The document provides a comprehensive guide on locating elements using XPath and CSS selectors in Selenium for web automation scripts. It explains the concept of locators, different types of XPath, their syntax, and comparison with CSS selectors, highlighting their strengths and limitations. Additionally, it covers methods such as contains(), starts-with(), and various XPath axes to facilitate finding elements in a more dynamic manner.
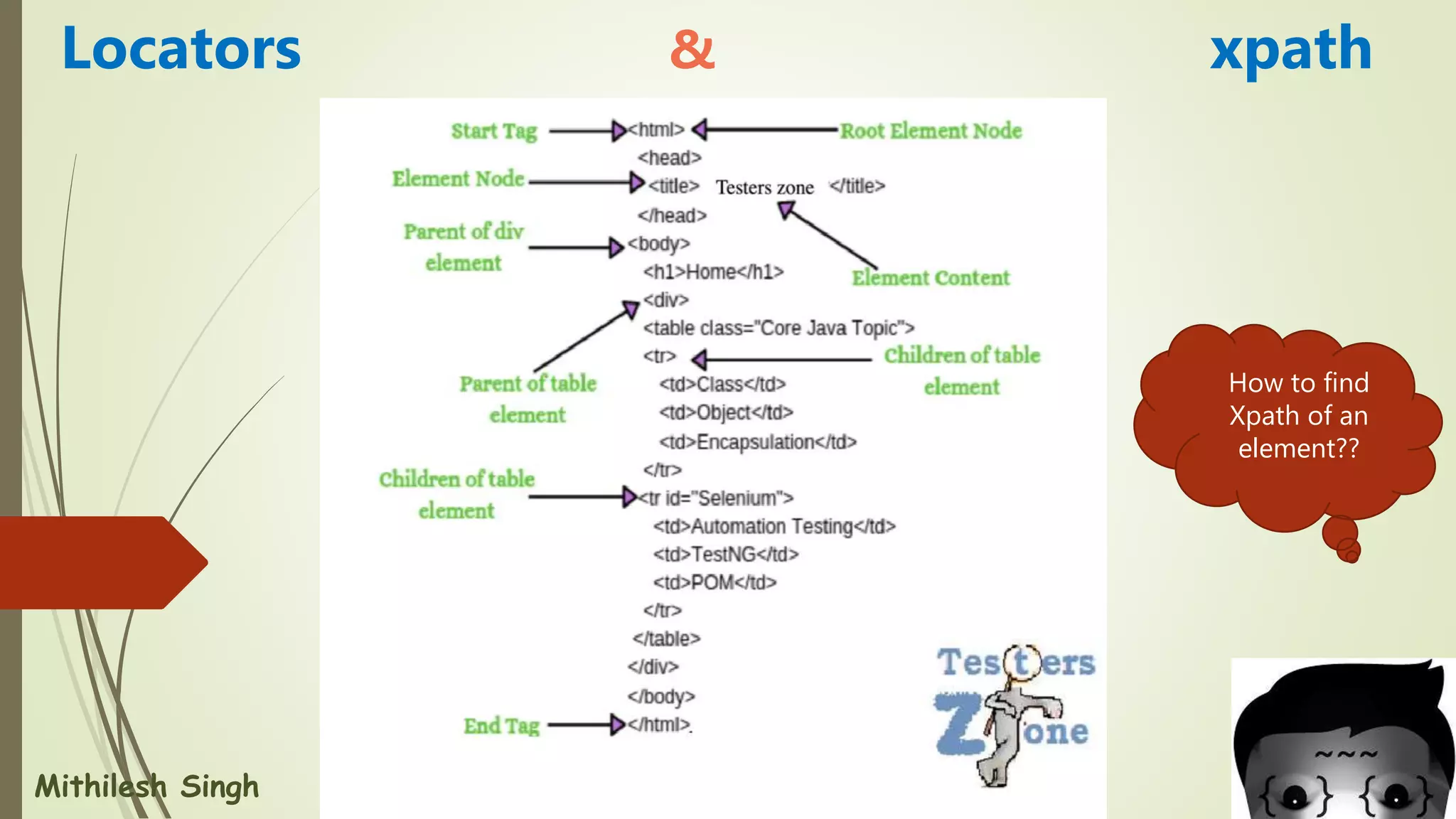


![Syntax of Xpath
XPath =
//tag_name[@Attribute_name =
“Value of attribute”]
// --> Select current node.
tag_name --> Tagname of the
particular node.
@ --> Select attribute.
Attribute_name --> Attribute name
of the node.
Value of attribute --> Value of the
attribute.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-5-2048.jpg)
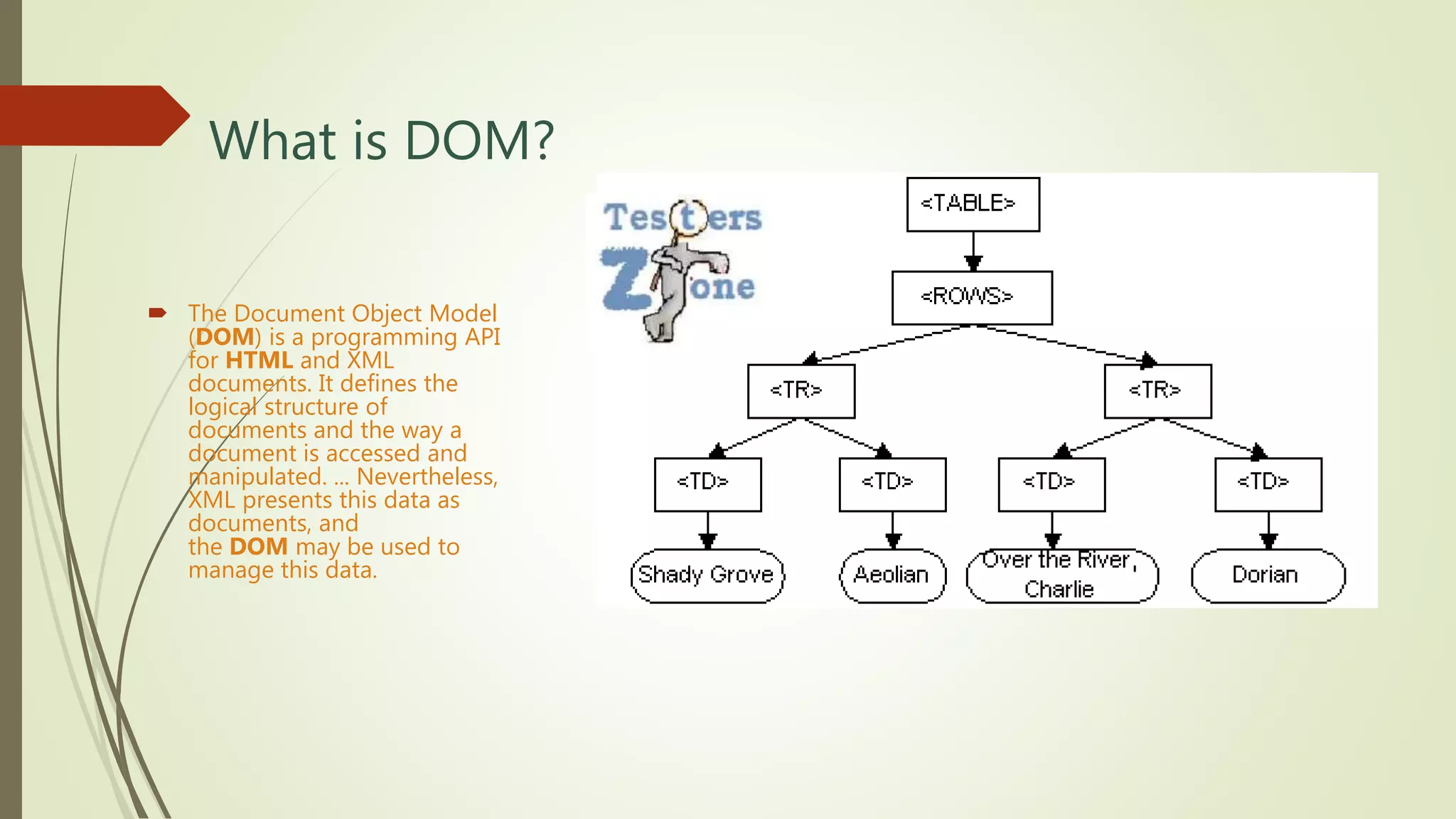
![Types of XPath
Absolute Xpath
Absolute XPath is the direct way of
finding the element. Moreover, it
starts from the first/root node of
the XML/HTML document and
goes all the way to the required
node following one node at a
time.
Example:
/html/body/div/header/a/img
Relative Xpath
Relative XPath starts from any node inside
the HTML DOM; it need not start from
the root node. It beings with a double
forward slash.
Example:
//img[@src= "/images/Testerszone.jpg"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-6-2048.jpg)
![Relative Xpath Syntax for Pre - defined locators:
Using text() : //*[text()='testers zone']
Using name() : //input[@name='Mithilesh']
Using id() : //input[@id='user-message‘]
Using class() : //input[@class='user-message']
LinkText() : //a[@href='http://testerszone.com/']
Note: We can use * in place of input, it will also work fine. Input is specific
tag name but * is generic(point out all the available tags in the DOM) we
can use for any tag name.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-7-2048.jpg)

![Use of Contains() in Xpath
• Contains() method always use in xpath to get the element using partial text.
• Whenever we have long text or dynamic text we go with contains().
Using text() : //*[contains(text(),'testers ')]
Using name() : //input[contains(@name,'Mith')]
Using id() : //input[contains(@id,'user-message‘)]
Using class() : //input[contains(@class,'user-message')]
Partial-LinkText() : //a[contains(@href,'testerszone.com']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-9-2048.jpg)
![Use of
Starts-with()
starts-with() method is used when we know
about the initial partial attribute value or
initial partial text associated with the web
element.
Syntax:
//a[starts-with(@id,'link-testers_')]
Note: inside the ' ' you have to mention the
partial text value, make sure you are getting
unique matching element with your xpath.
Simillar way we have ends_with() also. We use
end partial part of text.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-10-2048.jpg)
![Use of
OR & AND
Xpath=//input[@type='submit' and @name='btnLogin']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-11-2048.jpg)
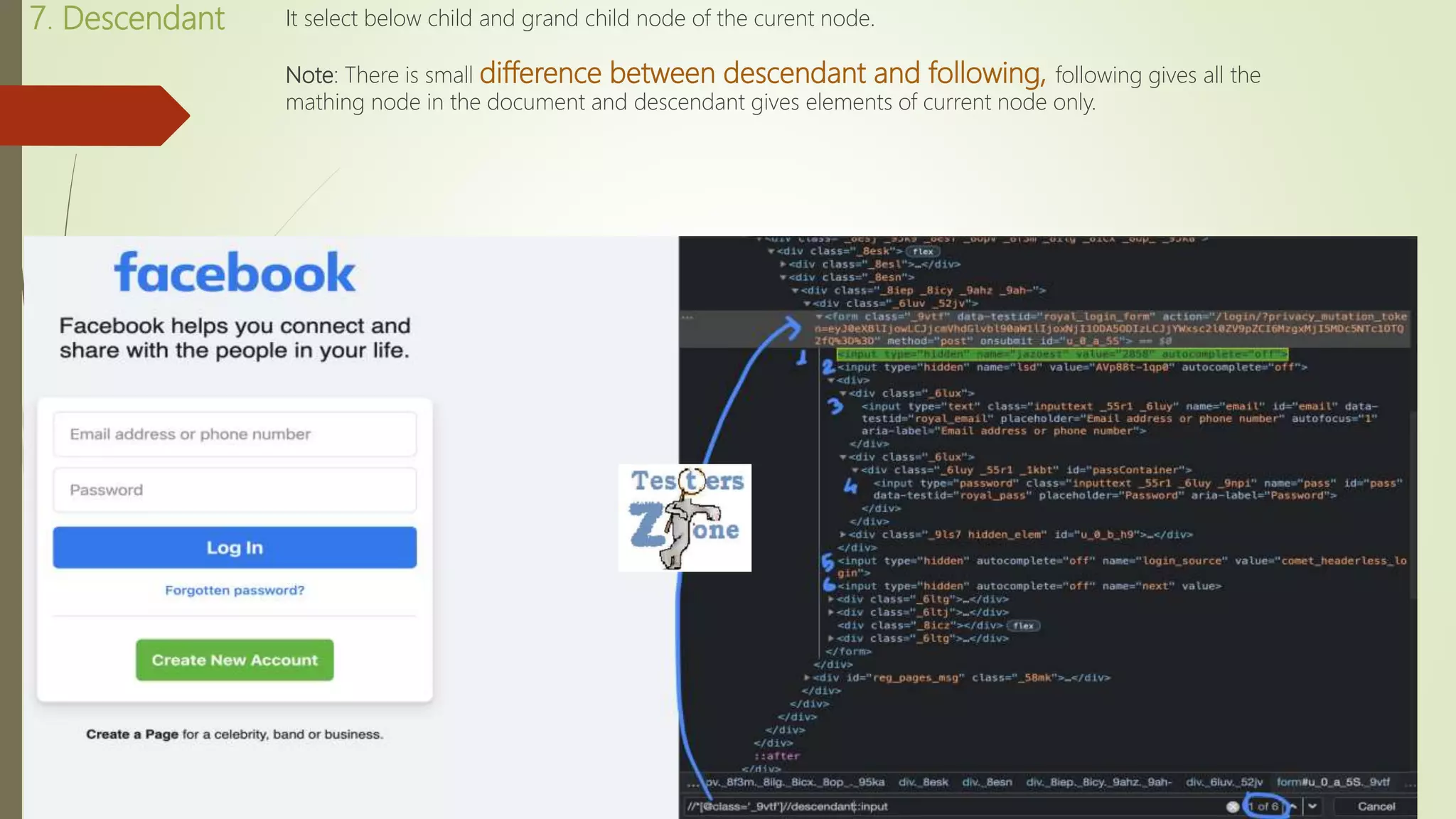
![XPath axes
method
Sometimes we don't get element very easily so we need to use axes method in xpath, we use this to find complex and dynamic
element also.
1. Following:
This will give you the count of total elements in a document of the current node and we can access them using index.
Syntax:
Xpath=//*[@type='text']//following::input](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-12-2048.jpg)
![2.Ancestor The ancestor axis selects all ancestors element (parent, grandparent, great-
grandparents, etc.) of the current node.
Syntax:
Xpath=//*[@type='text']//ancestor::div](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-13-2048.jpg)
![3. Child
Select all the child elements of the current node.
Xpath= //*[@class='ng-lns-c59-10']//child::tr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-14-2048.jpg)
![4. Preceding
Select all nodes that come before the current
node
Xpath= //*[@type='password']//preceding::input](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-15-2048.jpg)
![5. Following-sibling:
The following-sibling selects all sibling nodes after the current node at the same level. i.e. It will find the element
after the current node.
Xpath=//div[@id='nlplmgContainer']//following-
sibling::input](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-16-2048.jpg)
![6. Parent
It select the parent of the current node.
Xpath= //*[@type='password']//parent::div](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-17-2048.jpg)

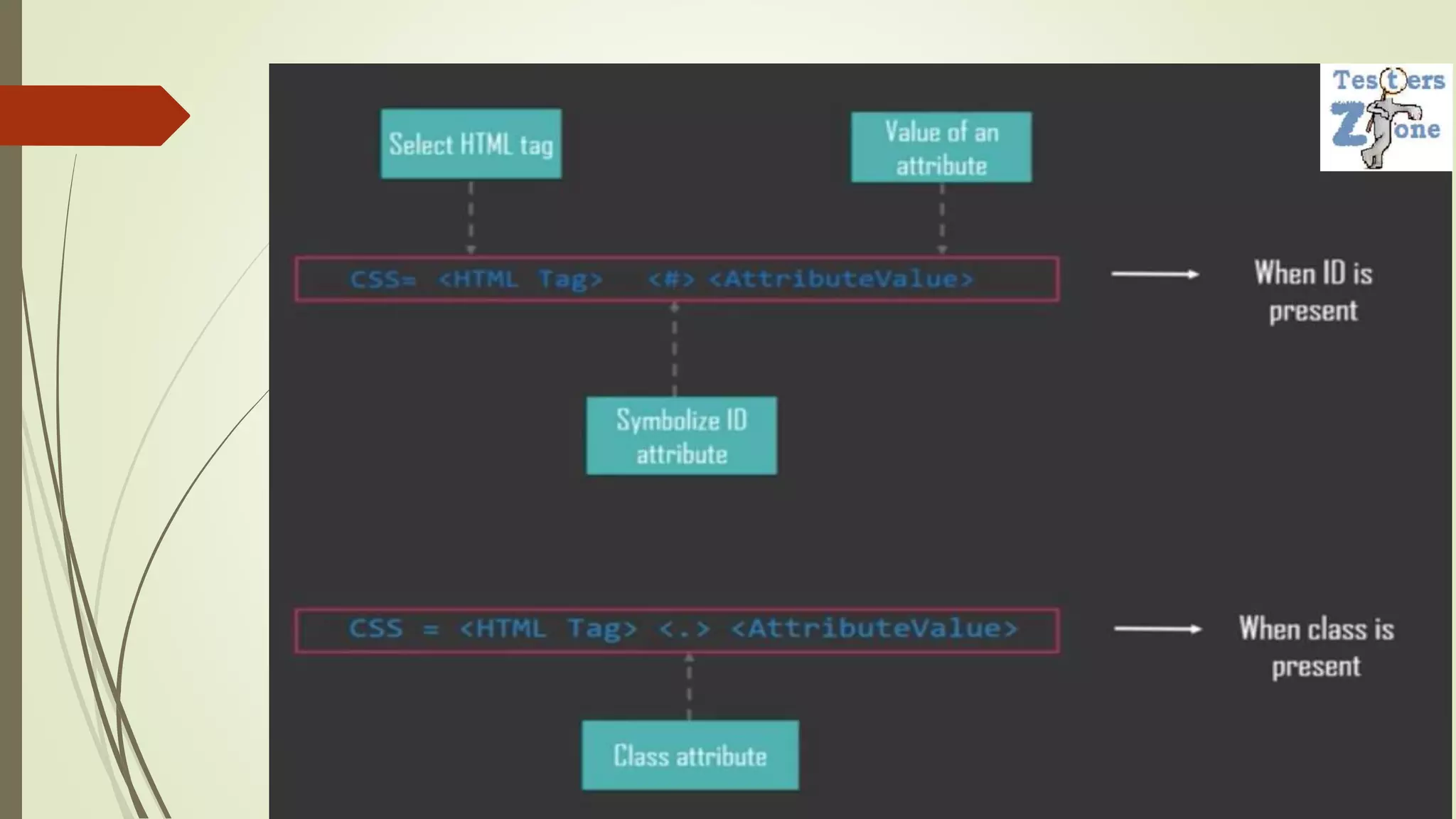


![Example
css = input[id$='mail']
css = input[id*='mai']
css = input[id^='ema']
using child selectors--> css = form>label>input[id=PersistentCookie]
using multiple node --> css = input[name=email][type=text]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selenium-locators-220510182354-e17ed02d/75/Selenium-Locators-23-2048.jpg)

