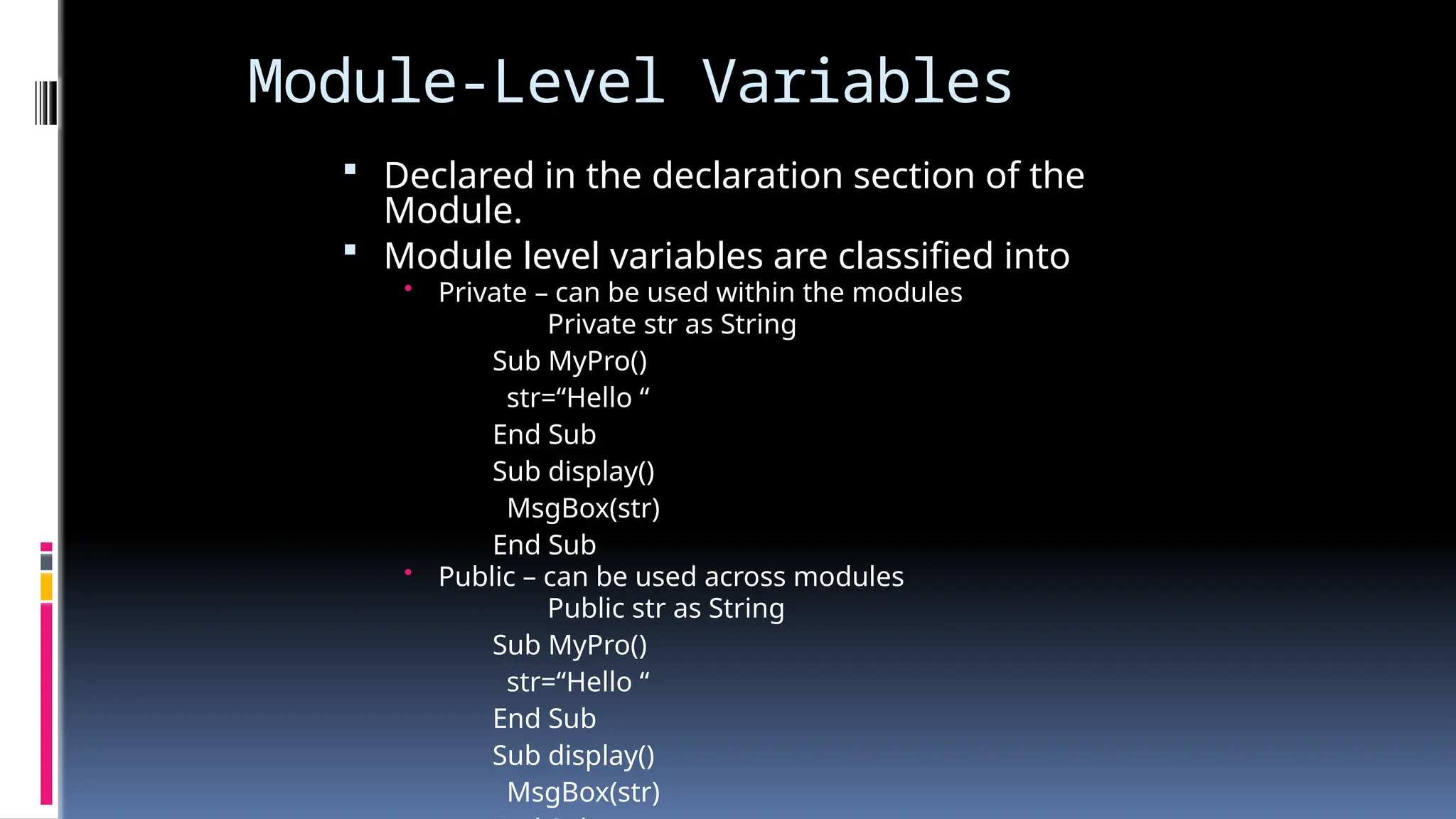
The document provides an overview of programming fundamentals in VB.NET, covering topics such as variables, constants, data types, operators, and control flow structures. It explains how to declare and initialize variables, the rules for naming them, and the different types of operators for mathematical and logical operations. Additionally, it discusses decision-making and looping constructs used to control program flow effectively.



![Declaring Variables
Dim statement is used to declare a
variable
Syntax
Dim VariableName [As type]
VariableName – name of the variable
type – data type
Declaration
Dim ivar
Dim svar=“Hello”
Dim ivar1,ivar2 as integer
Initialization
Dim ivar as Integer
ivar=25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentals-250130061210-b38ffb88/75/Fundamentals-of-Net-Programming-concepts-5-2048.jpg)


![Explicit declaration
Can be declared implicitly as well as
explicitly
Without declaring a variable ,if it is
used it is implicitly declared
Example
InCo=20*5
Option Explicit [on|off]
On – explicit declaration
Off – implicit declaration
Default - on](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentals-250130061210-b38ffb88/75/Fundamentals-of-Net-Programming-concepts-8-2048.jpg)

![Declaring Constants
Const Keyword is used to declare a
constant
Syntax
Const ConstantName [As type]
ConstantName – name of the constant
type – data type
Example
Const cd as integer =25
Dim ivar as Integer
if ivar =1000 then
MessageBox.show(“Discount offered is “ & cd &
“%”)
End if](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentals-250130061210-b38ffb88/75/Fundamentals-of-Net-Programming-concepts-12-2048.jpg)