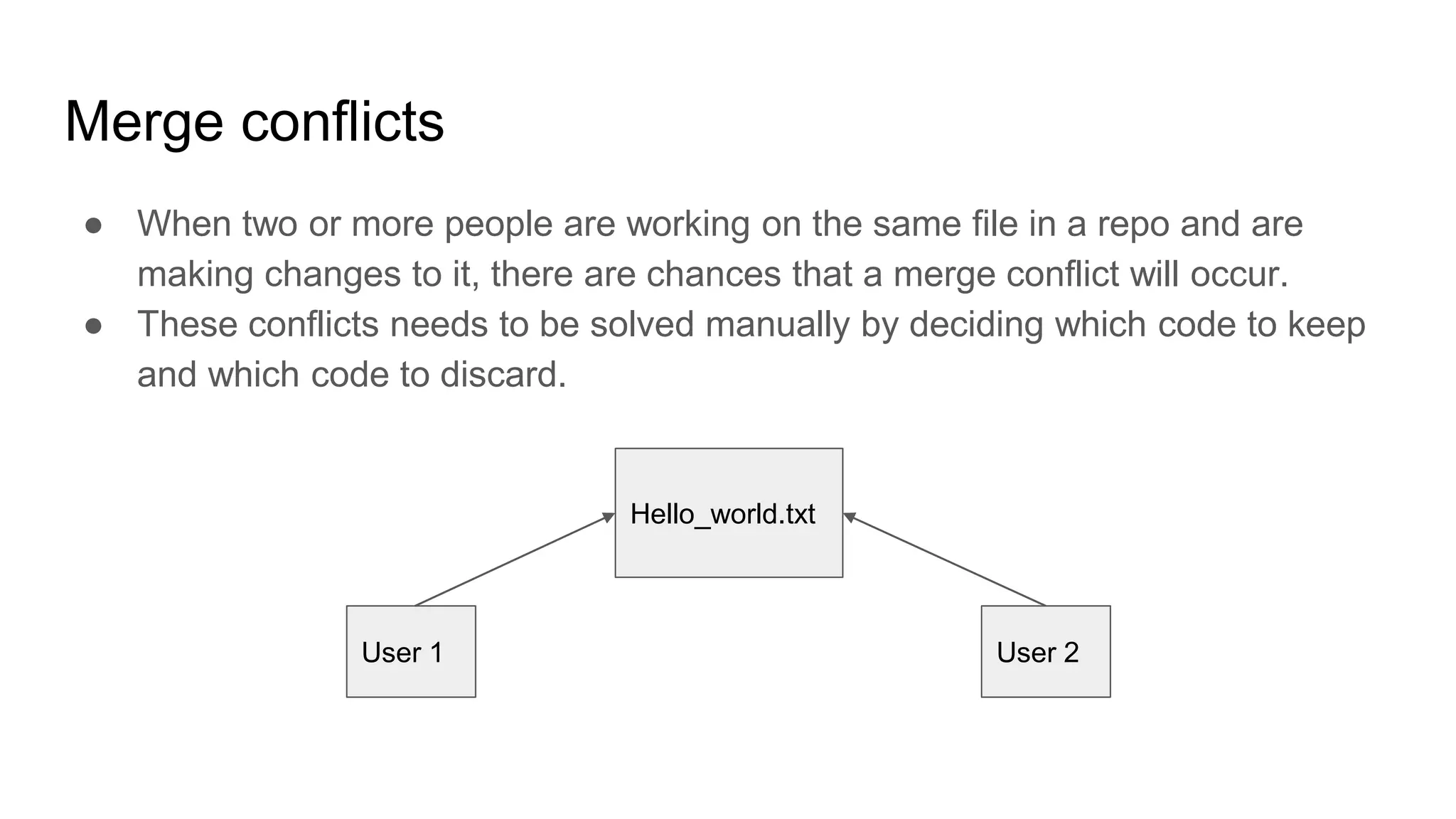
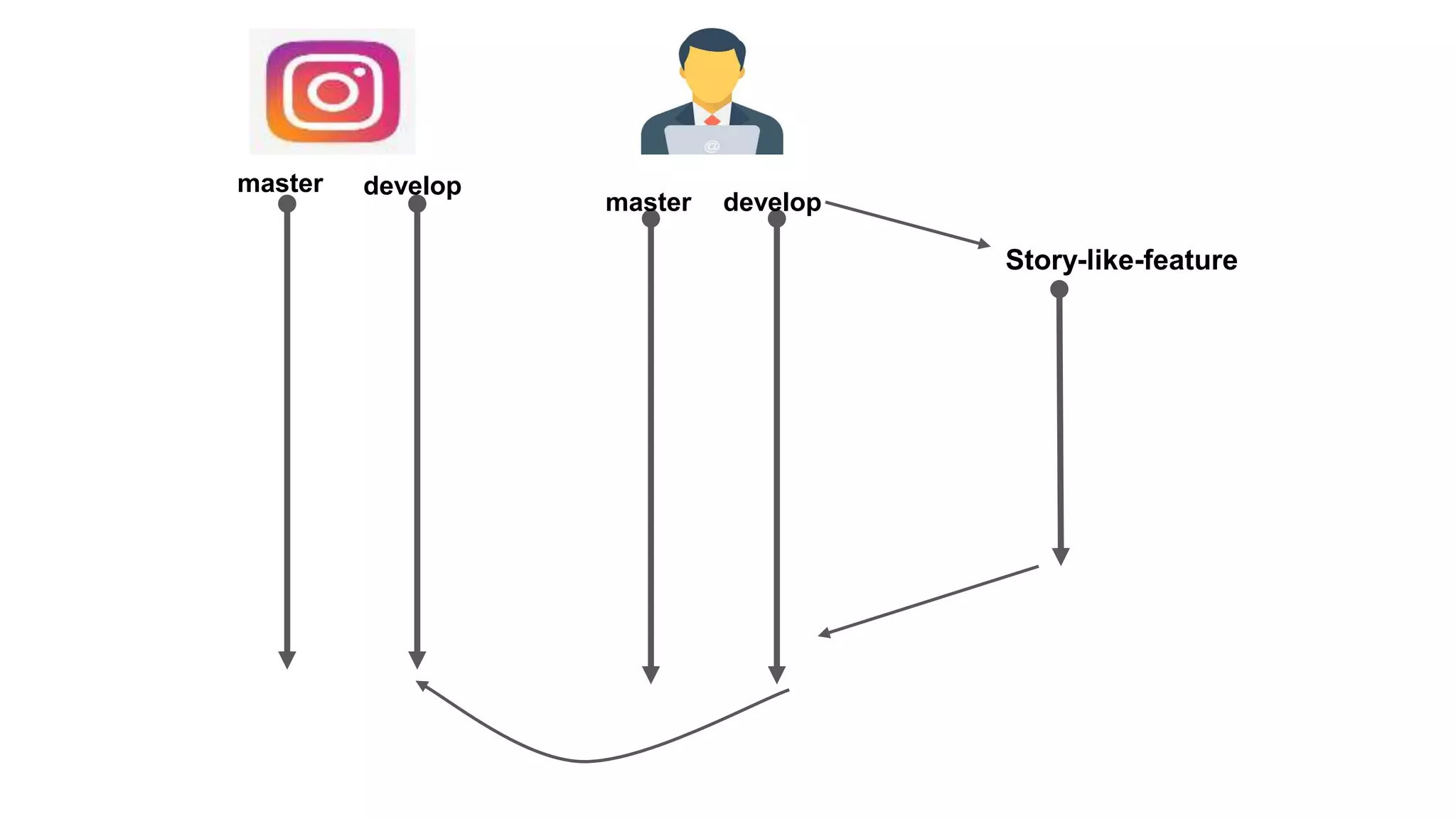
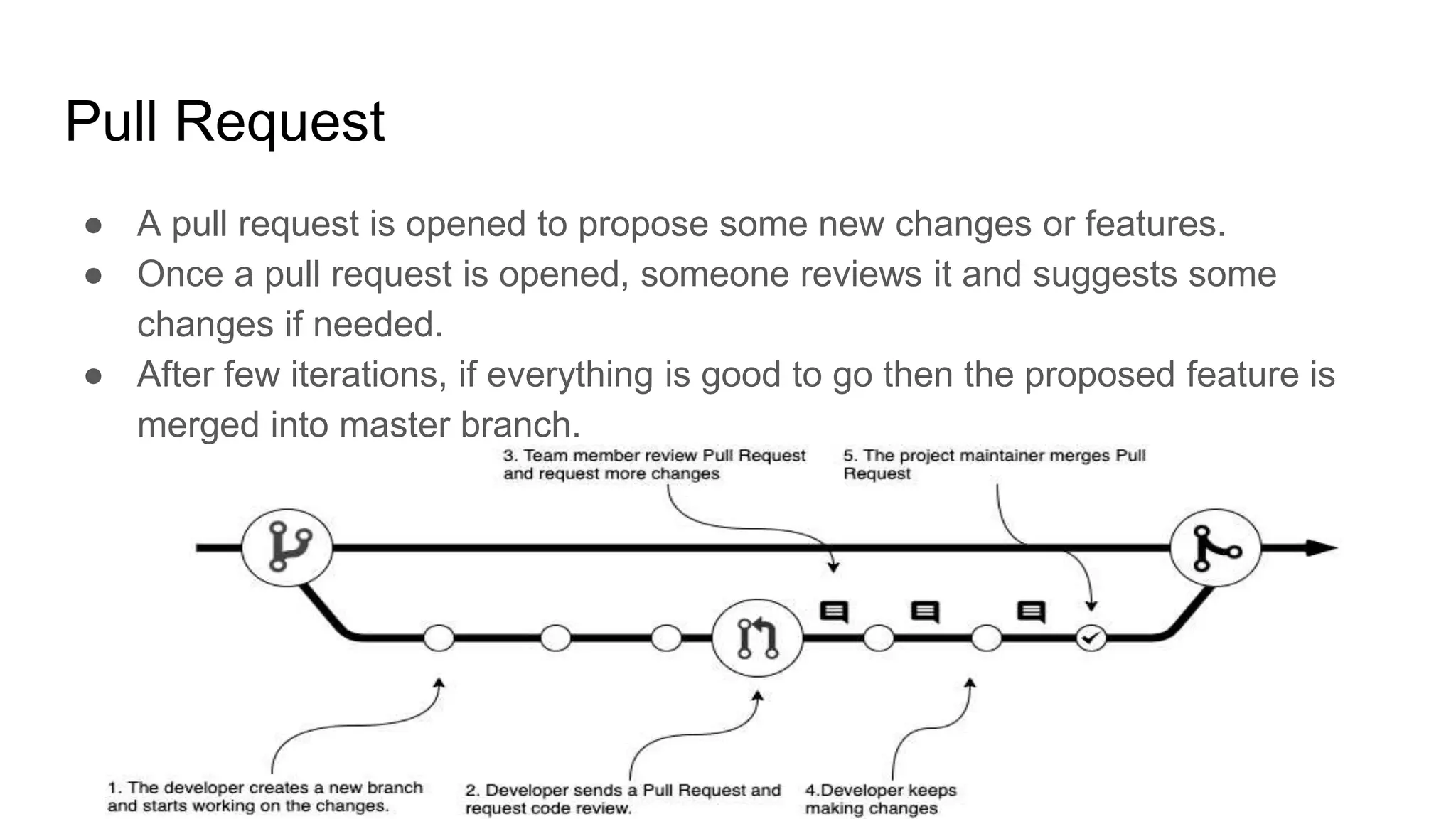
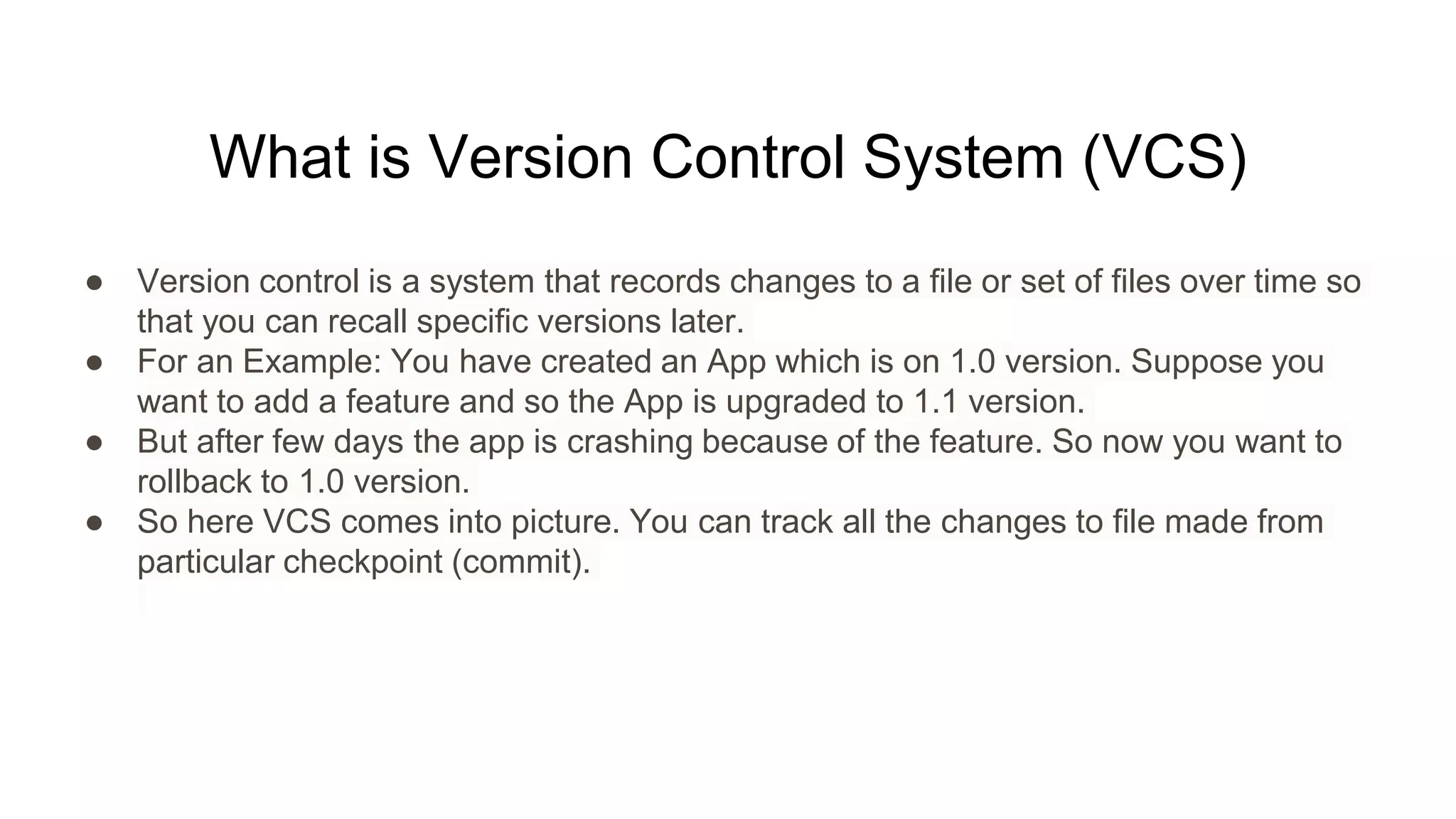
Git is an open source distributed version control system (VCS) developed by Linus Torvalds in 2005. Version control allows tracking changes to files over time through commits, enabling recall of specific versions. GitHub is a code hosting platform that allows collaboration on projects remotely using Git. Common Git commands include git init to create a repository, git add to stage files, git commit to save changes, and git push to sync a local repository with a remote one. Pull requests allow proposing and reviewing changes before merging into a main branch like master.





![git add
● git add [filename] - Add file contents to staging
area
● git add . - Add all the changed files to staging
area.
○ Staging Area - Git knows what files are changed,
but doesn’t know why changed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitandgithubfundamentals-200917130636/75/Git-and-github-fundamentals-8-2048.jpg)

![git diff
● git diff - Show changes between commits,
commit and working tree, etc
○ git diff [filename] - Shows the content
changed in file after last commit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitandgithubfundamentals-200917130636/75/Git-and-github-fundamentals-11-2048.jpg)


![git remote
● git remote - Adds a remote named <name> for
the repository at <url>
○ git remote add origin [url]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitandgithubfundamentals-200917130636/75/Git-and-github-fundamentals-14-2048.jpg)


![git branch
● git branch - List all the branches
○ git branch [branch-name] - Creates a branch
with name as [branch-name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitandgithubfundamentals-200917130636/75/Git-and-github-fundamentals-17-2048.jpg)
![git checkout
● git checkout - Switch branches or restore
working tree files.
○ git checkout [branch-name] - Checkout to
[branch-name]
○ Git checkout -b [branch-name] - Creates an
checkout to [branch-name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitandgithubfundamentals-200917130636/75/Git-and-github-fundamentals-18-2048.jpg)
![git merge
● git merge - Join two or more development
histories together
○ git merge [branch-name] - Merge a [branch-
name] with current branch.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitandgithubfundamentals-200917130636/75/Git-and-github-fundamentals-19-2048.jpg)