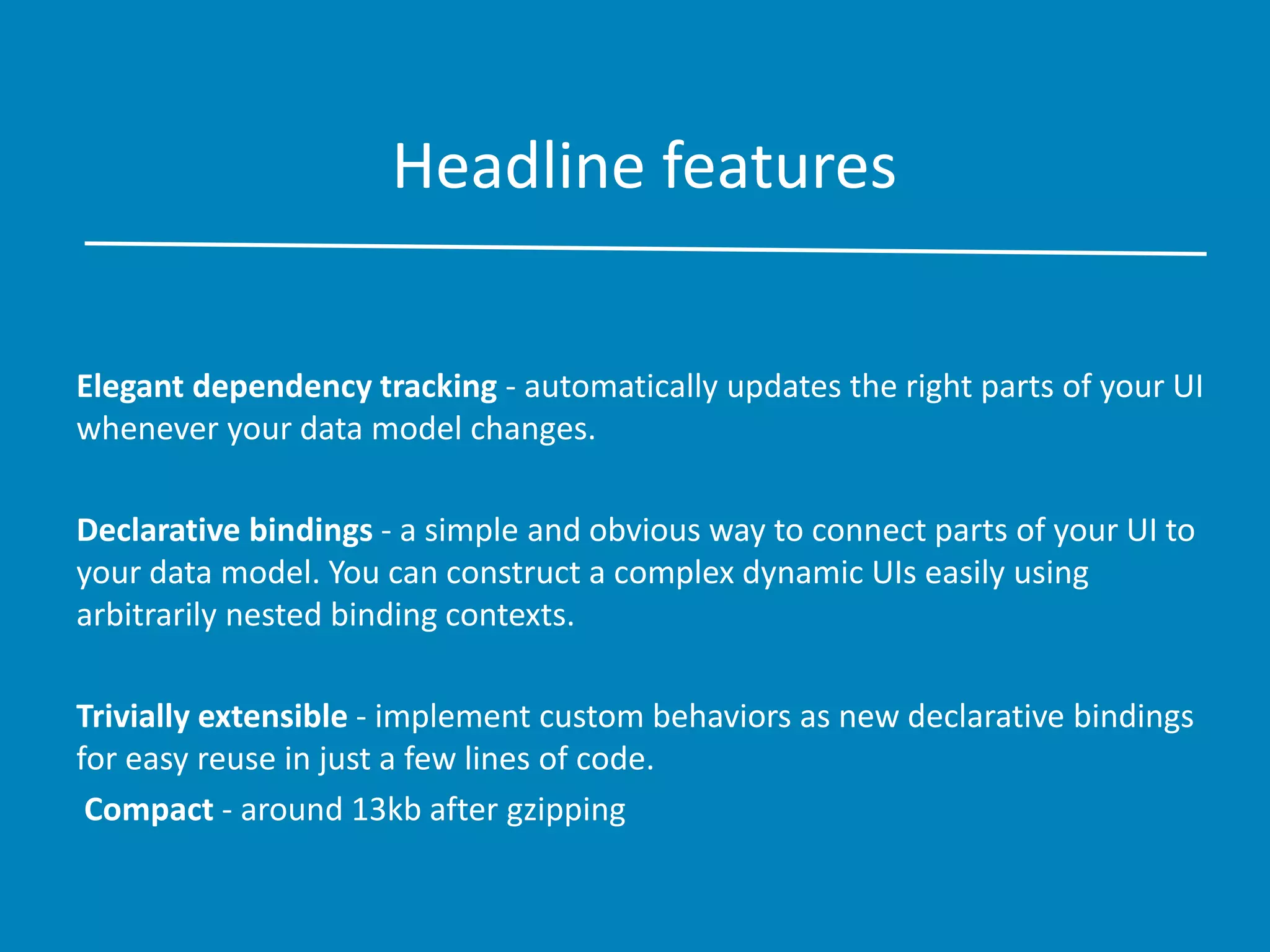
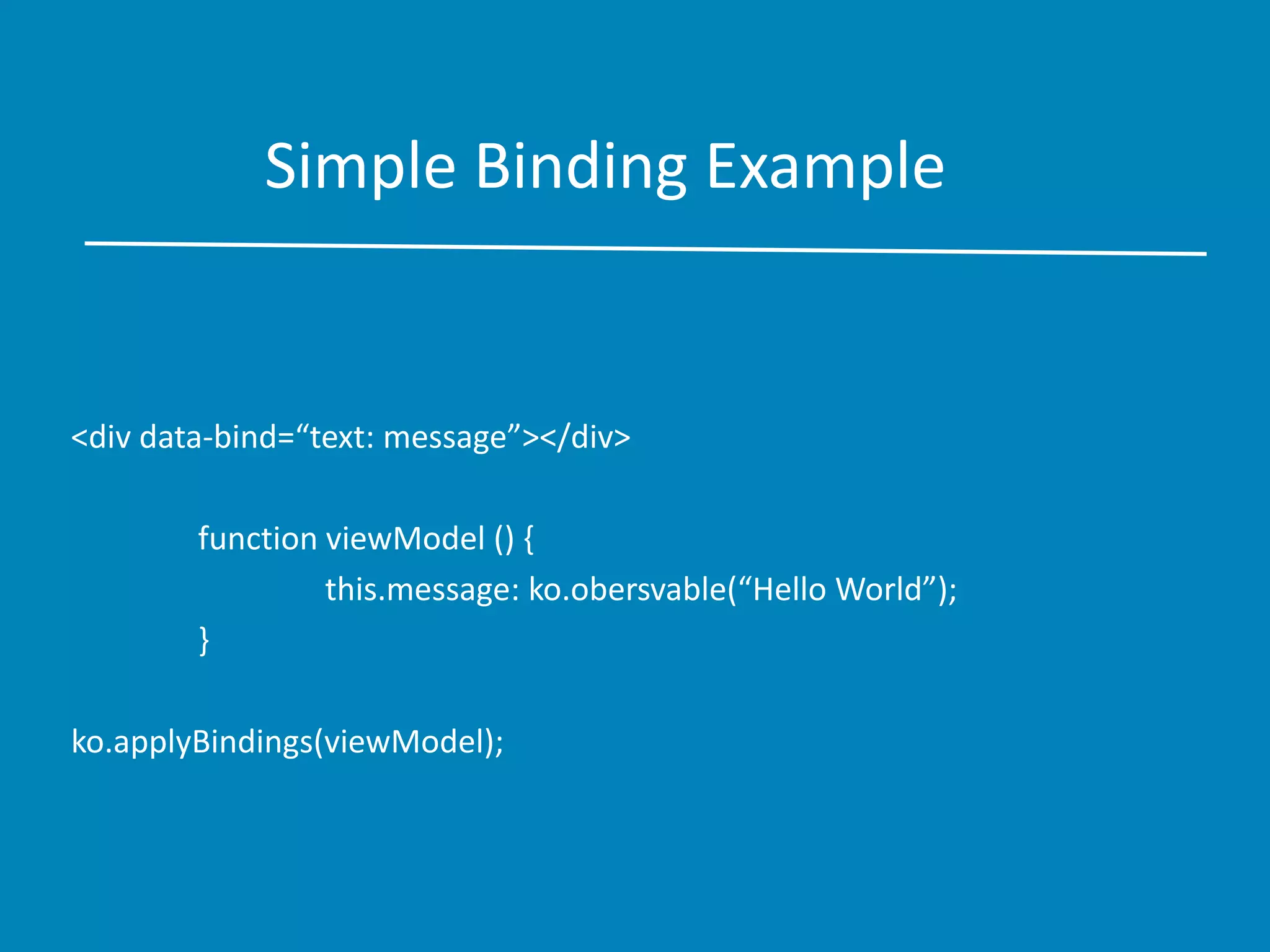
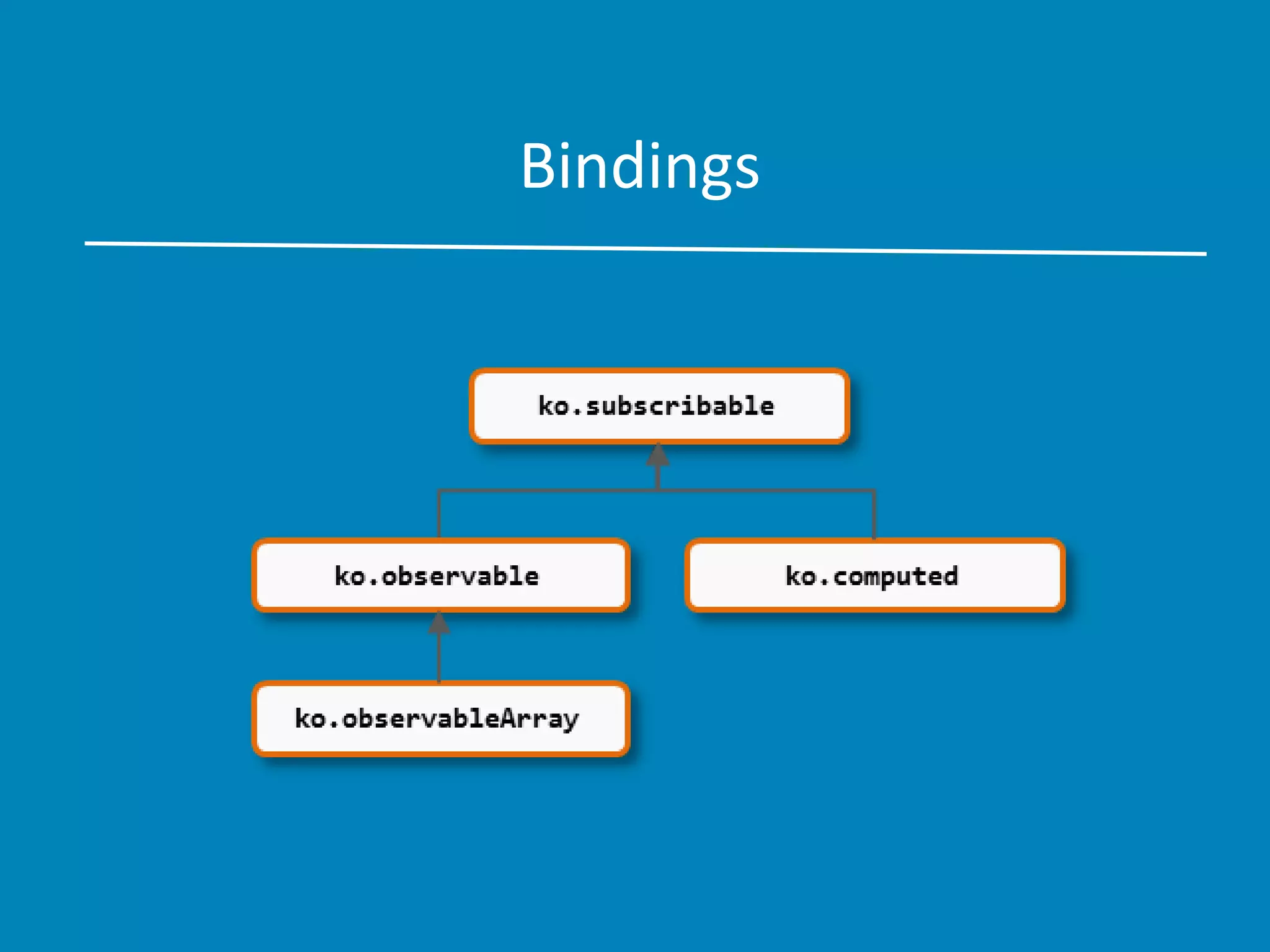
This document provides an overview of Knockout.js, emphasizing its application of the MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) pattern for creating responsive user interfaces. It details the advantages of using Knockout.js, such as its elegant dependency tracking, declarative bindings, and ease of extensibility, while also offering examples of common bindings and templates. Additionally, it covers testing and validation aspects, encouraging developers to experiment with the library.











![Control Flow Bindings - foreach
<ul data-bind="foreach: people“>
<li> <p data-bind="text: firstName"></li>
<li> <p data-bind="text: lastName"> </li>
</ul>
ko.applyBindings({
people: [ { firstName: 'Bert', lastName: 'Bertington' },
{ firstName: 'Charles', lastName: 'Charlesforth' }]
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knockoutjs-140326151017-phpapp02/75/Fundaments-of-Knockout-js-21-2048.jpg)
![Control Flow Bindings - If
<ul data-bind="foreach: planets">
<li>Planet: <b data-bind="text: name"> </b>
<div data-bind="if: capital">
Capital: <b data-bind="text: capital.cityName"> </b></div>
</li>
</ul>
ko.applyBindings({
planets: [ { name: 'Mercury', capital: null },
{ name: 'Earth', capital: { cityName: 'Barnsley' } } ]
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knockoutjs-140326151017-phpapp02/75/Fundaments-of-Knockout-js-22-2048.jpg)



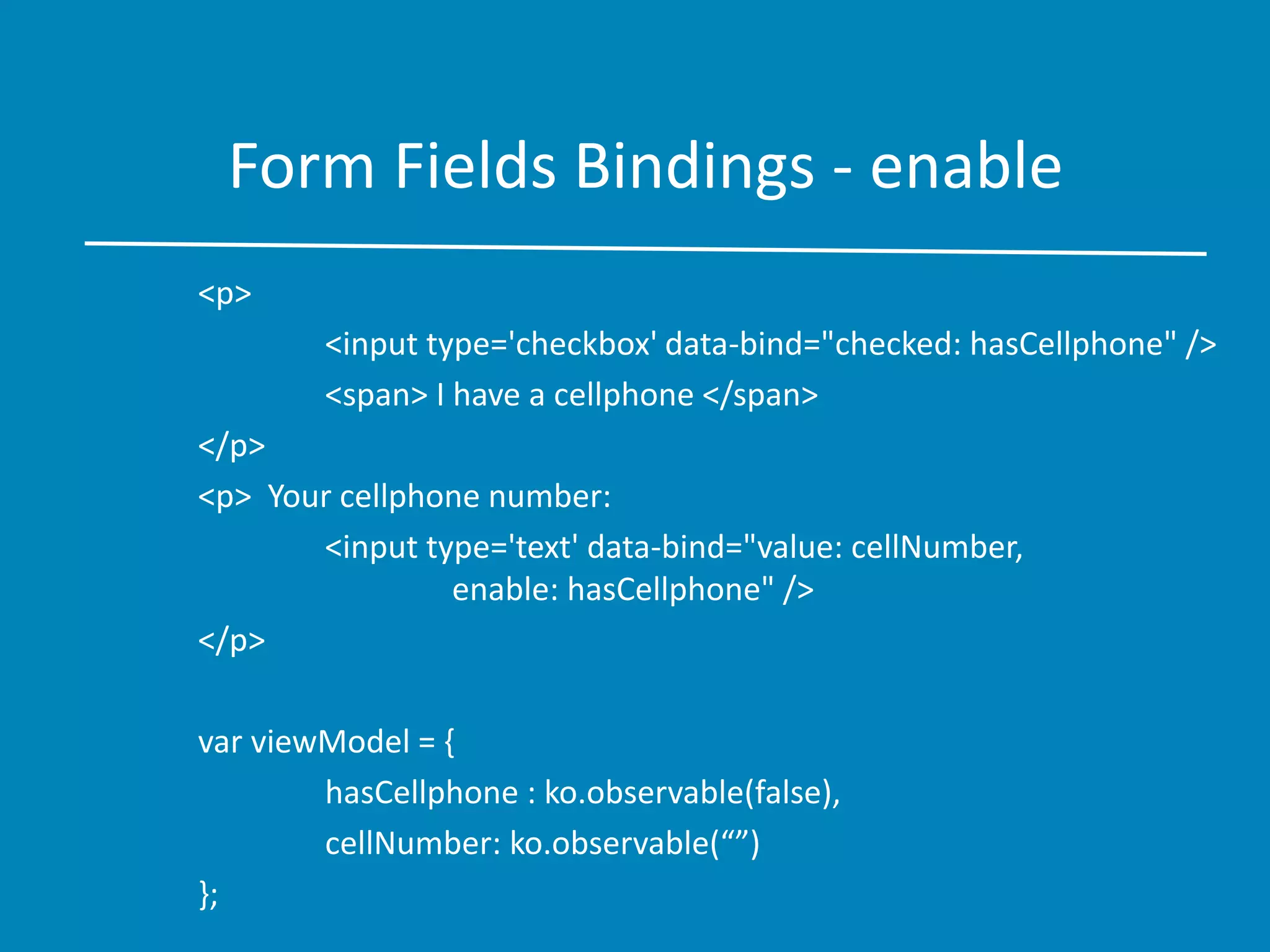

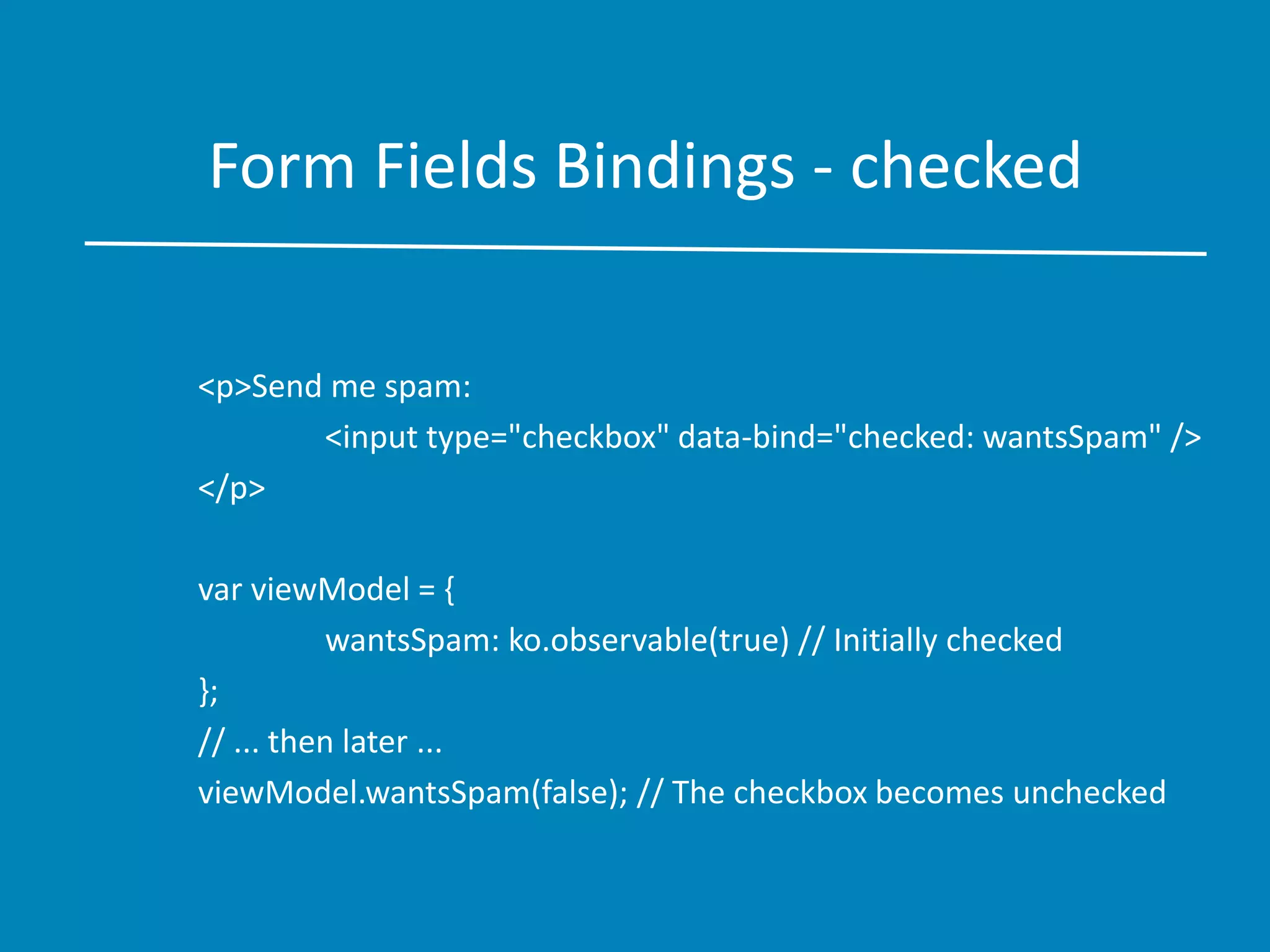

![Form Fields Bindings - options
<span>Destination country: </span>
<select data-bind="options: availableCountries"></select>
var viewModel = {
// These are the initial options
availableCountries: ko.observableArray(['France', 'Spain'])
};
// ... then later ...
viewModel.availableCountries.push('China'); // Adds another option](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knockoutjs-140326151017-phpapp02/75/Fundaments-of-Knockout-js-30-2048.jpg)