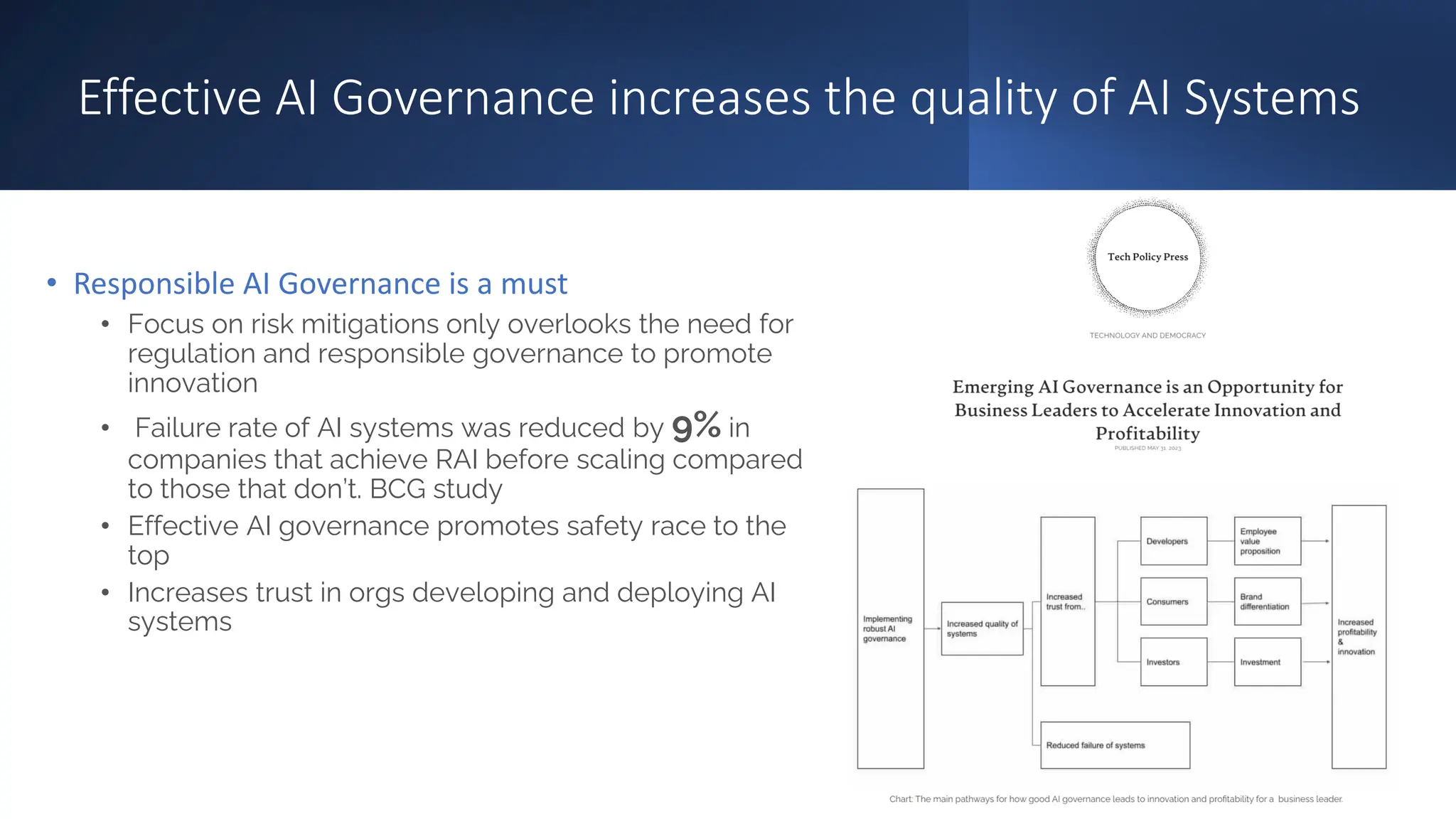
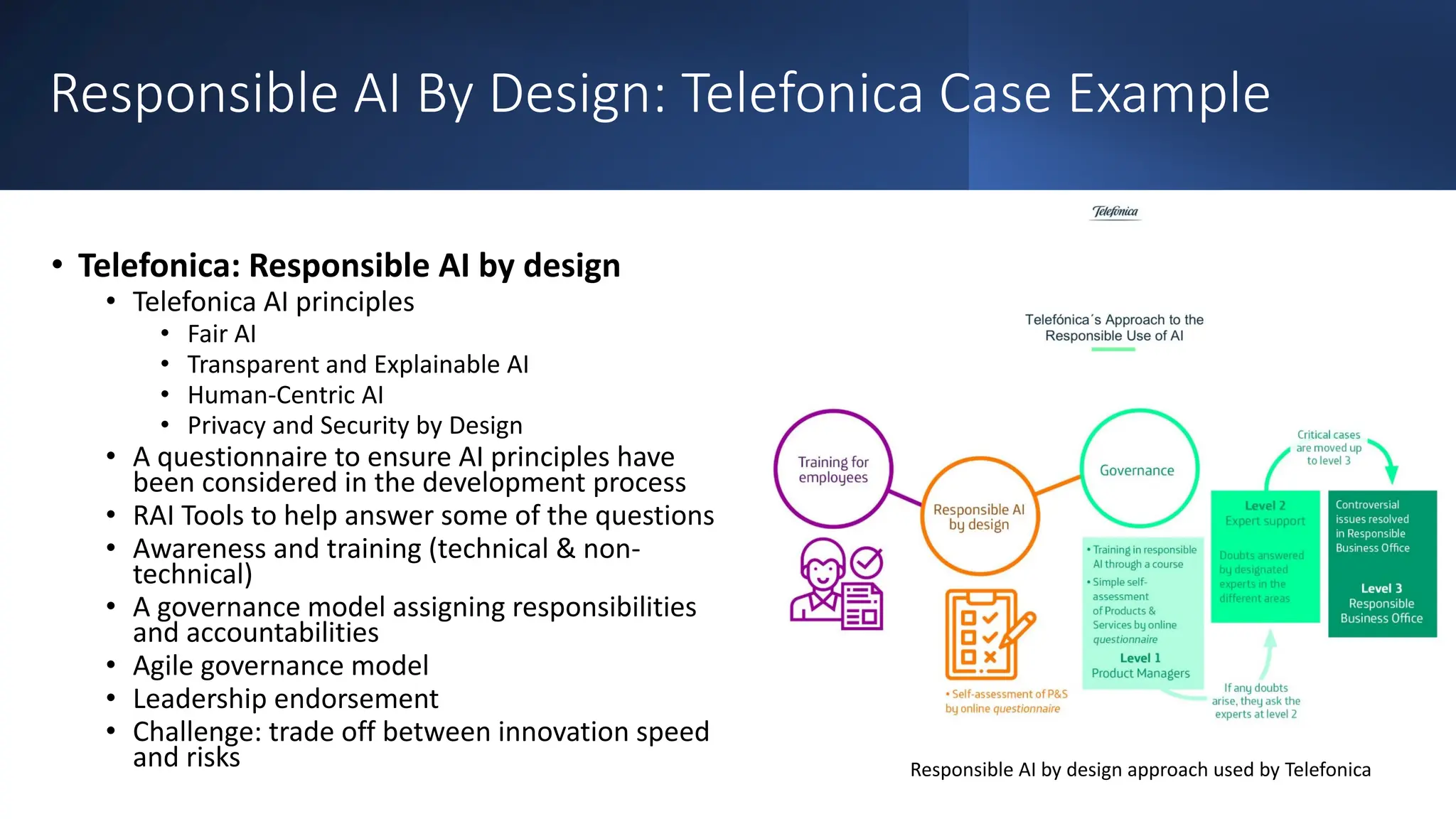
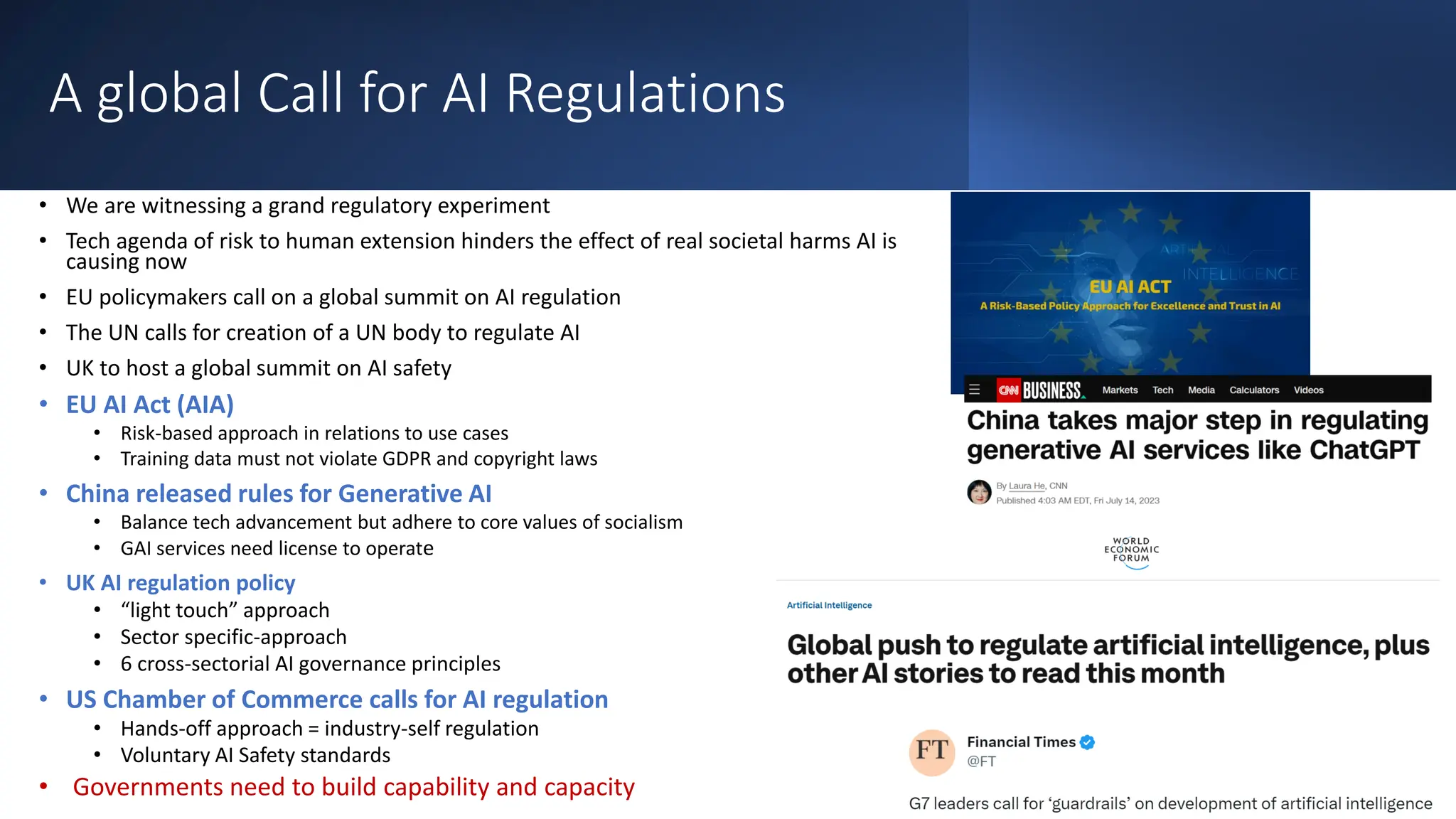
Generative AI: Responsible Path Forward
Dr. Saeed Aldhaheri discusses the potential and risks of generative AI and proposes a responsible path forward. He outlines that (1) while generative AI shows great economic potential and can augment human capabilities, it also poses new ethical risks if not developed responsibly. (2) Current approaches by the tech industry are not sufficient, and a human-centered perspective is needed. (3) Building responsible generative AI requires moving beyond technical solutions to address sociotechnical issues through principles of ethics by design, governance, risk frameworks, and responsible data practices.