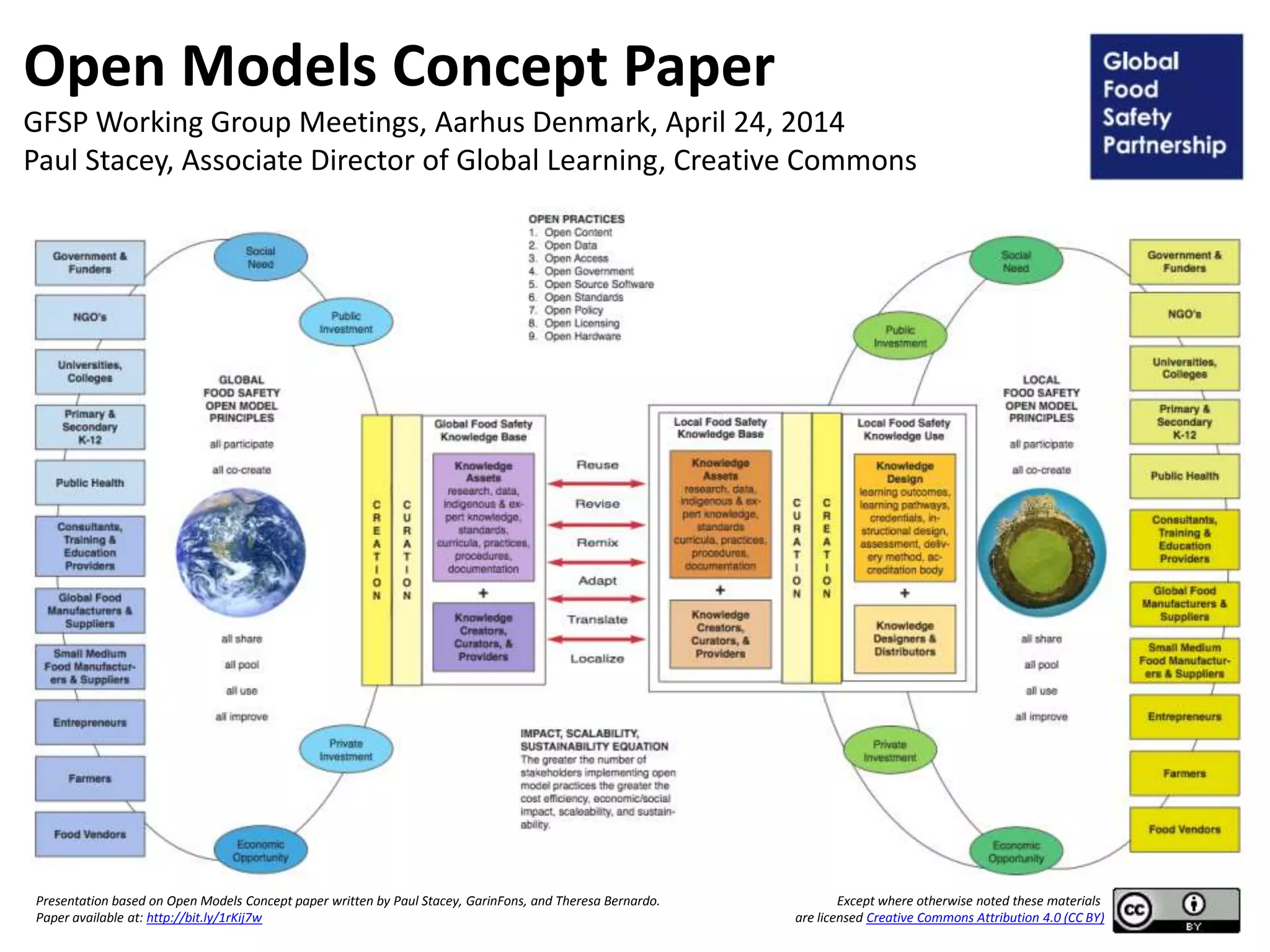
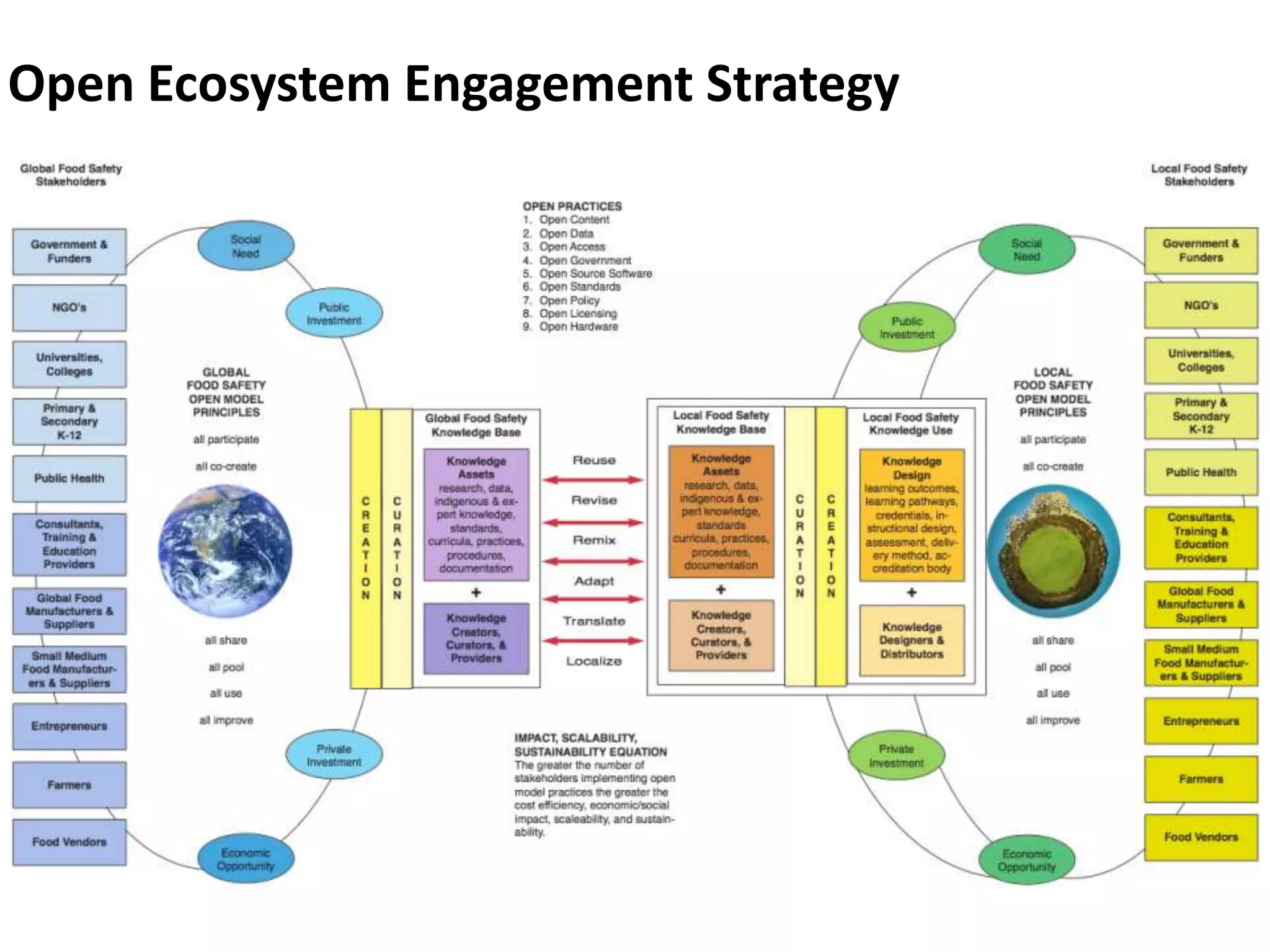
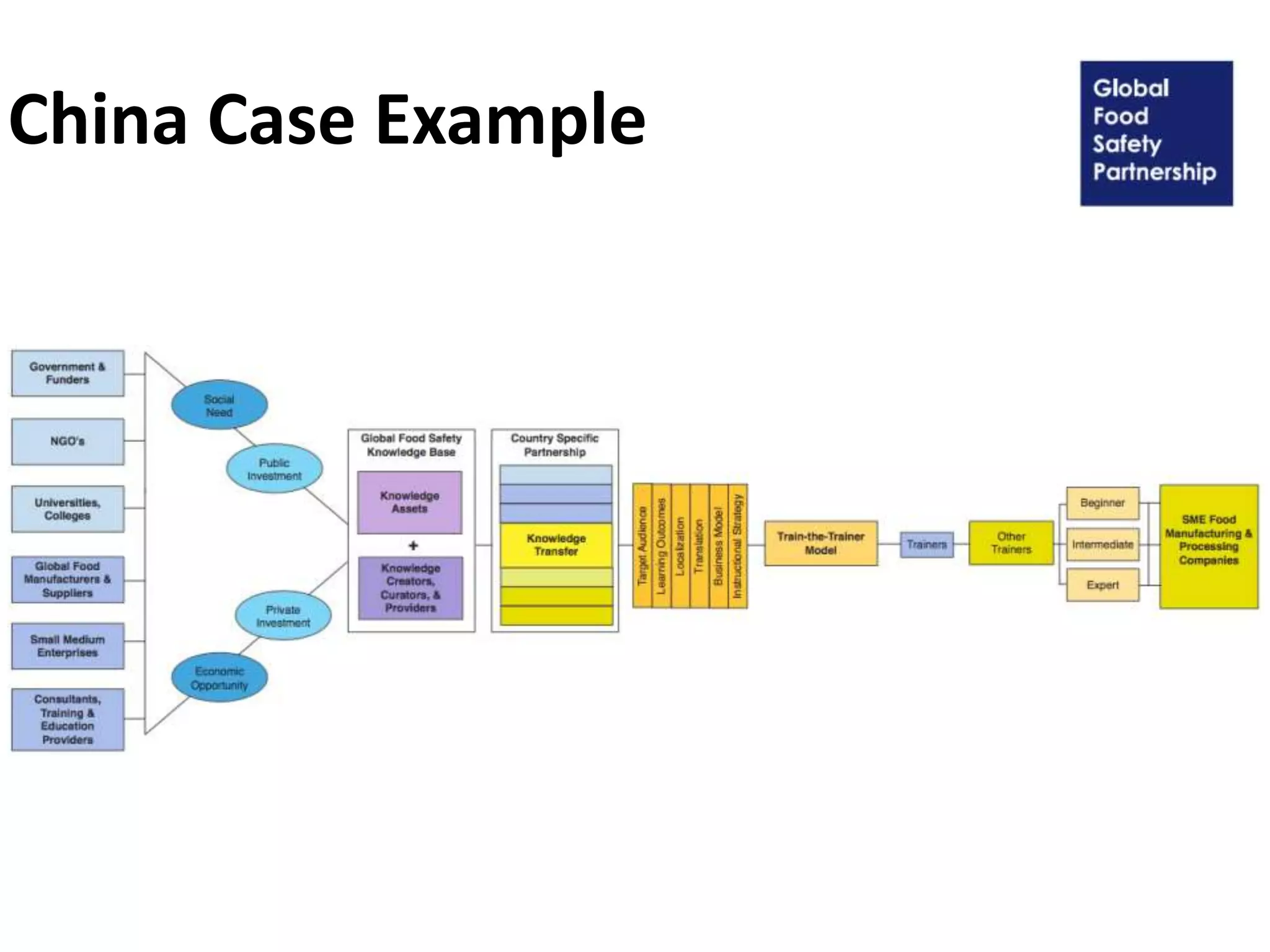
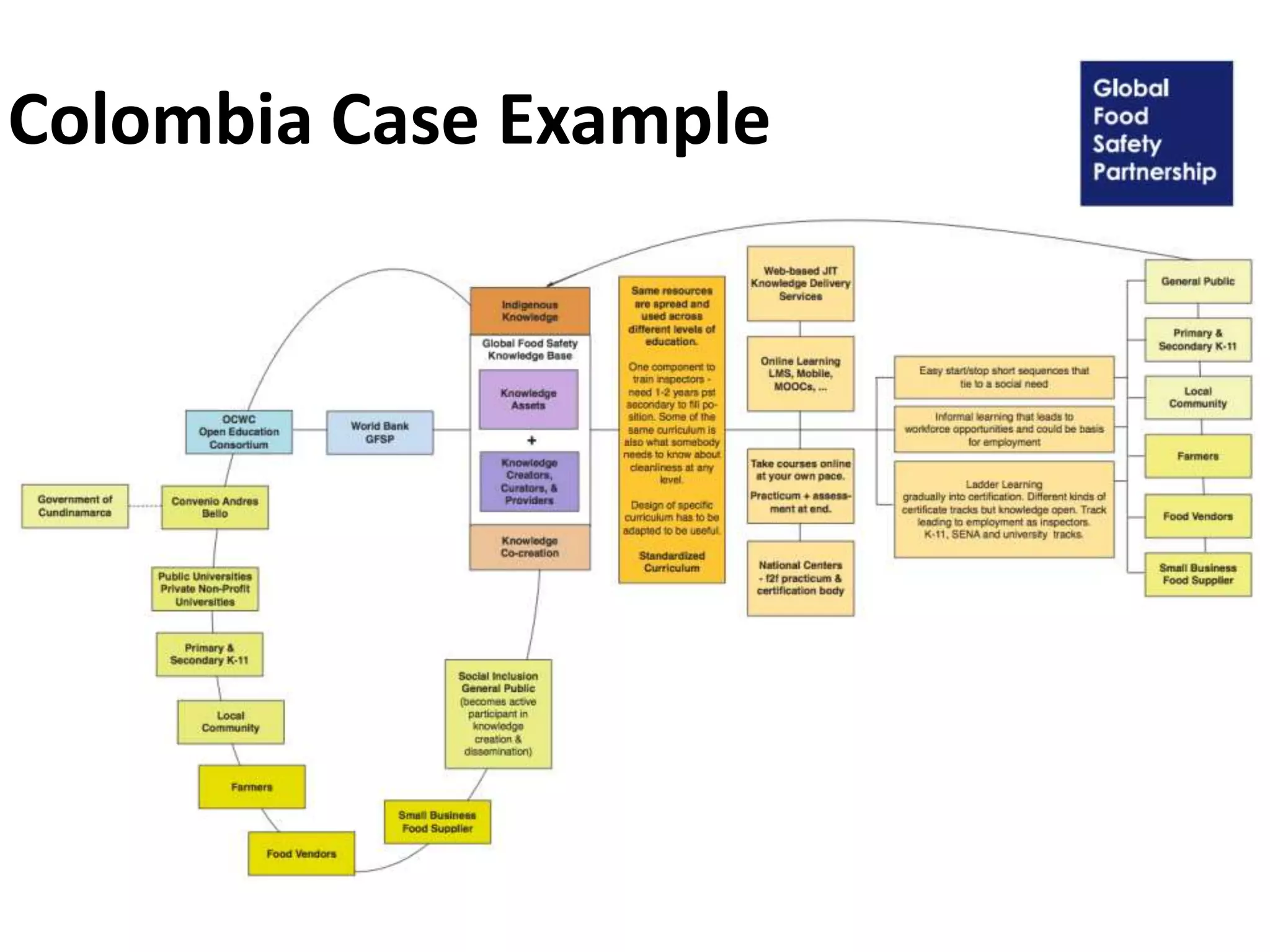
The document discusses the Open Models concept paper aimed at promoting the use of open practices among GFSP members, highlighting nine specific open strategies such as open content and open data. It provides case examples from China and Colombia, alongside policy recommendations to adopt and implement openness in operations, and suggests practical steps for innovation and business model creation. The paper outlines the importance of engaging stakeholders and making GFSP deliverables accessible through open licensing and shared resources.