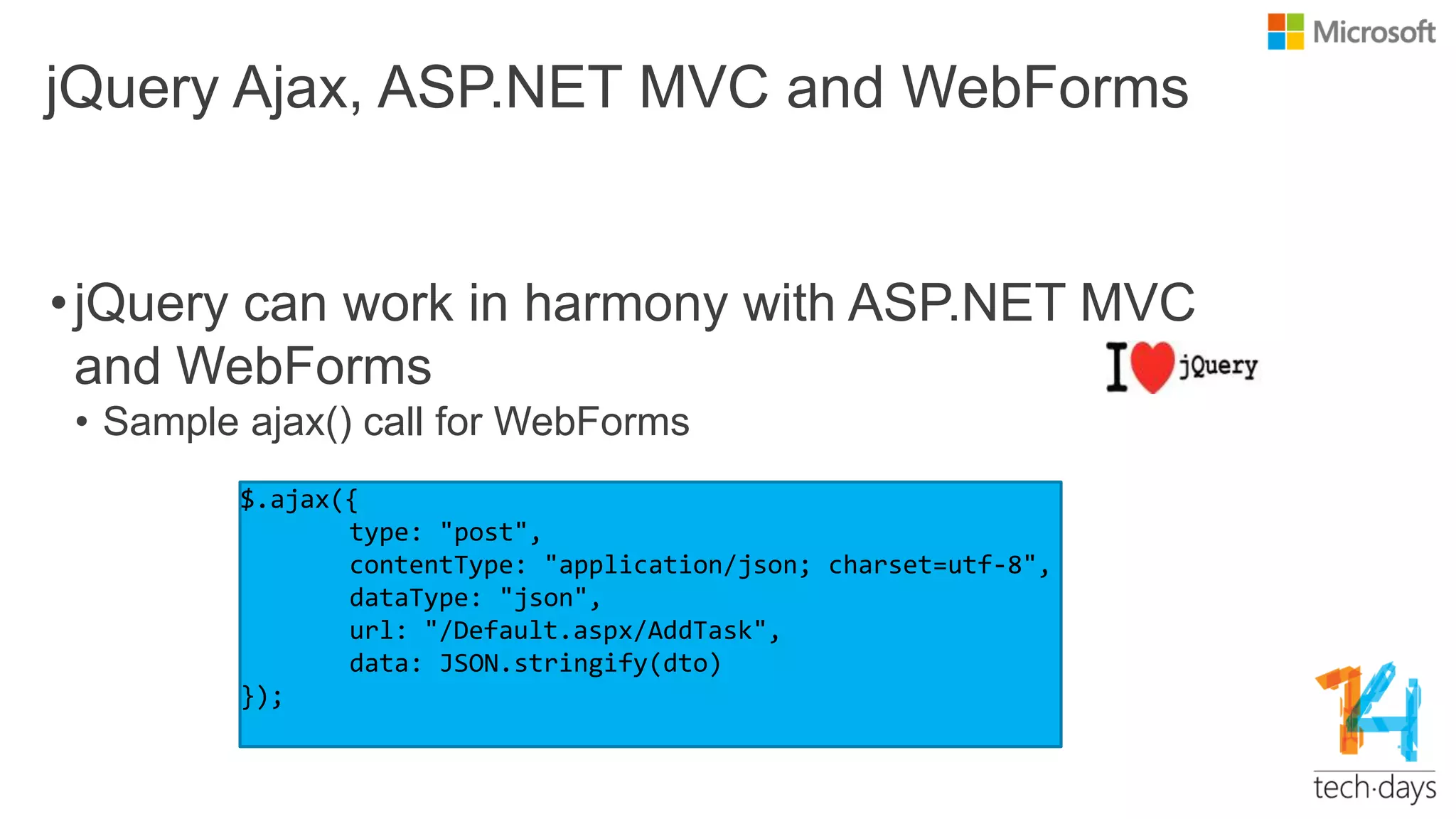
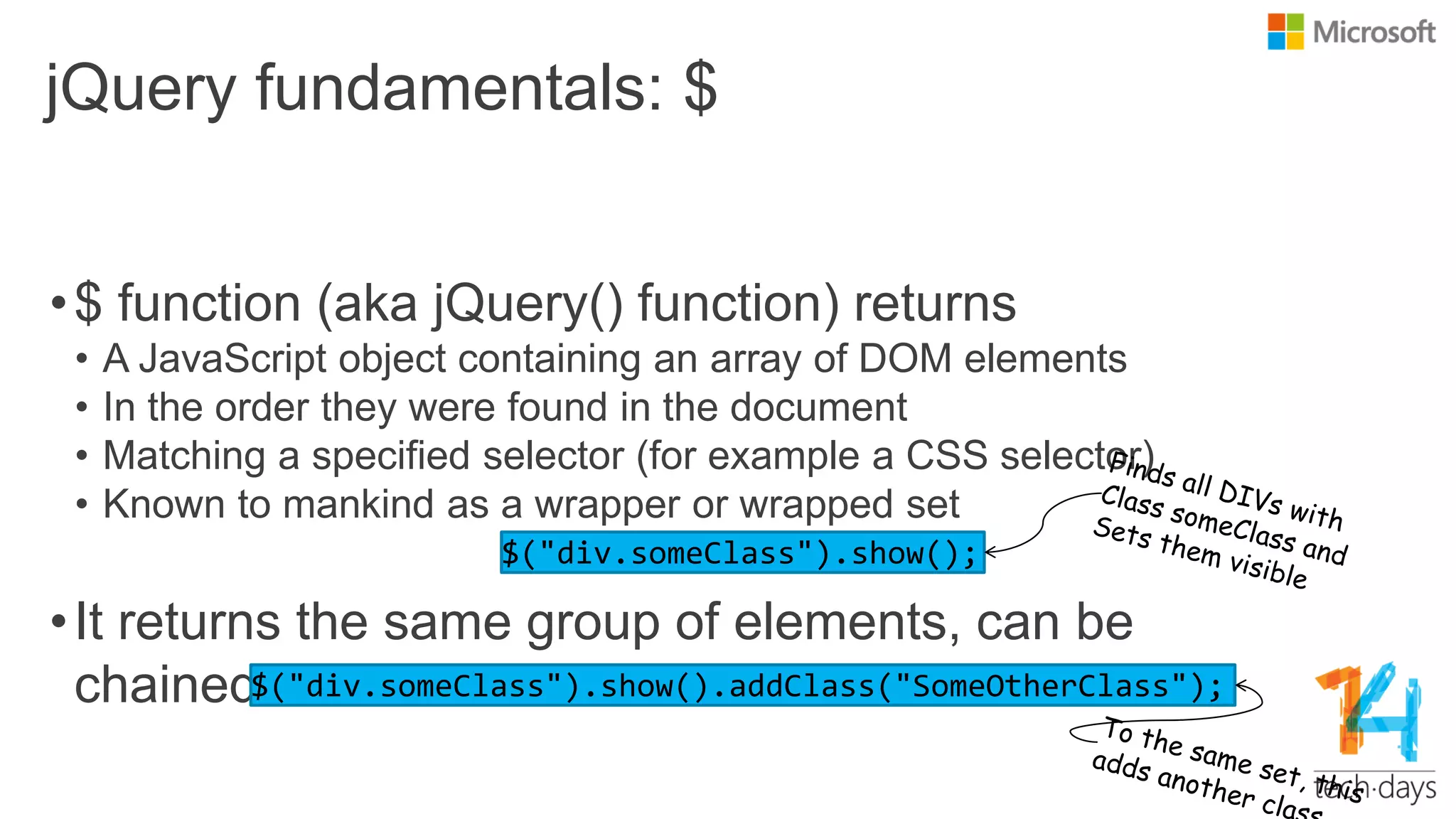
The document provides an overview of jQuery, a popular JavaScript library aimed at simplifying client-side scripting. It covers key fundamentals such as DOM manipulation, event handling, animations, AJAX requests, and jQuery UI features, emphasizing its lightweight nature, ease of use, and extensive community support. It also discusses the benefits of using jQuery in conjunction with various frameworks and offers guidance on writing plugins and utilizing CDNs.











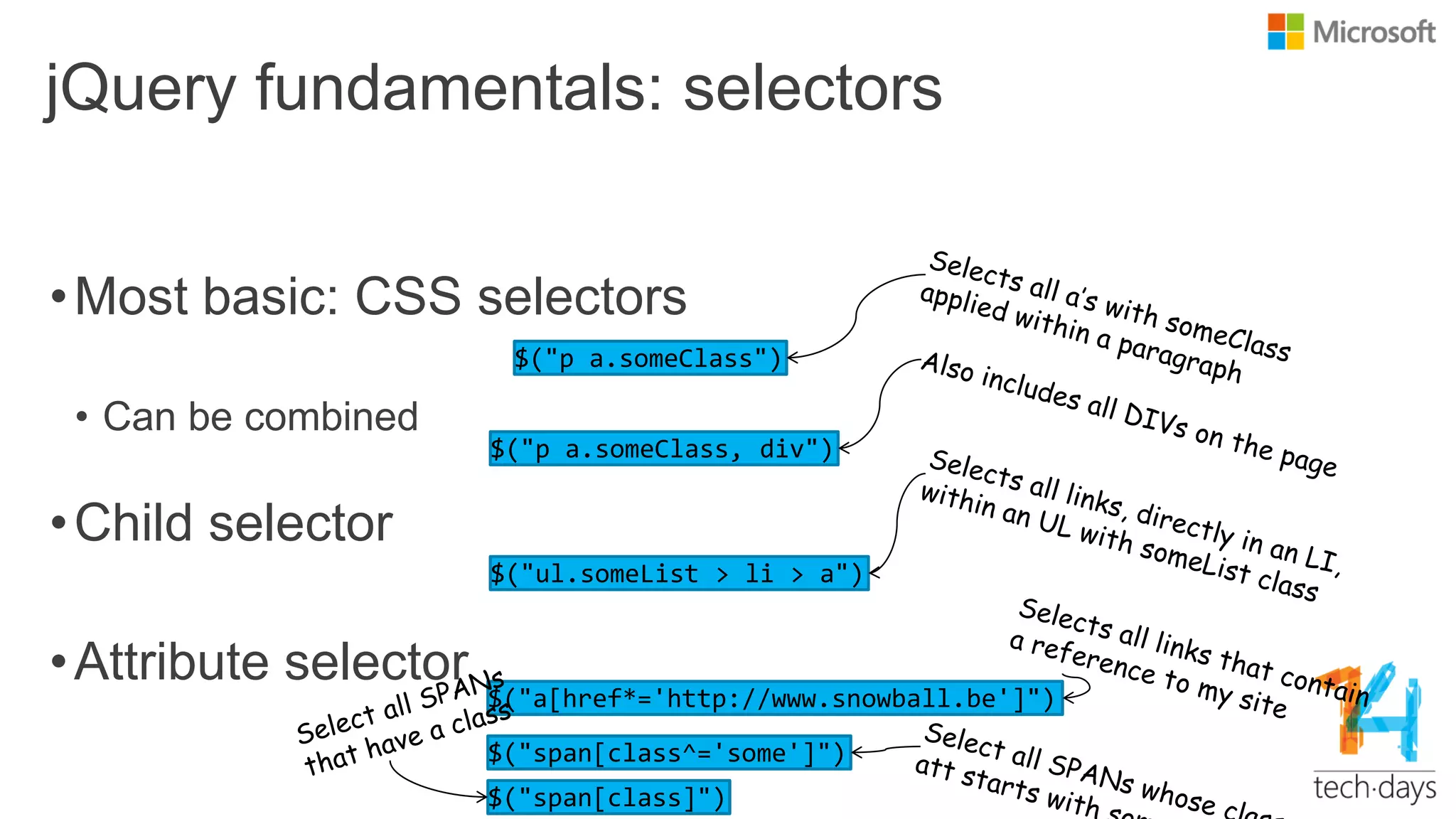
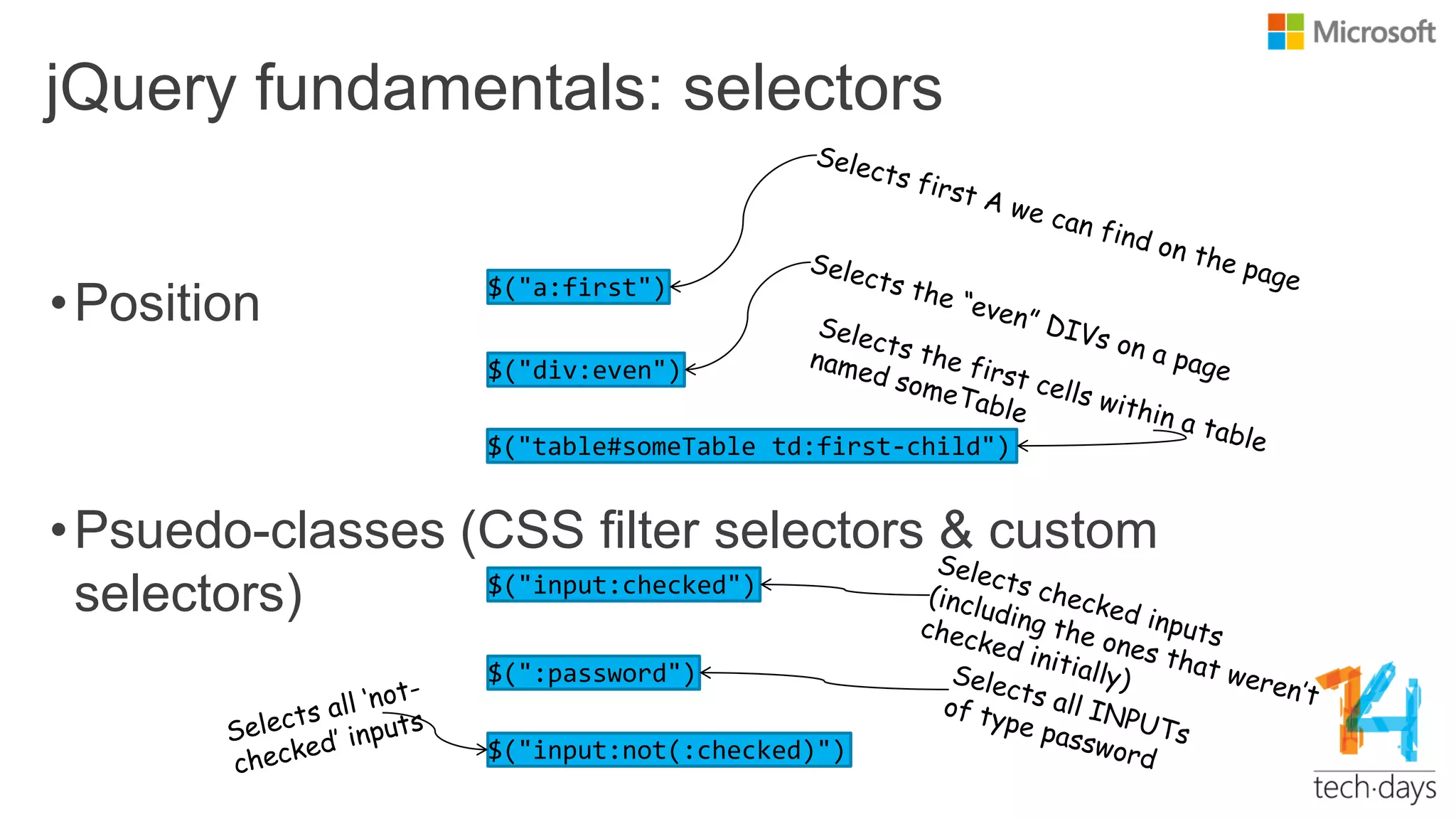
![More selectors
Full list at http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-
selectors/Pattern Meaning
* any element
E an element of type E
E[foo] an E element with a "foo" attribute
E[foo^="bar"]
an E element whose "foo" attribute value begins exactly
with the string "bar"
E:nth-child(n) an E element, the n-th child of its parent
E:first-child an E element, first child of its parent
E:empty an E element that has no children (including text nodes)
E:link
E:visited
an E element being the source anchor of a hyperlink of
which the target is not yet visited (:link) or already visited
(:visited)
E > F an F element child of an E element
E + F an F element immediately preceded by an E element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/getting-20started-20with-20jquery-20templated-140423100639-phpapp02/75/Getting-started-with-jQuery-15-2048.jpg)