The document discusses accessibility in web design, emphasizing the importance of accommodating users with disabilities through flexible, separable, and modifiable systems. It highlights the use of jQuery and HTML5 to improve the usability and accessibility of web applications, covering topics like enhanced keyboard navigation and the implementation of ARIA roles. The authors advocate for inclusive design practices and the ongoing evolution of web standards for a more accessible future.























![Without jQuery
function stripeListElements() {
// get the items from the list
var myItems = document.getElementsByTagName("li");
// skip line 0 as it's the header row
for(var i = 0; i < myItems.length; i++) {
if ((i % 2) === 0) {
myItems[i].className = "striped";
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theinclusiveweb-handsonwithhtml5andjquery-110601100344-phpapp02/75/The-Inclusive-Web-hands-on-with-HTML5-and-jQuery-24-2048.jpg)















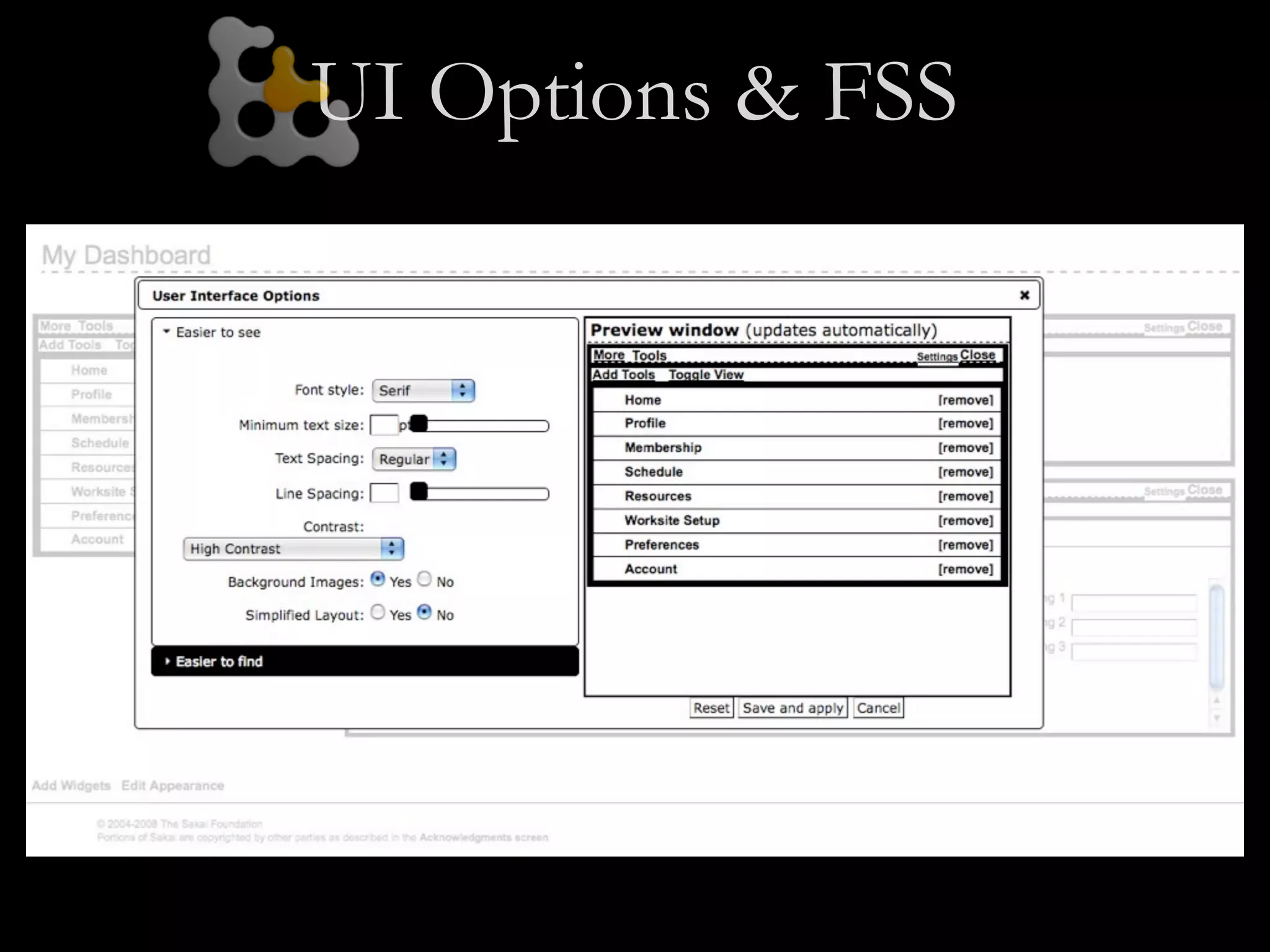
![Adding ARIA in code
// Identify the container as a list of tabs.
tabContainer.attr("role", "tablist");
// Give each tab the "tab" role.
tabs.attr("role", "tab");
// Give each panel the appropriate role, panels.attr("role",
"tabpanel");
panels.each(function (idx, panel) {
var tabForPanel = that.tabs.eq(idx);
// Relate the panel to the tab that labels it.
$(panel).attr("aria-labelledby", tabForPanel[0].id);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theinclusiveweb-handsonwithhtml5andjquery-110601100344-phpapp02/75/The-Inclusive-Web-hands-on-with-HTML5-and-jQuery-40-2048.jpg)





















![Getting the files
filesControl.change(function () {
that.events.onAdd.fire(filesControl[0].files);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theinclusiveweb-handsonwithhtml5andjquery-110601100344-phpapp02/75/The-Inclusive-Web-hands-on-with-HTML5-and-jQuery-69-2048.jpg)