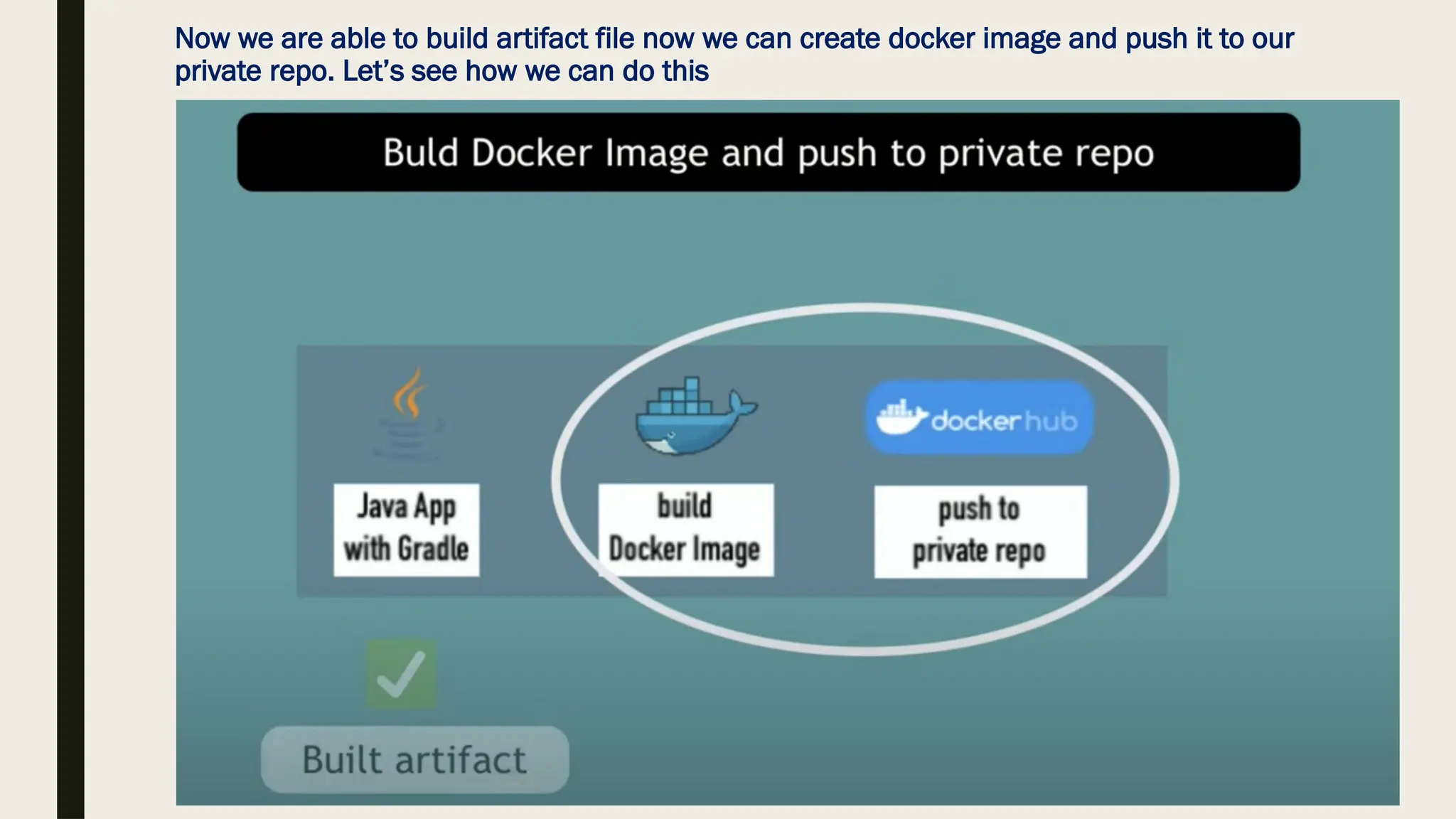
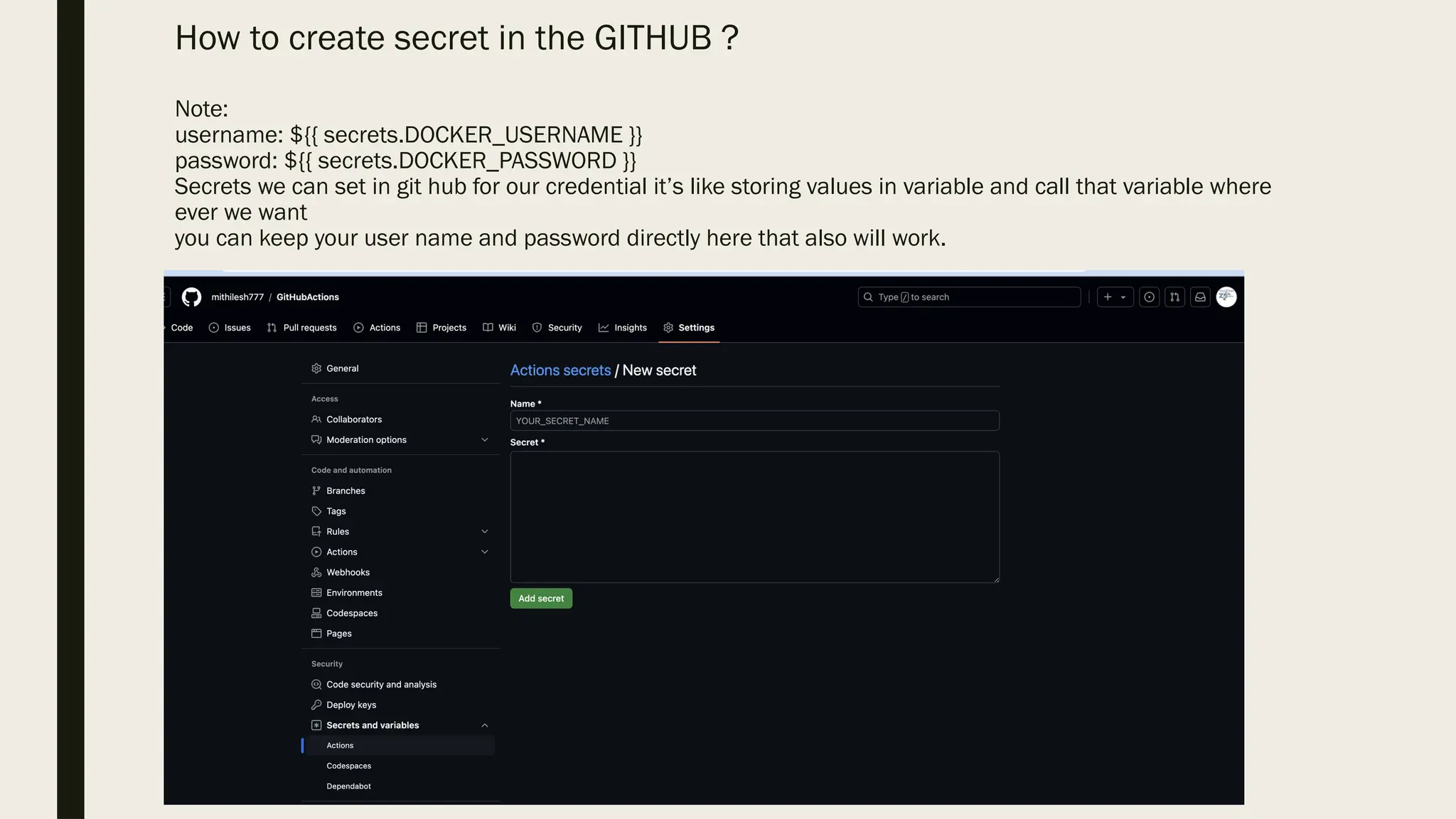
GitHub Actions automates software development workflows, allowing users to respond to events in repositories with automated actions. The Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) process is streamlined through GitHub Actions, which manages tools necessary for each phase to facilitate automatic builds and deployments. Users can configure actions based on project requirements and utilize predefined workflows to enhance collaboration and efficiency in development tasks.



![Note
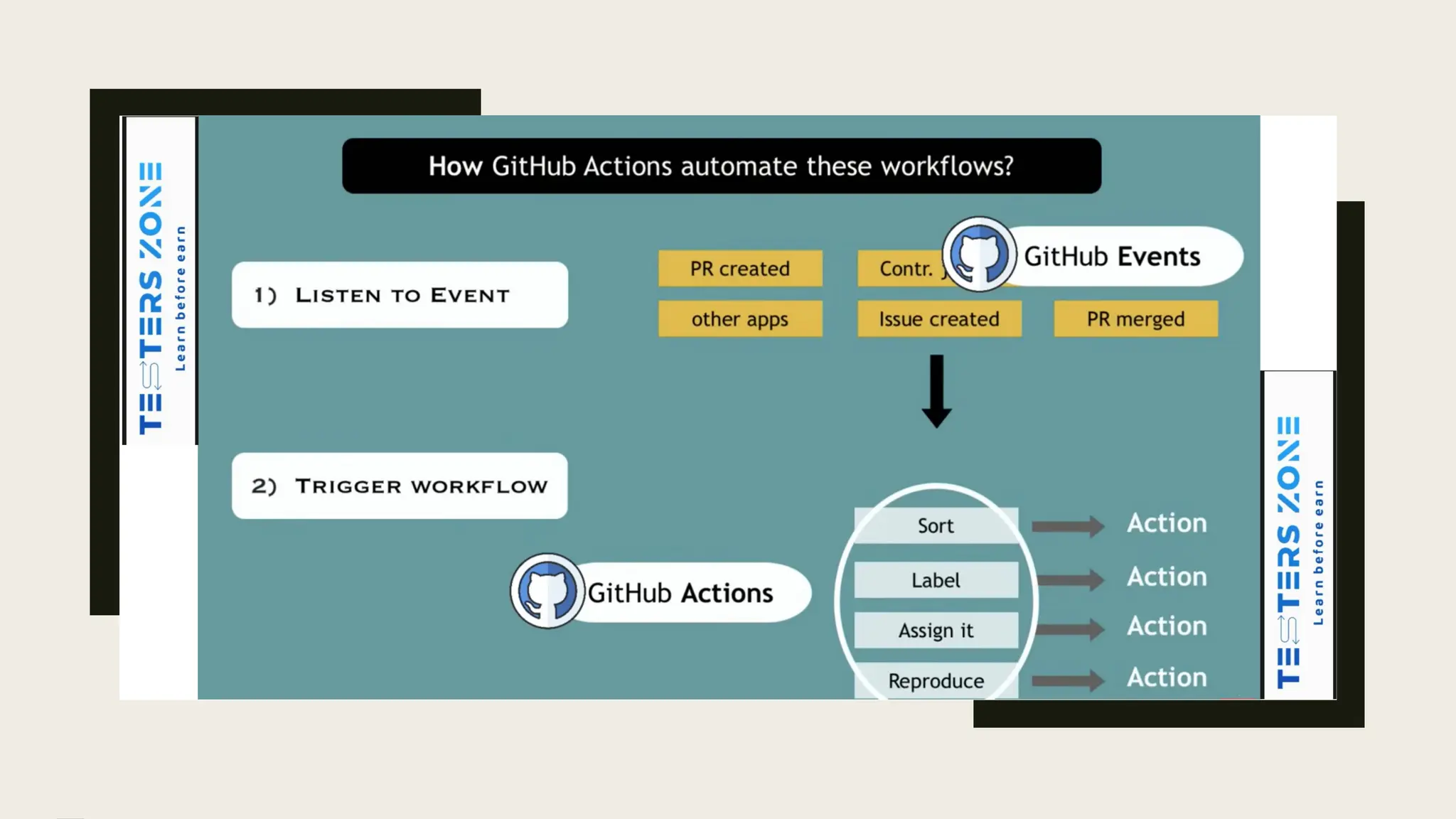
GITHUB Action act against GIT Events, Events might be anything like
Merge request
Create MR,
Raised Issue or any short of activity
Now what possible actions we might have against above events?
1. we can sort the issues based on priority or date
2. We can put labels on the tickets
3. We can assign some of the unassigned tickets to the dev.
4. We can try to reproduce the issue once it logged or after fixes
All these actions instead of performing manually we can do automatically with the
help if GitHub Actions[ ss attached in next slide]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/githubactions-cicd-240922060634-91b31550/75/GITHUB_ACTIONS_CICD_OVERVIEW_FOR_BEGINNERS-4-2048.jpg)

![ Once will click on configure we will get this kind of template
name: Java CI with Gradle
on:
push:
branches: [ "testerszone/sep2024" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "testerszone/sep2024" ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up JDK 17
uses: actions/setup-java@v4
with:
java-version: '17'
distribution: 'temurin'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/githubactions-cicd-240922060634-91b31550/75/GITHUB_ACTIONS_CICD_OVERVIEW_FOR_BEGINNERS-11-2048.jpg)
![Syntax Explanation:
■ name: Java CI with Gradle —> This is Optional field defines name of the workflow.
■ on: This is required field where we mention the events which triggers the workflow.
e.g.
if we want to define action for the push request against master branch then we need to create event for push
request like this
push:
branches: [ master ]
■ Note:
to explore more about the type of events you can visit this
link:
https://docs.github.com/en/actions/writing-workflows/choosing-when-your-workflow-runs/events-that-trigger-wo
rkflows#about-events-that-trigger-workflows
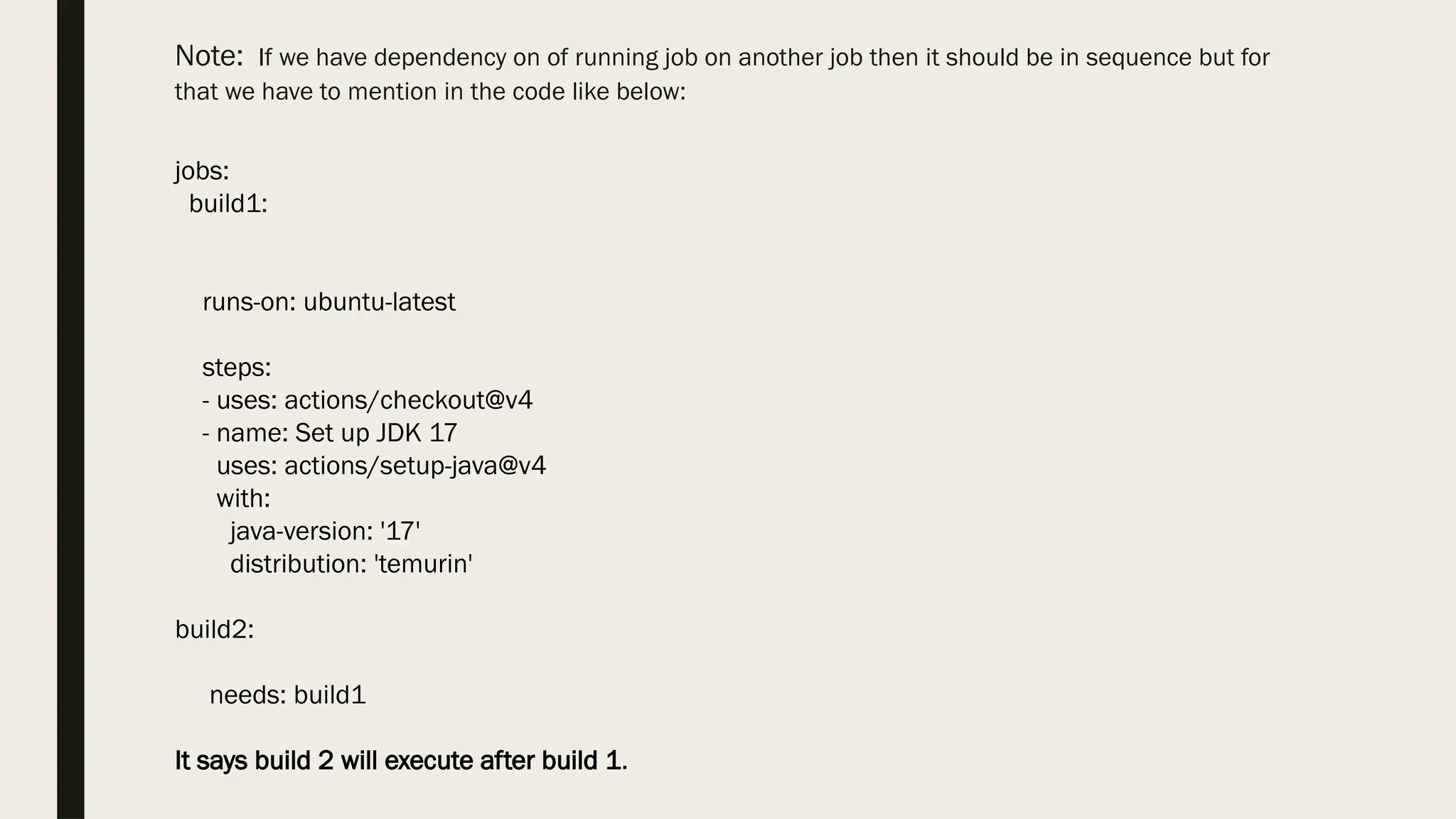
■ jobs: it groups set of actions. We can have multiple job under jobs tag and each job will be having its name.
e.g. if there is build job then we can define like this
jobs:
build:
■ Steps: It can run commands, set up tasks or run an action
■ Uses: it selects predefine code for an action hosted under path actions/
to check the pre-defined action you can visit this link: https://github.com/actions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/githubactions-cicd-240922060634-91b31550/75/GITHUB_ACTIONS_CICD_OVERVIEW_FOR_BEGINNERS-12-2048.jpg)
![Syntax Explanation:
■ runs-on: we can define OS where work flow will execute, it might be window Mac or
ubuntu.
If we want to execute on more than one OS that also can be managed easily with
below snippet of code
runs-on: ${{matrix.os}}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [ubuntu-latest, windows-latest, macOS-latest]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/githubactions-cicd-240922060634-91b31550/75/GITHUB_ACTIONS_CICD_OVERVIEW_FOR_BEGINNERS-13-2048.jpg)
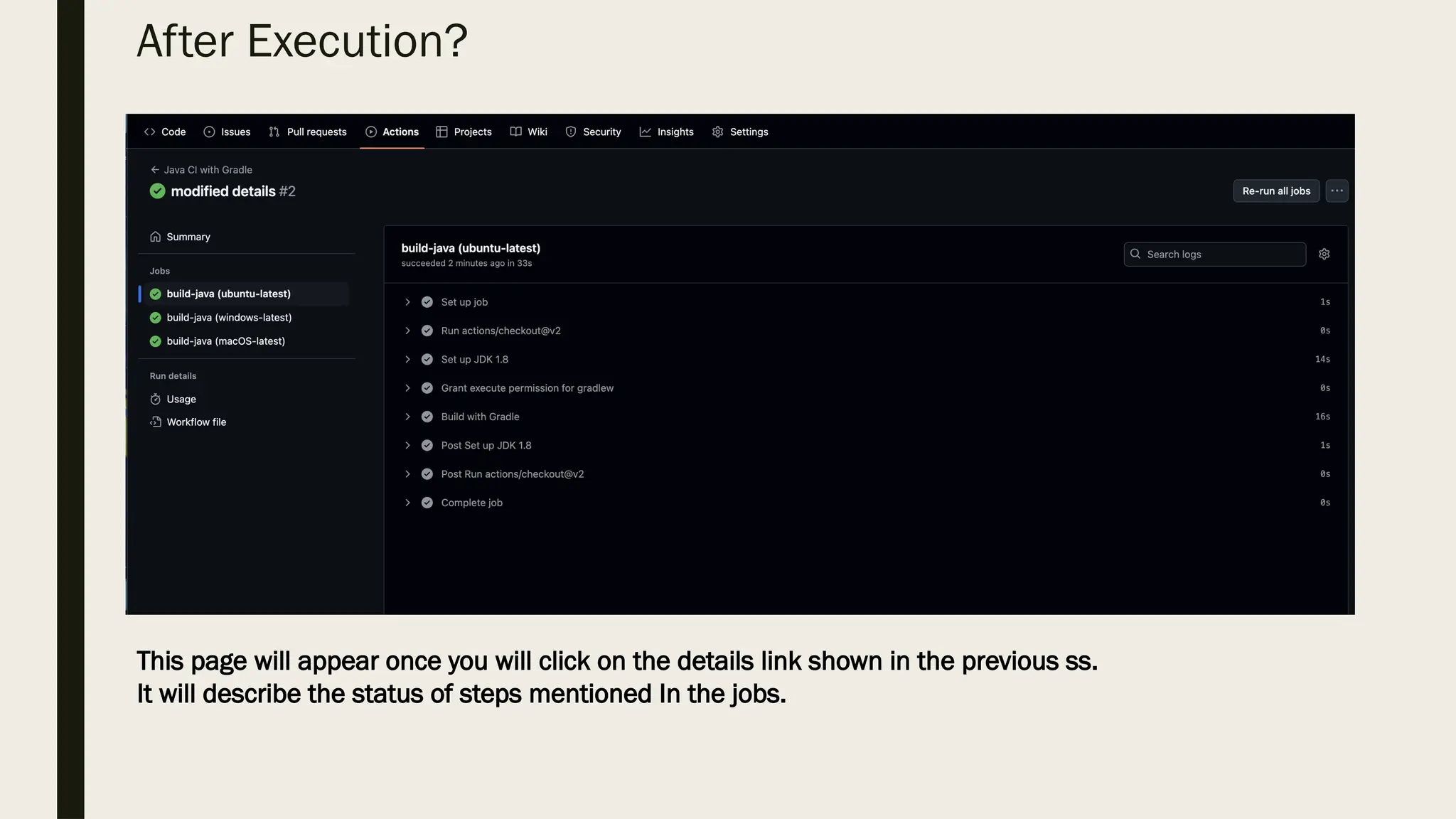
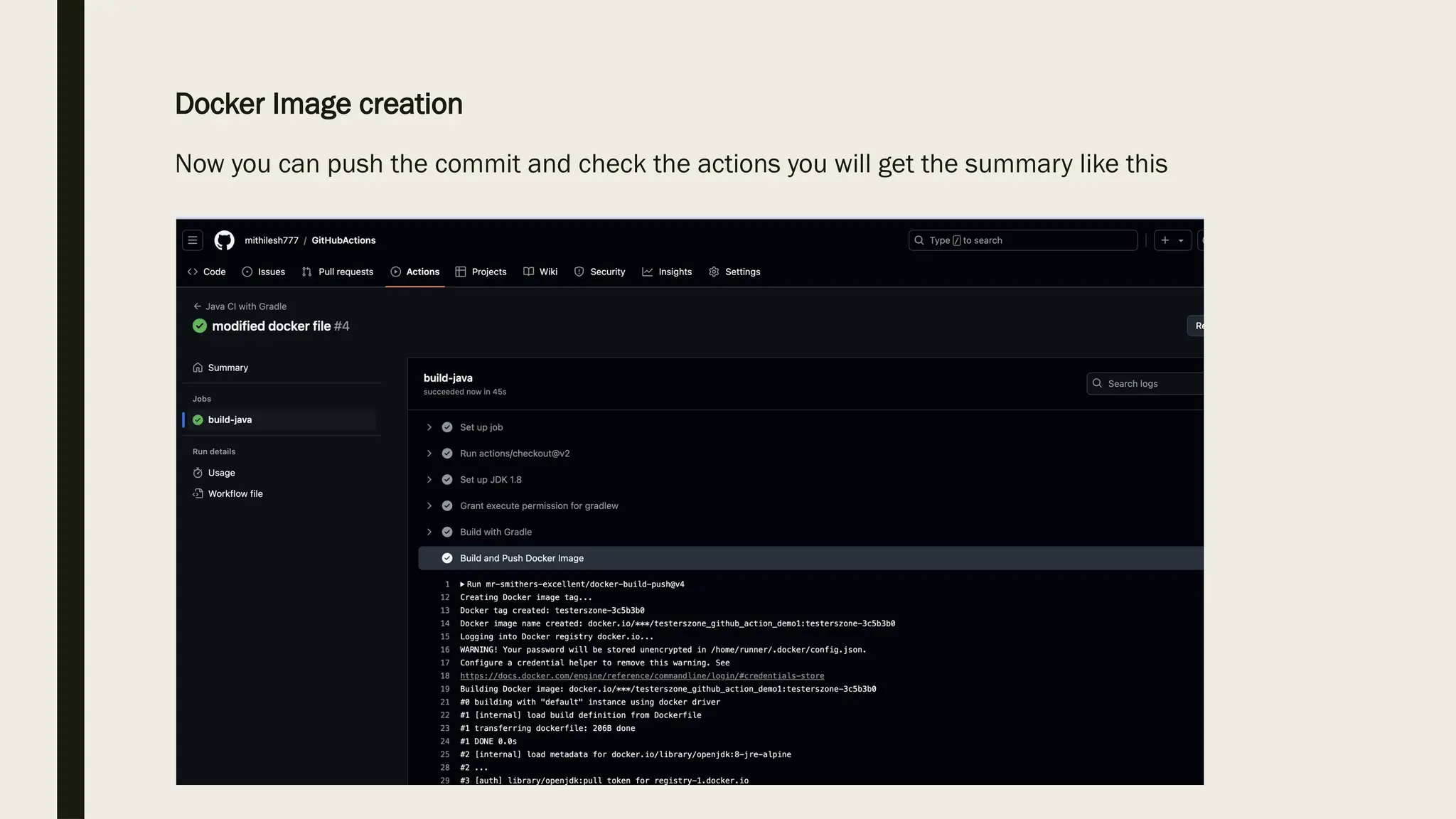
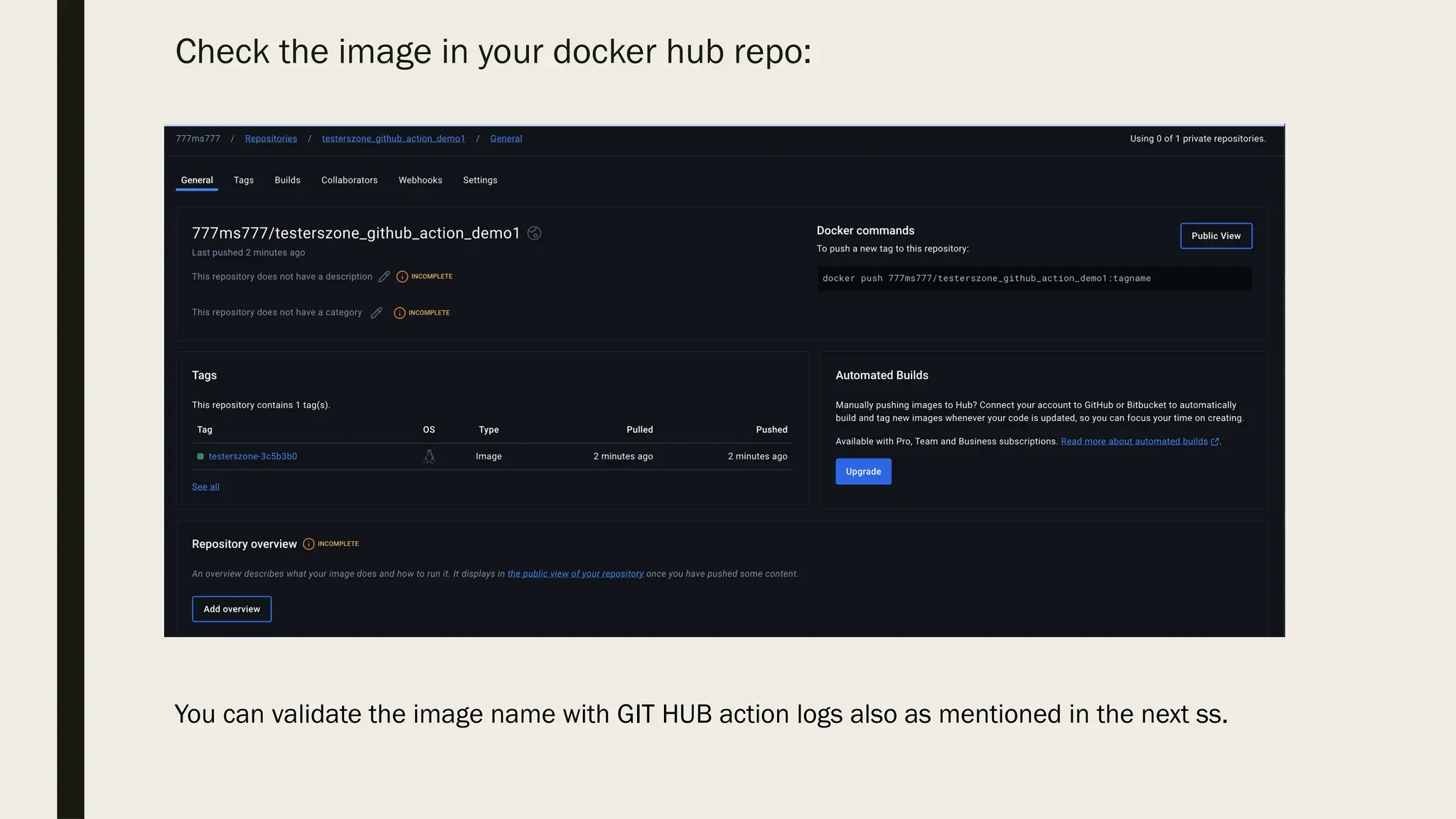
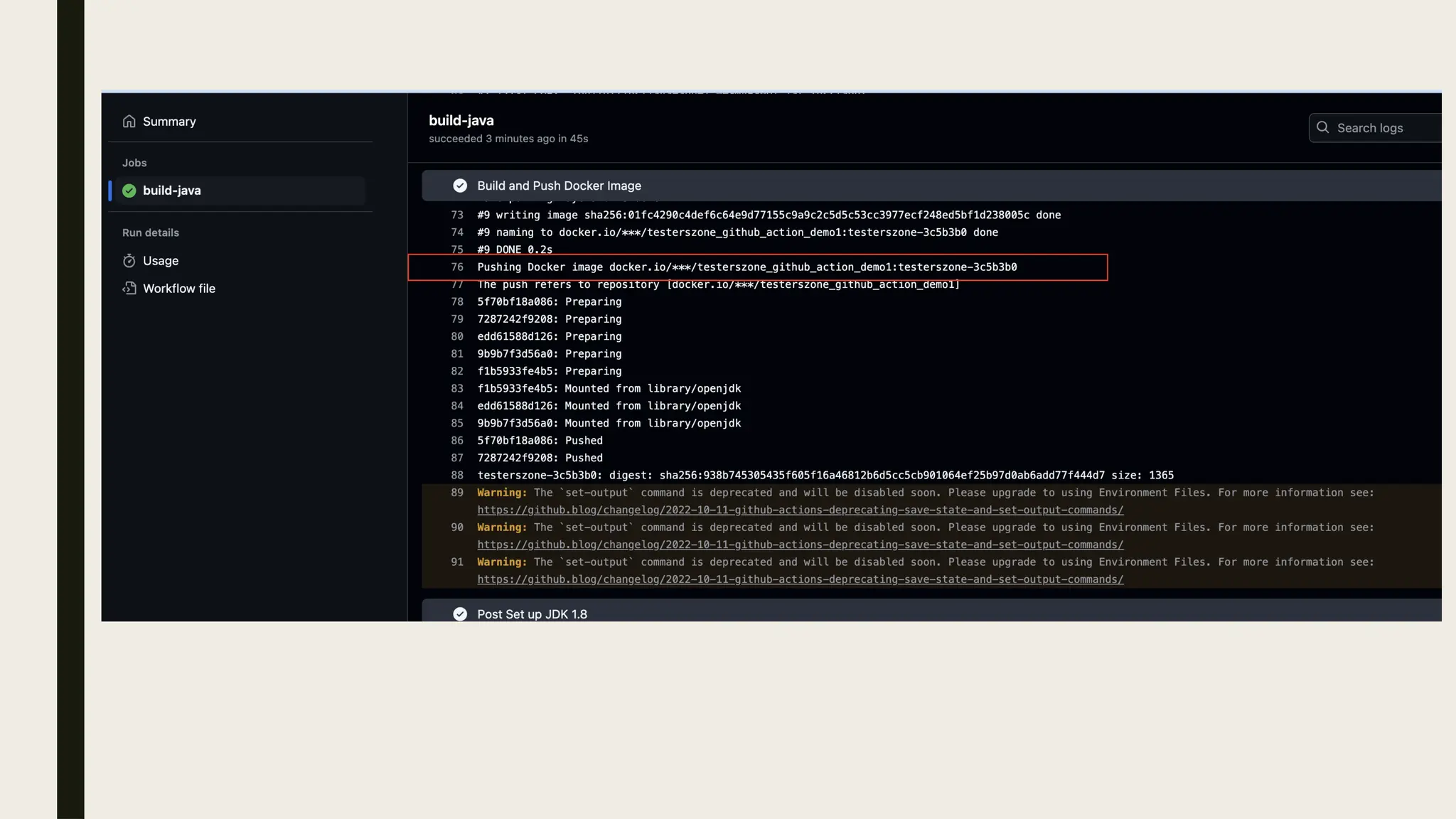
![ How does execution look like?
Once we push the commit to the specified branch [I used master] then action will
trigger and can observe like mentioned in the ss.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/githubactions-cicd-240922060634-91b31550/75/GITHUB_ACTIONS_CICD_OVERVIEW_FOR_BEGINNERS-14-2048.jpg)