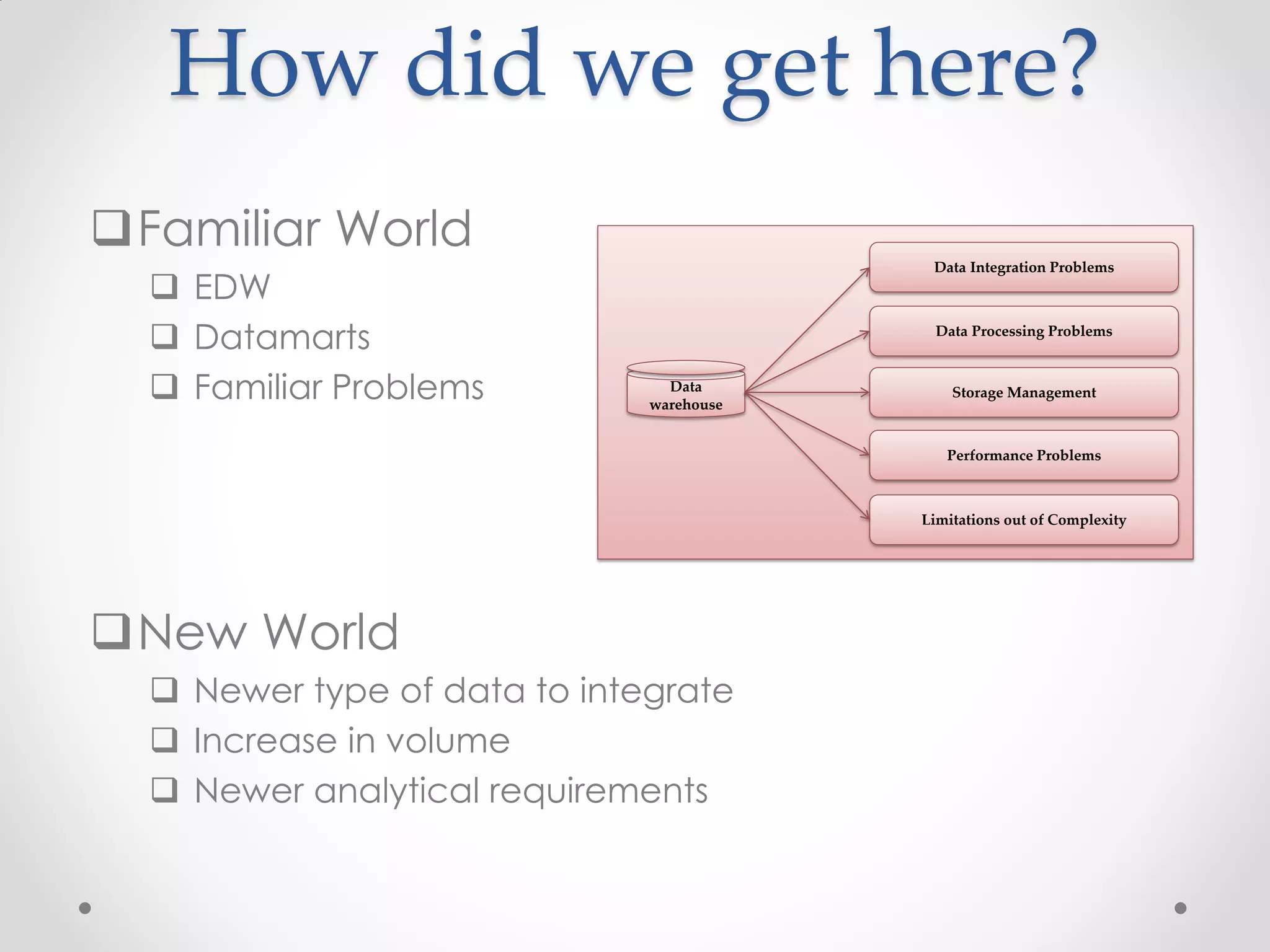
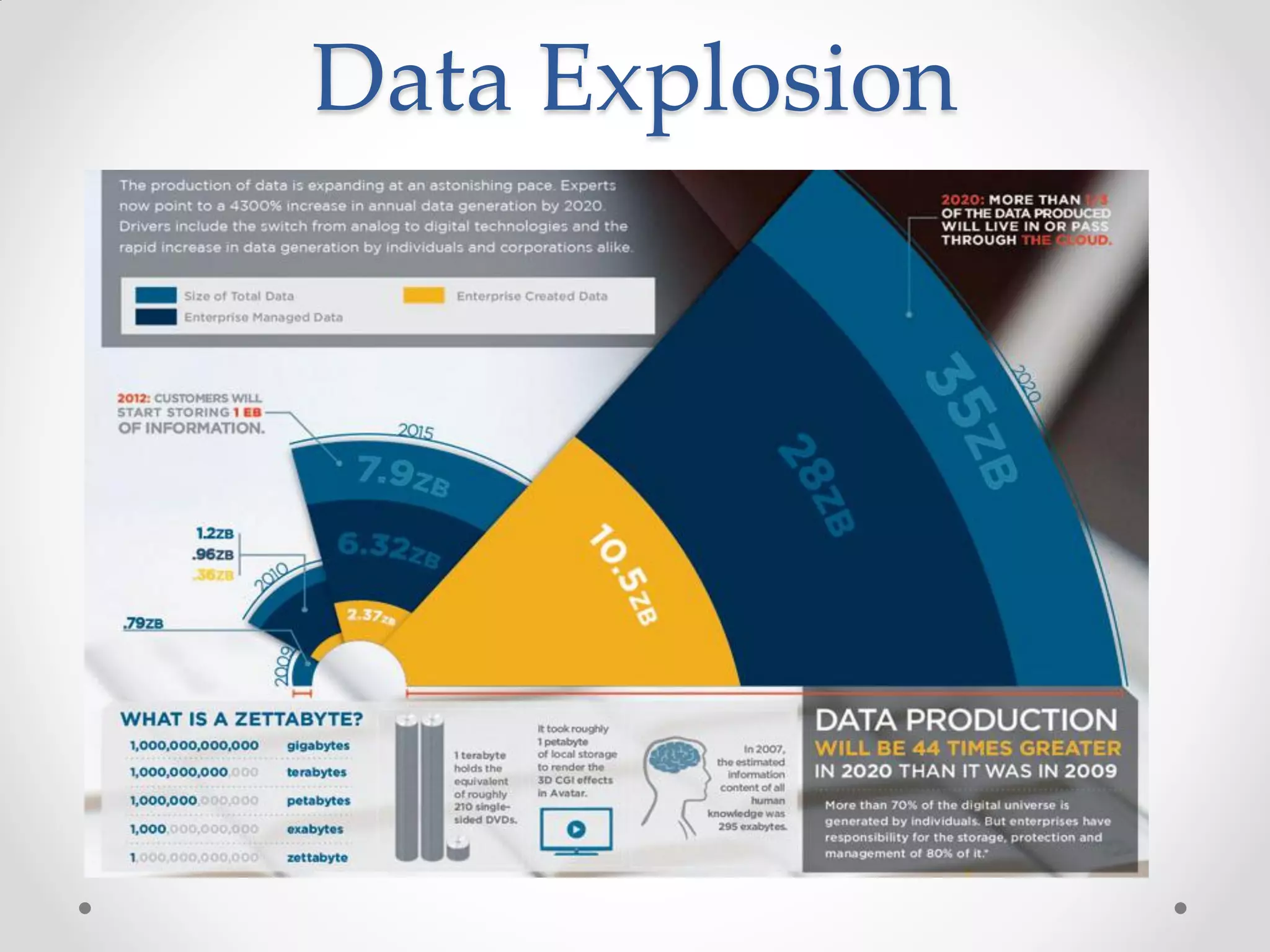
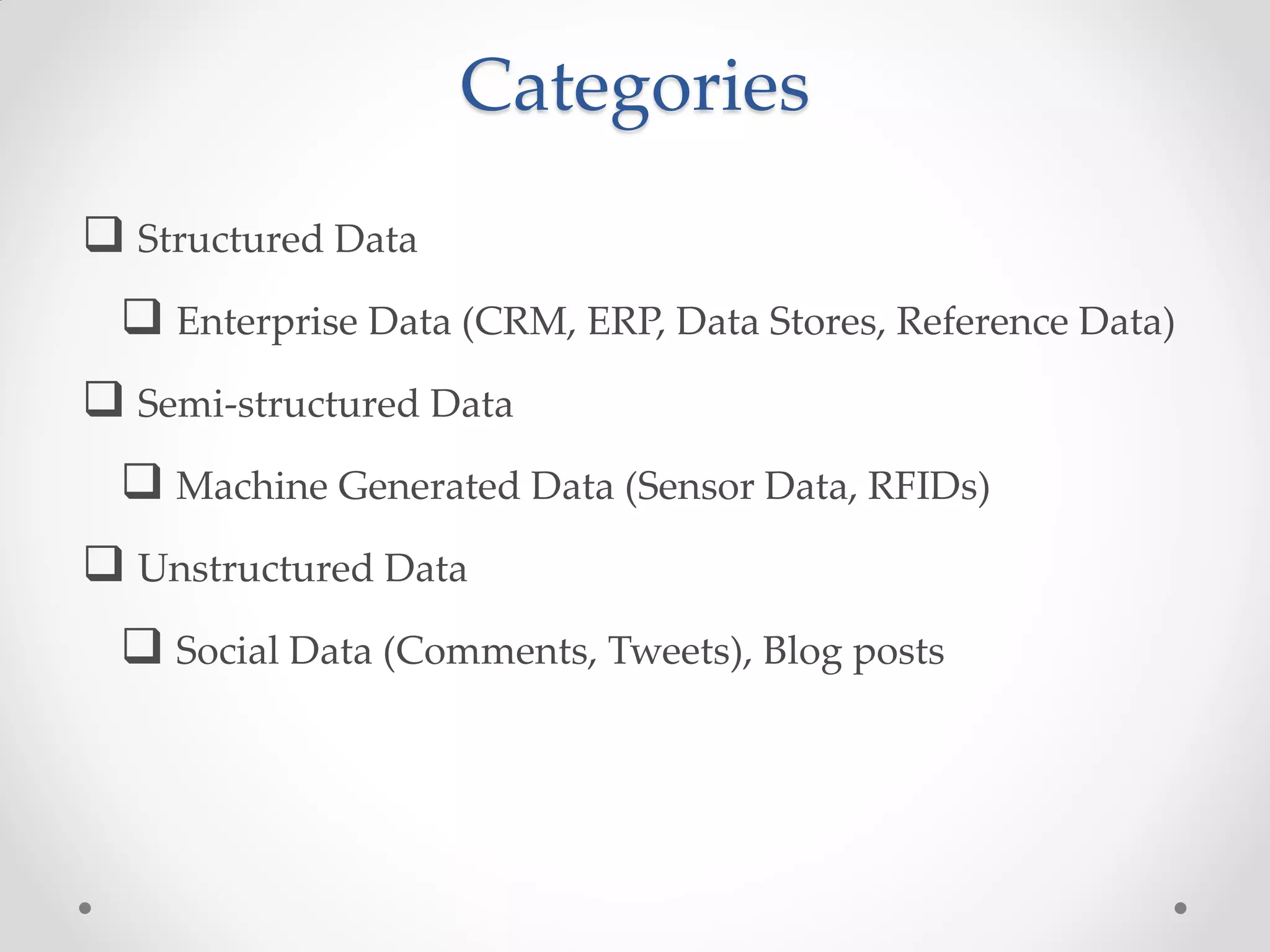
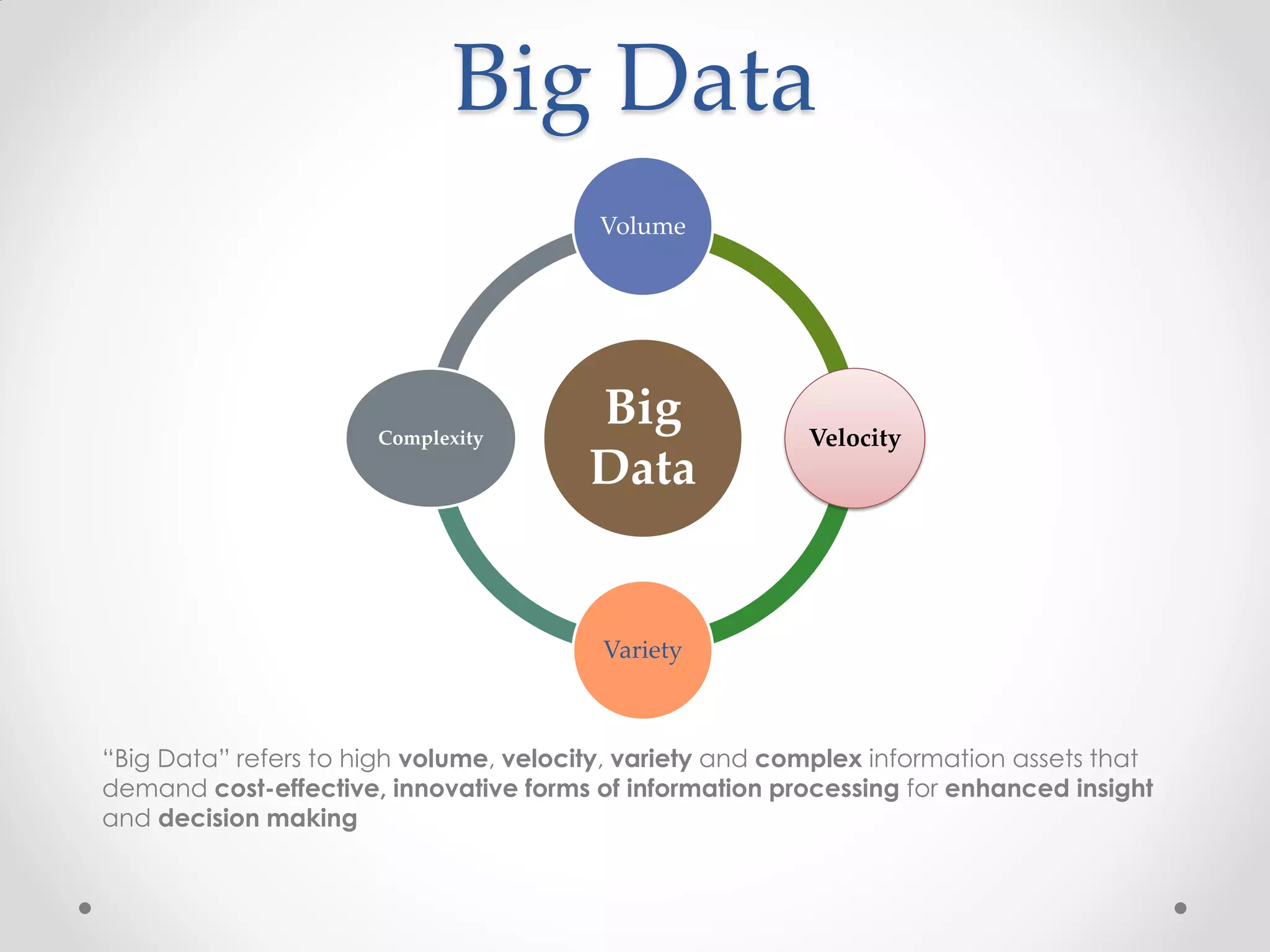
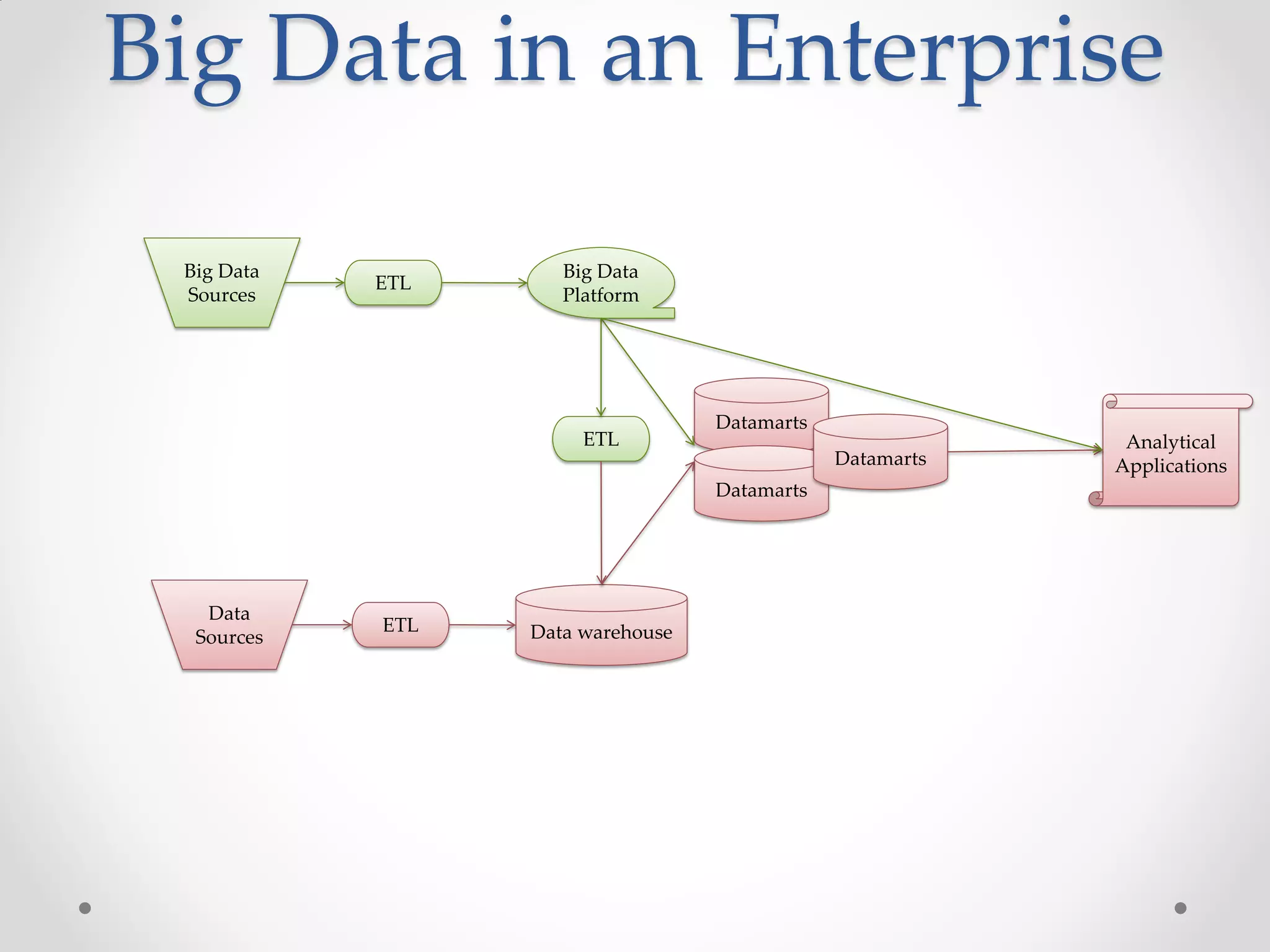
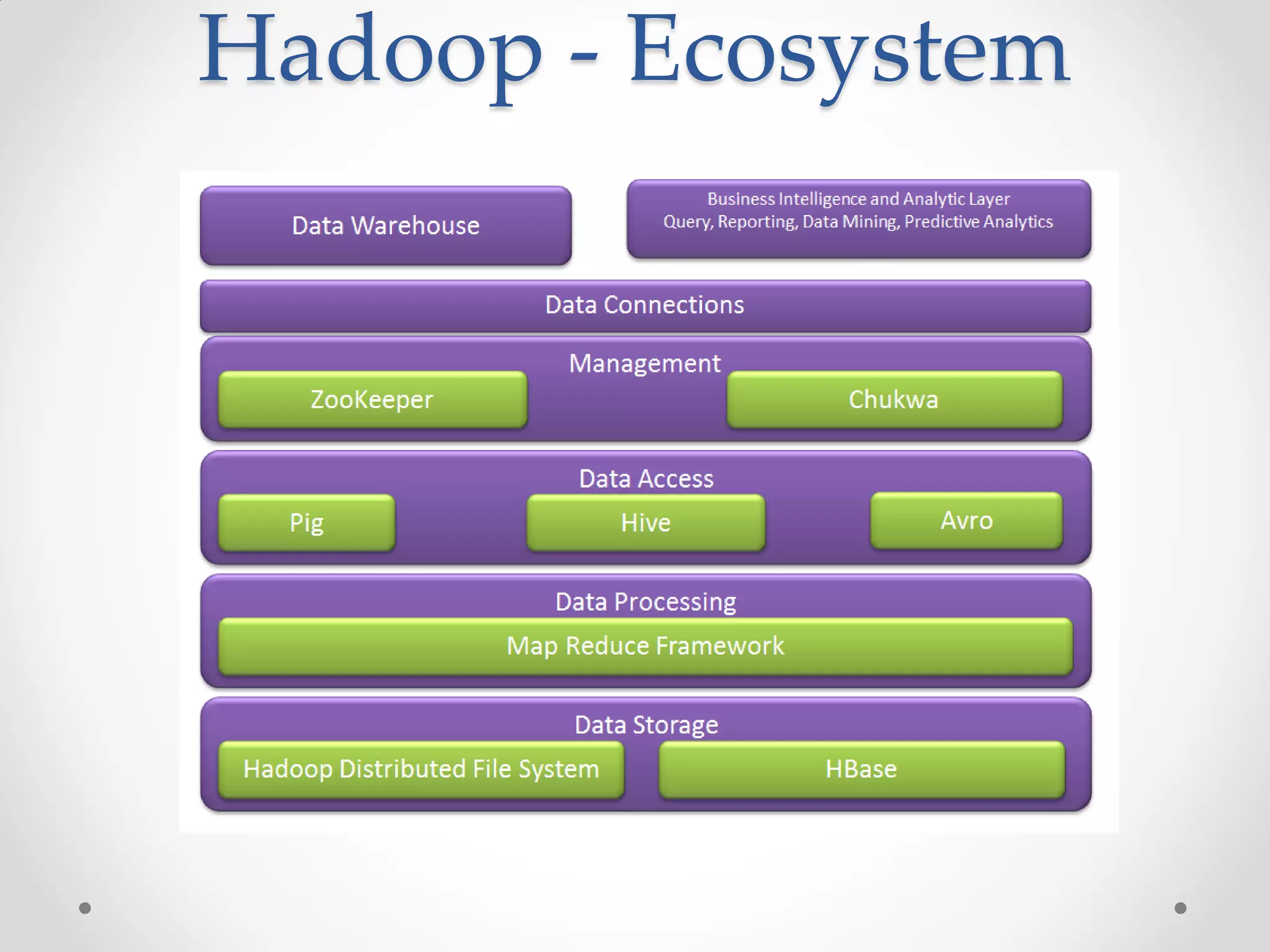
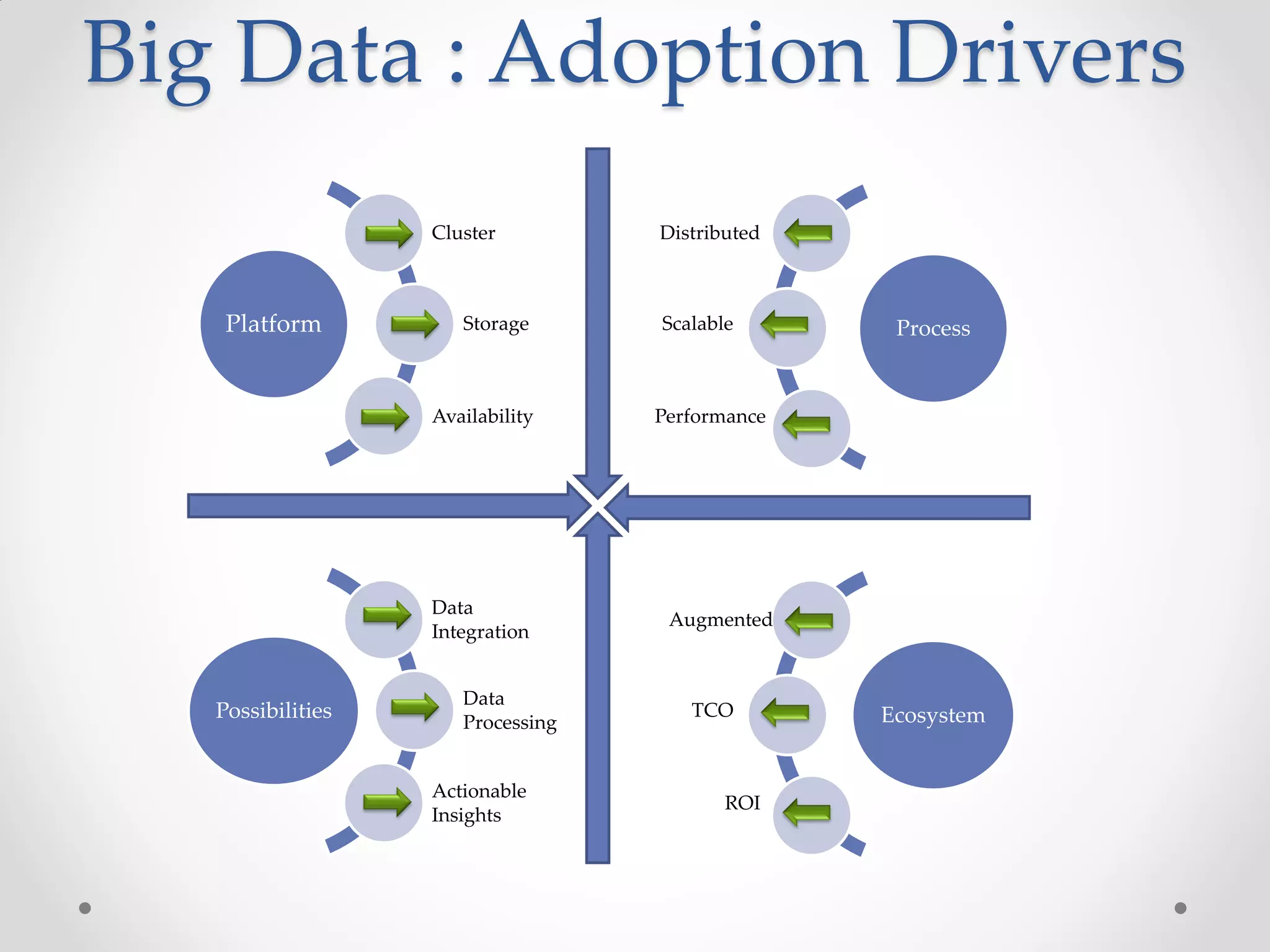
This document discusses big data and how enterprises are adopting big data solutions. It describes how data has exploded in terms of volume, velocity, and variety. Big data now includes structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from sources like sensors, social media, and machine logs. The document outlines how Hadoop has become a popular big data platform that provides scalable and cost-effective storage and processing of large, complex datasets. It also discusses how enterprises are using big data for applications like predictive analytics, social intelligence, and mobile analytics to drive insights and decisions.