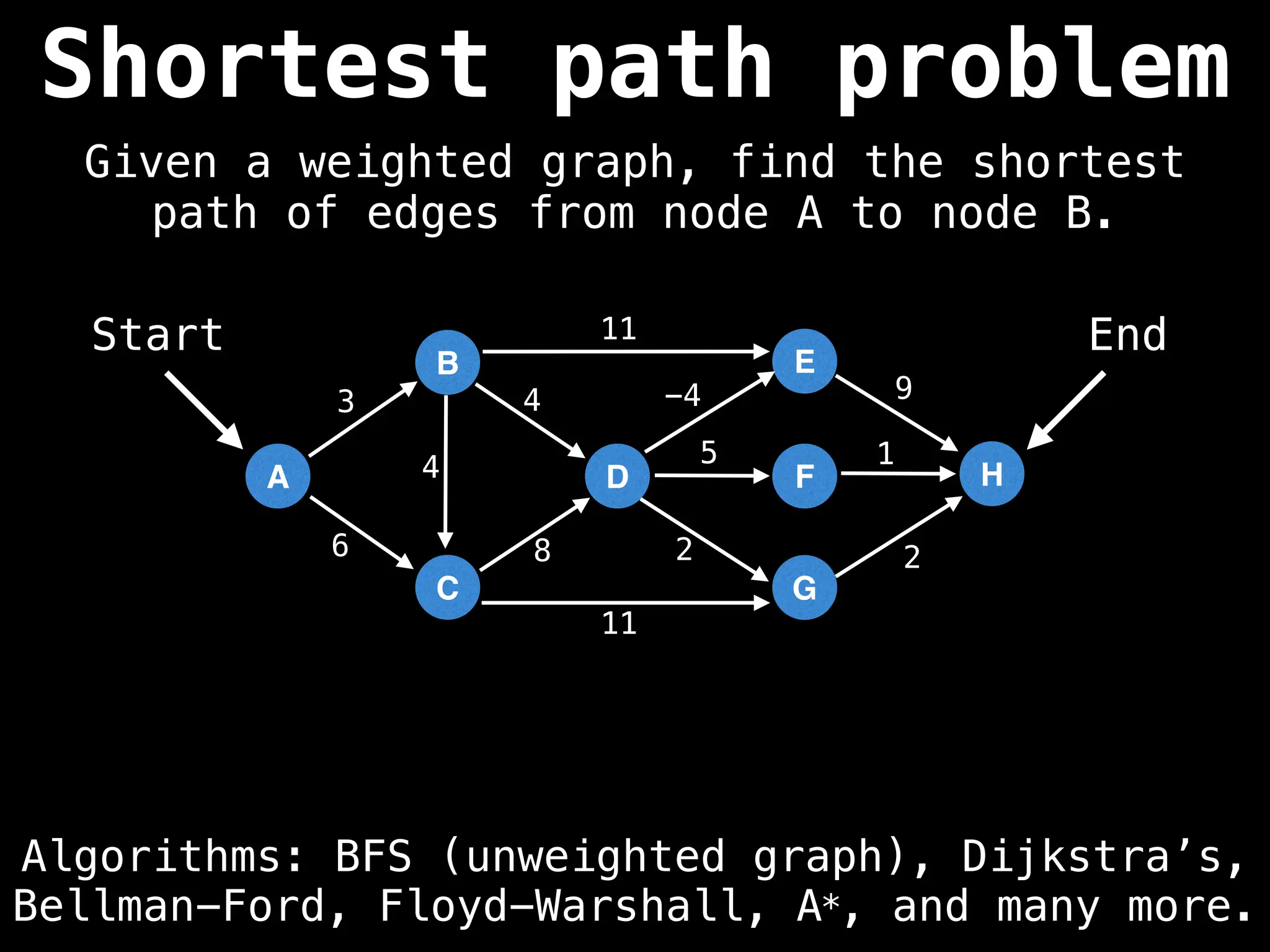
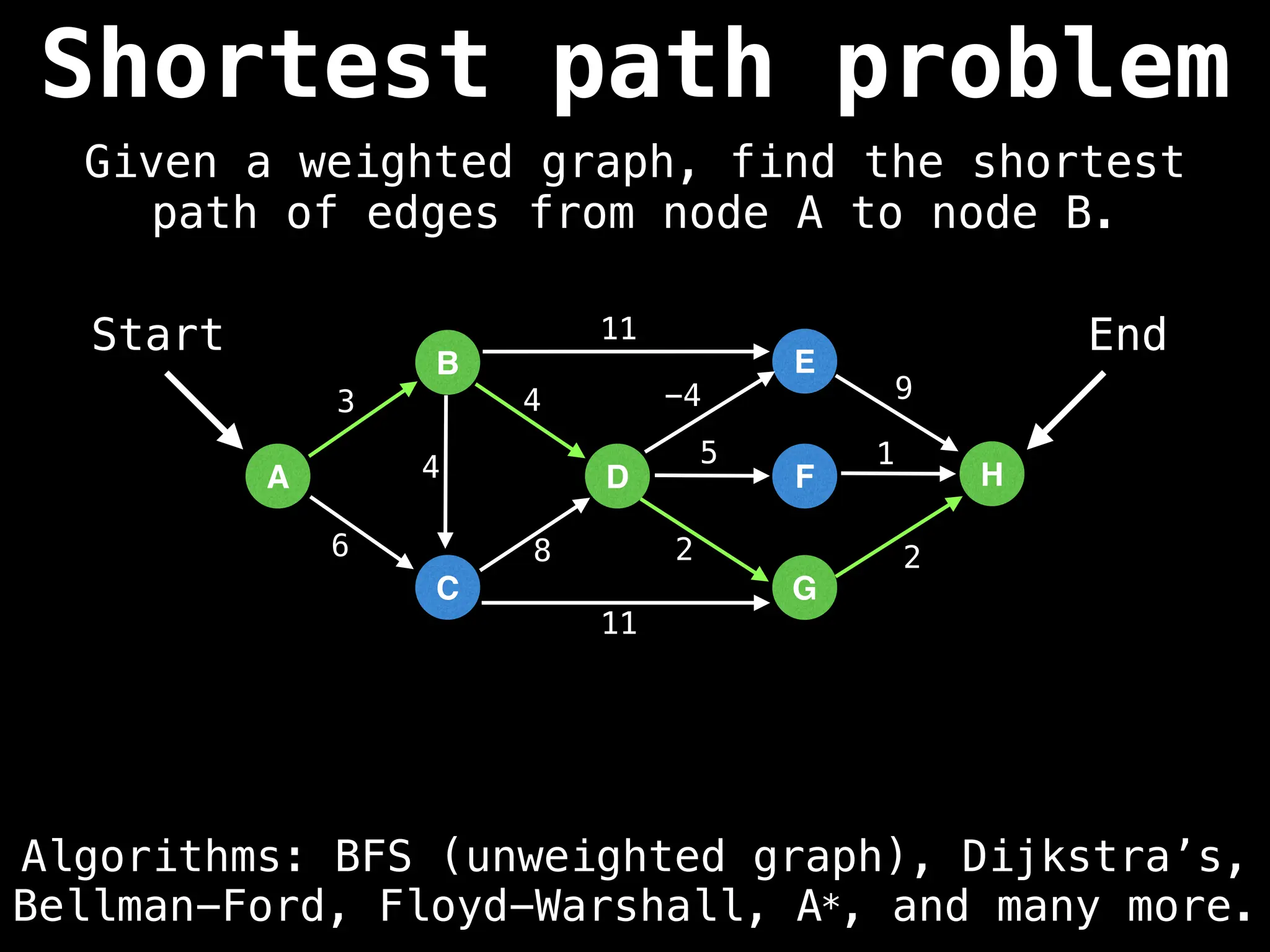
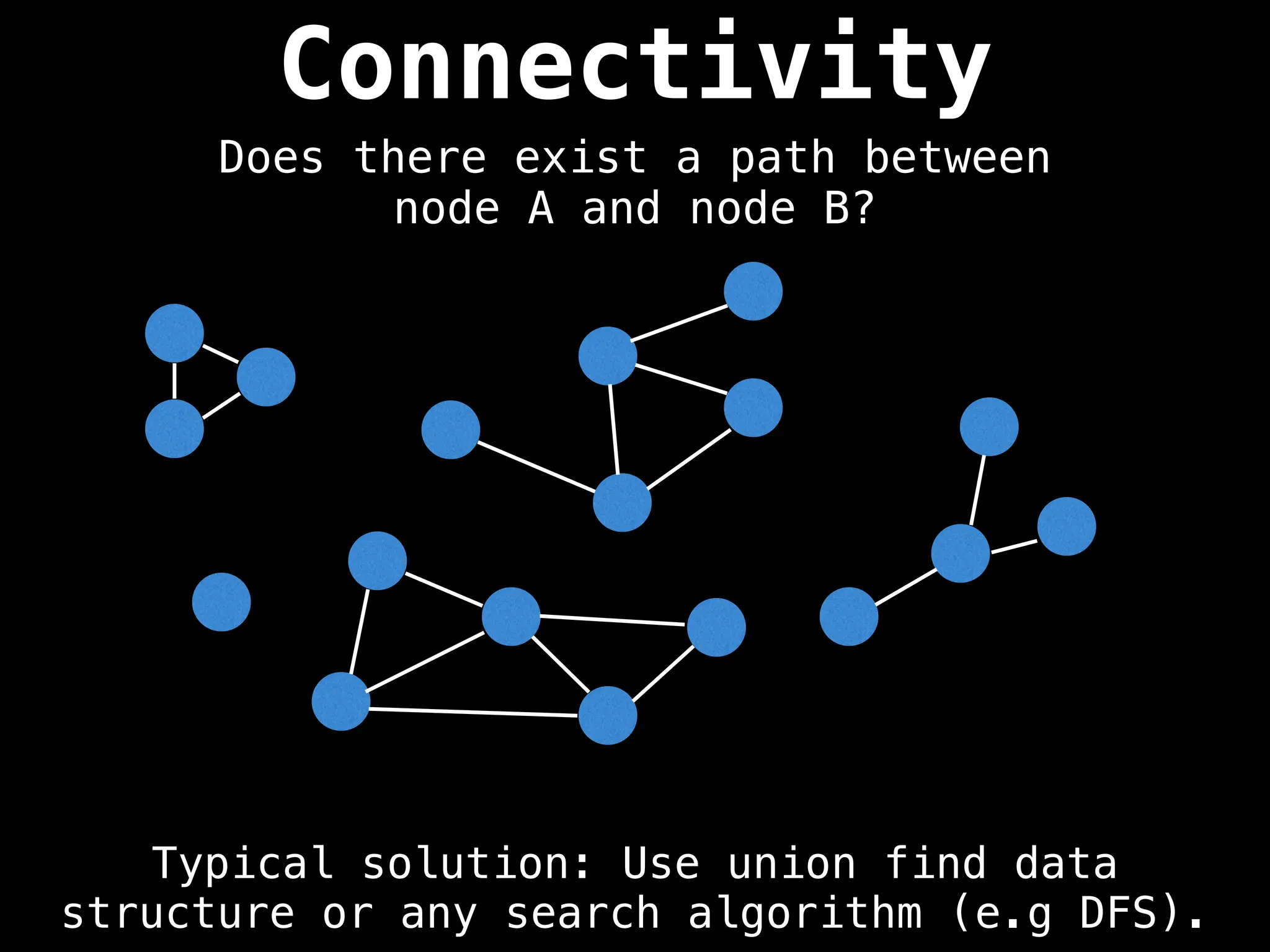
Graph theory algorithms are computational procedures that operate on graph structures (nodes and edges) to find solutions to problems involving relationships, connections, and paths within networks. Common algorithms include Breadth-First Search (BFS) and Depth-First Search (DFS) for traversal, Dijkstra's and Bellman-Ford for shortest paths, and Prim's and Kruskal's for finding minimum spanning trees. These algorithms are widely used in various fields, such as social network analysis, route optimization, and logistics.
Core Concepts
Graph:
A collection of nodes (vertices) and edges, where edges represent the relationships or connections between nodes.
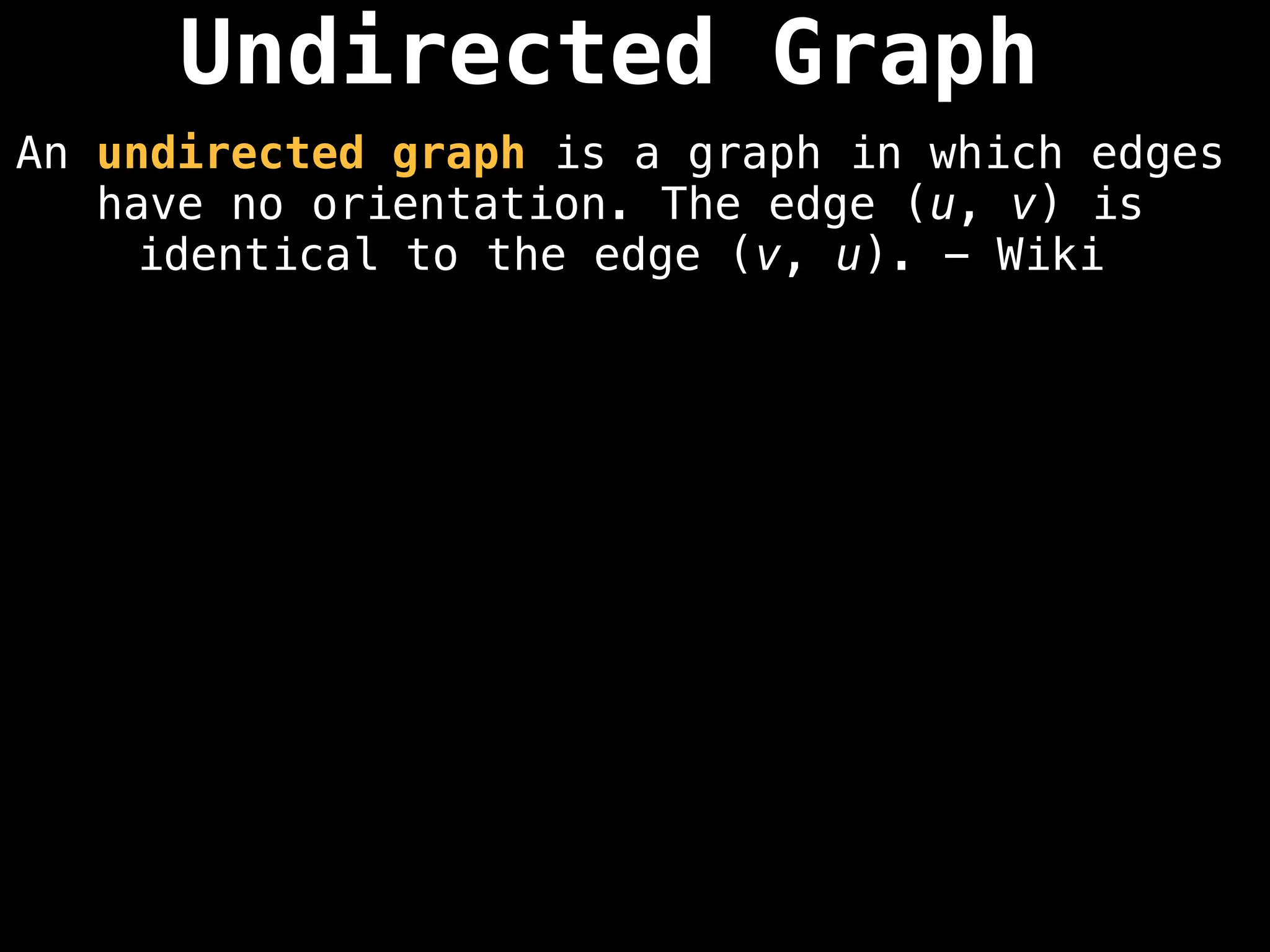
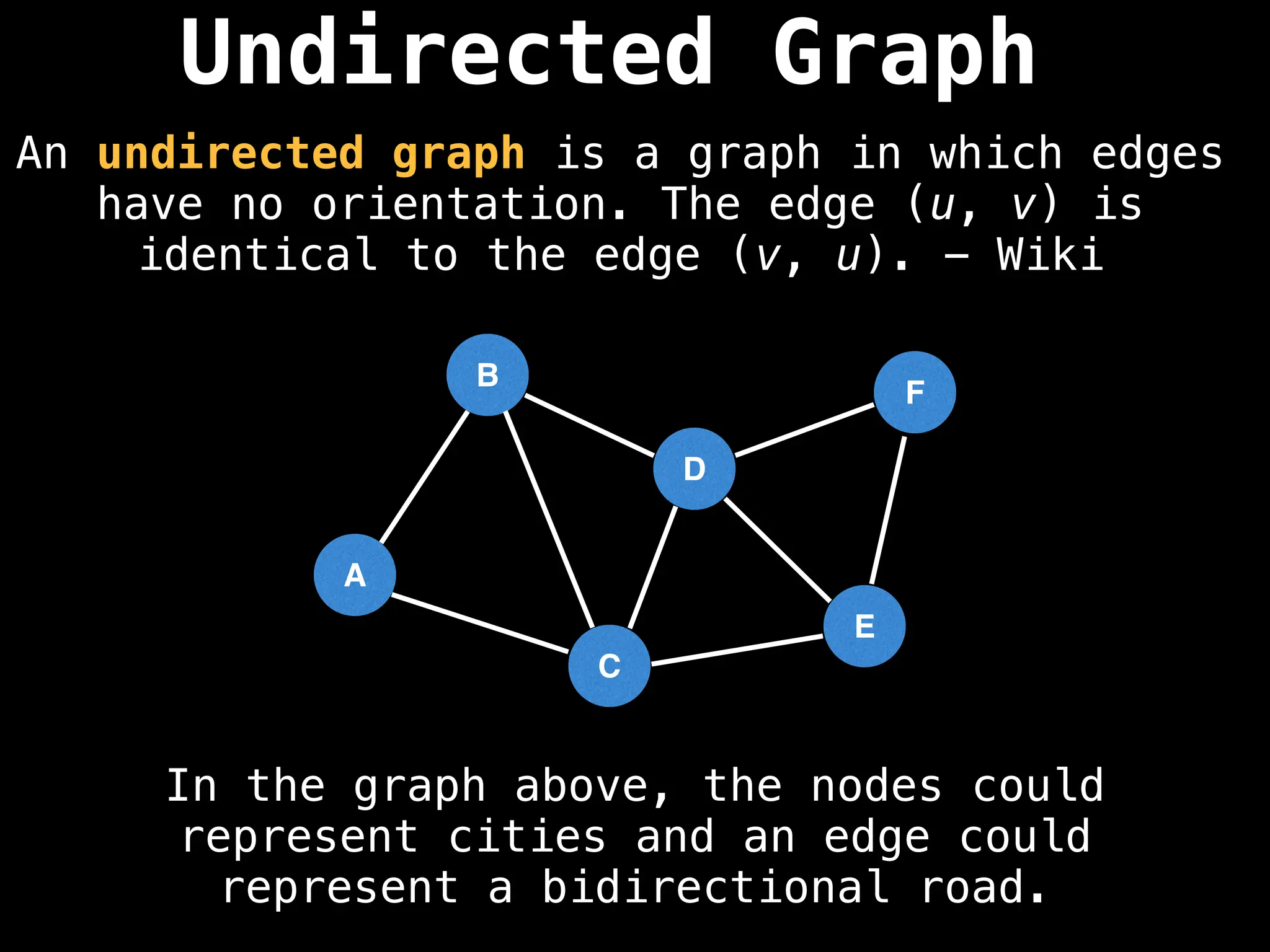
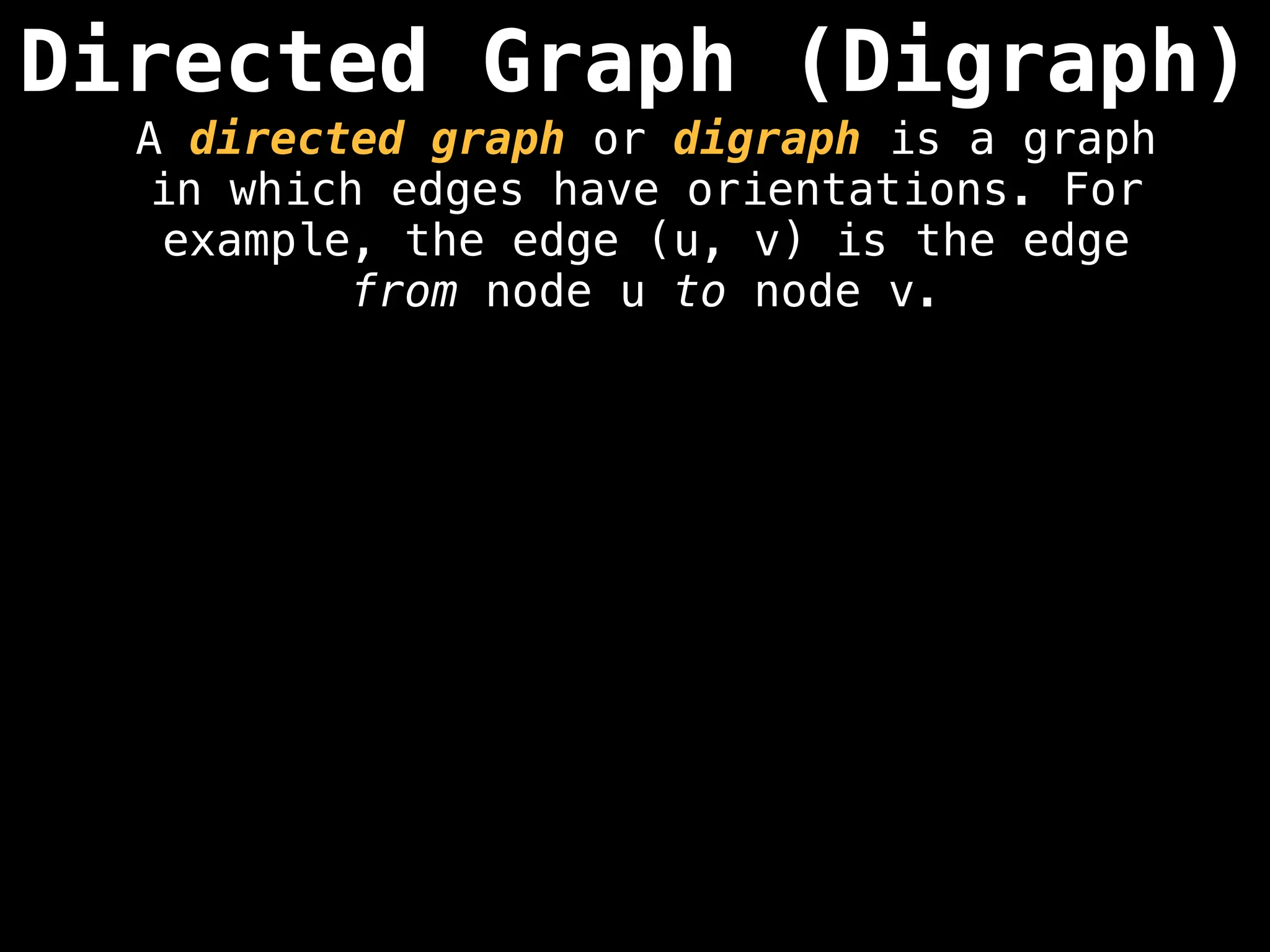
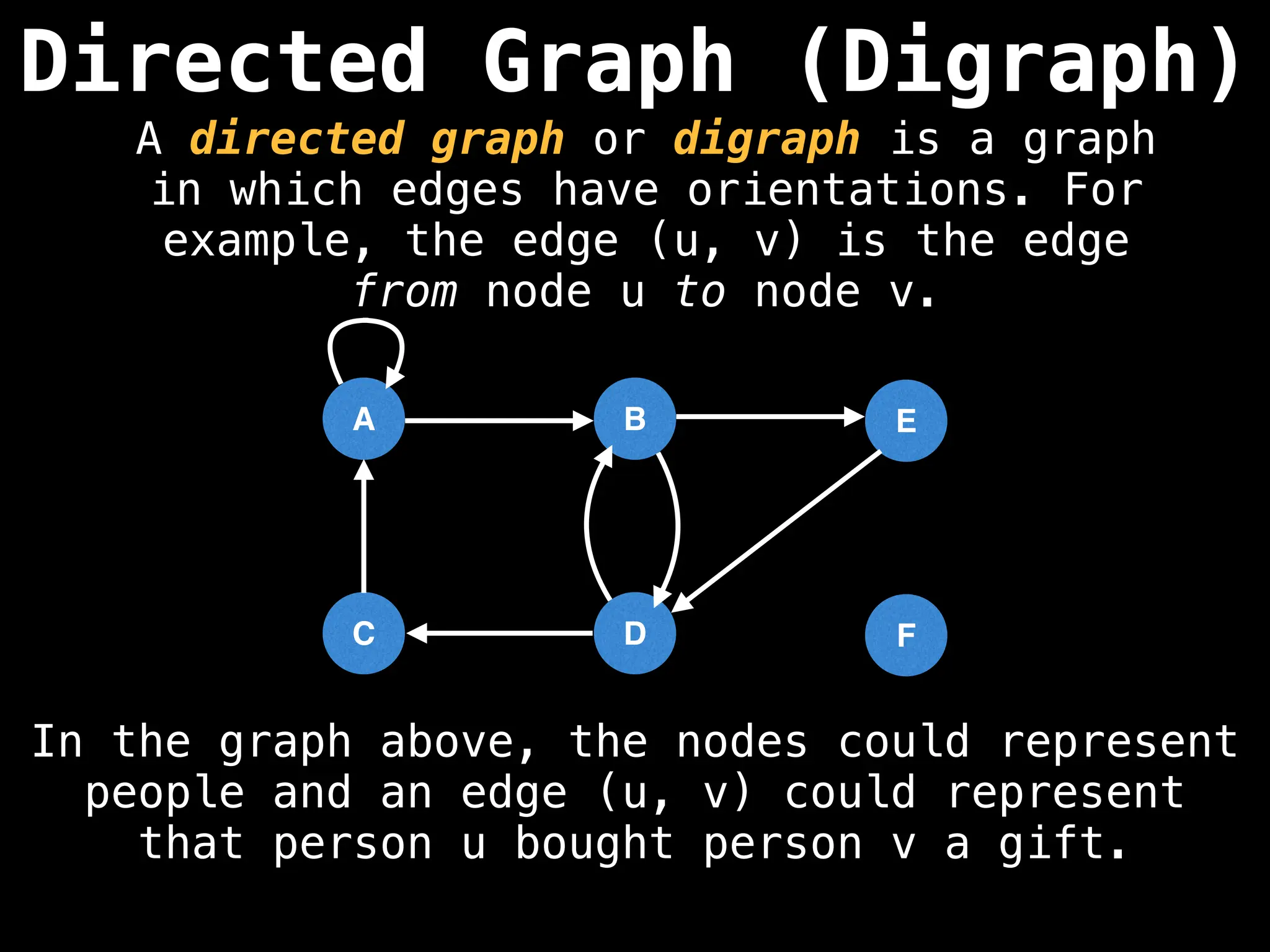
Directed vs. Undirected Graphs:
Edges in undirected graphs are bidirectional, while edges in directed graphs have a specific direction.
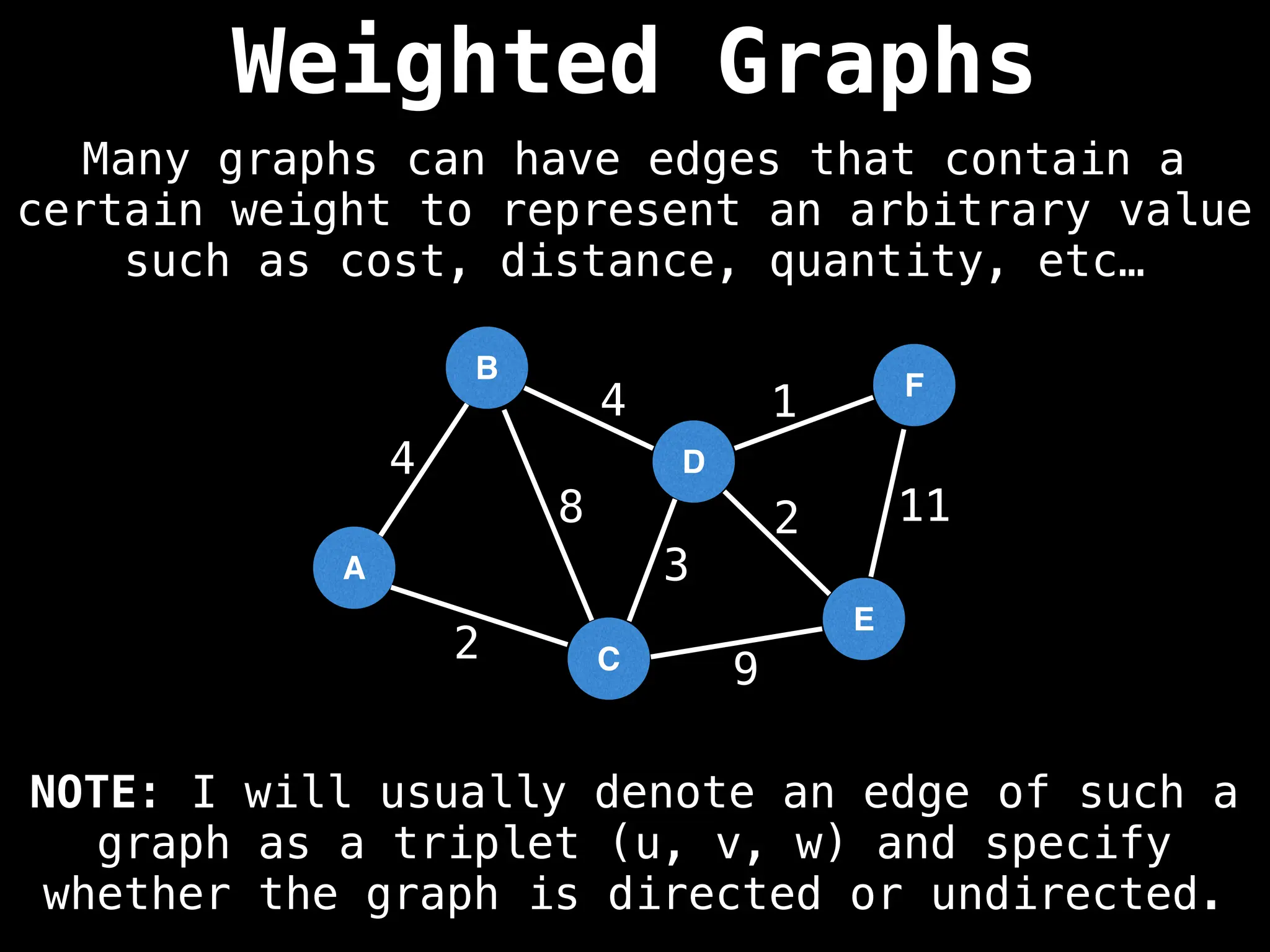
Weighted vs. Unweighted Graphs:
Edges in weighted graphs have numerical values (weights), which can represent cost or distance, while unweighted graphs do not.
Common Algorithms
Traversal Algorithms:
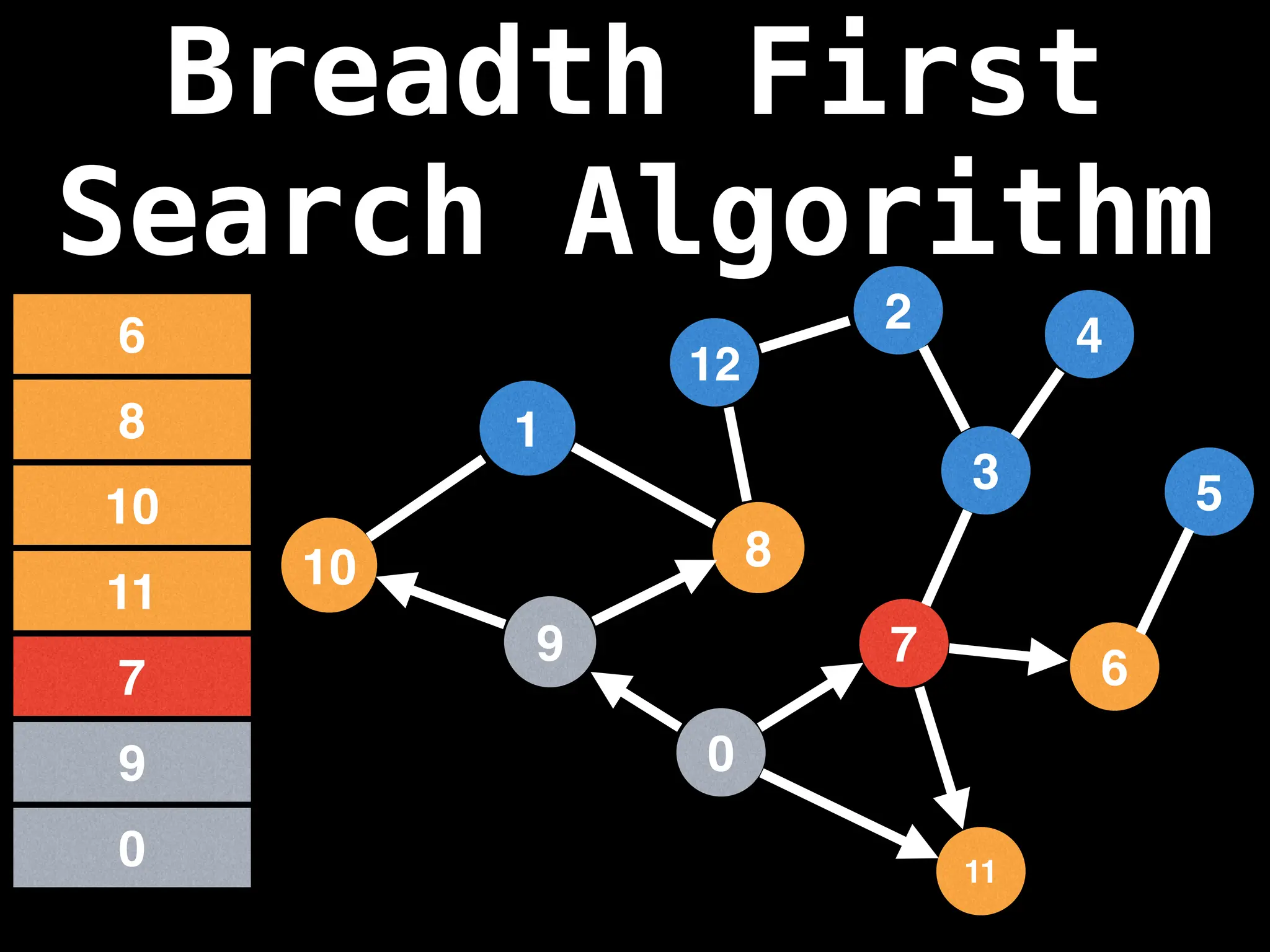
Breadth-First Search (BFS): Explores a graph level by level, exploring all neighbors of a node before moving to the next level.
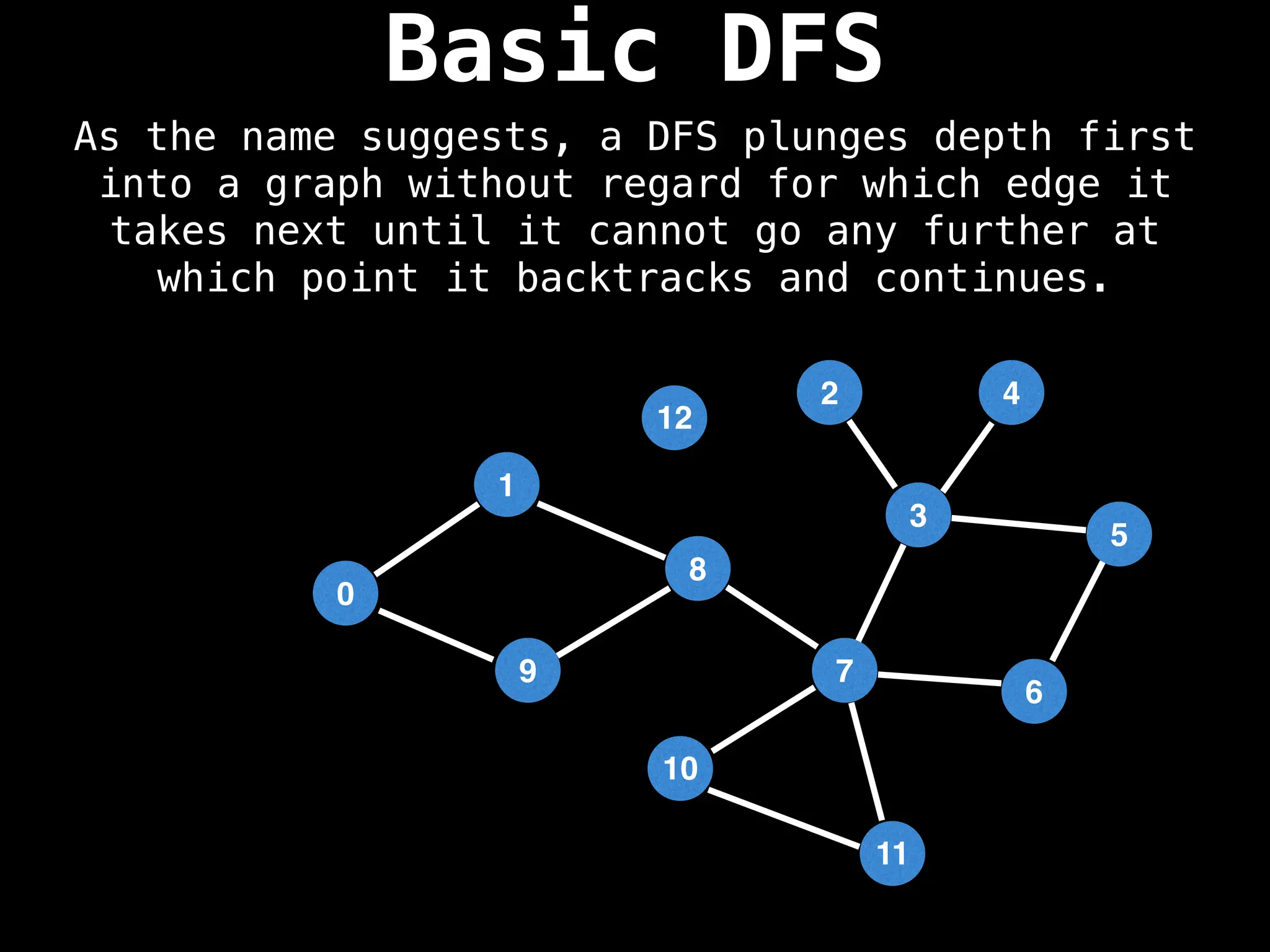
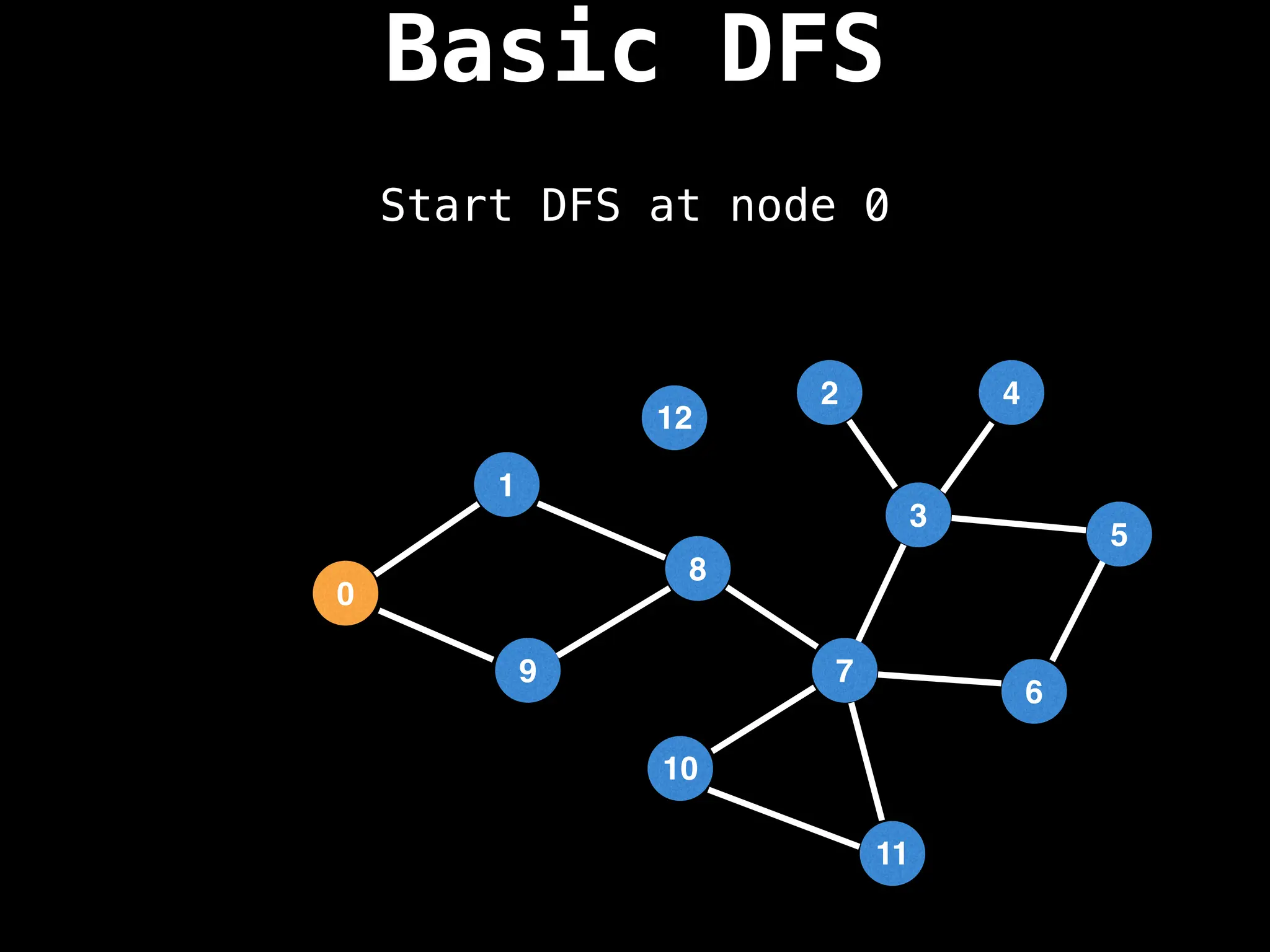
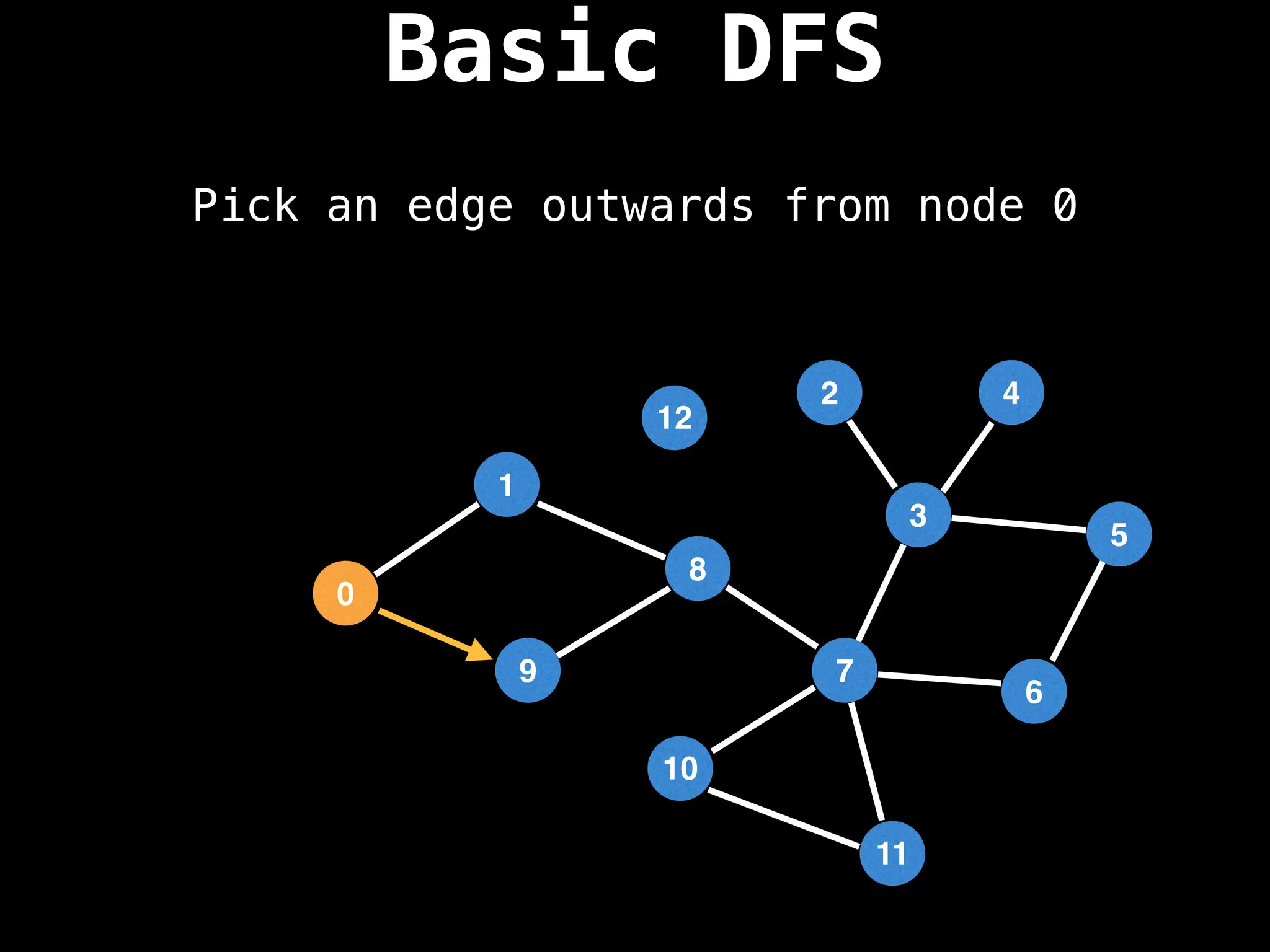
Depth-First Search (DFS): Explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
Shortest Path Algorithms:
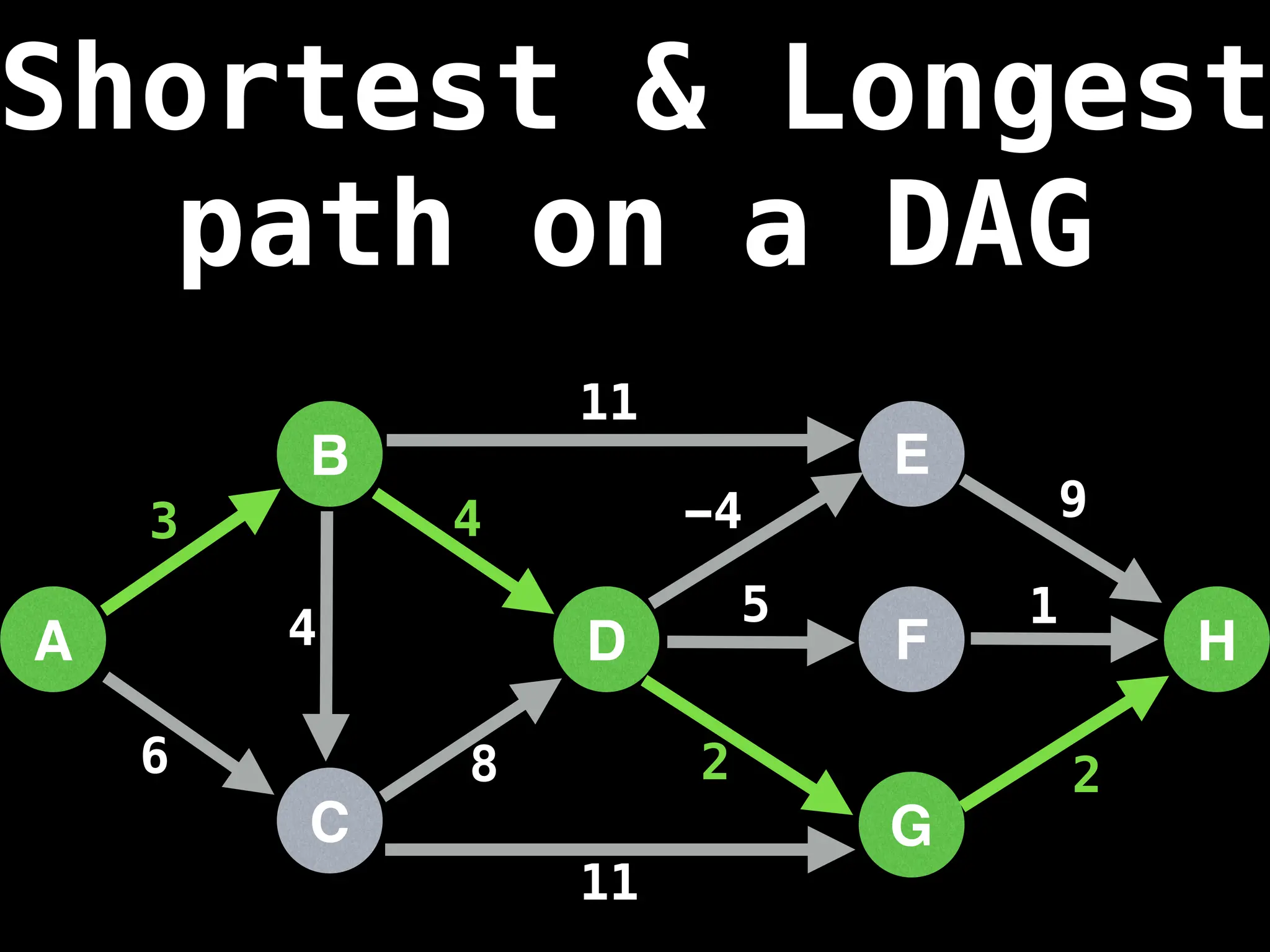
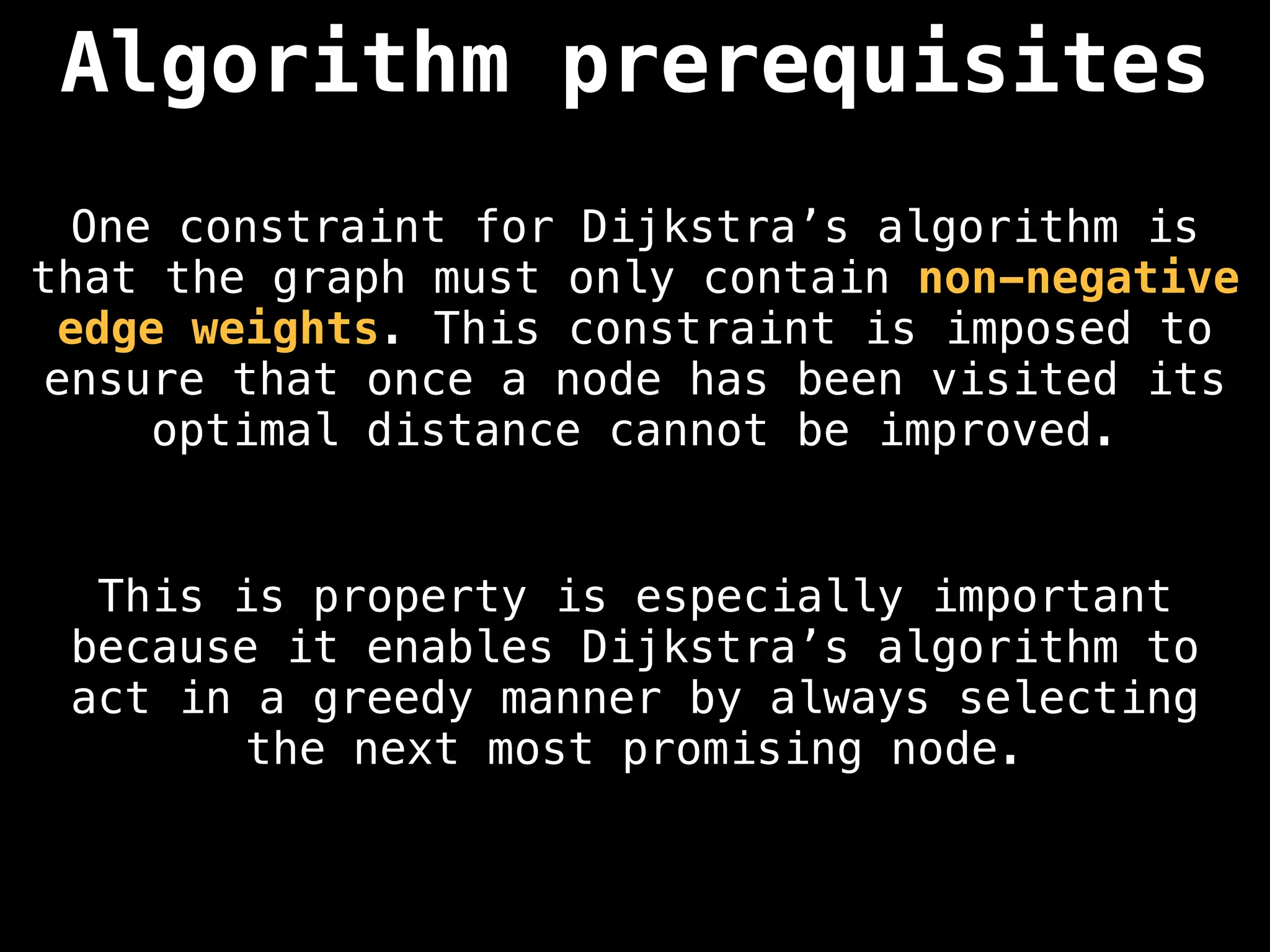
Dijkstra's Algorithm: Finds the shortest paths from a single source node to all other nodes in a graph with non-negative edge weights.
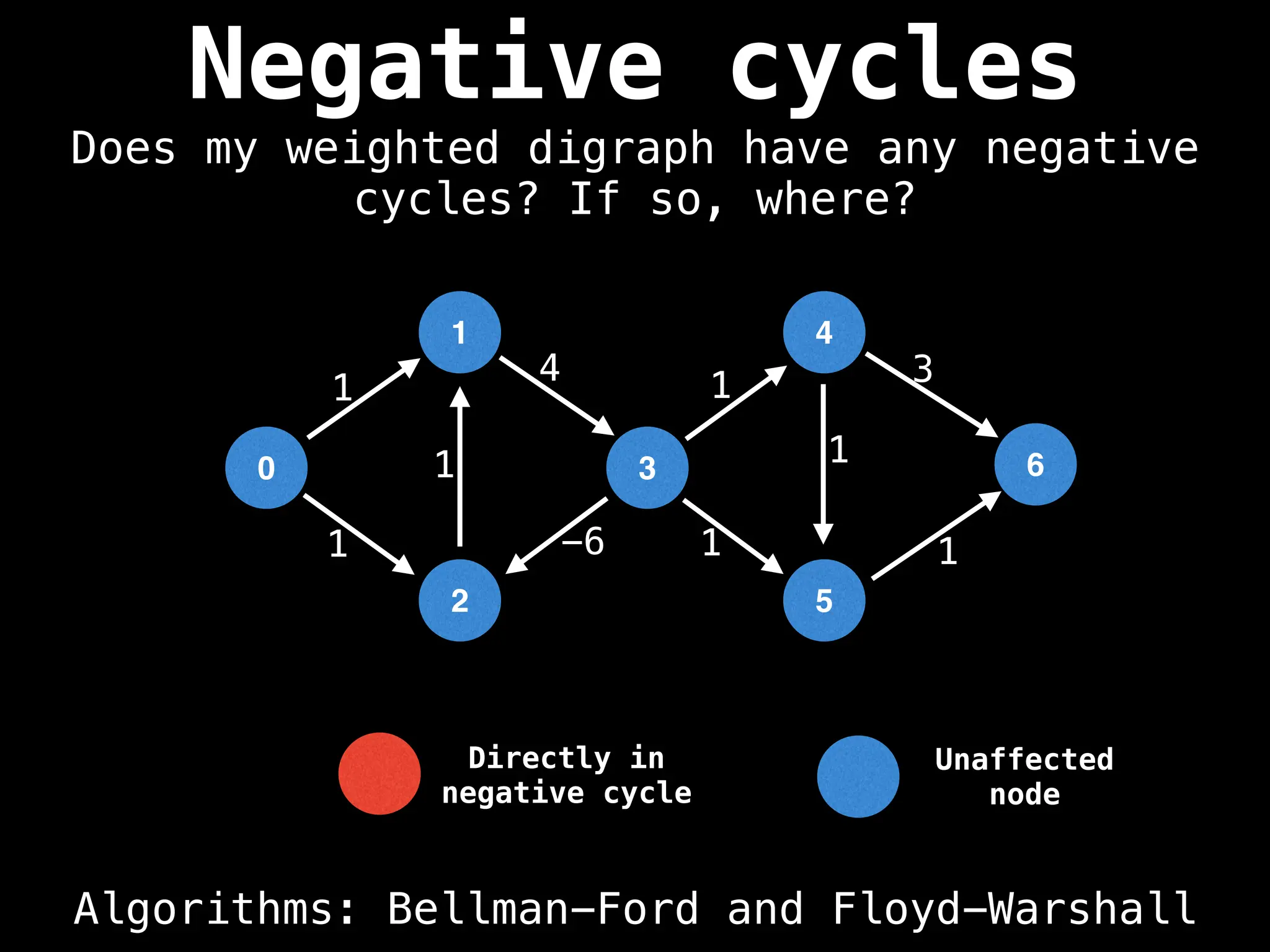
Bellman-Ford Algorithm: Finds shortest paths from a single source to all other nodes, even with negative edge weights (but no negative cycles).
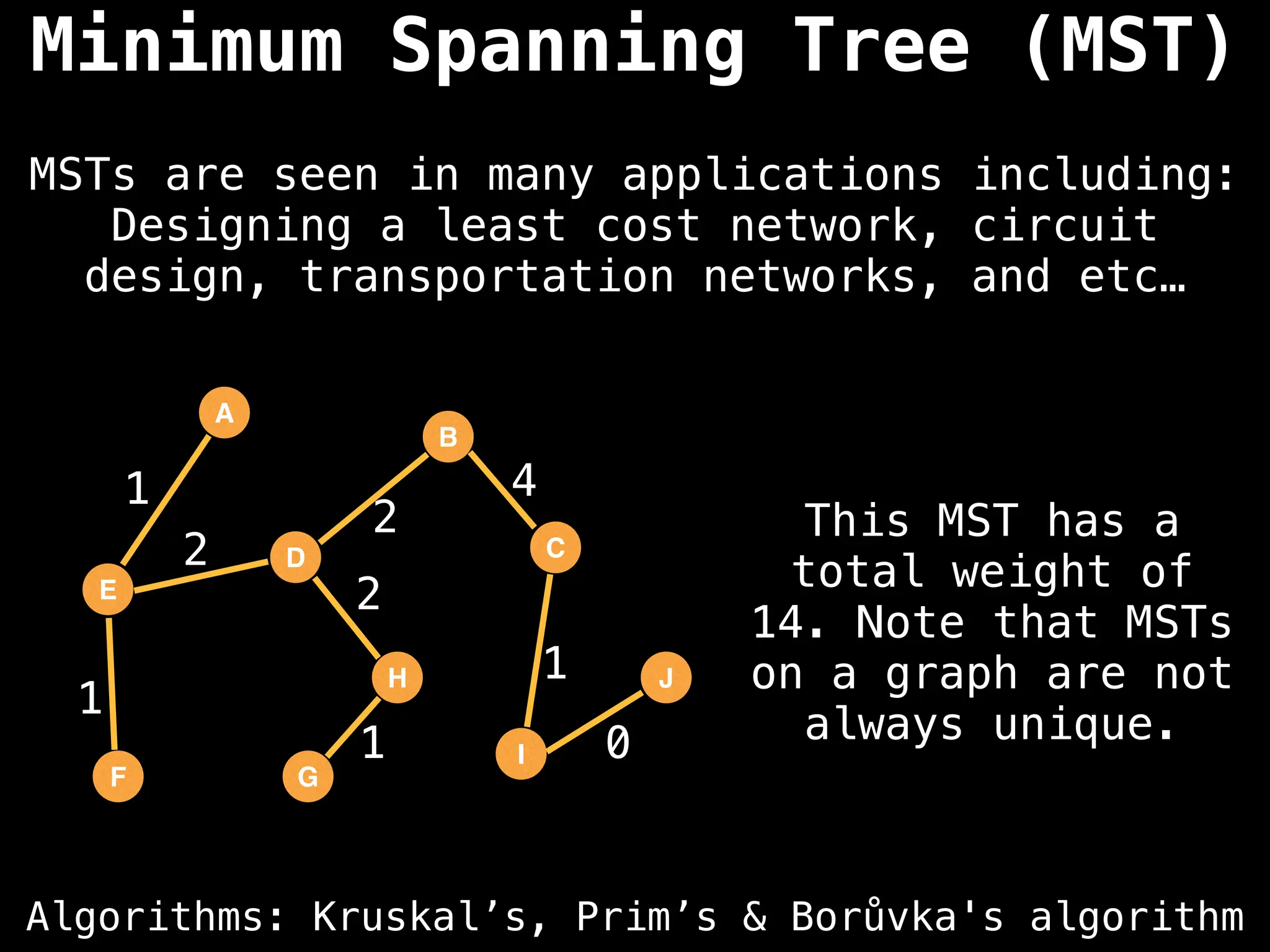
Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) Algorithms:
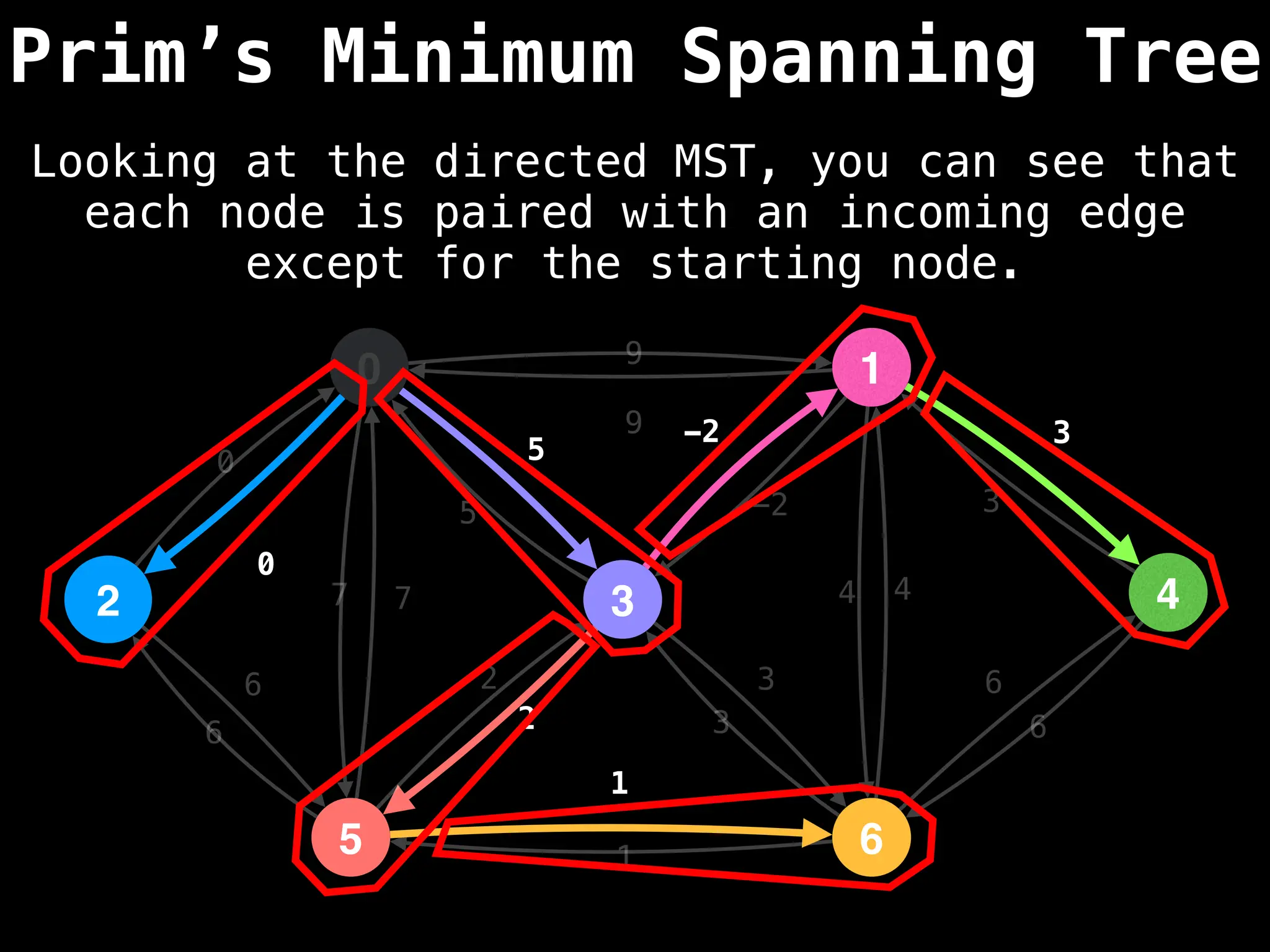
Prim's Algorithm: Builds an MST by starting from an arbitrary vertex and adding the cheapest edge that connects a vertex in the growing tree to one outside the tree.
Kruskal's Algorithm: Builds an MST by sorting all edges by weight and adding them to the tree as long as they don't form a cycle.
Applications
Social Networks: Analyzing user influence, community detection, and relationship patterns.
Transportation & Navigation: Finding the shortest or most efficient routes between locations.
Logistics: Optimizing delivery routes and supply chains.
Bioinformatics: Modeling biological networks and analyzing relationships in biological data.
Web Analysis: Understanding the structure of web pages and how users navigate them.
Applications of the 20 Most Popular Graph Algorithms - Memgraph
11 Mar 2022 — Johnson's algorithm finds the shortest paths between every pair of vertices in an edge-weighted directed graph. Edge we...
Memgraph
Applications of the 20 Most Popular Graph Algorithms
11 Mar 2022 — The Bellman-Ford algorithm uses Dijkstra's algorithm to find the shortest path from a source node to all other nodes in...
Memgraph
Graph Algorithms for Technical Interviews - Full Course
4 Aug 2021 — and technically I would have to double traverse some nodes like B and D over here. so overall in this yellow. coloring I...



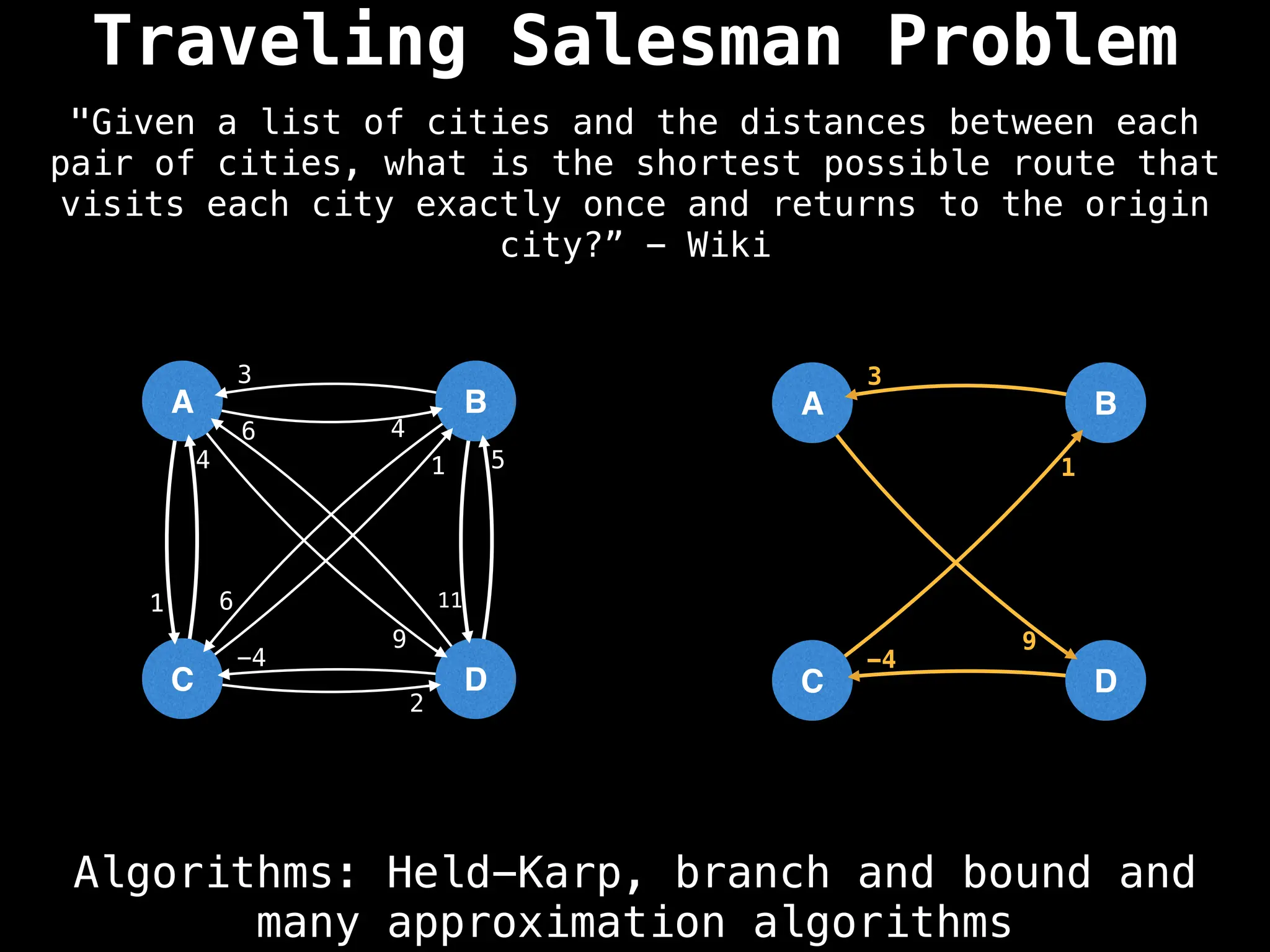
![Adjacency Matrix
0 4 1 9
3 0 6 11
4 1 0 2
6 5 -4 0
A B C D
A
B
C
D
A
C
B
D
4
9
1
3
6 11
4 1
2
6
5
-4
A adjacency matrix m is a very simple way to
represent a graph. The idea is that the cell
m[i][j] represents the edge weight of going
from node i to node j.
NOTE: It is often assumed that the edge of
going from a node to itself has a cost of zero.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-19-2048.jpg)

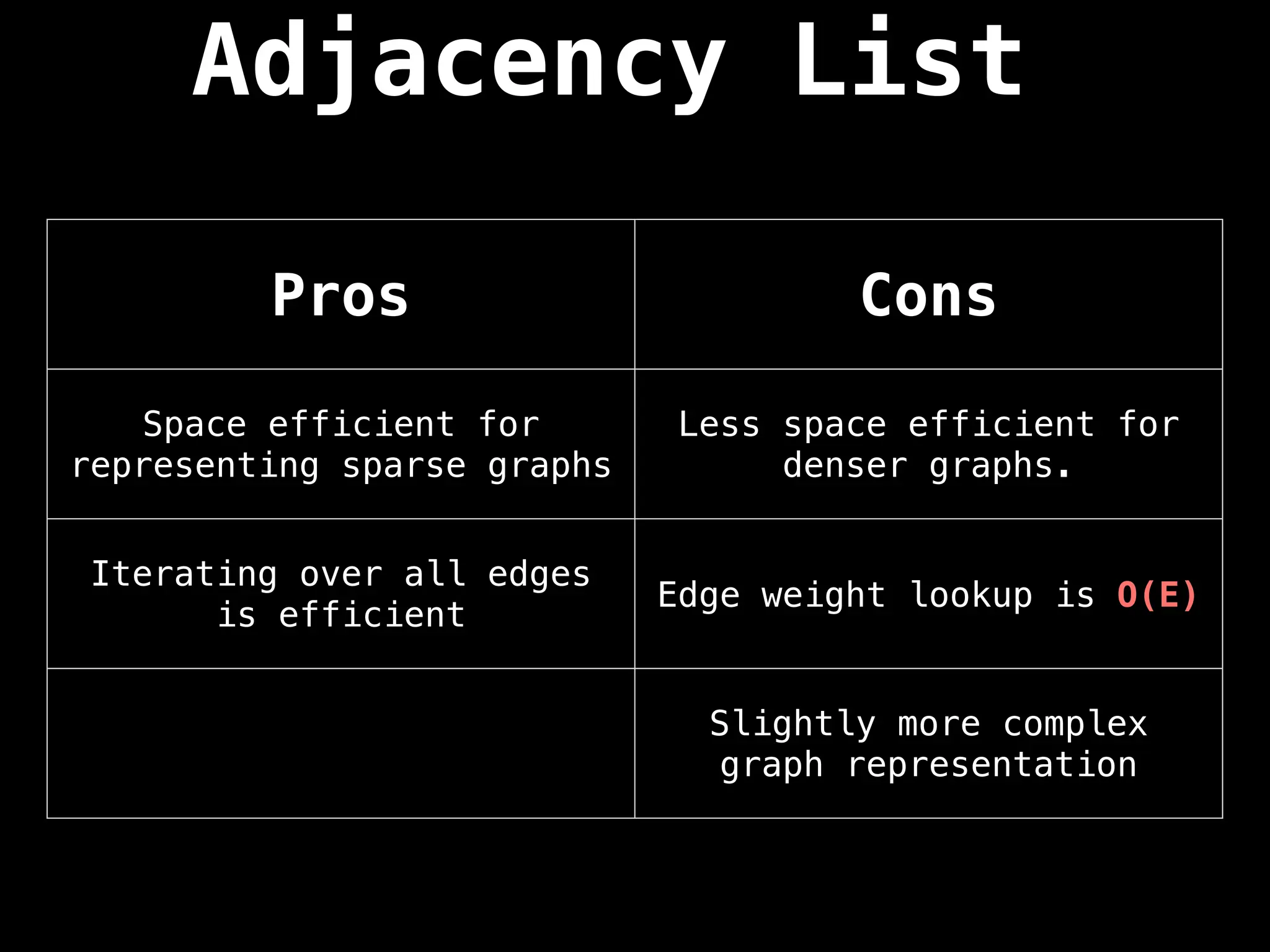
![Adjacency List
An adjacency list is a way to represent a
graph as a map from nodes to lists of edges.
A -> [(B,4),(C,1)]
B -> [(C,6)]
C -> [(A,4),(B,1),(D,2)]
D -> []
A
C
B
D
4
1 6
4 1
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-21-2048.jpg)
![A -> [(B,4),(C,1)]
B -> [(C,6)]
C -> [(A,4),(B,1),(D,2)]
D -> []
Adjacency List
A
C
B
D
4
1 6
4 1
2
Node C can reach
Node A with cost 4
Node B with cost 1
Node D with cost 2
An adjacency list is a way to represent a
graph as a map from nodes to lists of edges.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-22-2048.jpg)
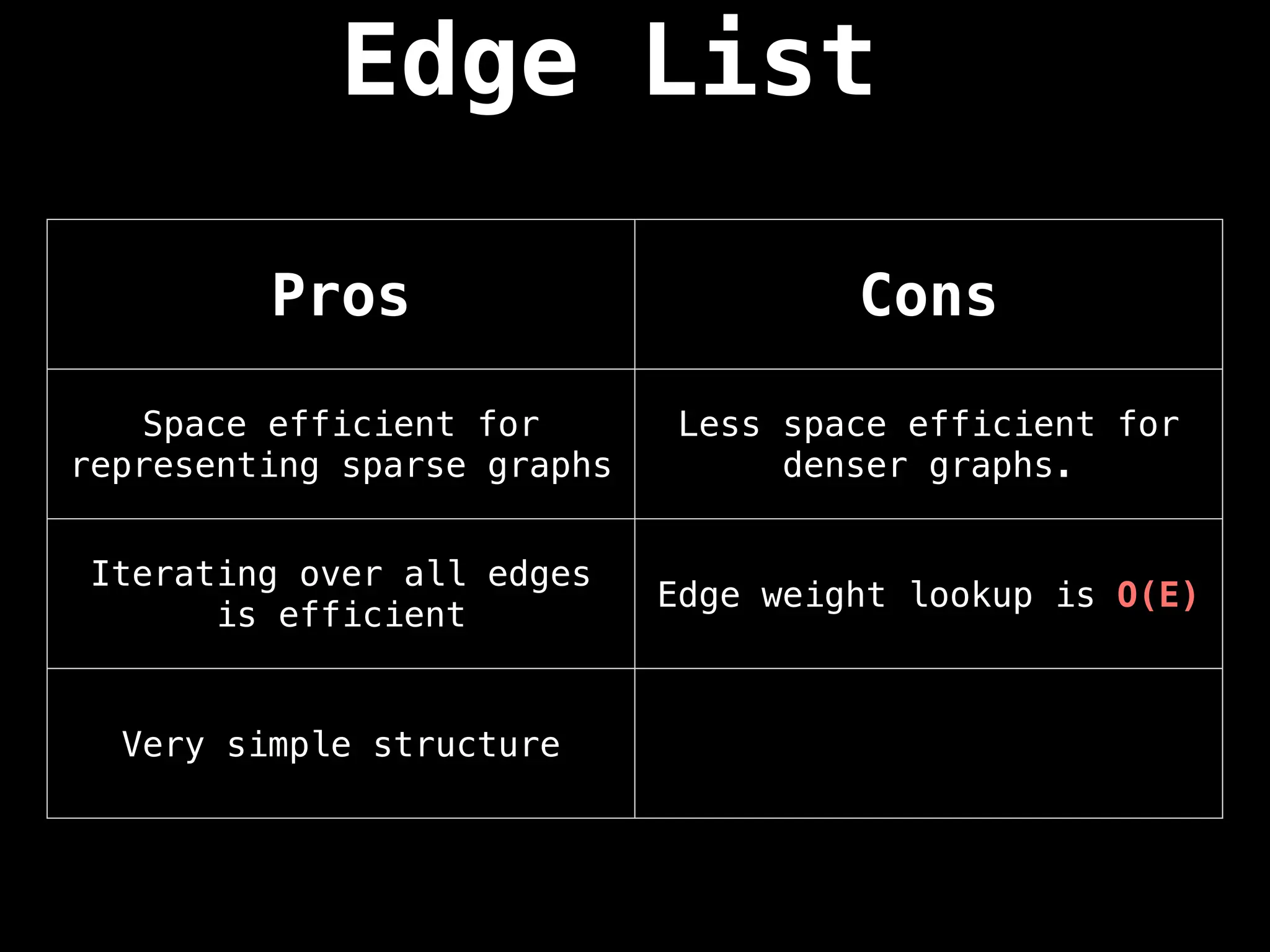
![Edge List
This representation is seldomly used because
of its lack of structure. However, it is
conceptually simple and practical in a
handful of algorithms.
[(C,A,4), (A,C,1),
(B,C,6), (A,B,4),
(C,B,1), (C,D,2)]
A
C
B
D
4
1 6
4 1
2
An edge list is a way to represent a graph
simply as an unordered list of edges. Assume
the notation for any triplet (u,v,w) means:
“the cost from node u to node v is w”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-24-2048.jpg)




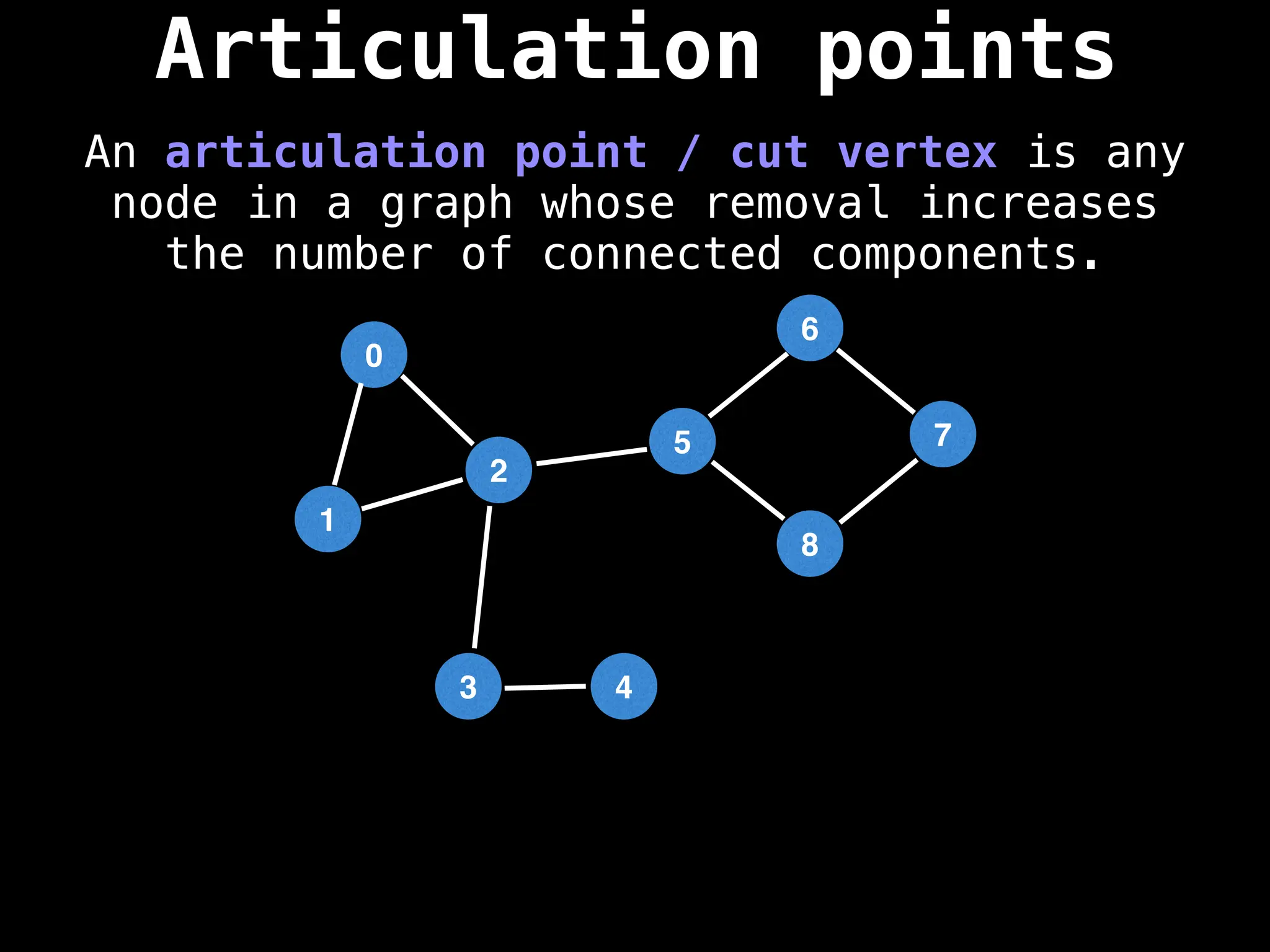
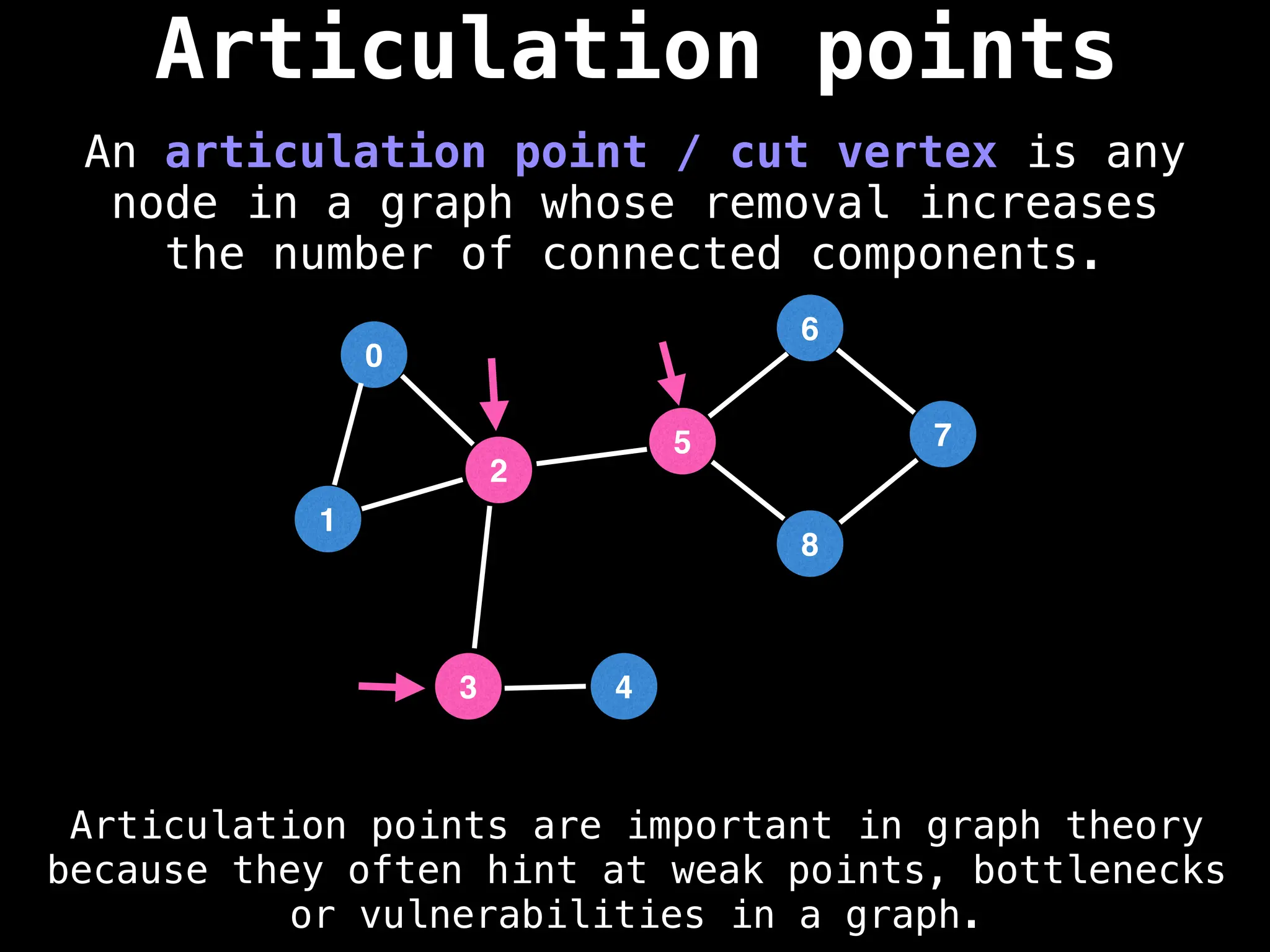
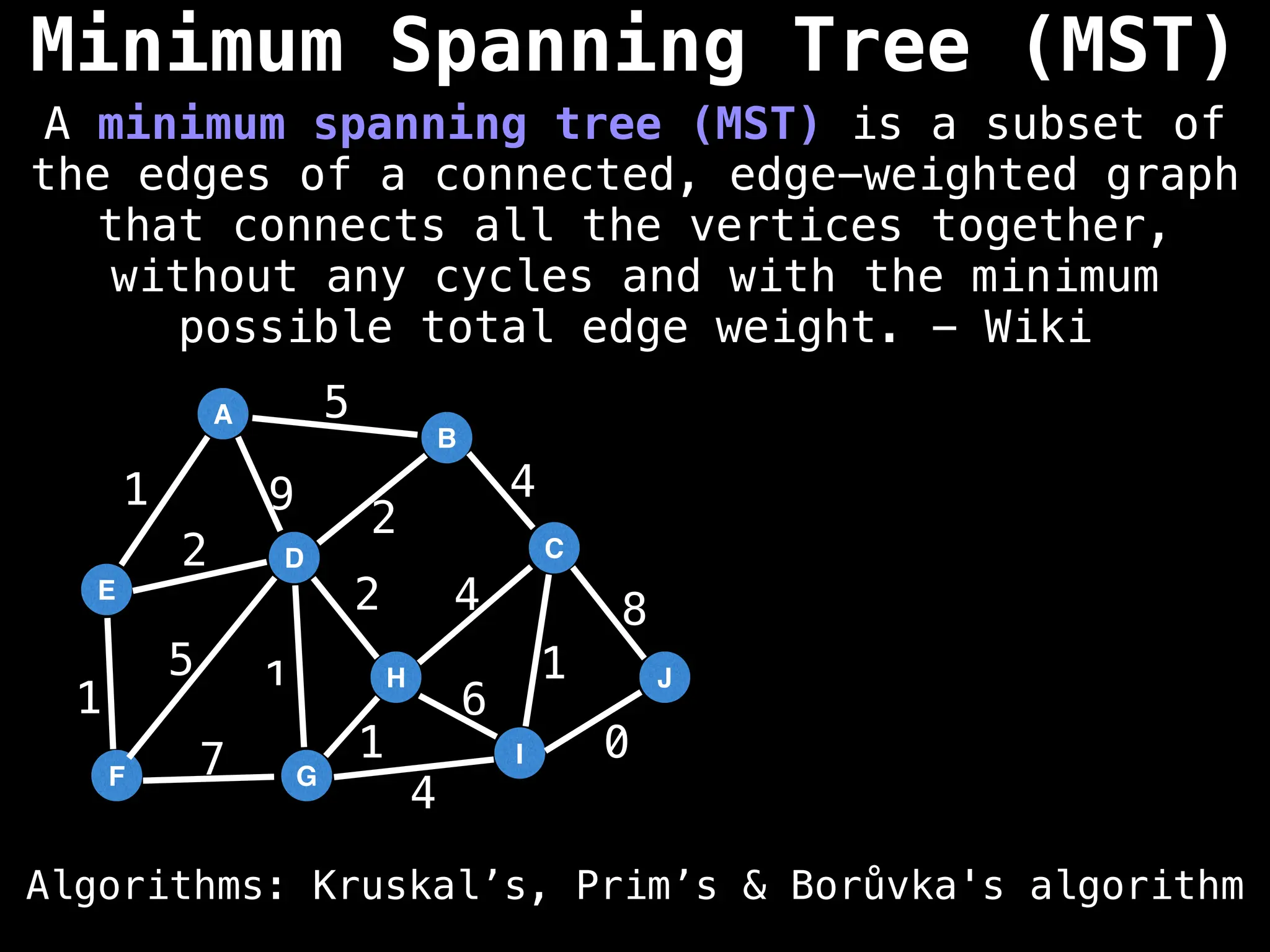
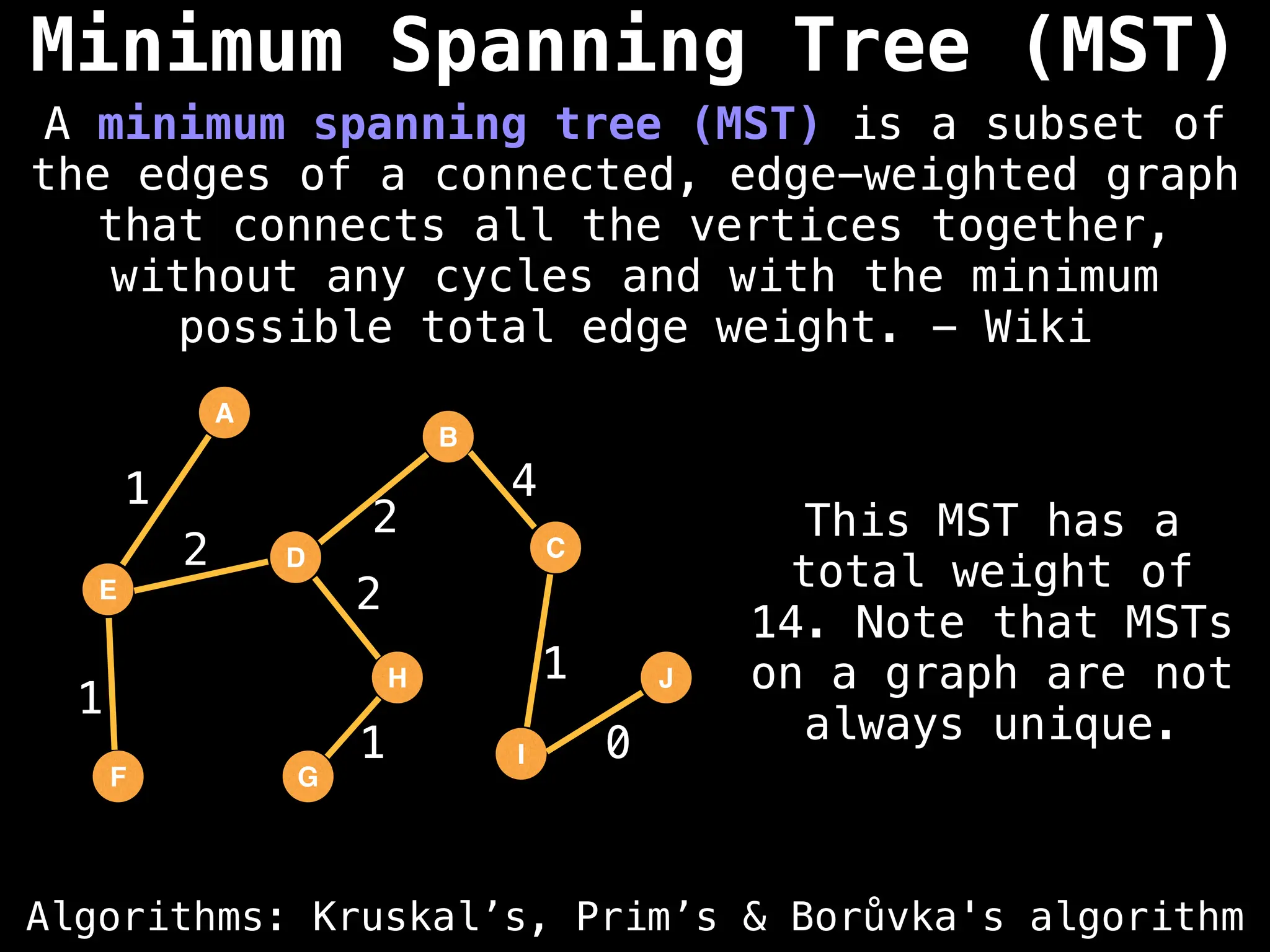



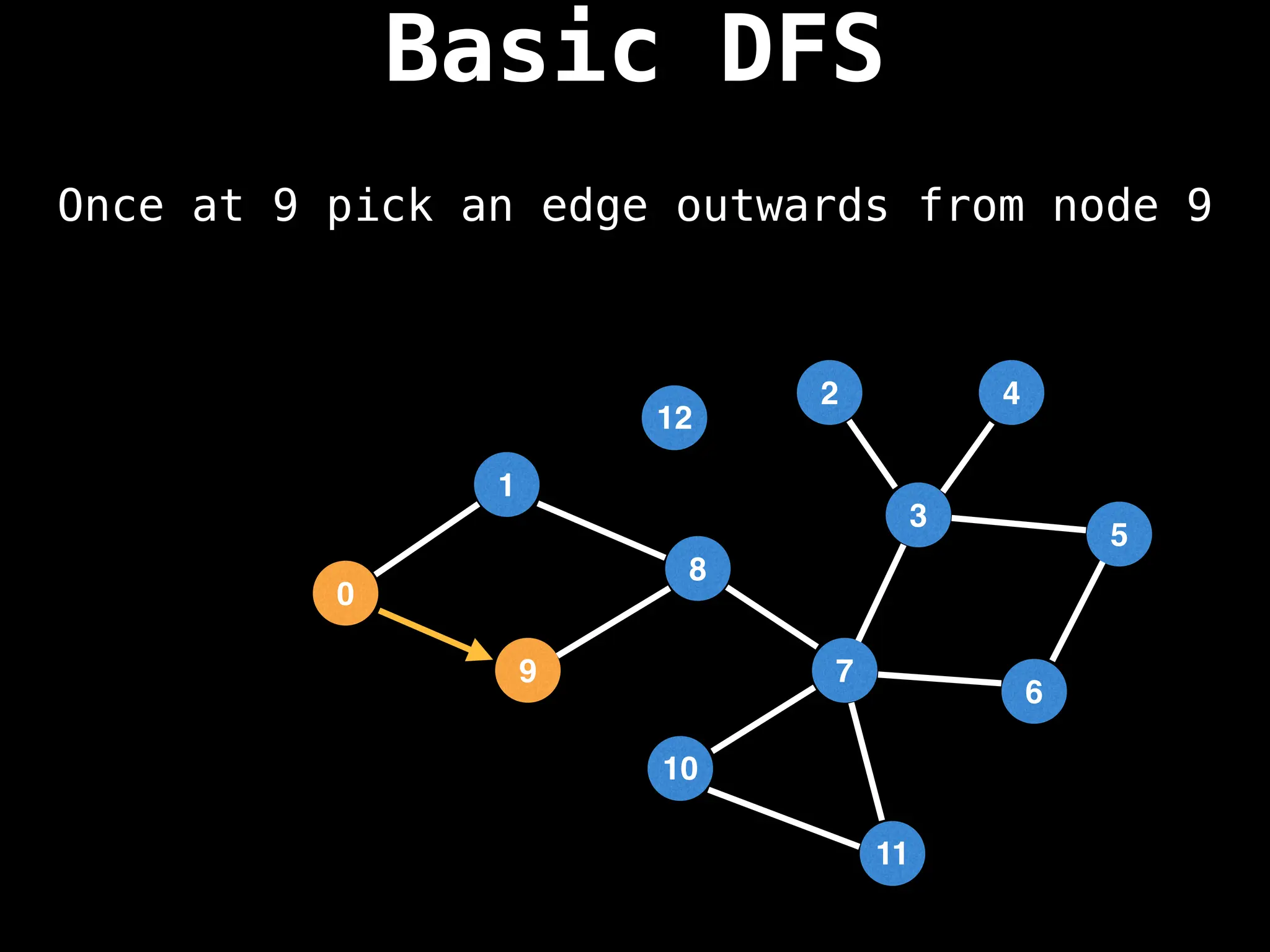
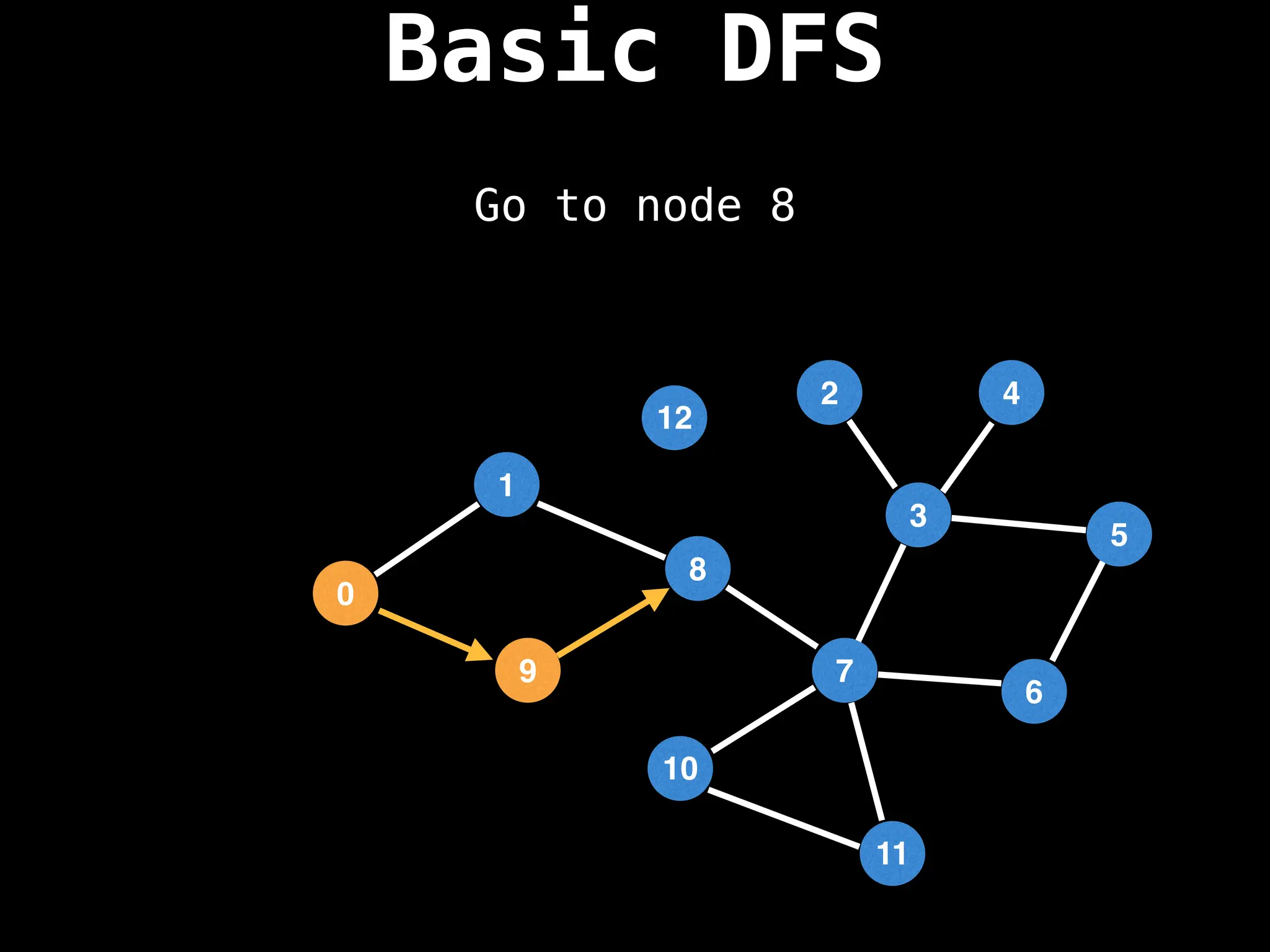
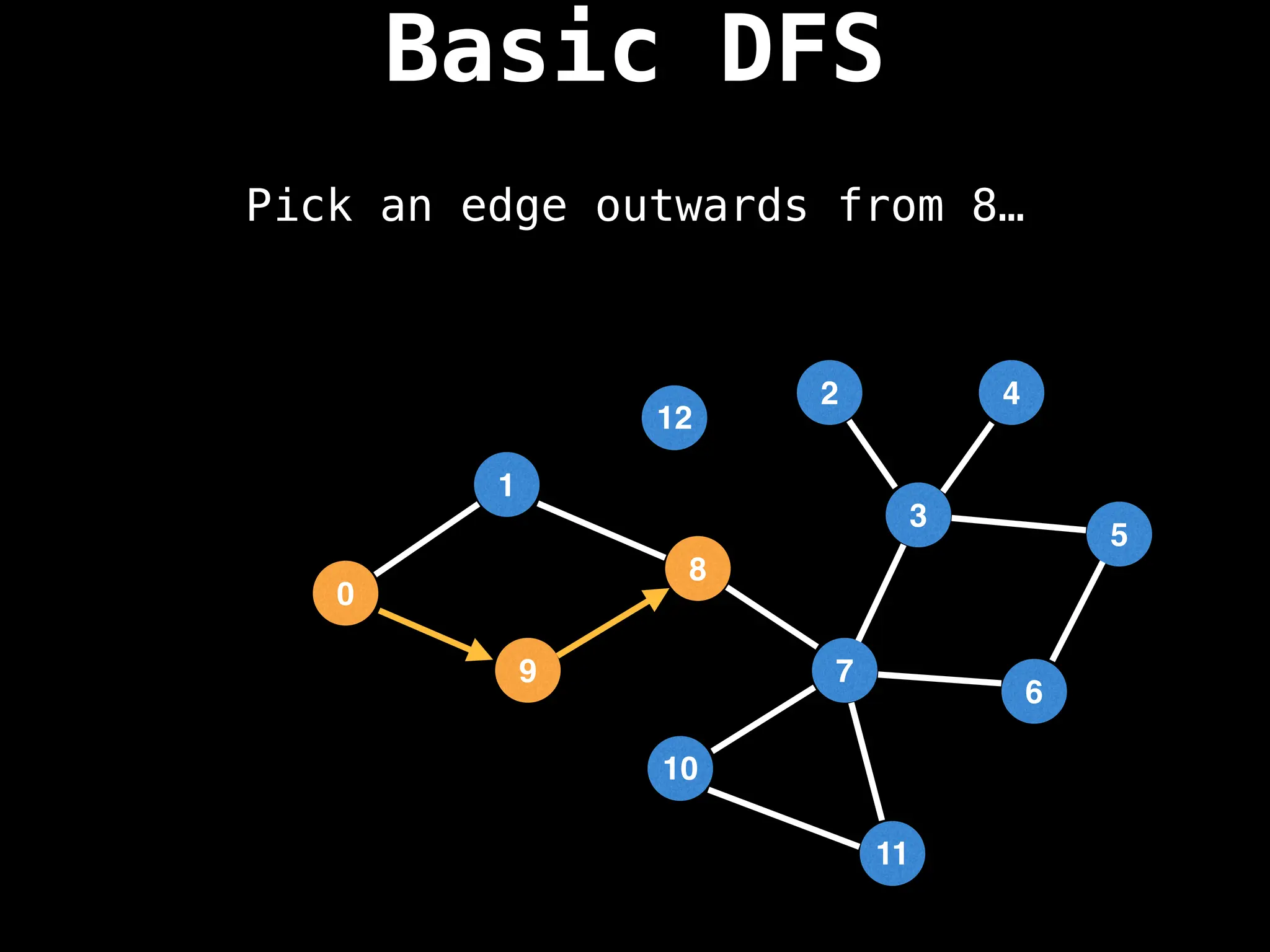
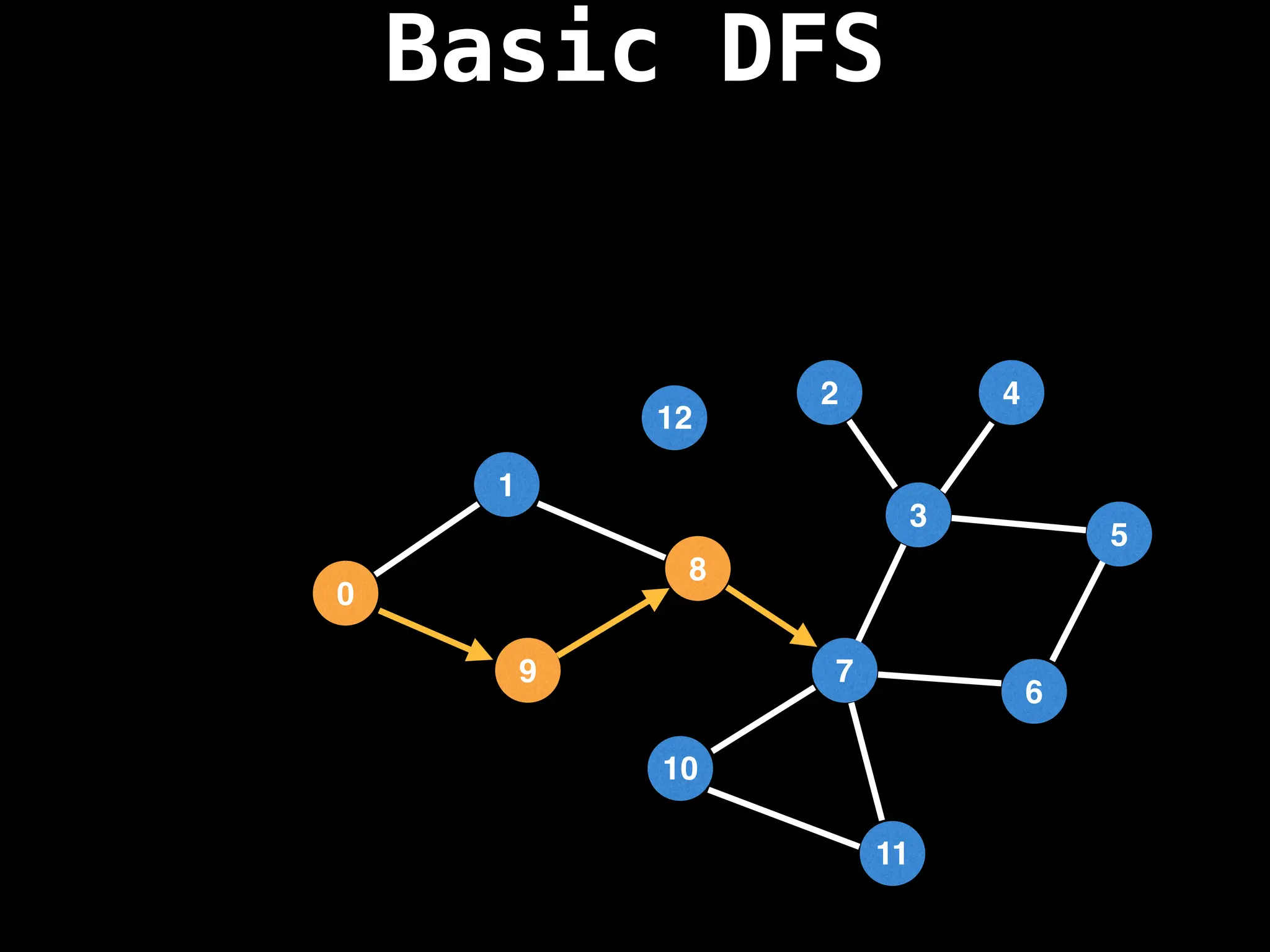
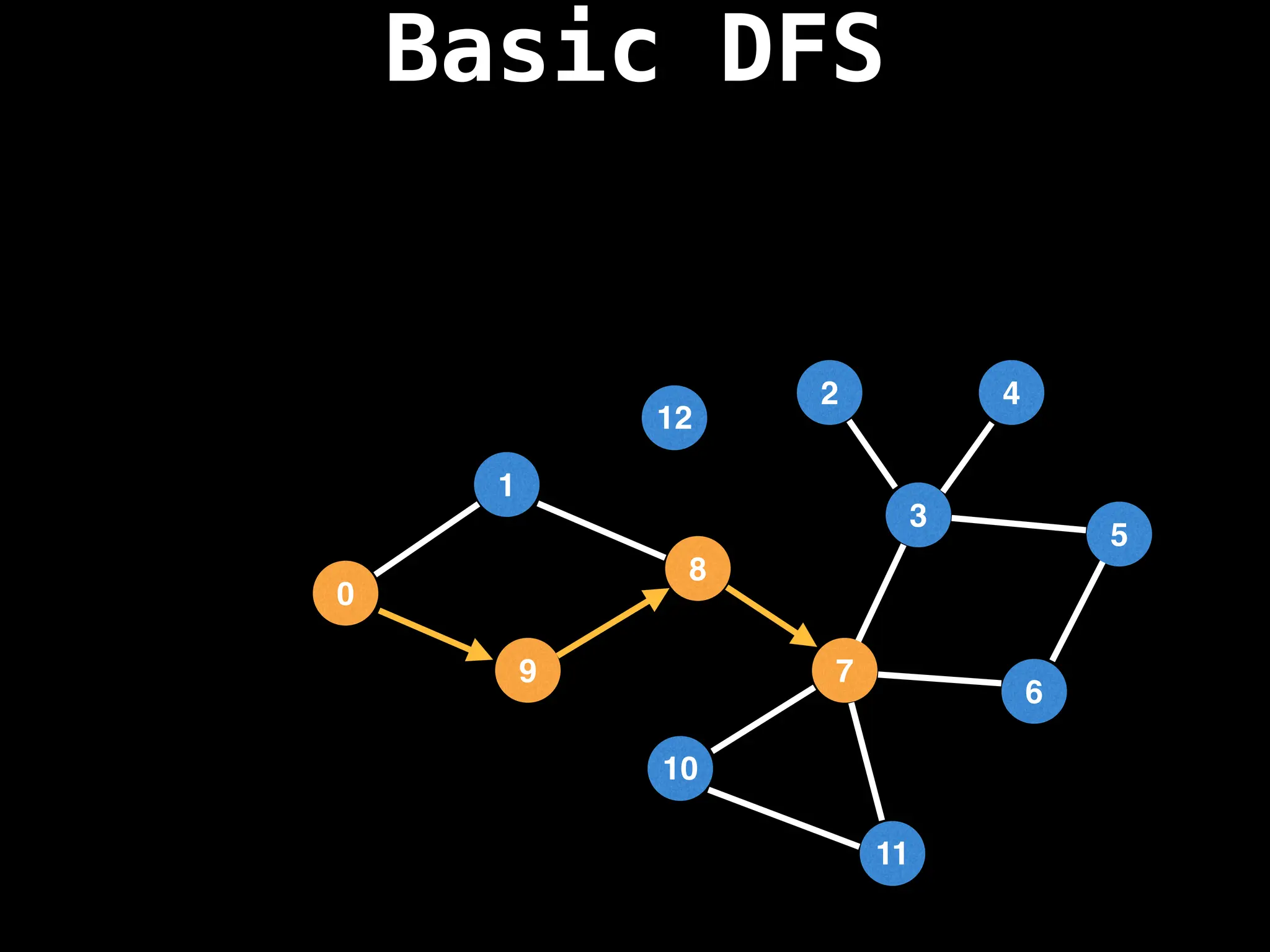
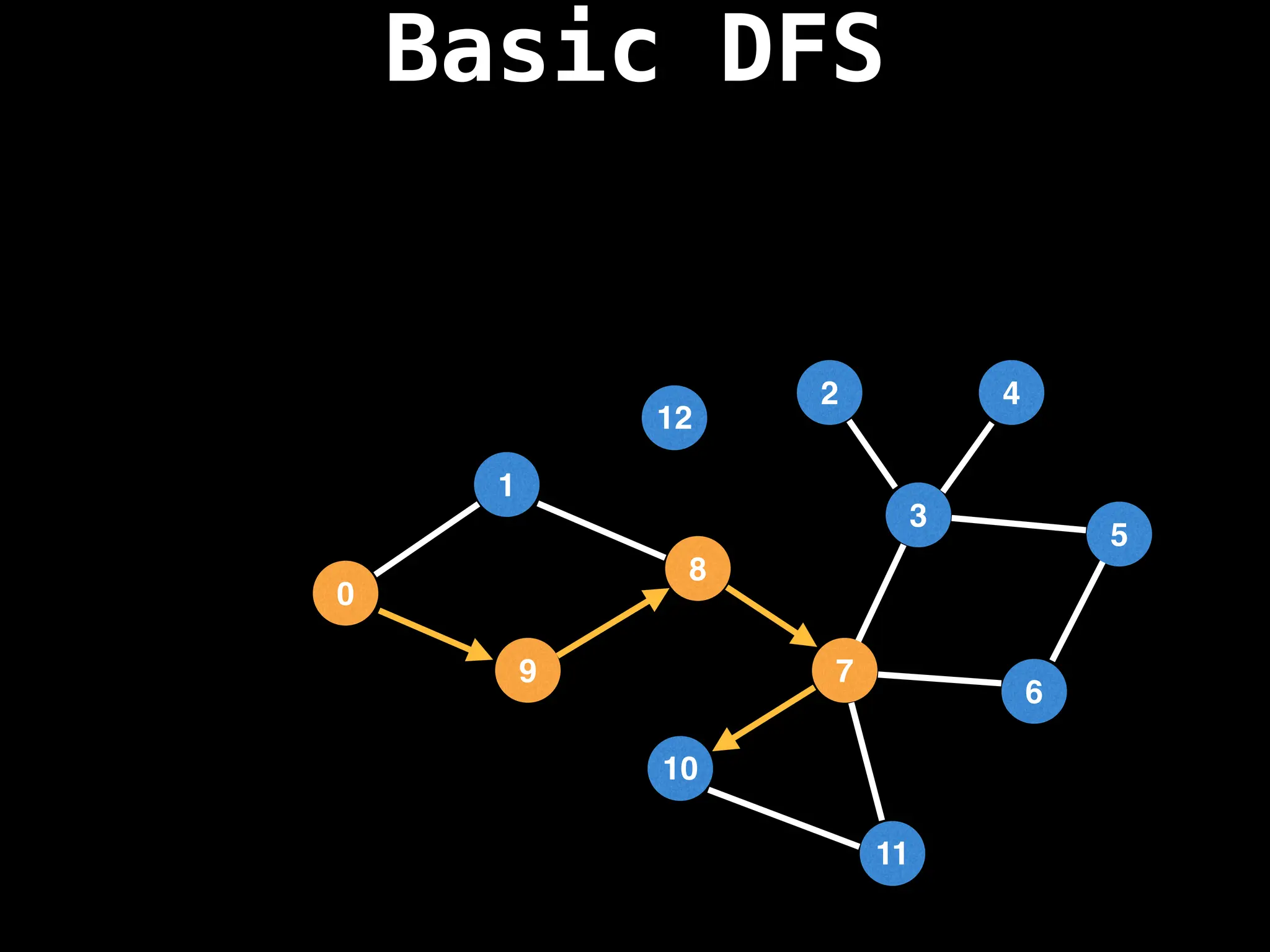
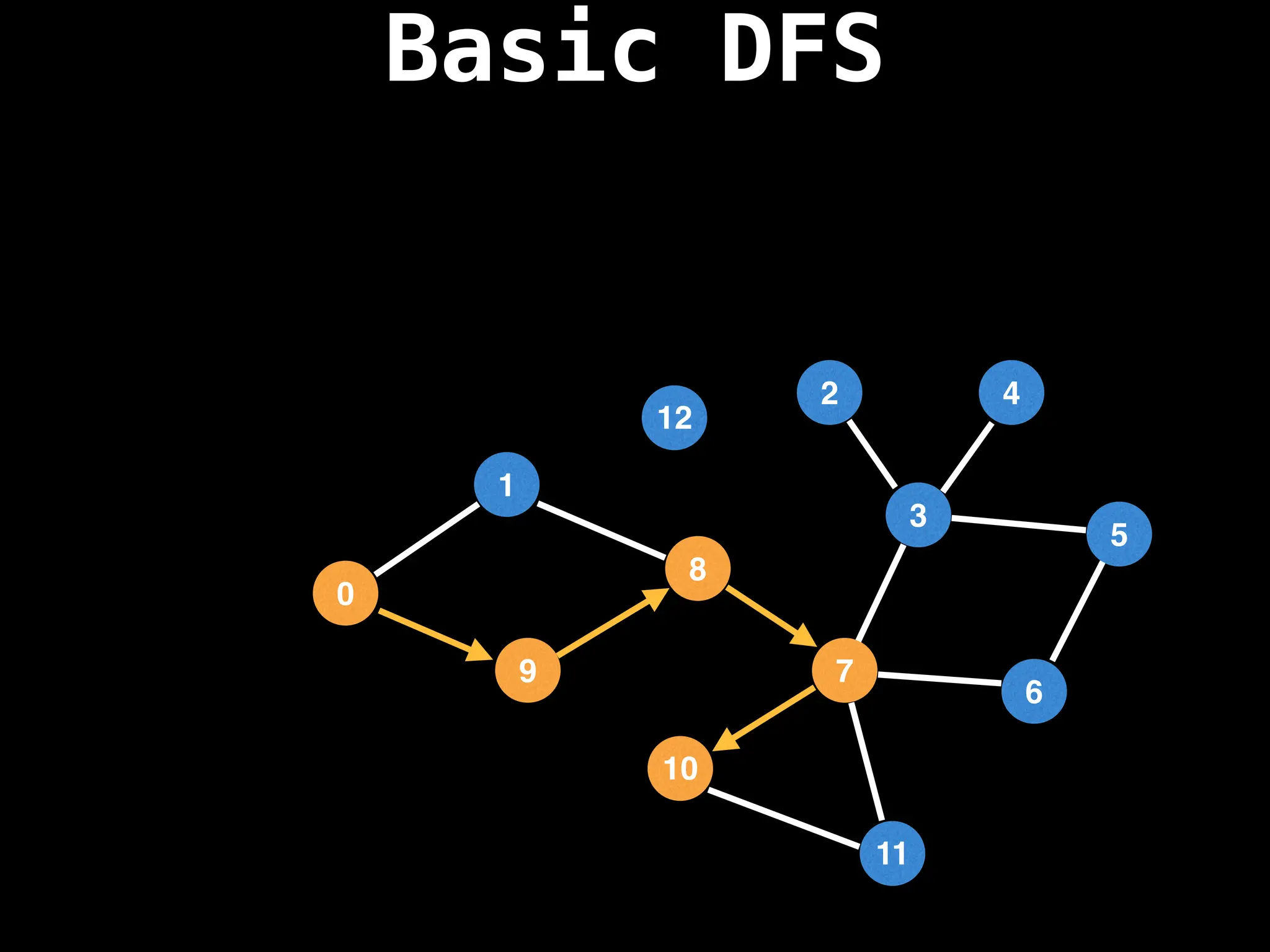
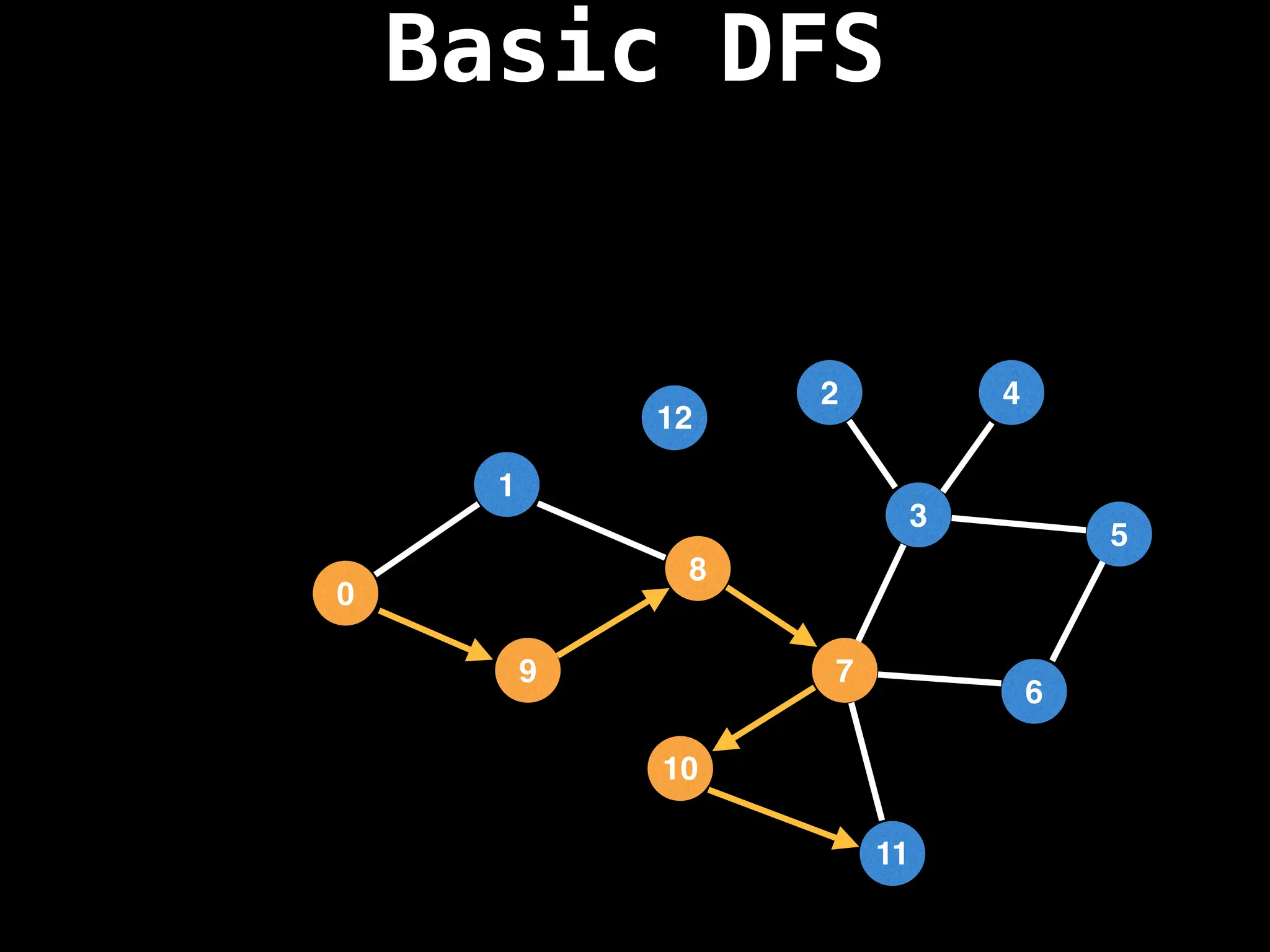
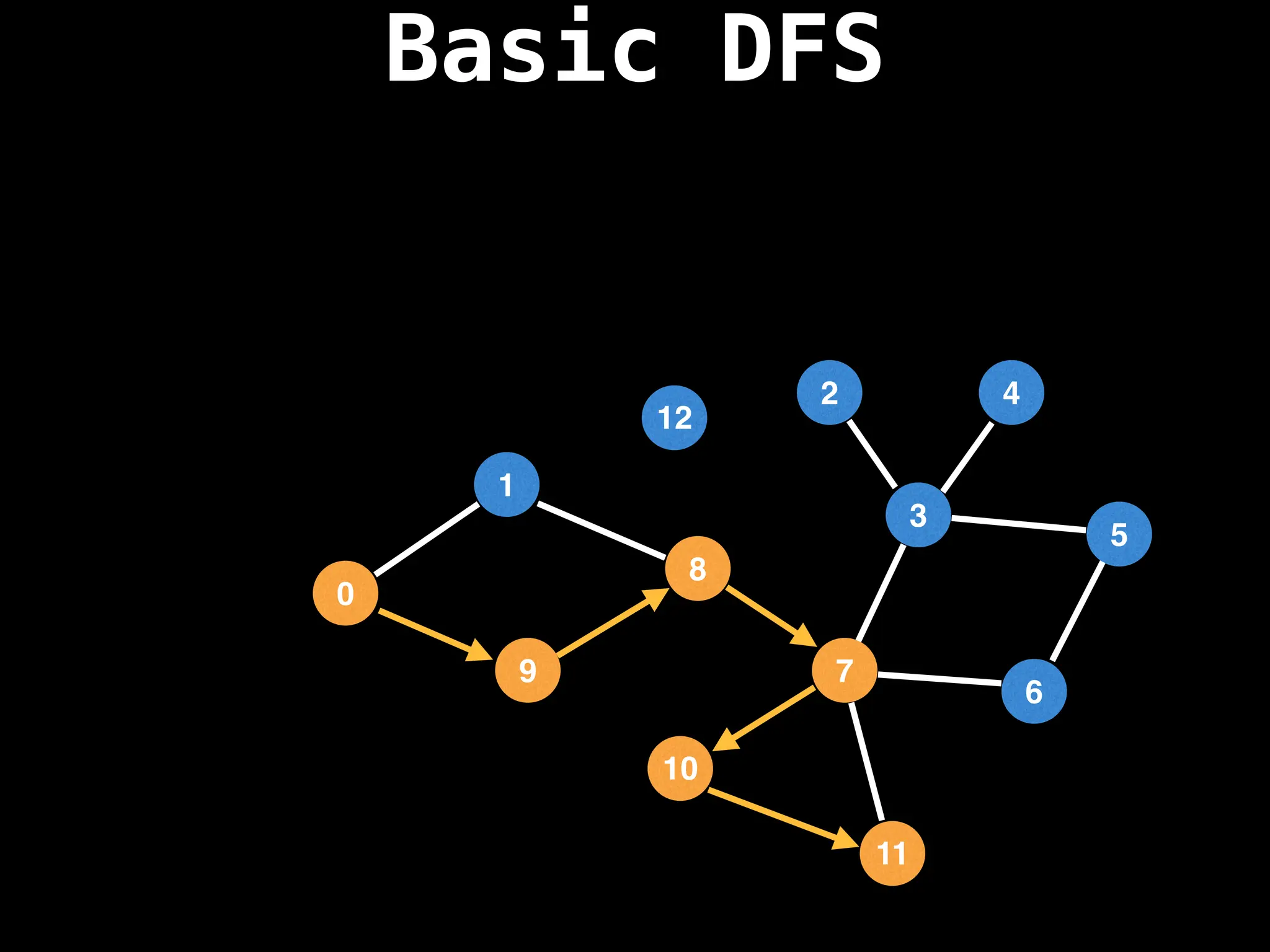
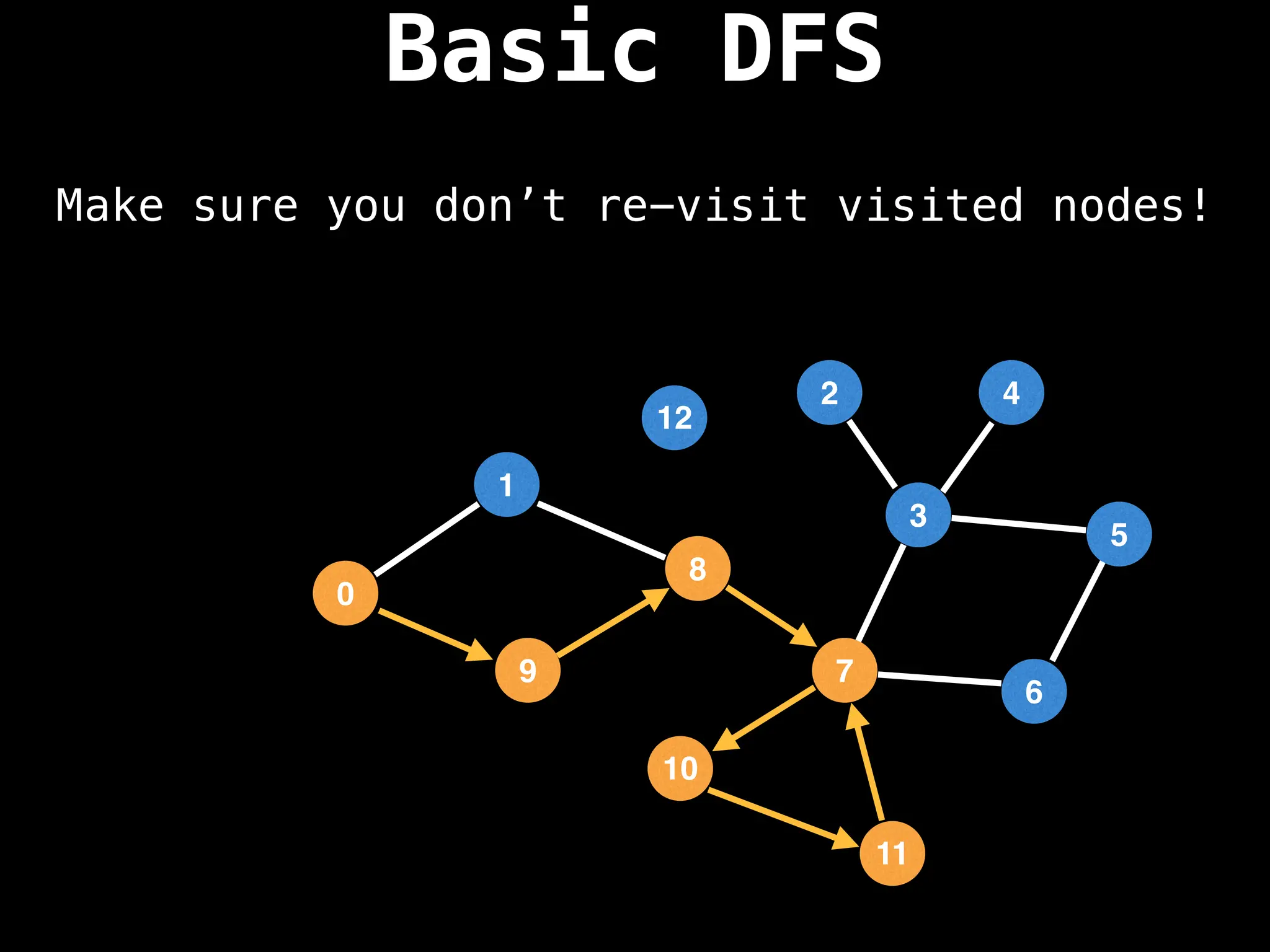
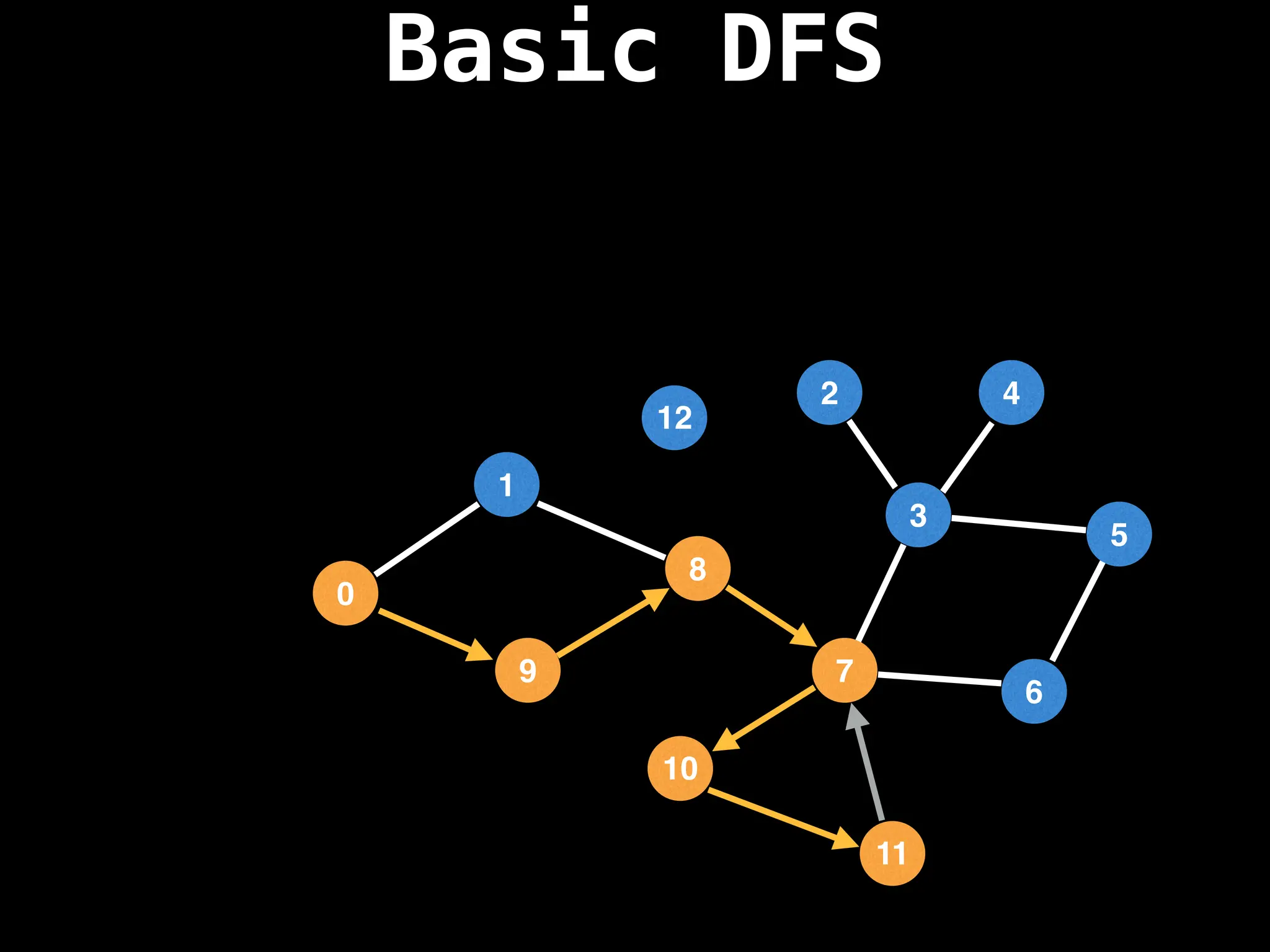
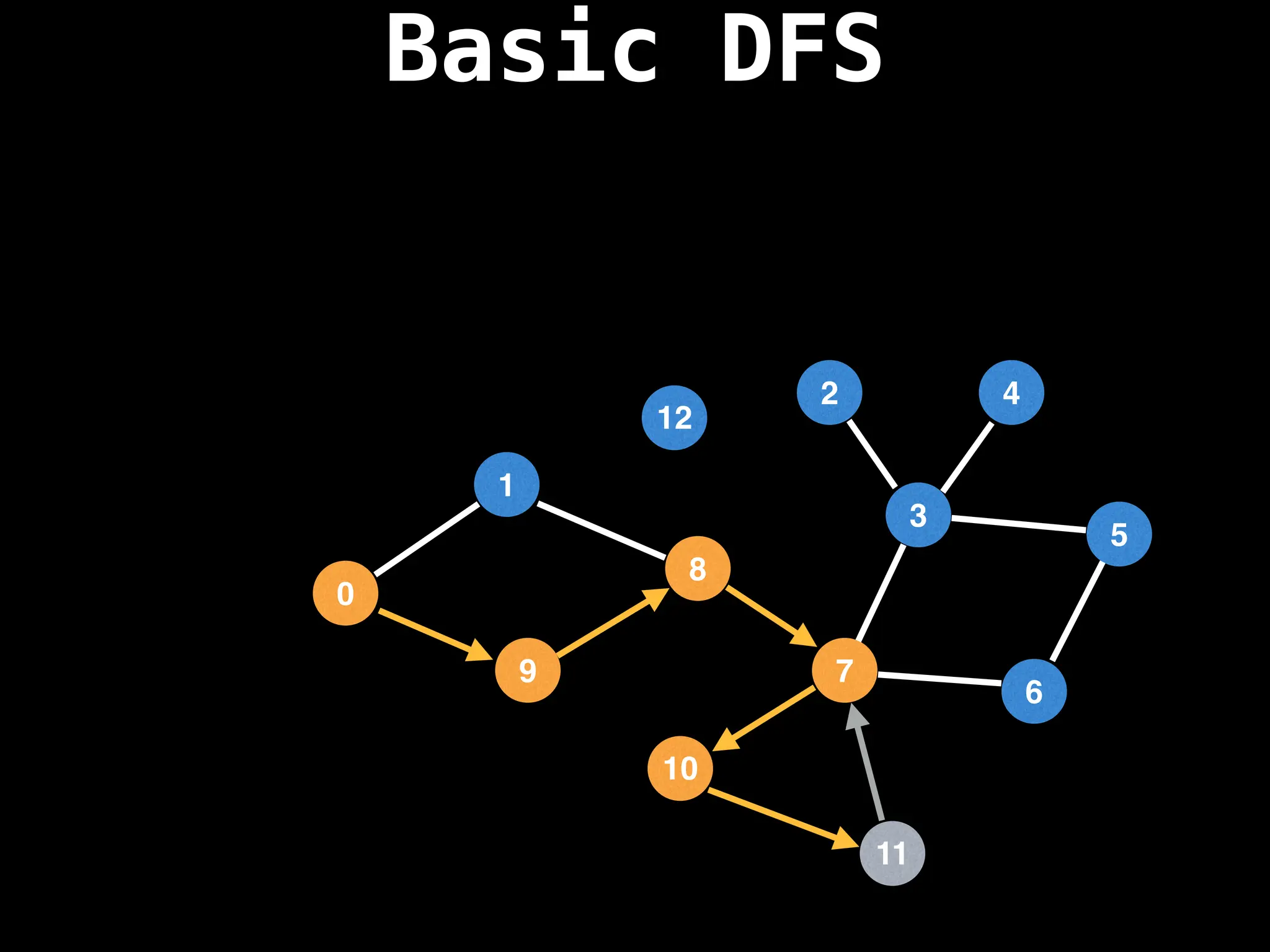
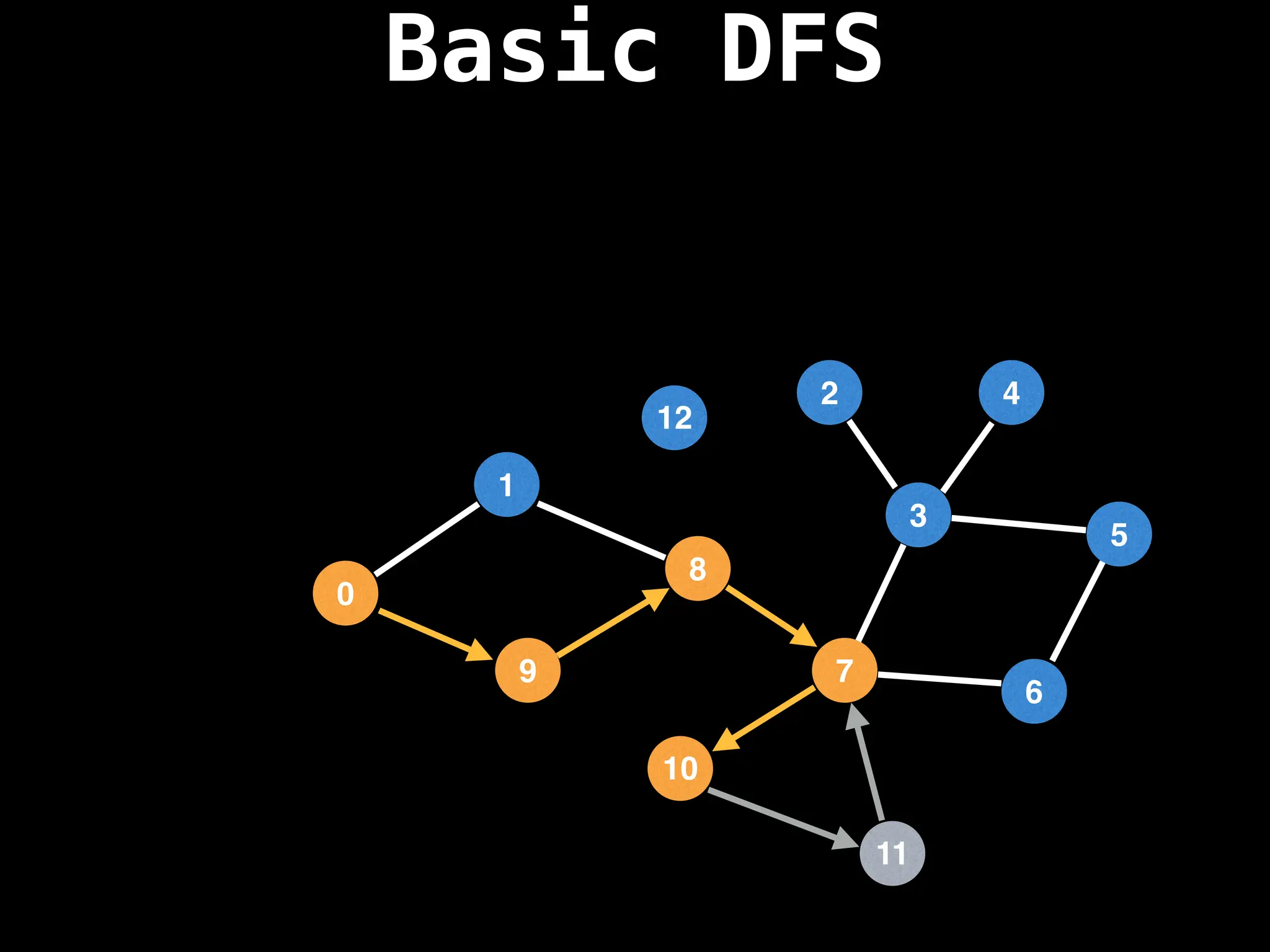
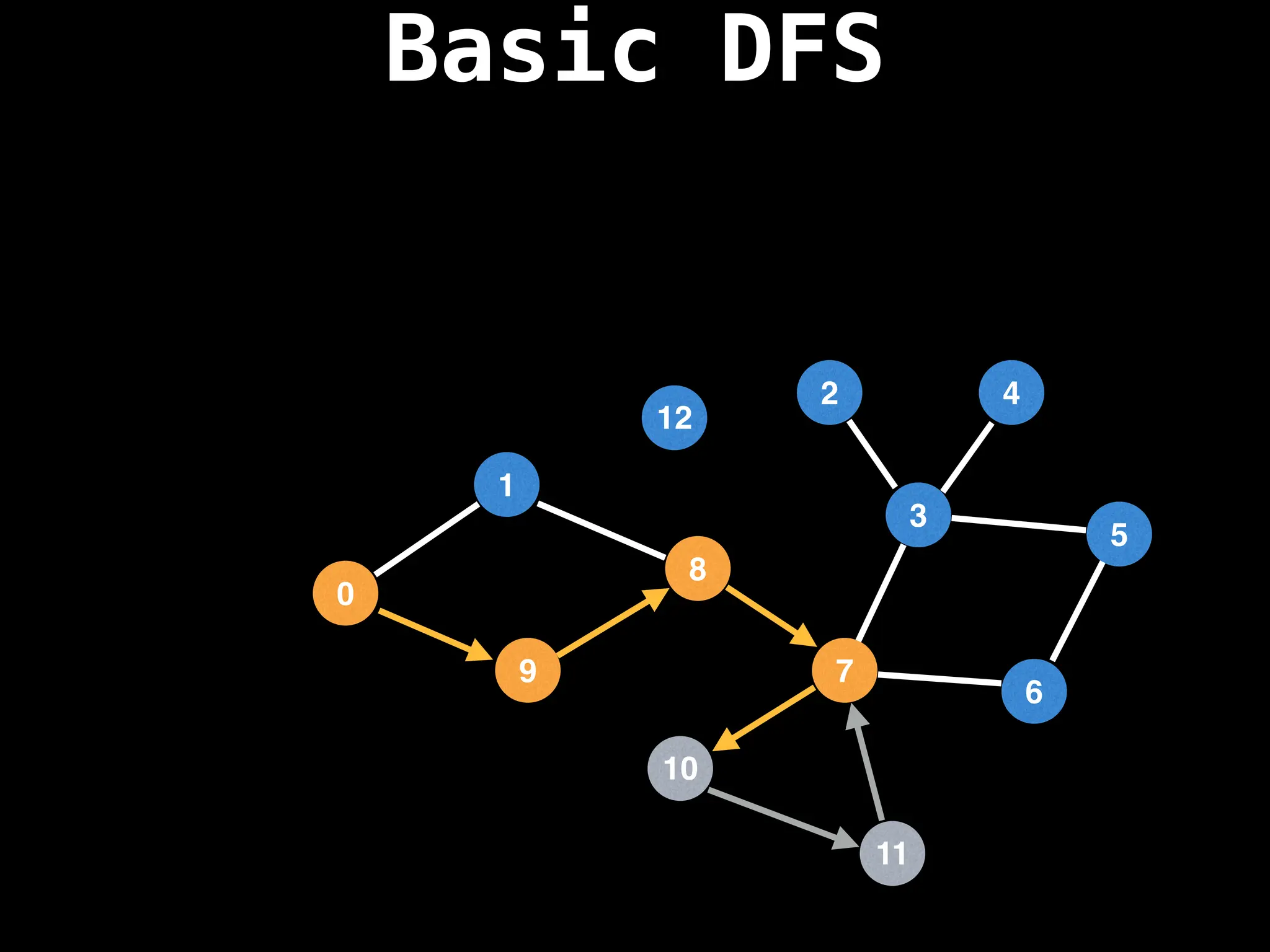
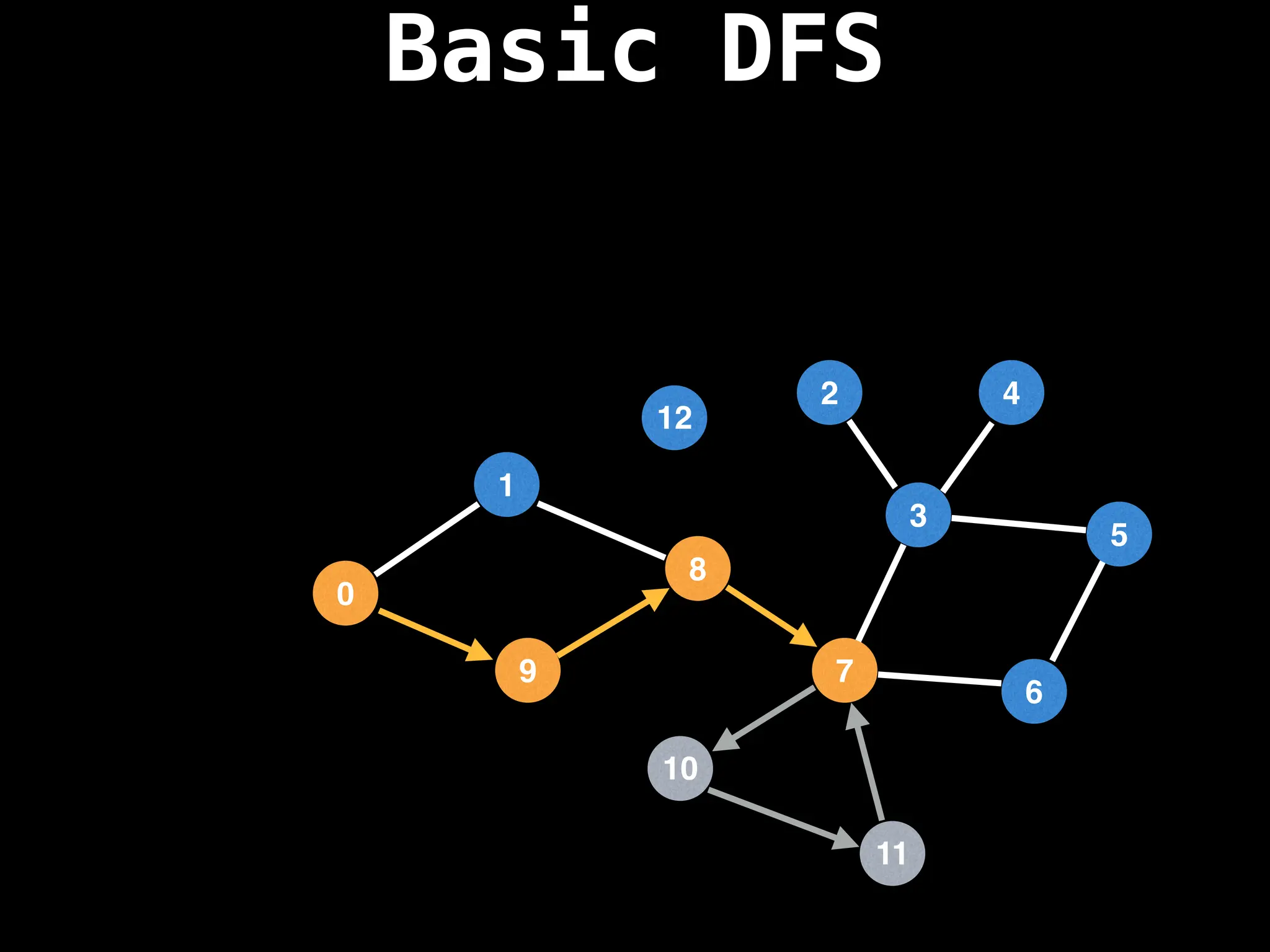
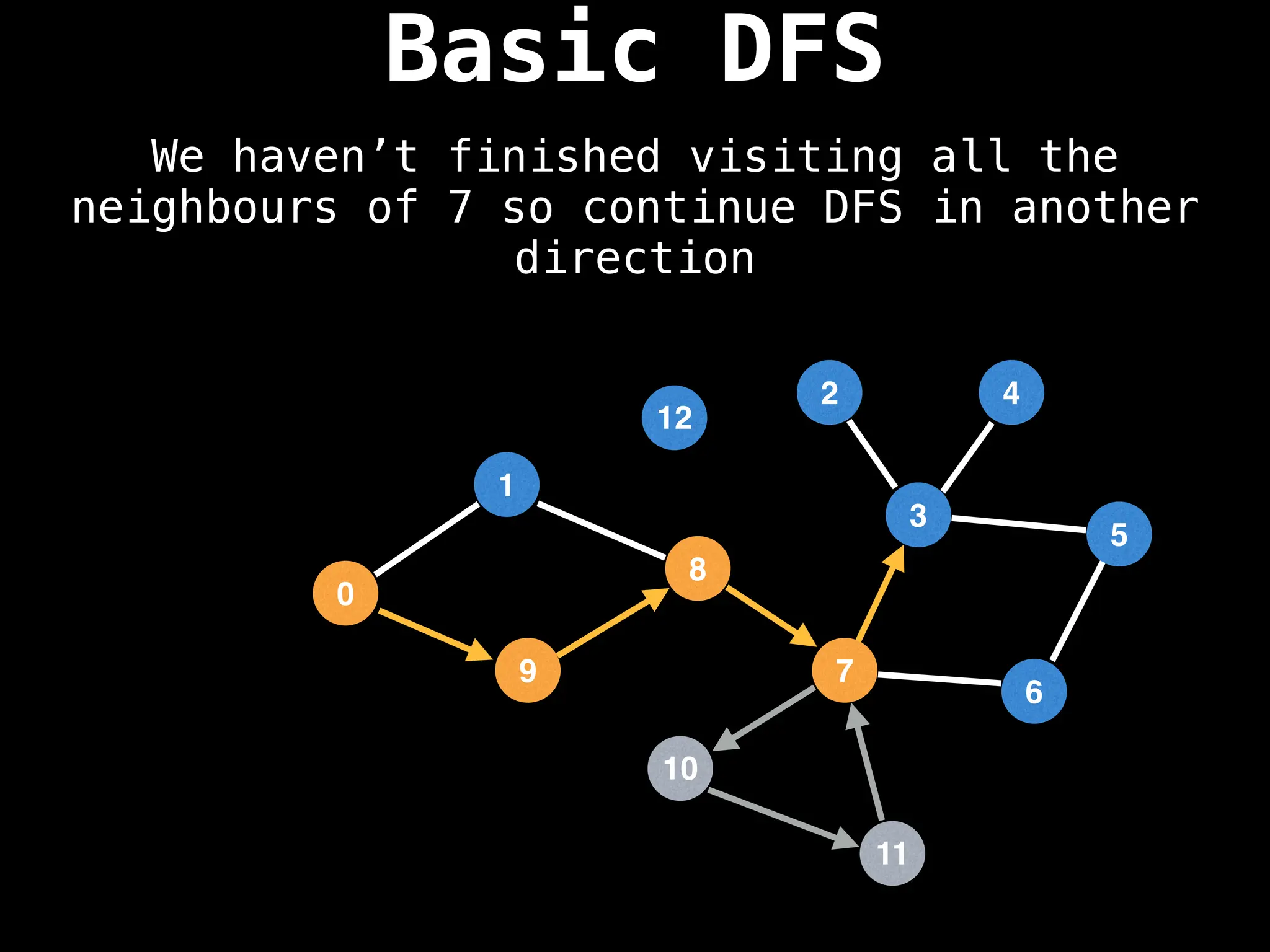
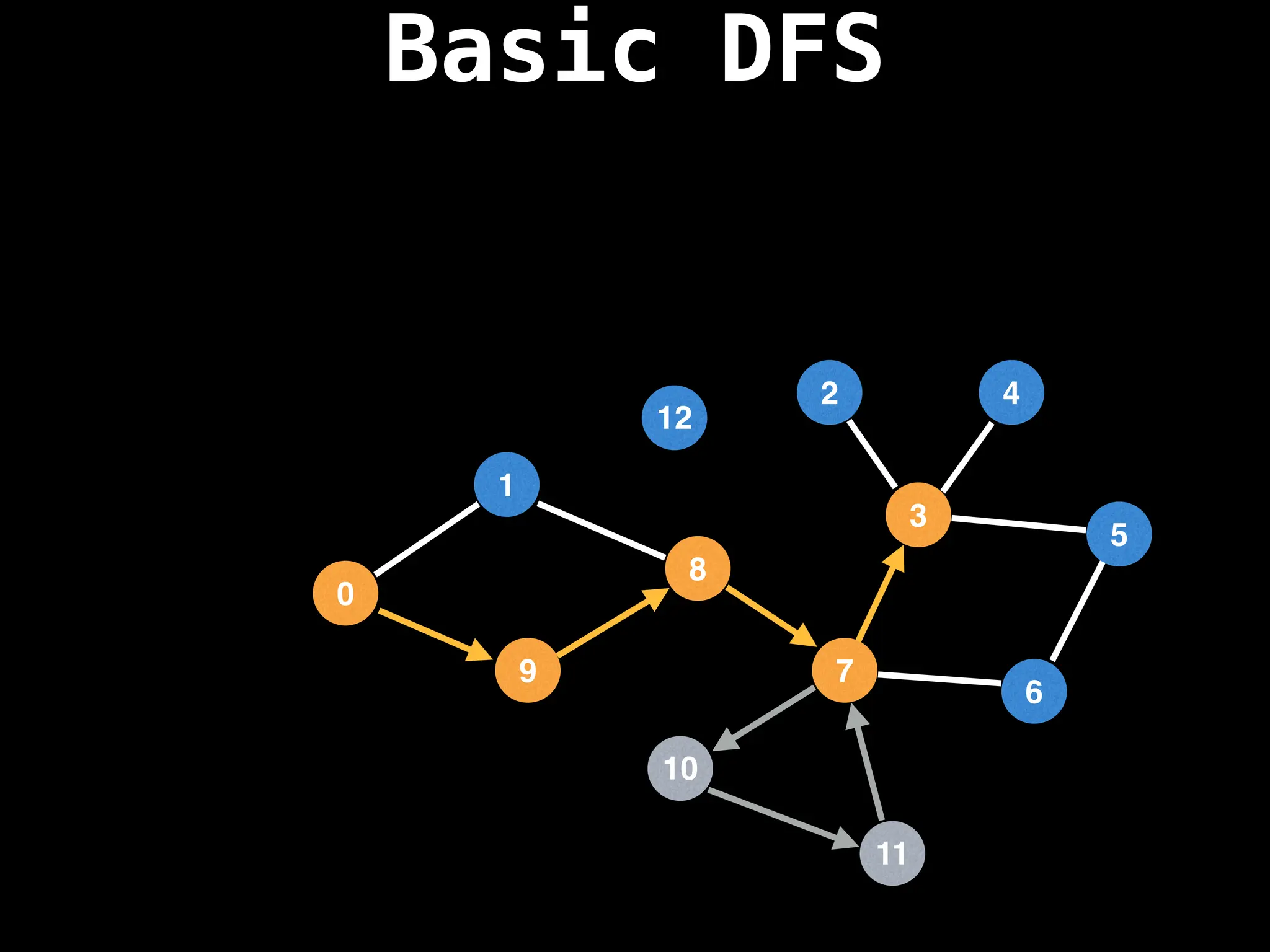
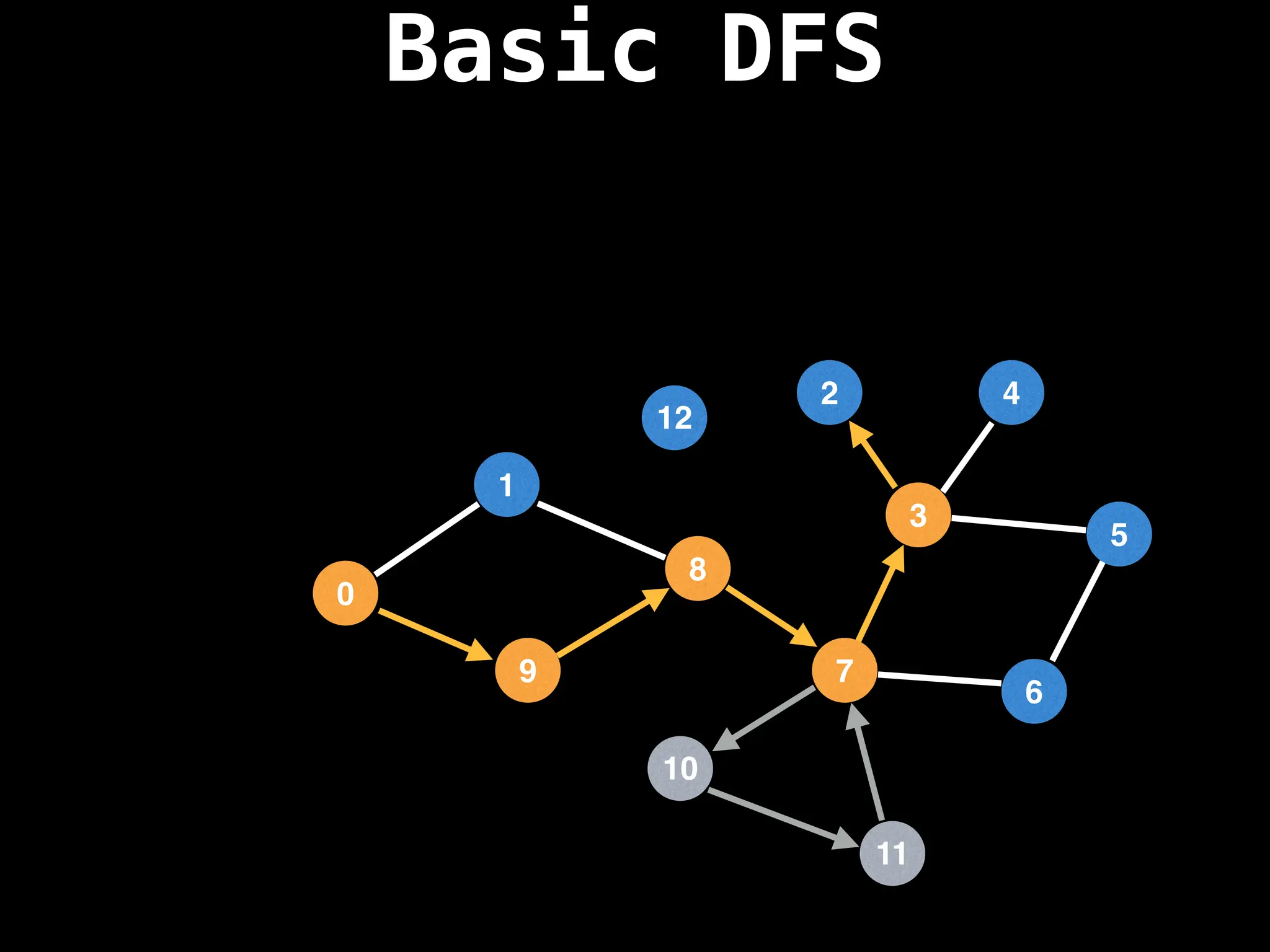
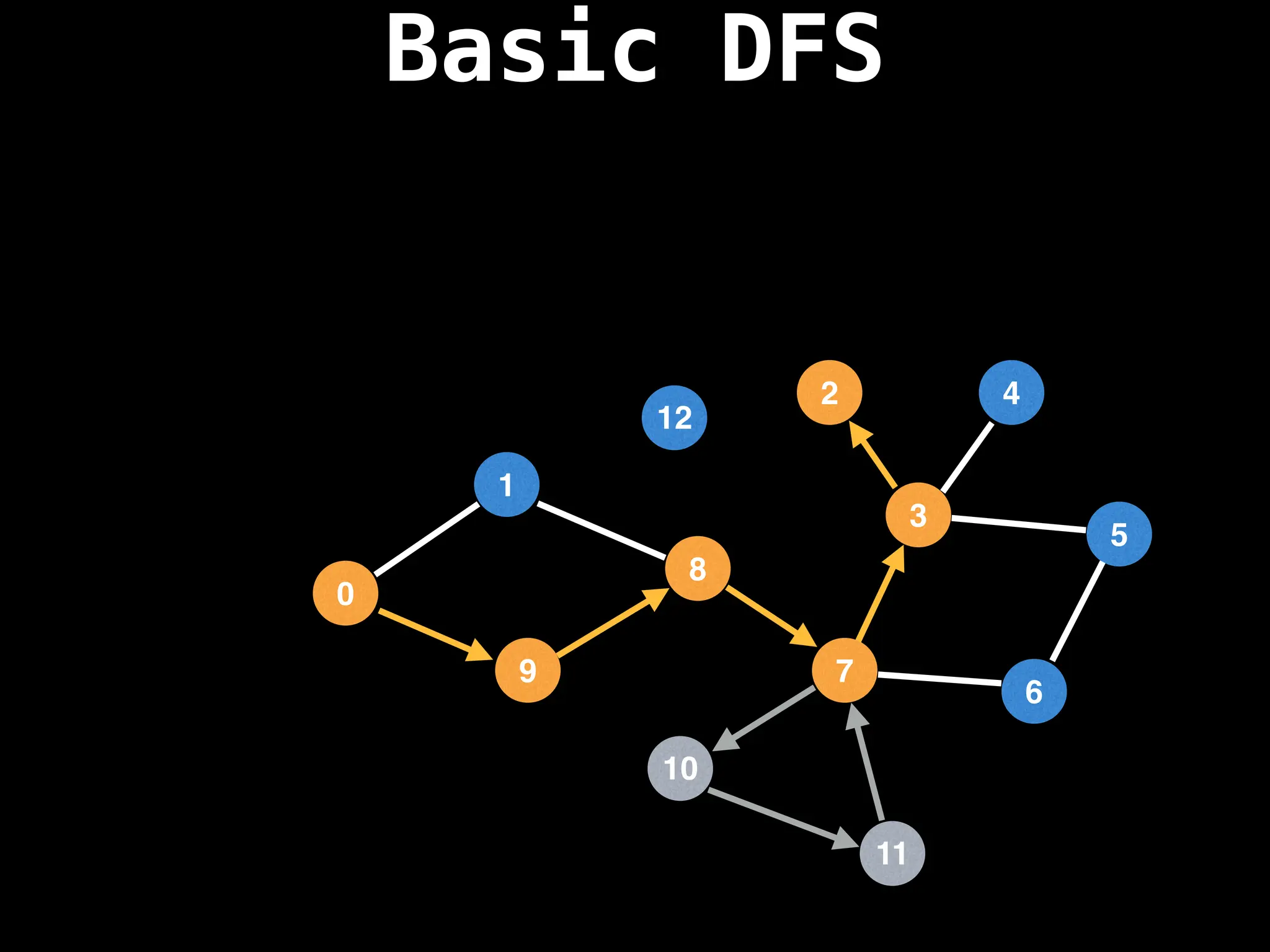
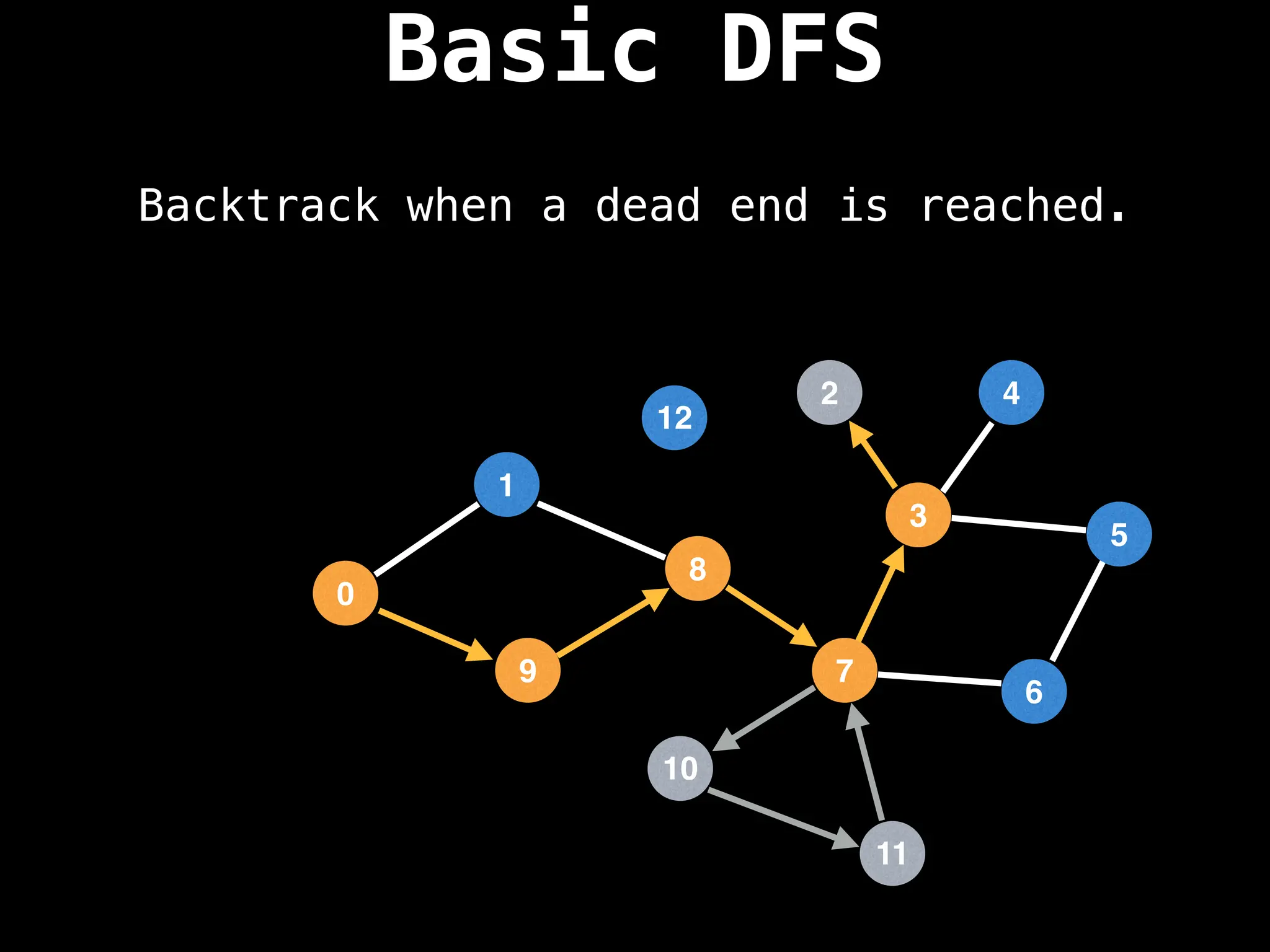
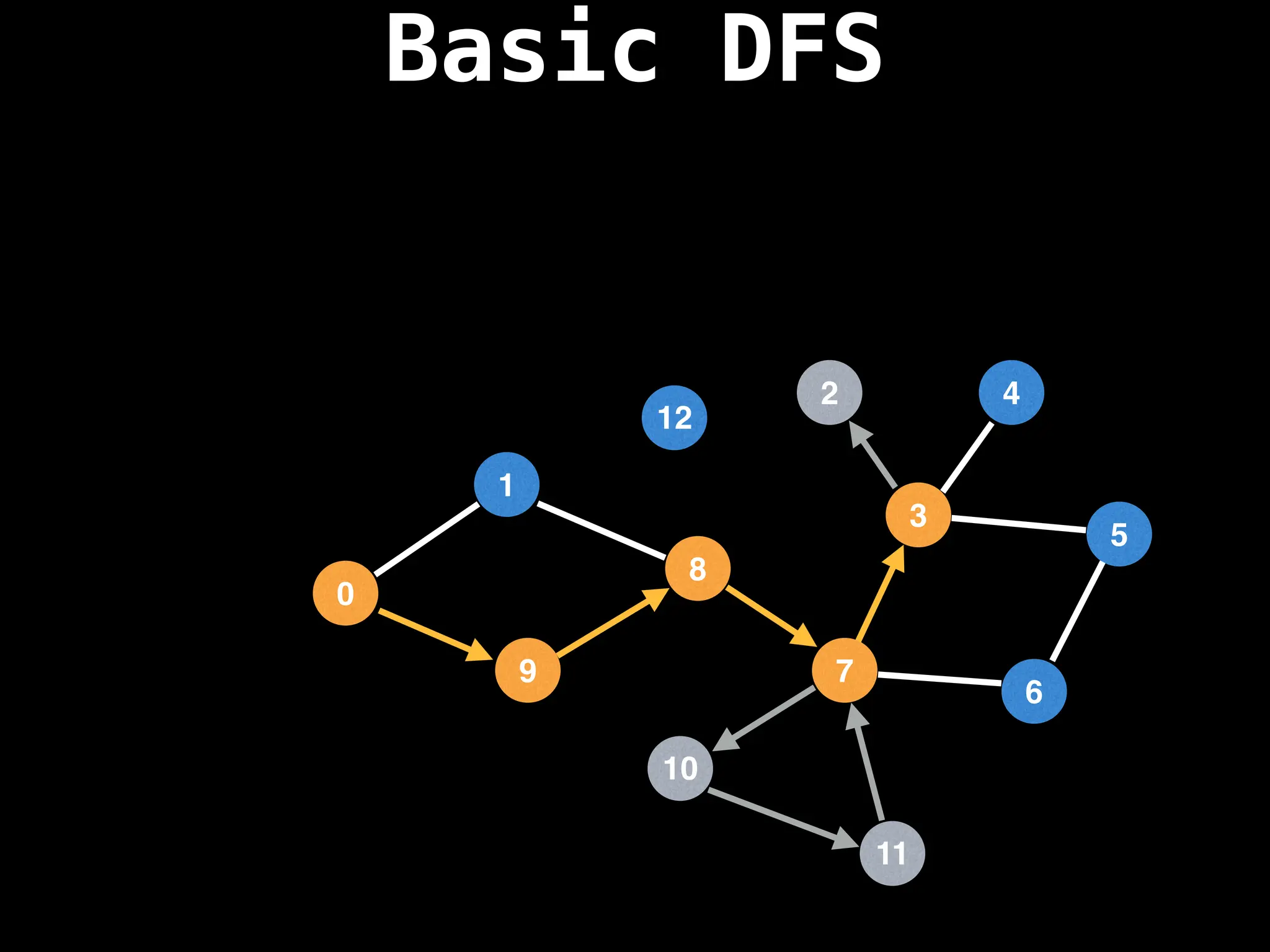
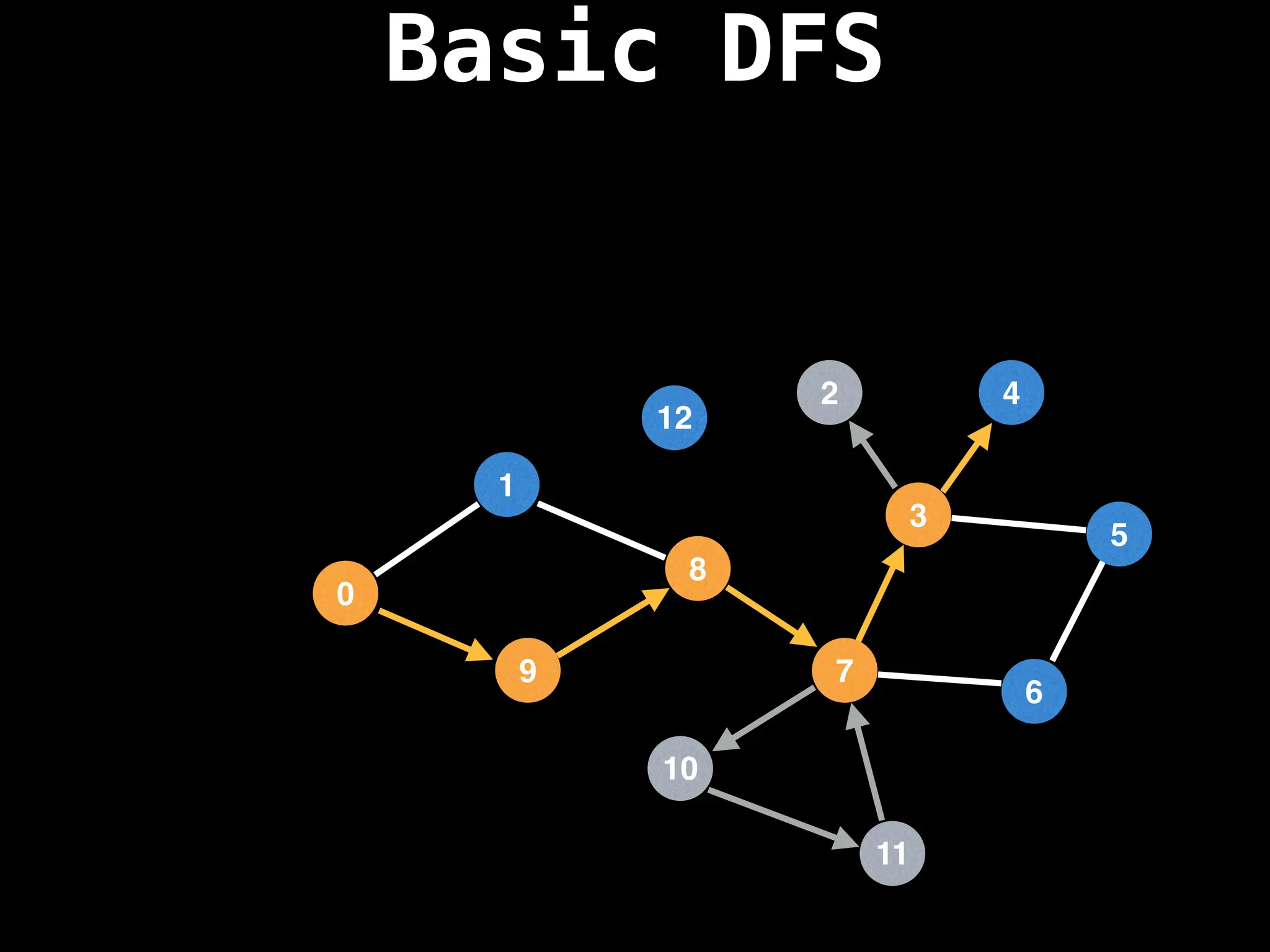
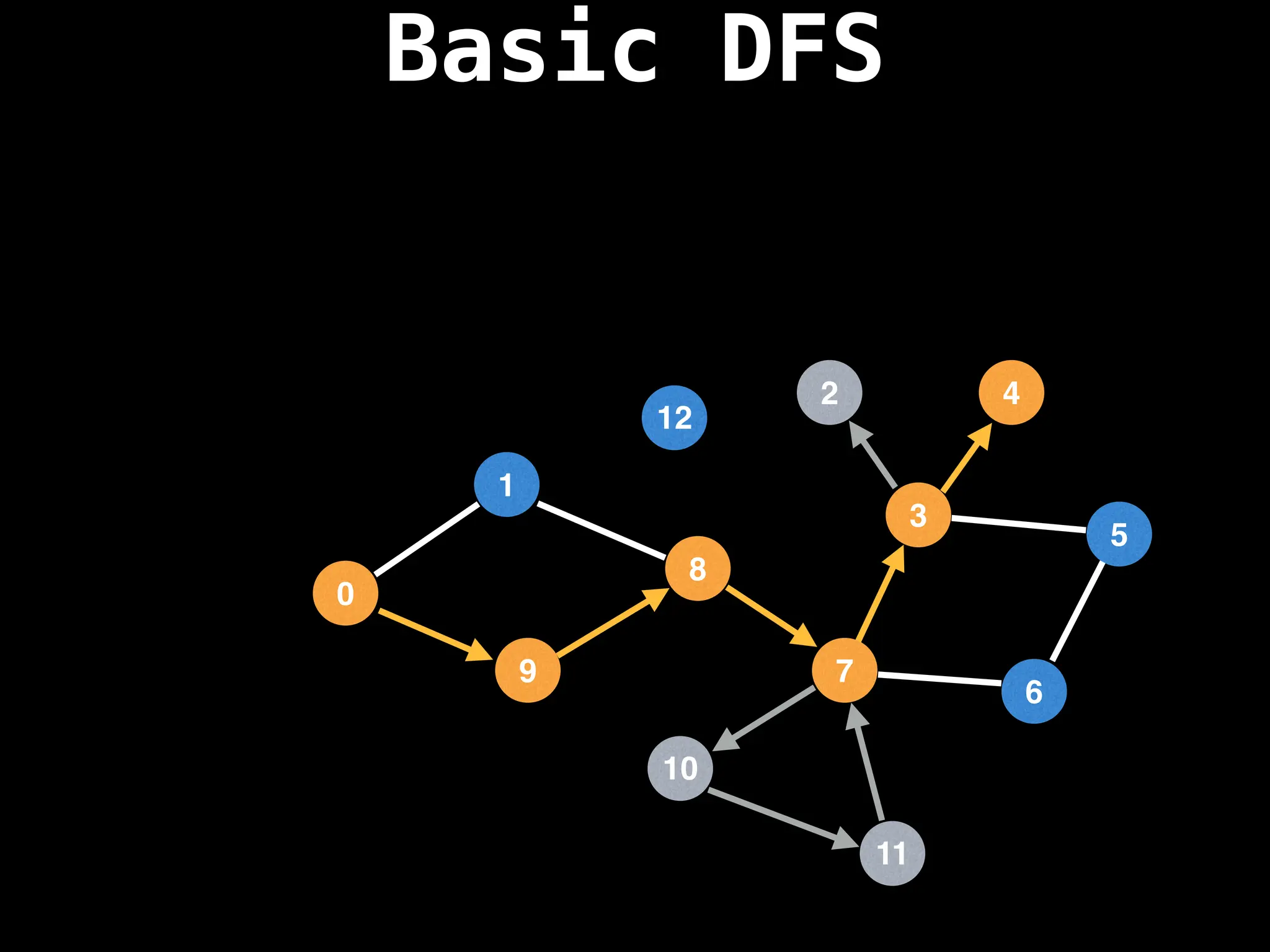
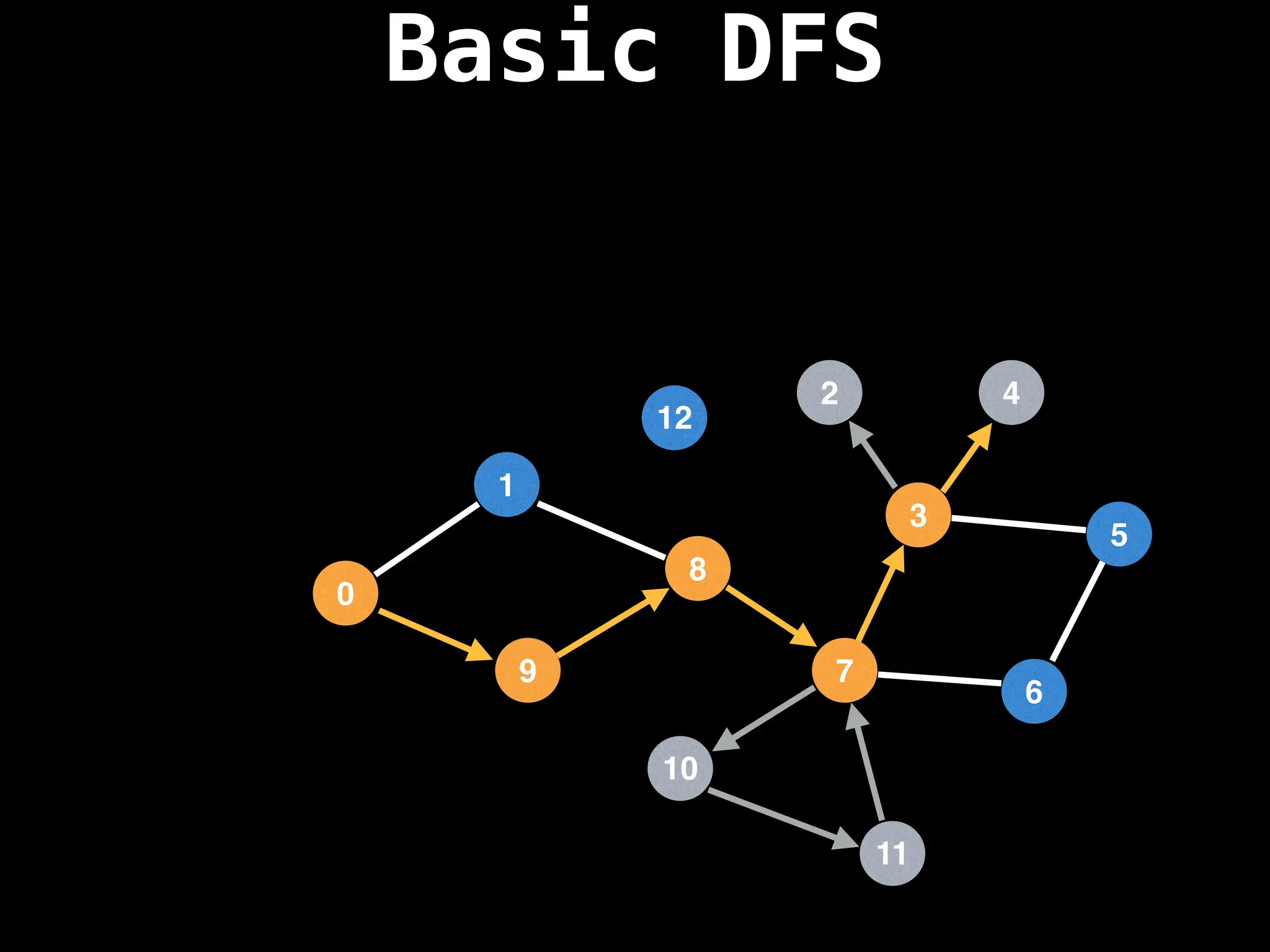
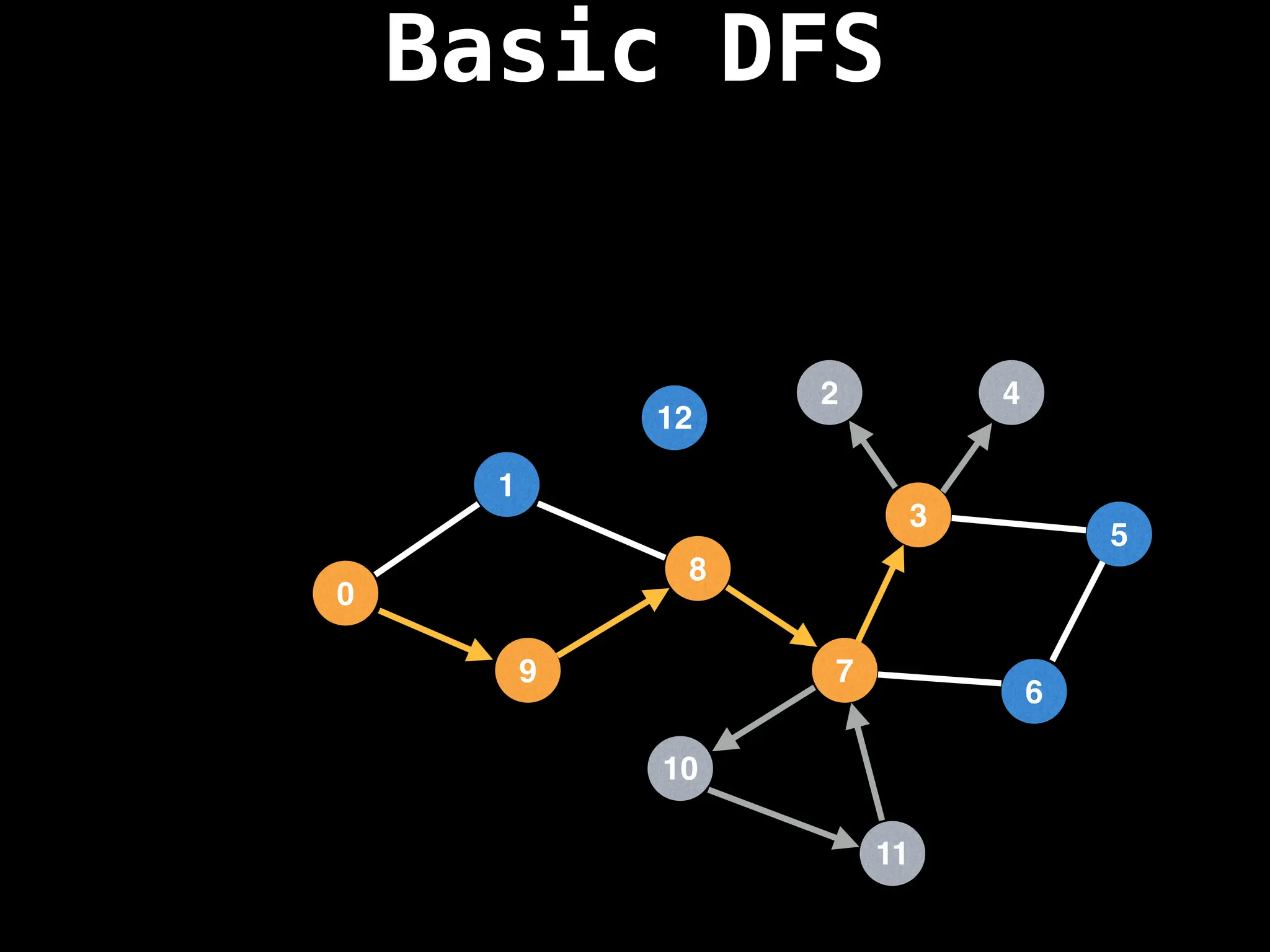
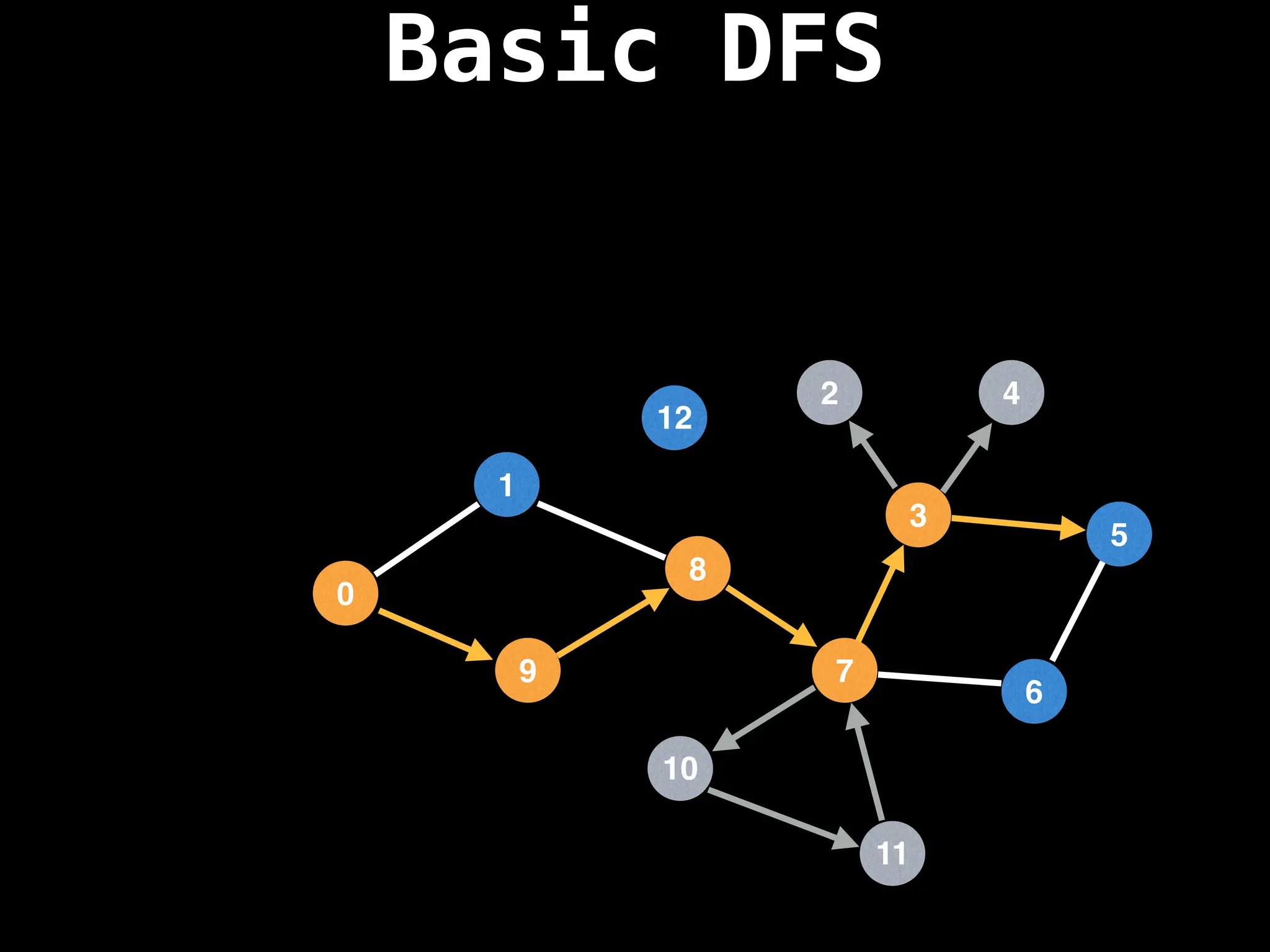
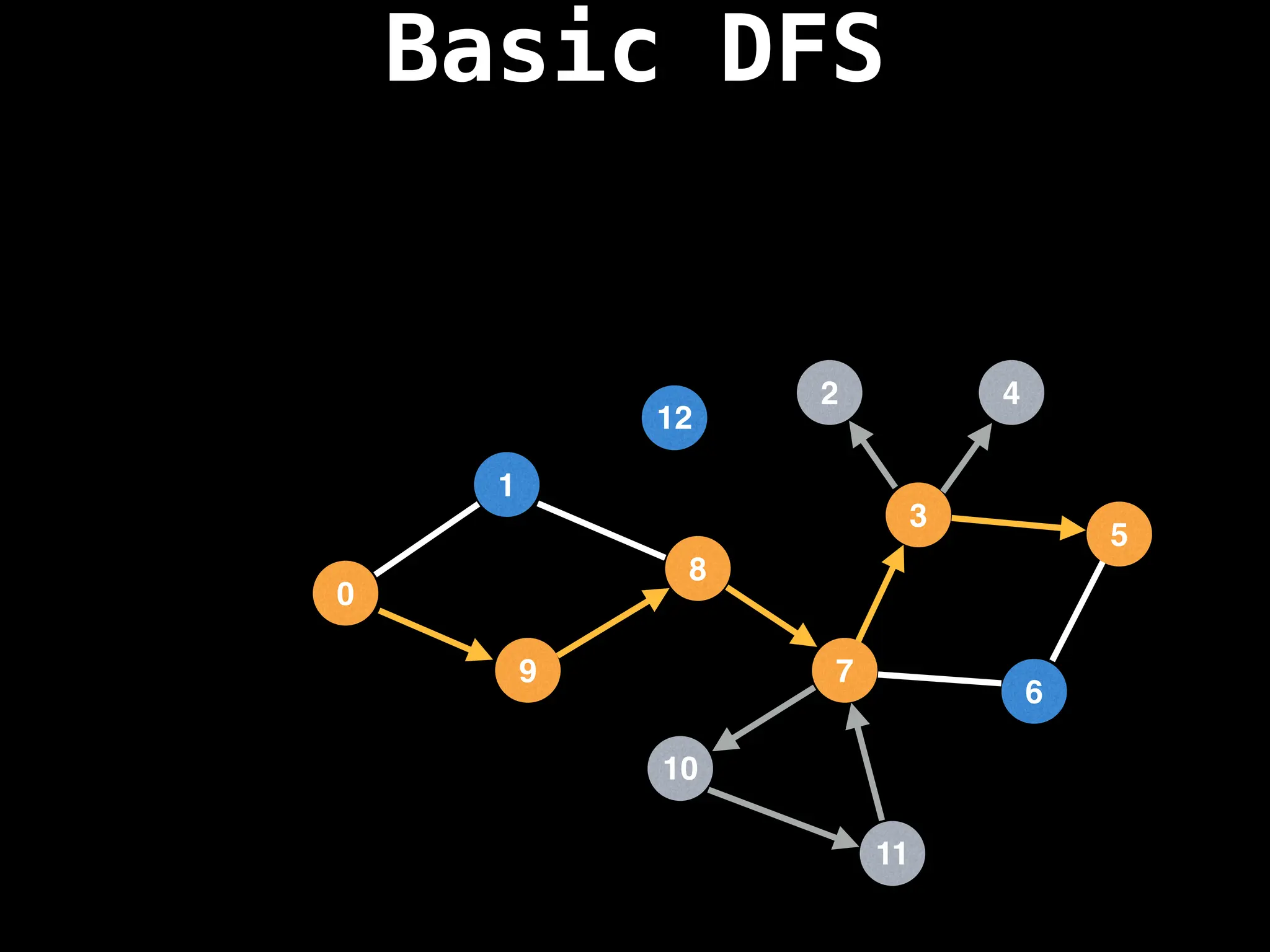
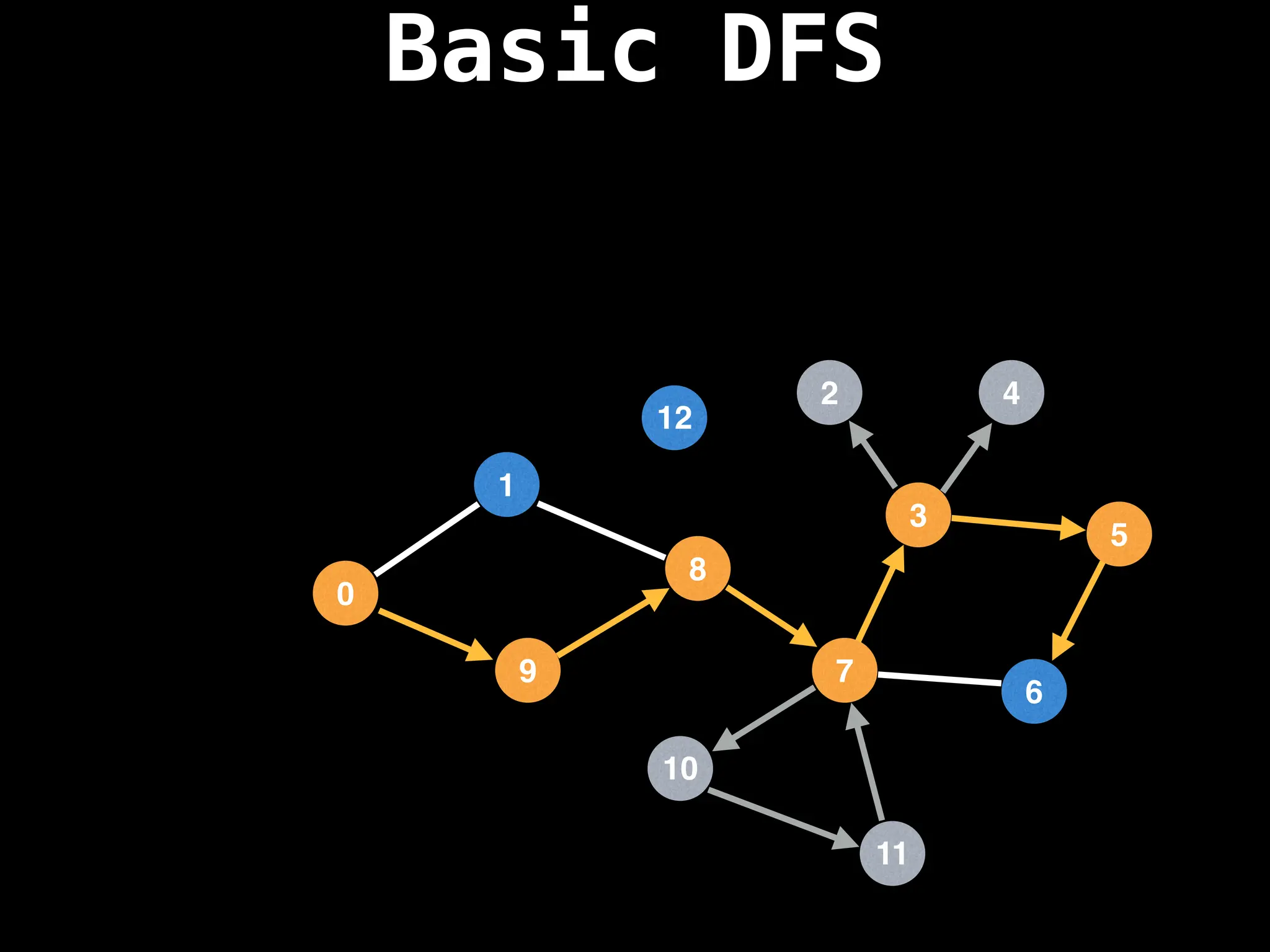
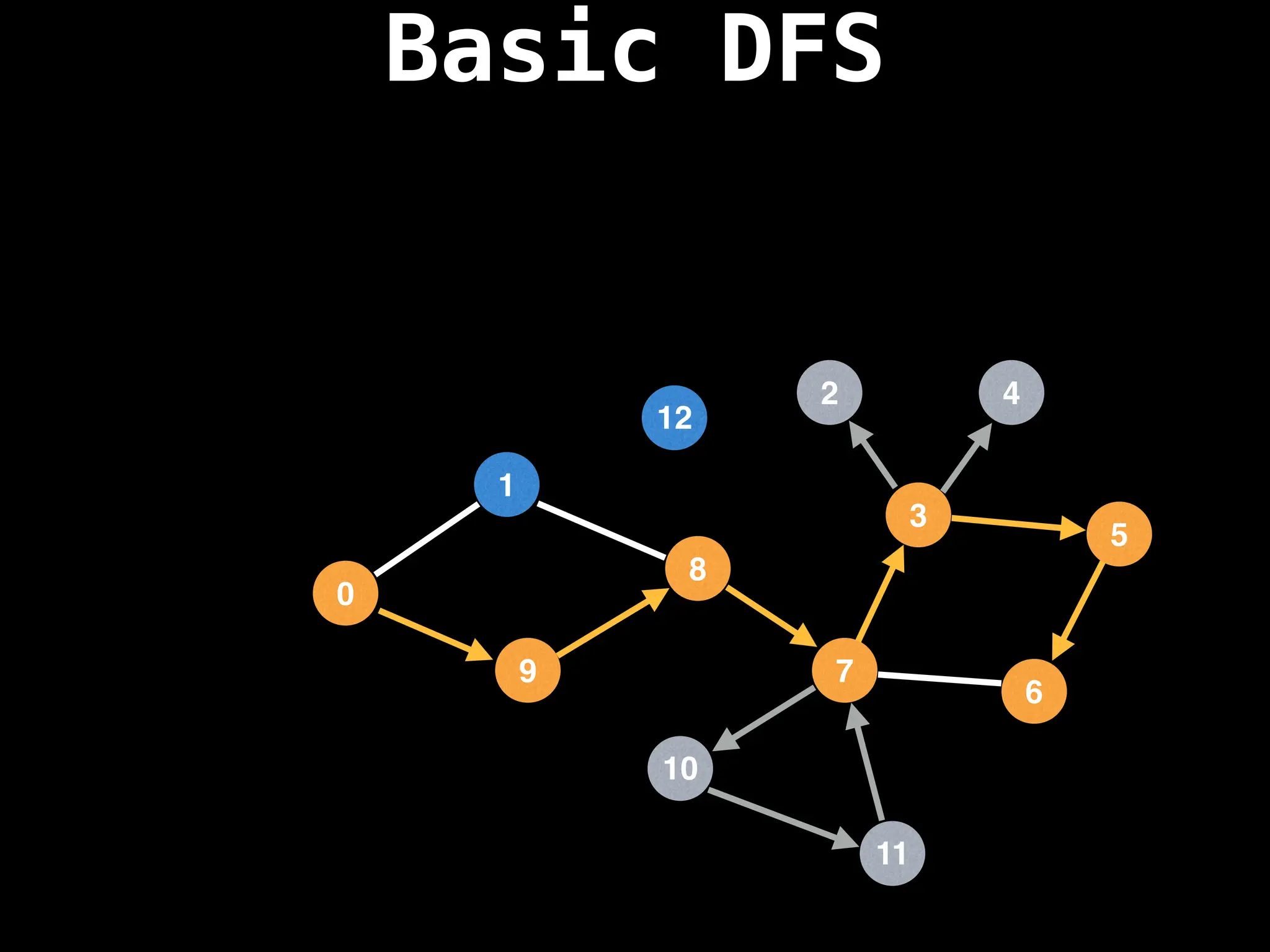
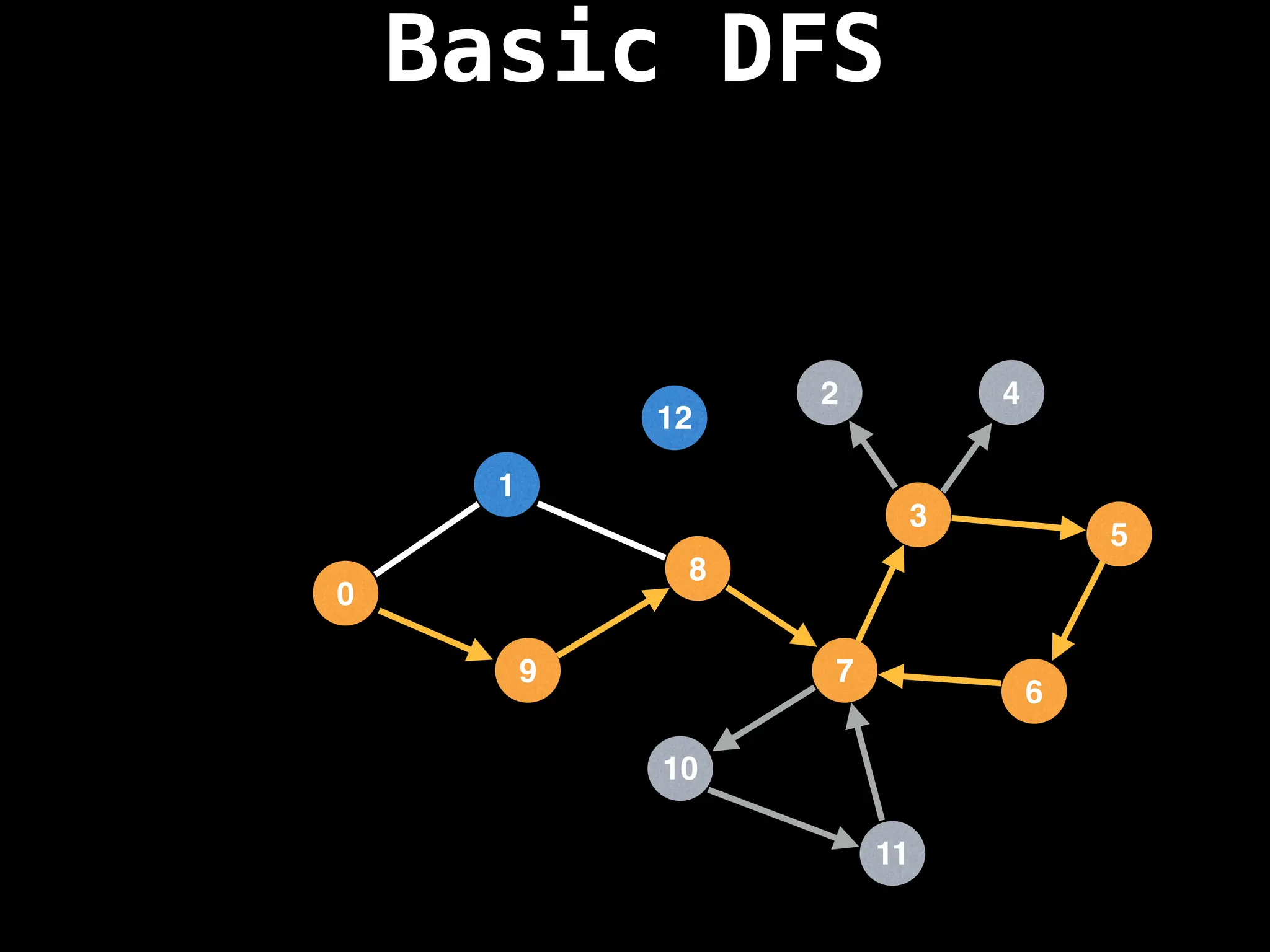
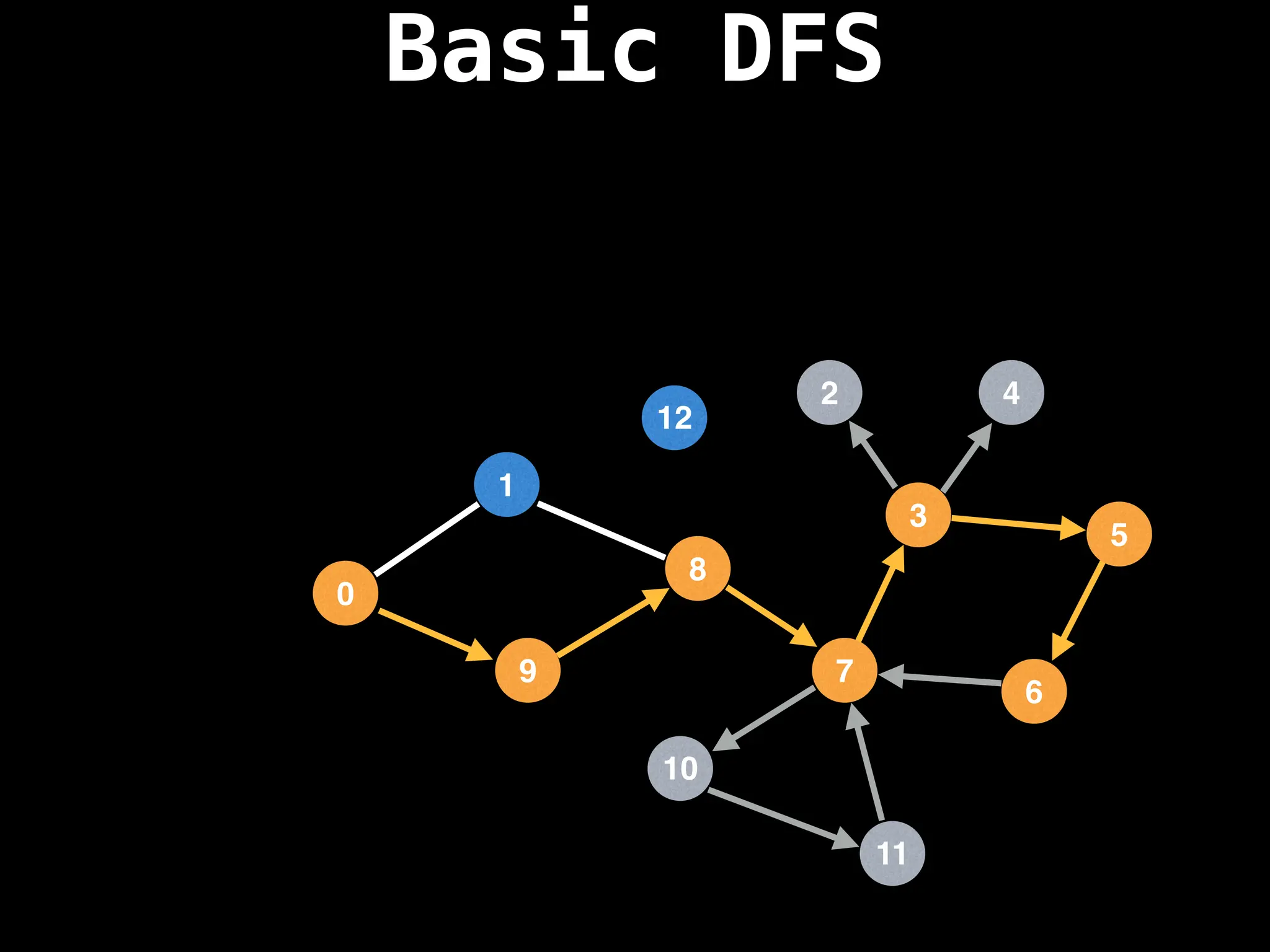
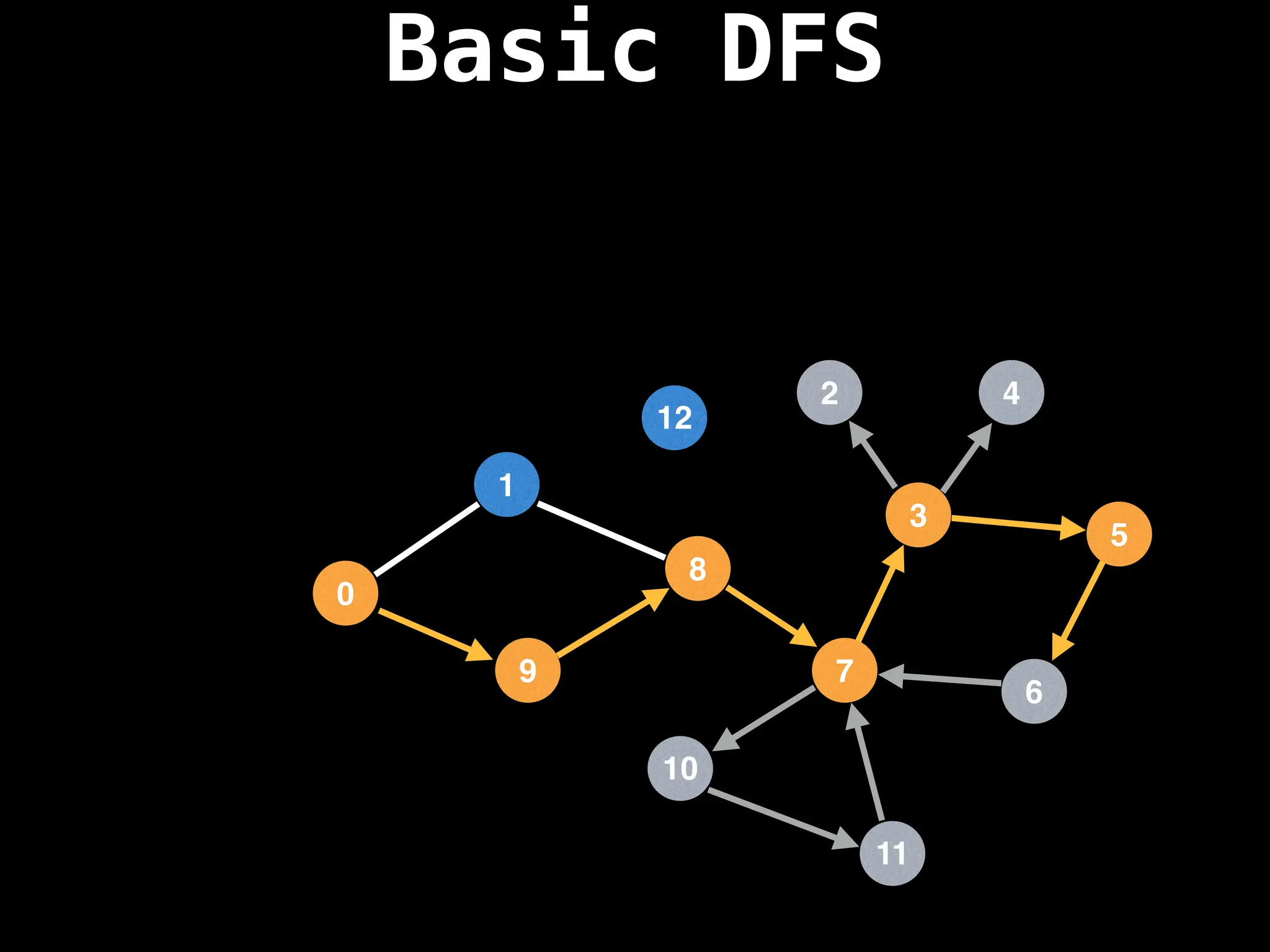
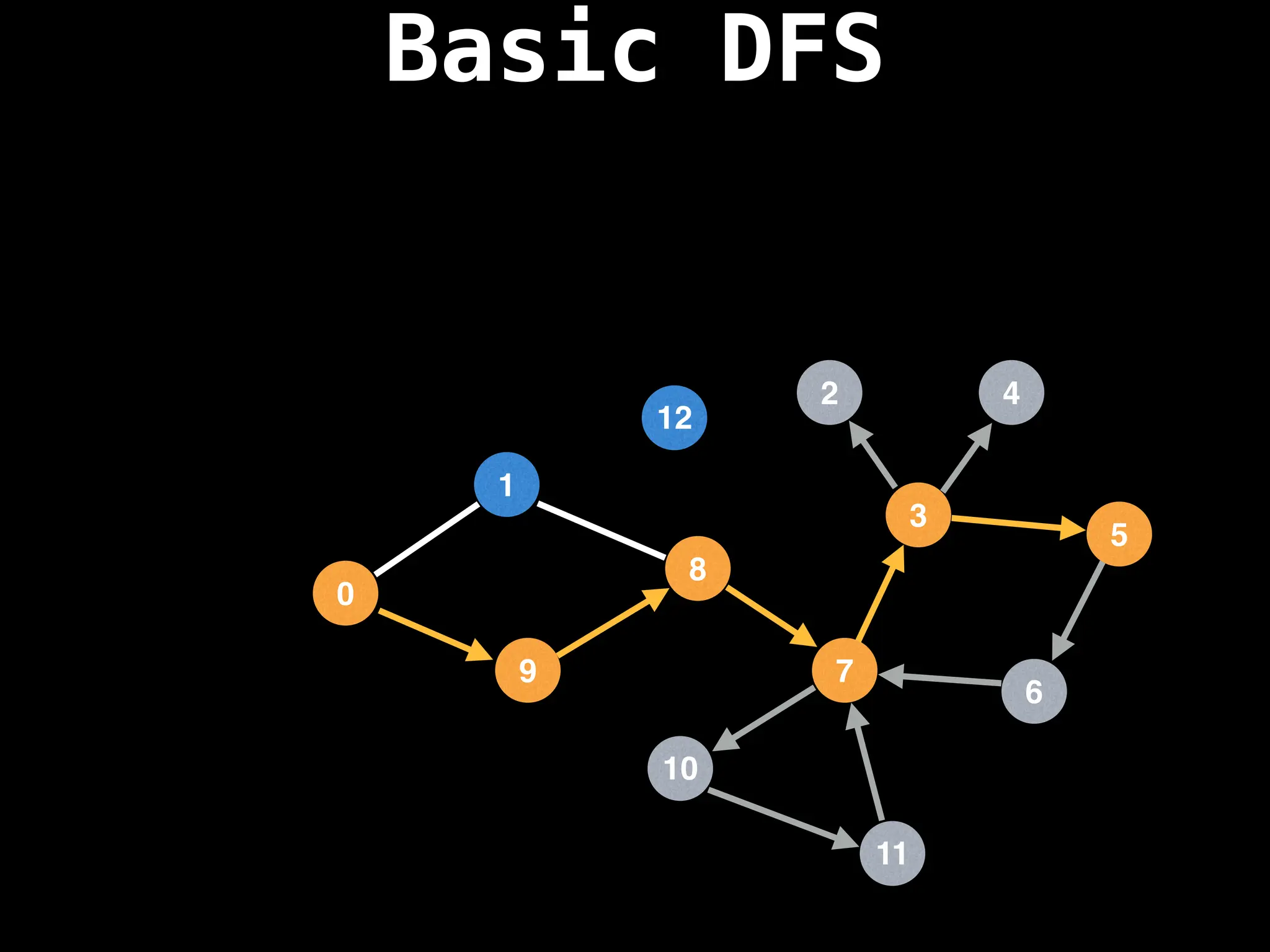
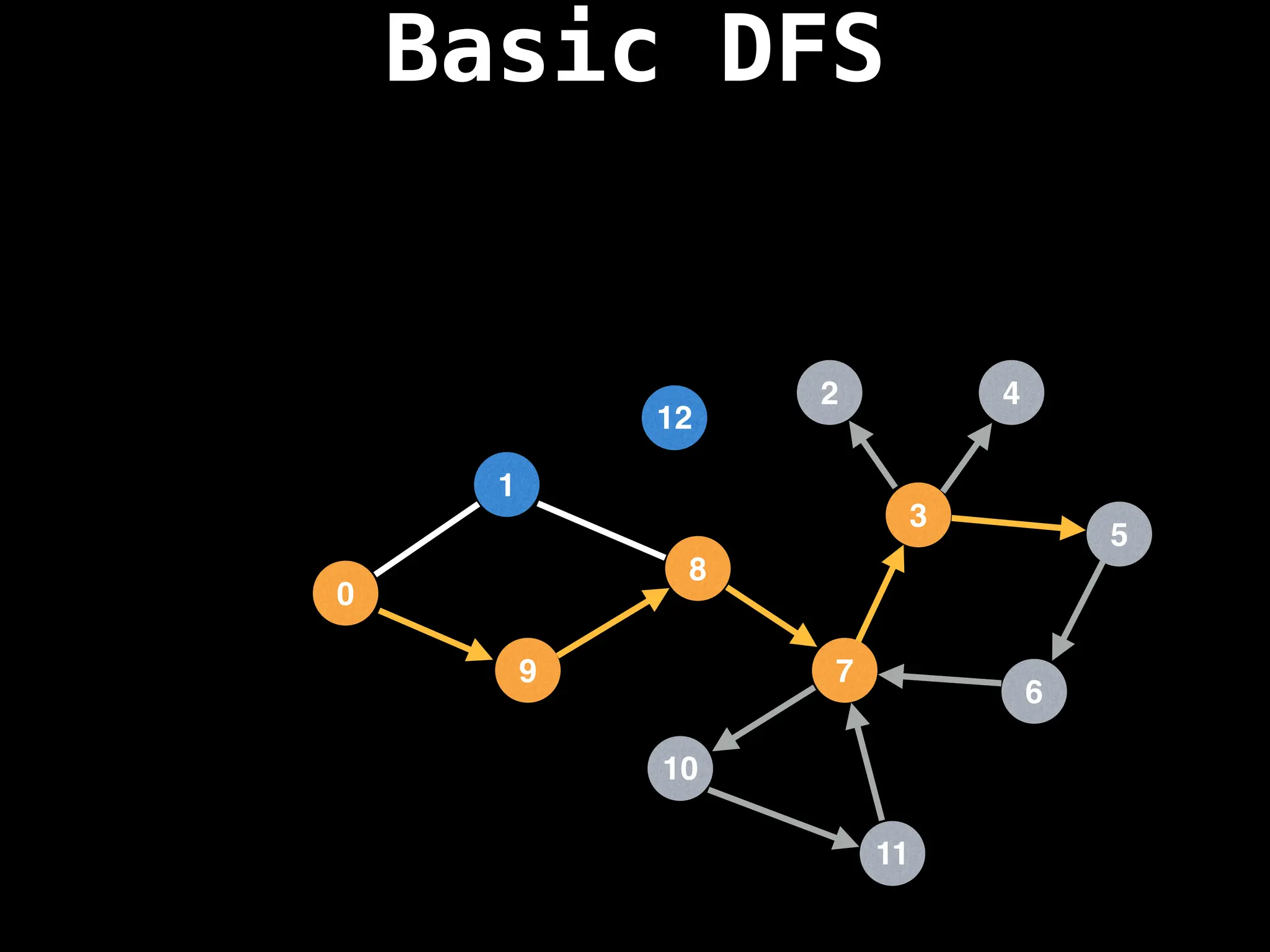
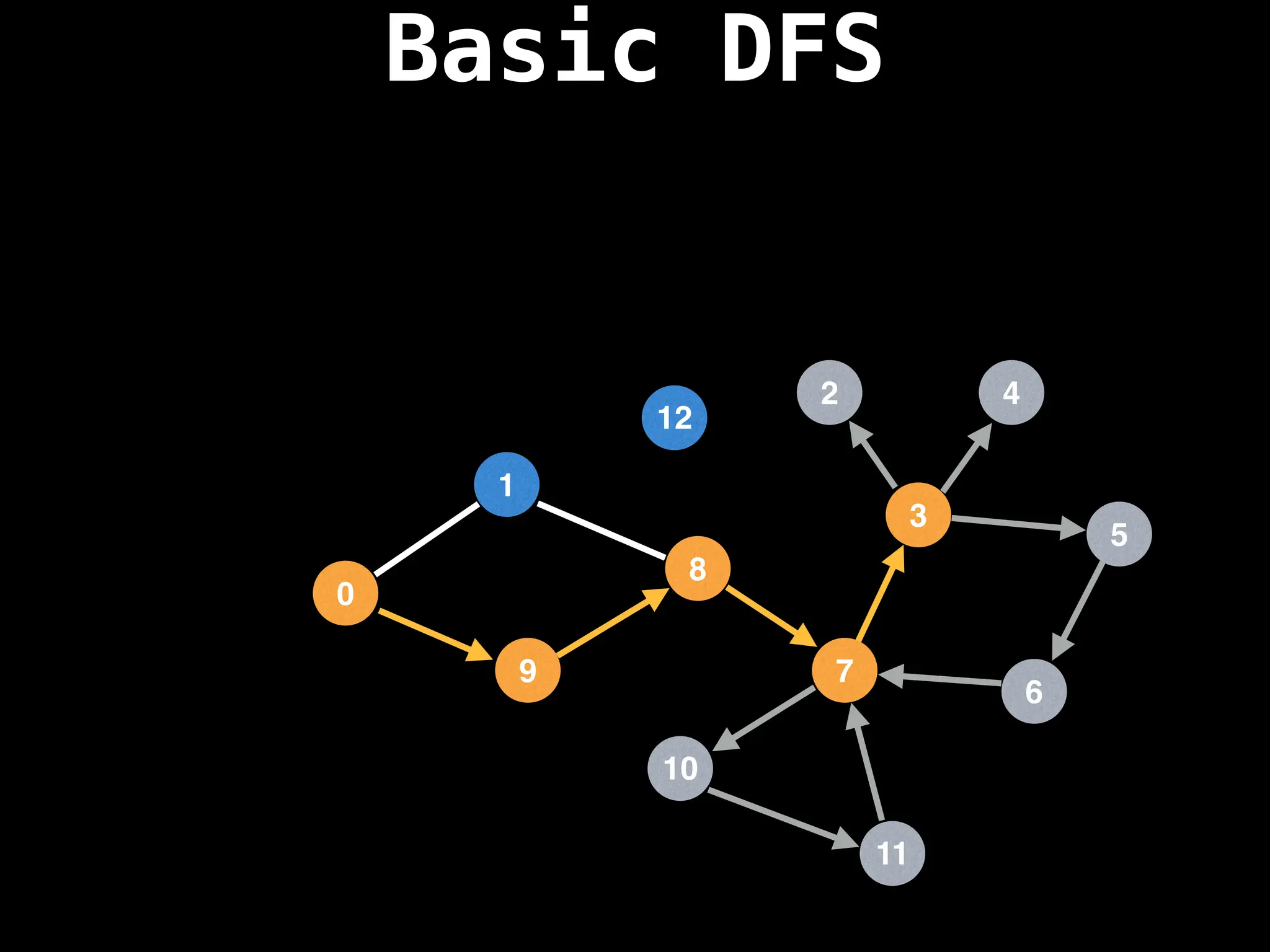
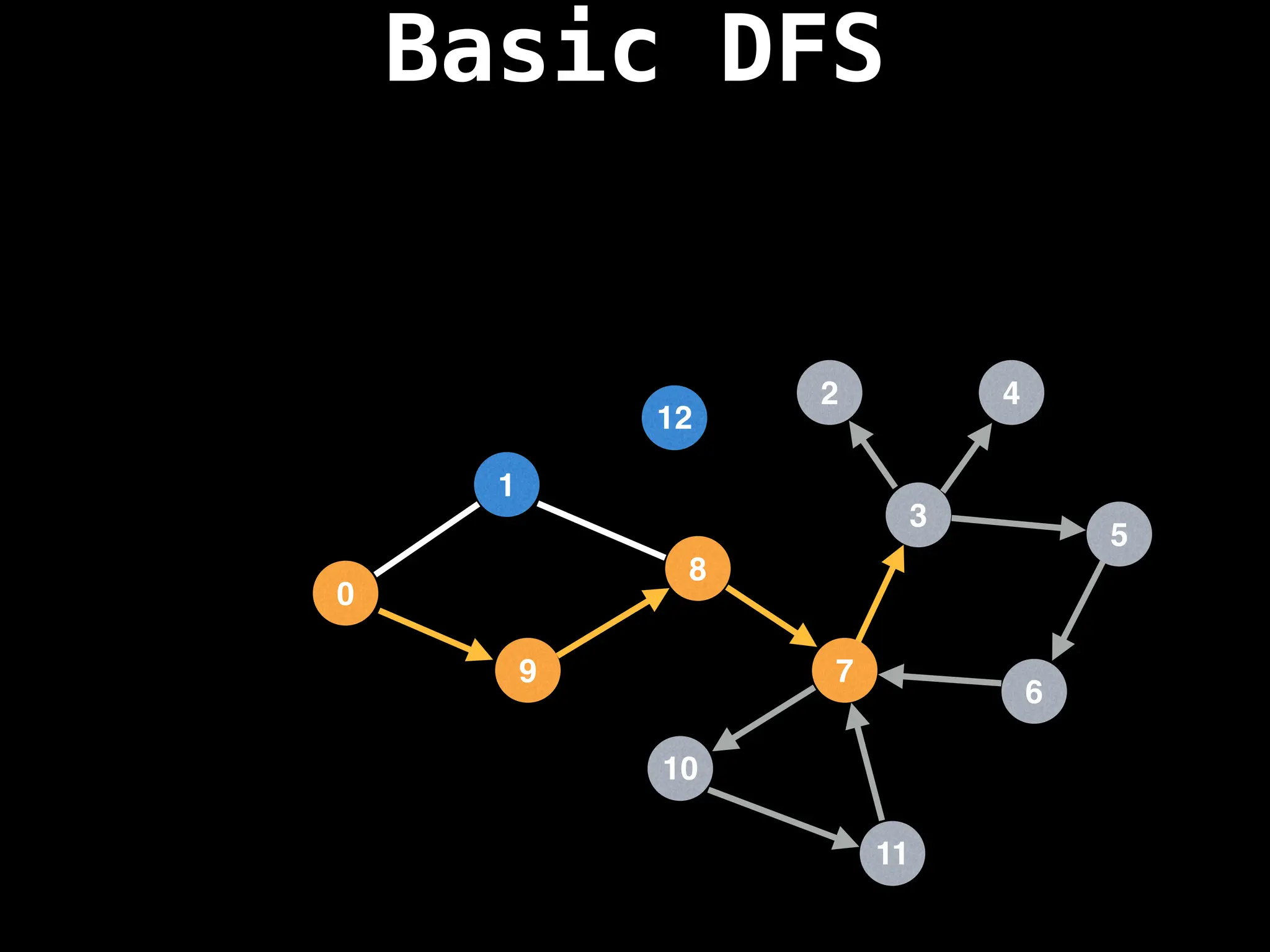
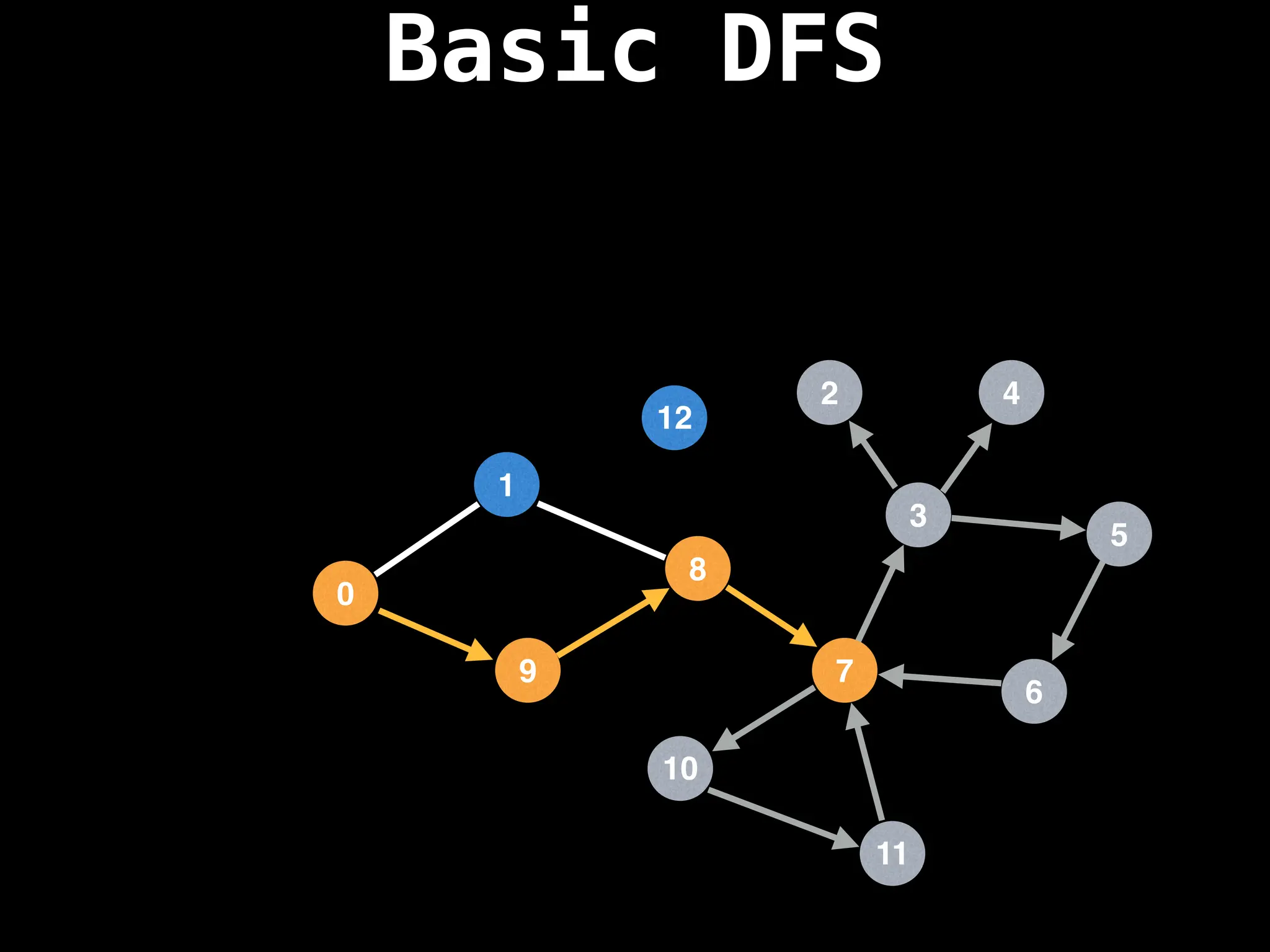
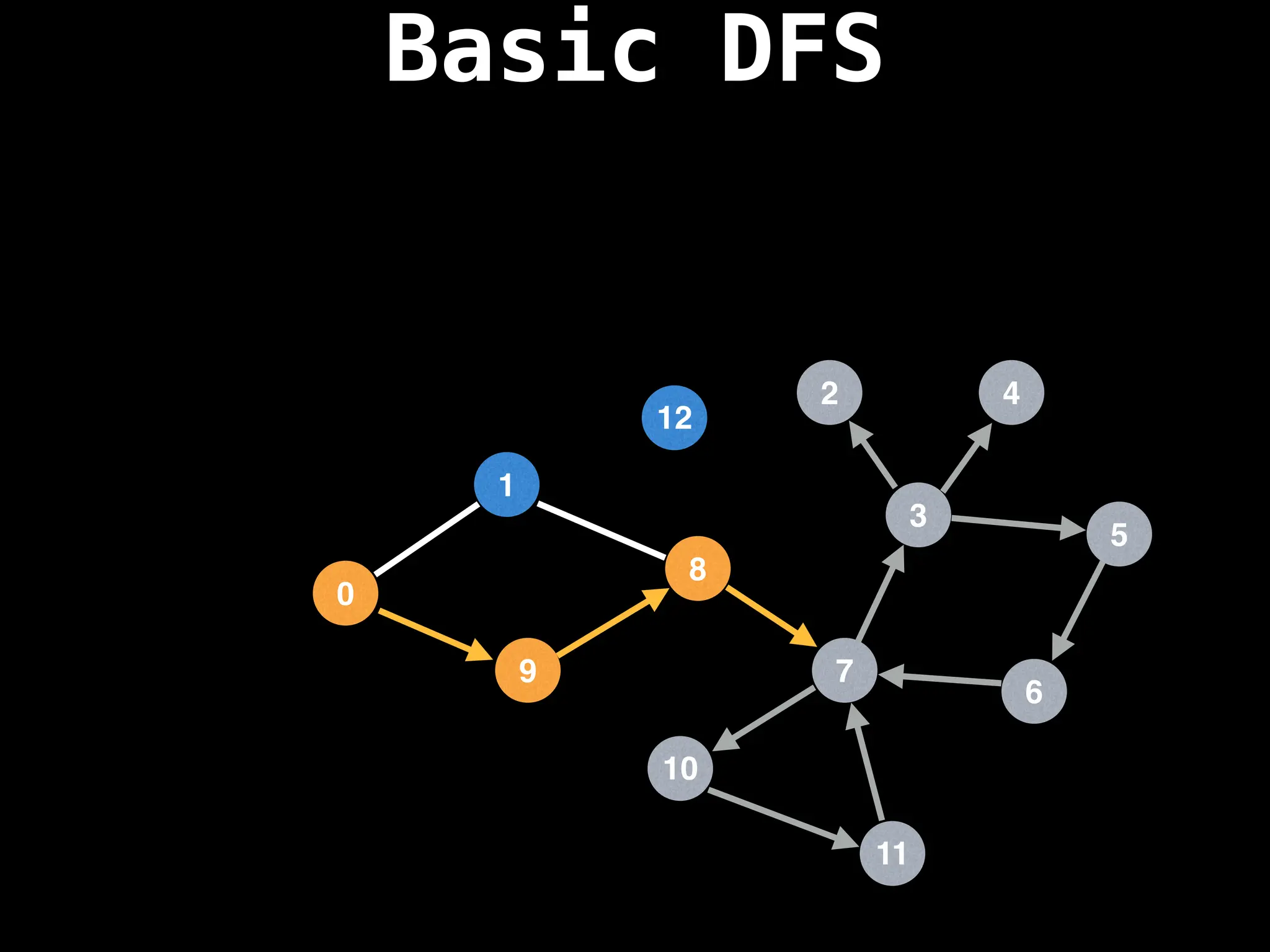
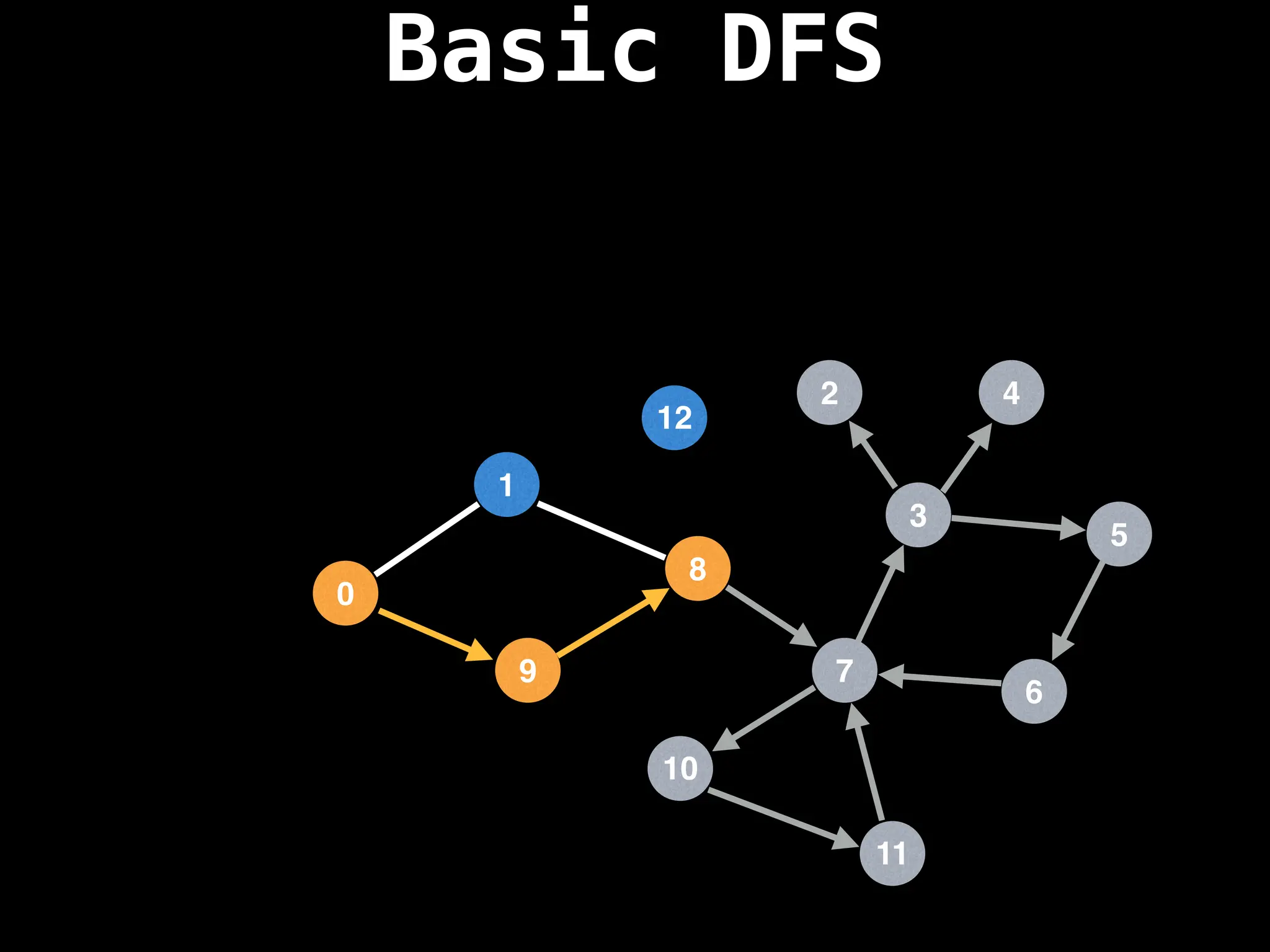
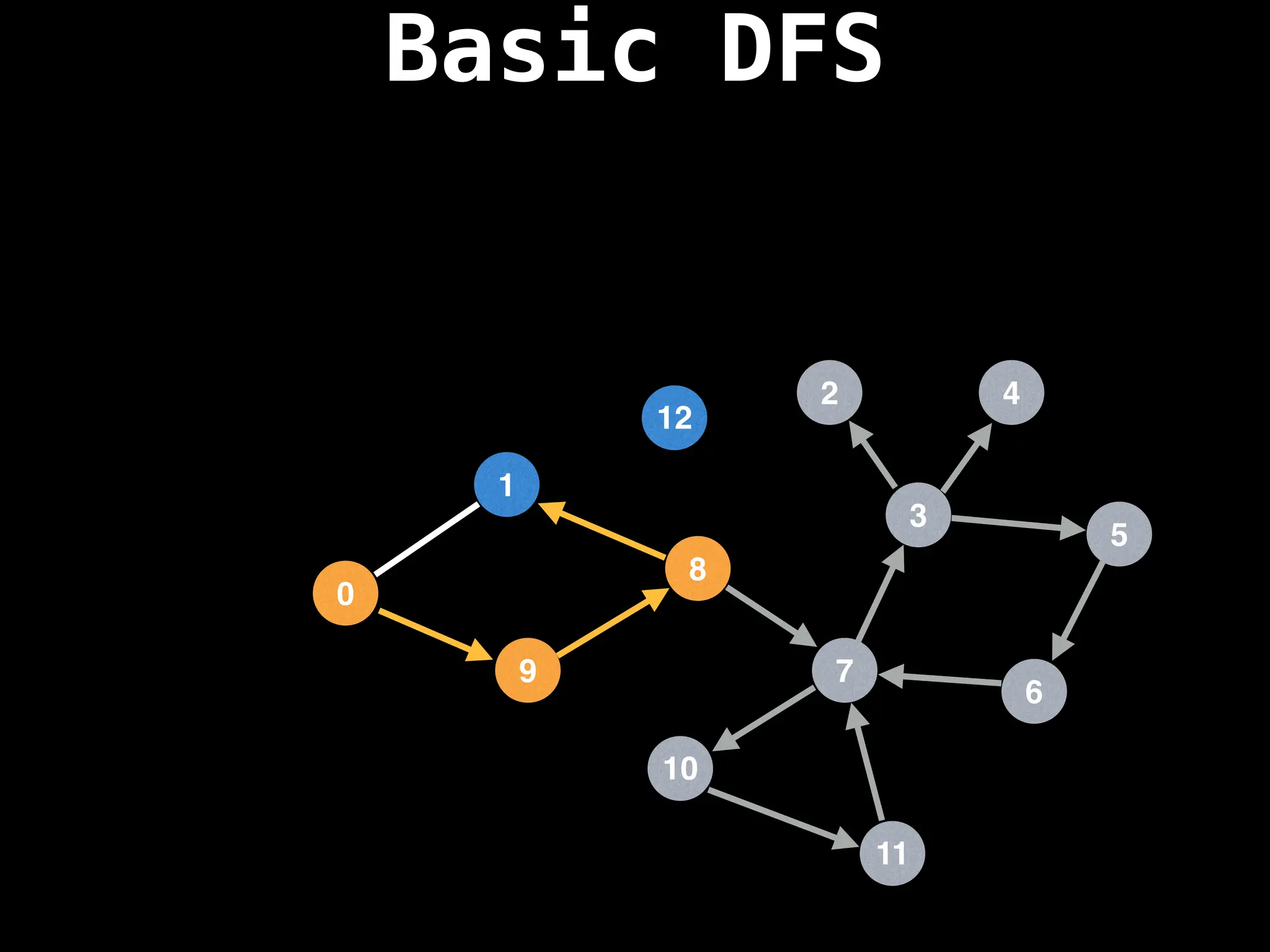
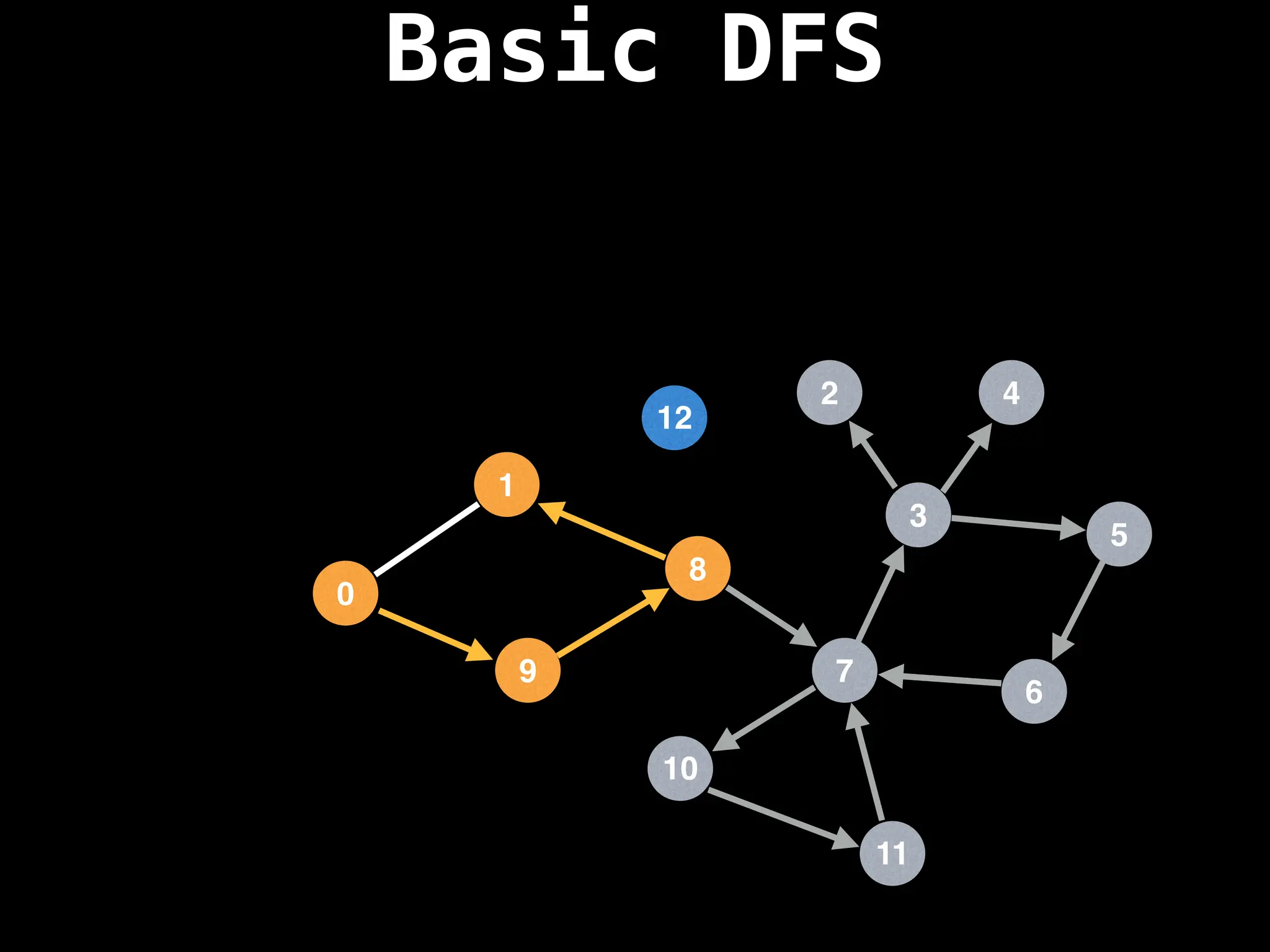
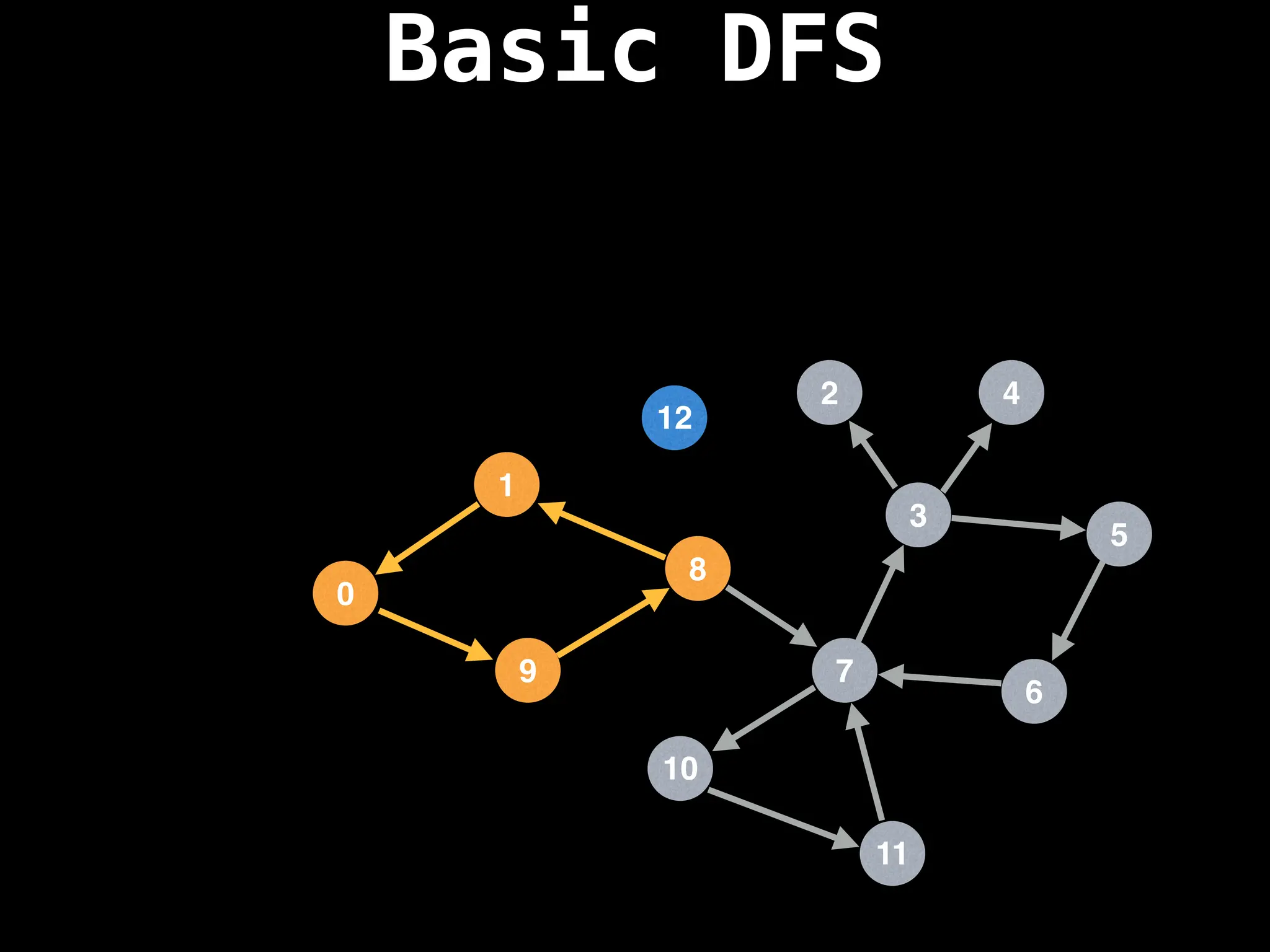
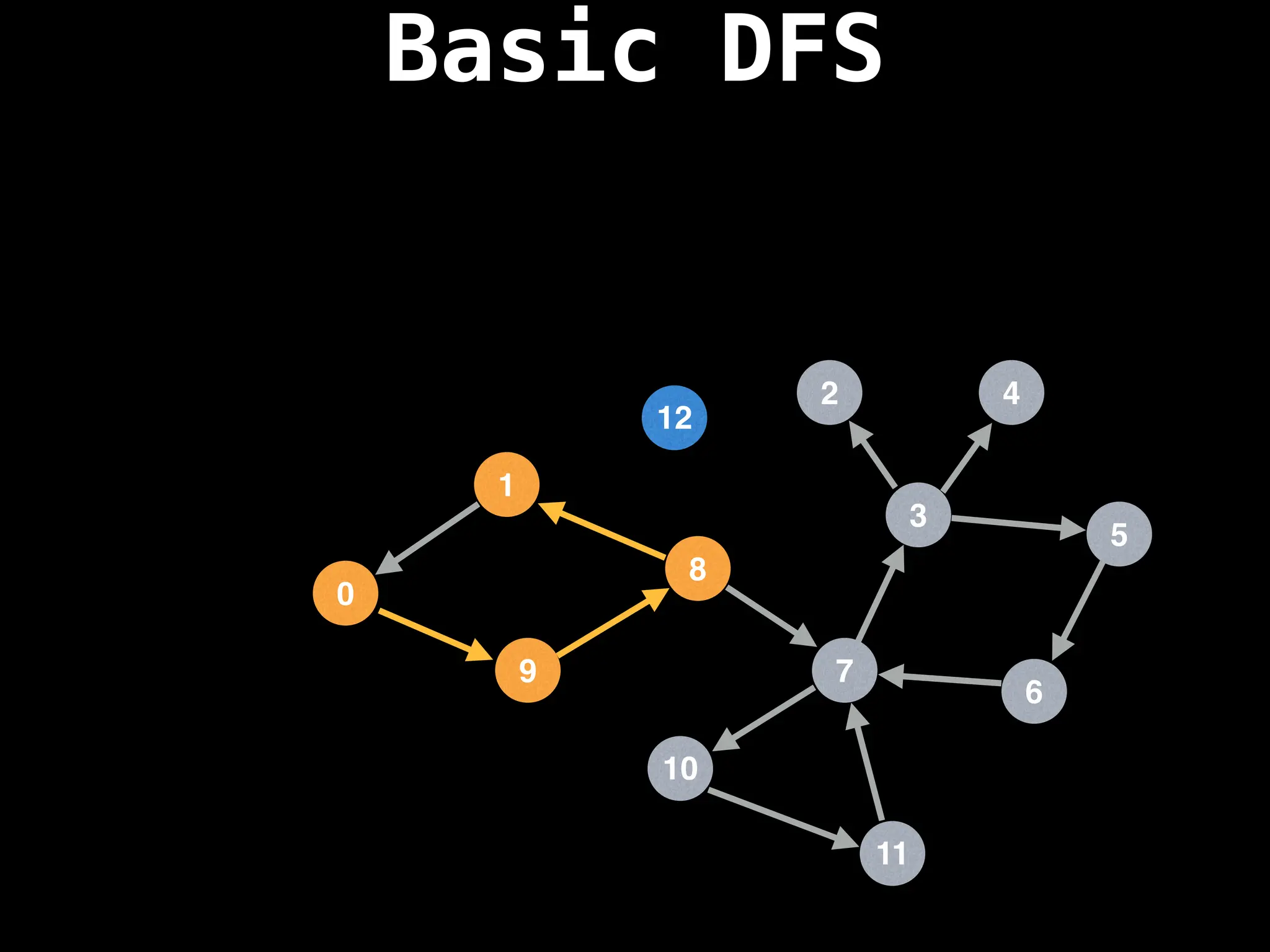
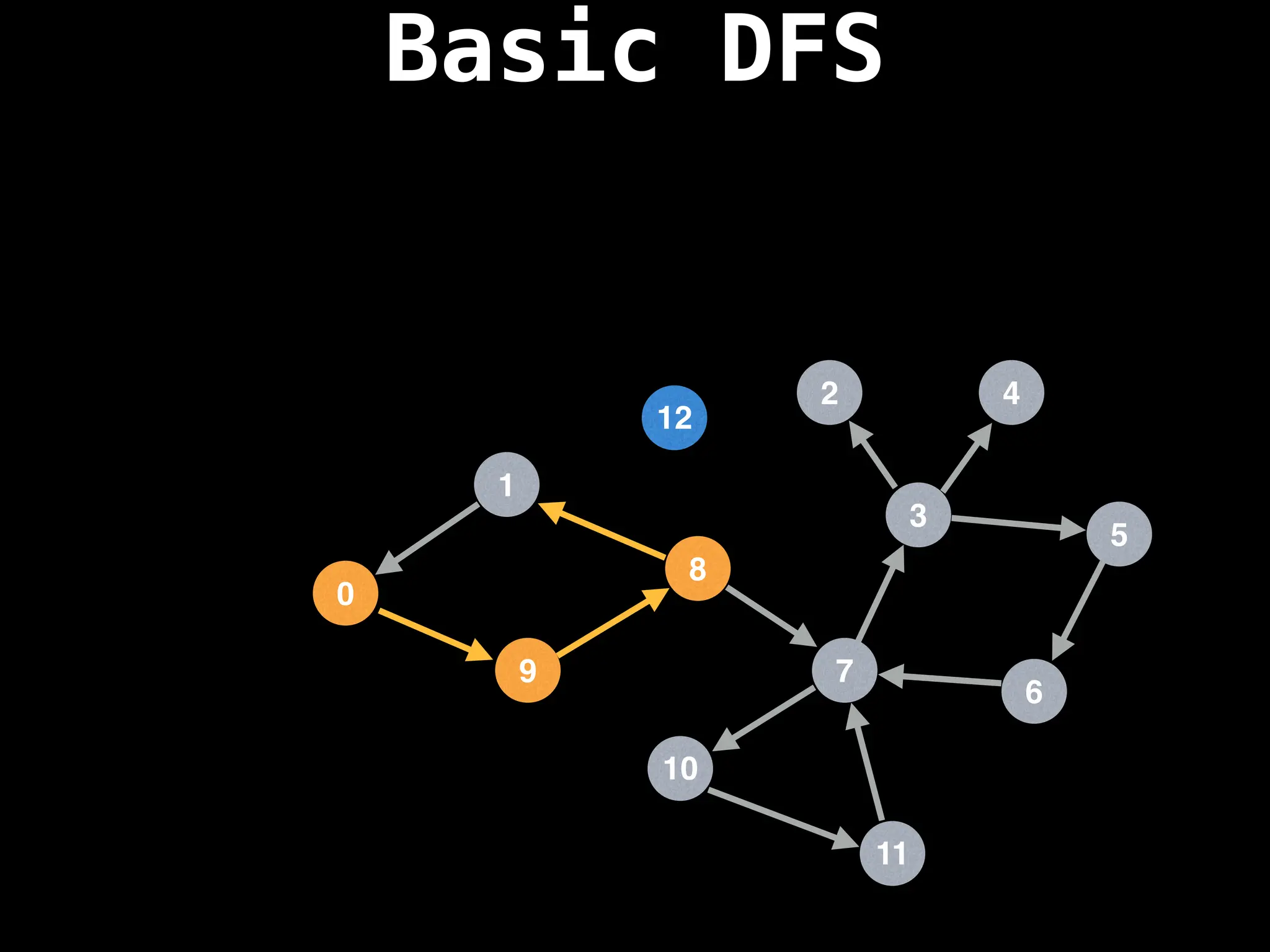
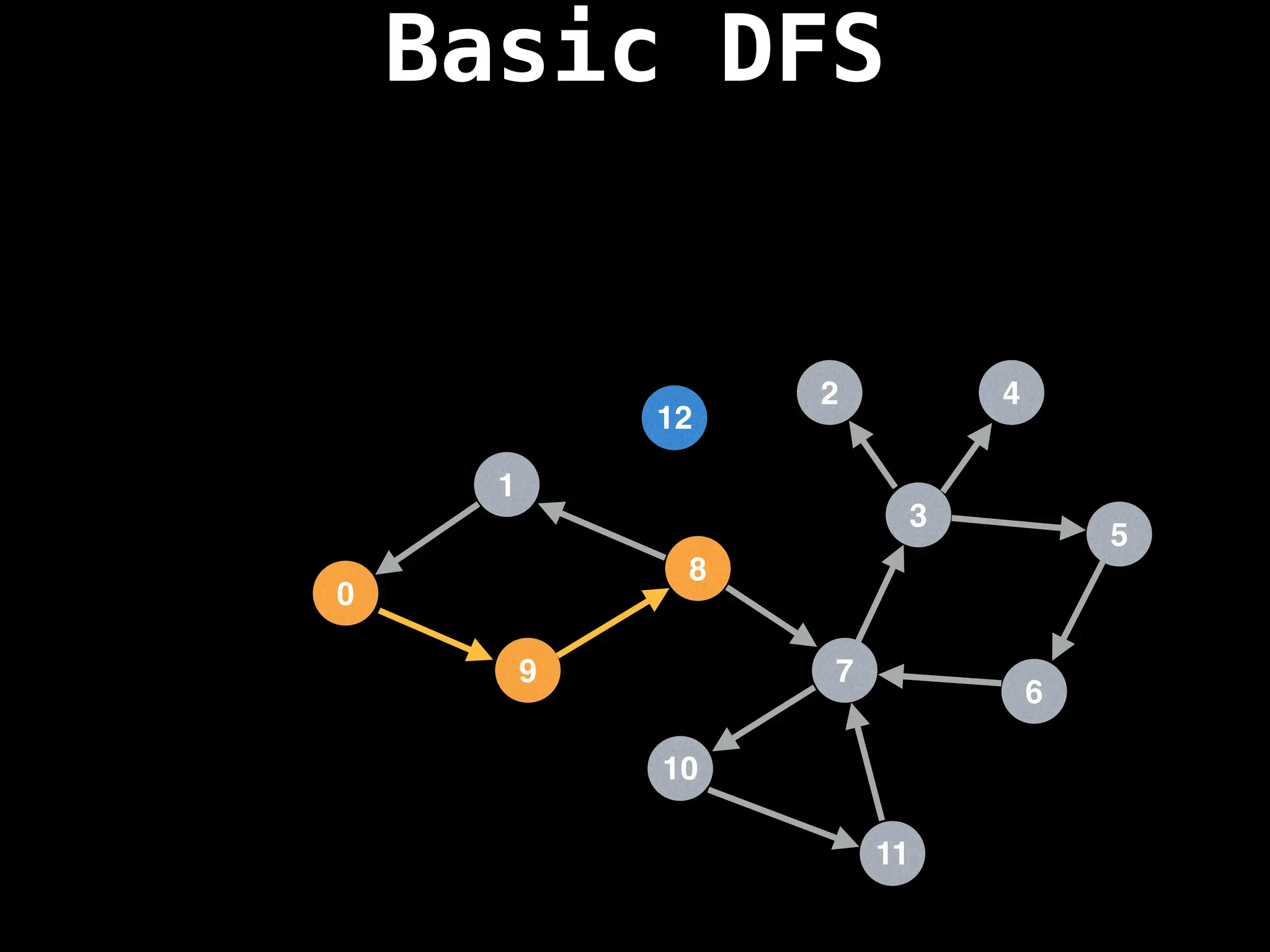
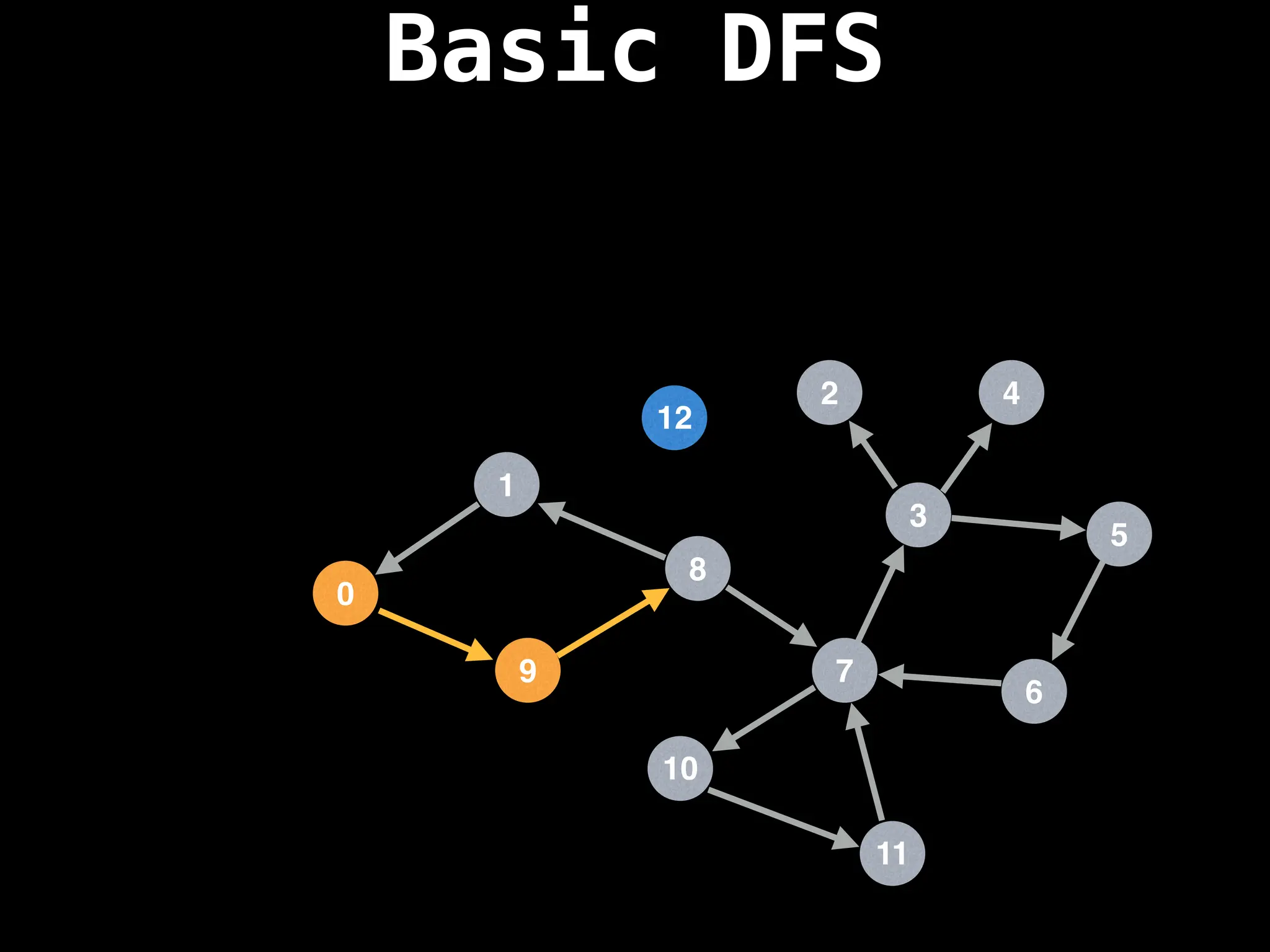
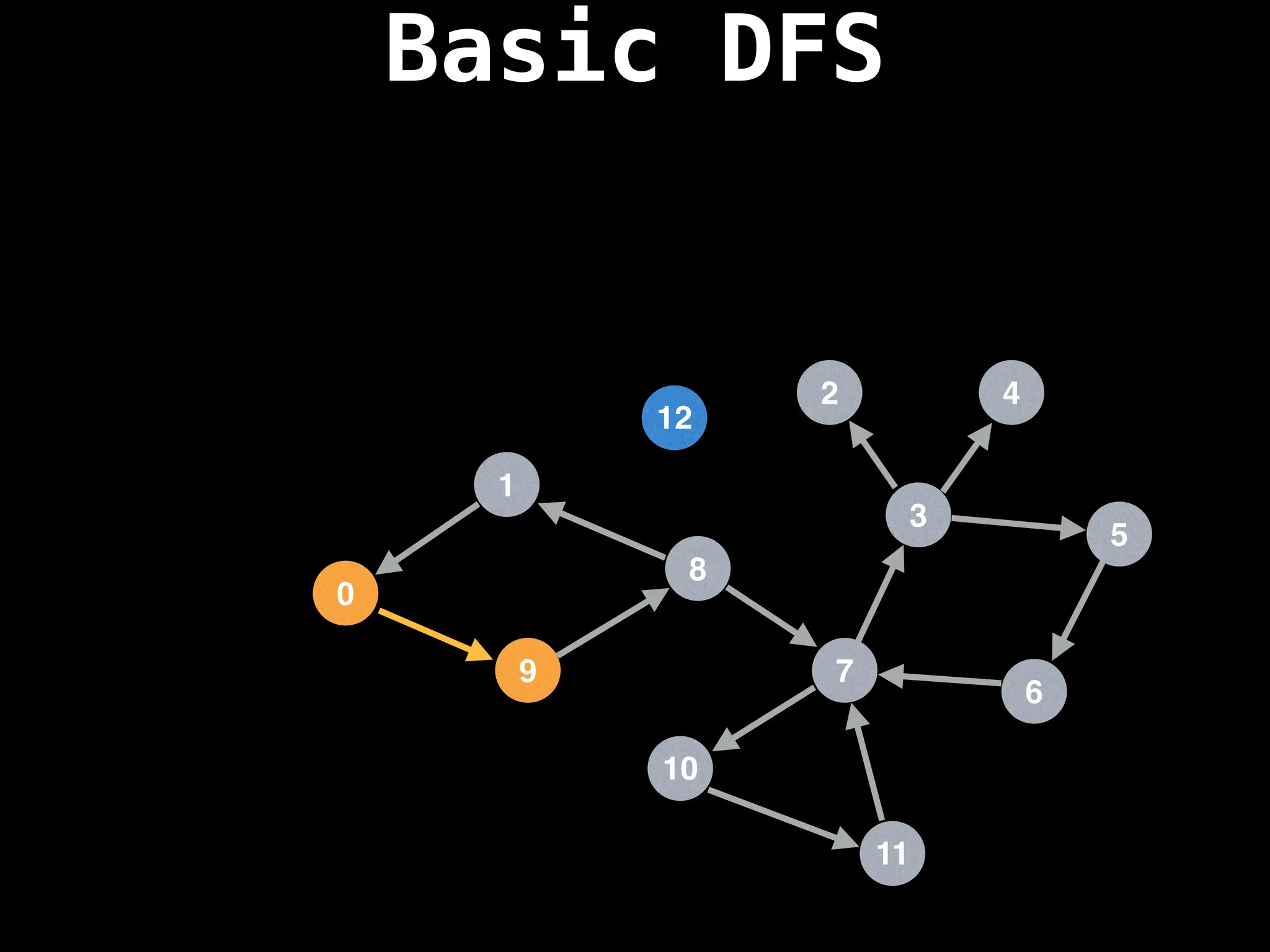
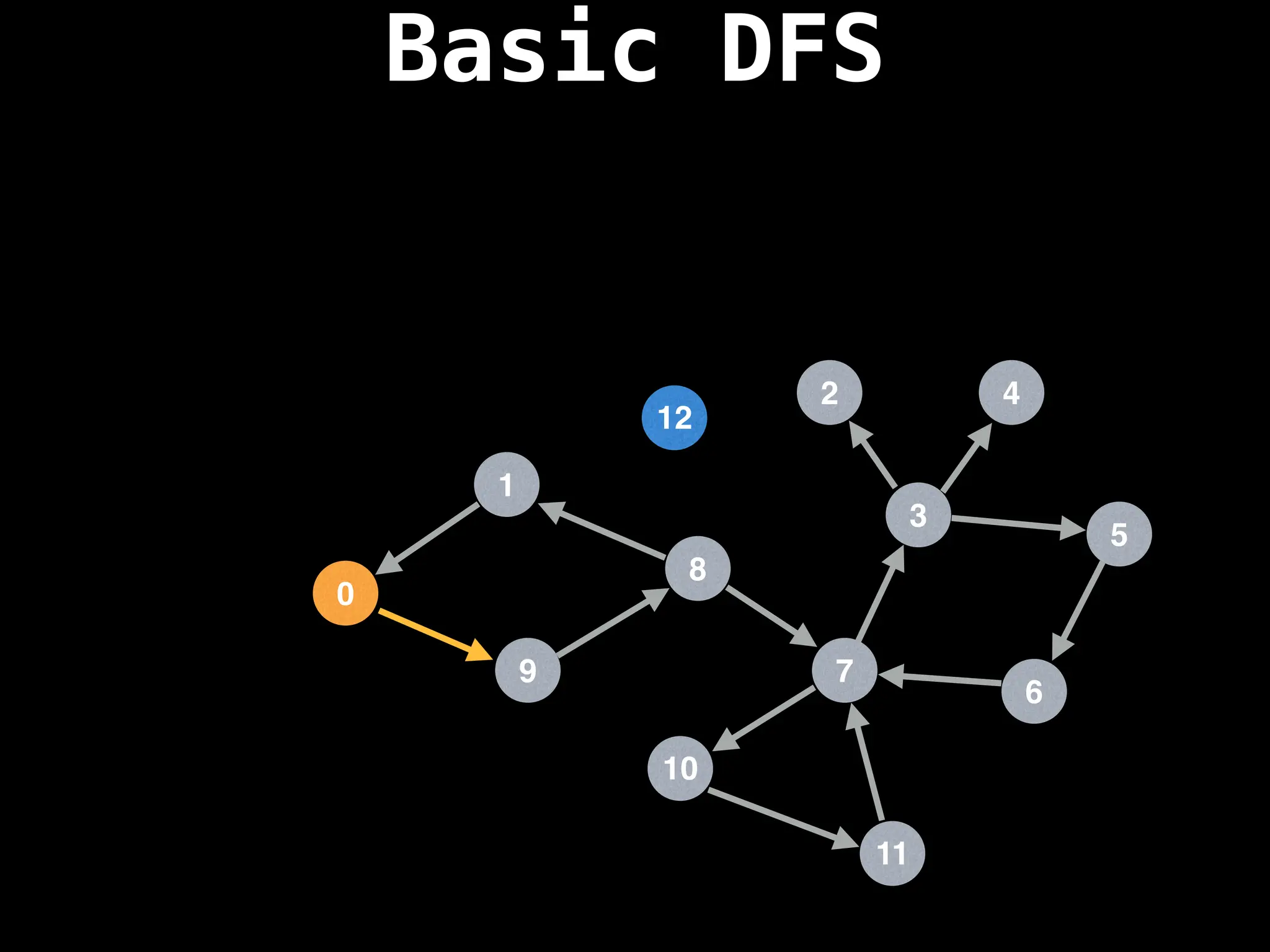
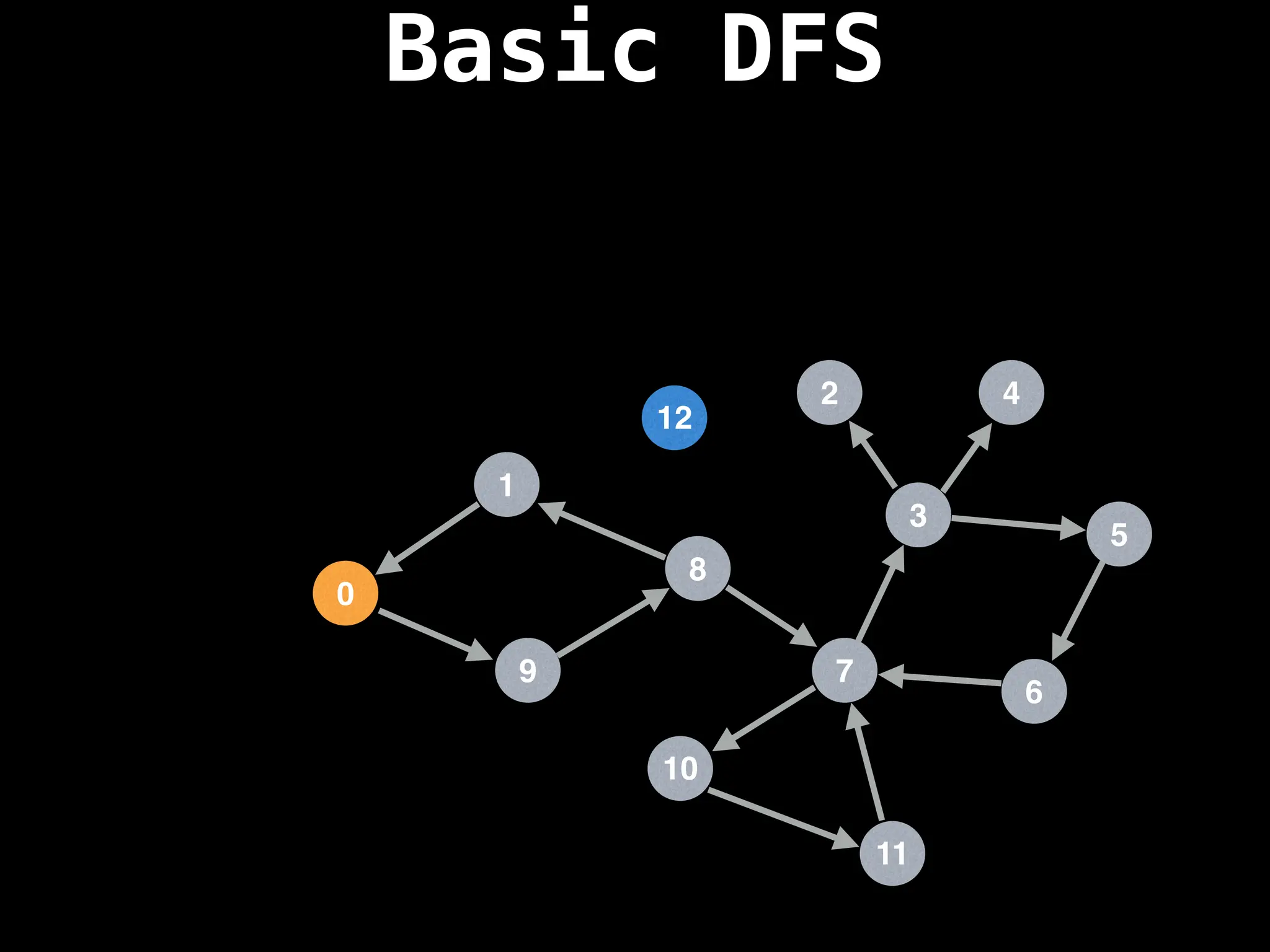
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-110-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-111-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-112-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-113-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-114-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-115-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-116-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function dfs(at):
if visited[at]: return
visited[at] = true
neighbours = graph[at]
for next in neighbours:
dfs(next)
# Start DFS at node zero
start_node = 0
dfs(start_node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-117-2048.jpg)
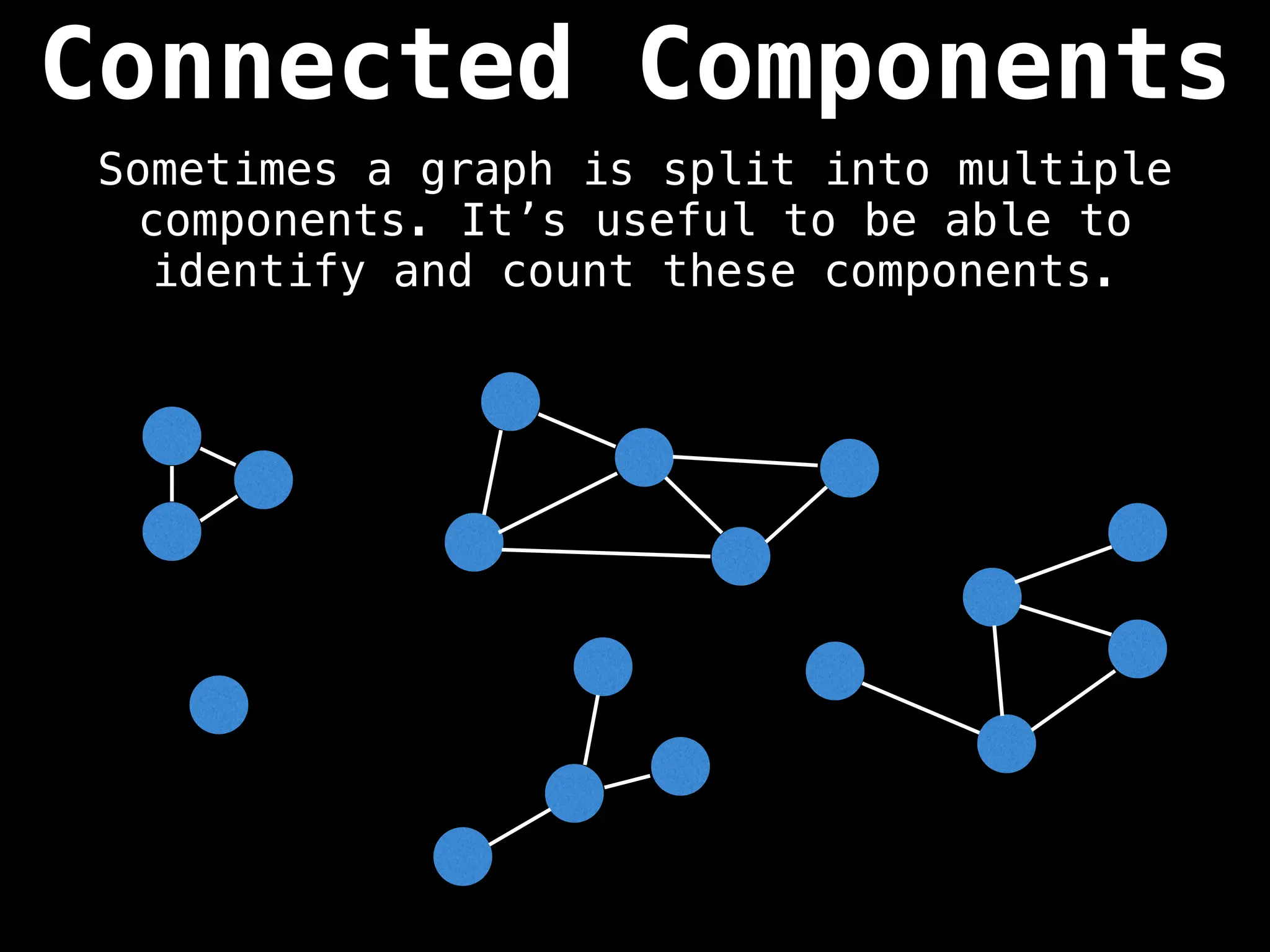
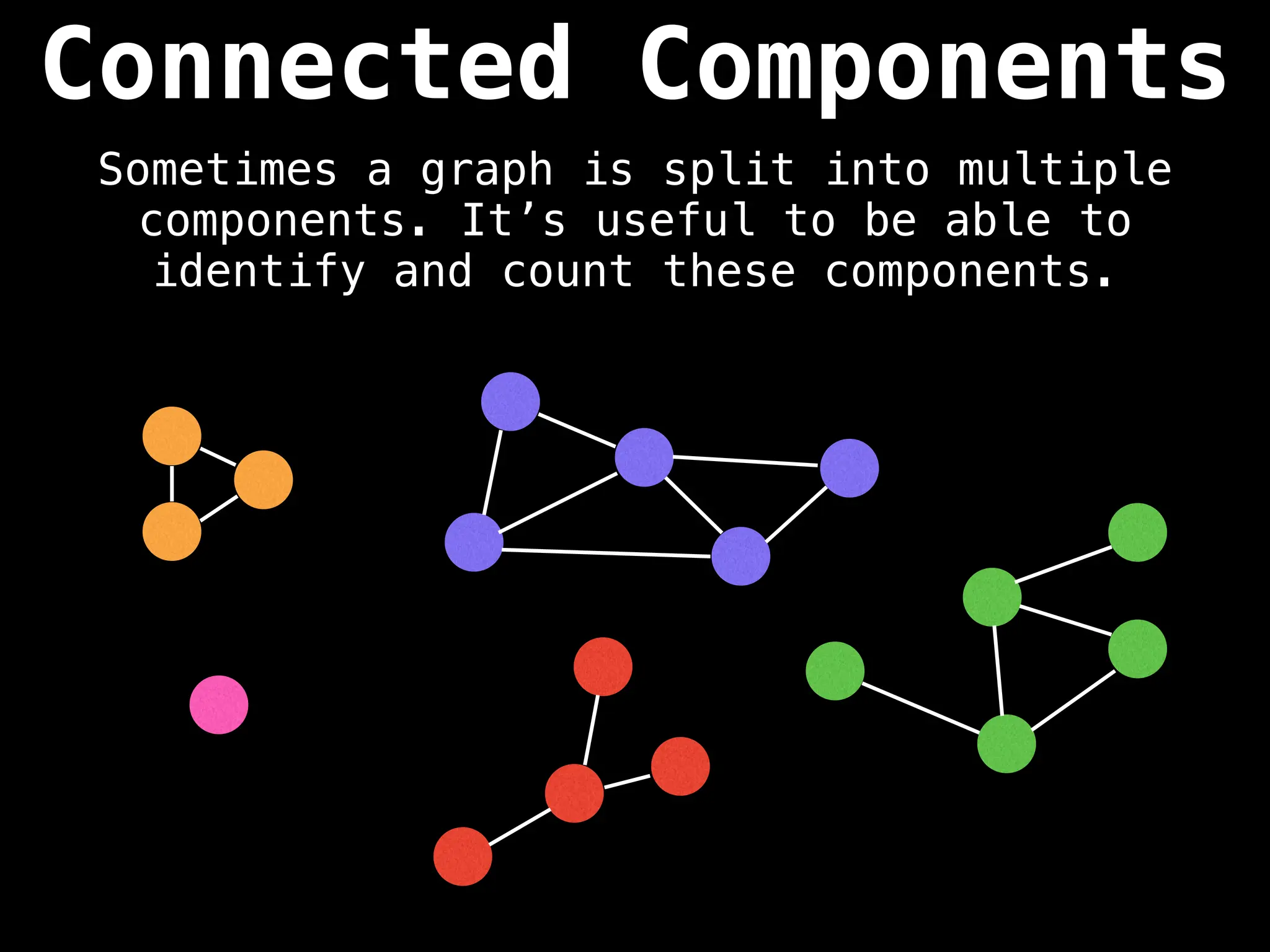
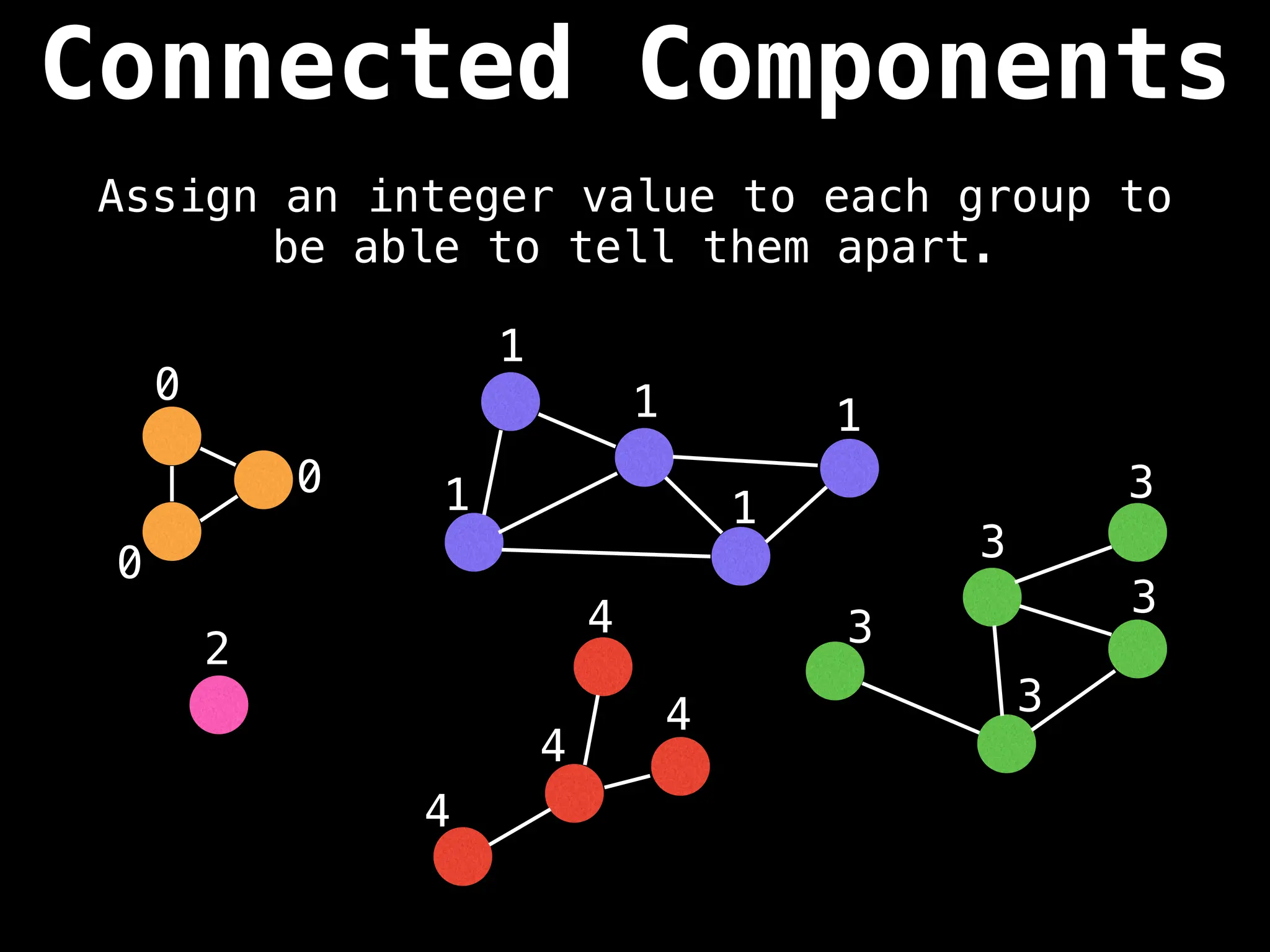
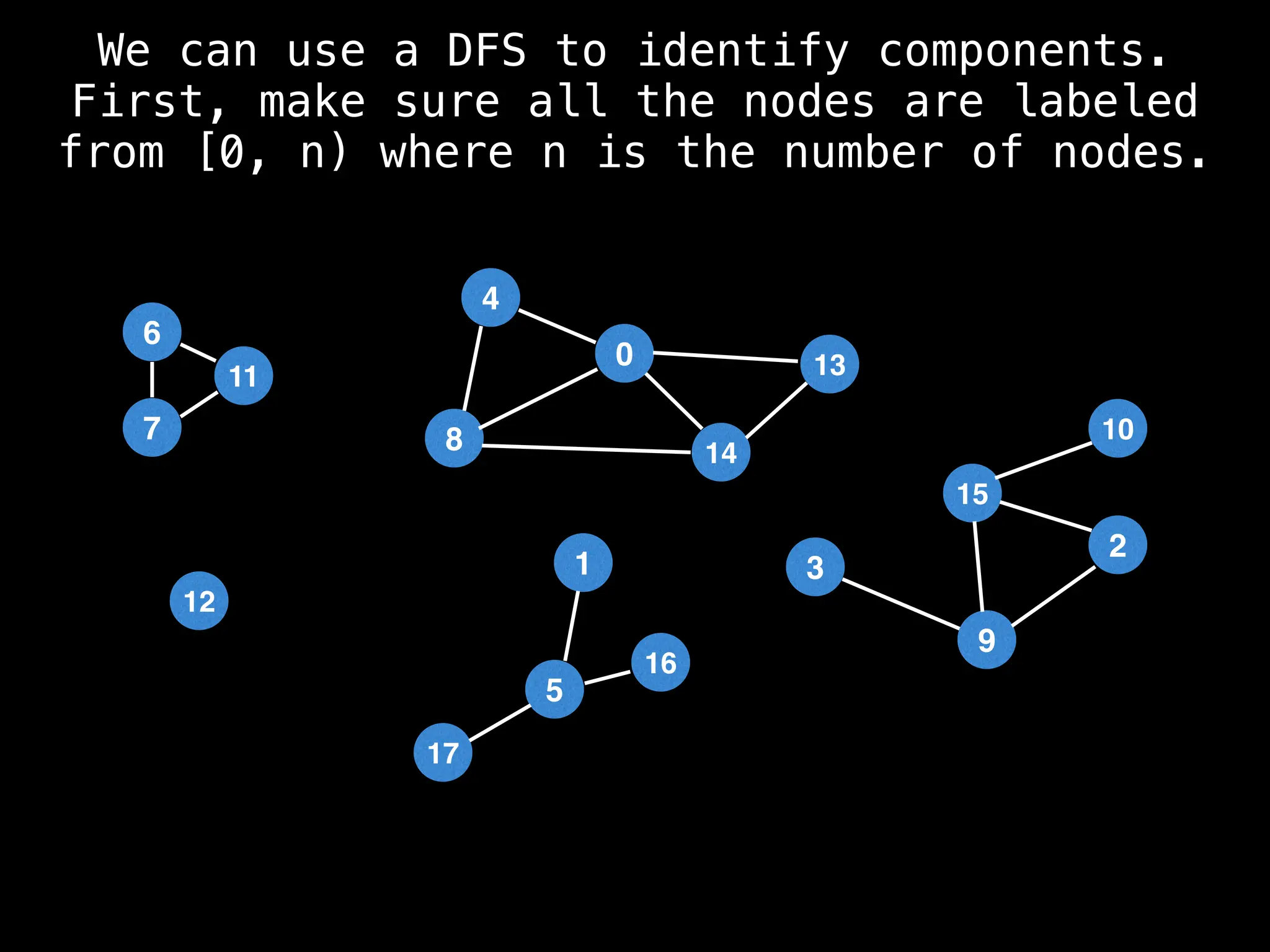
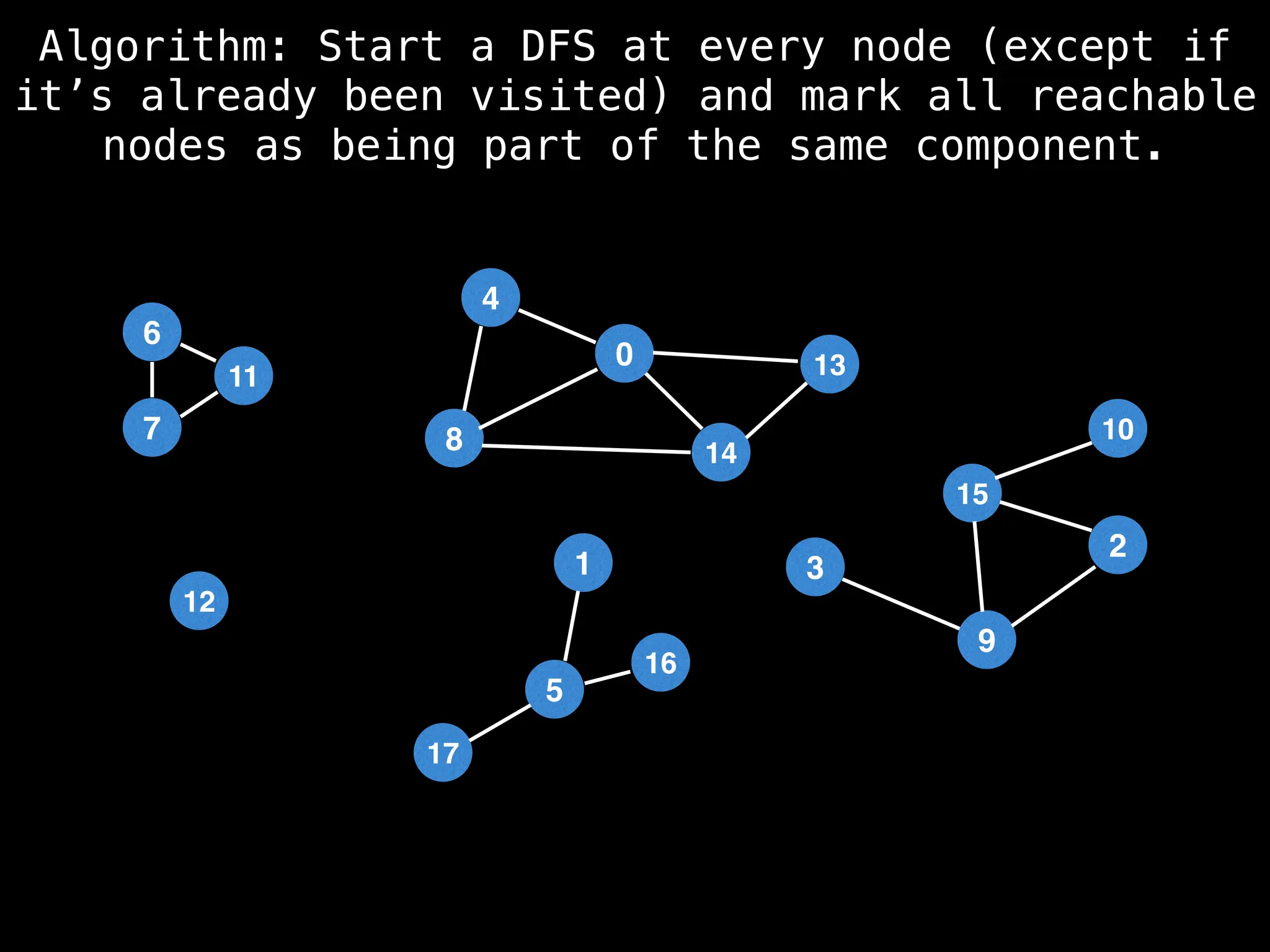
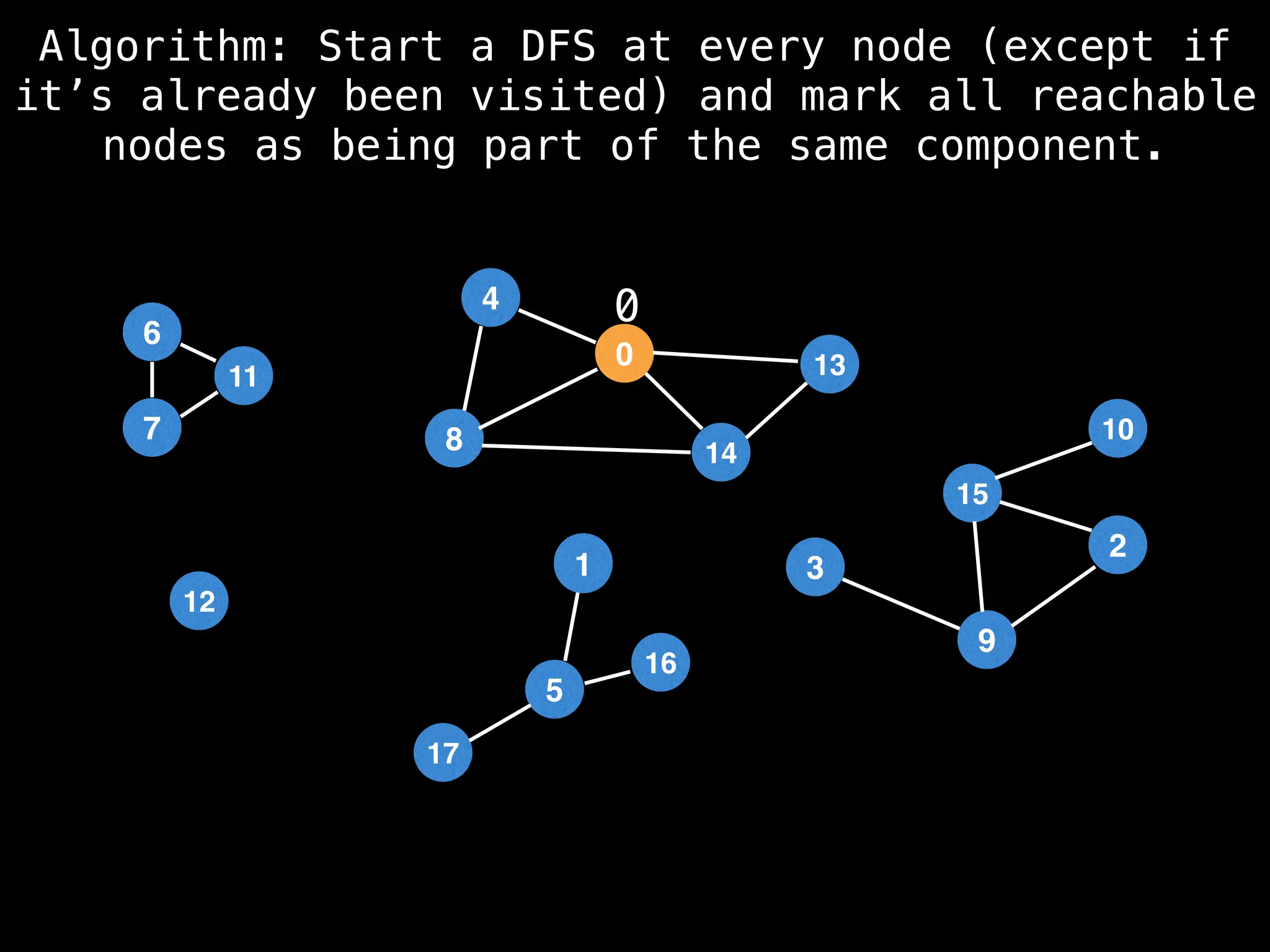
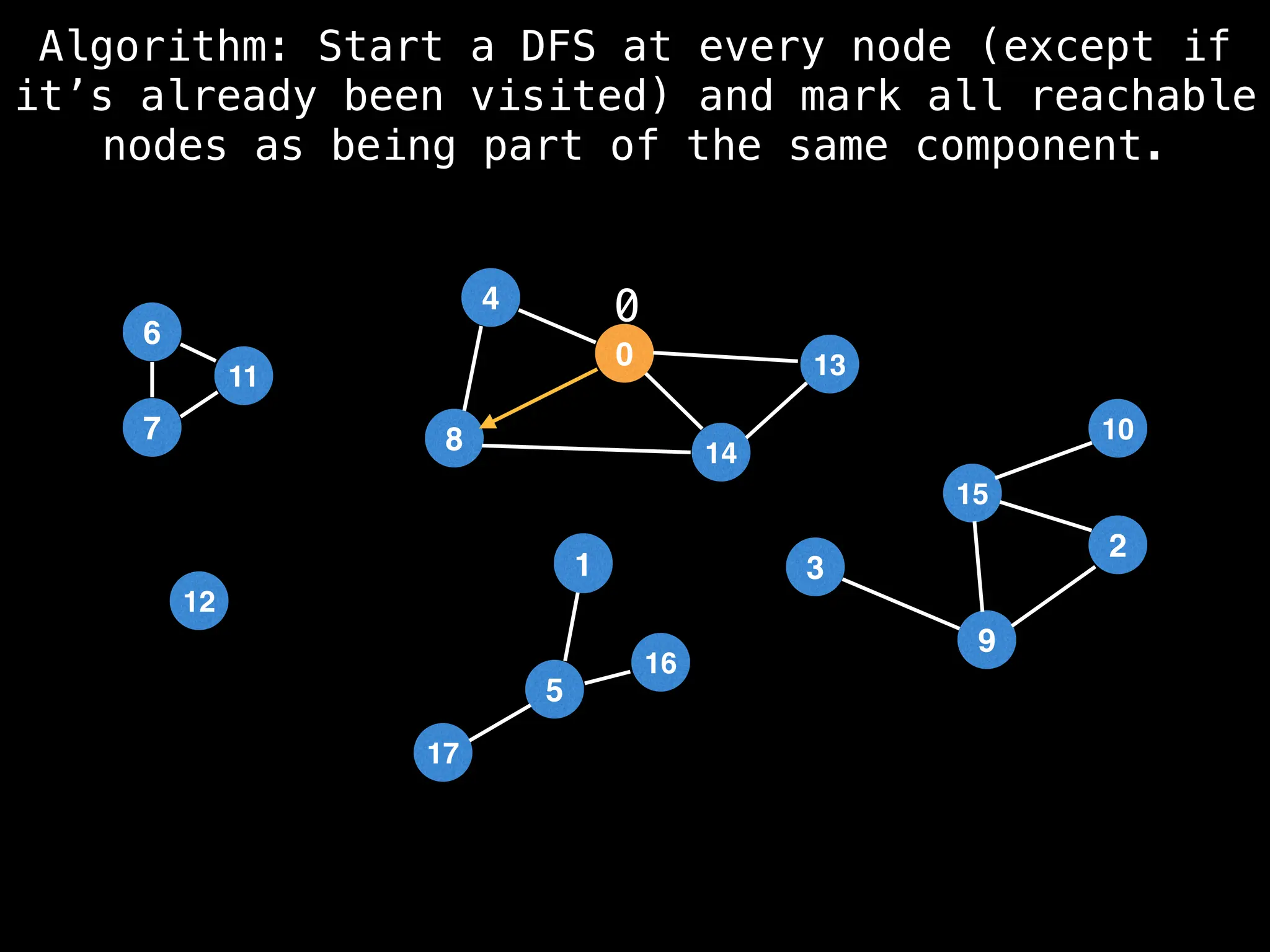
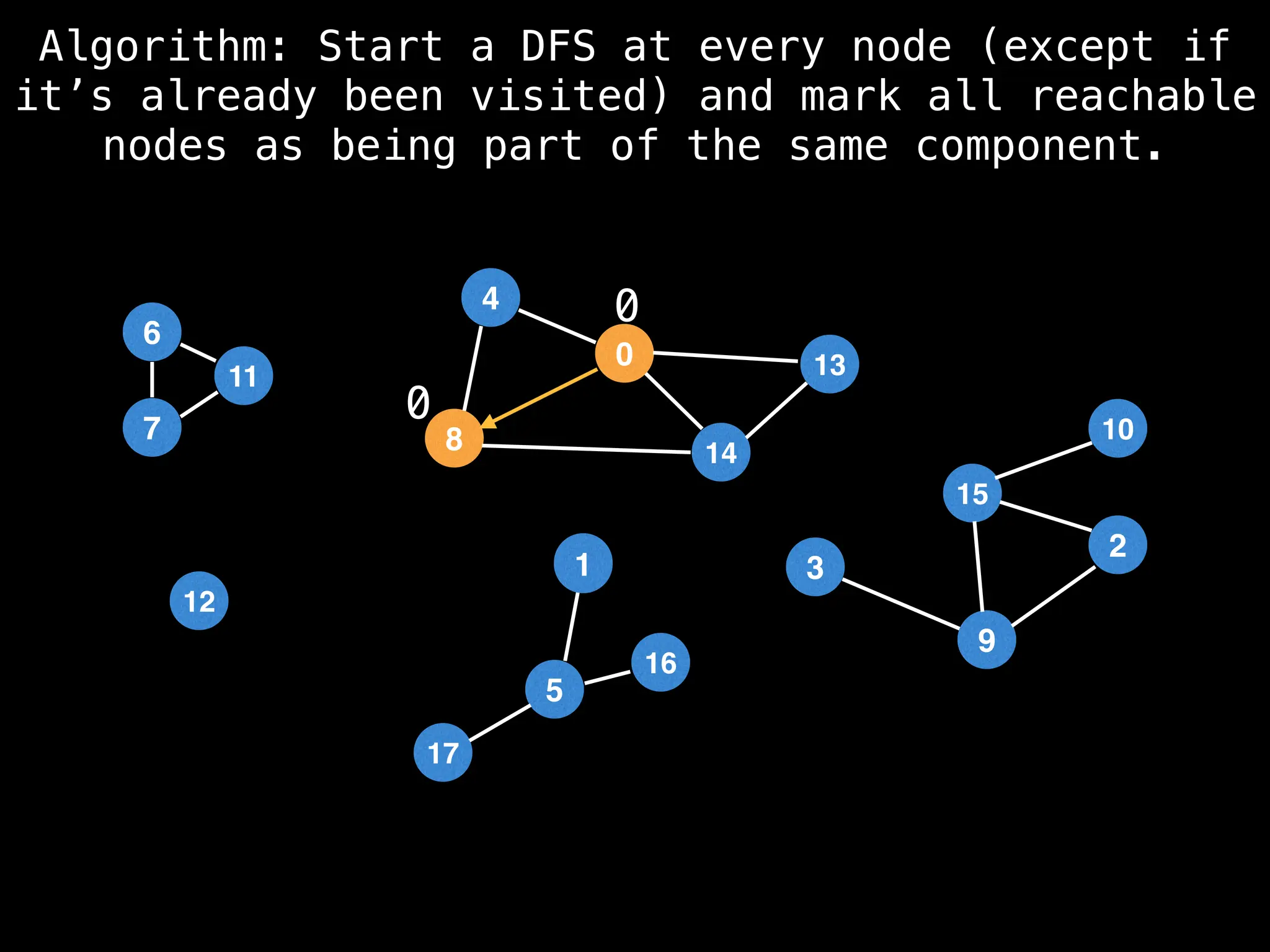
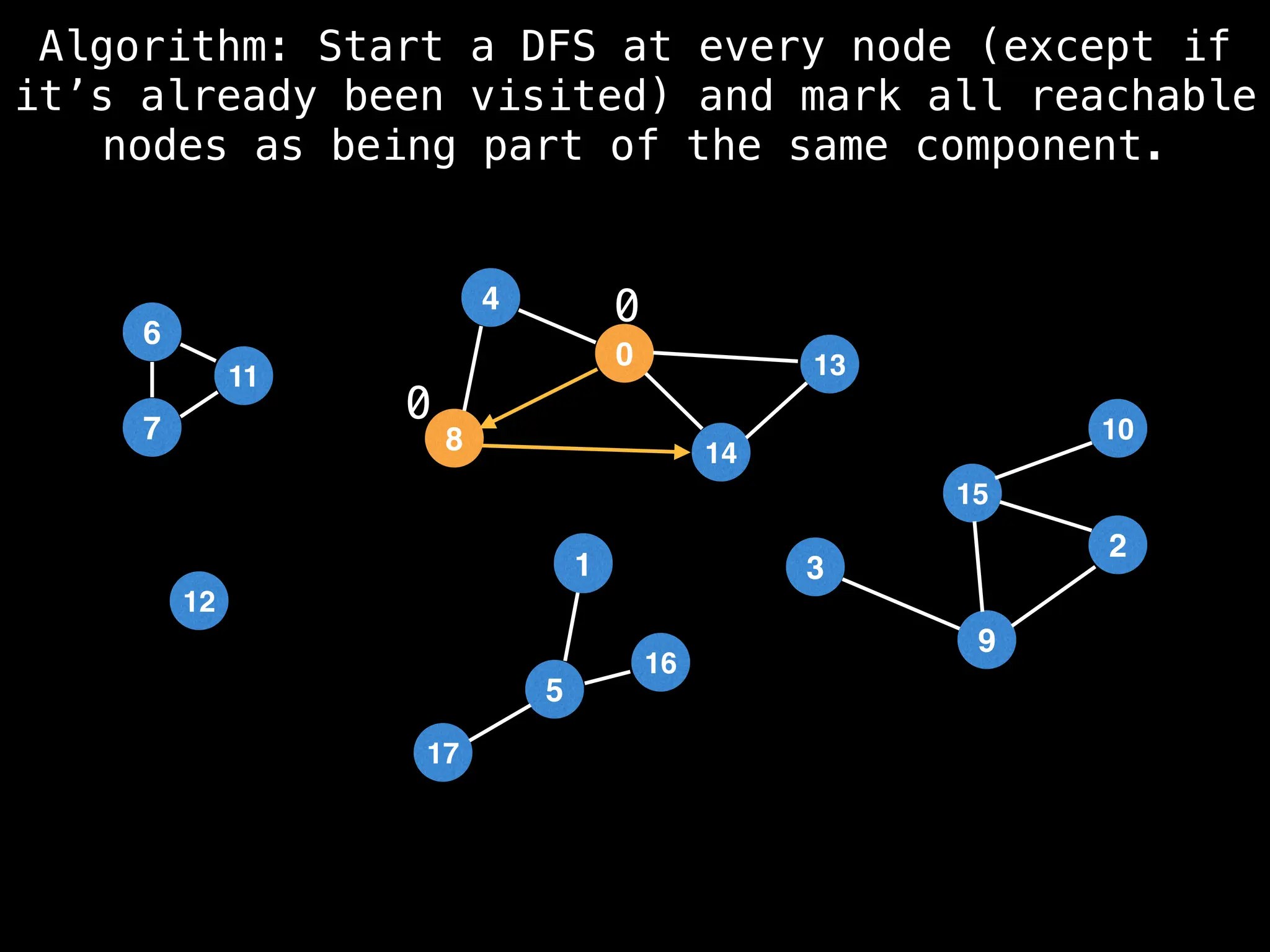
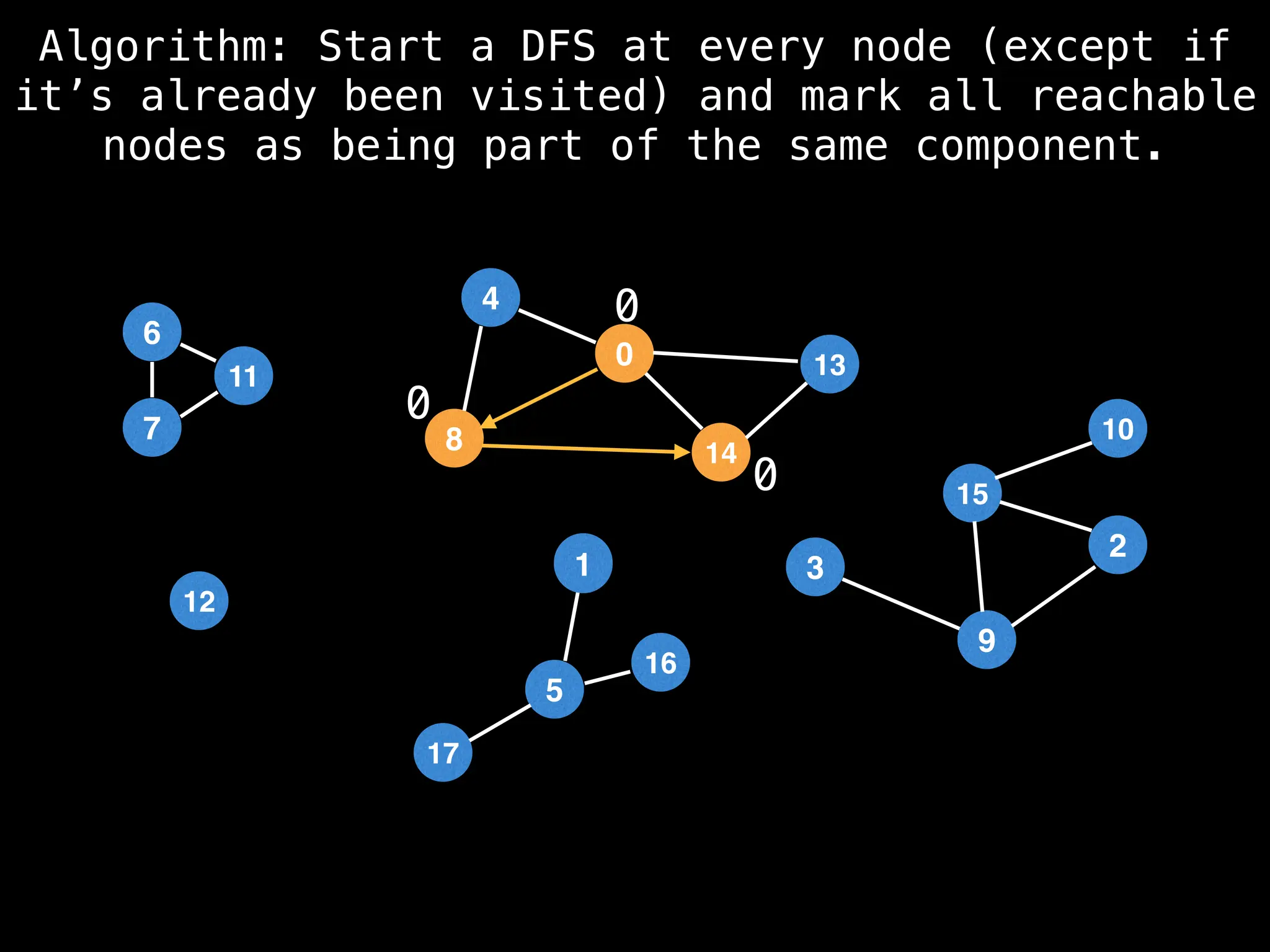
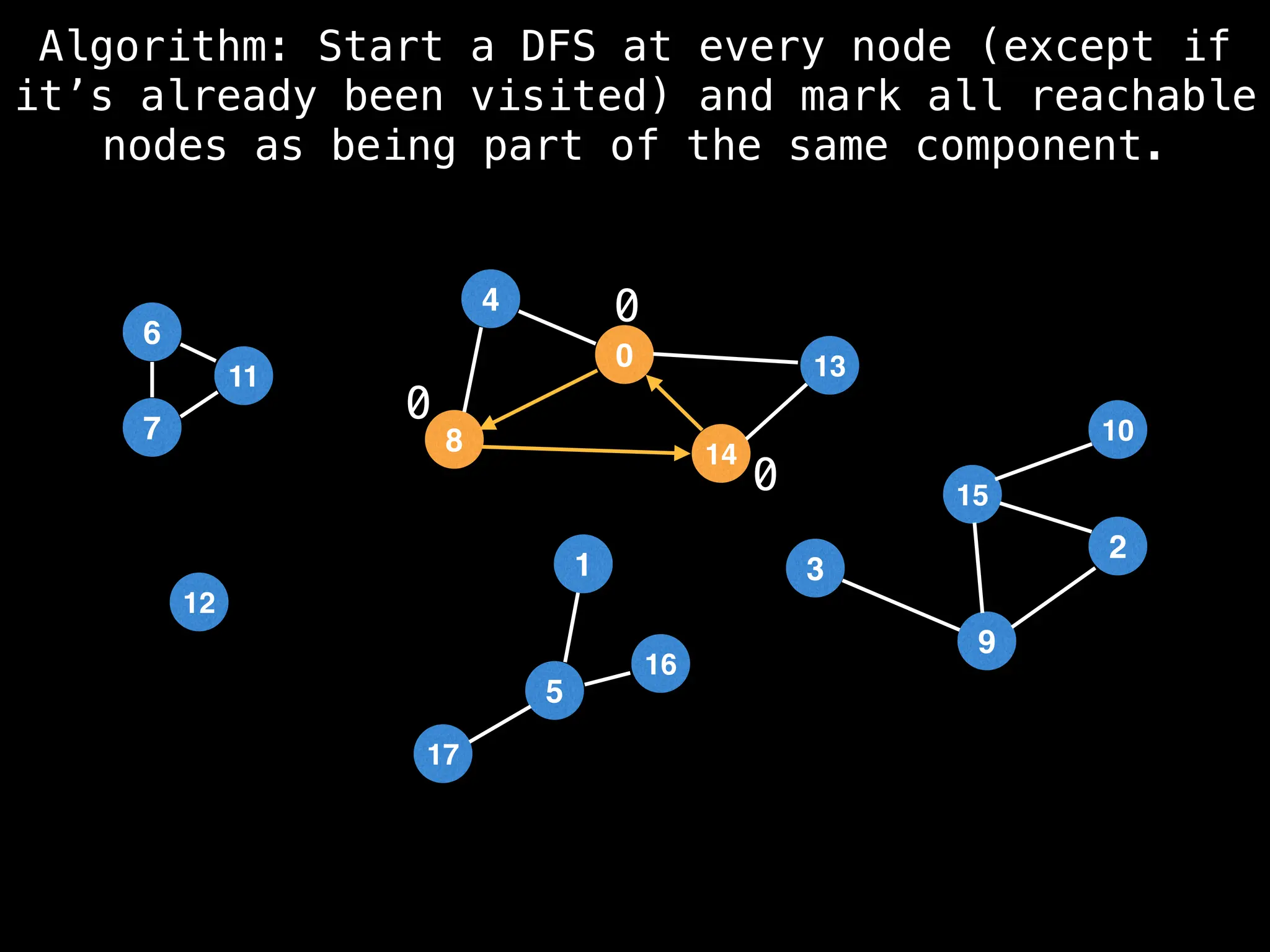
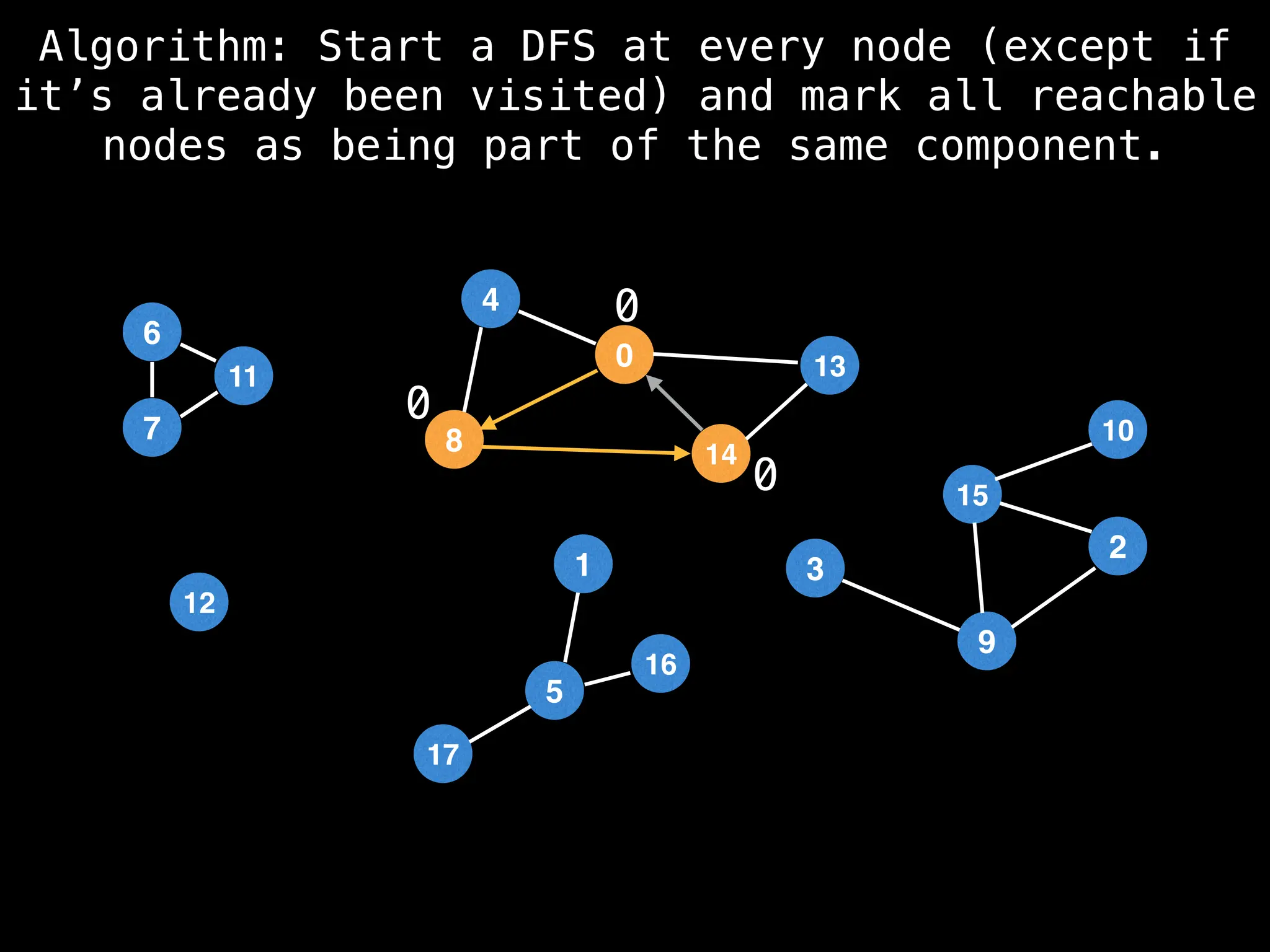
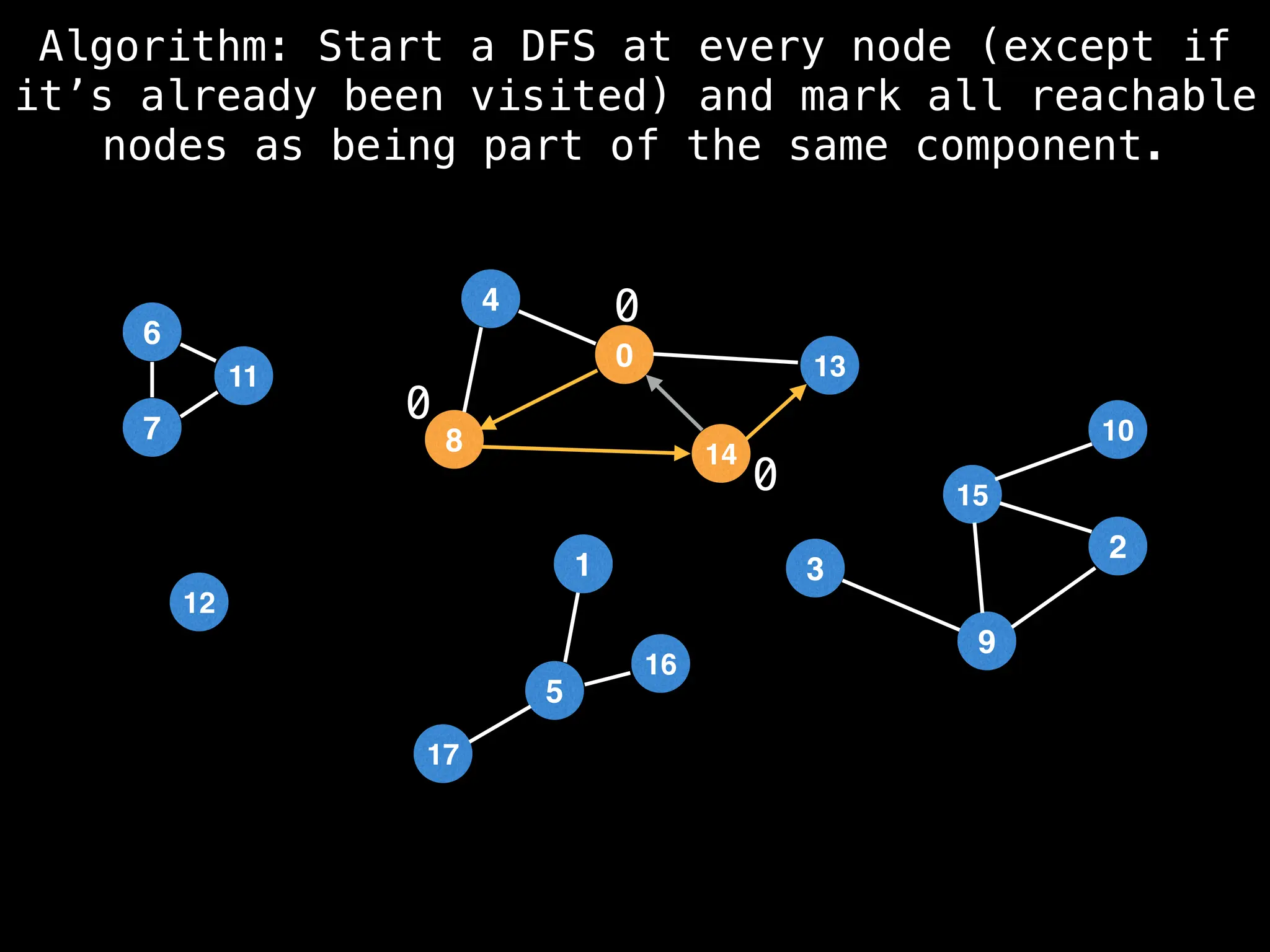
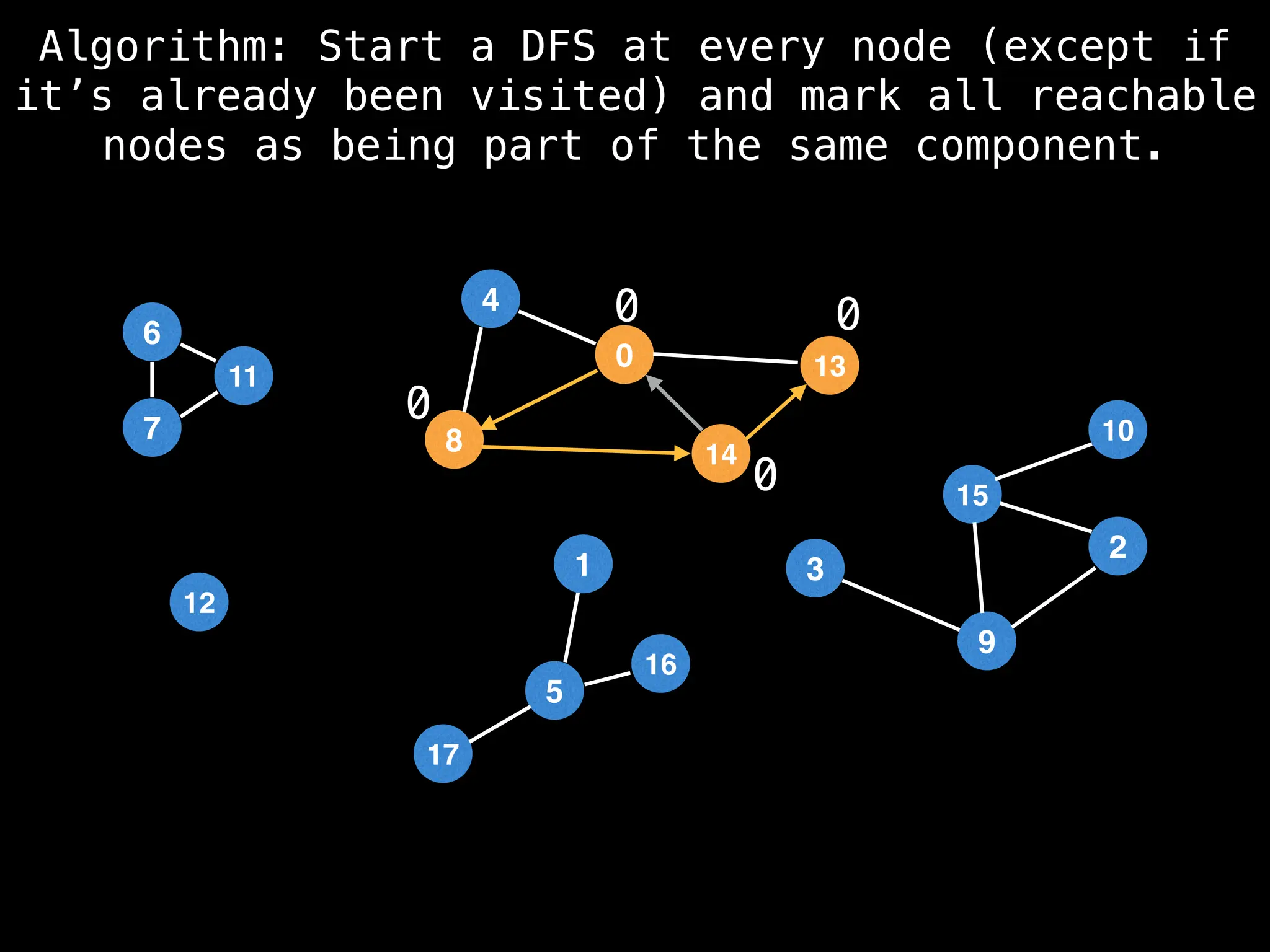
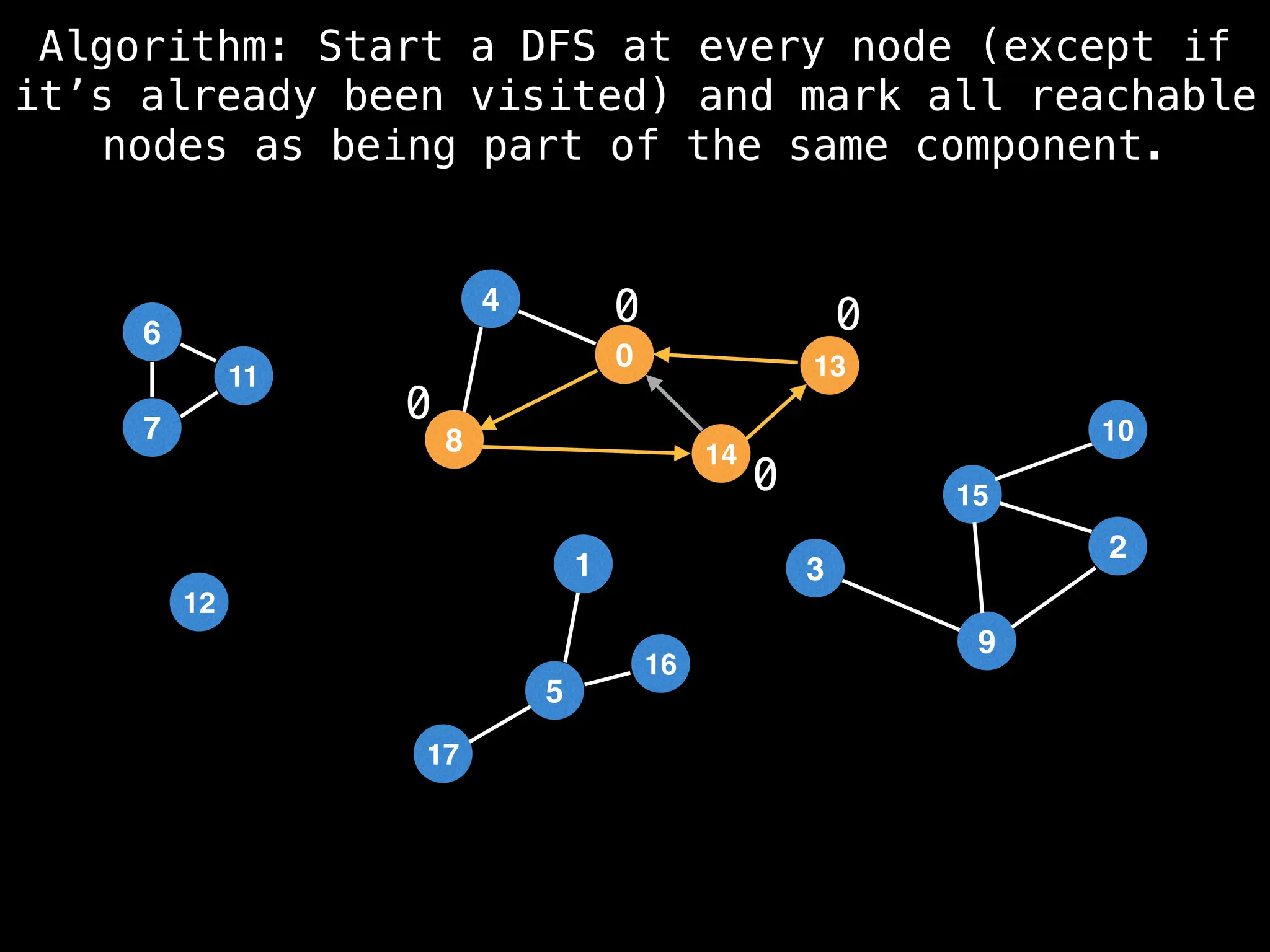
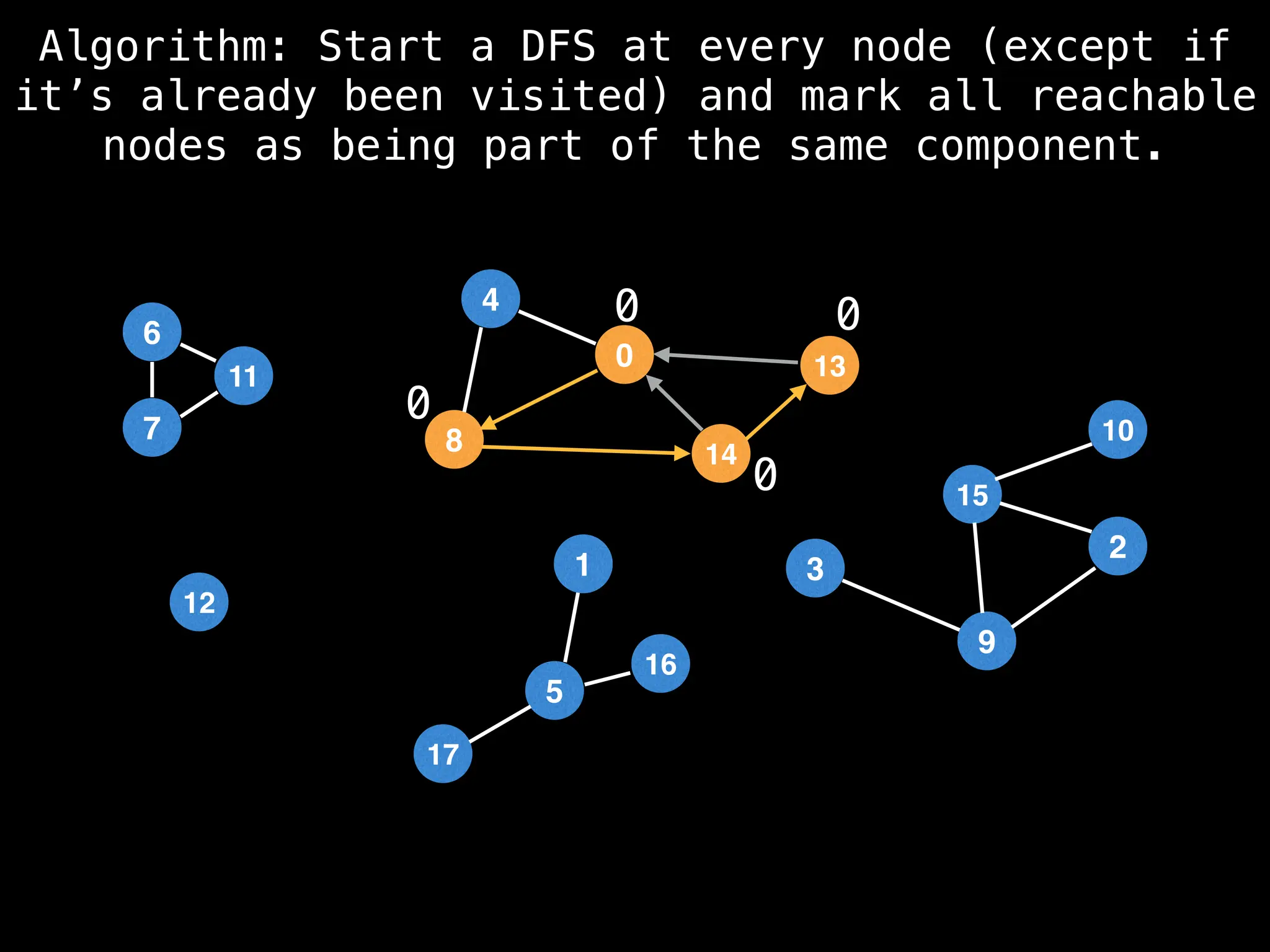
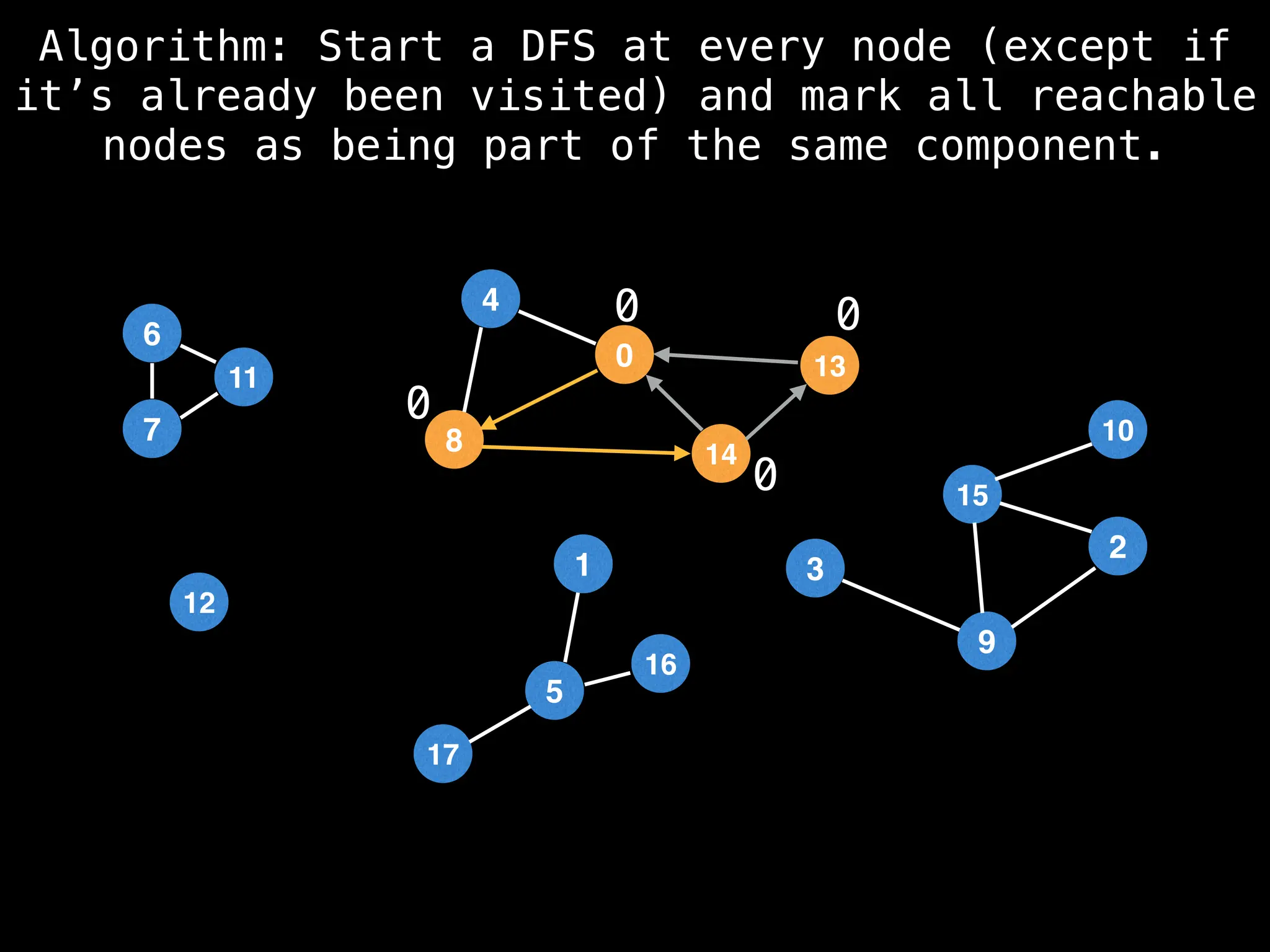
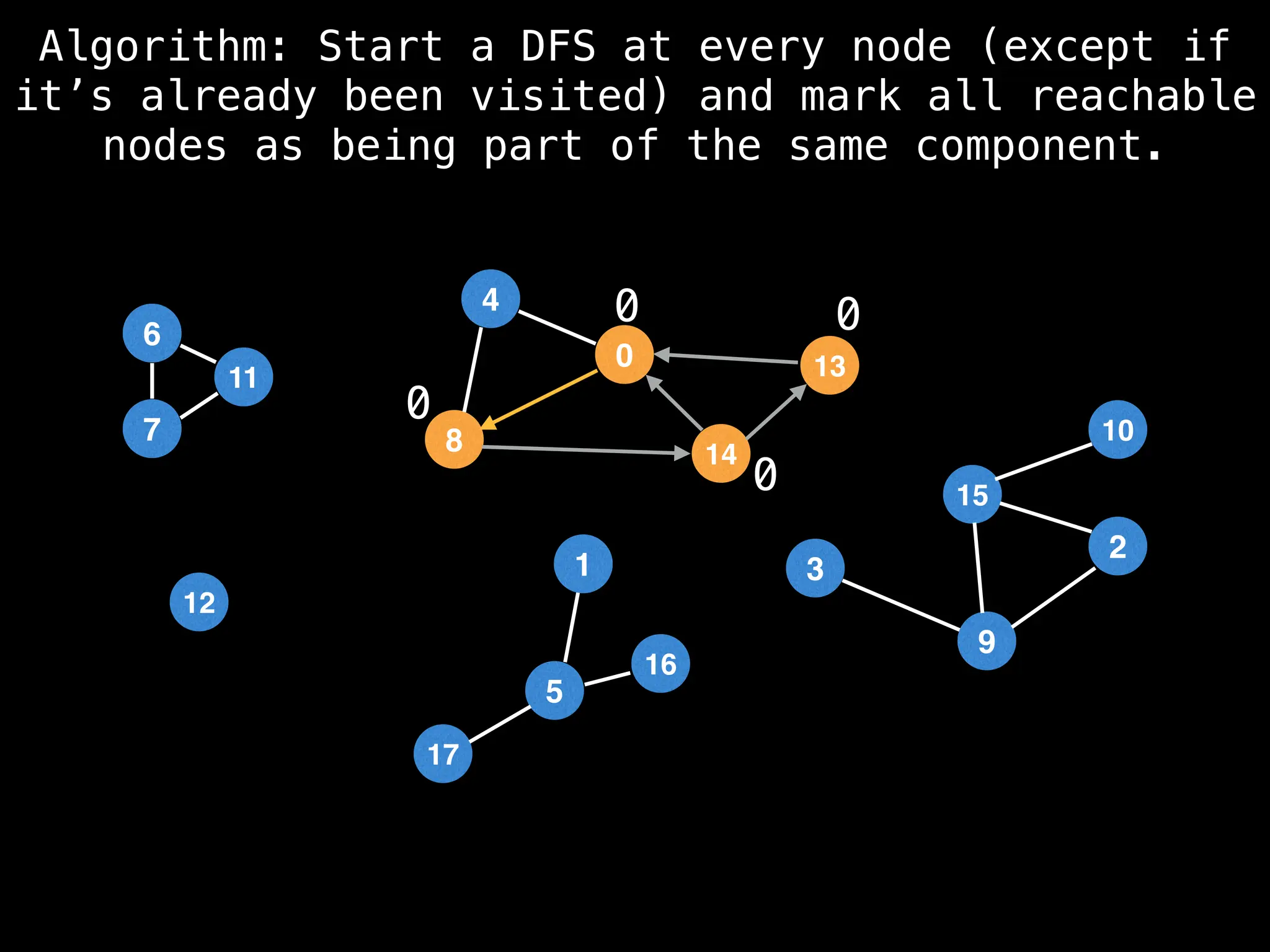
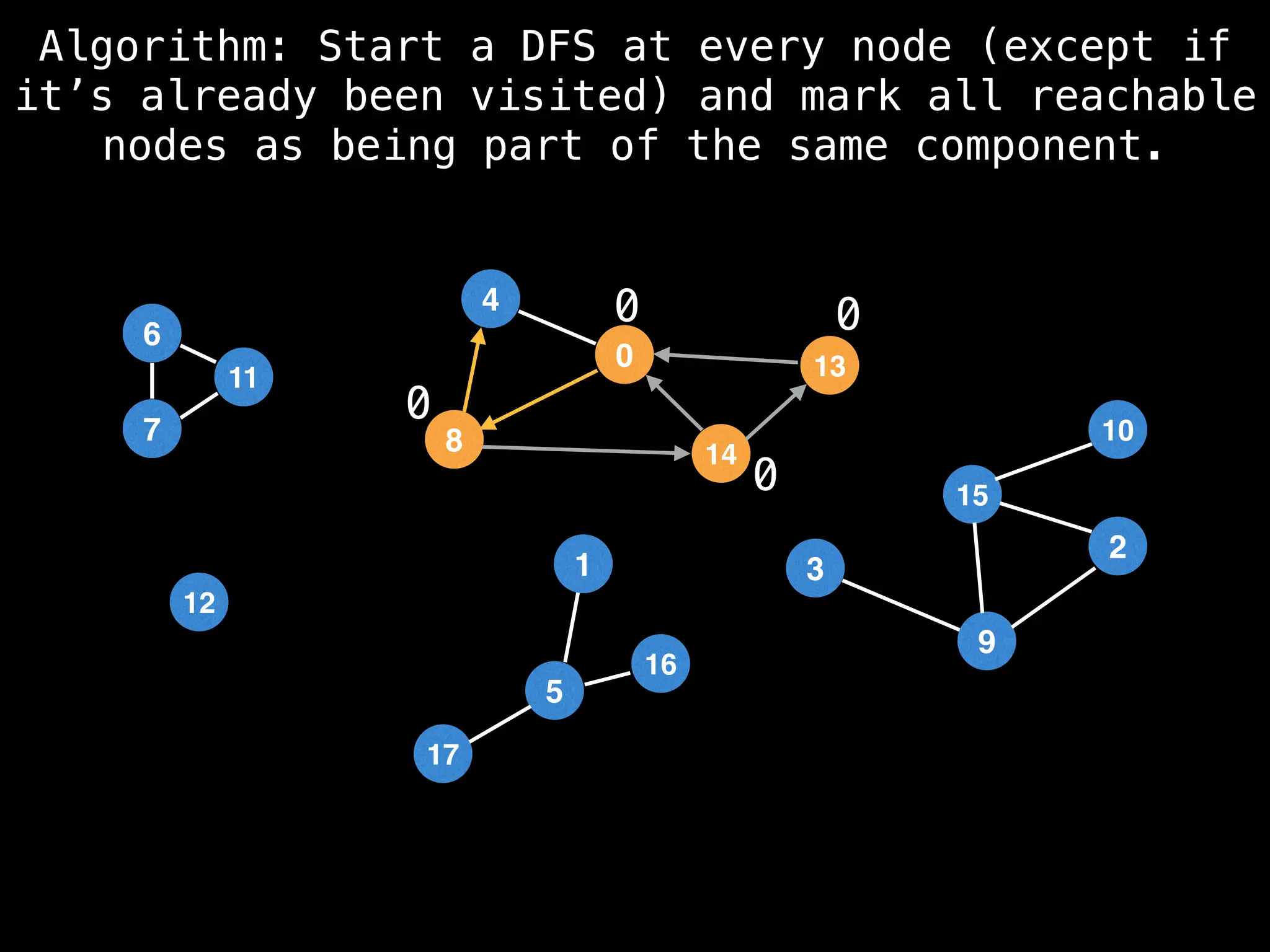
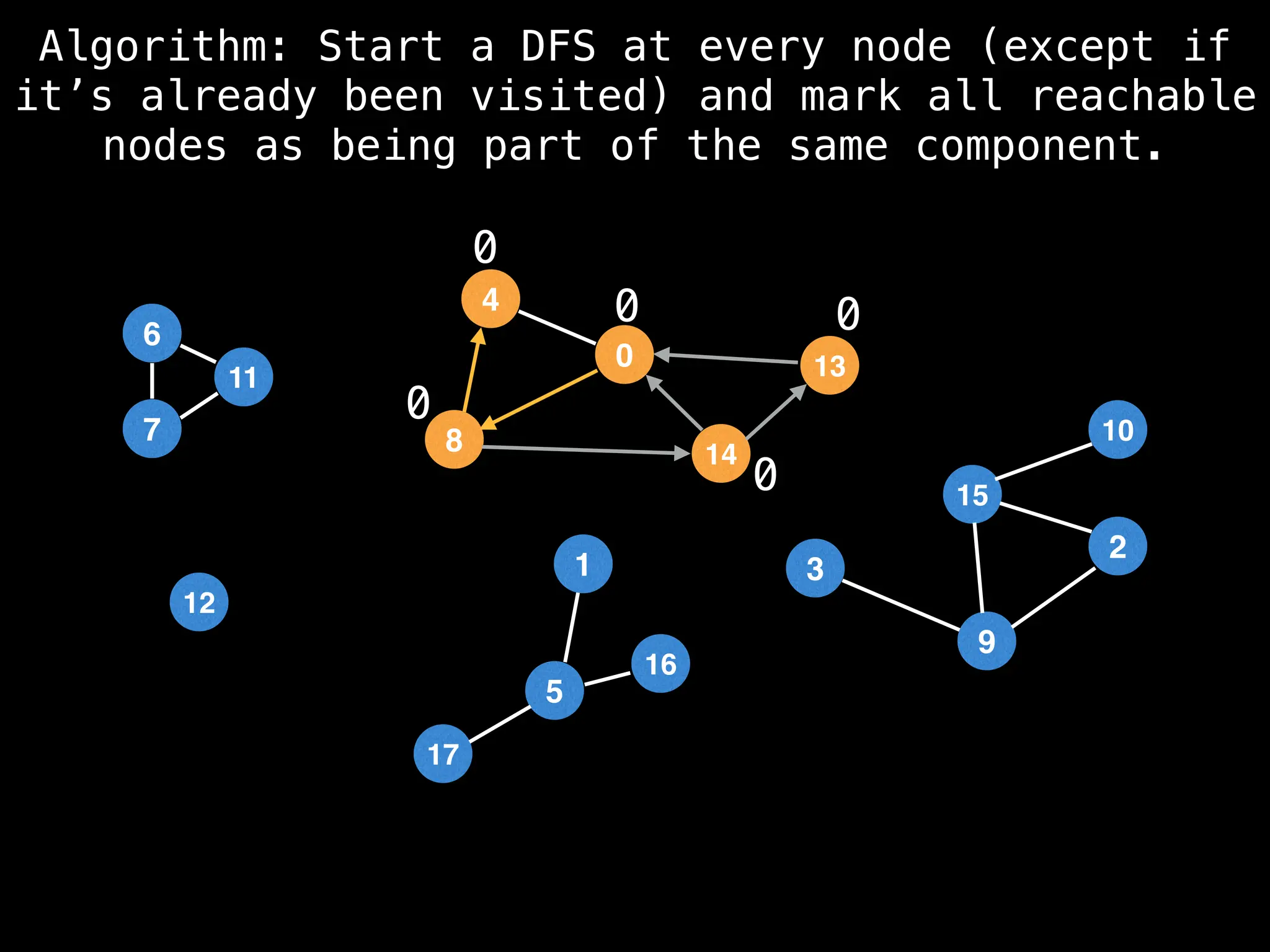
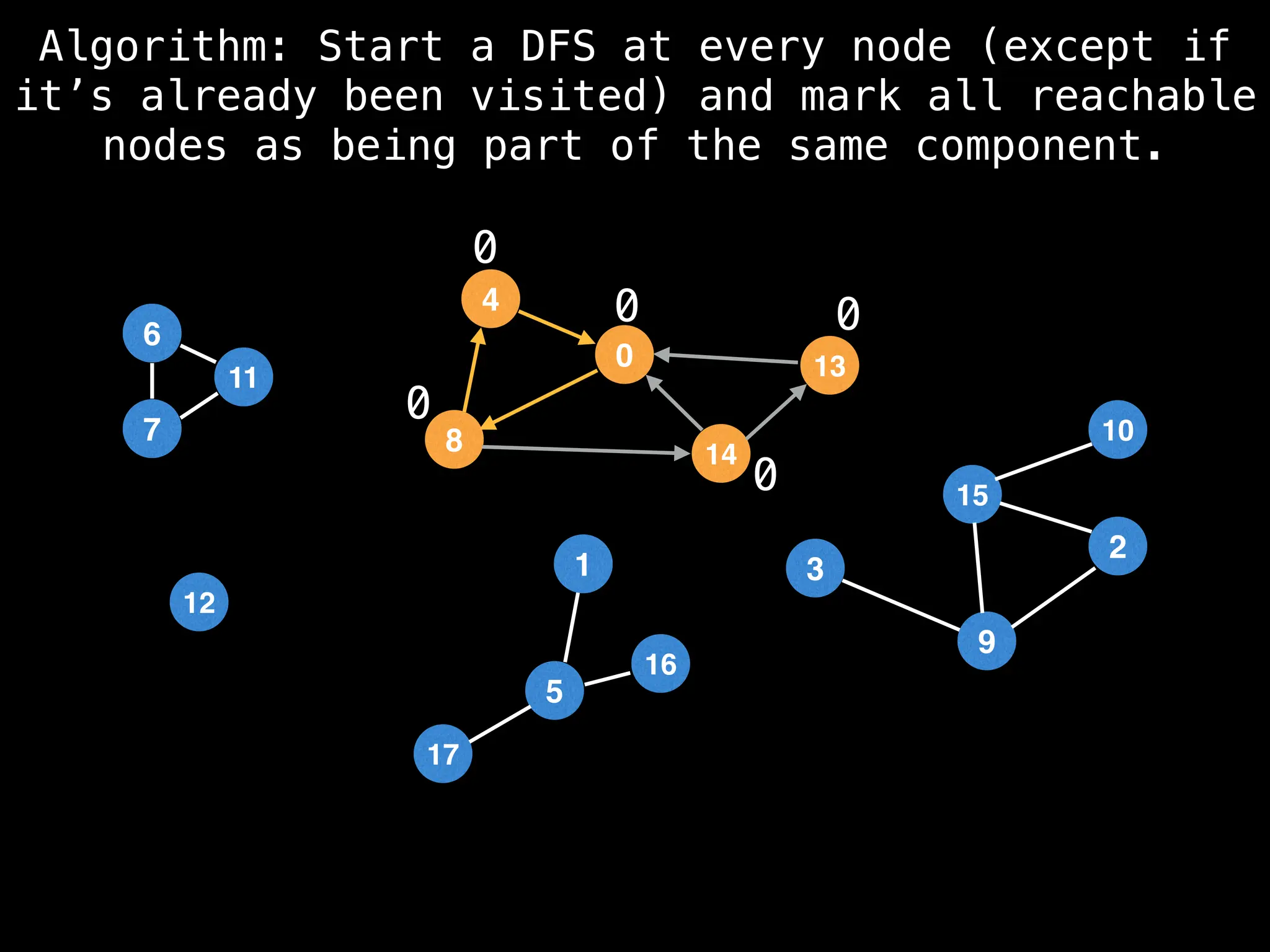
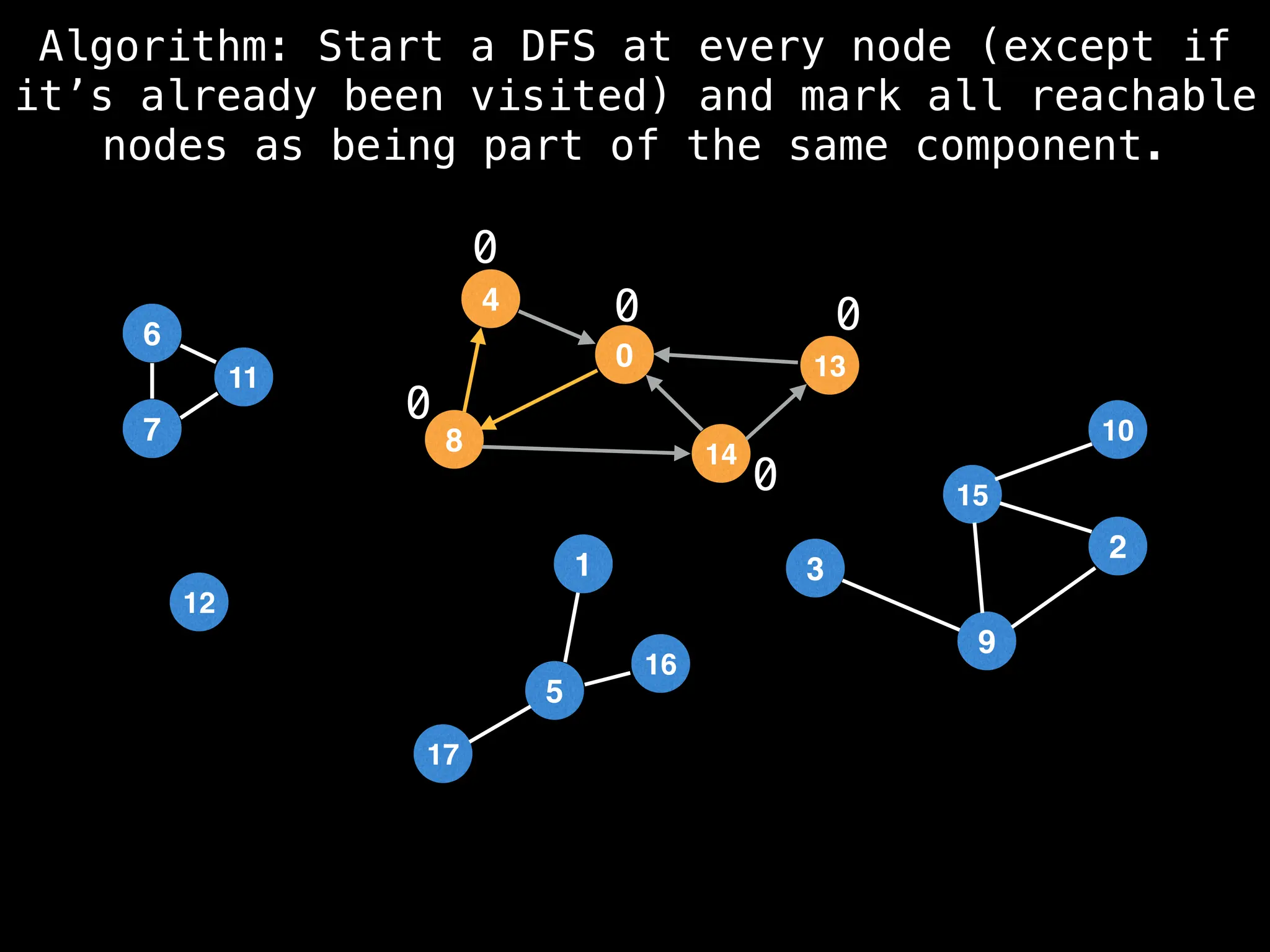
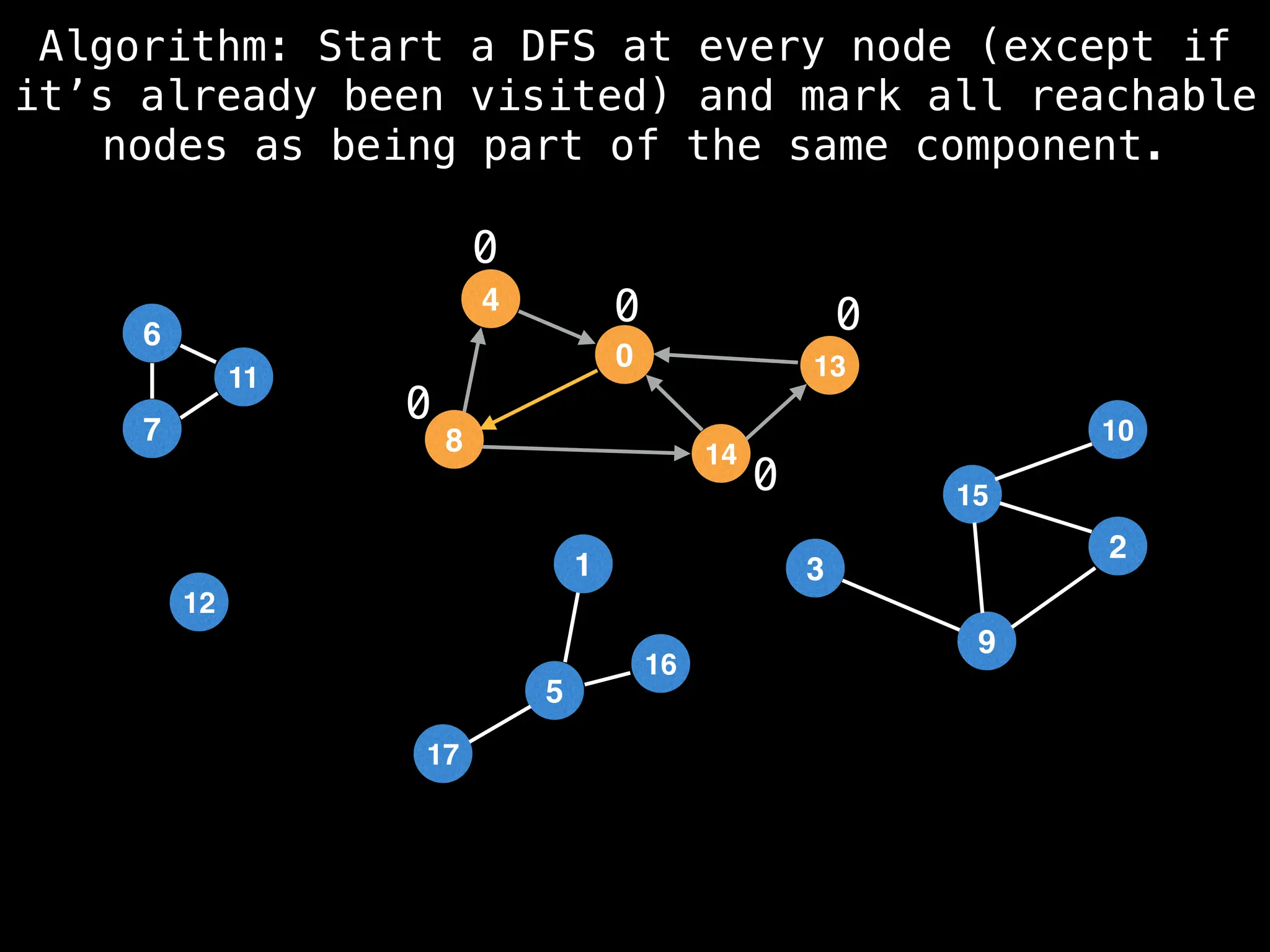
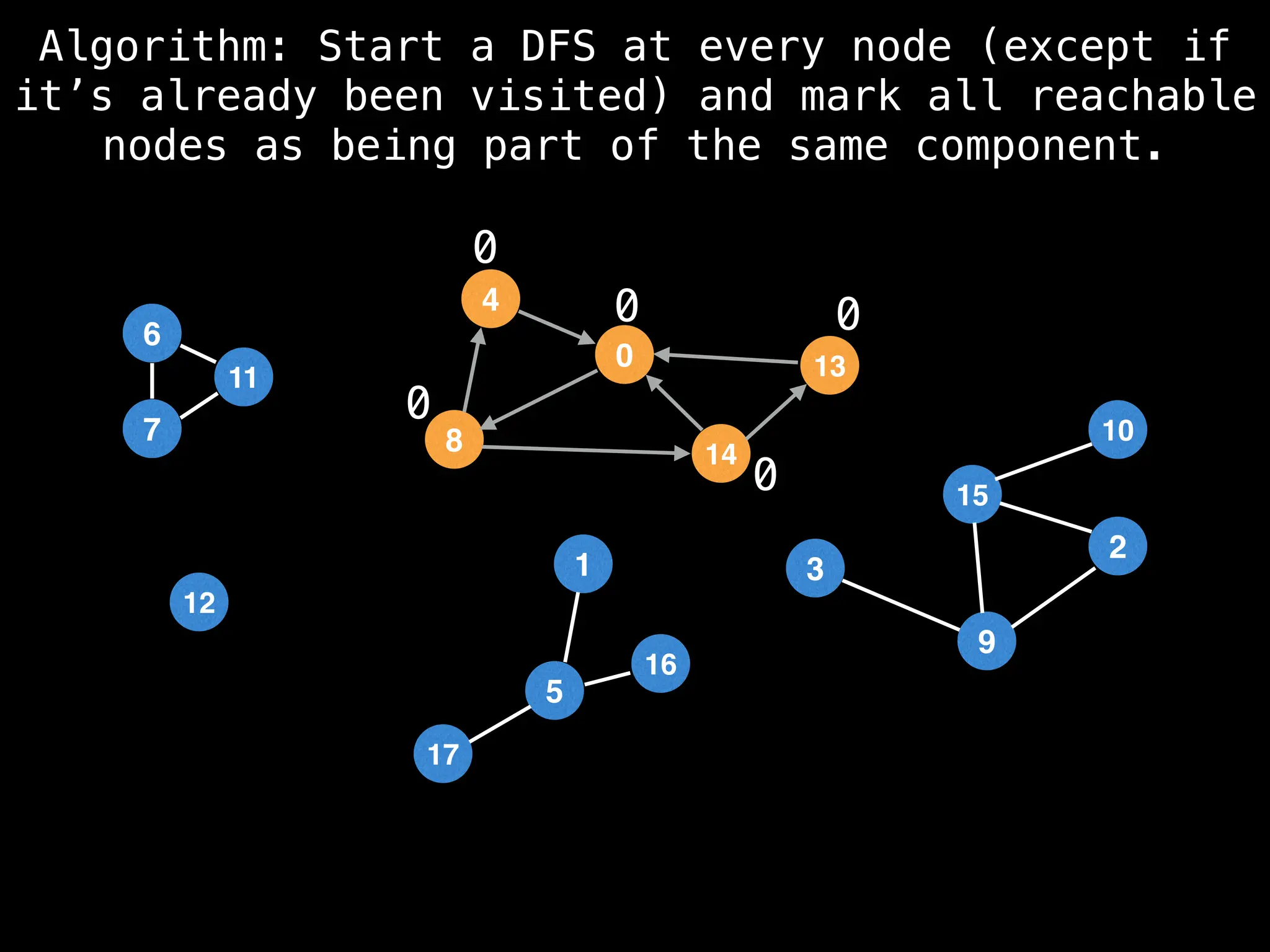
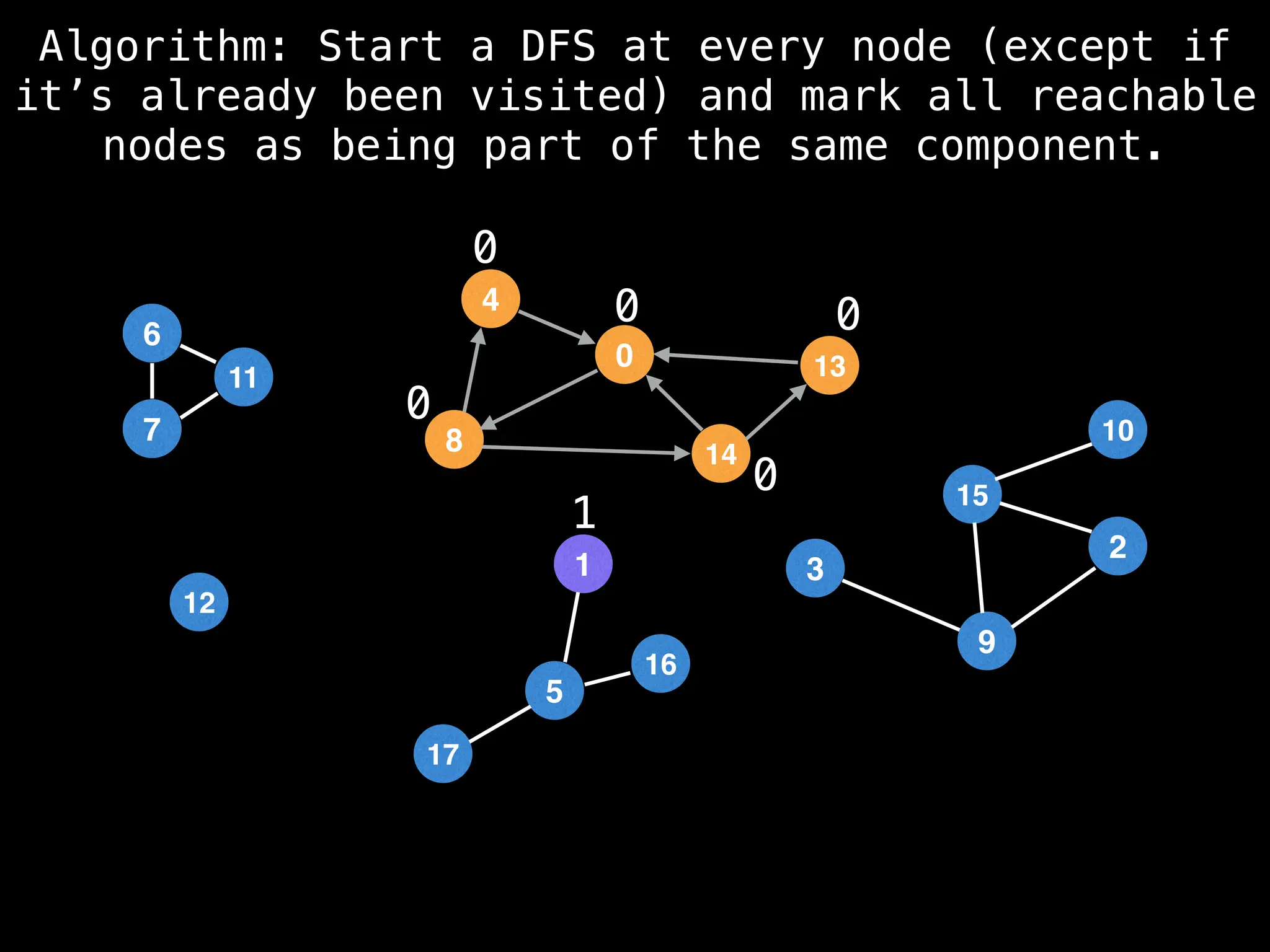
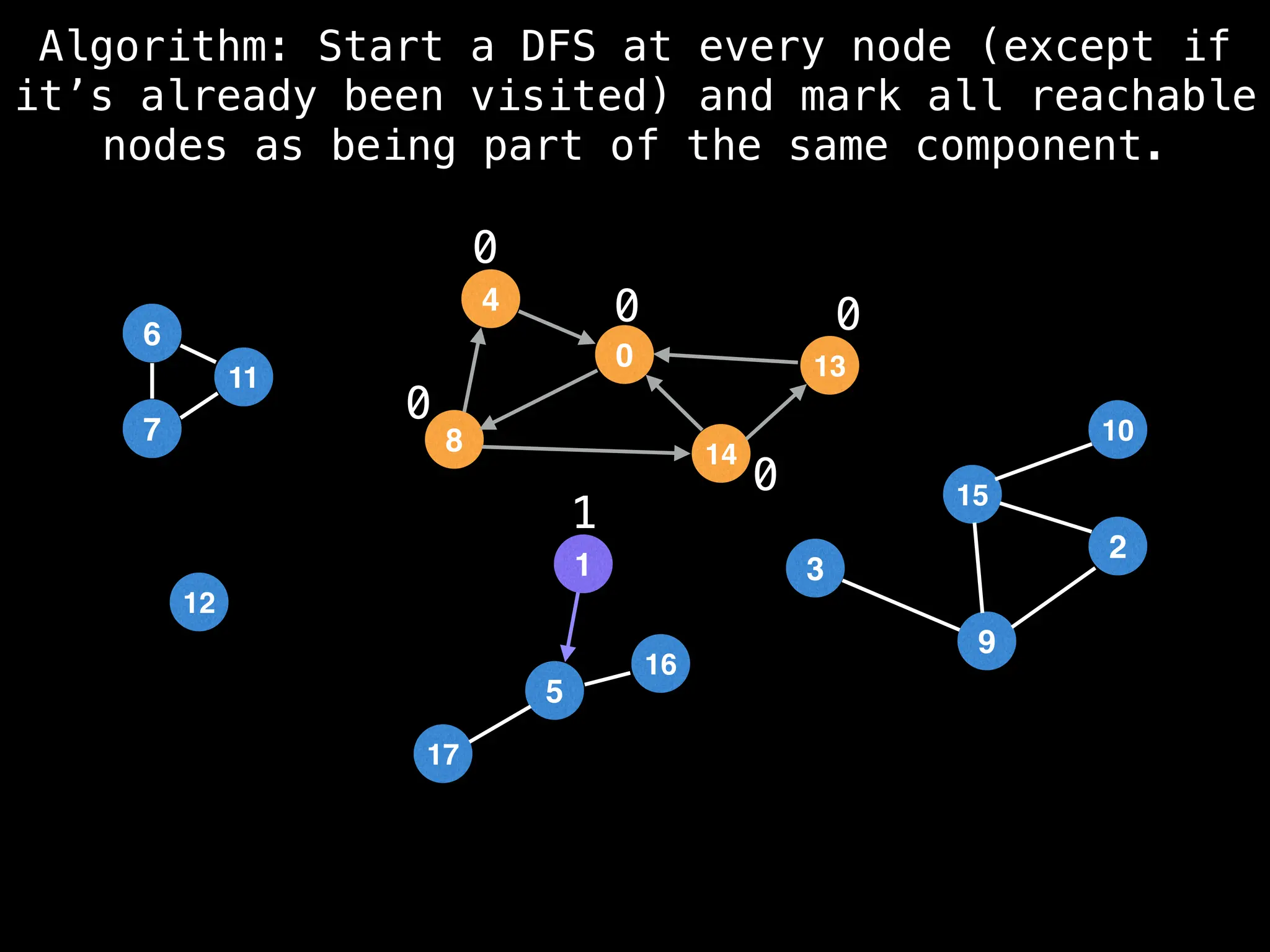
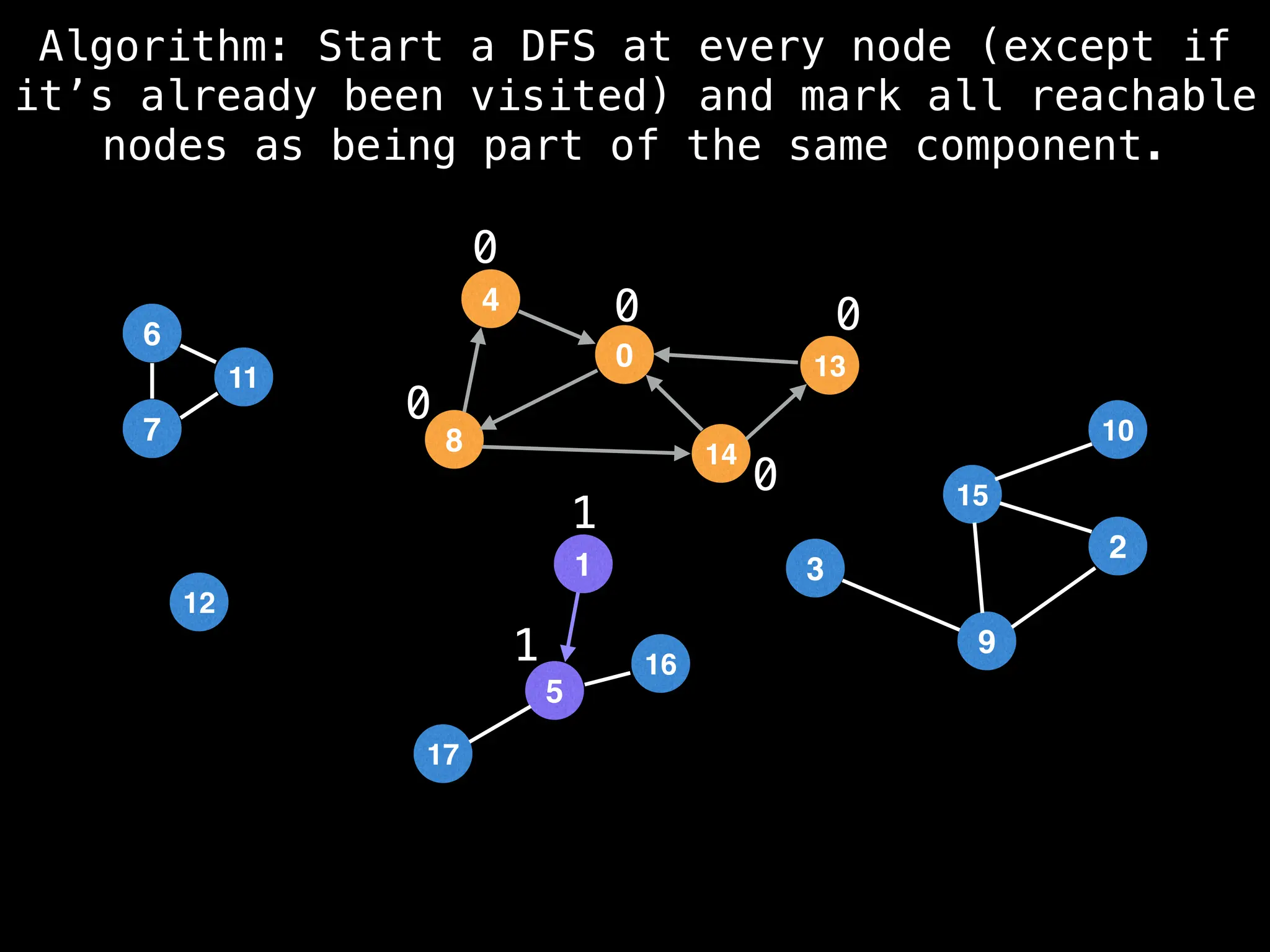
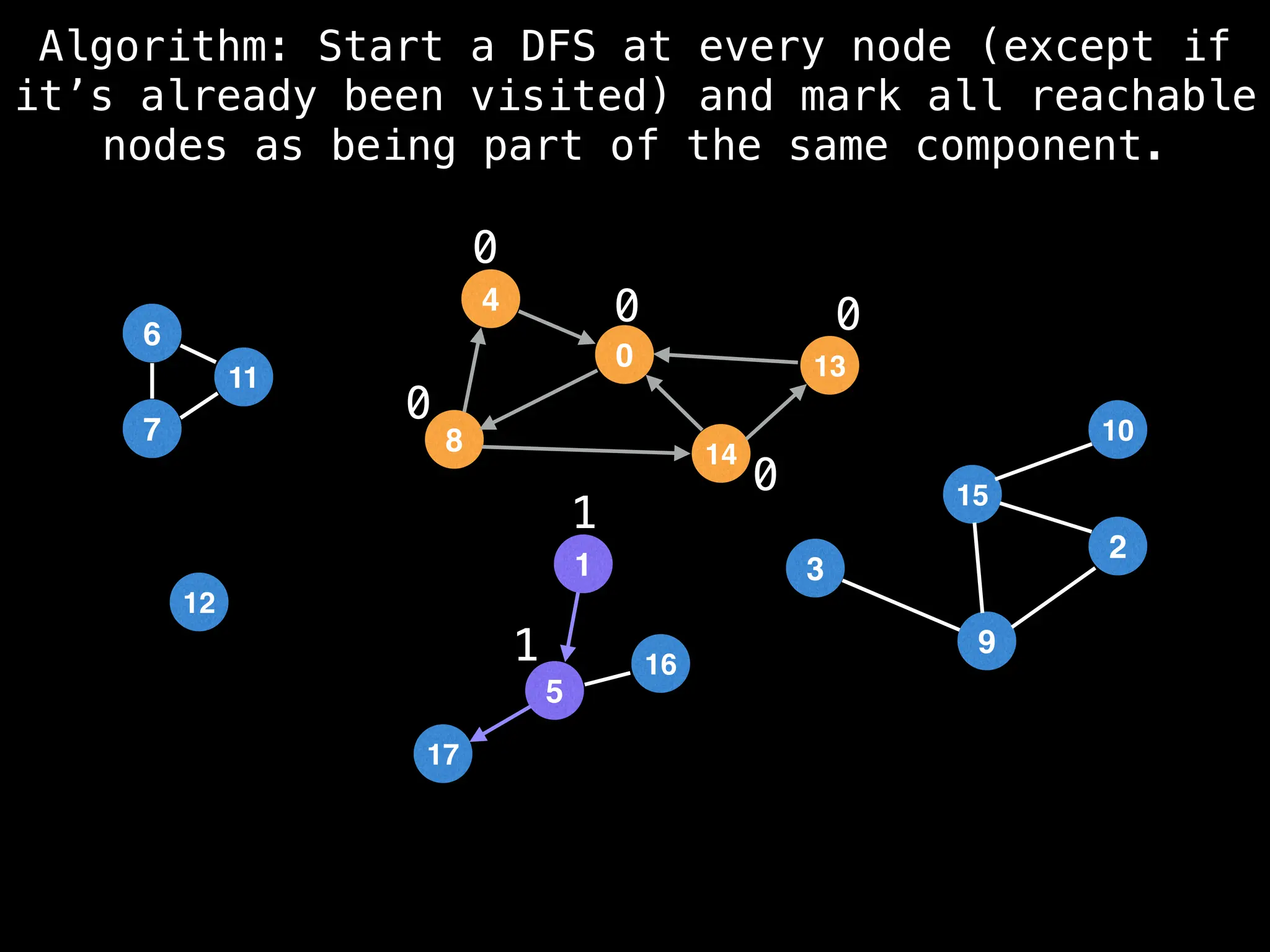
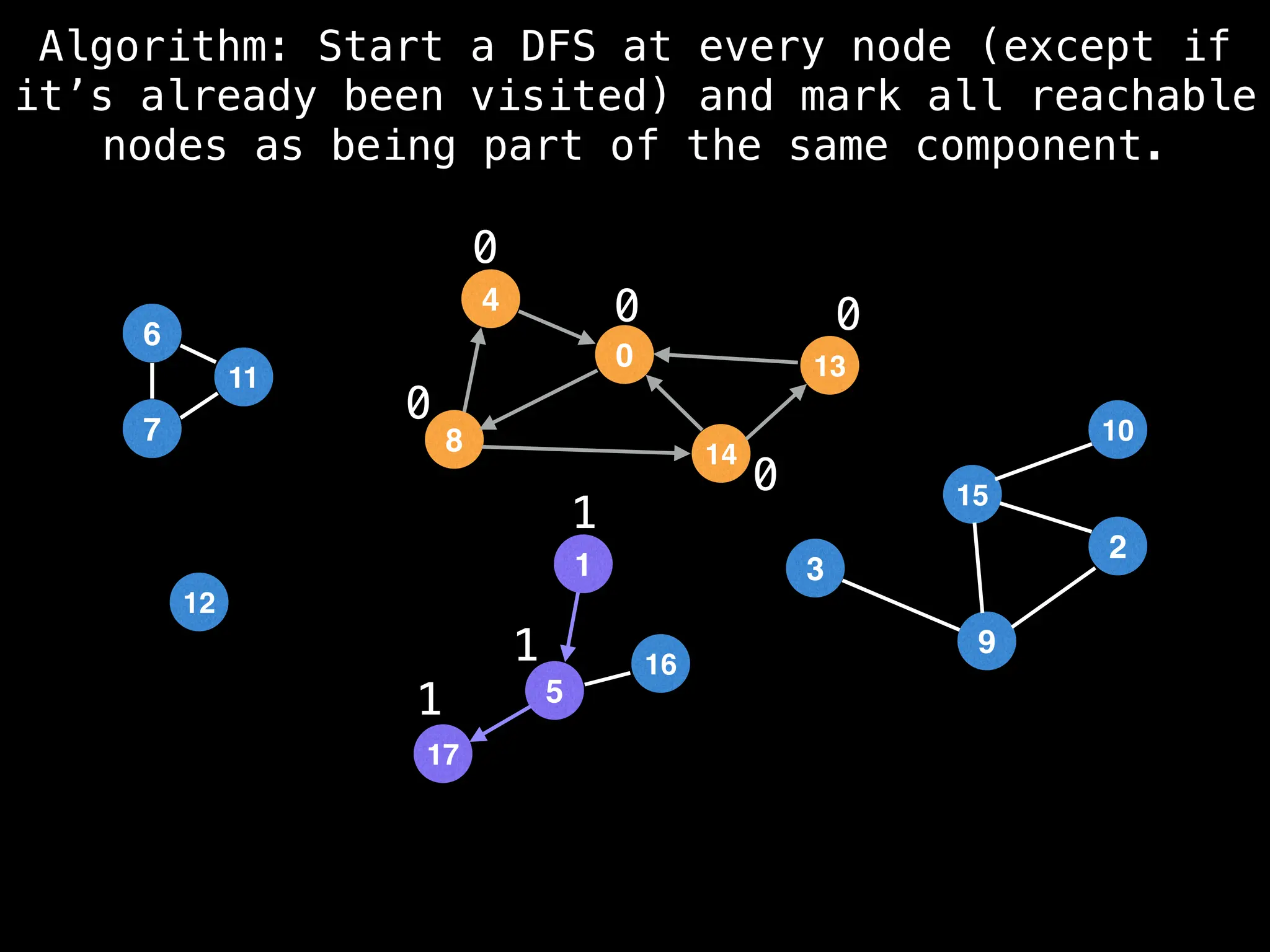
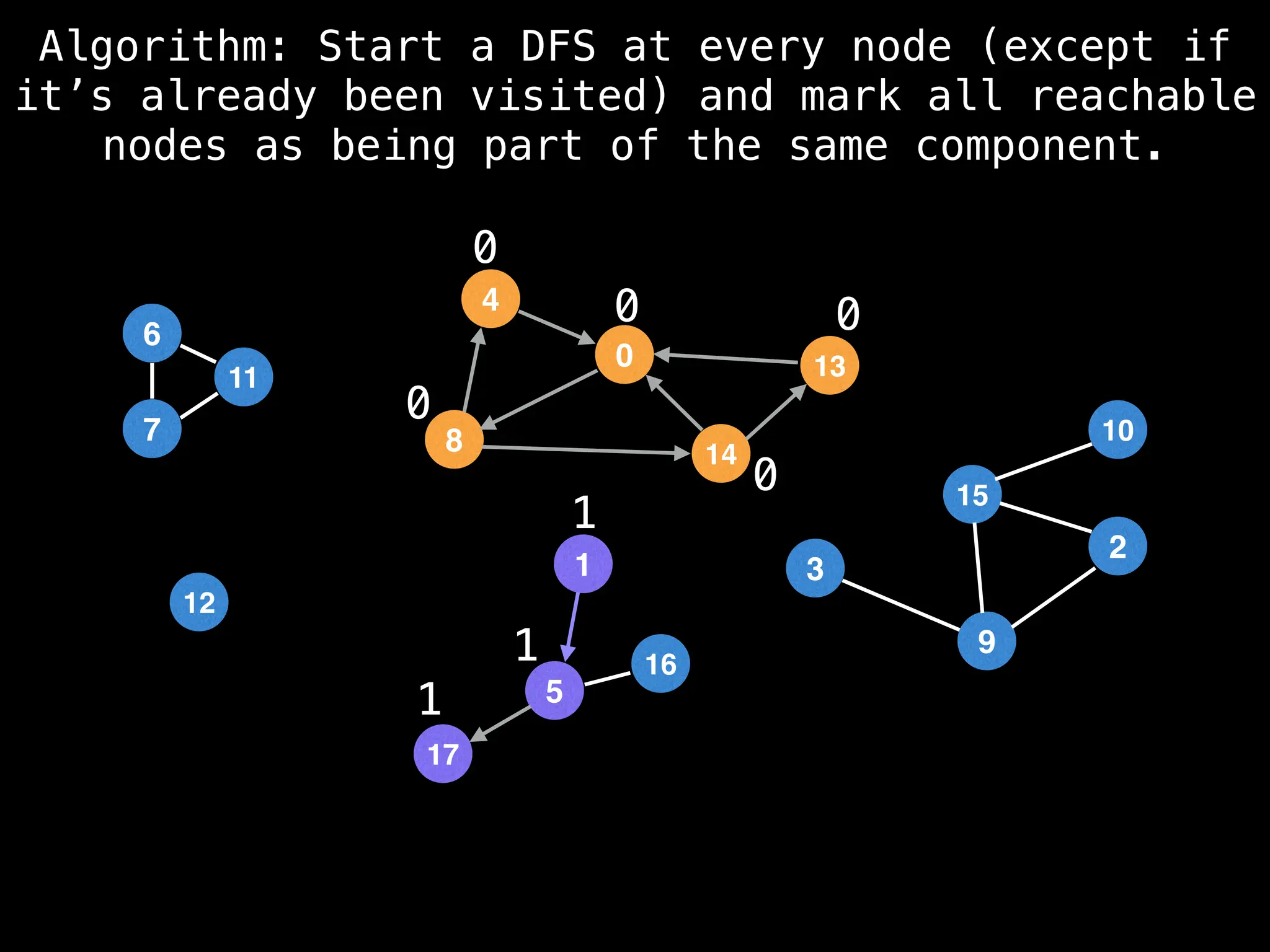
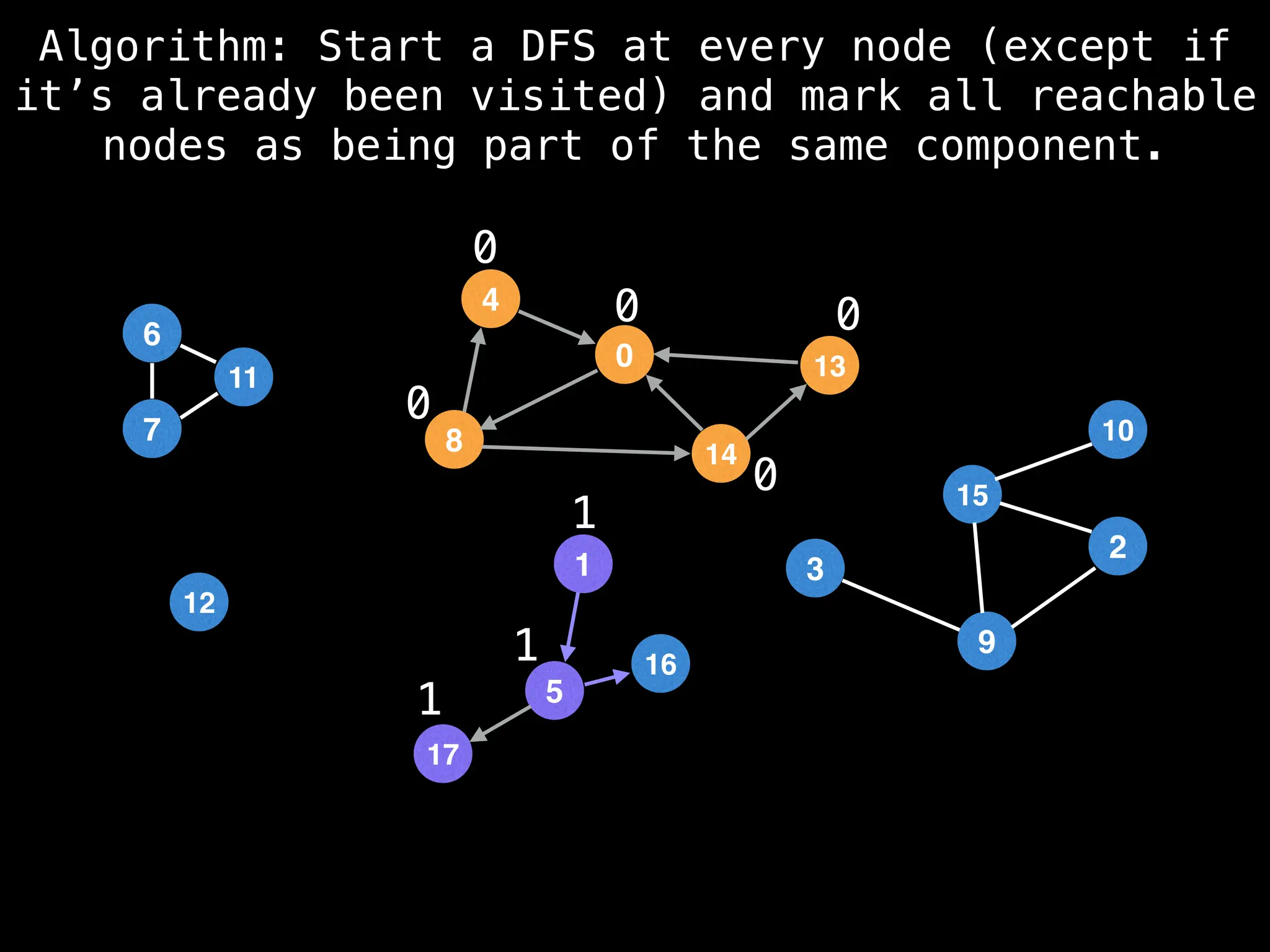
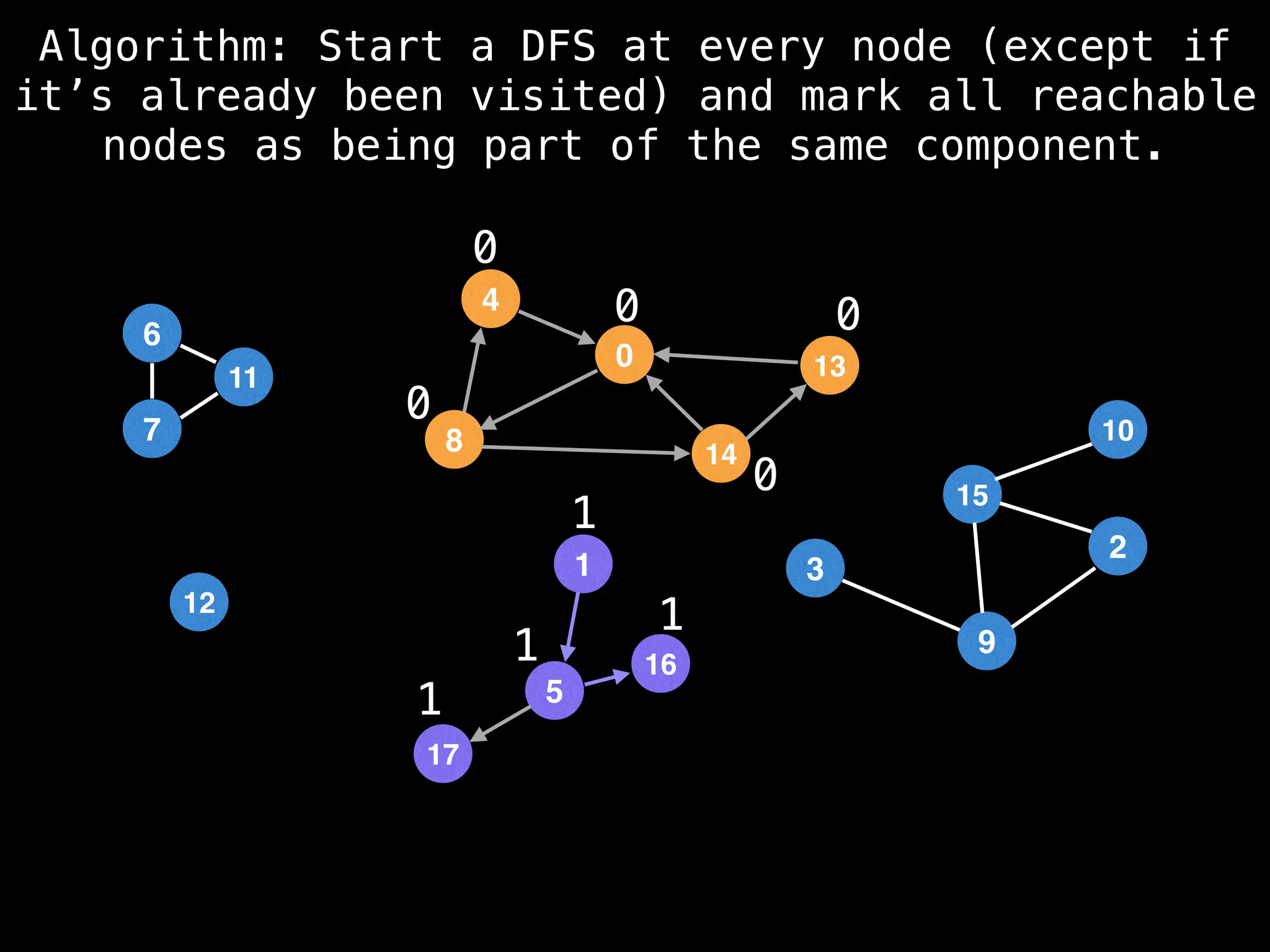
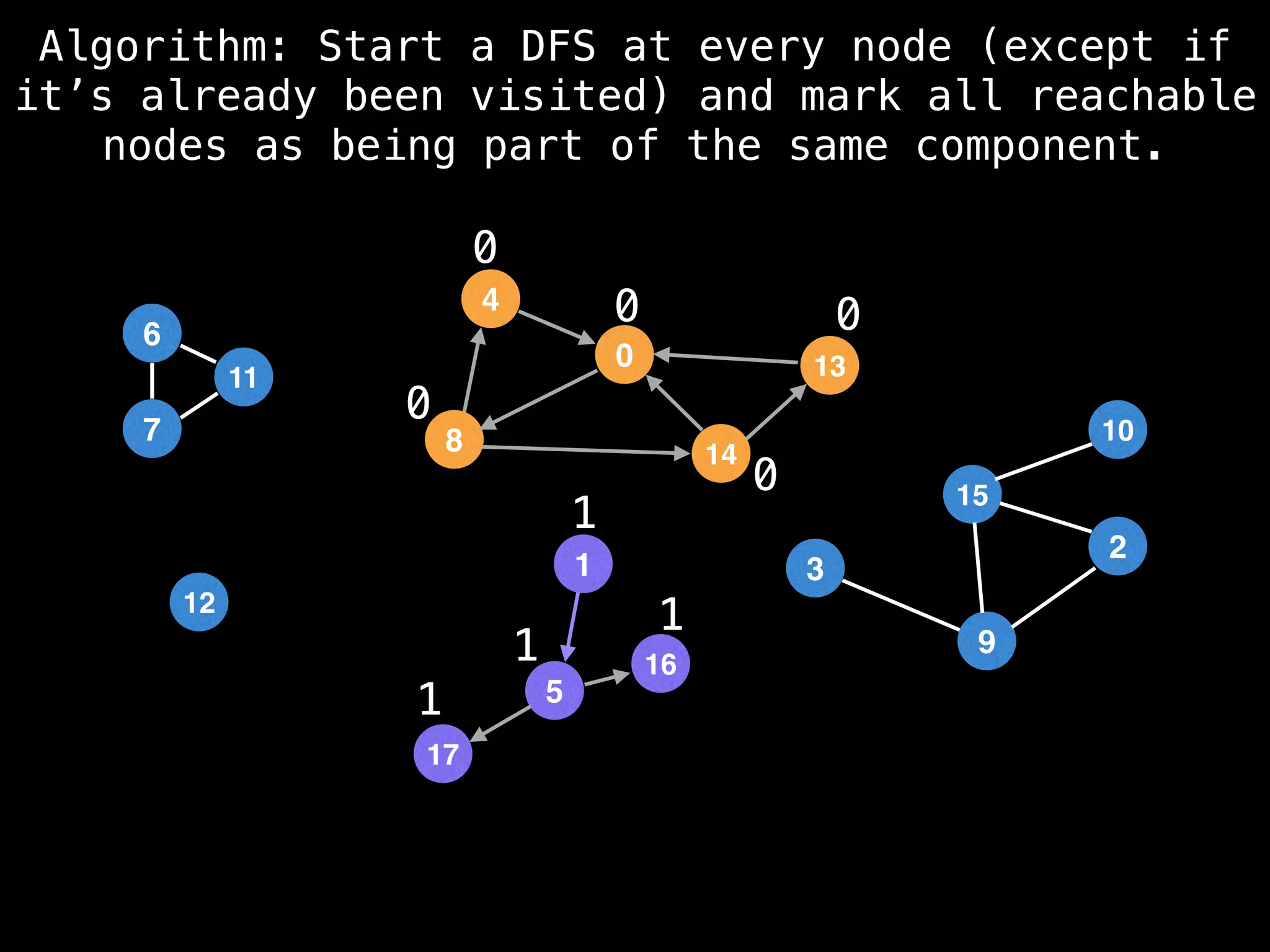
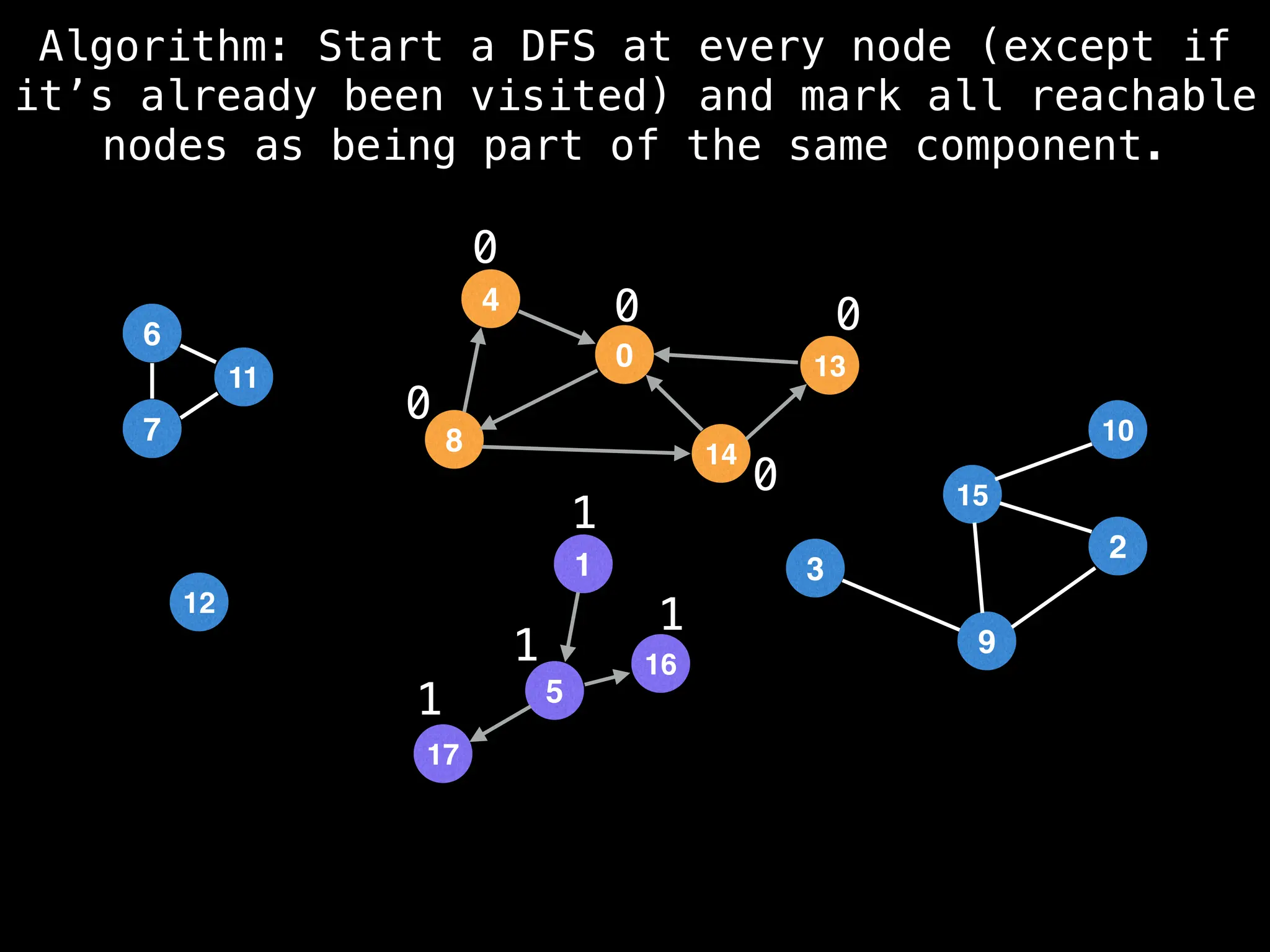
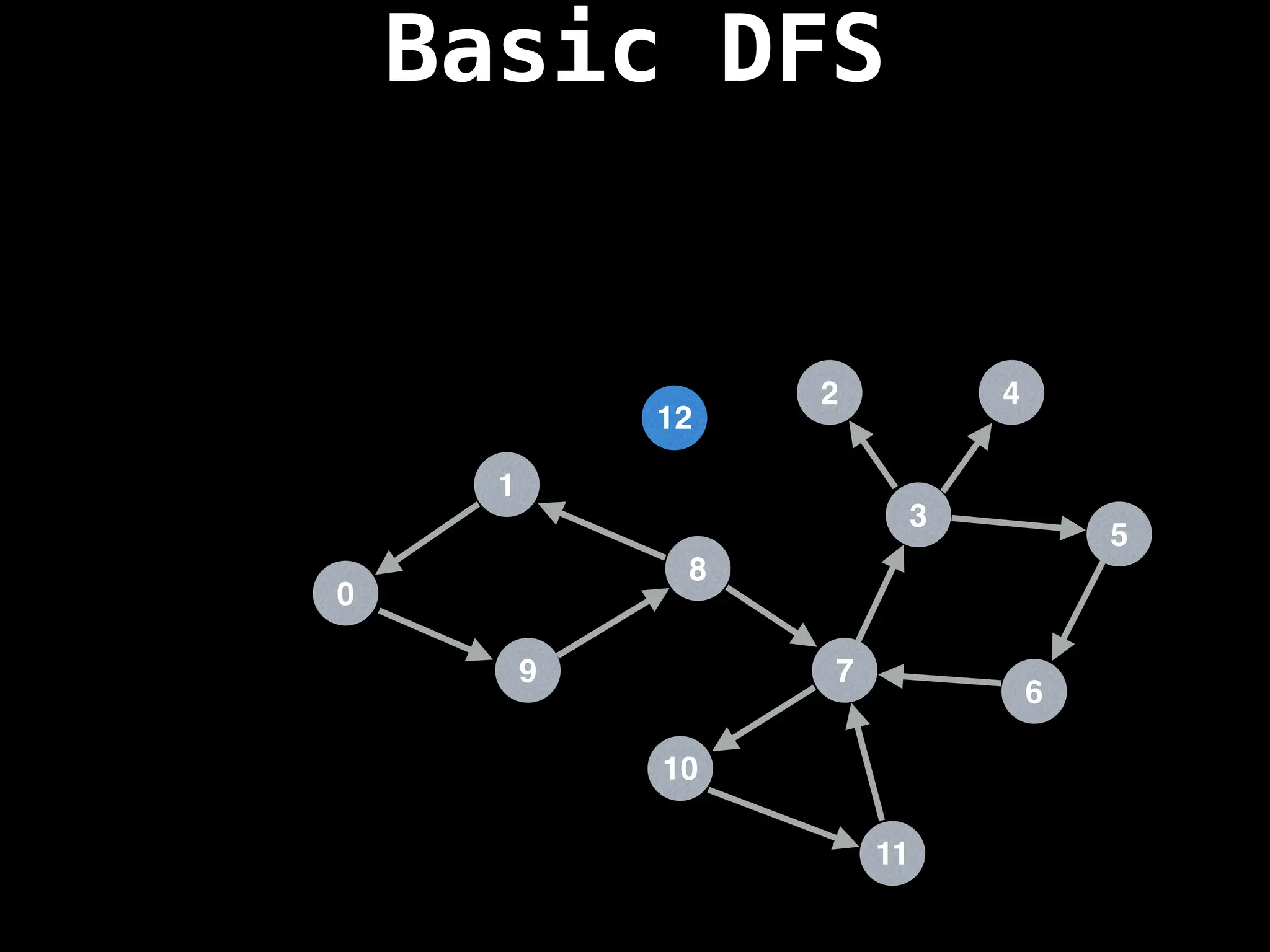
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
count = 0
components = empty integer array # size n
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
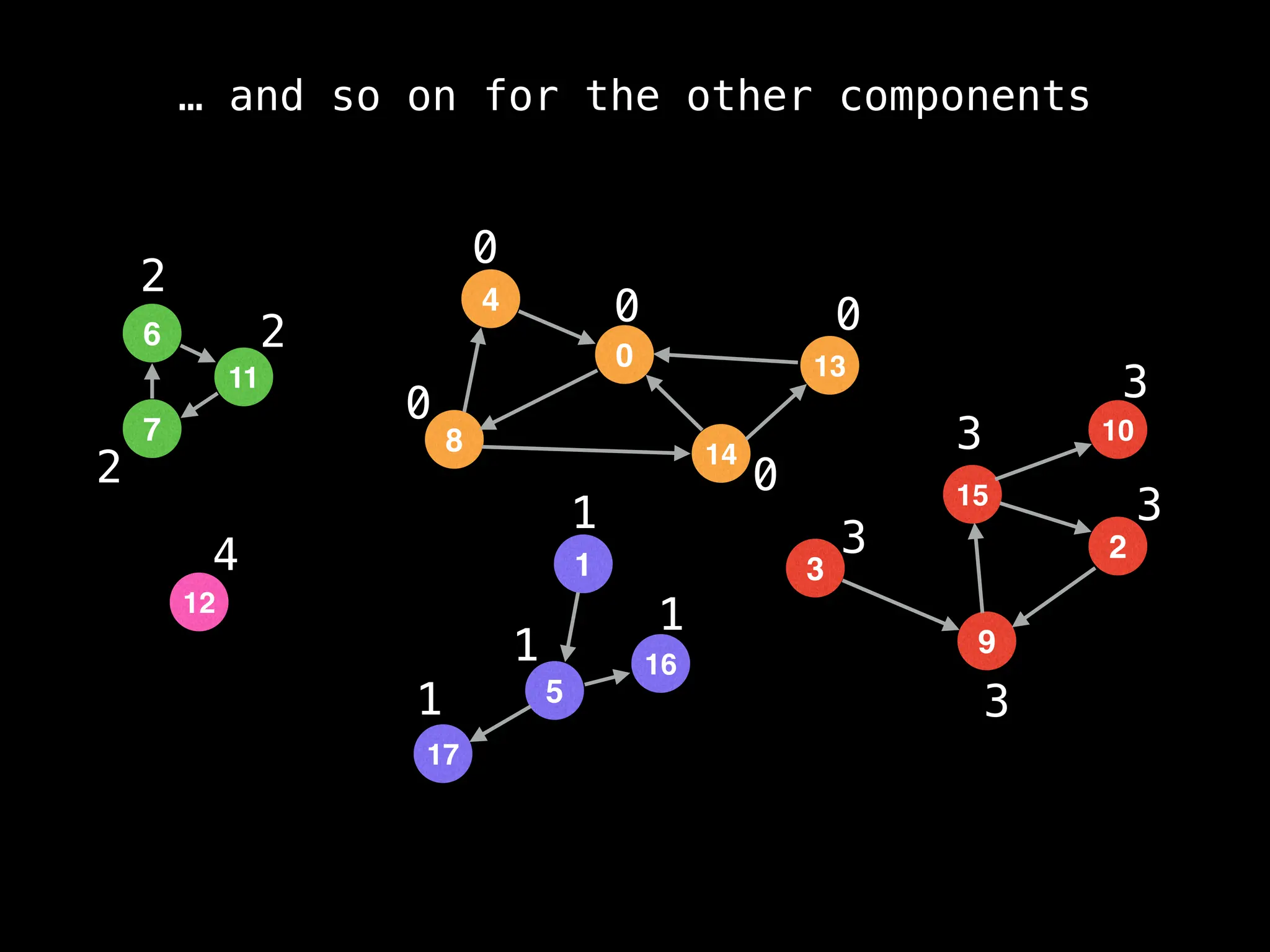
function findComponents():
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if !visited[i]:
count++
dfs(i)
return (count, components)
function dfs(at):
visited[at] = true
components[at] = count
for (next : g[at]):
if !visited[next]:
dfs(next)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-154-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
count = 0
components = empty integer array # size n
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function findComponents():
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if !visited[i]:
count++
dfs(i)
return (count, components)
function dfs(at):
visited[at] = true
components[at] = count
for (next : g[at]):
if !visited[next]:
dfs(next)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-155-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
count = 0
components = empty integer array # size n
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function findComponents():
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if !visited[i]:
count++
dfs(i)
return (count, components)
function dfs(at):
visited[at] = true
components[at] = count
for (next : g[at]):
if !visited[next]:
dfs(next)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-156-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
count = 0
components = empty integer array # size n
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function findComponents():
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if !visited[i]:
count++
dfs(i)
return (count, components)
function dfs(at):
visited[at] = true
components[at] = count
for (next : g[at]):
if !visited[next]:
dfs(next)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-157-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
count = 0
components = empty integer array # size n
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function findComponents():
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if !visited[i]:
count++
dfs(i)
return (count, components)
function dfs(at):
visited[at] = true
components[at] = count
for (next : g[at]):
if !visited[next]:
dfs(next)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-158-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
count = 0
components = empty integer array # size n
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function findComponents():
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if !visited[i]:
count++
dfs(i)
return (count, components)
function dfs(at):
visited[at] = true
components[at] = count
for (next : g[at]):
if !visited[next]:
dfs(next)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-159-2048.jpg)
![# Global or class scope variables
n = number of nodes in the graph
g = adjacency list representing graph
count = 0
components = empty integer array # size n
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
function findComponents():
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if !visited[i]:
count++
dfs(i)
return (count, components)
function dfs(at):
visited[at] = true
components[at] = count
for (next : g[at]):
if !visited[next]:
dfs(next)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-160-2048.jpg)




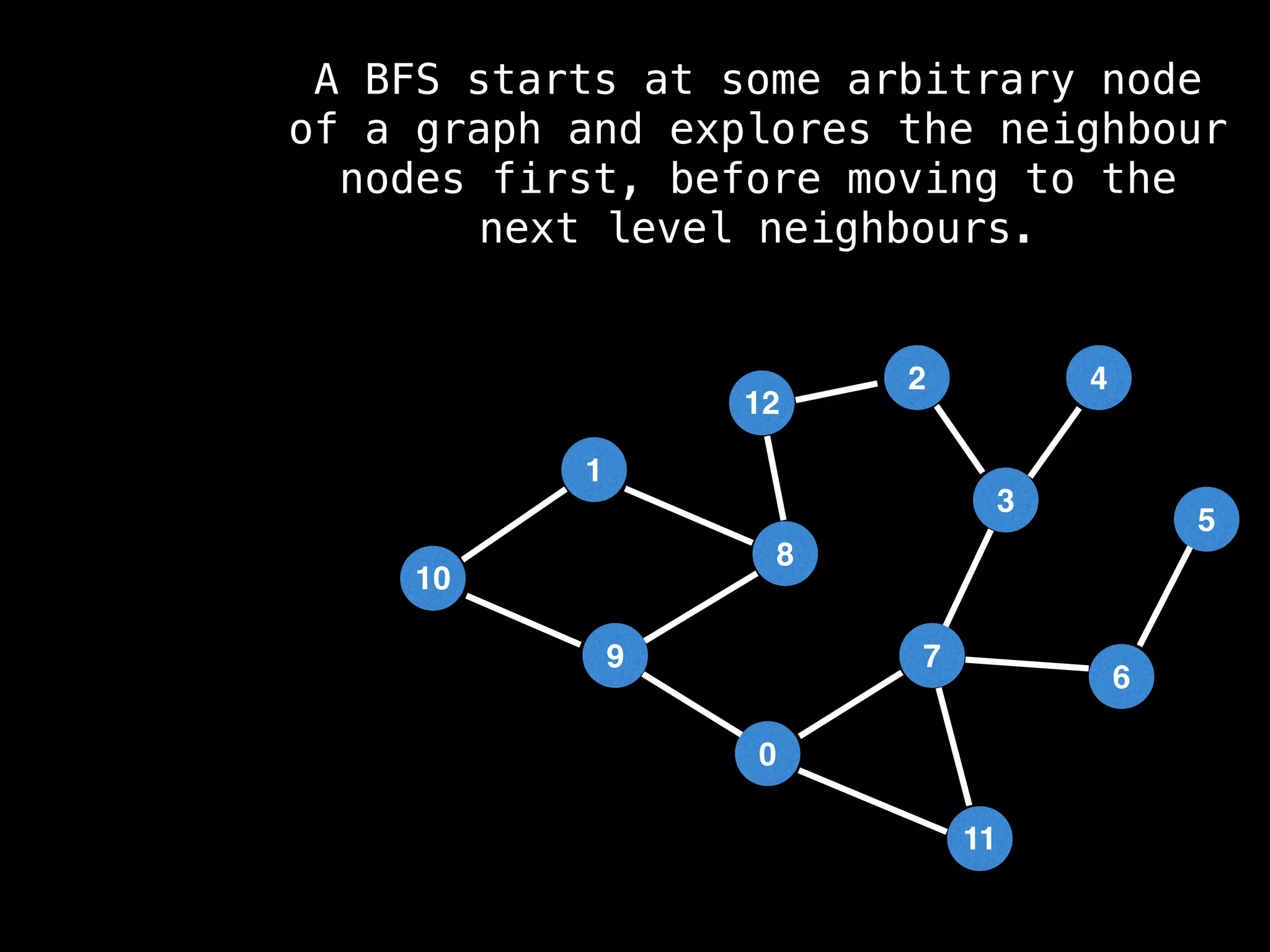
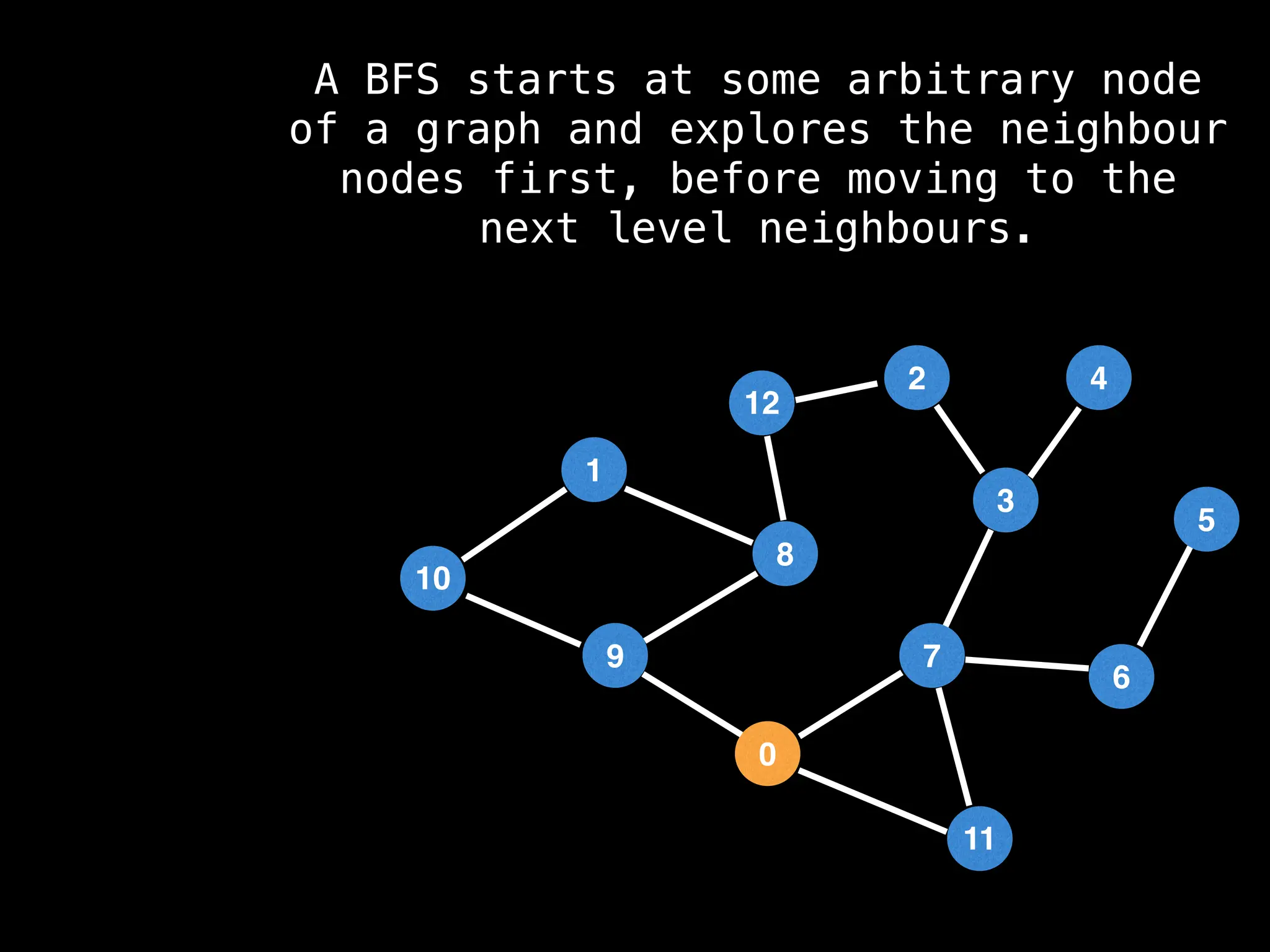
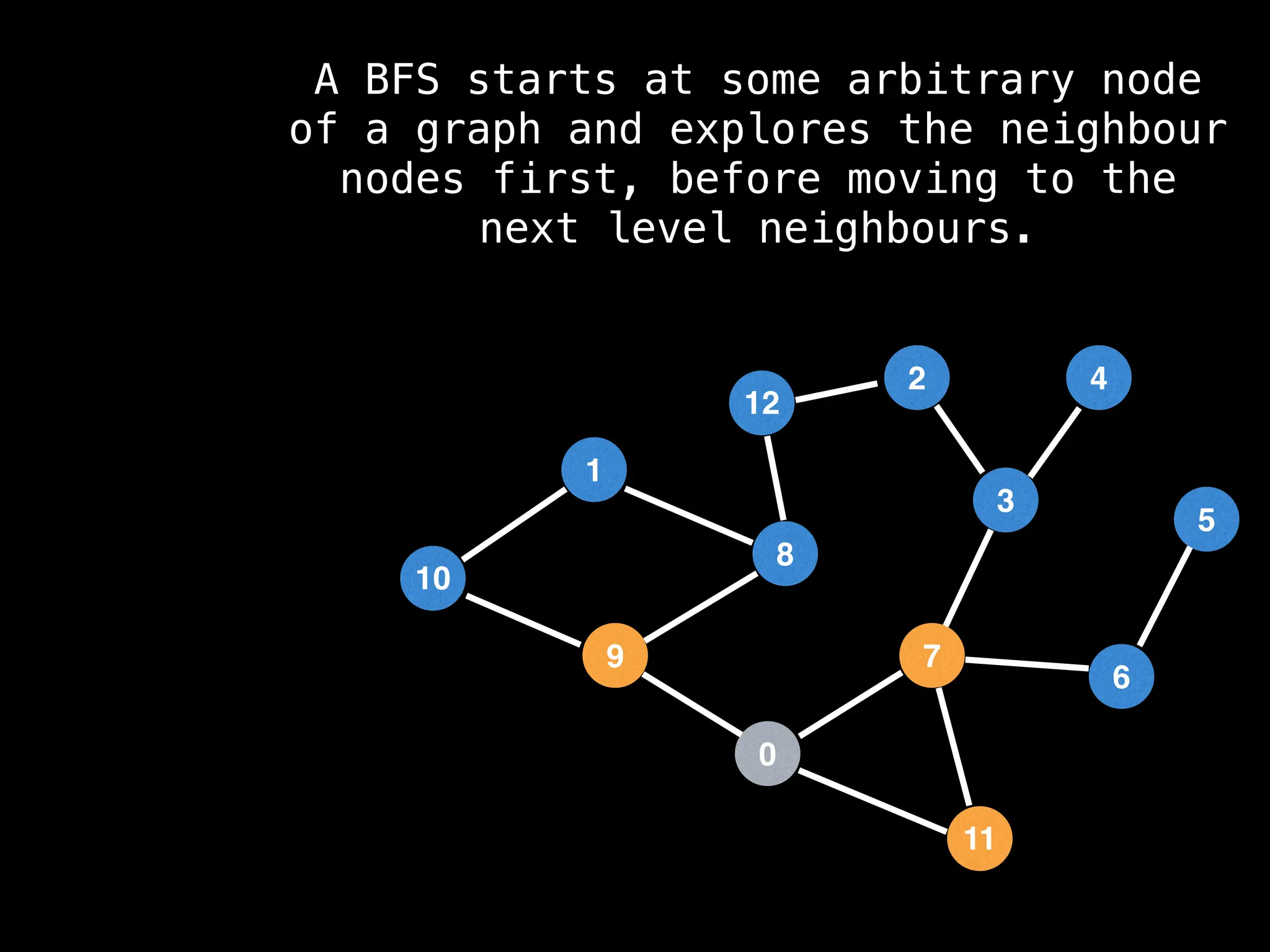
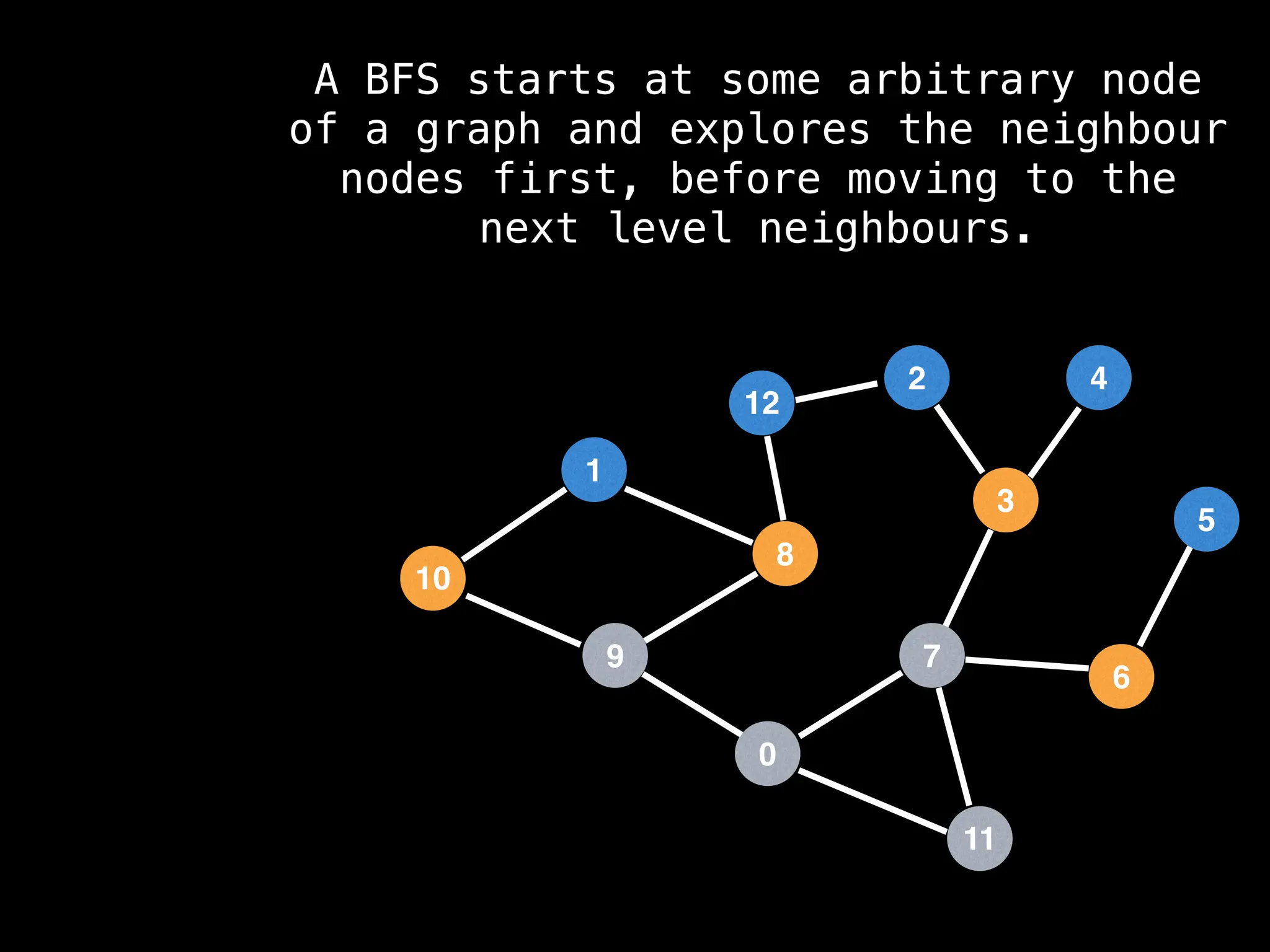
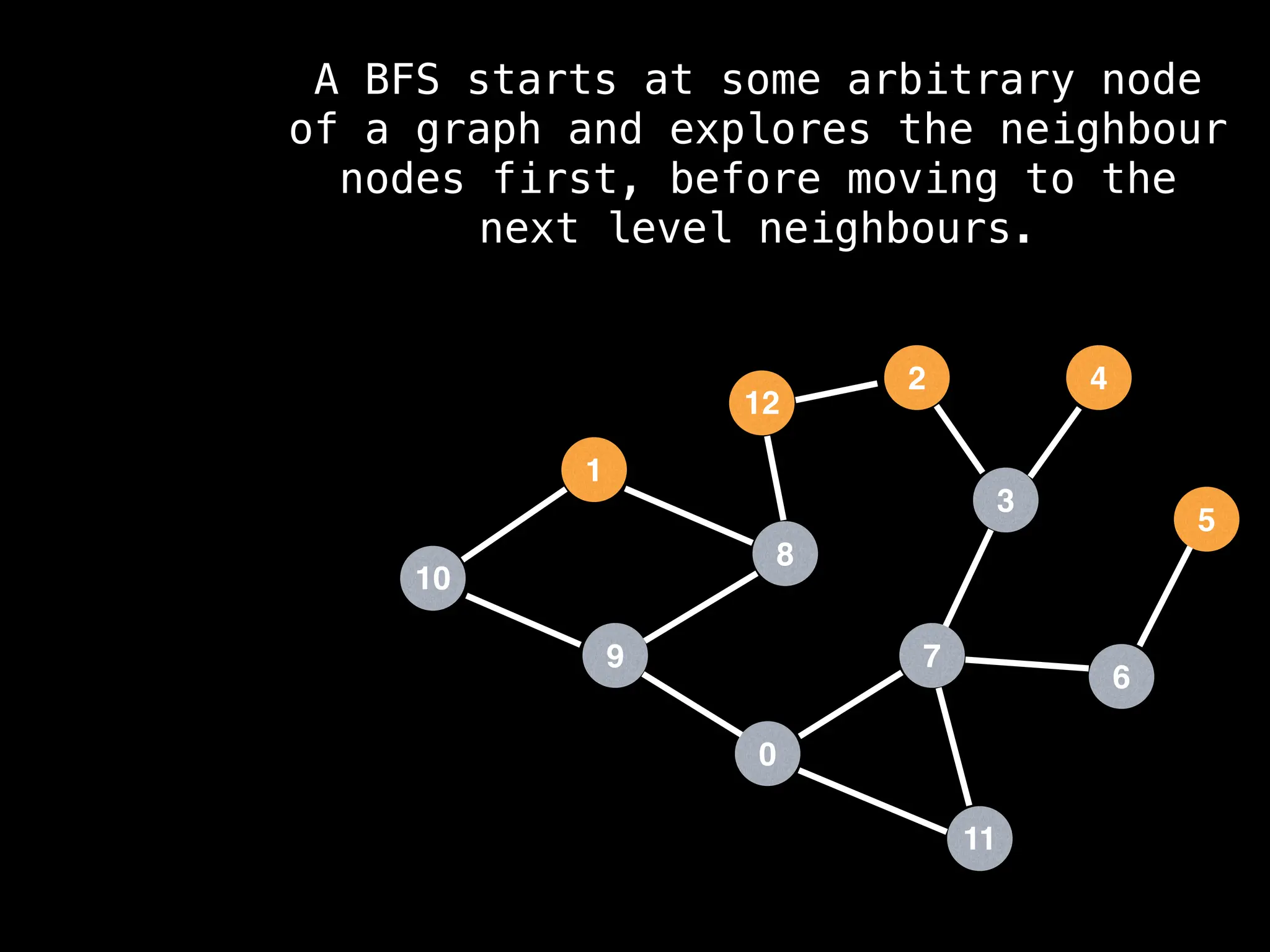
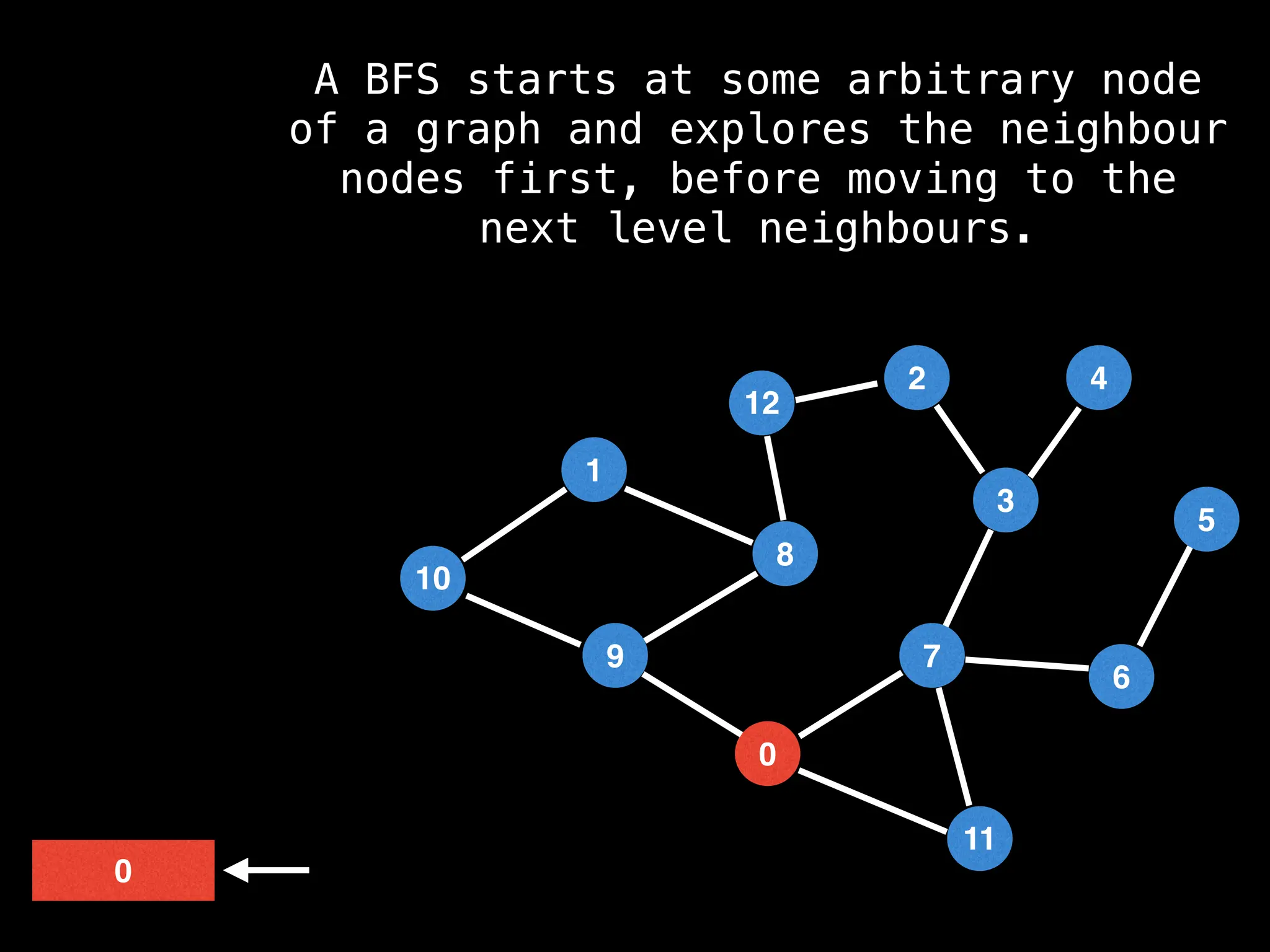
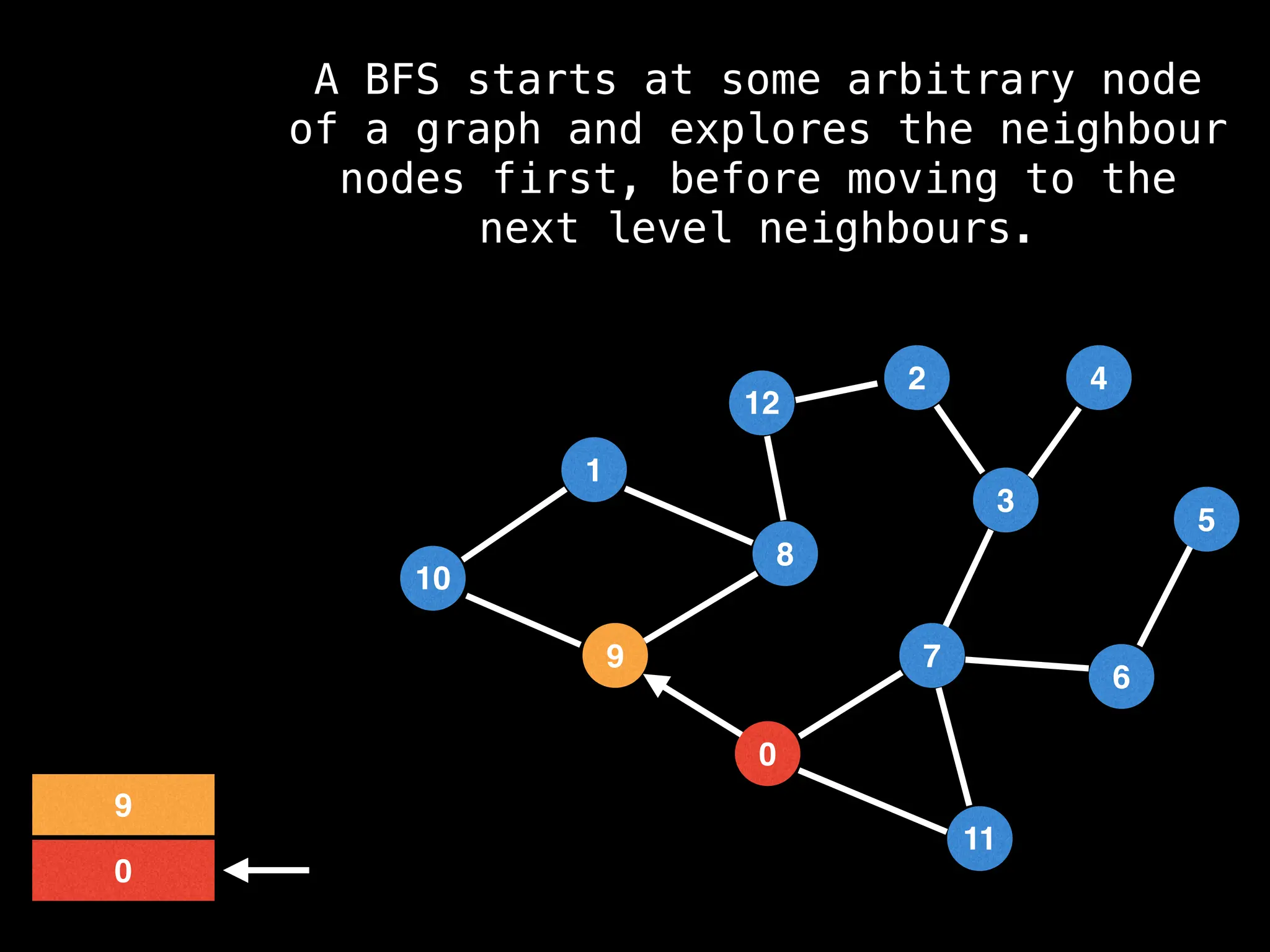
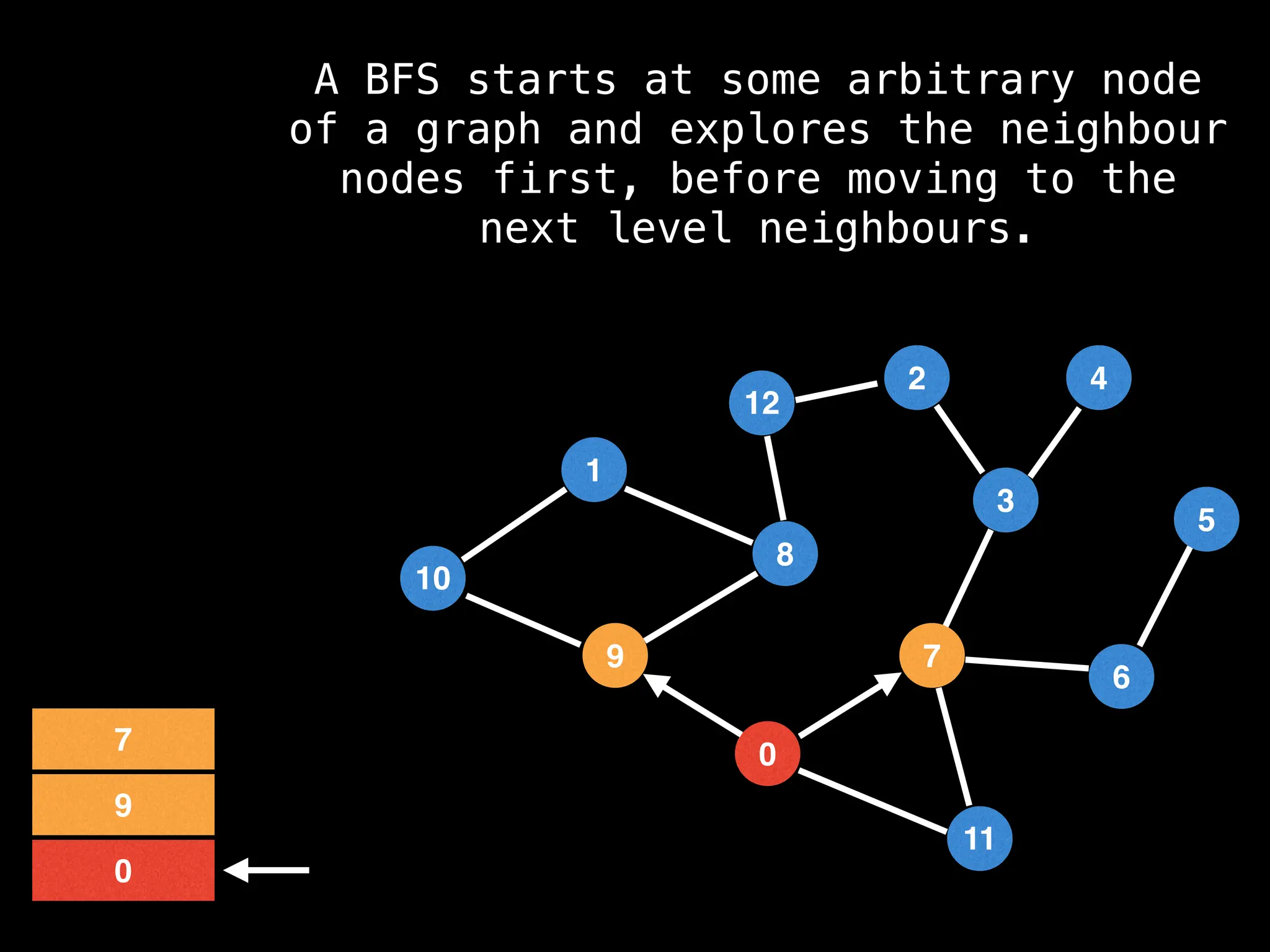
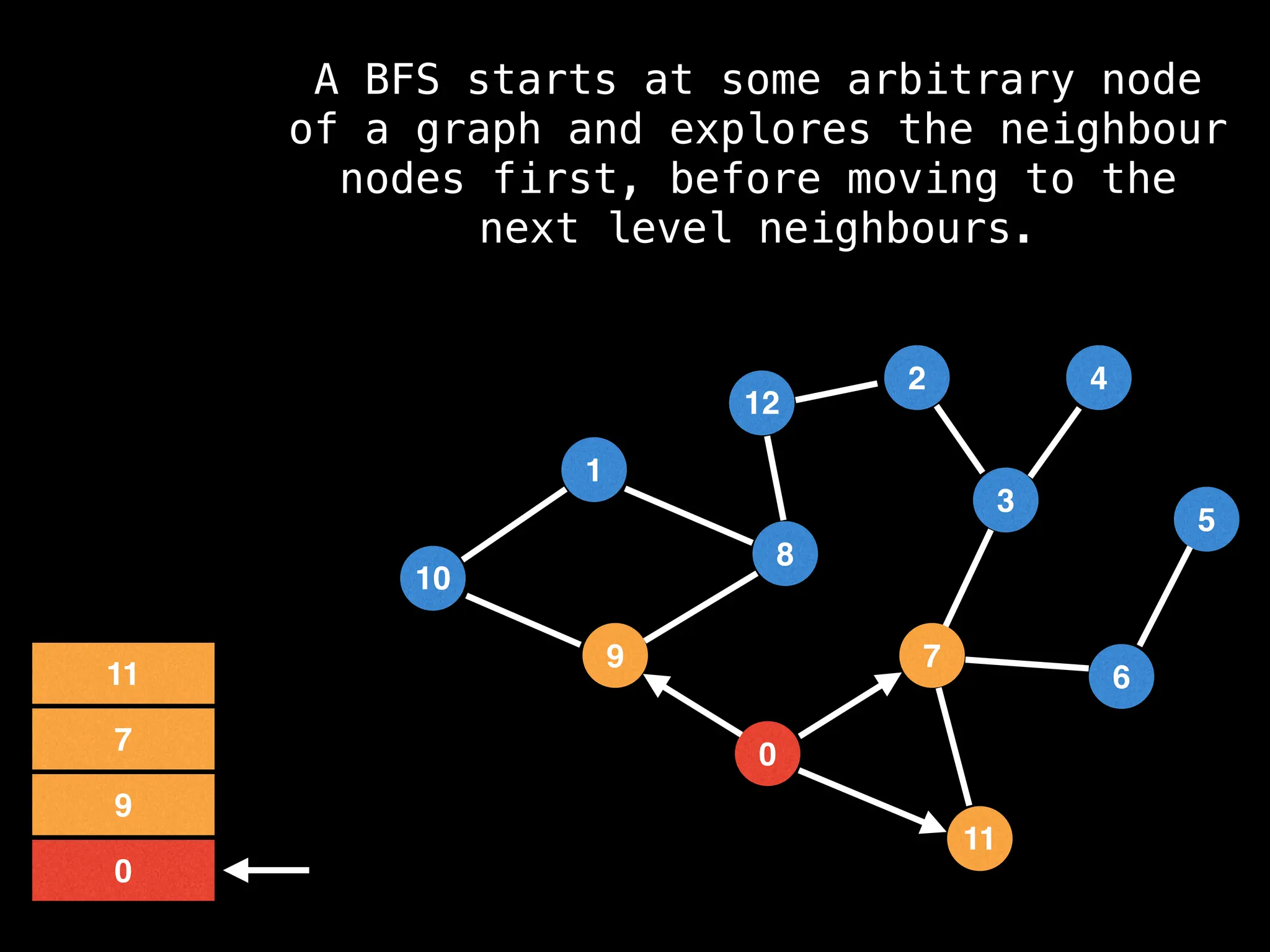
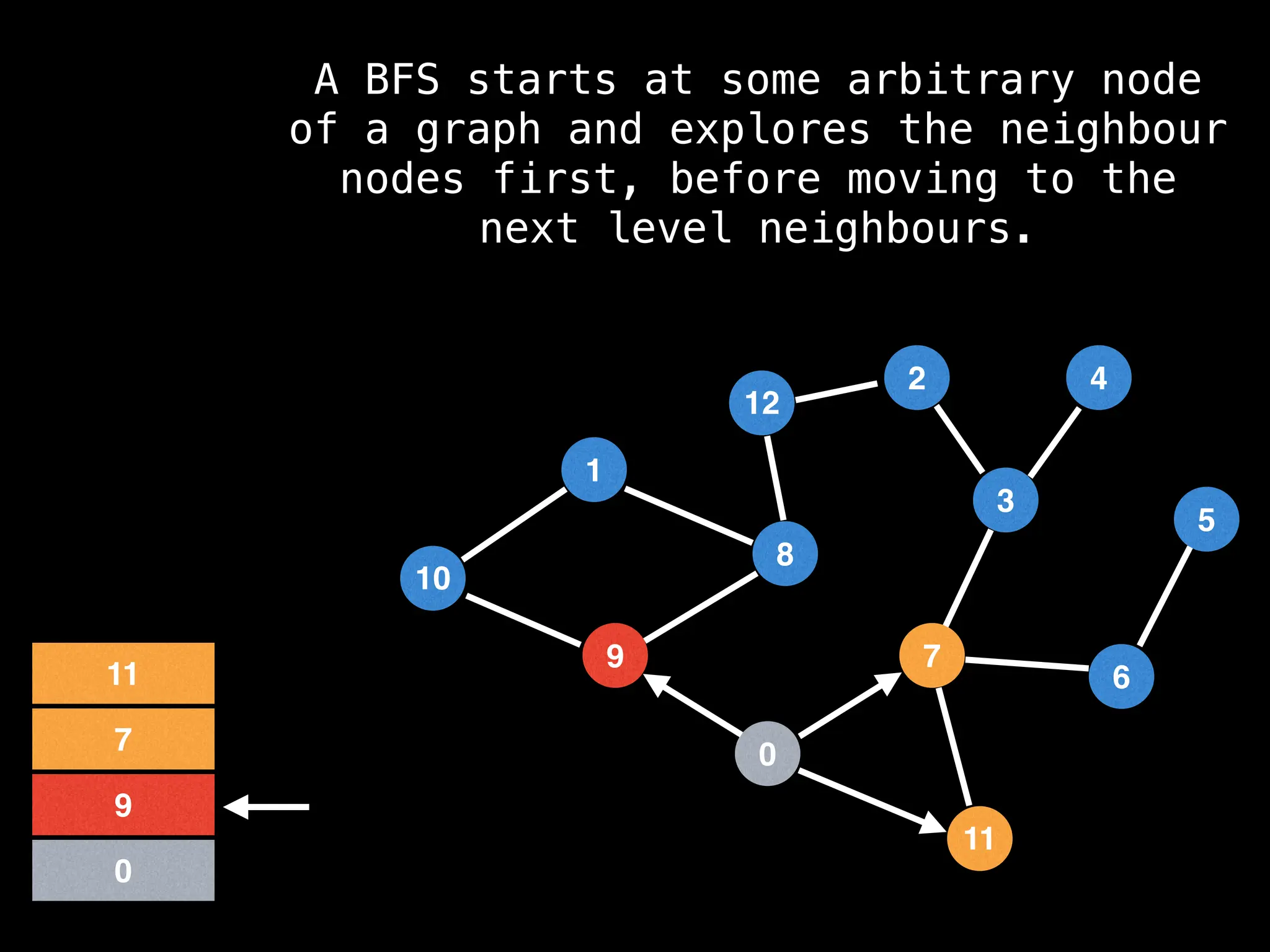
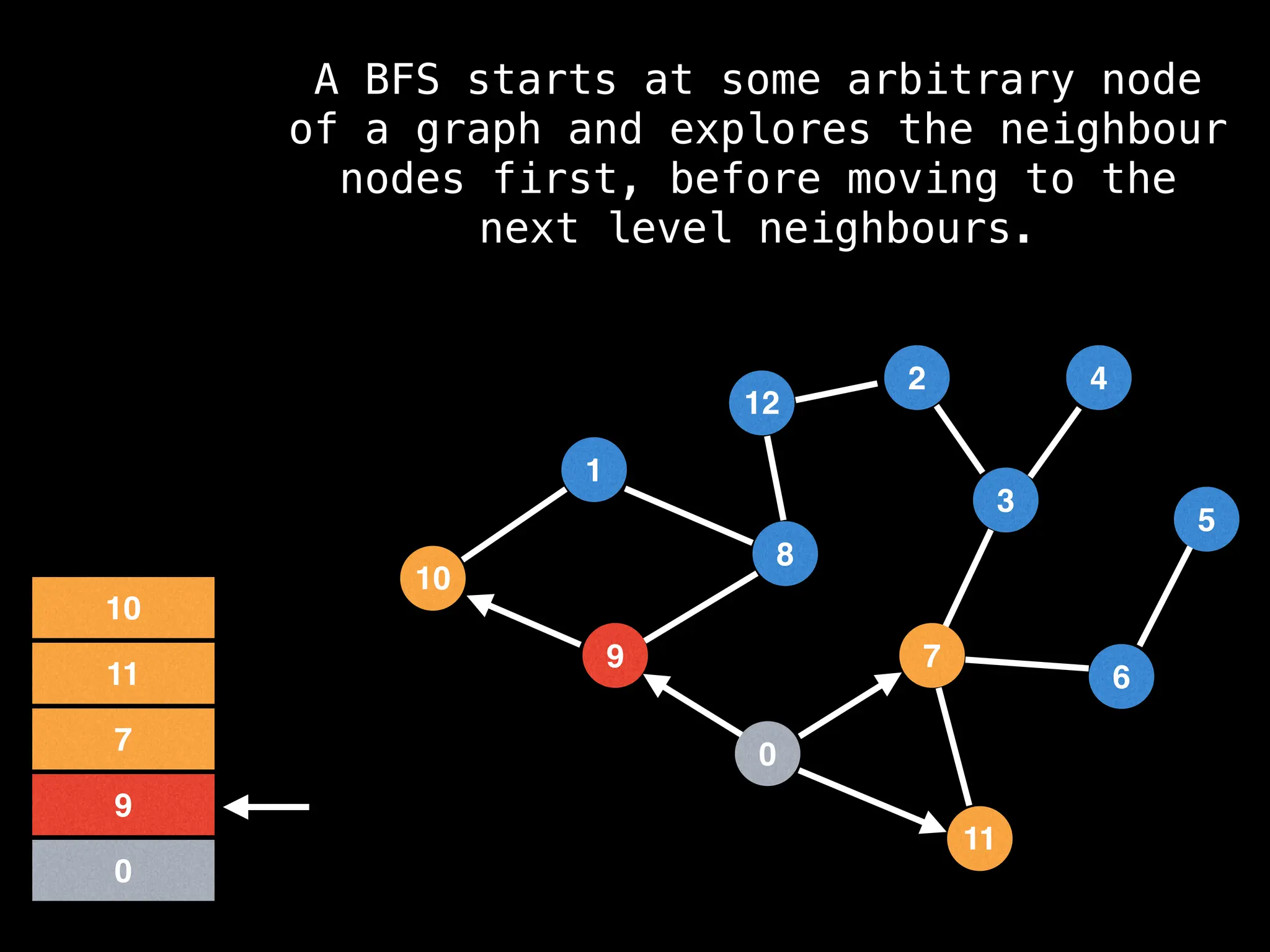
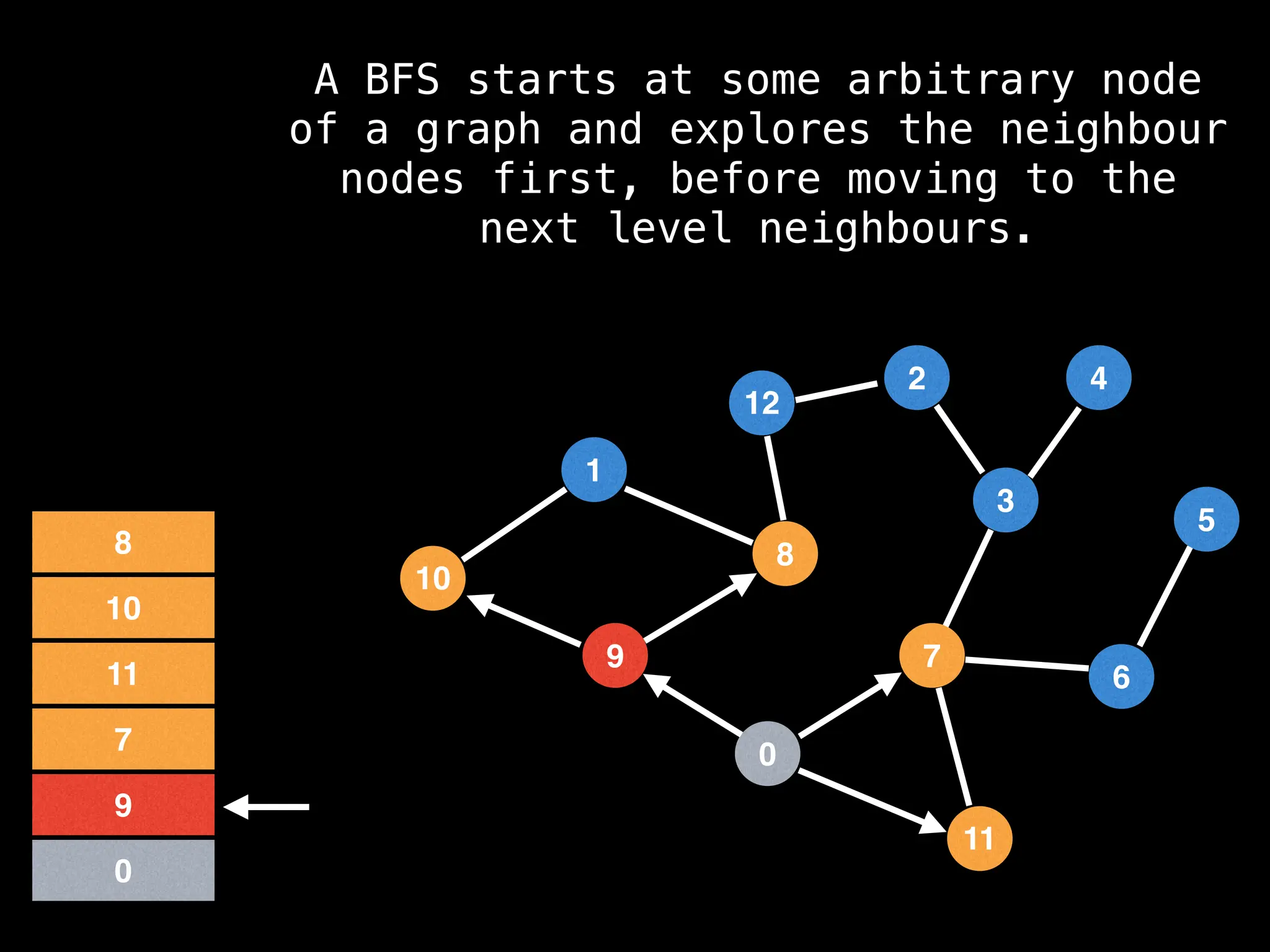
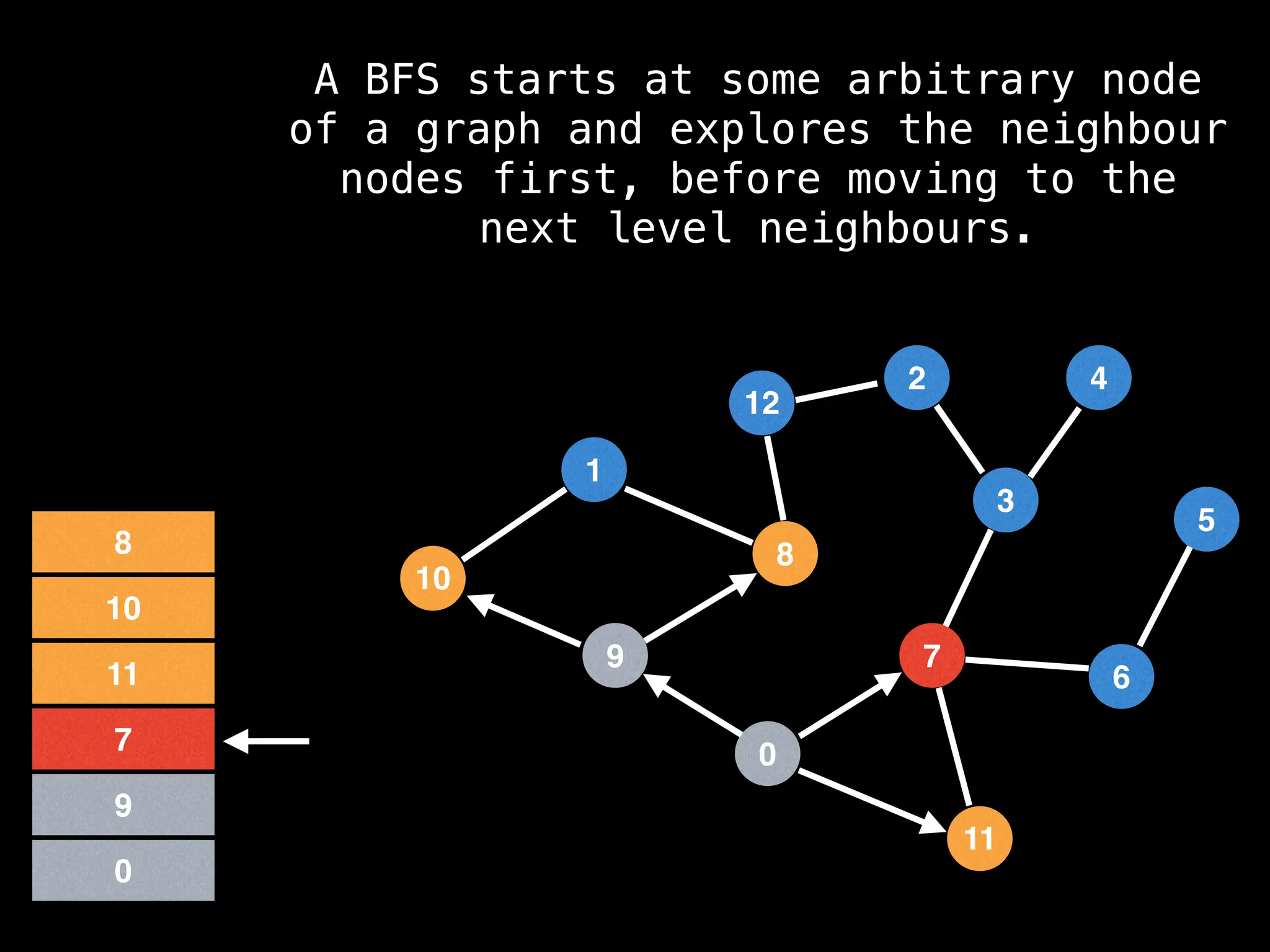
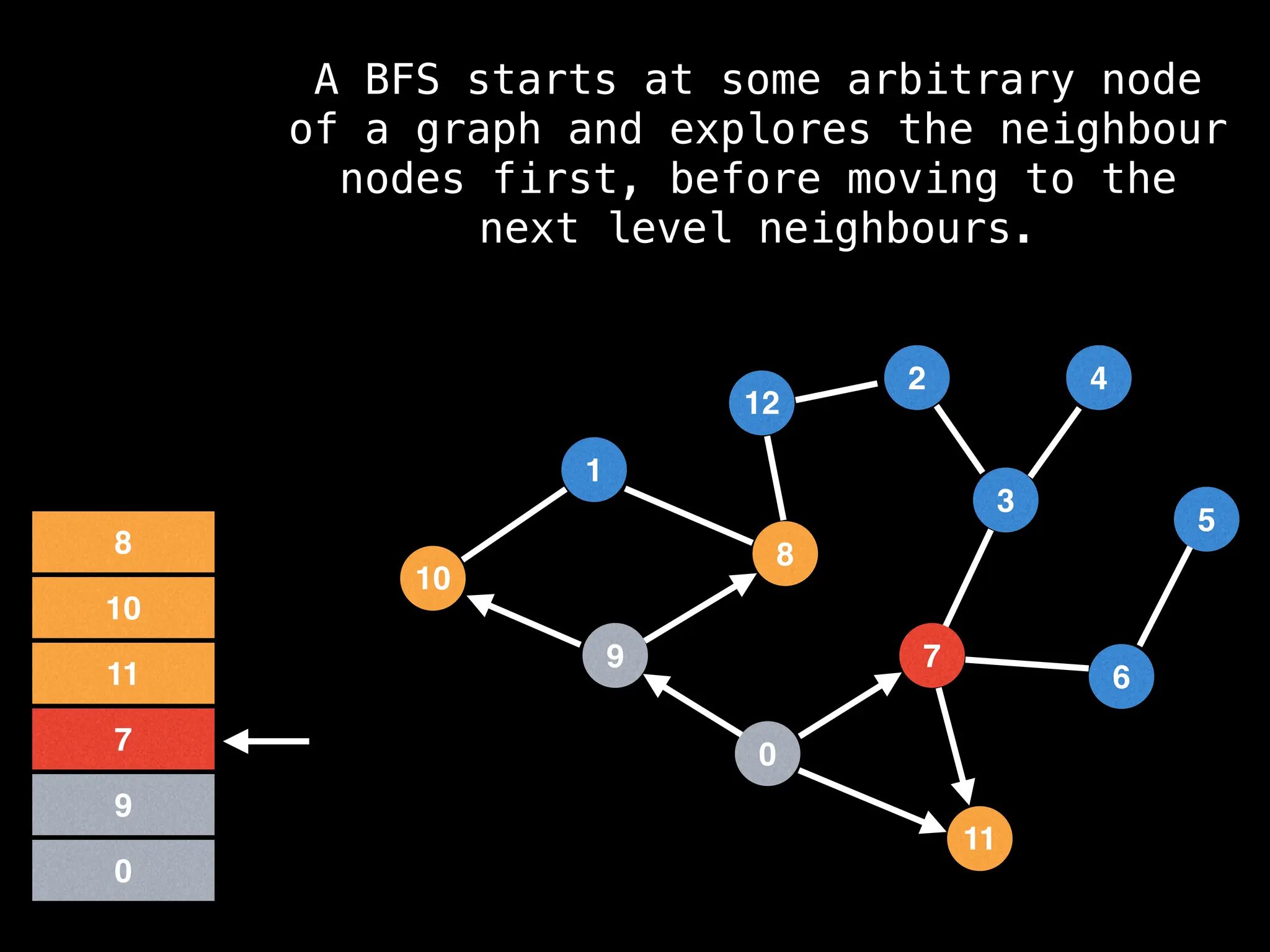
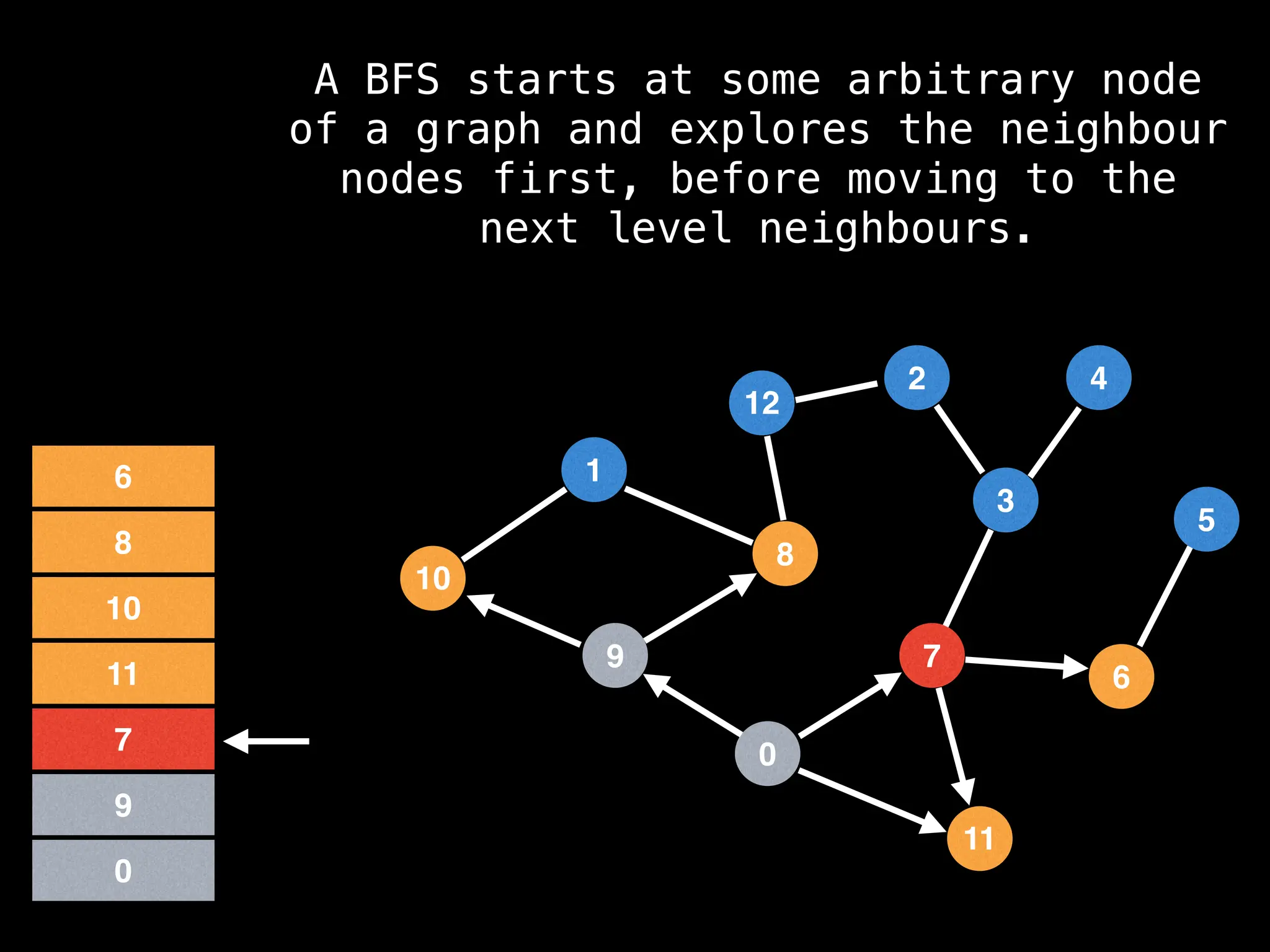
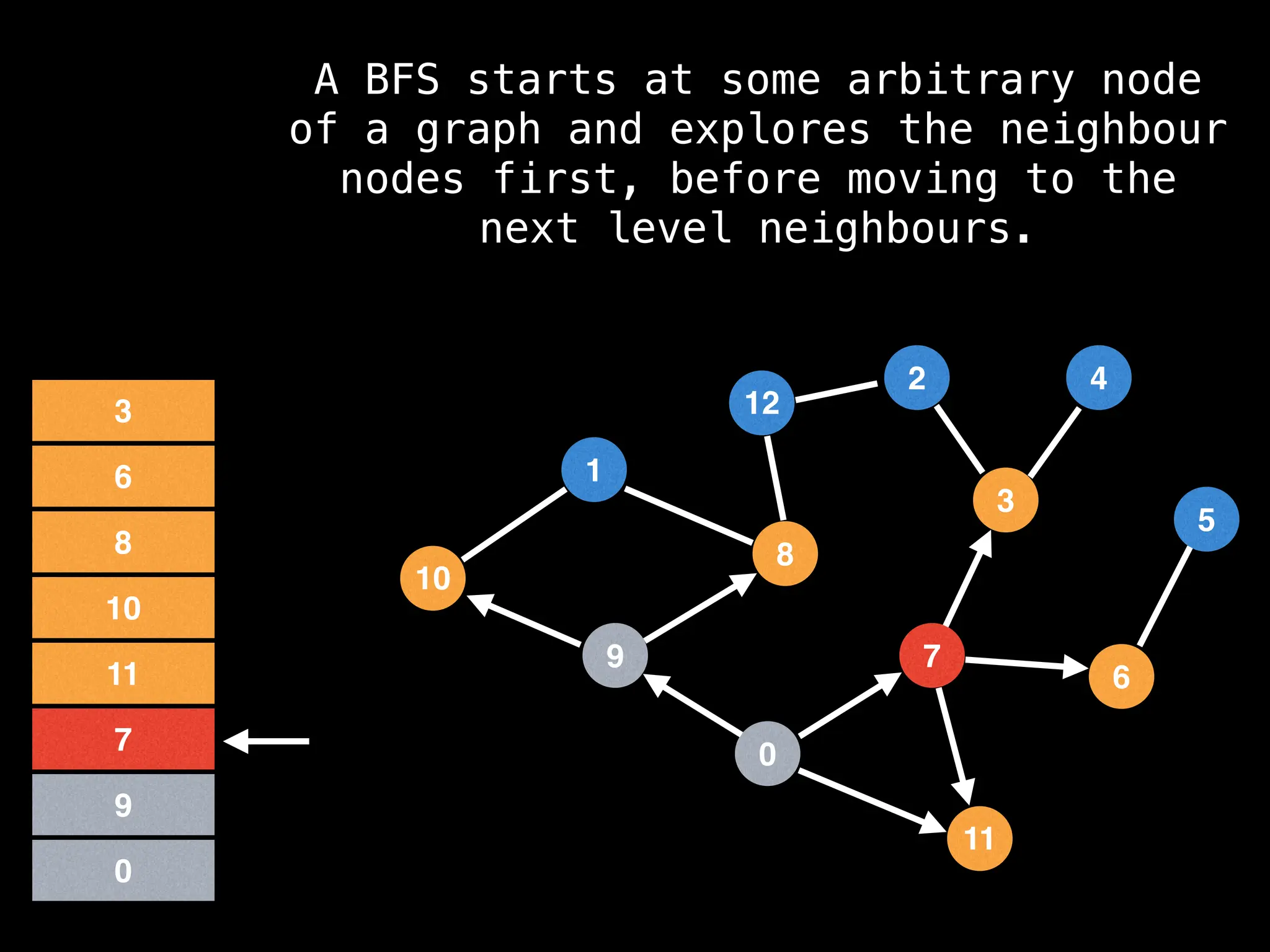
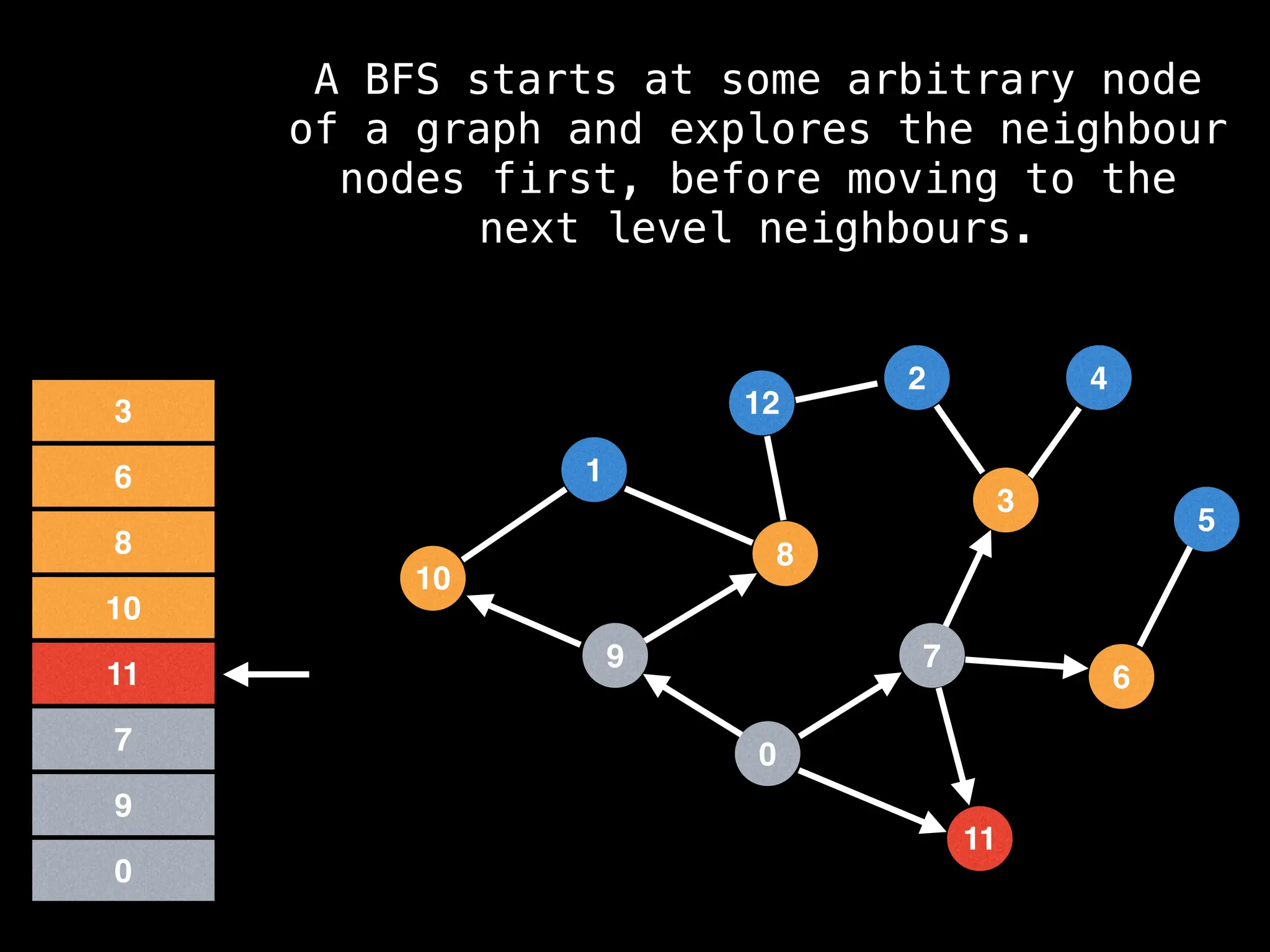
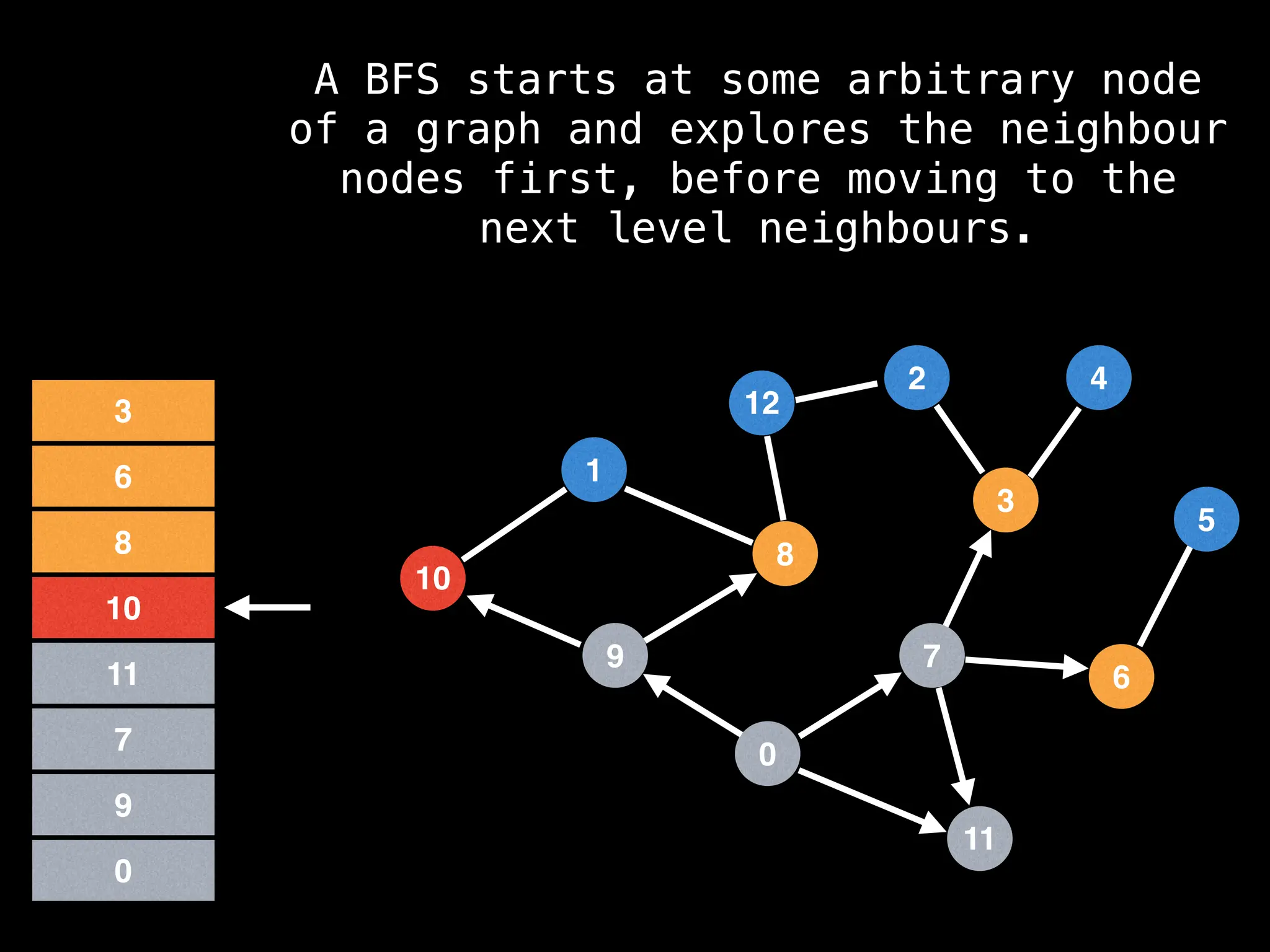
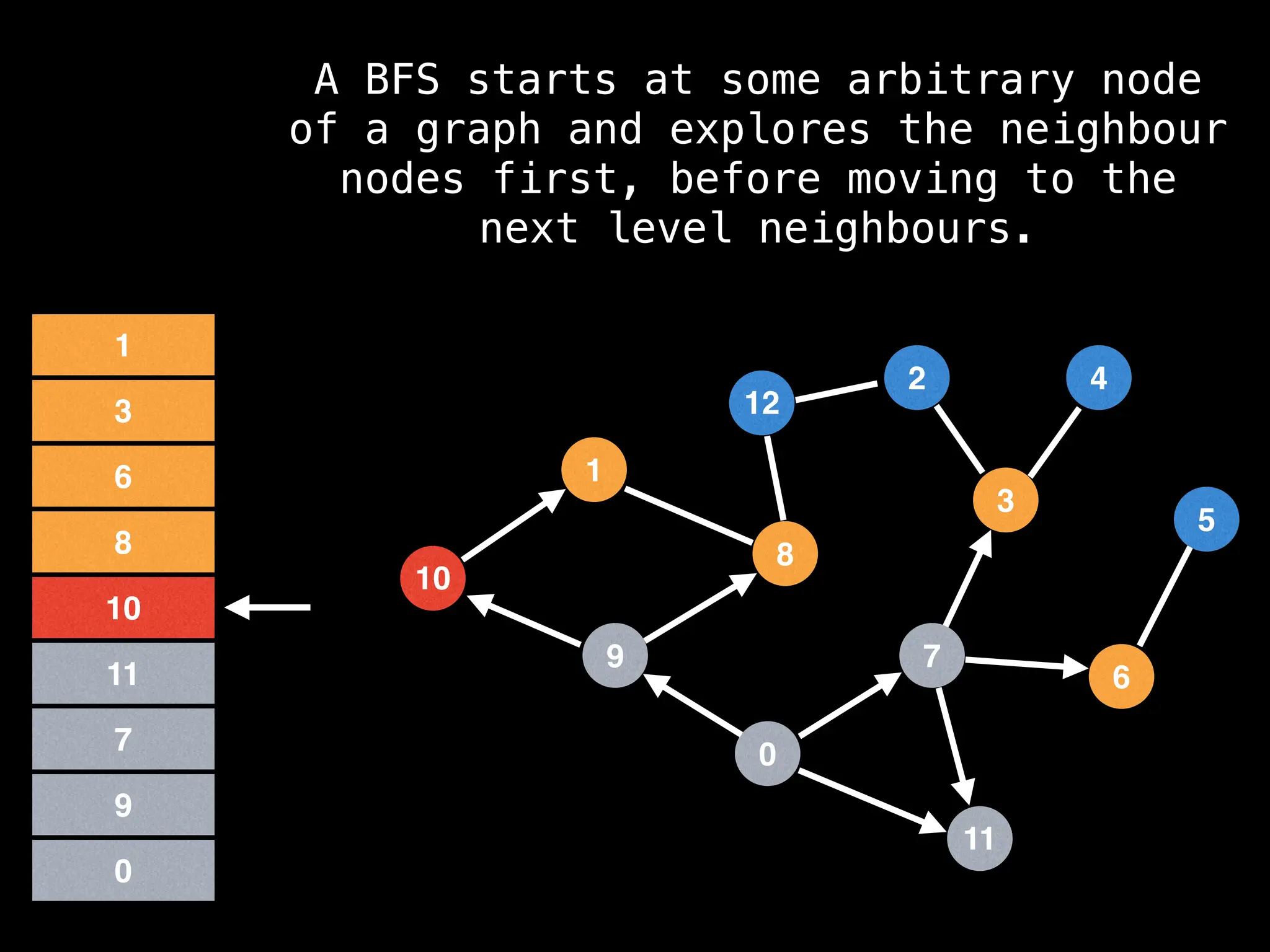
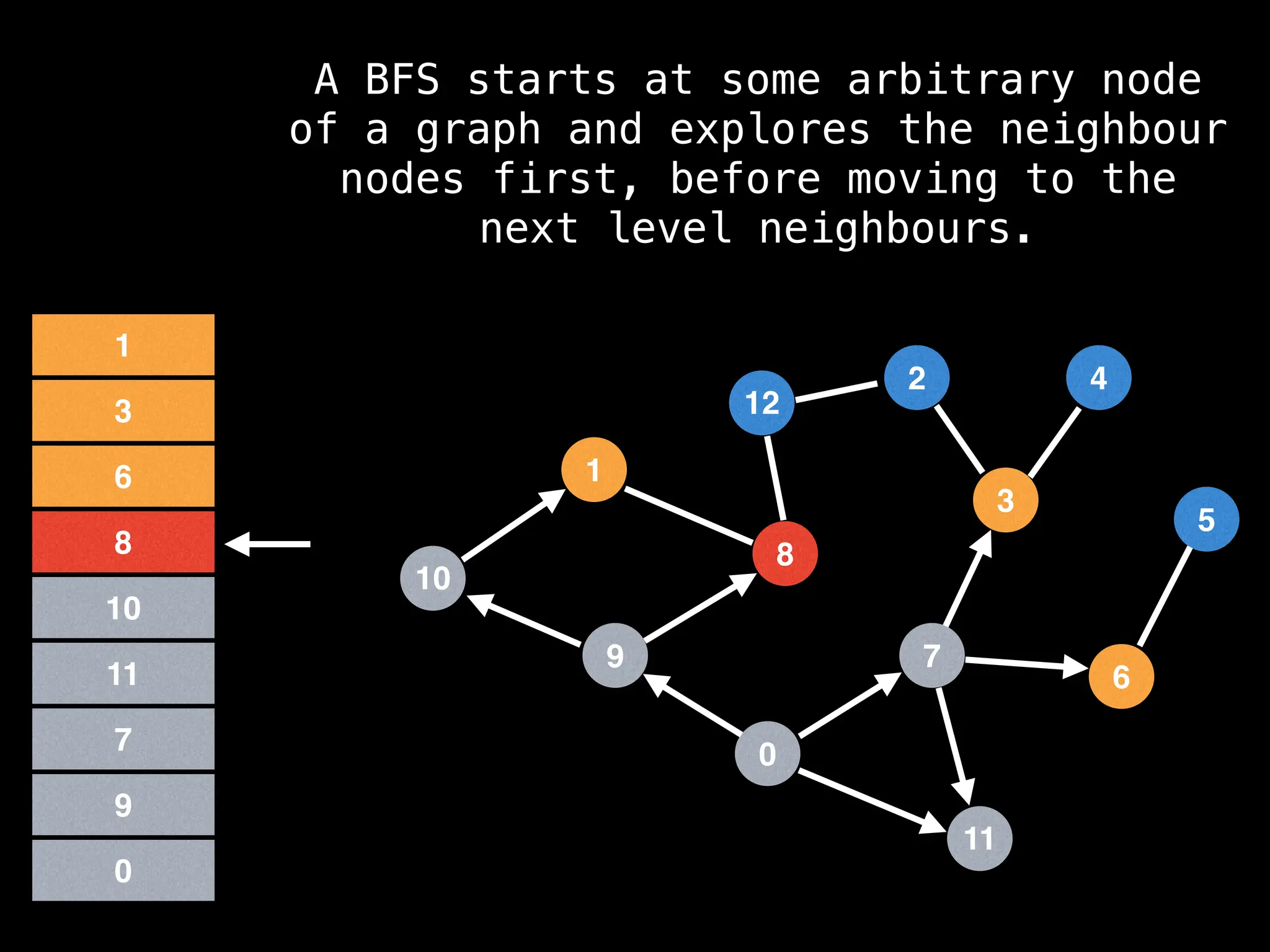
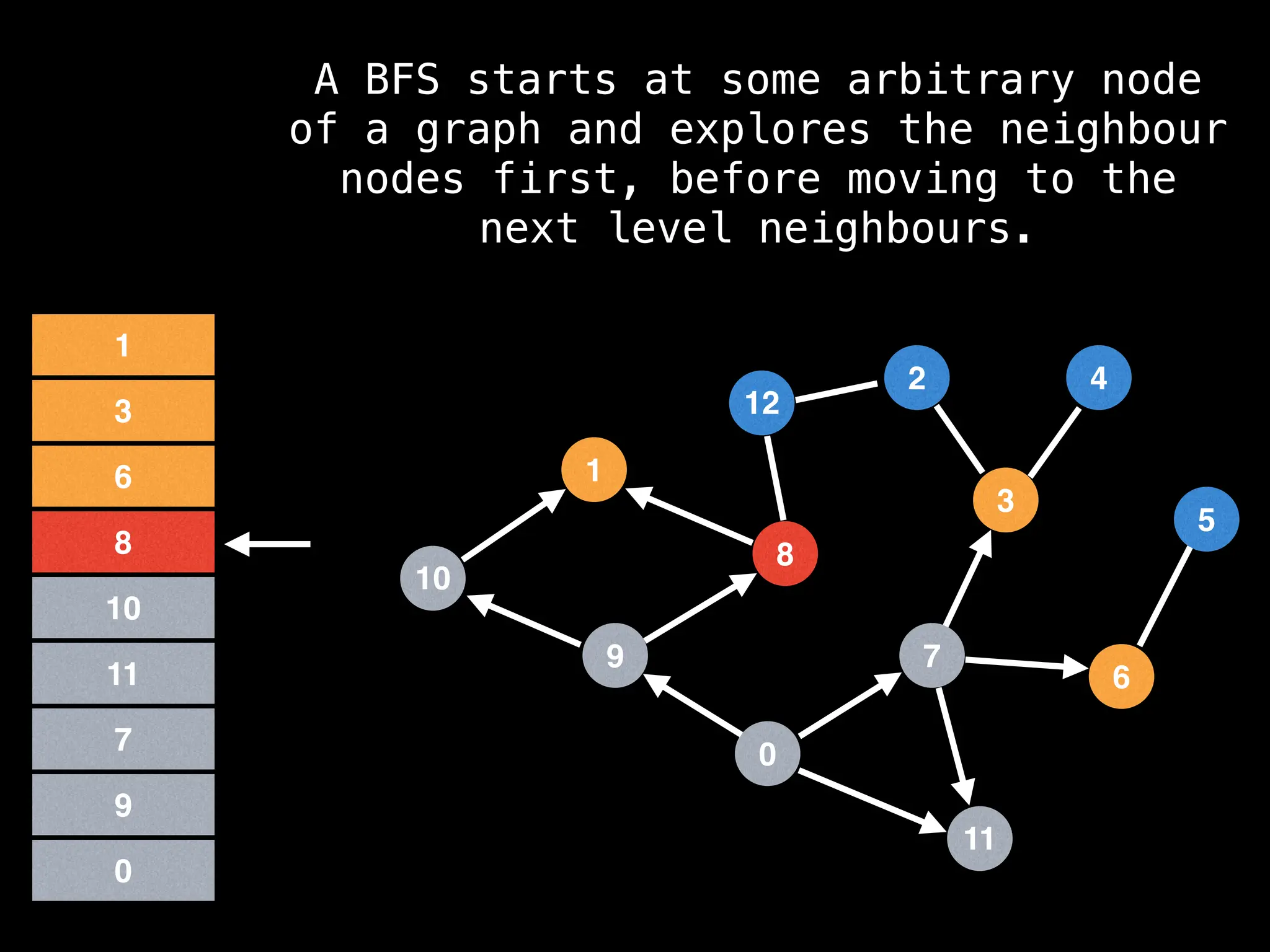
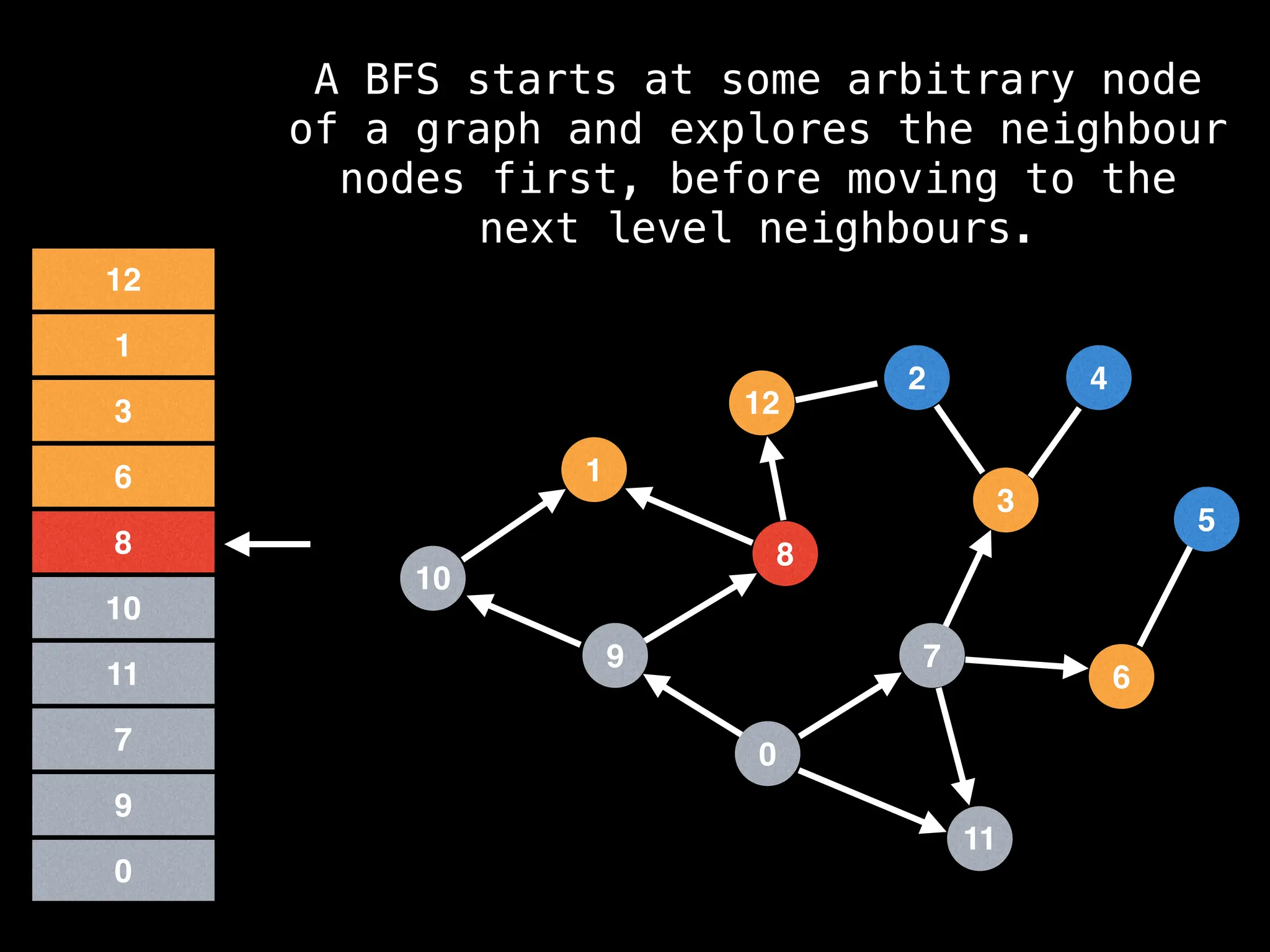
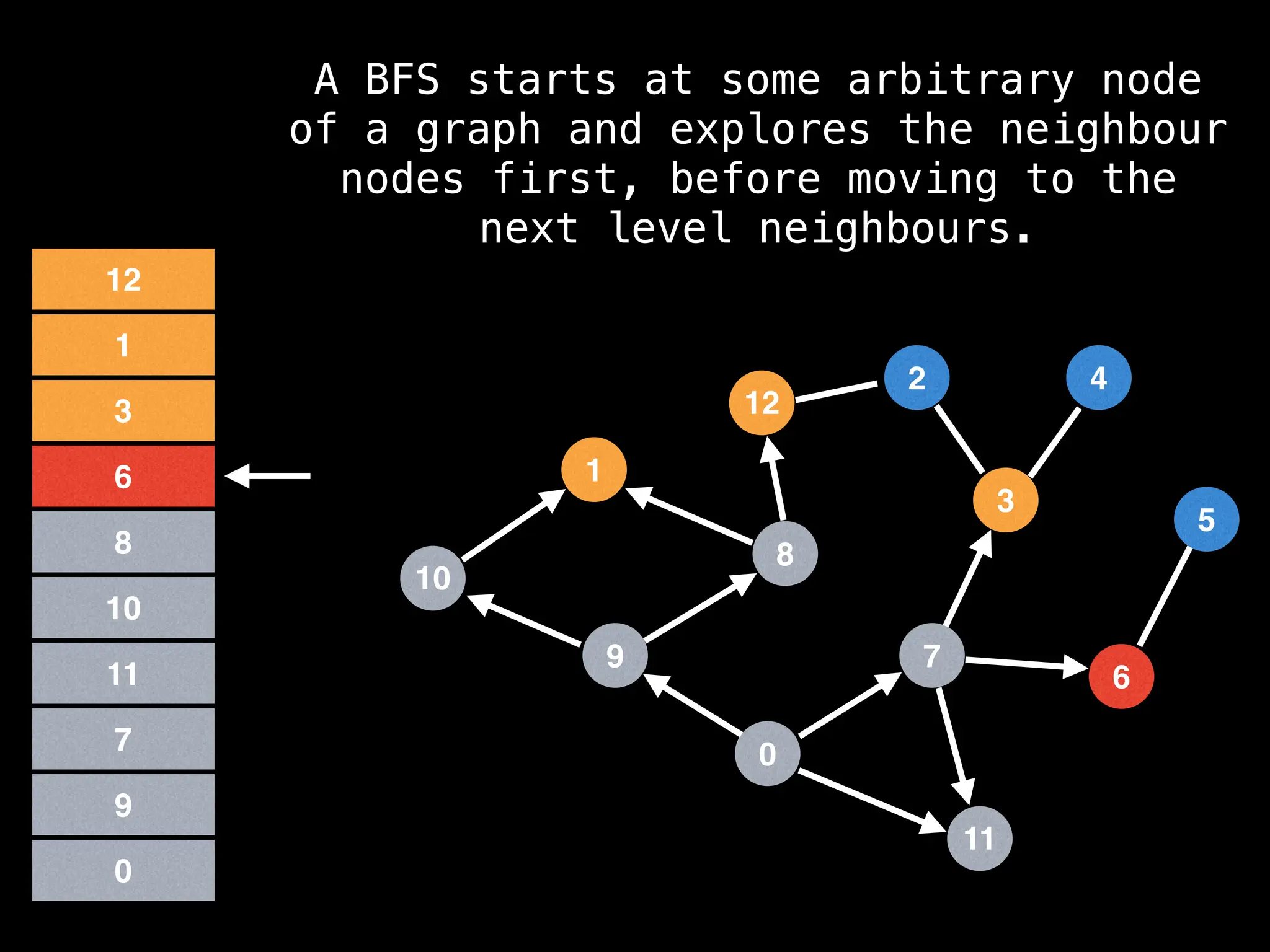
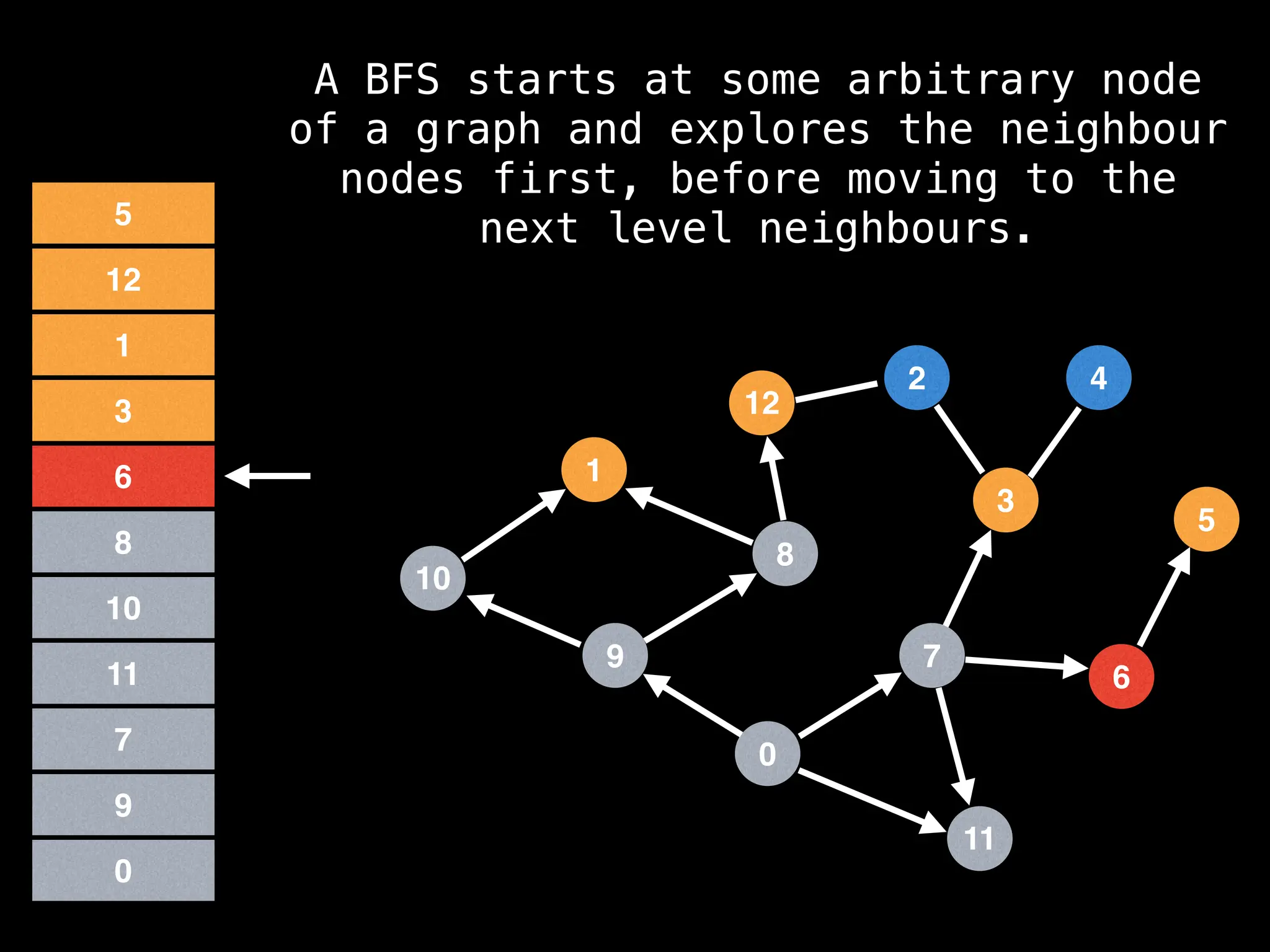
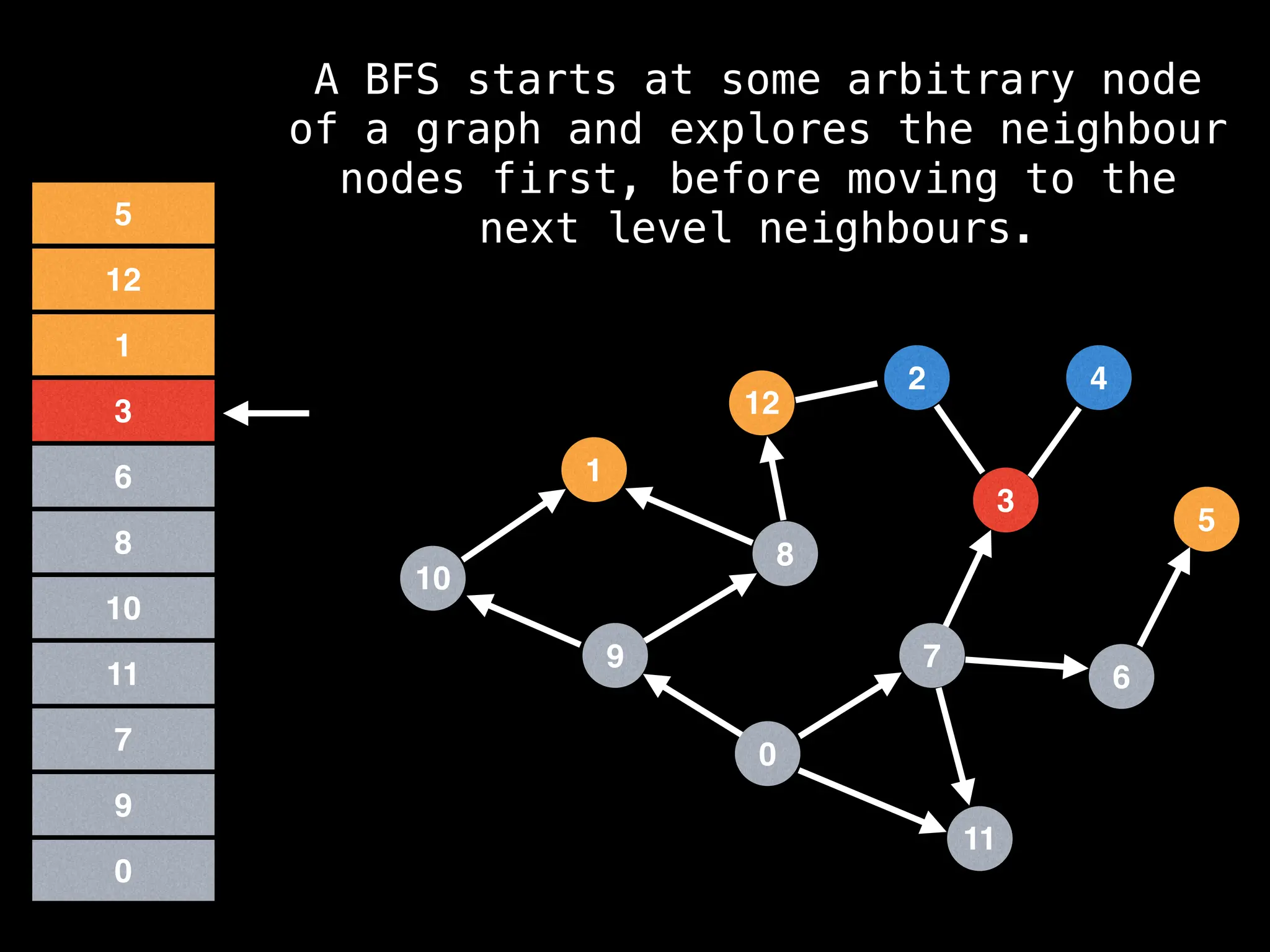
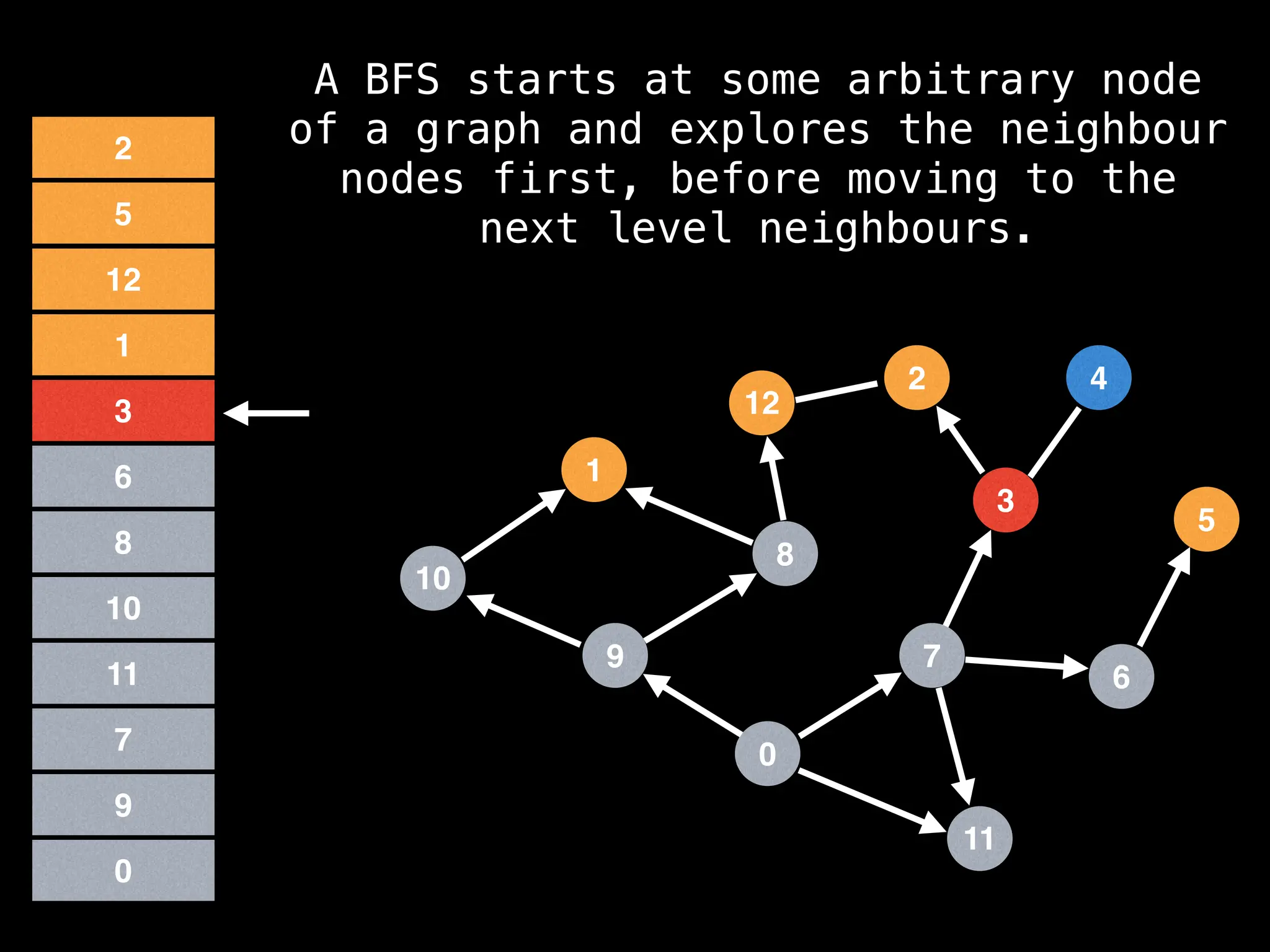
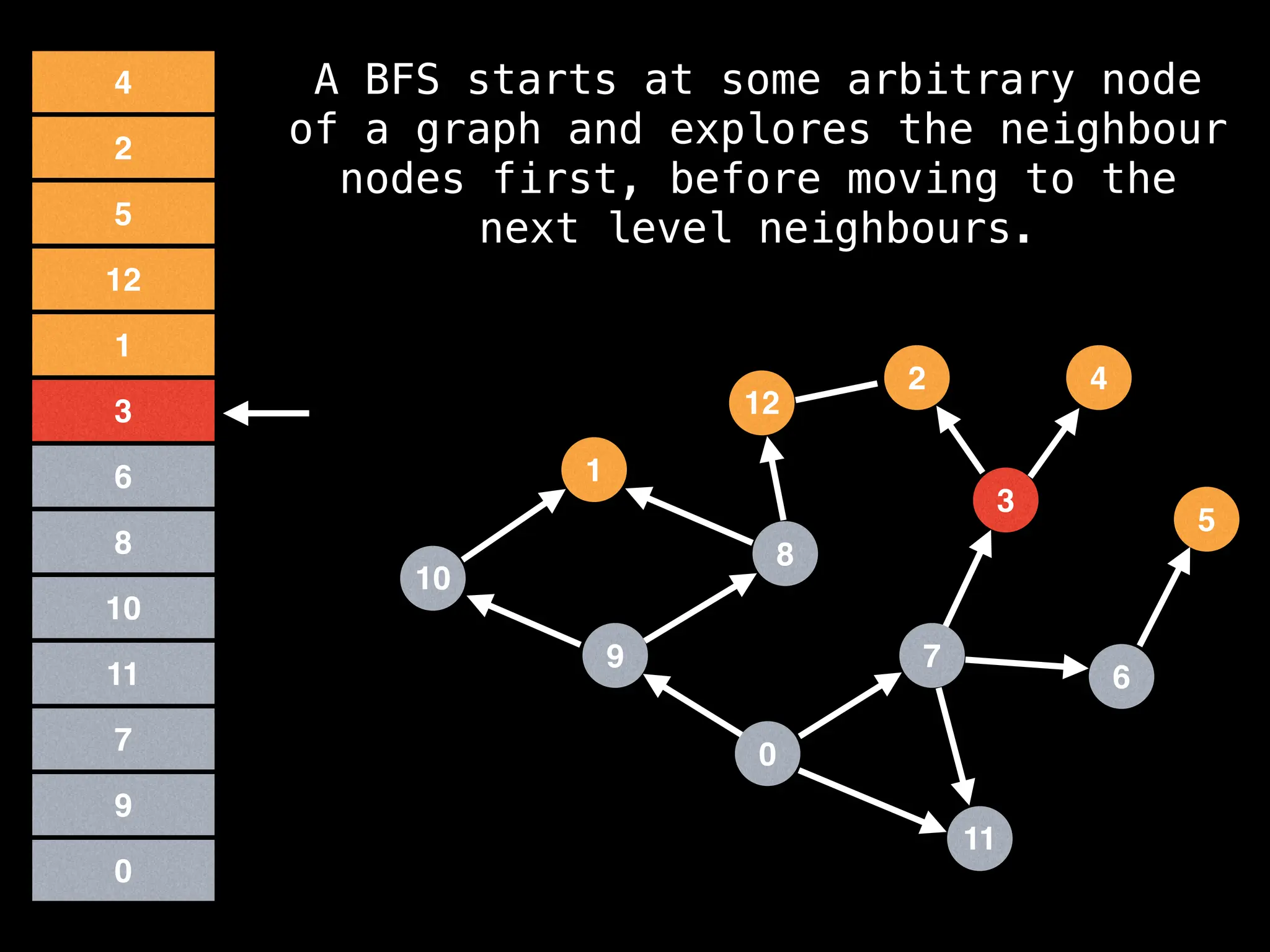
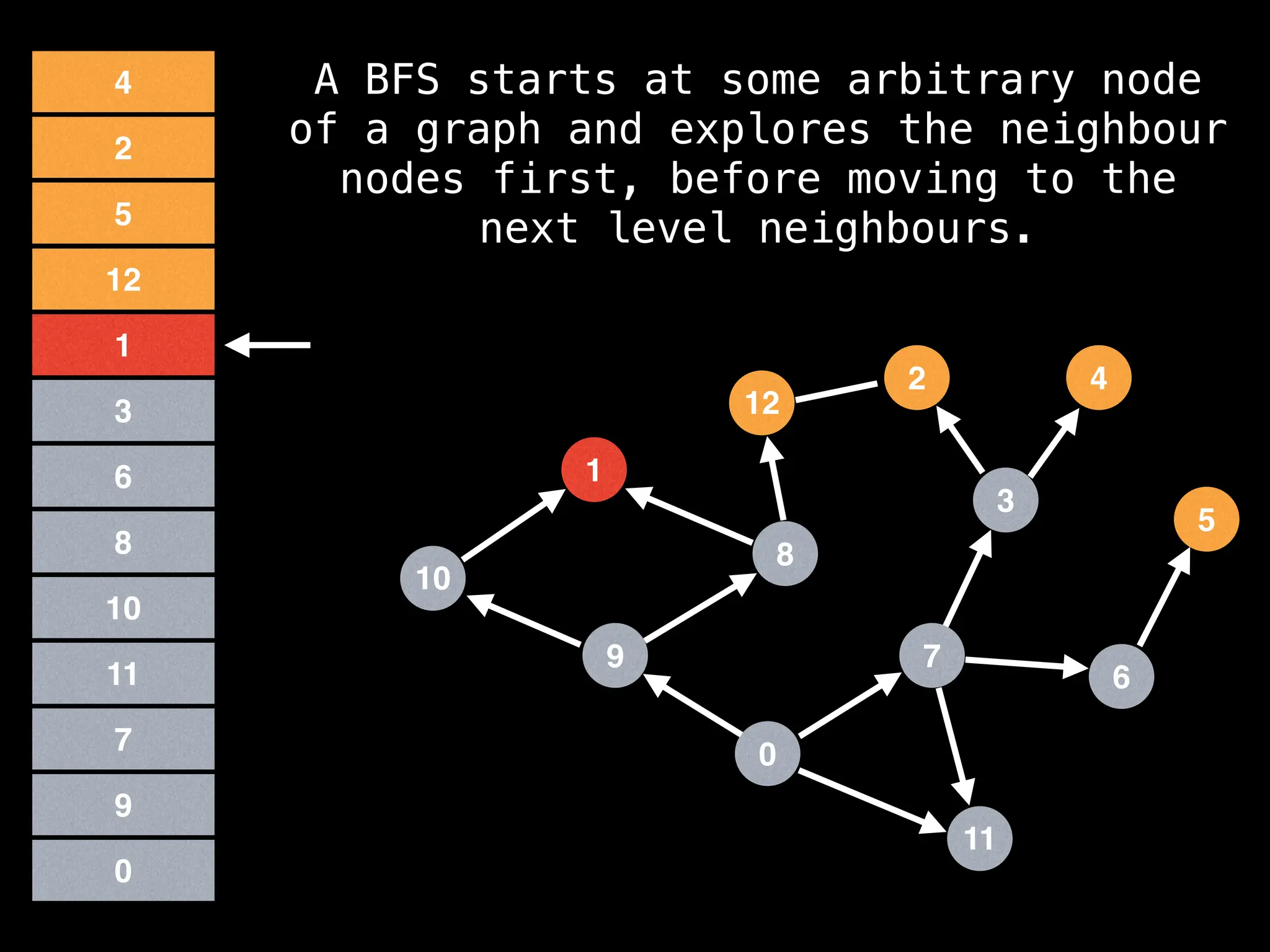
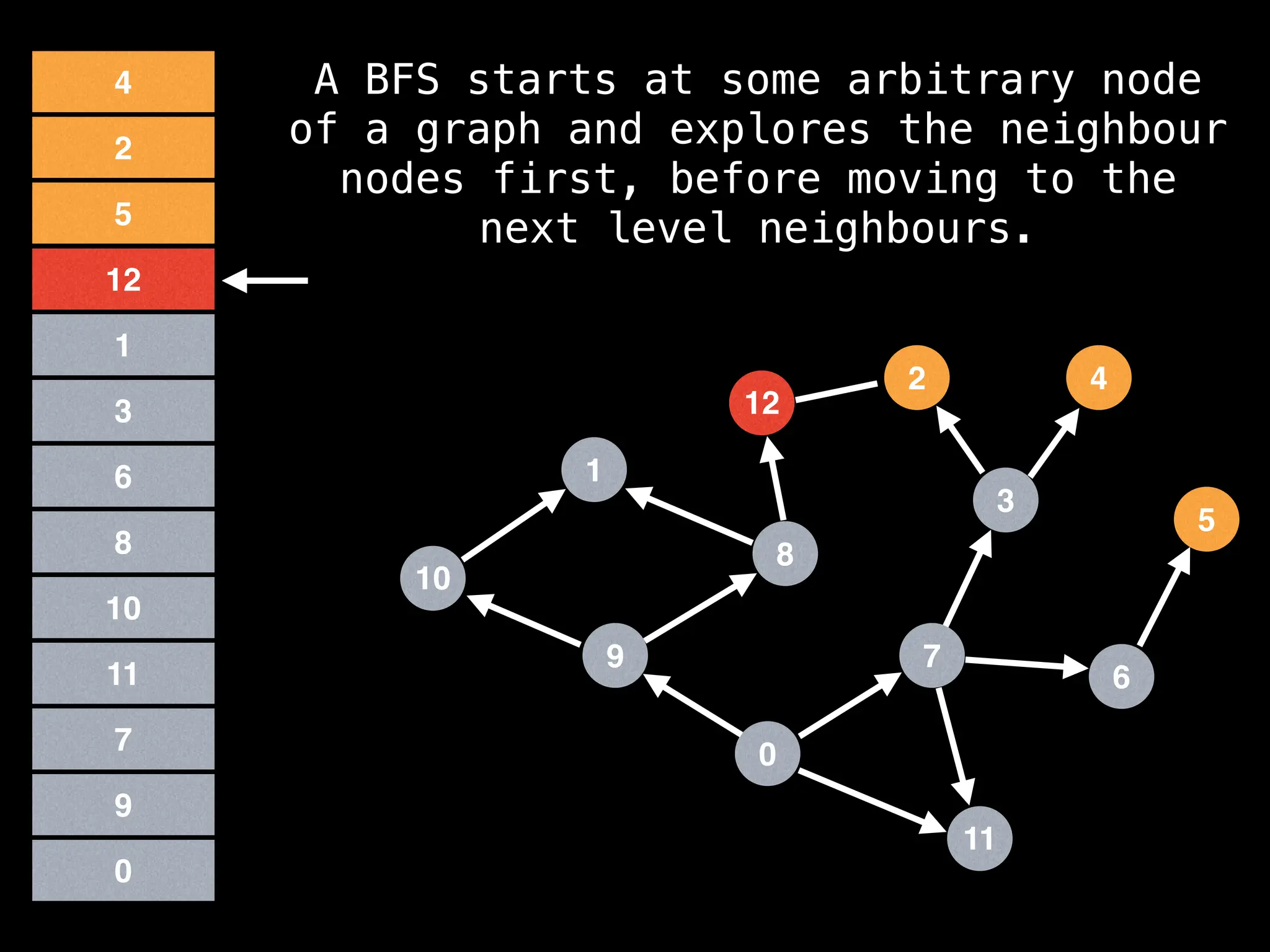
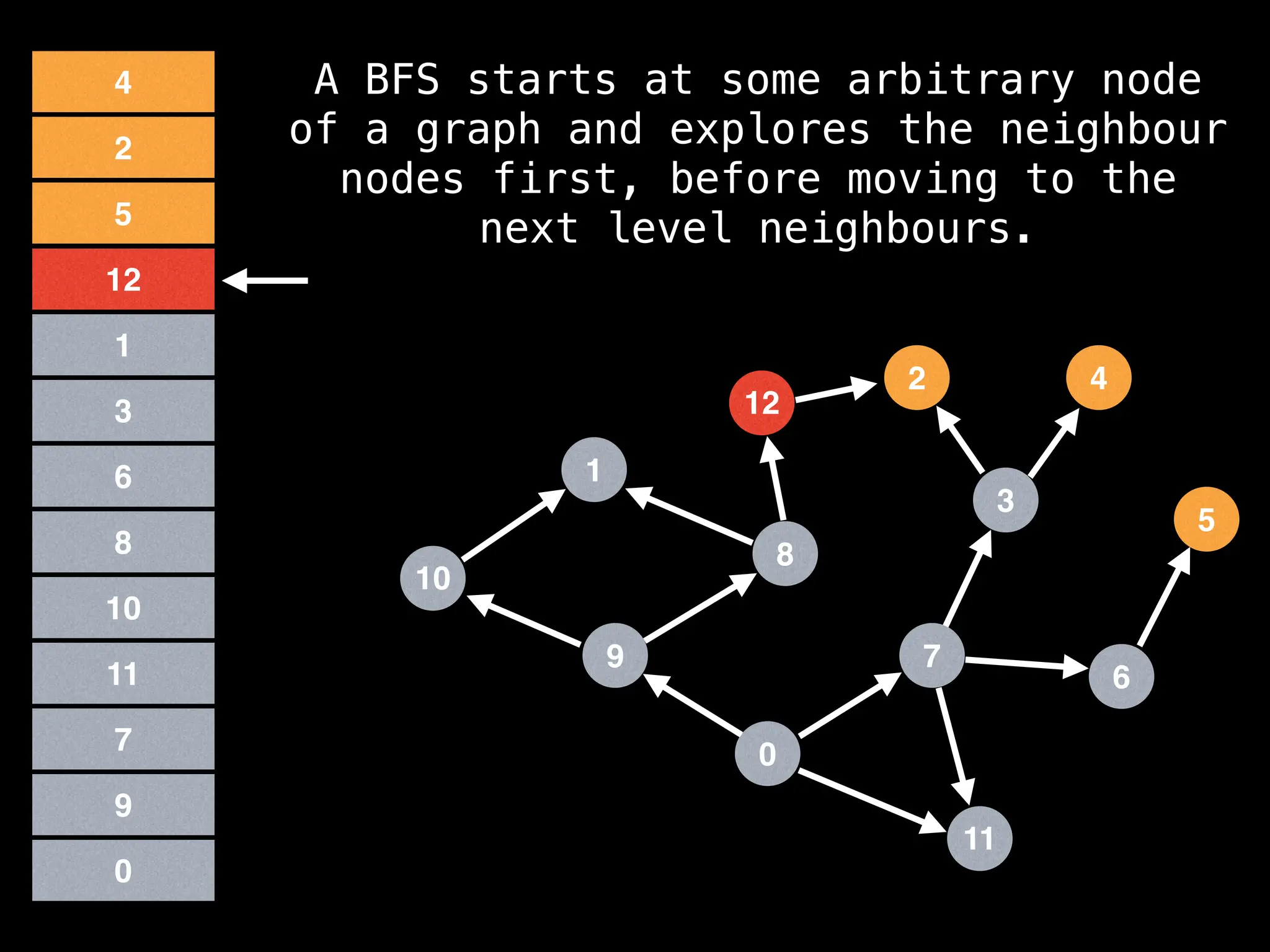
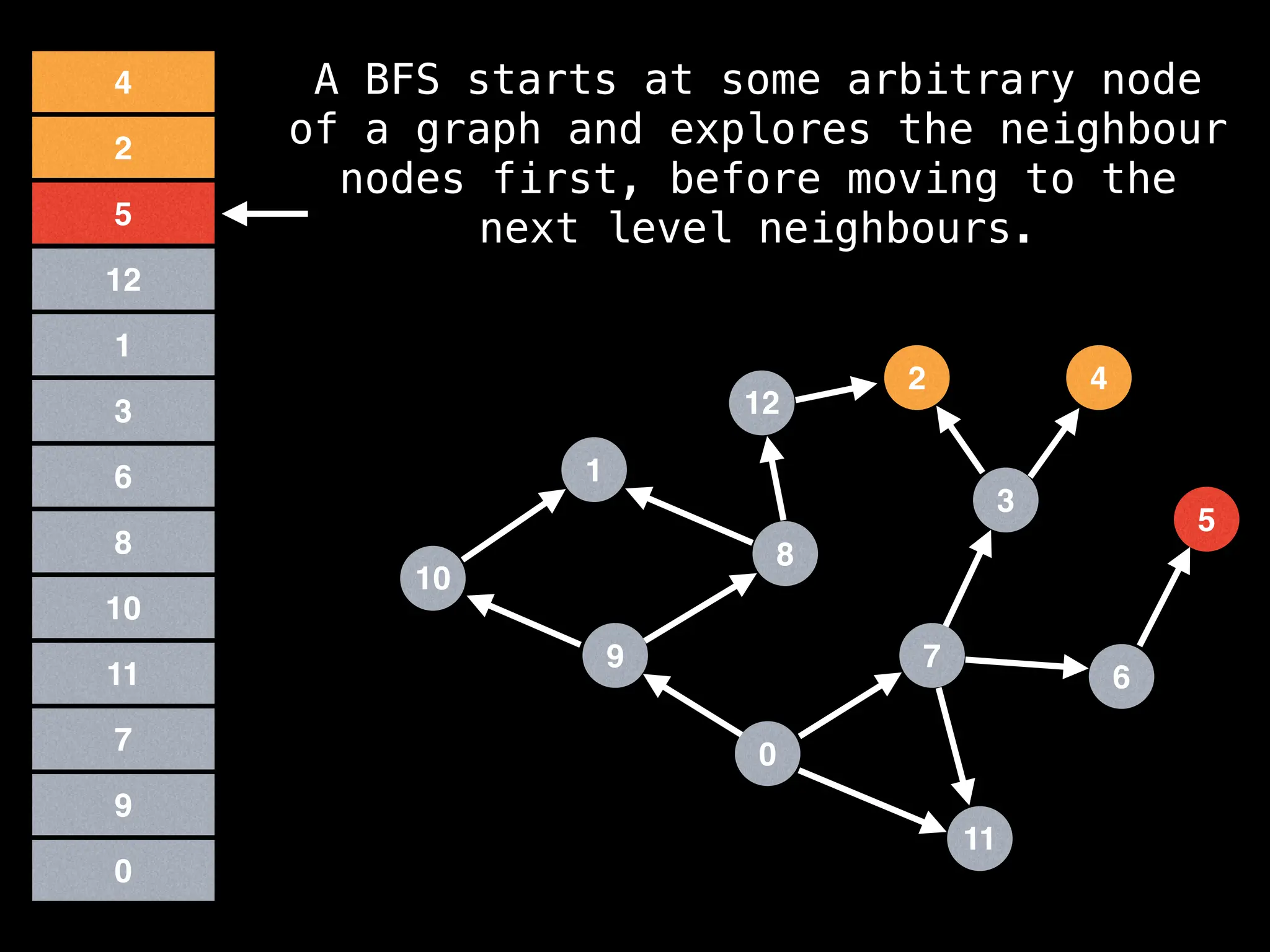
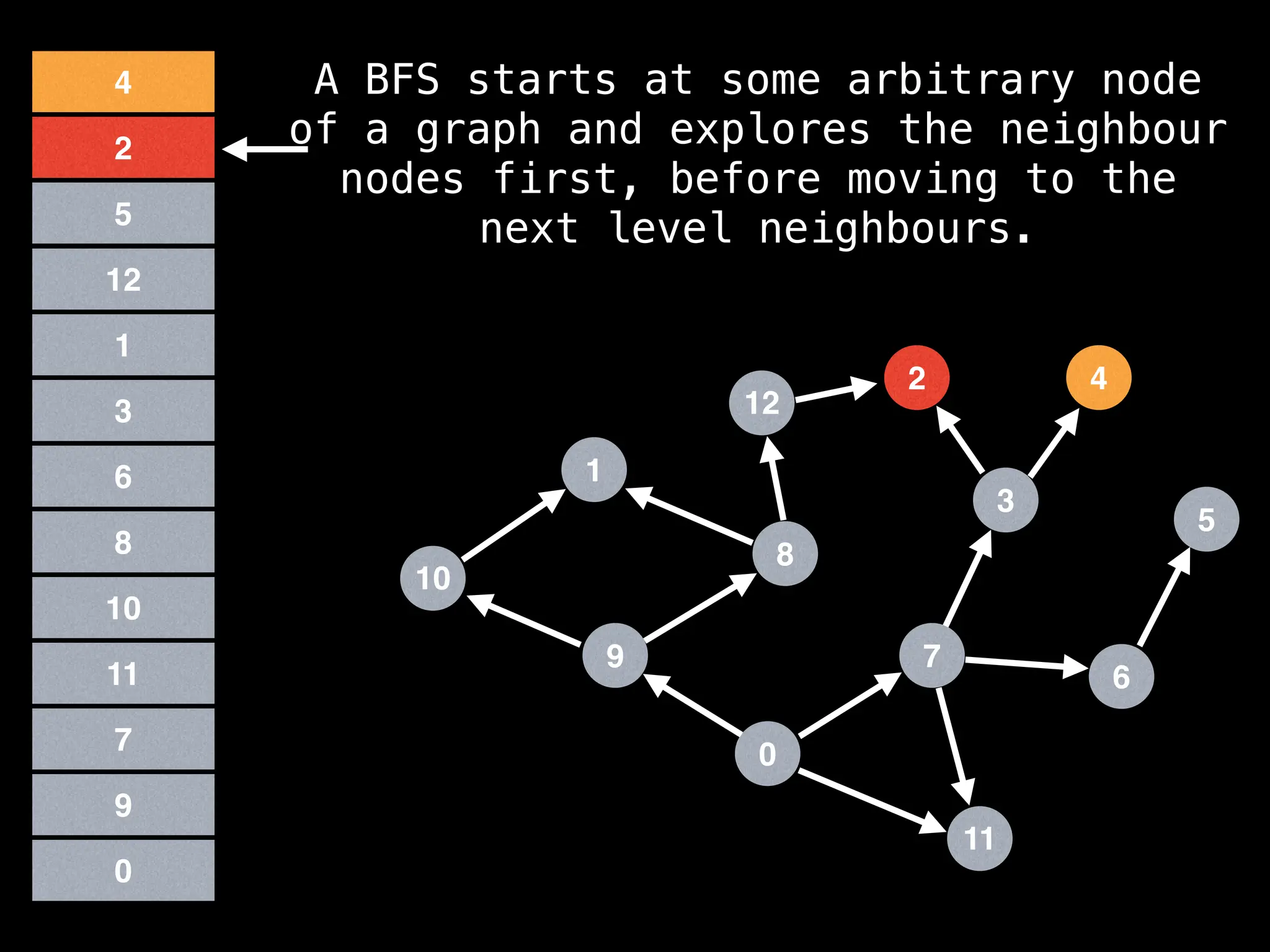
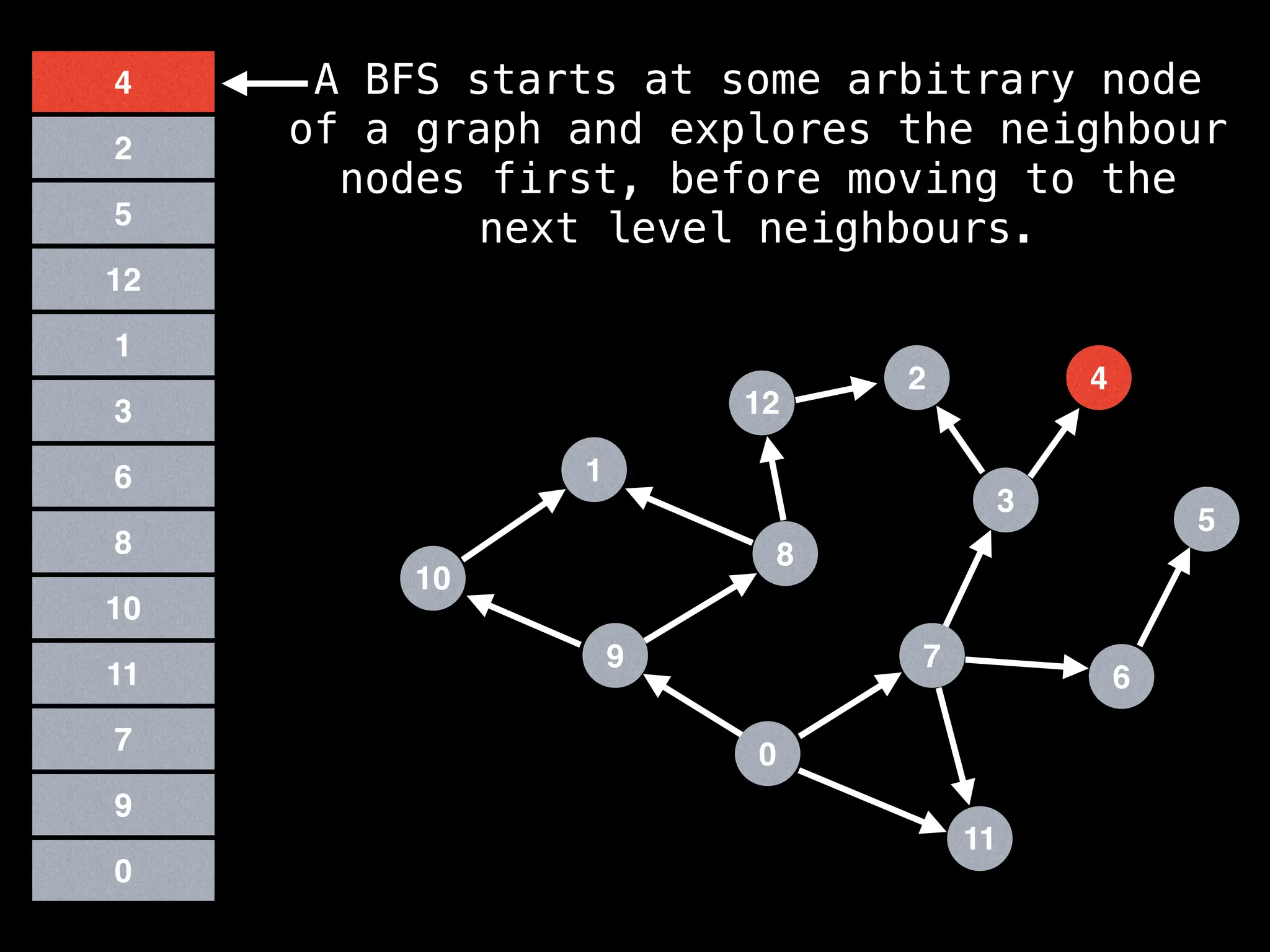
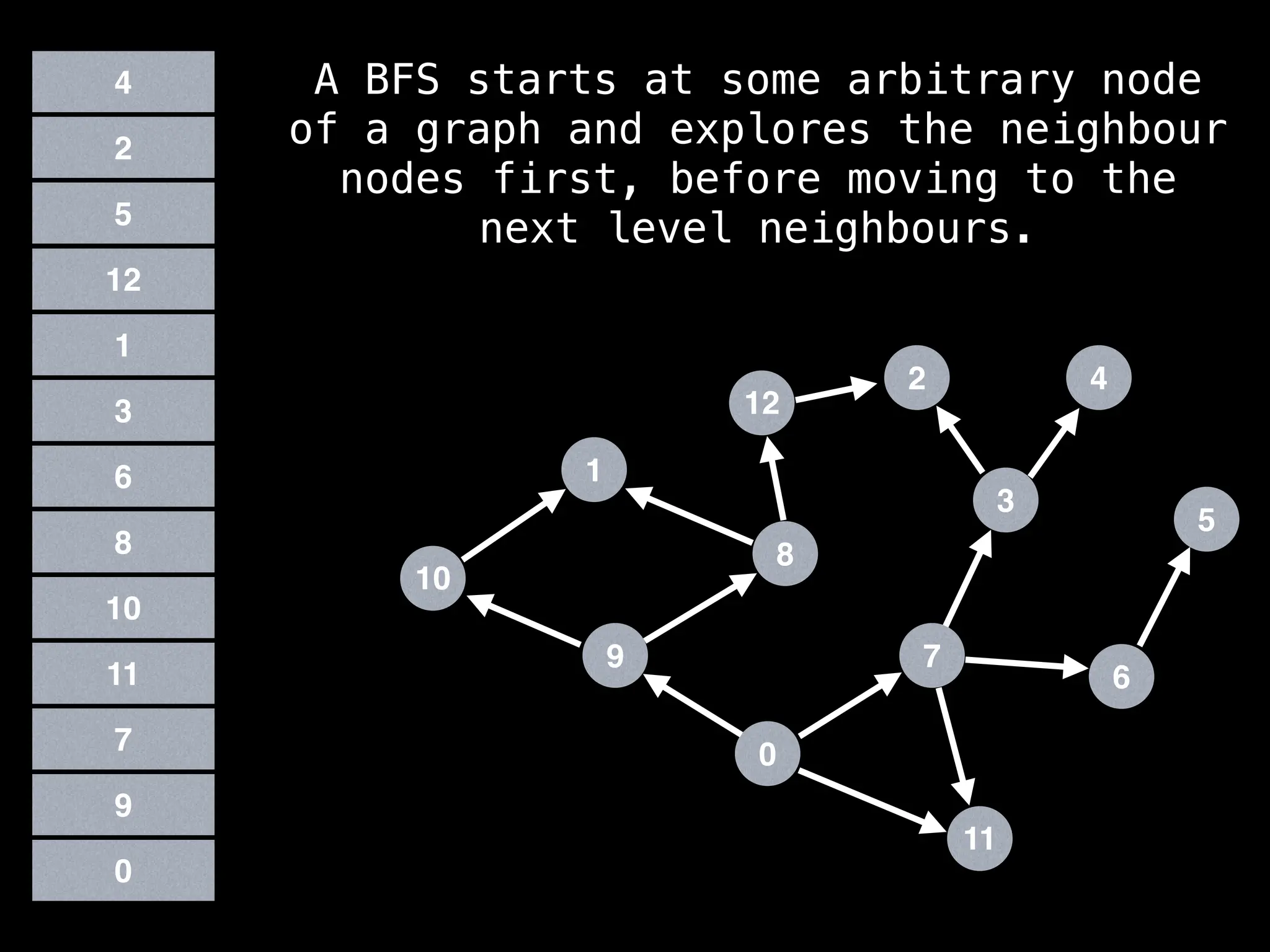
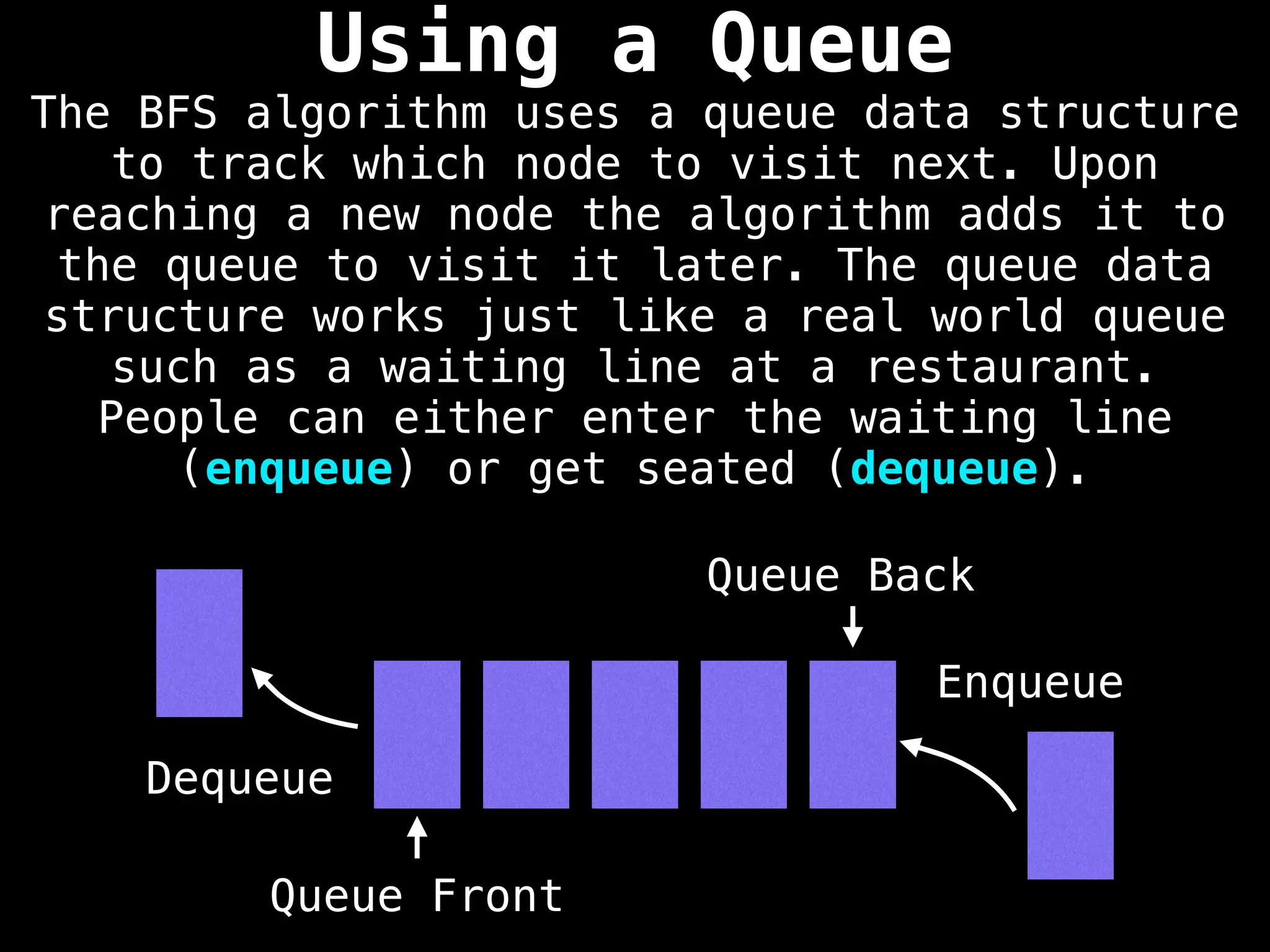
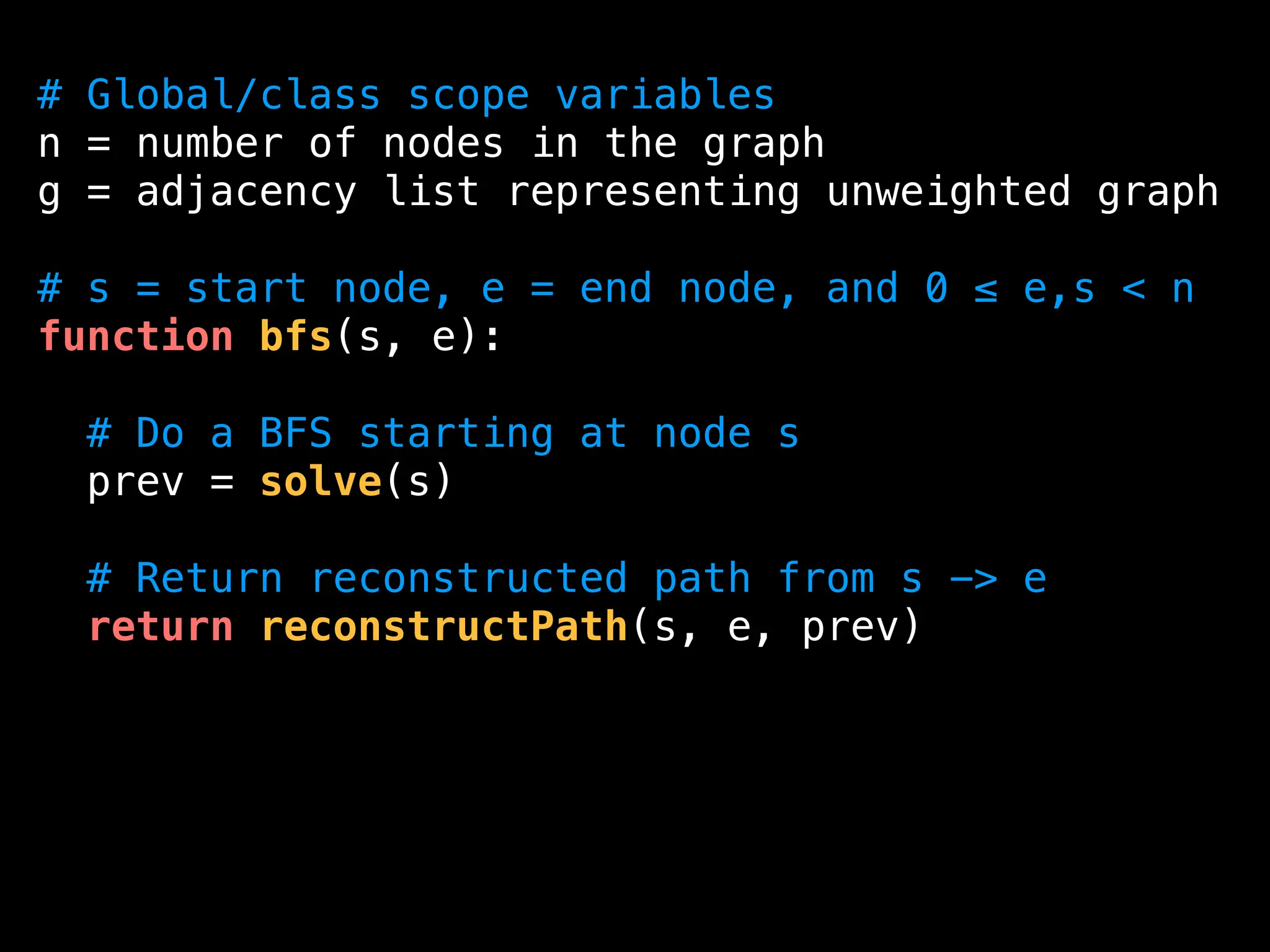
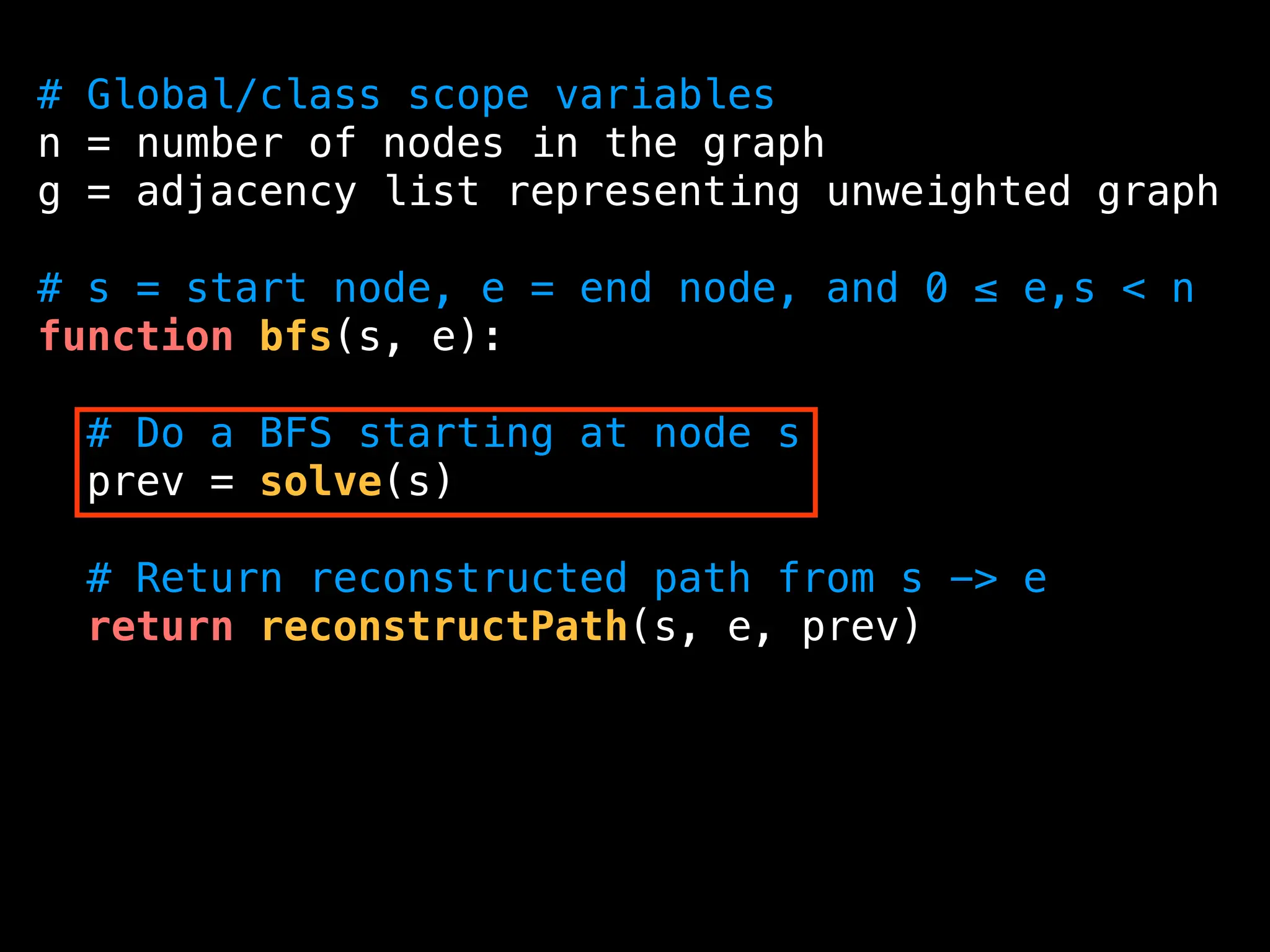
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-208-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-209-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-210-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-211-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-212-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-213-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-214-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-215-2048.jpg)
![function solve(s):
q = queue data structure with enqueue and dequeue
q.enqueue(s)
visited = [false, …, false] # size n
visited[s] = true
prev = [null, …, null] # size n
while !q.isEmpty():
node = q.dequeue()
neighbours = g.get(node)
for(next : neighbours):
if !visited[next]:
q.enqueue(next)
visited[next] = true
prev[next] = node
return prev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-216-2048.jpg)
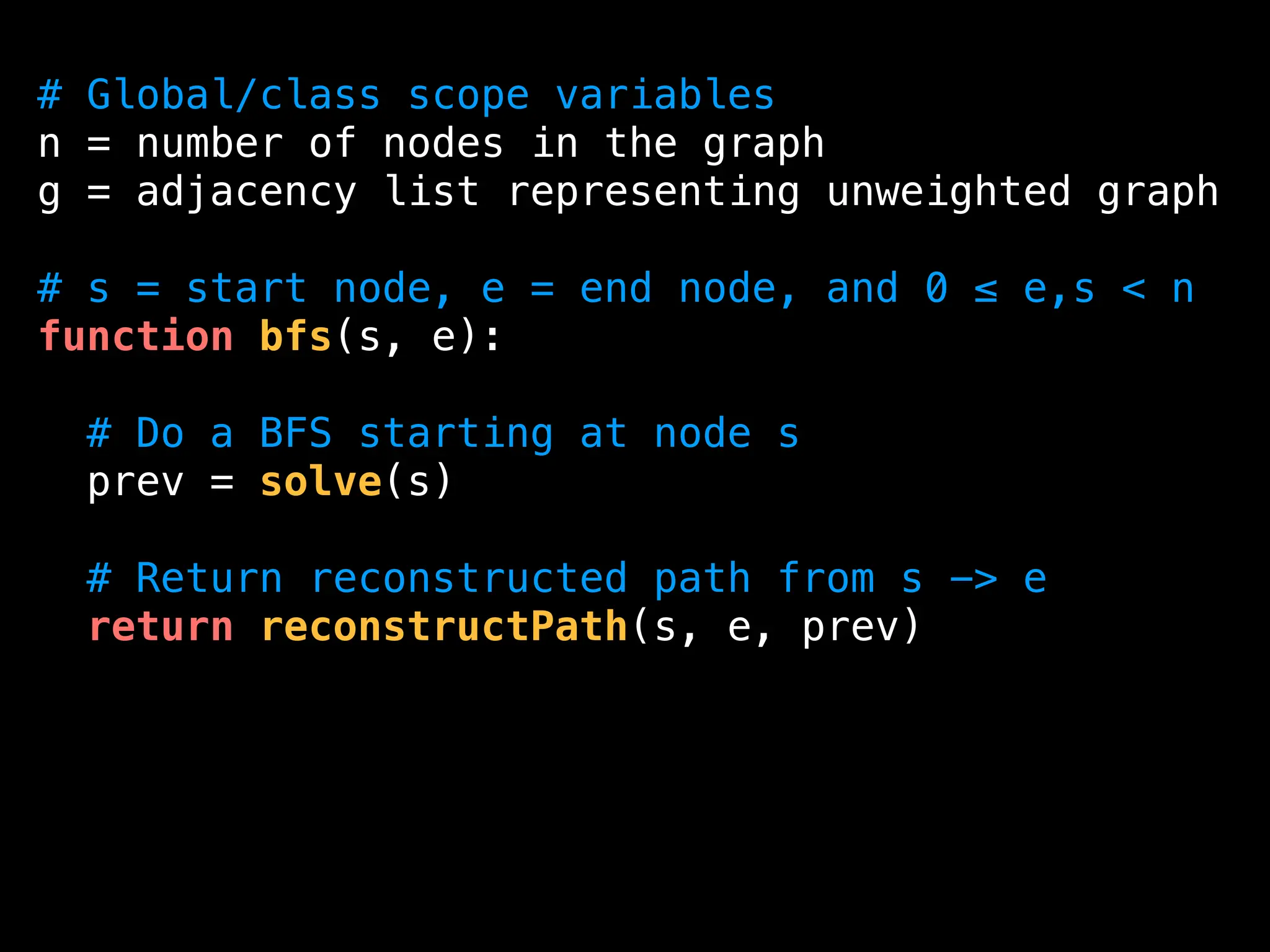
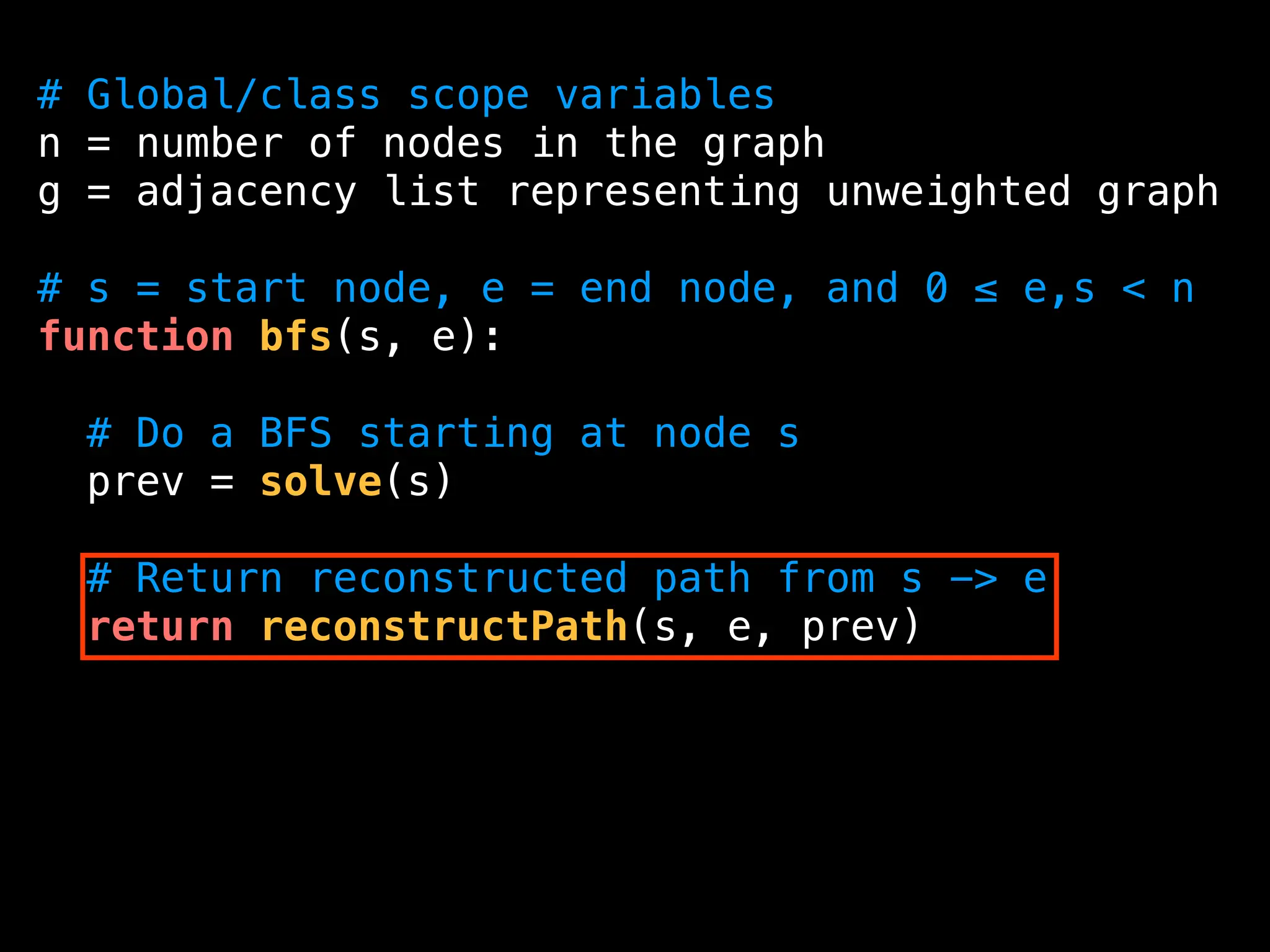
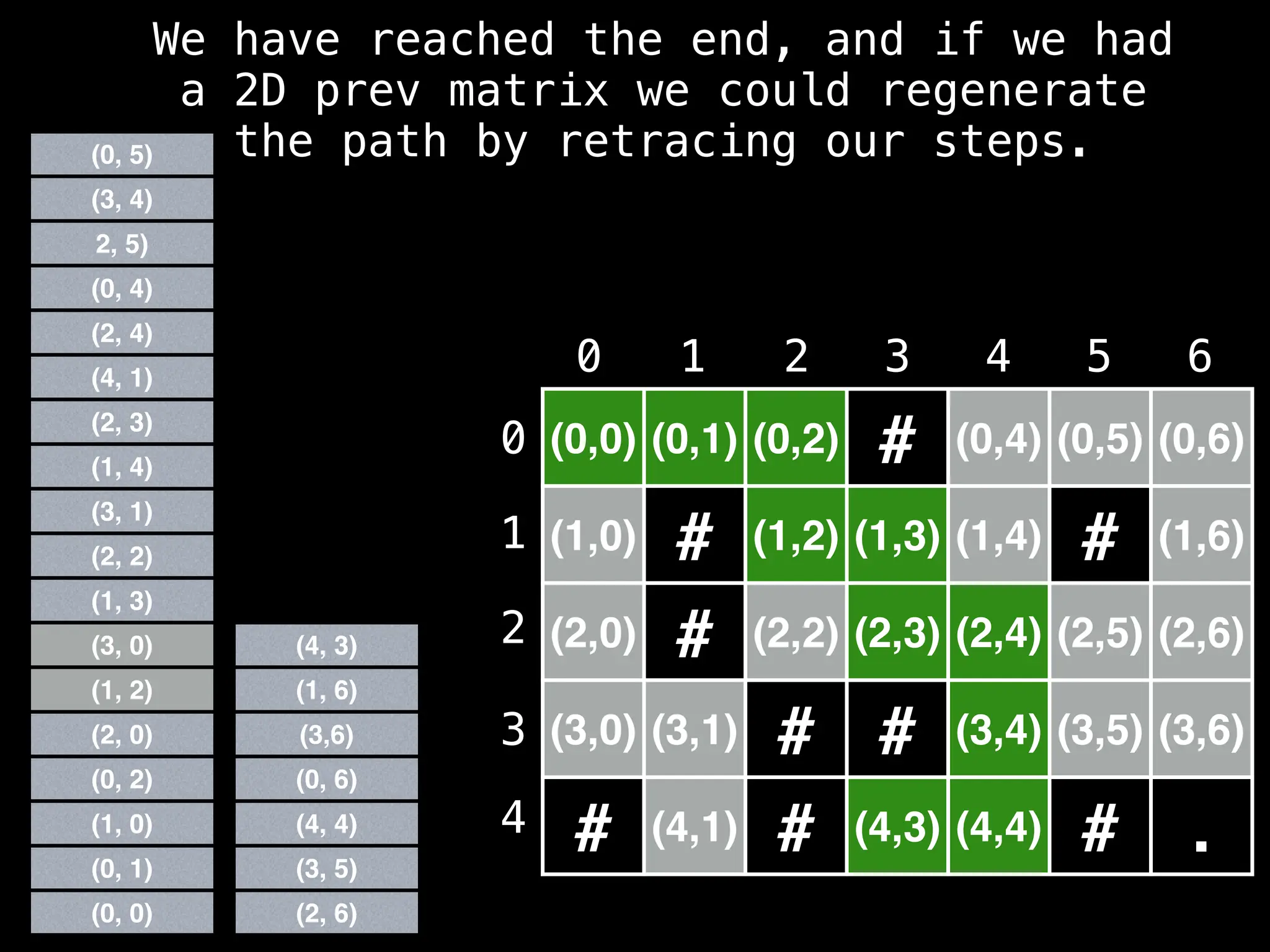
![function reconstructPath(s, e, prev):
# Reconstruct path going backwards from e
path = []
for(at = e; at != null; at = prev[at]):
path.add(at)
path.reverse()
# If s and e are connected return the path
if path[0] == s:
return path
return []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-219-2048.jpg)
![function reconstructPath(s, e, prev):
# Reconstruct path going backwards from e
path = []
for(at = e; at != null; at = prev[at]):
path.add(at)
path.reverse()
# If s and e are connected return the path
if path[0] == s:
return path
return []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-220-2048.jpg)
![function reconstructPath(s, e, prev):
# Reconstruct path going backwards from e
path = []
for(at = e; at != null; at = prev[at]):
path.add(at)
path.reverse()
# If s and e are connected return the path
if path[0] == s:
return path
return []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-221-2048.jpg)
![function reconstructPath(s, e, prev):
# Reconstruct path going backwards from e
path = []
for(at = e; at != null; at = prev[at]):
path.add(at)
path.reverse()
# If s and e are connected return the path
if path[0] == s:
return path
return []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-222-2048.jpg)




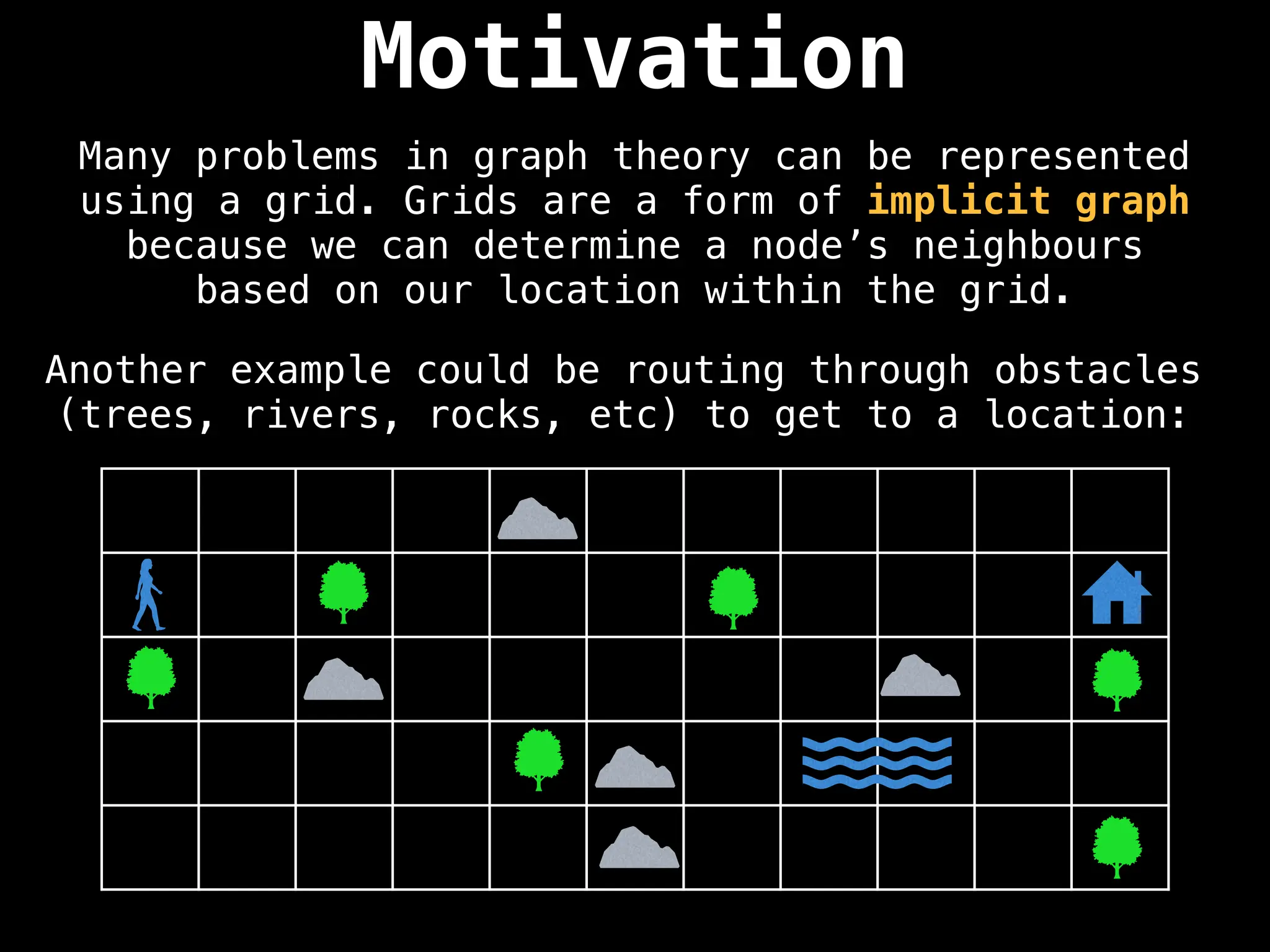
![IMPORTANT: Assume the grid is unweighted and
cells connect left, right, up and down.
0 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
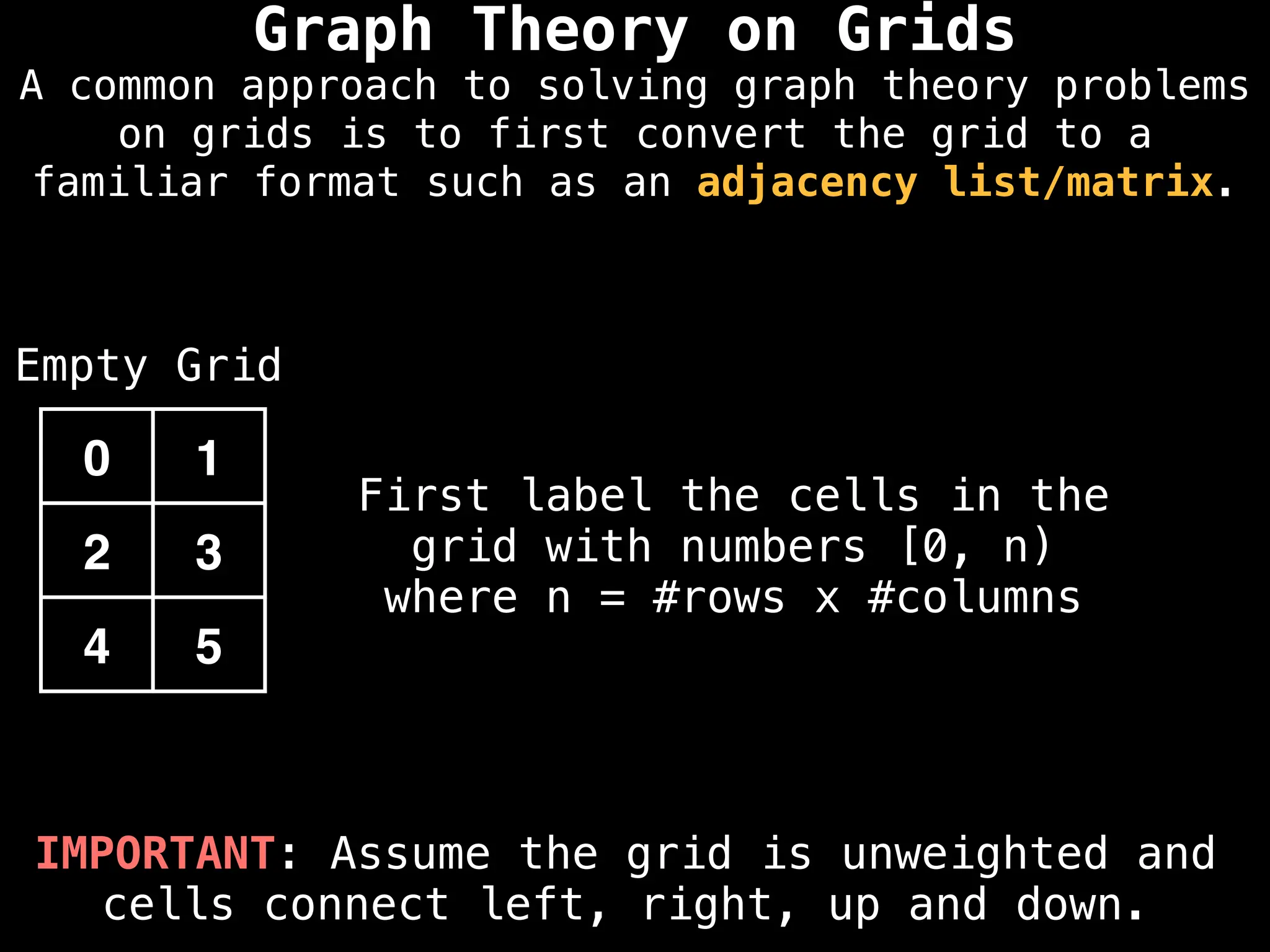
Empty Grid
Graph Theory on Grids
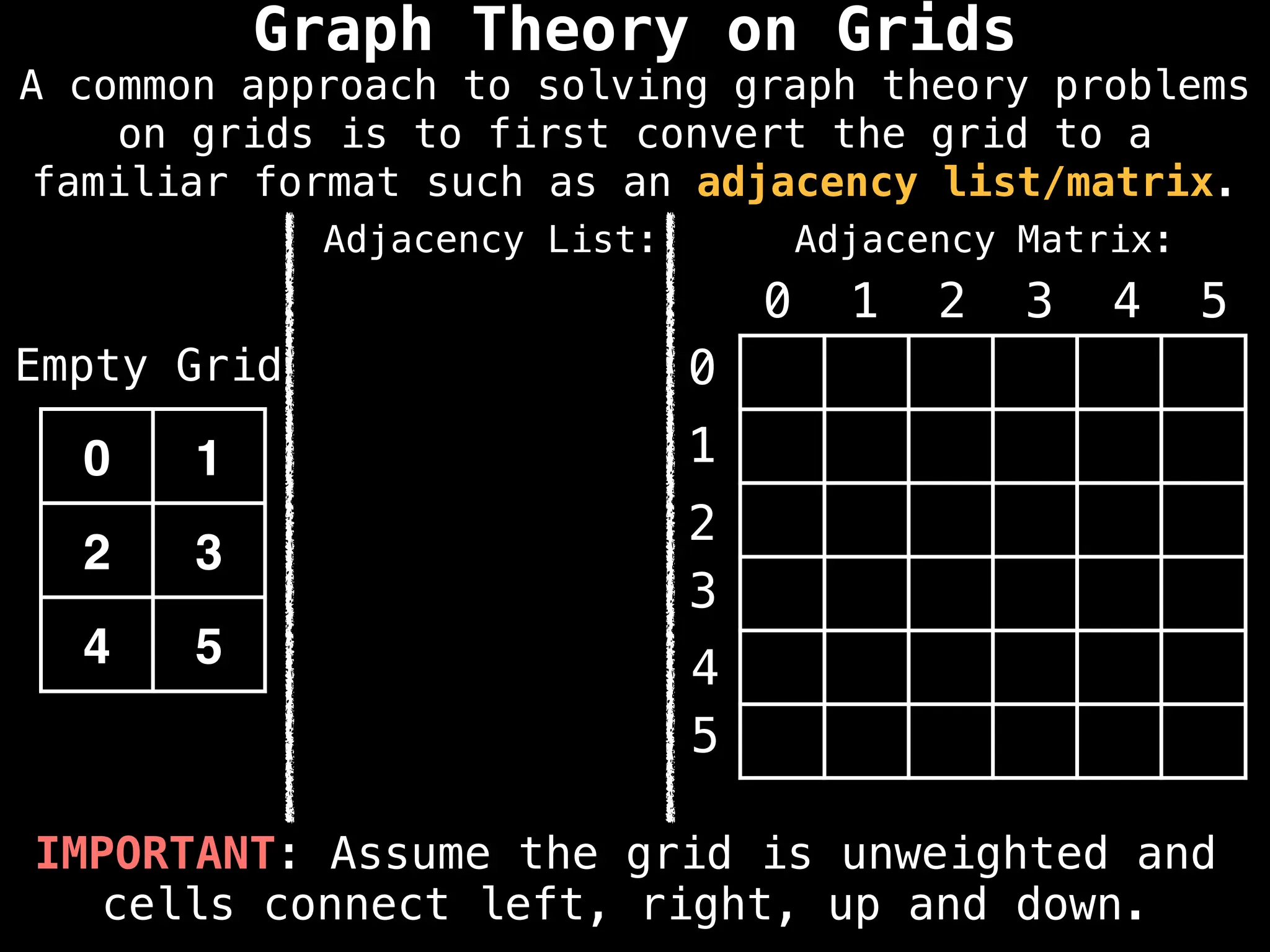
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
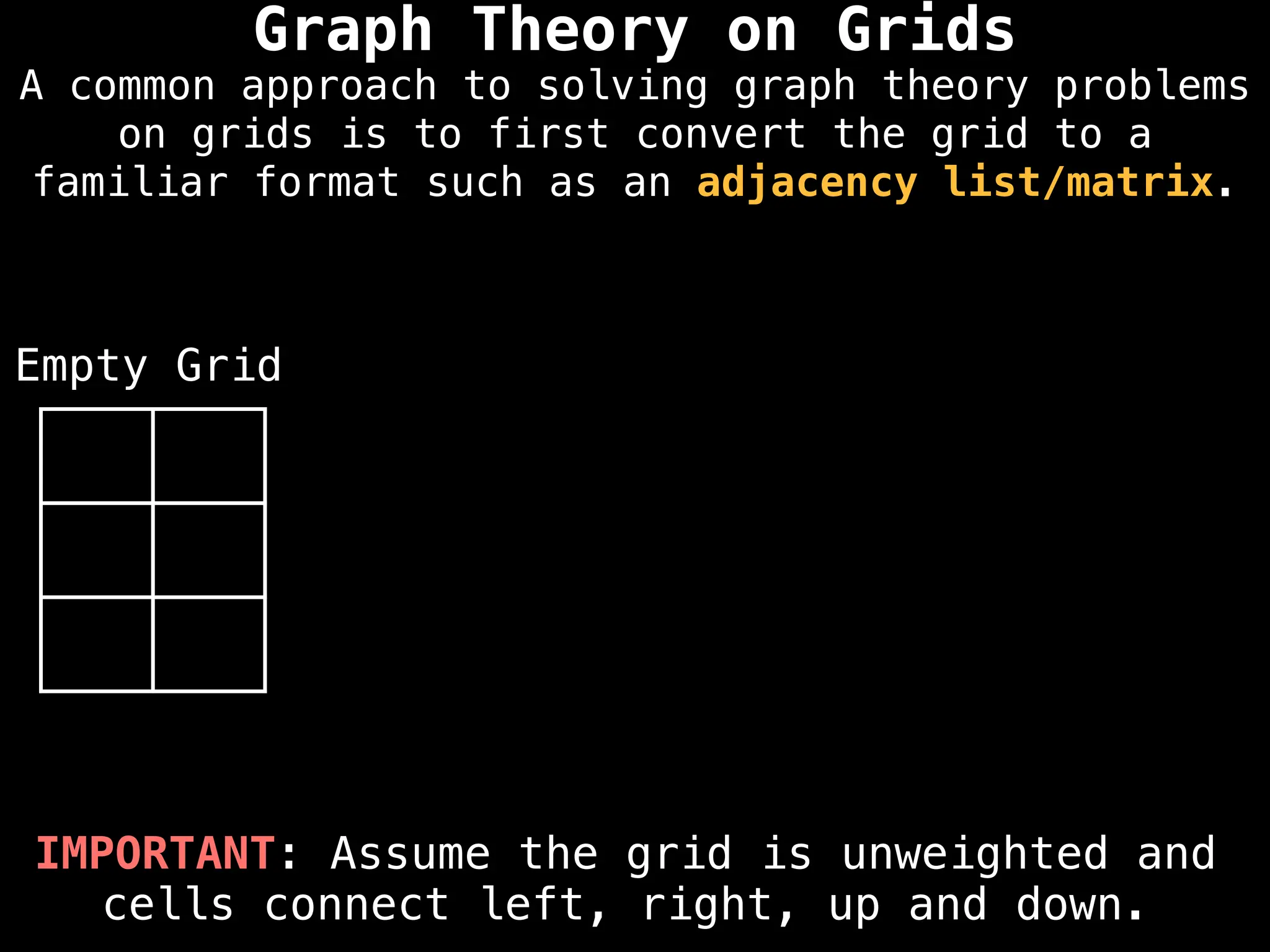
A common approach to solving graph theory problems
on grids is to first convert the grid to a
familiar format such as an adjacency list/matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-234-2048.jpg)
![IMPORTANT: Assume the grid is unweighted and
cells connect left, right, up and down.
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
Empty Grid
Graph Theory on Grids
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
1 -> [0, 3]
A common approach to solving graph theory problems
on grids is to first convert the grid to a
familiar format such as an adjacency list/matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-235-2048.jpg)
![IMPORTANT: Assume the grid is unweighted and
cells connect left, right, up and down.
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
Empty Grid
Graph Theory on Grids
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
1 -> [0, 3]
2 -> [0, 3, 4]
A common approach to solving graph theory problems
on grids is to first convert the grid to a
familiar format such as an adjacency list/matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-236-2048.jpg)
![IMPORTANT: Assume the grid is unweighted and
cells connect left, right, up and down.
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 1
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
Empty Grid
Graph Theory on Grids
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
1 -> [0, 3]
2 -> [0, 3, 4]
3 -> [1, 2, 5]
A common approach to solving graph theory problems
on grids is to first convert the grid to a
familiar format such as an adjacency list/matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-237-2048.jpg)
![IMPORTANT: Assume the grid is unweighted and
cells connect left, right, up and down.
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 1
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
Empty Grid
Graph Theory on Grids
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
1 -> [0, 3]
2 -> [0, 3, 4]
3 -> [1, 2, 5]
4 -> [2, 5]
A common approach to solving graph theory problems
on grids is to first convert the grid to a
familiar format such as an adjacency list/matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-238-2048.jpg)
![IMPORTANT: Assume the grid is unweighted and
cells connect left, right, up and down.
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
Empty Grid
Graph Theory on Grids
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
1 -> [0, 3]
2 -> [0, 3, 4]
3 -> [1, 2, 5]
4 -> [2, 5]
5 -> [3, 4]
A common approach to solving graph theory problems
on grids is to first convert the grid to a
familiar format such as an adjacency list/matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-239-2048.jpg)
![IMPORTANT: Assume the grid is unweighted and
cells connect left, right, up and down.
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
Empty Grid
Graph Theory on Grids
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
1 -> [0, 3]
2 -> [0, 3, 4]
3 -> [1, 2, 5]
4 -> [2, 5]
5 -> [3, 4]
A common approach to solving graph theory problems
on grids is to first convert the grid to a
familiar format such as an adjacency list/matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-240-2048.jpg)

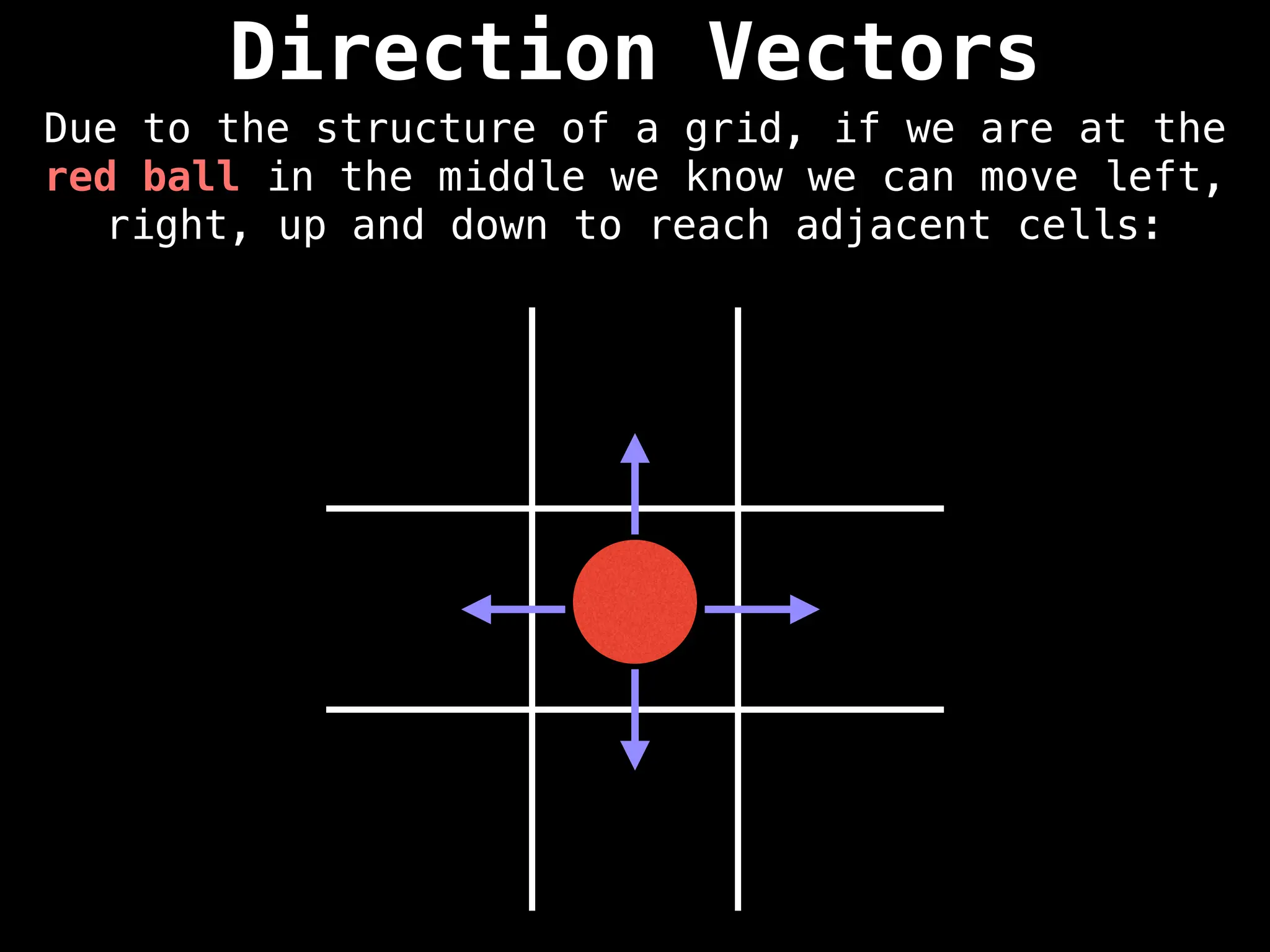
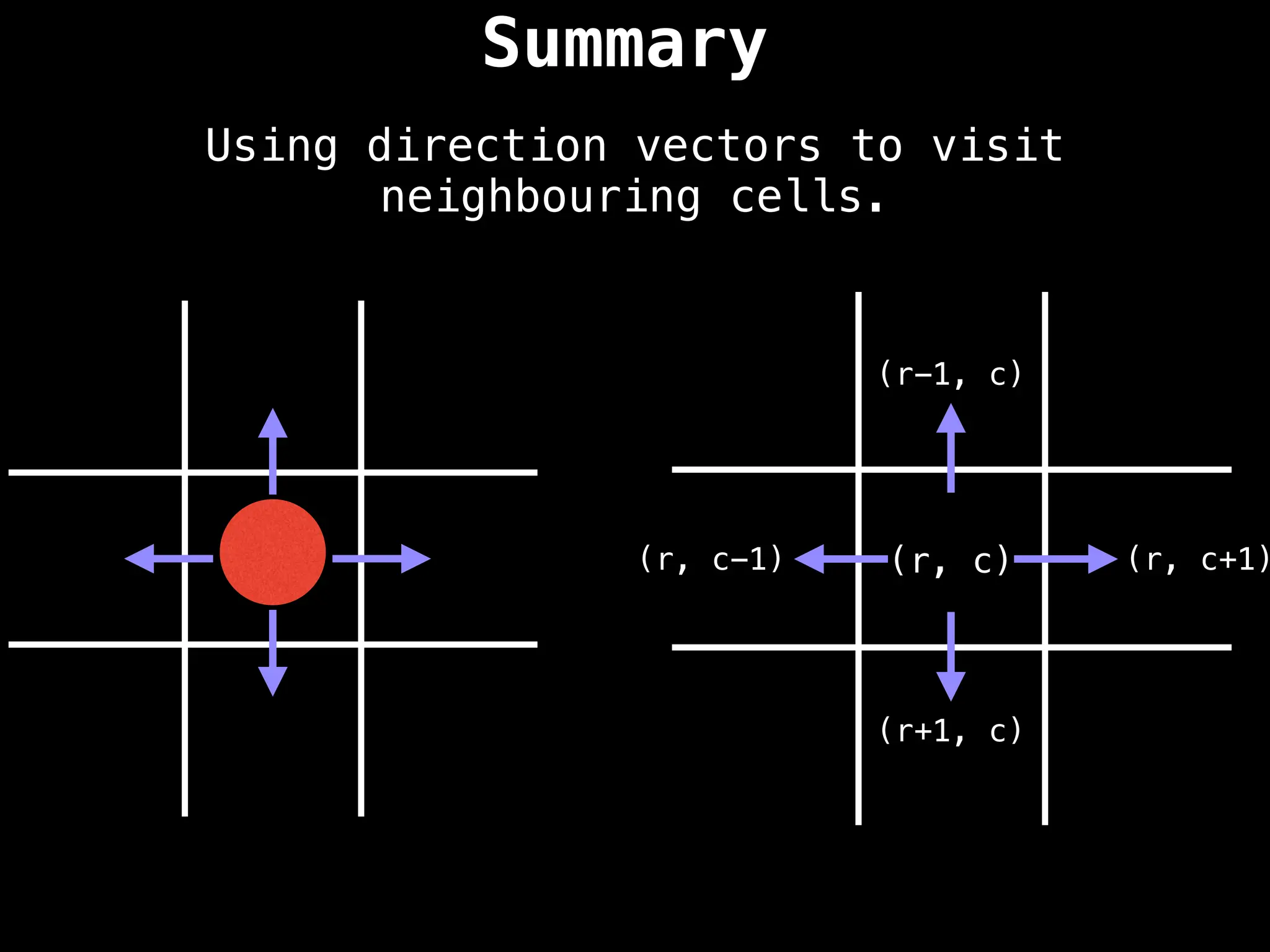
![Direction Vectors
Mathematically, if the red ball is at the row-
column coordinate (r, c) we can add the row
vectors [-1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], and [0, -1] to
reach adjacent cells.
(r, c)
(r-1, c)
(r+1, c)
(r, c+1)
(r, c-1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-243-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
If the problem you are trying to solve allows
moving diagonally then you can also include the
row vectors: [-1, -1], [-1, 1], [1, 1], [1, -1]
(r, c)
(r-1, c)
(r+1, c)
(r, c+1)
(r, c-1)
(r-1, c+1)
(r+1, c+1)
(r+1, c-1)
(r-1, c-1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-244-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
This makes it very easy to access neighbouring
cells from the current row-column position:
# Define the direction vectors for
# north, south, east and west.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip invalid cells. Assume R and
# C for the number of rows and columns
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
#(rr, cc) is a neighbouring cell of (r, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-245-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
This makes it very easy to access neighbouring
cells from the current row-column position:
# Define the direction vectors for
# north, south, east and west.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip invalid cells. Assume R and
# C for the number of rows and columns
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
#(rr, cc) is a neighbouring cell of (r, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-246-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
This makes it very easy to access neighbouring
cells from the current row-column position:
# Define the direction vectors for
# north, south, east and west.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip invalid cells. Assume R and
# C for the number of rows and columns
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
#(rr, cc) is a neighbouring cell of (r, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-247-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
This makes it very easy to access neighbouring
cells from the current row-column position:
# Define the direction vectors for
# north, south, east and west.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip invalid cells. Assume R and
# C for the number of rows and columns
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
#(rr, cc) is a neighbouring cell of (r, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-248-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
This makes it very easy to access neighbouring
cells from the current row-column position:
# Define the direction vectors for
# north, south, east and west.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip invalid cells. Assume R and
# C for the number of rows and columns
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
#(rr, cc) is a neighbouring cell of (r, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-249-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
This makes it very easy to access neighbouring
cells from the current row-column position:
# Define the direction vectors for
# north, south, east and west.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip invalid cells. Assume R and
# C for the number of rows and columns
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
#(rr, cc) is a neighbouring cell of (r, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-250-2048.jpg)
![Direction Vectors
This makes it very easy to access neighbouring
cells from the current row-column position:
# Define the direction vectors for
# north, south, east and west.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip invalid cells. Assume R and
# C for the number of rows and columns
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
#(rr, cc) is a neighbouring cell of (r, c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-251-2048.jpg)



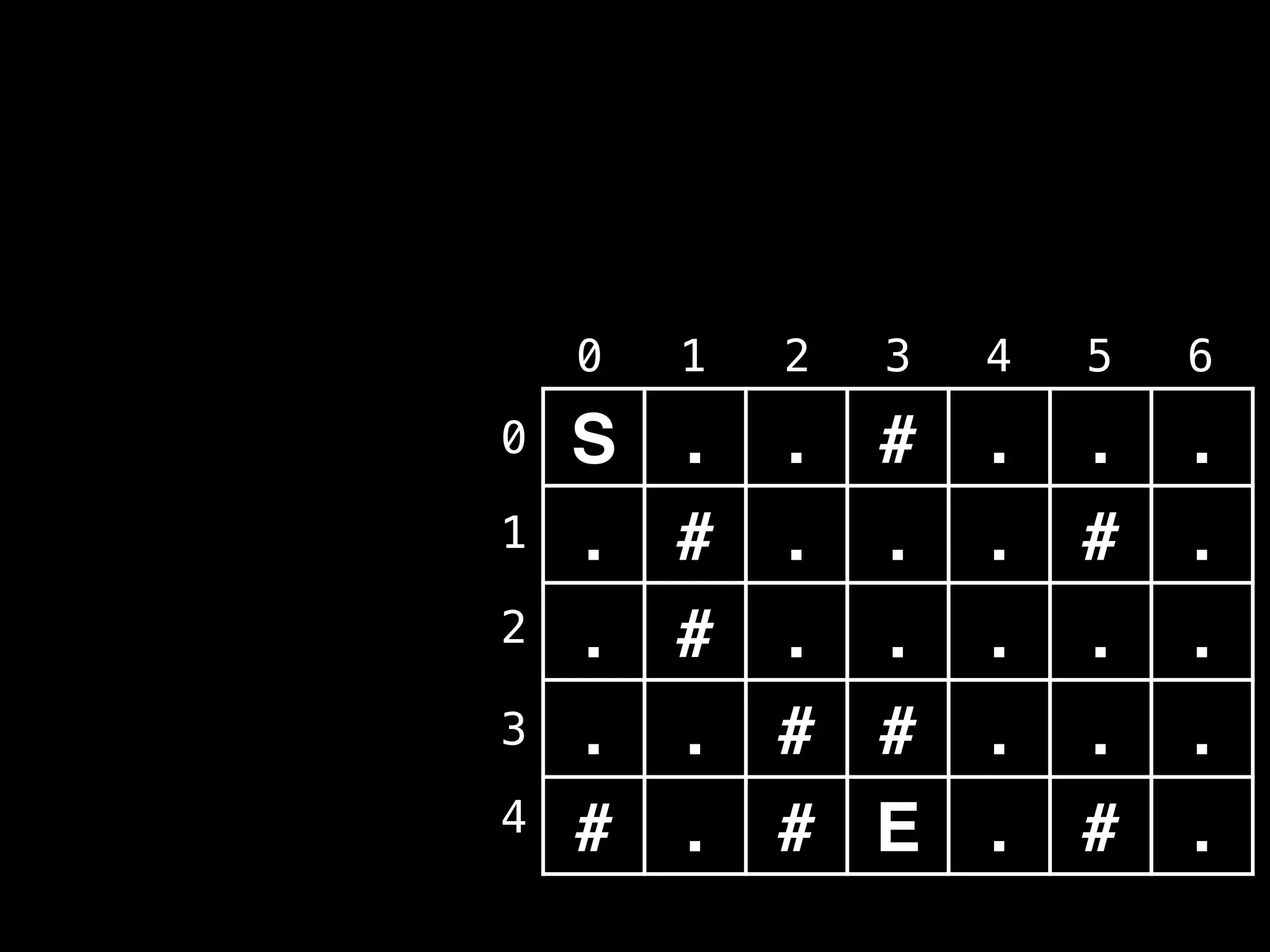

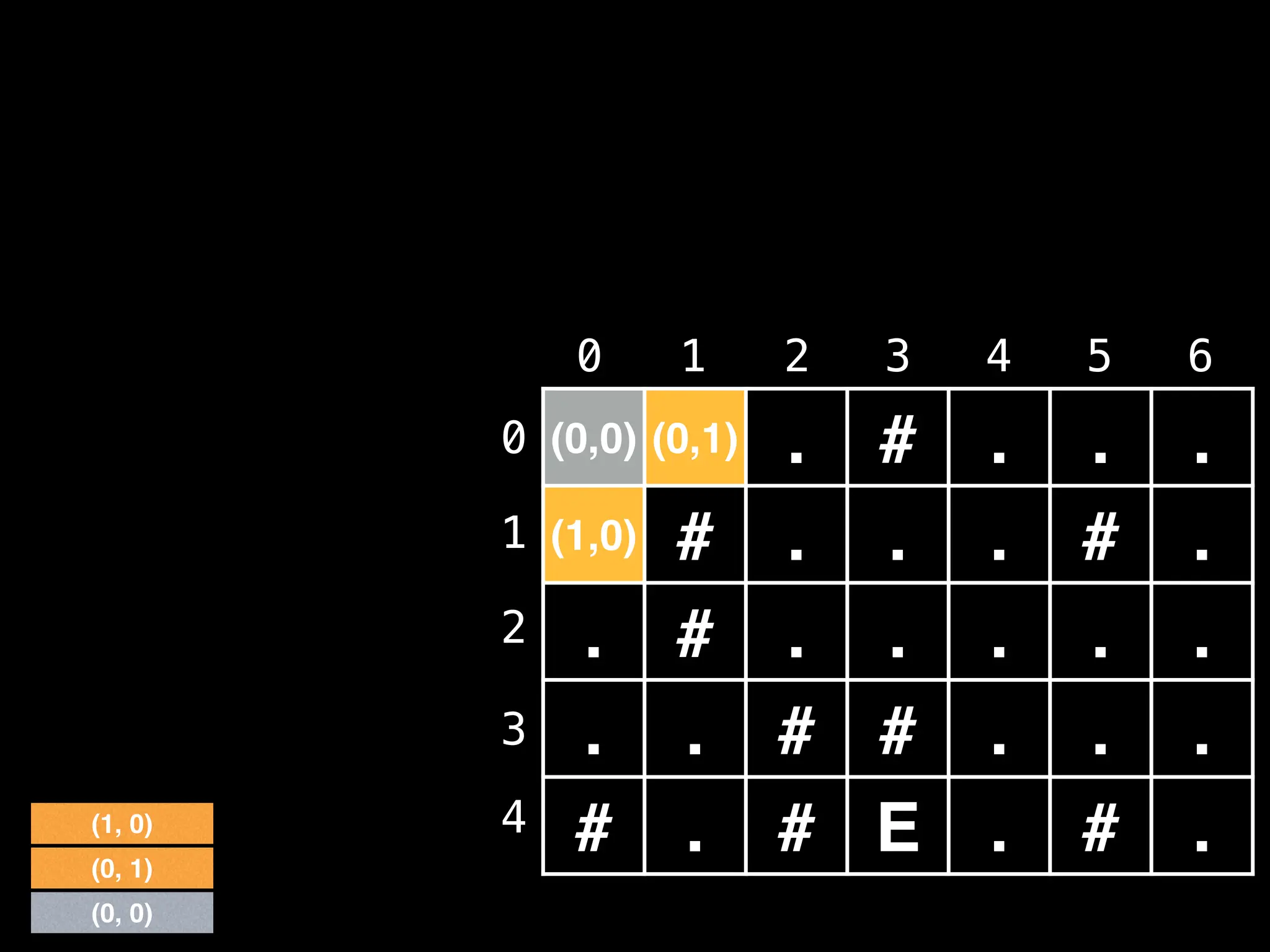
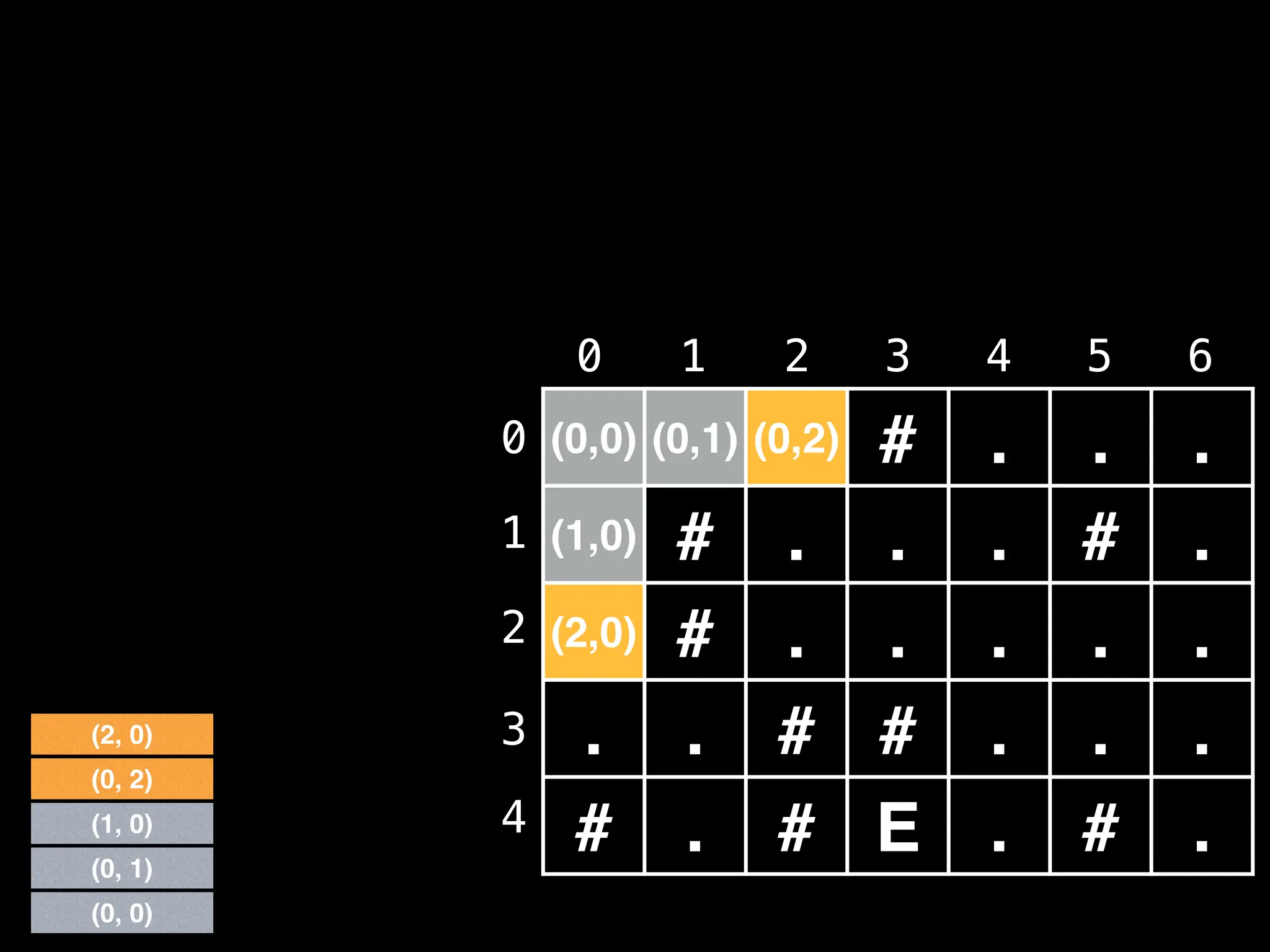
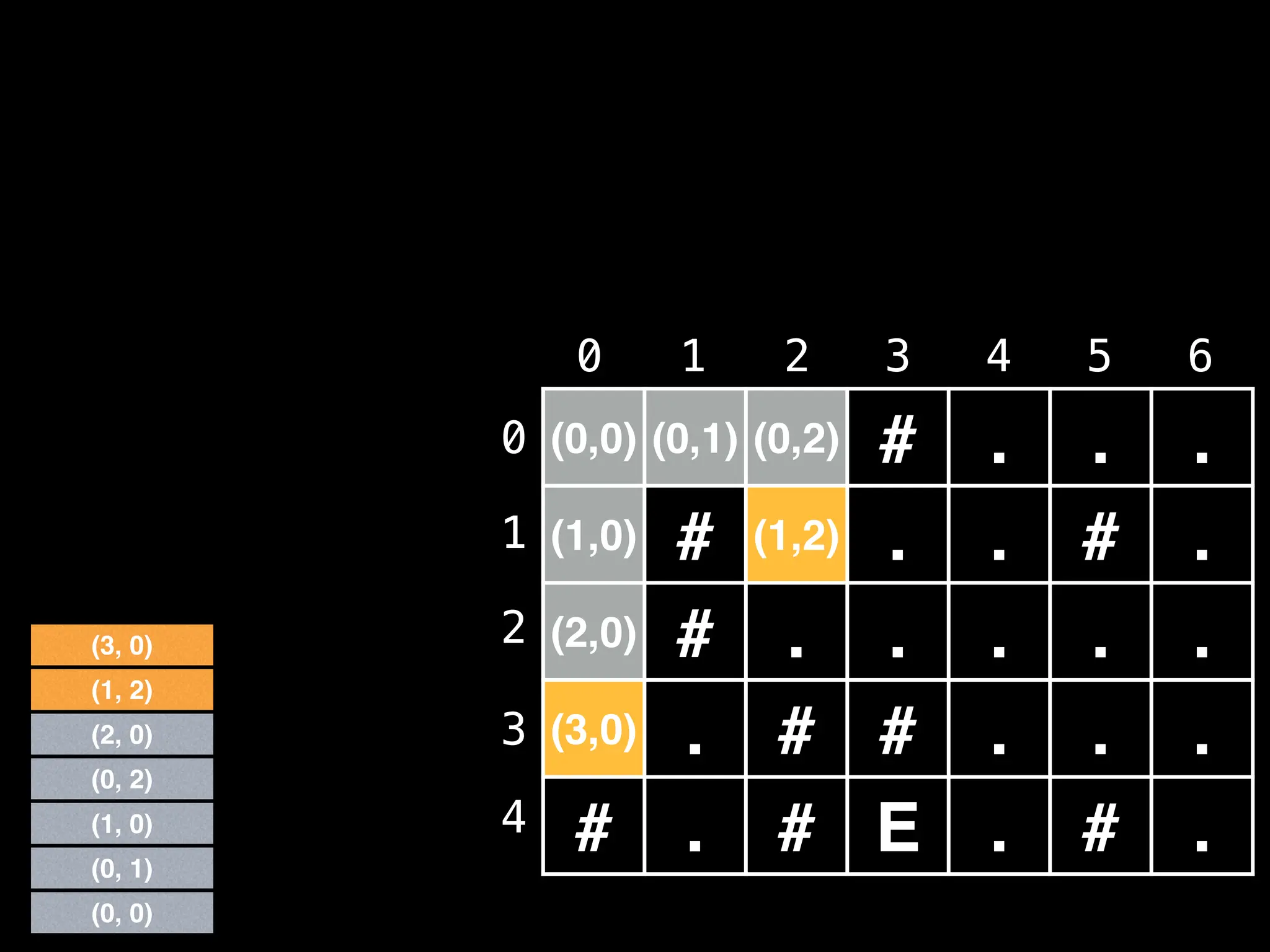
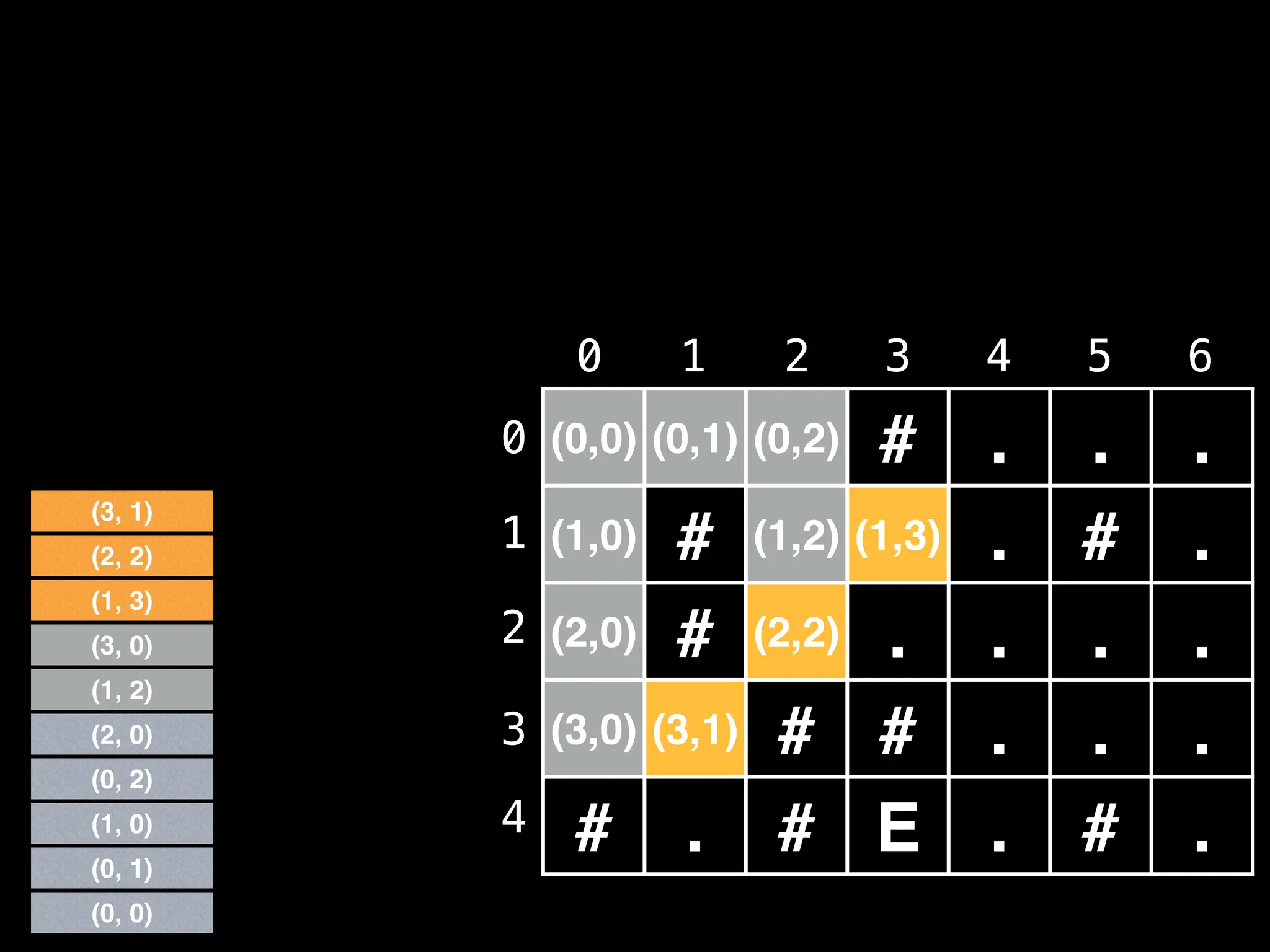
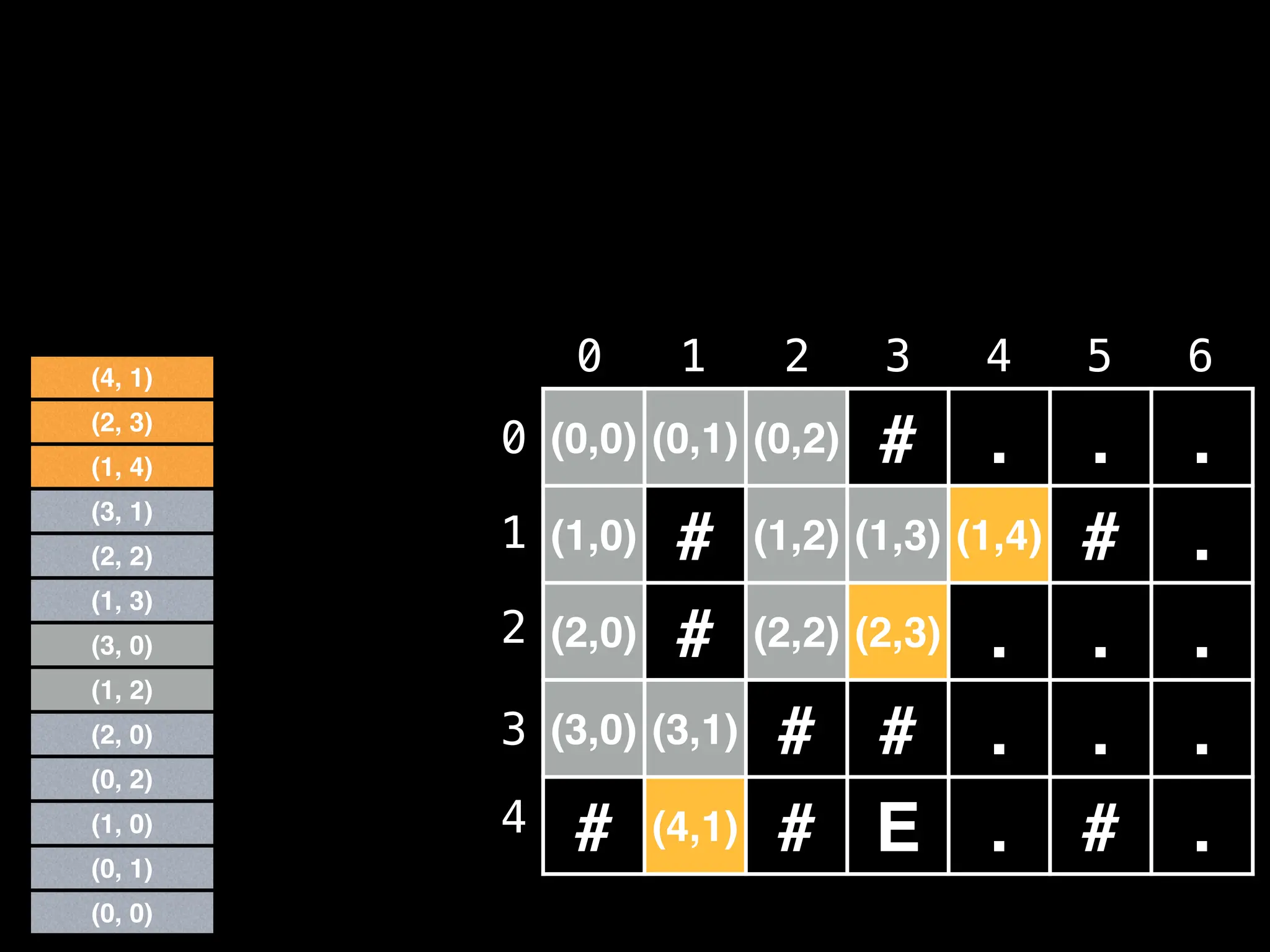
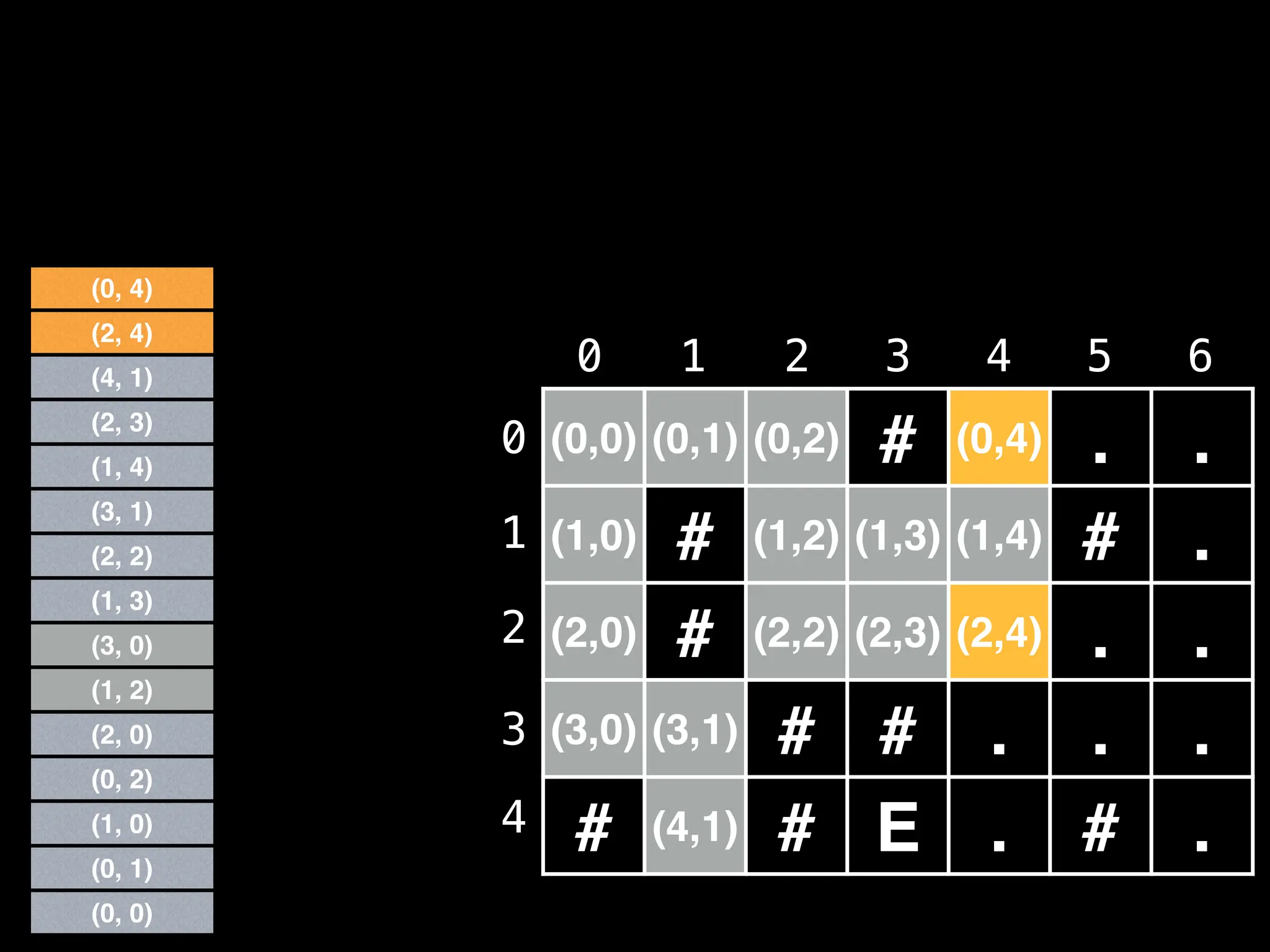
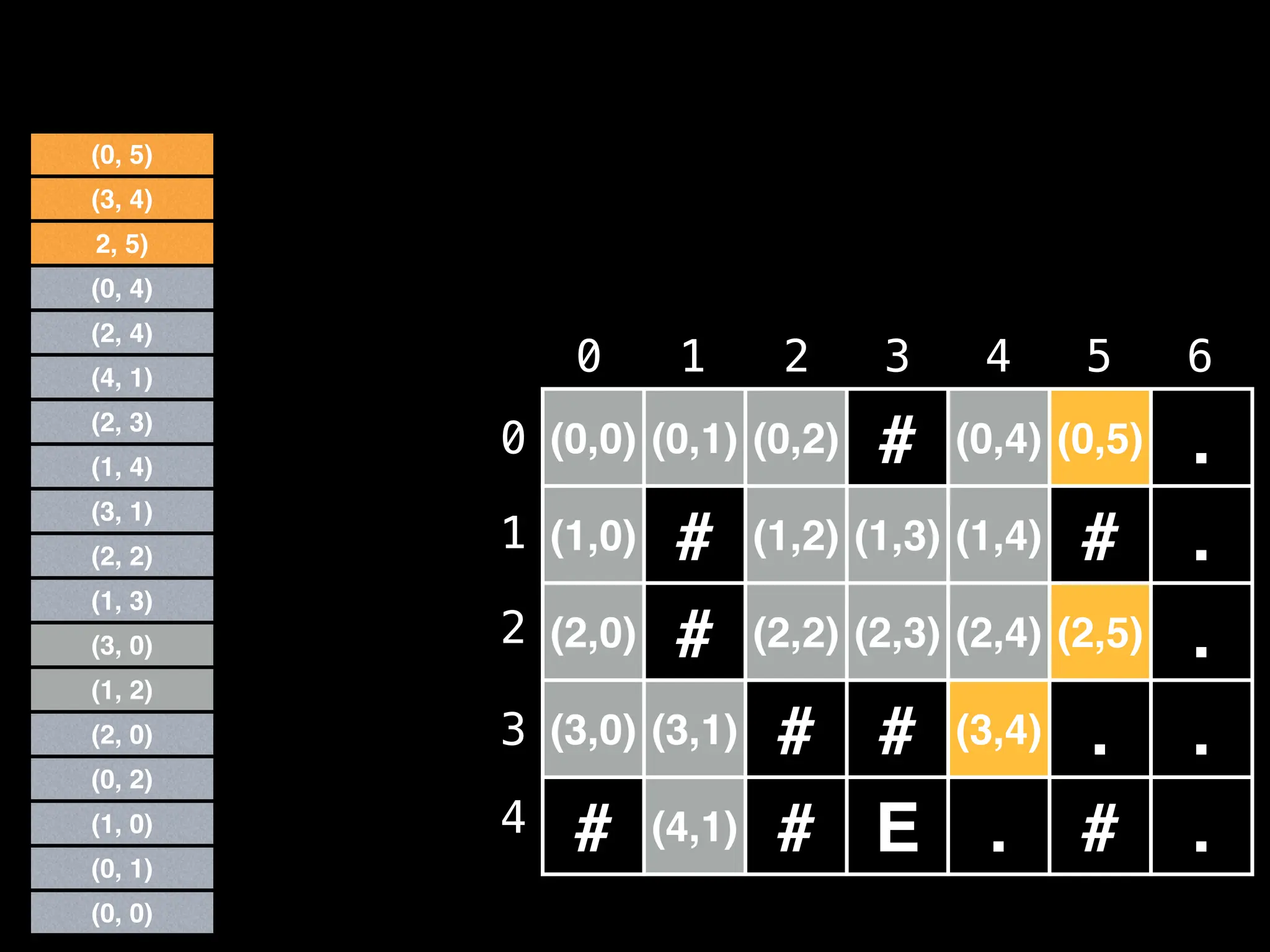
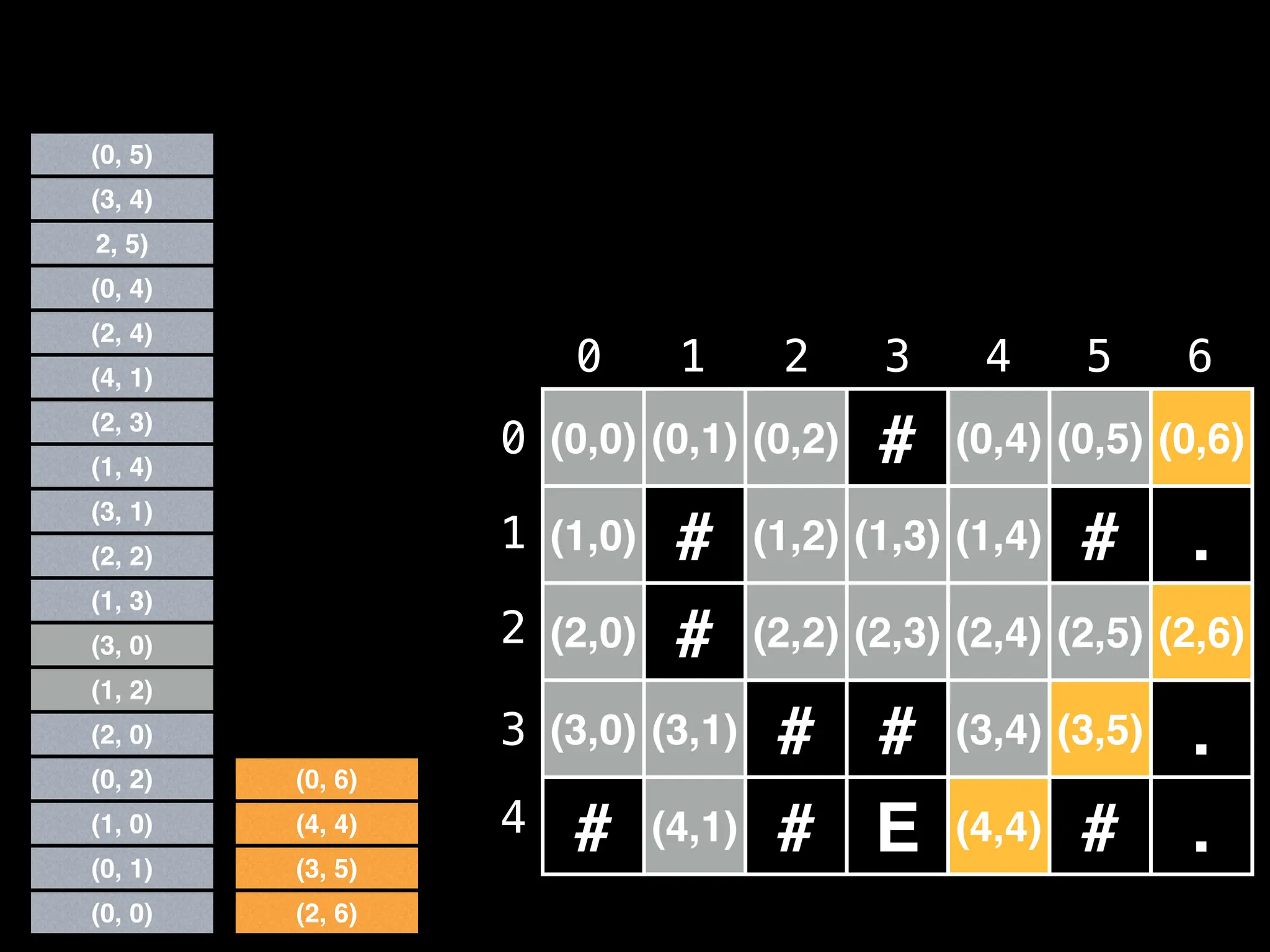
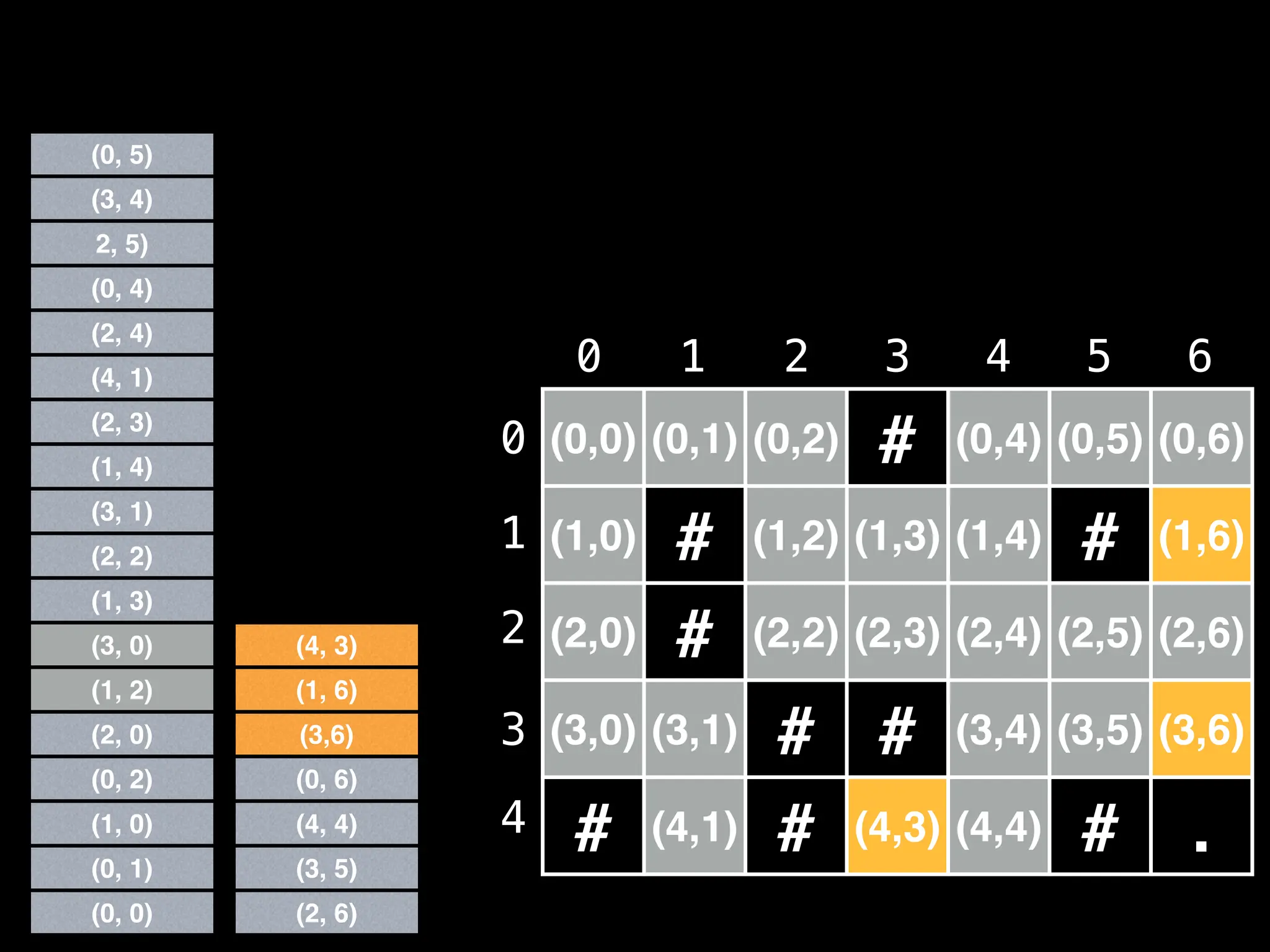

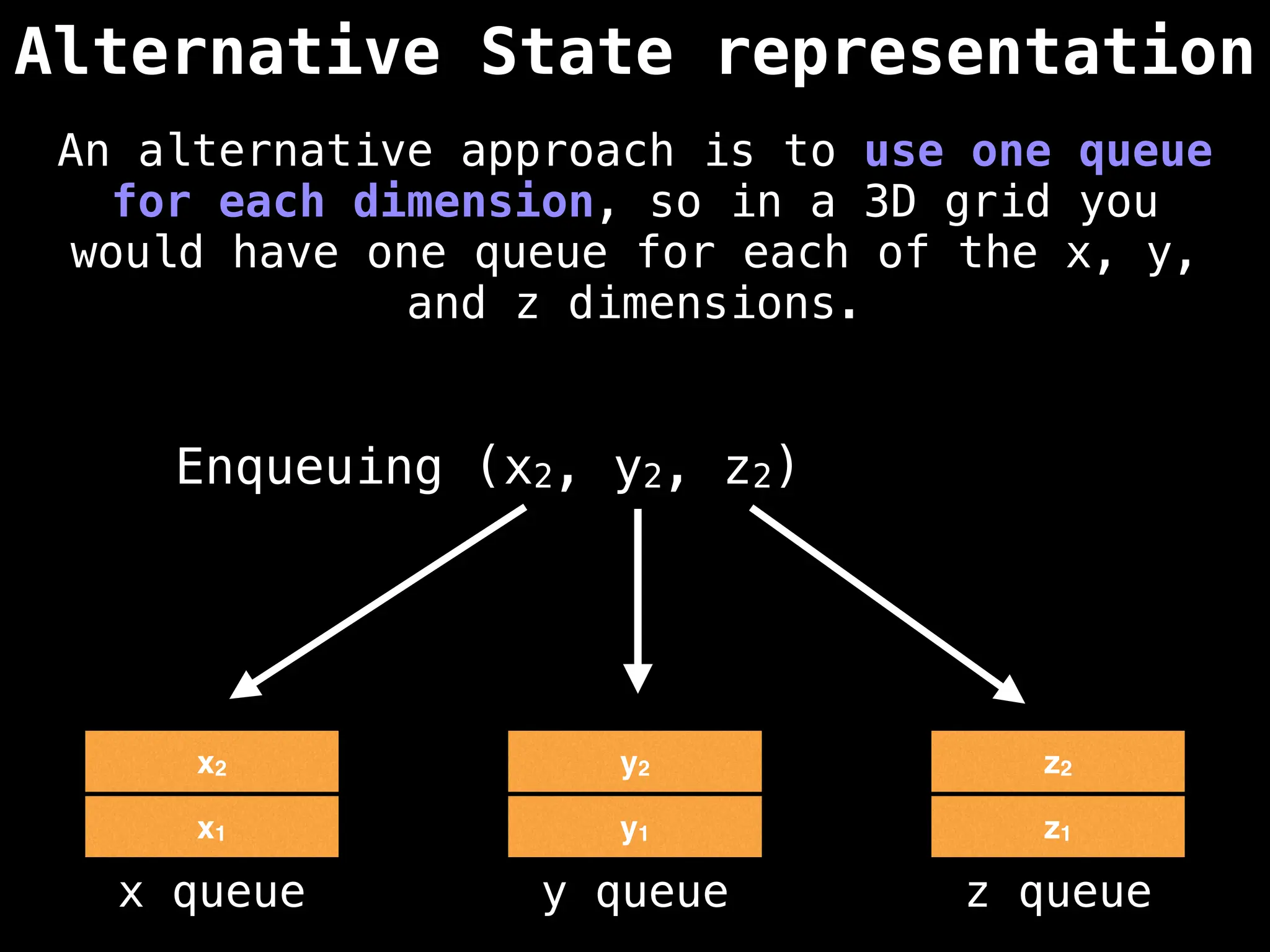
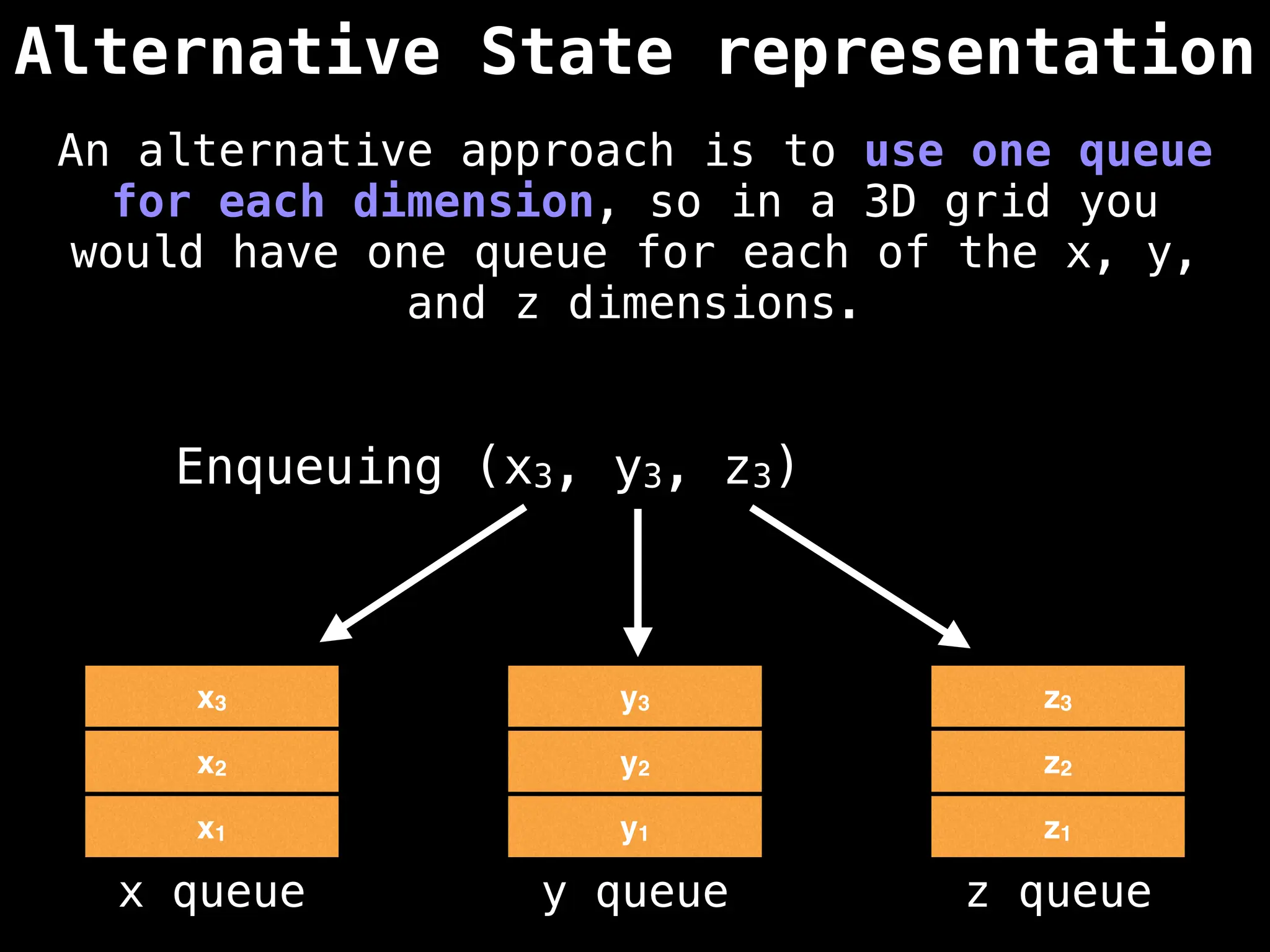
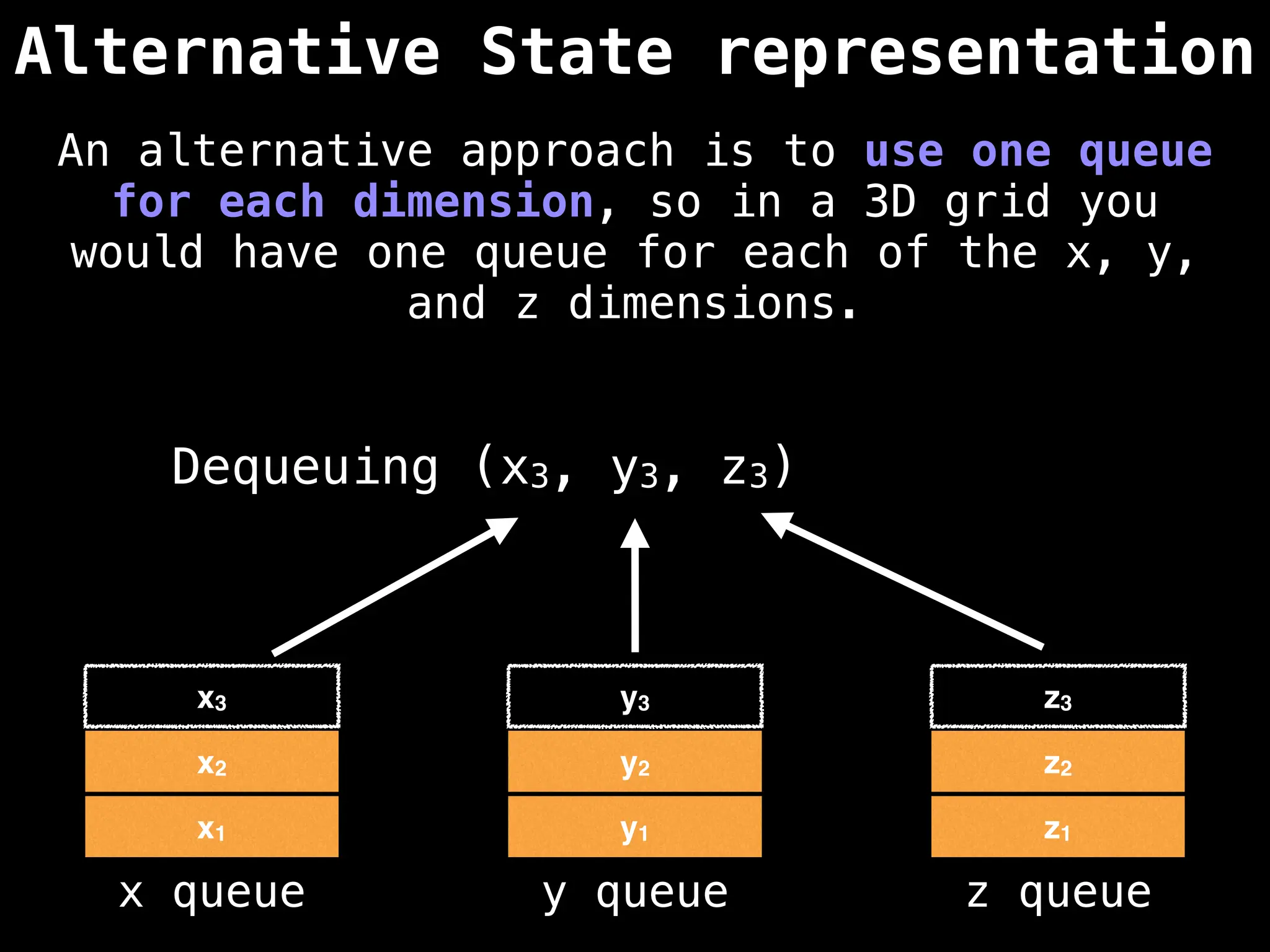
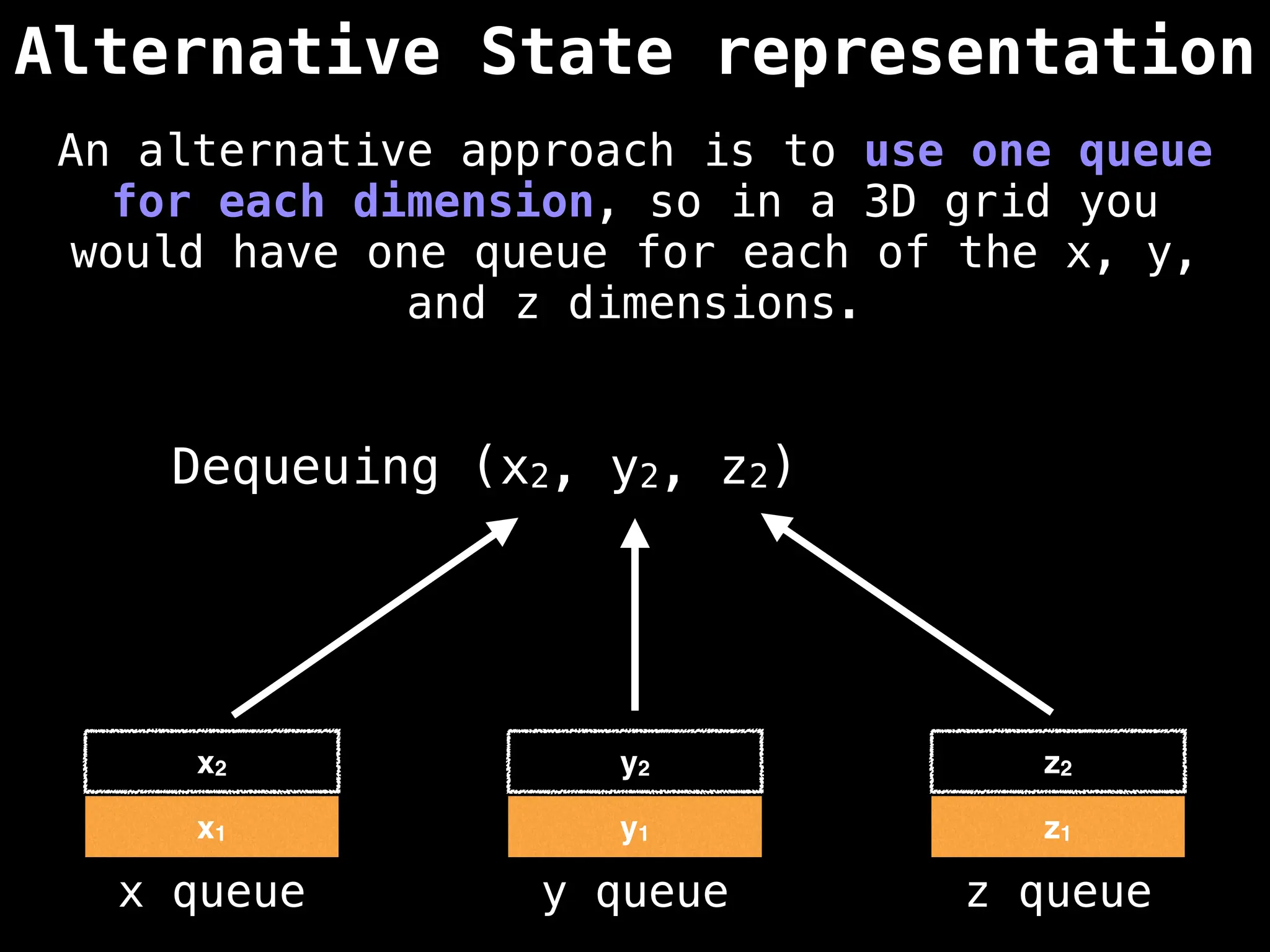

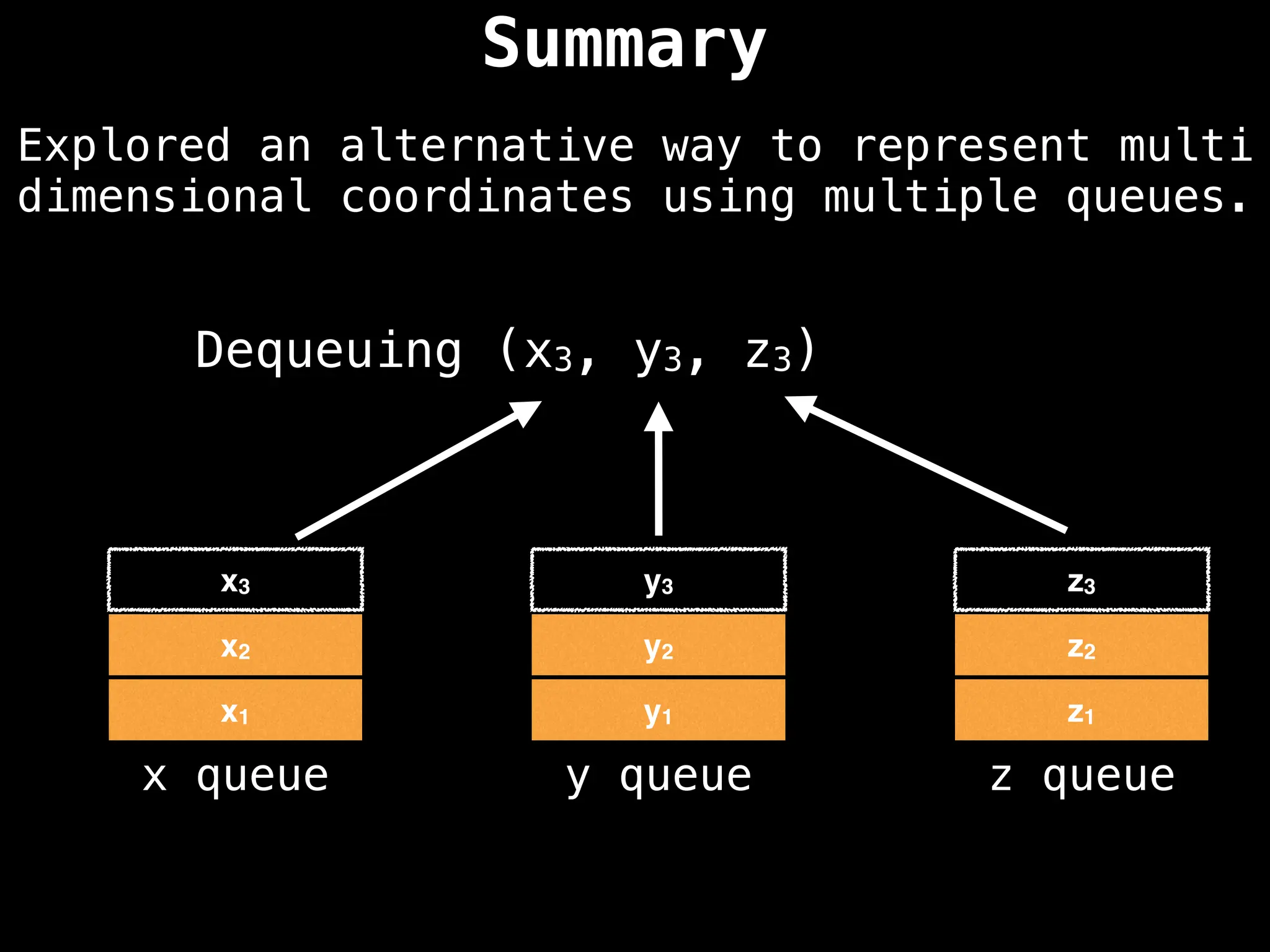
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-275-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-276-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-277-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-278-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-279-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-280-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-281-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
R, C = … # R = number of rows, C = number of columns
m = … # Input character matrix of size R x C
sr, sc = … # ’S’ symbol row and column values
rq, cq = … # Empty Row Queue (RQ) and Column Queue (CQ)
# Variables used to track the number of steps taken.
move_count = 0
nodes_left_in_layer = 1
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
# Variable used to track whether the ‘E’ character
# ever gets reached during the BFS.
reached_end = false
# R x C matrix of false values used to track whether
# the node at position (i, j) has been visited.
visited = …
# North, south, east, west direction vectors.
dr = [-1, +1, 0, 0]
dc = [ 0, 0, +1, -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-282-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-283-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-284-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-285-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-286-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-287-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-288-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-289-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-290-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-291-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-292-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-293-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-294-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-295-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-296-2048.jpg)
![function explore_neighbours(r, c):
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++):
rr = r + dr[i]
cc = c + dc[i]
# Skip out of bounds locations
if rr < 0 or cc < 0: continue
if rr >= R or cc >= C: continue
# Skip visited locations or blocked cells
if visited[rr][cc]: continue
if m[rr][cc] == ‘#’: continue
rq.enqueue(rr)
cq.enqueue(cc)
visited[rr][cc] = true
nodes_in_next_layer++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-297-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-298-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-299-2048.jpg)
![function solve():
rq.enqueue(sr)
cq.enqueue(sc)
visited[sr][sc] = true
while rq.size() > 0: # or cq.size() > 0
r = rq.dequeue()
c = cq.dequeue()
if m[r][c] == ‘E’:
reached_end = true
break
explore_neighbours(r, c)
nodes_left_in_layer—-
if nodes_left_in_layer == 0:
nodes_left_in_layer = nodes_in_next_layer
nodes_in_next_layer = 0
move_count++
if reached_end:
return move_count
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-300-2048.jpg)
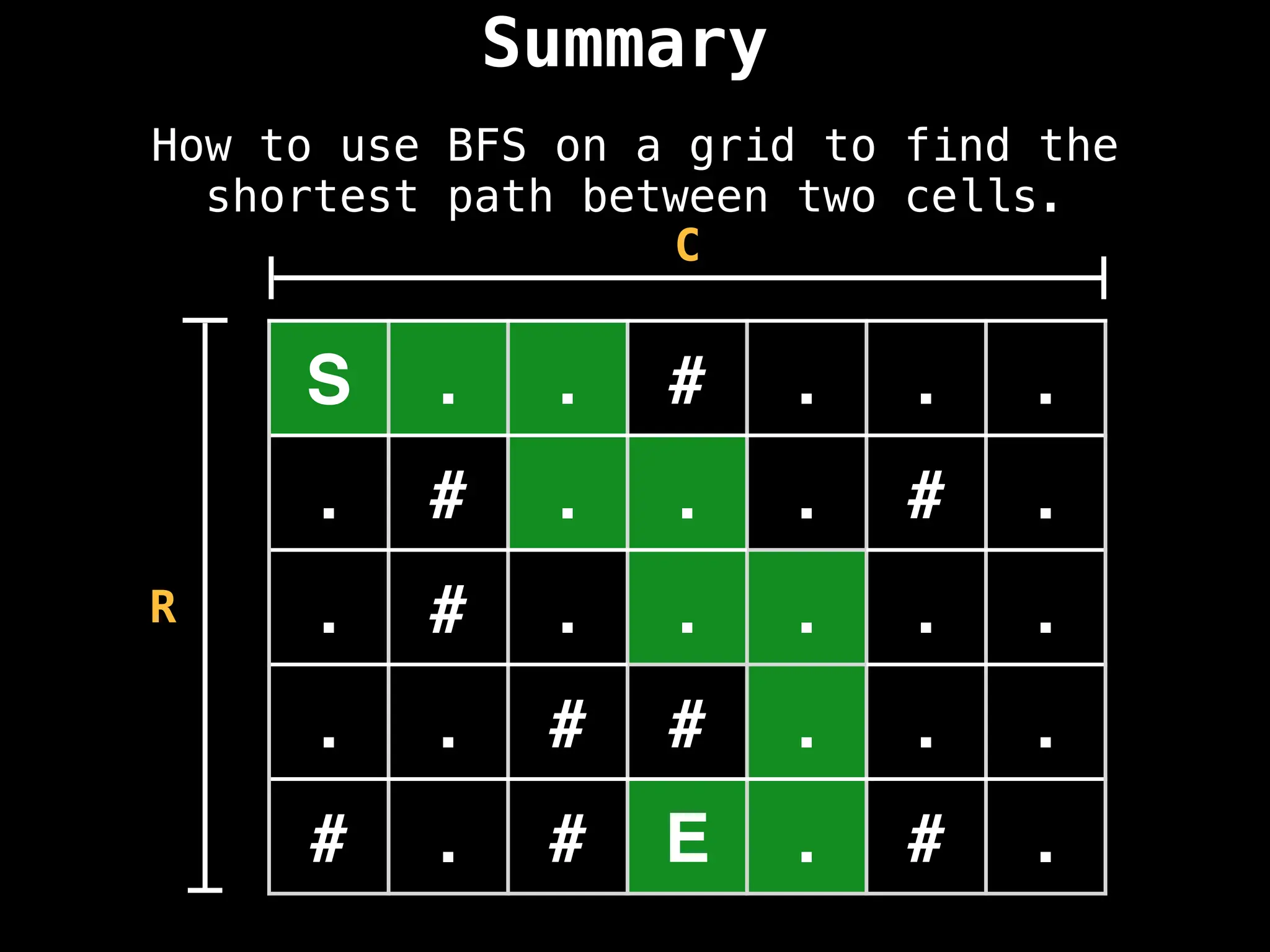
![Summary
Representing a grid as an adjacency list and
adjacency matrix.
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 1
2 3
4 5
Empty Grid
Adjacency Matrix:
Adjacency List:
0 -> [1, 2]
1 -> [0, 3]
2 -> [0, 3, 4]
3 -> [1, 2, 5]
4 -> [2, 5]
5 -> [3, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-301-2048.jpg)




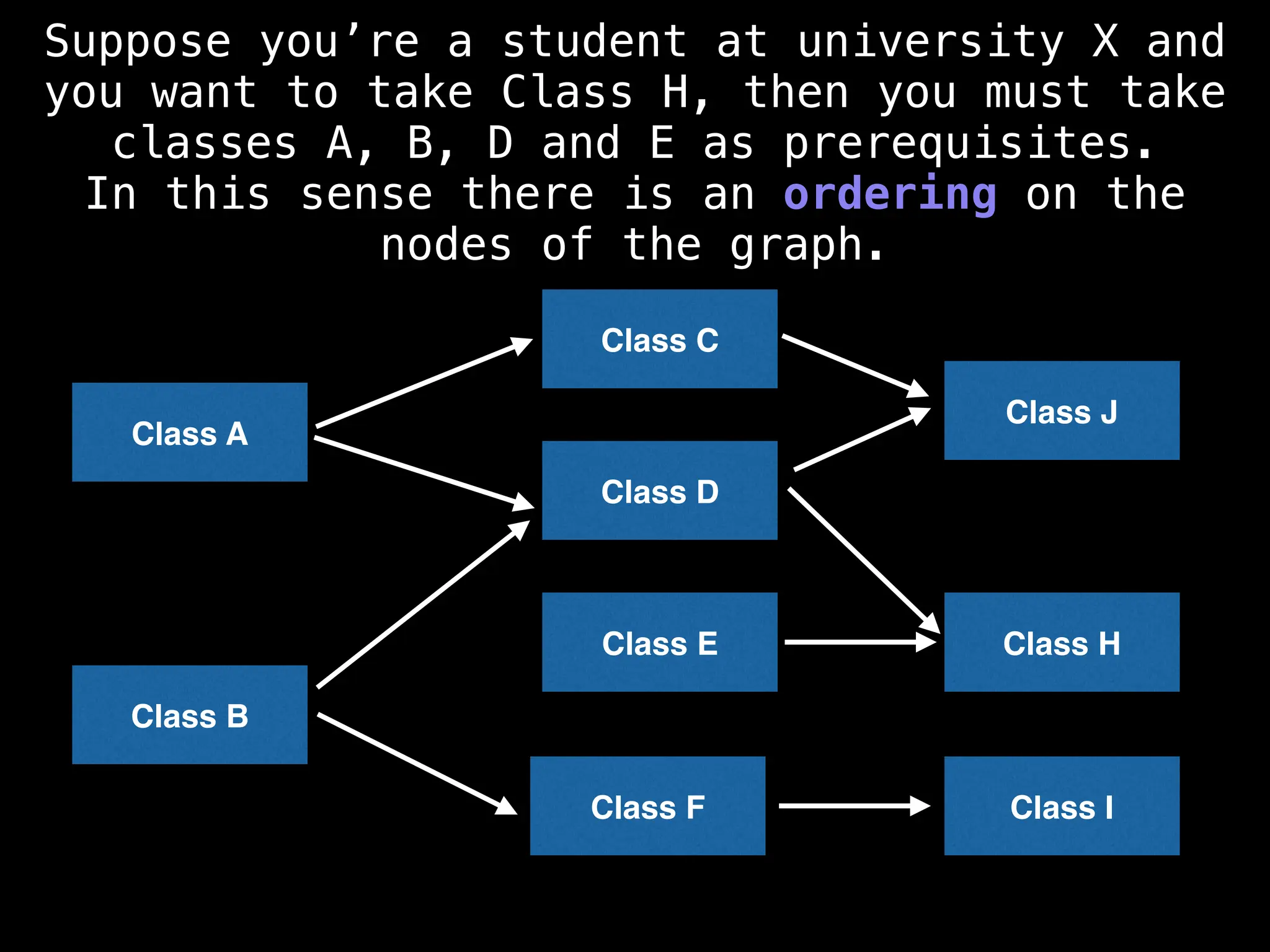
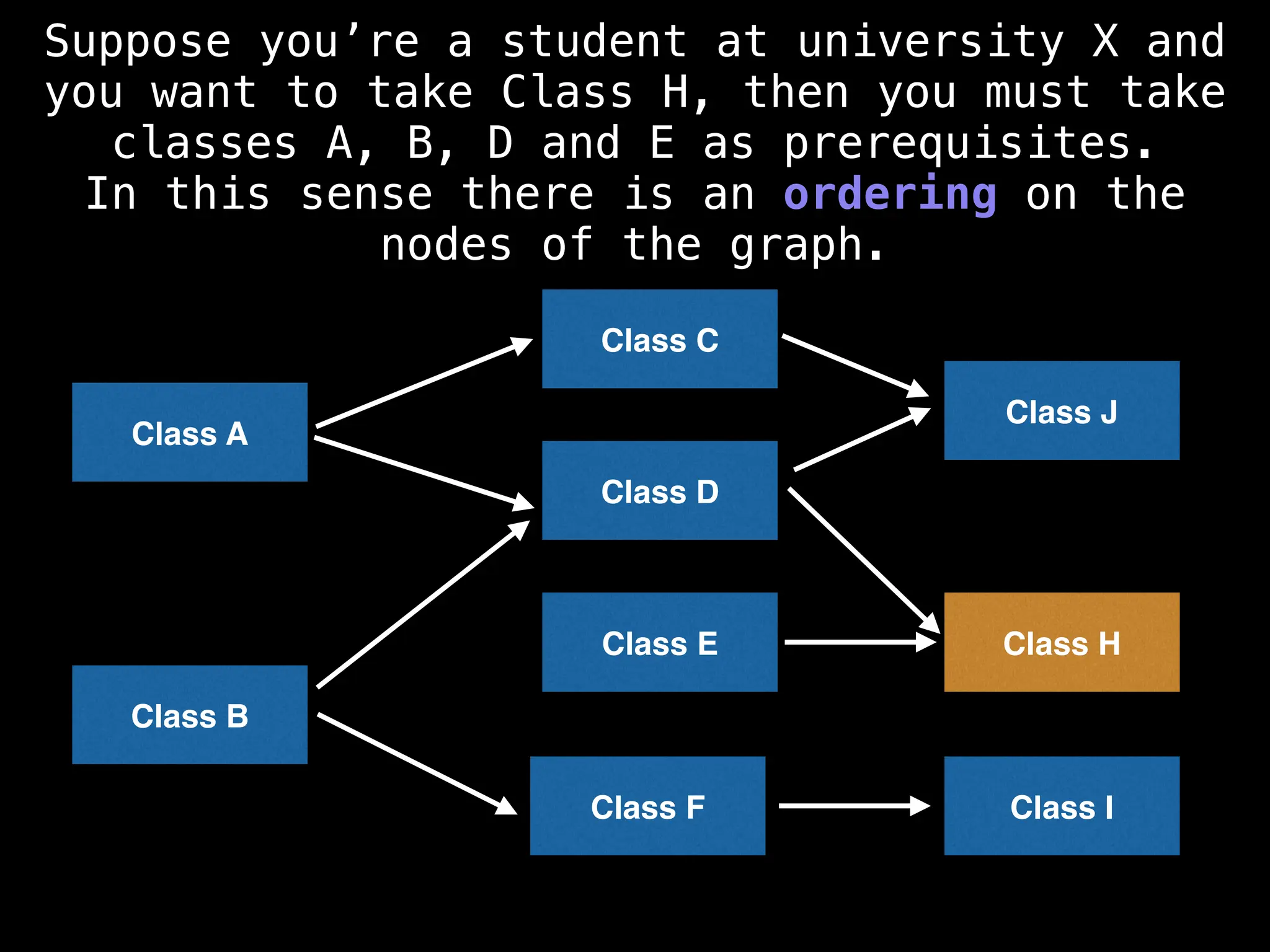
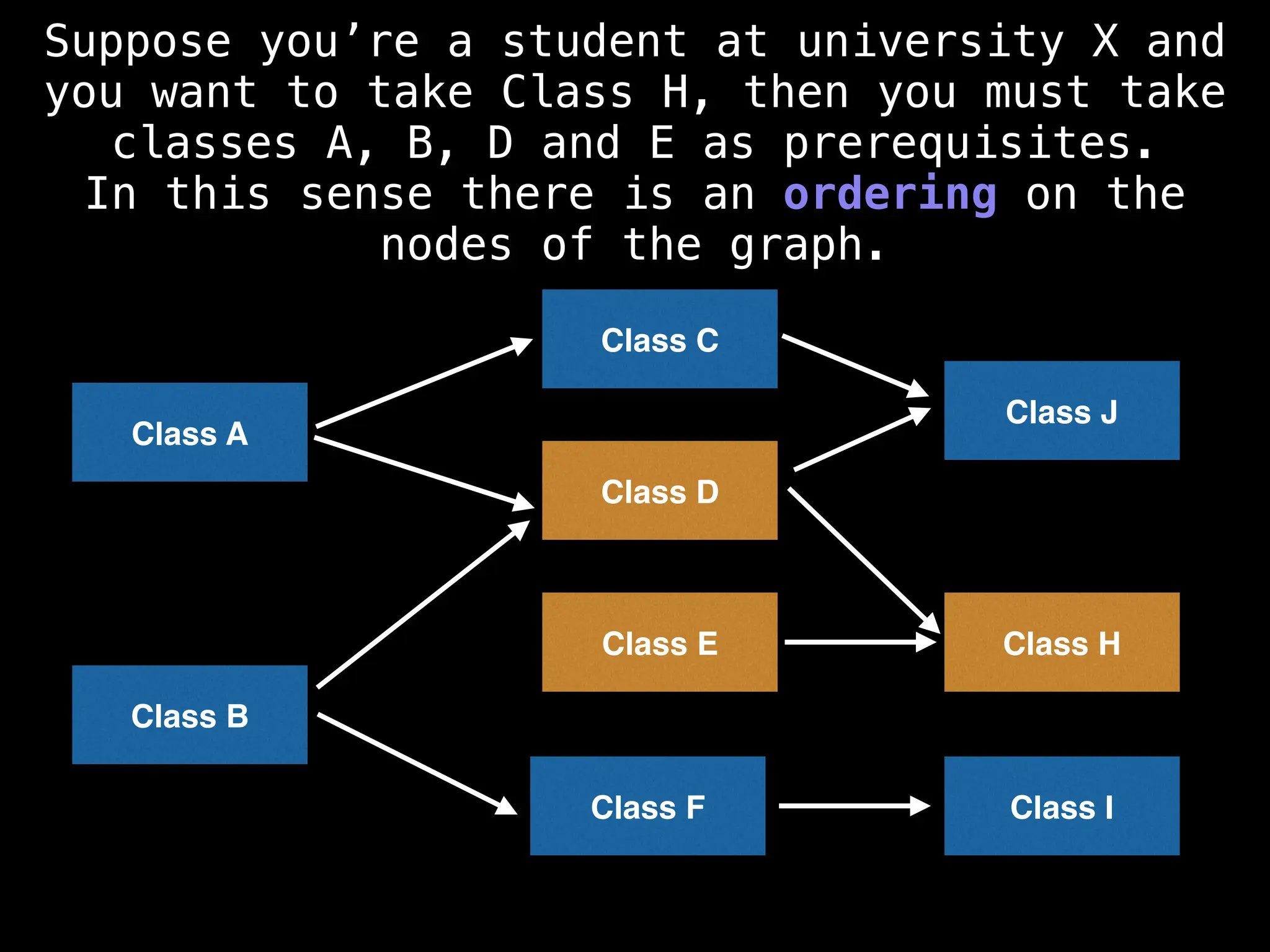
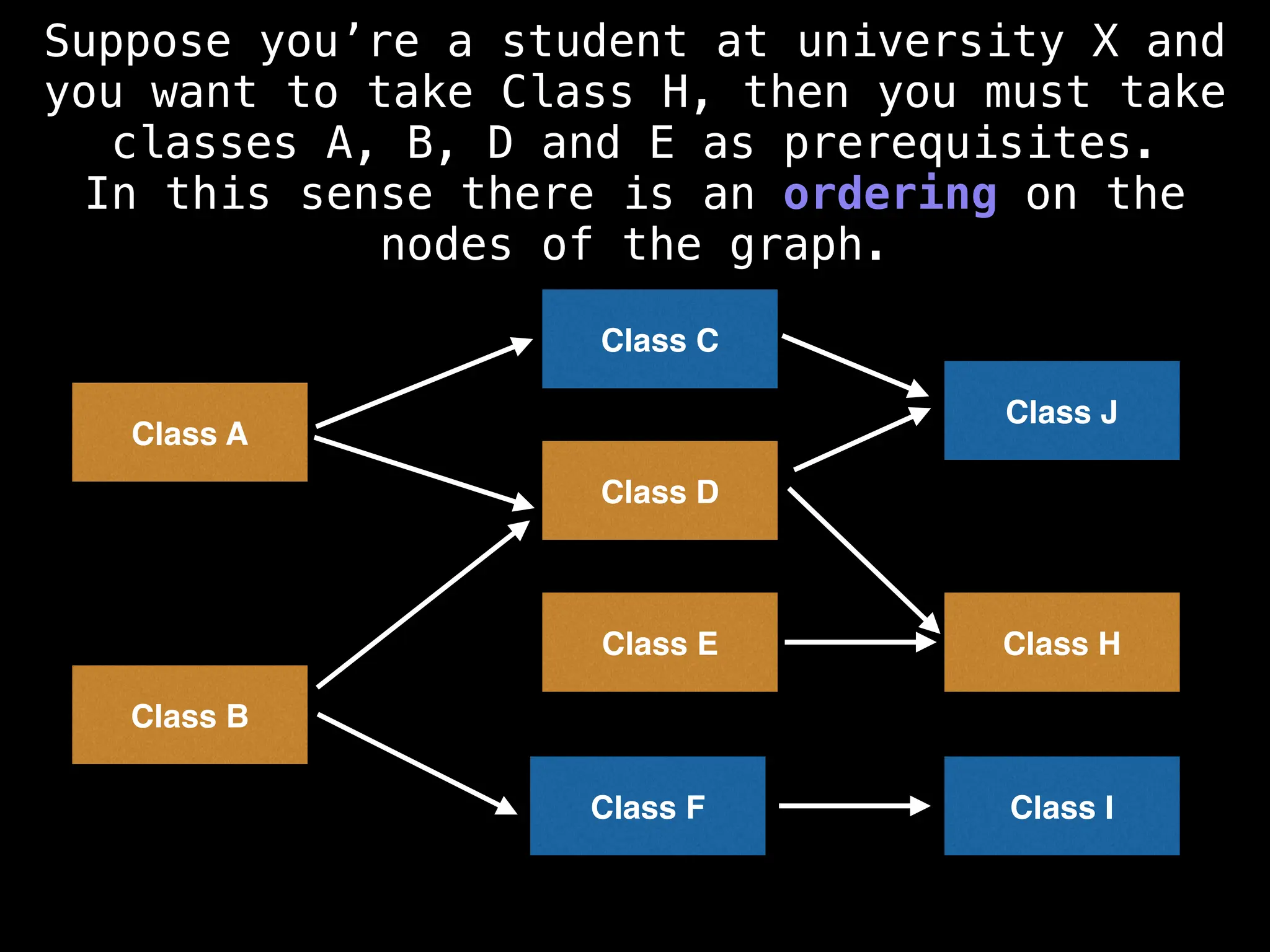
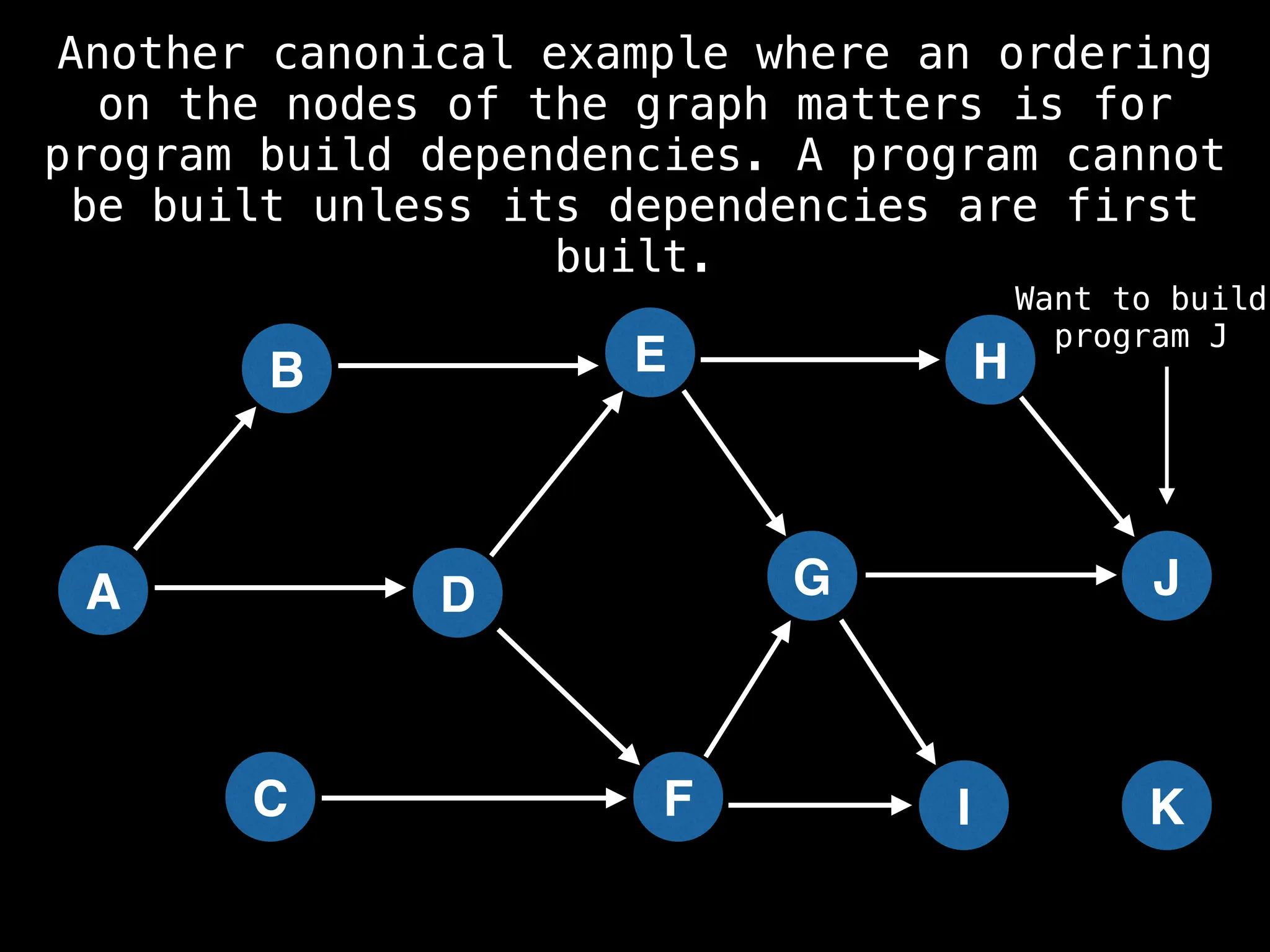
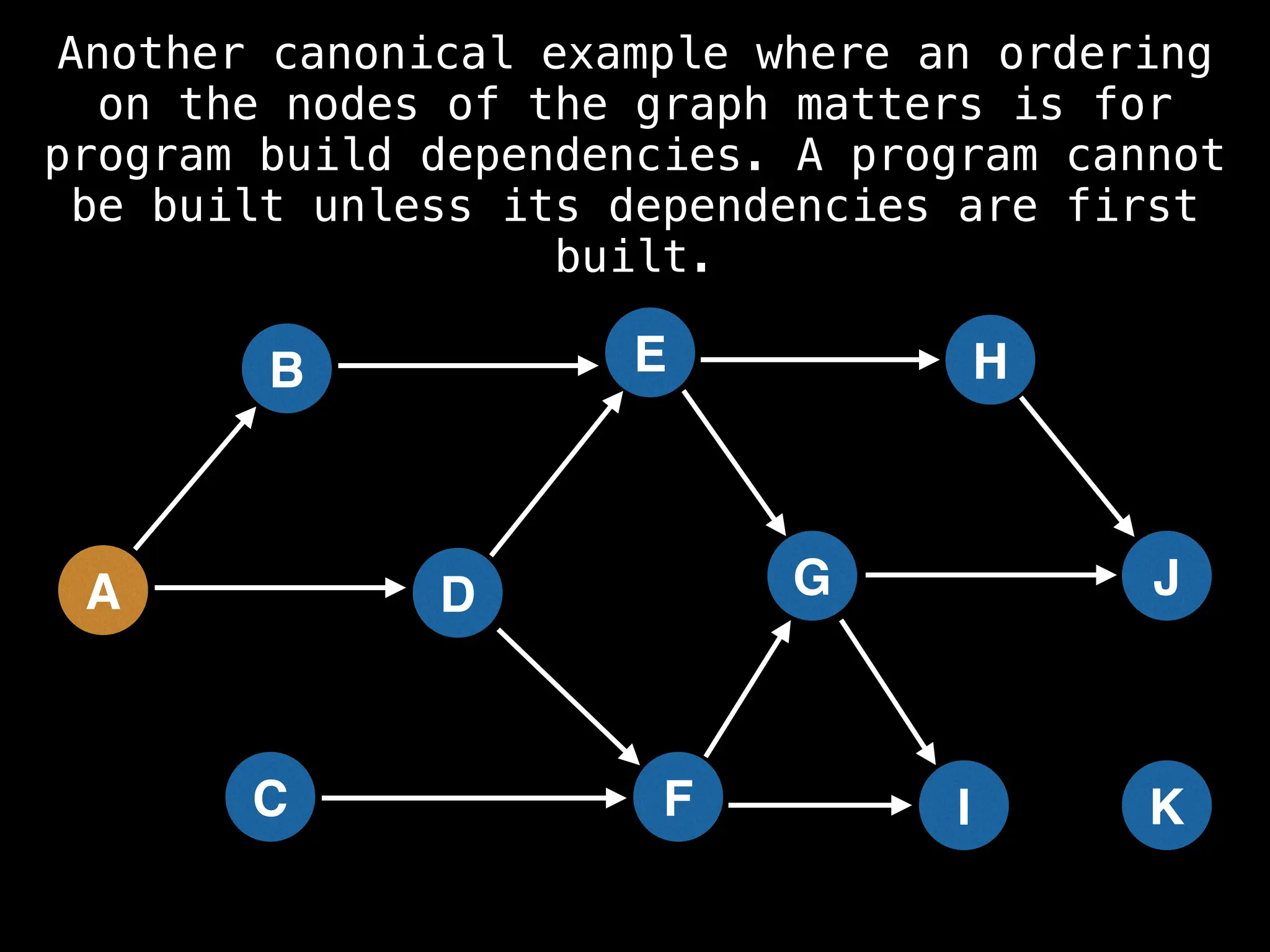
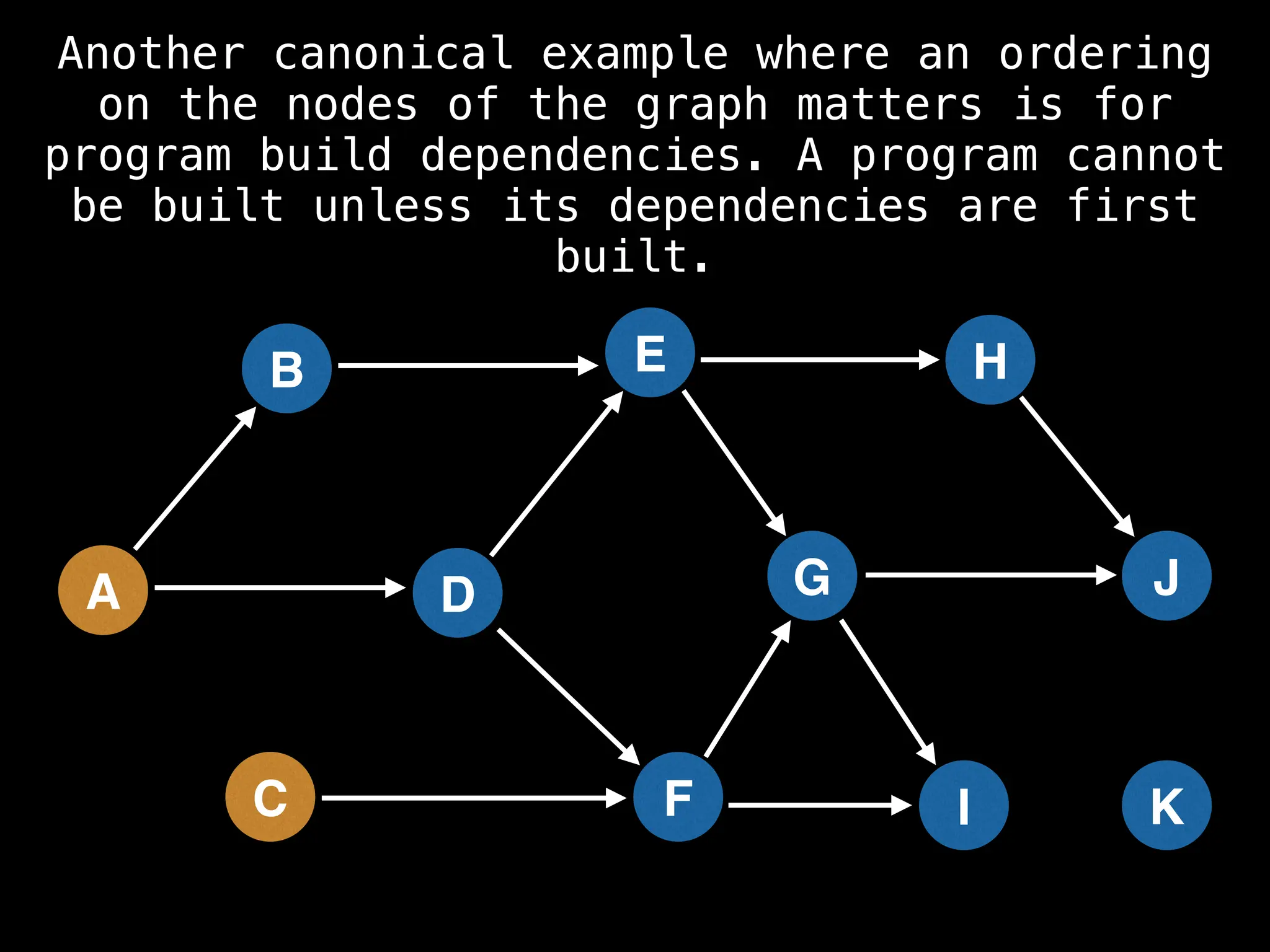
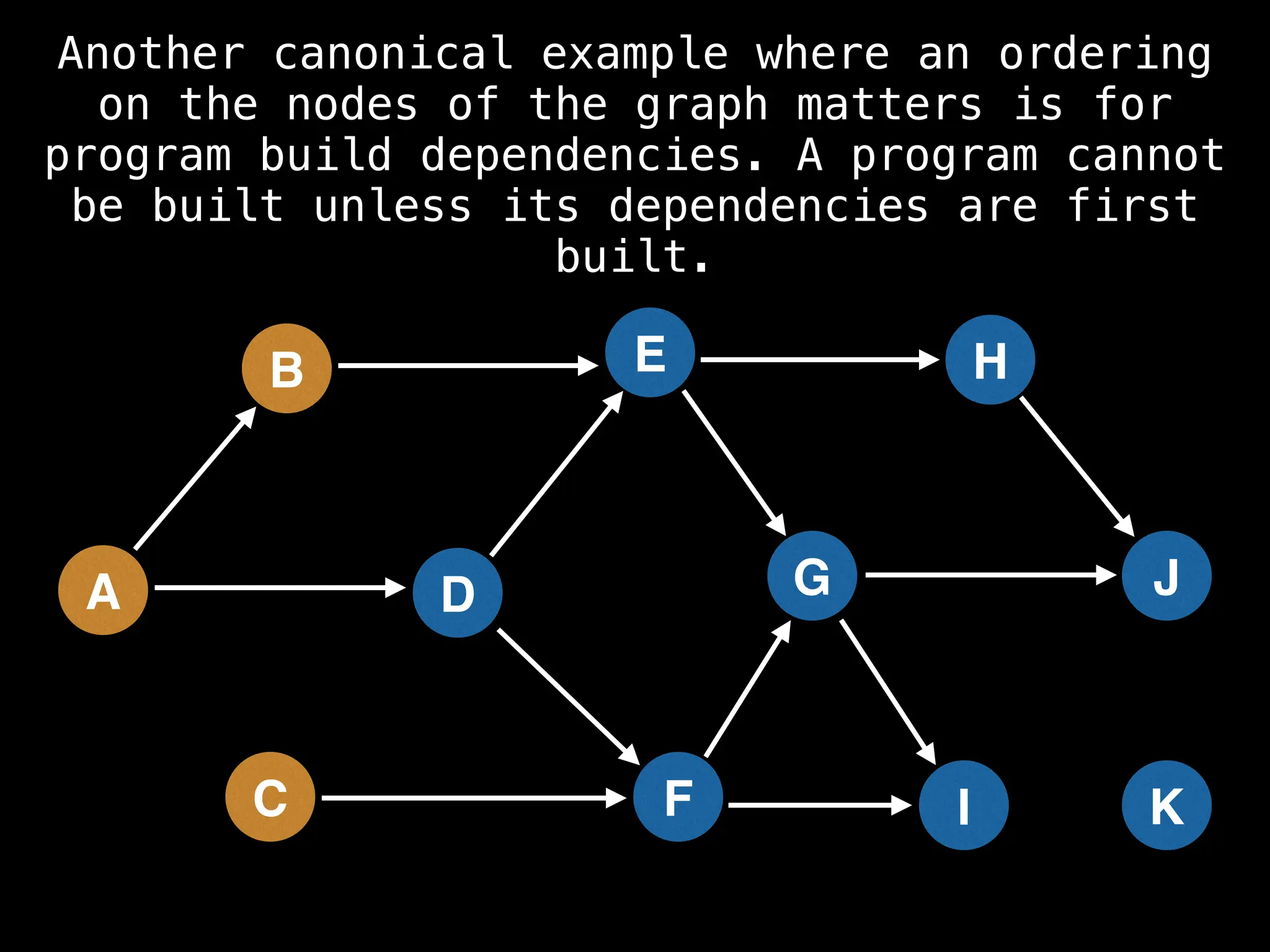
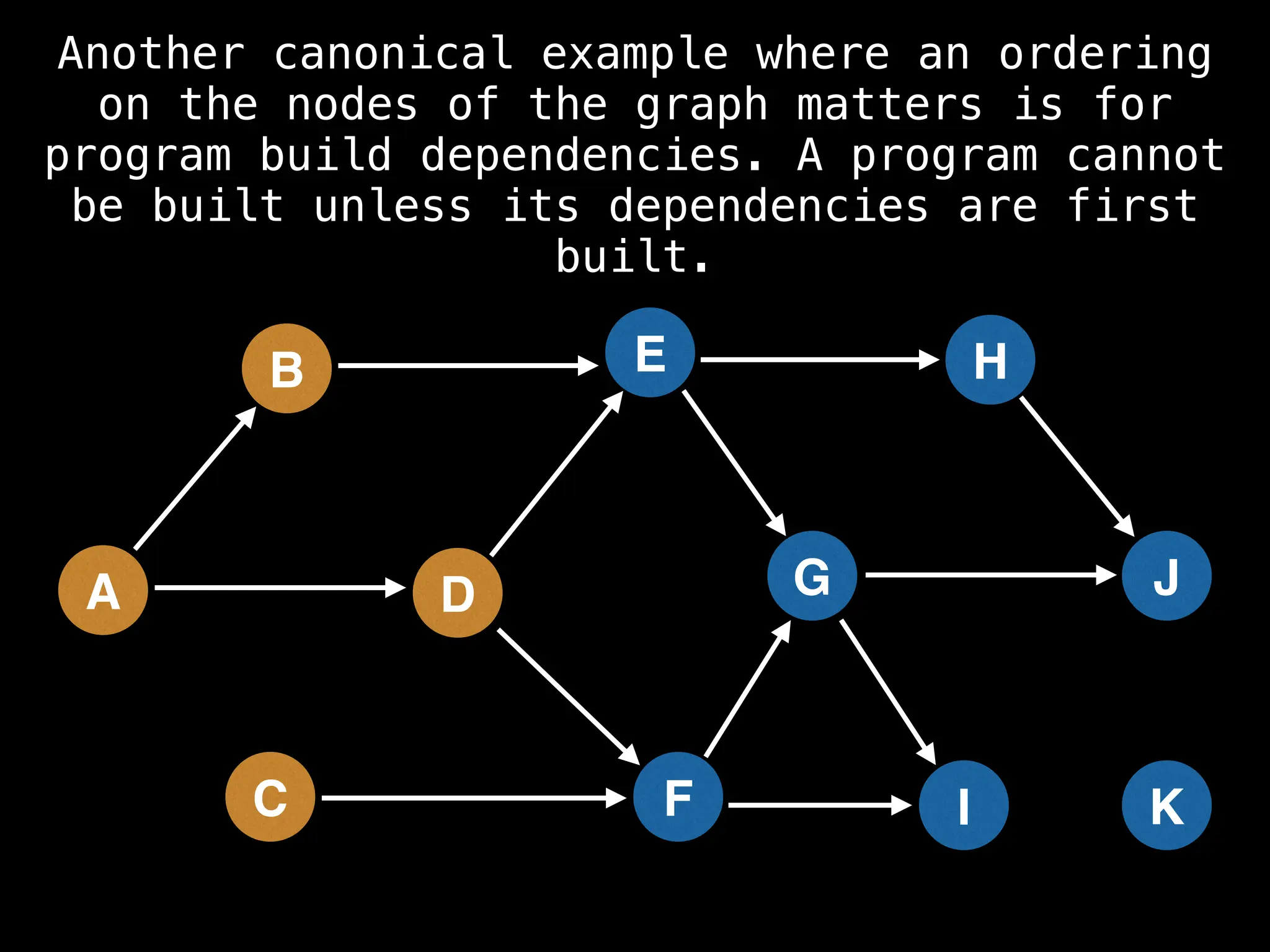
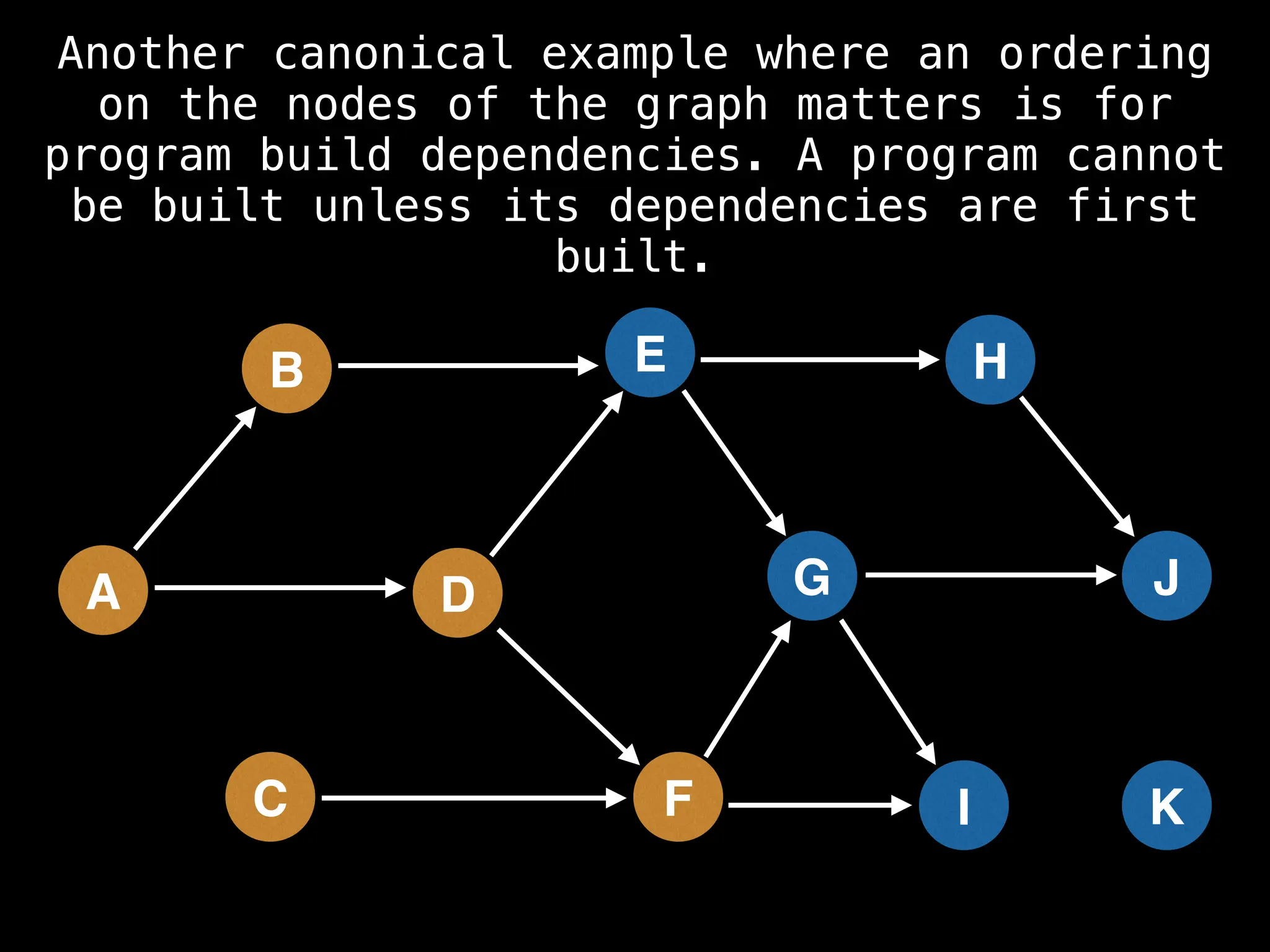
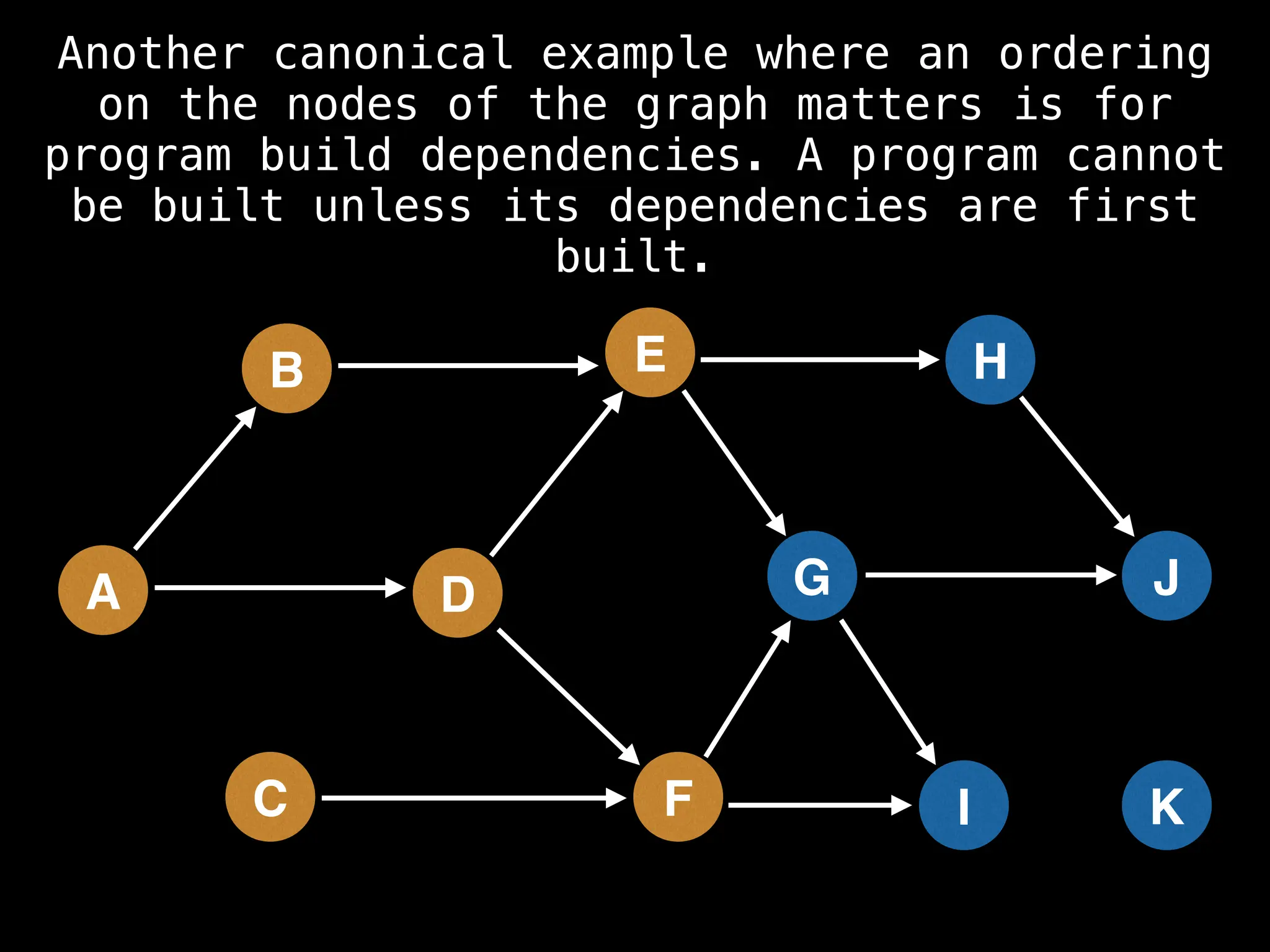
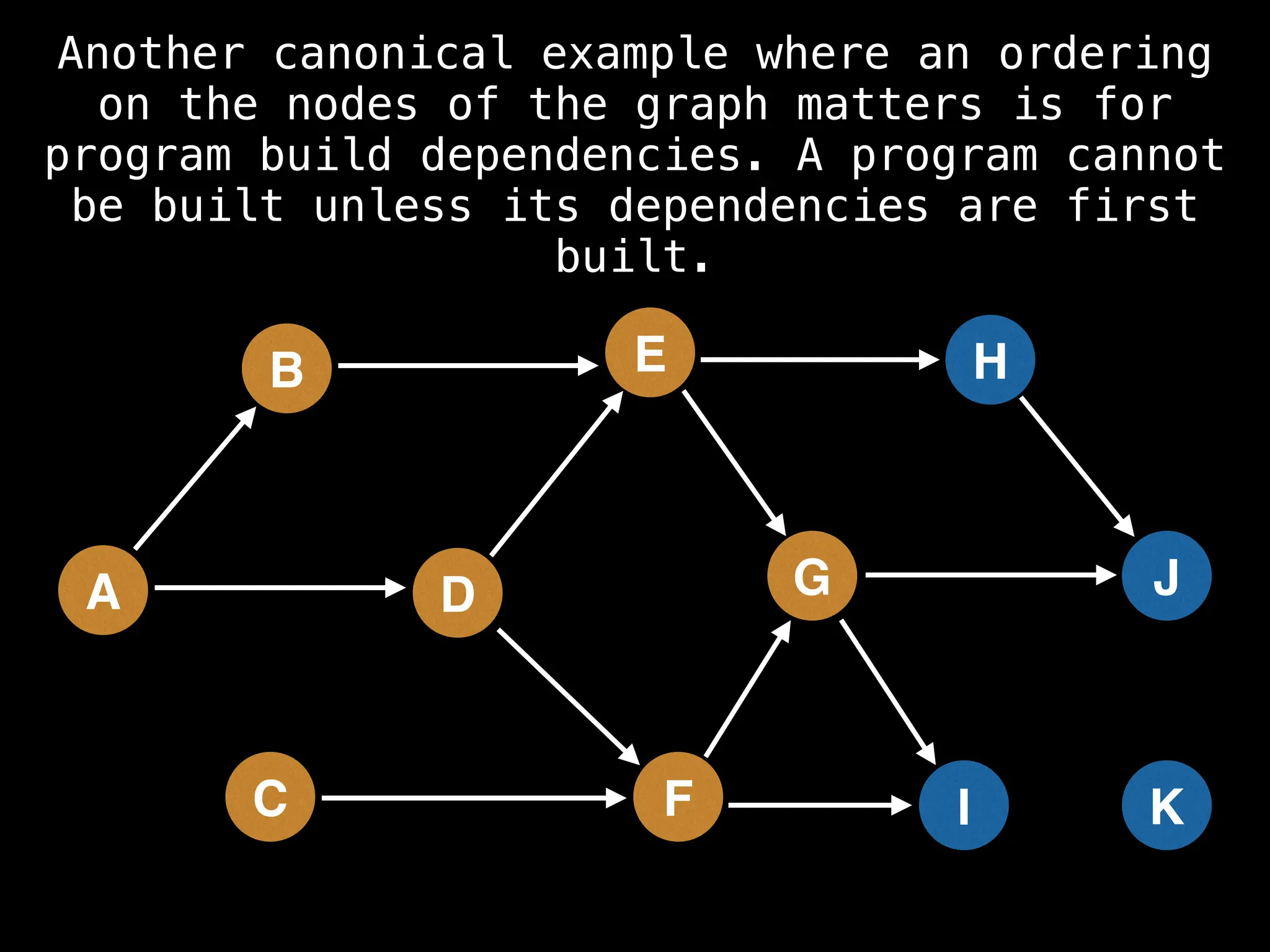
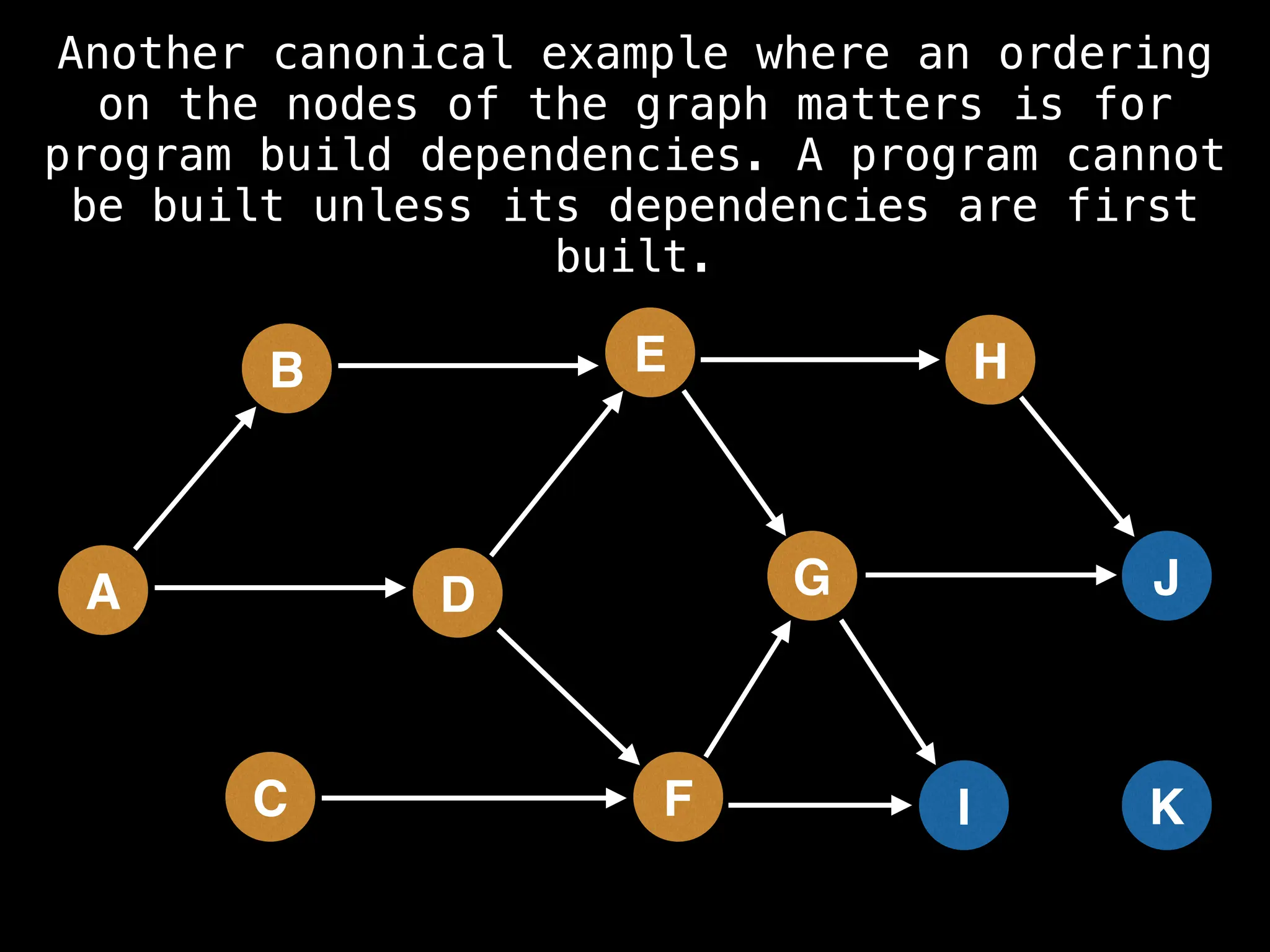
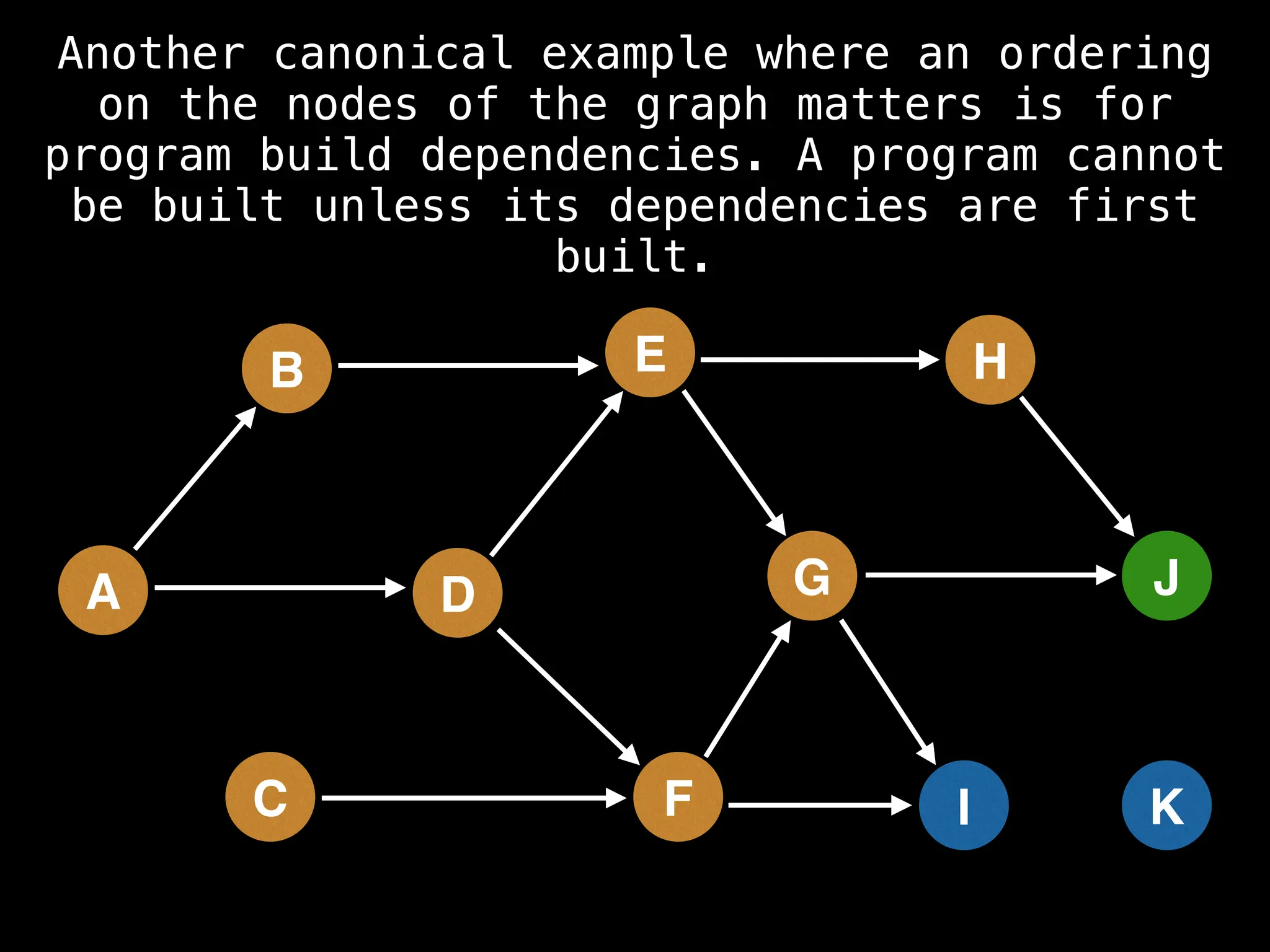
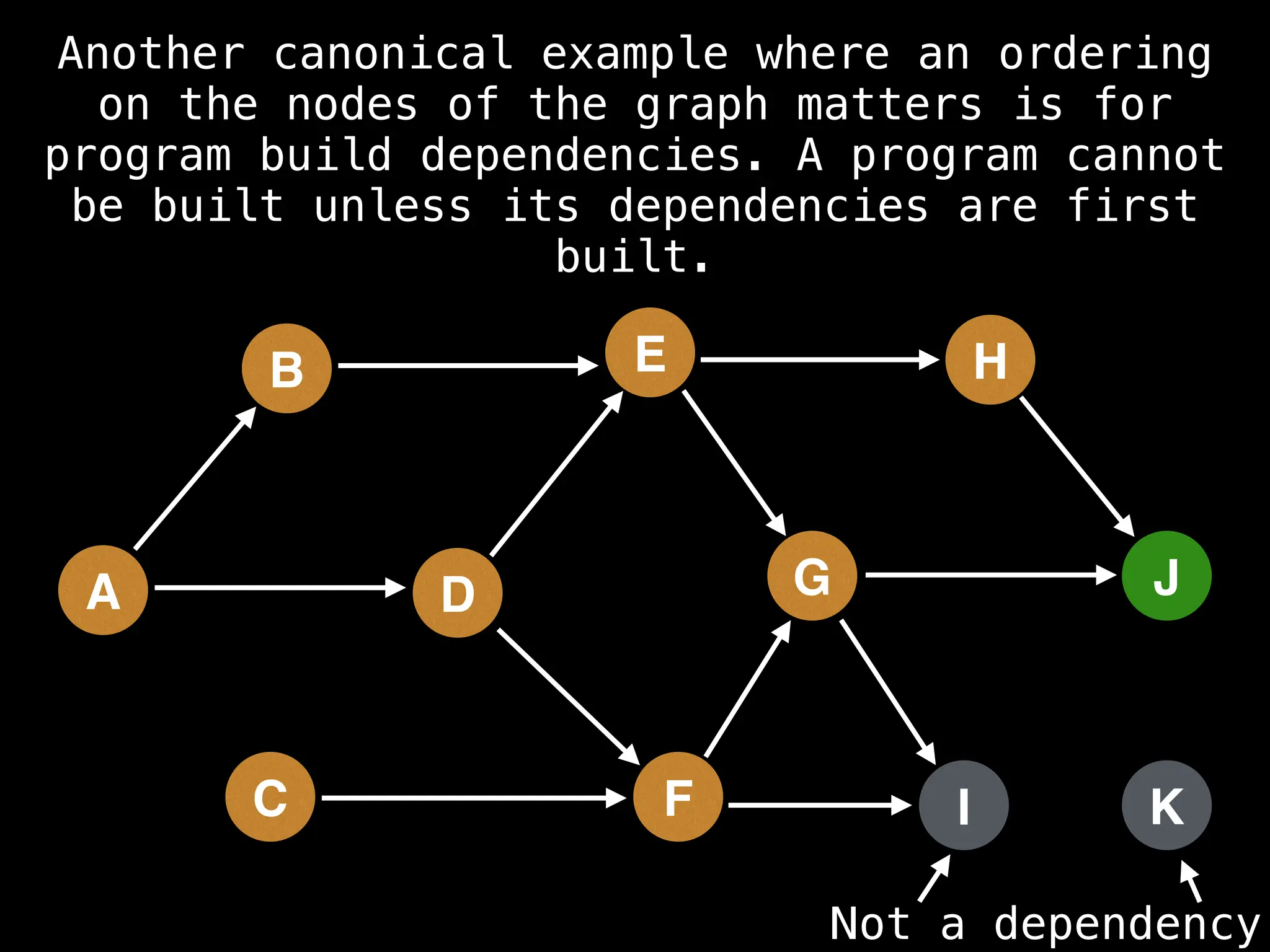
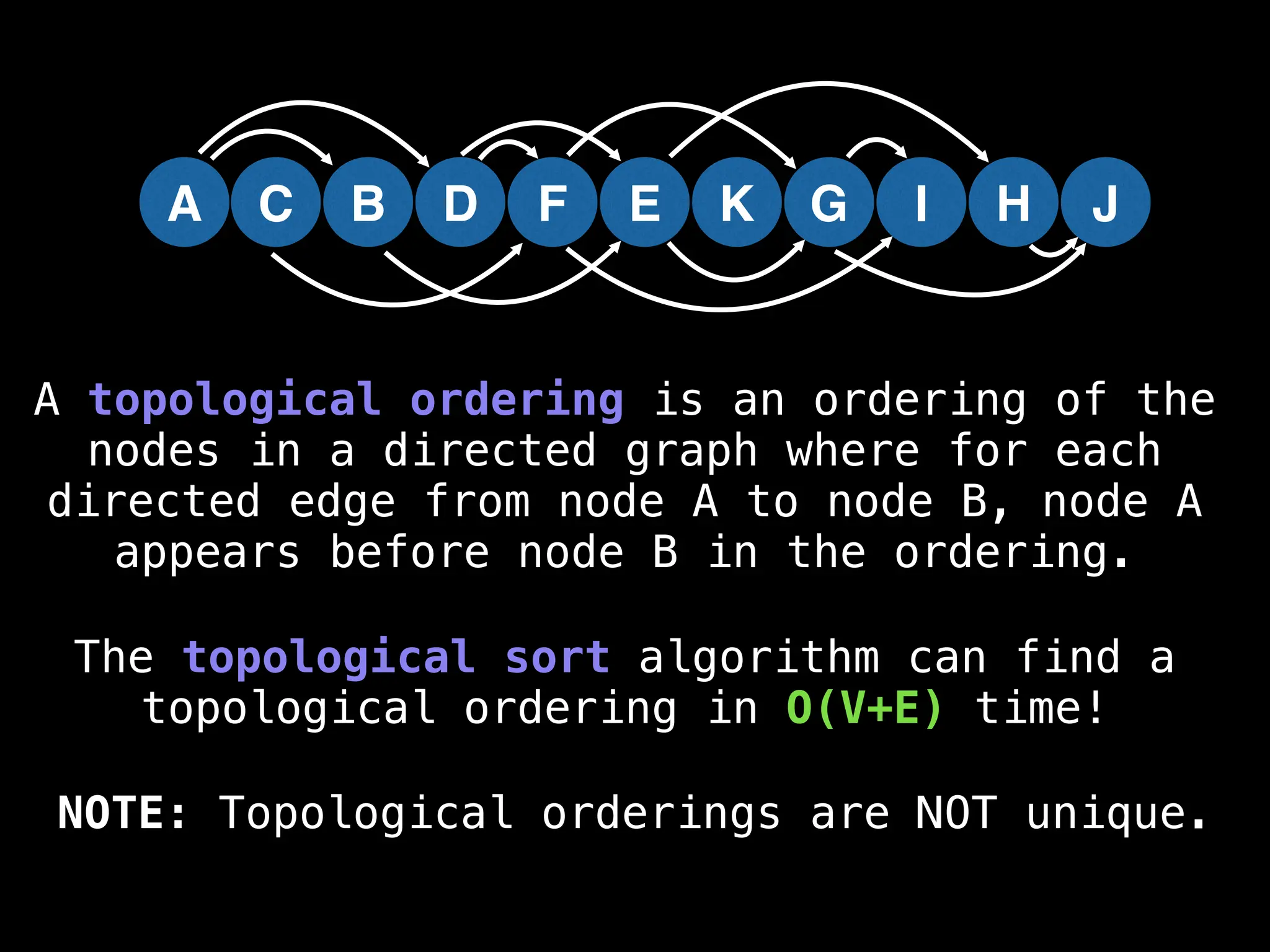
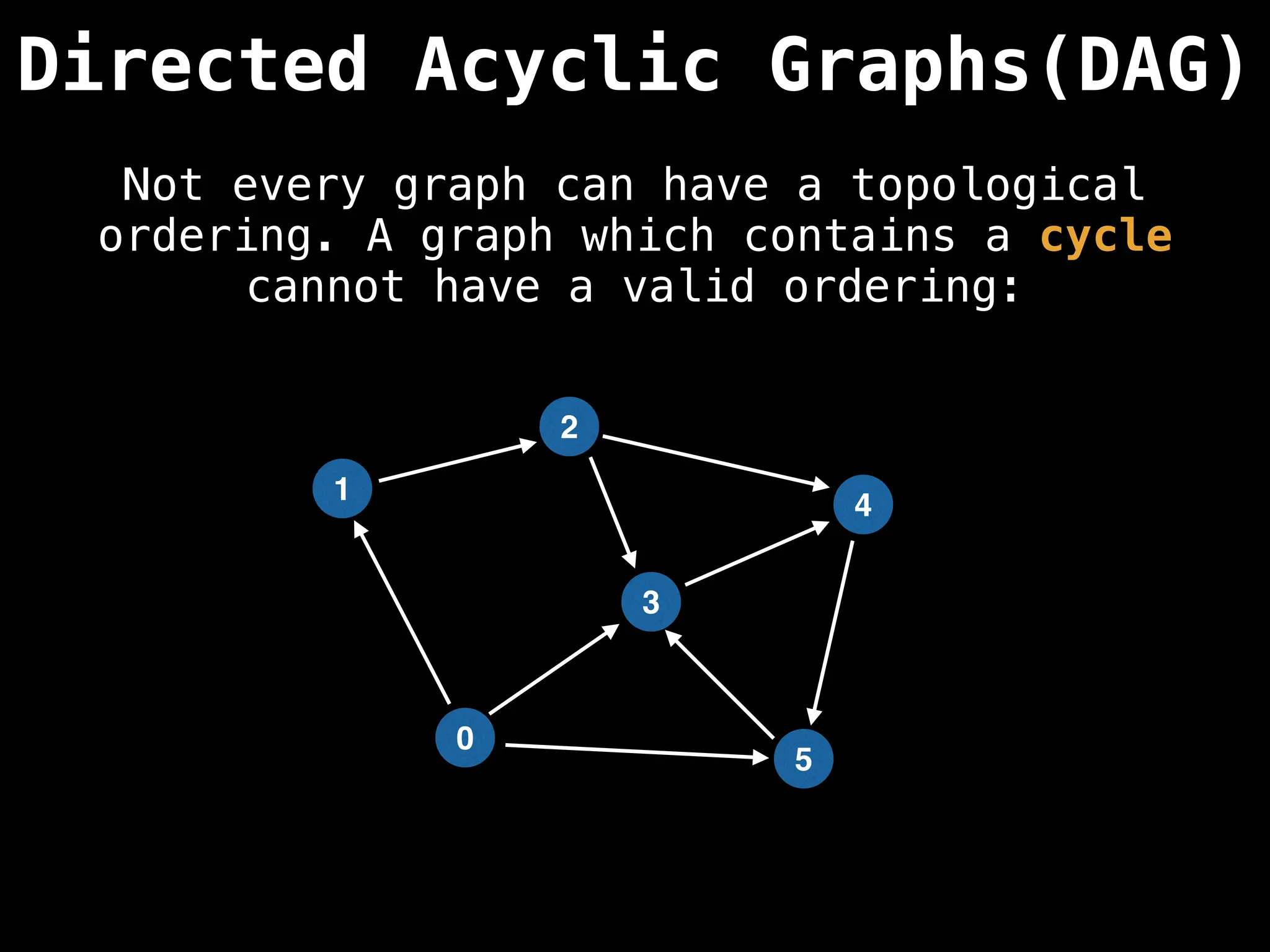
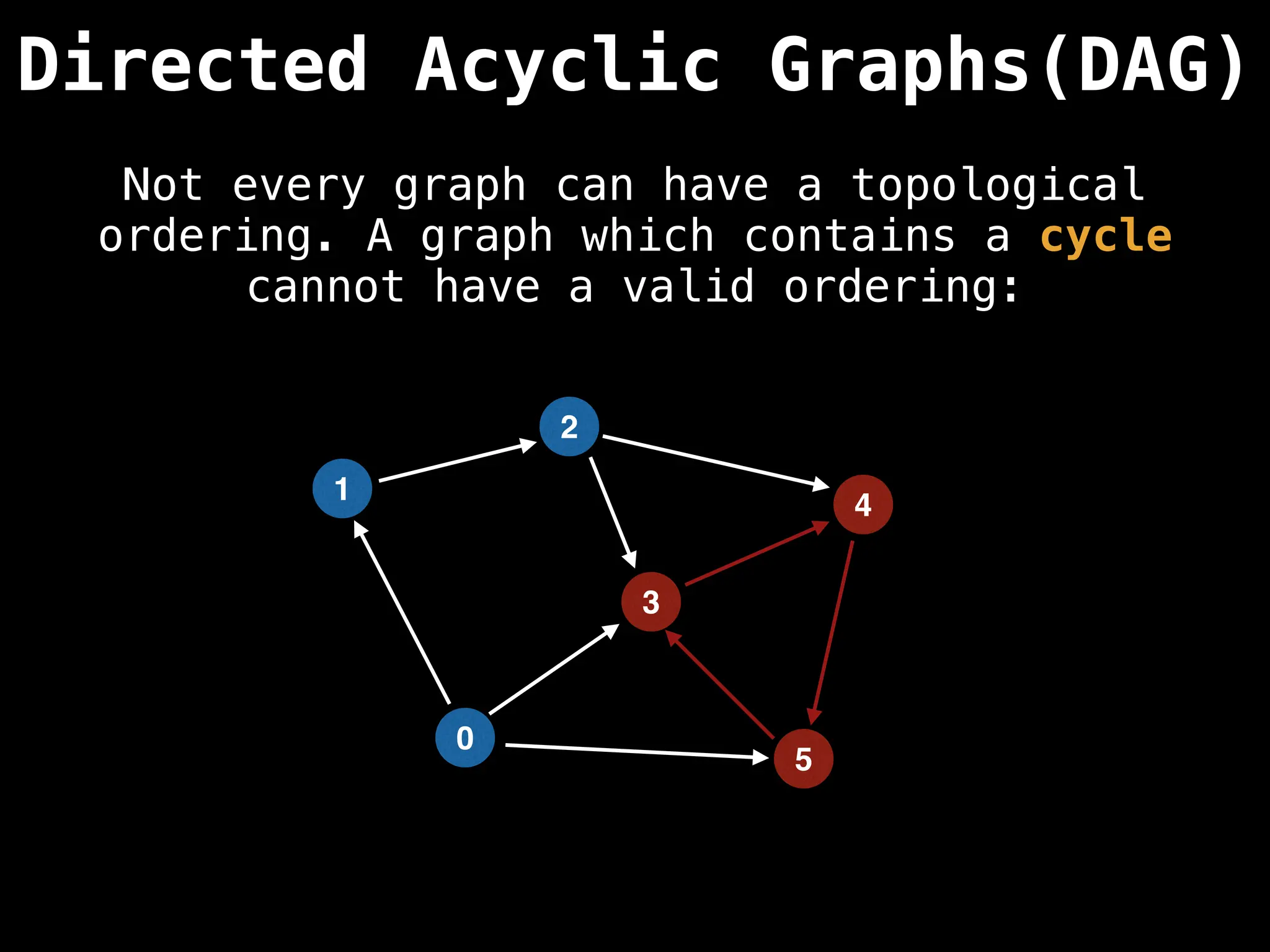
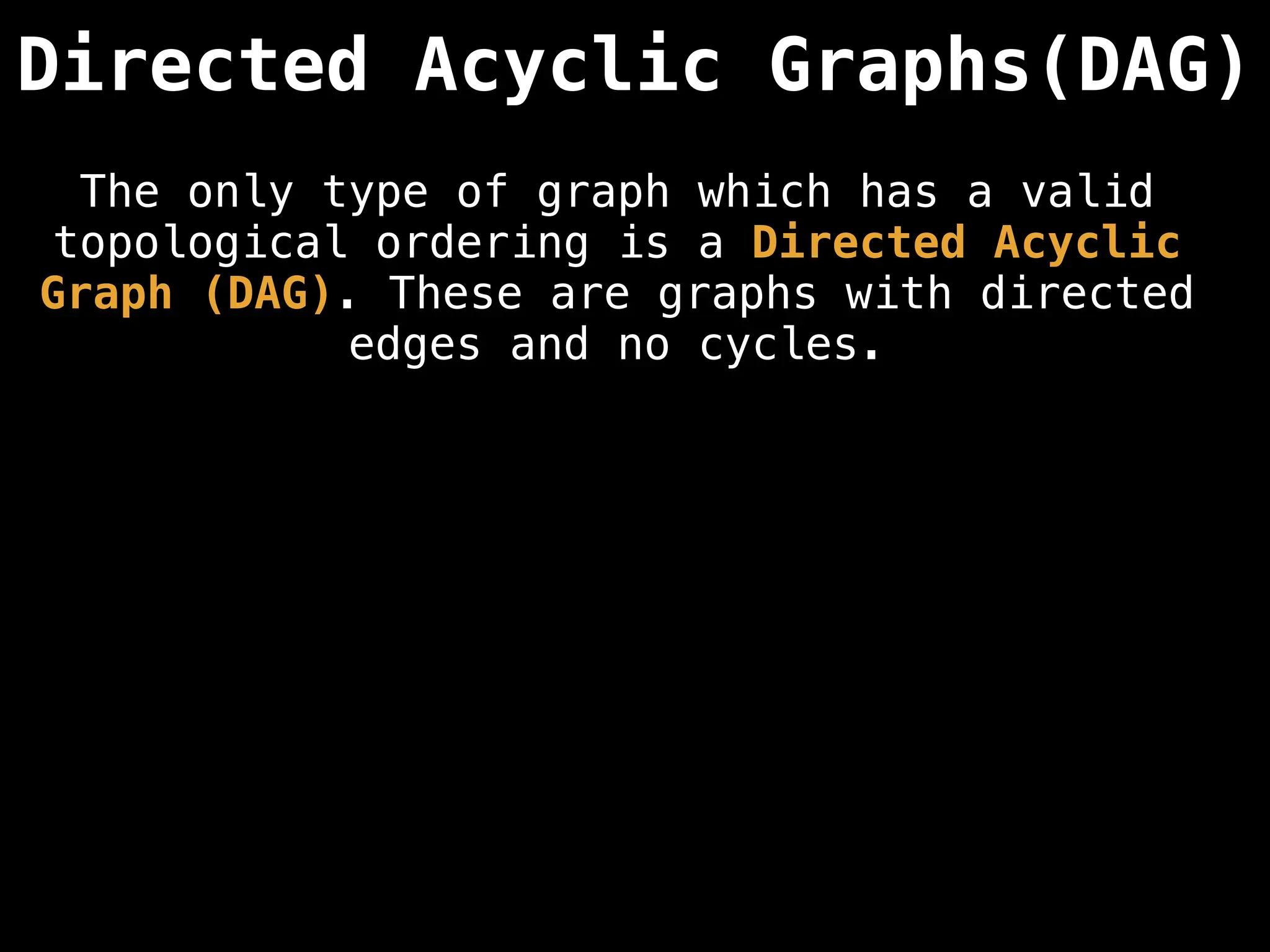
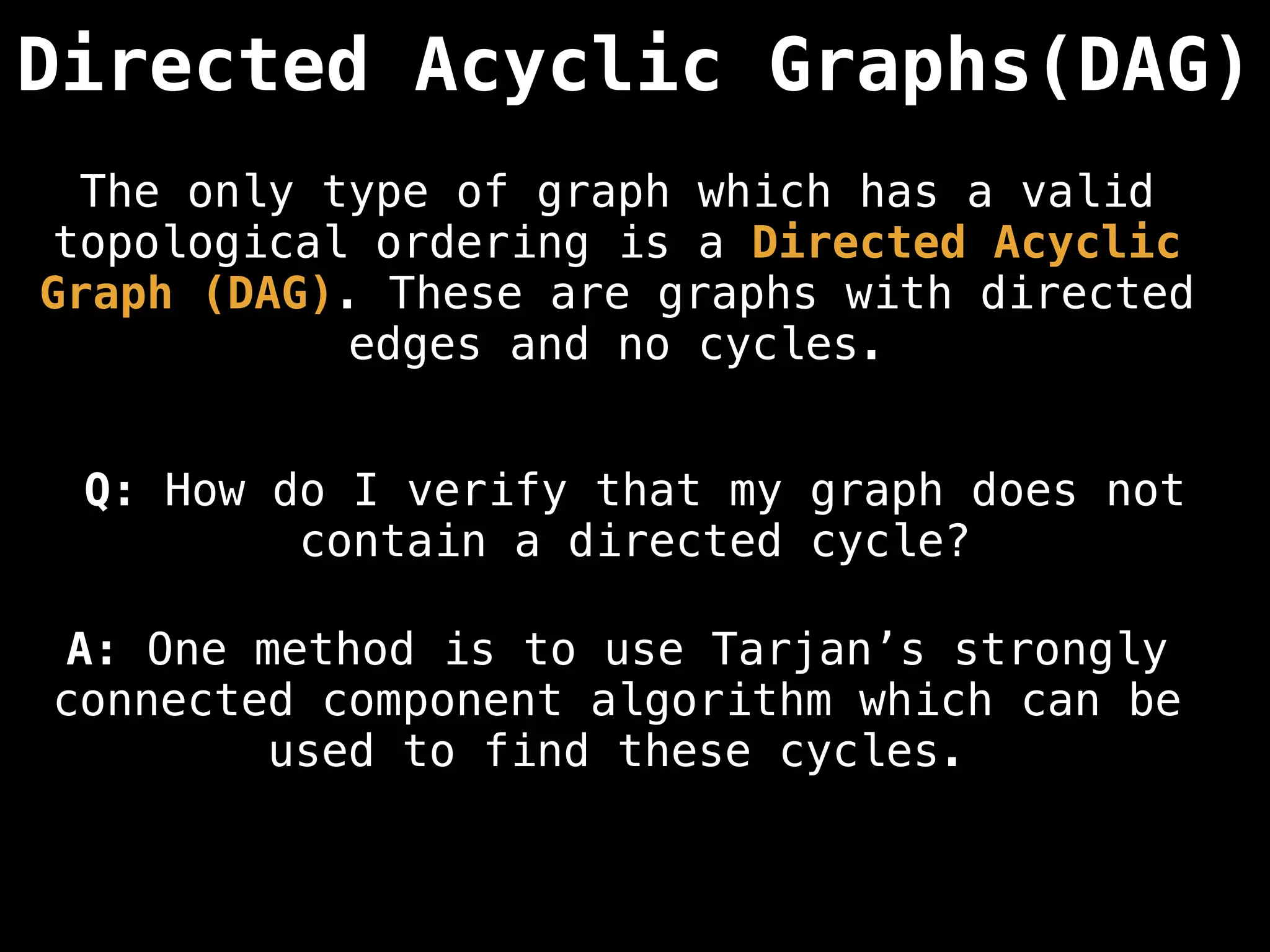
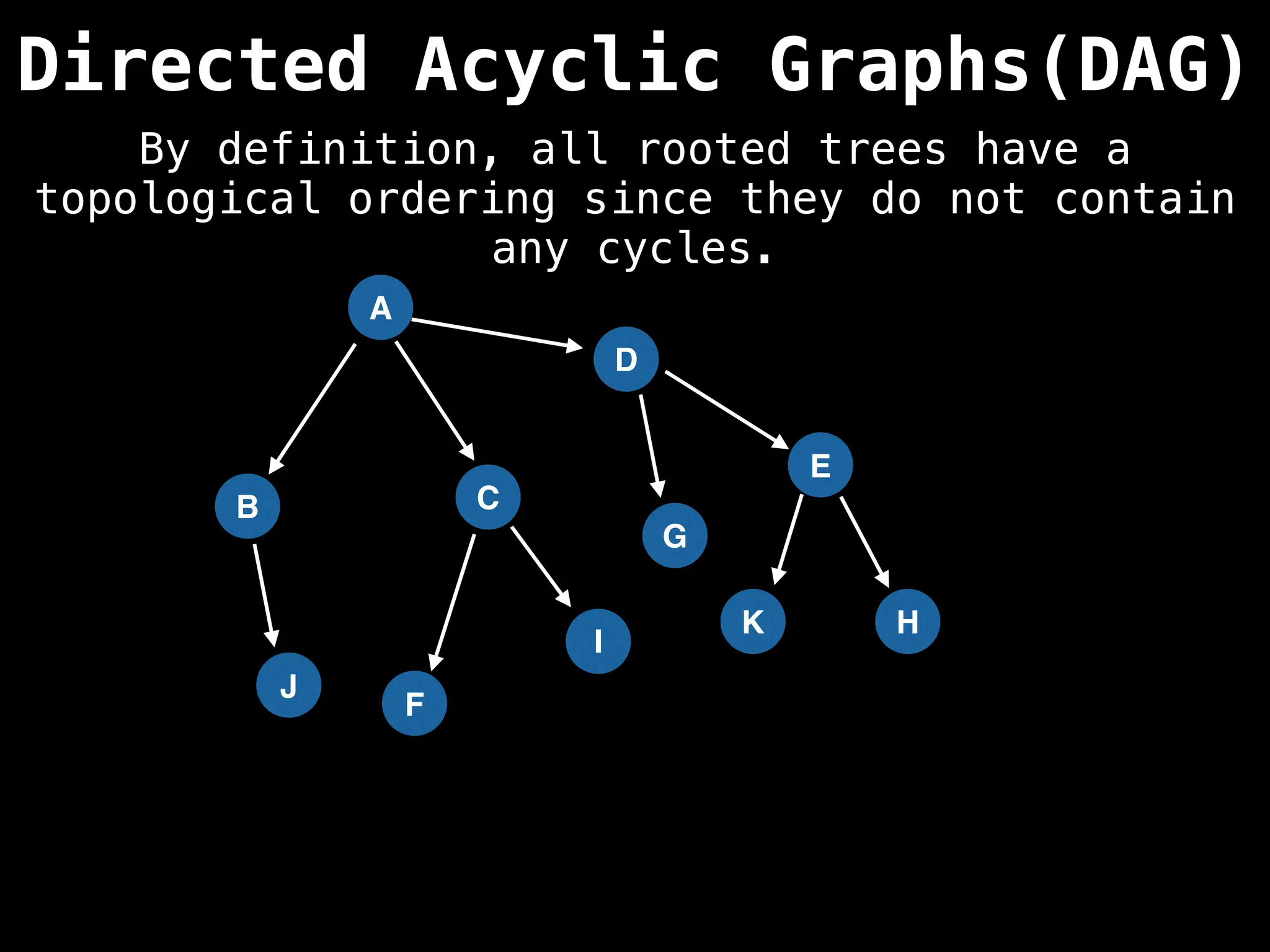
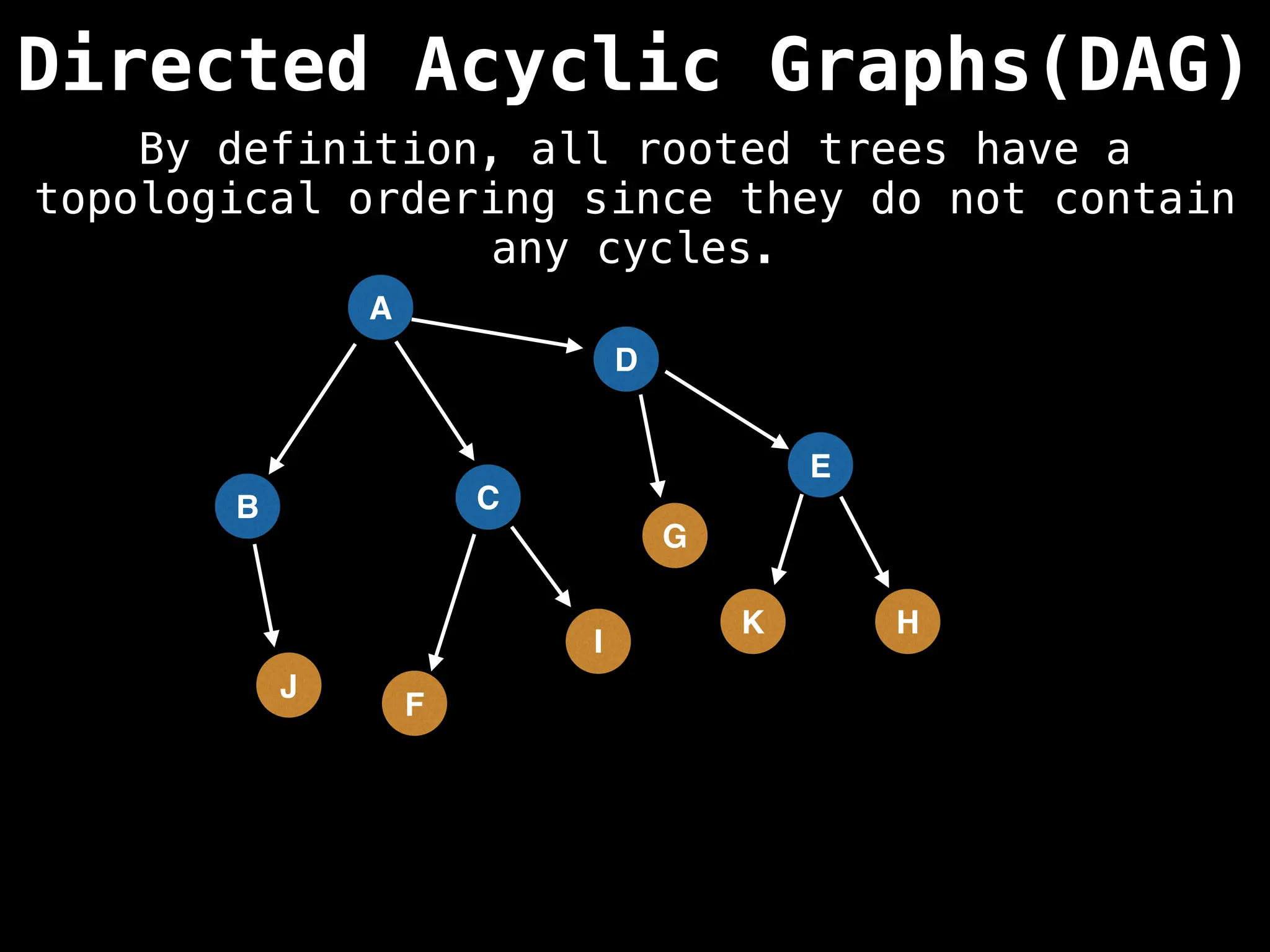
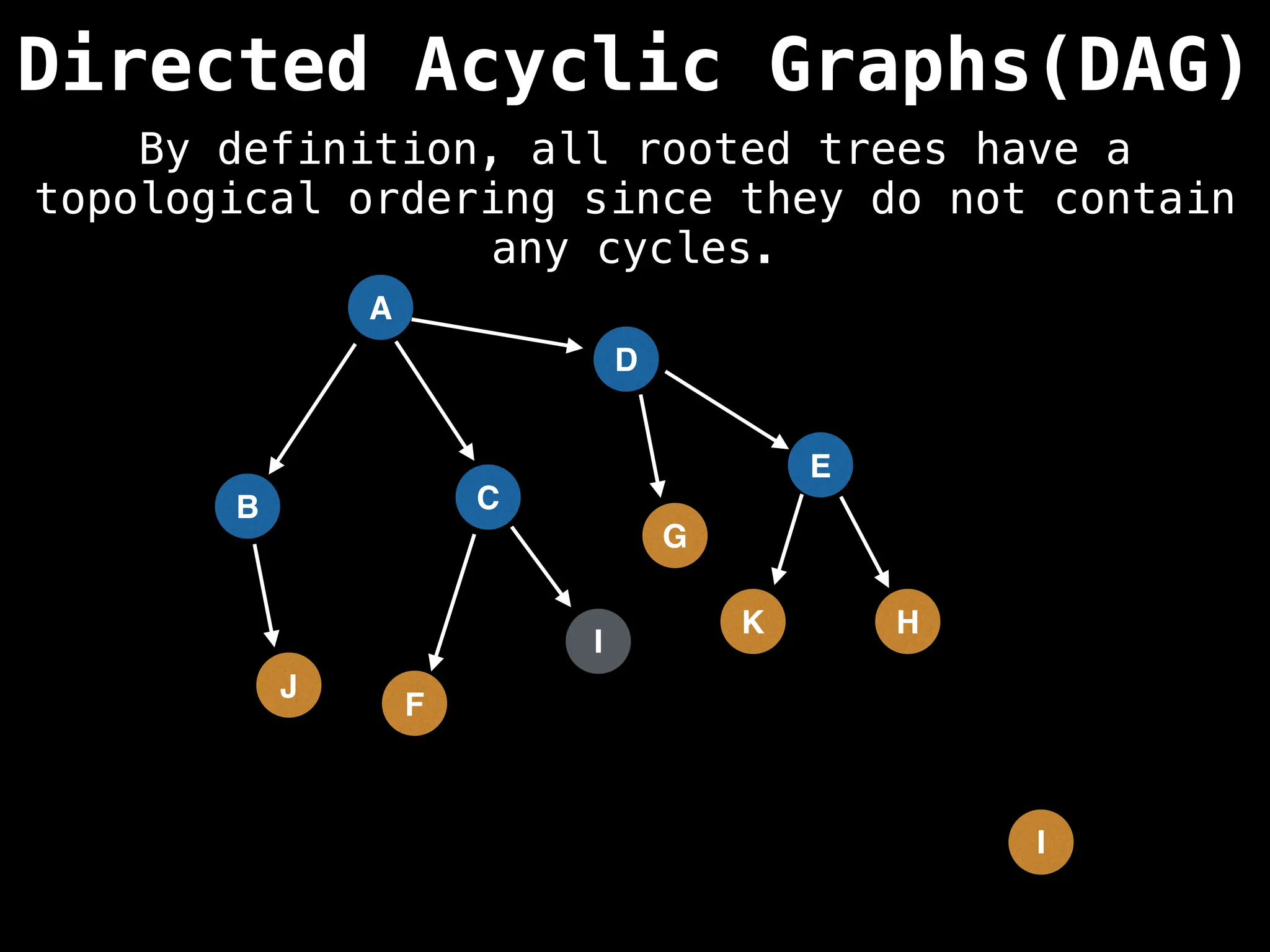
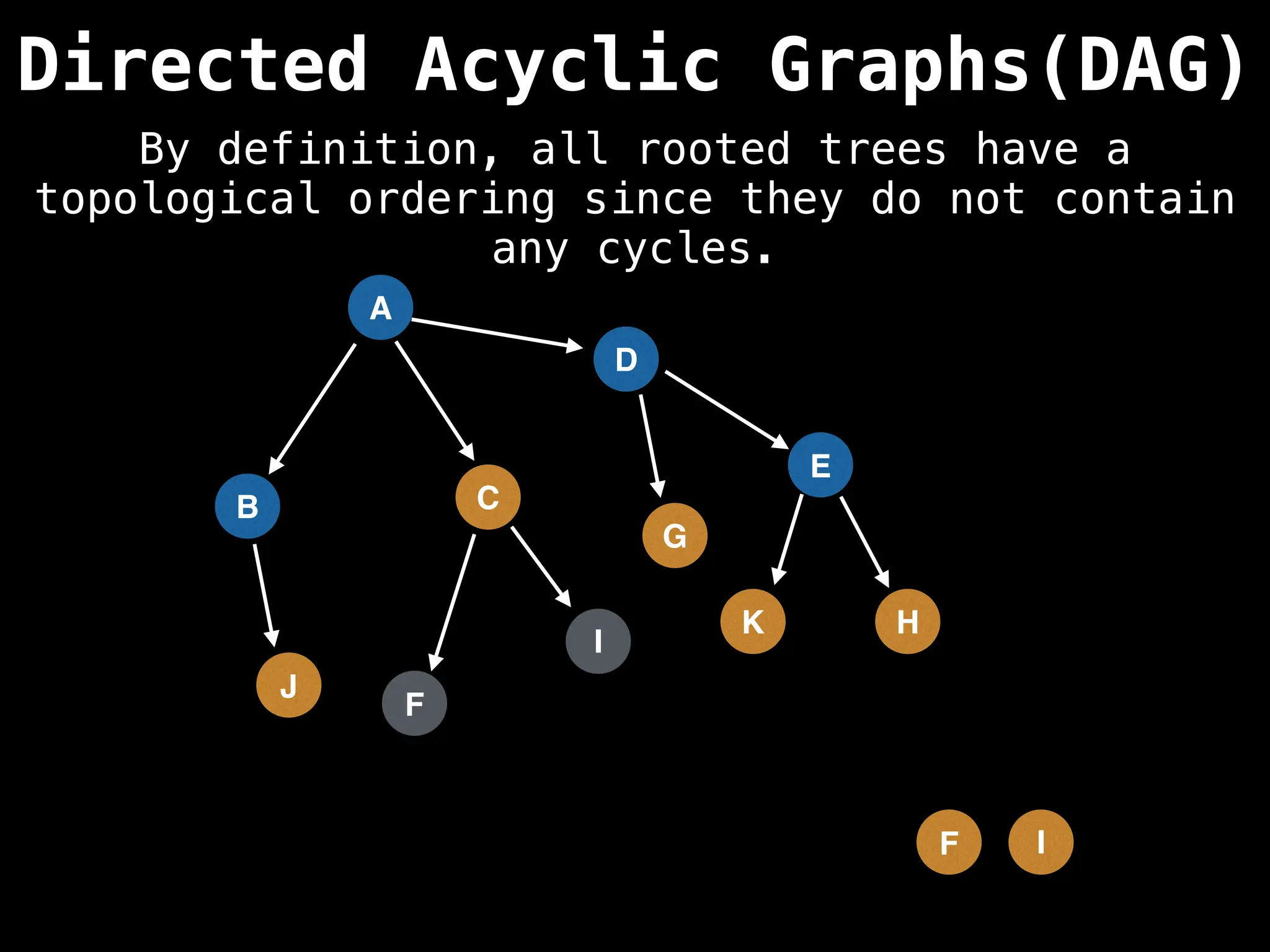
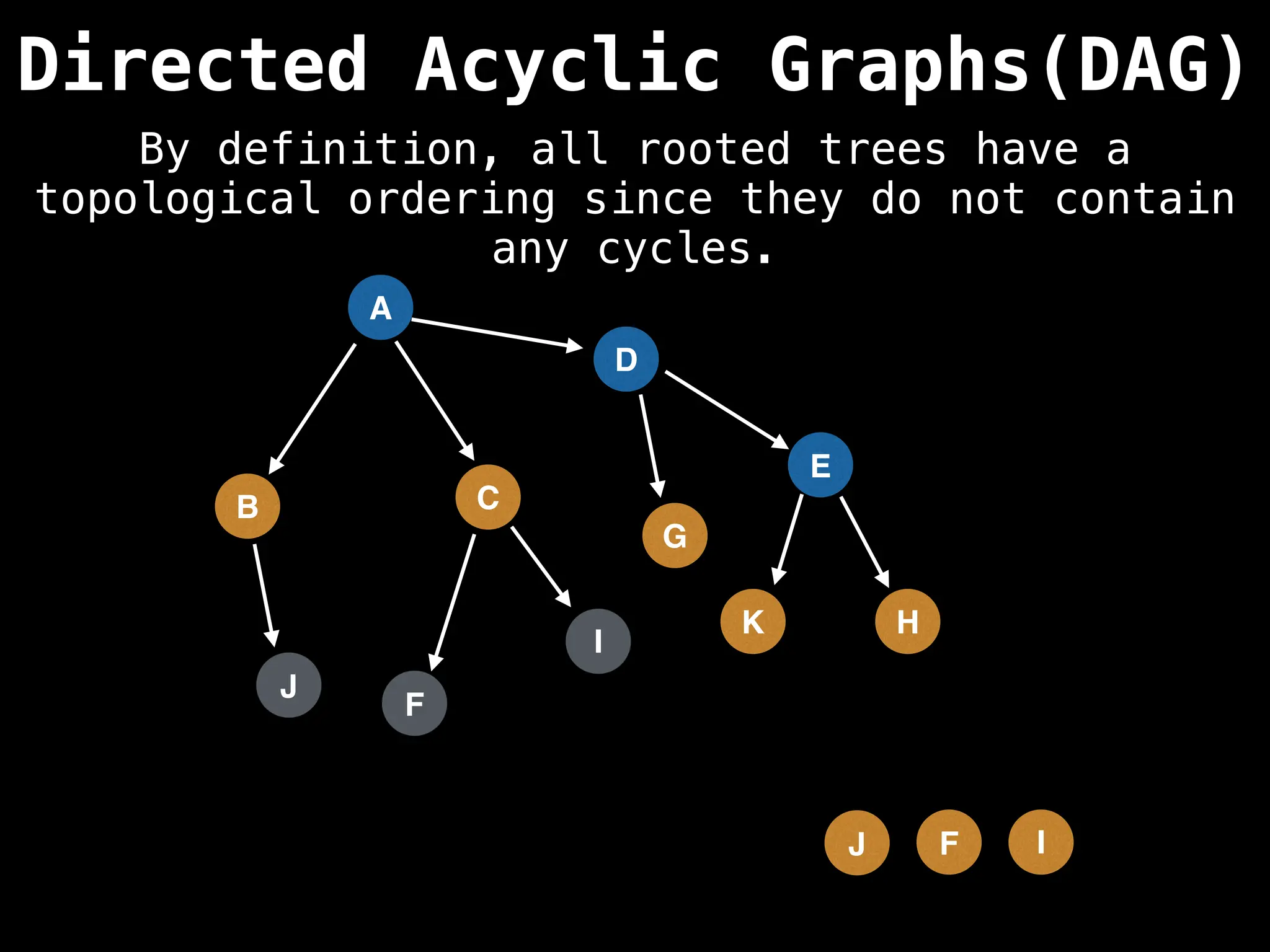
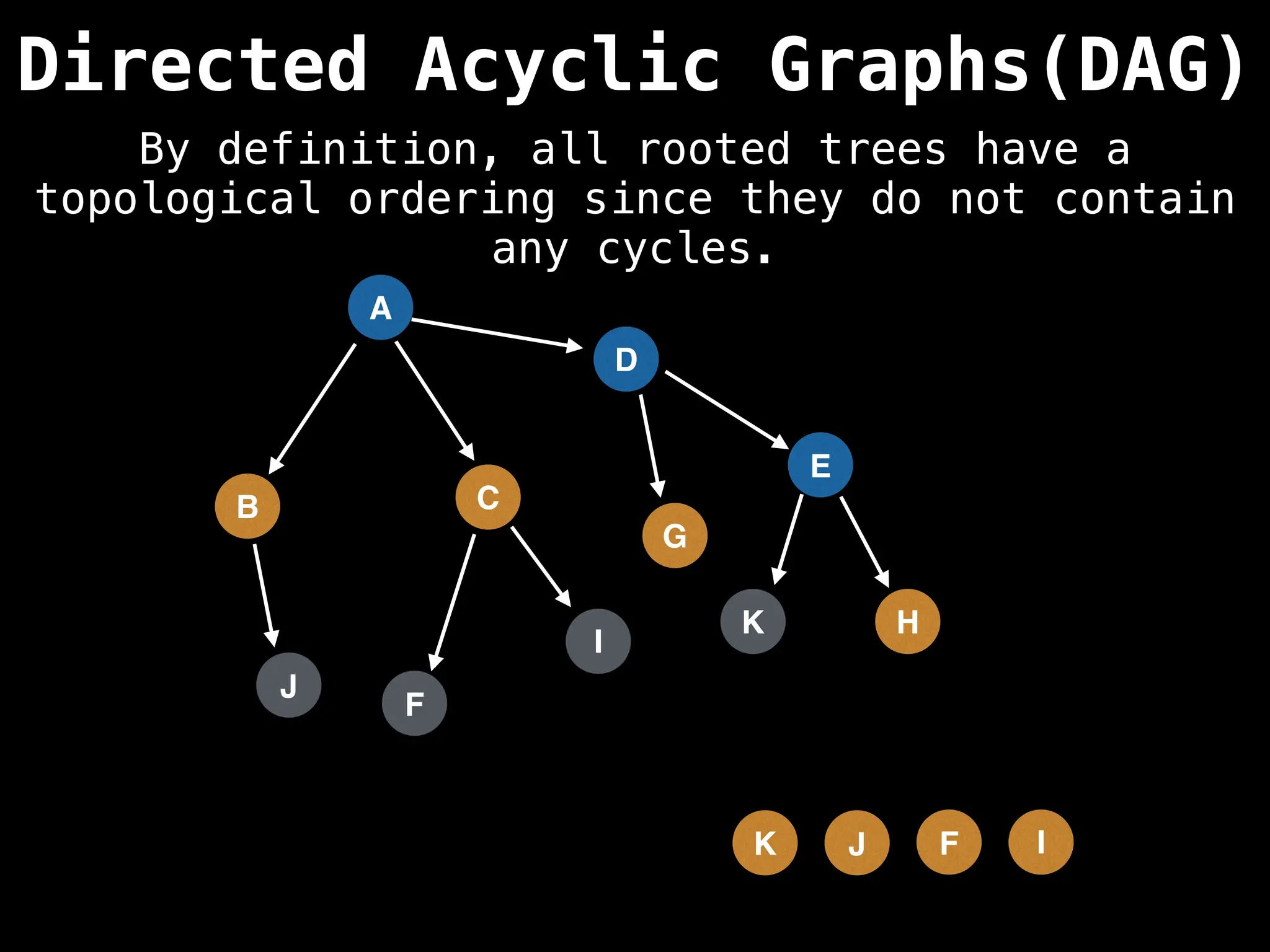
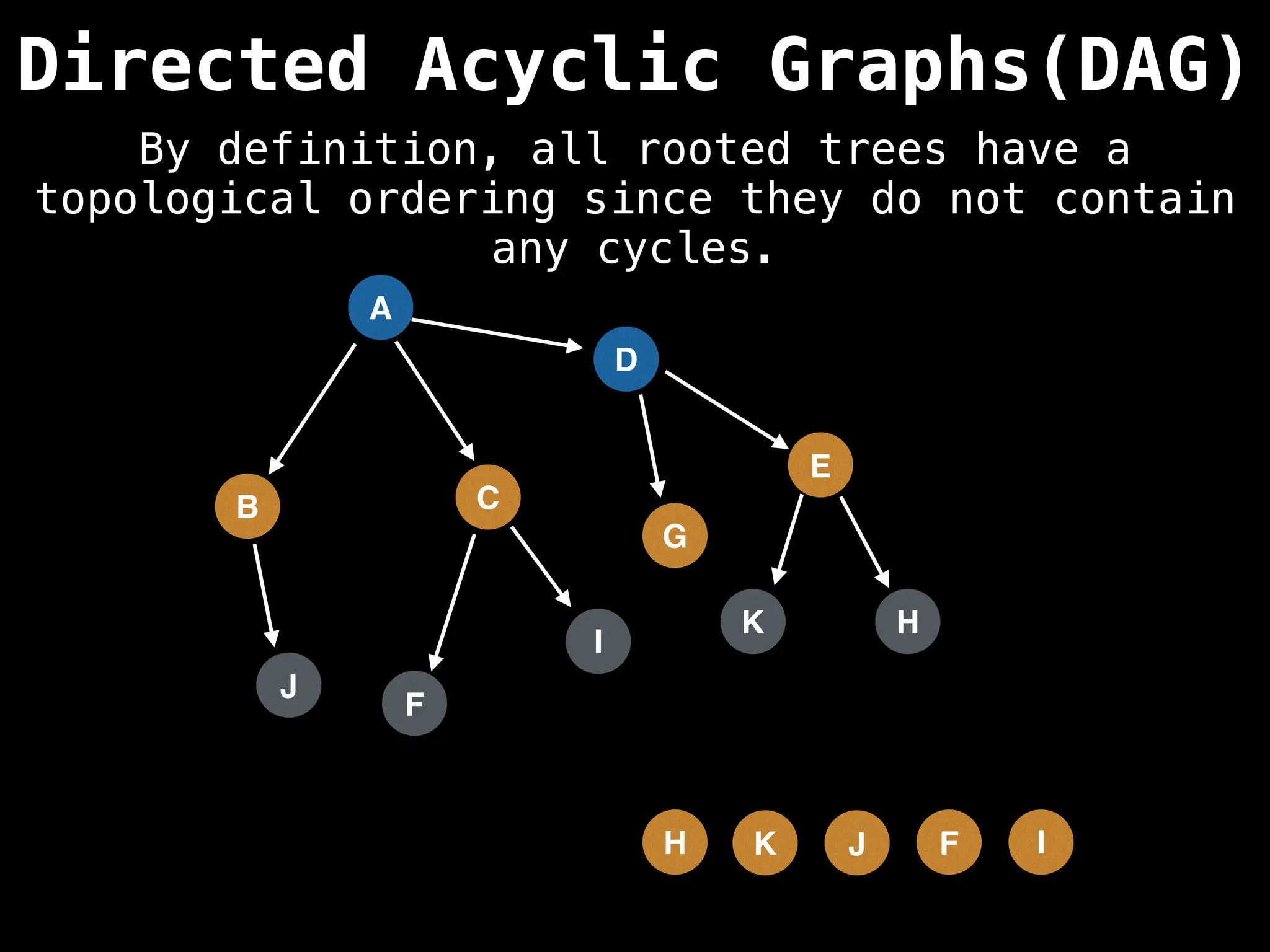
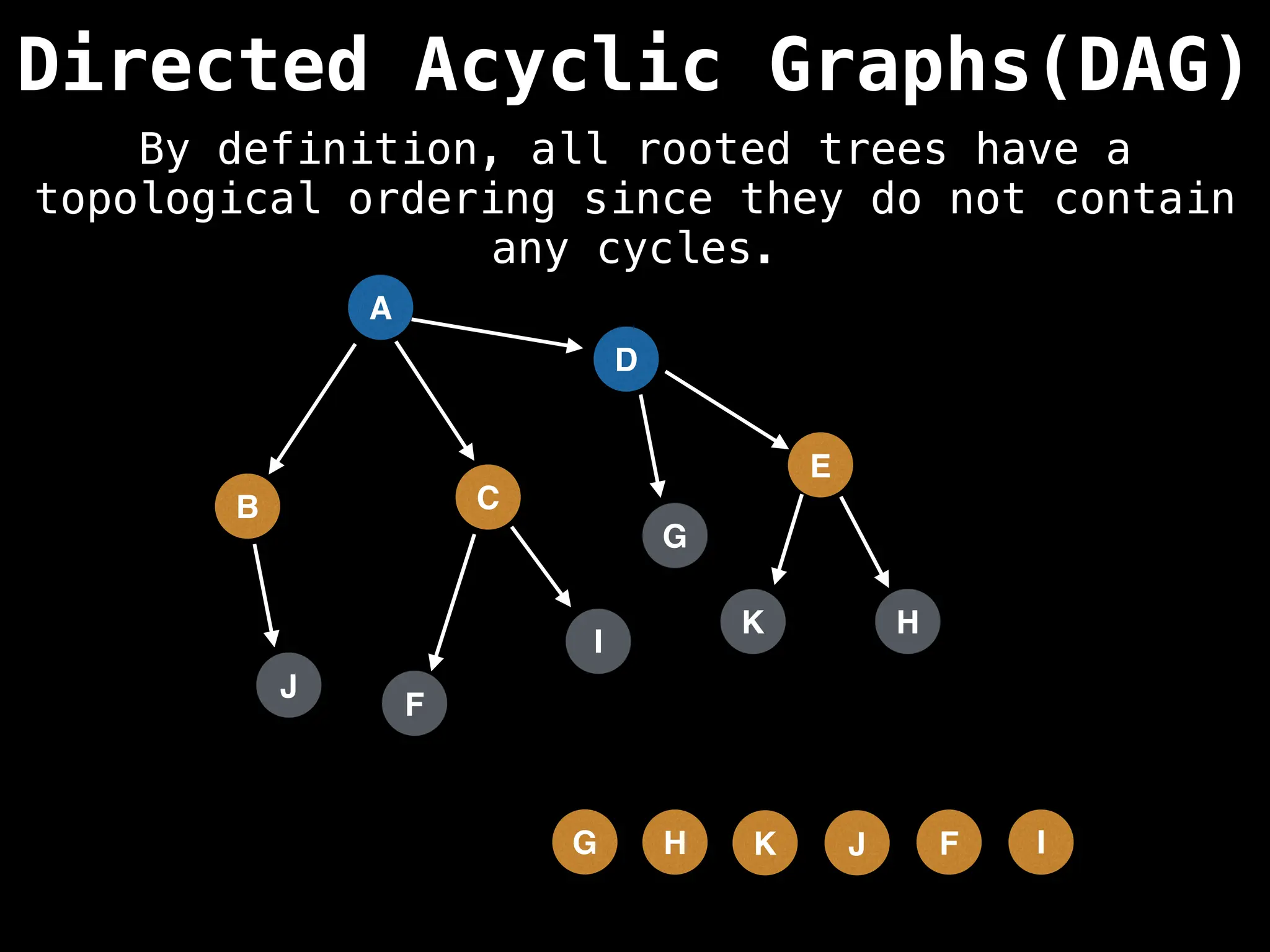
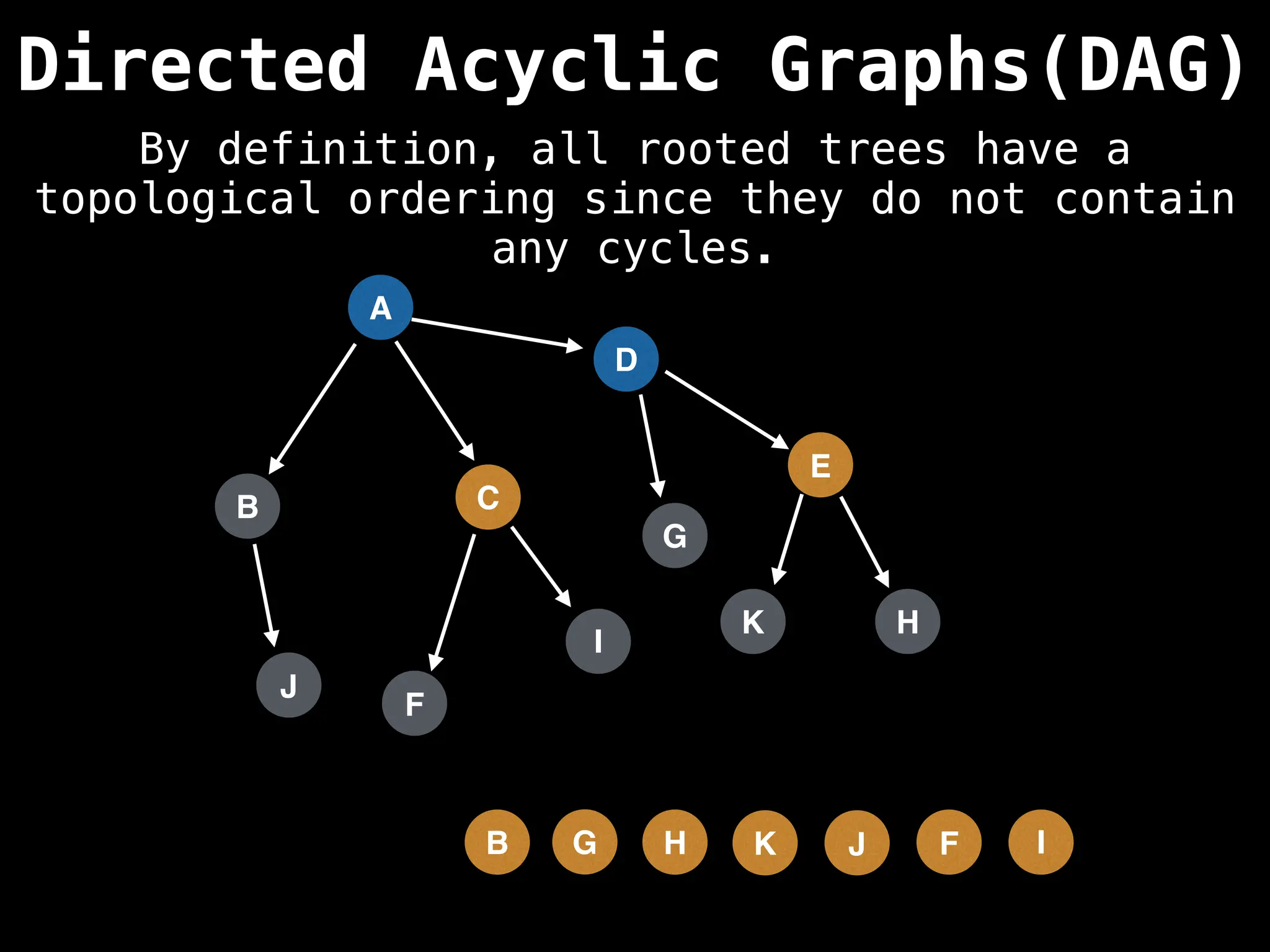
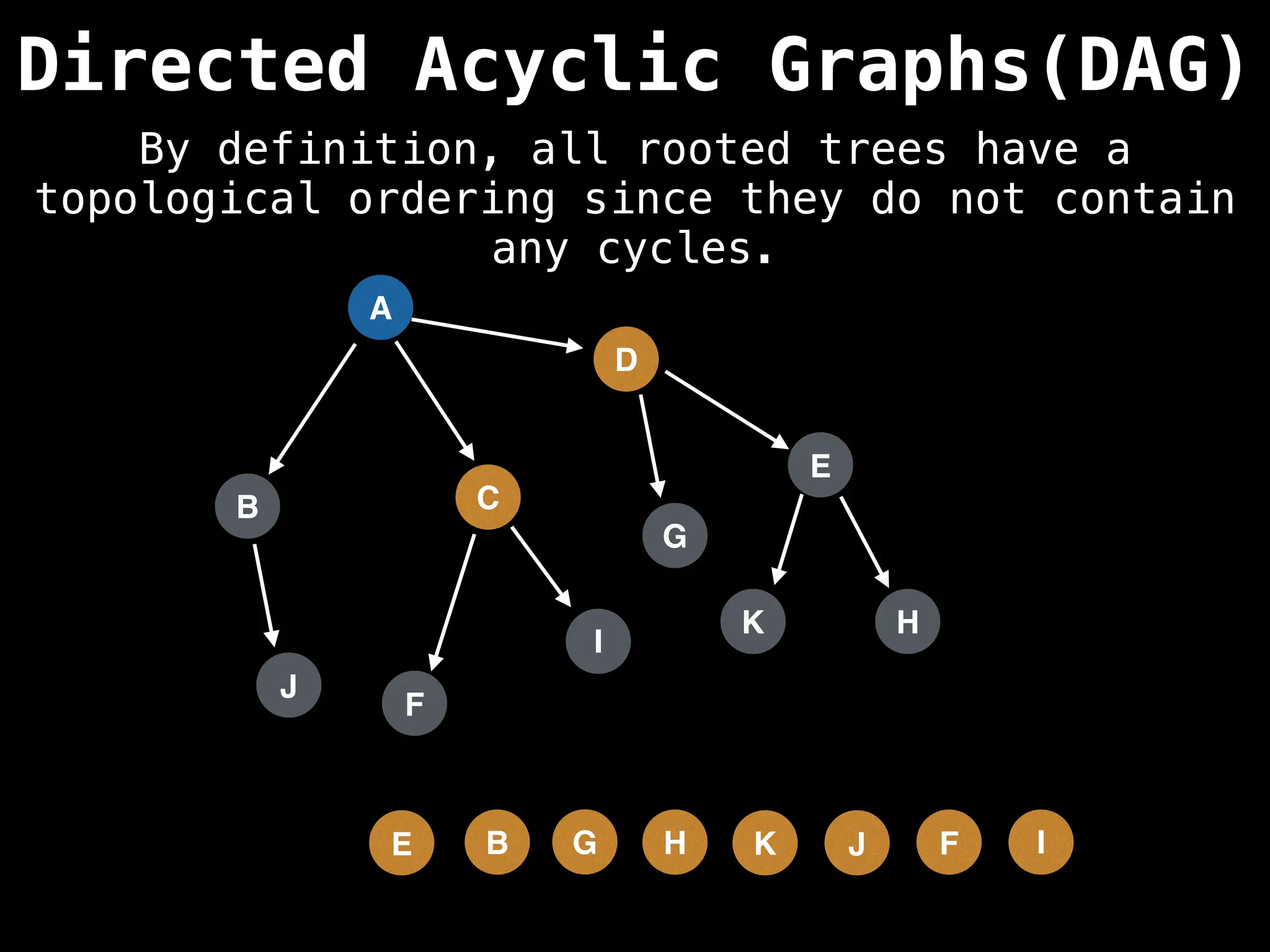
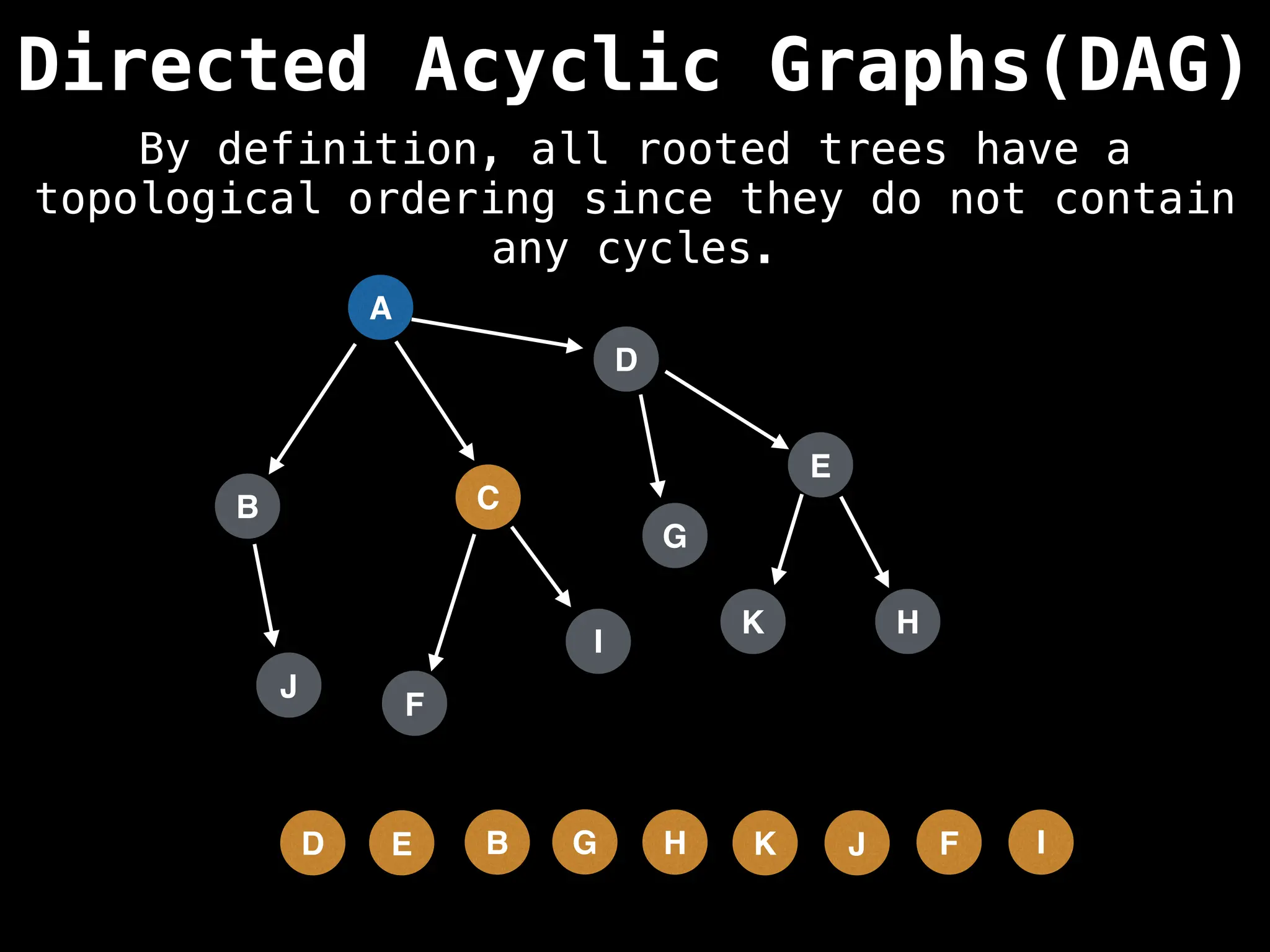
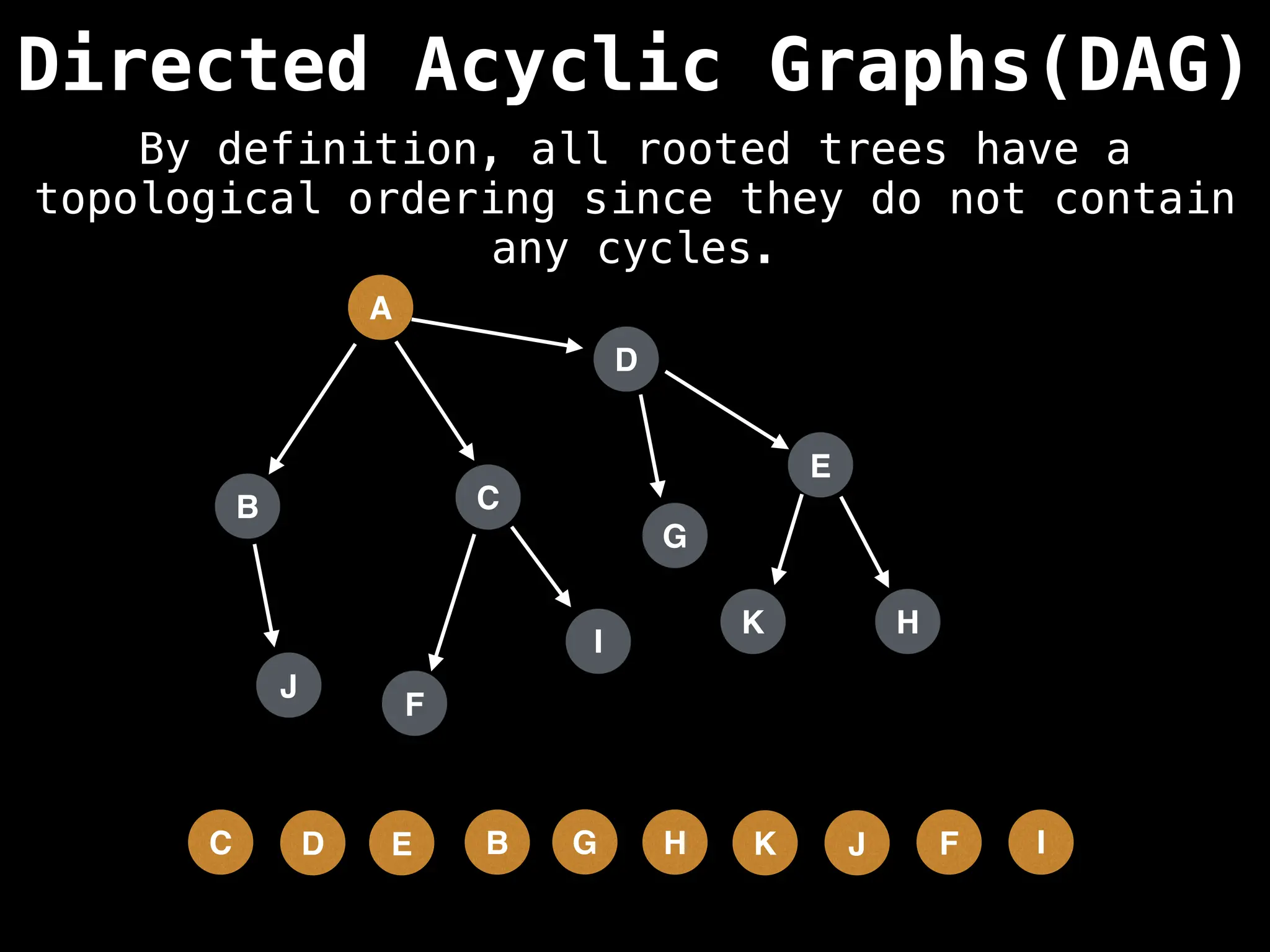
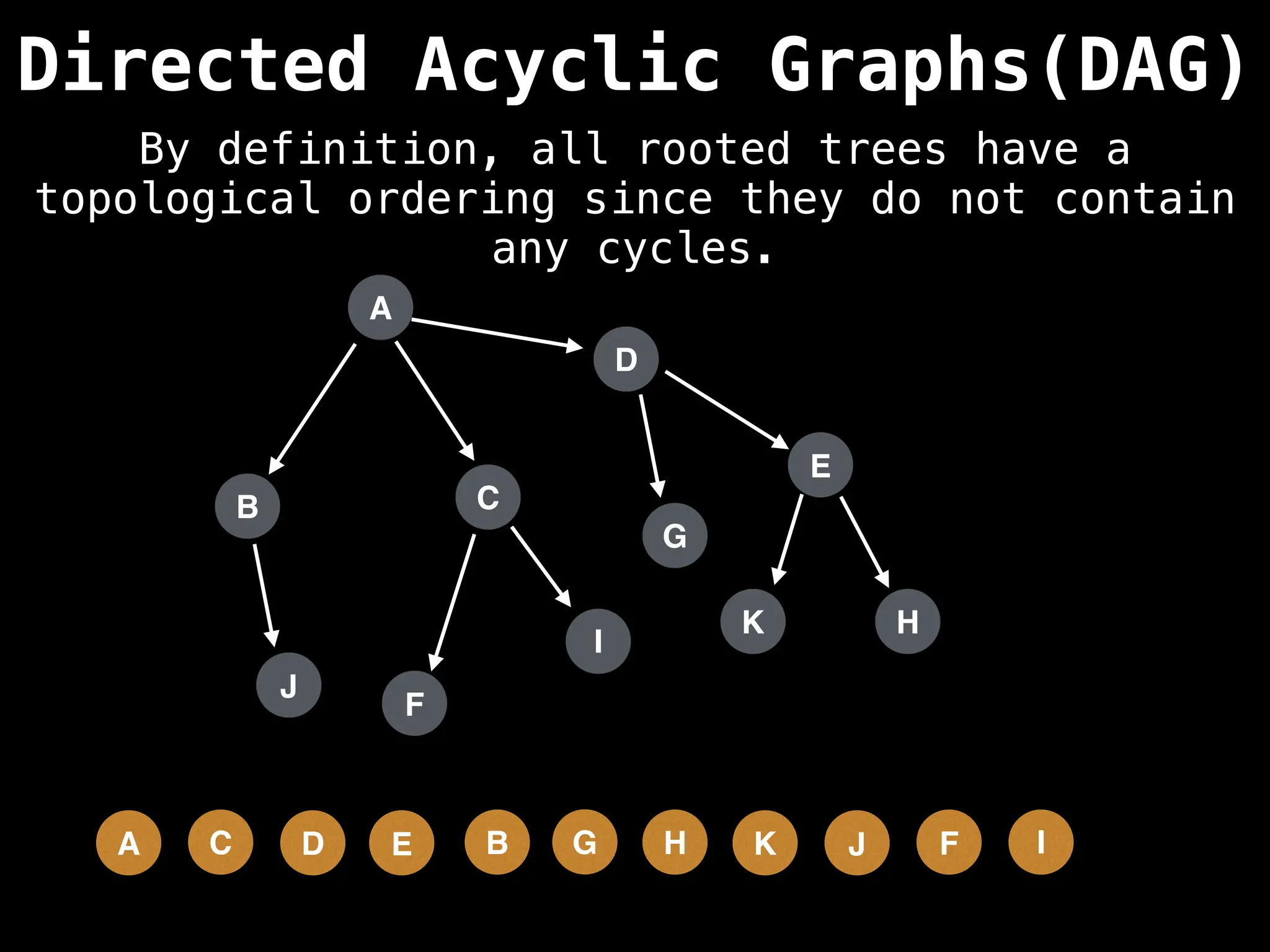
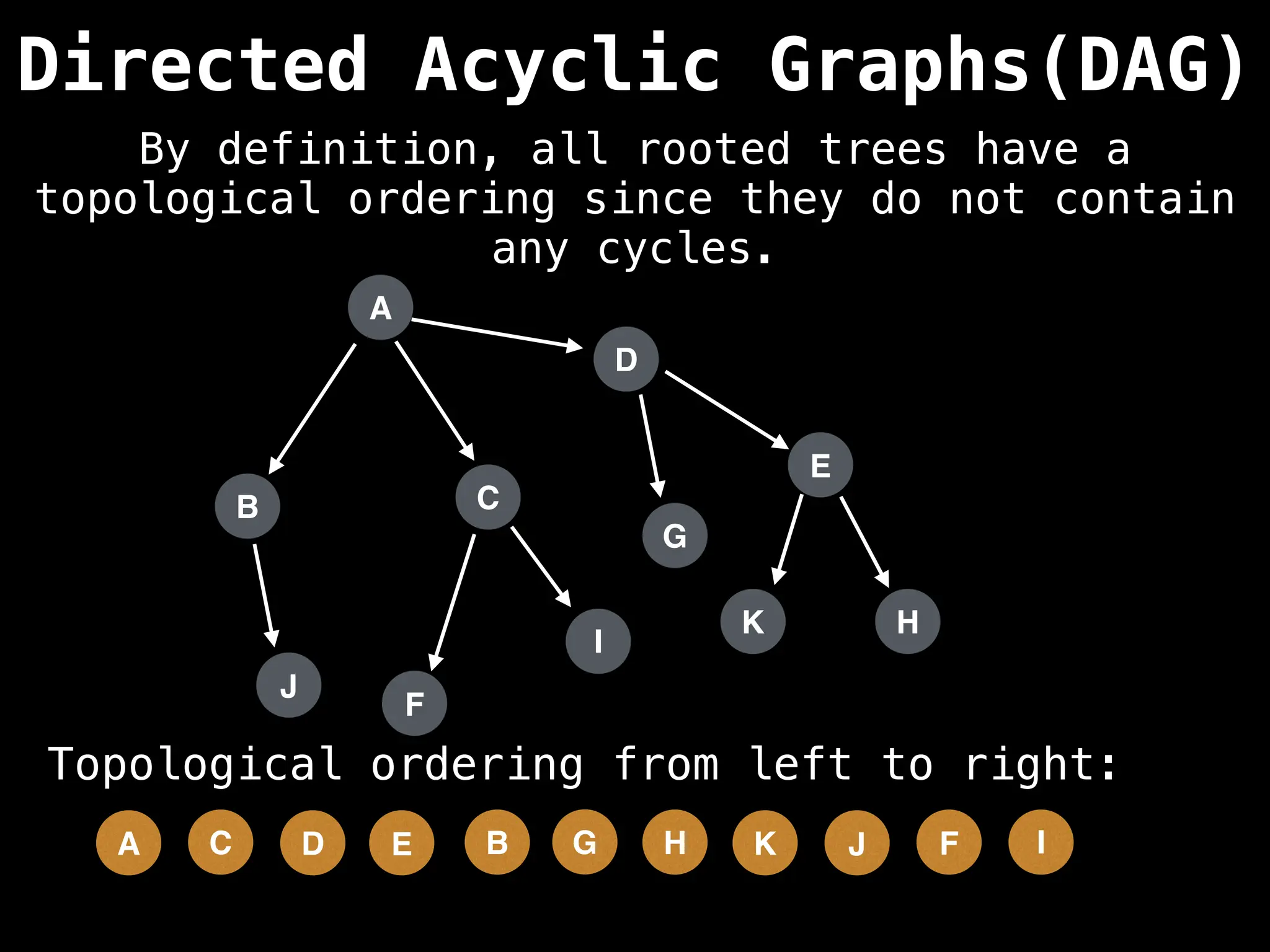

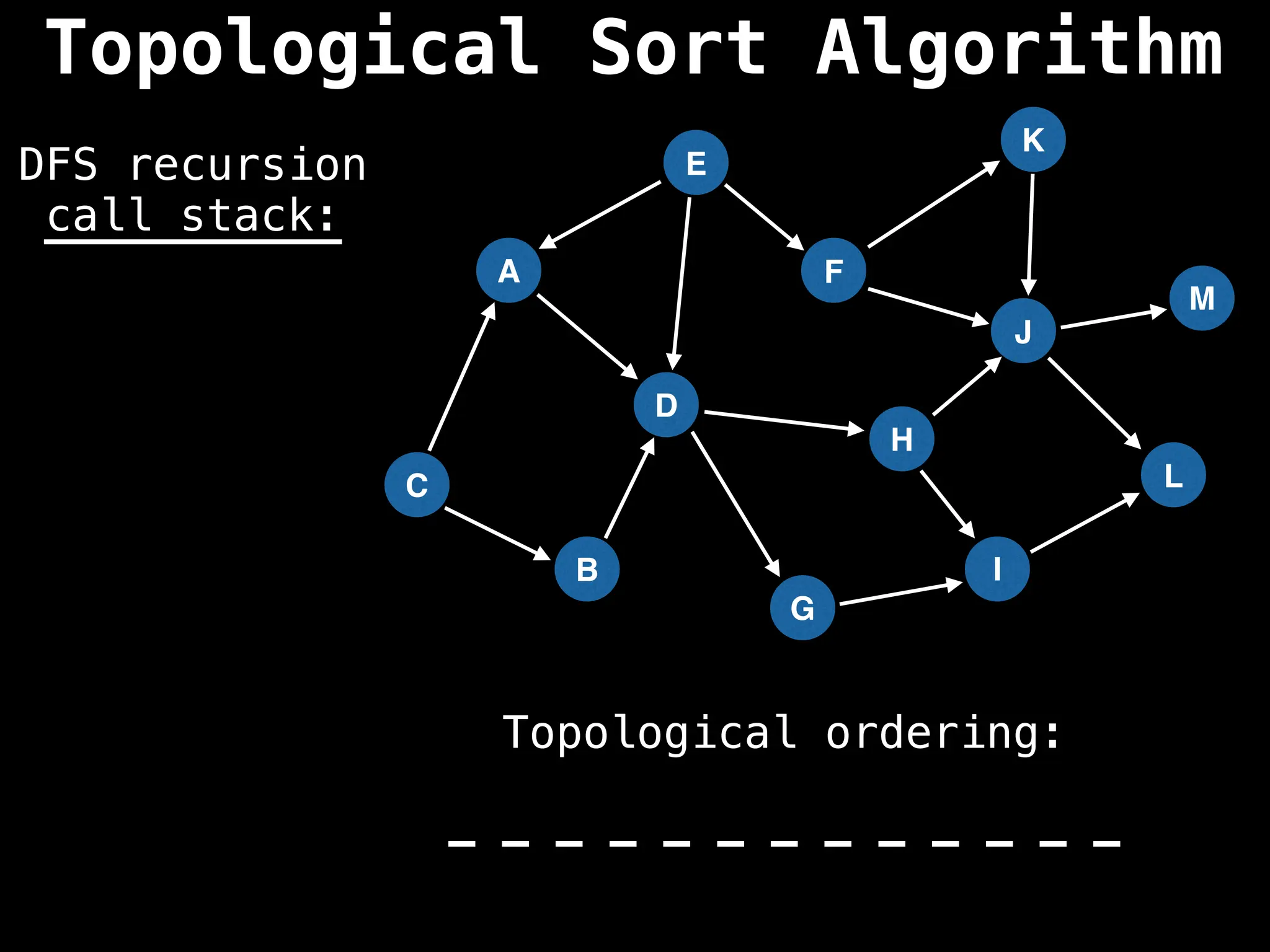
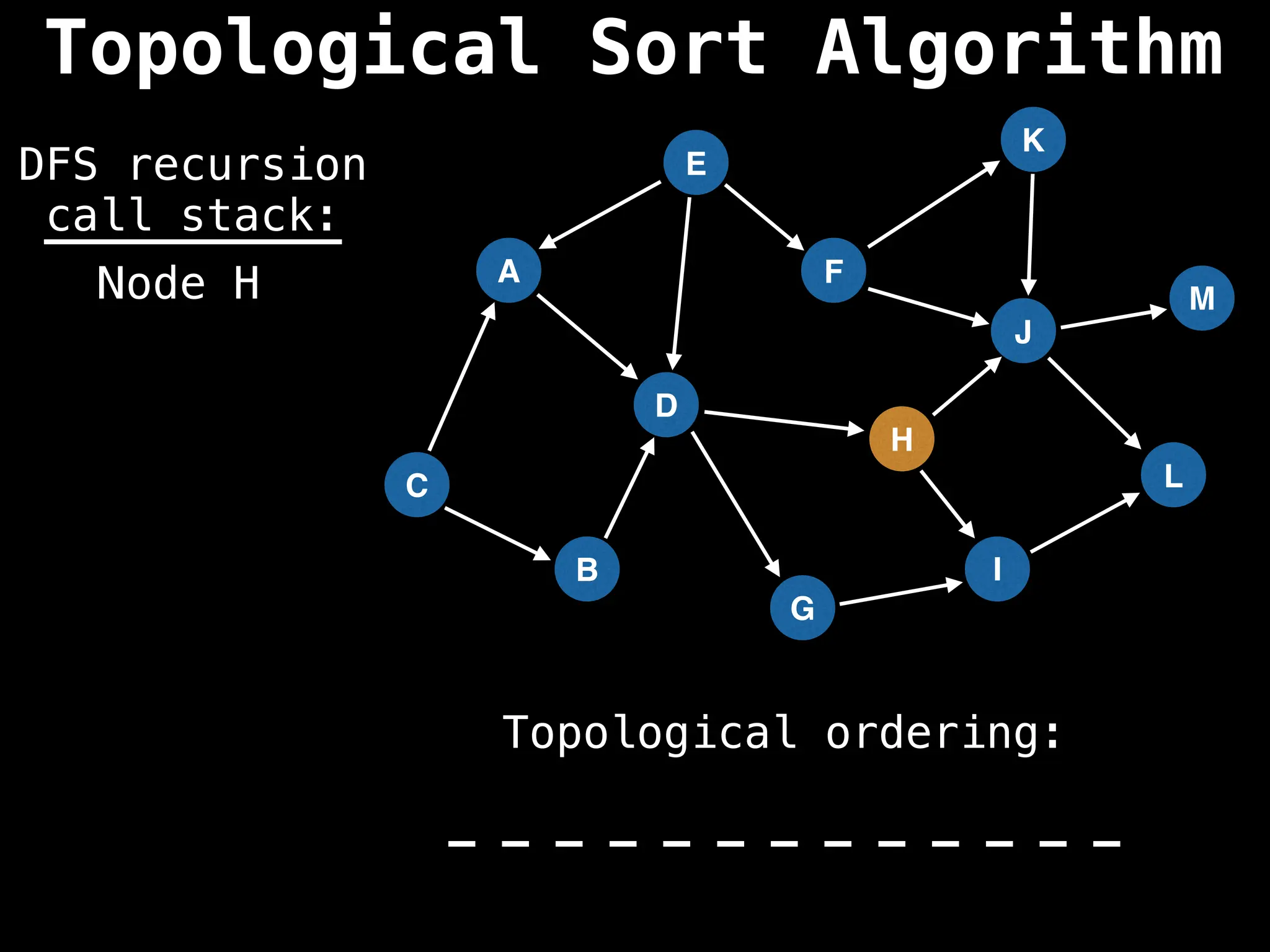
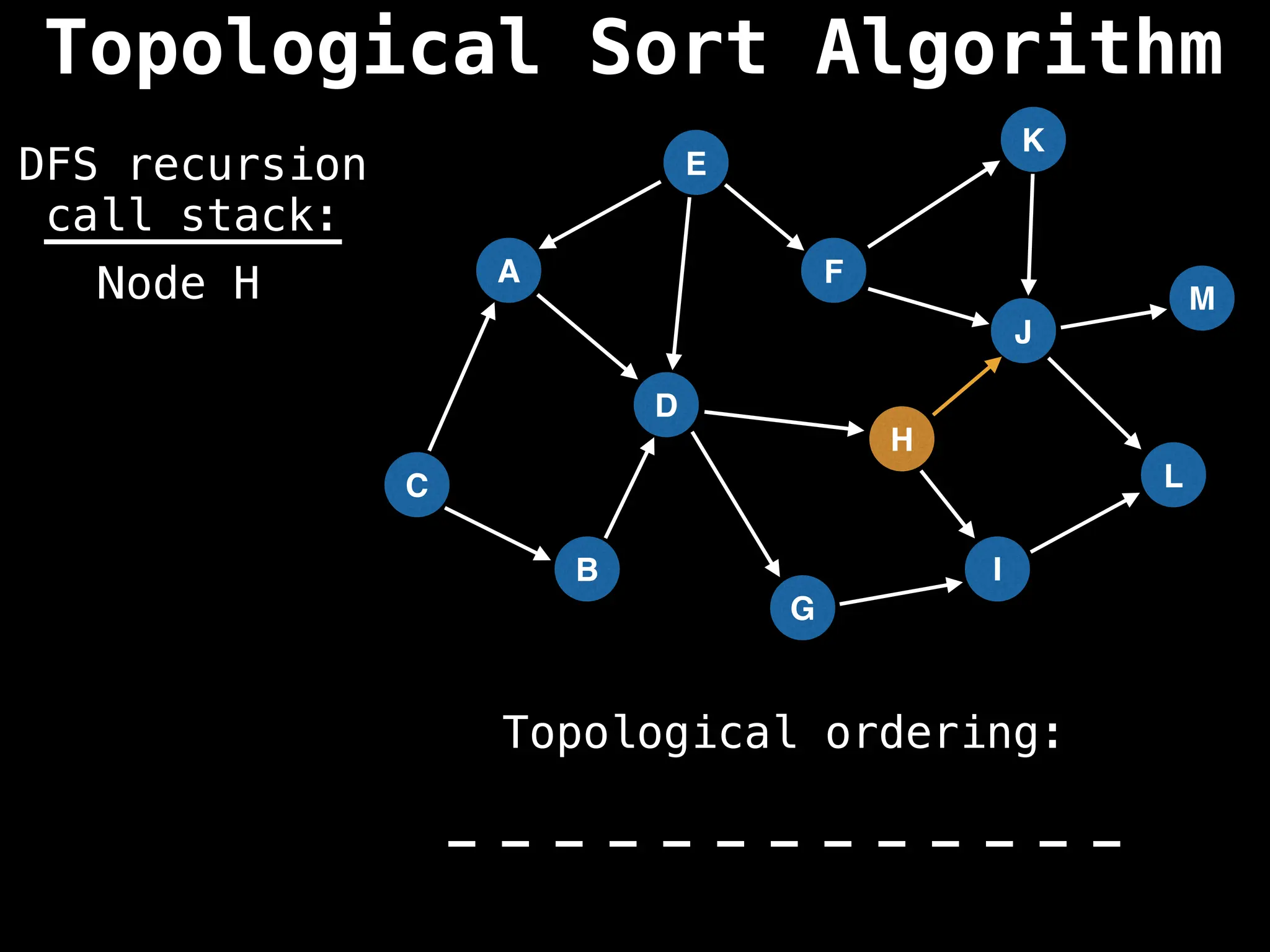
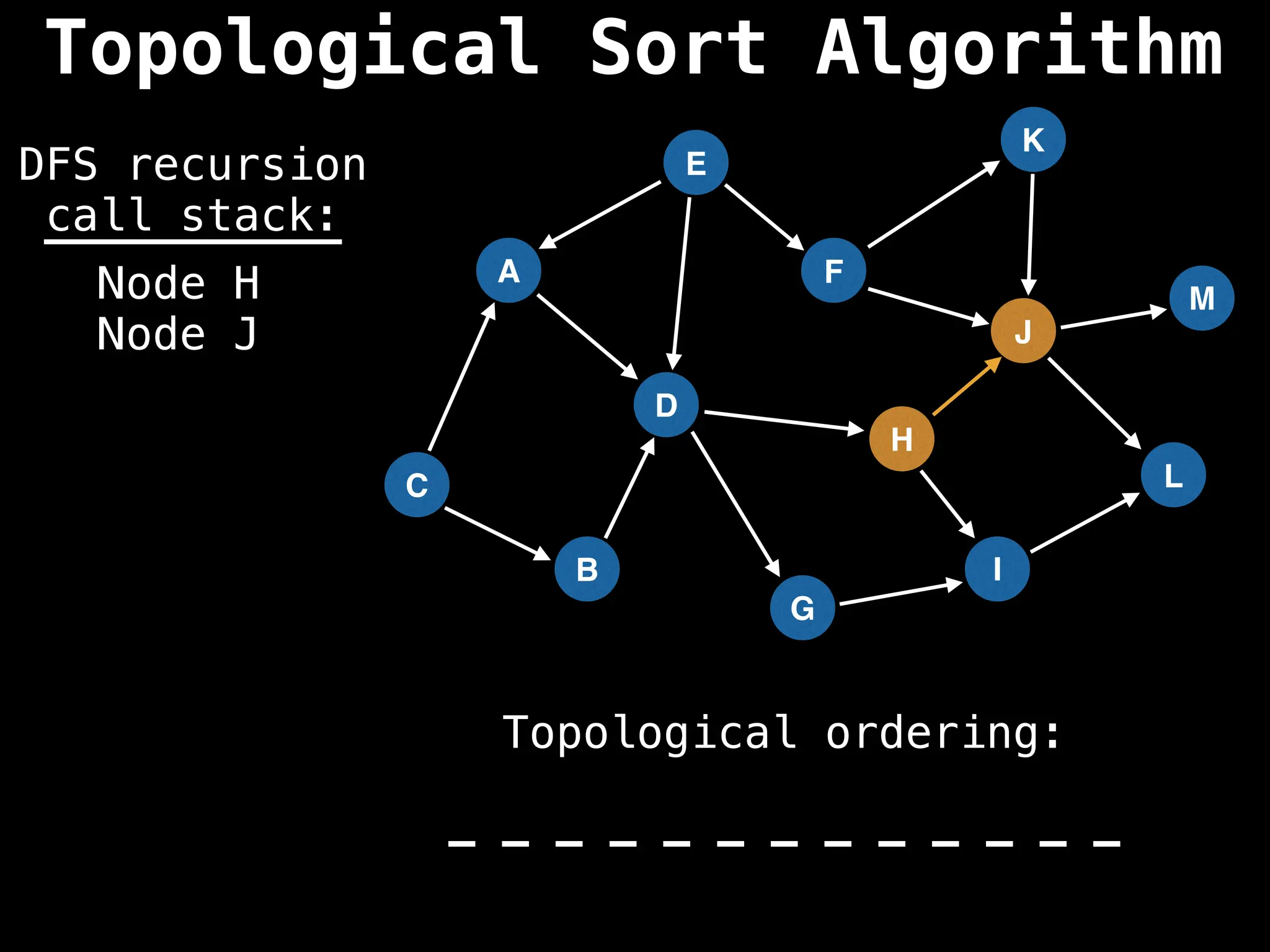
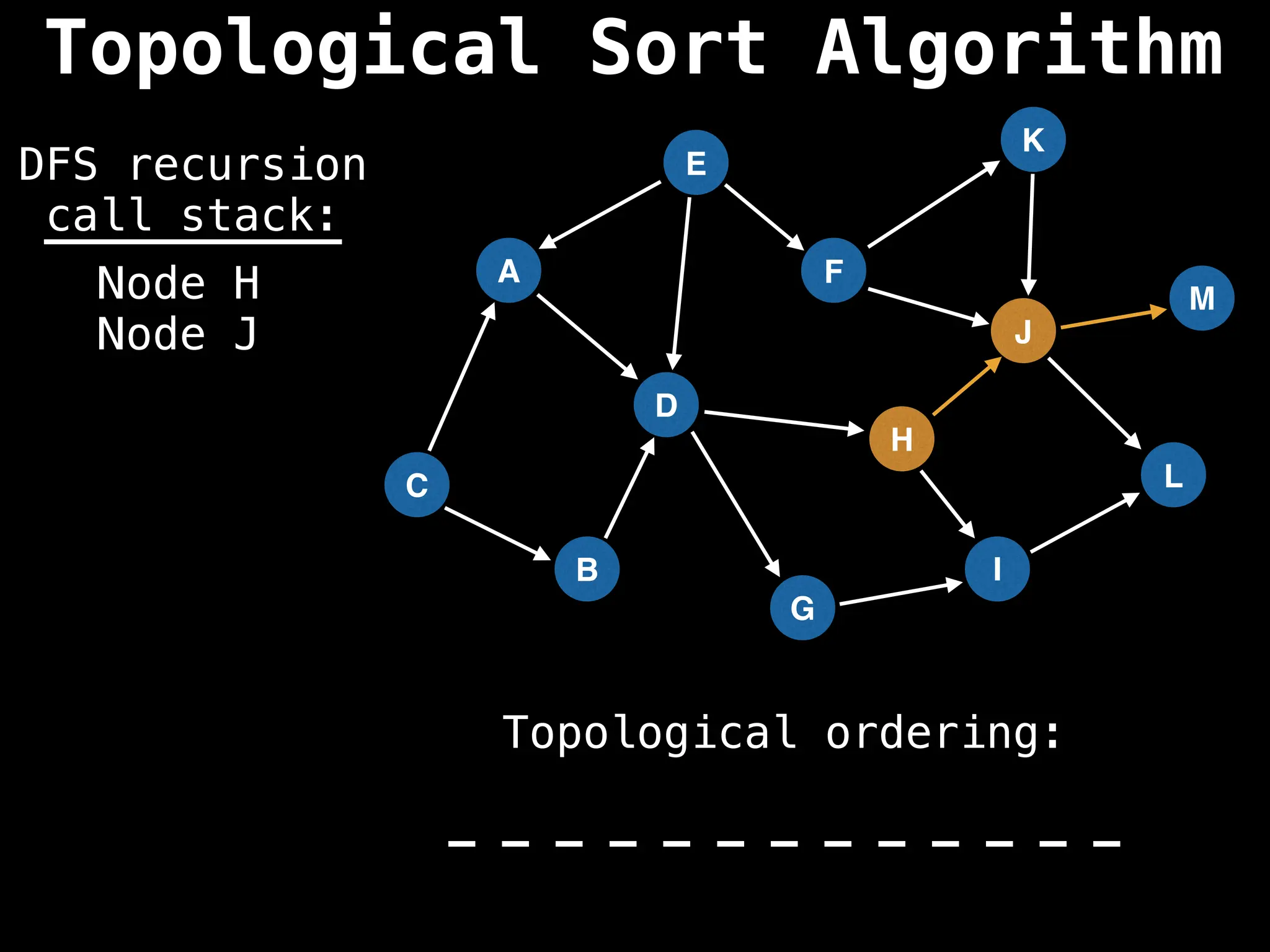
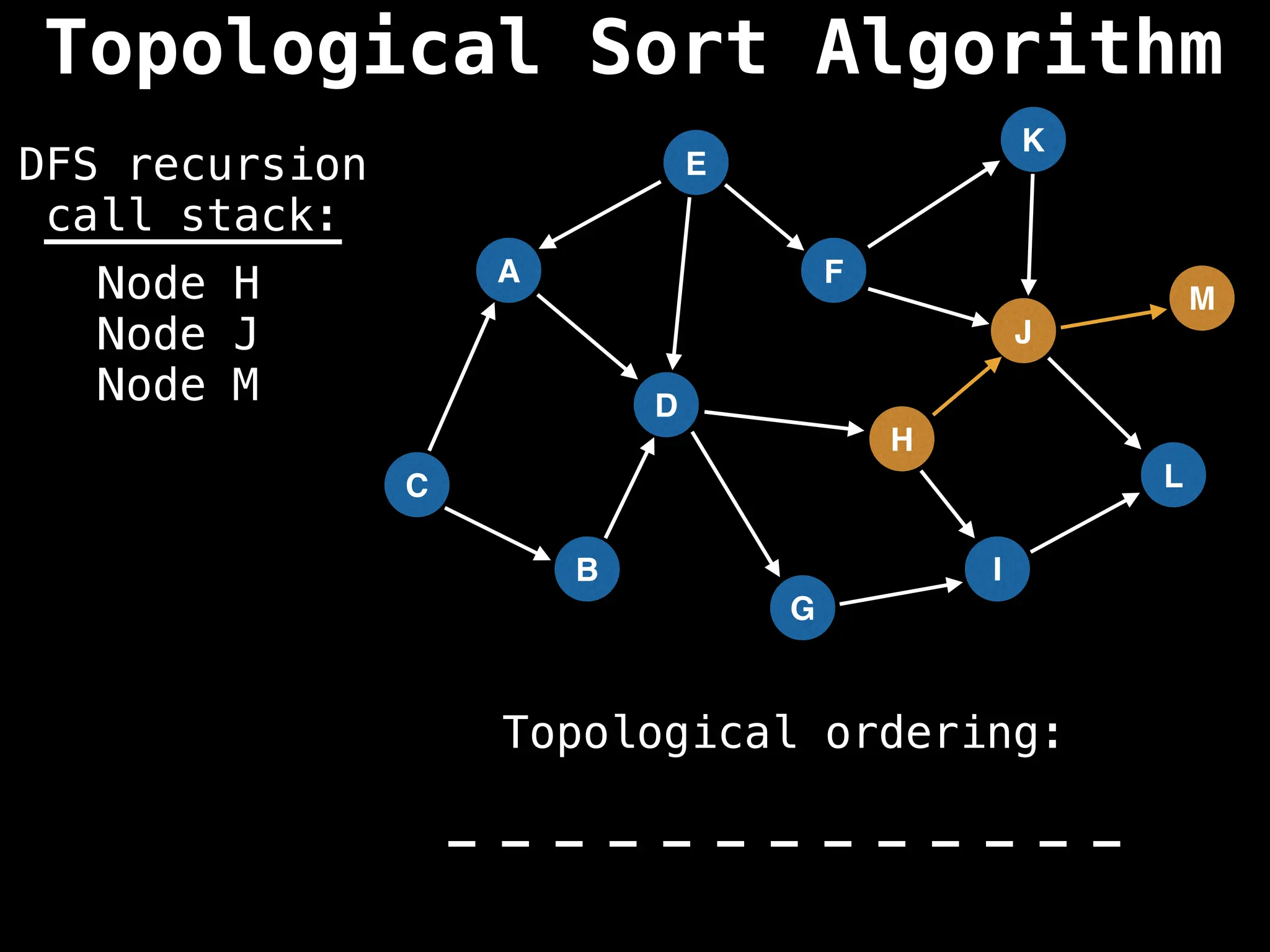
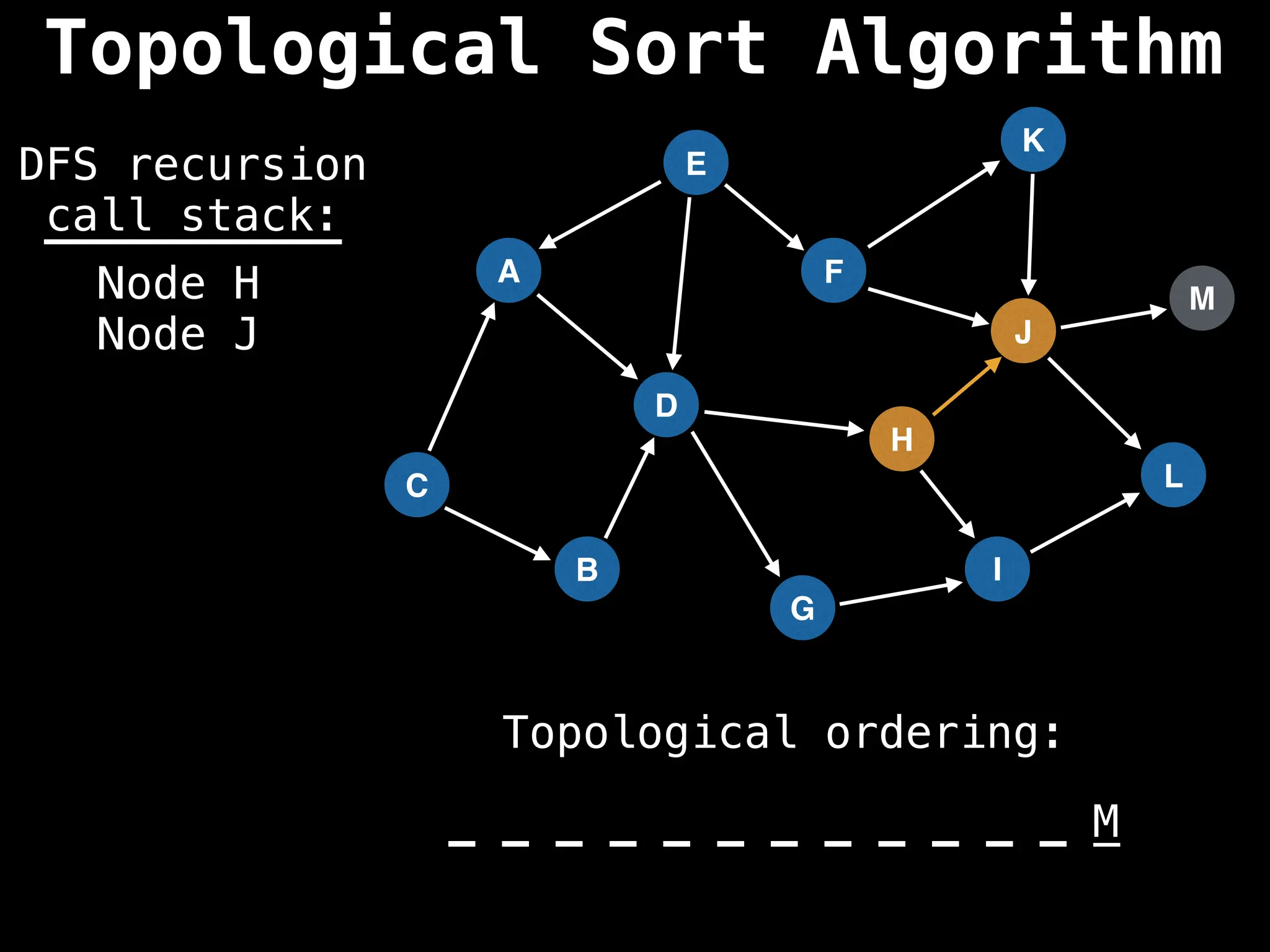
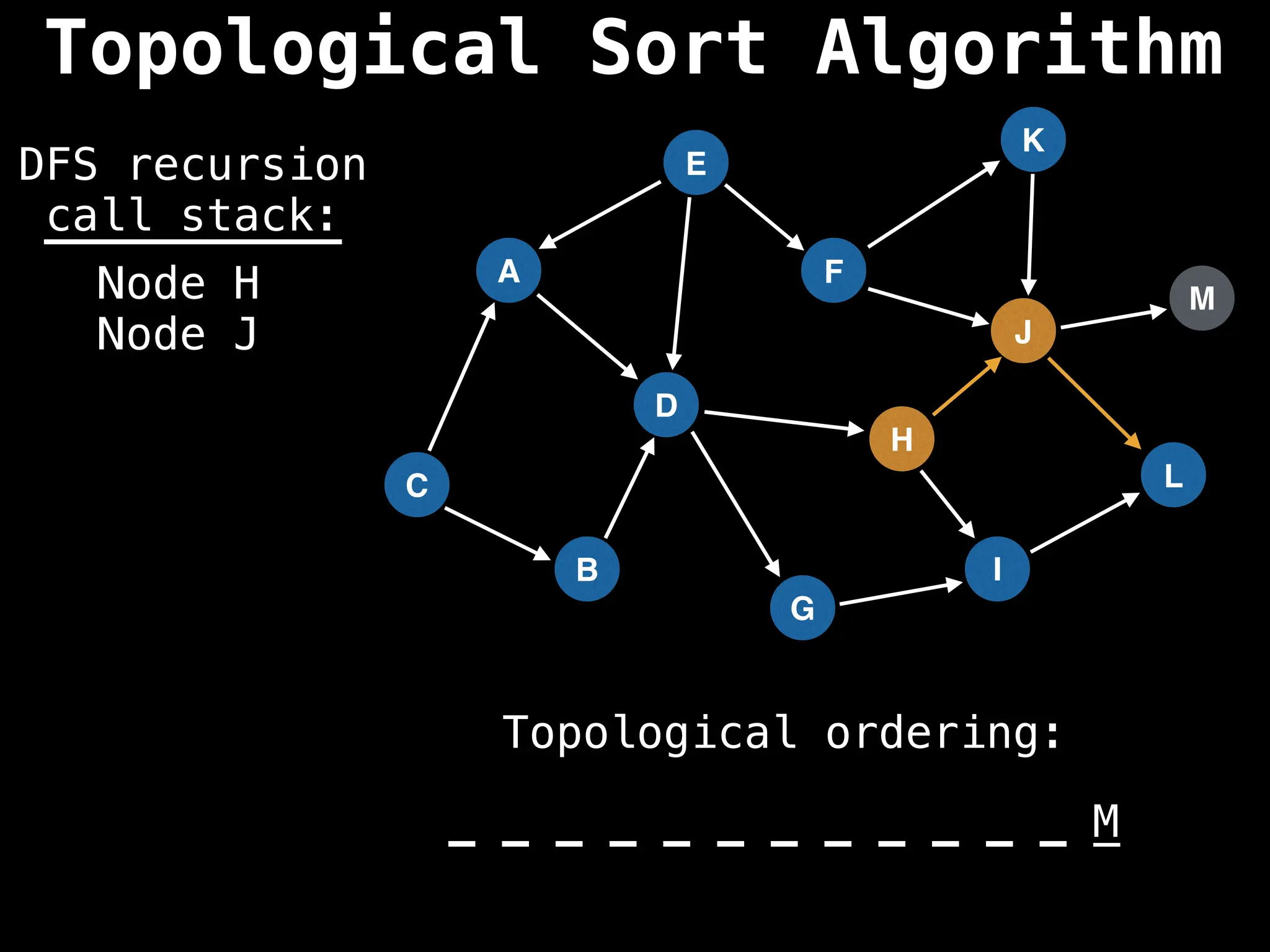
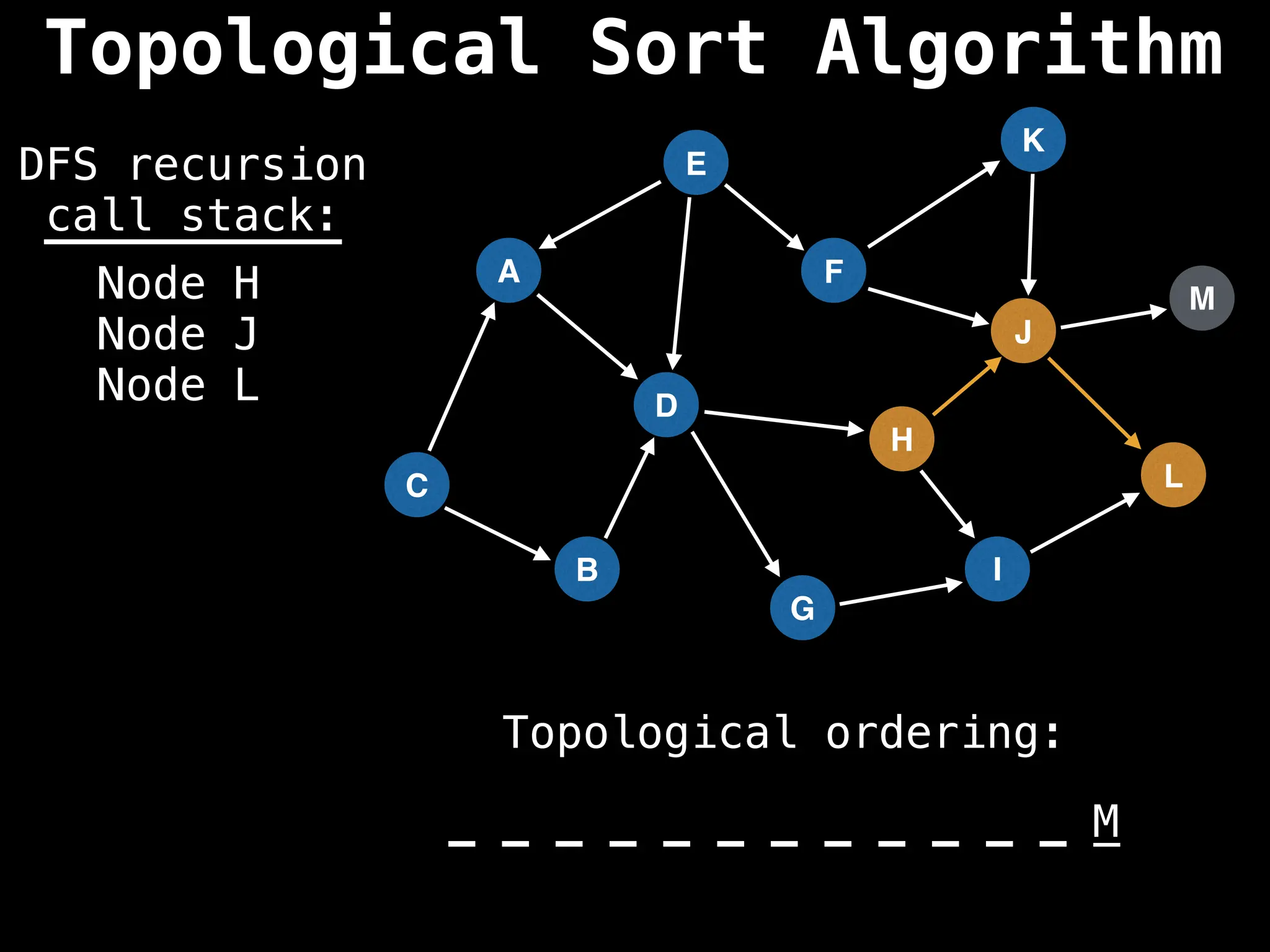
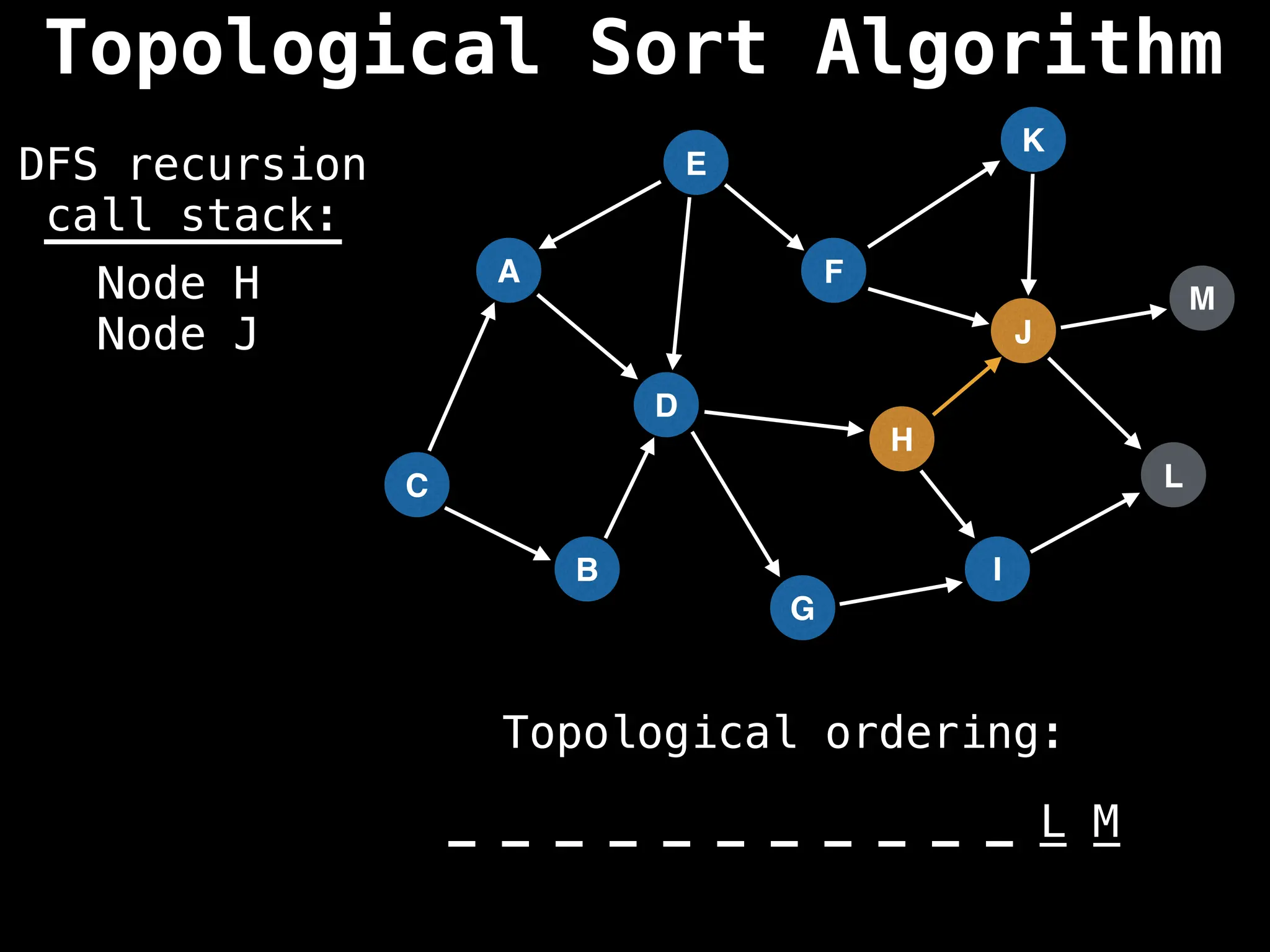
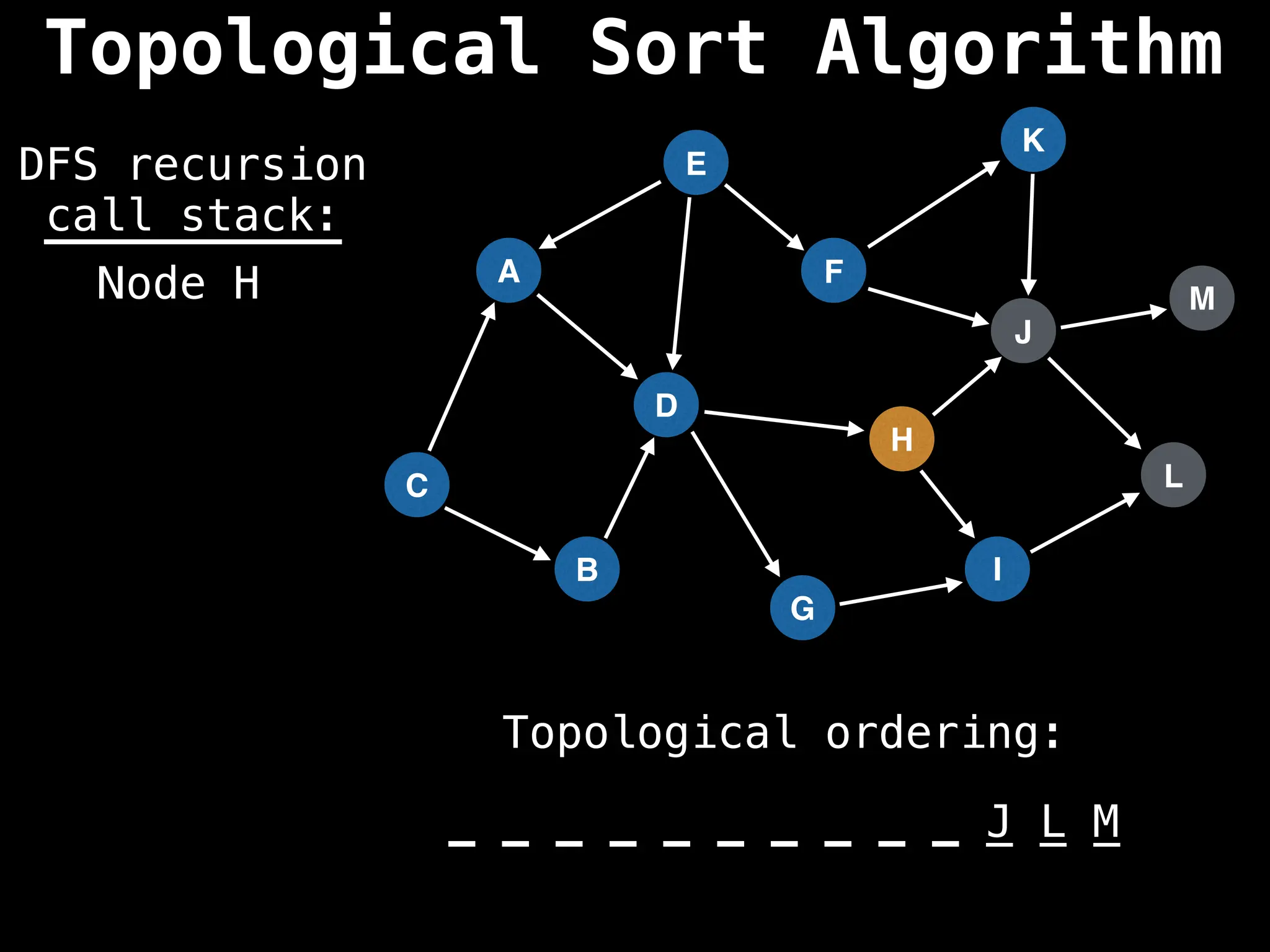
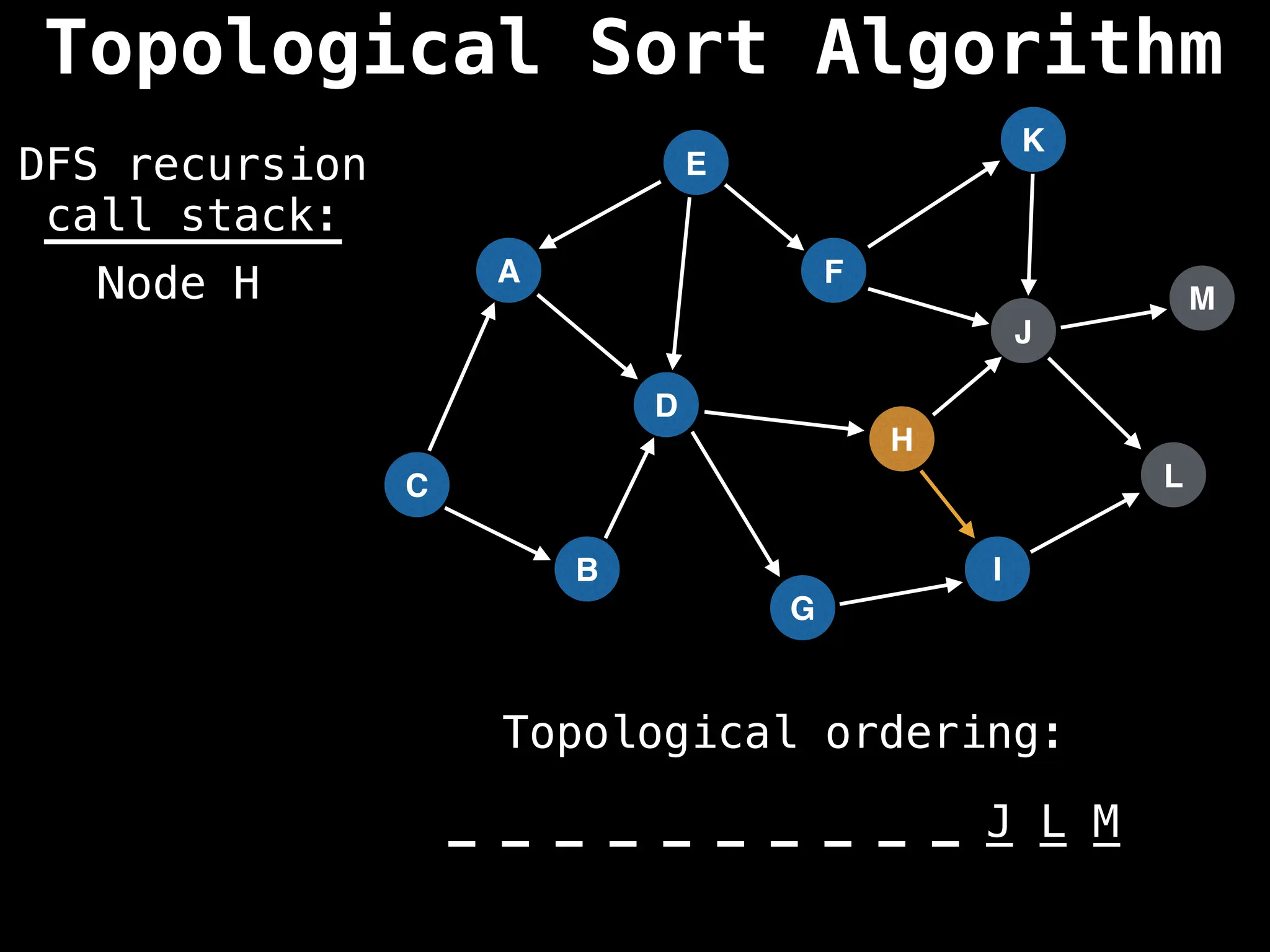
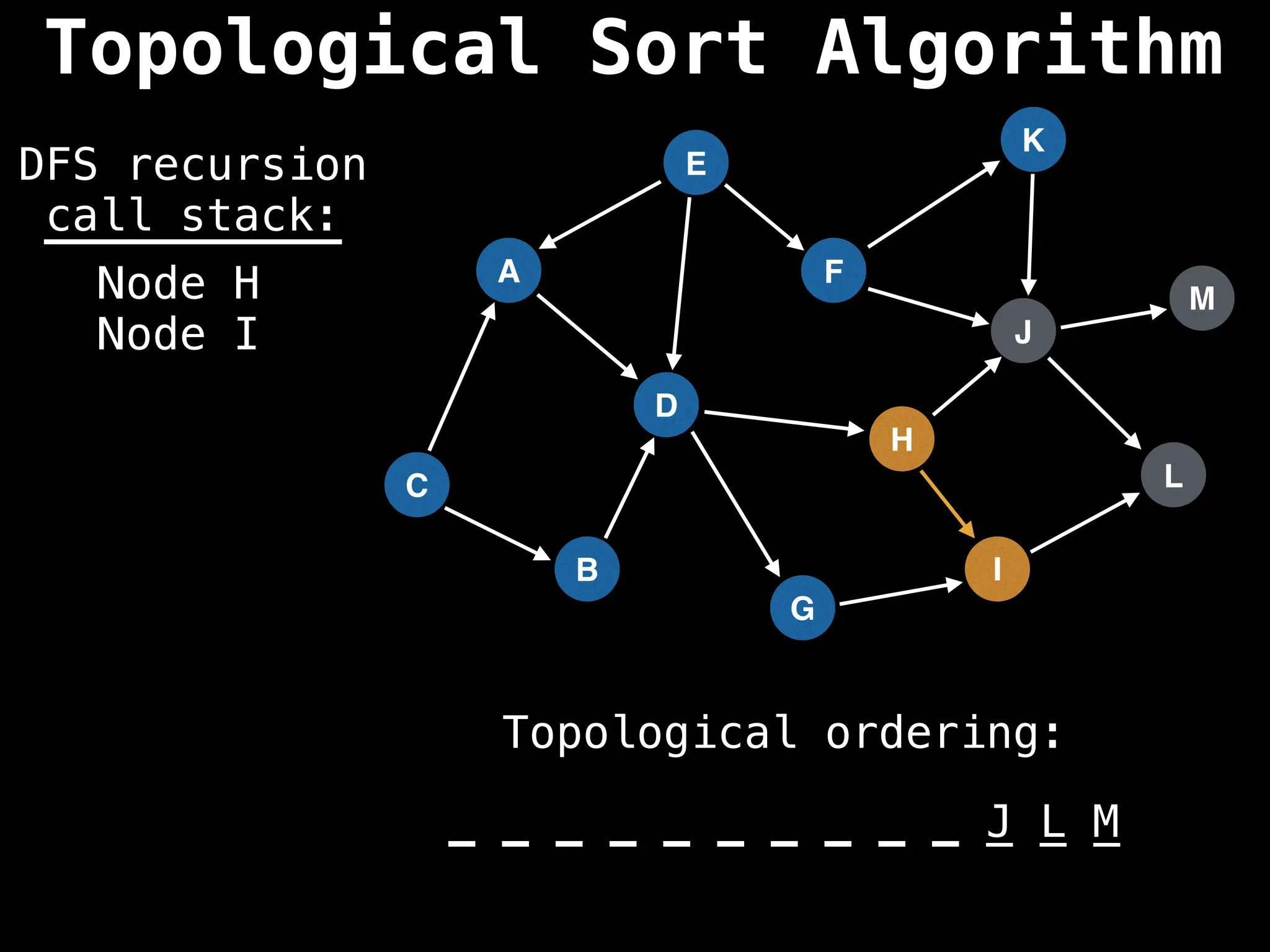
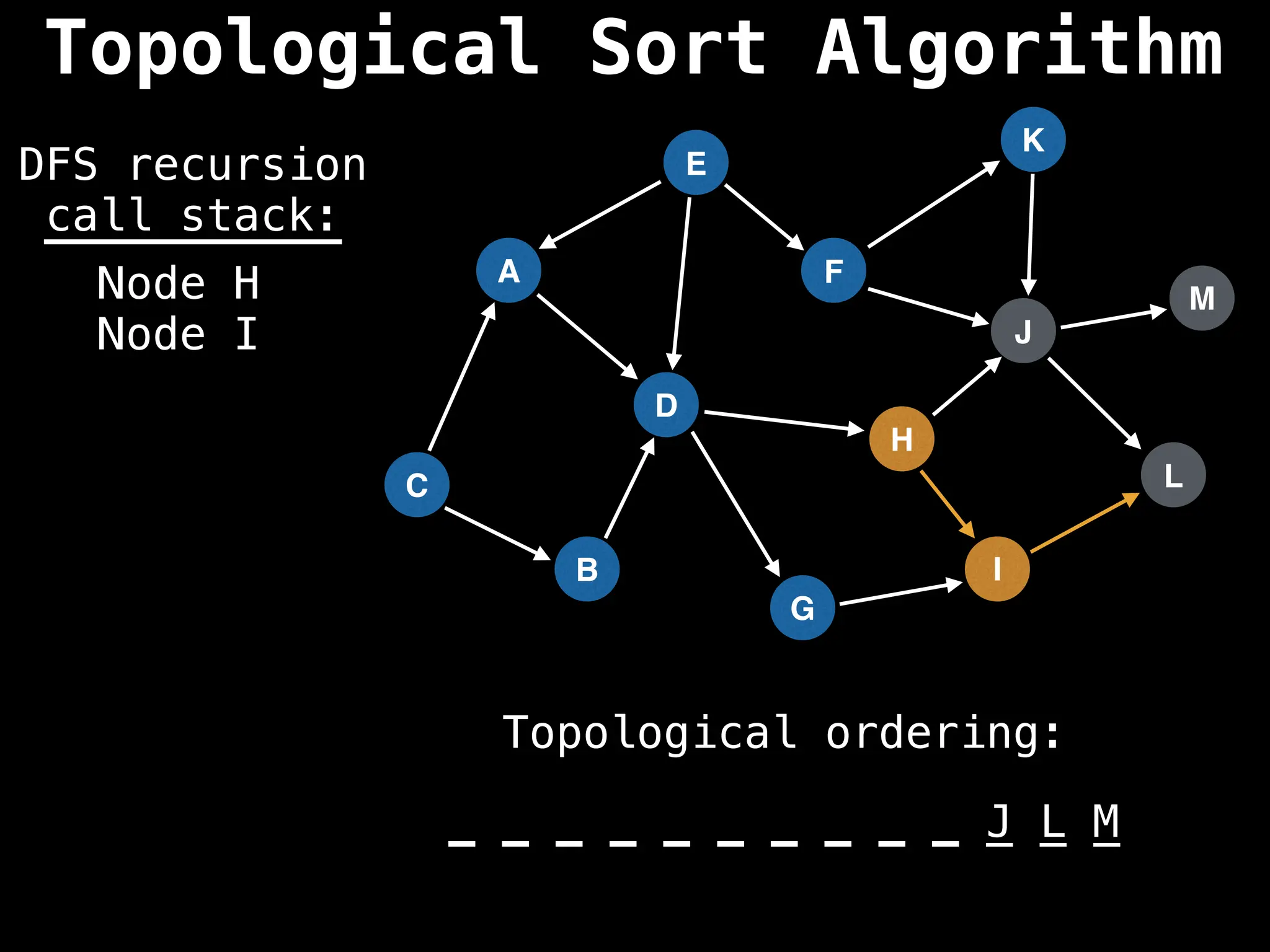
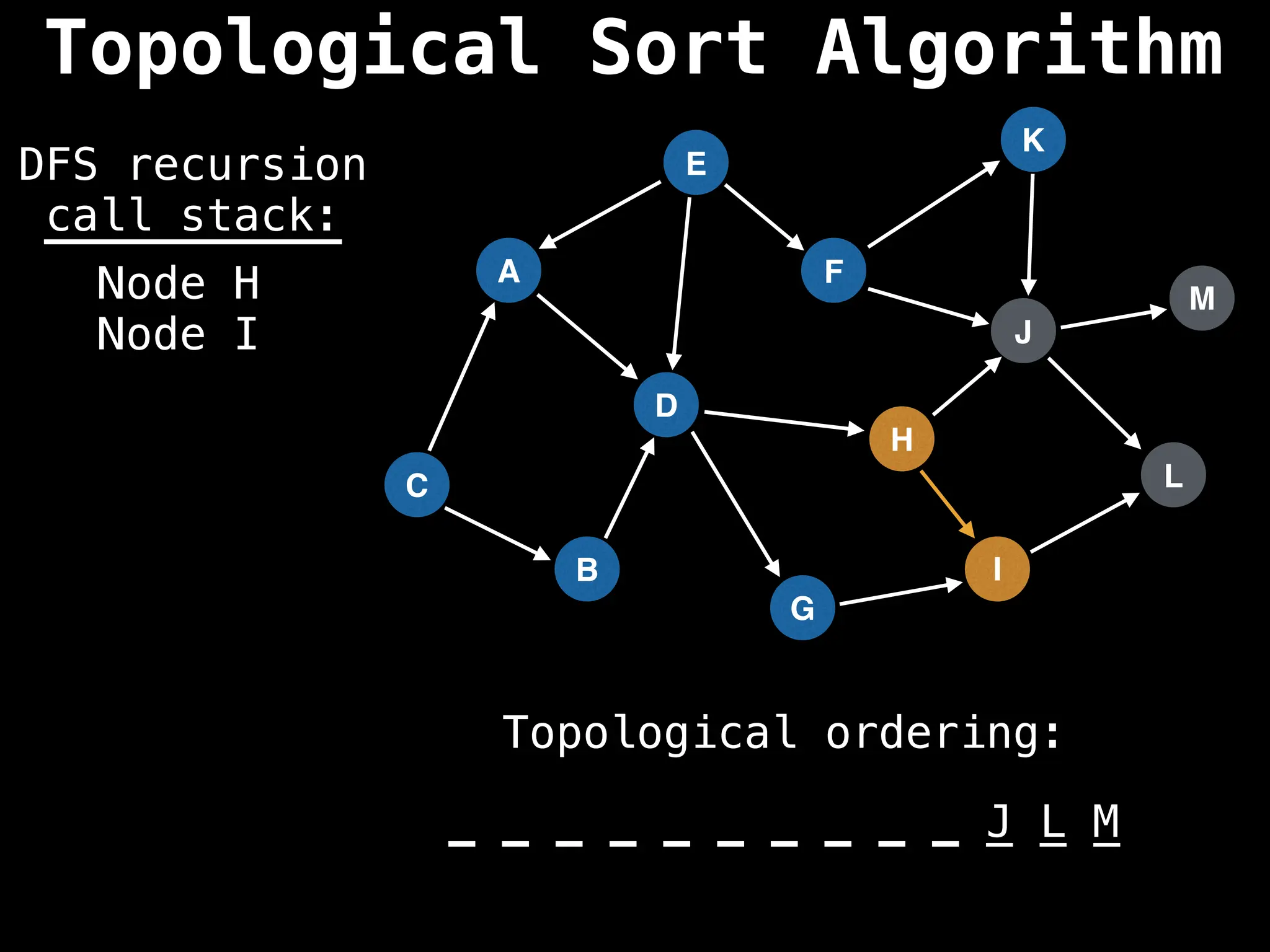
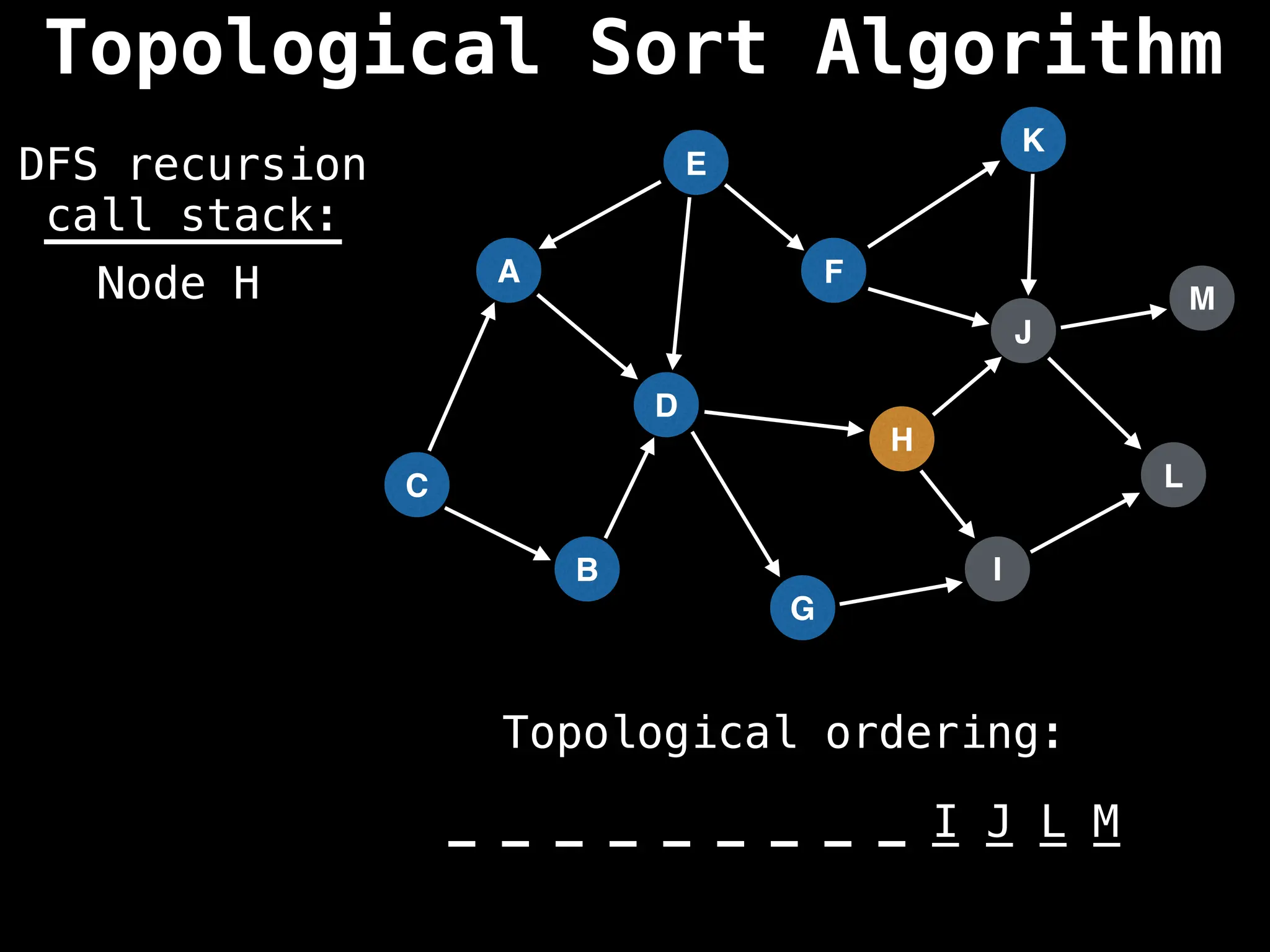
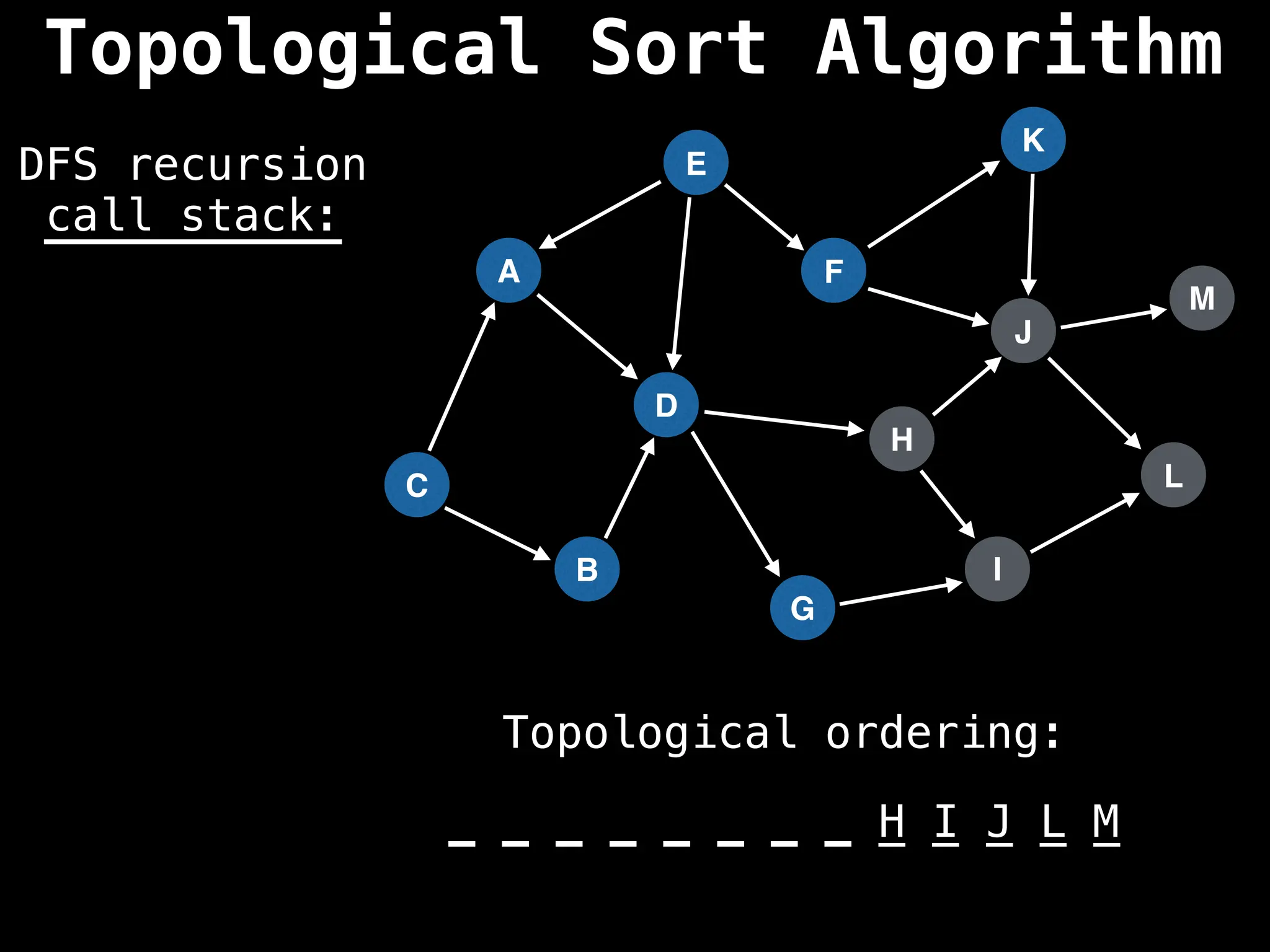
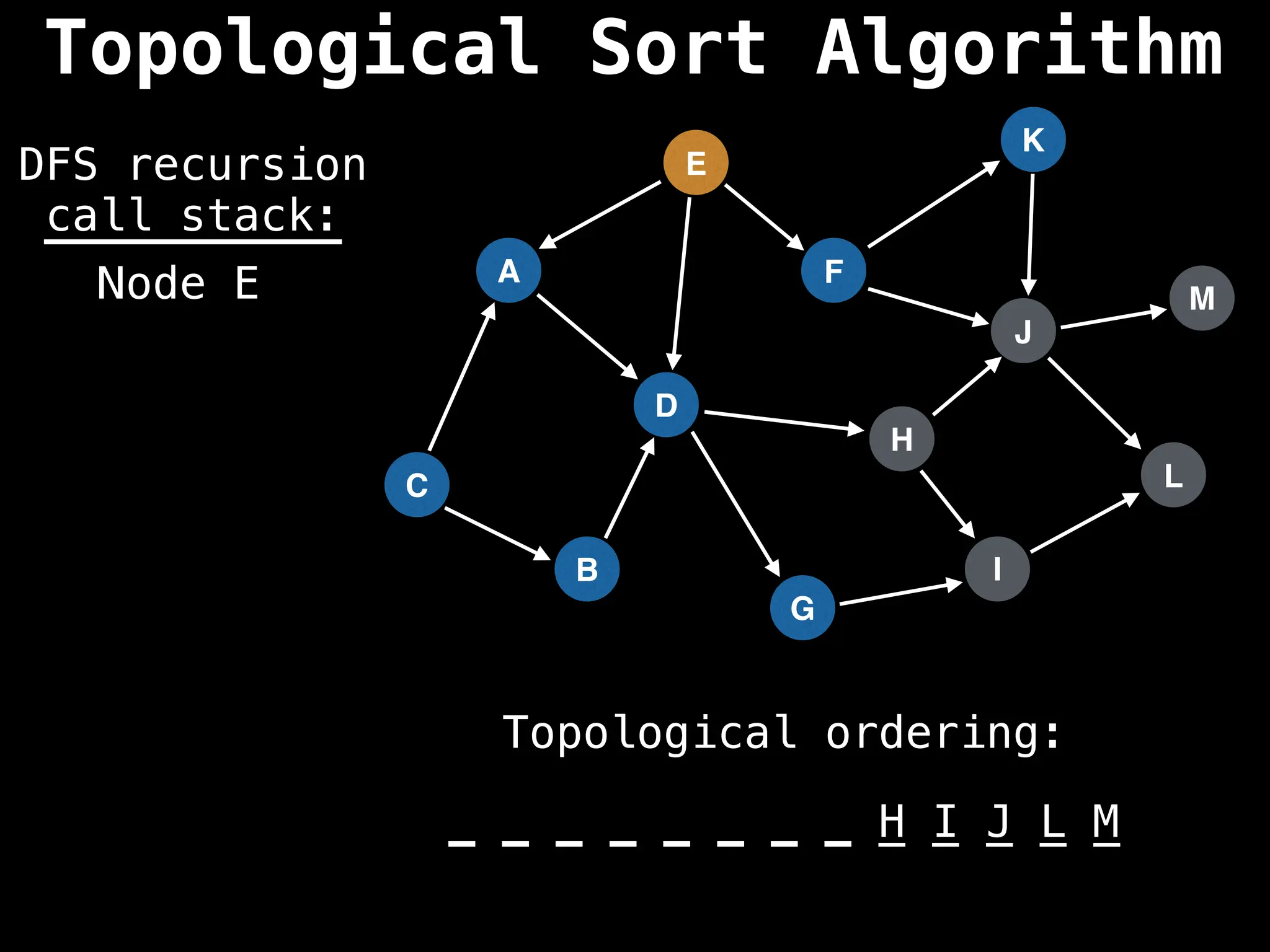
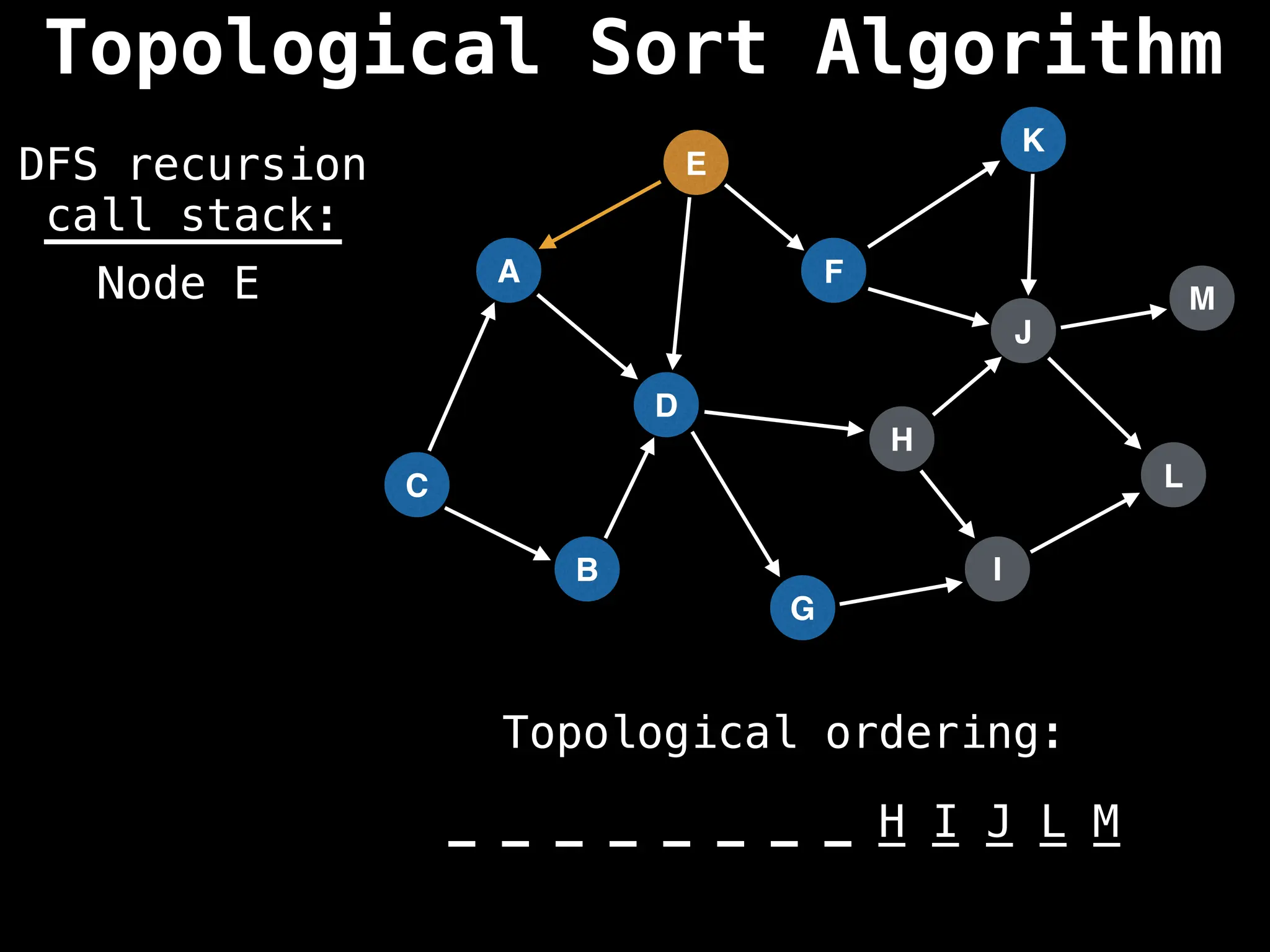
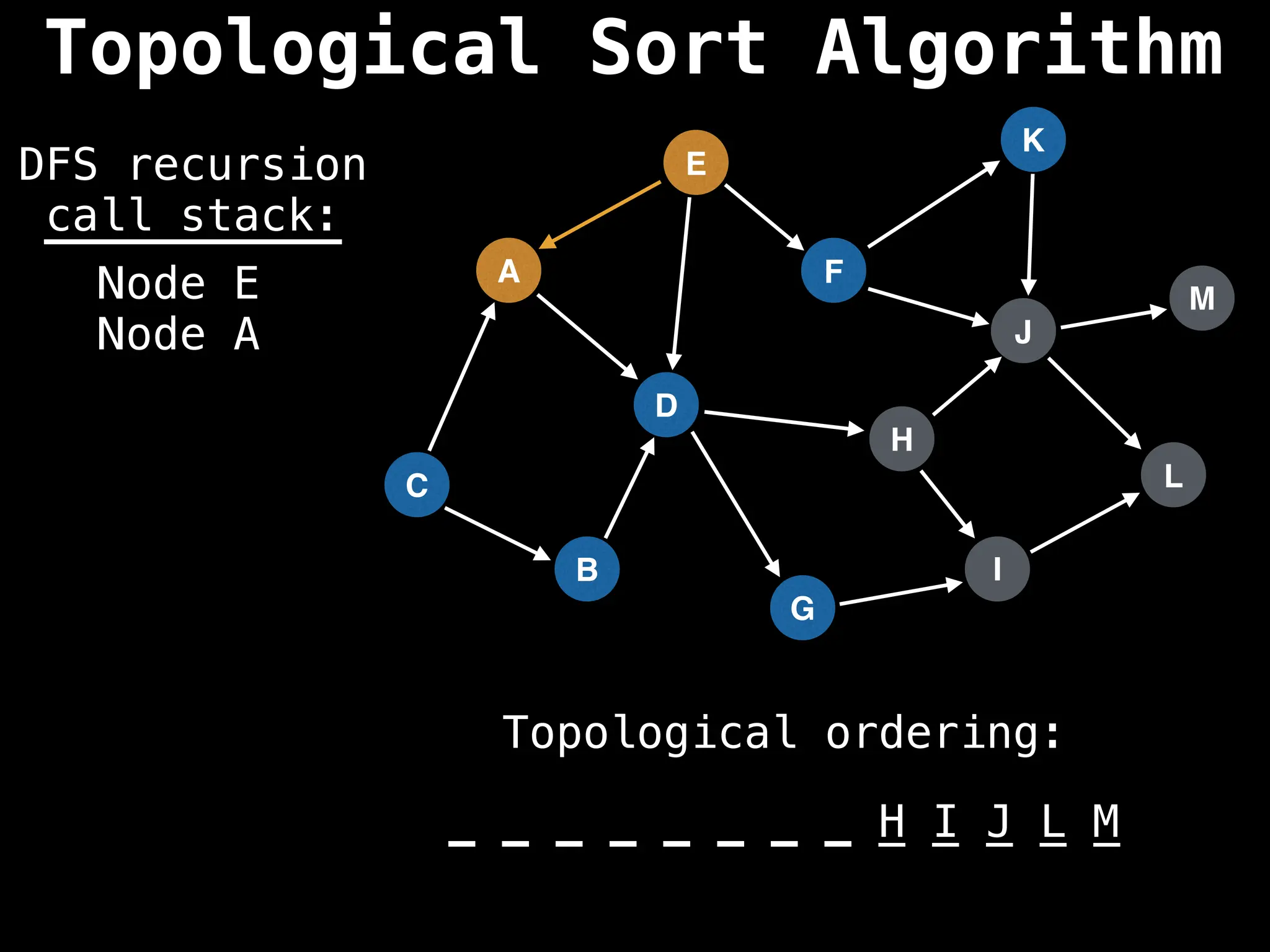
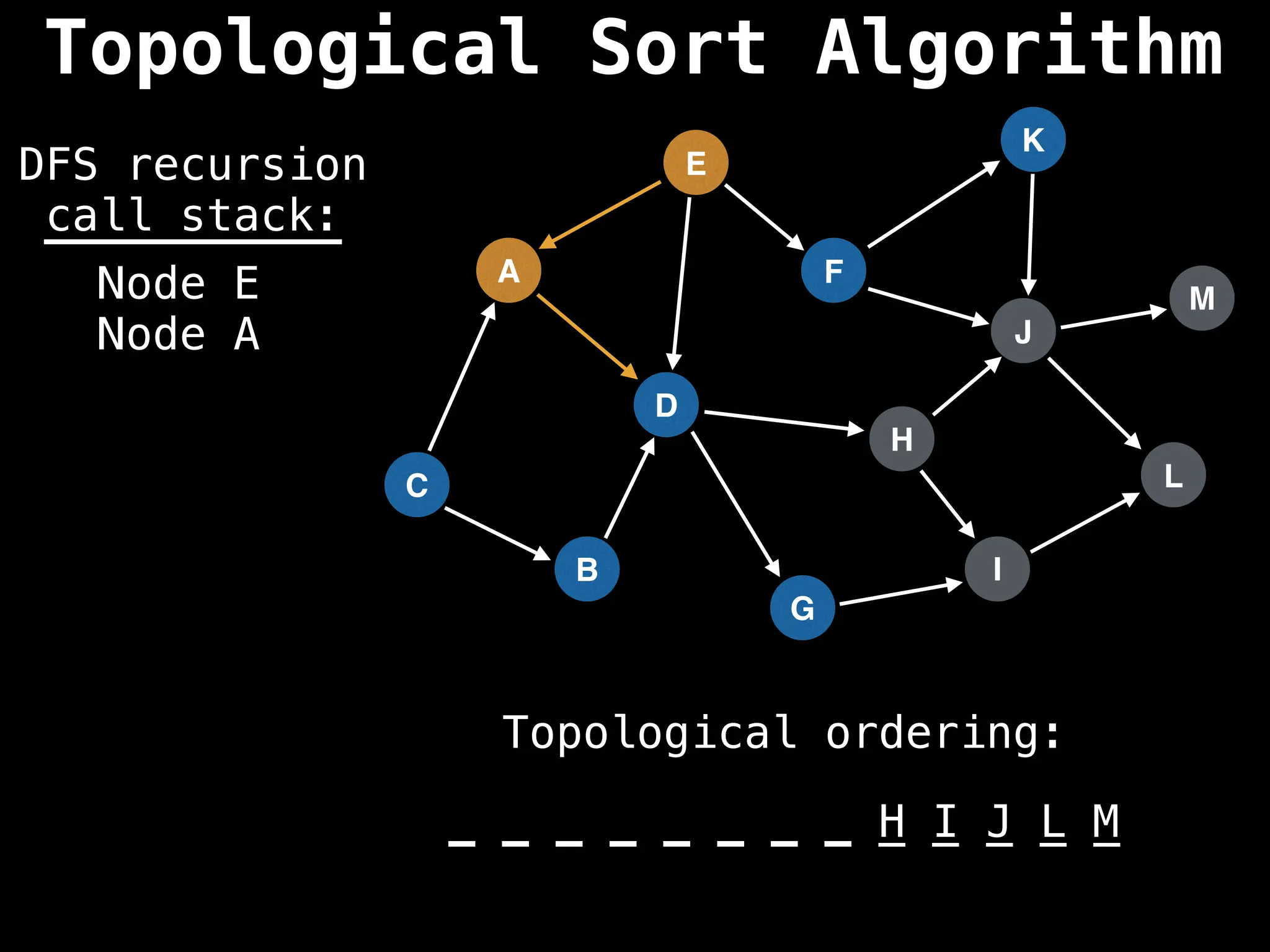
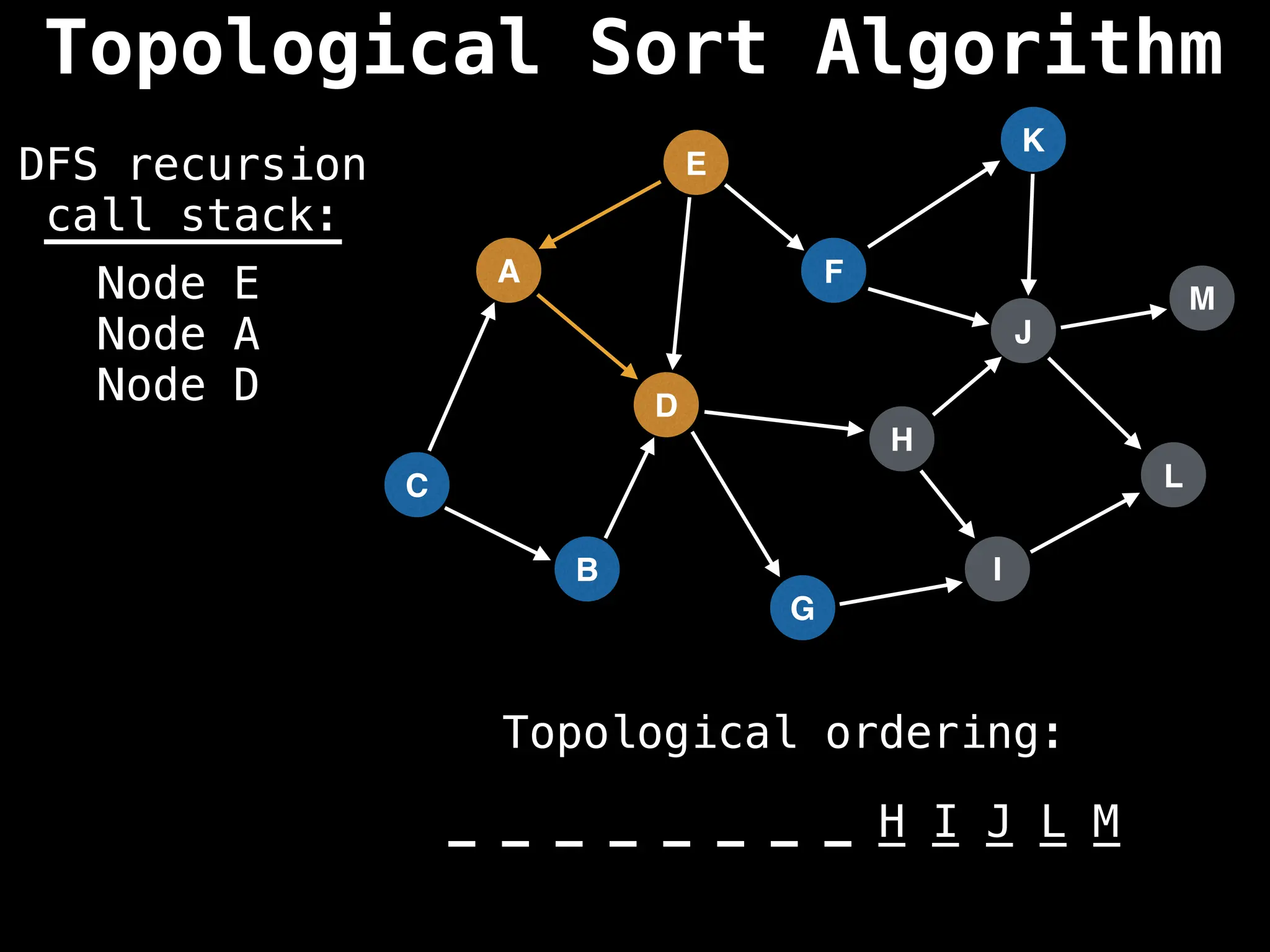
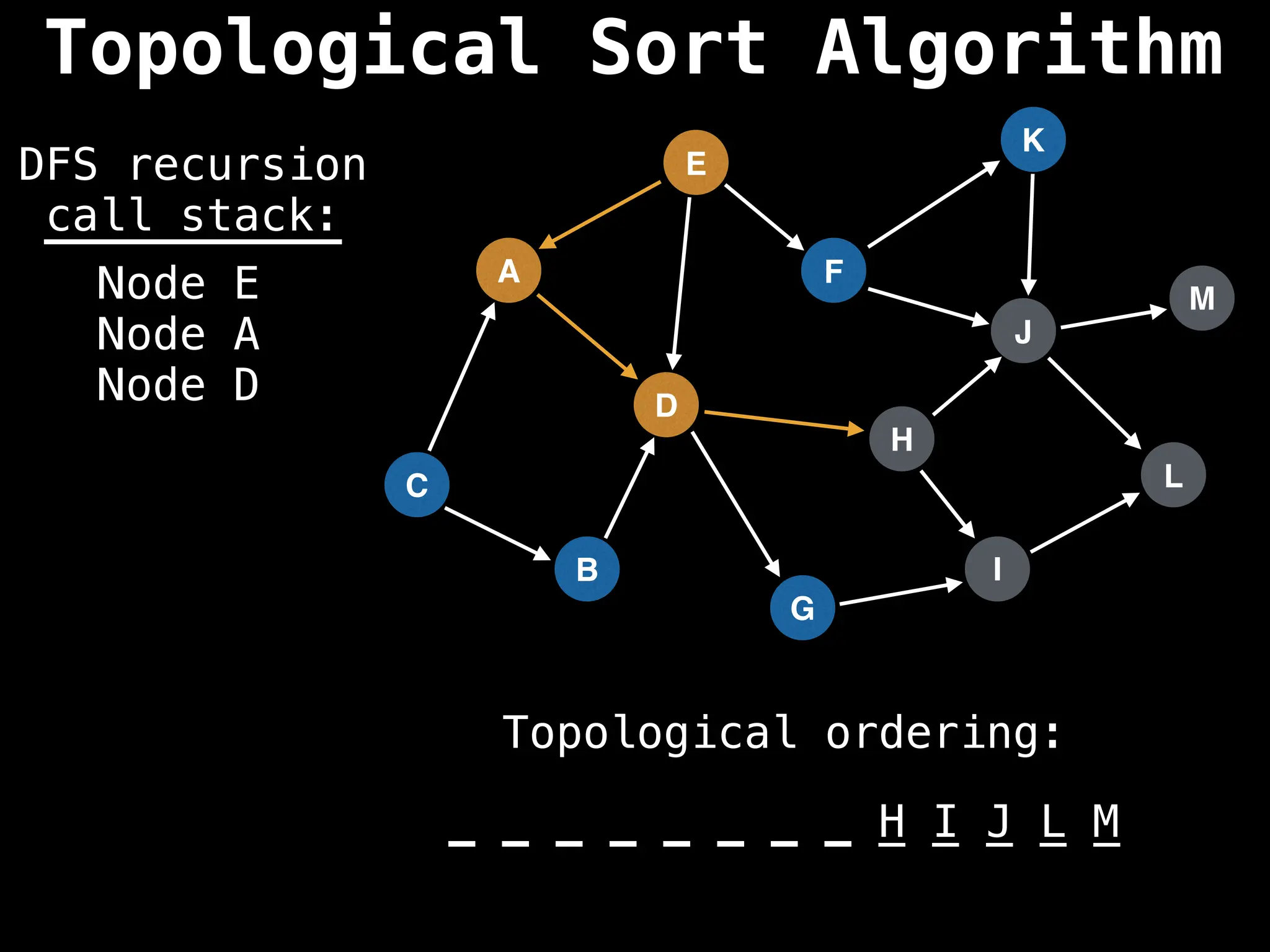
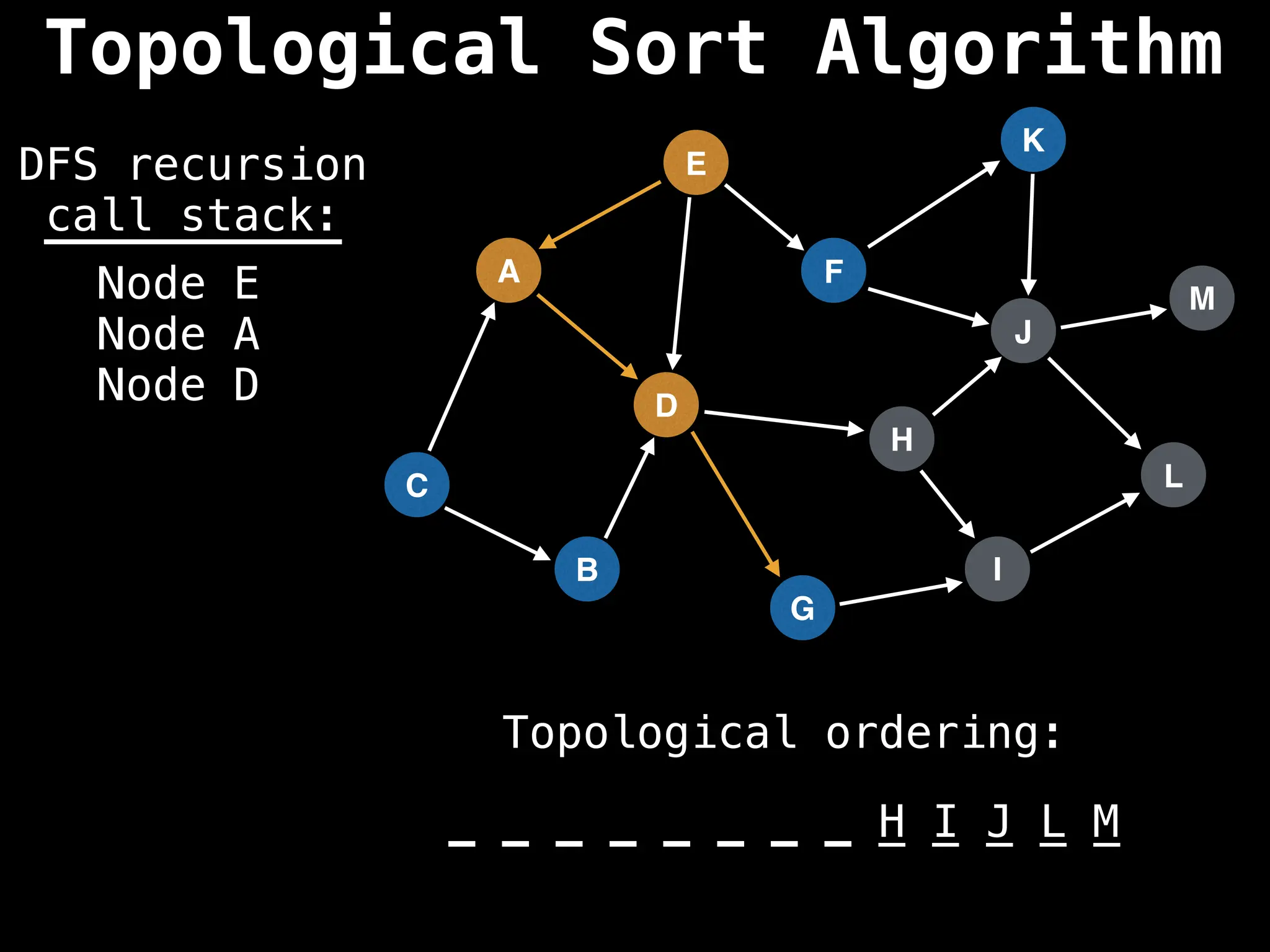
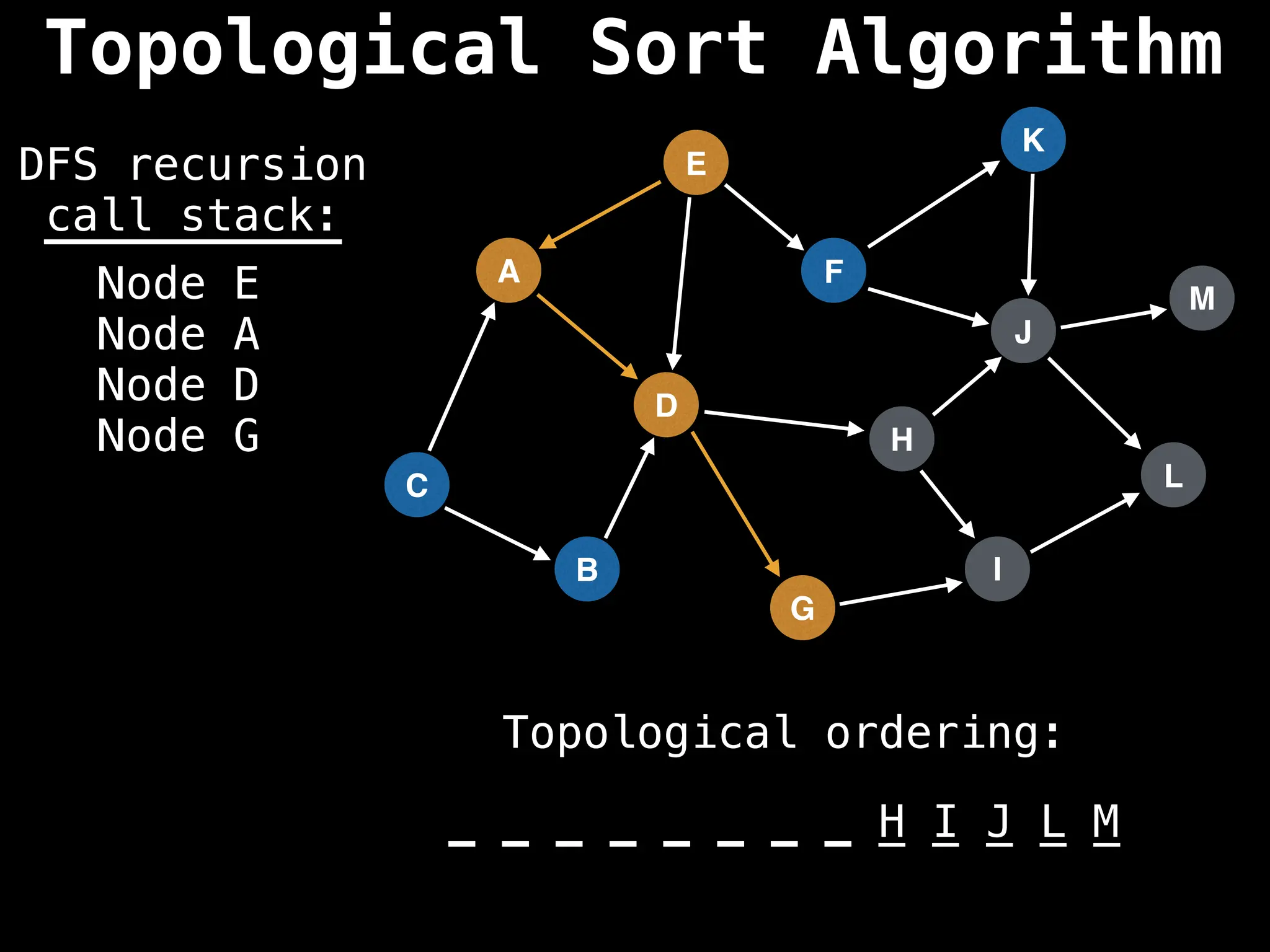
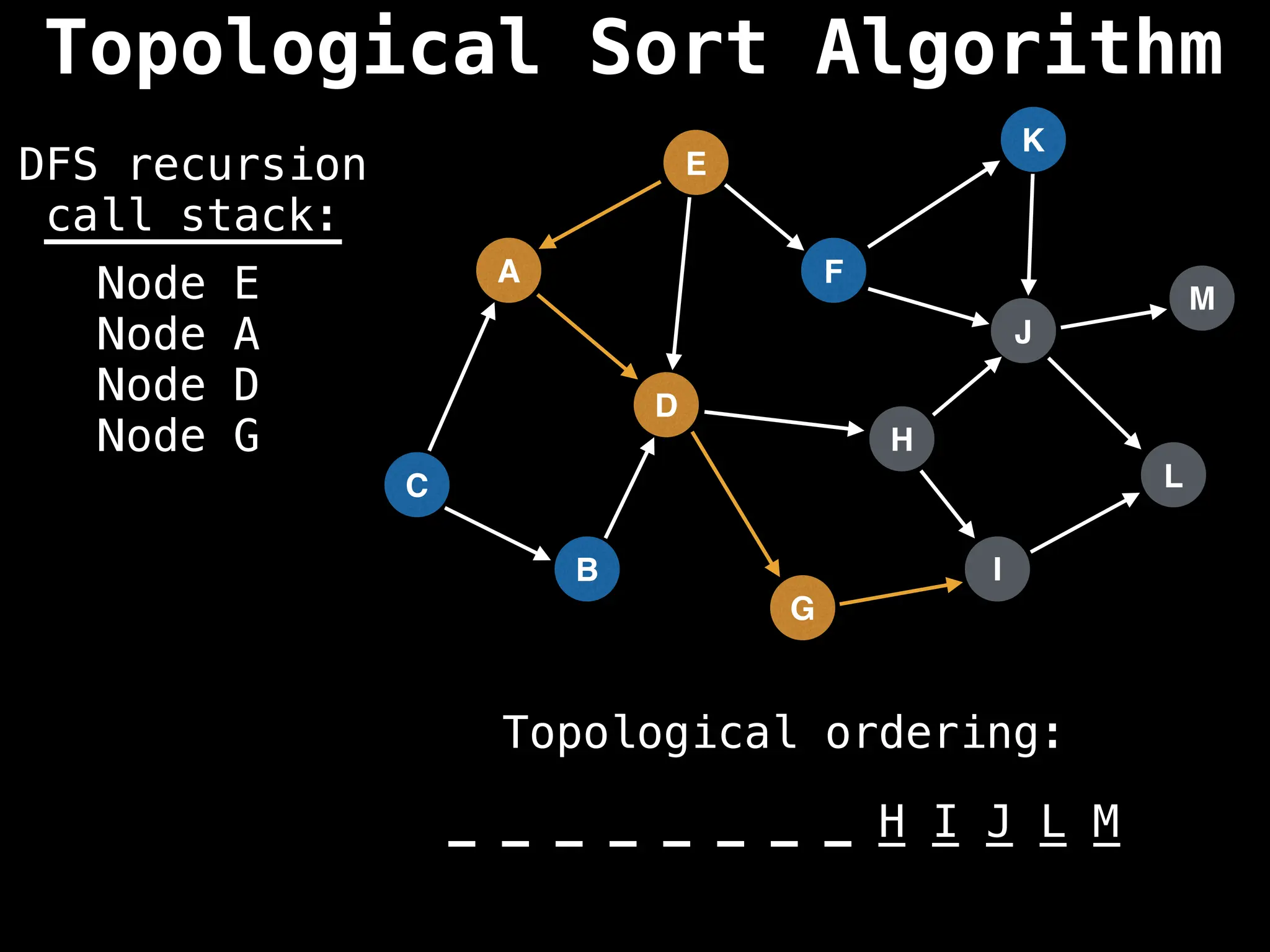
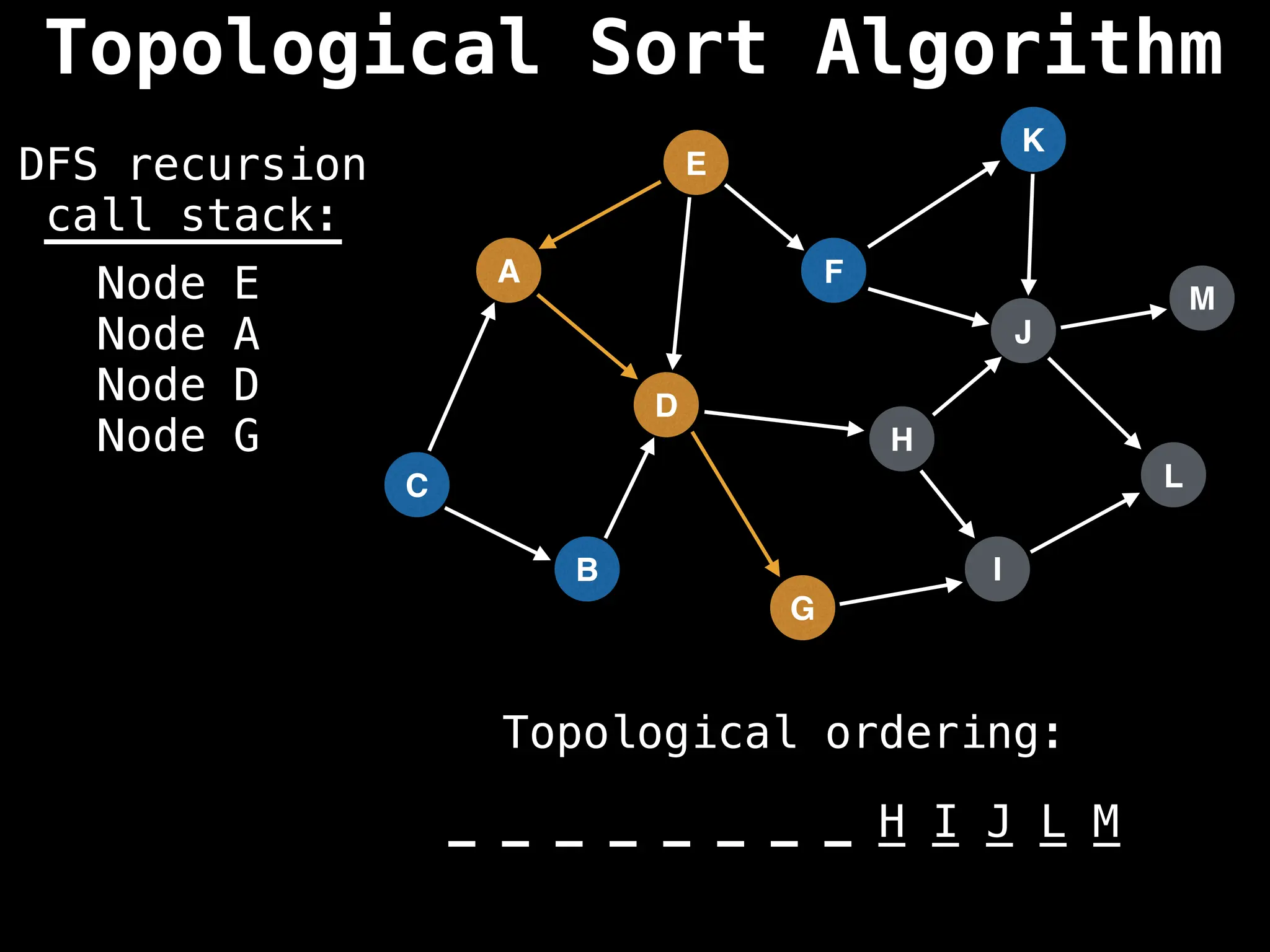
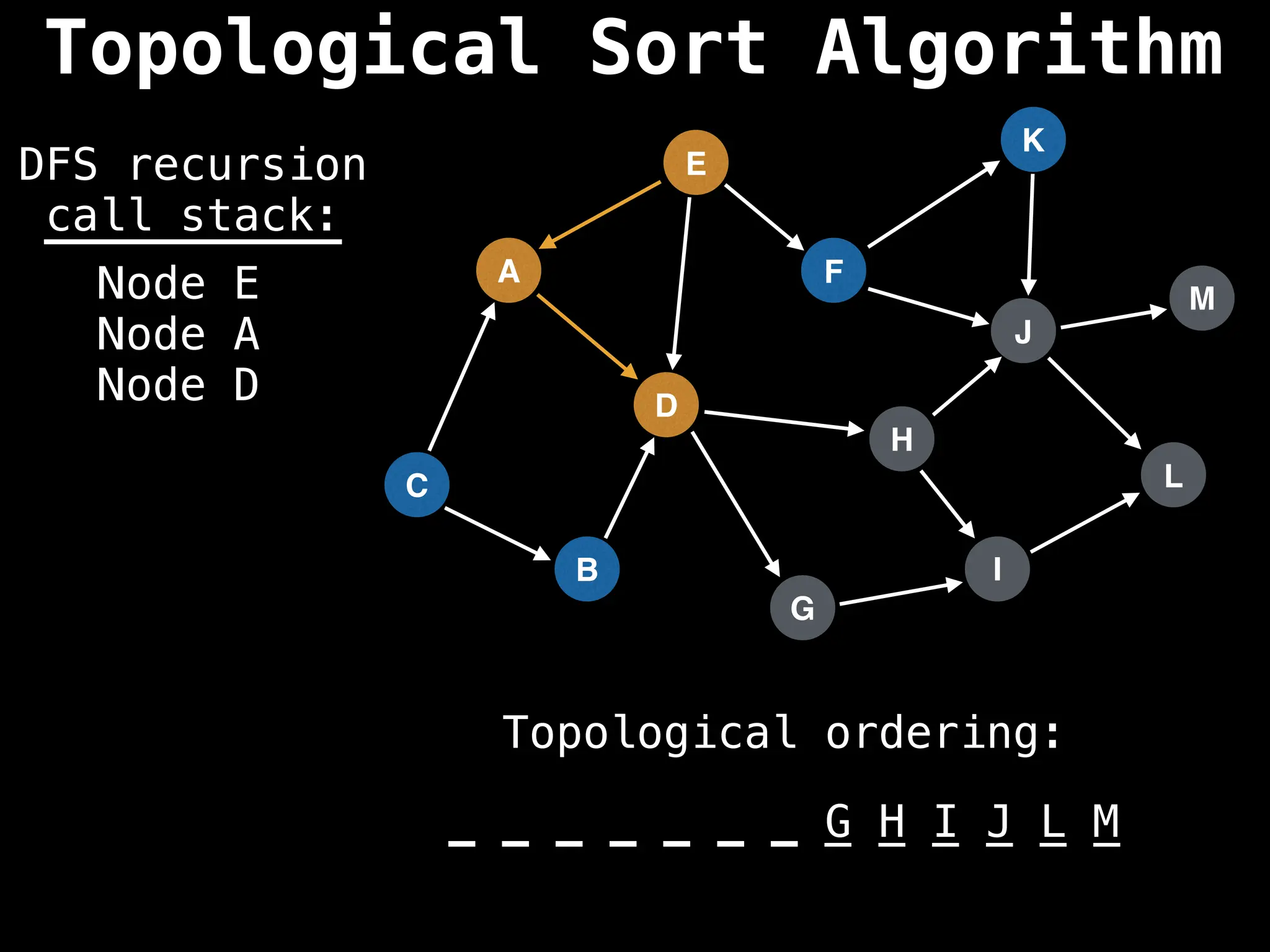
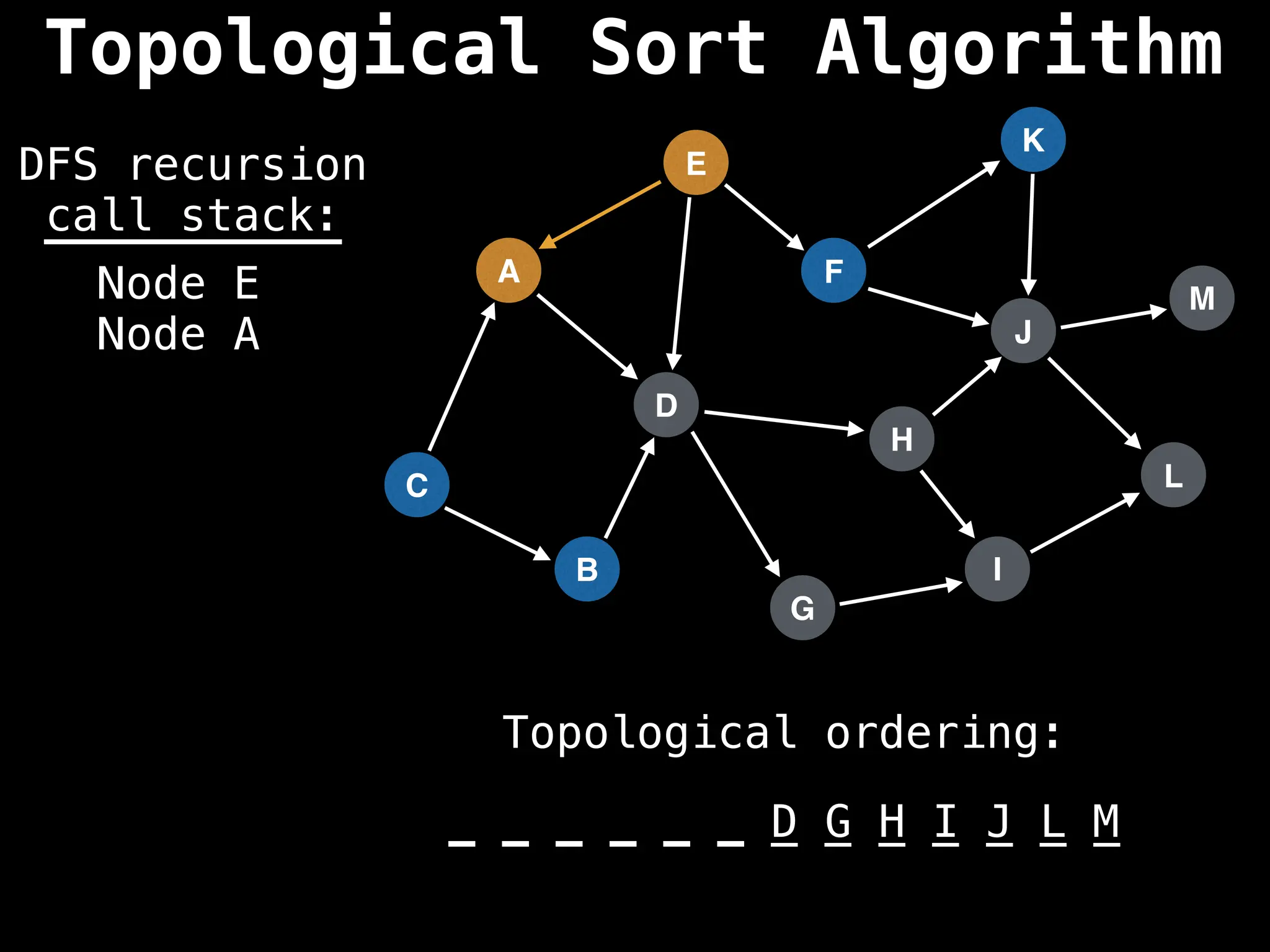
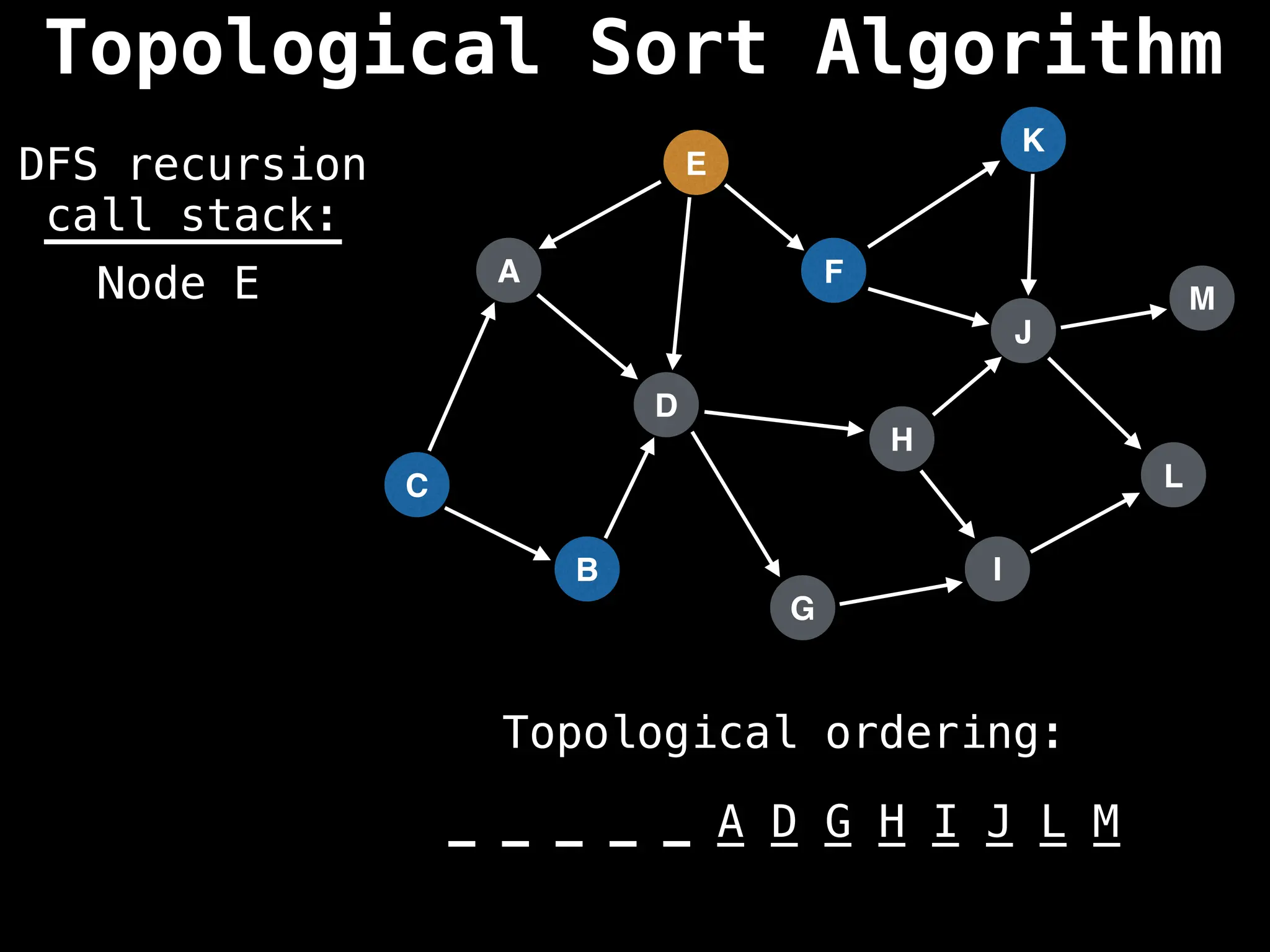
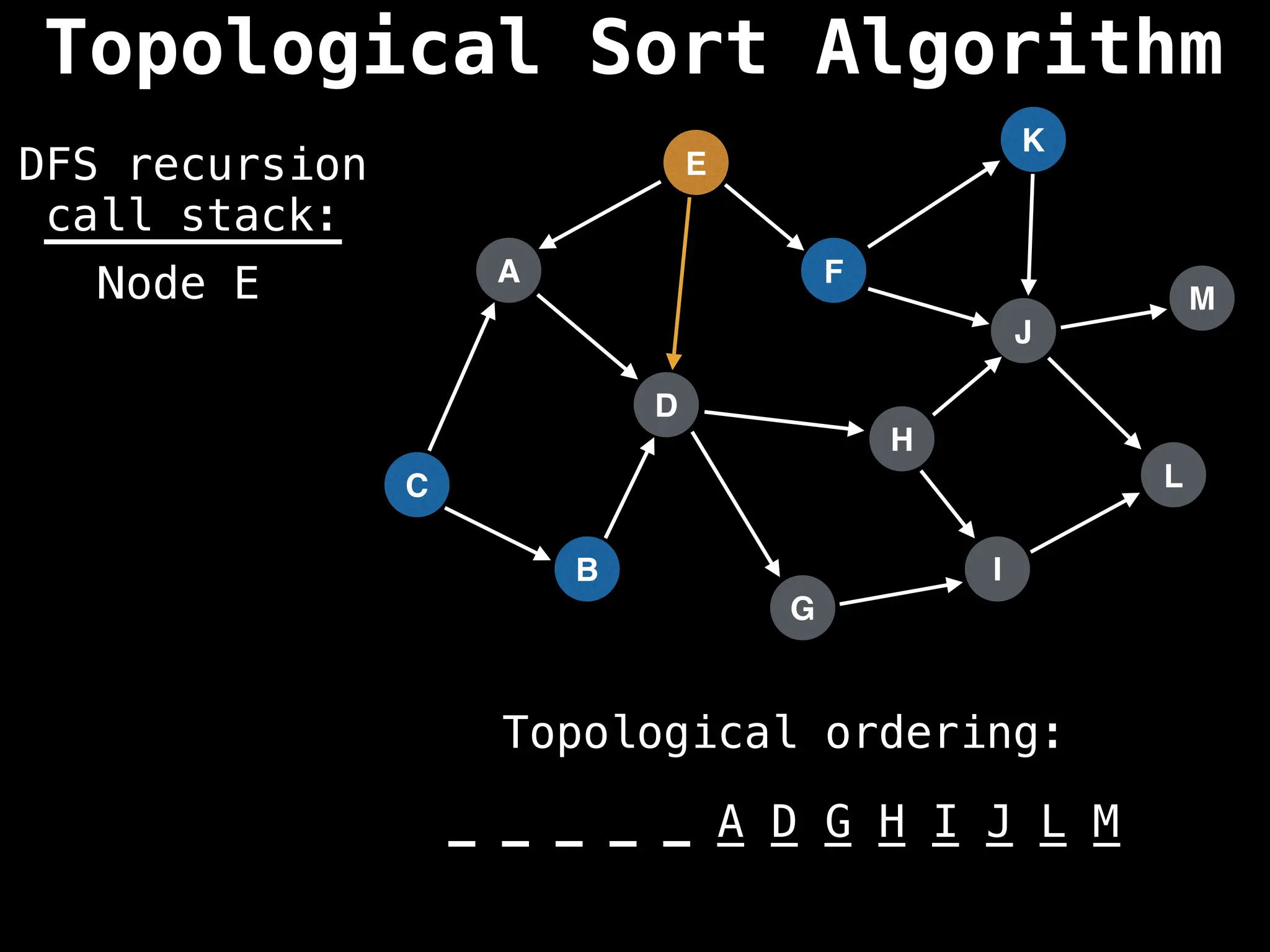
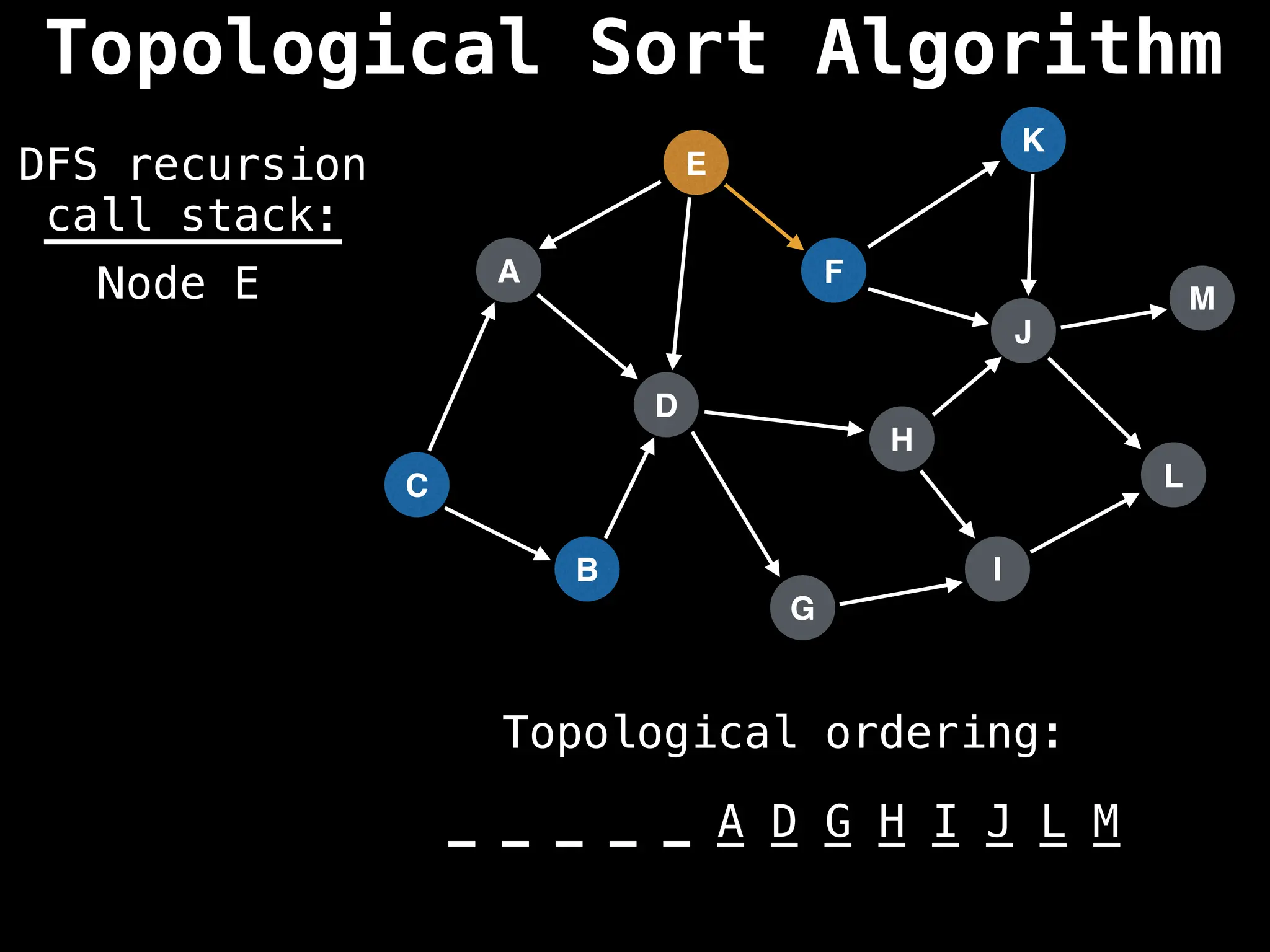
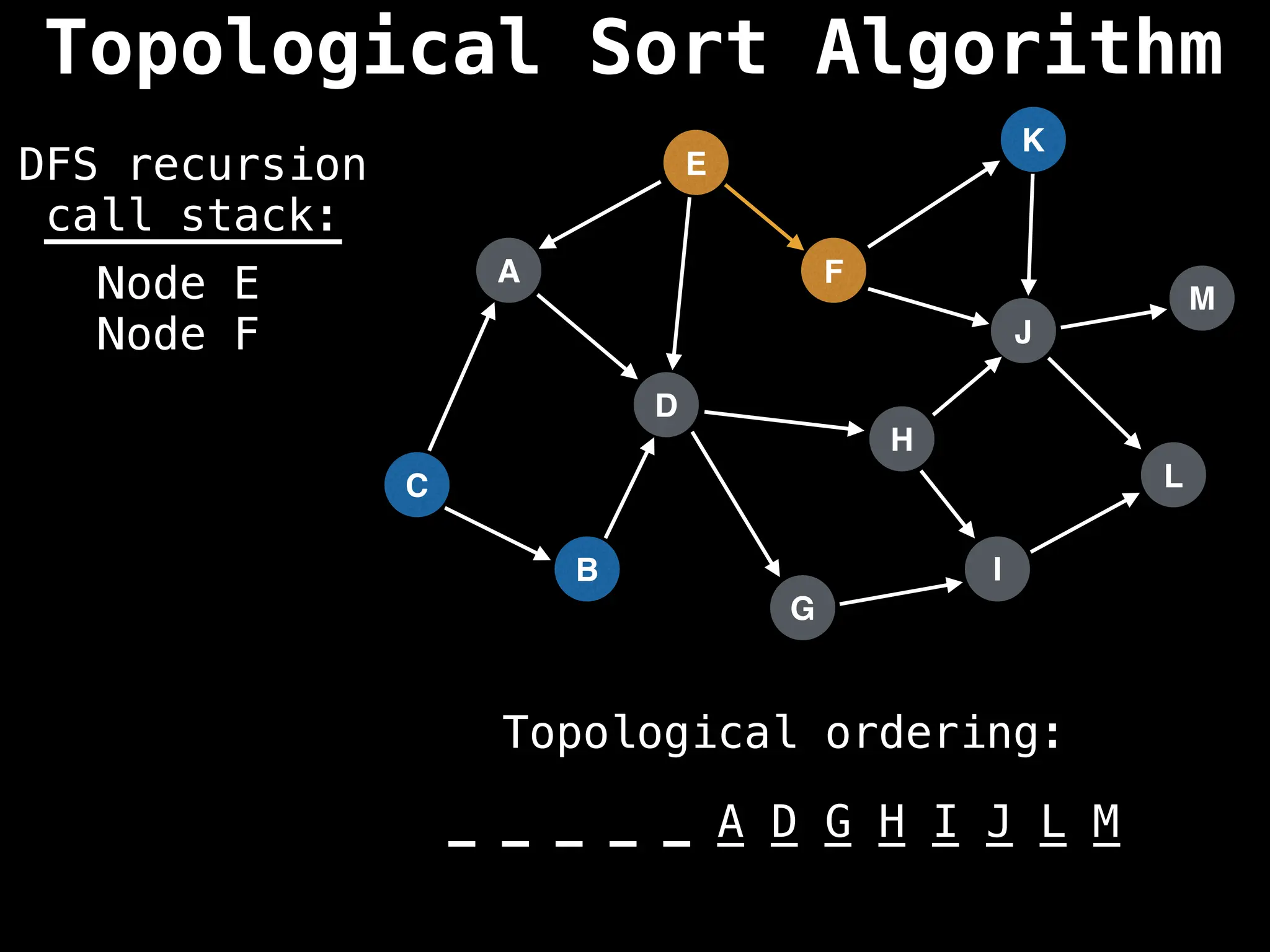
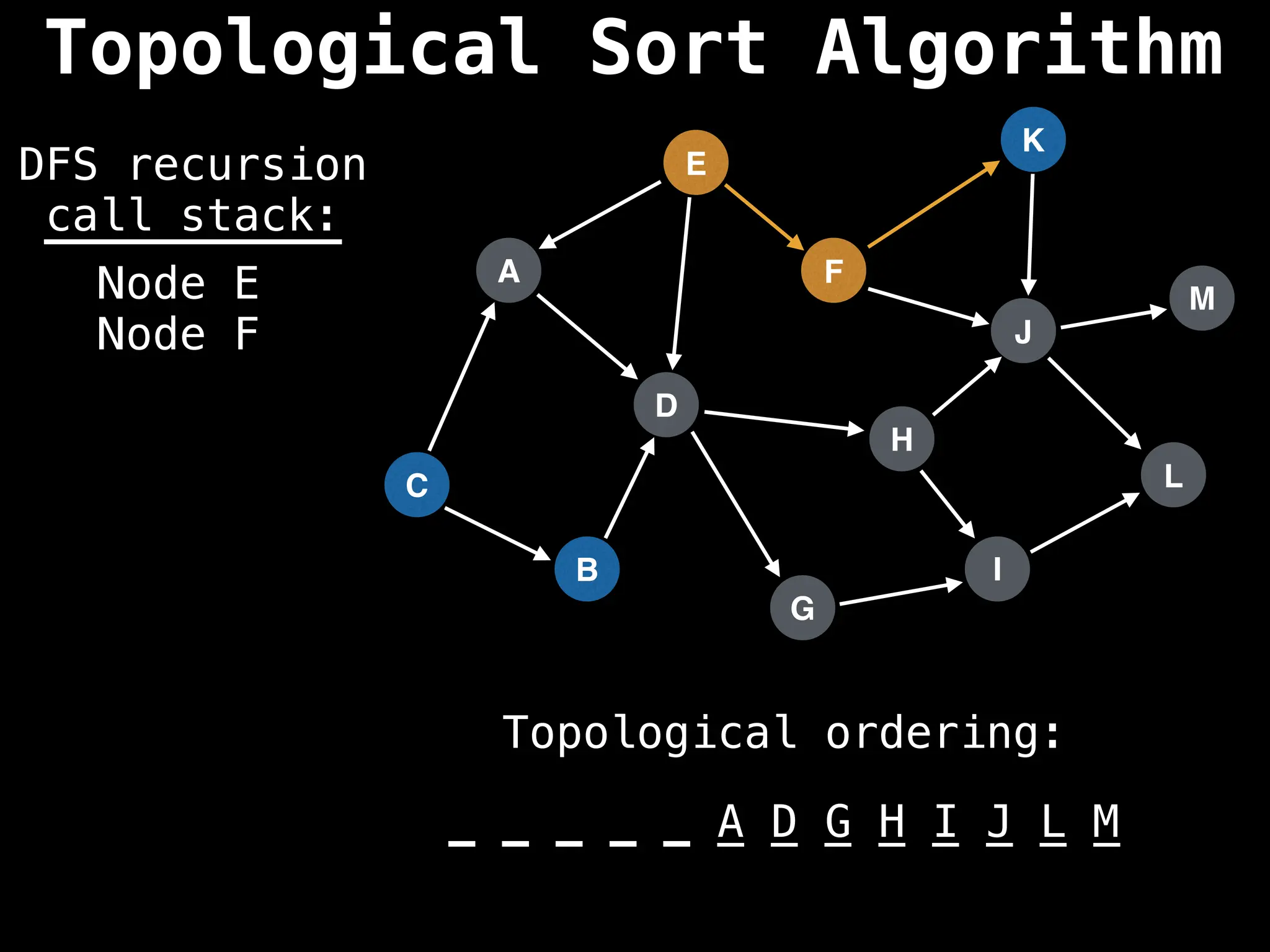
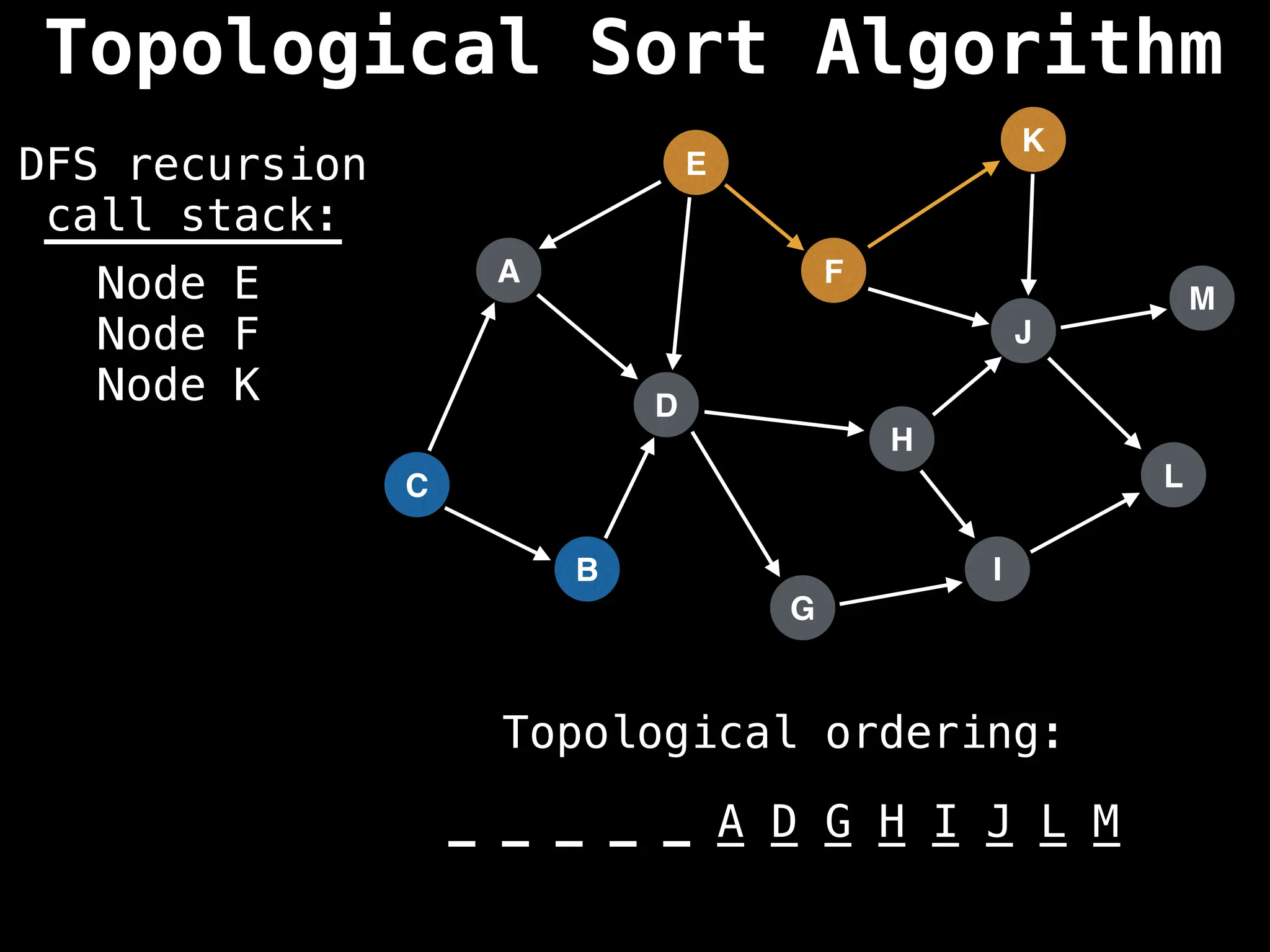
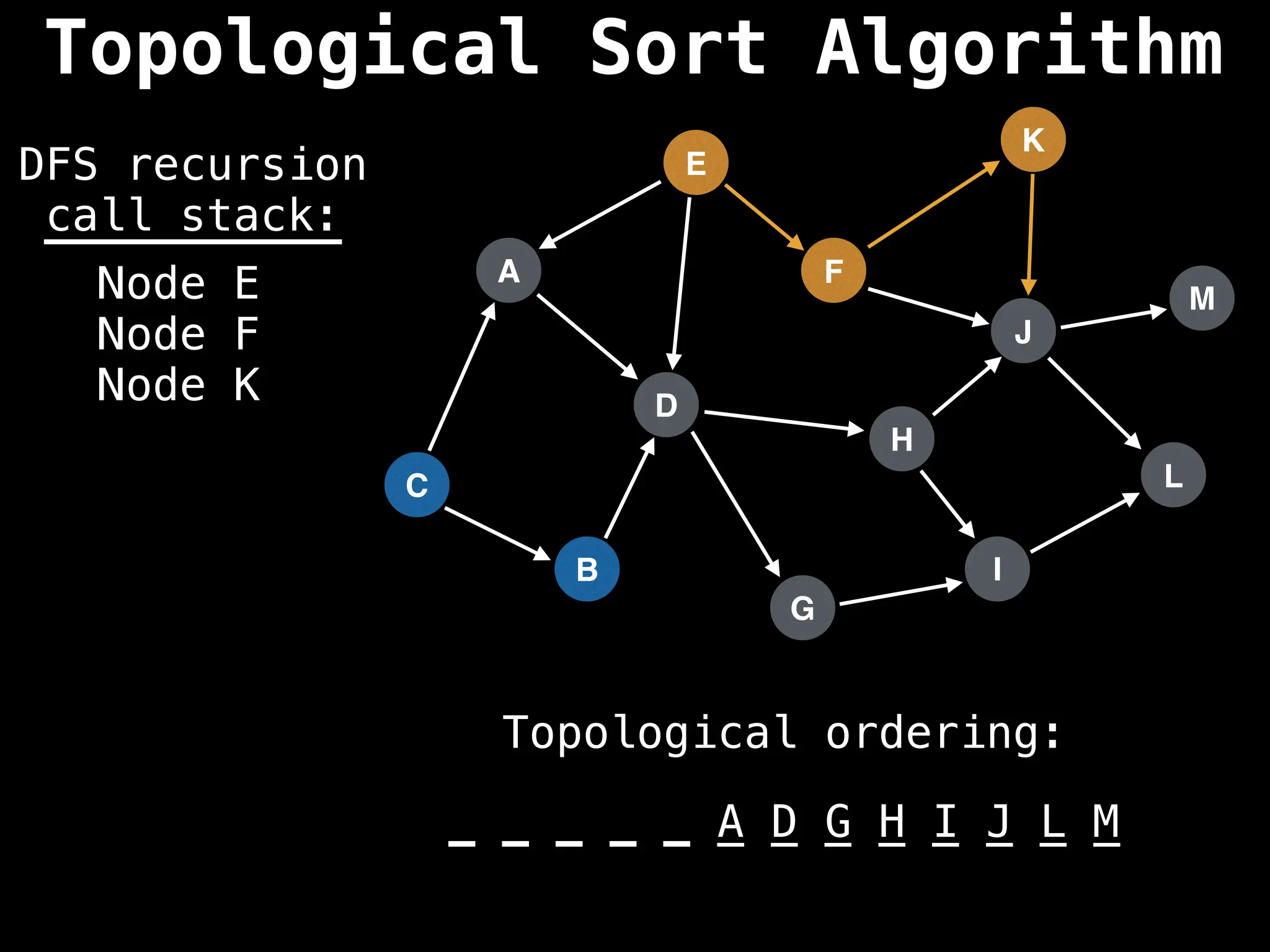
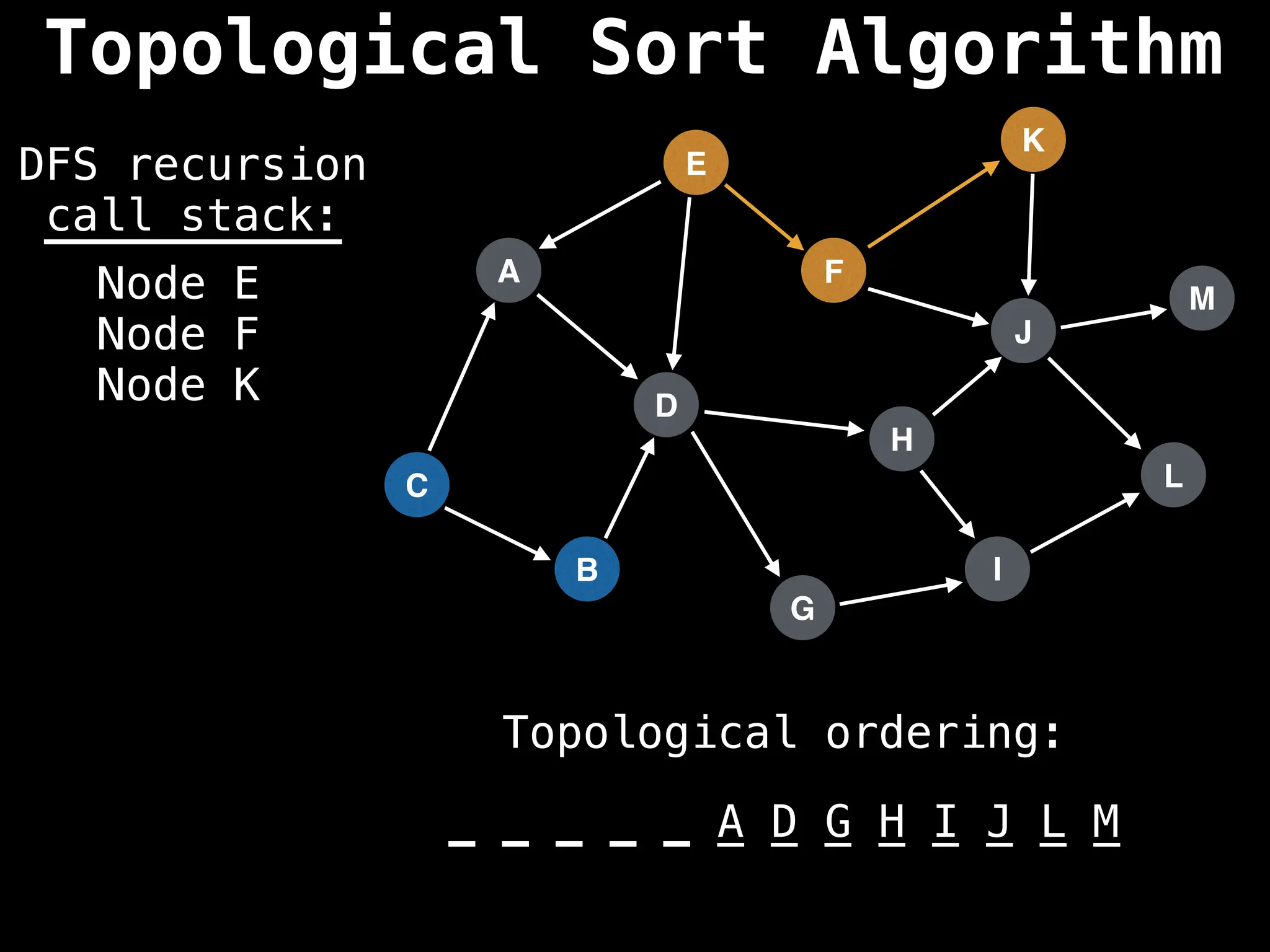
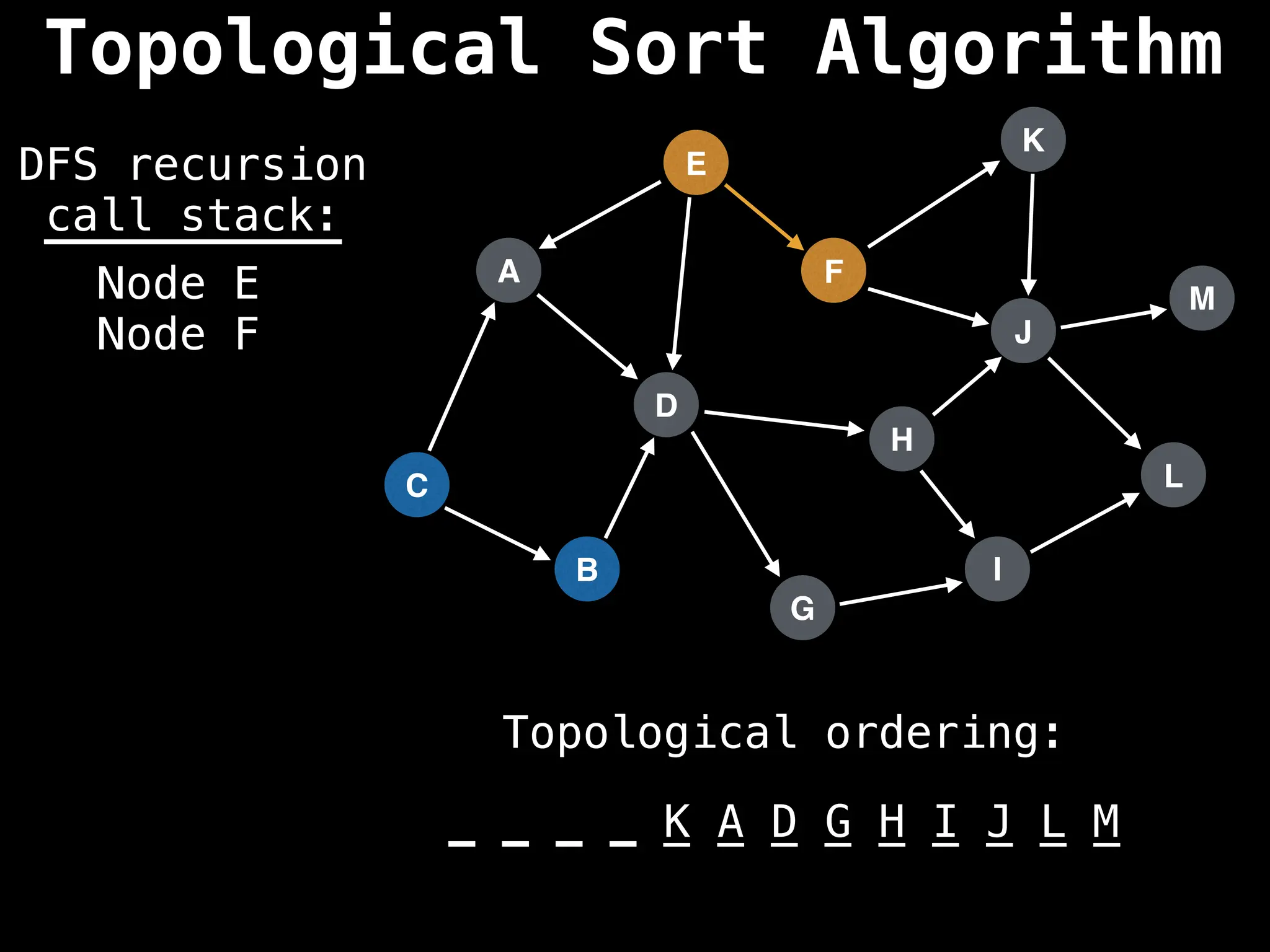
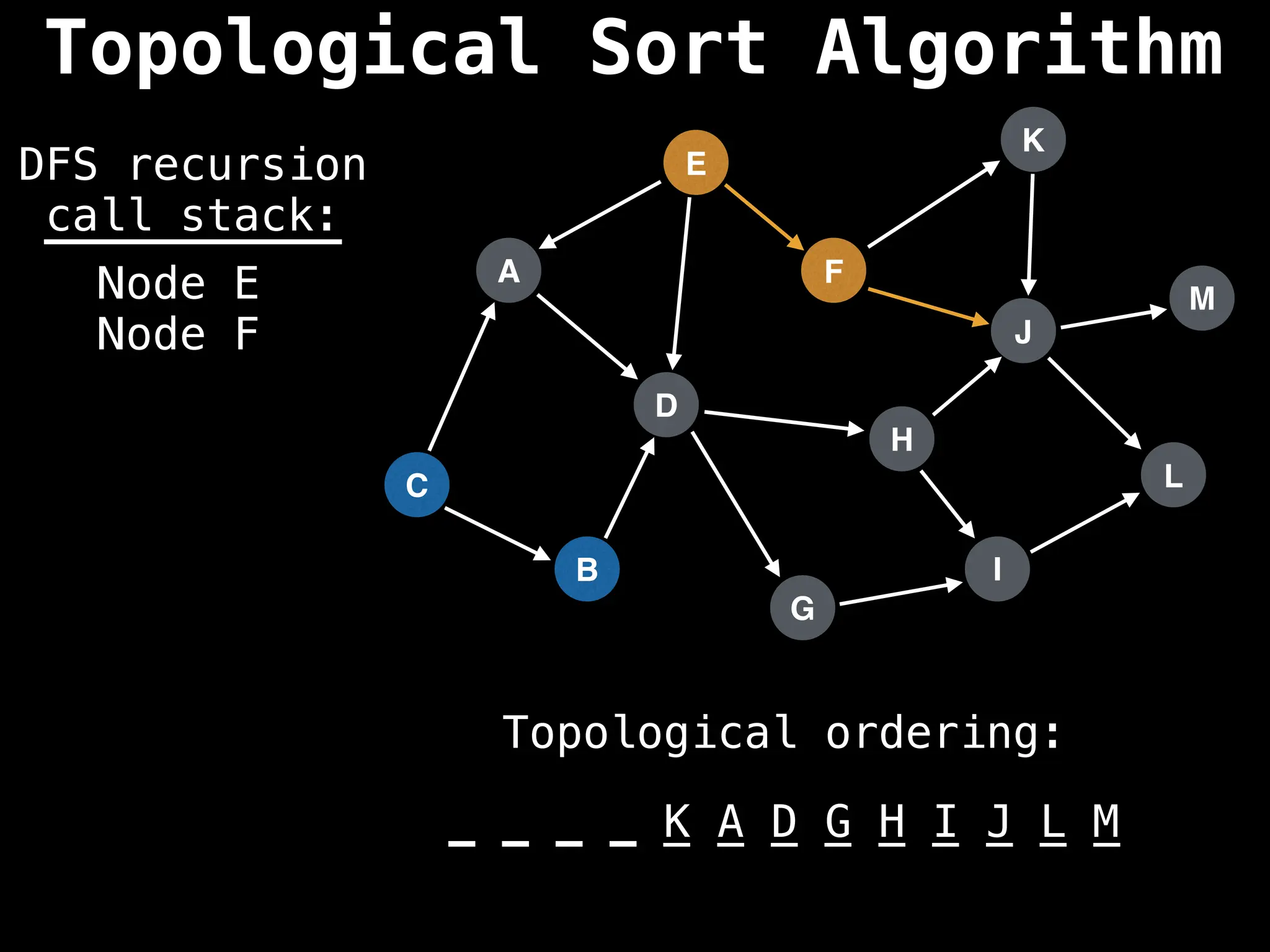
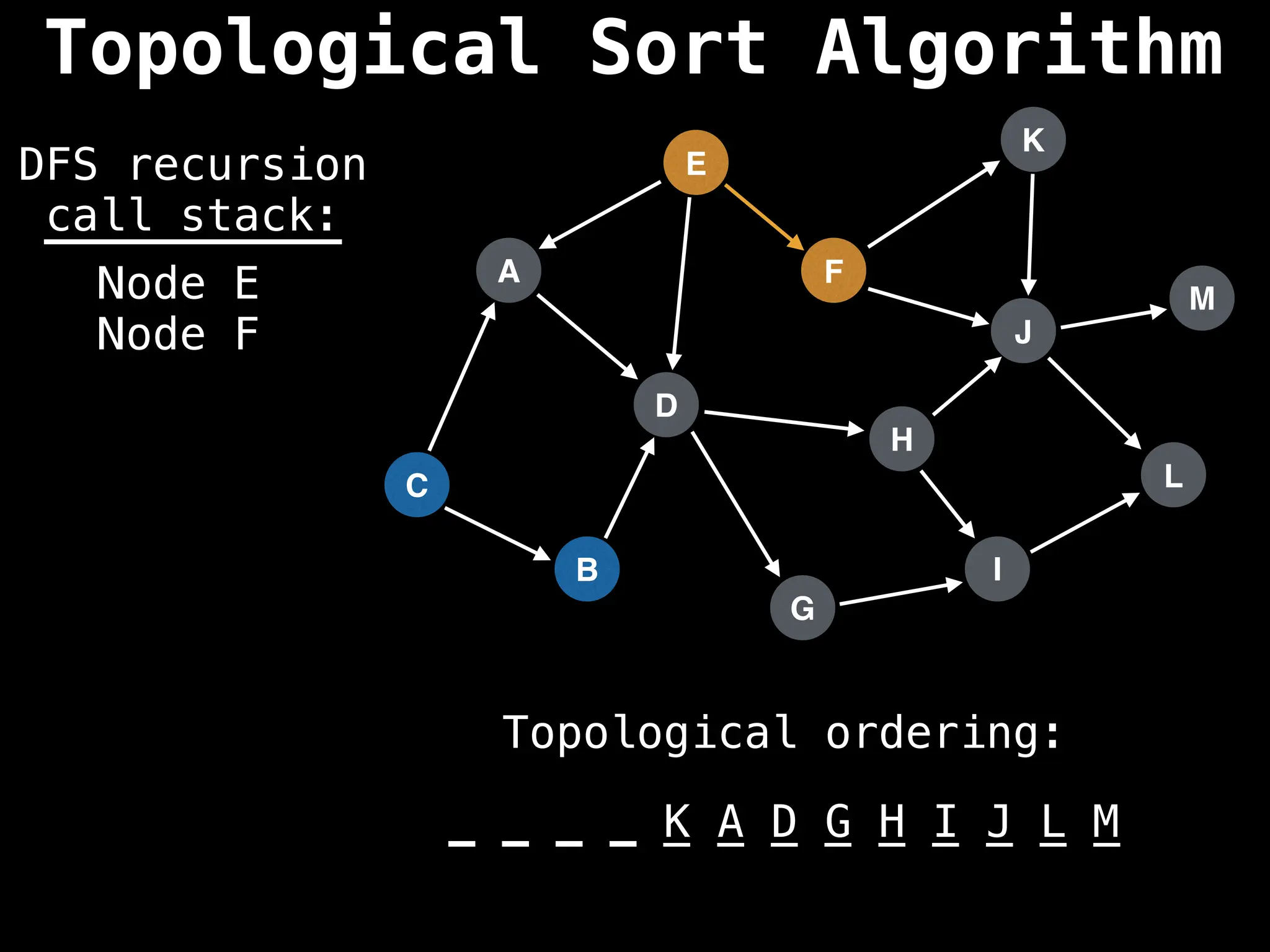
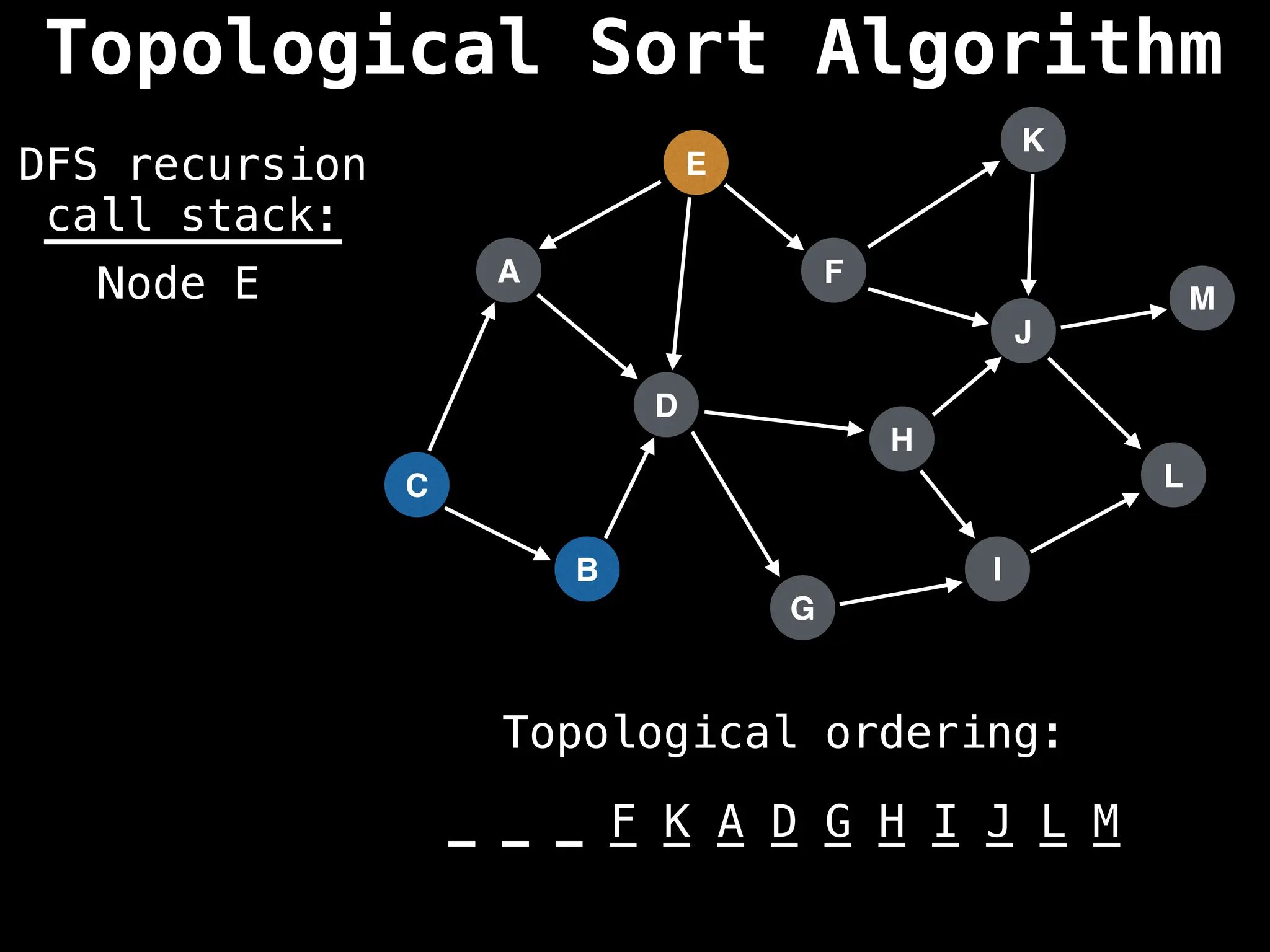
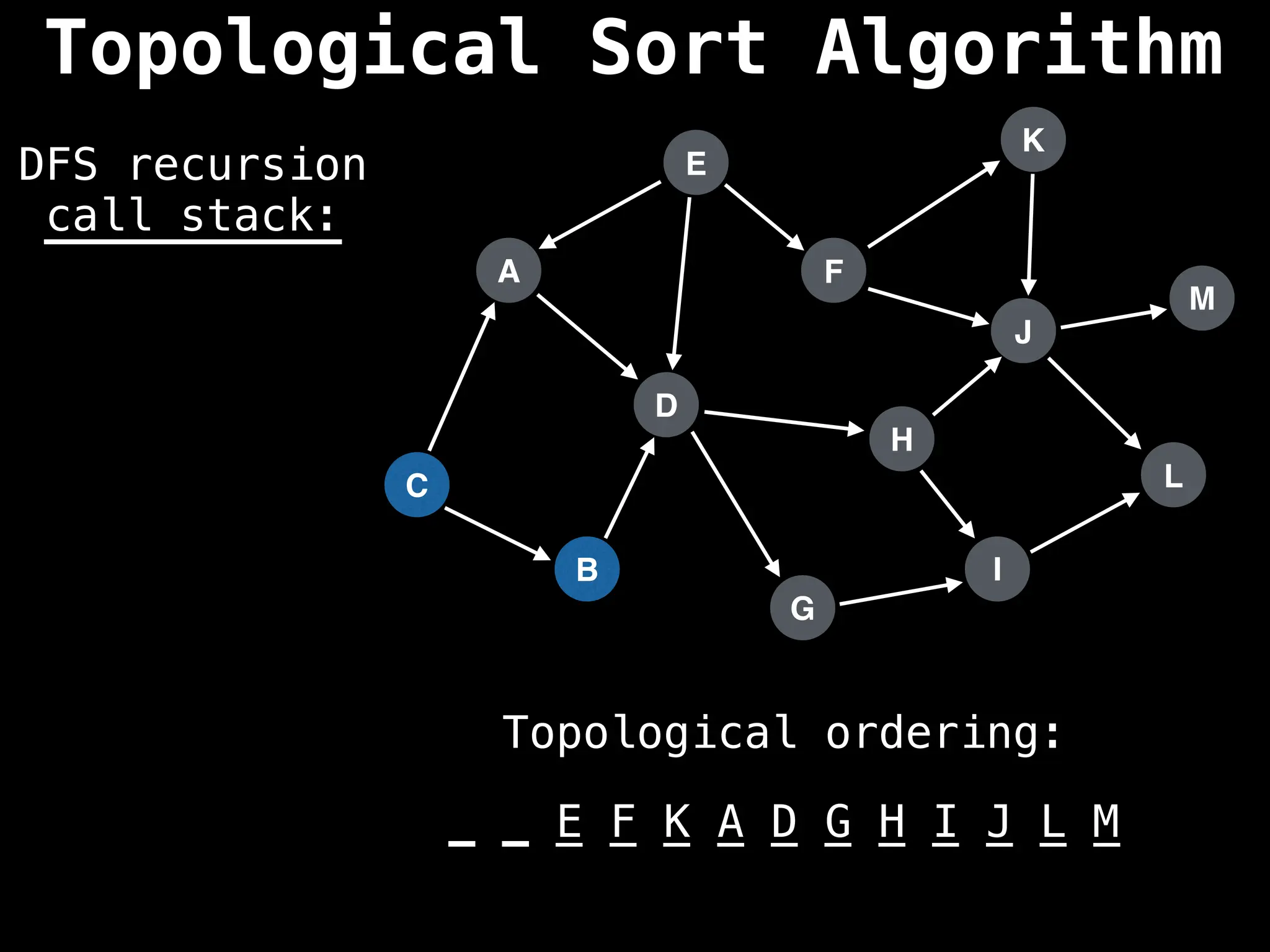
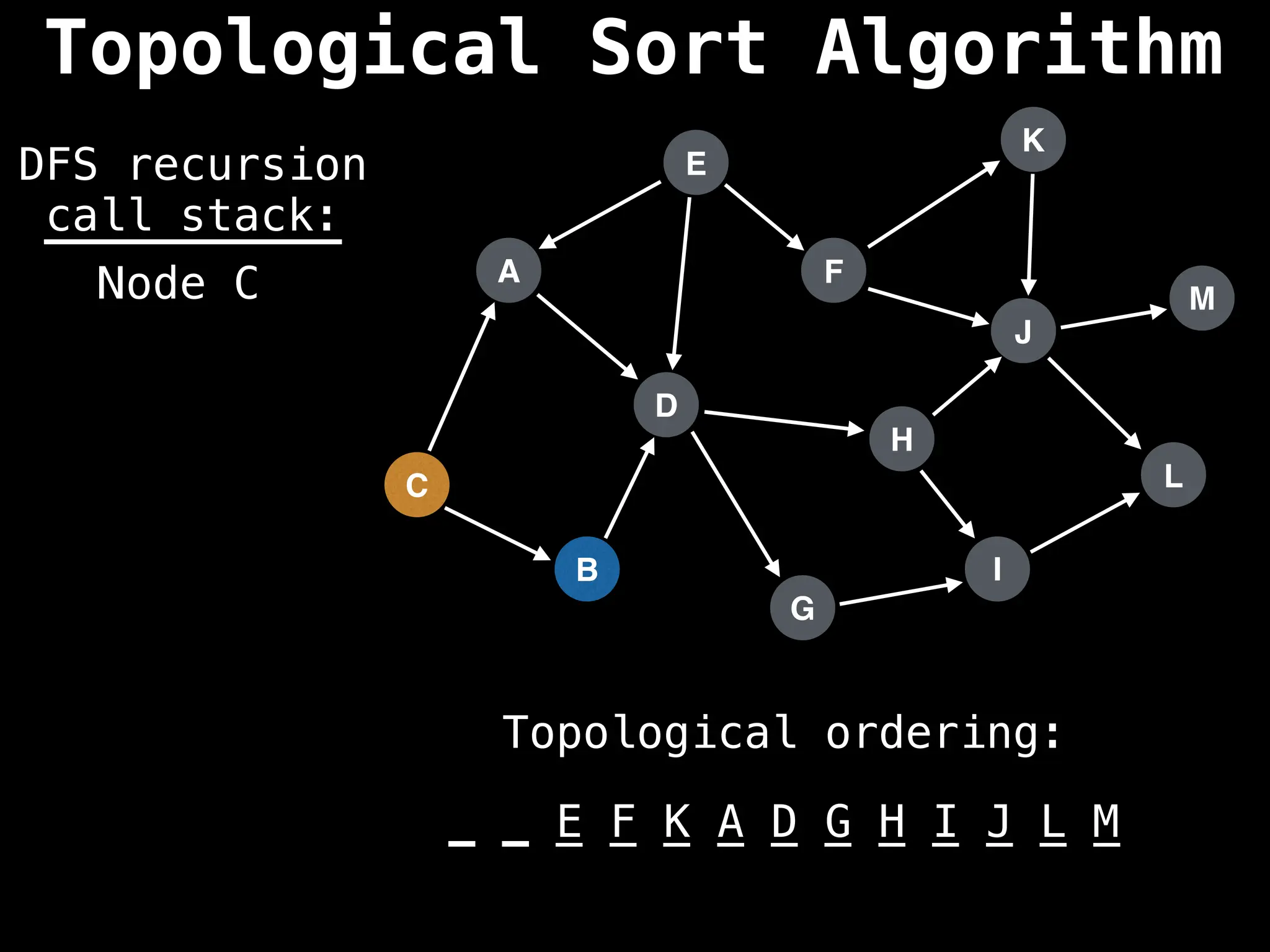
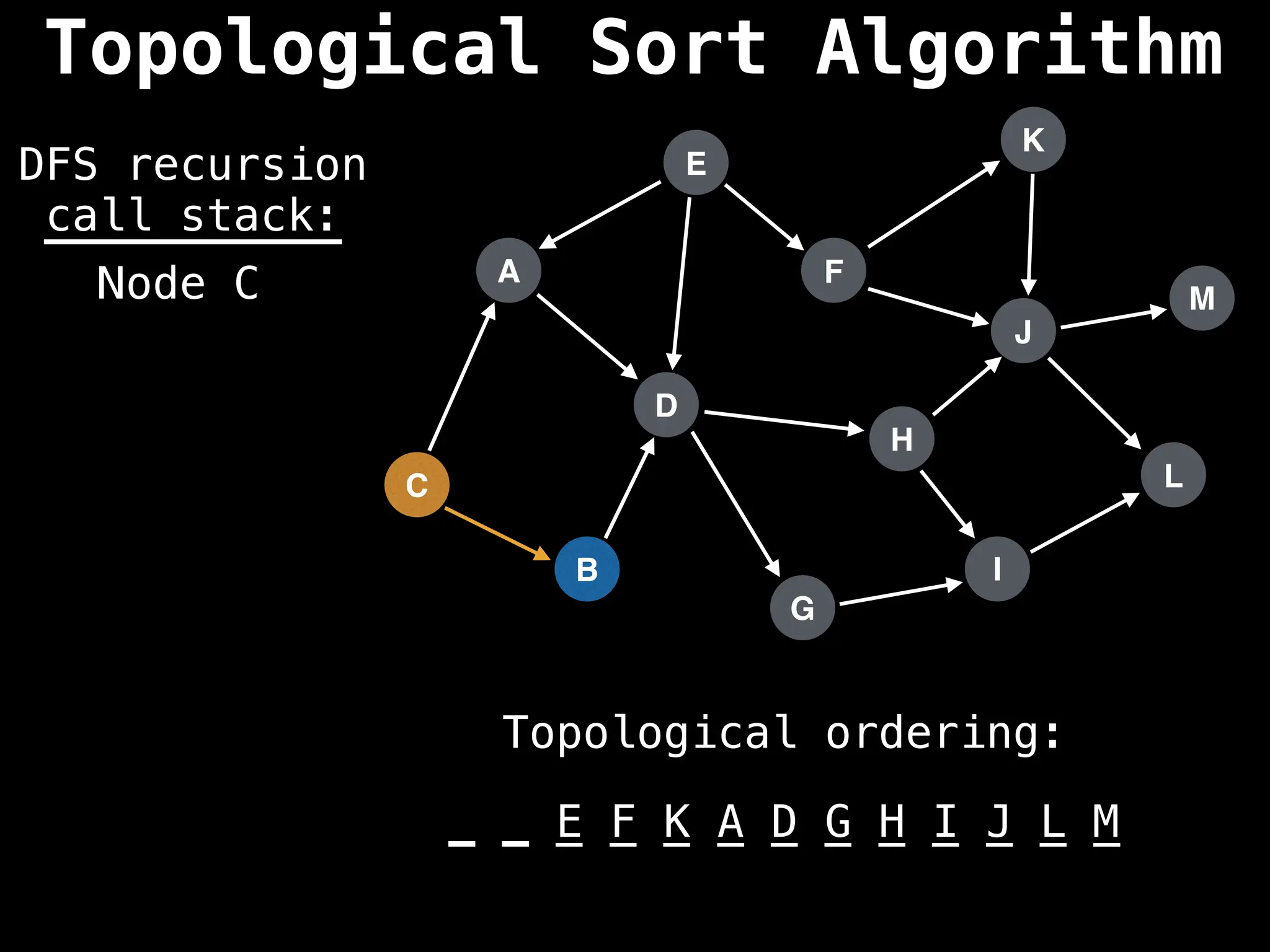
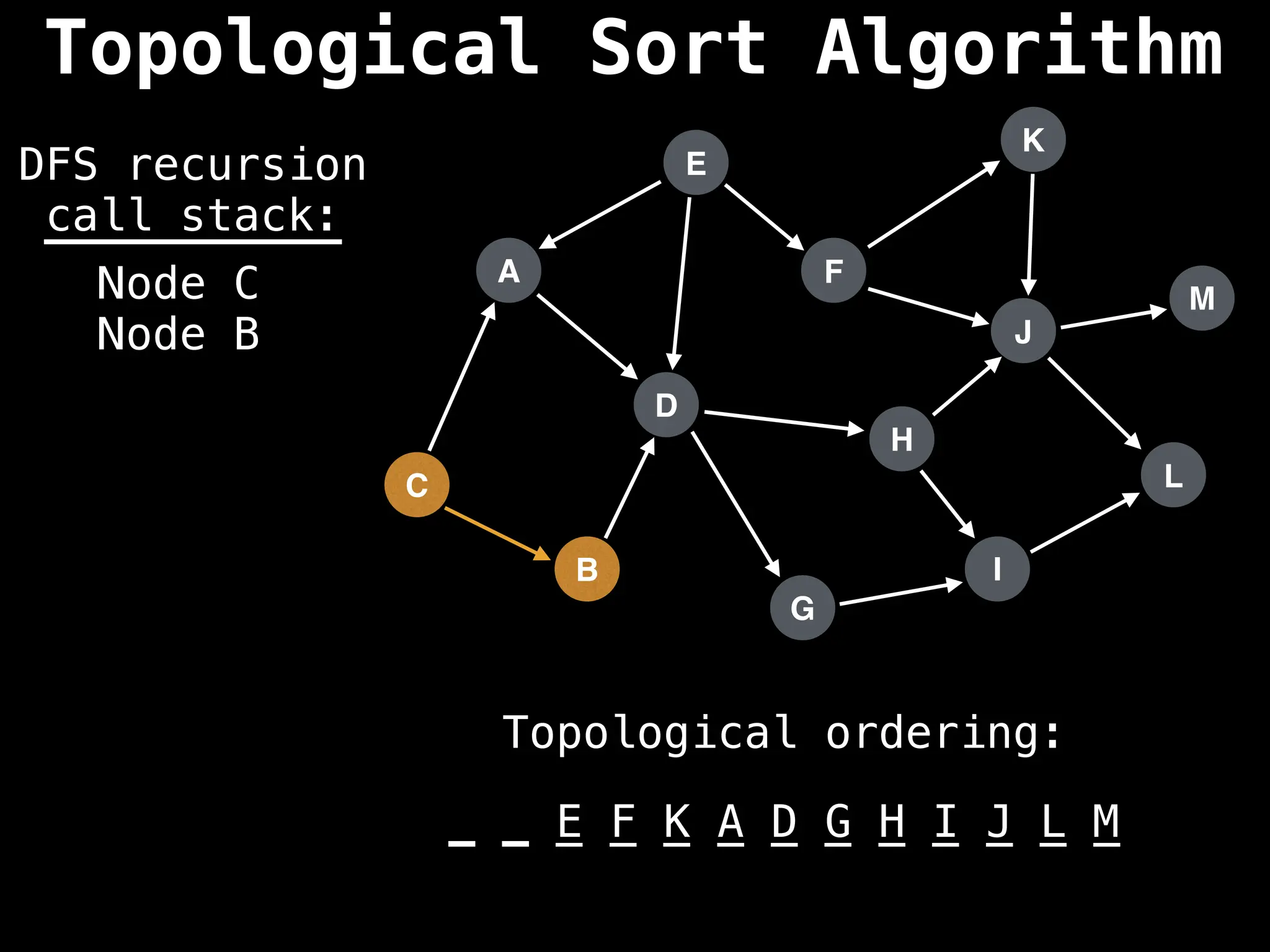
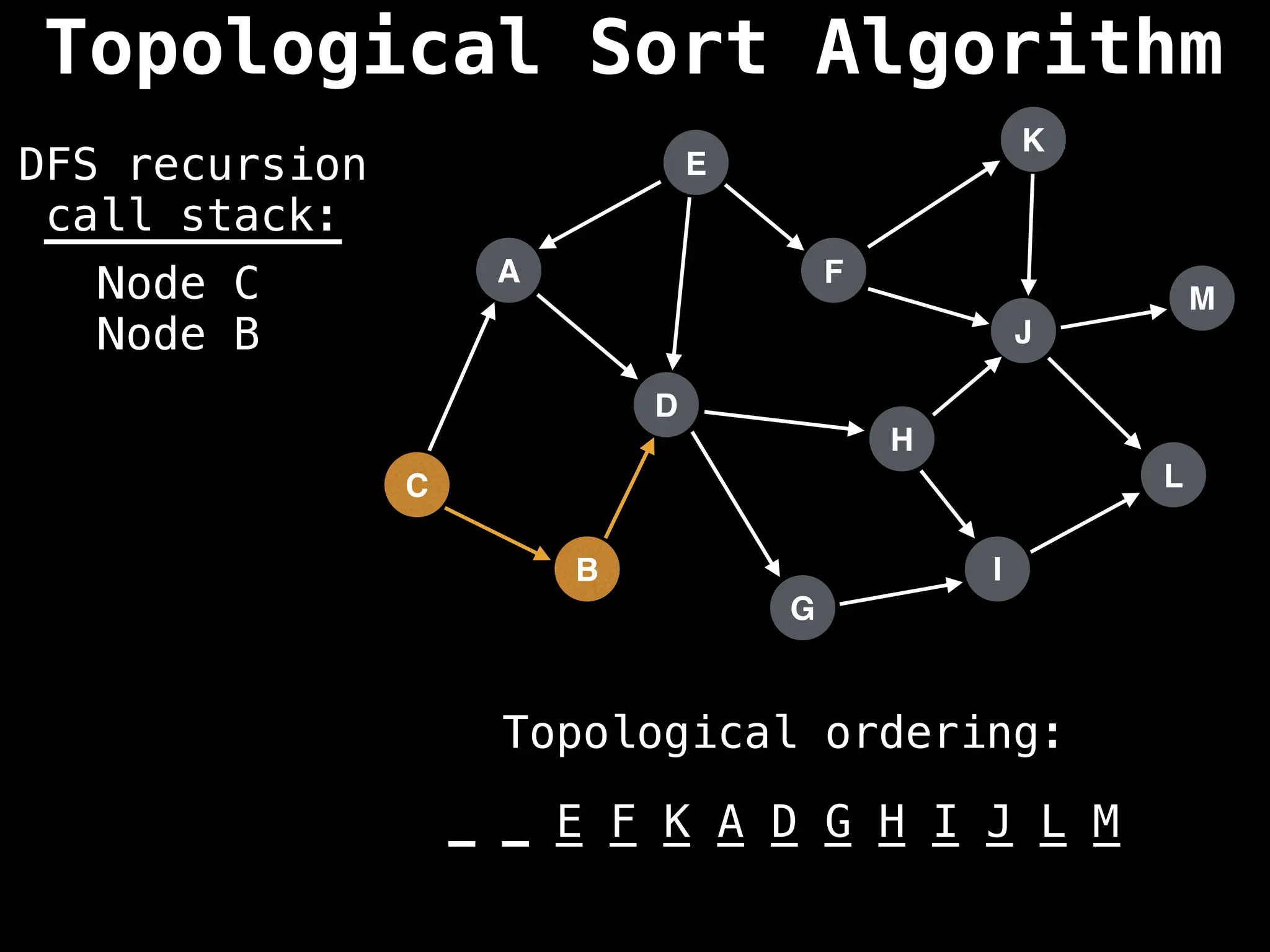
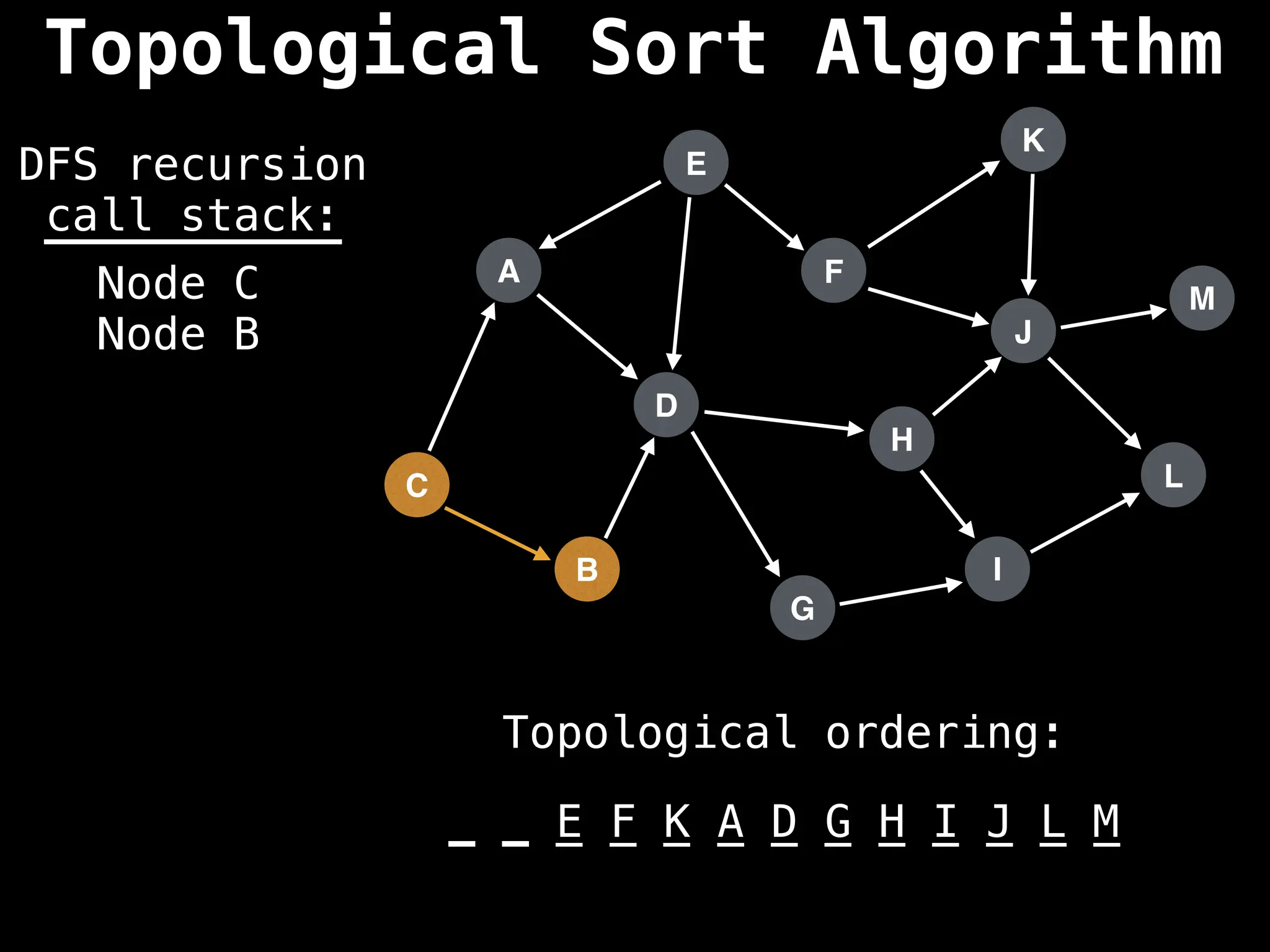
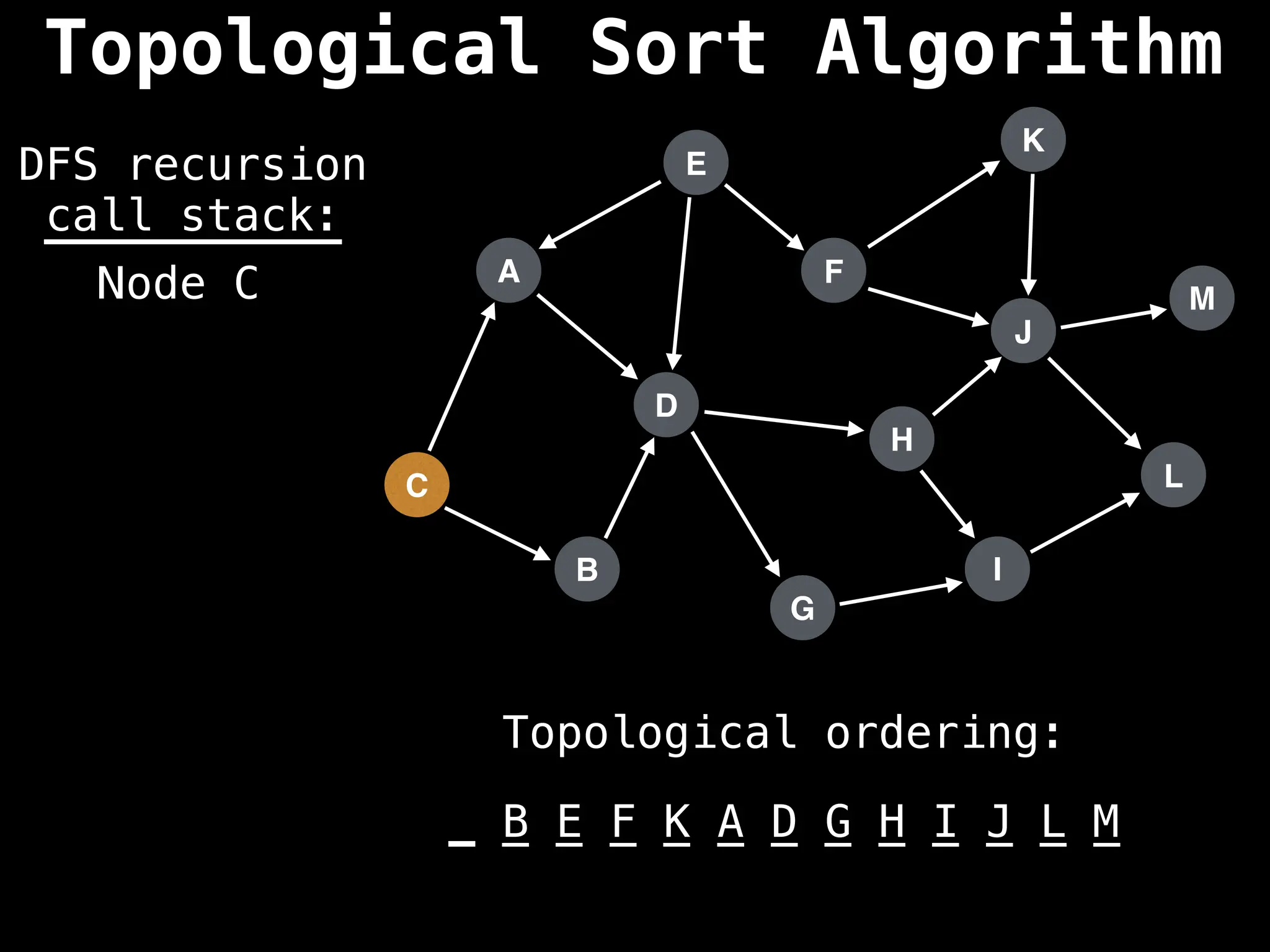
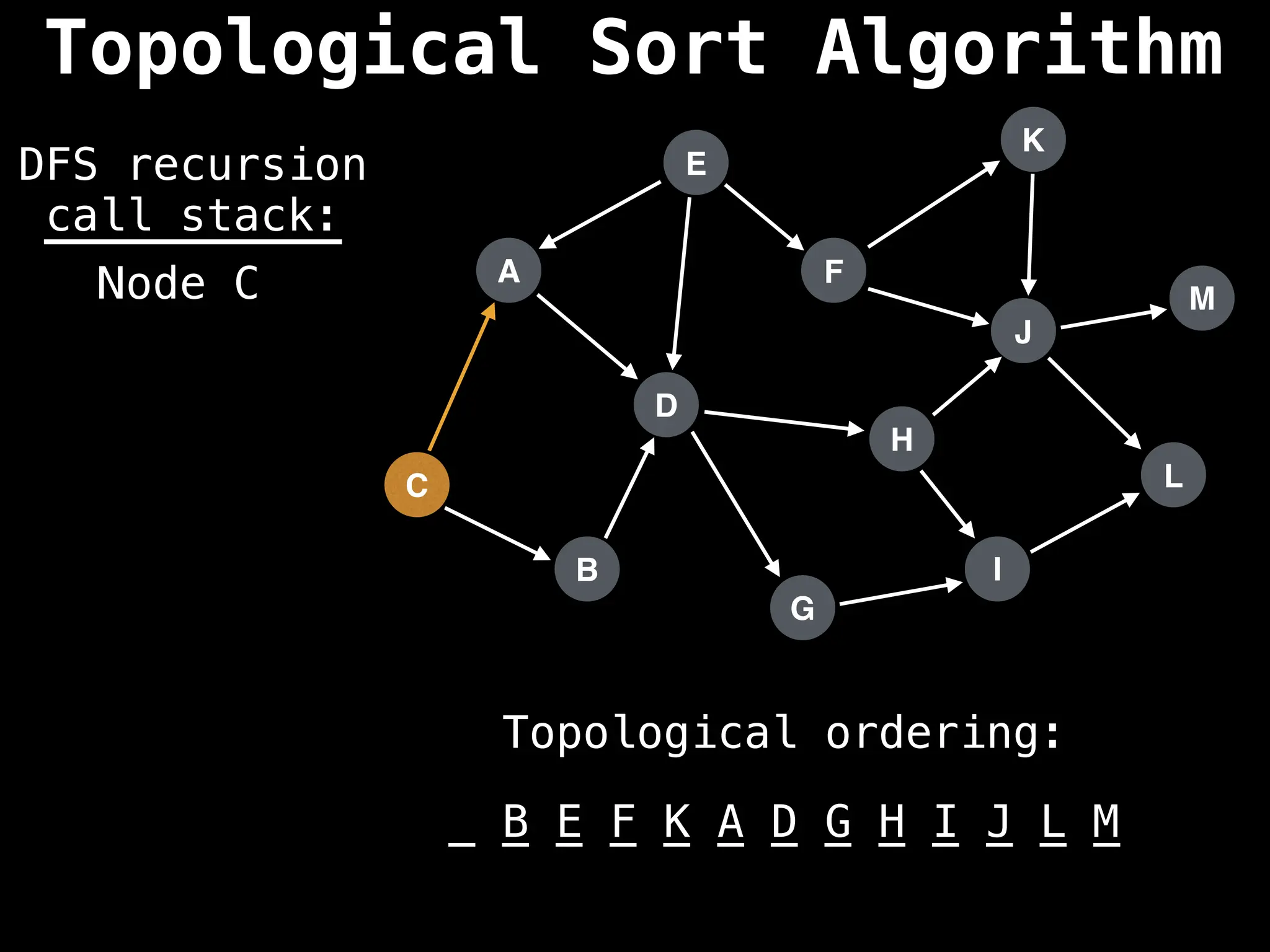
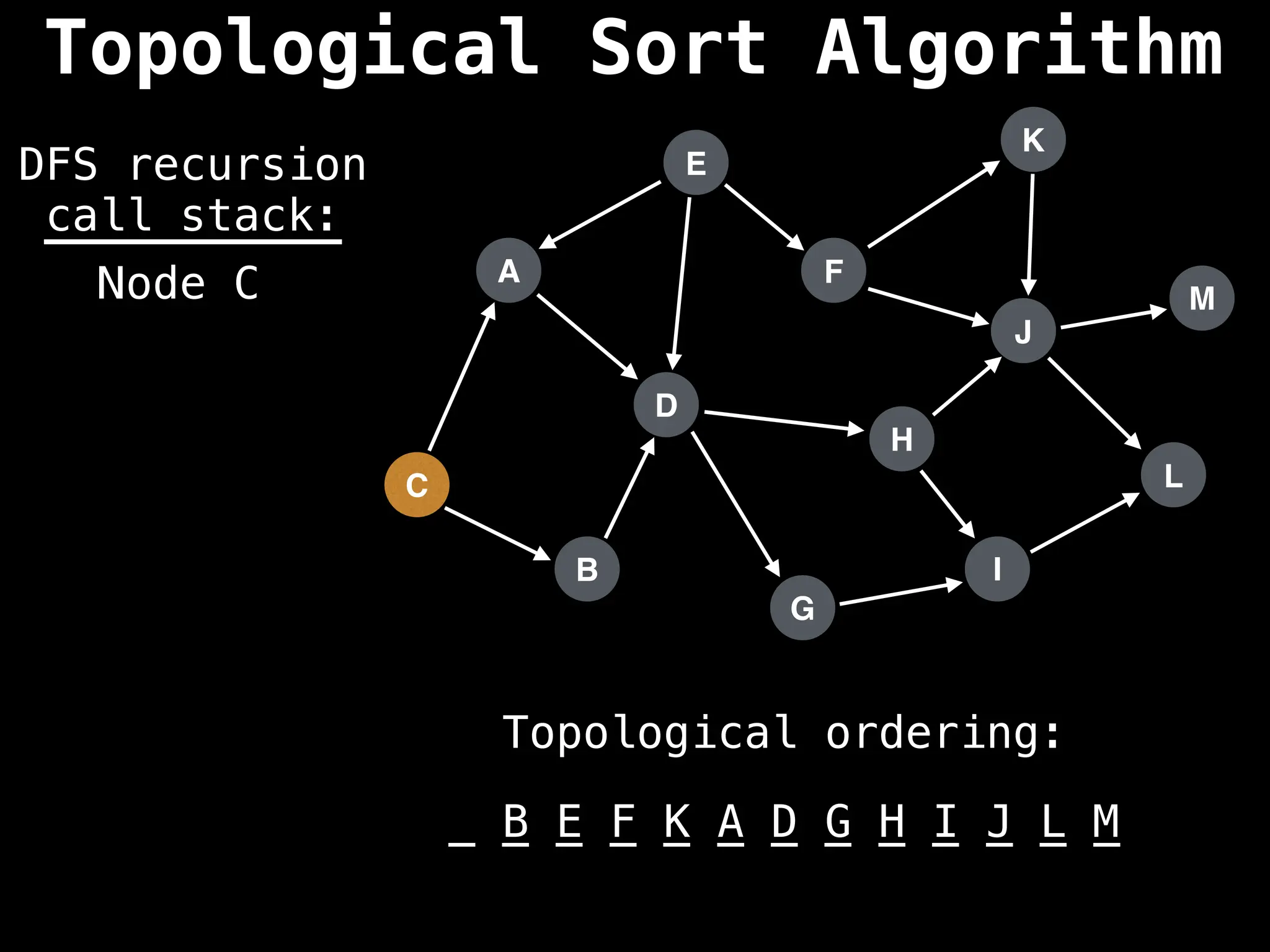
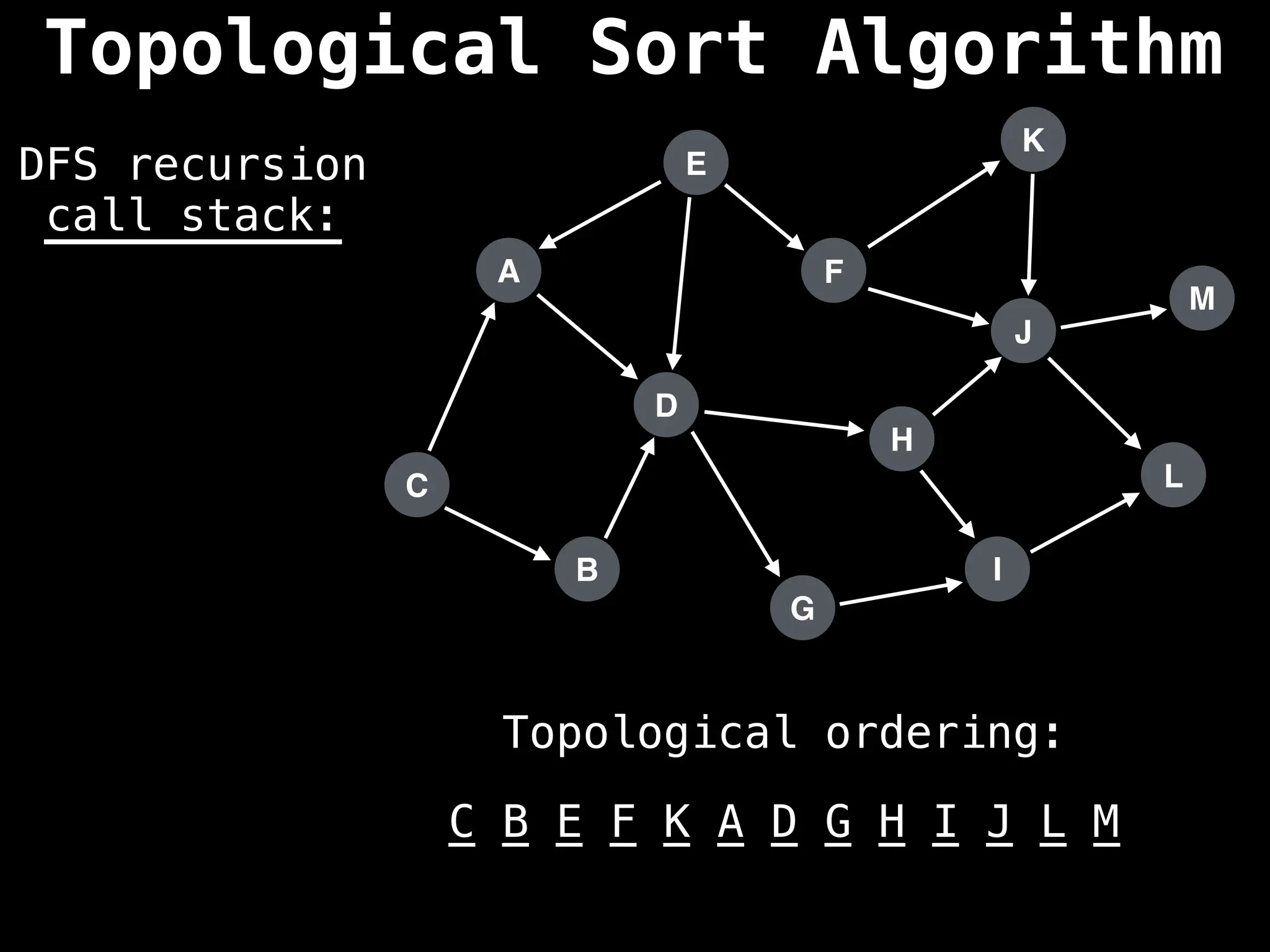
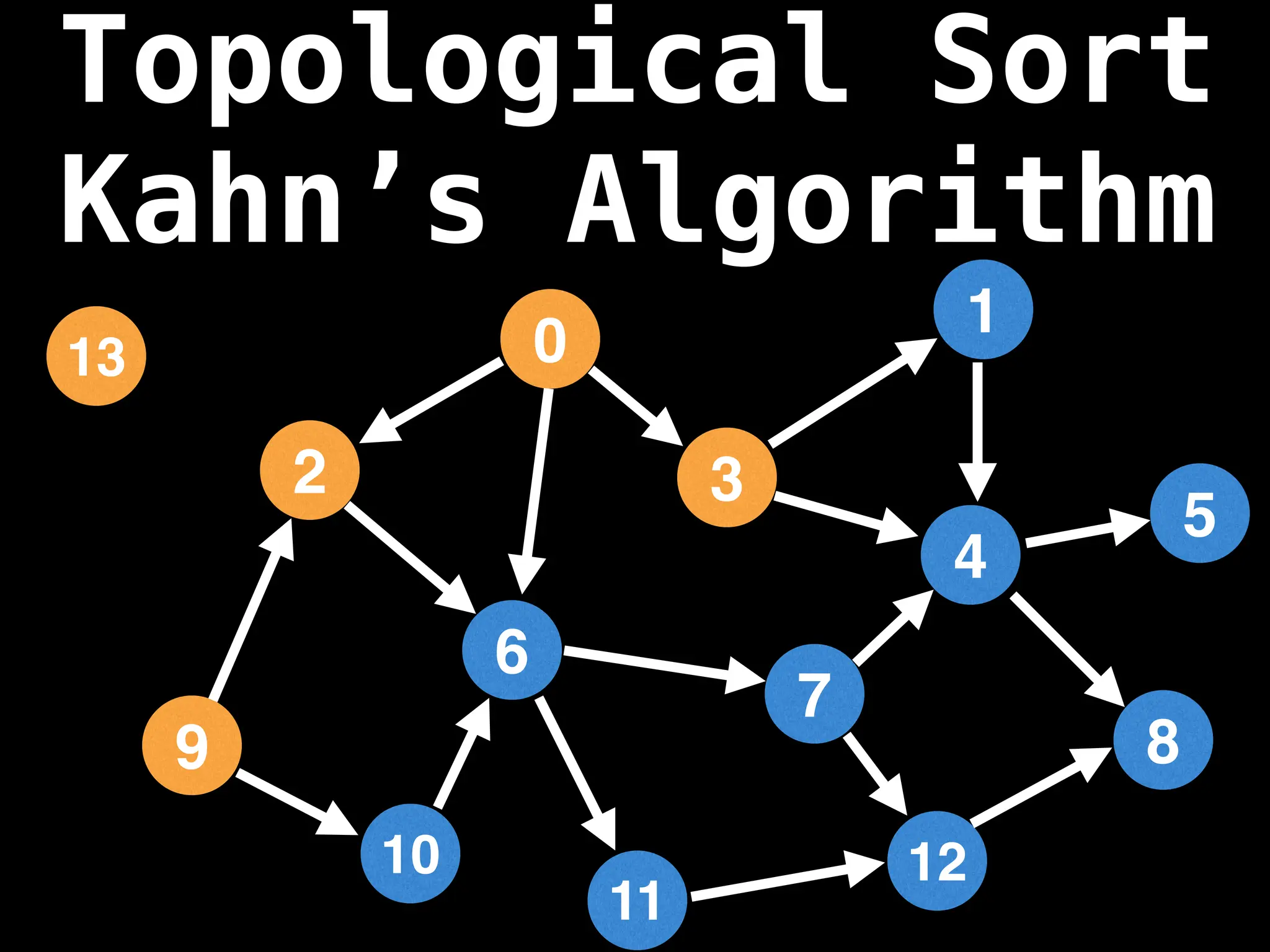
![# Assumption: graph is stored as adjacency list
function topsort(graph):
N = graph.numberOfNodes()
V = [false,…,false] # Length N
ordering = [0,…,0] # Length N
i = N - 1 # Index for ordering array
for(at = 0; at < N; at++):
if V[at] == false:
visitedNodes = []
dfs(at, V, visitedNodes, graph)
for nodeId in visitedNodes:
ordering[i] = nodeId
i = i - 1
return ordering
Topsort pseudocode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-397-2048.jpg)
![# Execute Depth First Search (DFS)
function dfs(at, V, visitedNodes, graph):
V[at] = true
edges = graph.getEdgesOutFromNode(at)
for edge in edges:
if V[edge.to] == false:
dfs(edge.to, V, visitedNodes, graph)
visitedNodes.add(at)
Topsort pseudocode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-398-2048.jpg)
![# Assumption: graph is stored as adjacency list
function topsort(graph):
N = graph.numberOfNodes()
V = [false,…,false] # Length N
ordering = [0,…,0] # Length N
i = N - 1 # Index for ordering array
for(at = 0; at < N; at++):
if V[at] == false:
visitedNodes = []
dfs(at, V, visitedNodes, graph)
for nodeId in visitedNodes:
ordering[i] = nodeId
i = i - 1
return ordering
Topsort pseudocode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-399-2048.jpg)
![# Assumption: graph is stored as adjacency list
function topsort(graph):
N = graph.numberOfNodes()
V = [false,…,false] # Length N
ordering = [0,…,0] # Length N
i = N - 1 # Index for ordering array
for(at = 0; at < N; at++):
if V[at] == false:
visitedNodes = []
dfs(at, V, visitedNodes, graph)
for nodeId in visitedNodes:
ordering[i] = nodeId
i = i - 1
return ordering
Topsort pseudocode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-400-2048.jpg)
![# Assumption: graph is stored as adjacency list
function topsort(graph):
N = graph.numberOfNodes()
V = [false,…,false] # Length N
ordering = [0,…,0] # Length N
i = N - 1 # Index for ordering array
for(at = 0; at < N; at++):
if V[at] == false:
i = dfs(i, at, V, ordering, graph)
return ordering
Topsort Optimization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-401-2048.jpg)
![# Execute Depth First Search (DFS)
function dfs(i, at, V, ordering, graph):
V[at] = true
edges = graph.getEdgesOutFromNode(at)
for edge in edges:
if V[edge.to] == false:
i = dfs(i, edge.to, V, ordering, graph)
ordering[i] = at
return i - 1
Topsort Optimization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-402-2048.jpg)

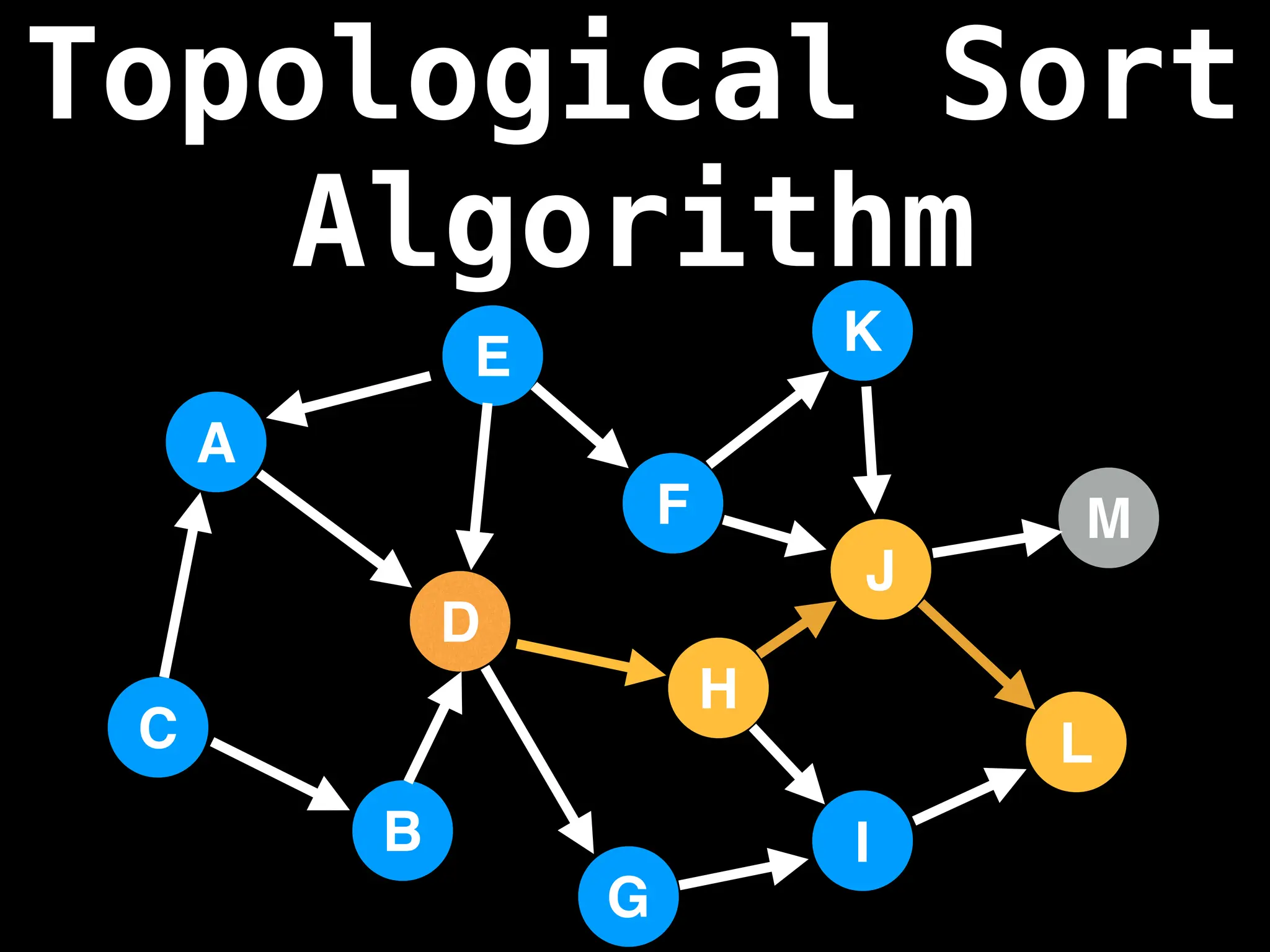

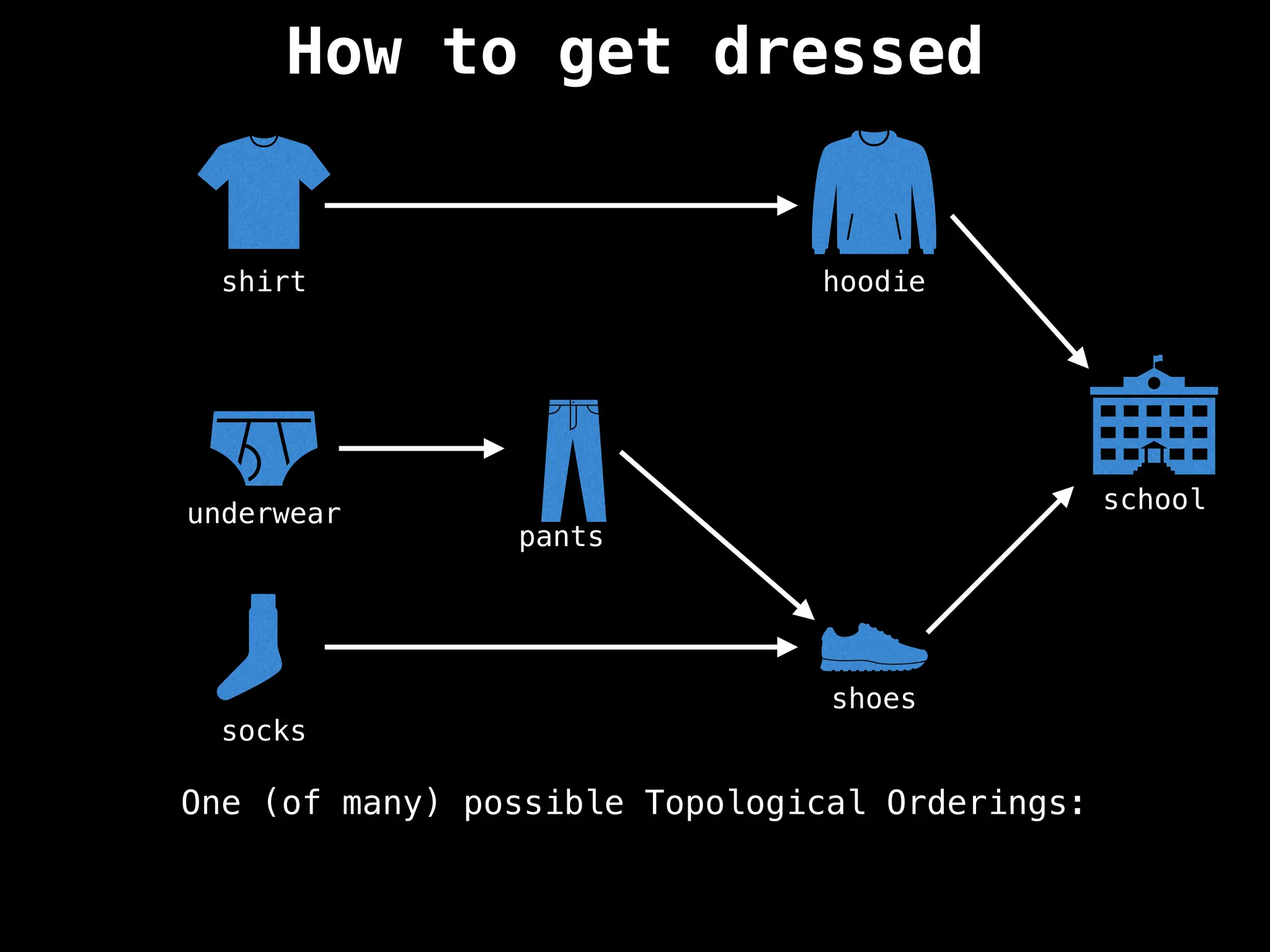
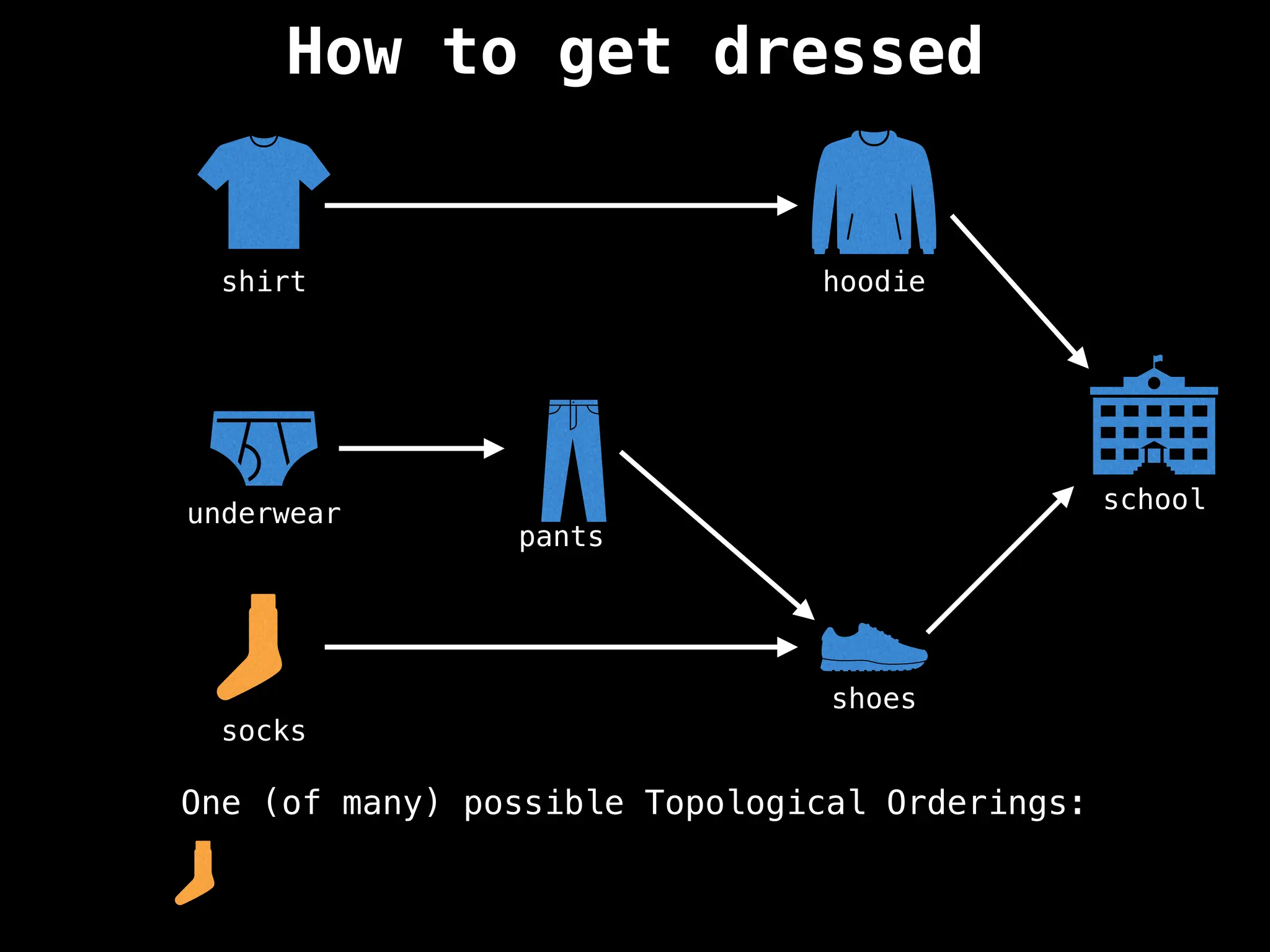
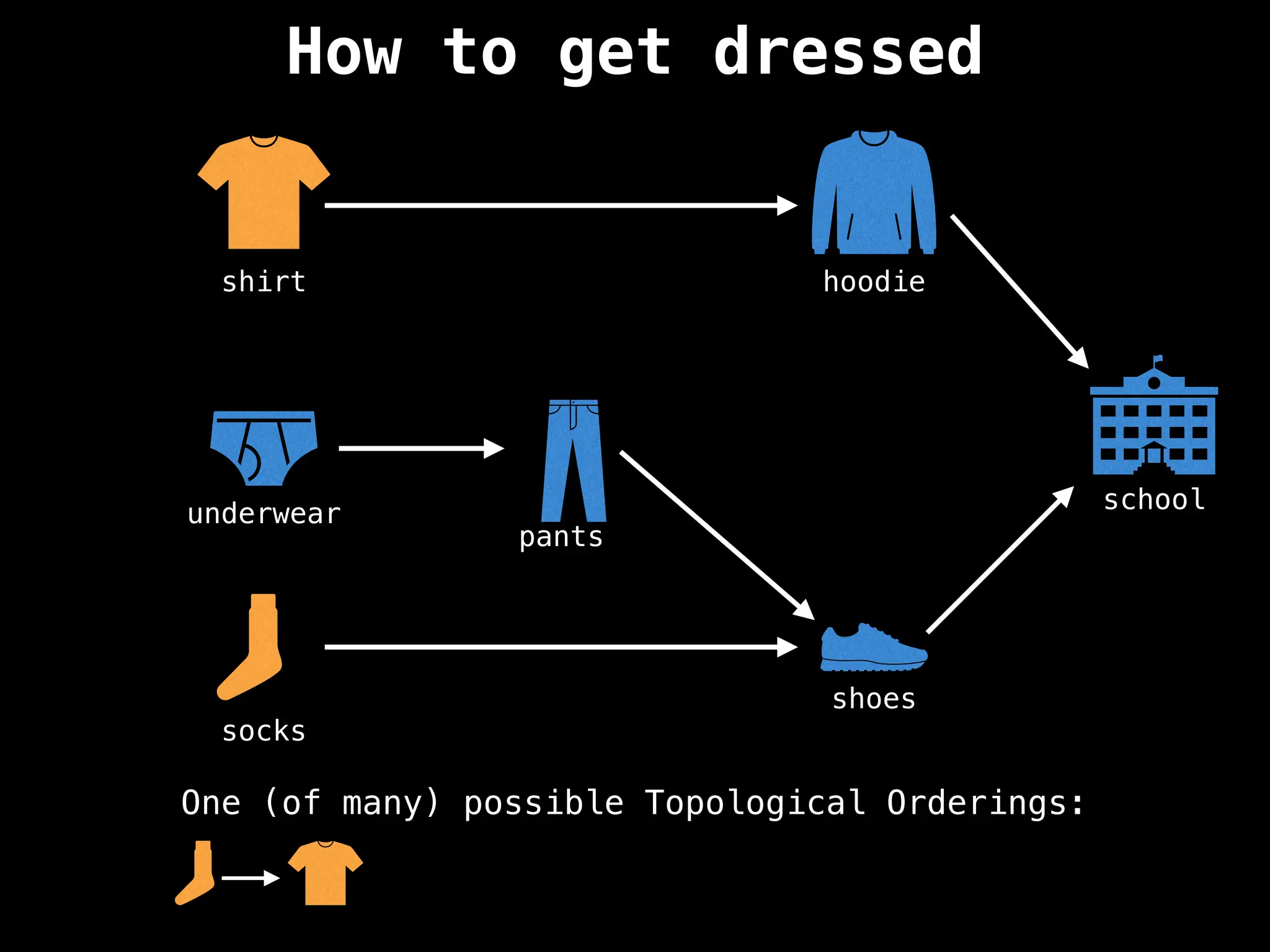
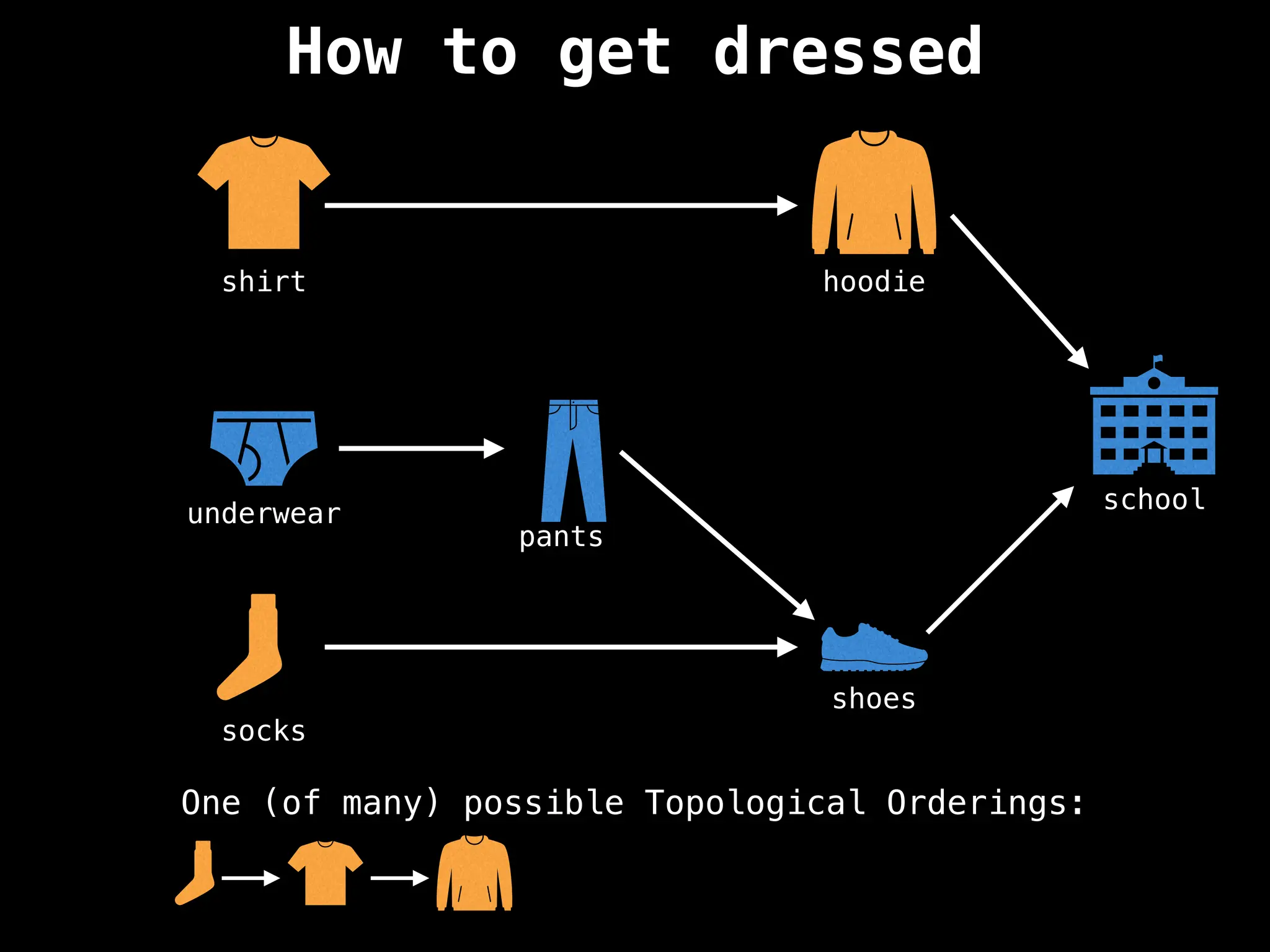
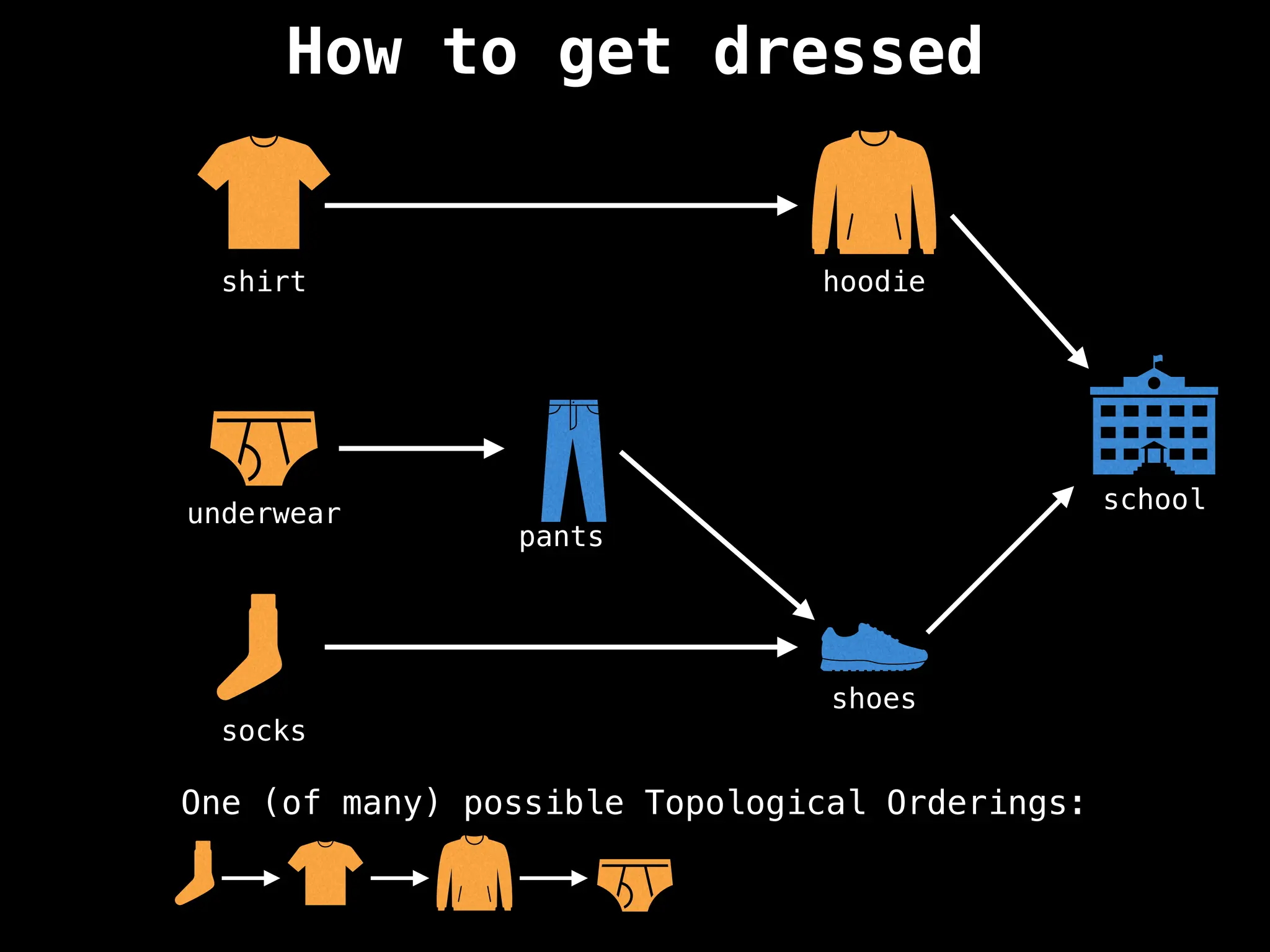
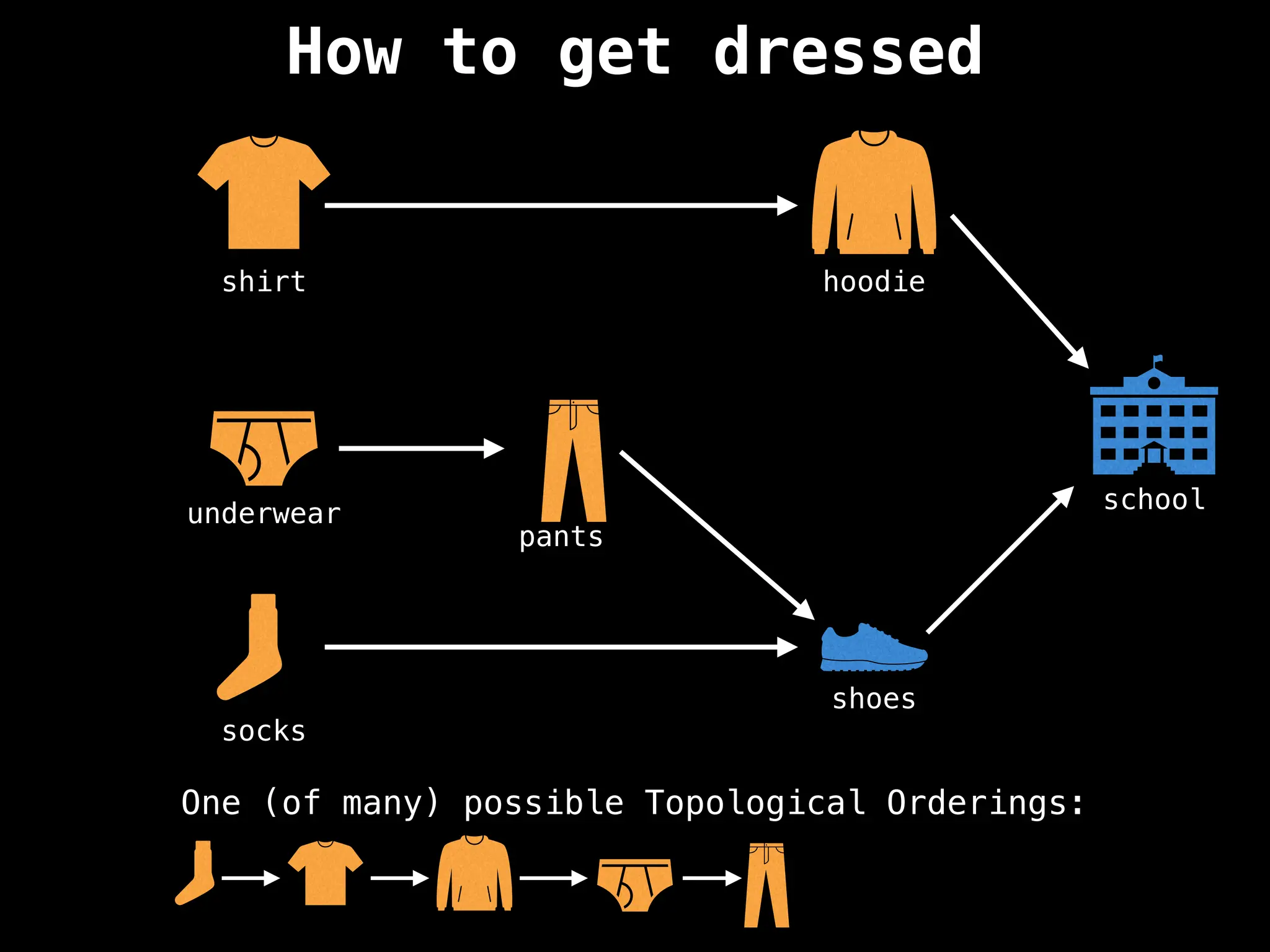
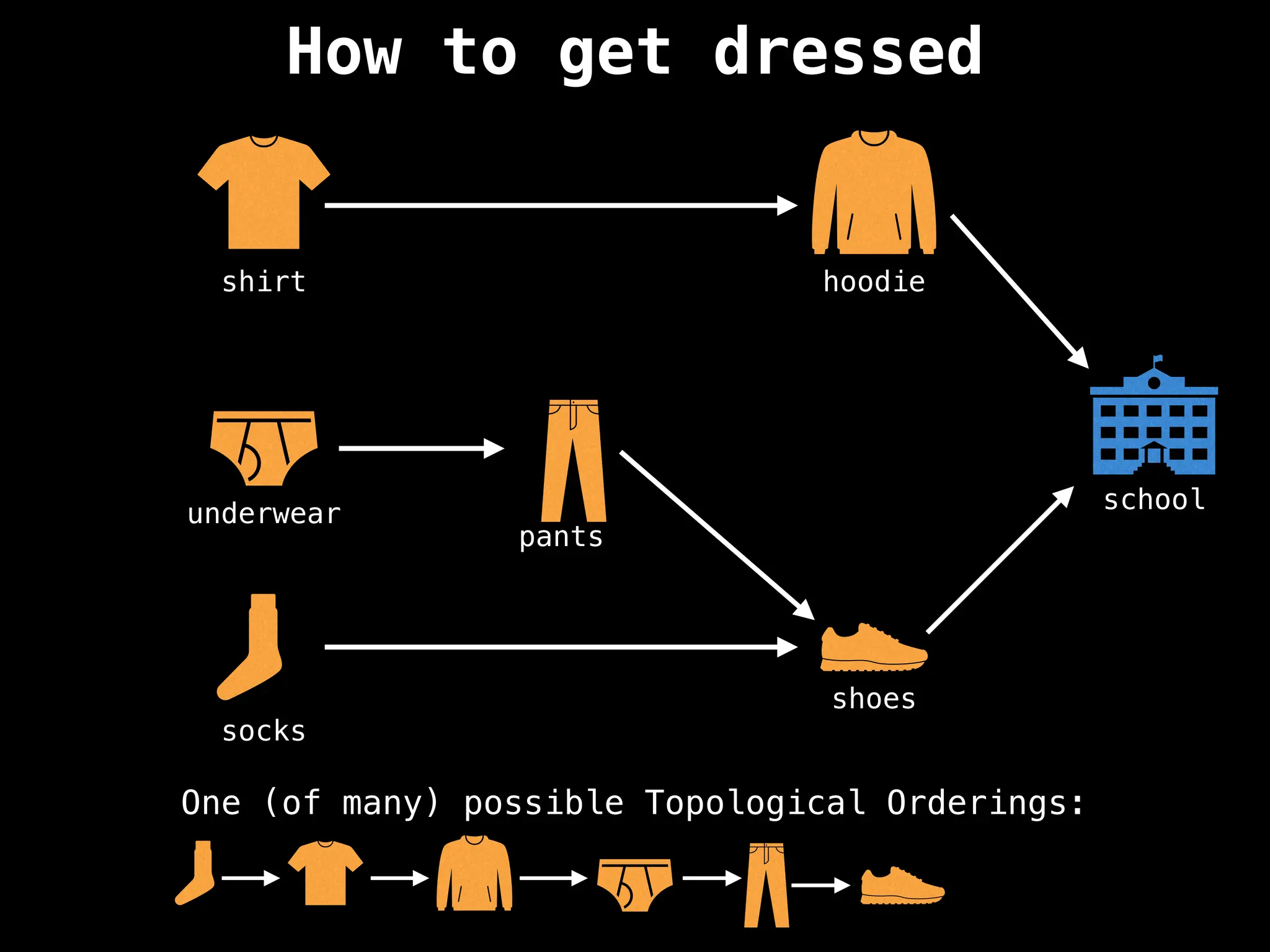
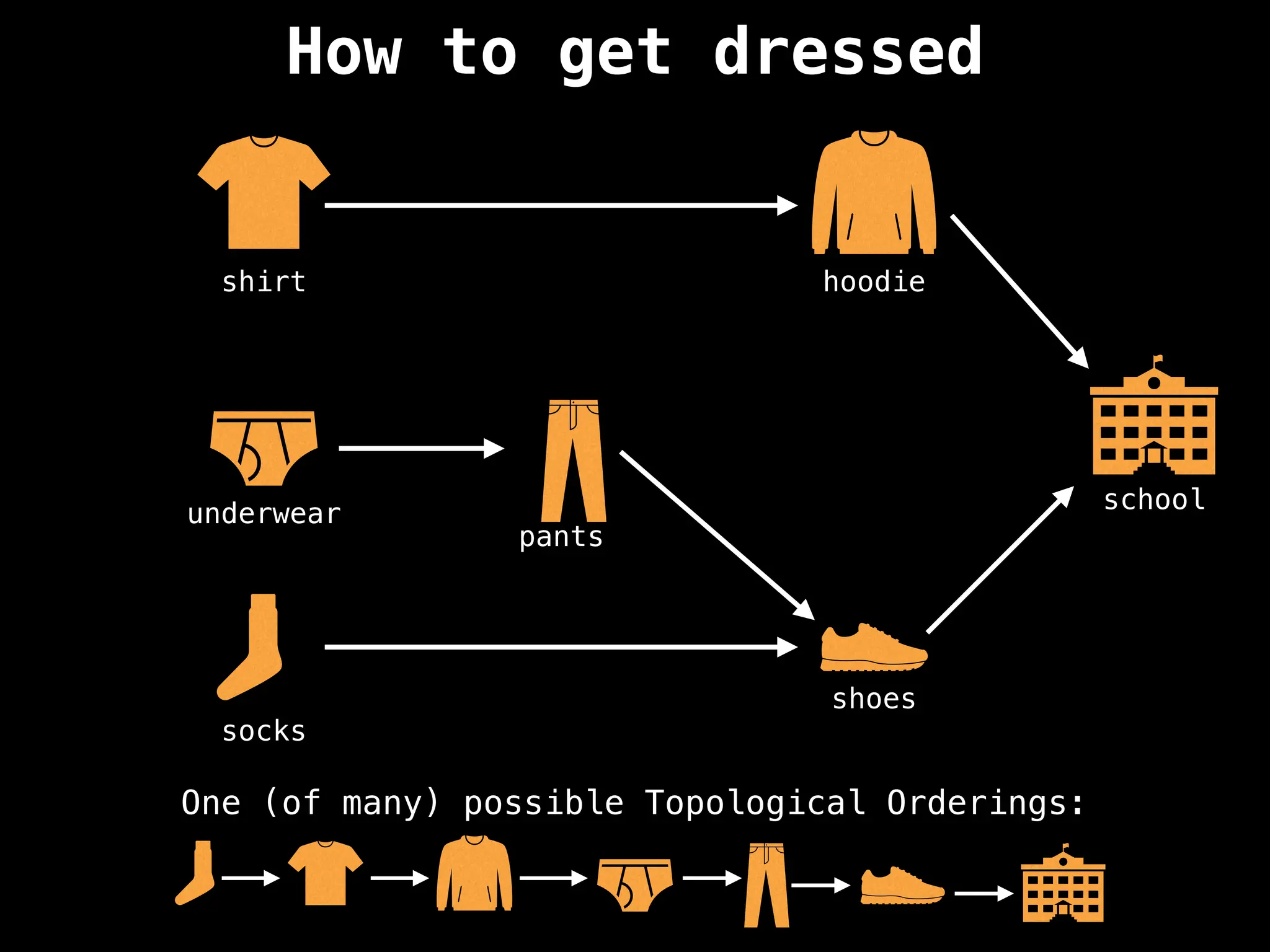

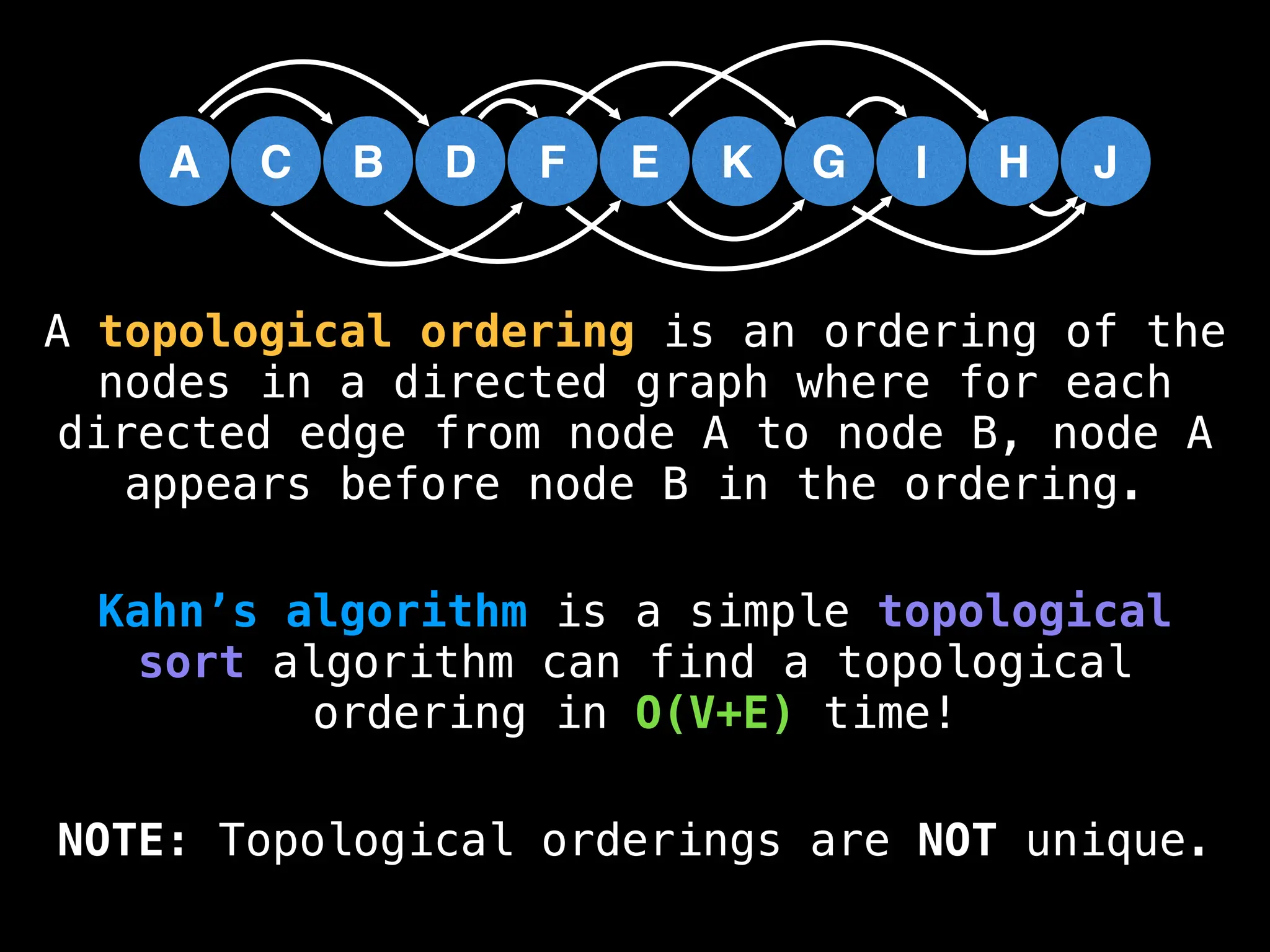
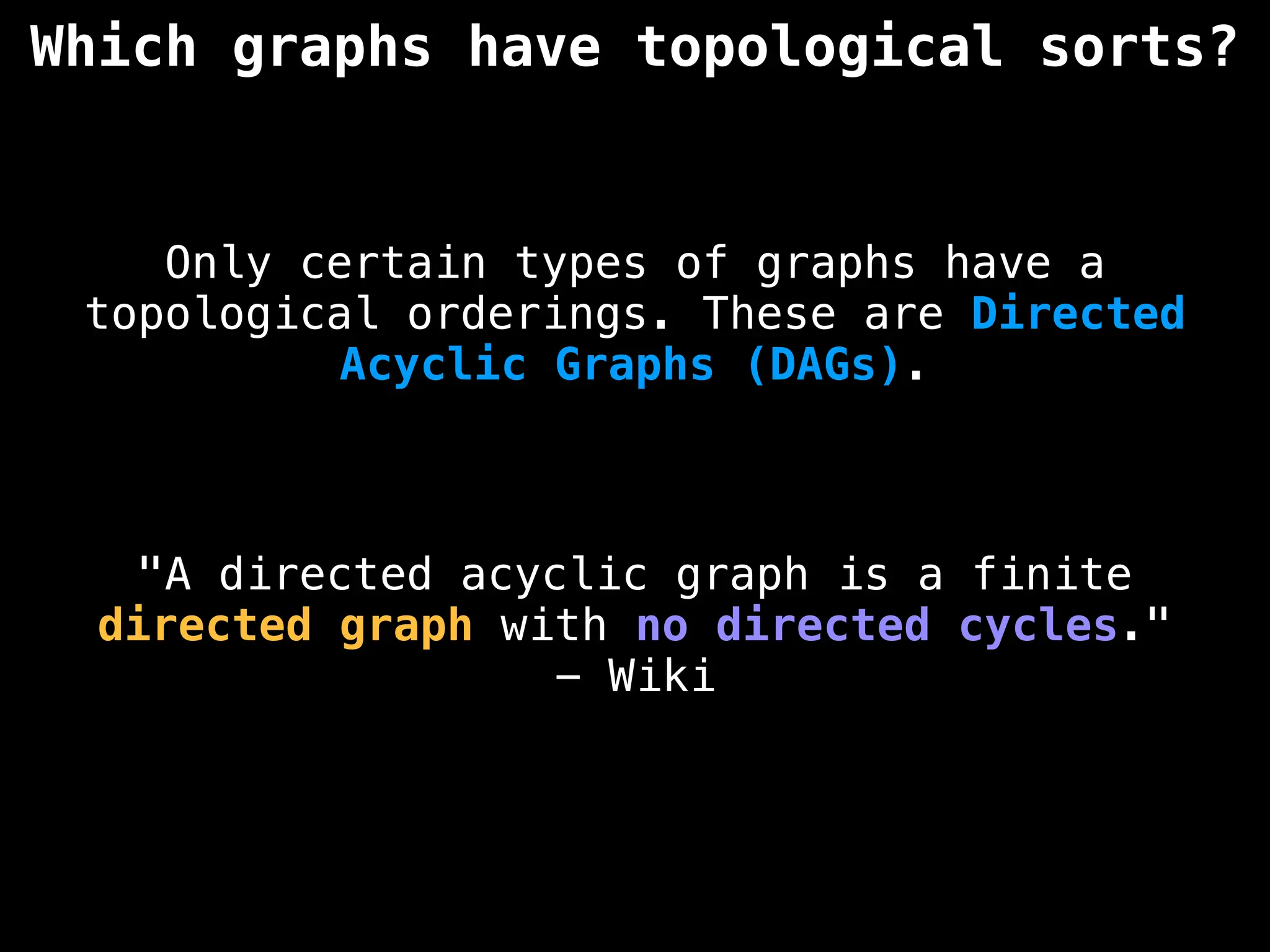
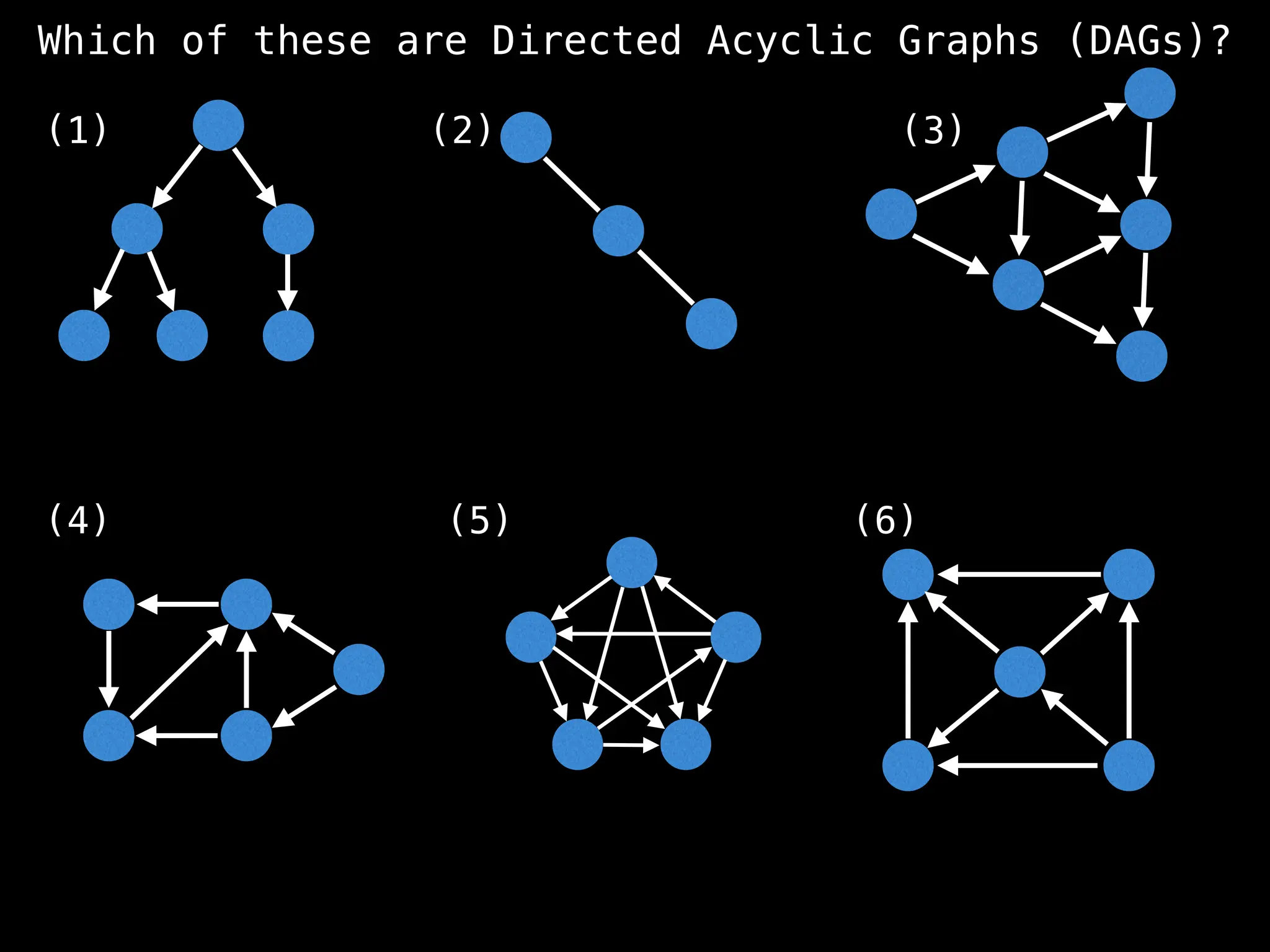
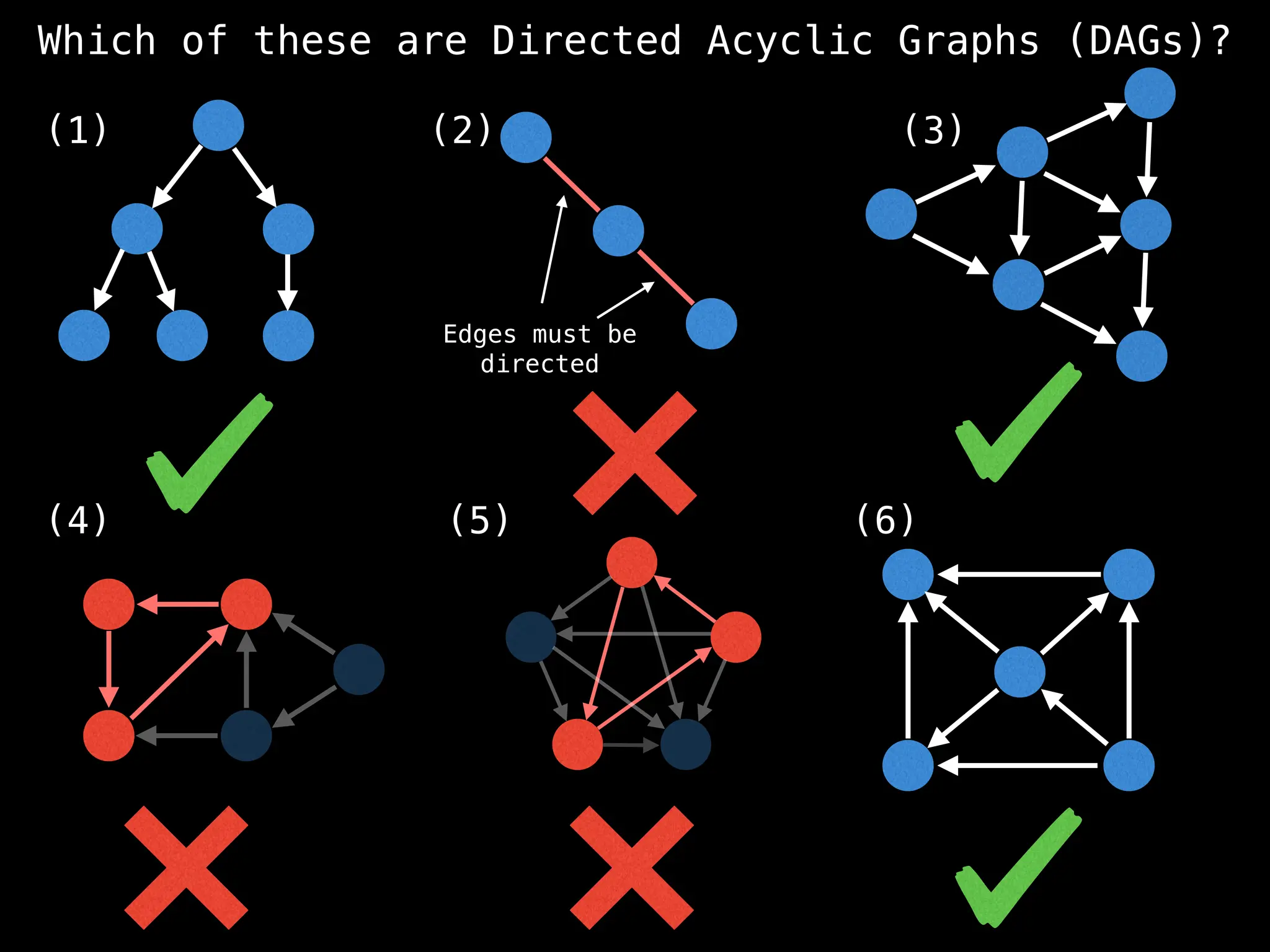
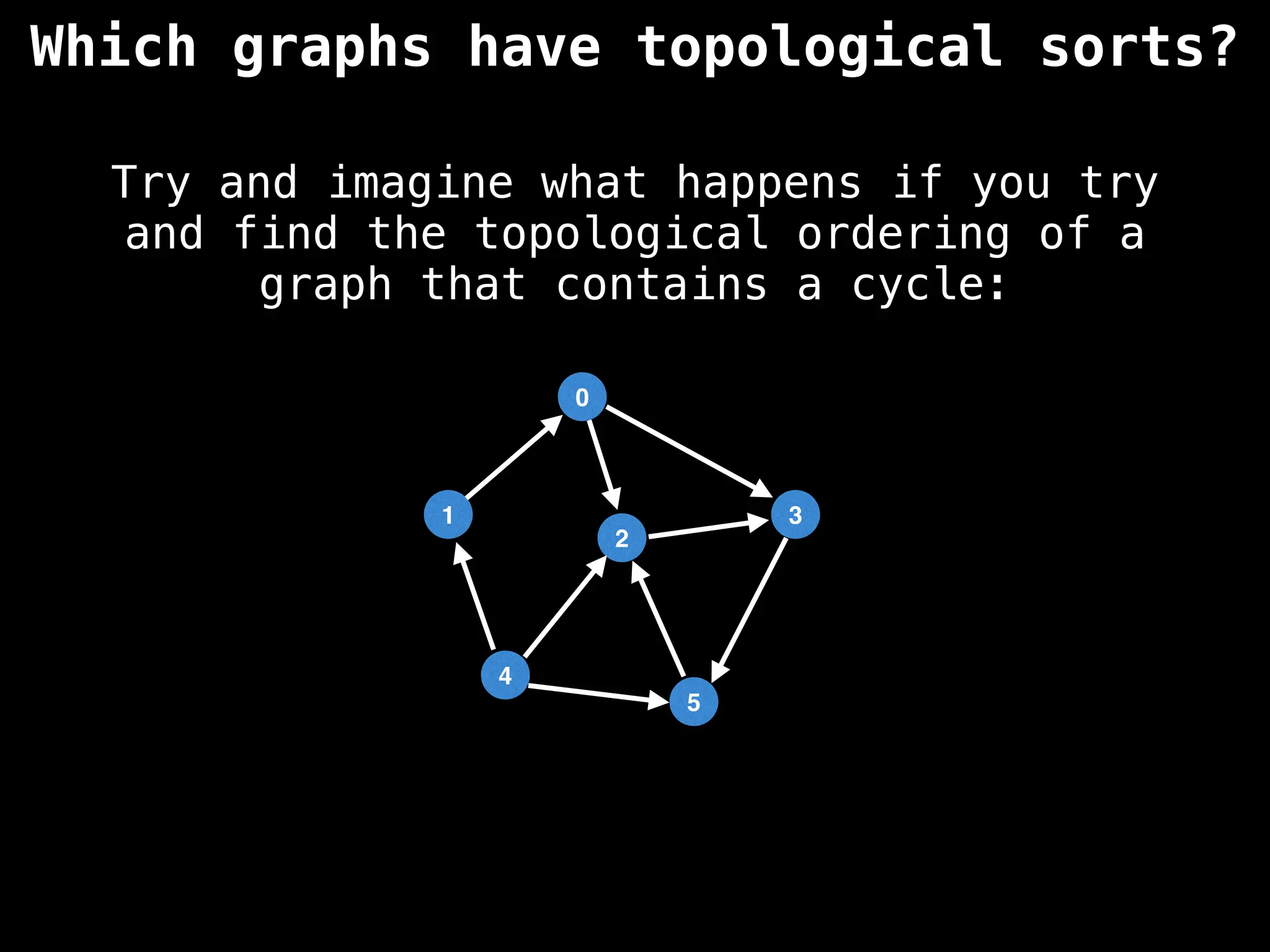
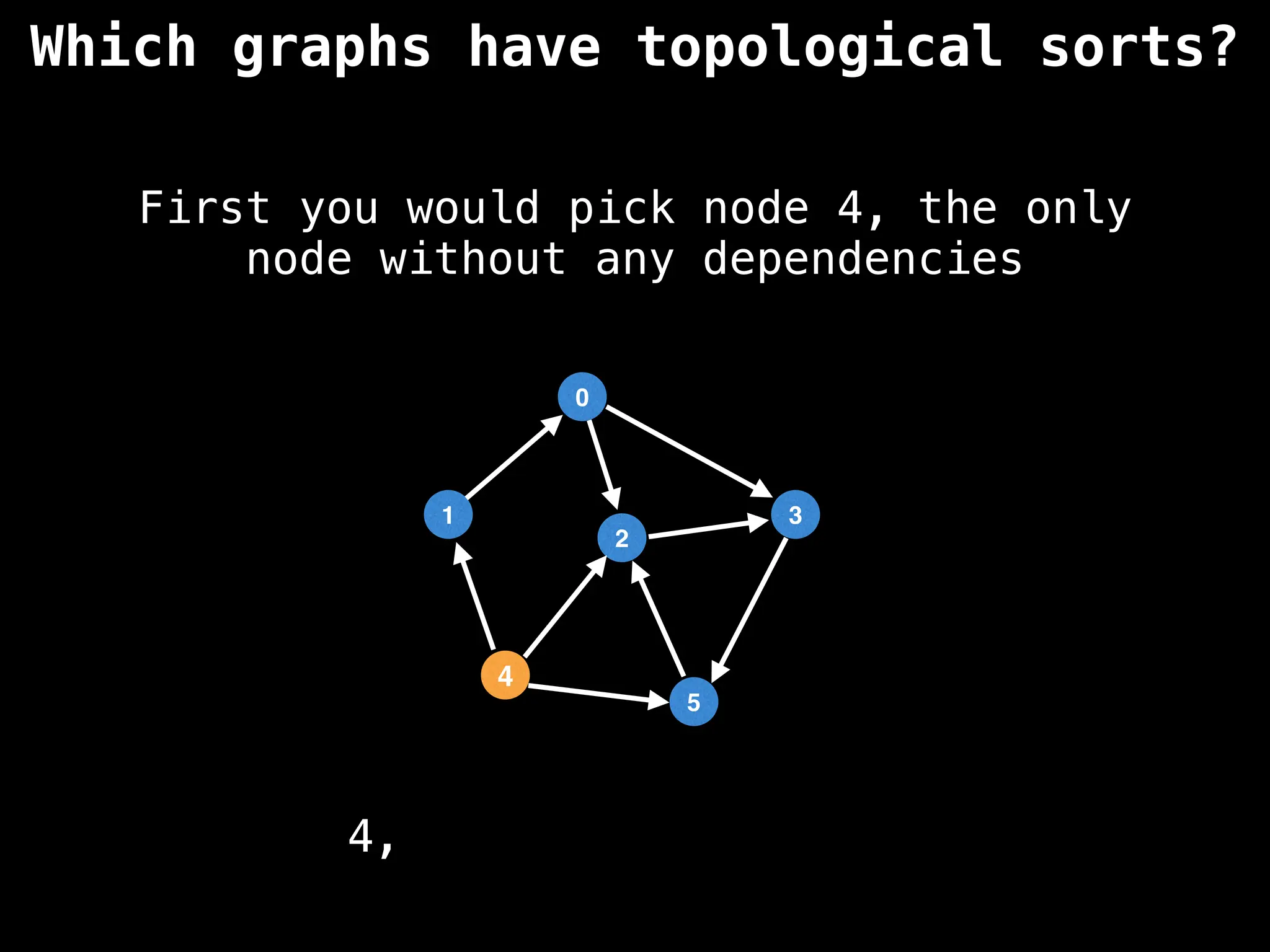
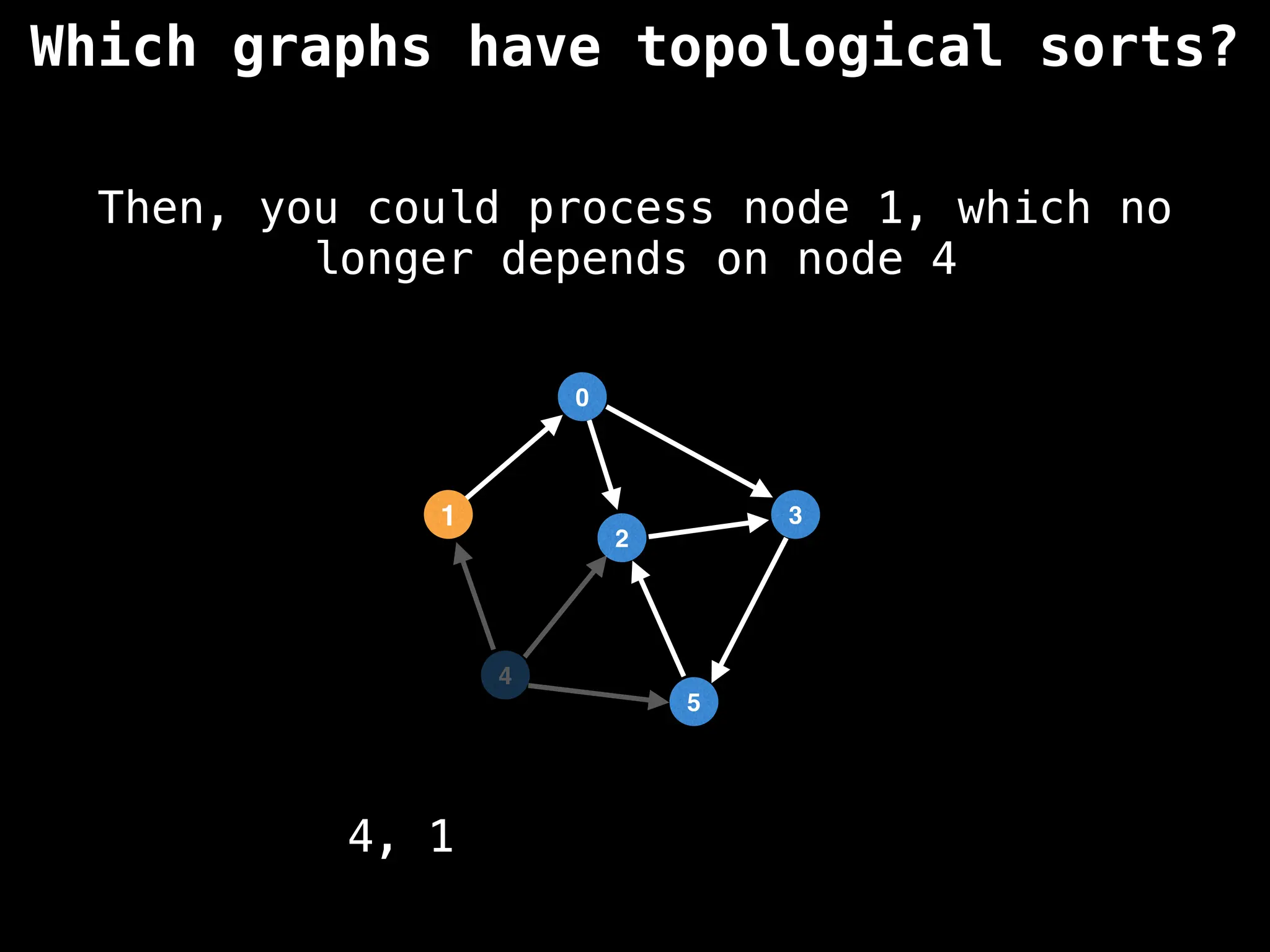
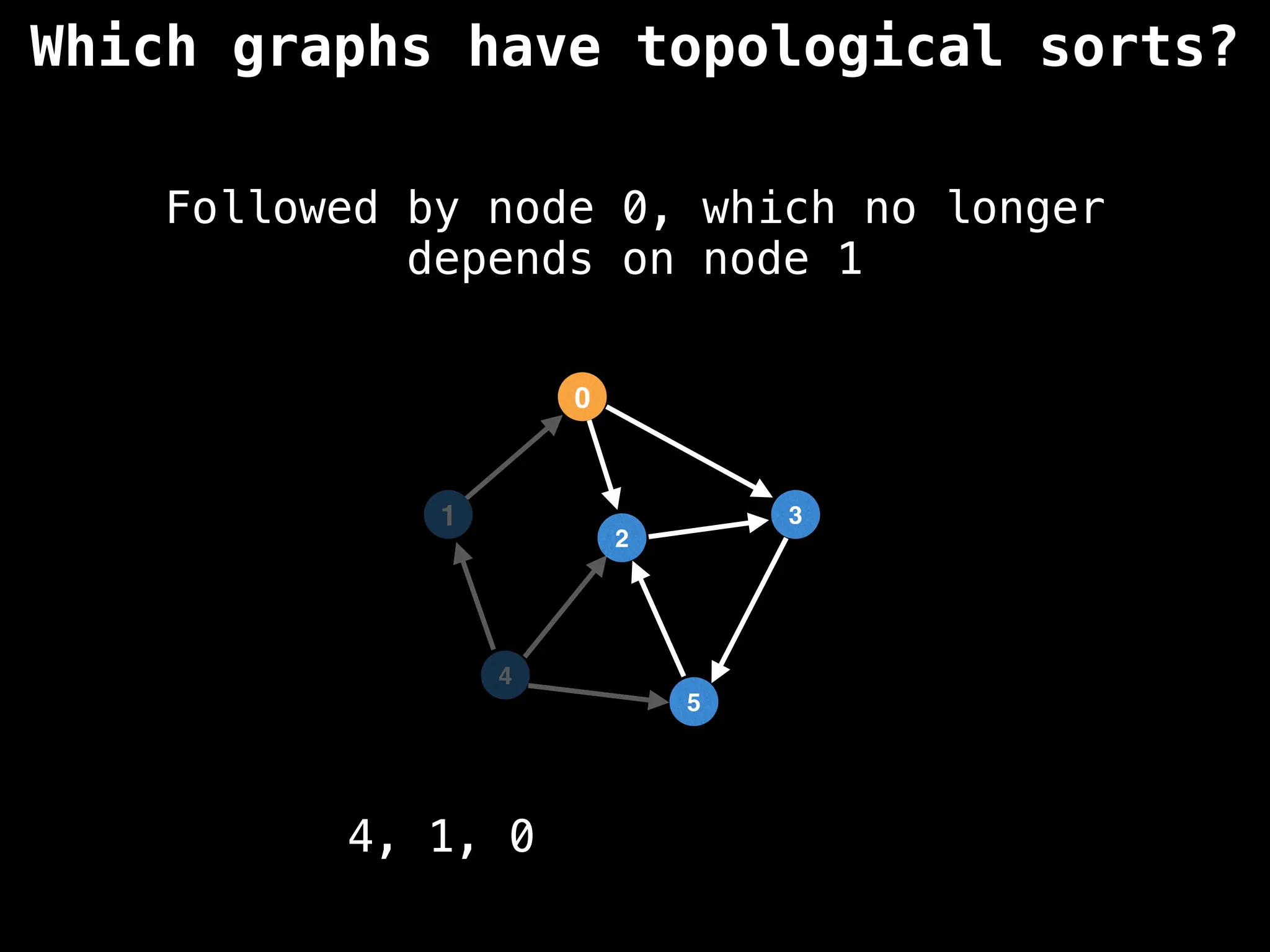
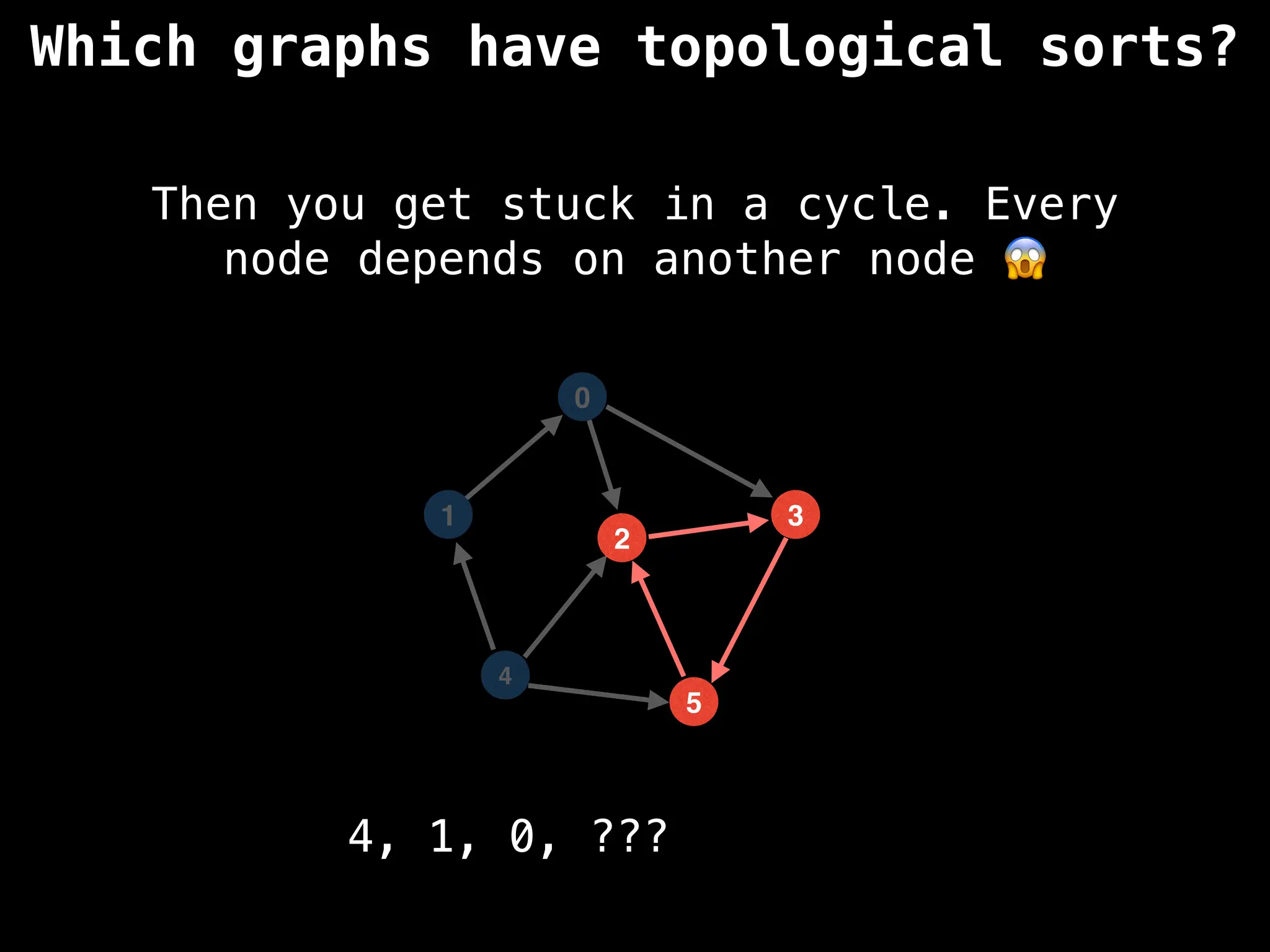

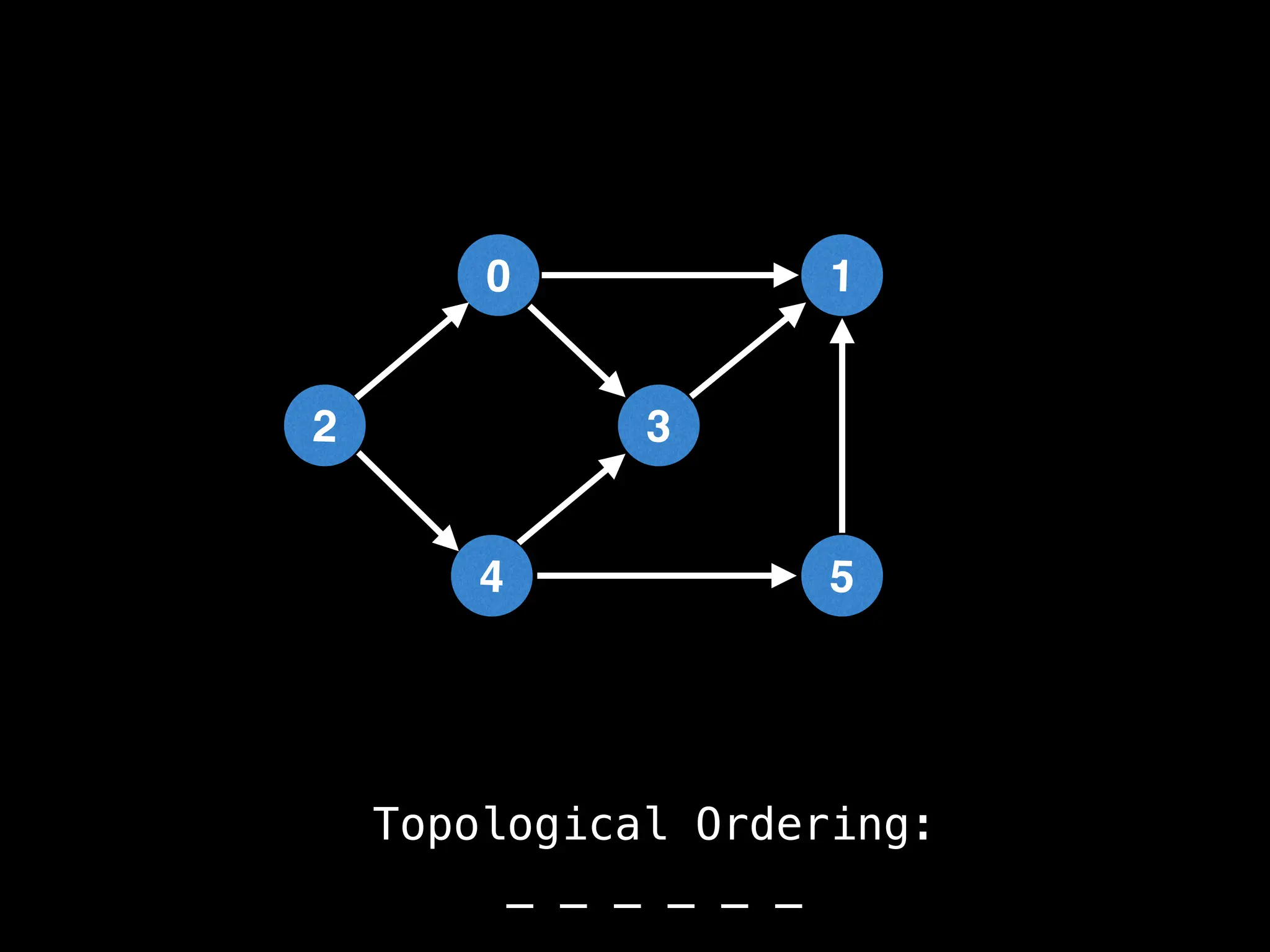
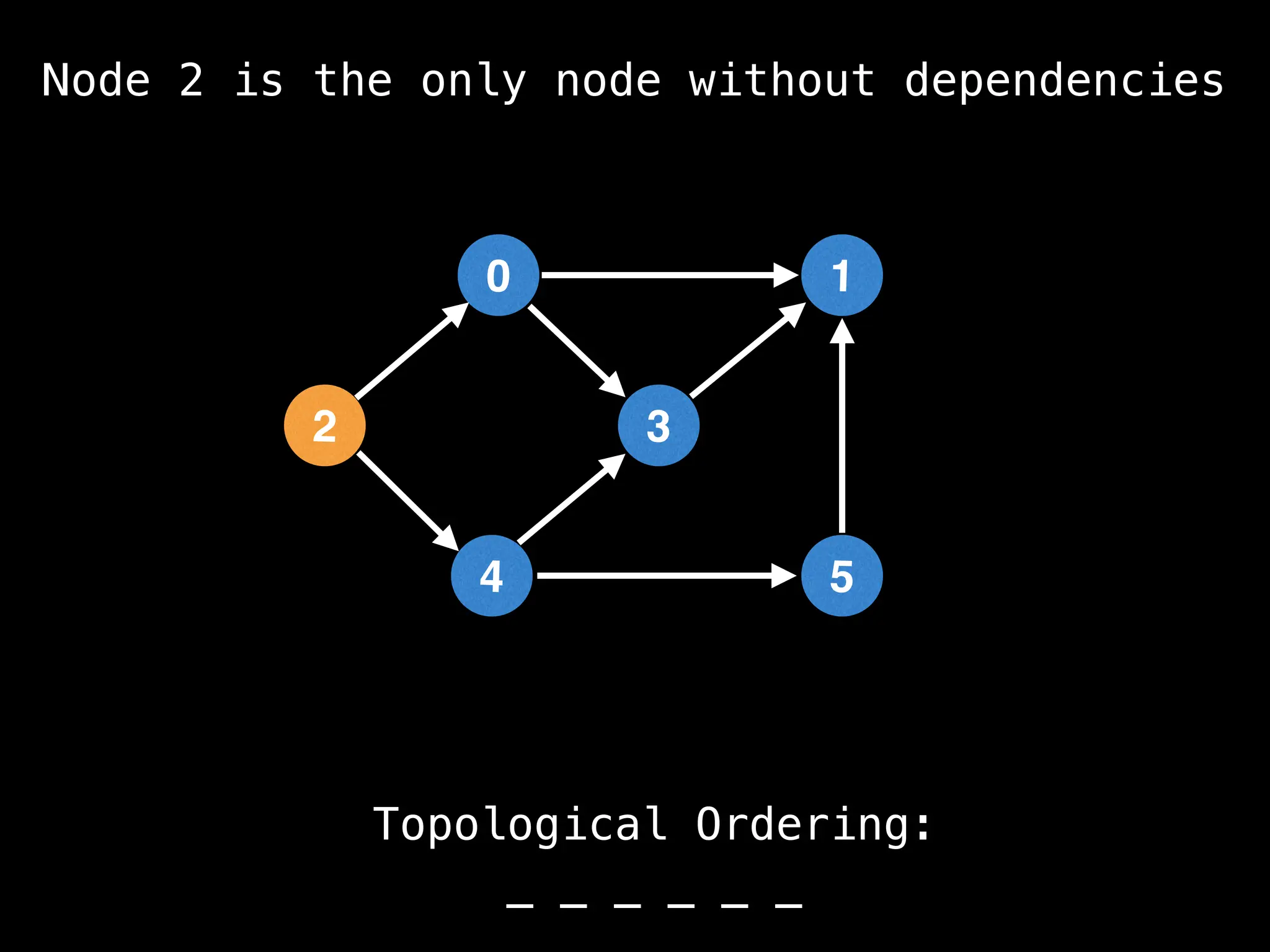
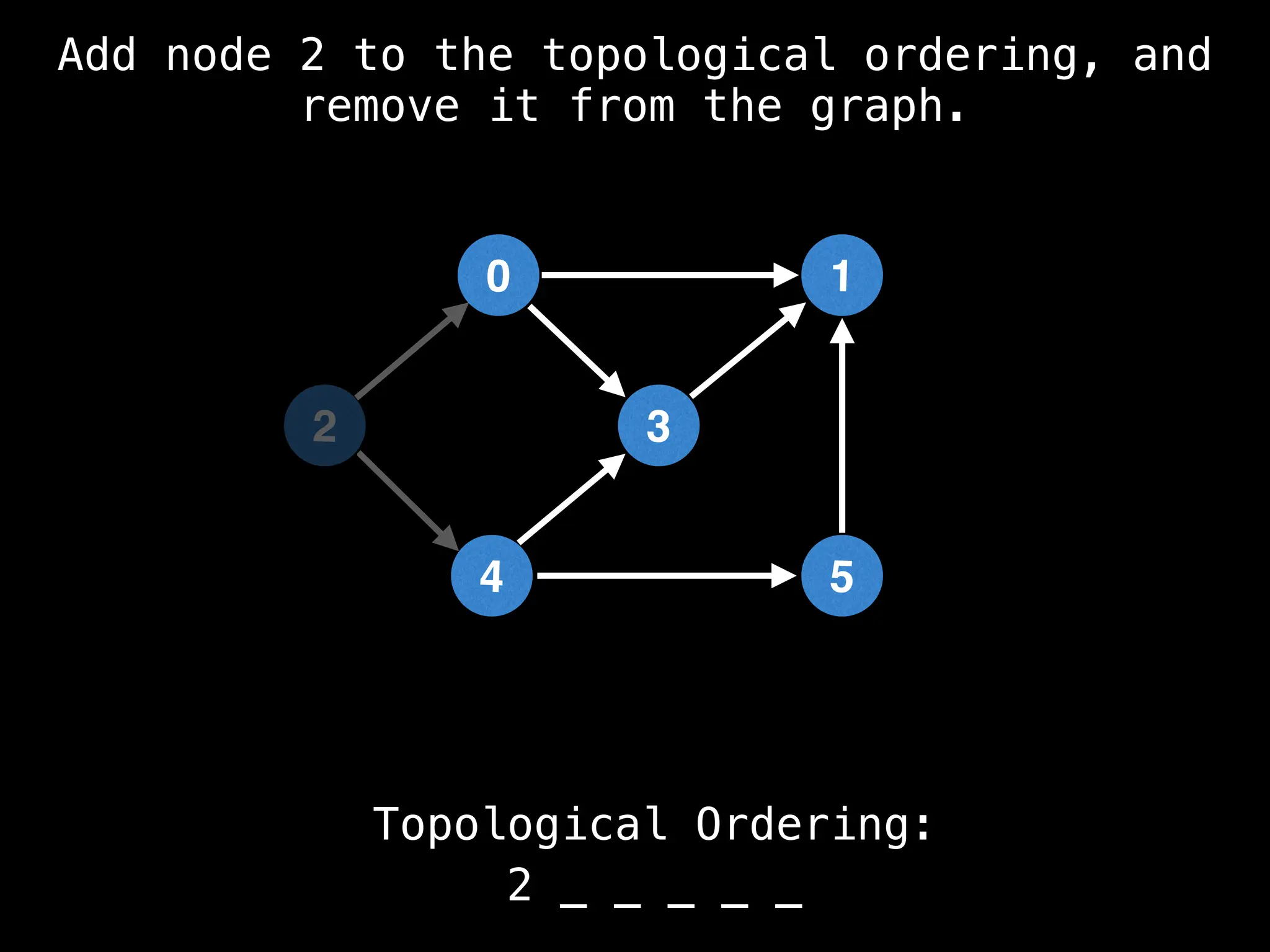
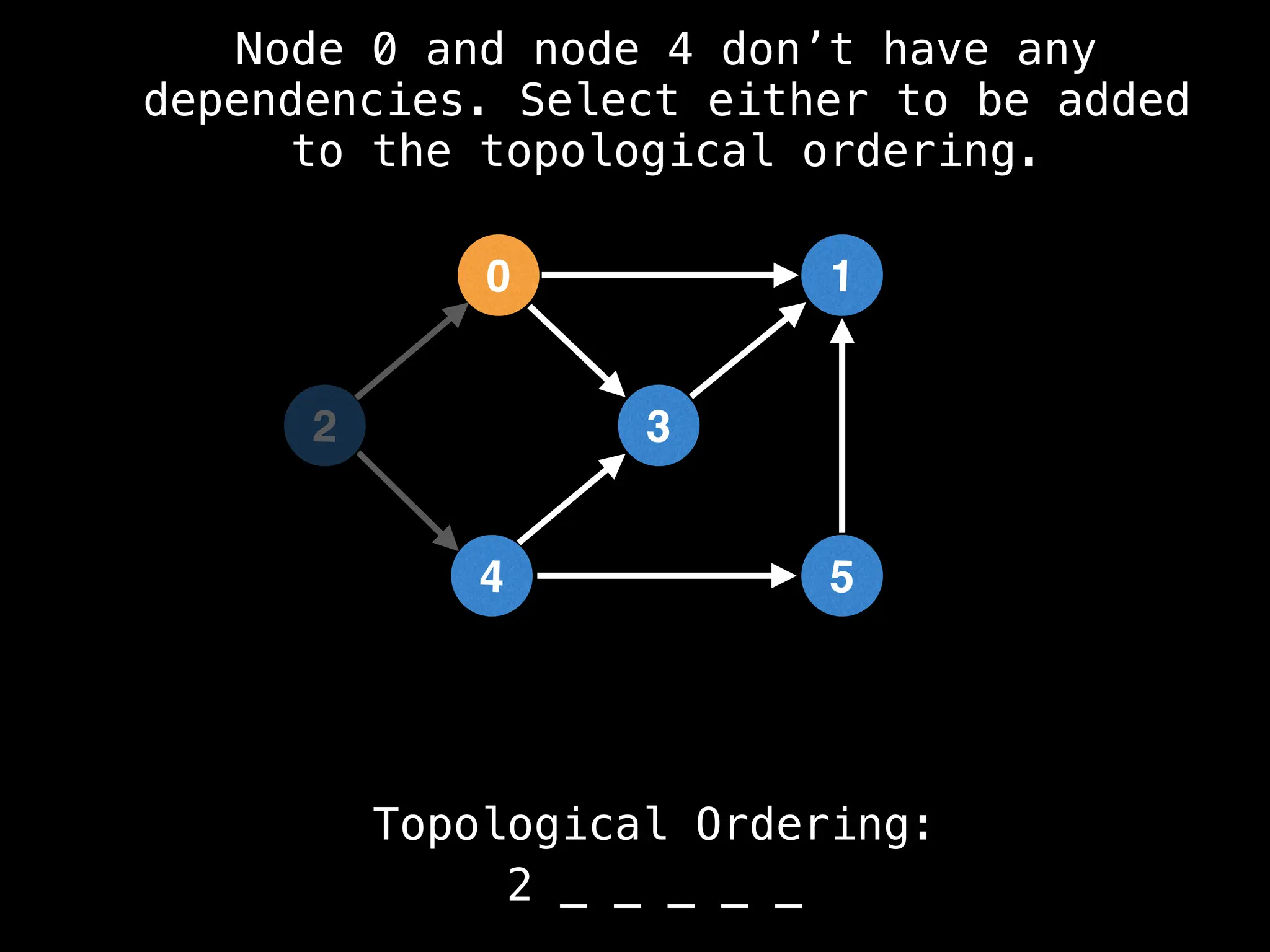
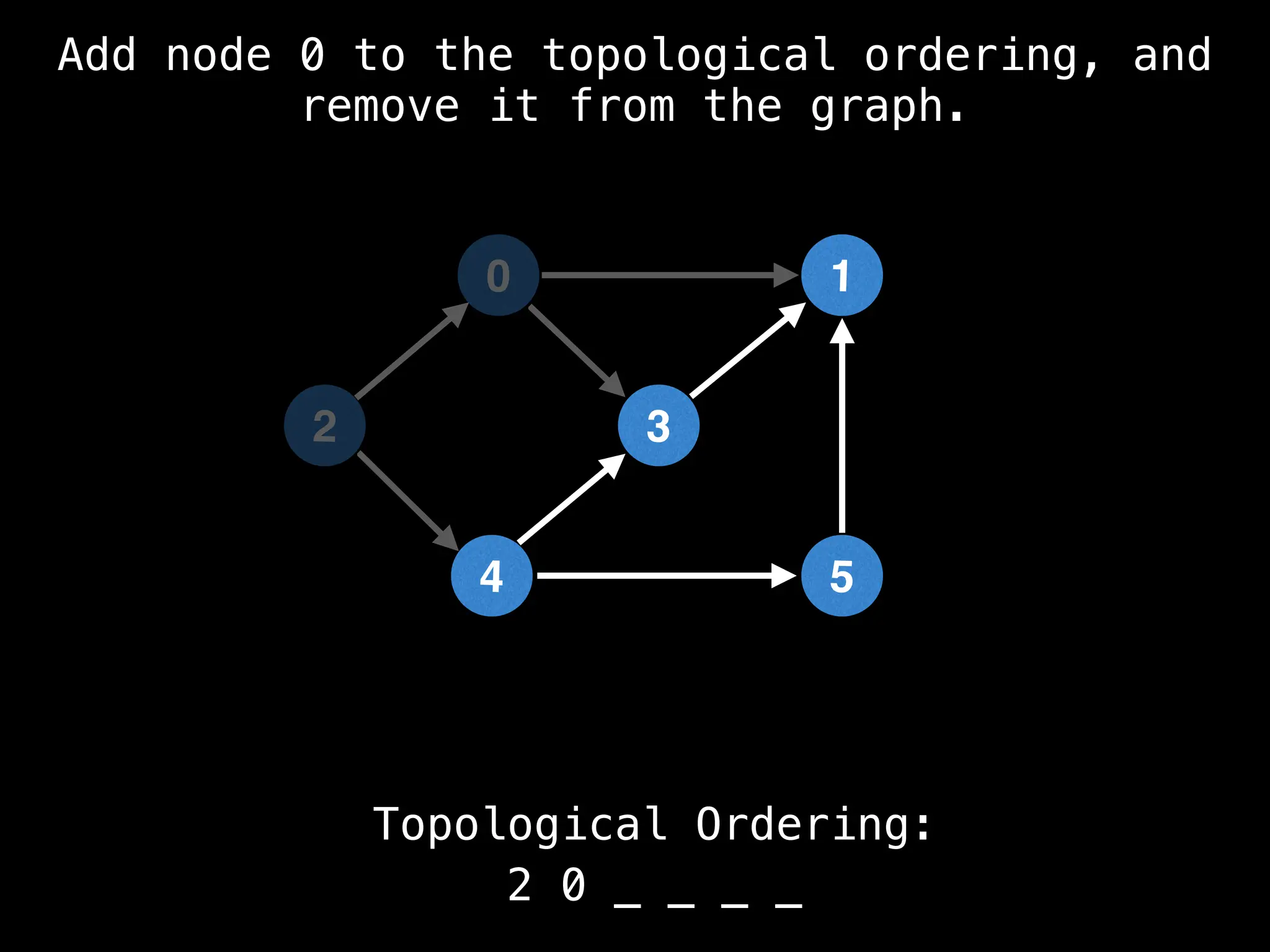
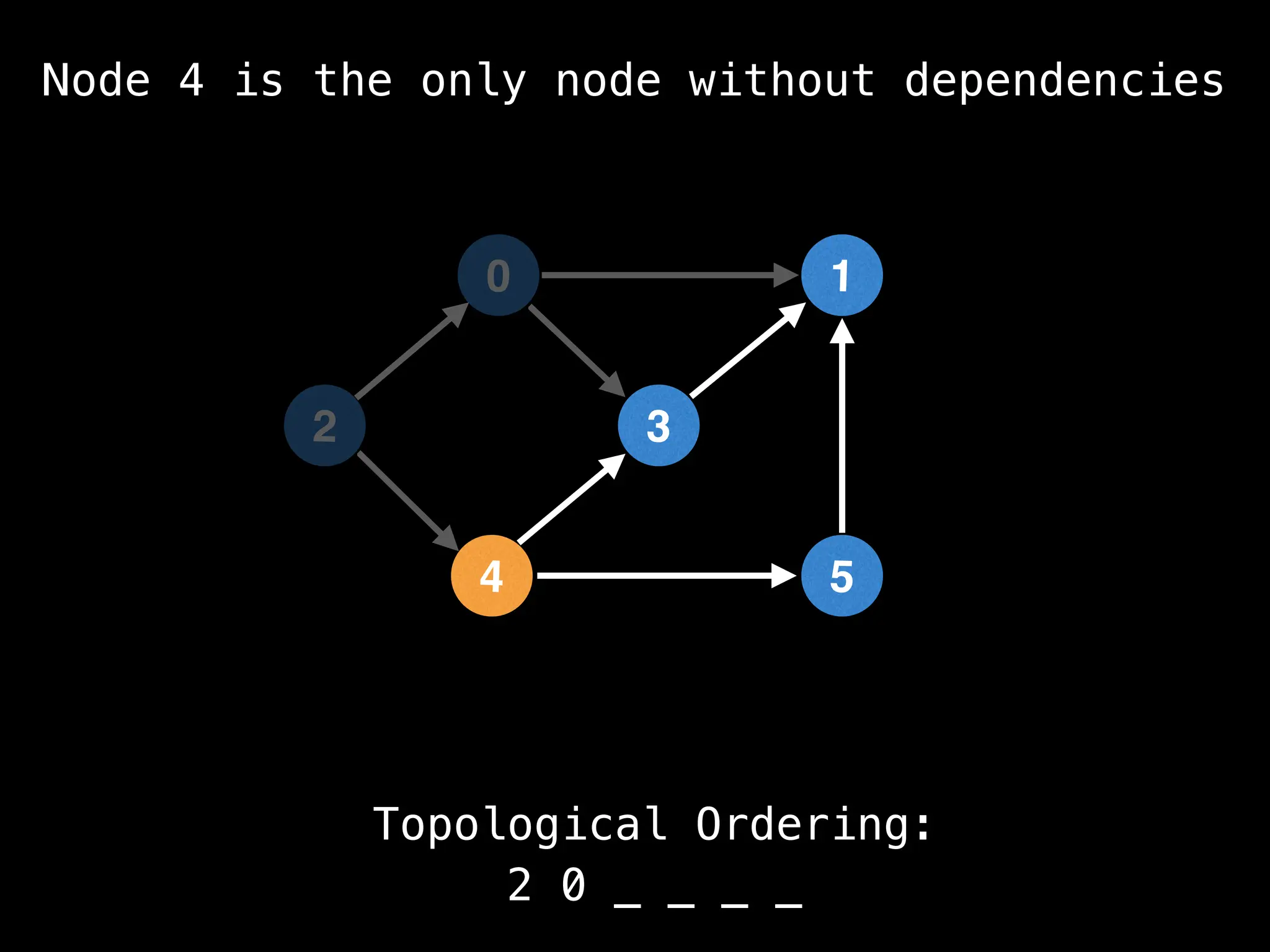
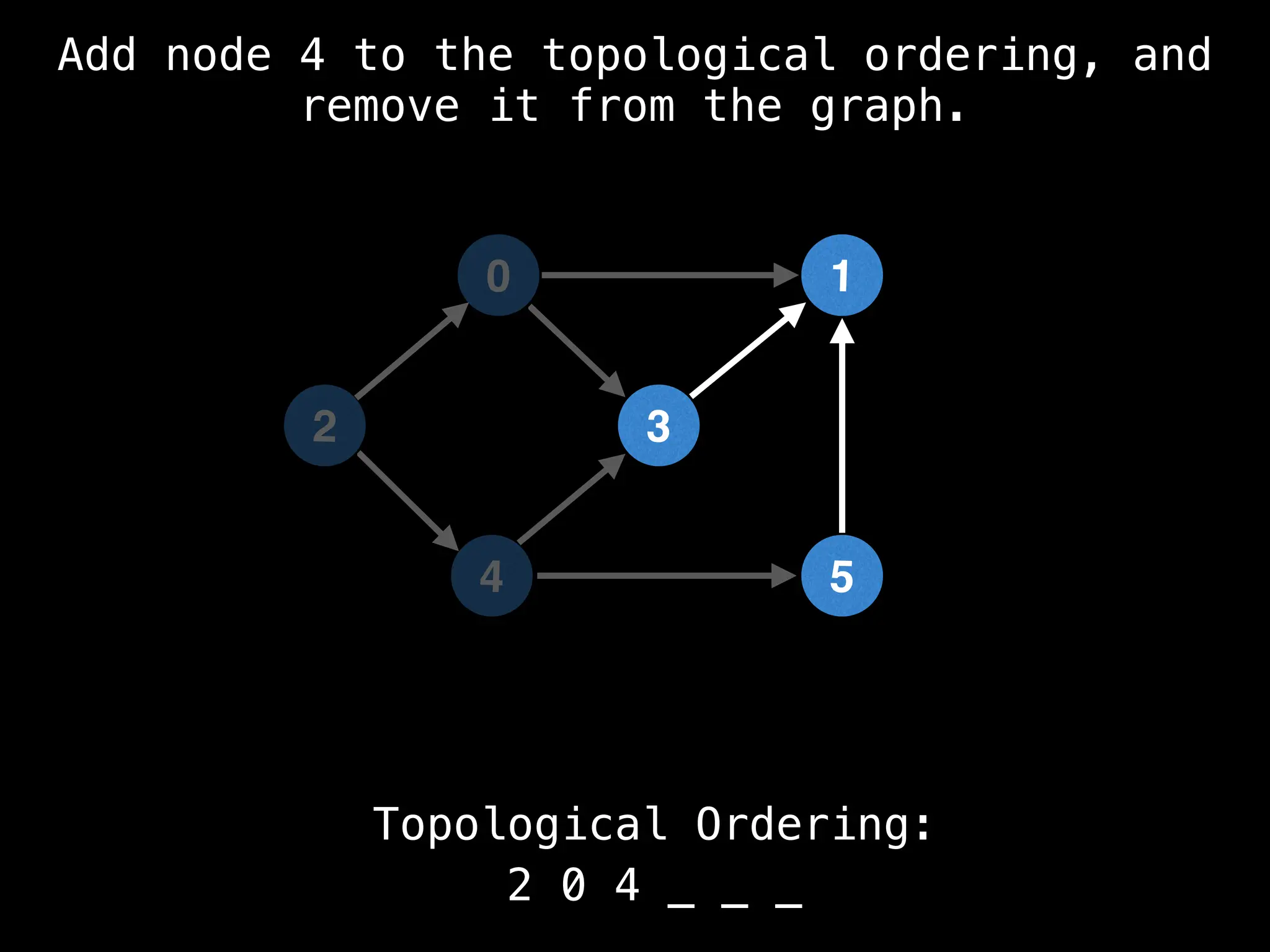
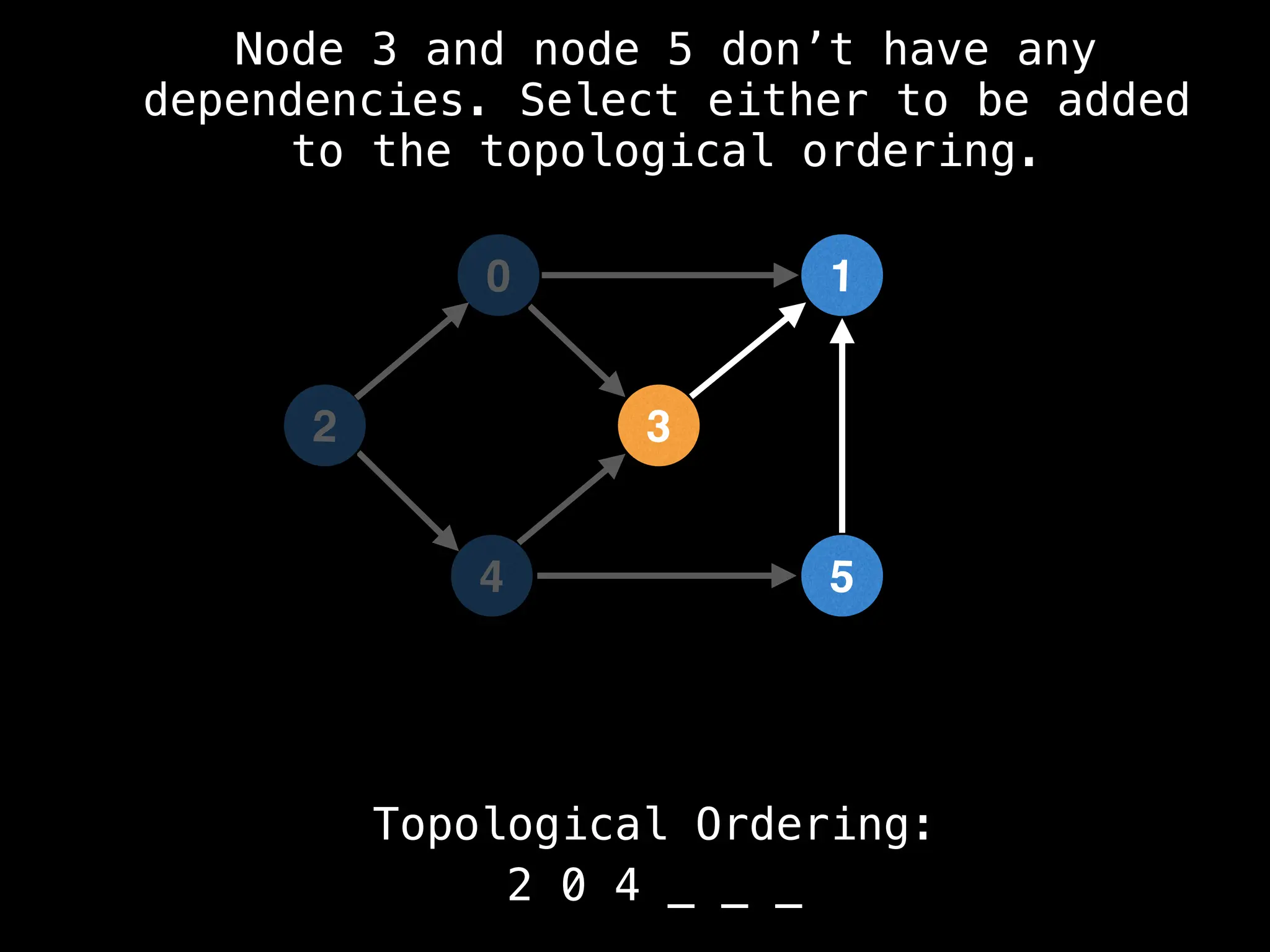
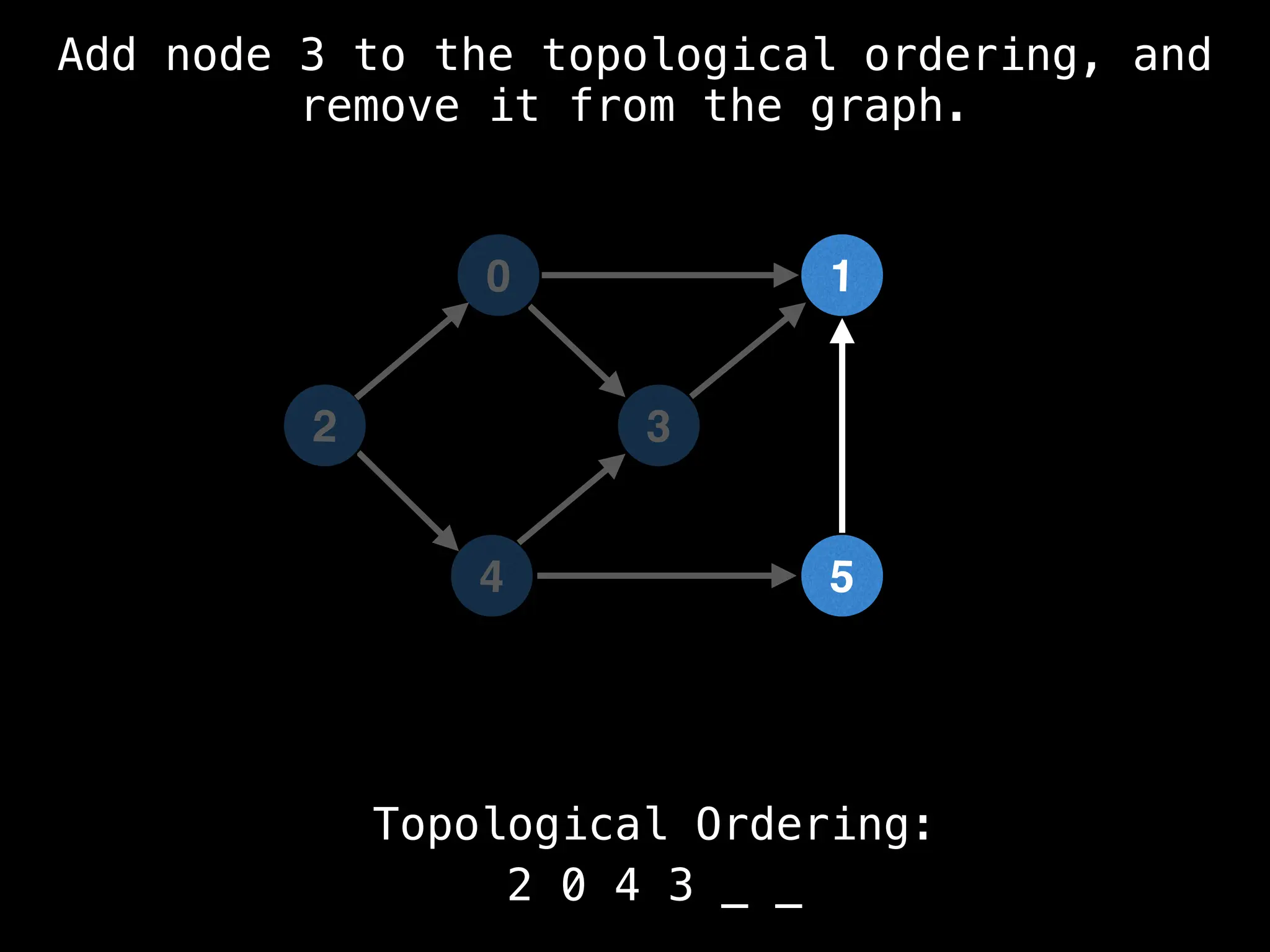
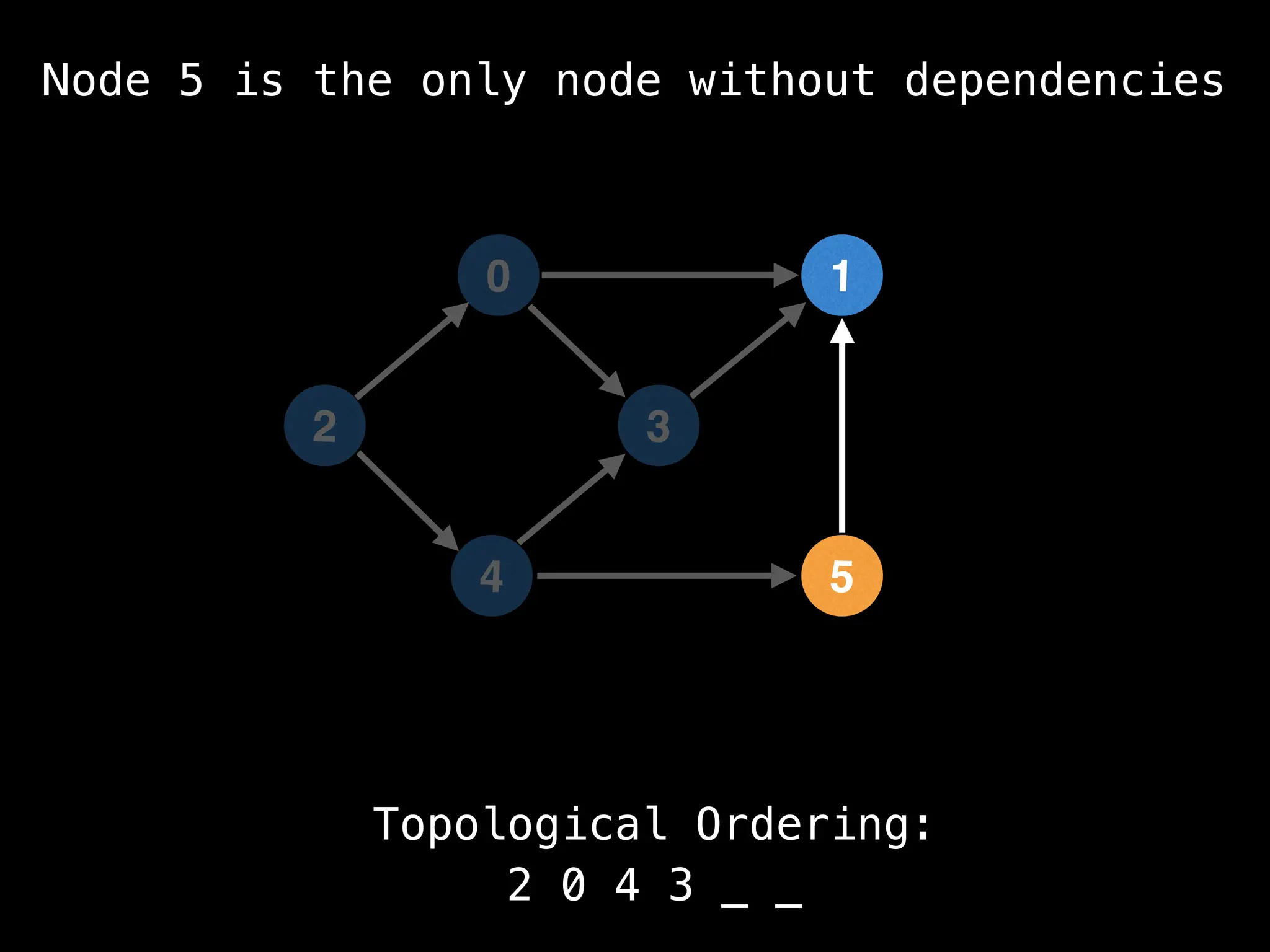
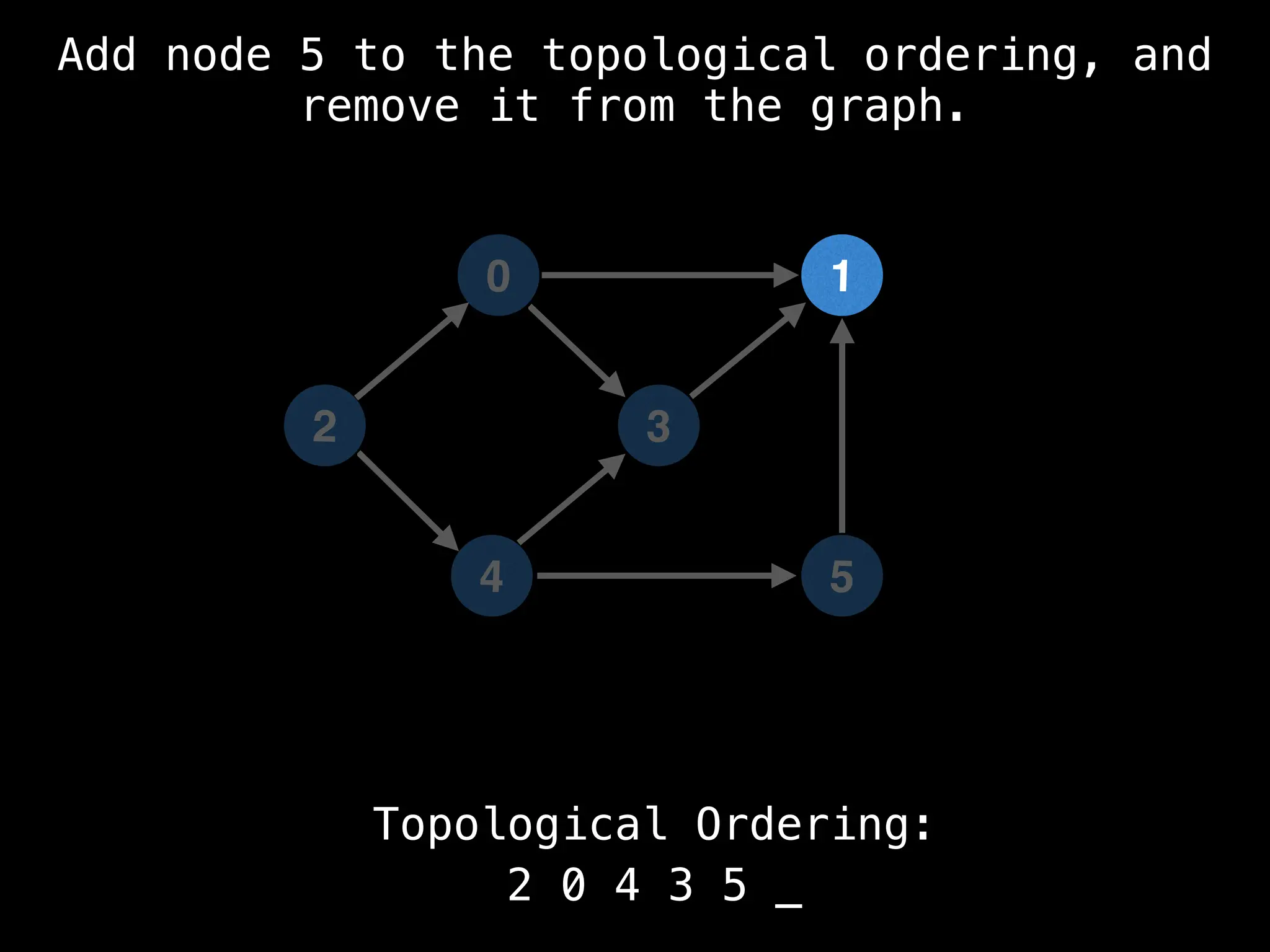
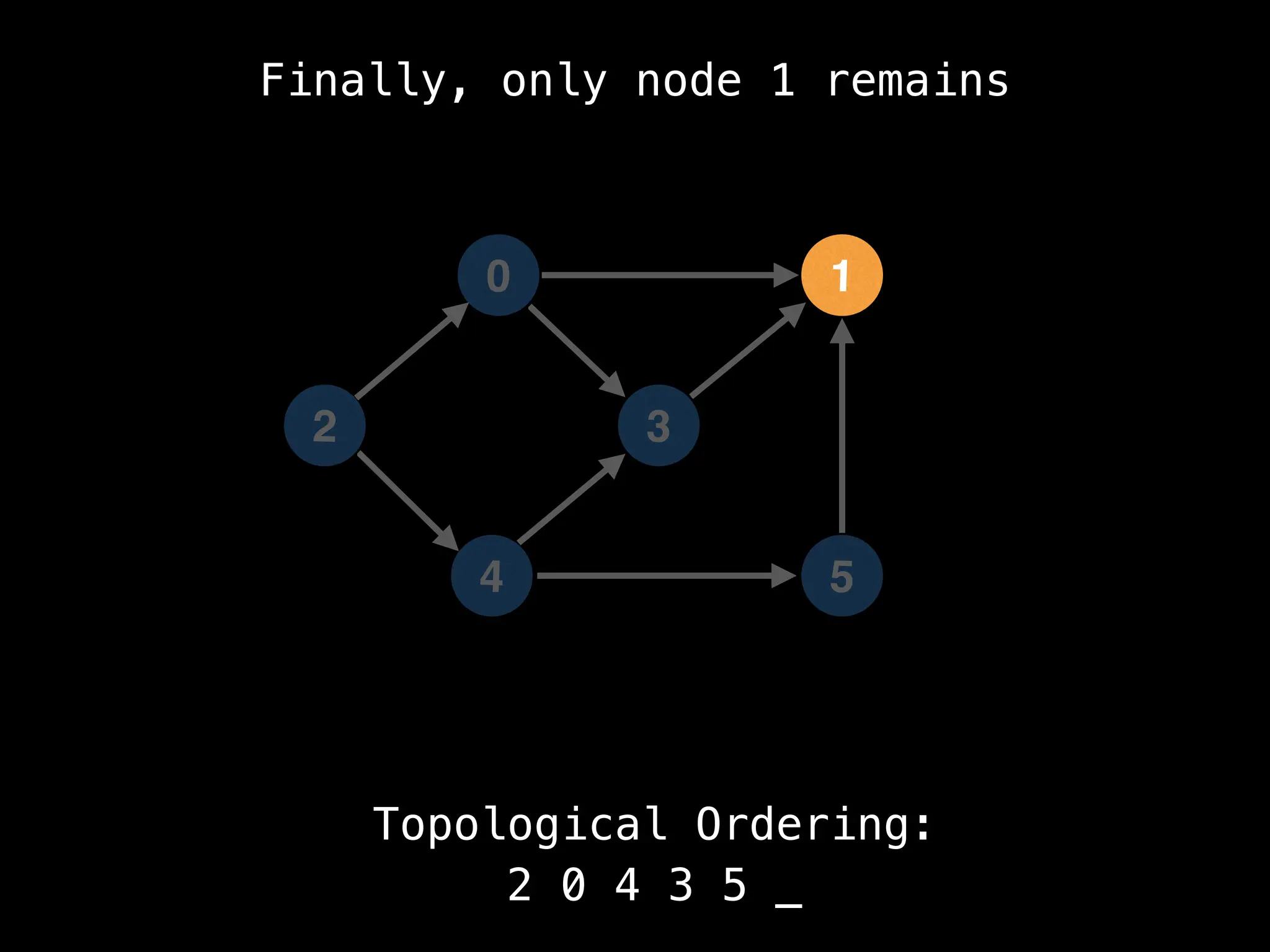
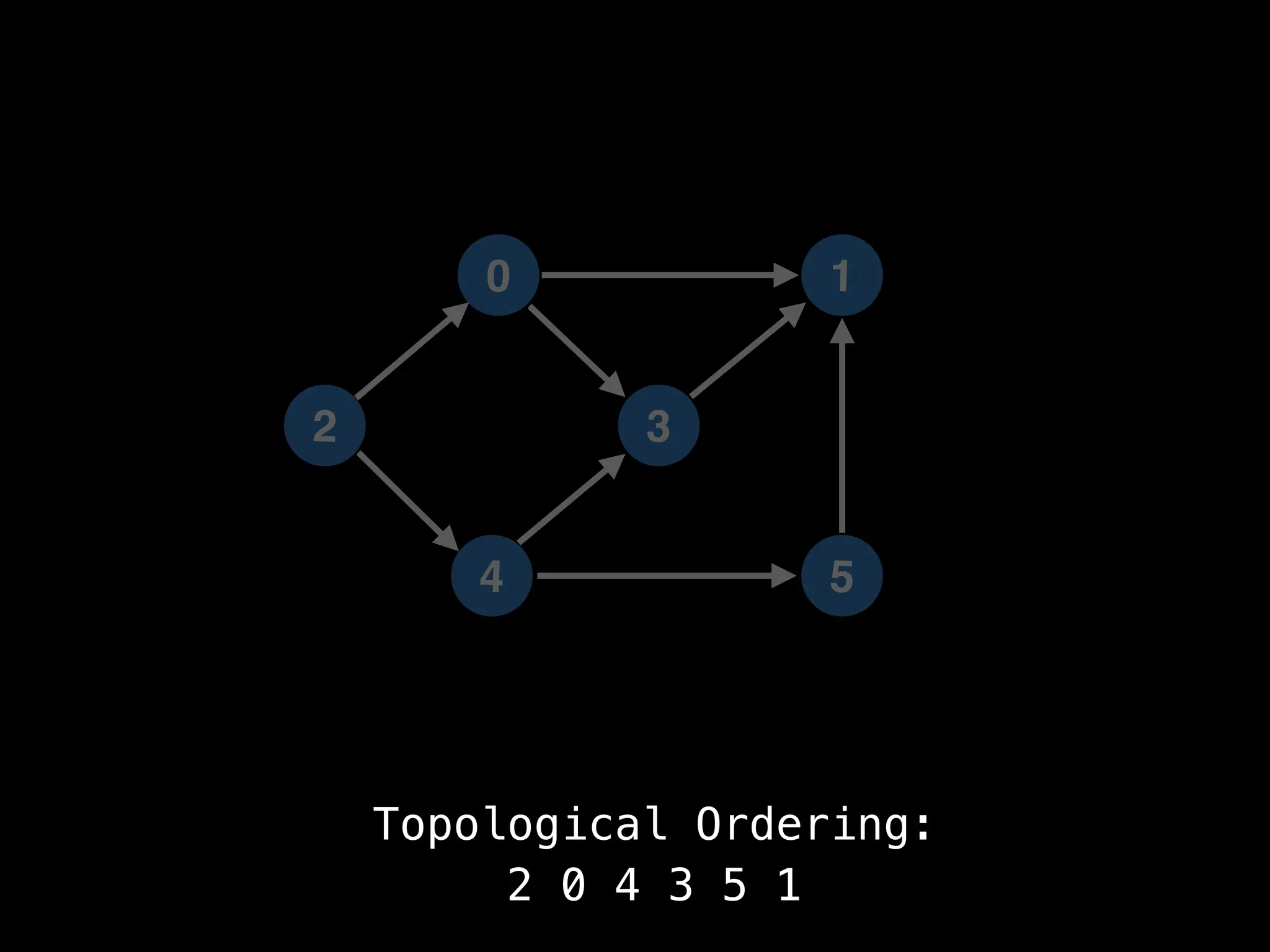
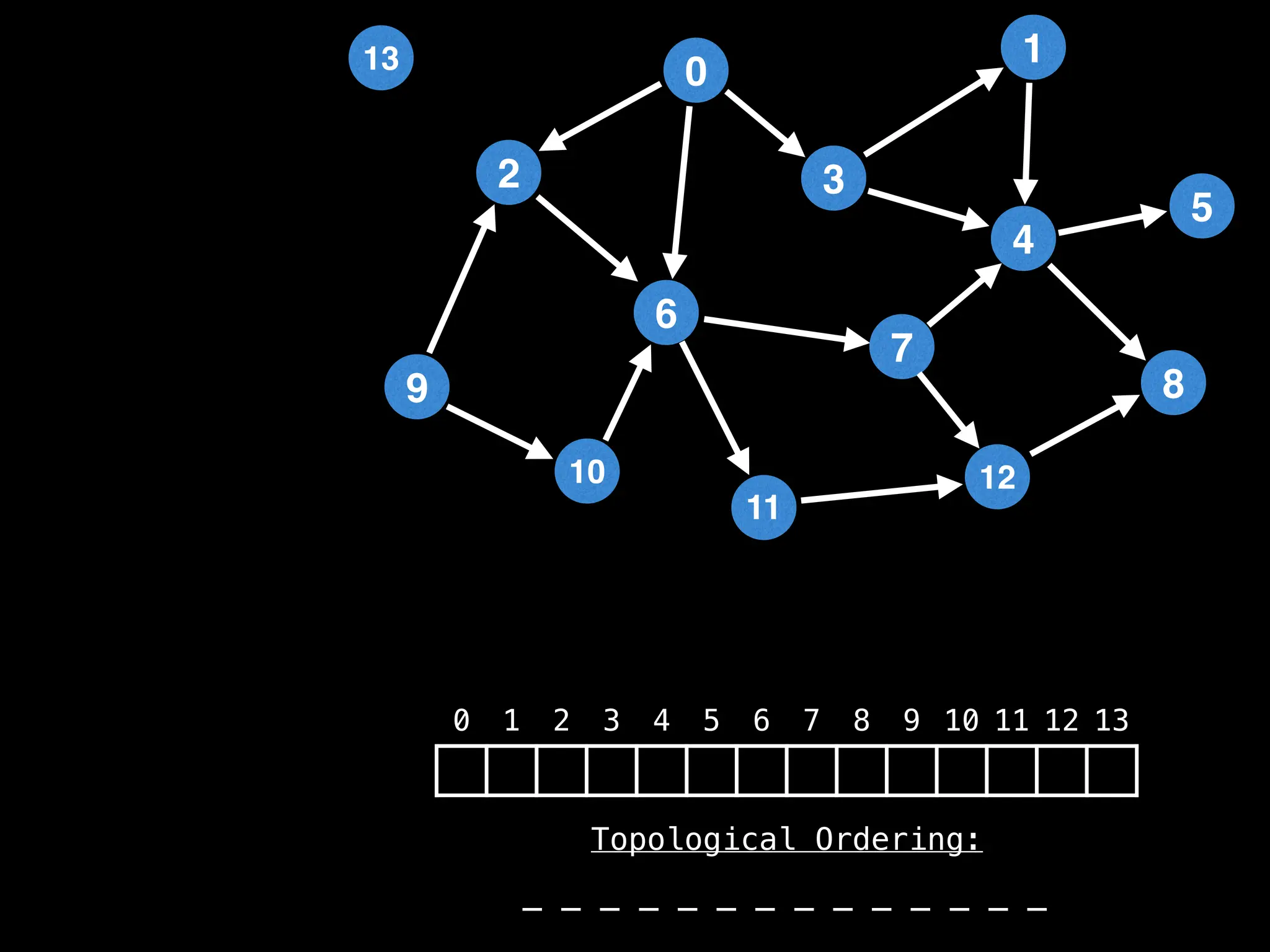
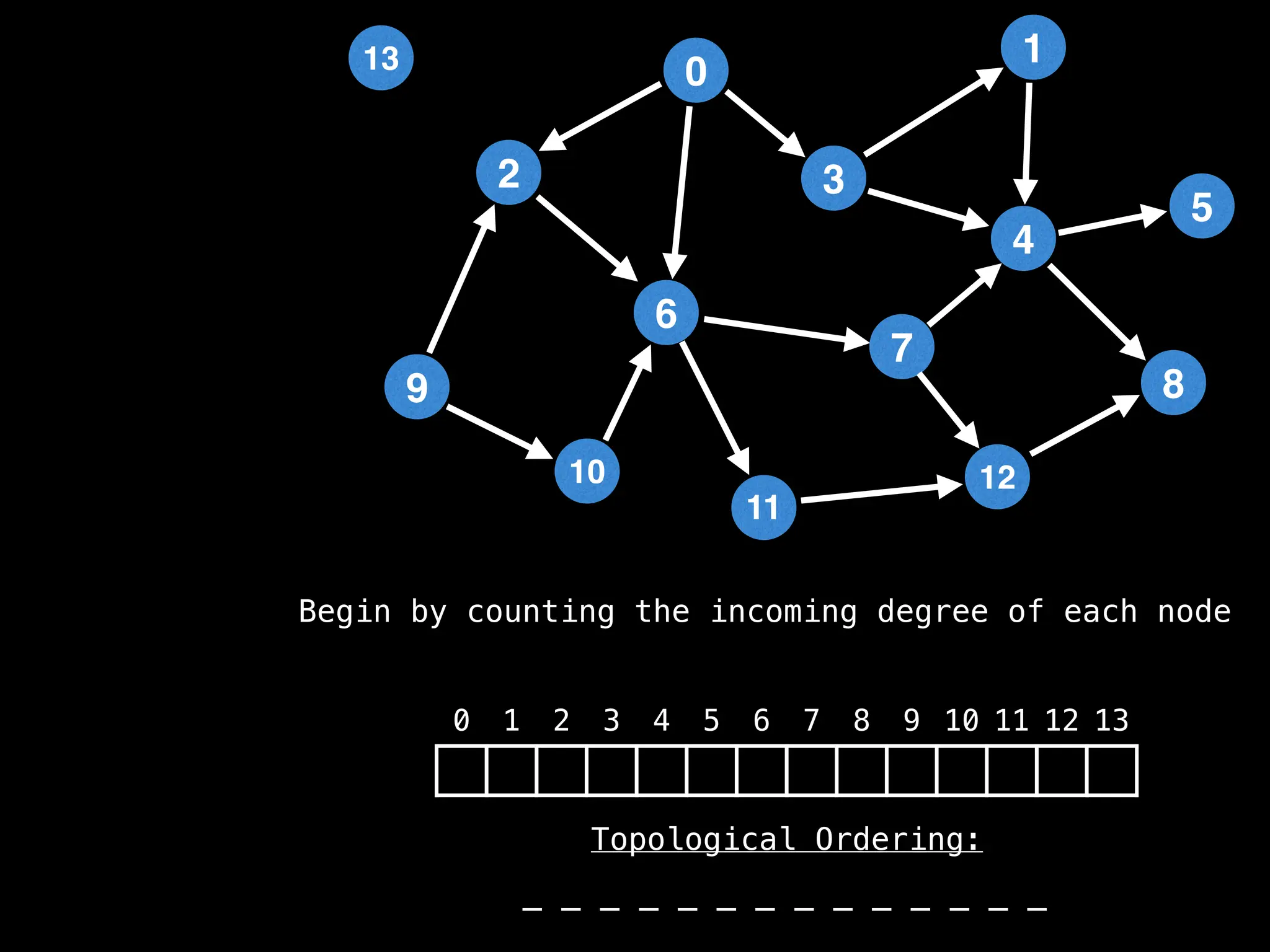
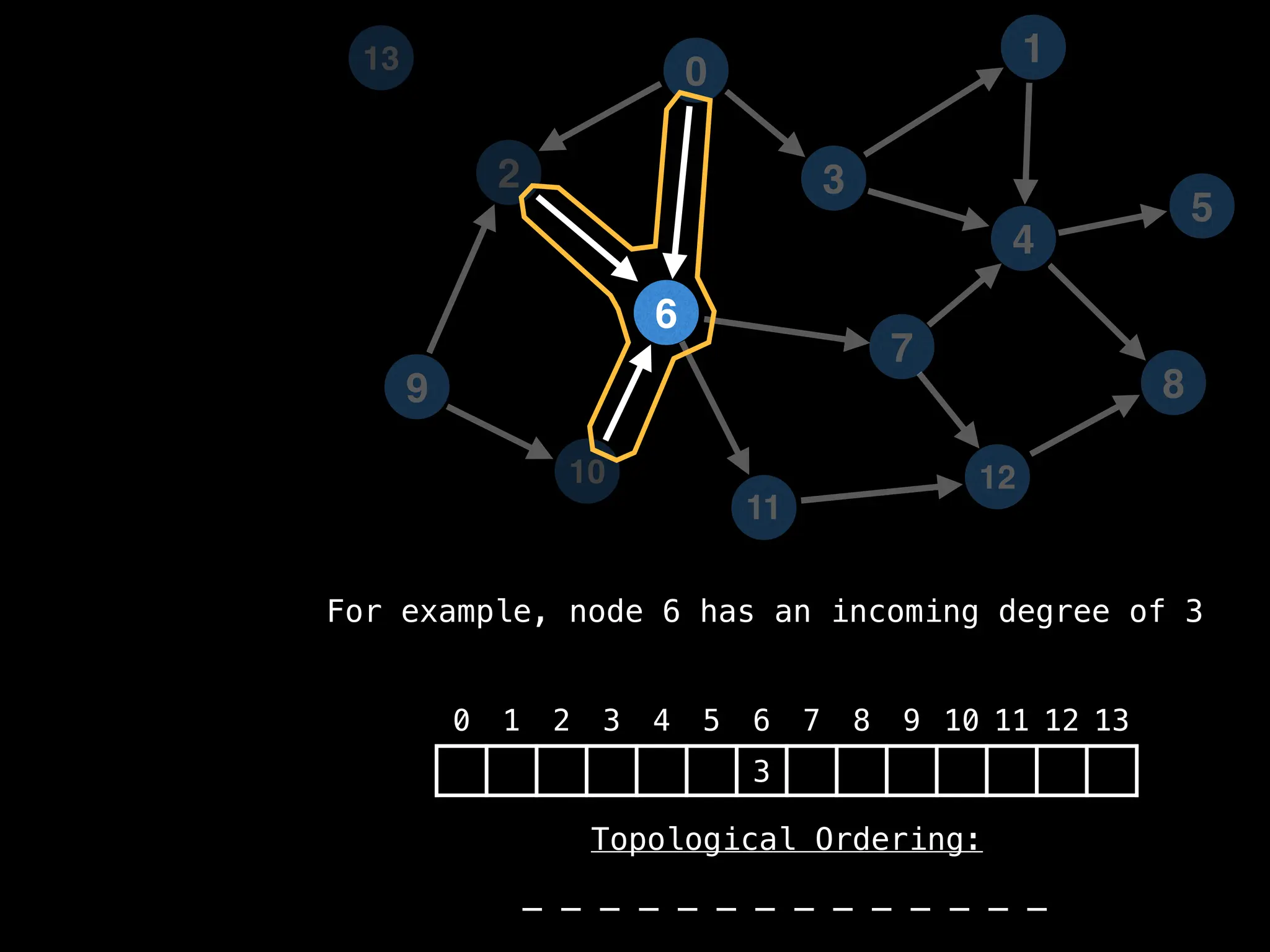
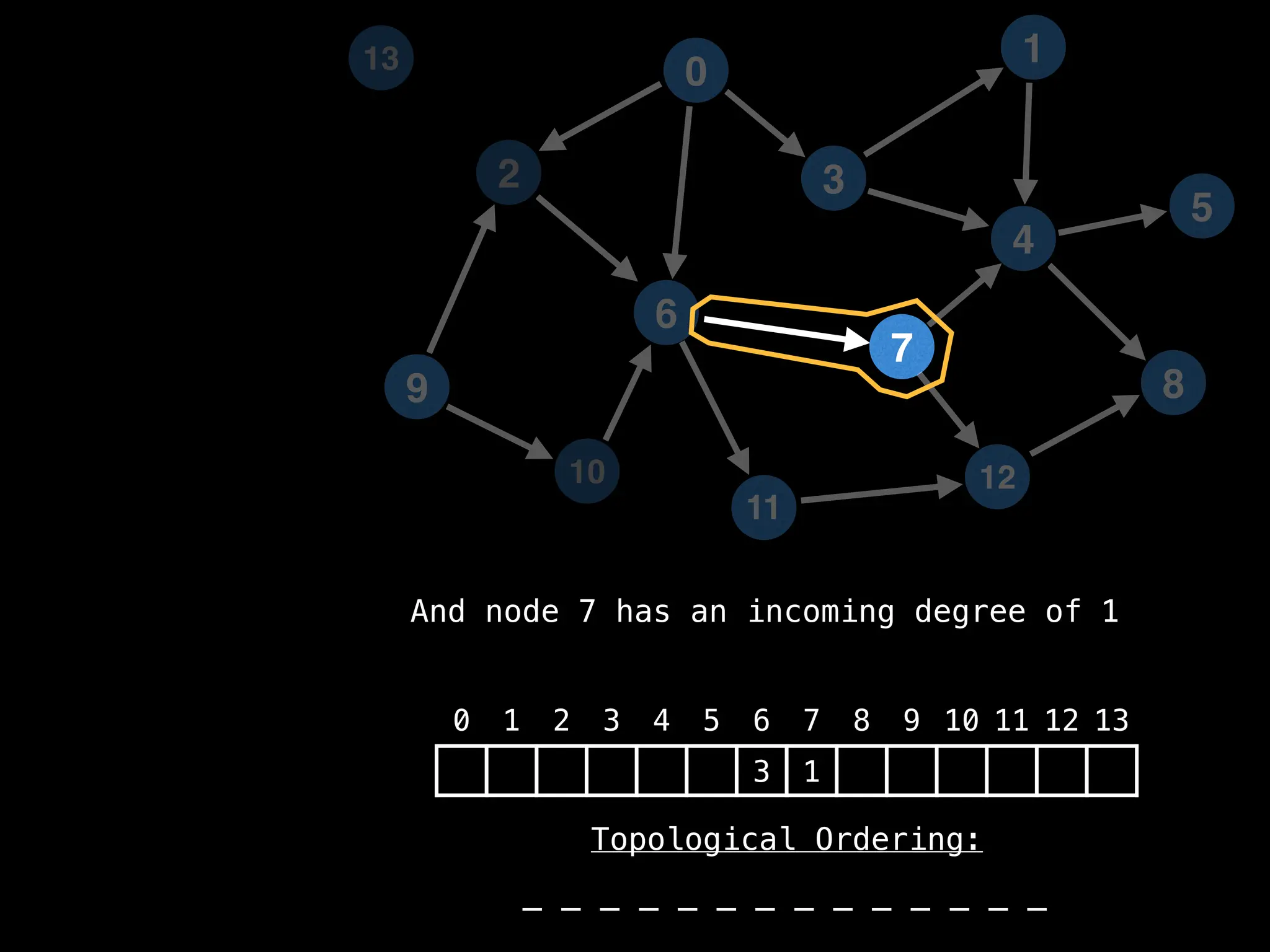
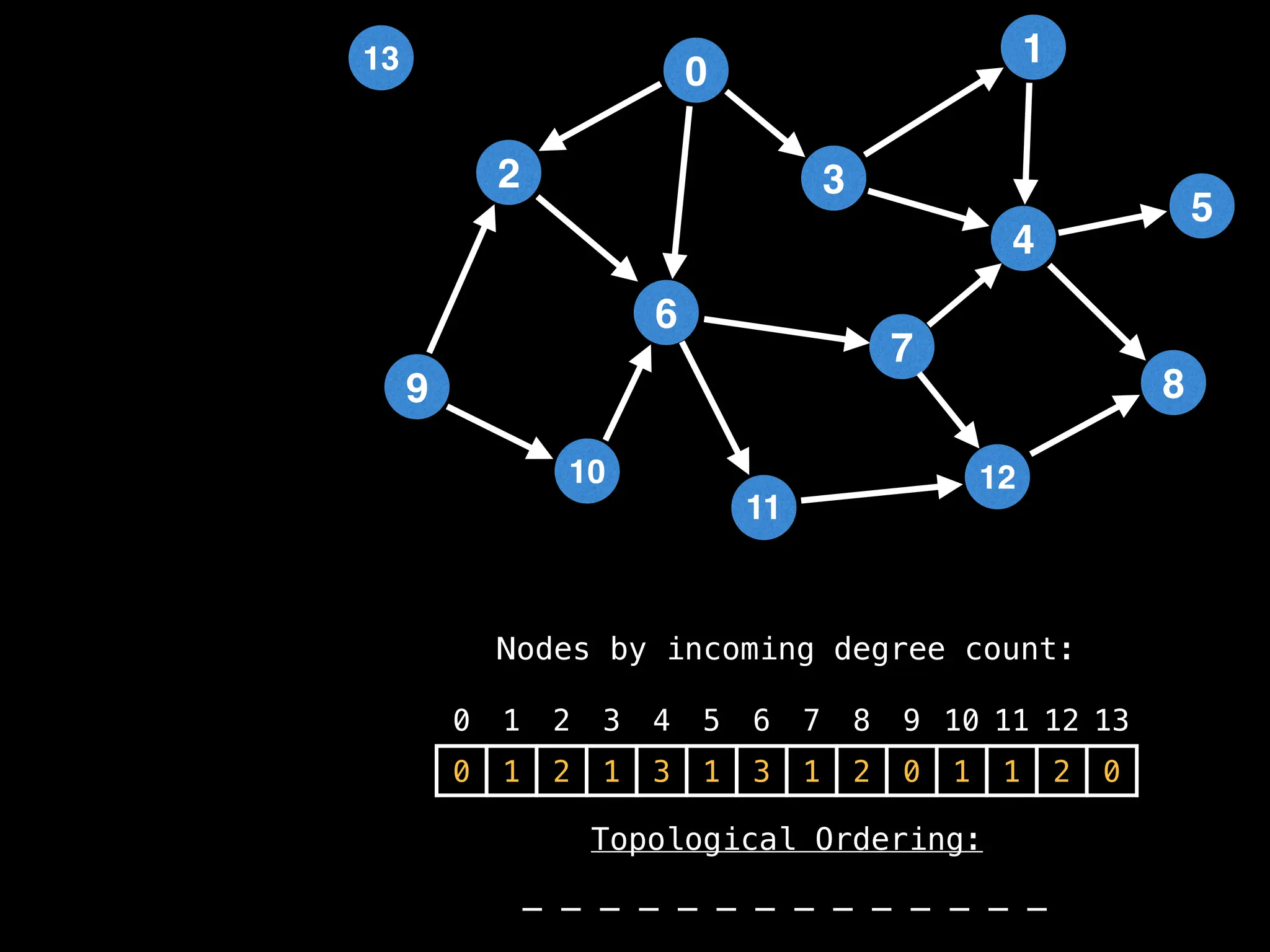
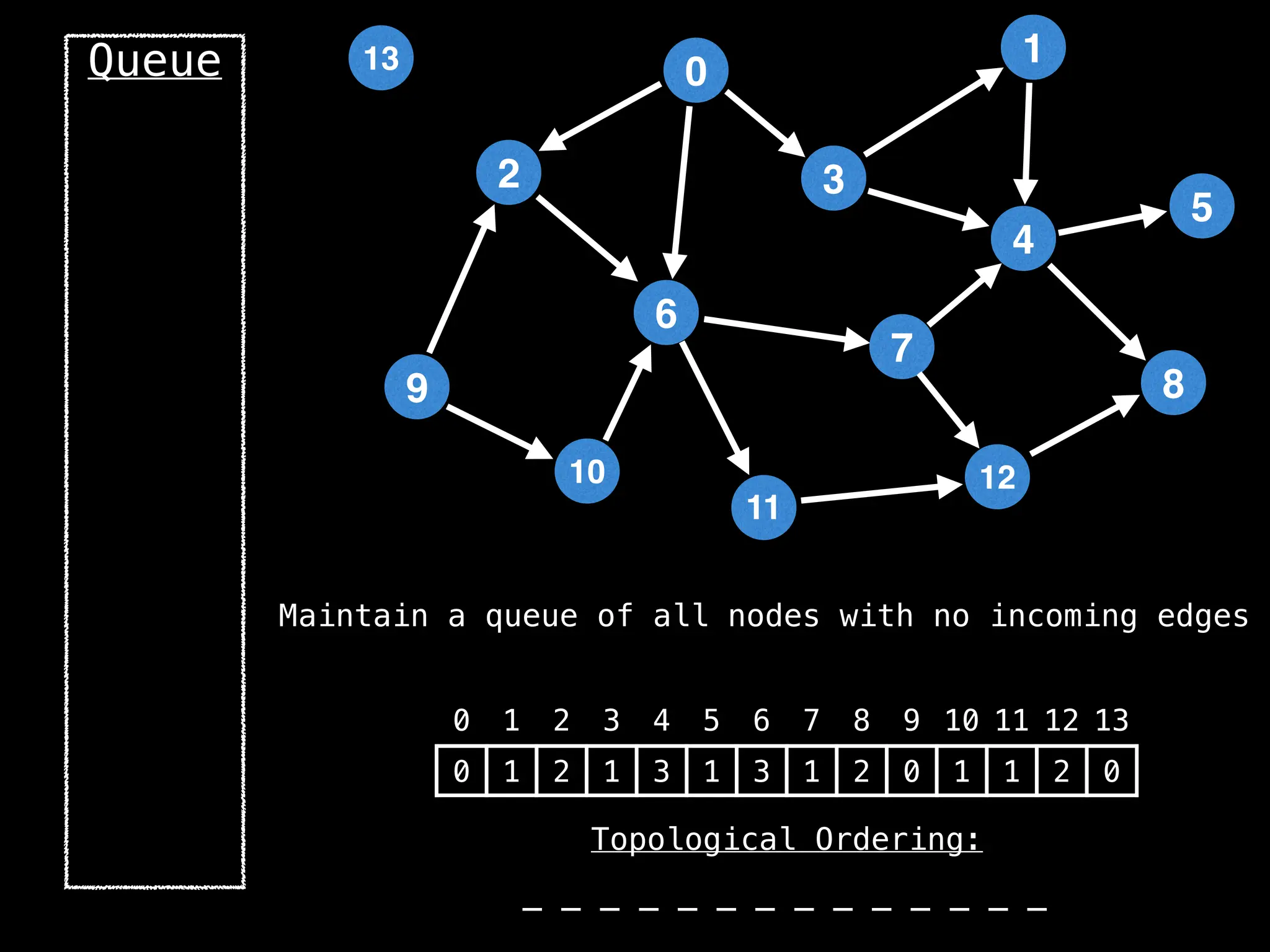
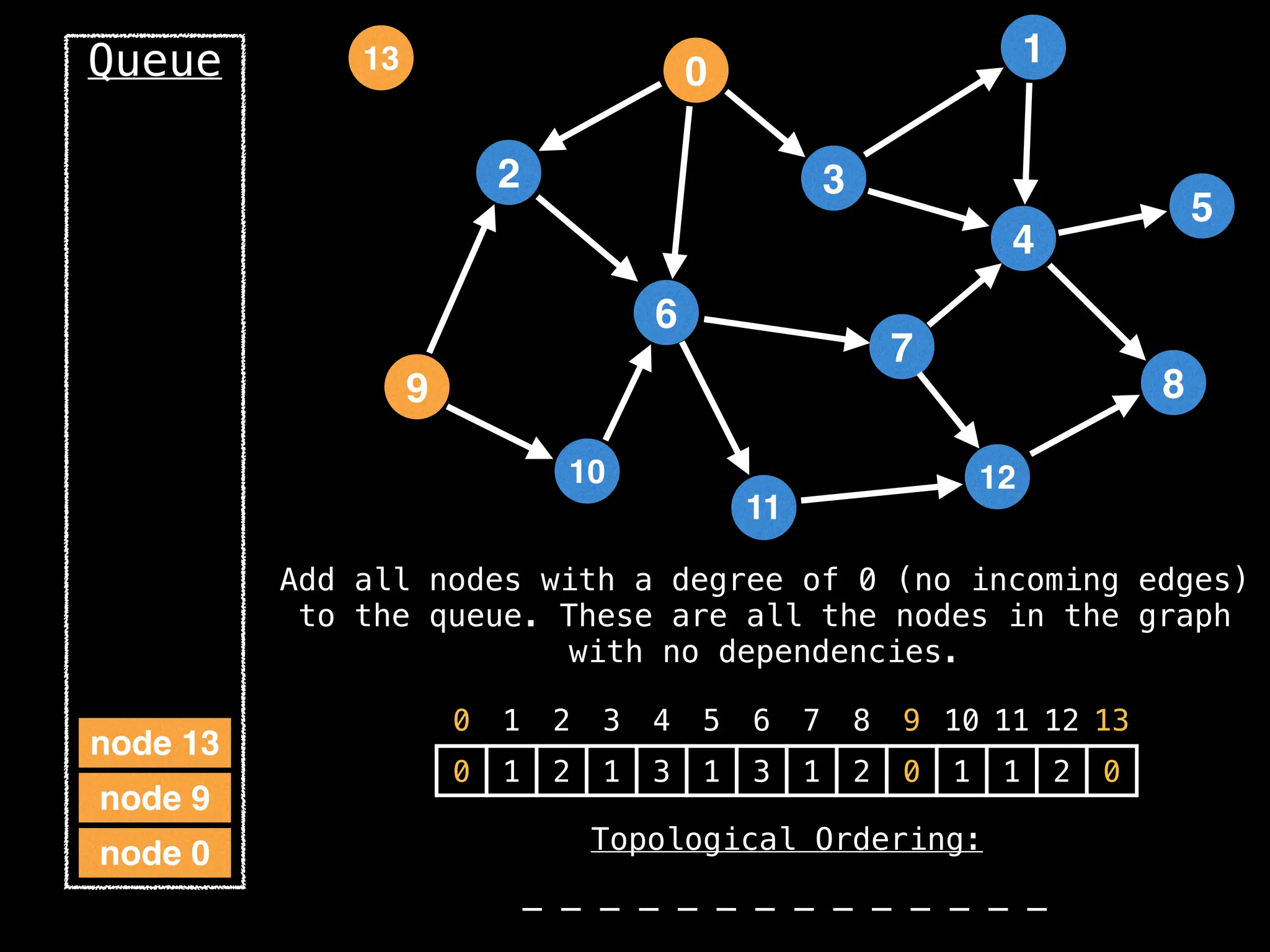
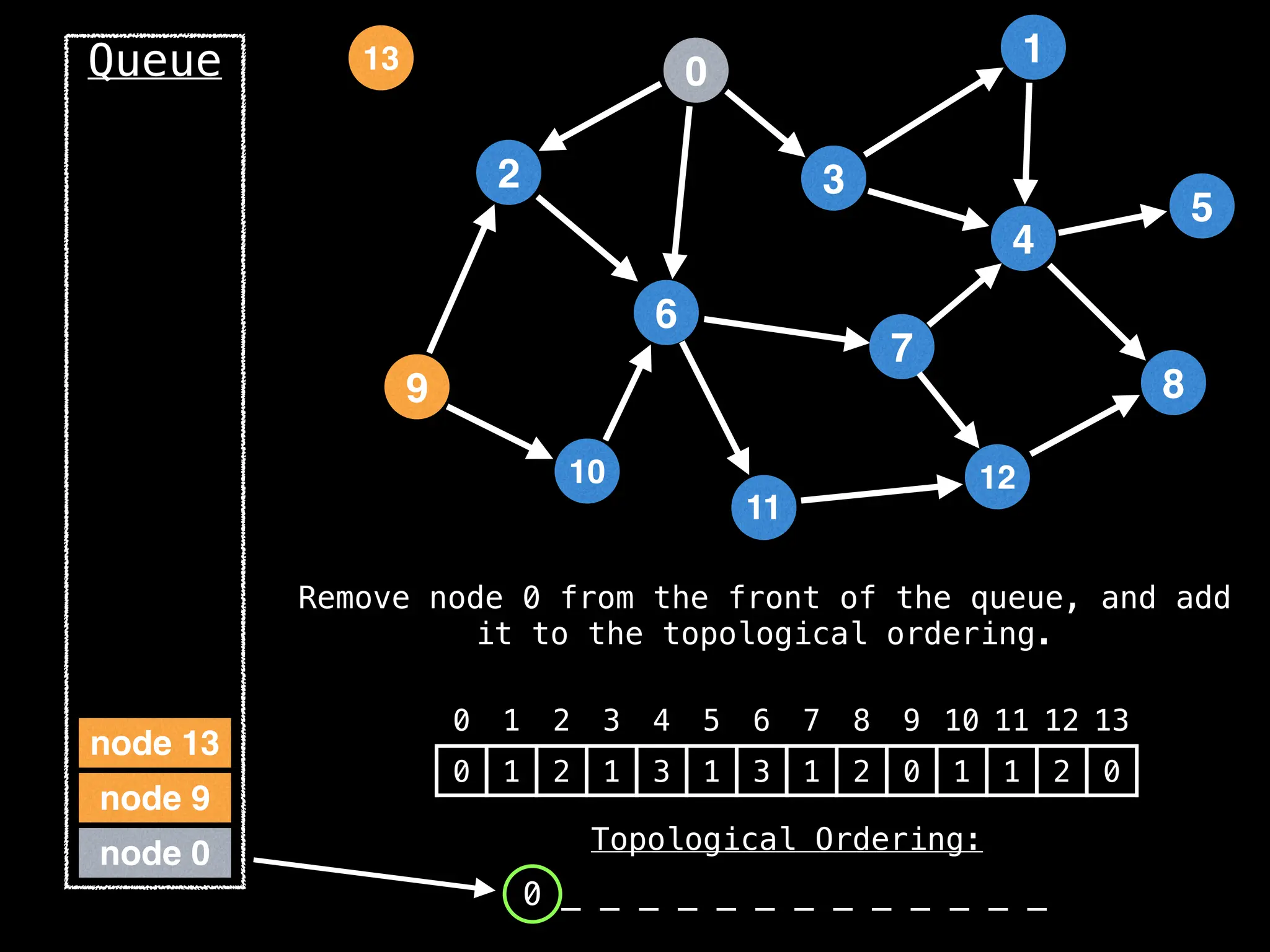
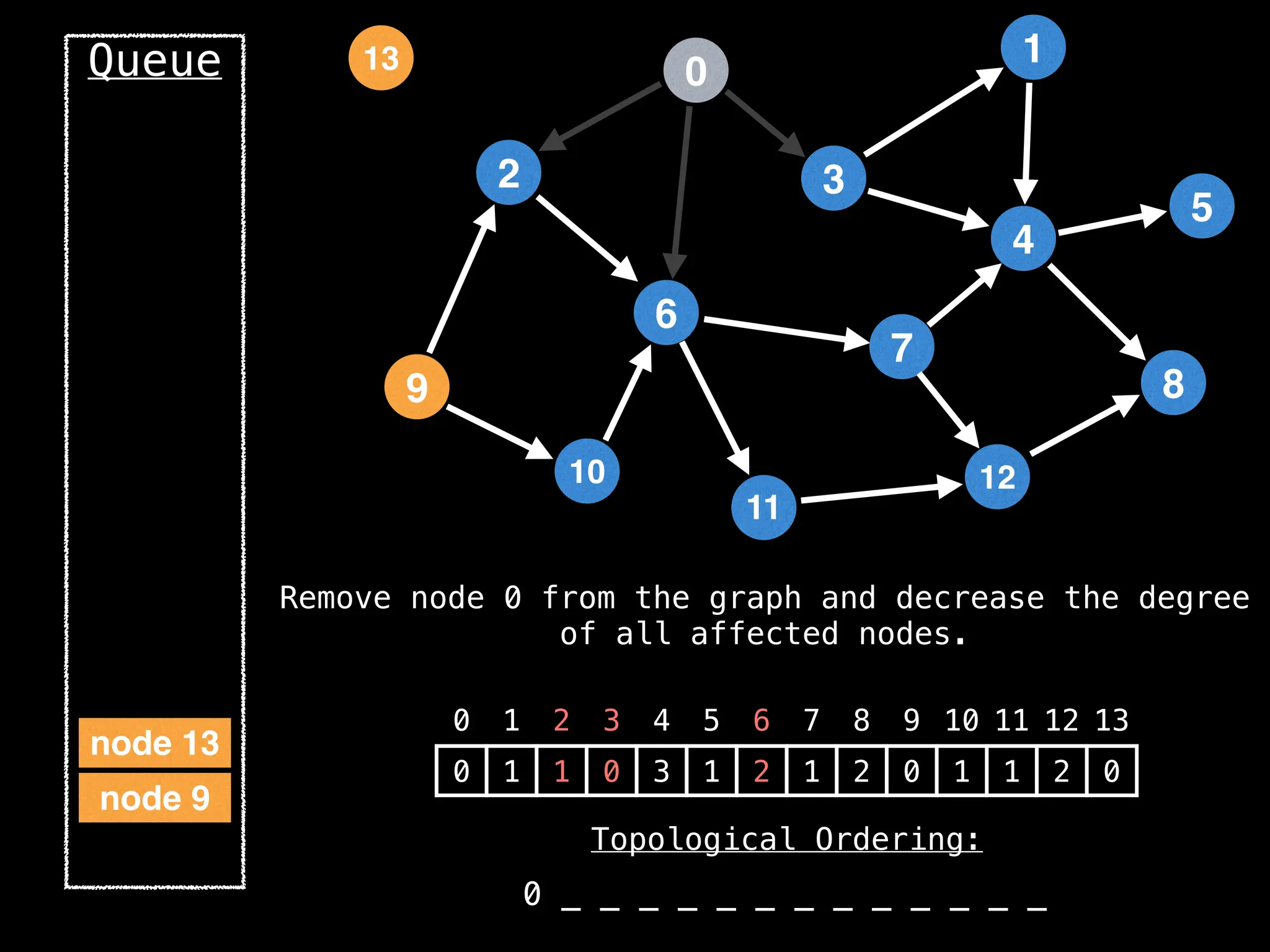
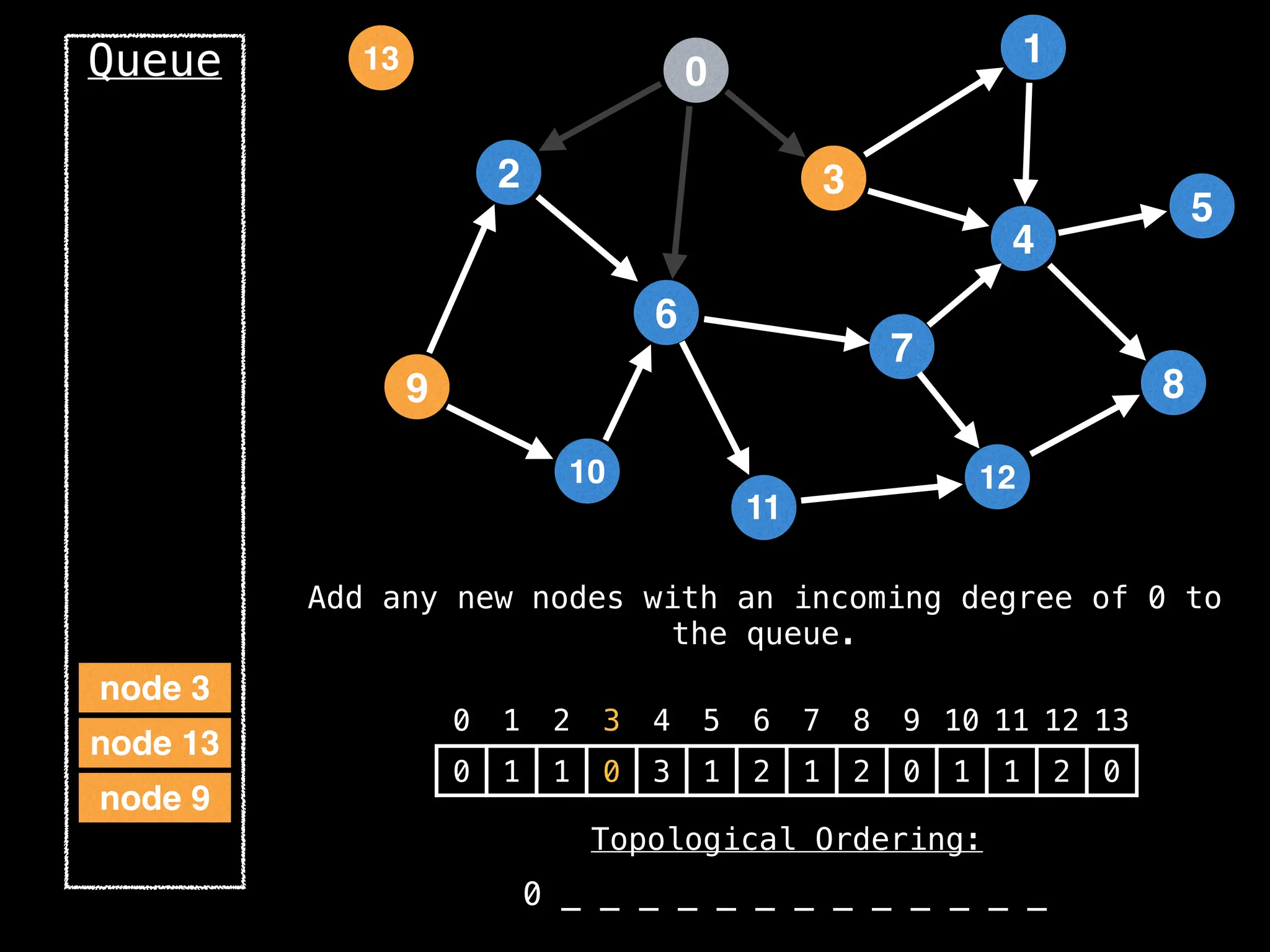
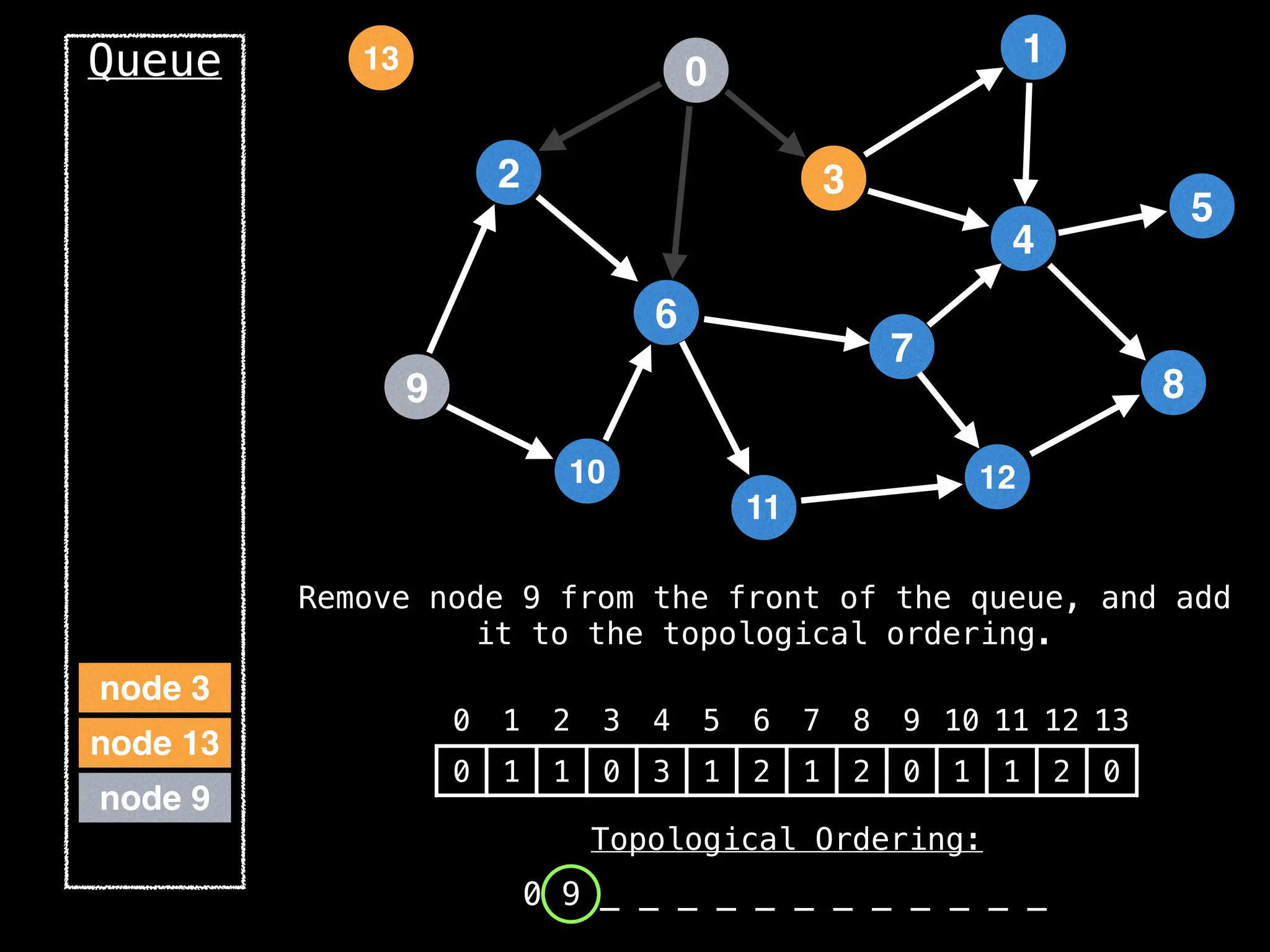
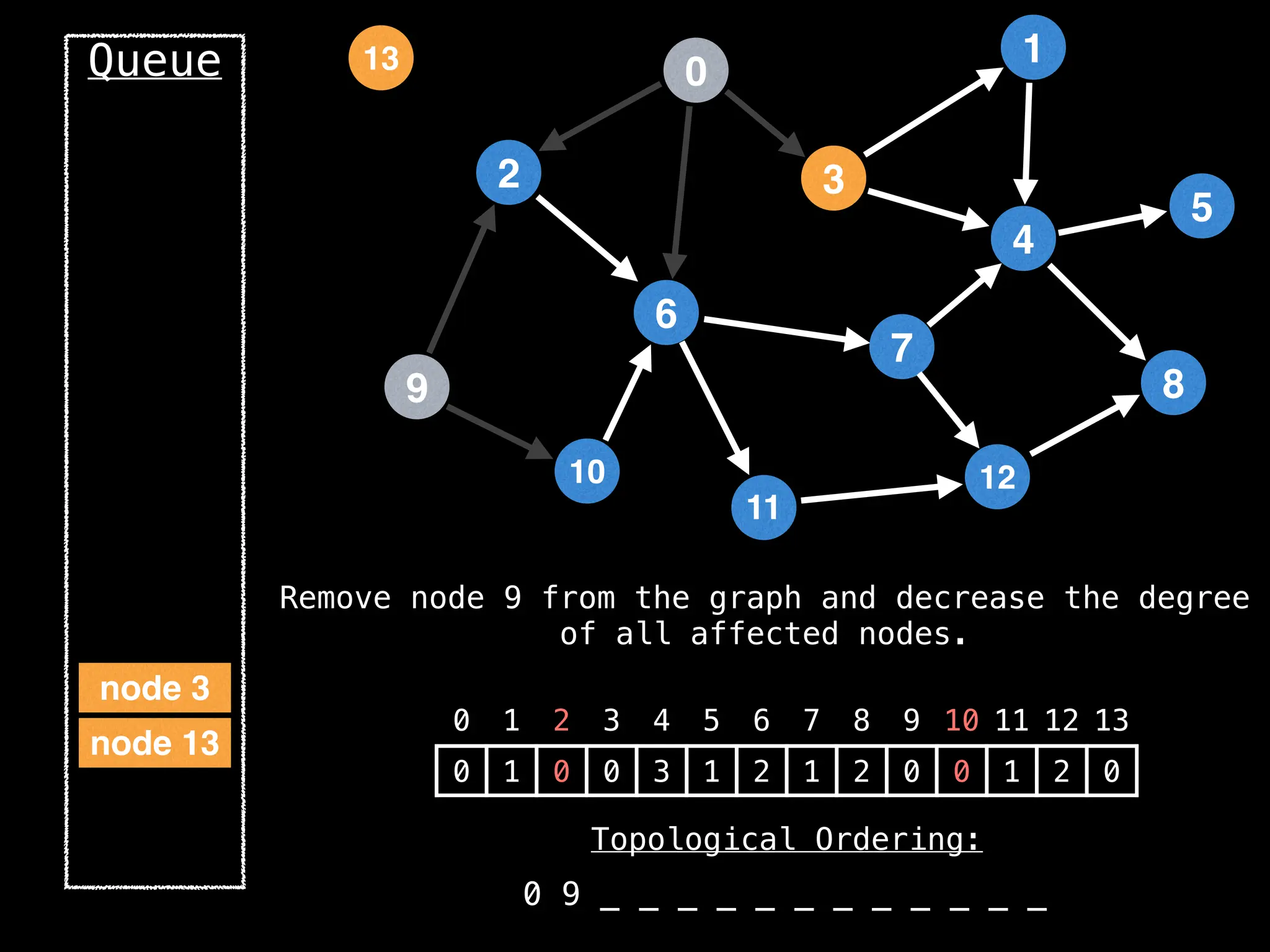
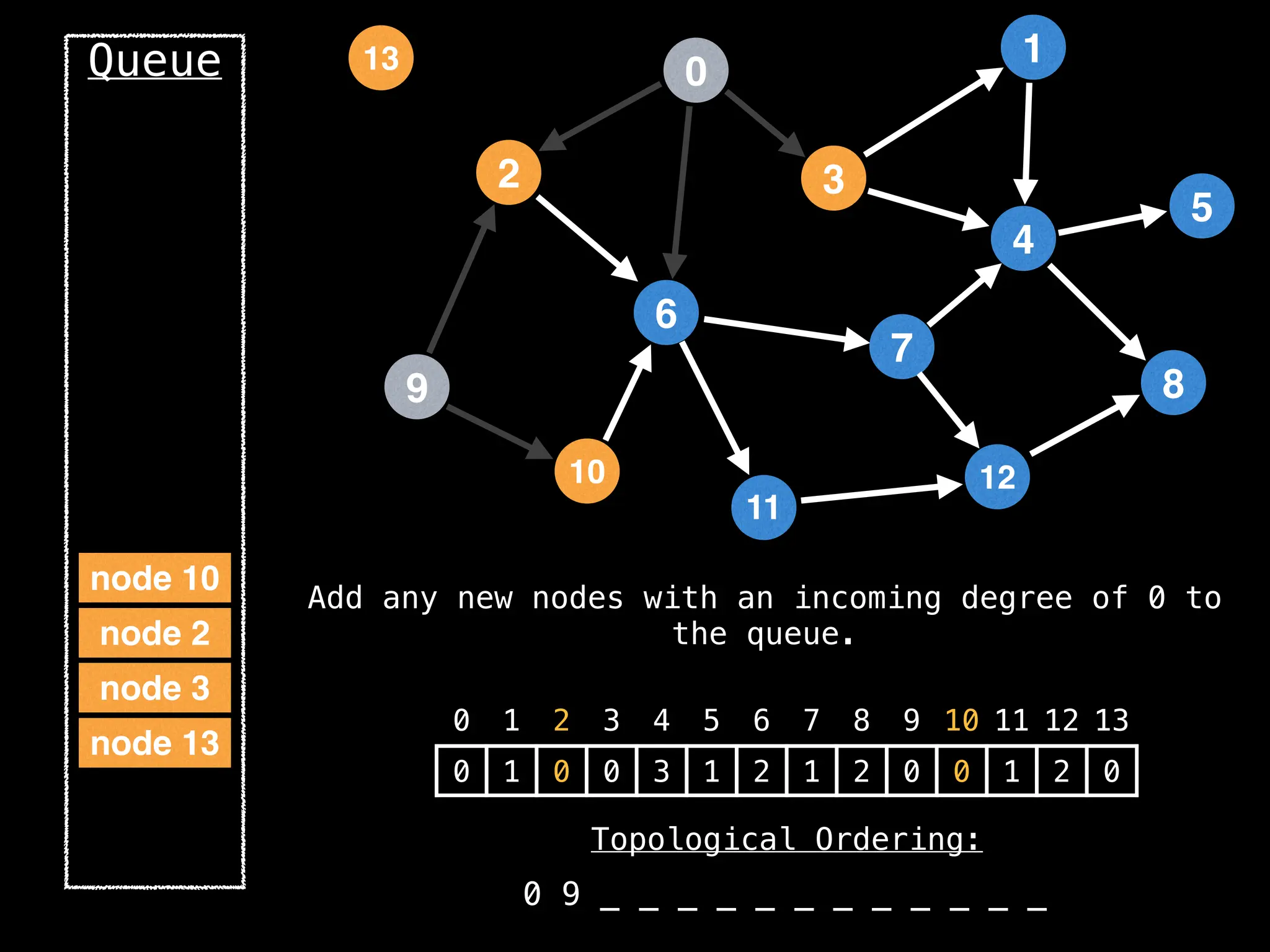
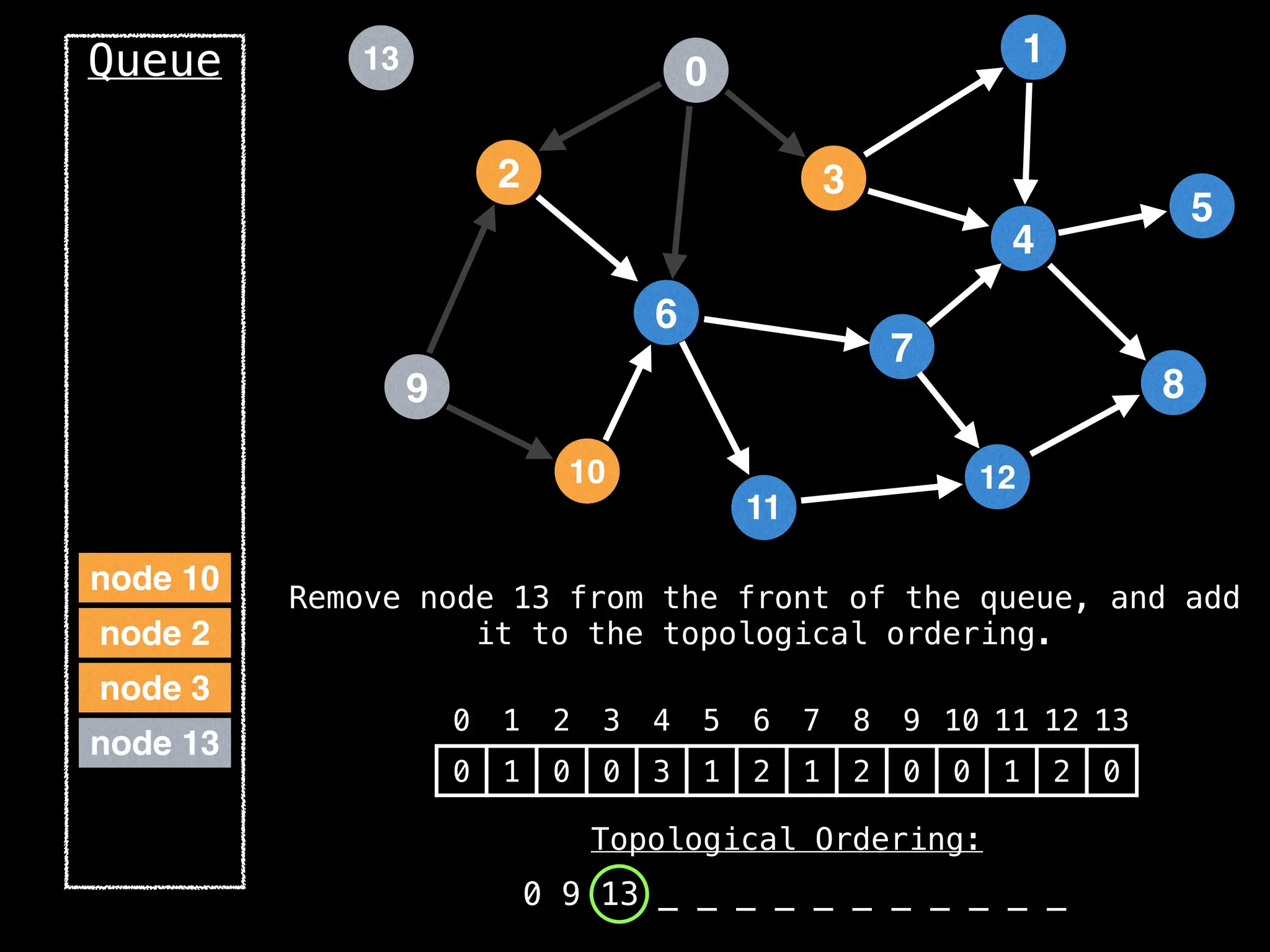
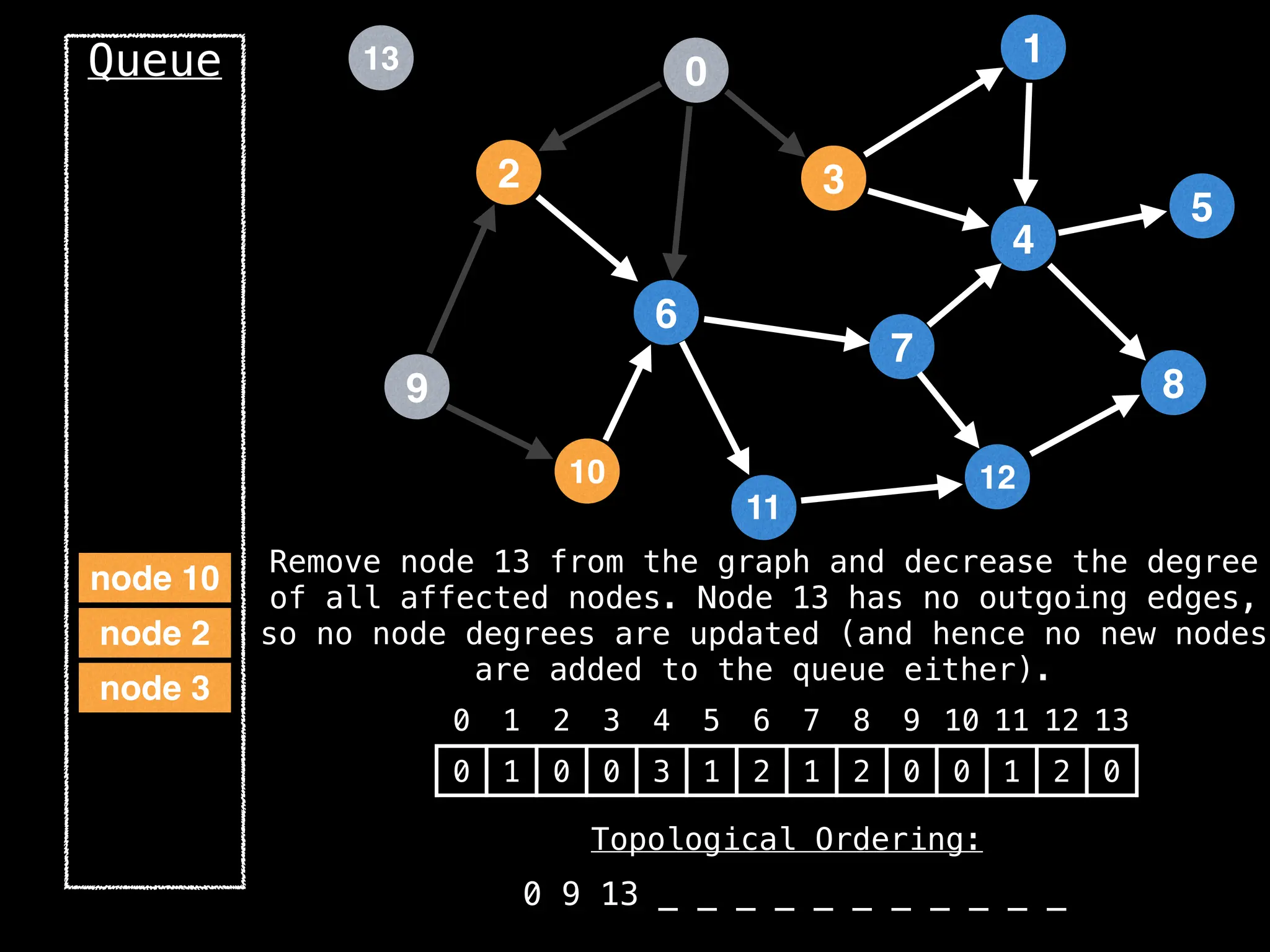
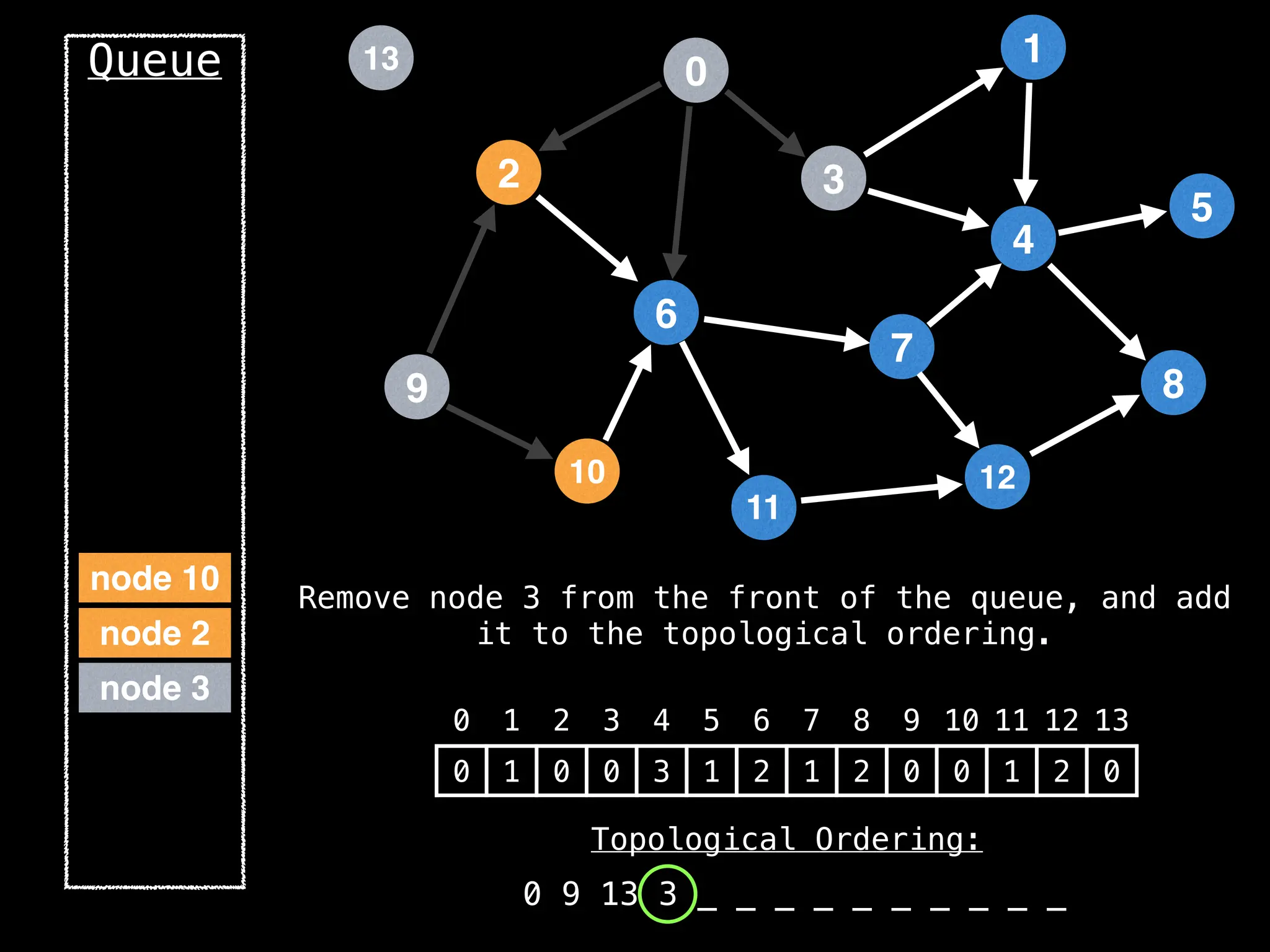
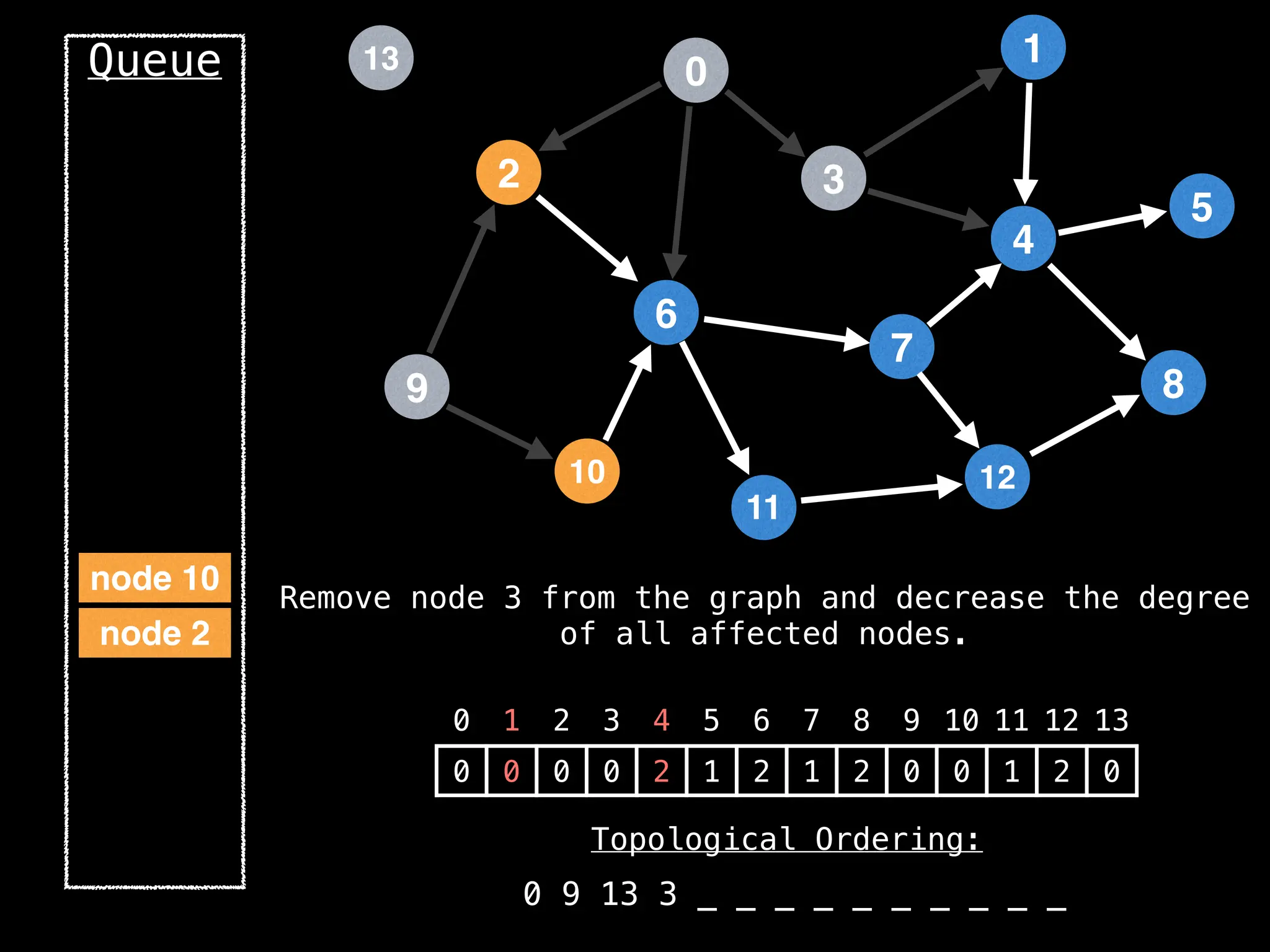
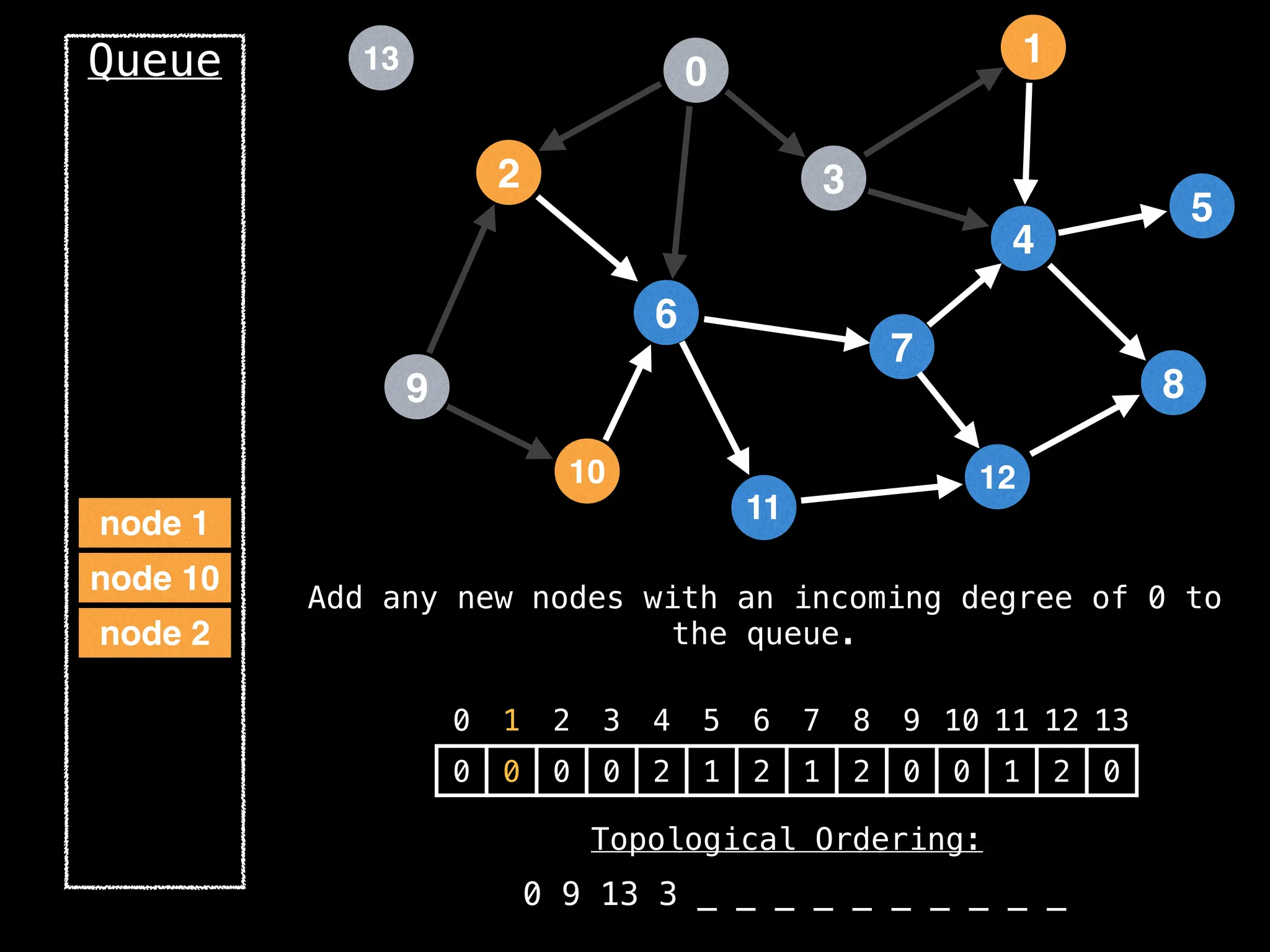
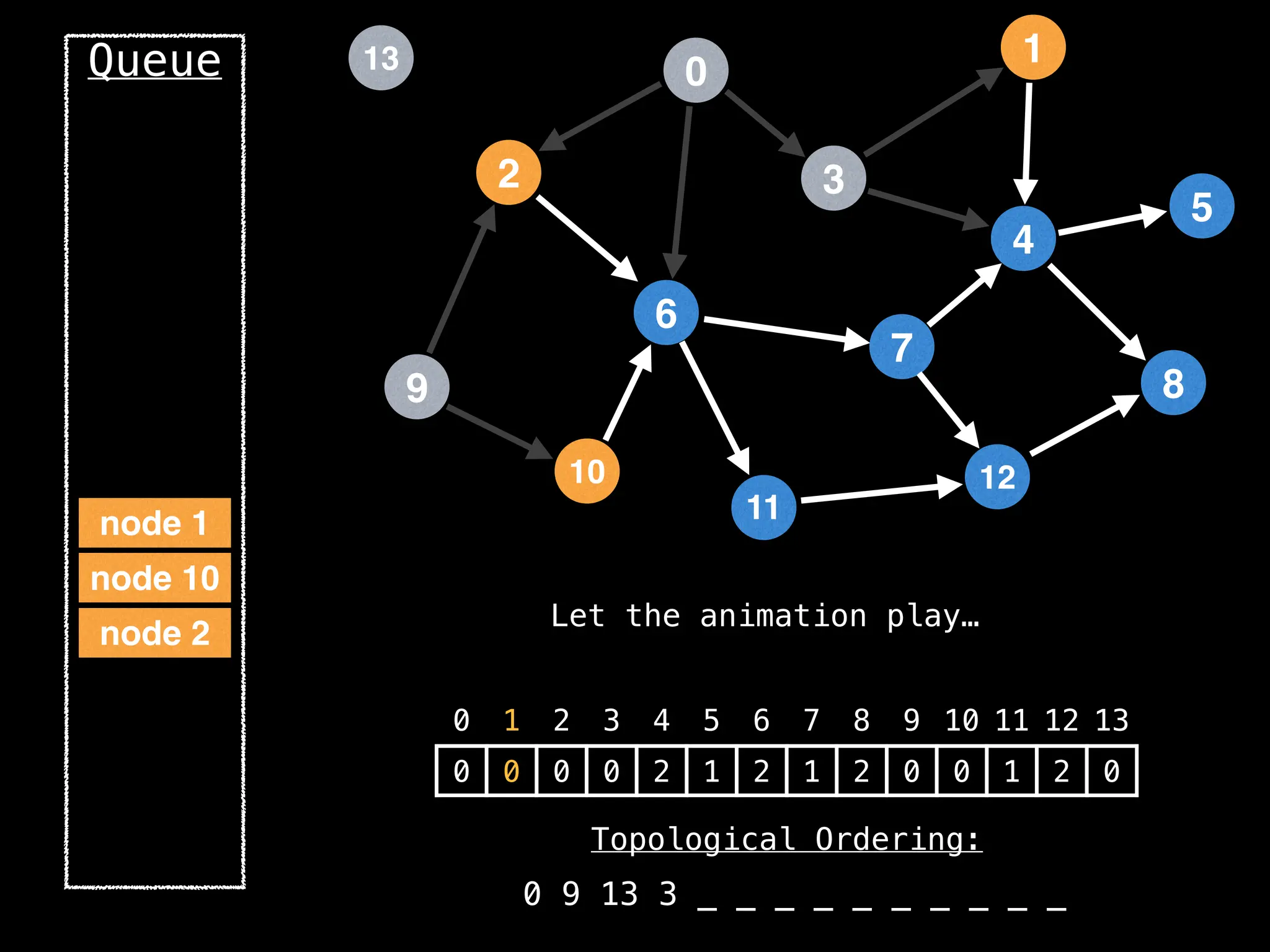
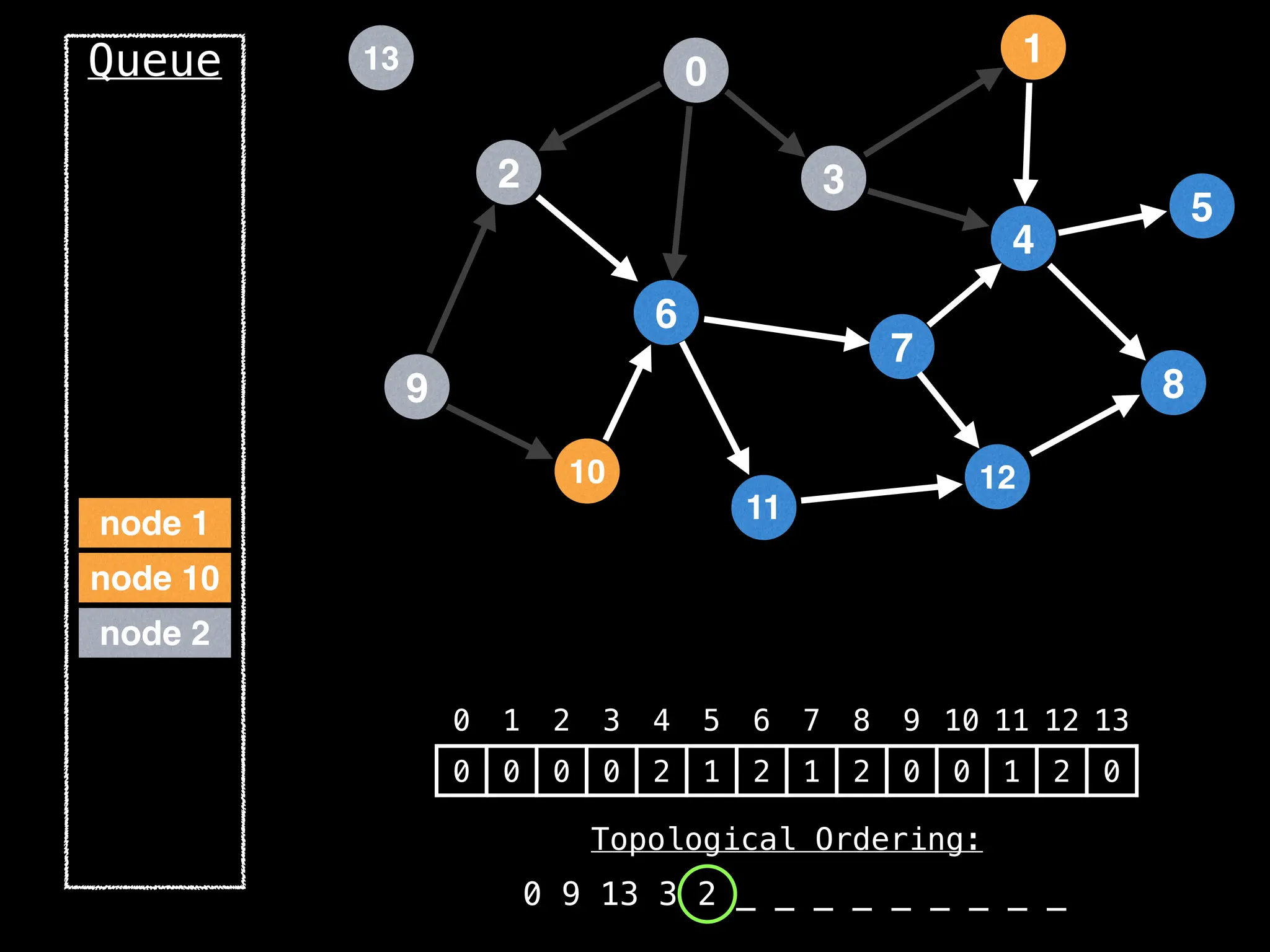
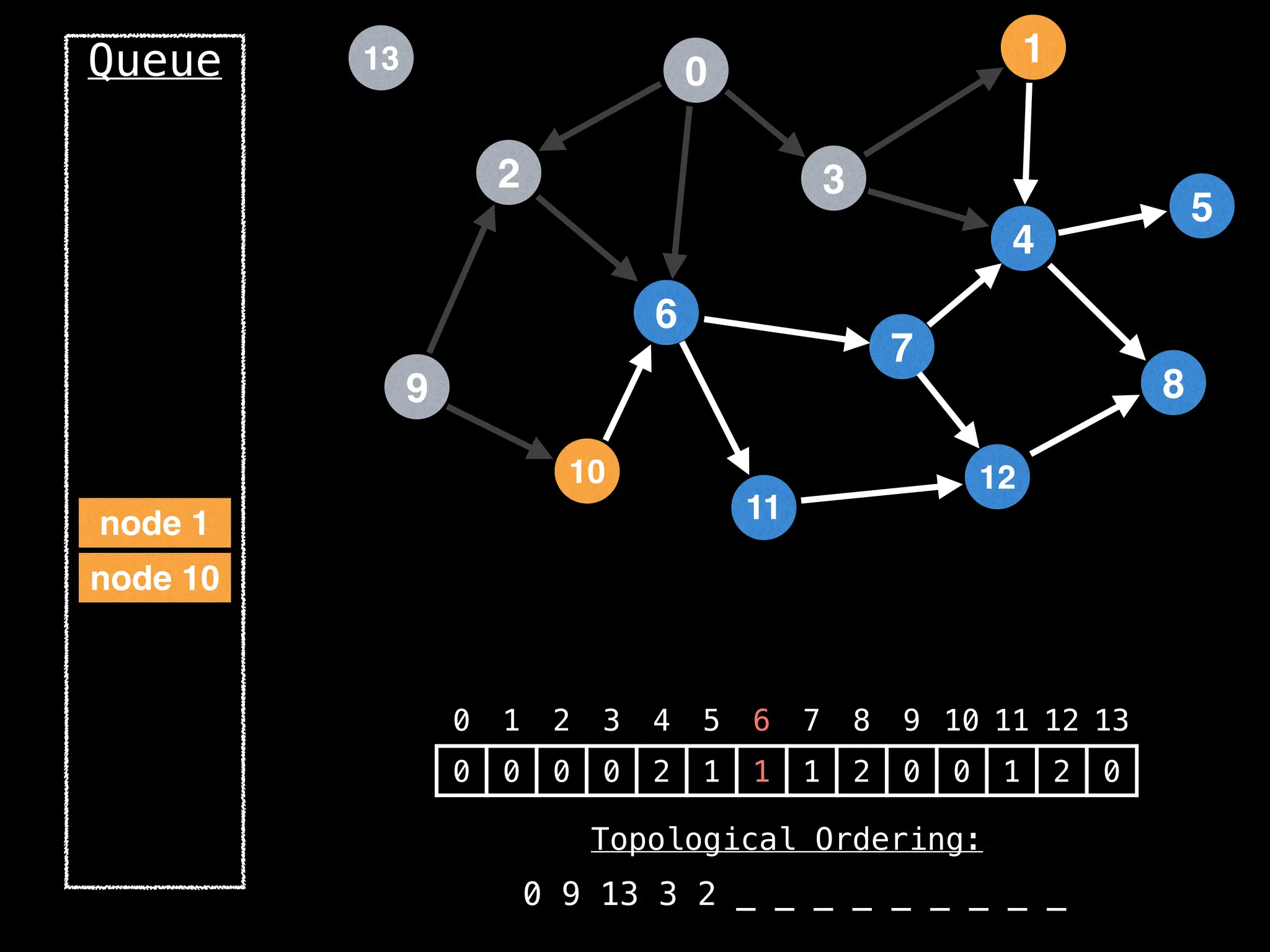
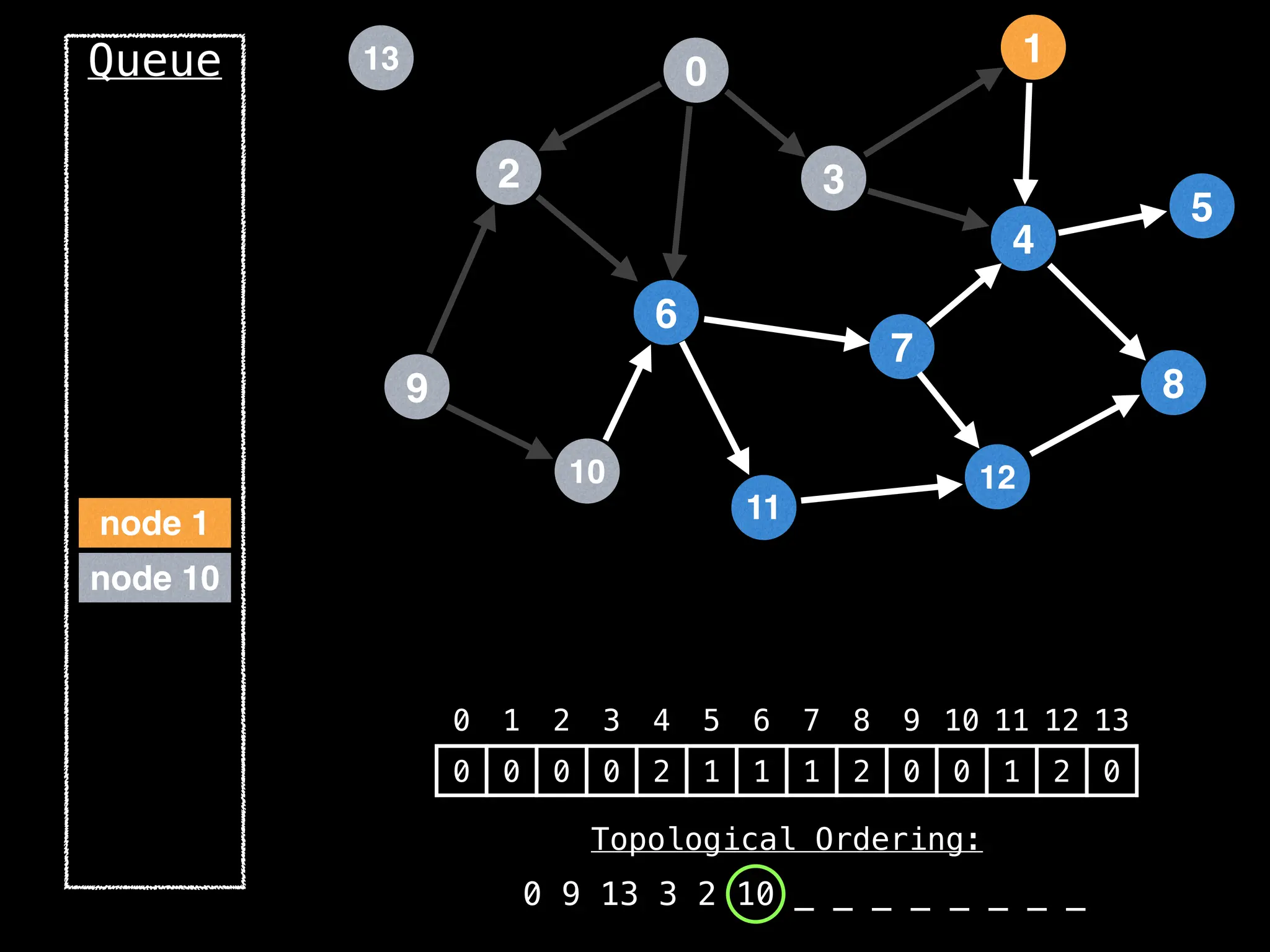
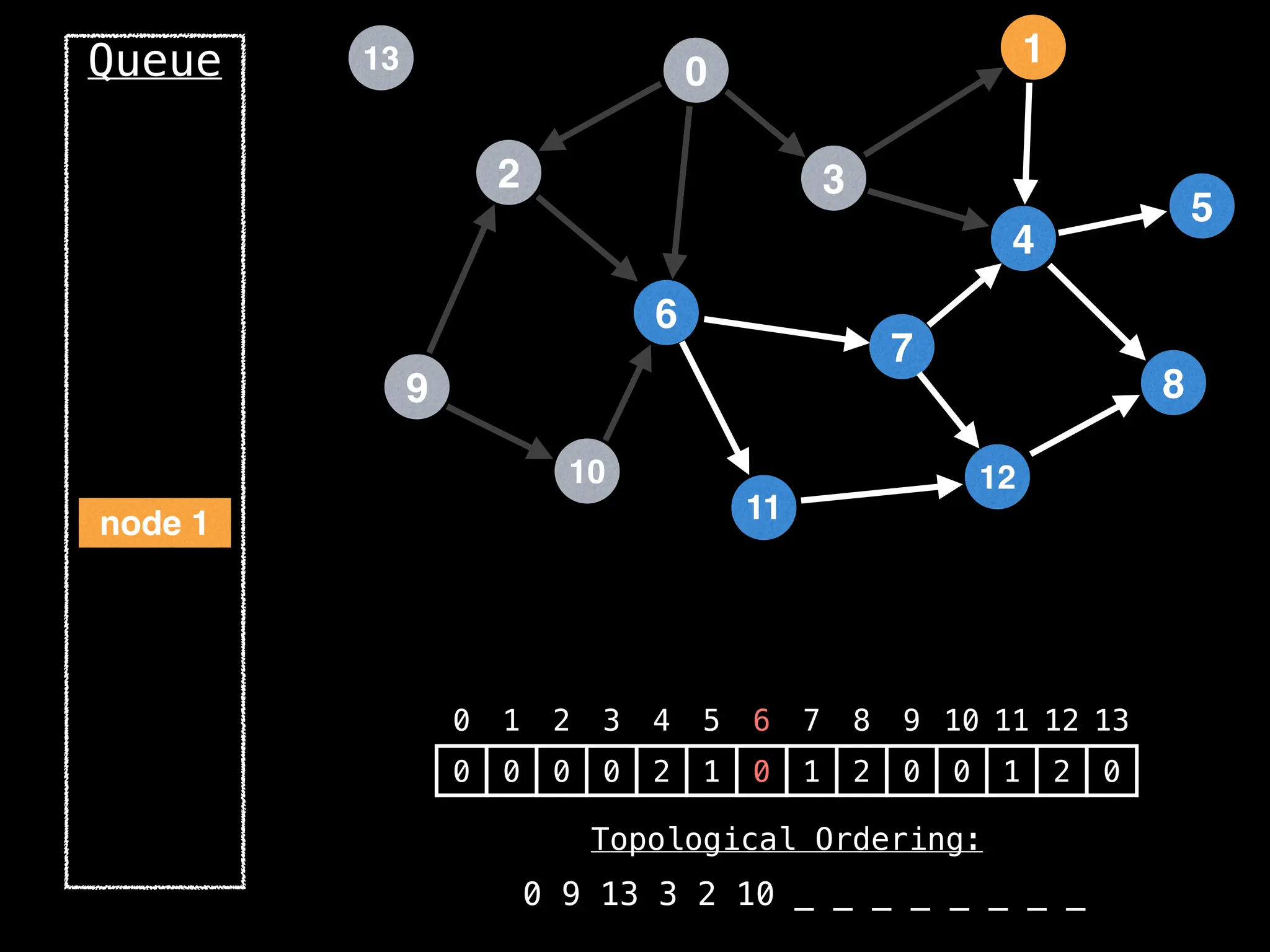
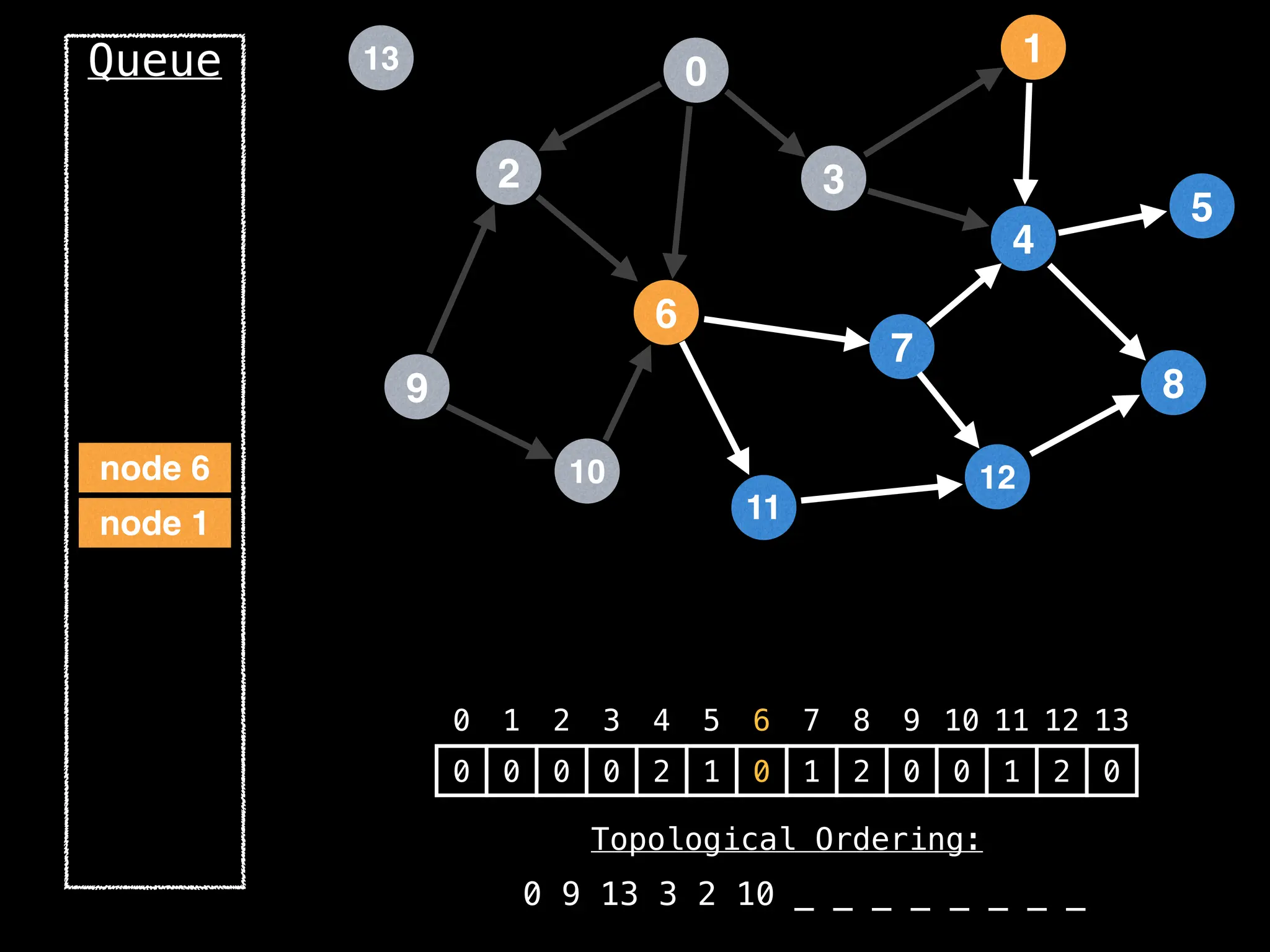
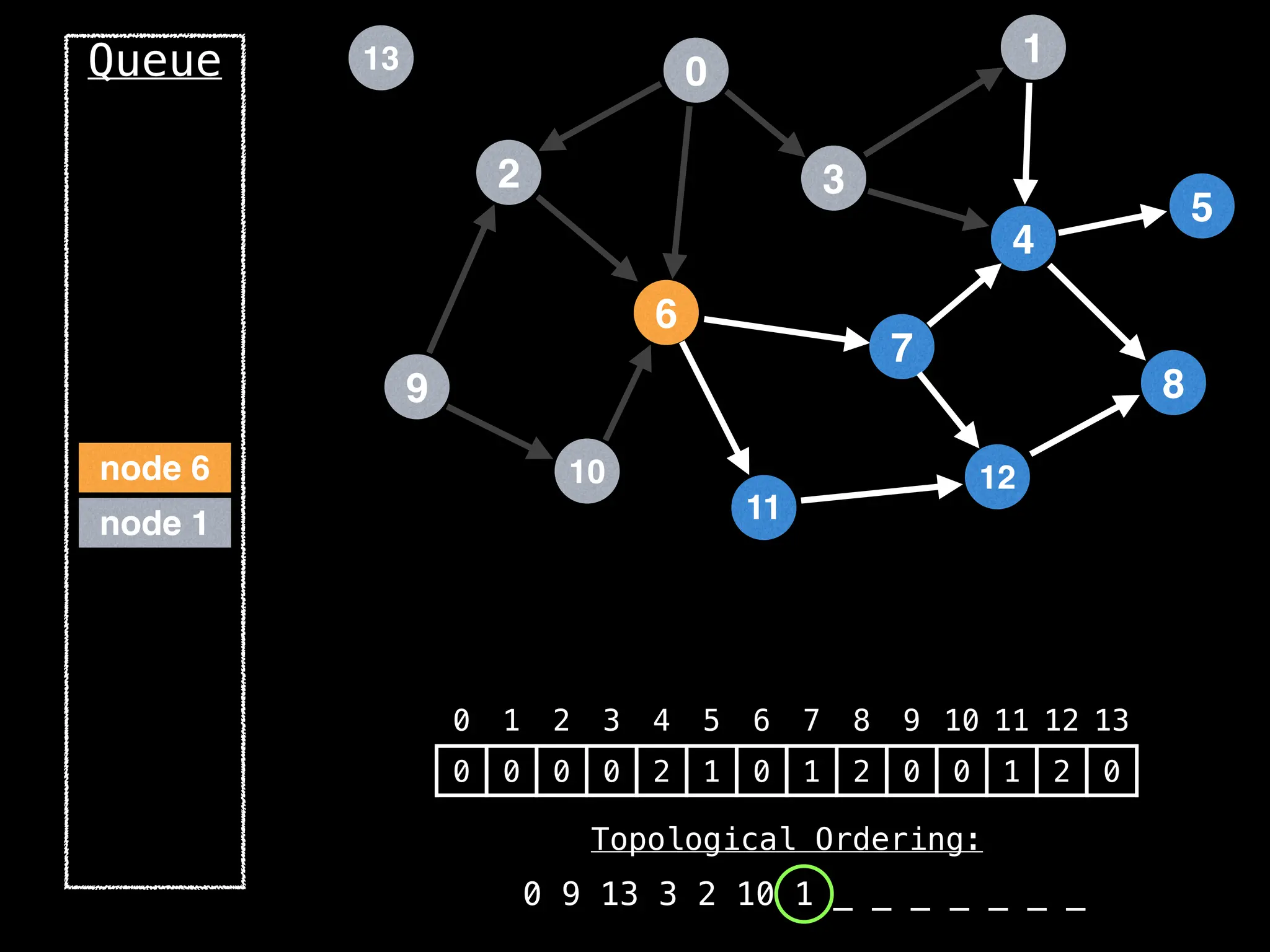
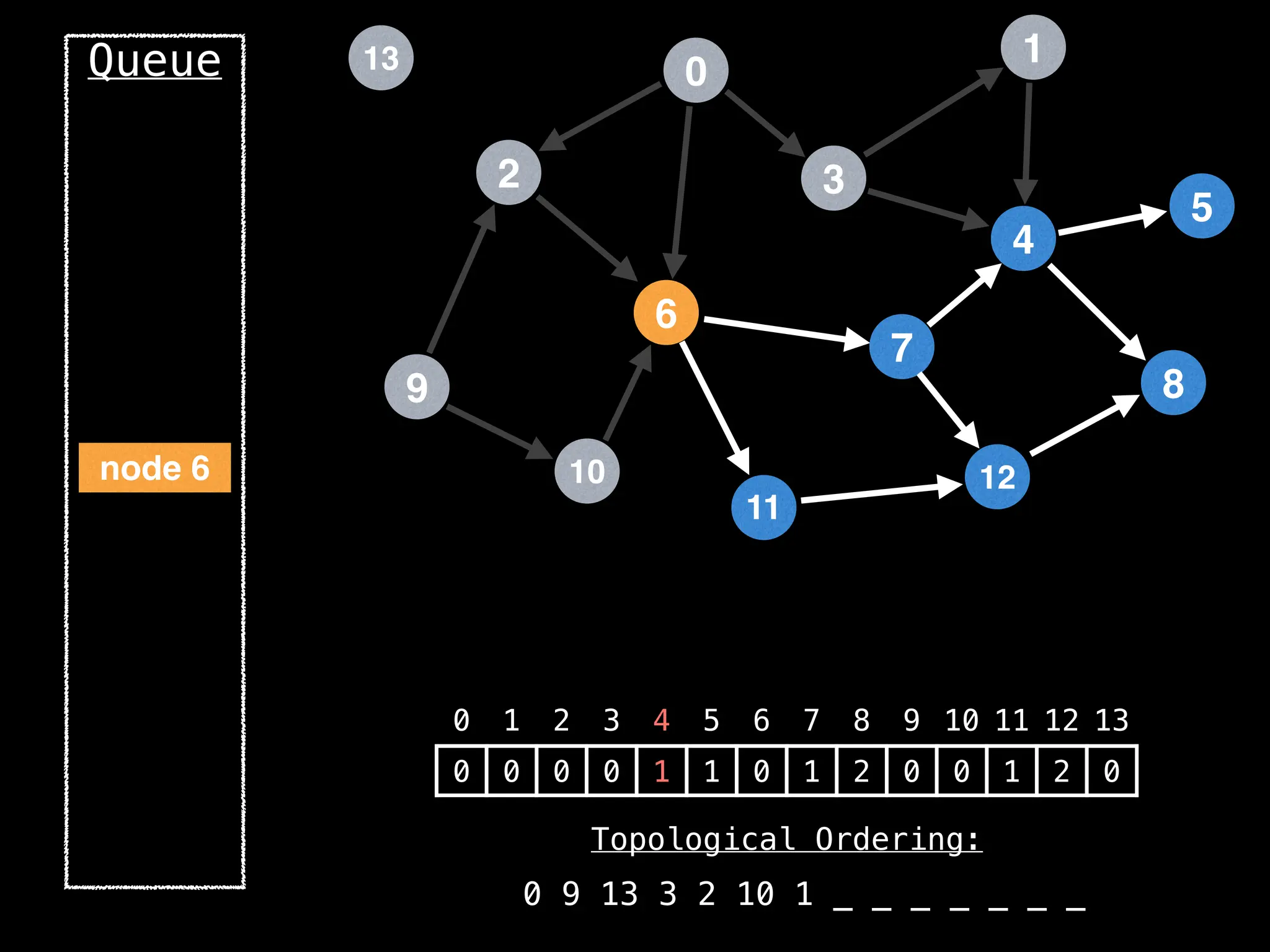
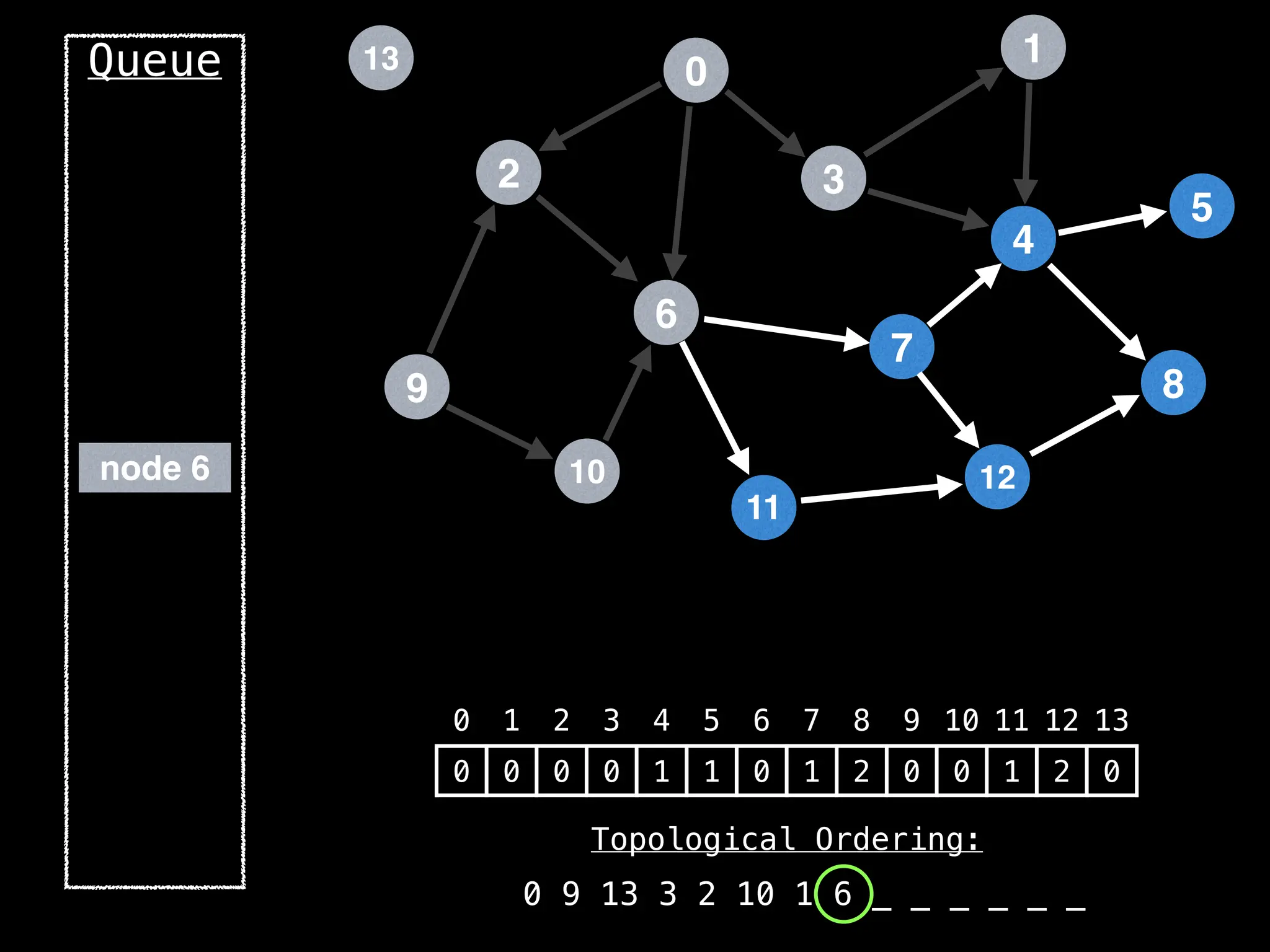
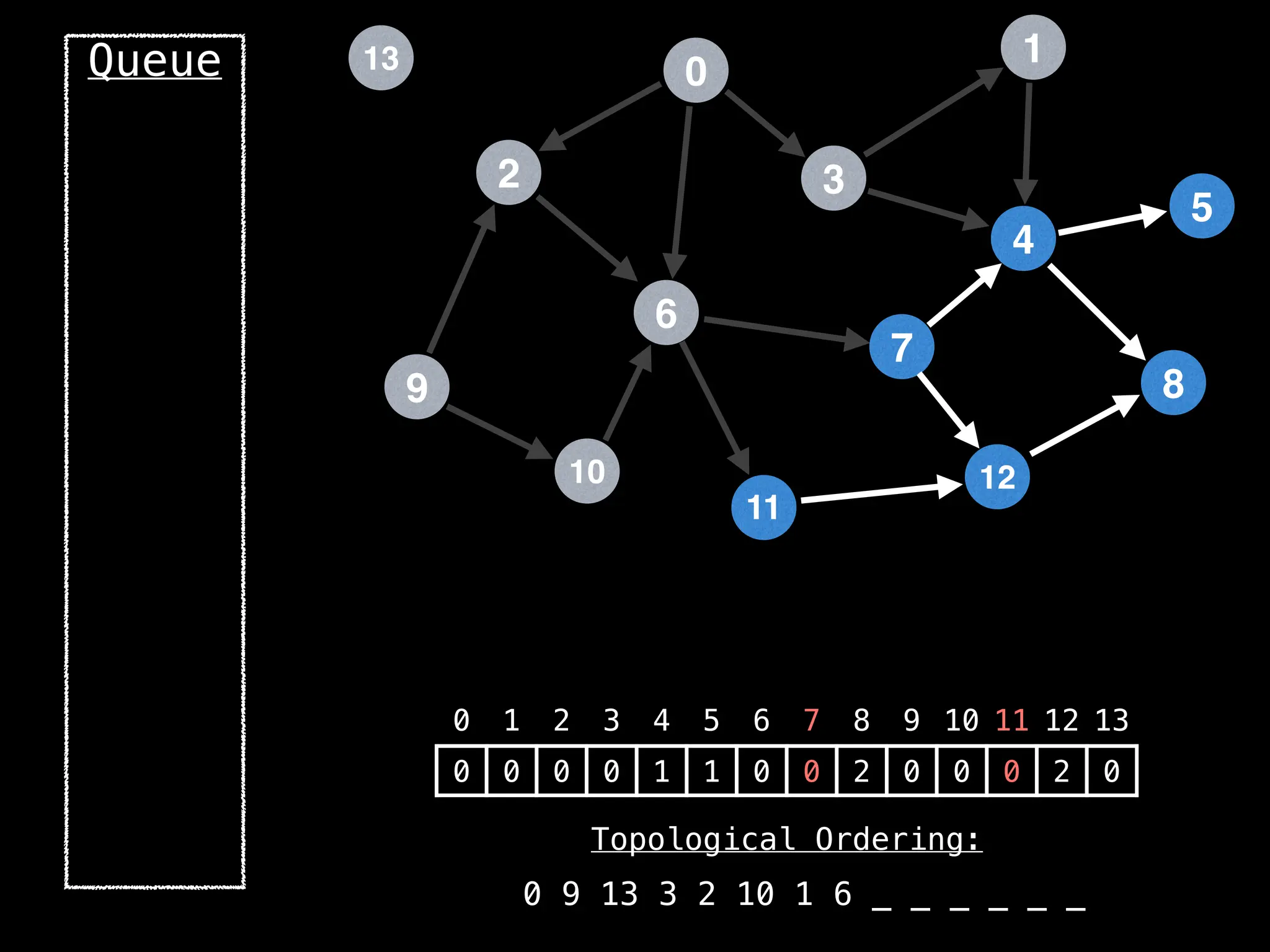
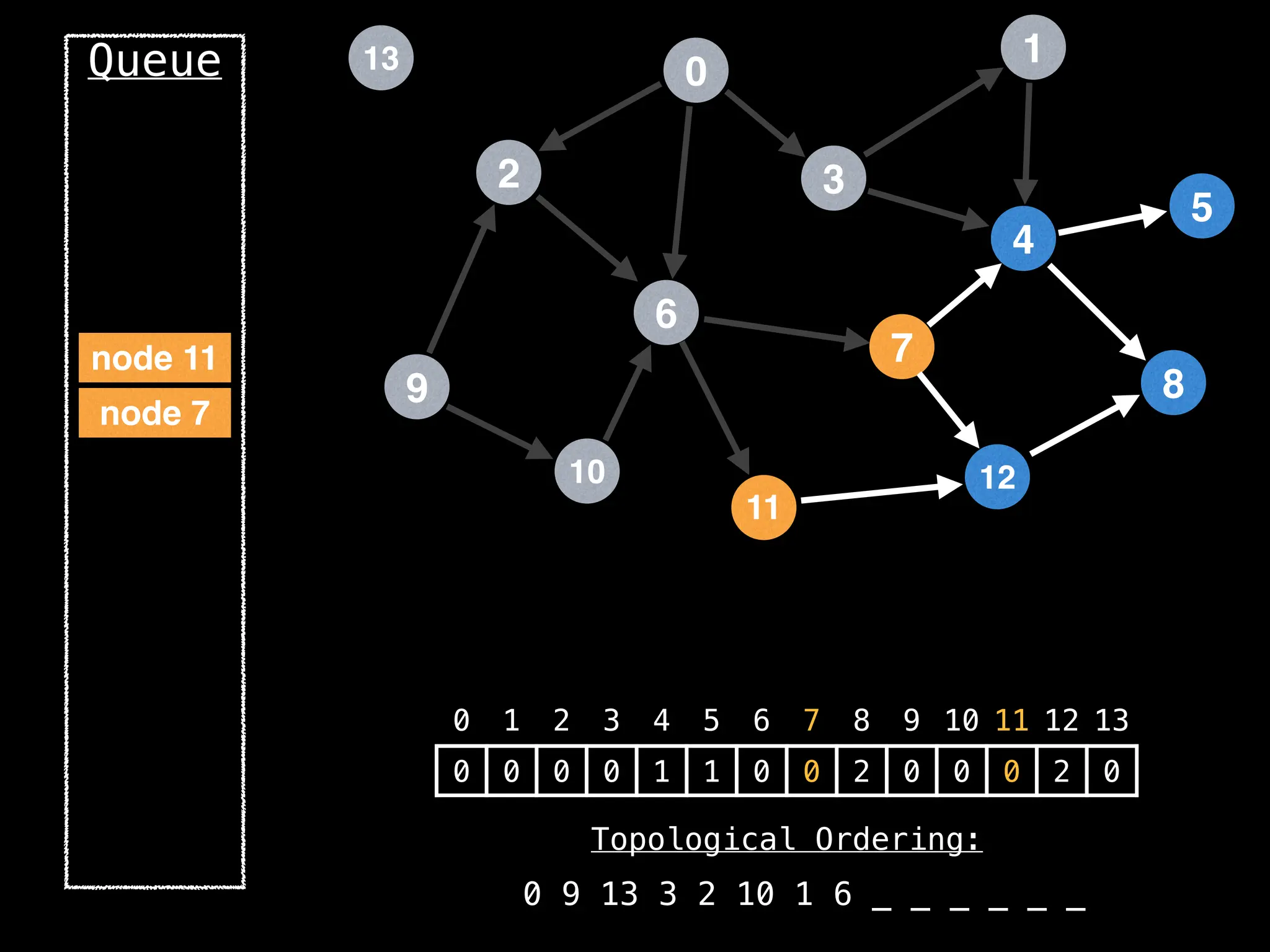
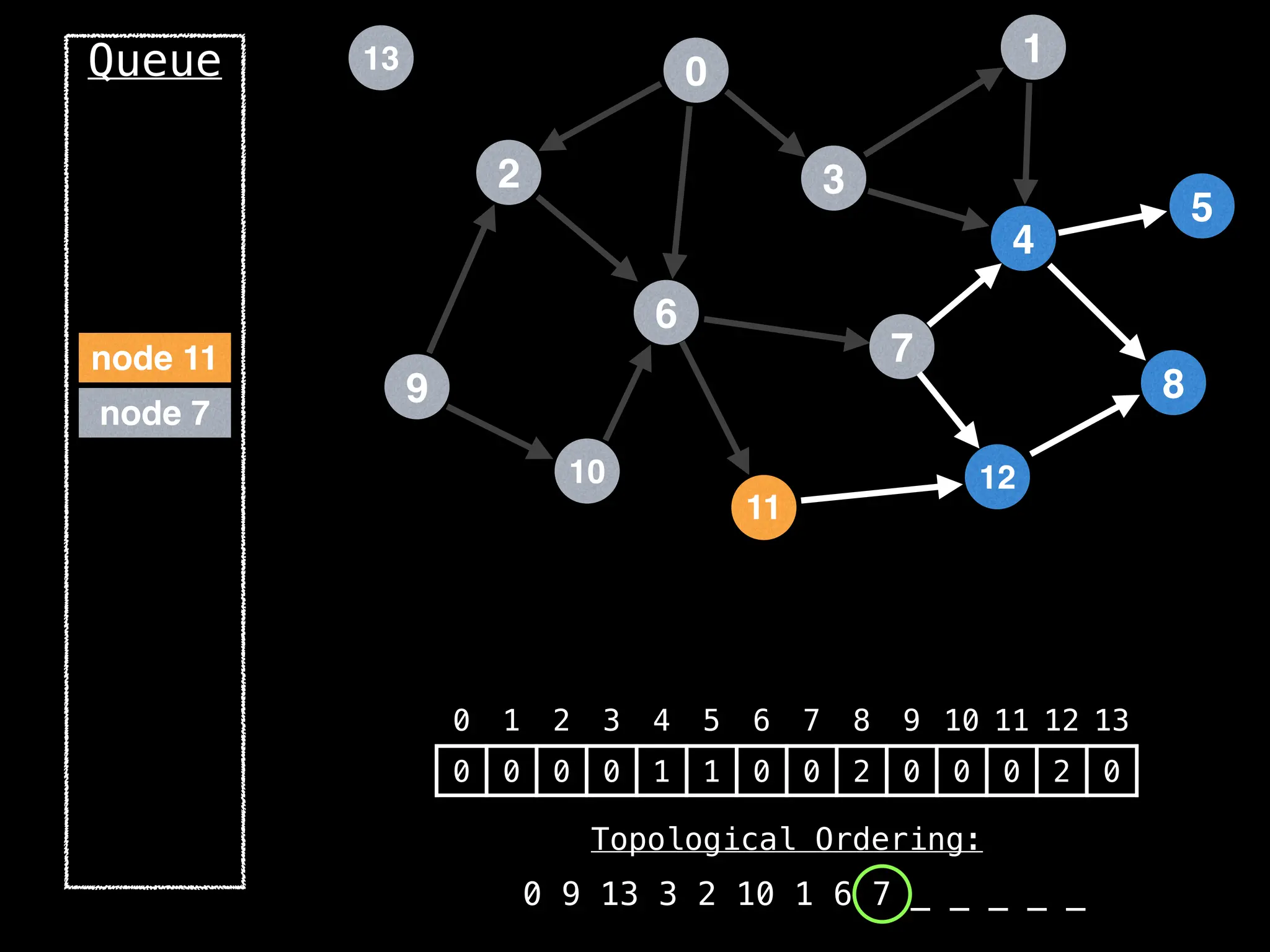
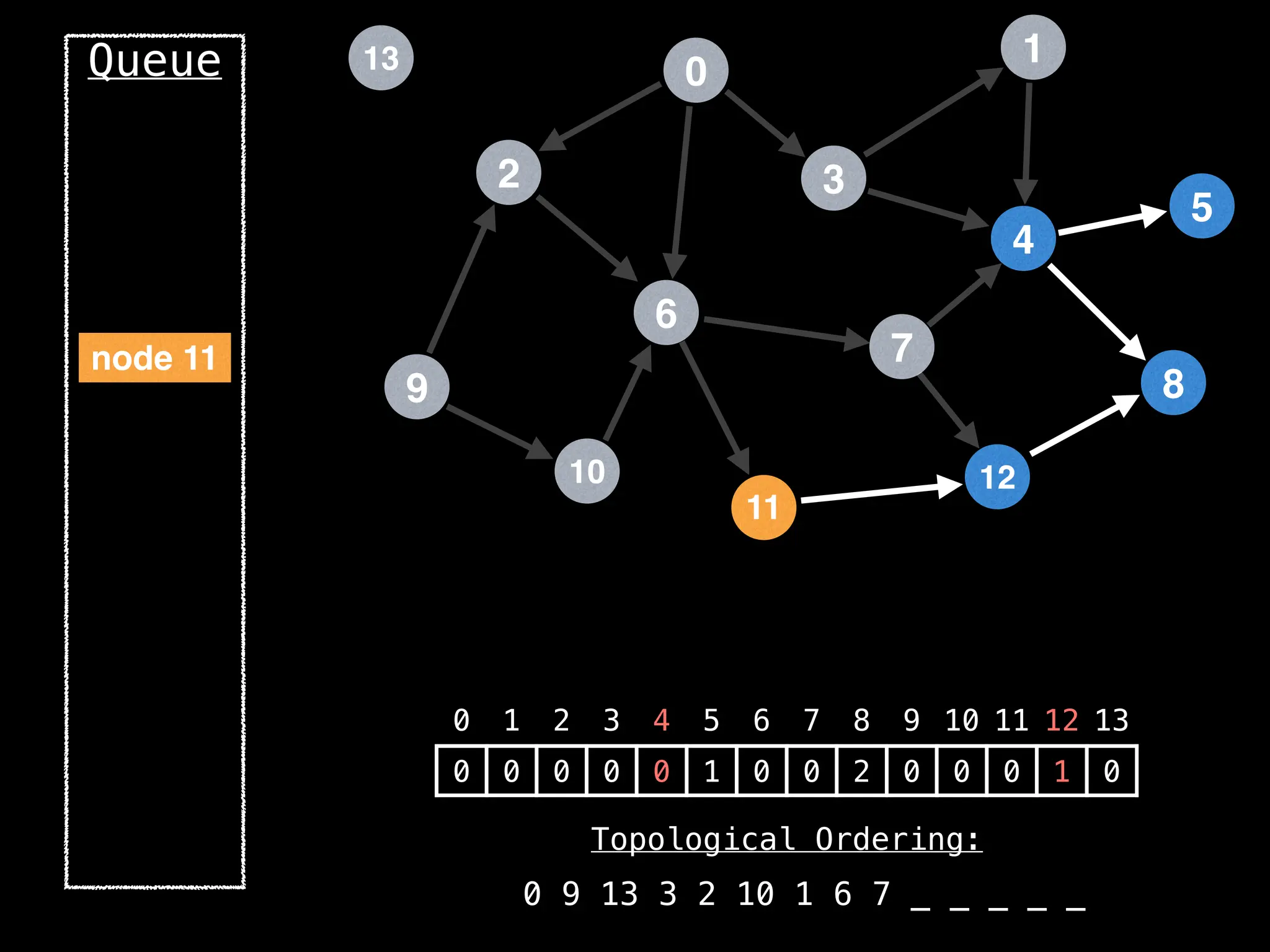
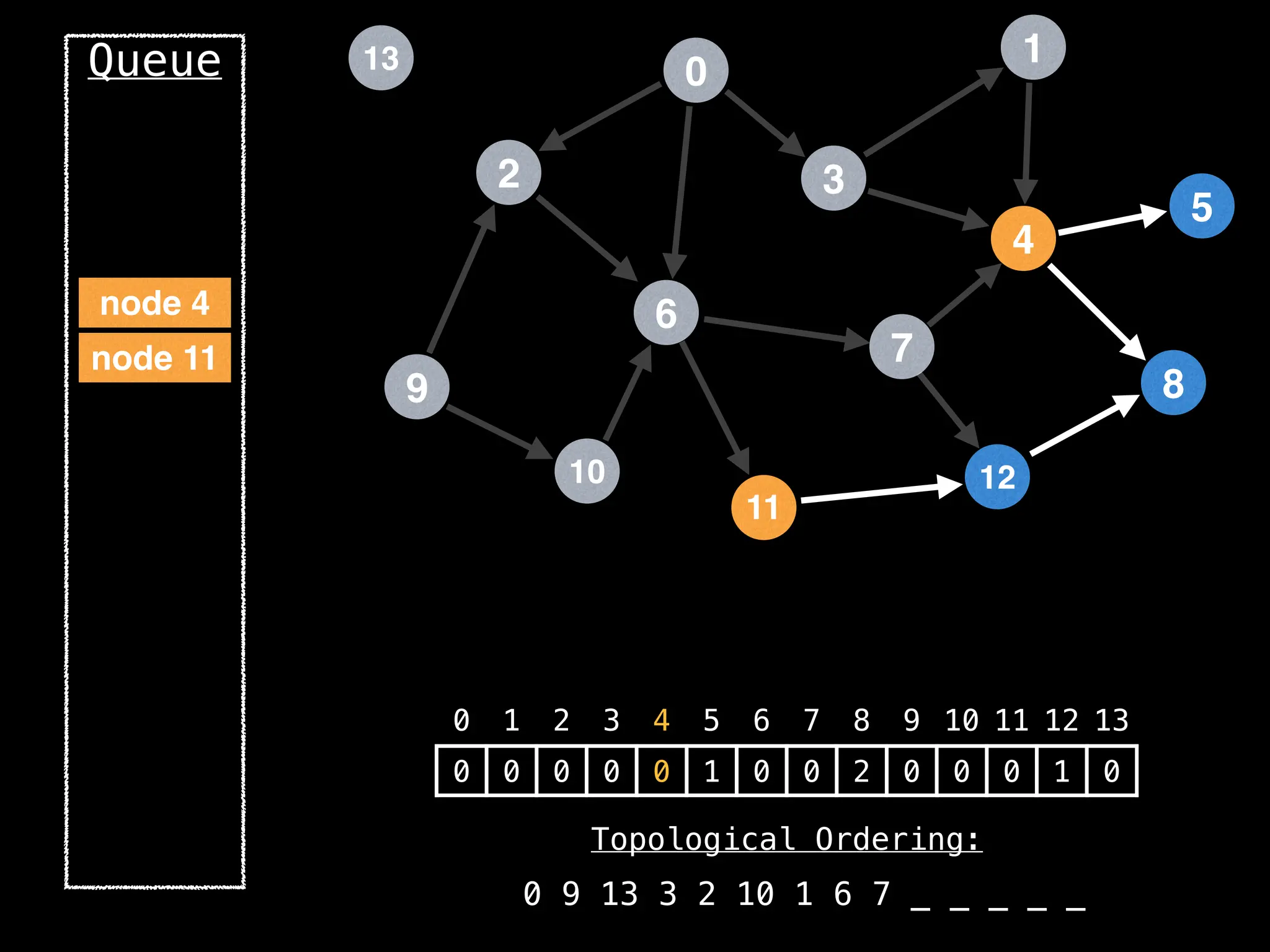
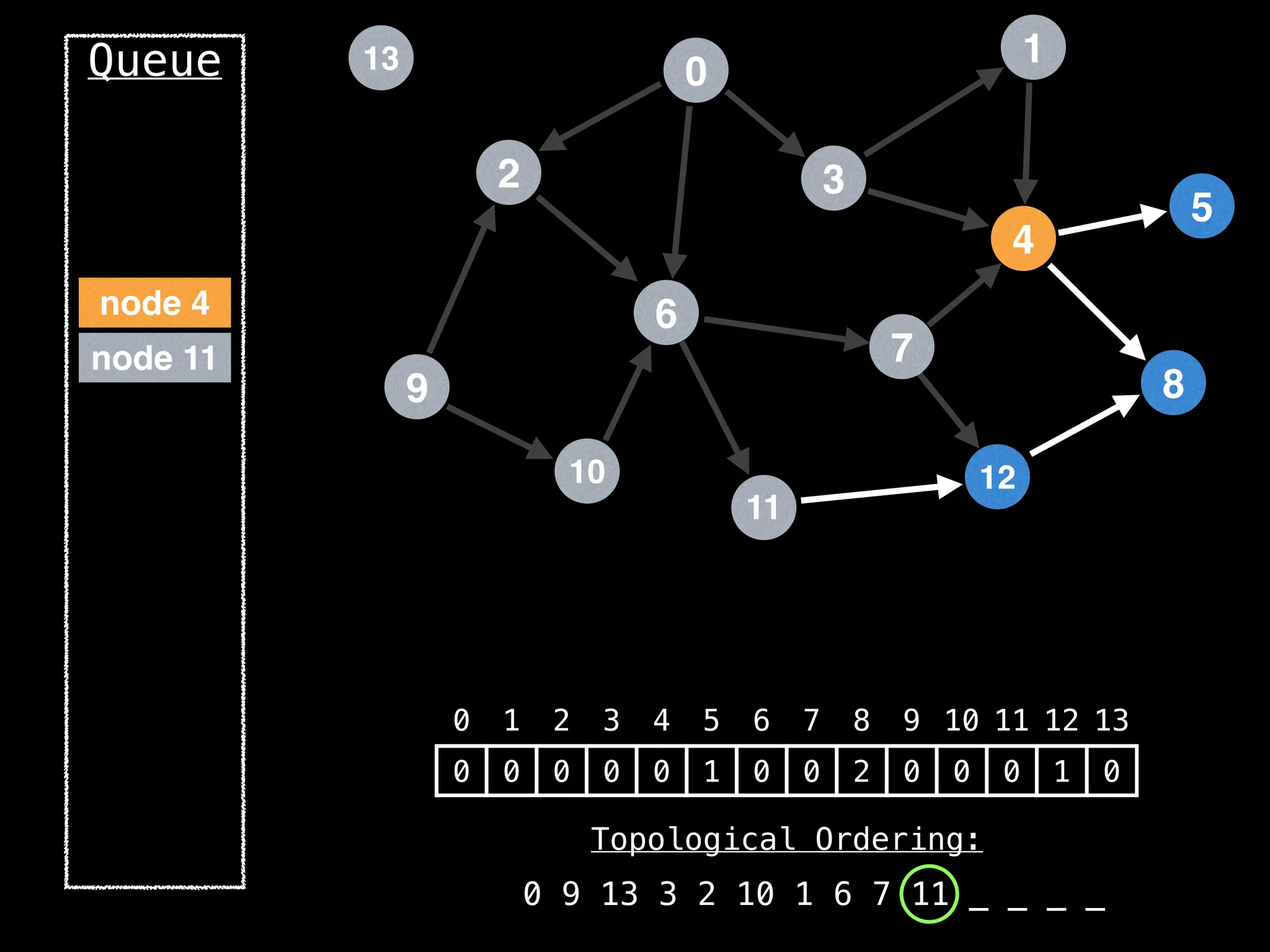
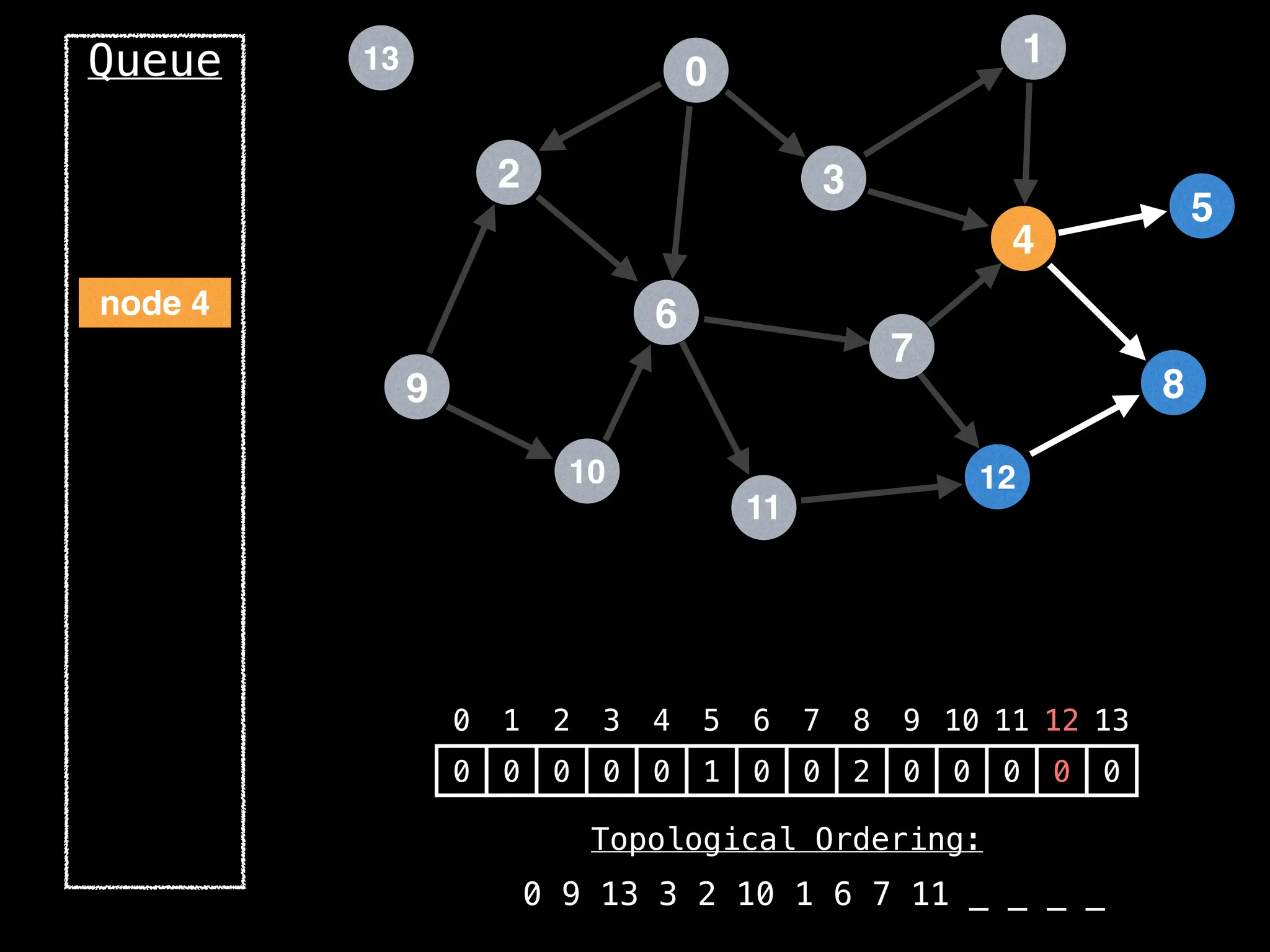
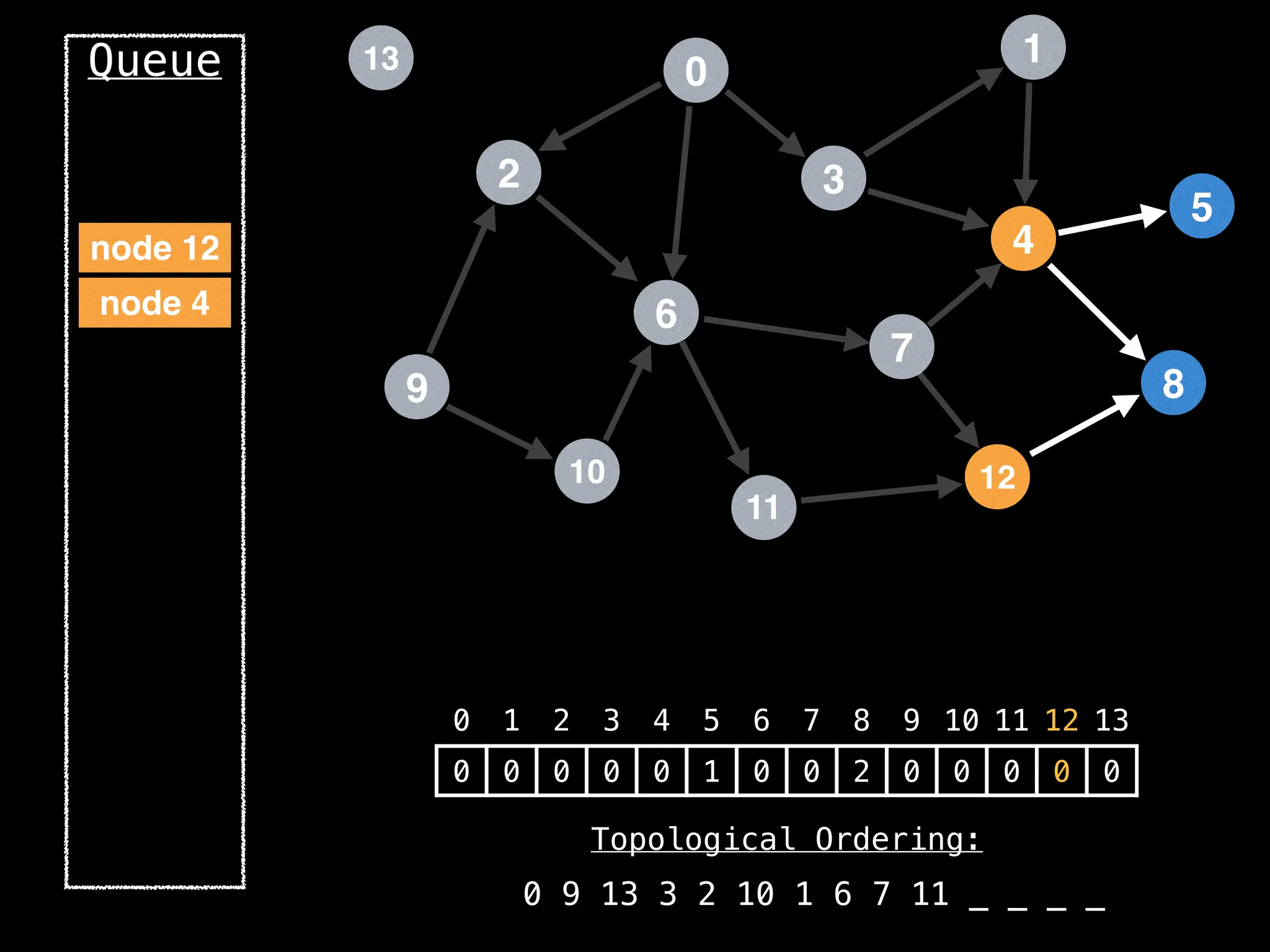
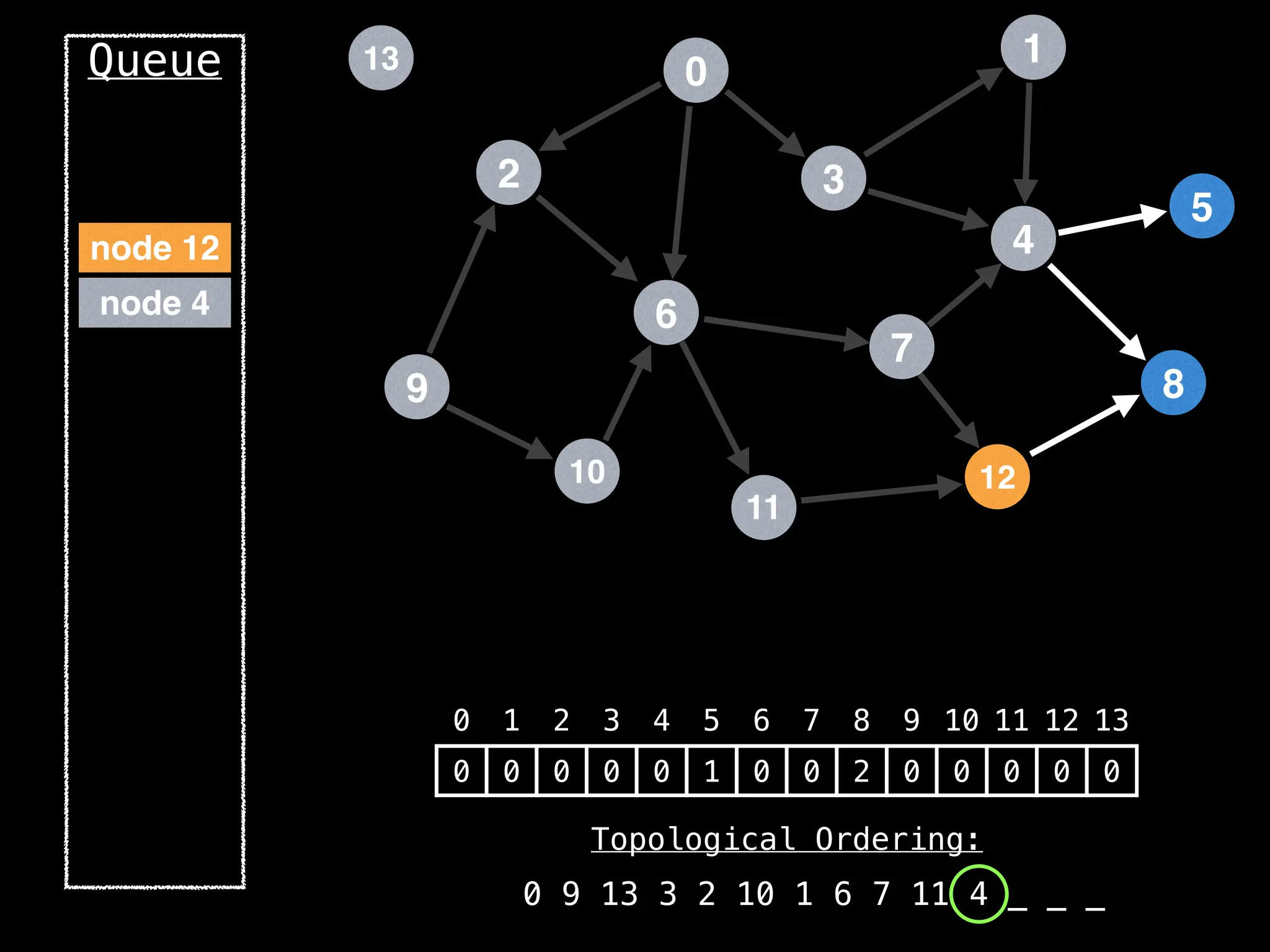
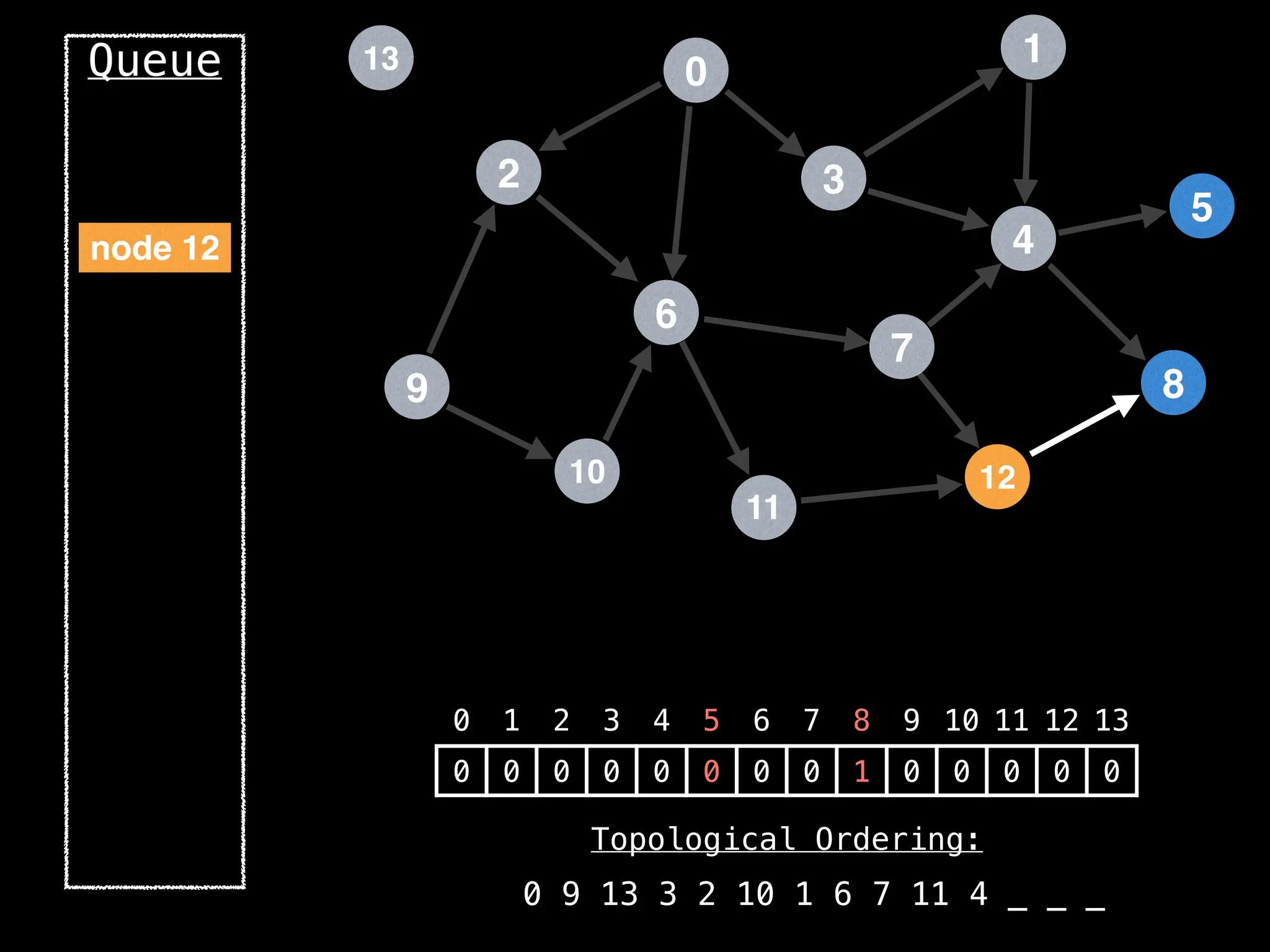
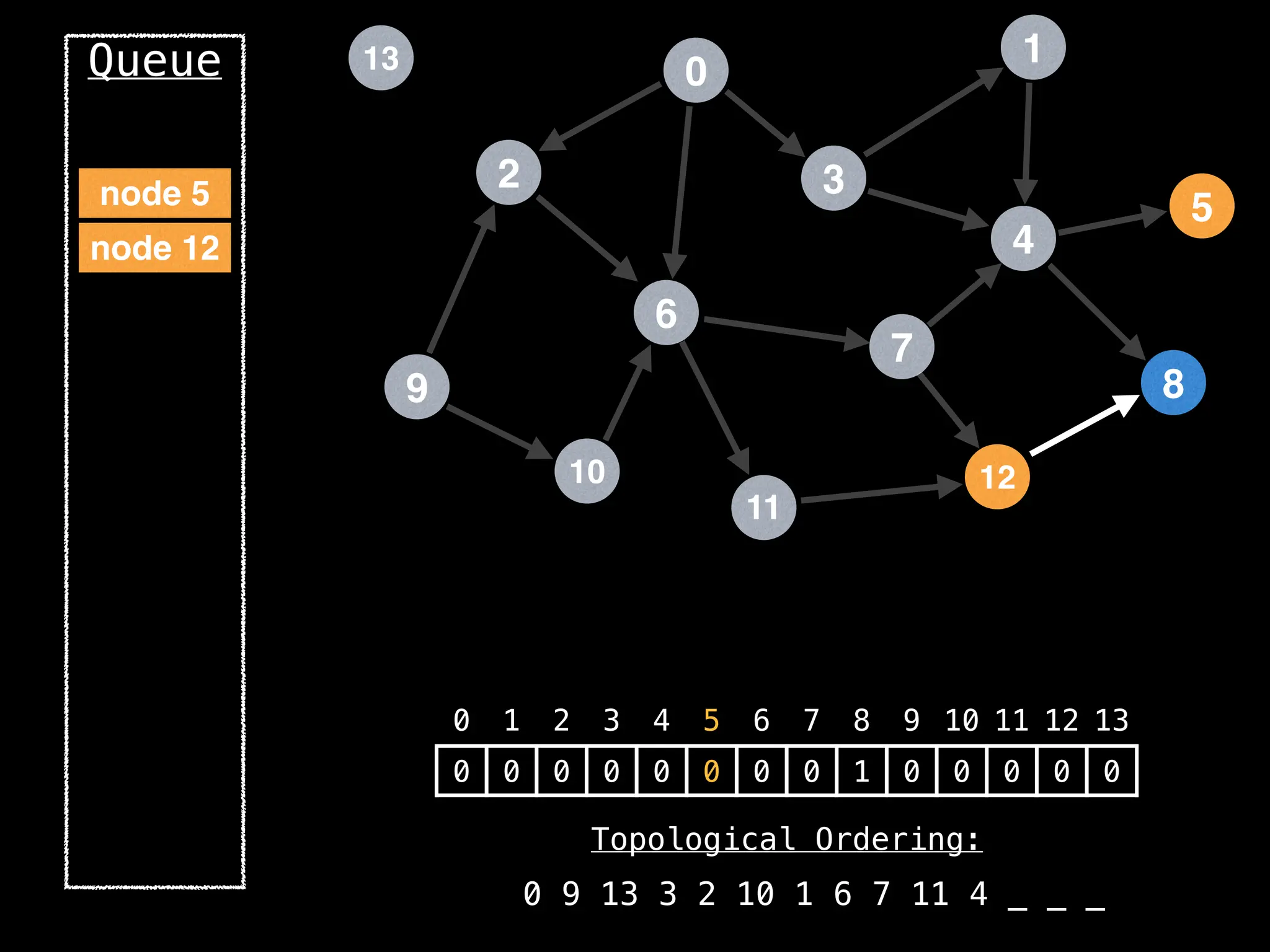
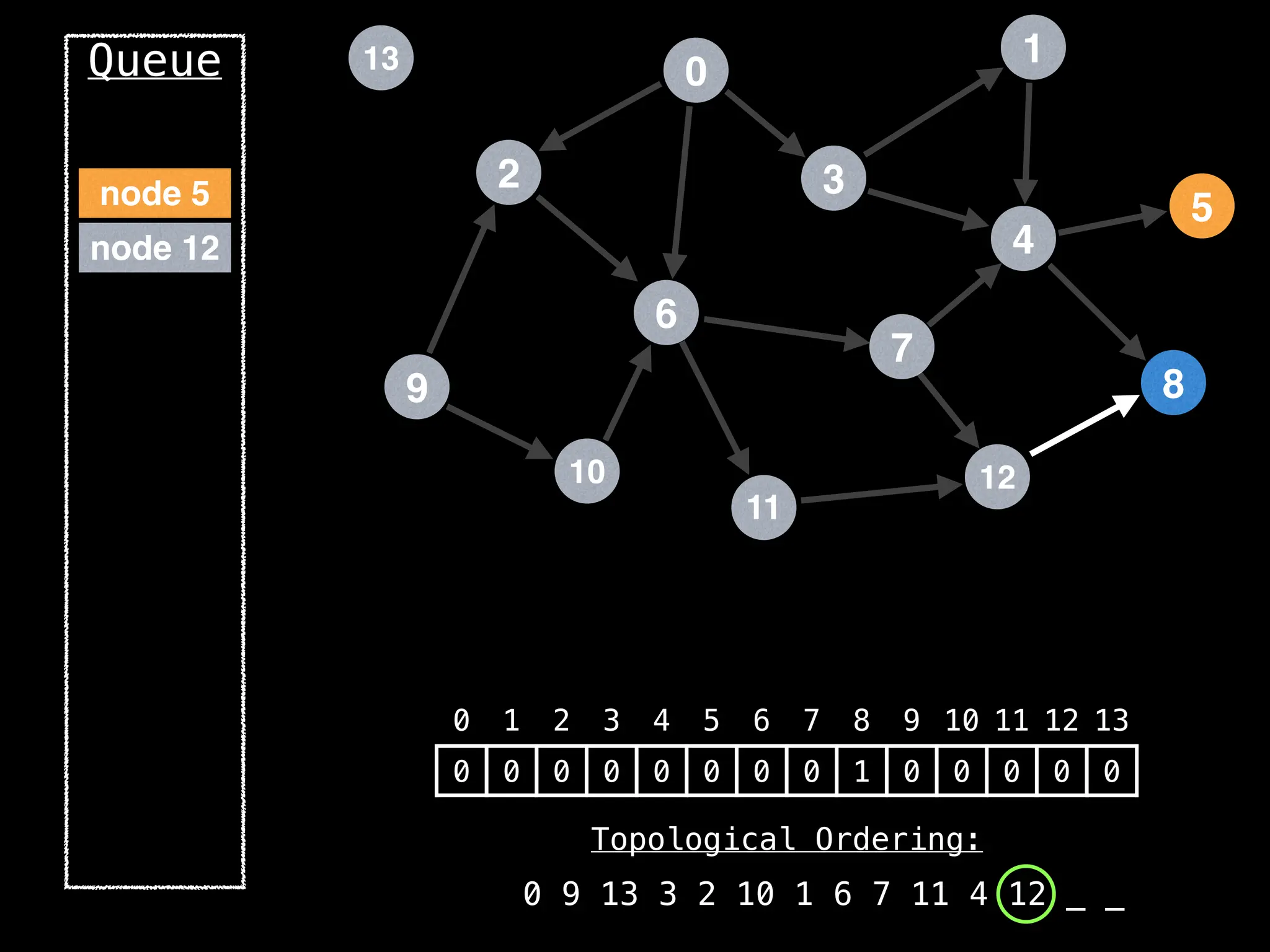
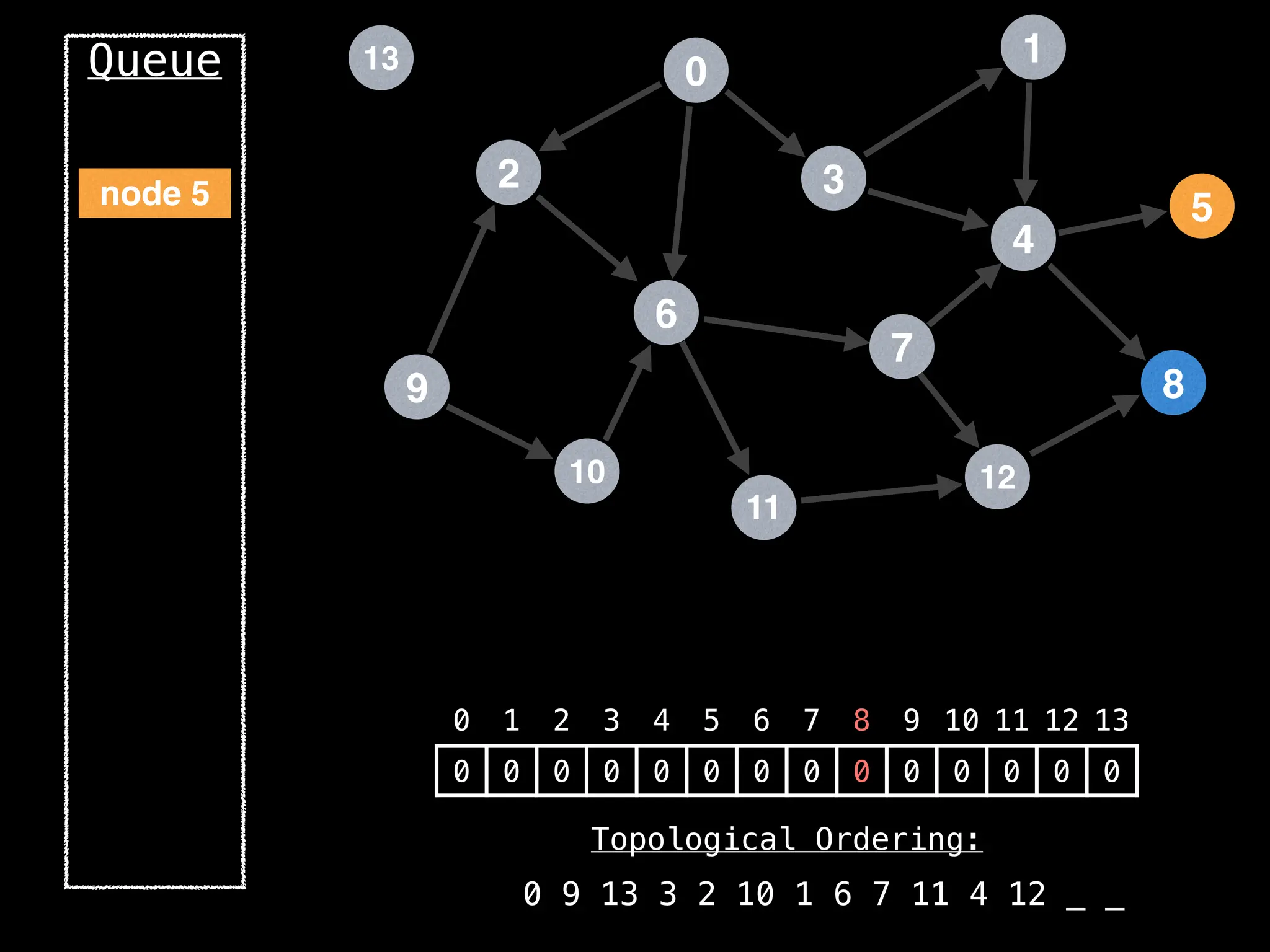
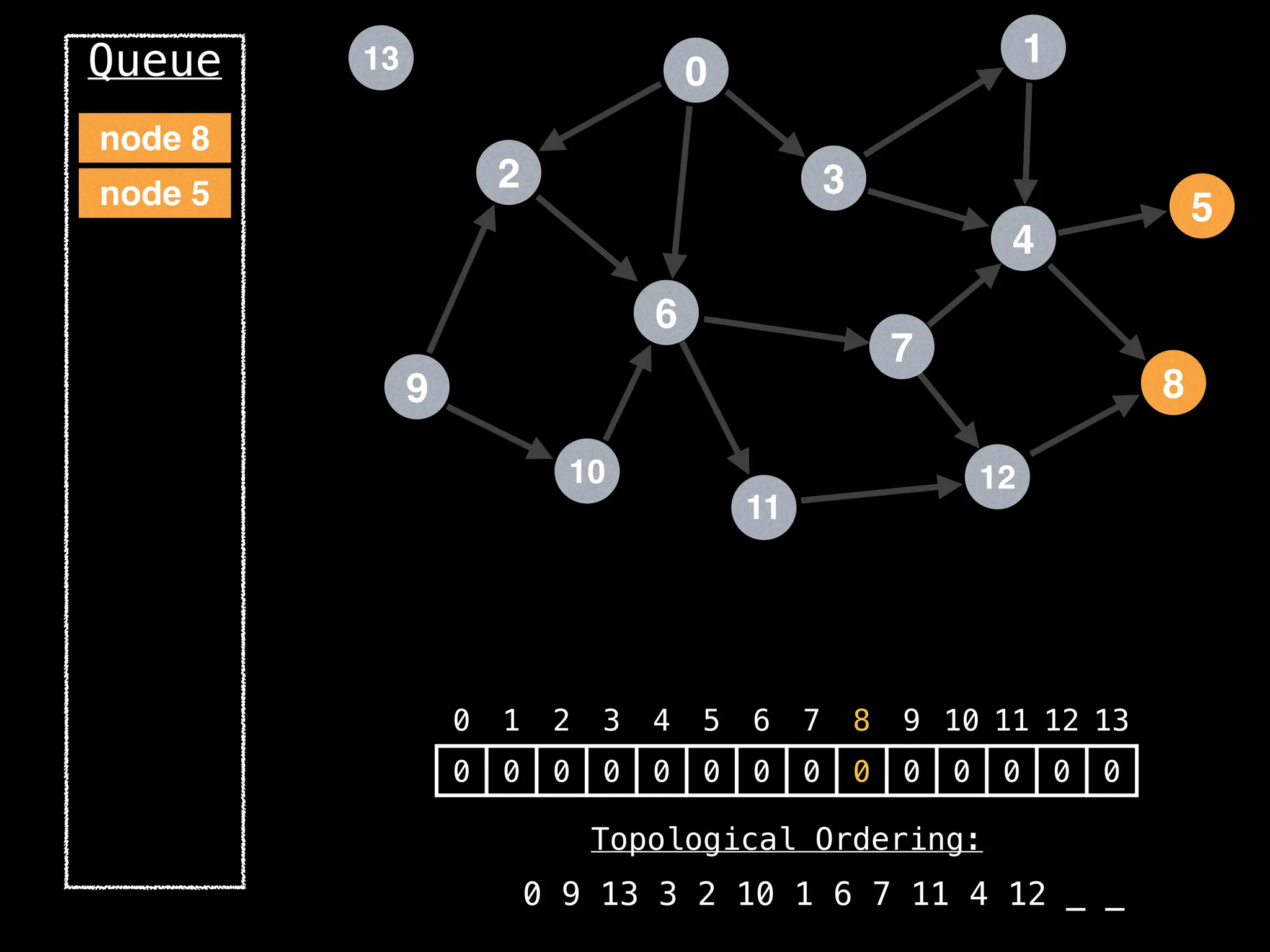
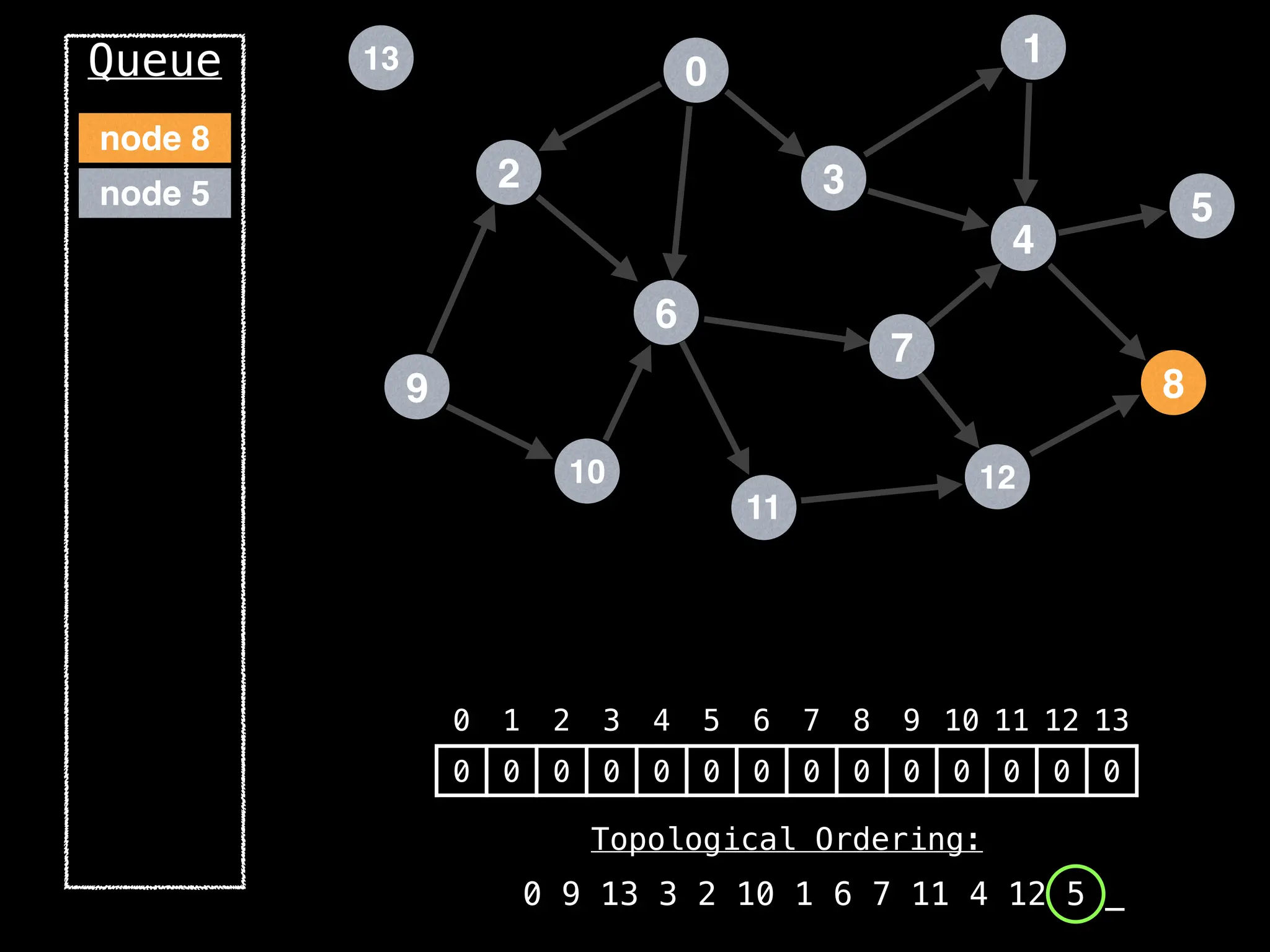
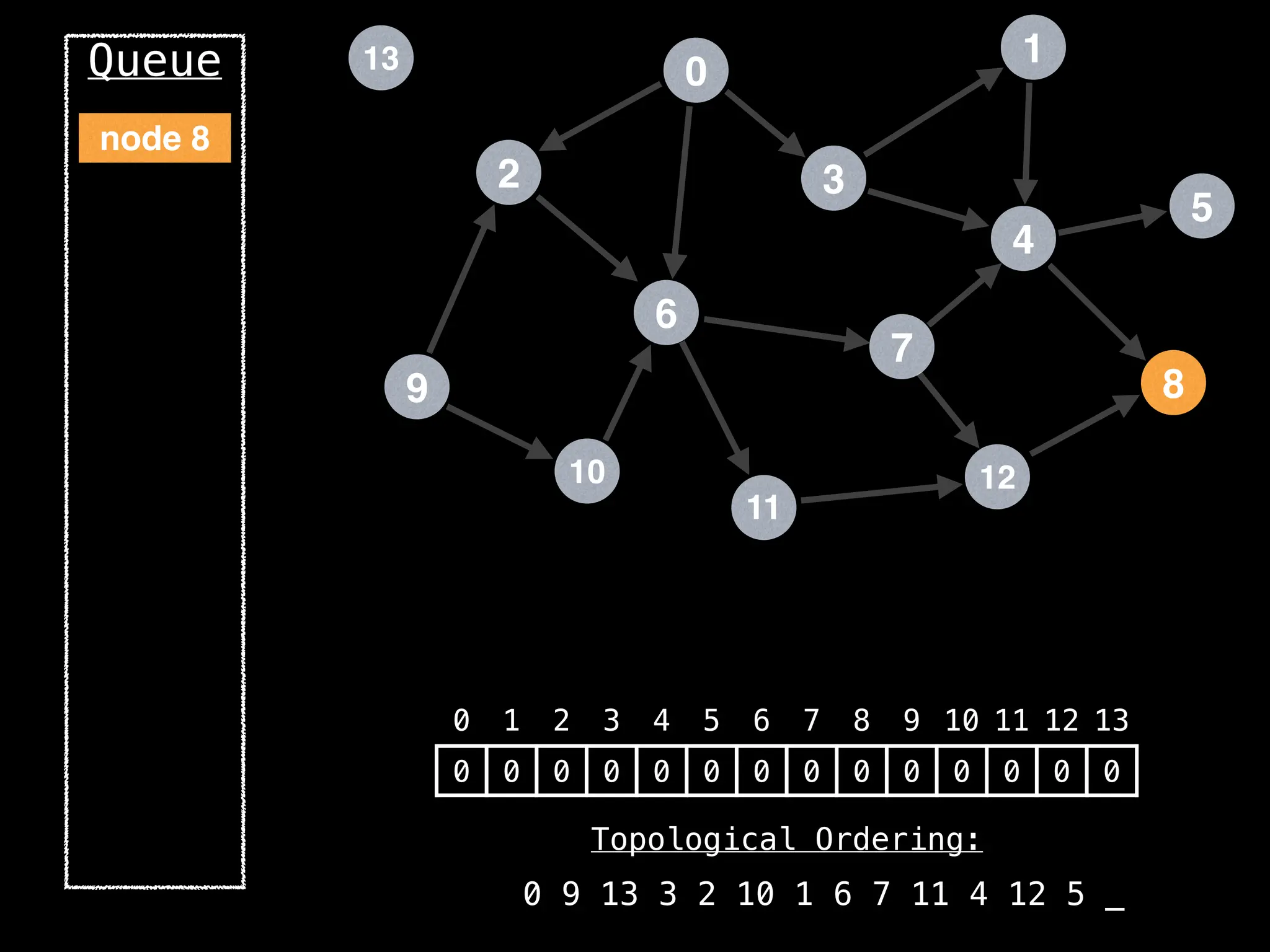
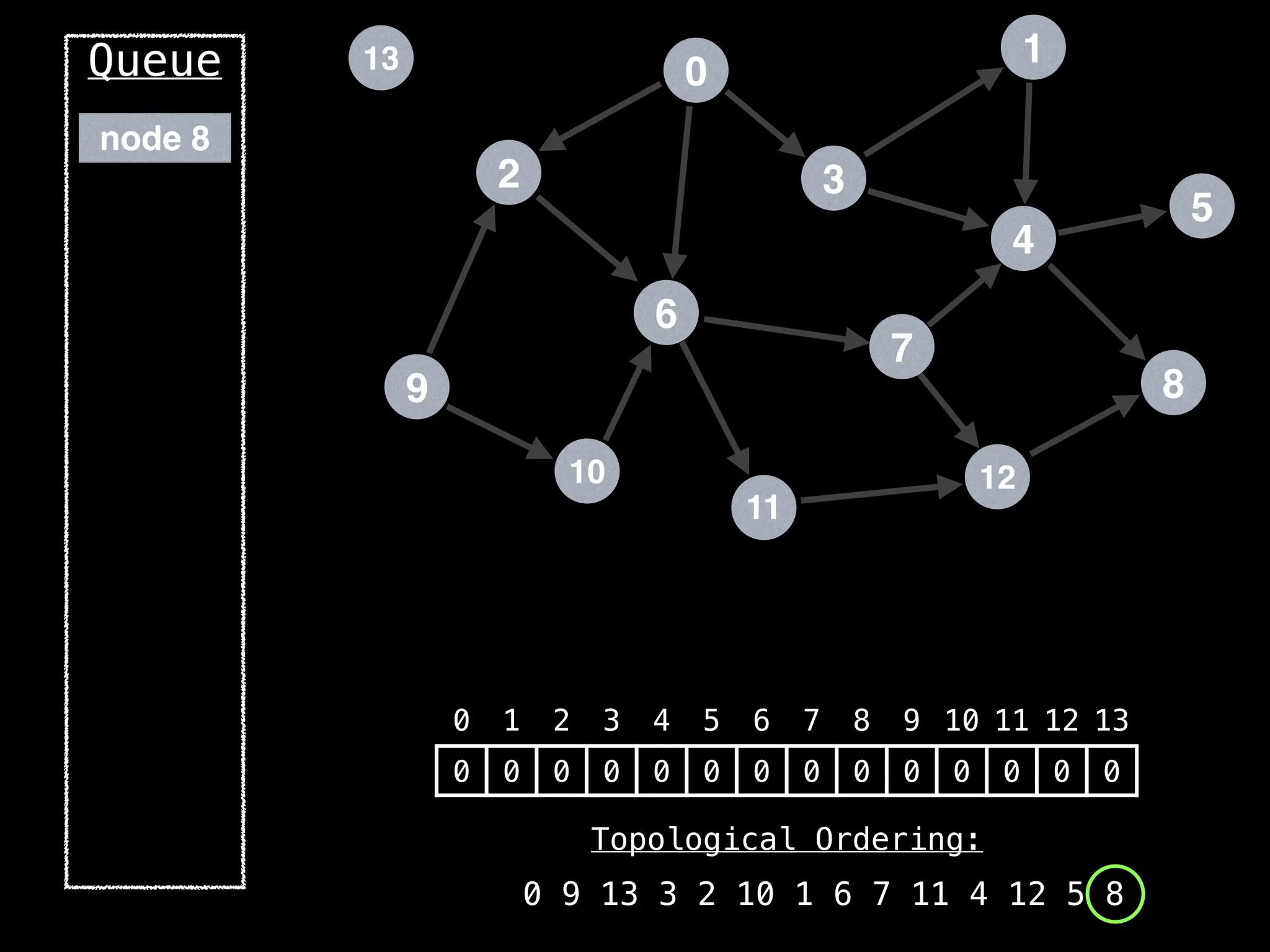
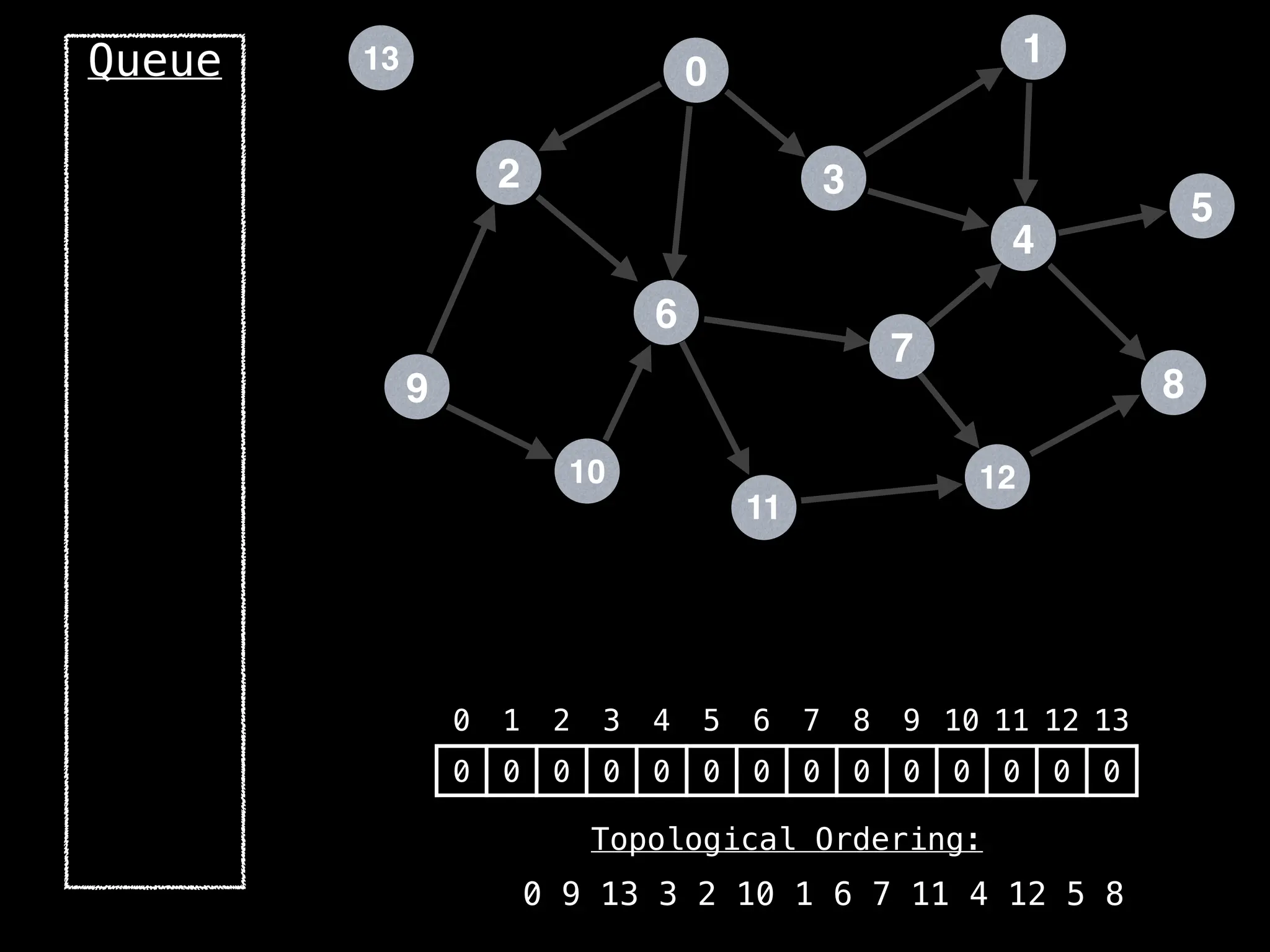
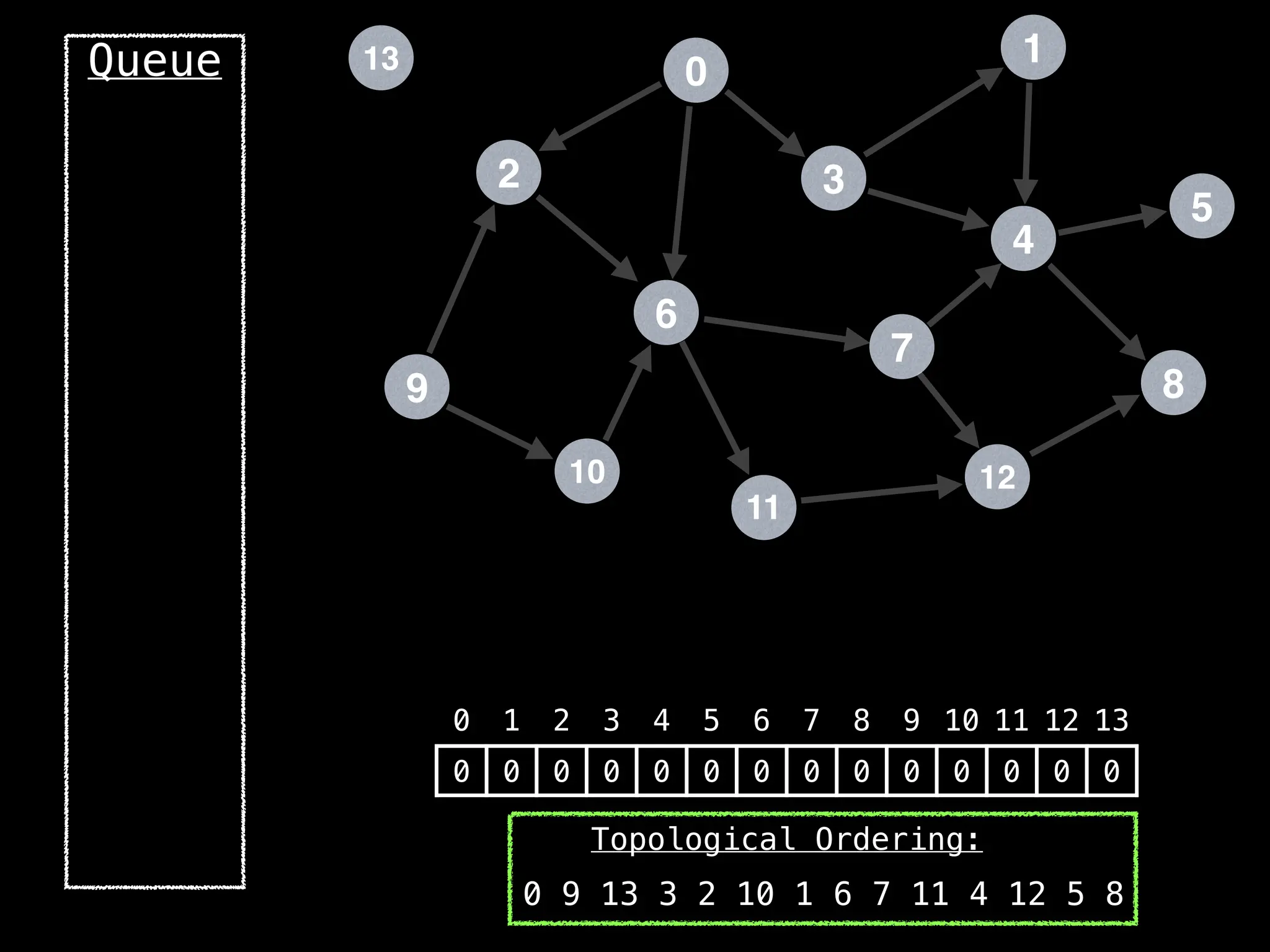
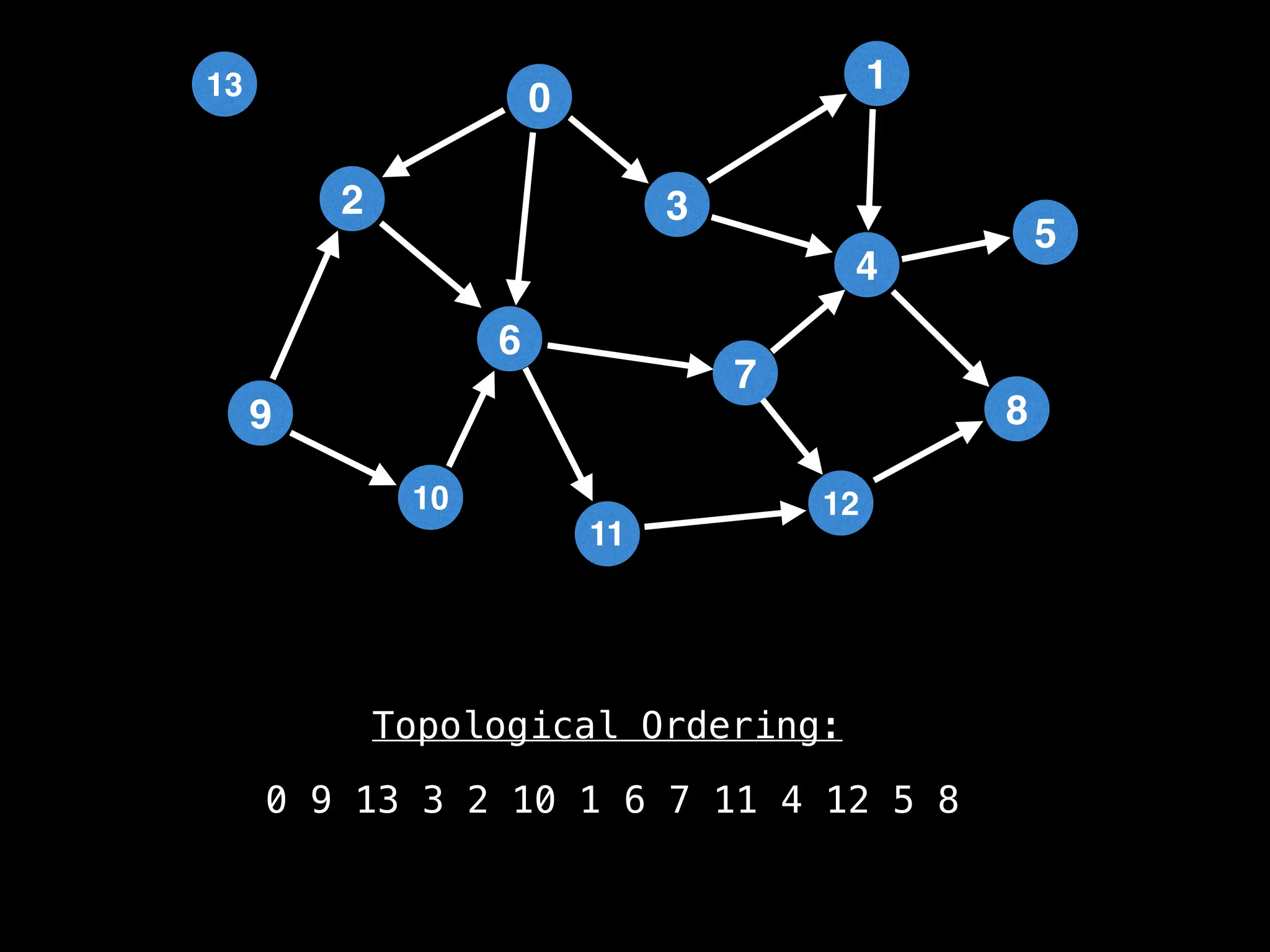
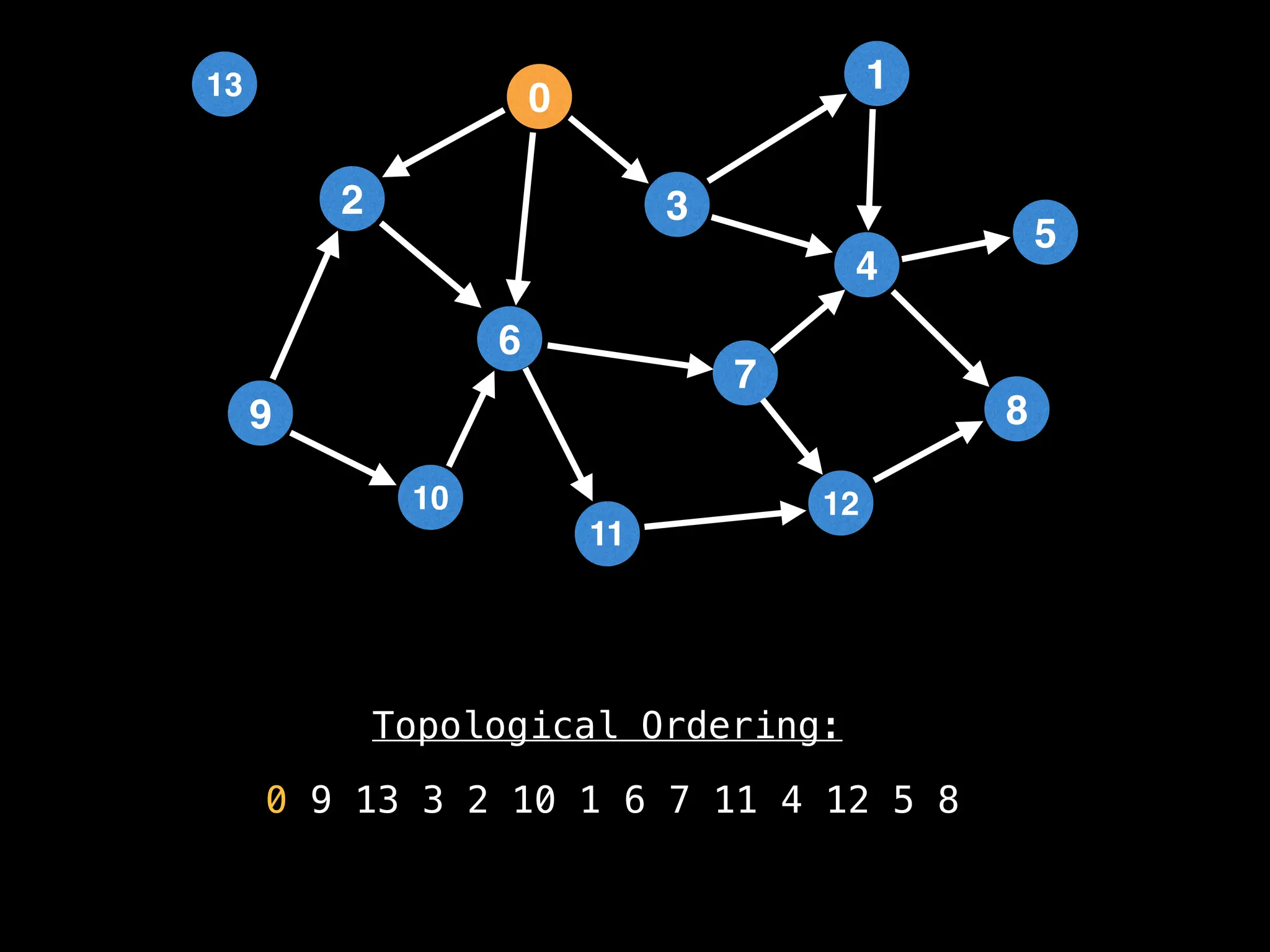
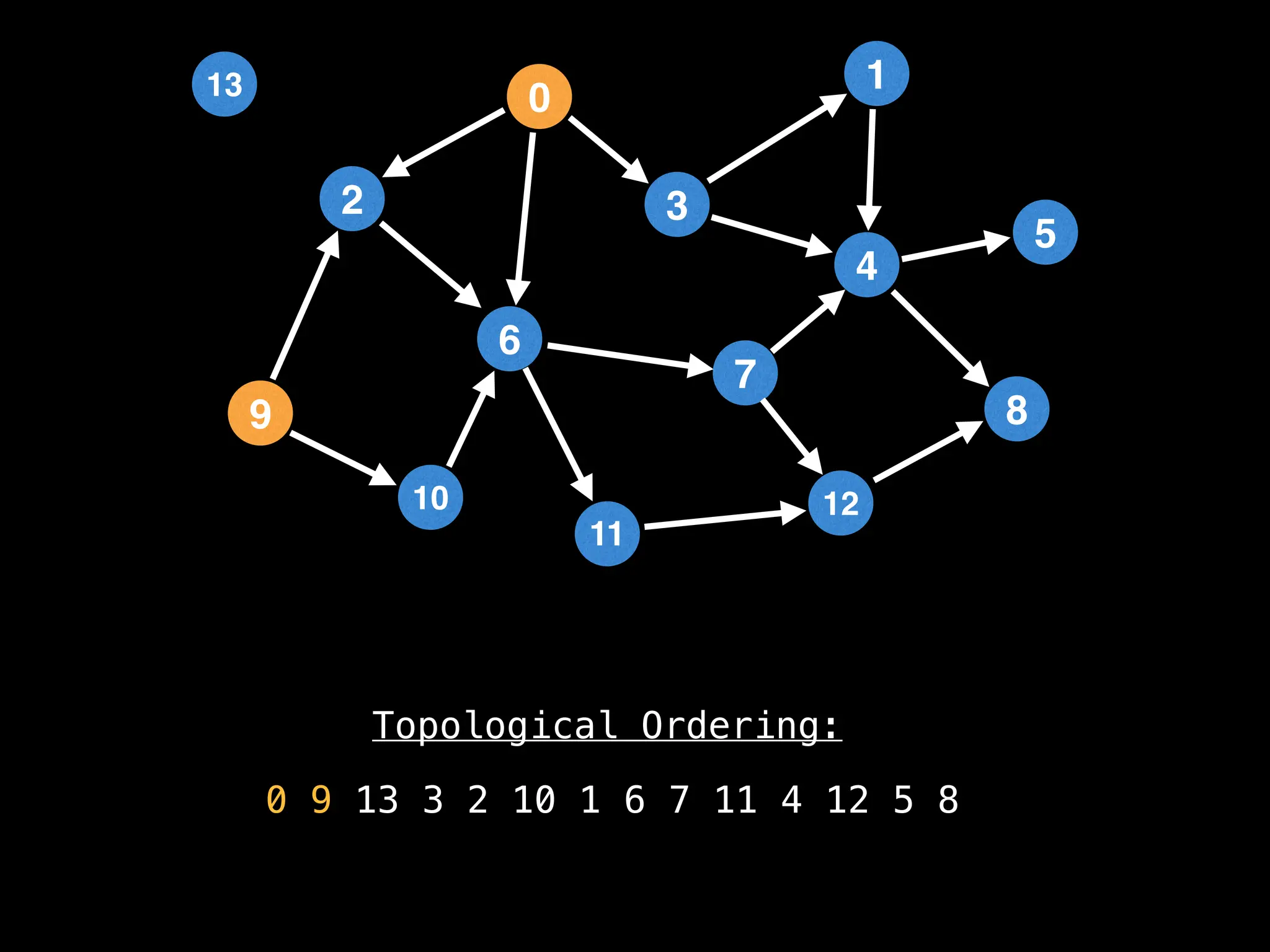
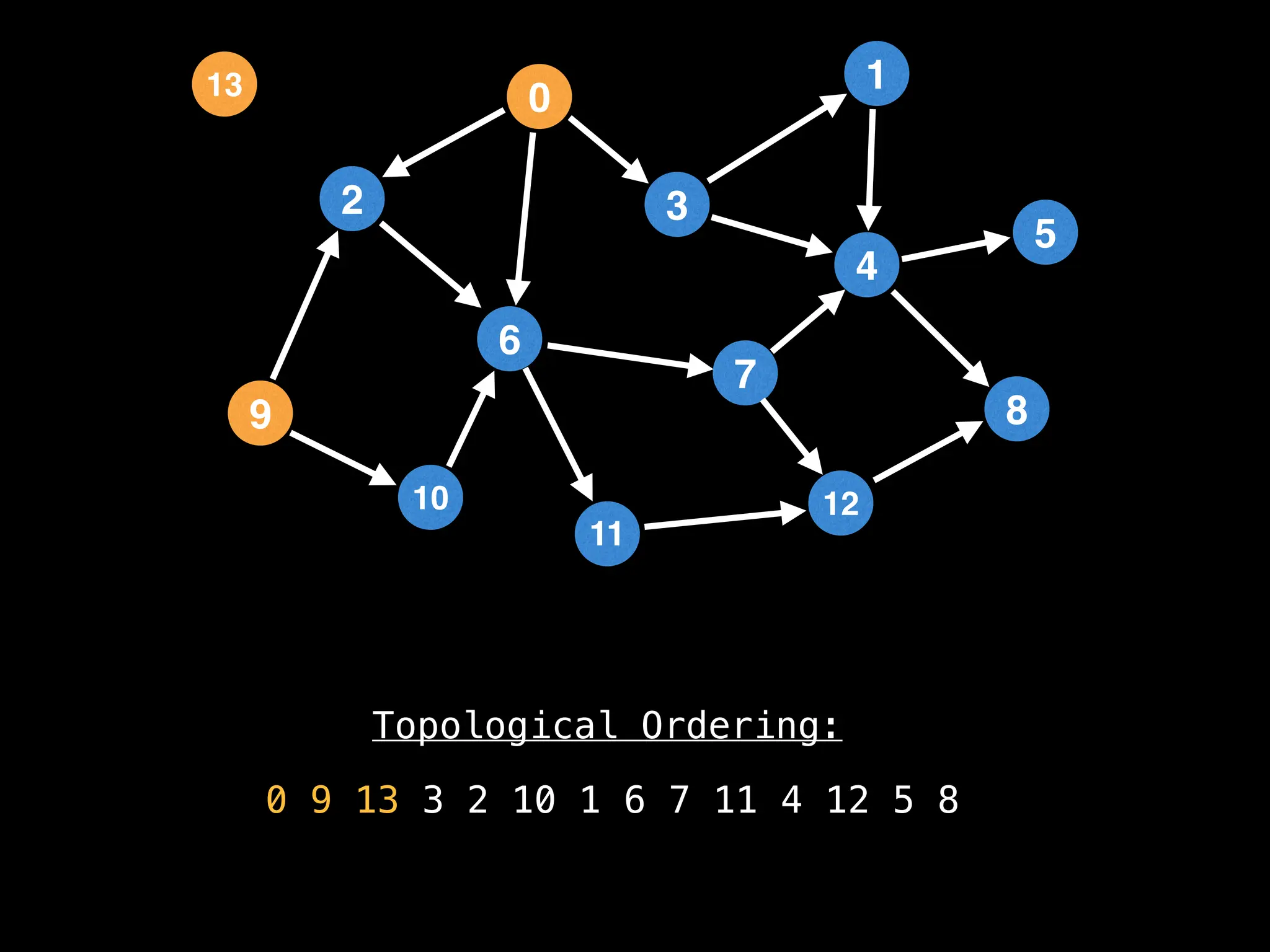
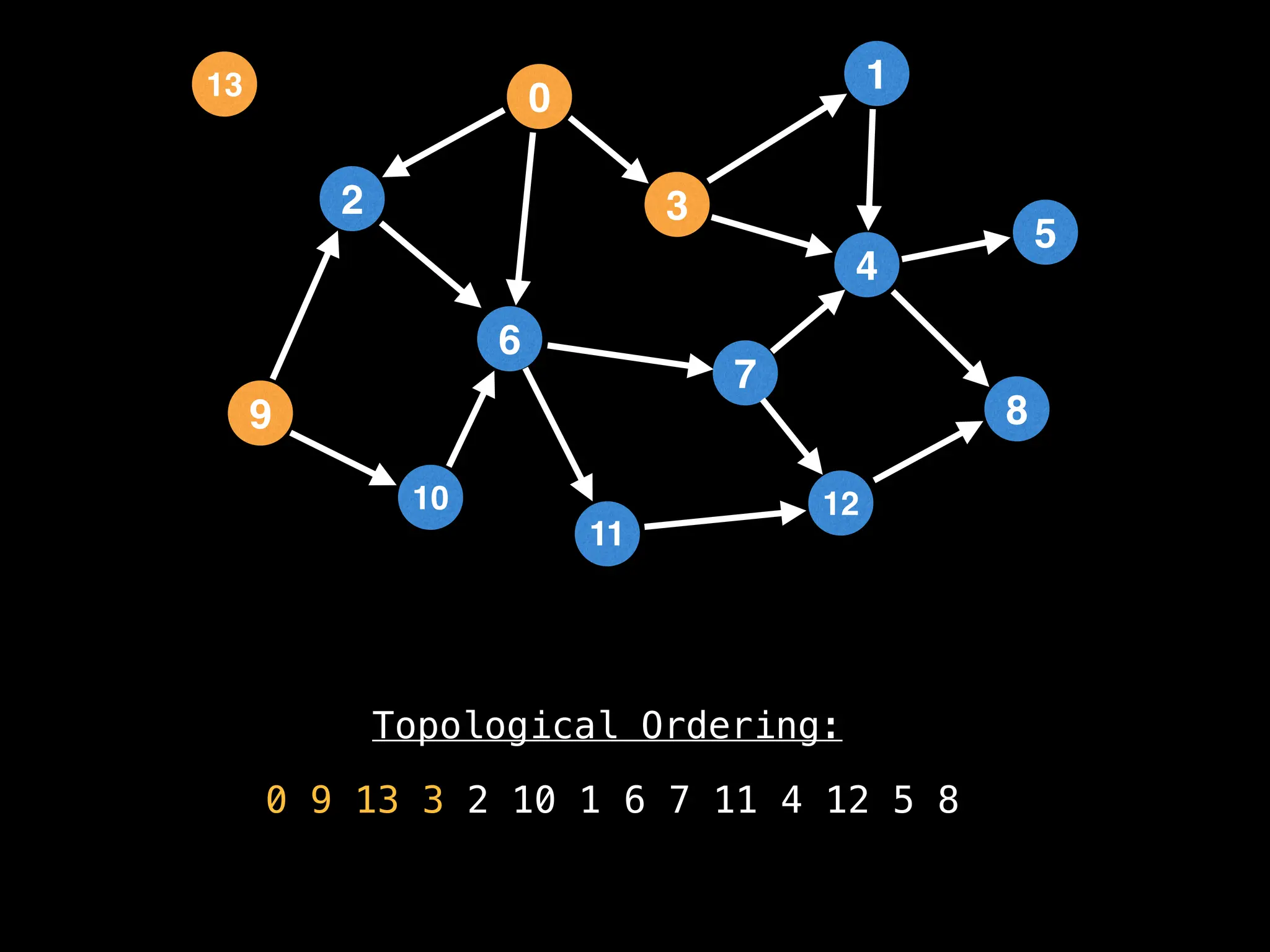
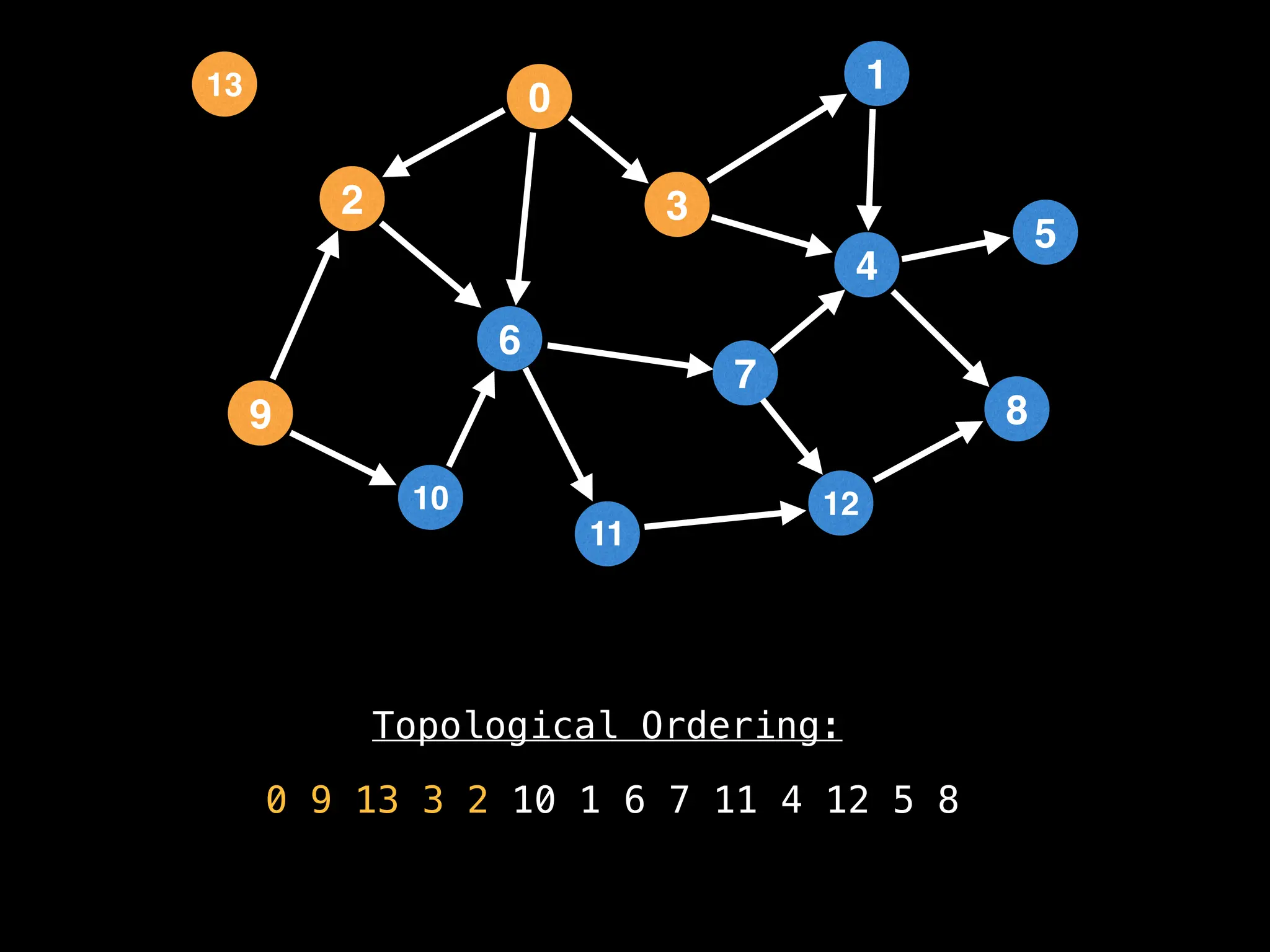
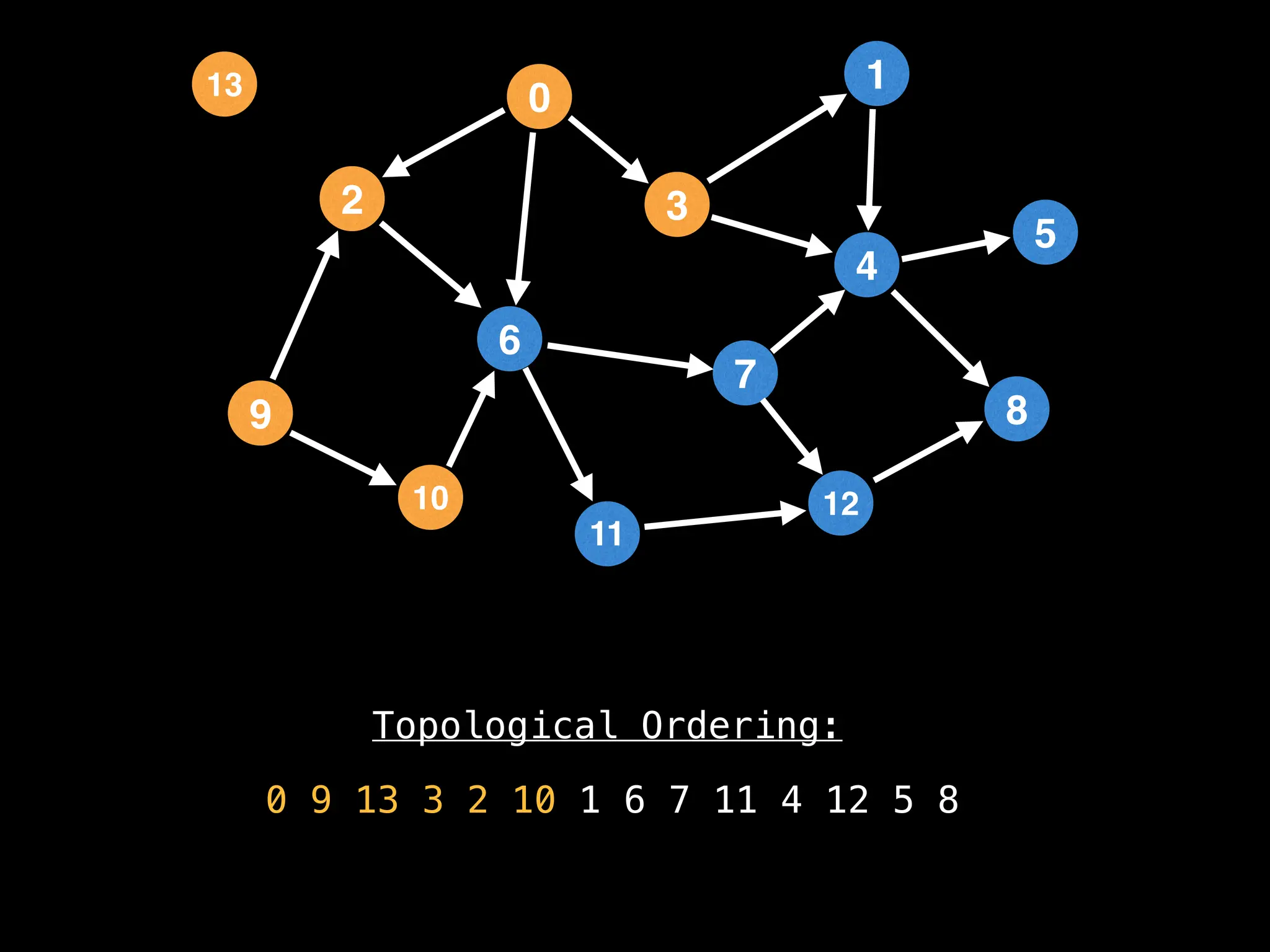
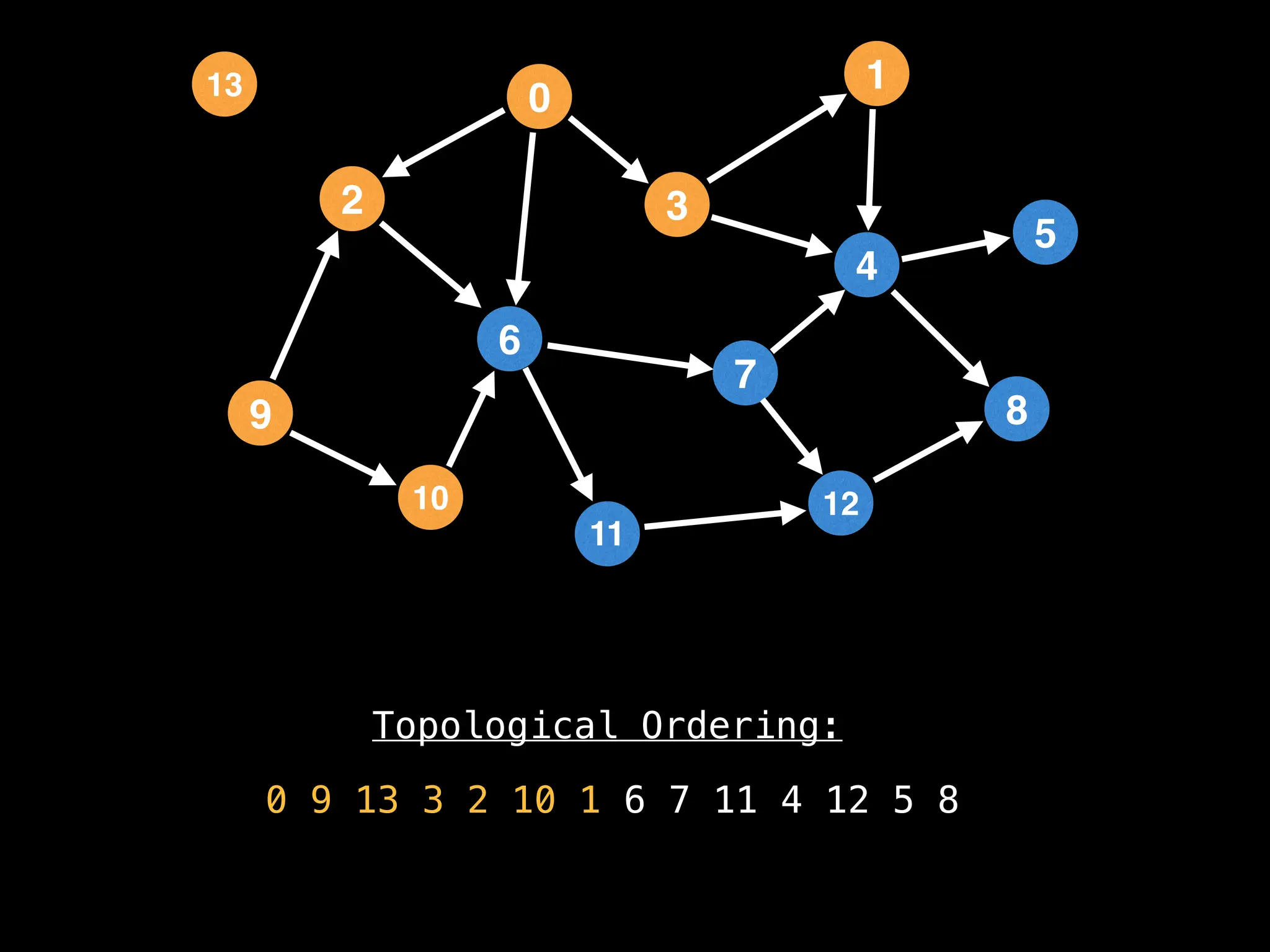
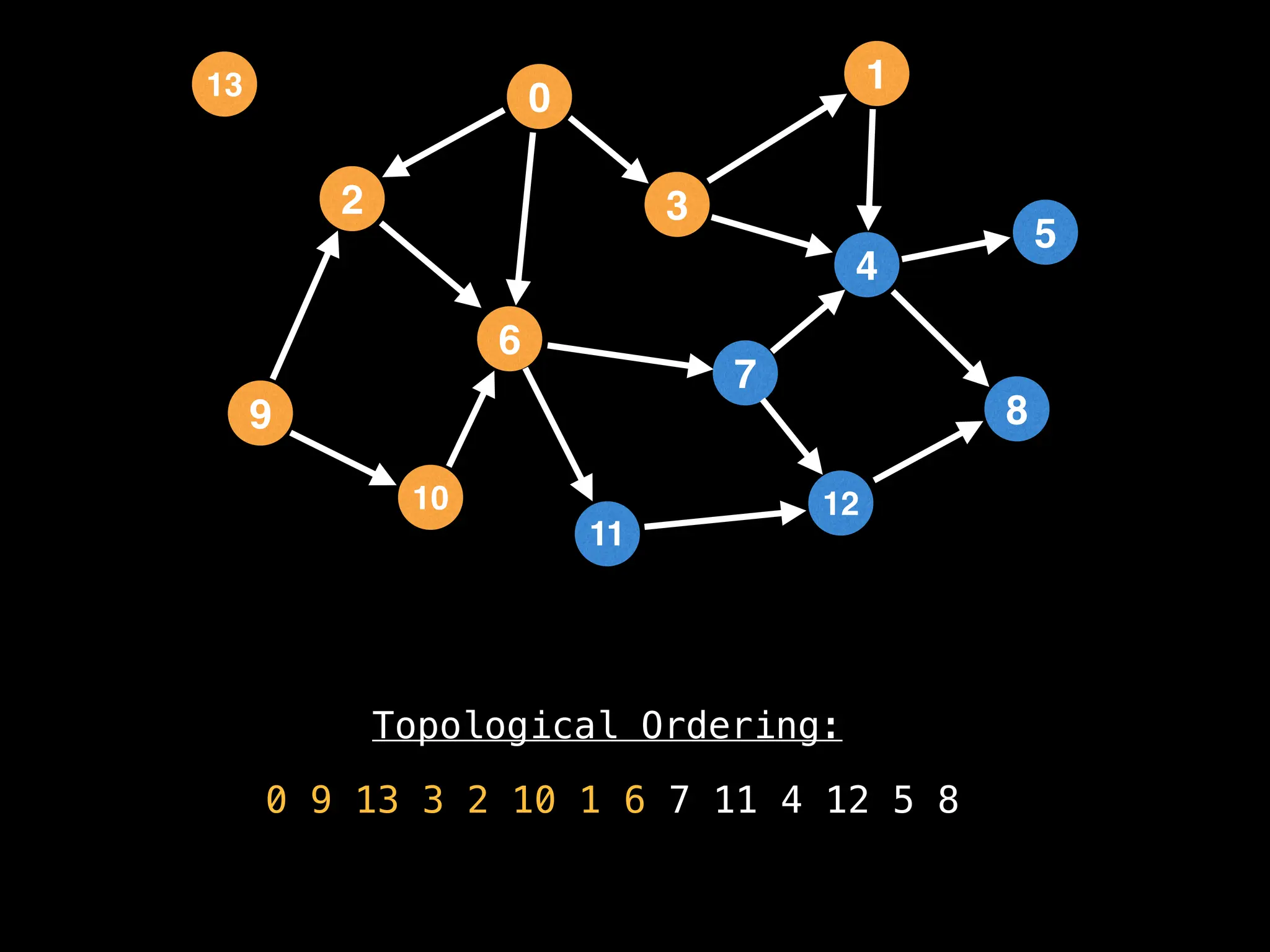
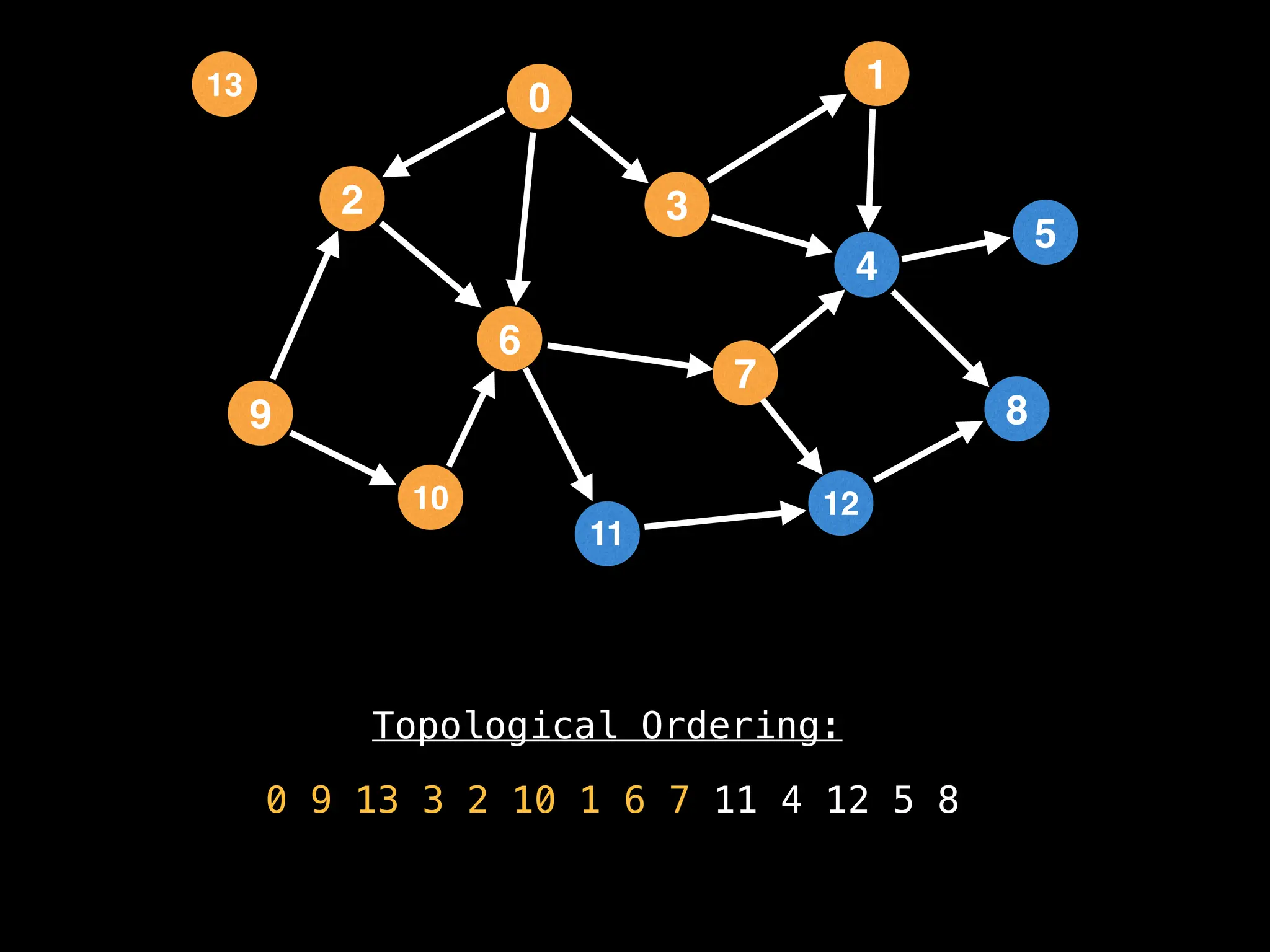
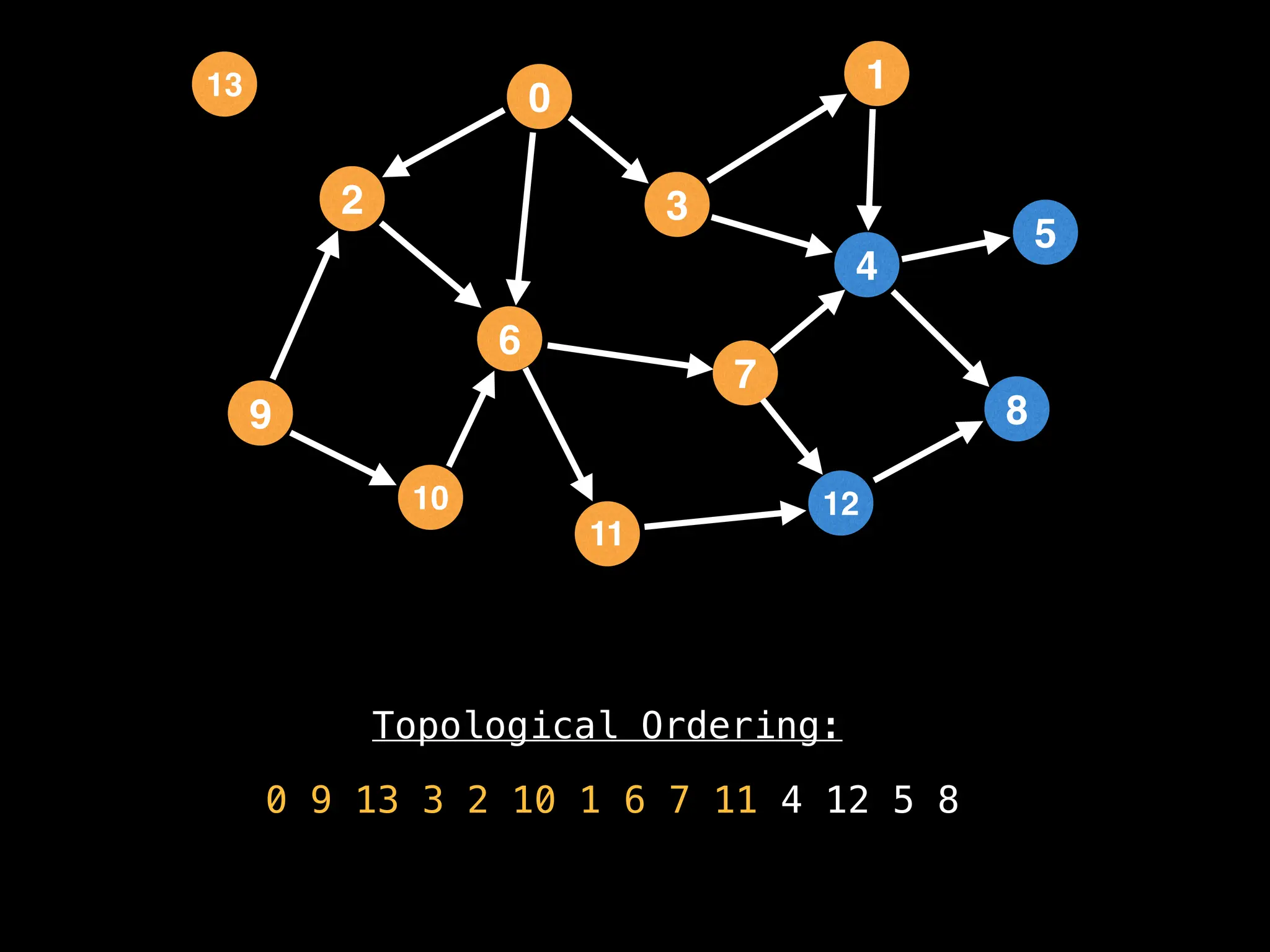
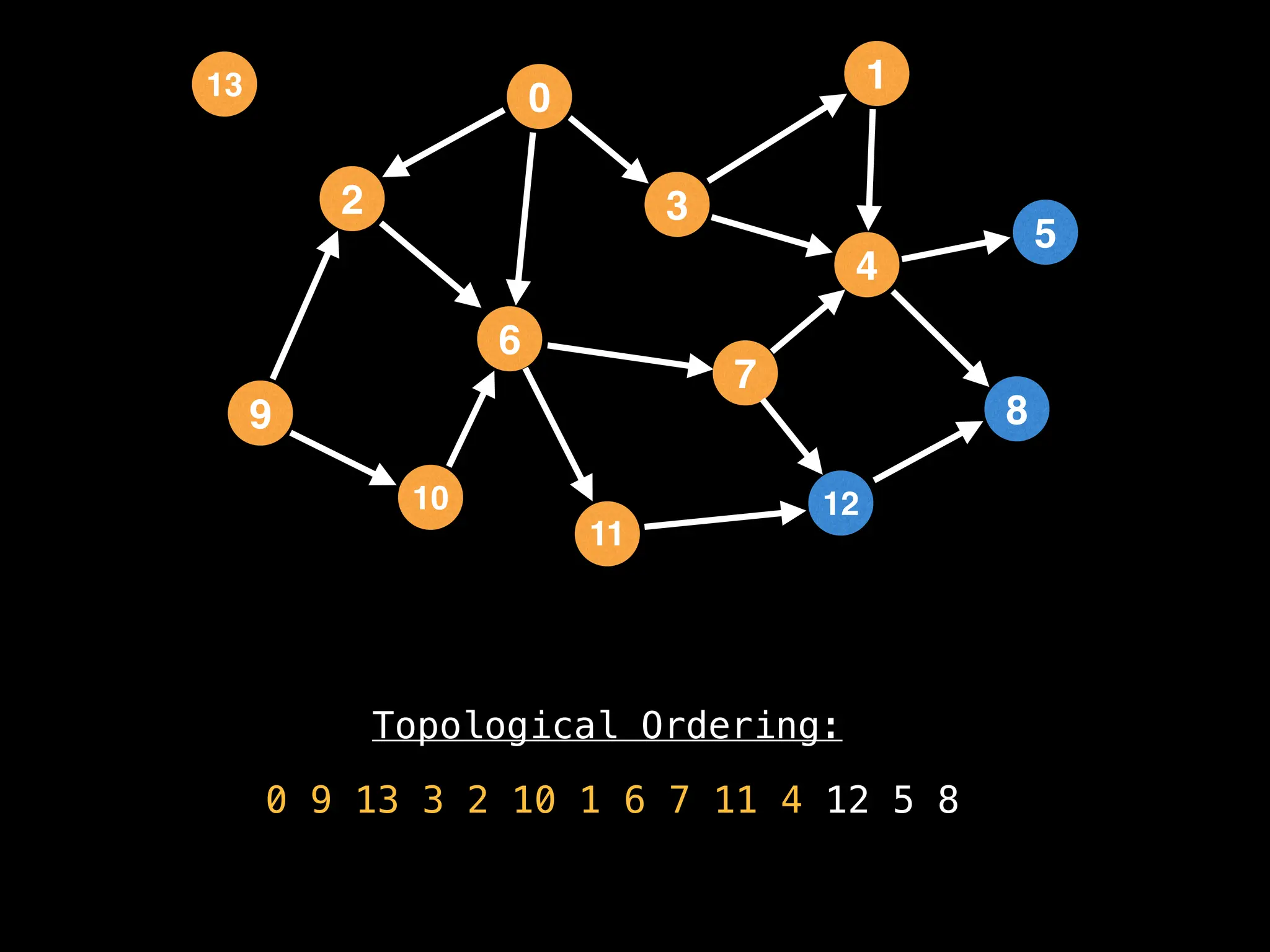
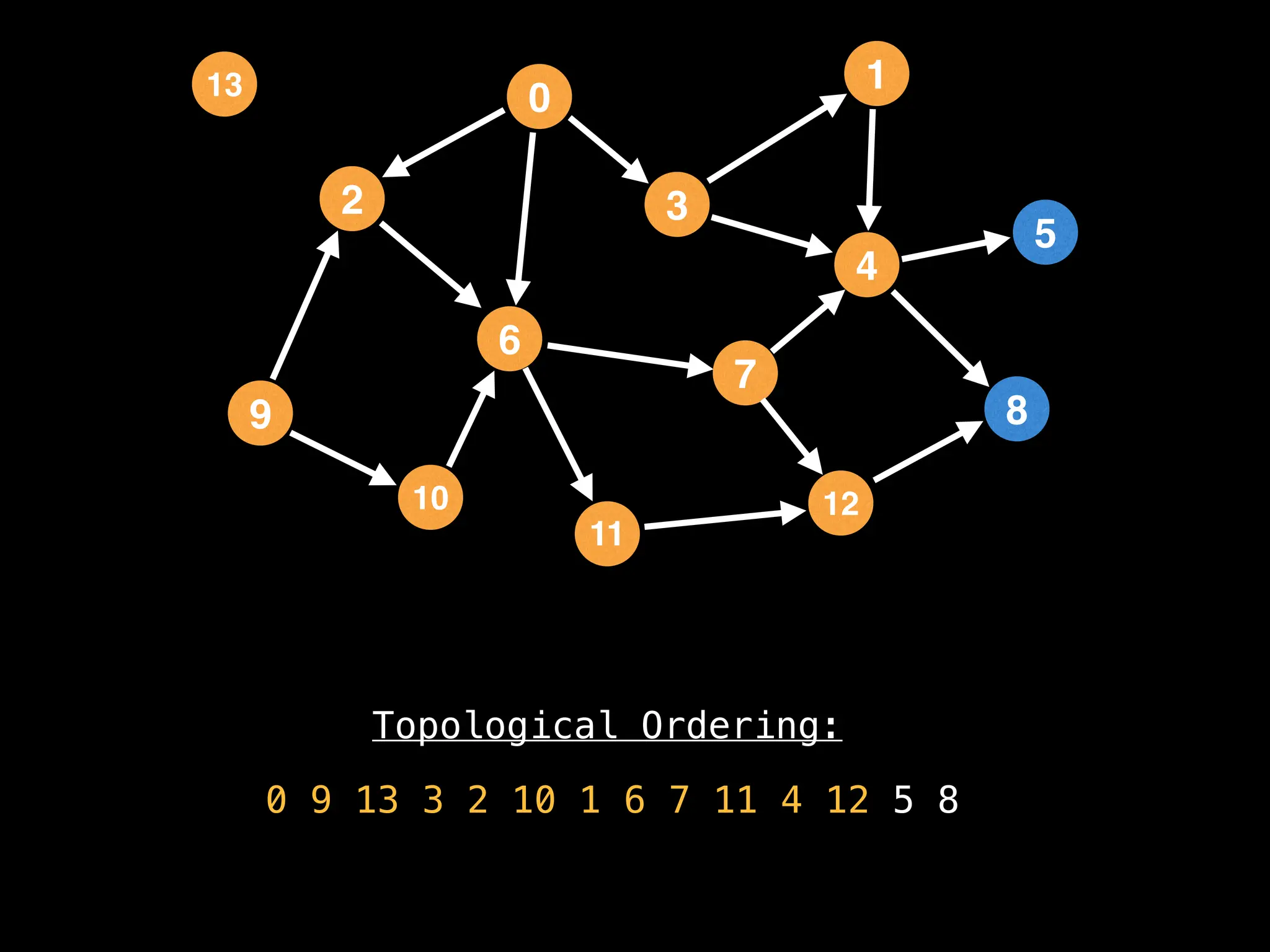
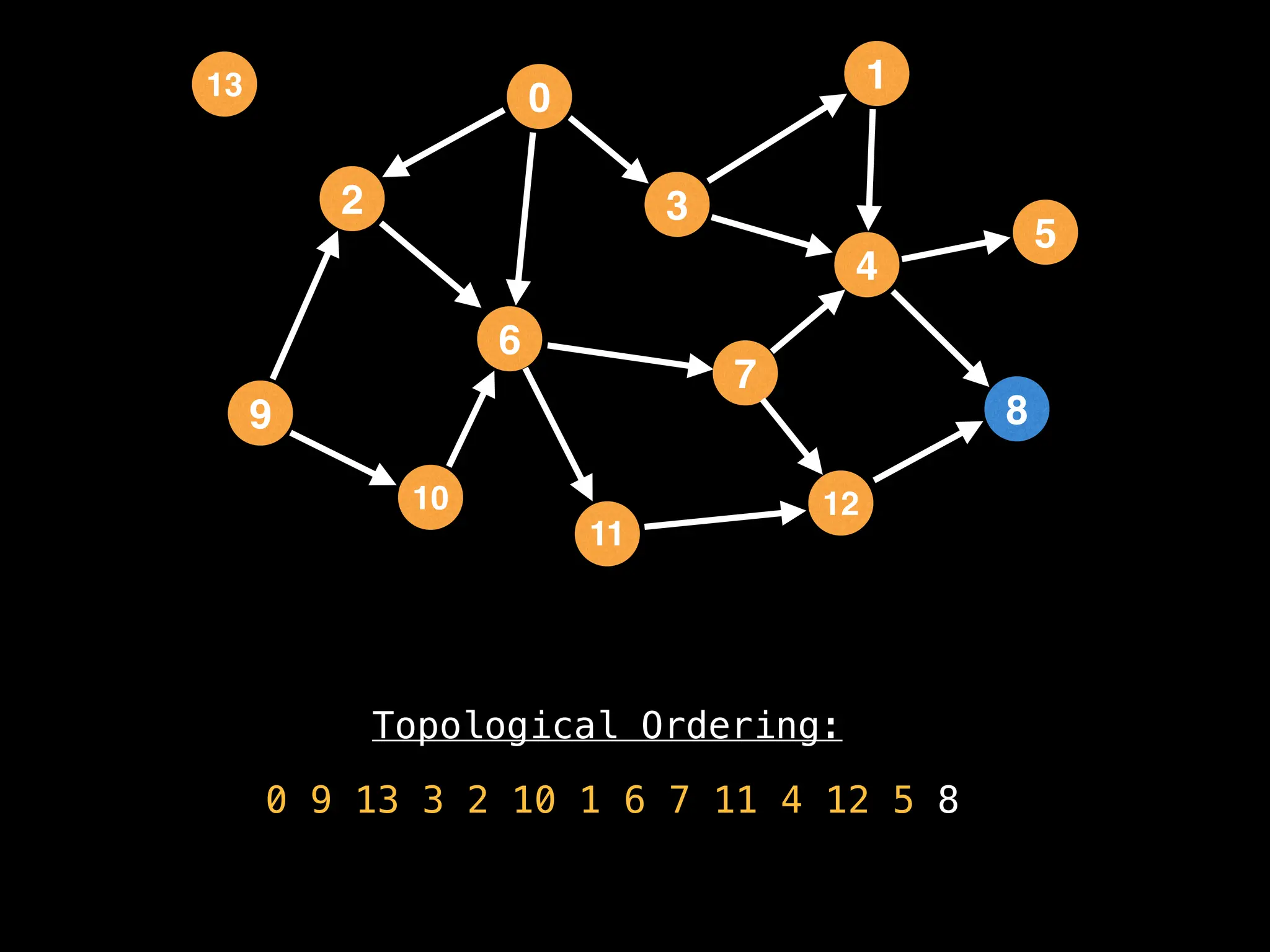
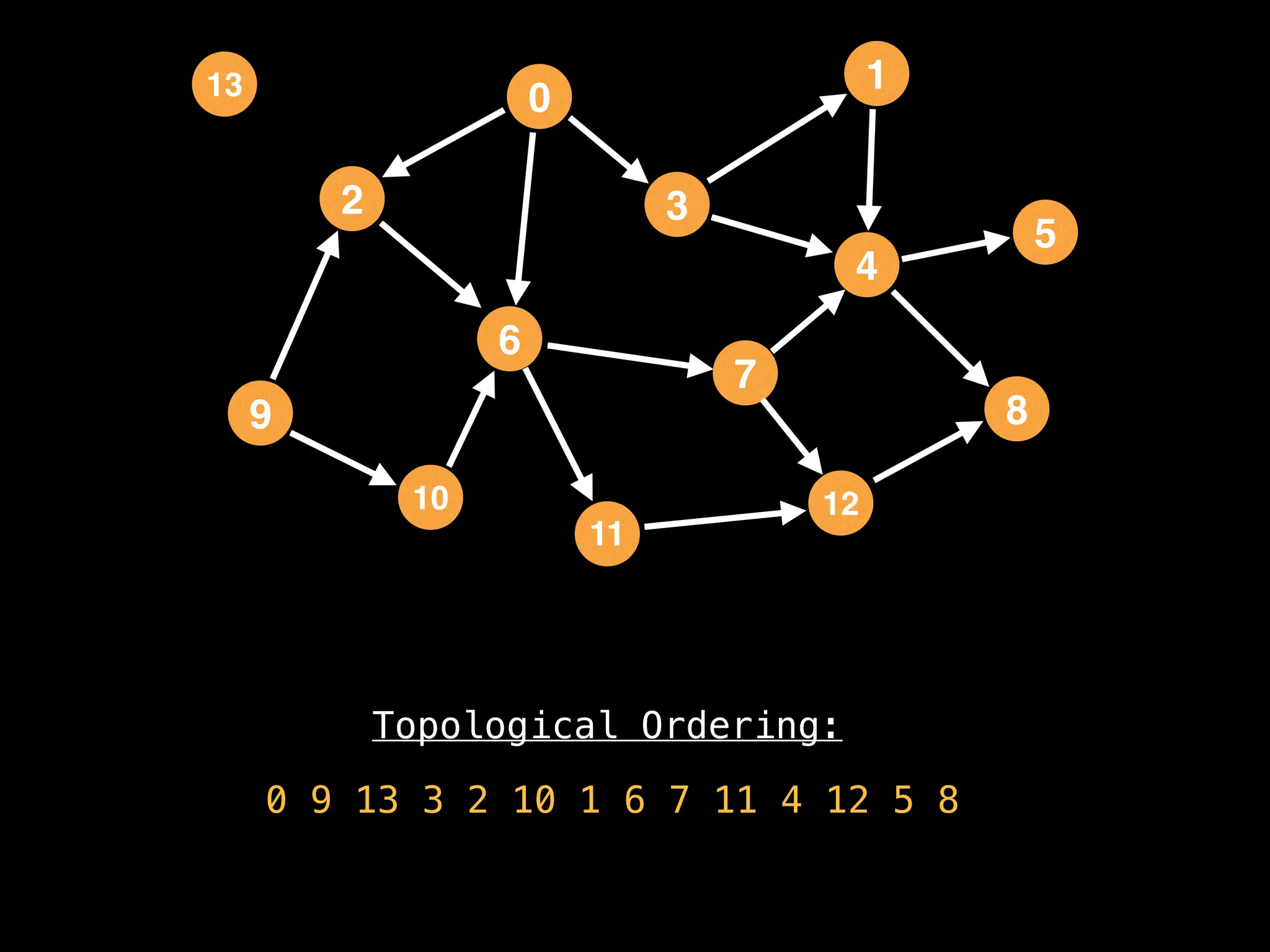
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-501-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-502-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-503-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-504-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-505-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-506-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-507-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-508-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-509-2048.jpg)
![# `g` is a directed acyclic graph represented as an adjacency list.
function FindTopologicalOrdering(g):
n = g.size()
in_degree = [0,0,…,0,0] # size n
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
for (to in g[i]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] + 1
# `q` always contains the set nodes with no incoming edges.
q = … # empty integer queue data structure
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (in_degree[i] == 0):
q.enqueue(i)
index = 0
order = [0,0,…0,0] # size n
while (!q.isEmpty()):
at = q.dequeue()
order[index++] = at
for (to in g[at]):
in_degree[to] = in_degree[to] - 1
if in_degree[to] == 0:
q.enqueue(to)
if index != n:
return null # Oops, graph contains a cycle
return order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-510-2048.jpg)

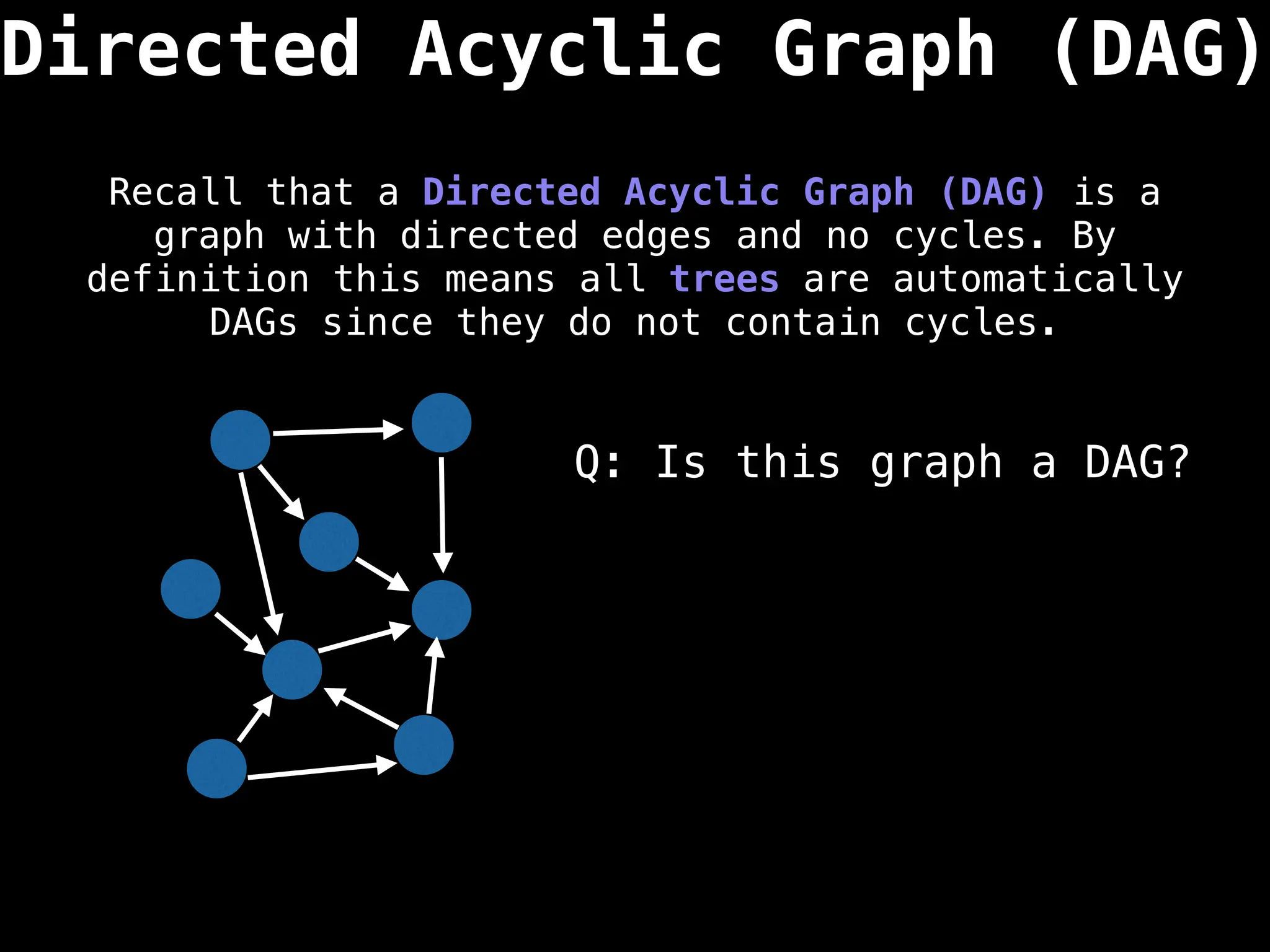
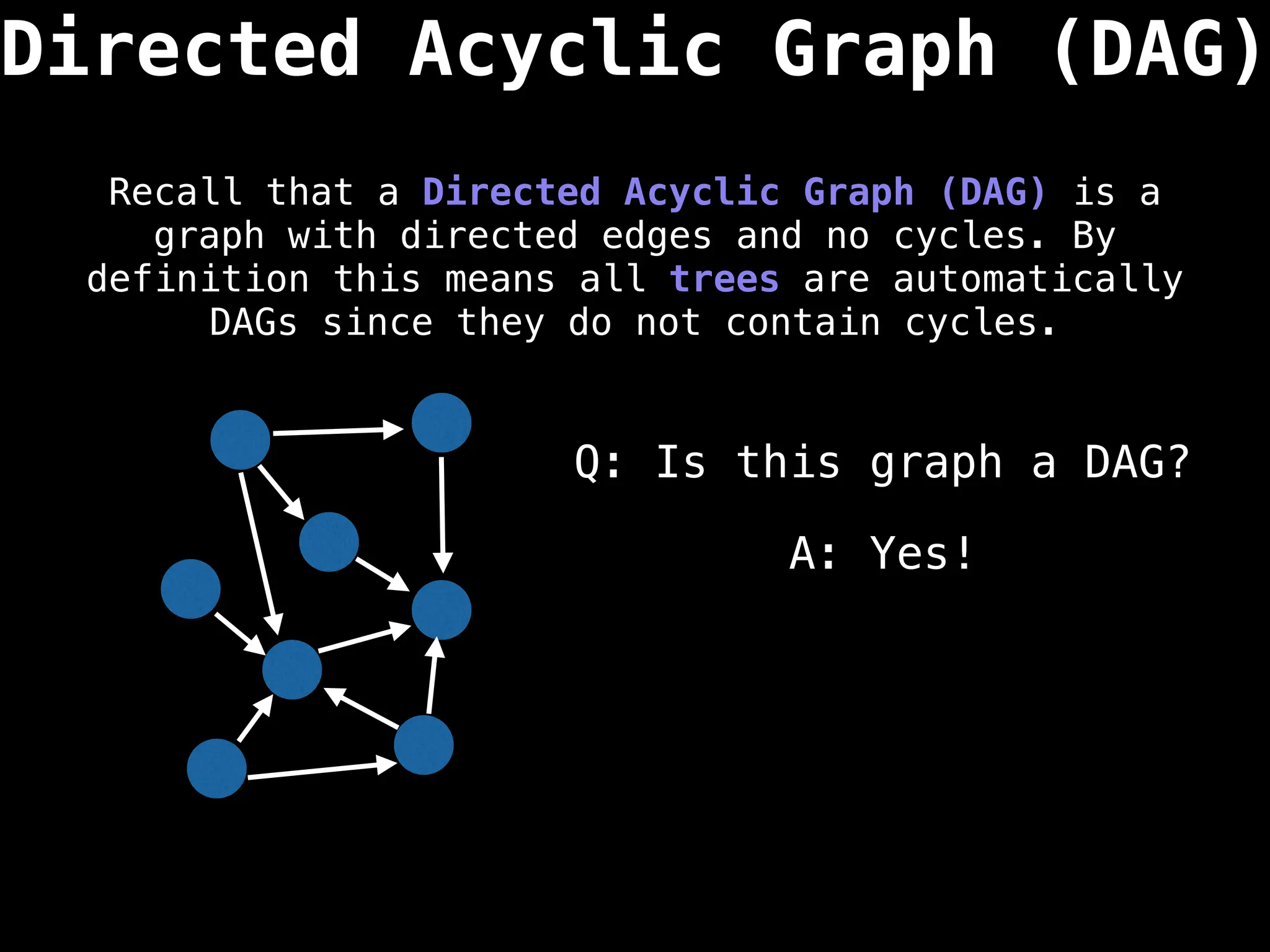
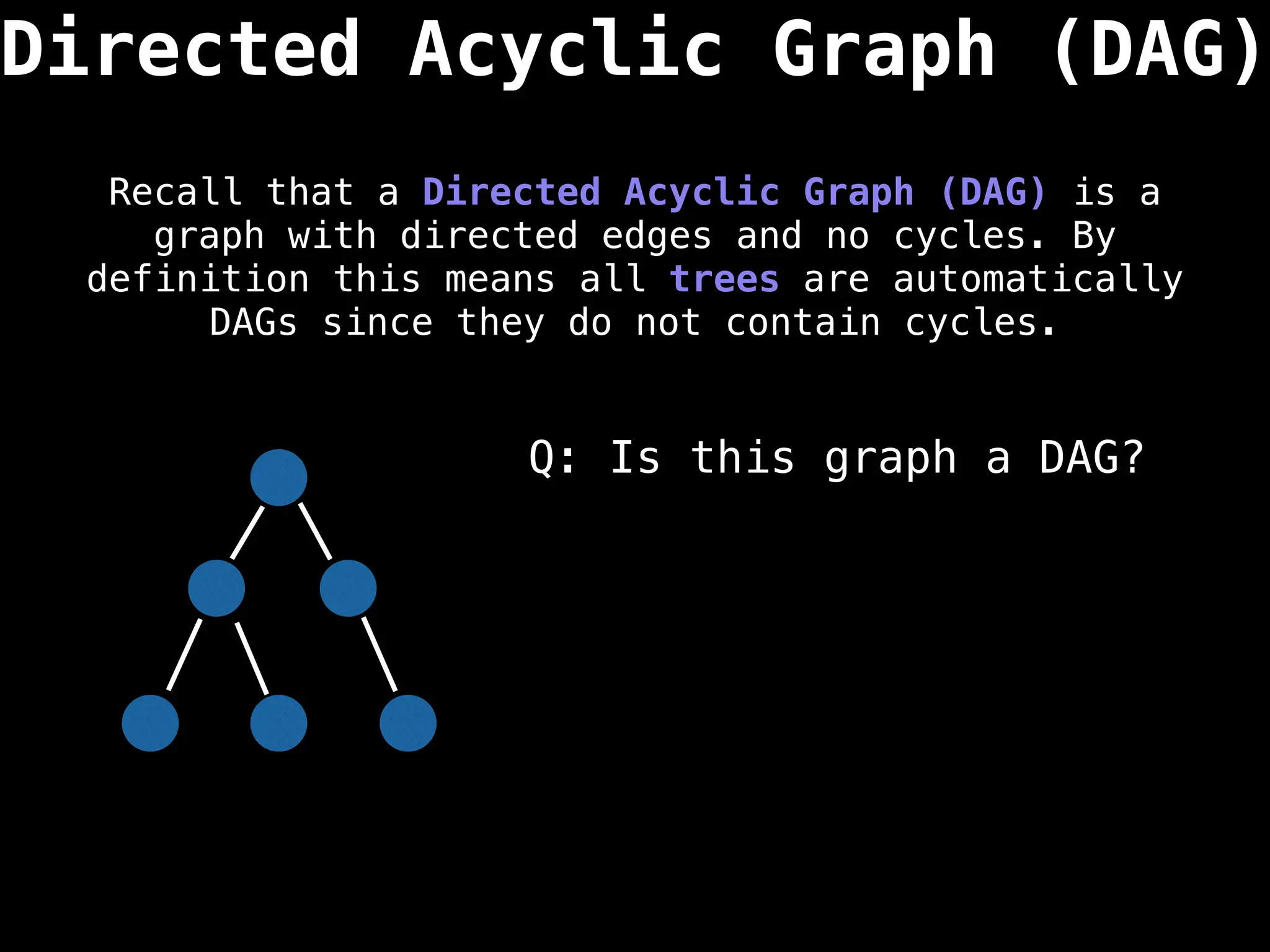
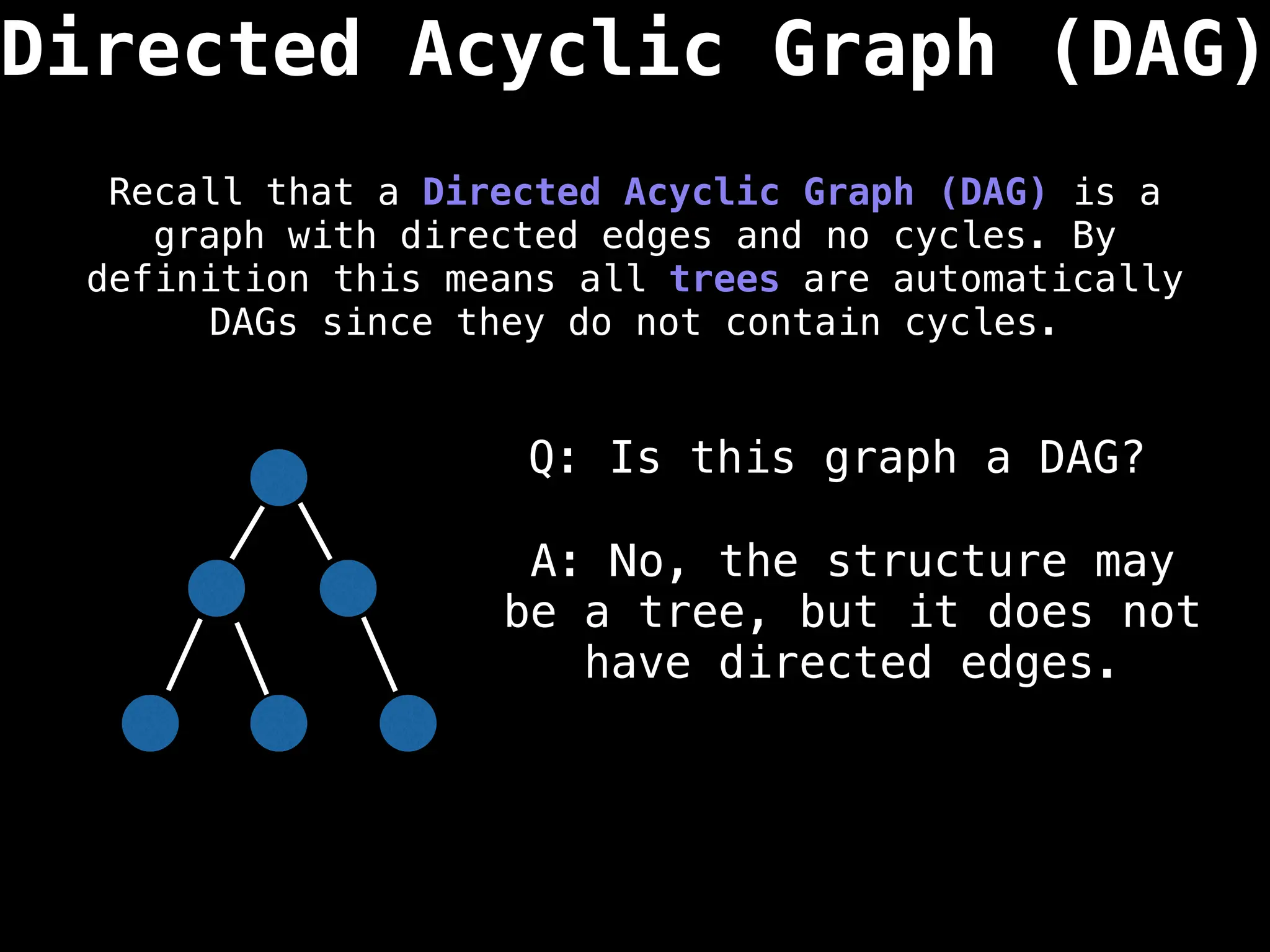
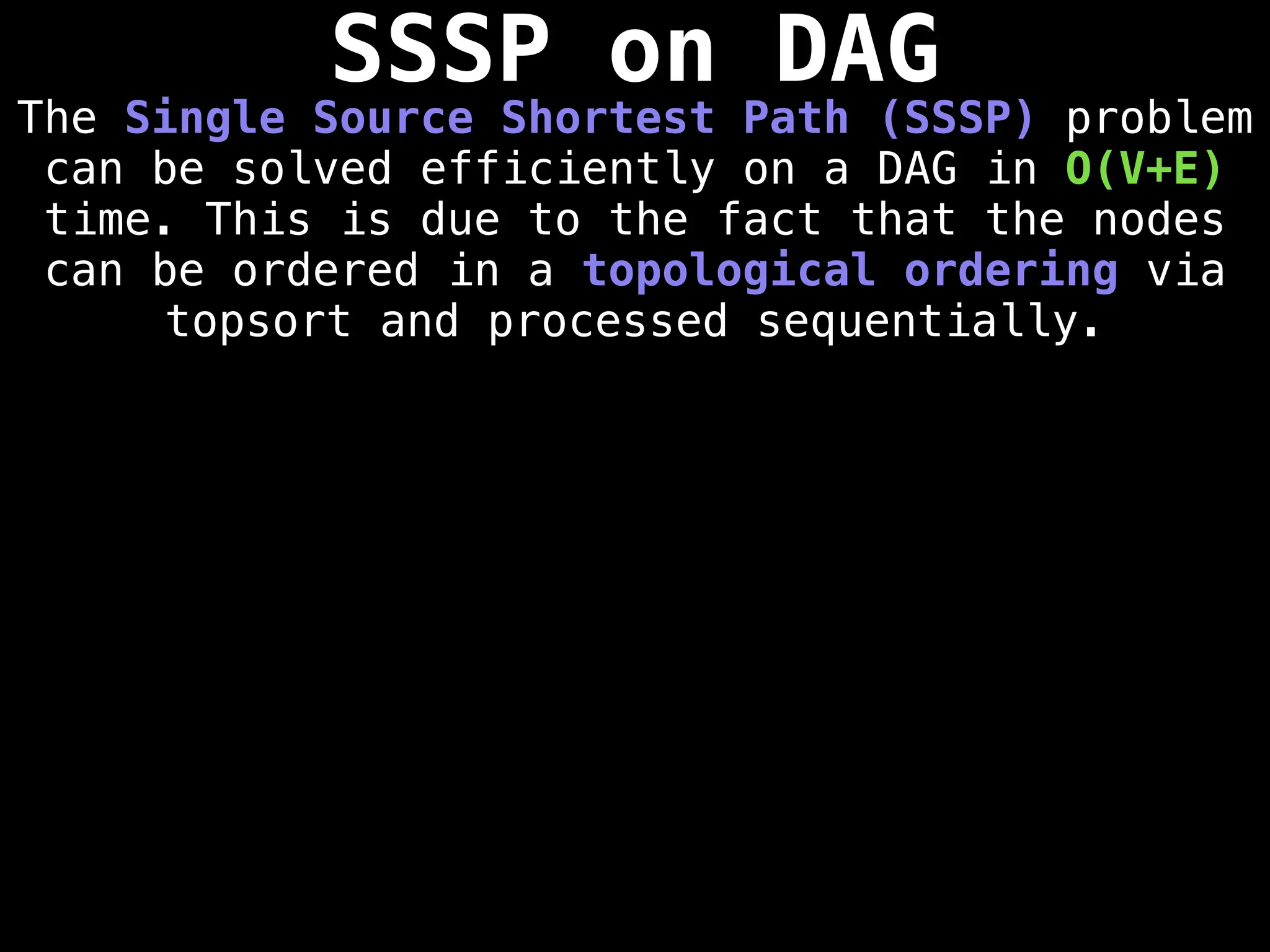
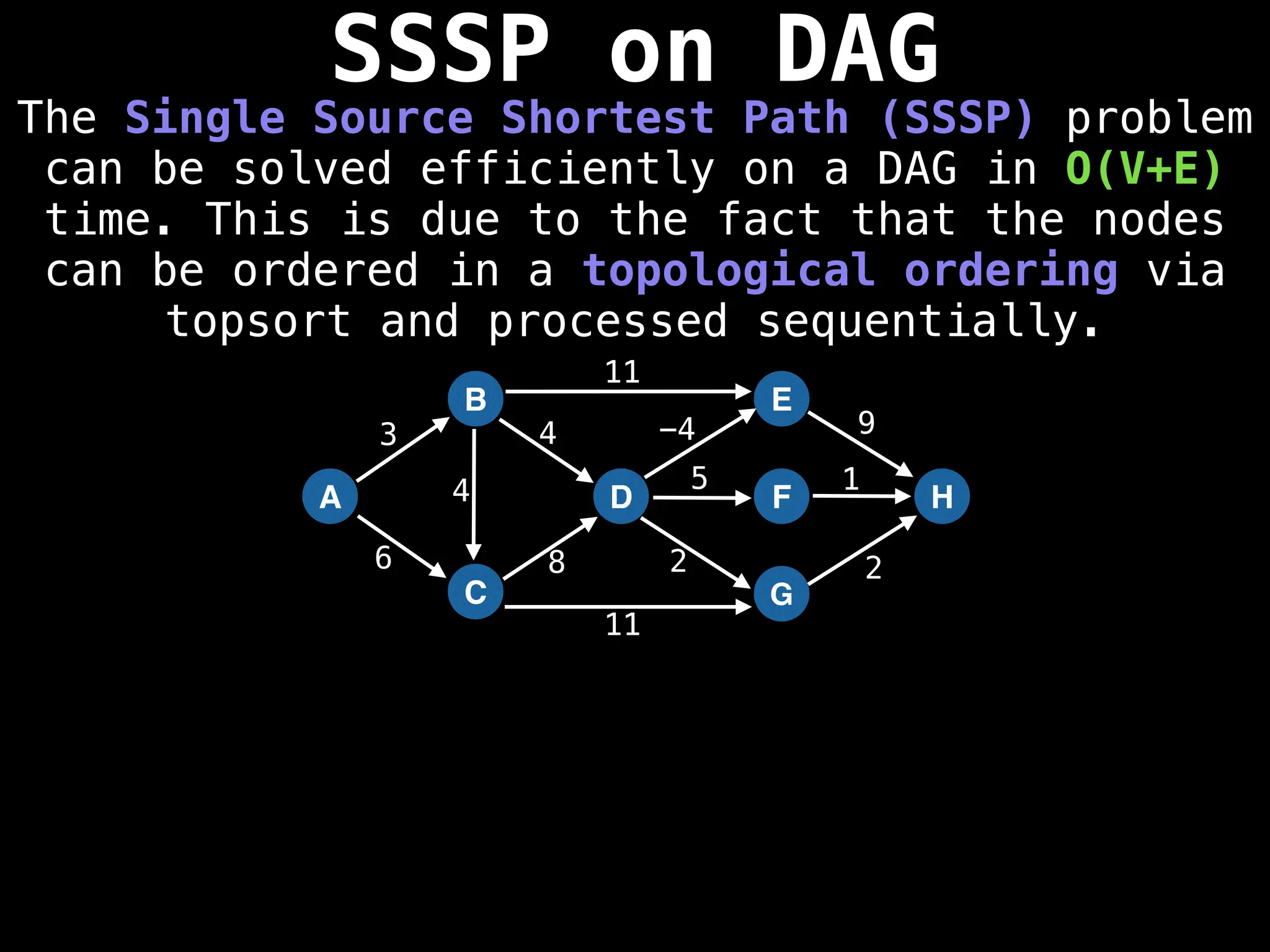
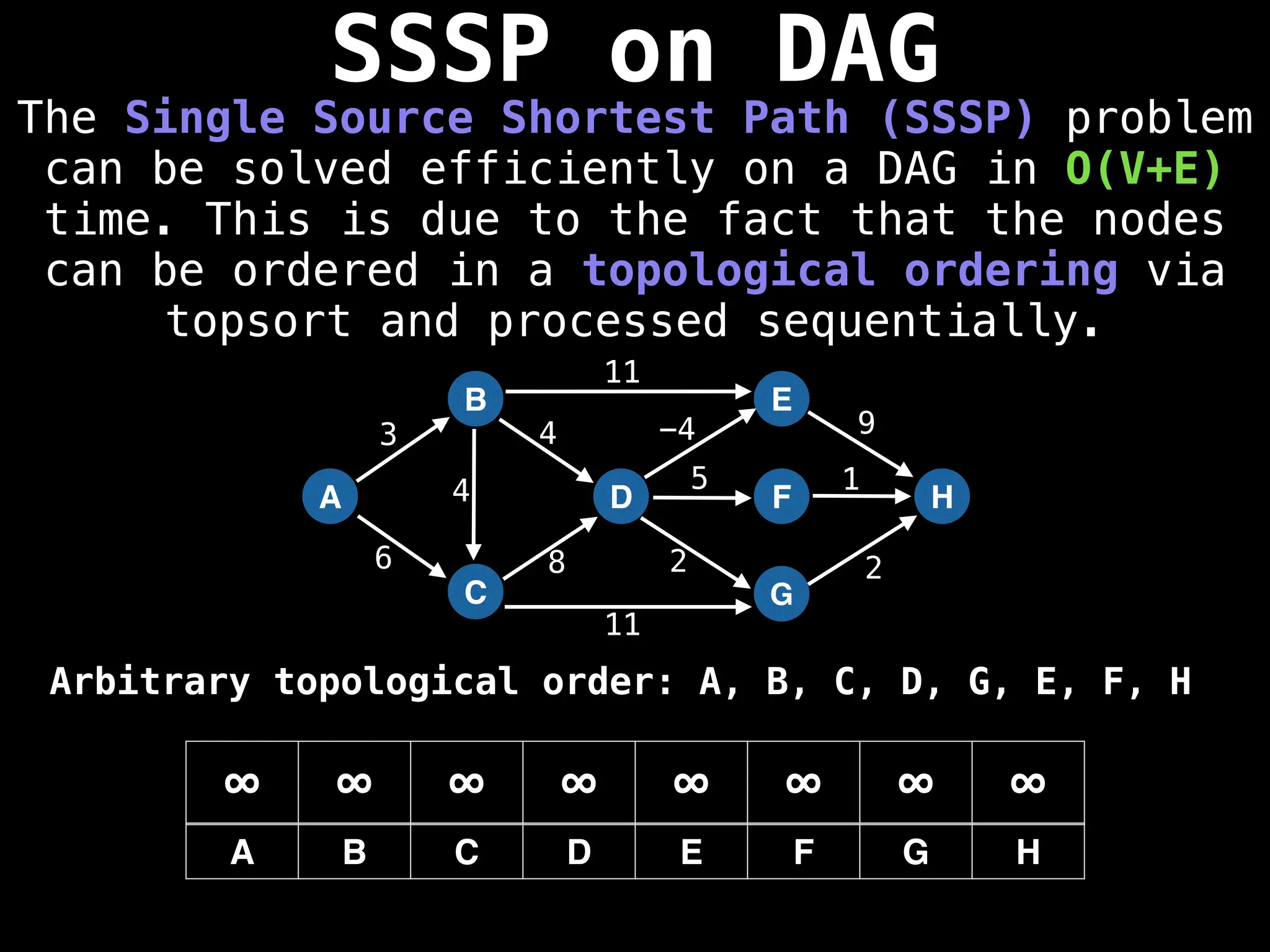
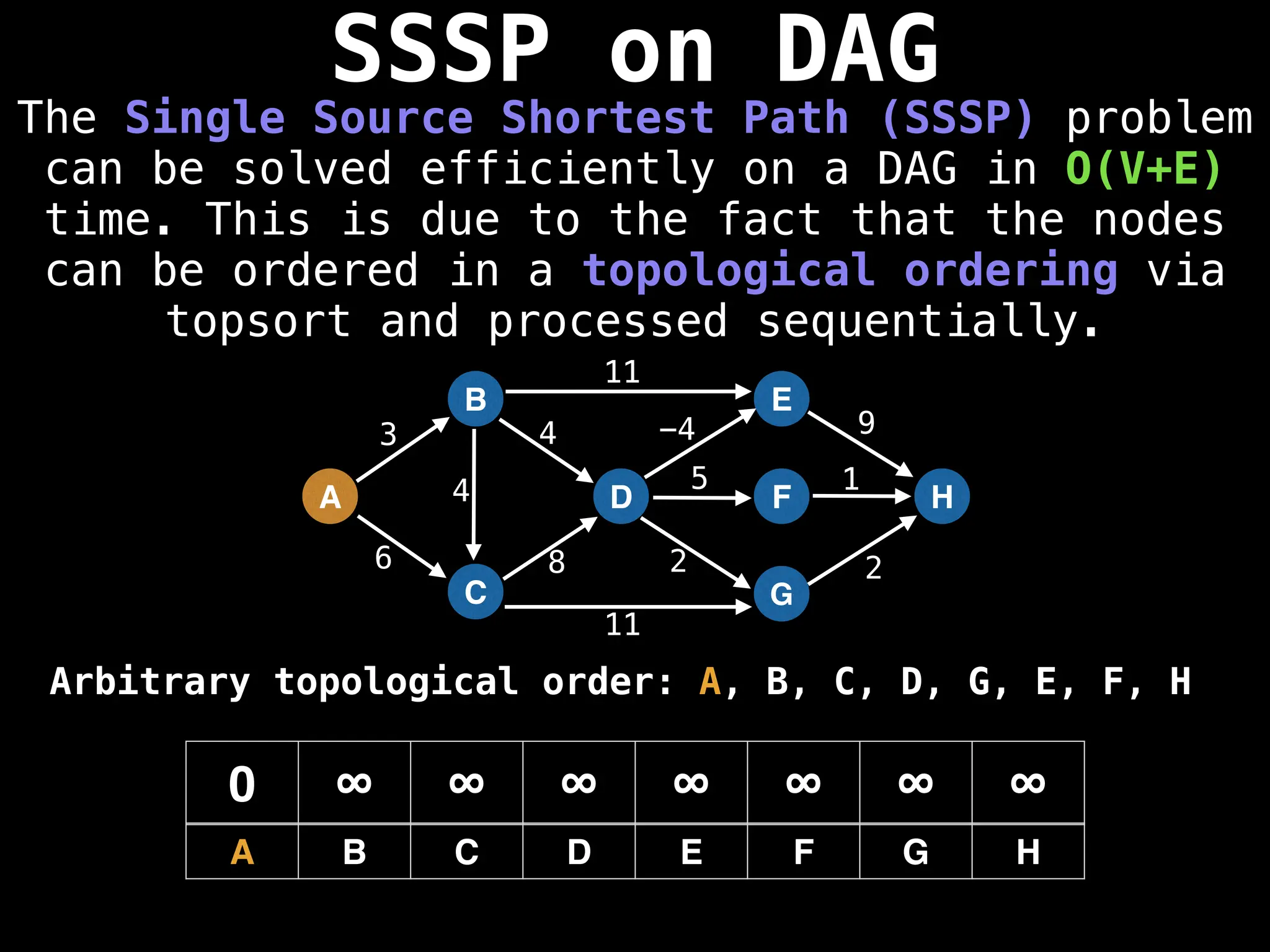
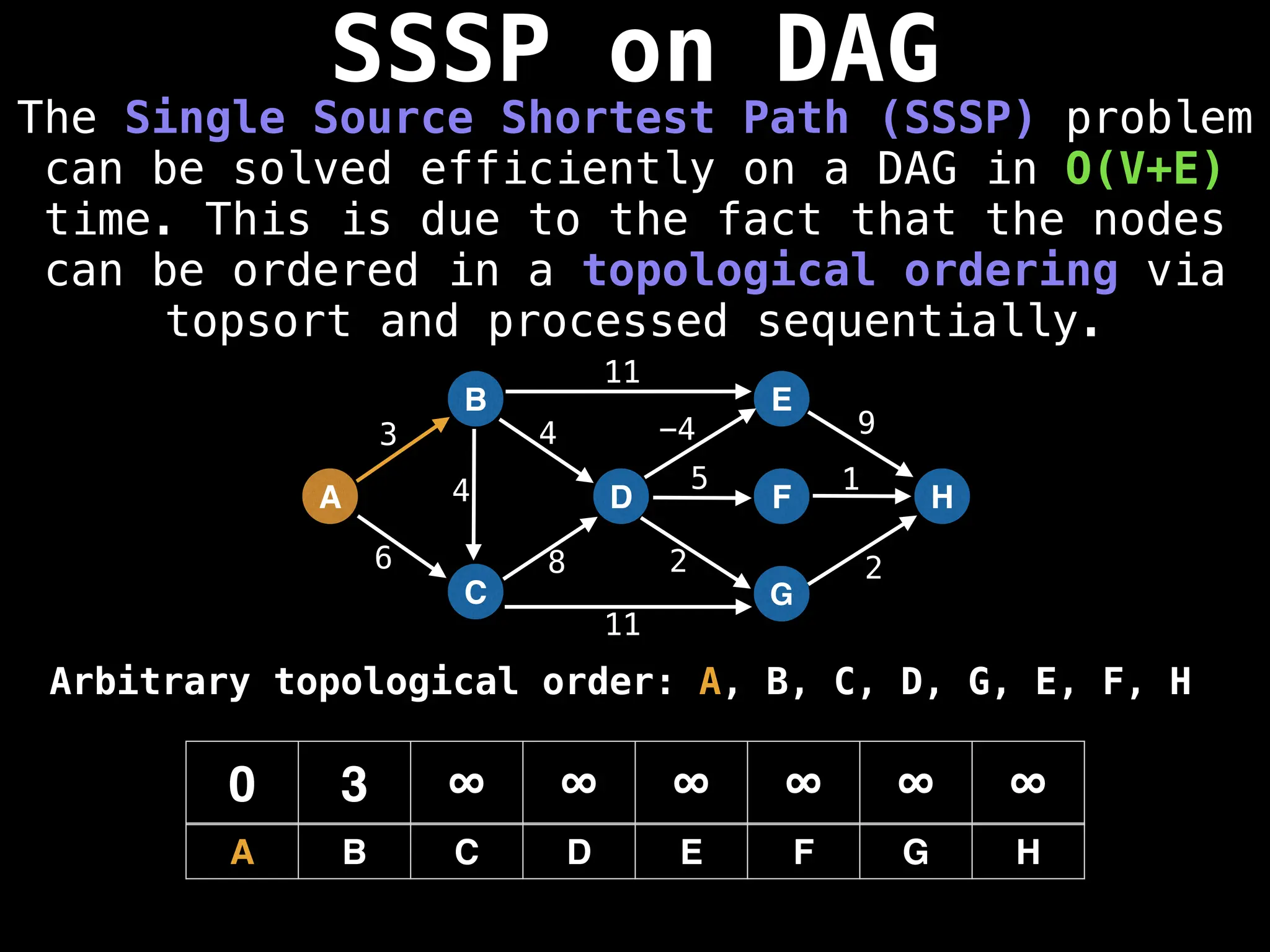
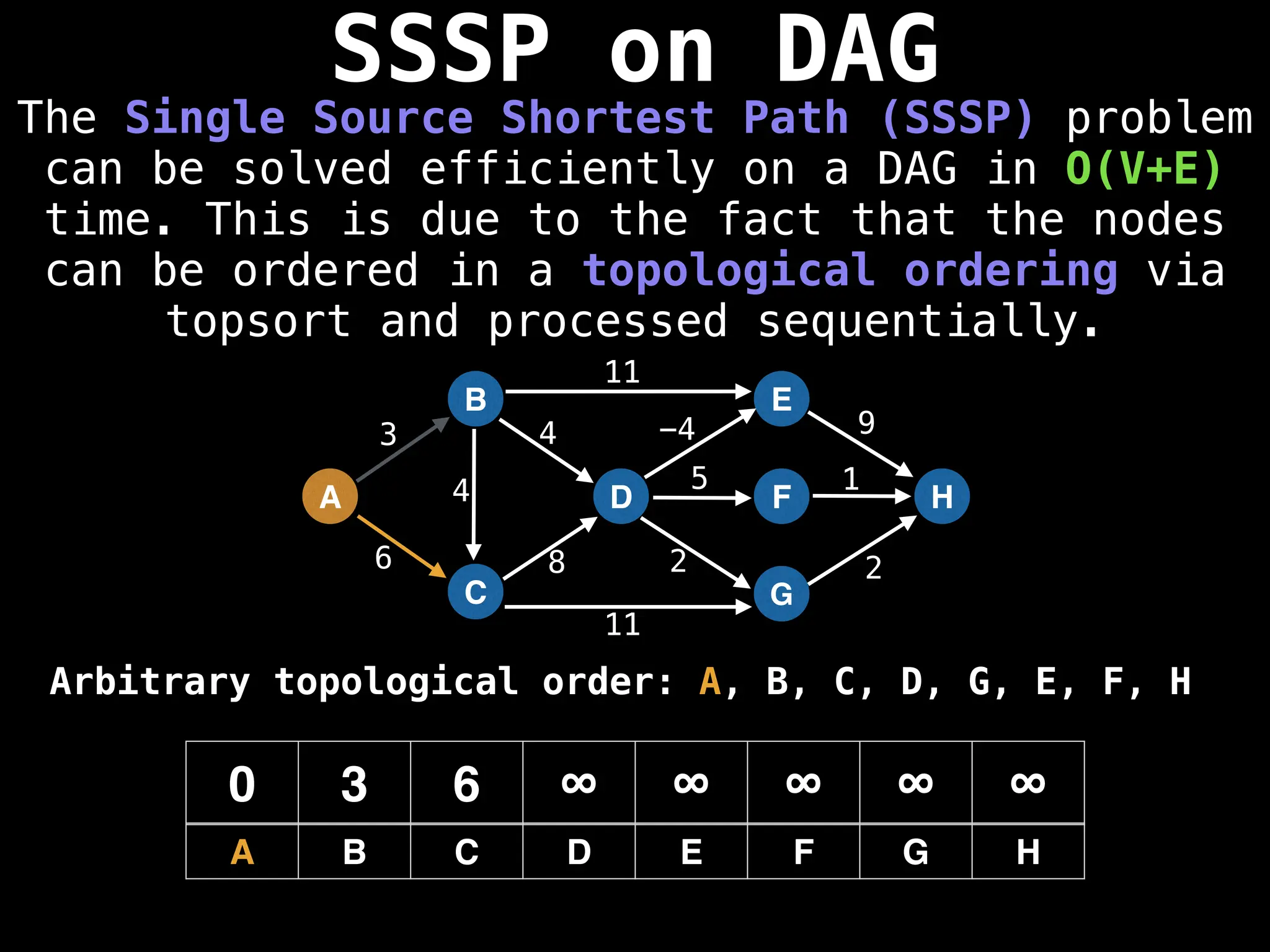
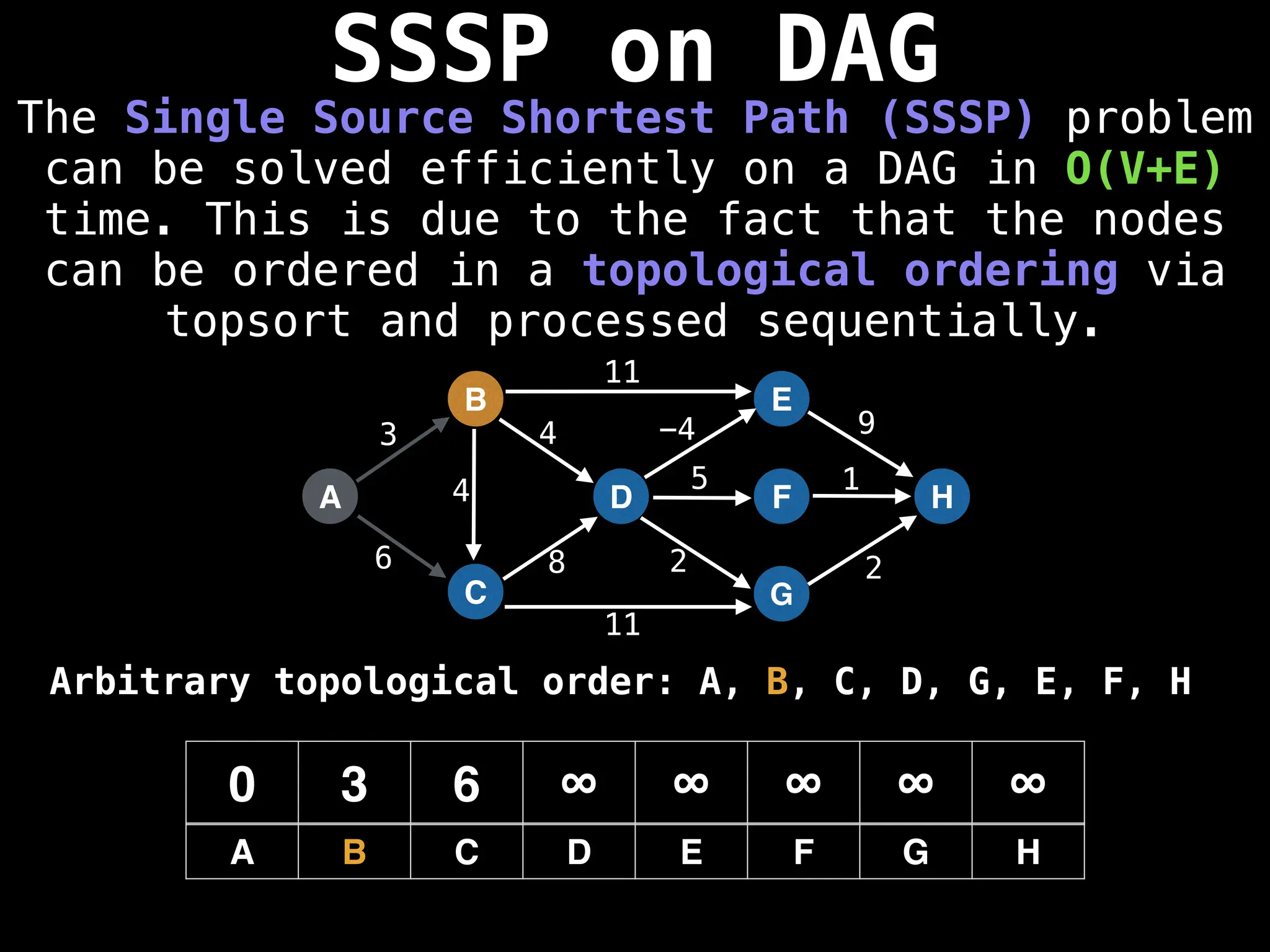
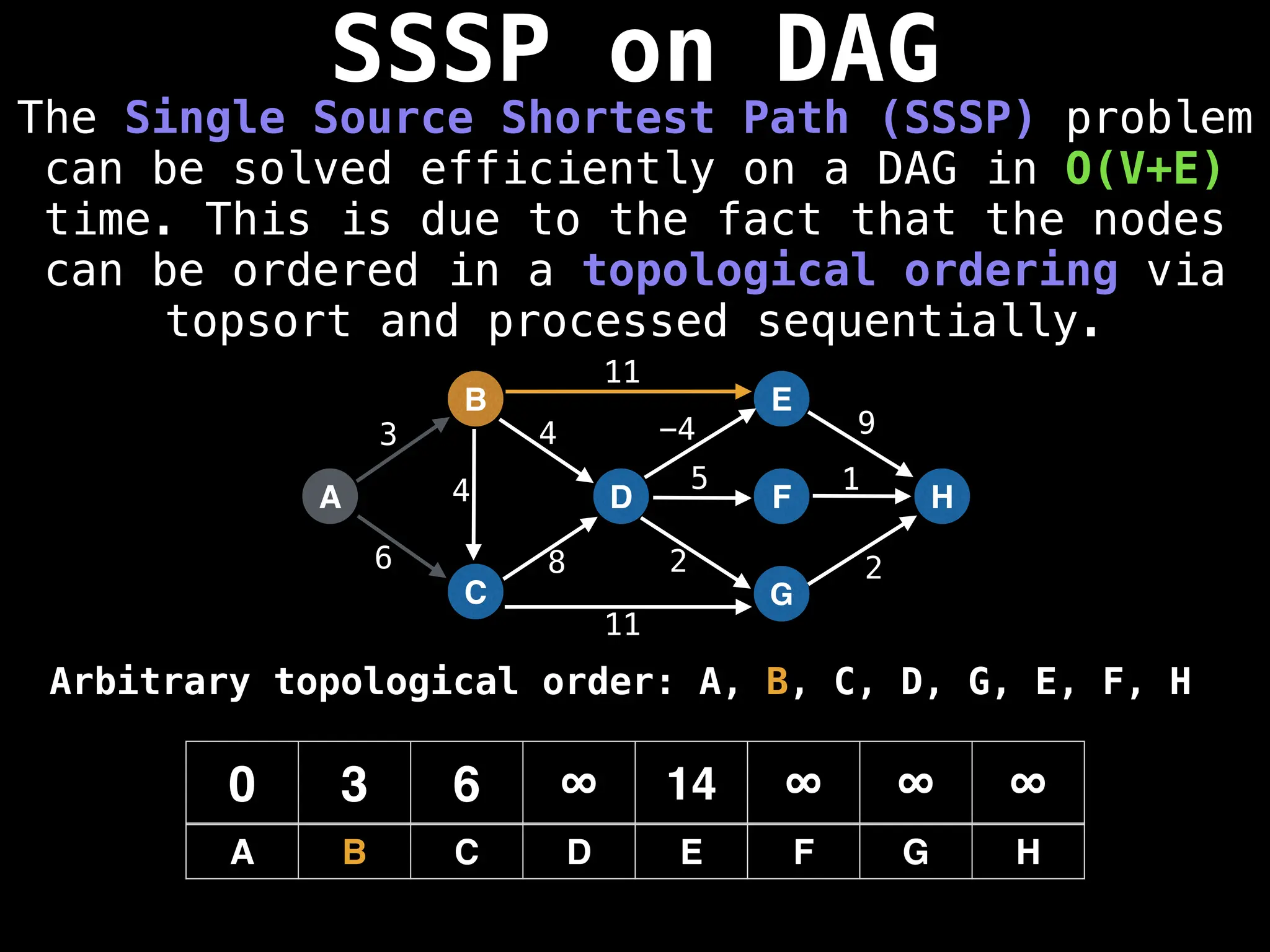
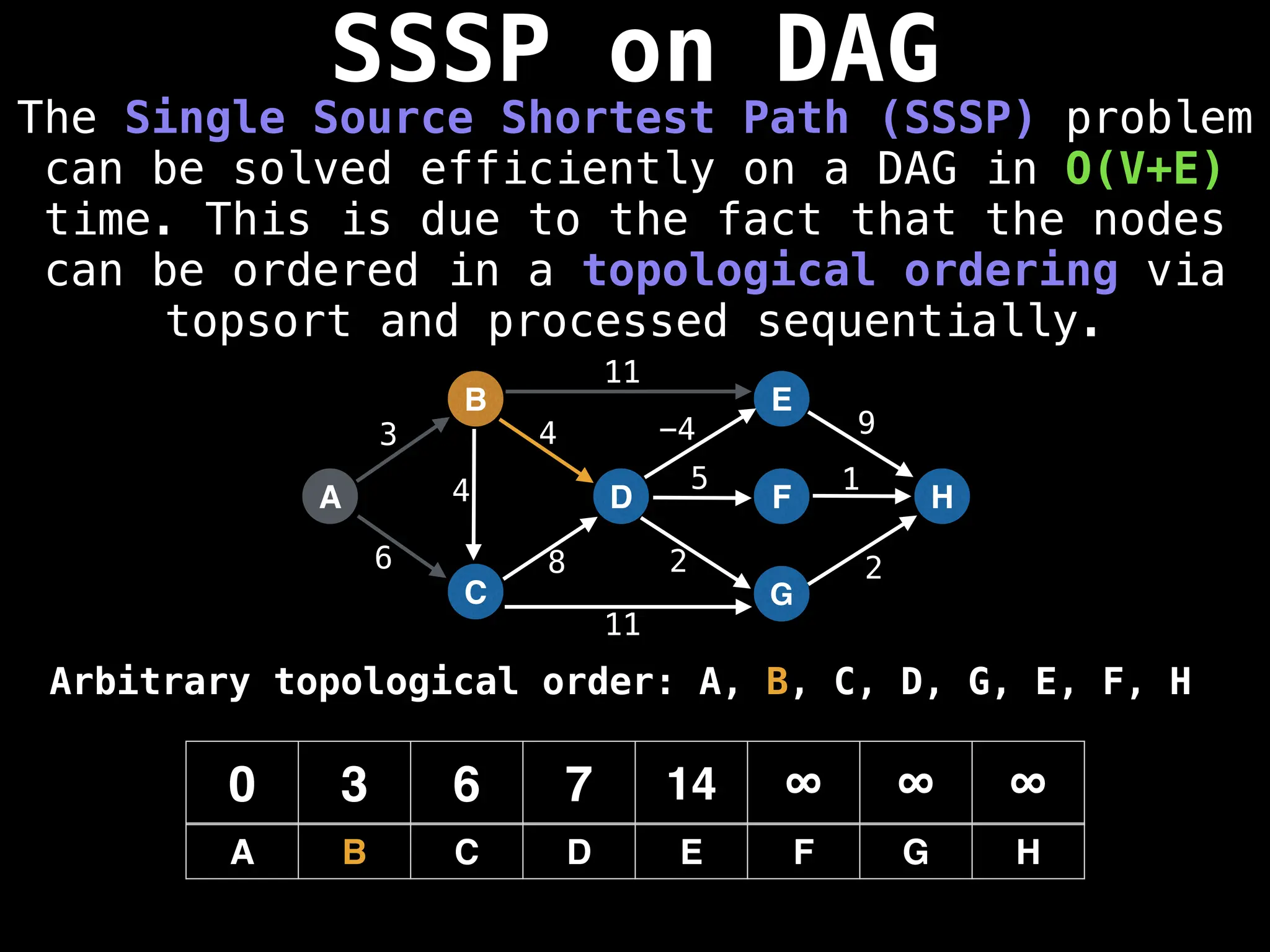
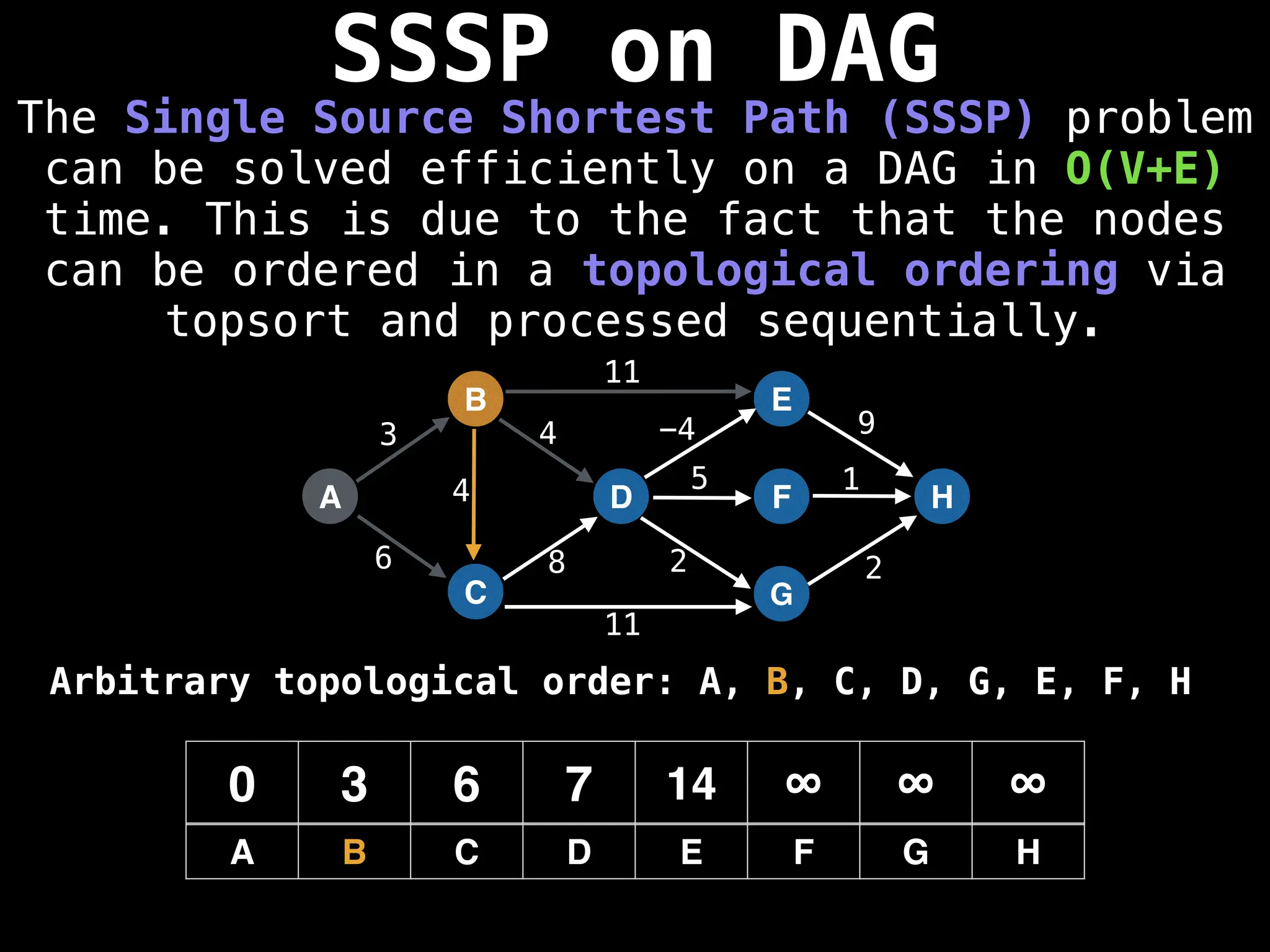
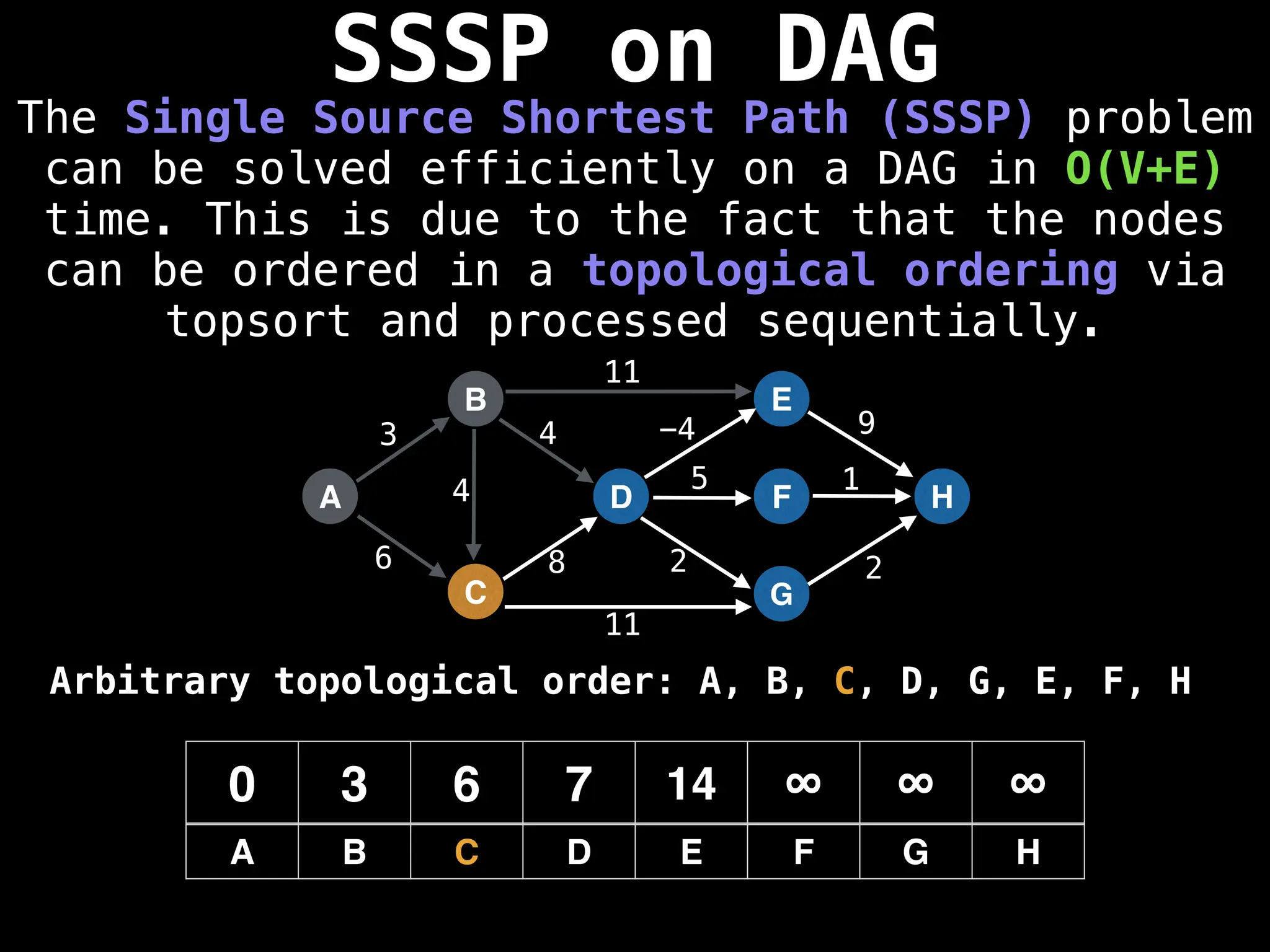
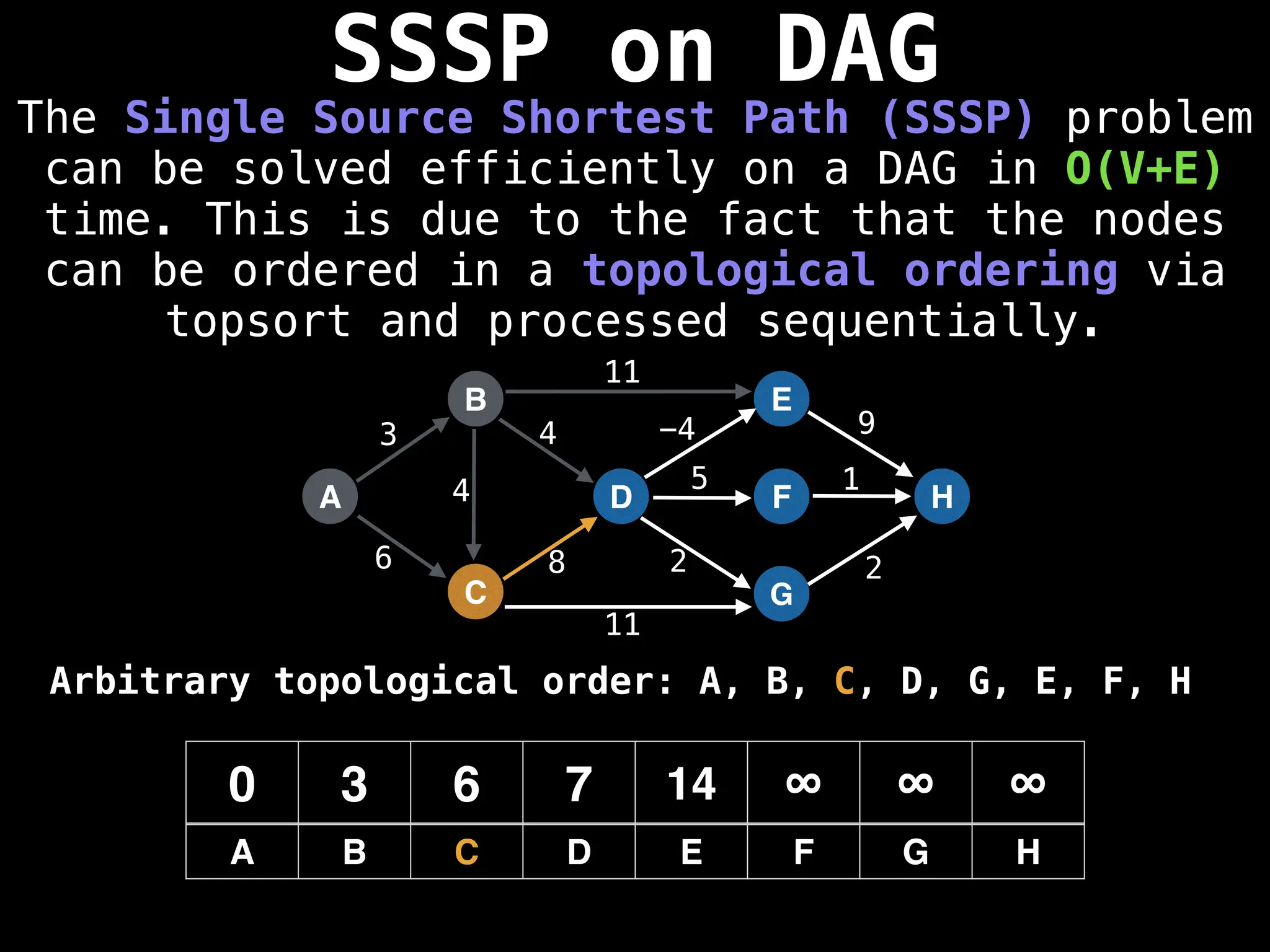
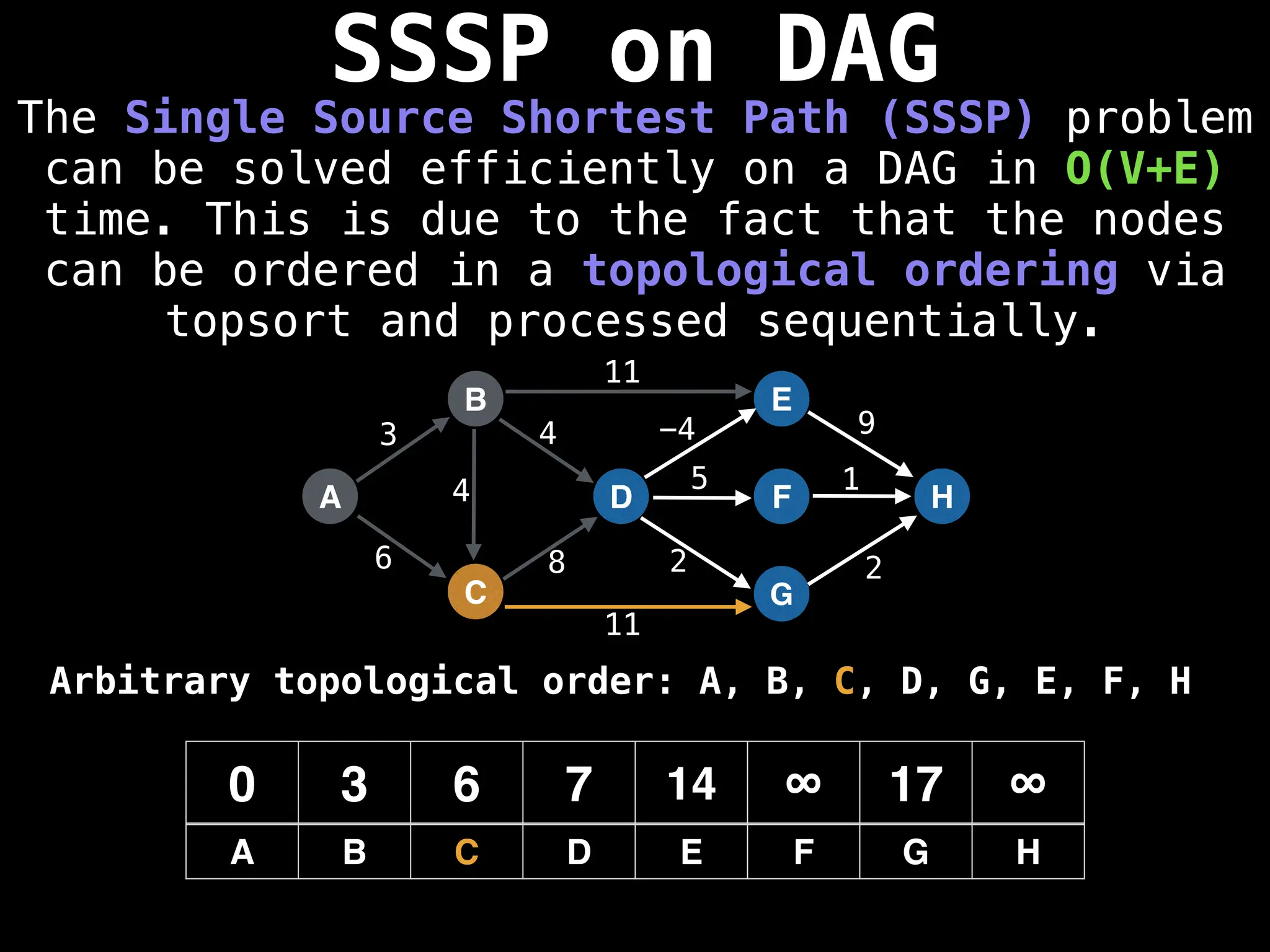
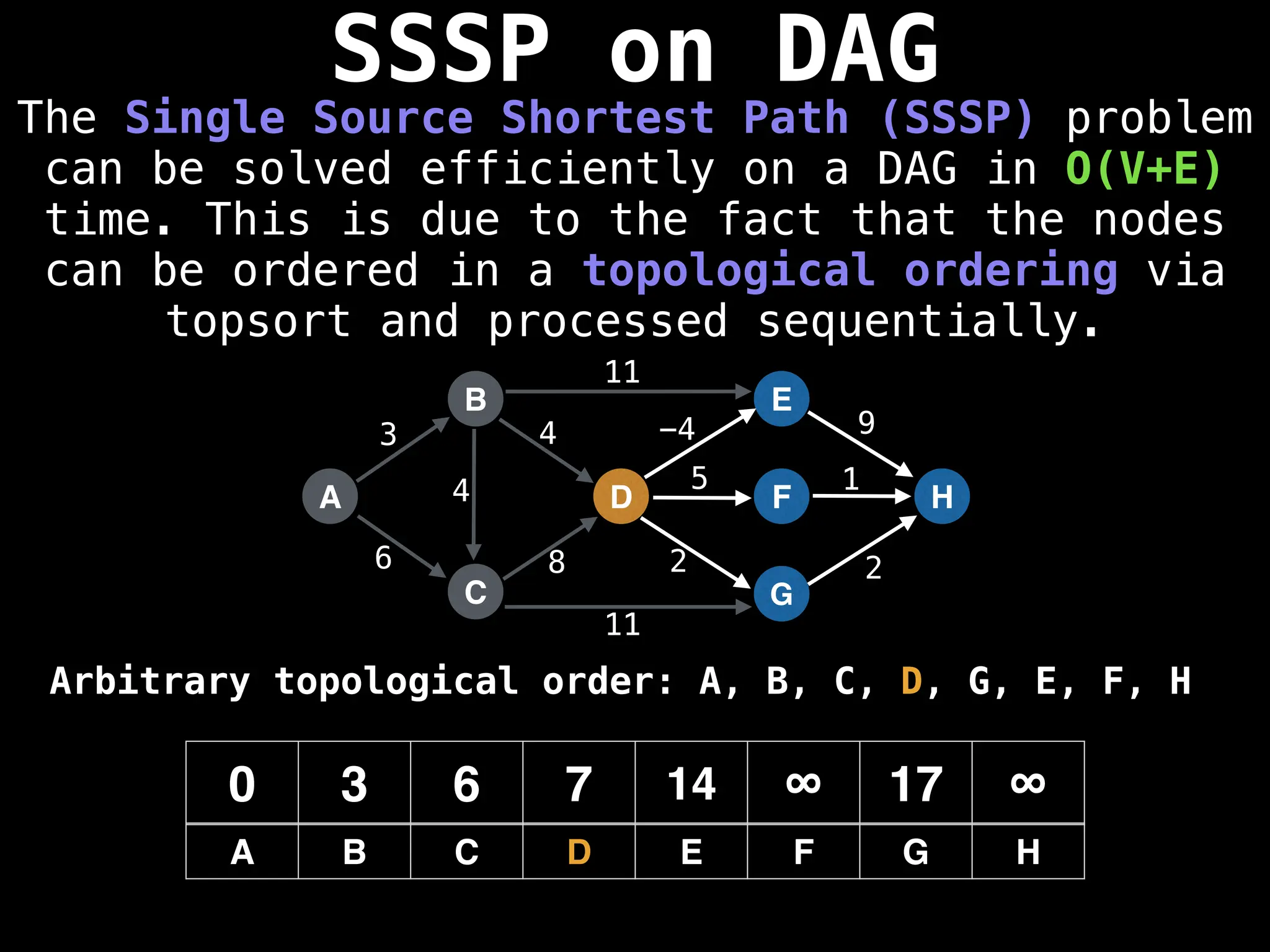
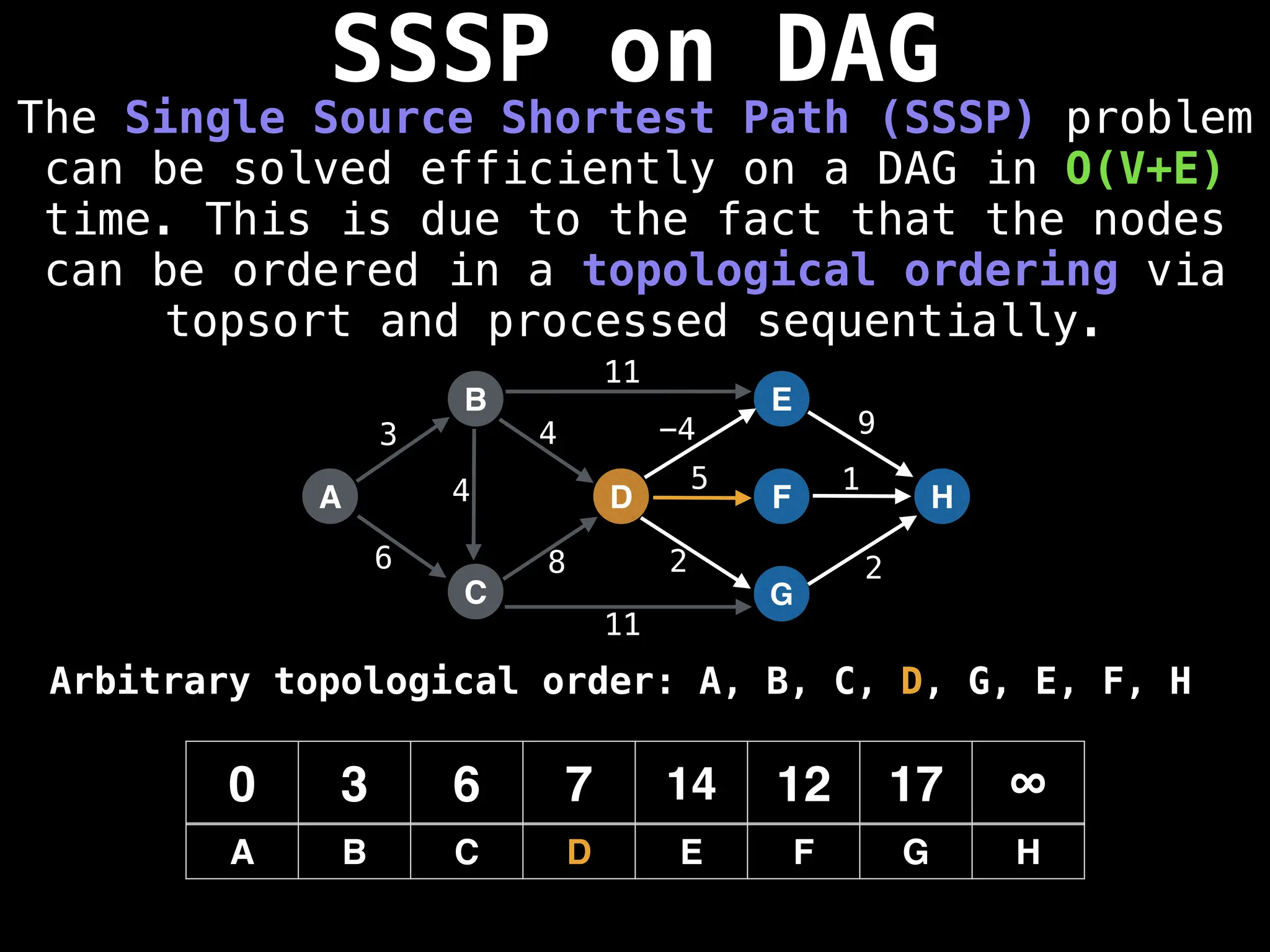
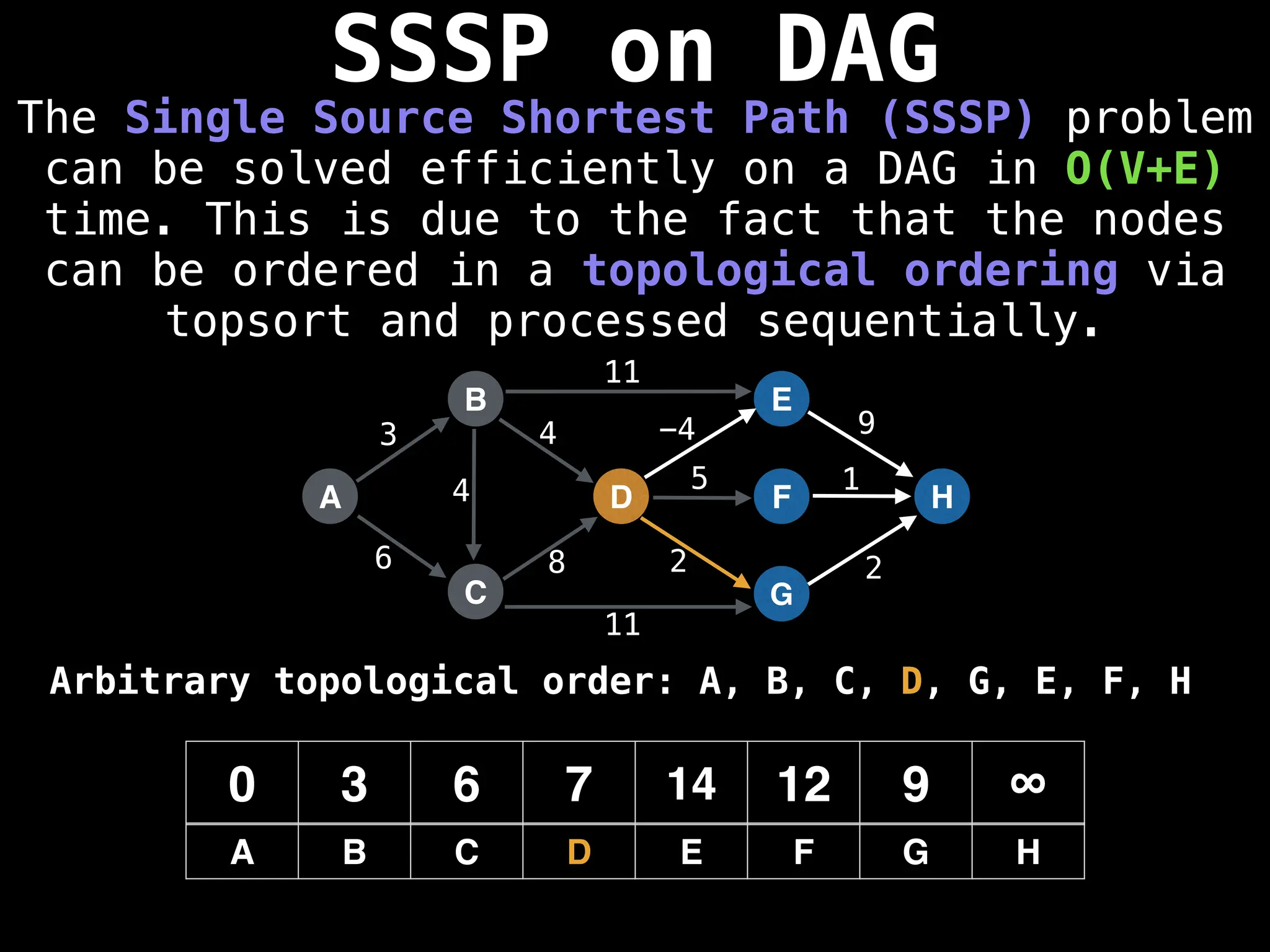
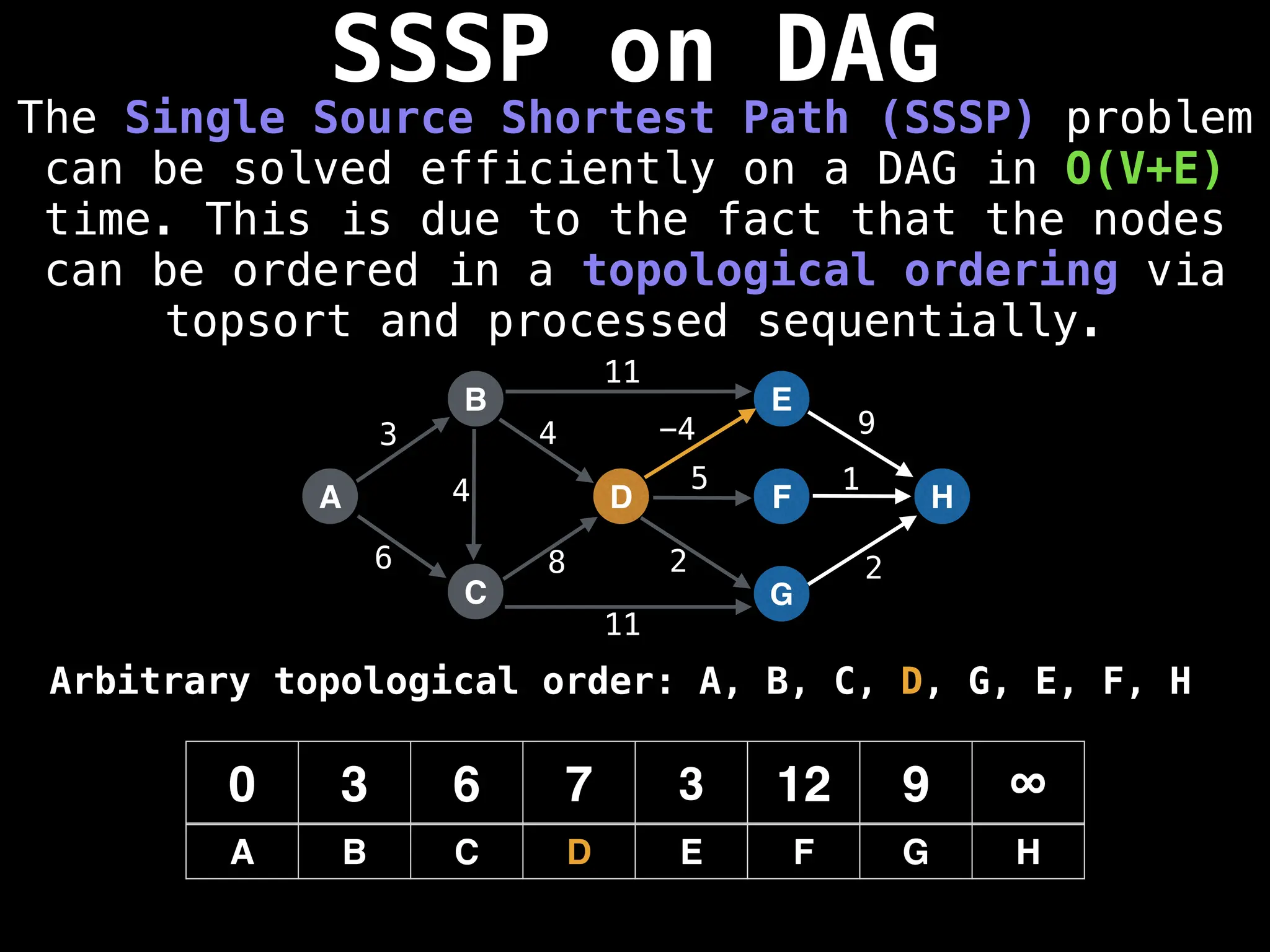
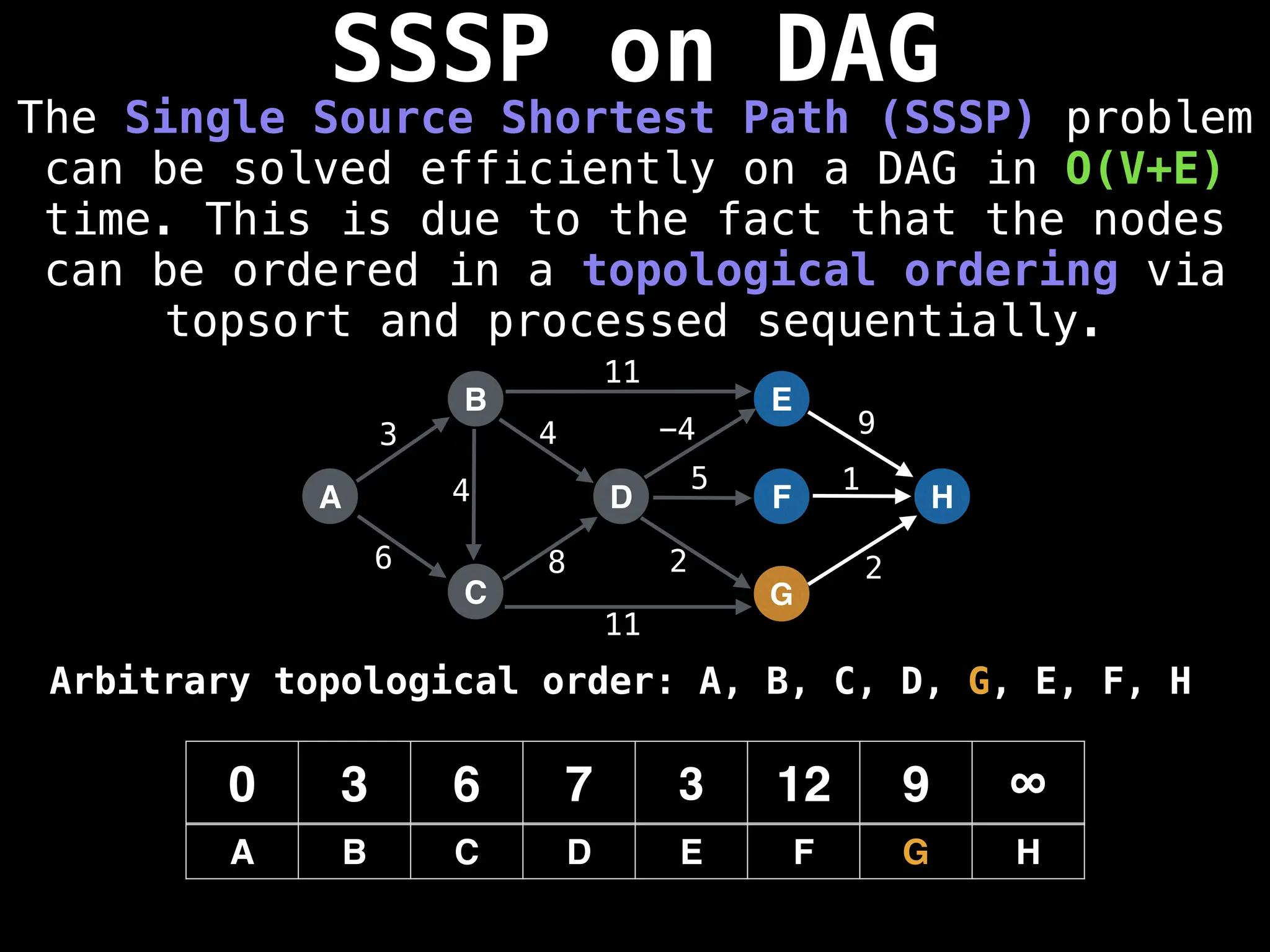
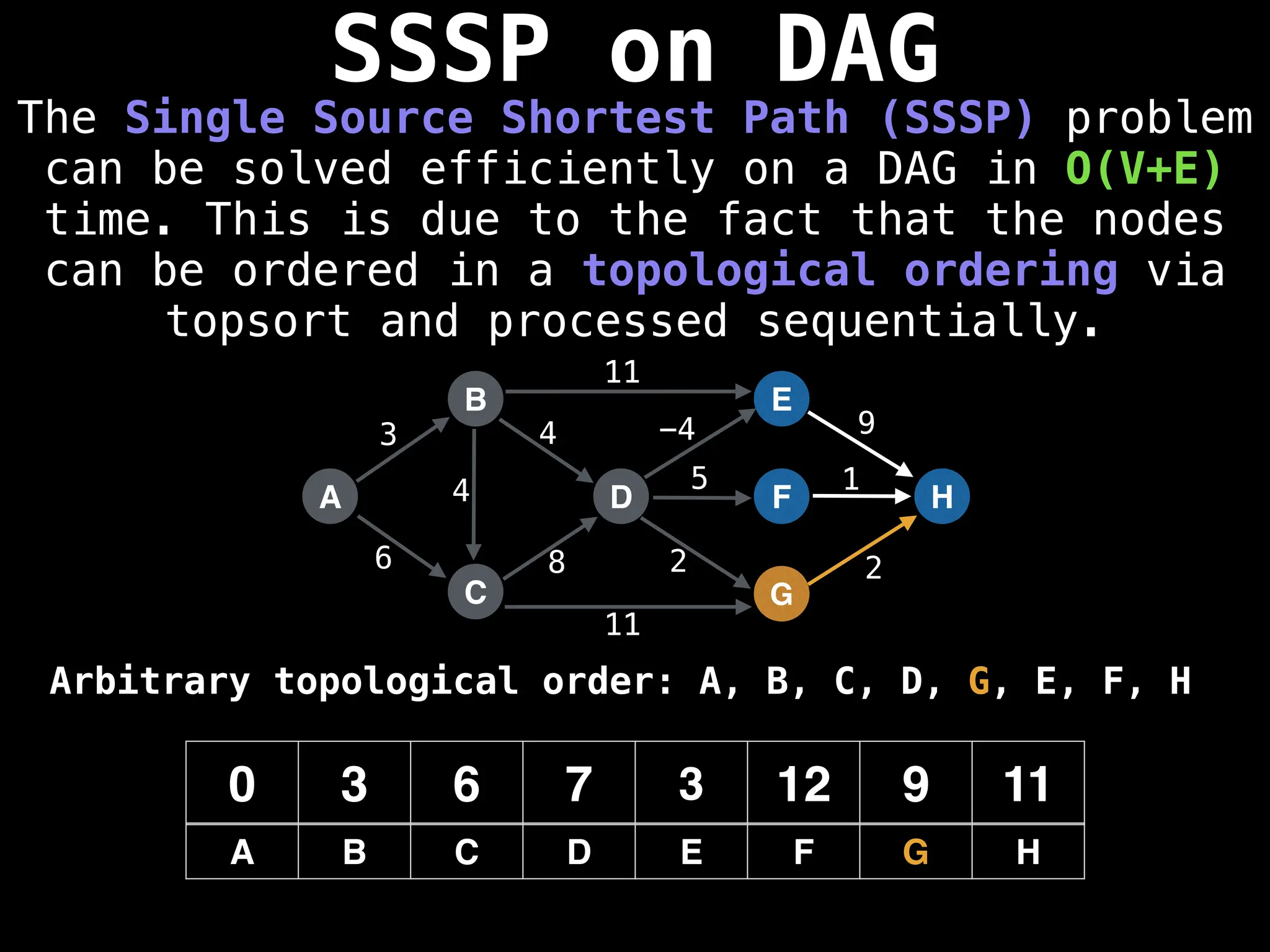
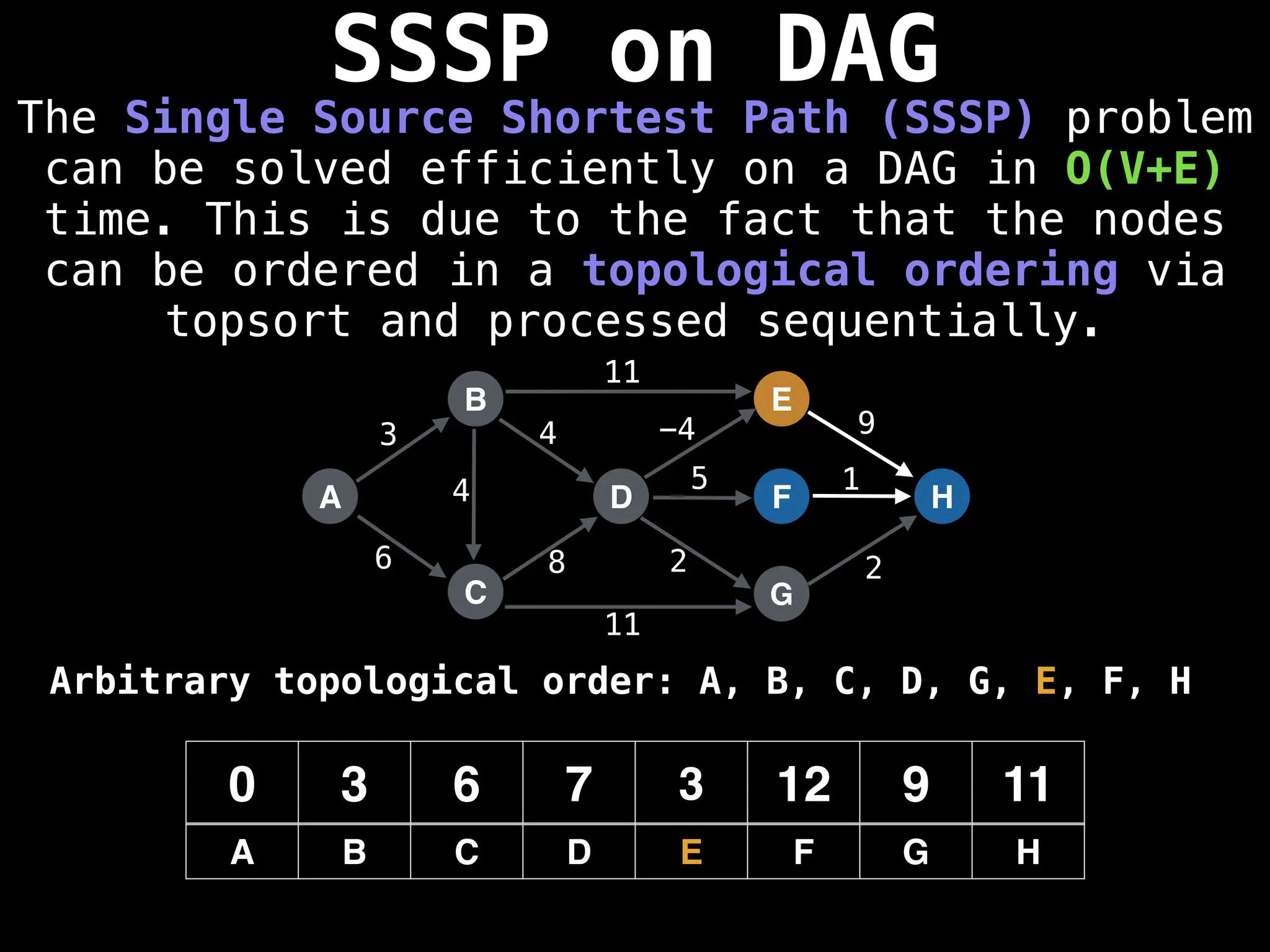
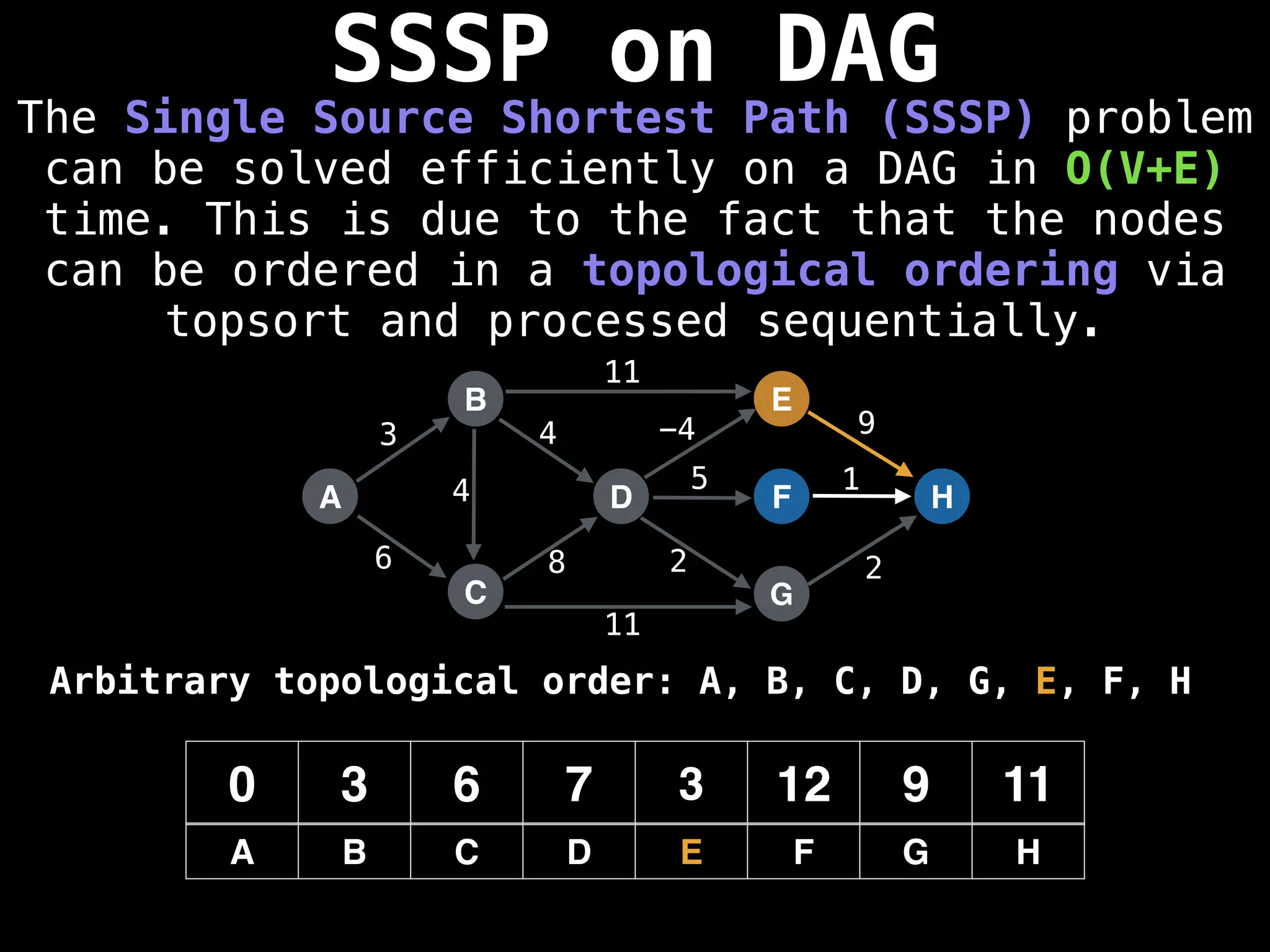
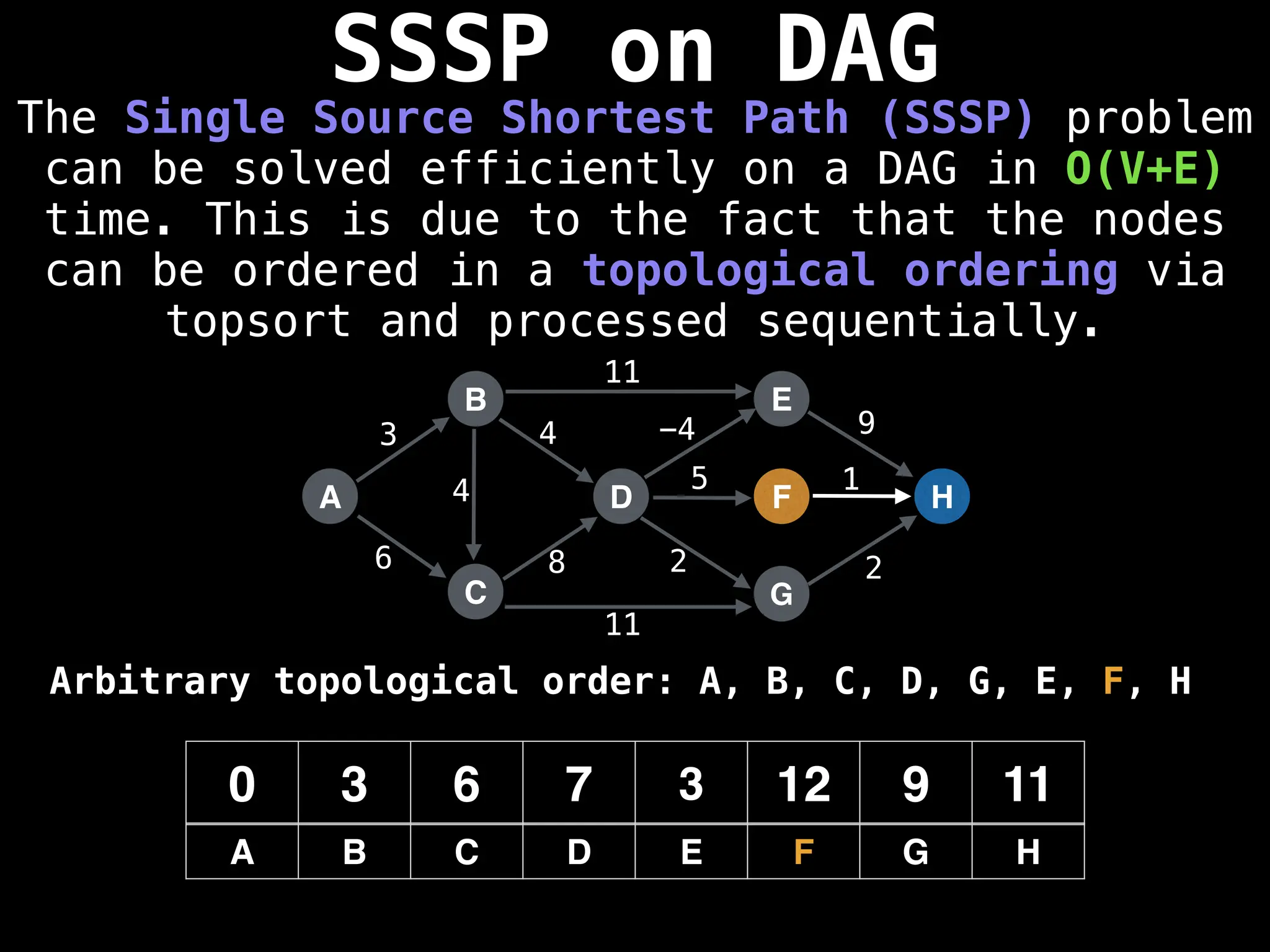
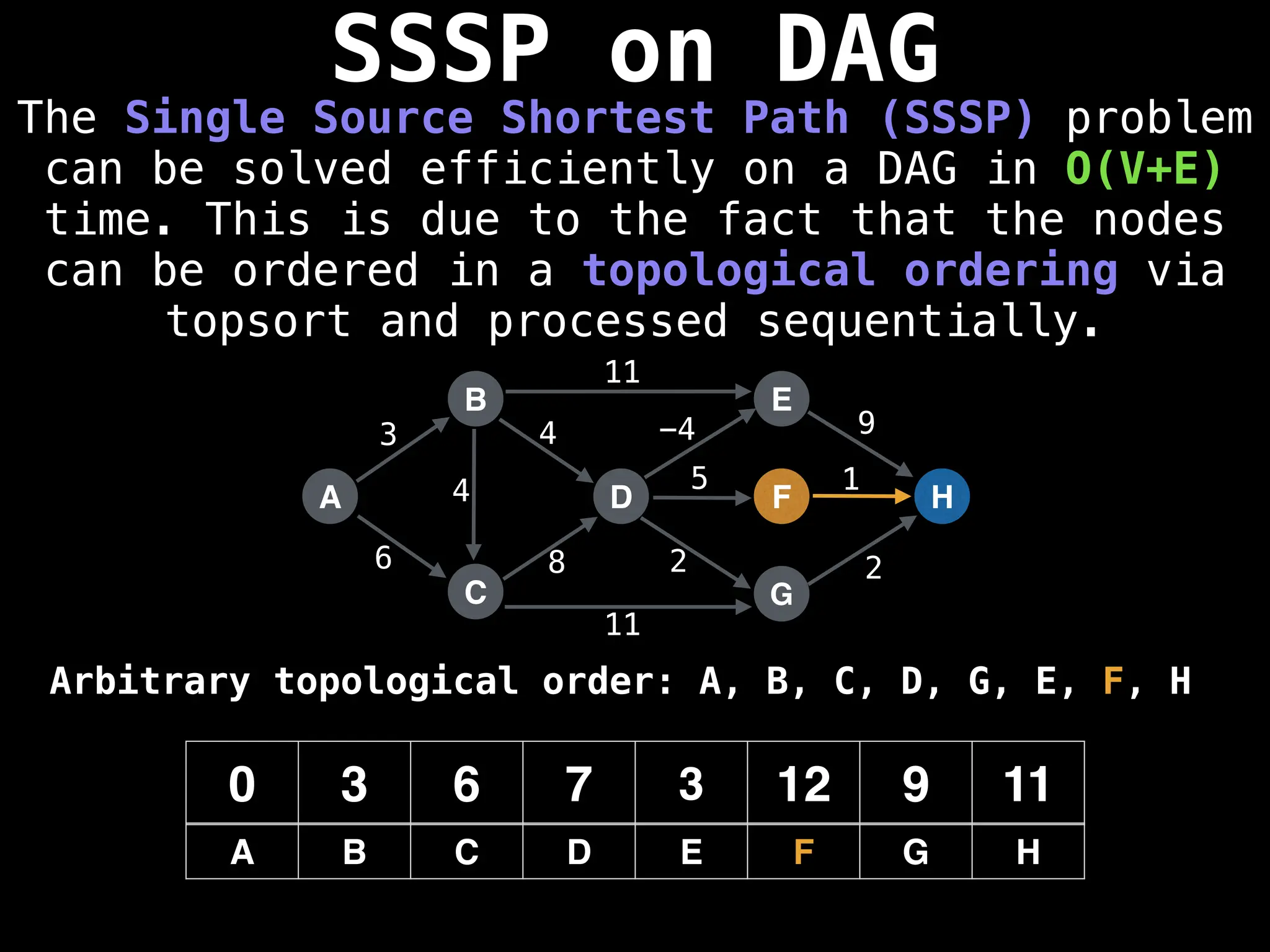
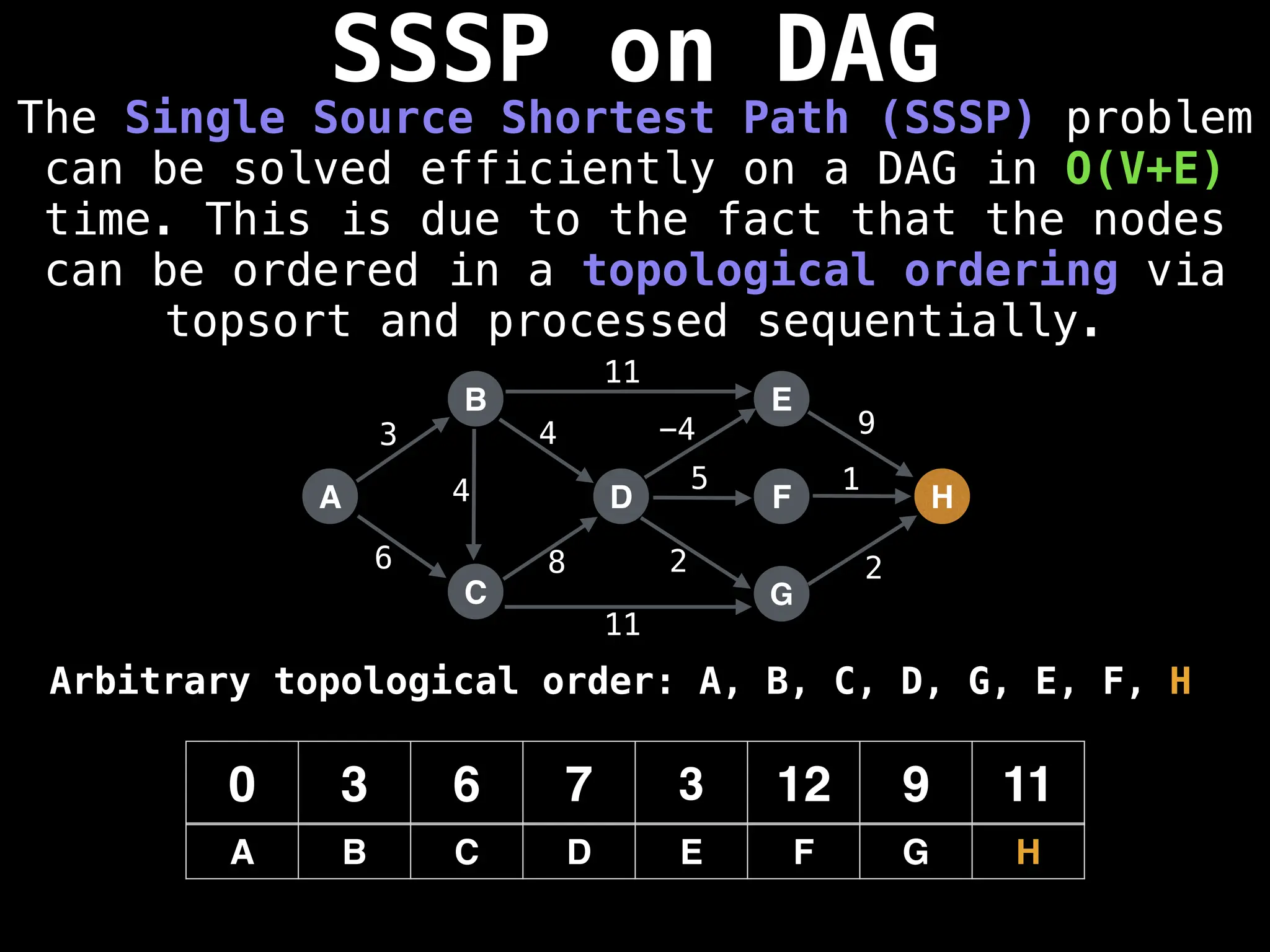
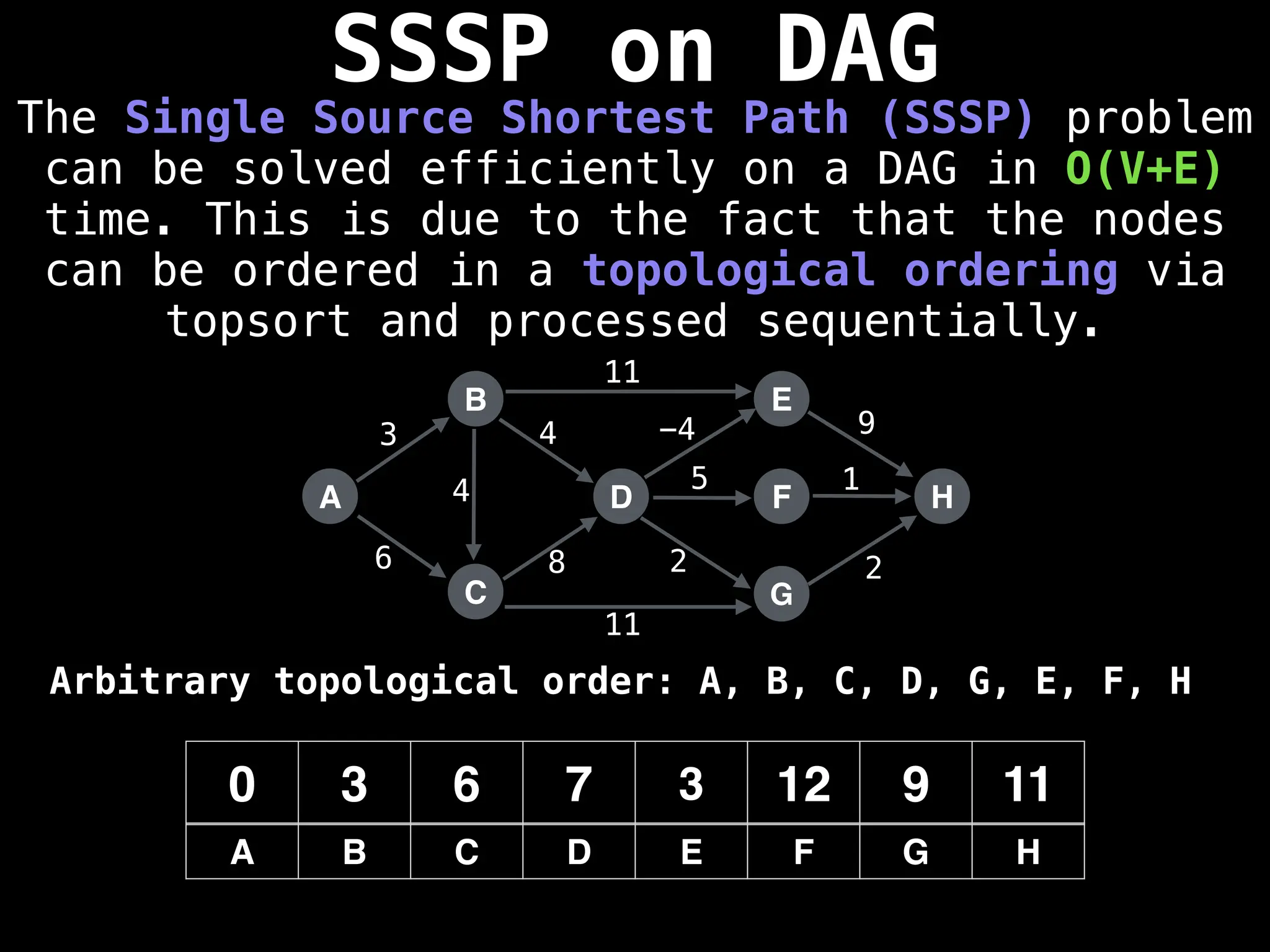
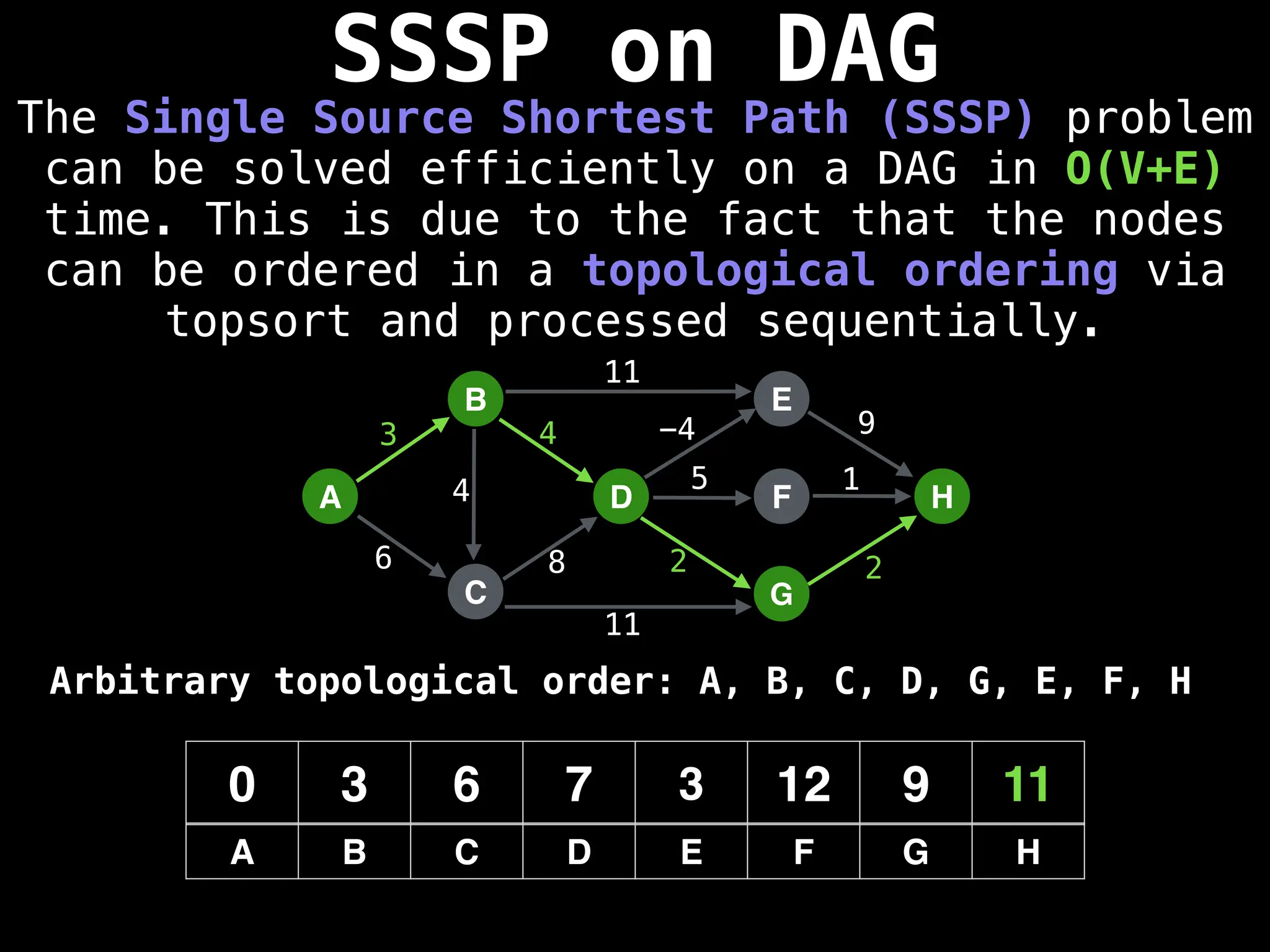
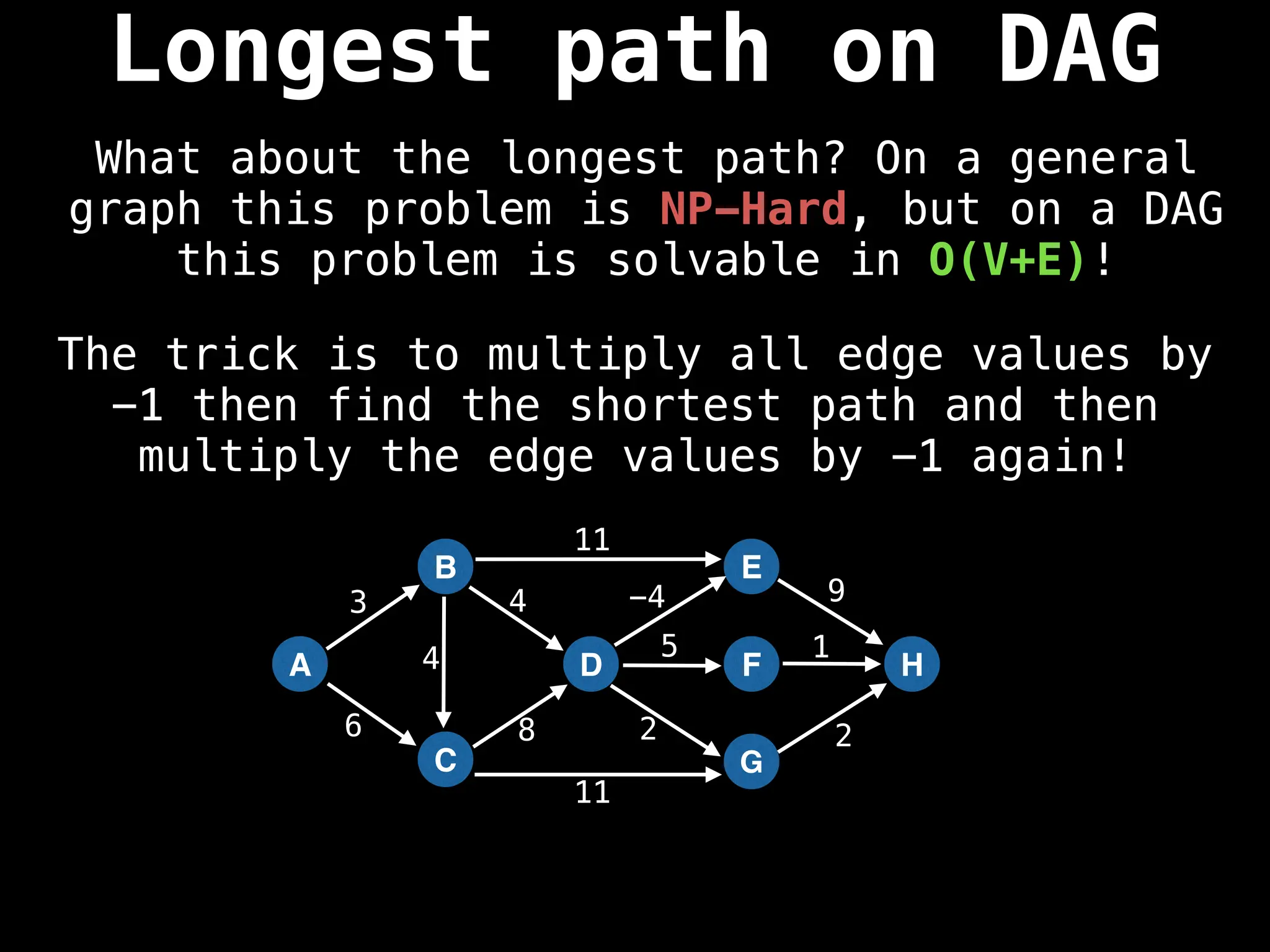
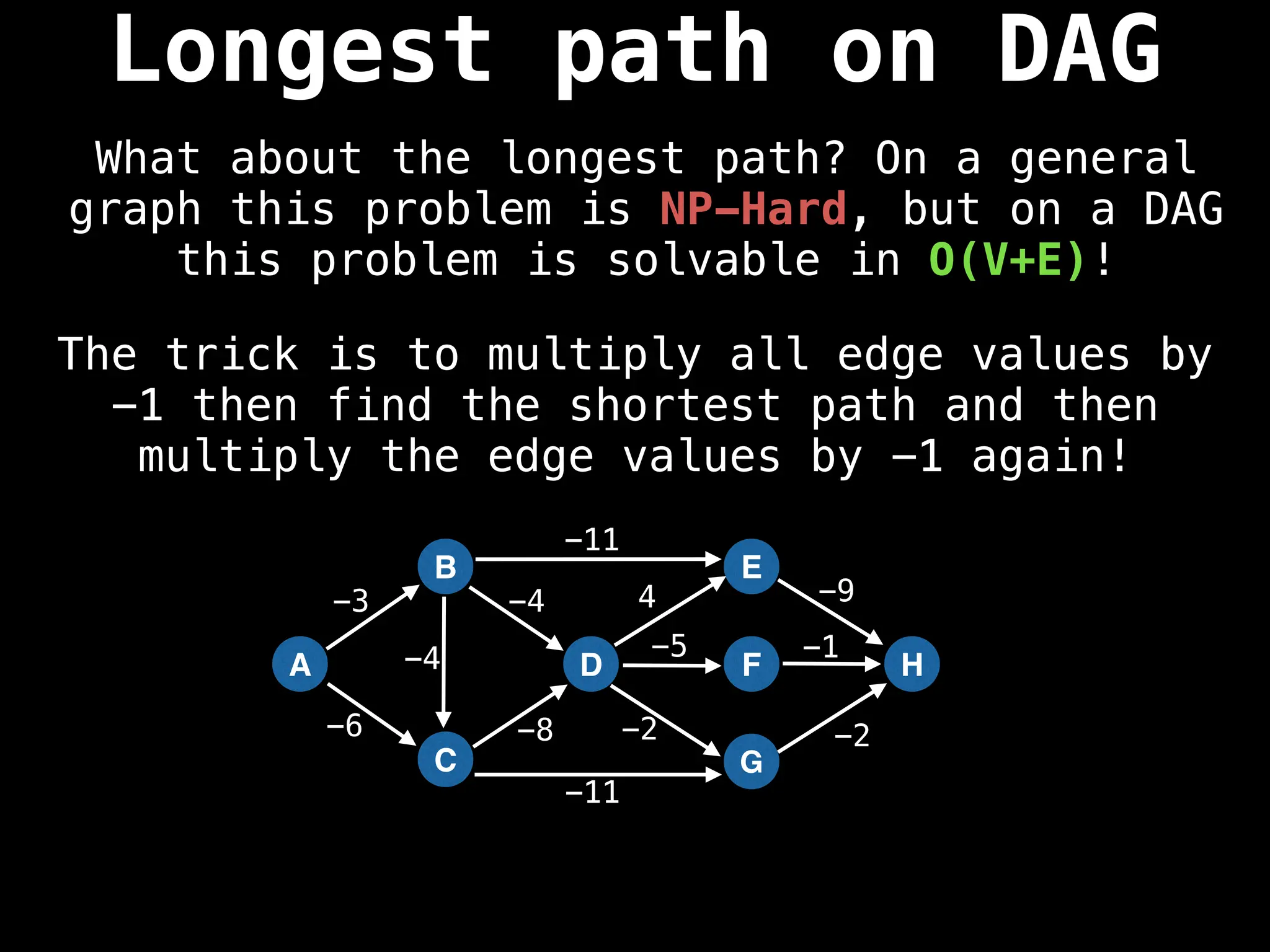
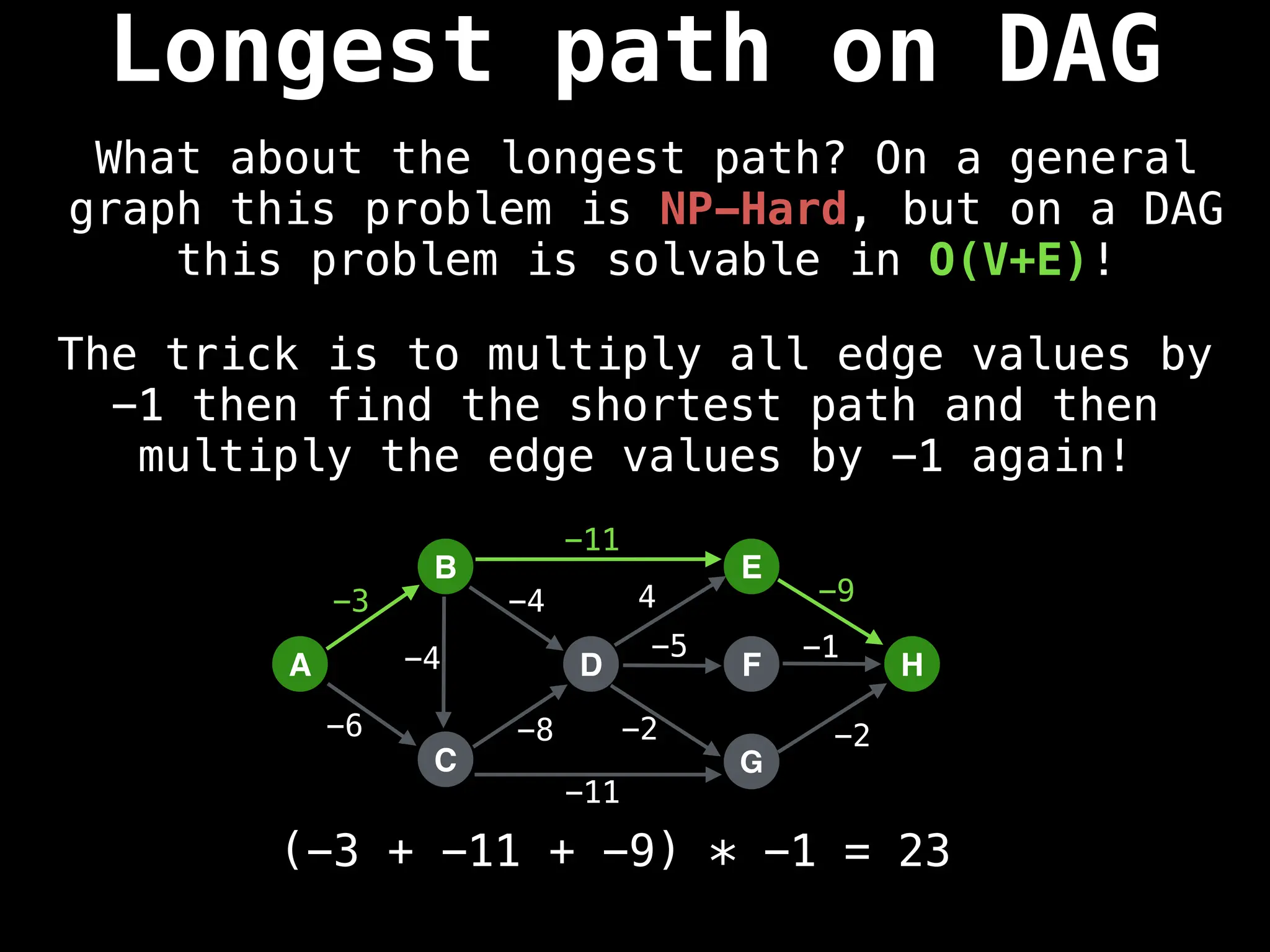





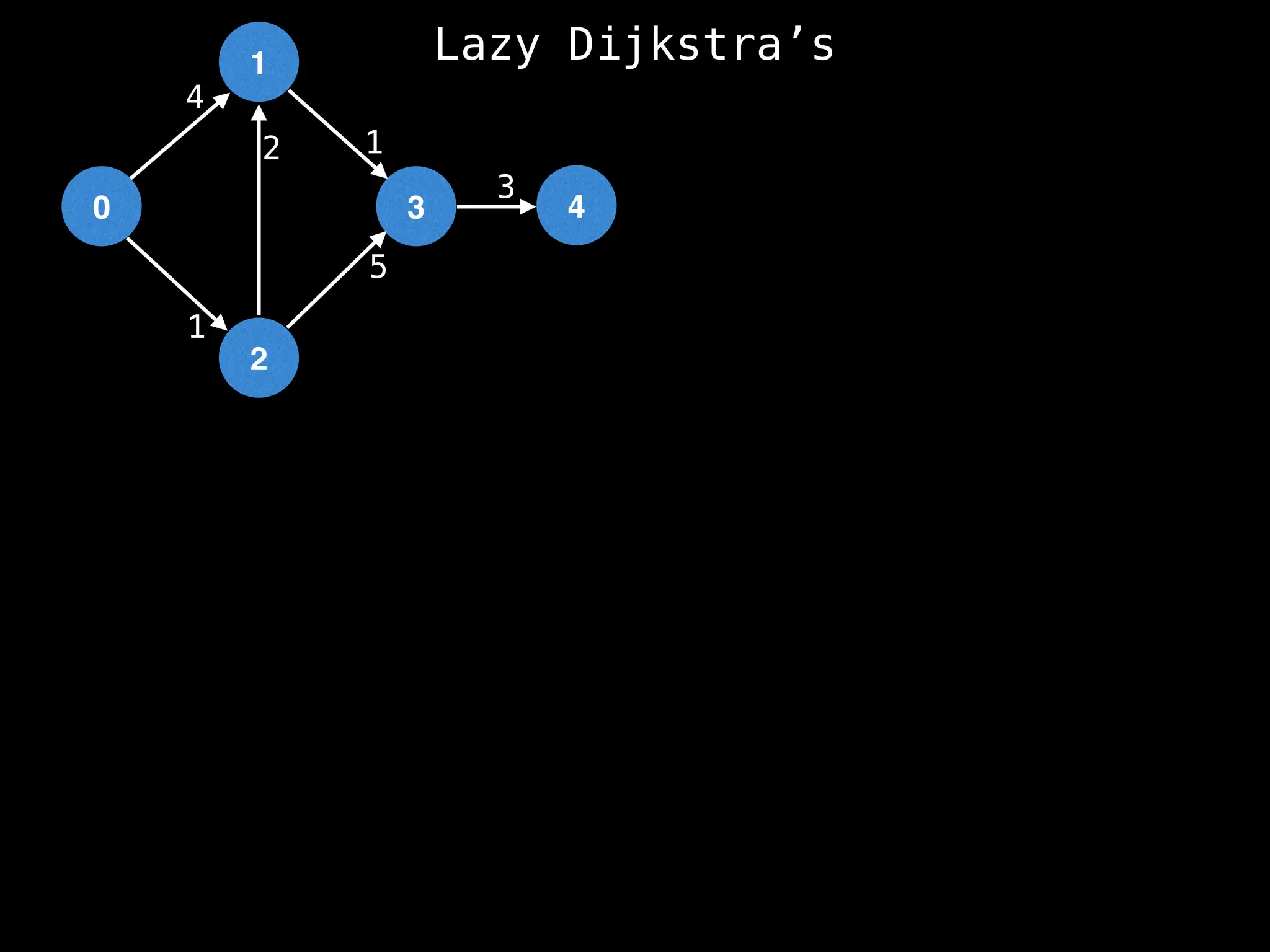
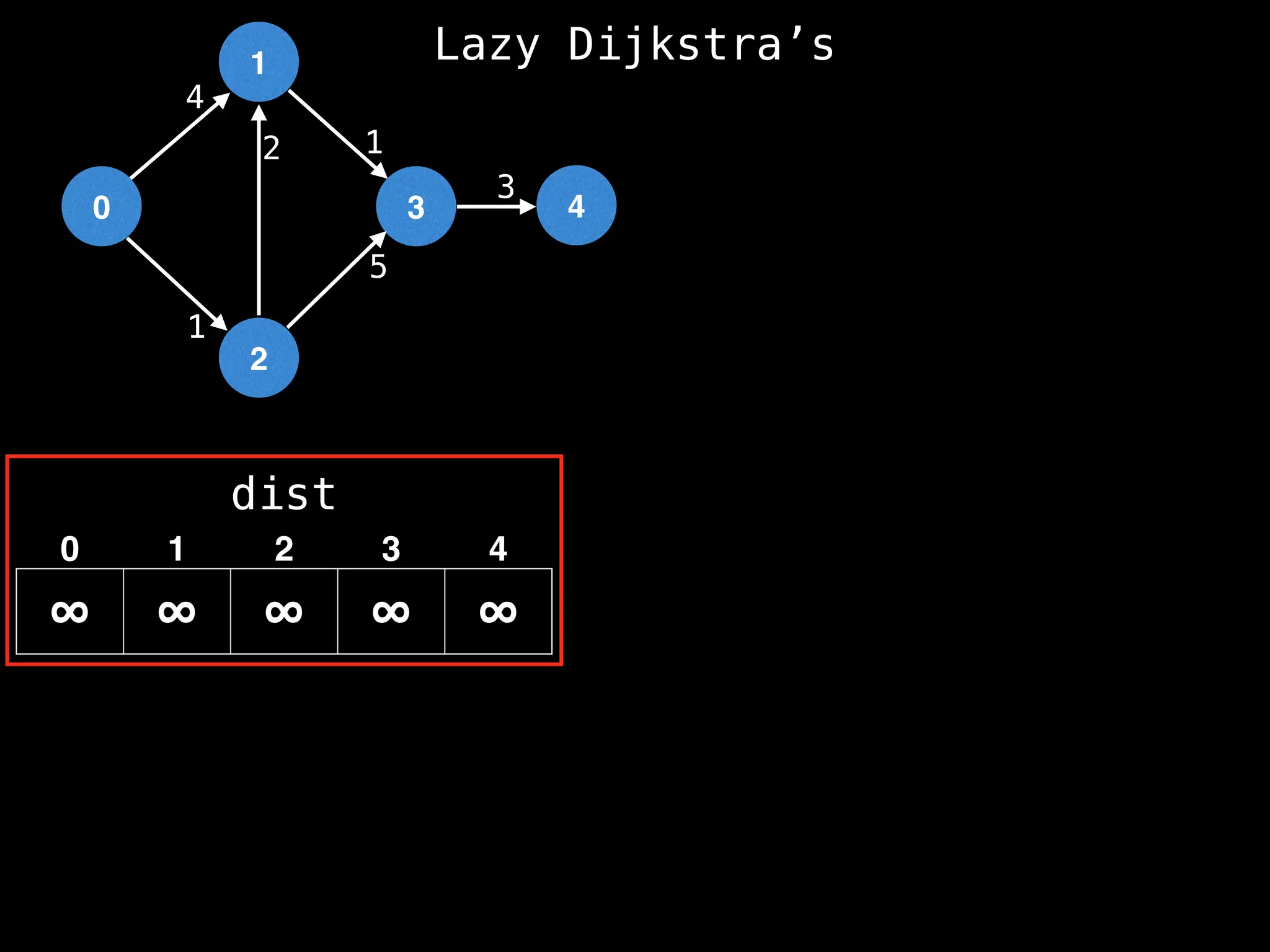
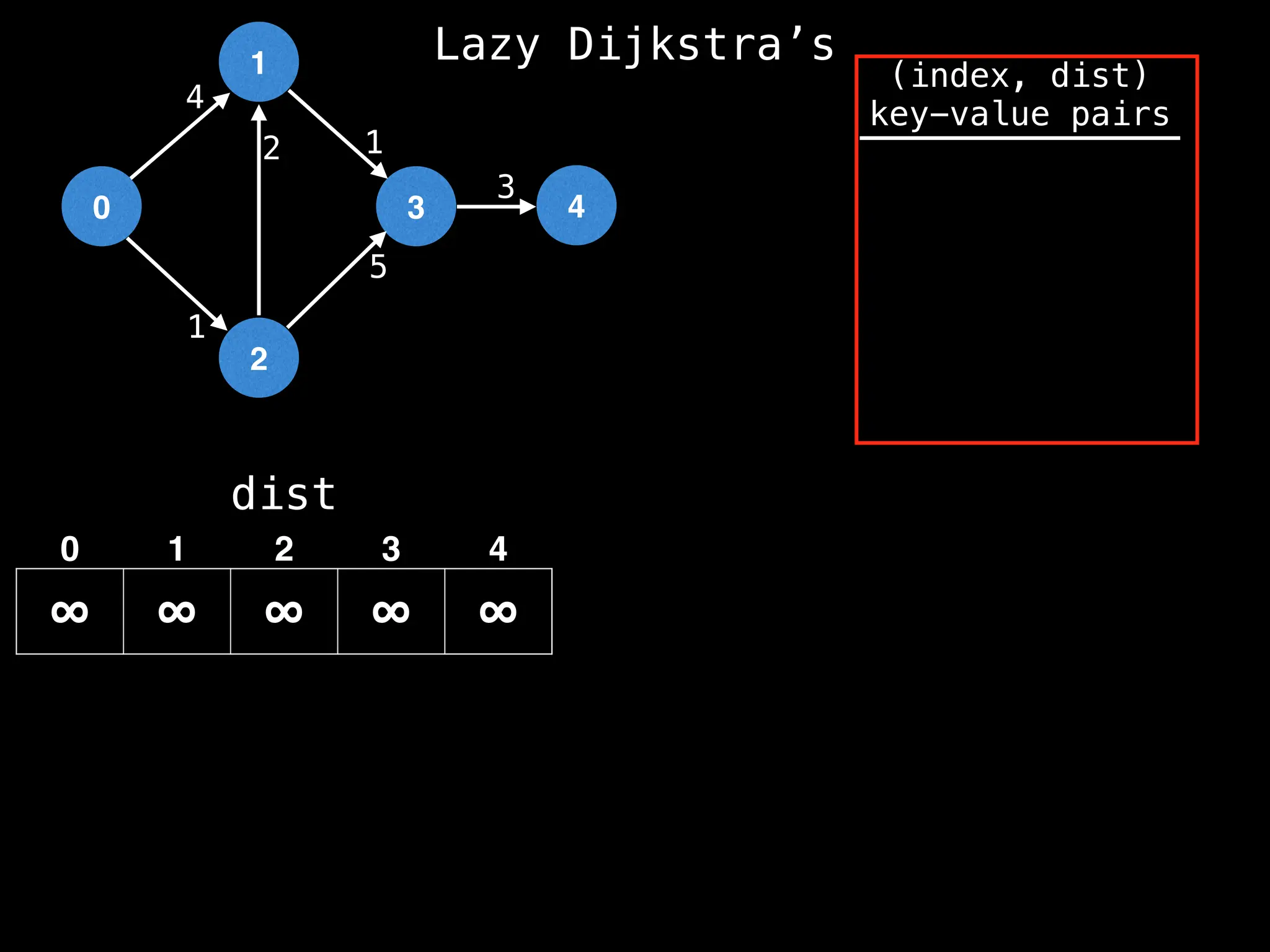
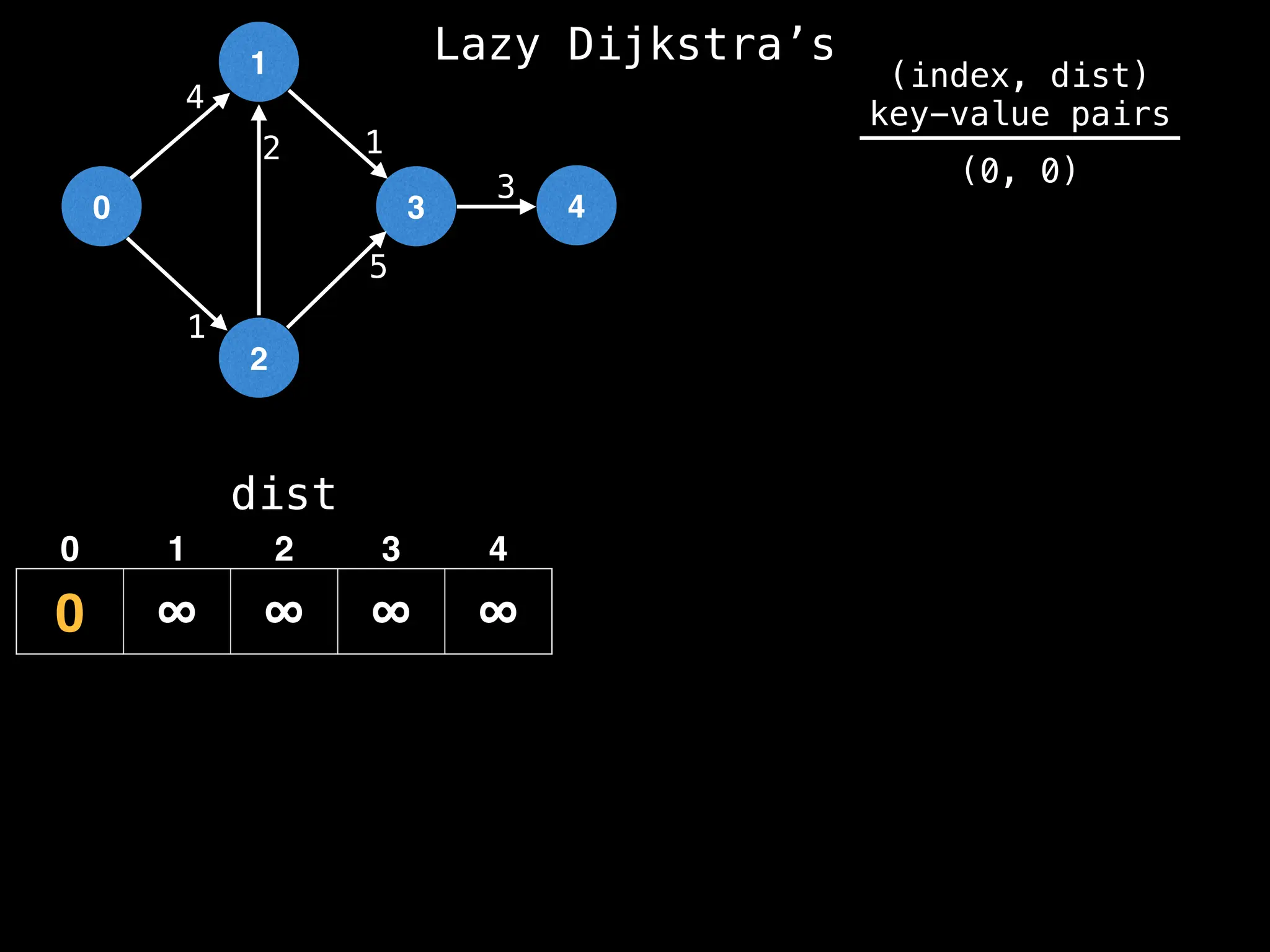
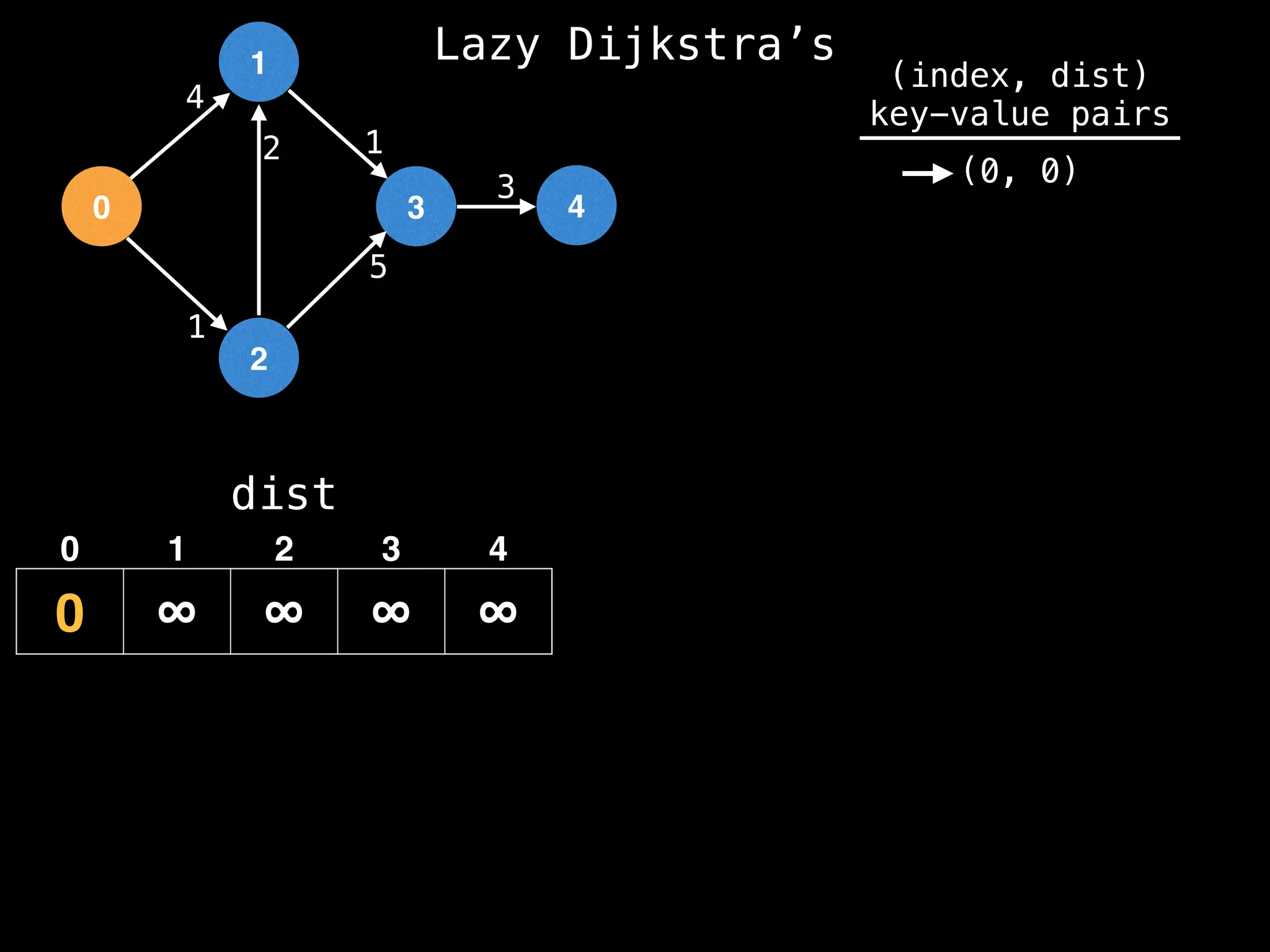
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 4 ∞ ∞ ∞
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
Best distance from node 0 to node 1 is:
dist[0] + edge.cost = 0 + 4 = 4
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-565-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 4 1 ∞ ∞
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
Best distance from node 0 to node 2 is:
dist[0] + edge.cost = 0 + 1 = 1
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-566-2048.jpg)
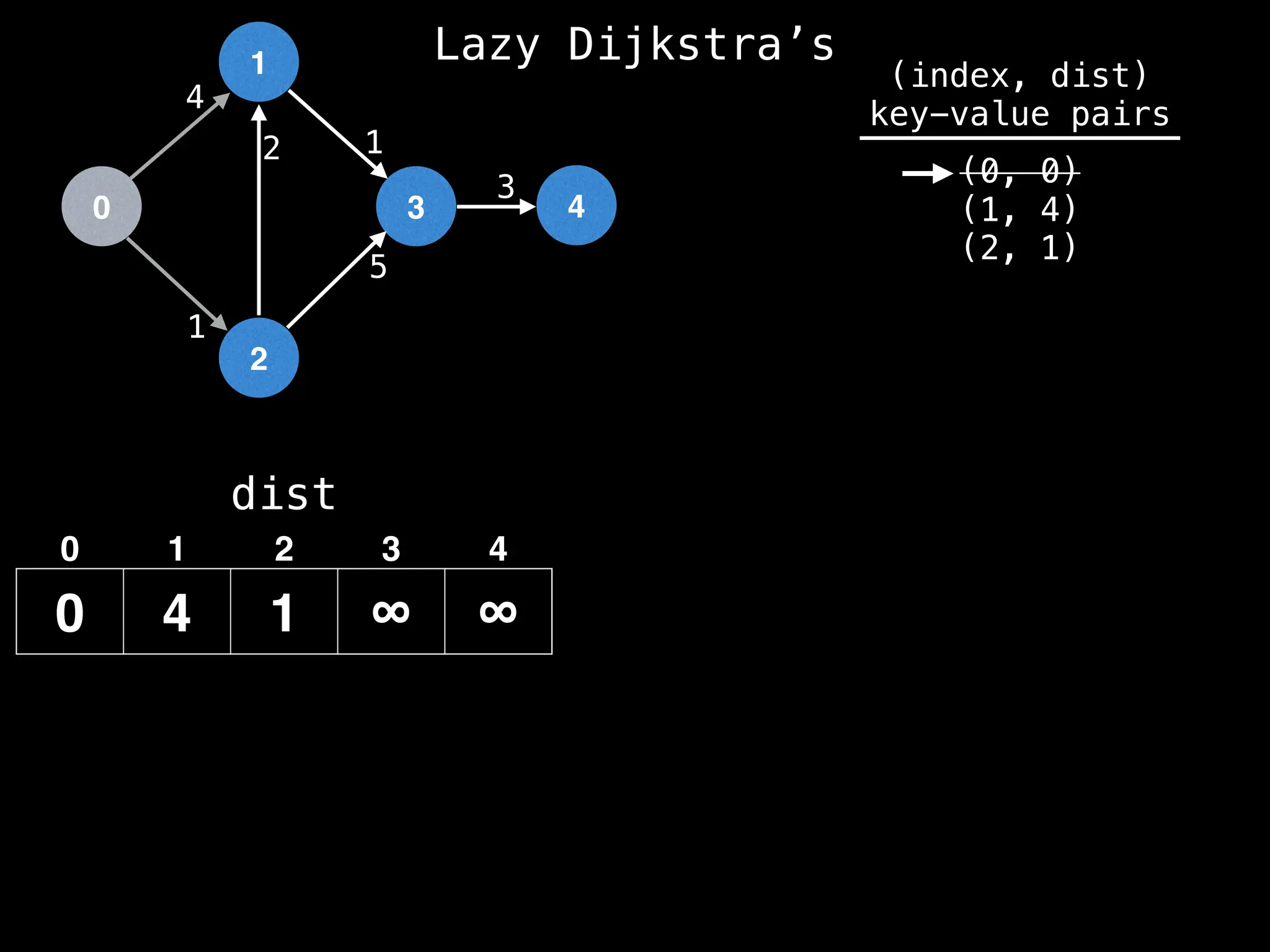
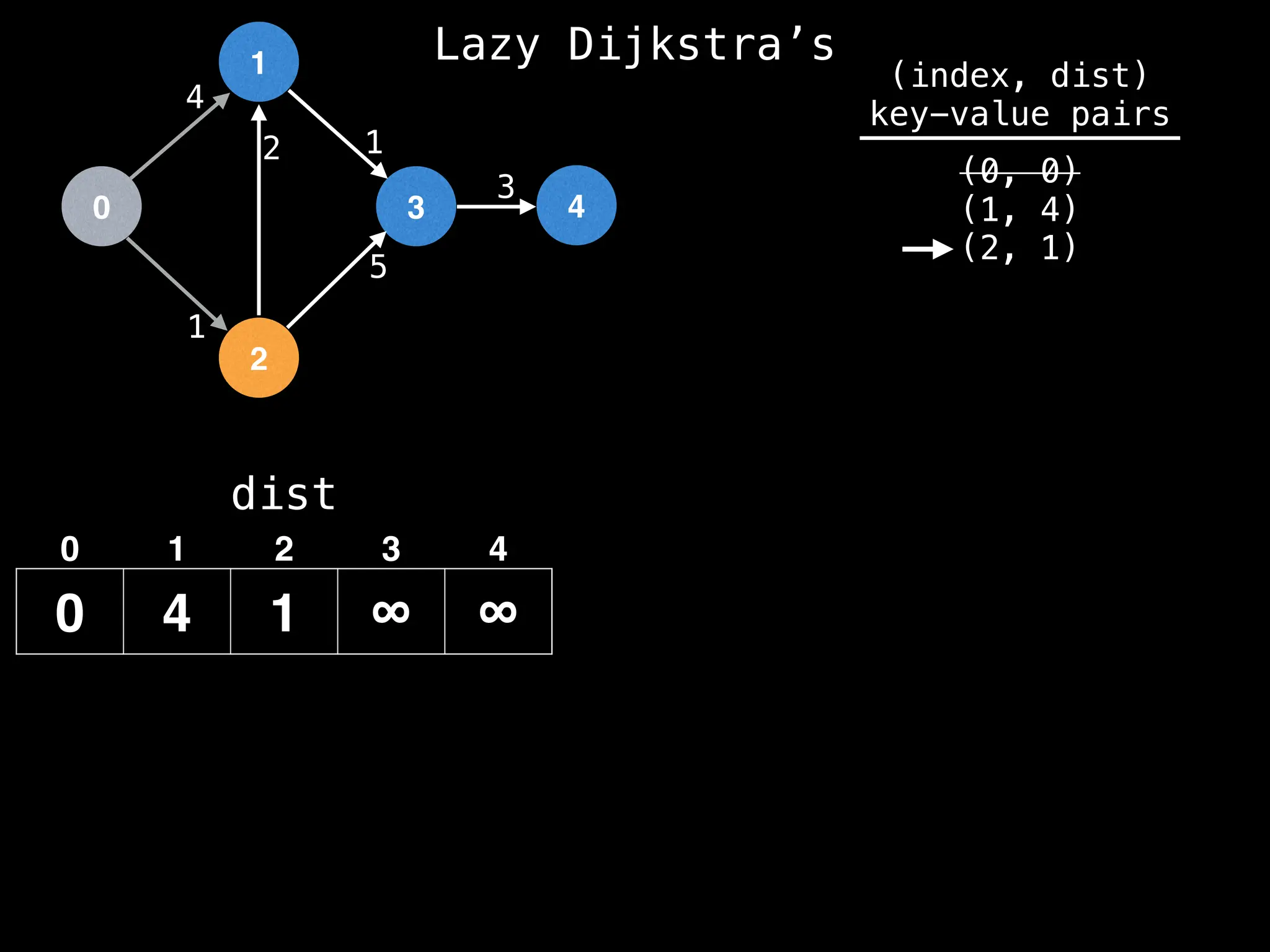
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 3 1 ∞ ∞
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
(1, 3)
Best distance from node 2 to node 1 is:
dist[2] + edge.cost = 1 + 2 = 3
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-569-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 3 1 6 ∞
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
(1, 3)
(3, 6)
Best distance from node 2 to node 3 is:
dist[2] + edge.cost = 1 + 5 = 6
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-570-2048.jpg)
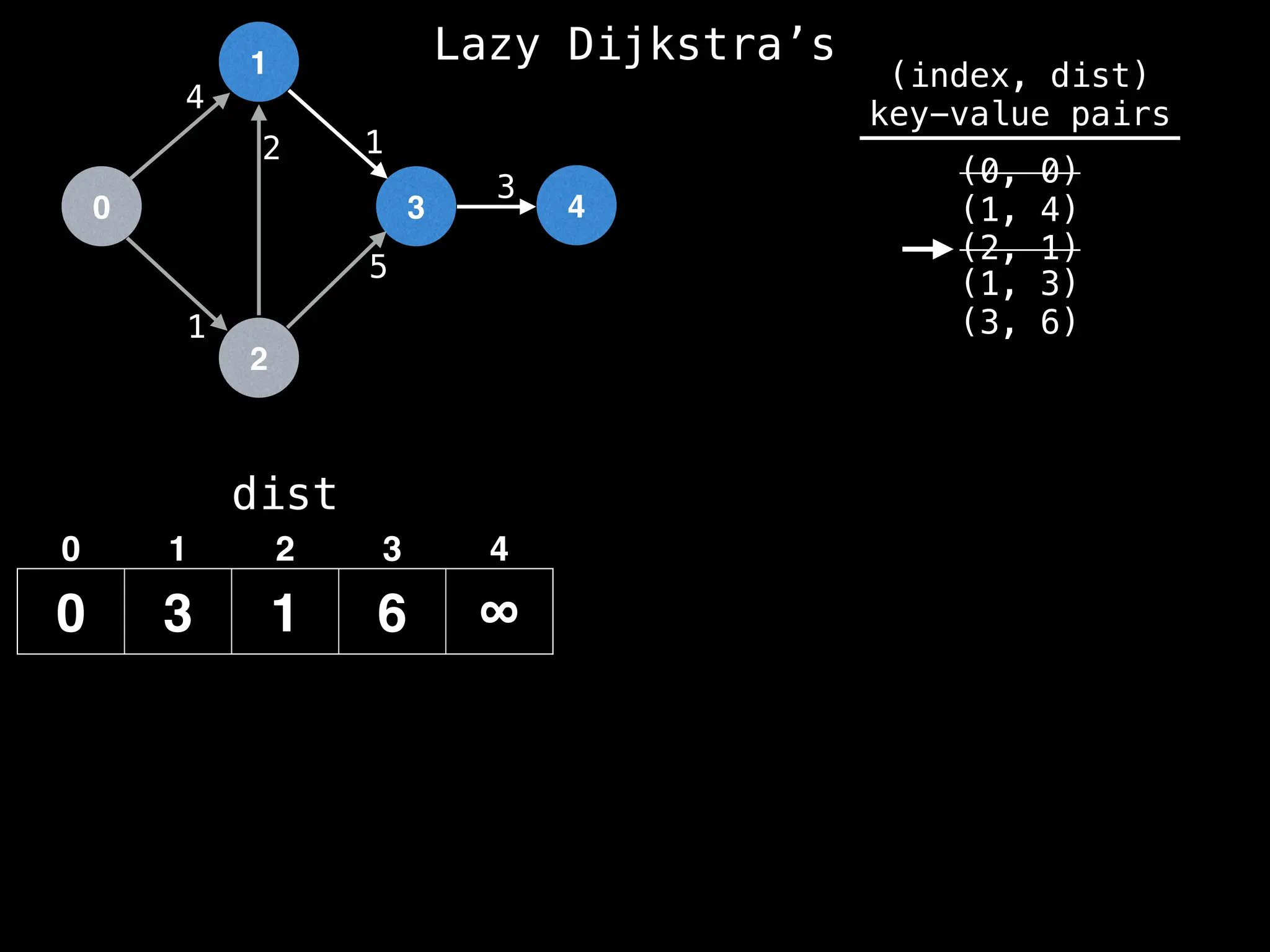
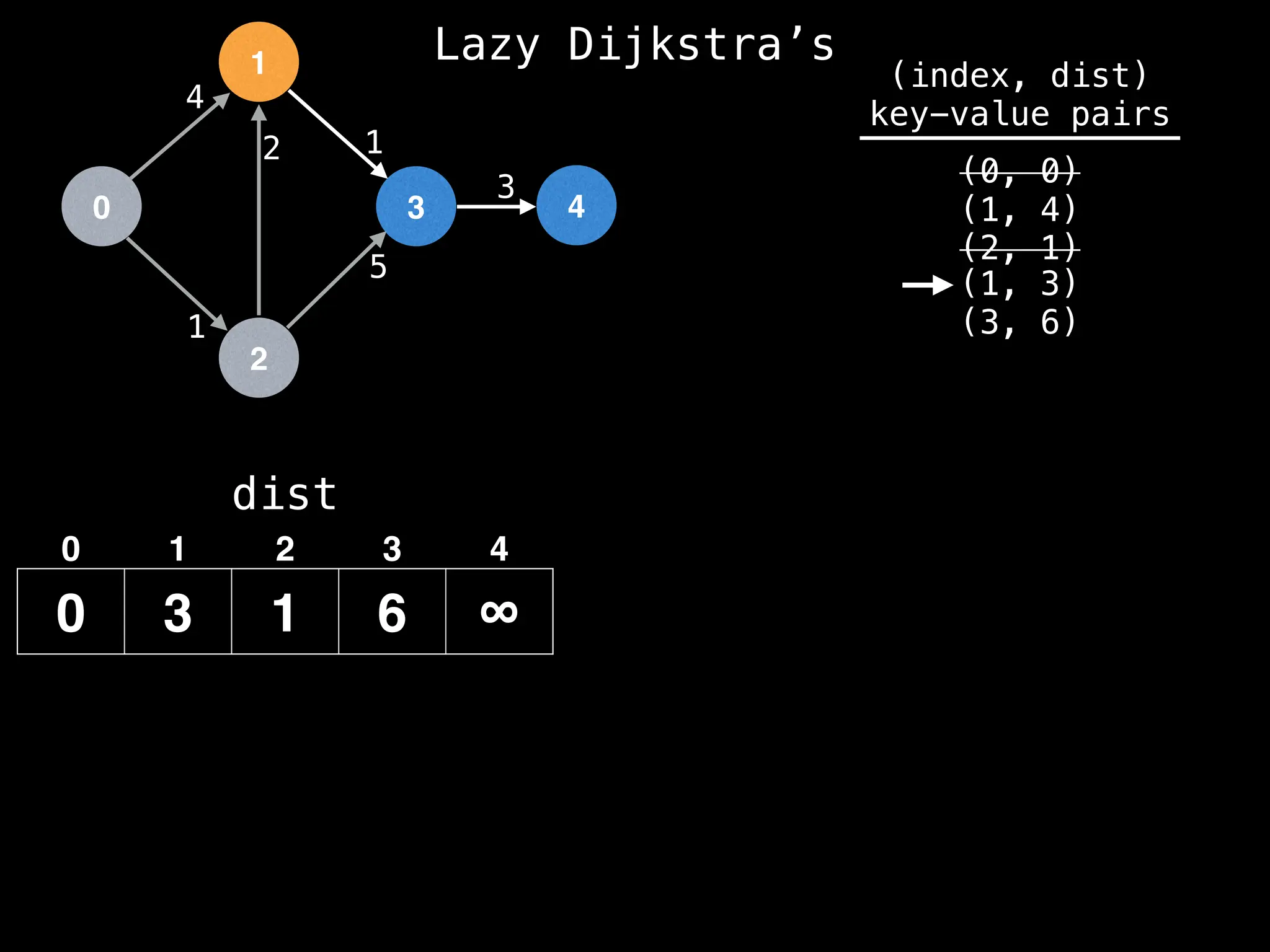
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 3 1 4 ∞
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
(1, 3)
(3, 6)
(3, 4)
Best distance from node 1 to node 3 is:
dist[1] + edge.cost = 3 + 1 = 4
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-573-2048.jpg)
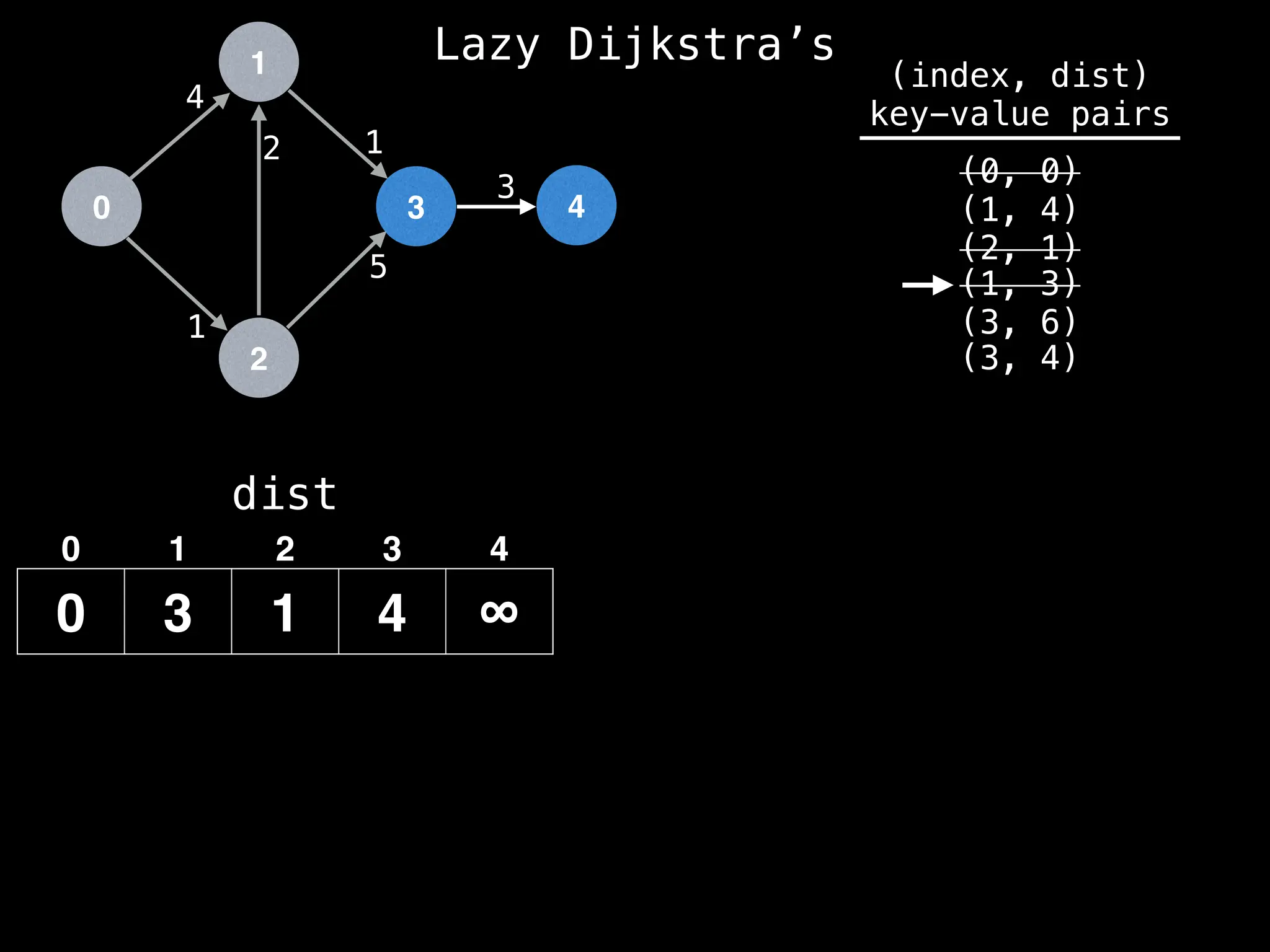
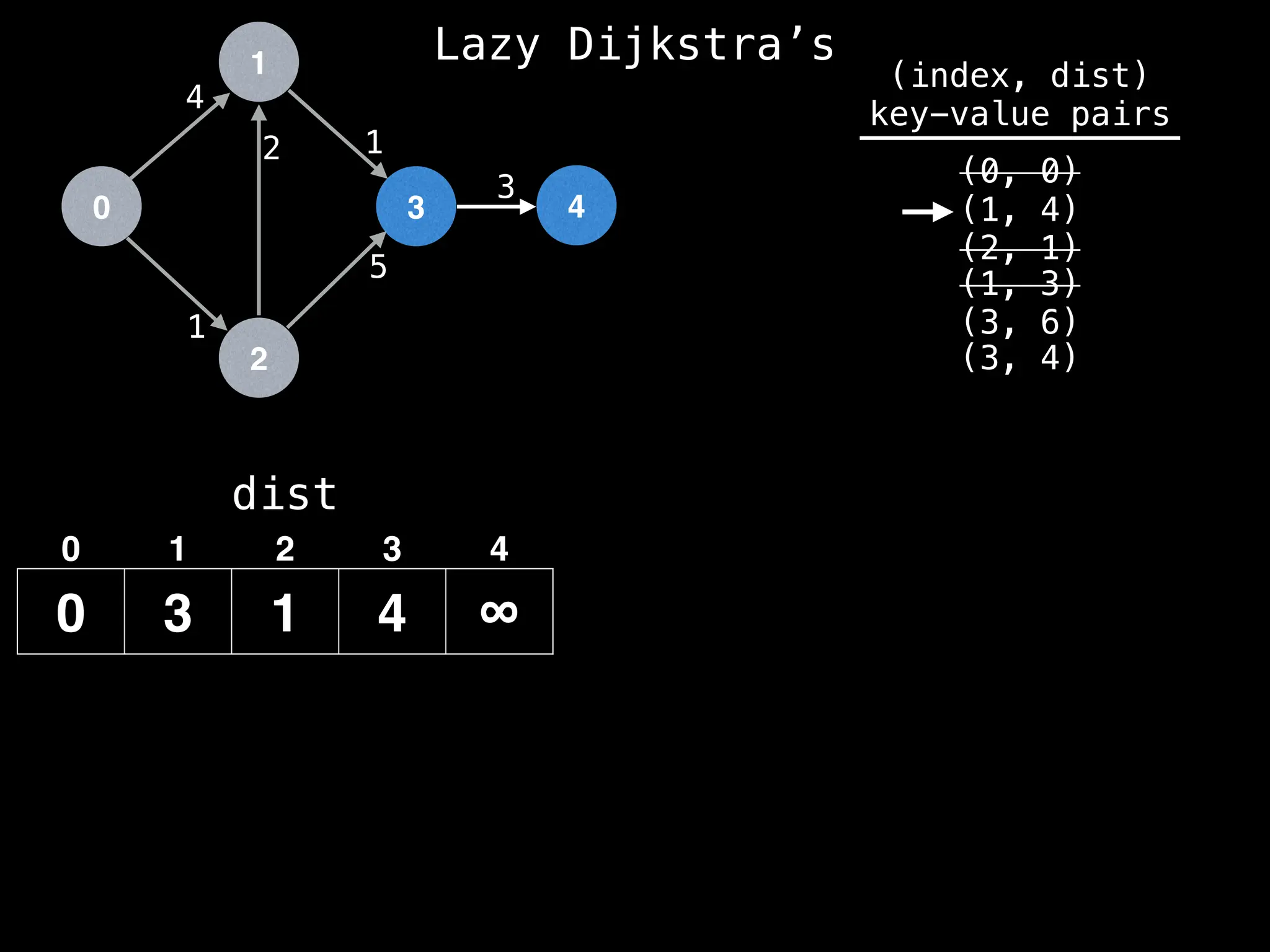
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 3 1 4 ∞
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
(1, 3)
(3, 6)
(3, 4)
We have already found a better route to get to
node 1 (since dist[1] has value 3) so we can
ignore this entry in the PQ.
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-576-2048.jpg)
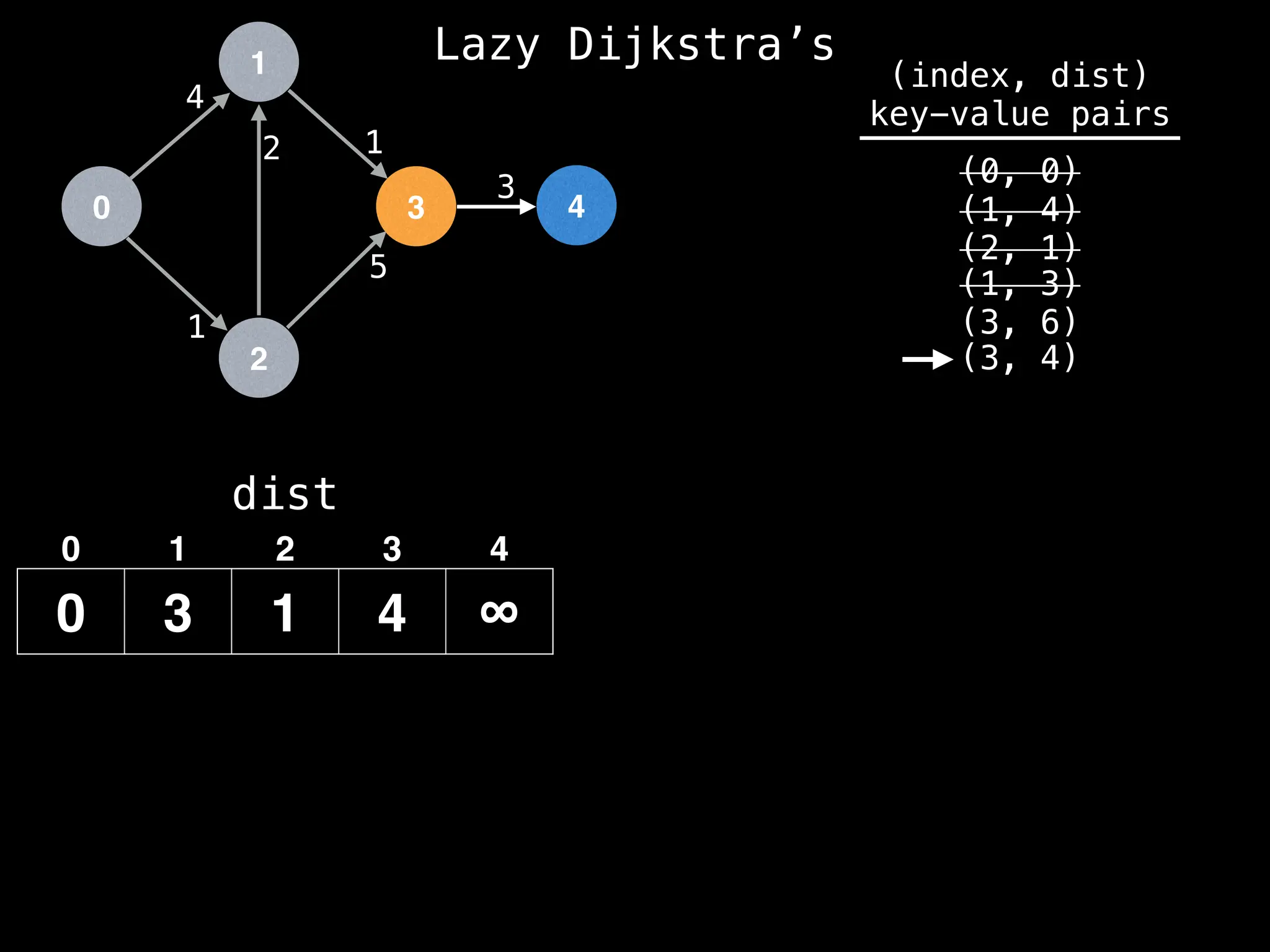
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 3 1 4 7
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
(1, 3)
(3, 6)
(3, 4)
(4, 7)
Best distance from node 3 to node 4 is:
dist[3] + edge.cost = 4 + 3 = 7
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-578-2048.jpg)
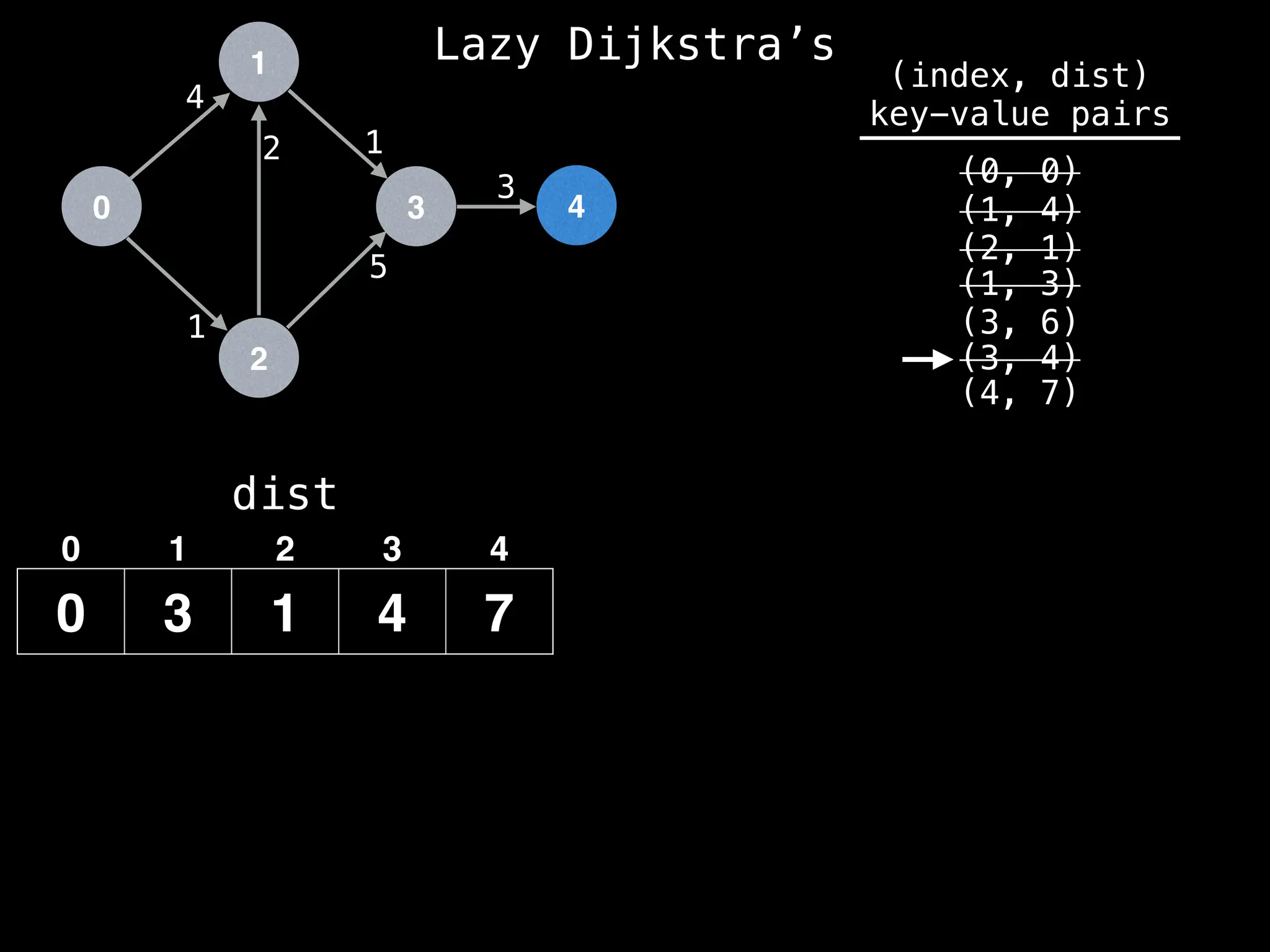
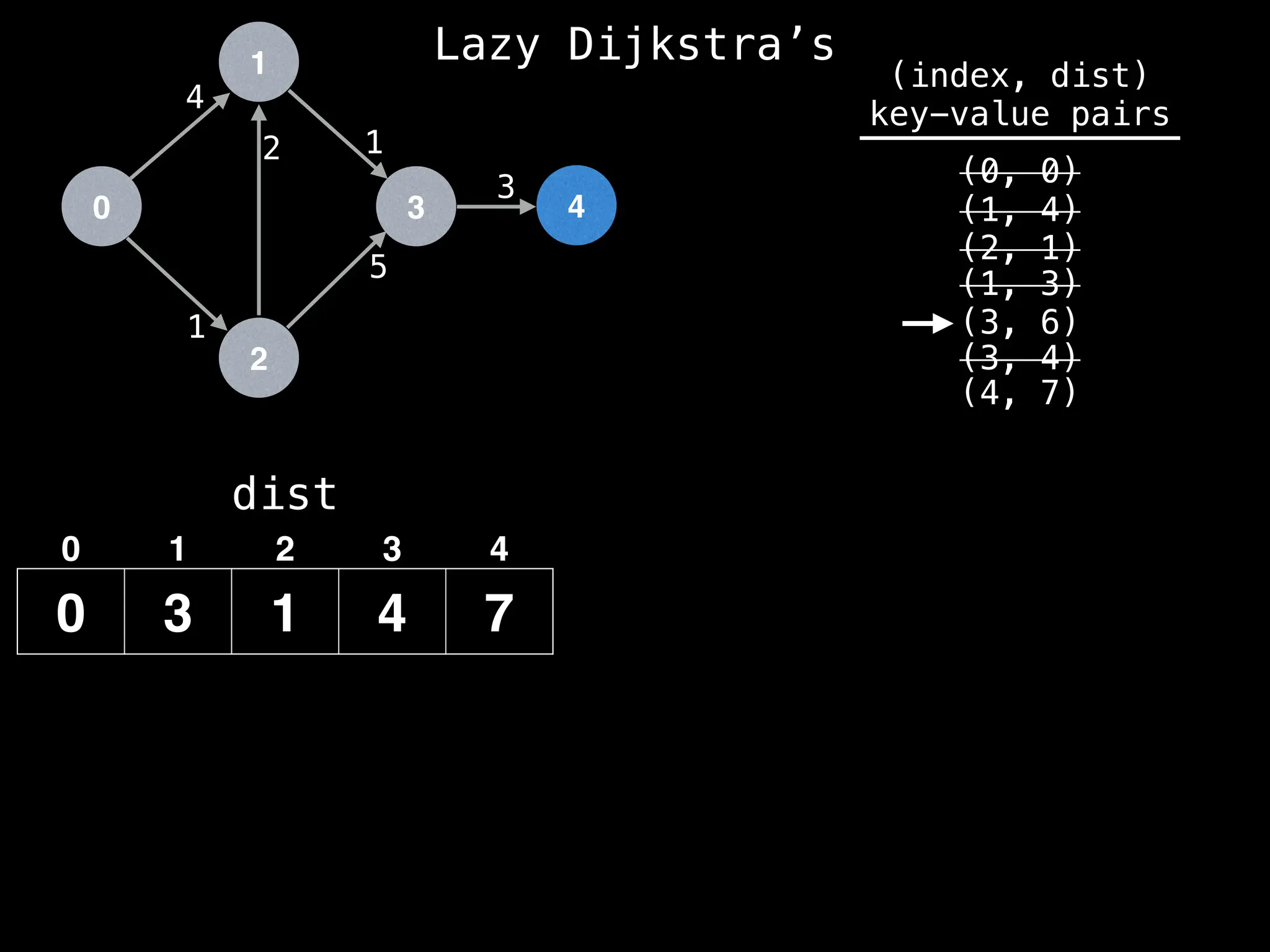
![0
1
2
3 4
1
2 1
5
3
4
dist
0 3 1 4 7
0 1 2 3 4
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
(1, 3)
(3, 6)
(3, 4)
(4, 7)
We have already found a better route to get to
node 3 (since dist[3] has value 4) so we can
ignore this entry in the PQ.
Lazy Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-581-2048.jpg)
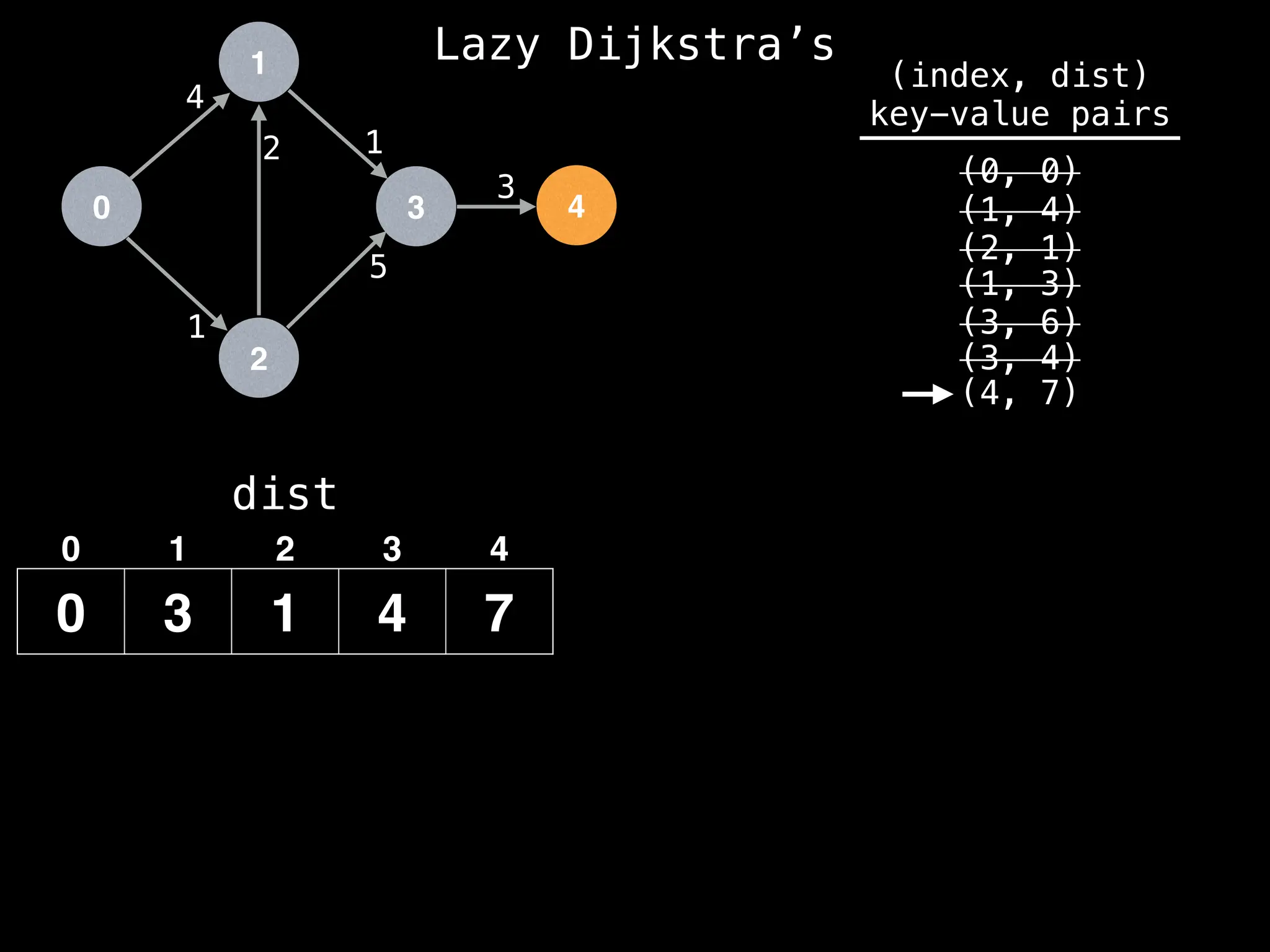
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-584-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-585-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-586-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist
Assume PQ stores (node index, best distance) pairs
sorted by minimum distance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-587-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-588-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-589-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-590-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-591-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist
In practice most standard libraries do not support the
decrease key operation for PQs. A way to get around
this is to add a new (node index, best distance) pair
every time we update the distance to a node.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-592-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist
As a result, it is possible to have duplicate node
indices in the PQ. This is not ideal, but inserting a
new key-value pair in O(log(n)) is much faster than
searching for the key in the PQ which takes O(n)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-593-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-594-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
if dist[index] < minValue: continue
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return dist
A neat optimization we can do which ignores stale (index,
dist) pairs in our PQ is to skip nodes where we already
found a better path routing through others nodes before we
got to processing this node.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-595-2048.jpg)
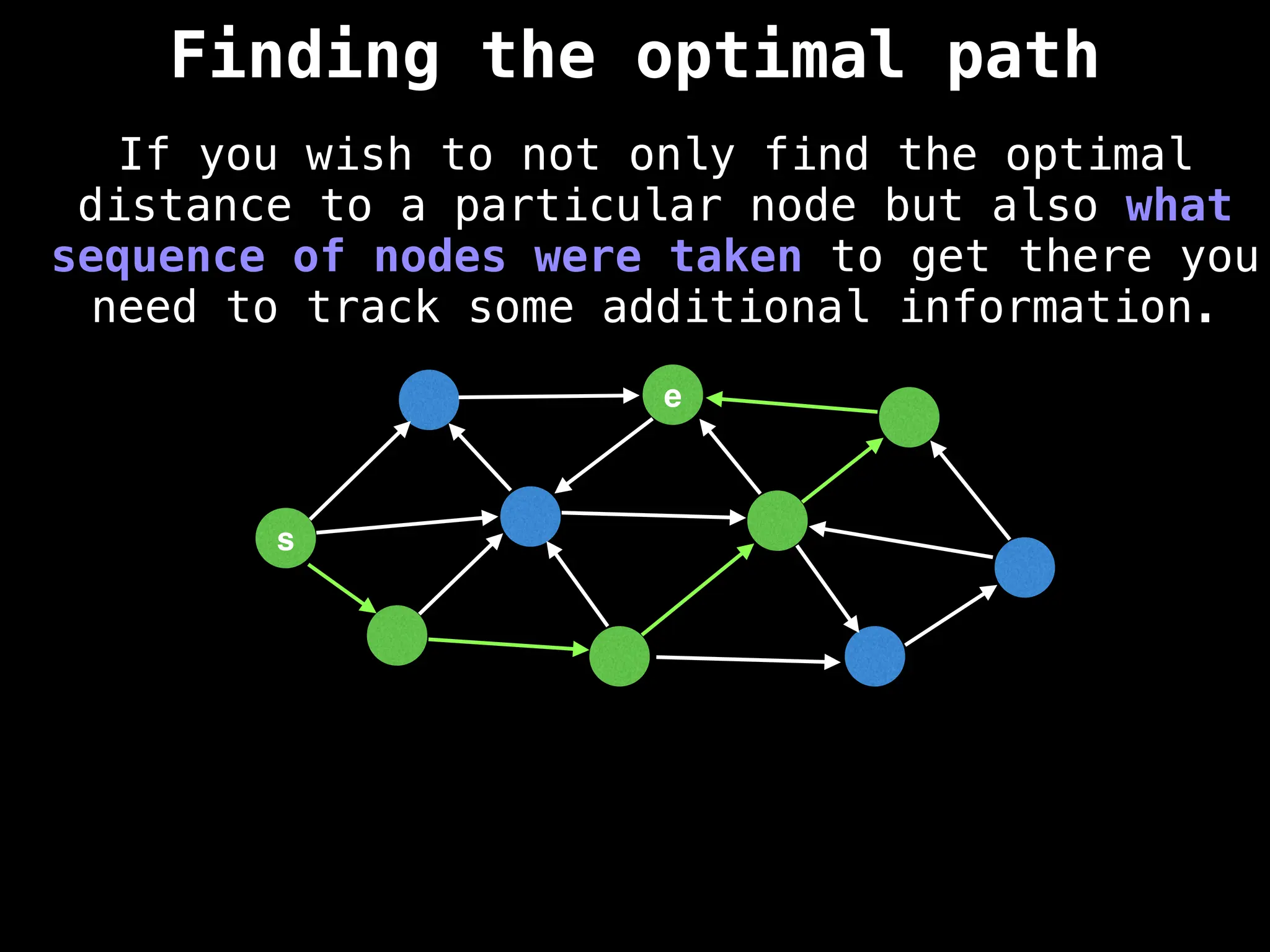
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s and
# the prev array to reconstruct the shortest path itself
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
prev = [null, null, …, null] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
if dist[index] < minValue: continue
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
prev[edge.to] = index
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
return (dist, prev)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-597-2048.jpg)
![# Finds the shortest path between two nodes.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
# e - the index of the end node (0 ≤ e < n)
function findShortestPath(g, n, s, e):
dist, prev = dijkstra(g, n, s)
path = []
if (dist[e] == ∞) return path
for (at = e; at != null; at = prev[at])
path.add(at)
path.reverse()
return path](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-598-2048.jpg)
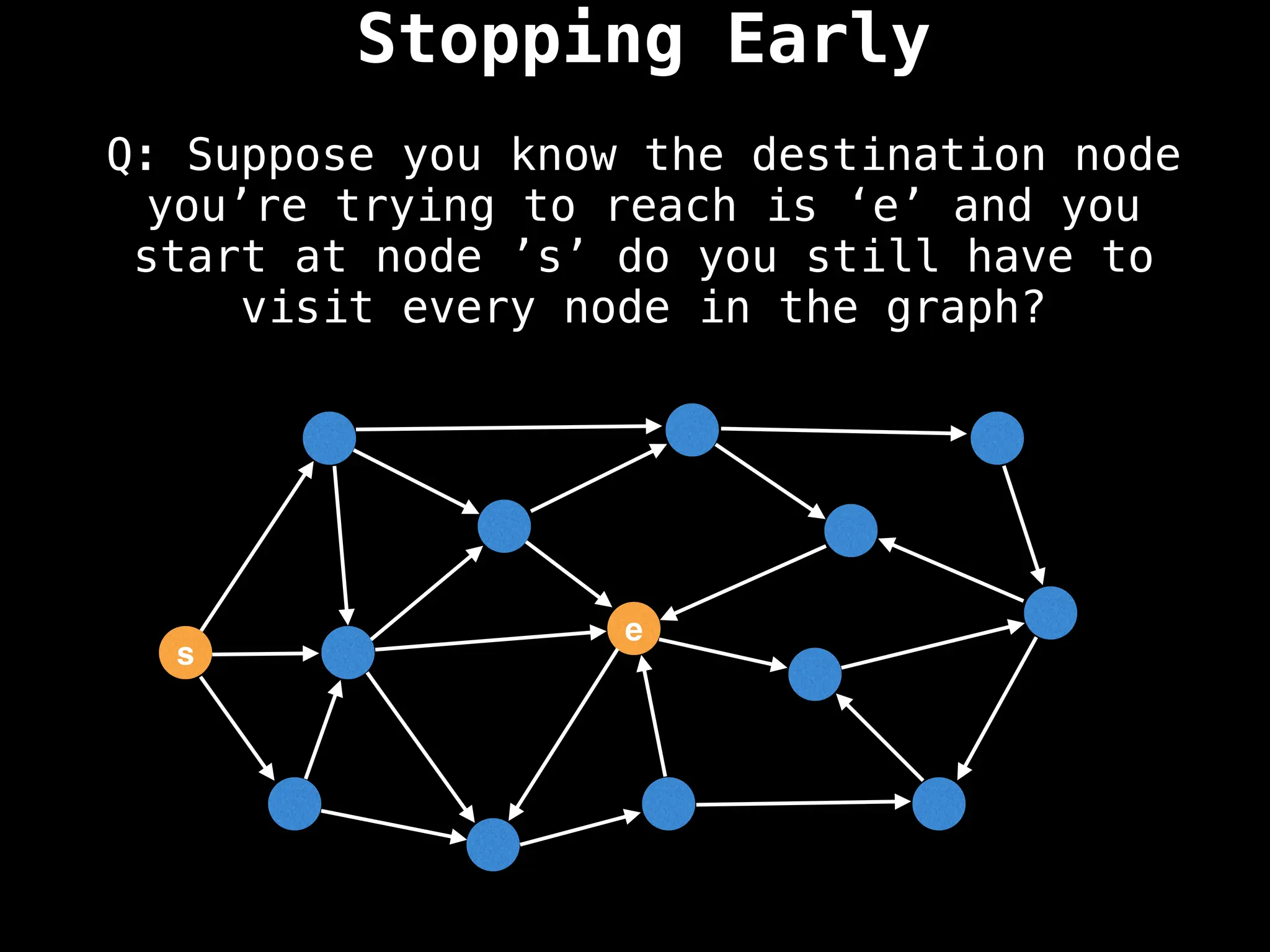
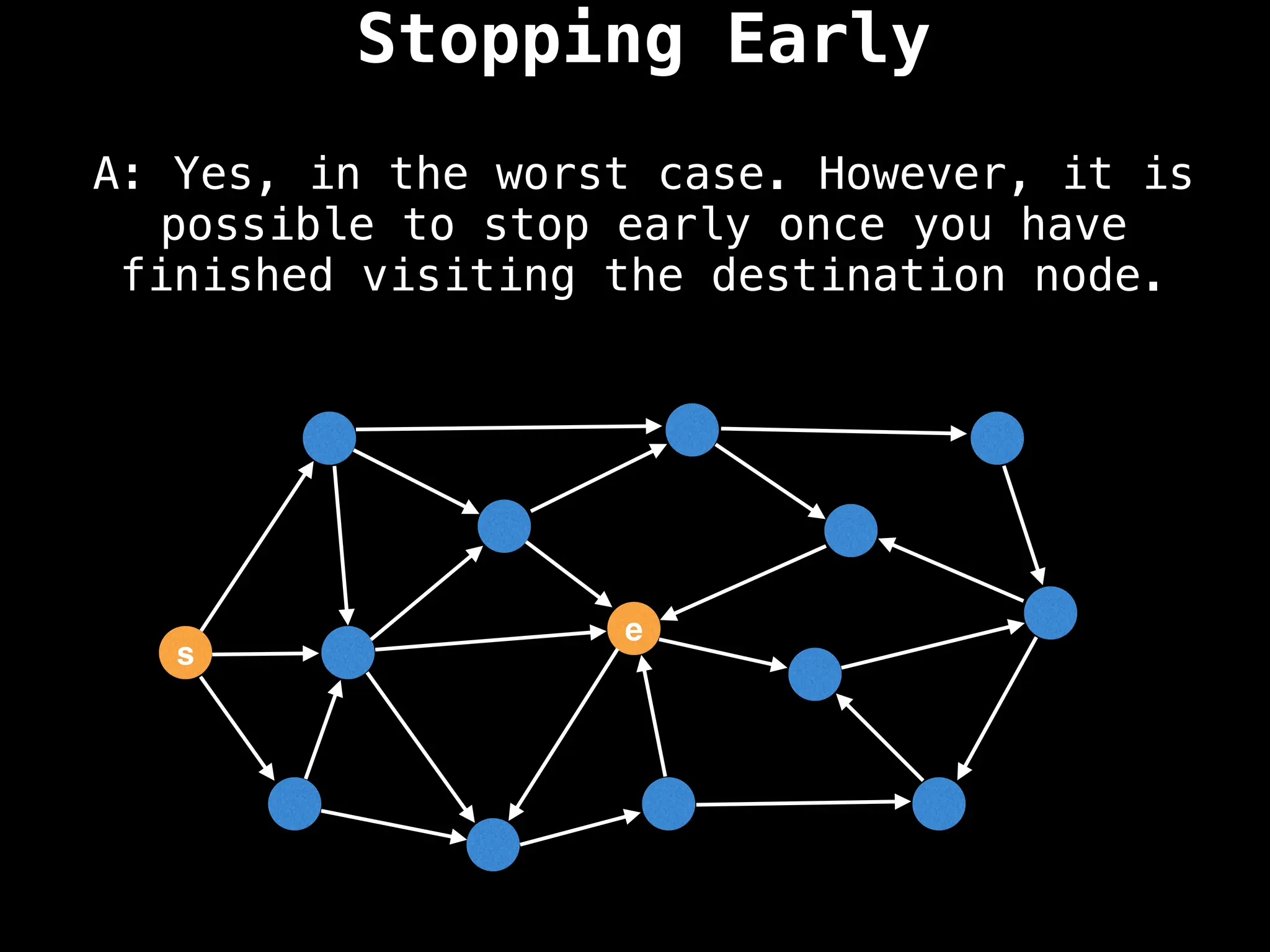
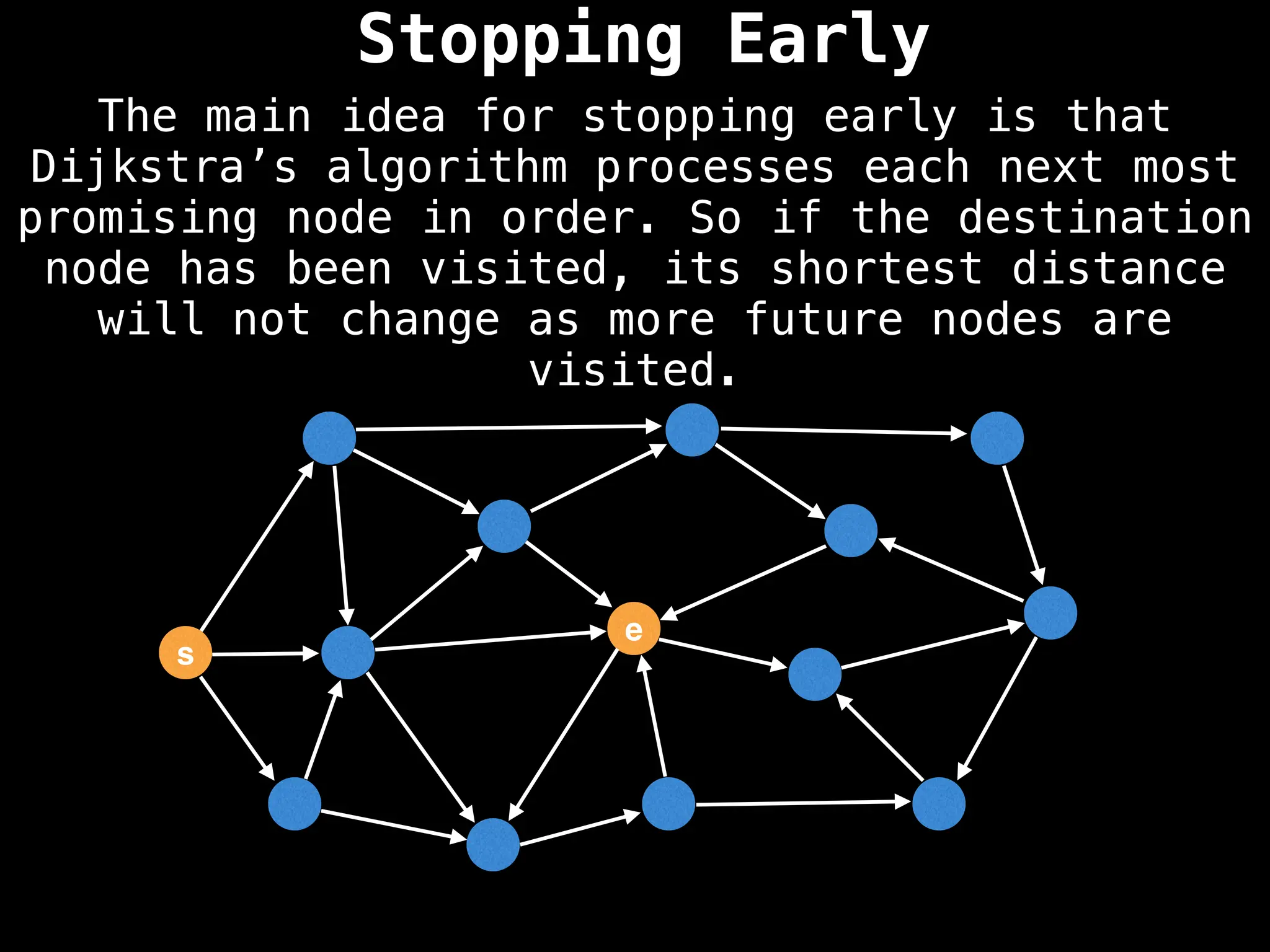
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns the shortest distance
# between nodes ’s’ and ‘e’. If there is no path, ∞ is returned.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
# e - the index of the end node (0 ≤ e < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s, e):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
pq = empty priority queue
pq.insert((s, 0))
while pq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = pq.poll()
vis[index] = true
if dist[index] < minValue: continue
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
pq.insert((edge.to, newDist))
if index == e:
return dist[e]
return ∞](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-602-2048.jpg)
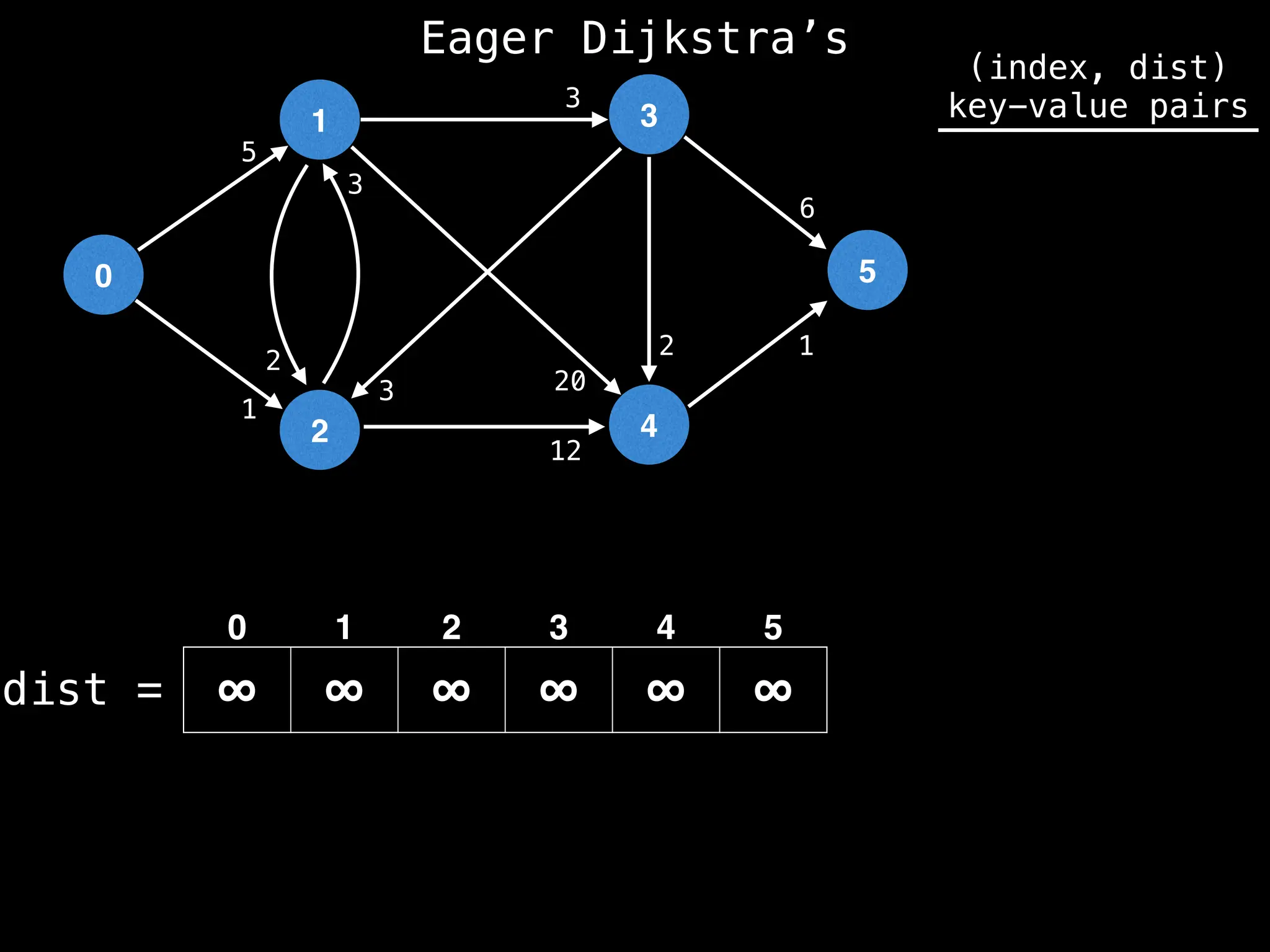
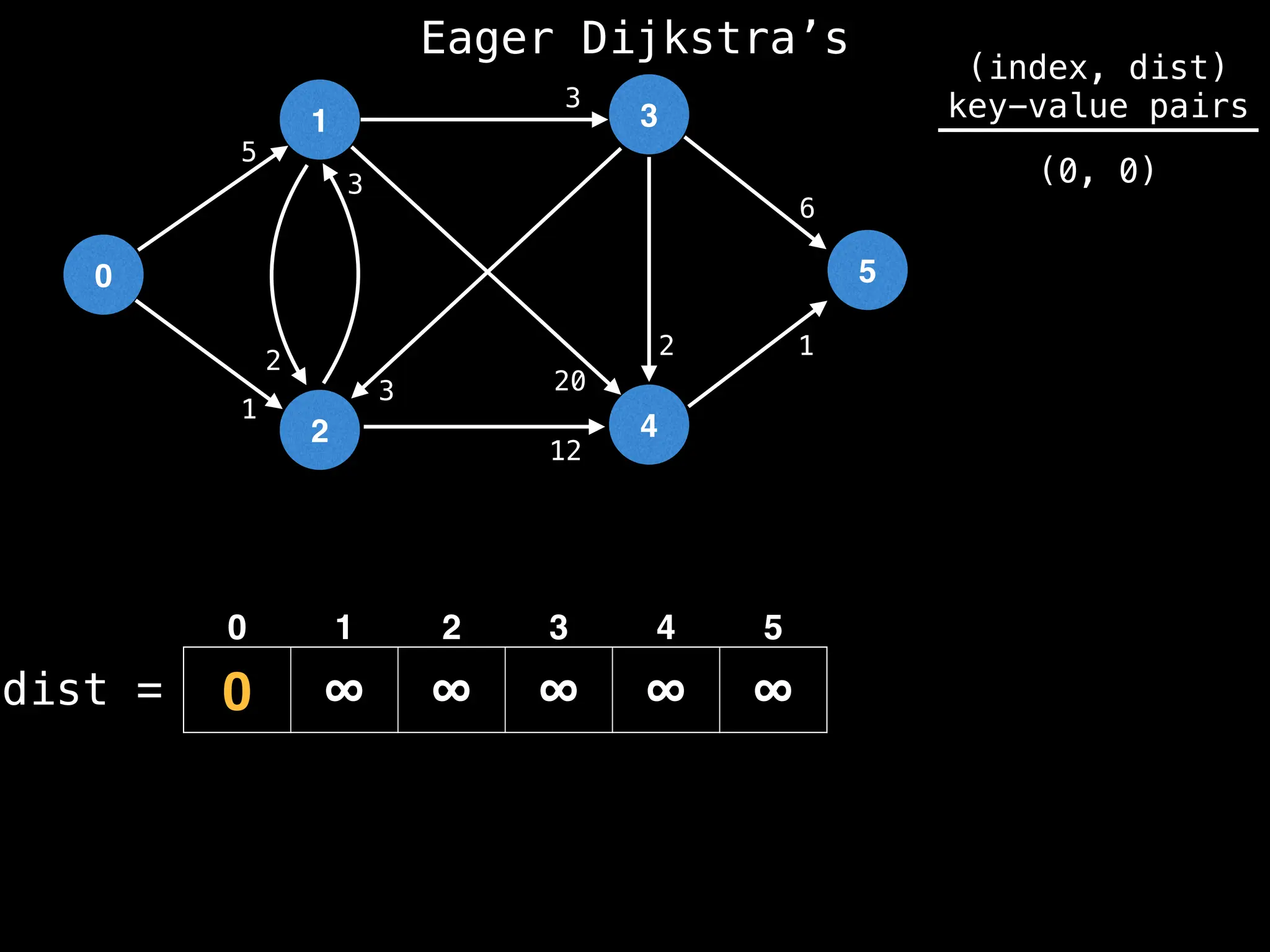
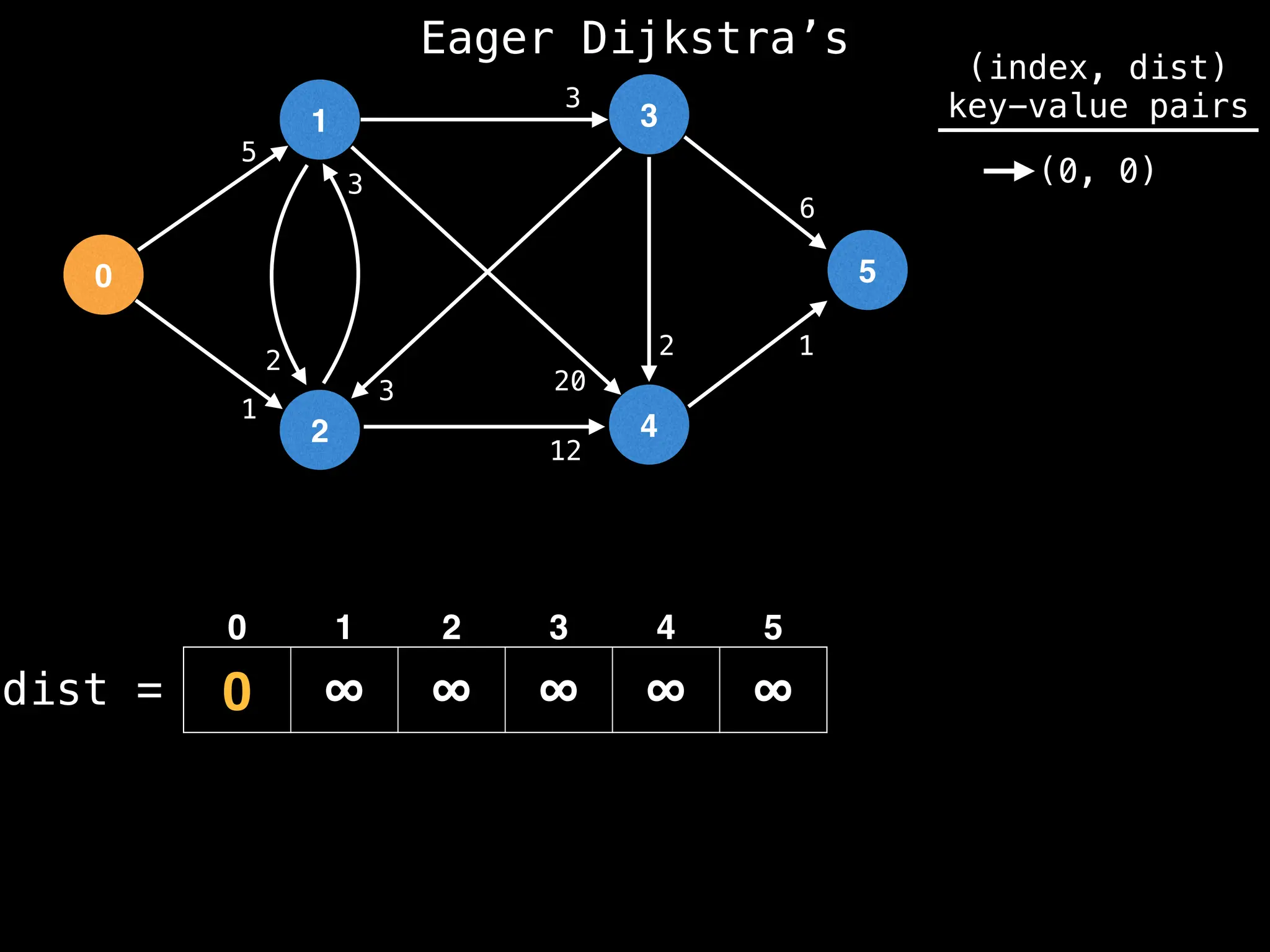
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
1
2
3
2
3
12
20
3
6
0 5 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 5)
0 1 2 3 4 5
Best distance from node 0 to node 1:
dist[0] + edge.cost = 0 + 5 = 5
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-608-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
1
2
3
2
3
12
20
3
6
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 5)
(2, 1)
0 5 1 ∞ ∞ ∞
0 1 2 3 4 5
Best distance from node 0 to node 2:
dist[0] + edge.cost = 0 + 1 = 1
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-609-2048.jpg)
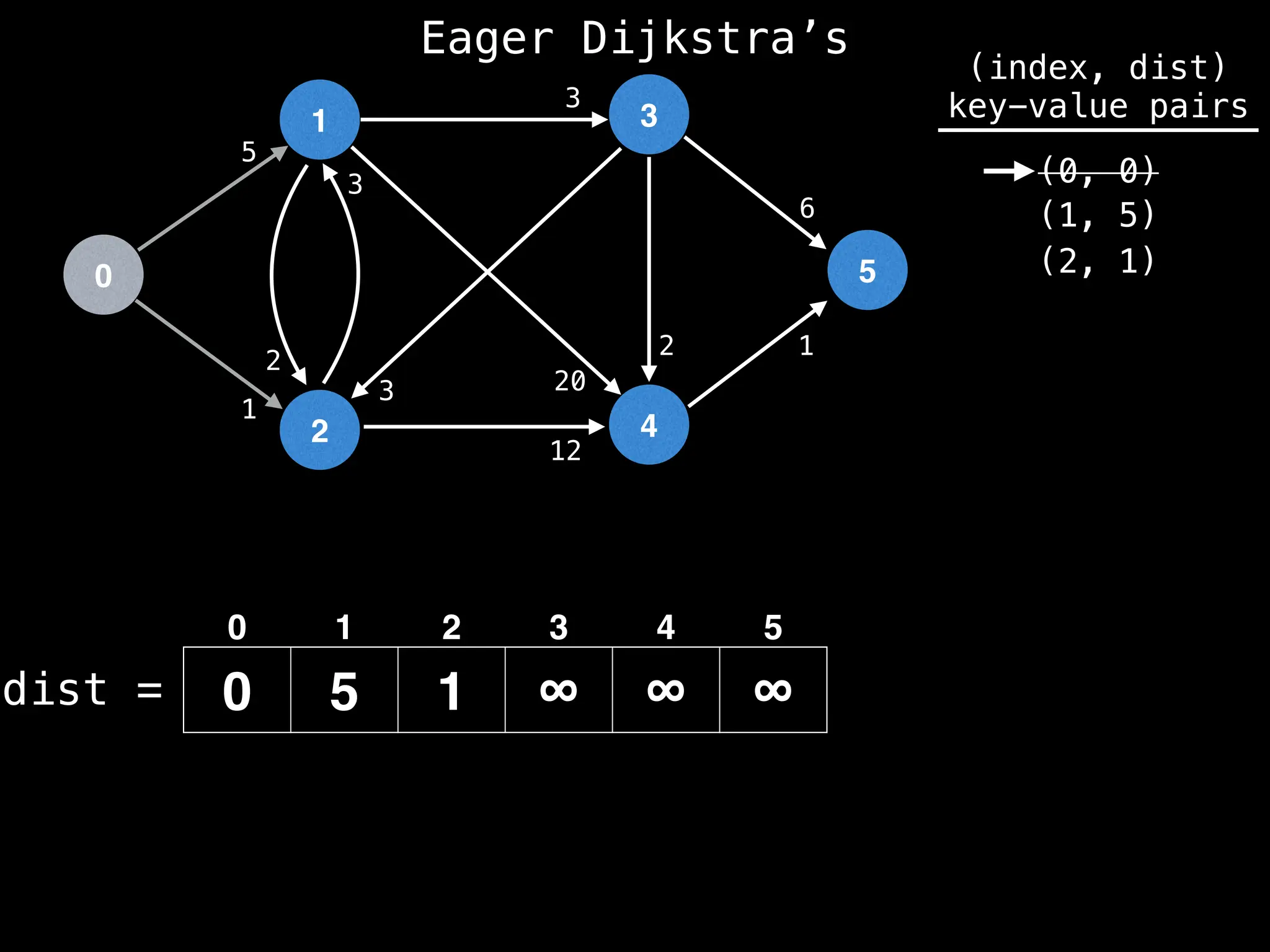
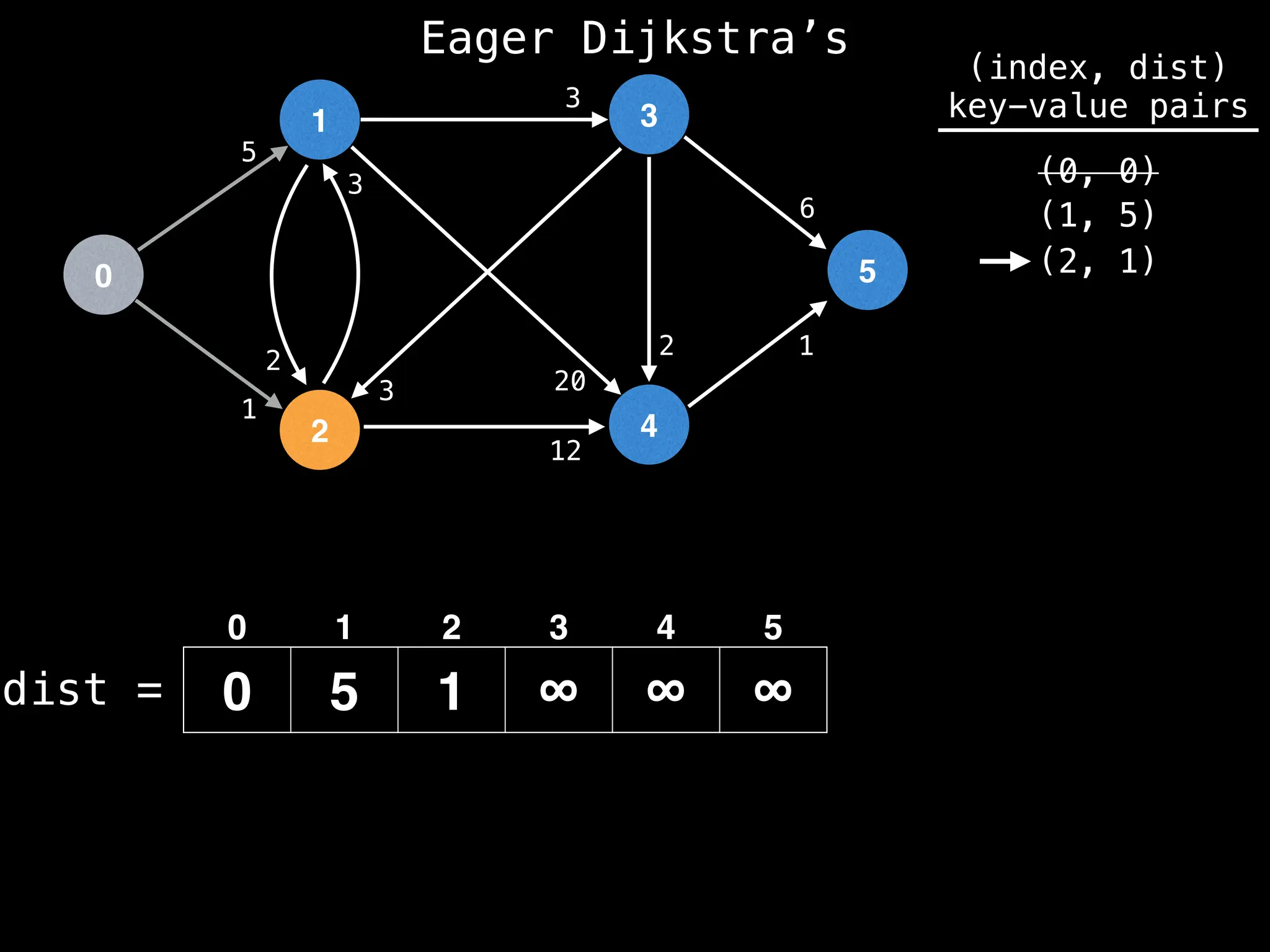
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
12
1
2
3
2
3
20
3
6
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 5)
(2, 1)
0 5 1 ∞ 13 ∞
0 1 2 3 4 5
(4, 13)
Best distance from node 2 to node 4:
dist[2] + edge.cost = 1 + 12 = 13
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-612-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
12
1
2
3
2
3
20
3
6
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
0 4 1 ∞ 13 ∞
0 1 2 3 4 5
(4, 13)
Best distance from node 2 to node 1:
dist[2] + edge.cost = 1 + 3 = 4
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-613-2048.jpg)
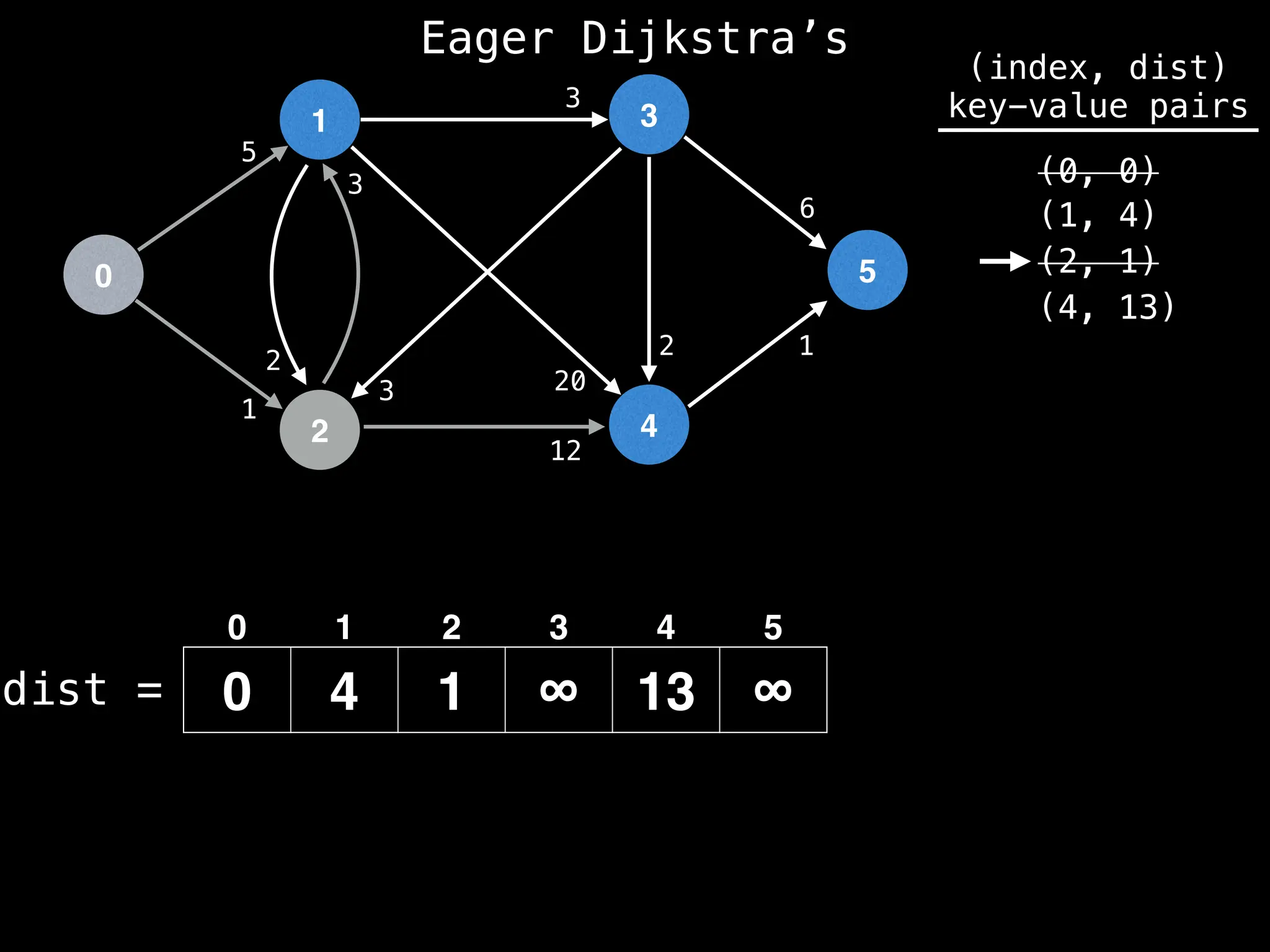
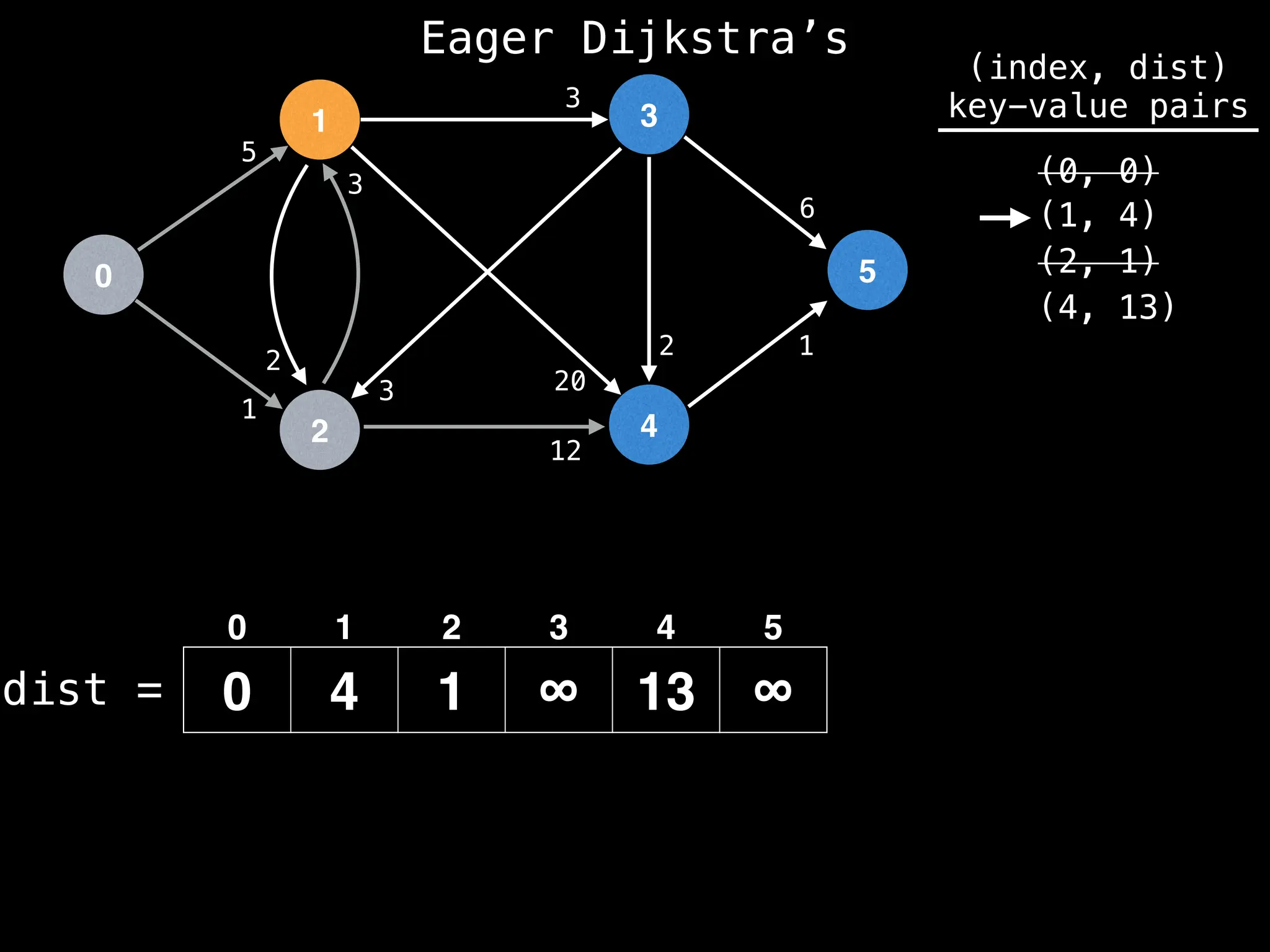
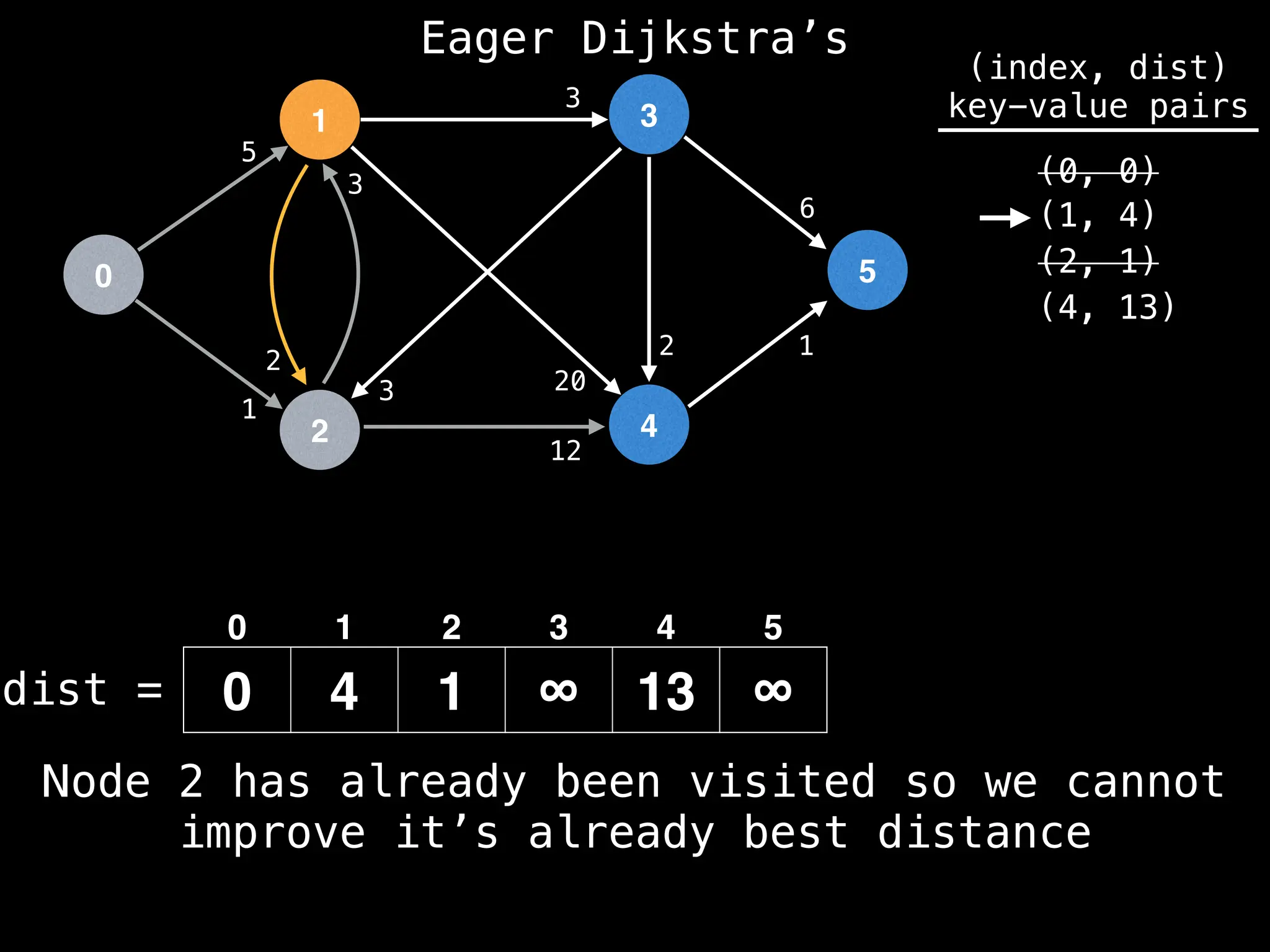
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
12
1
2
3
2
3
20
3
6
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
0 4 1 ∞ 13 ∞
(4, 13)
0 1 2 3 4 5
dist[1] + edge.cost = 4 + 20 = 24 > dist[4] = 13
so we cannot update best distance.
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-617-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
12
1
2
3
2
3
20
3
6
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
0 4 1 7 13 ∞
(4, 13)
0 1 2 3 4 5
(3, 7)
Best distance from node 1 to node 3:
dist[1] + edge.cost = 4 + 3 = 7
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-618-2048.jpg)
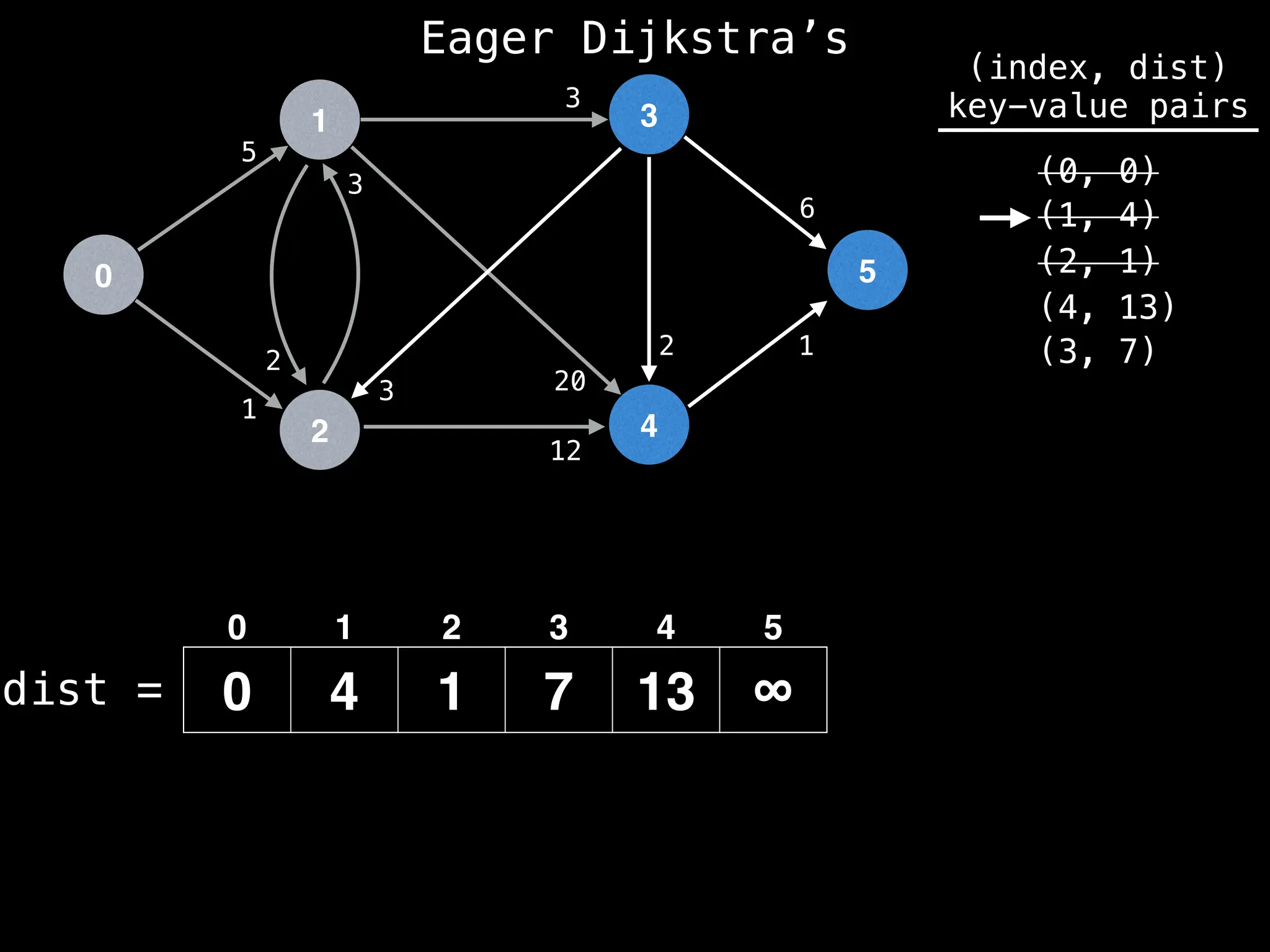
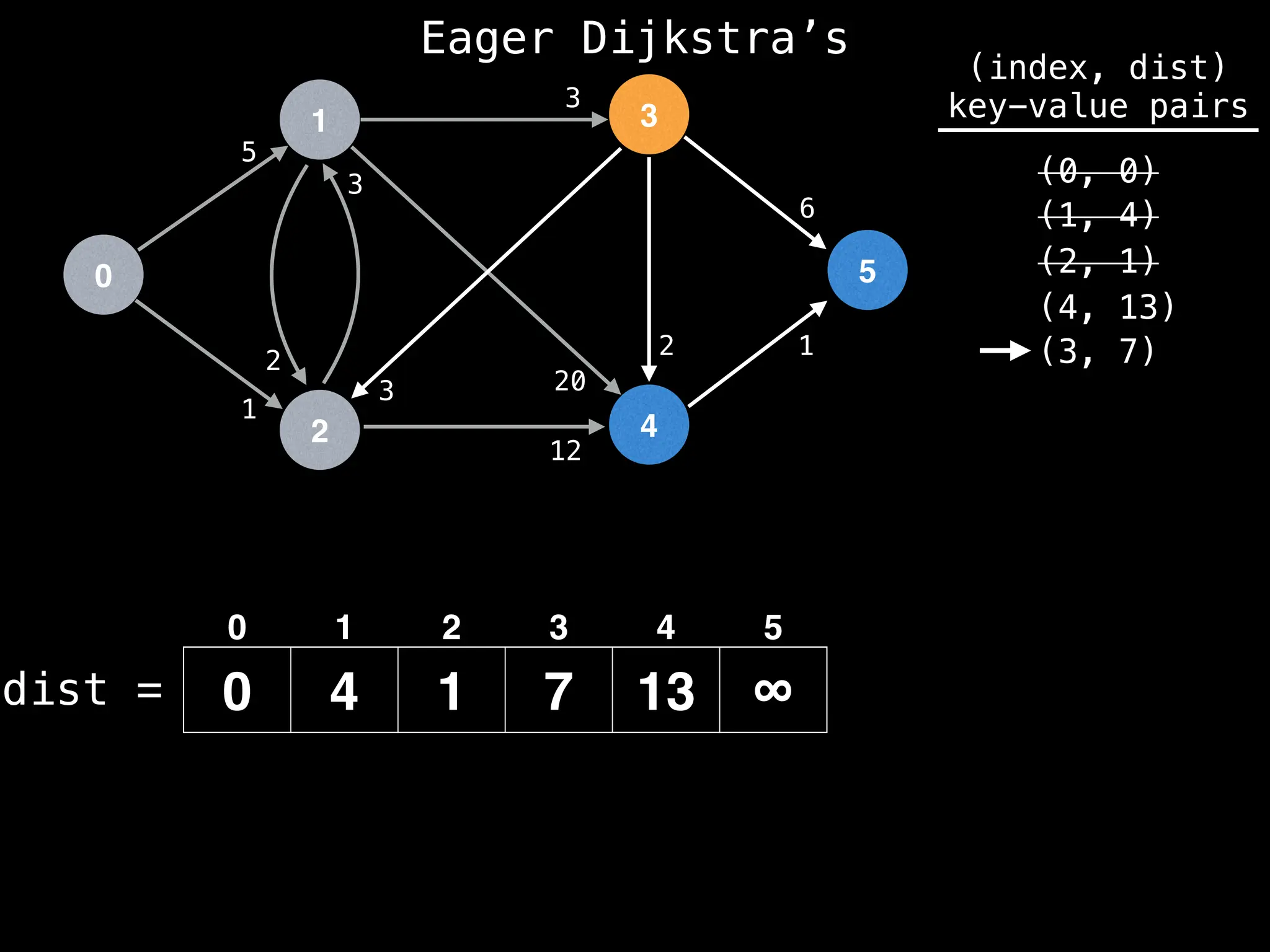
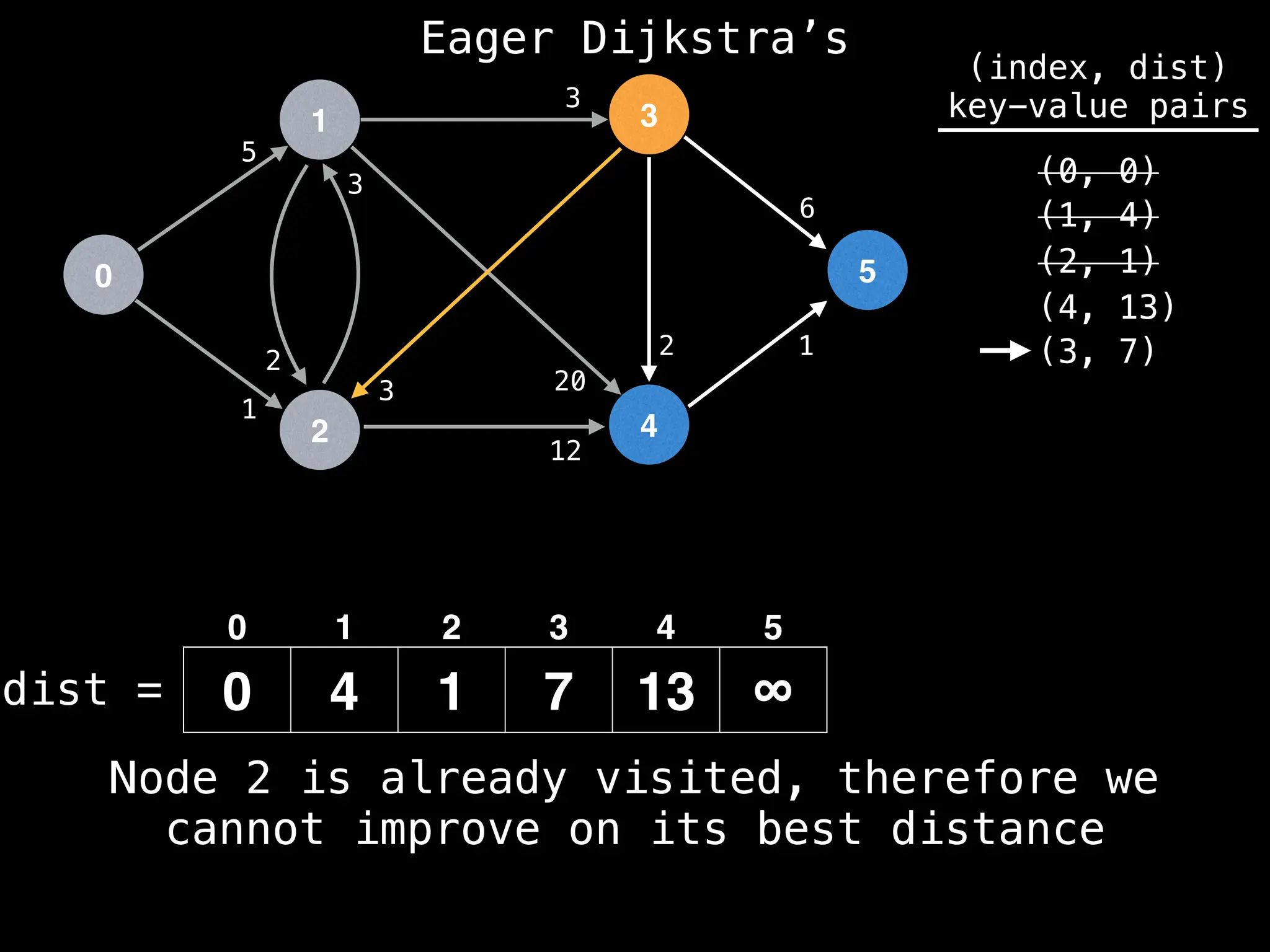
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
12
1
2
3
2
3
20
3
6
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
0 4 1 7 9 ∞
(4, 9)
0 1 2 3 4 5
(3, 7)
Best distance from node 3 to node 4:
dist[3] + edge.cost = 7 + 2 = 9
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-622-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
12
1
2
6
3
2
3
20
3
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
0 4 1 7 9 13
(4, 9)
0 1 2 3 4 5
(3, 7)
(5, 13)
Best distance from node 3 to node 5:
dist[3] + edge.cost = 7 + 6 = 13
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-623-2048.jpg)
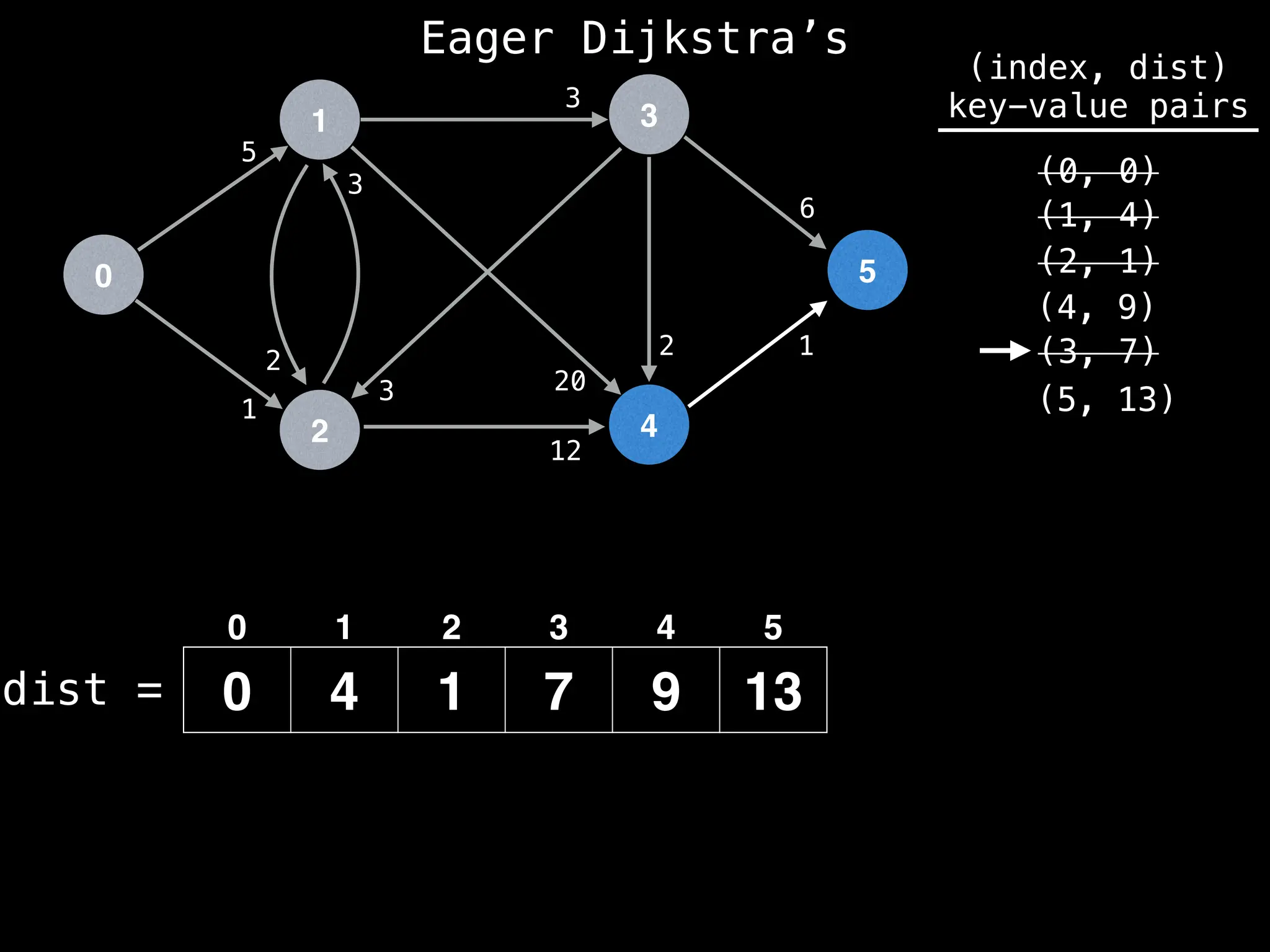
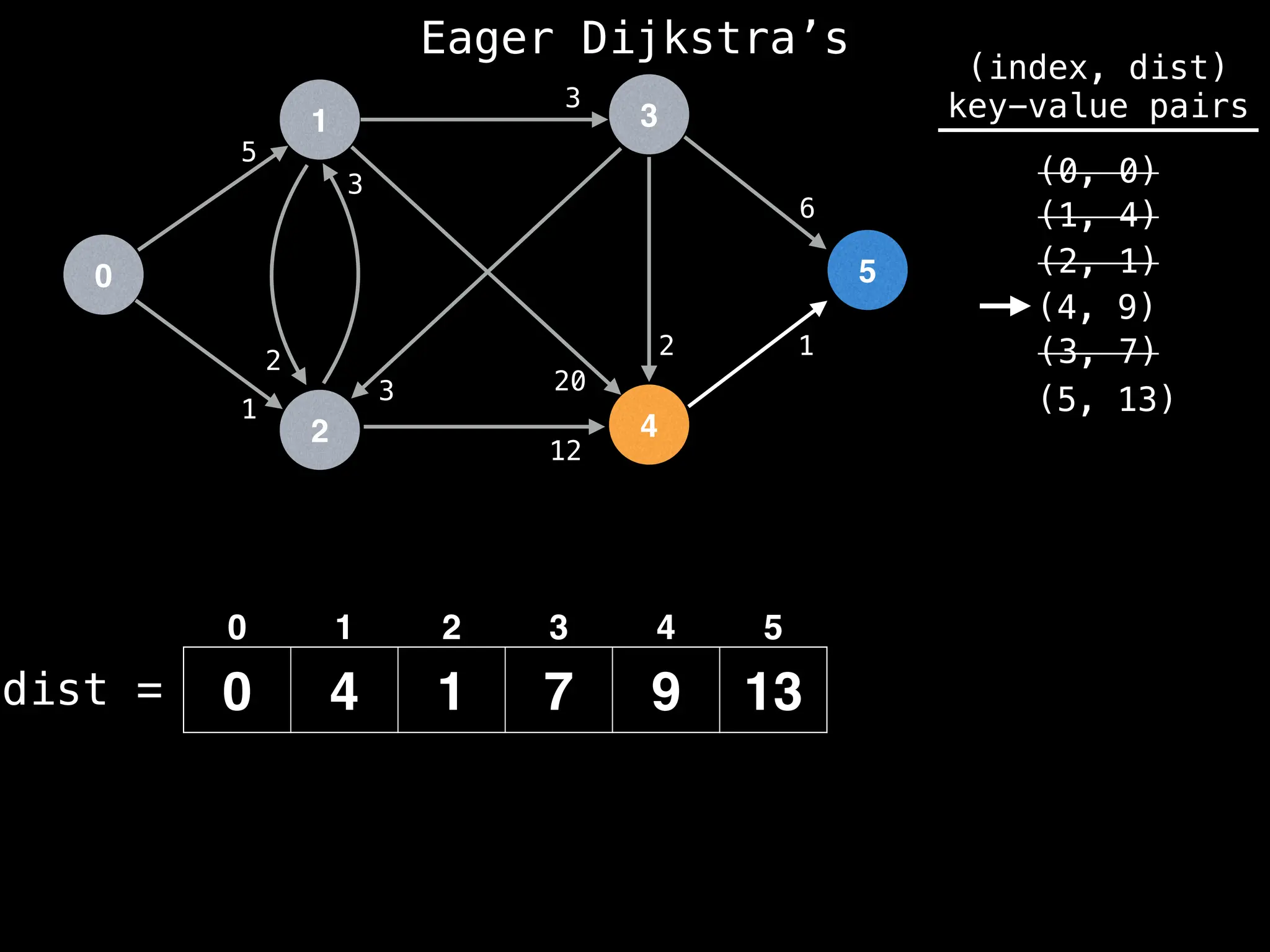
![0
1
2
3
4
5
5
1
12
1
2
6
3
2
3
20
3
dist =
(index, dist)
key-value pairs
(0, 0)
(1, 4)
(2, 1)
0 4 1 7 9 10
(4, 9)
0 1 2 3 4 5
(3, 7)
(5, 10)
Best distance from node 4 to node 5:
dist[3] + edge.cost = 9 + 1 = 10
Eager Dijkstra’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-626-2048.jpg)
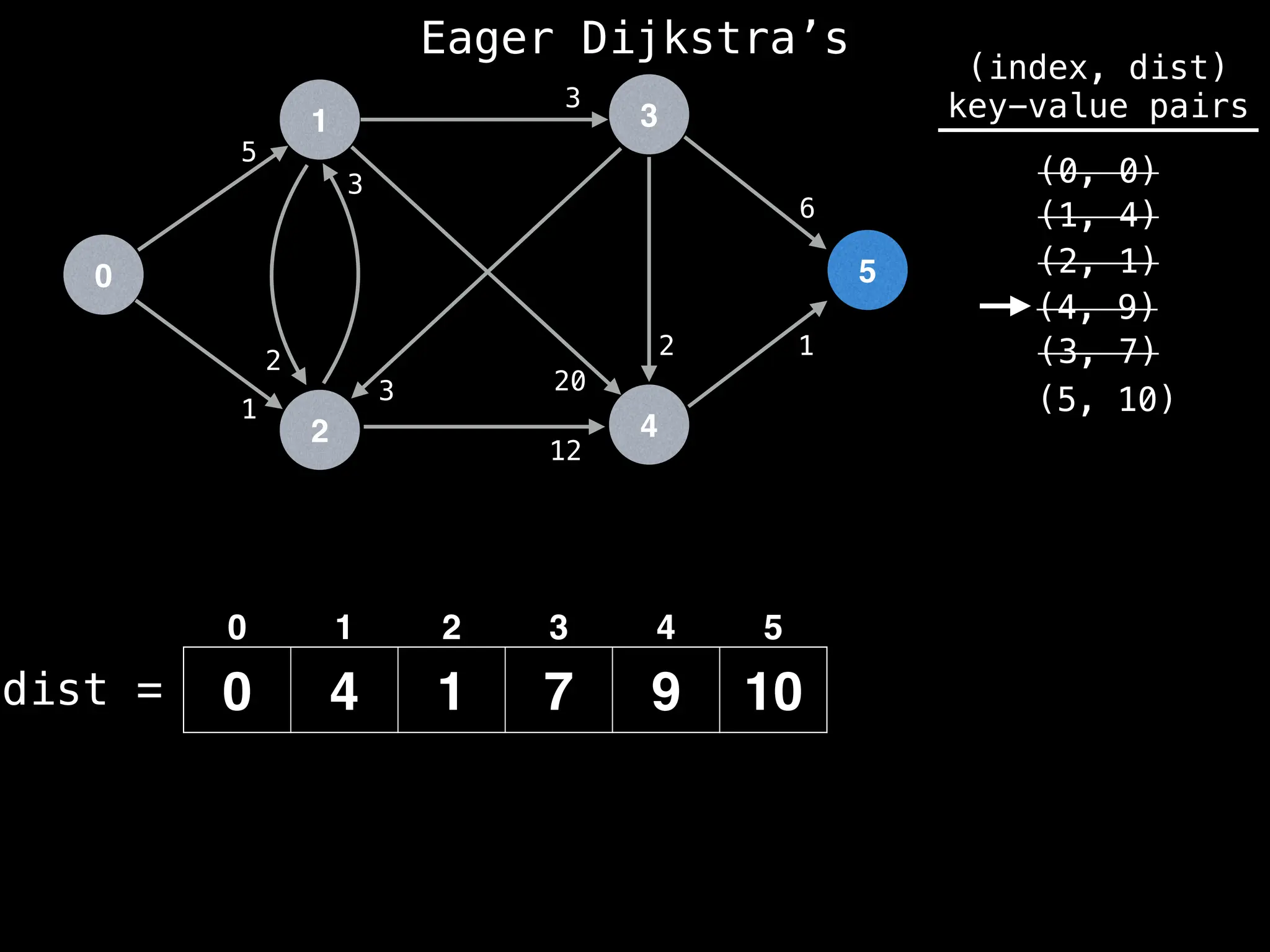
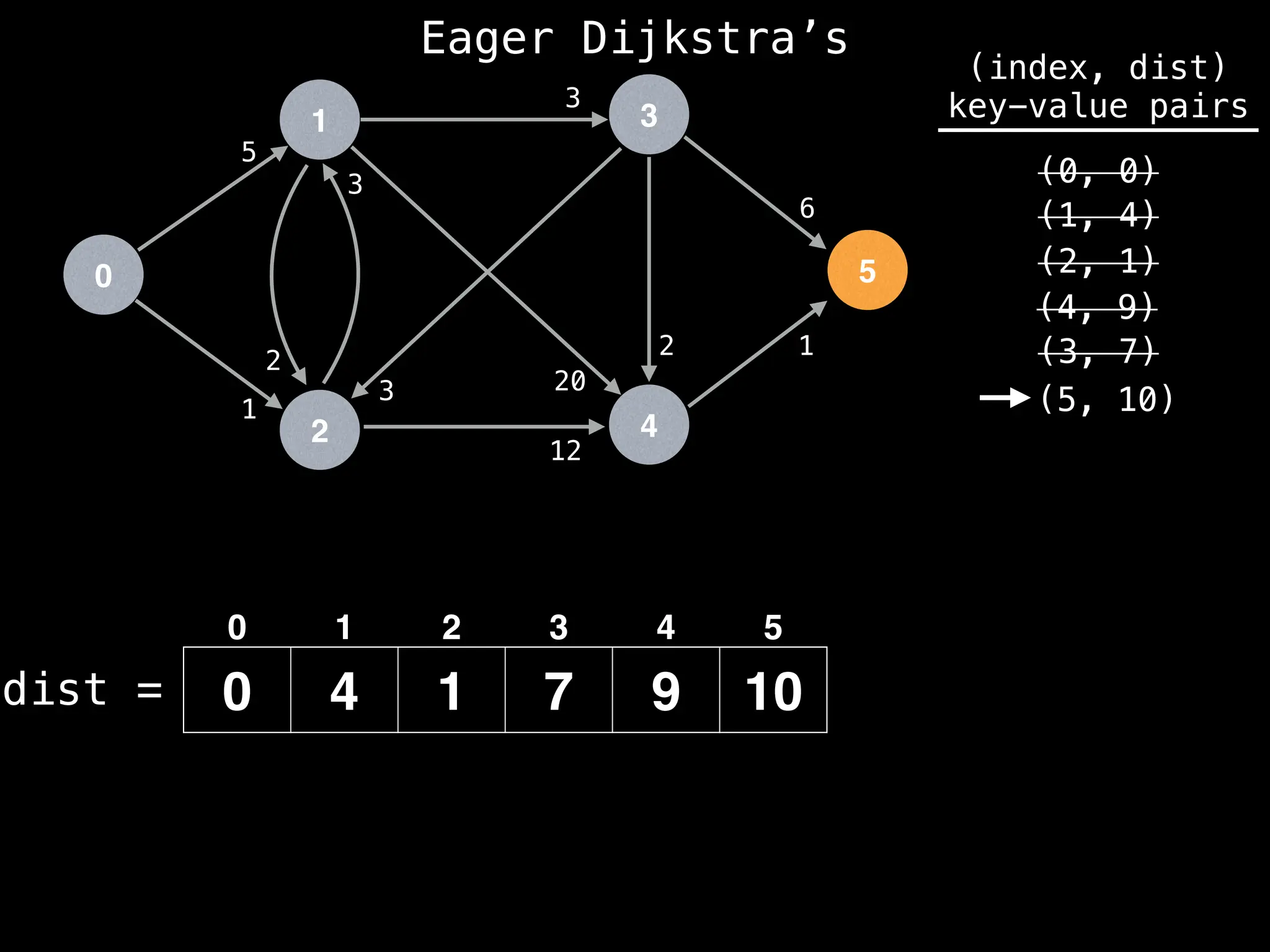
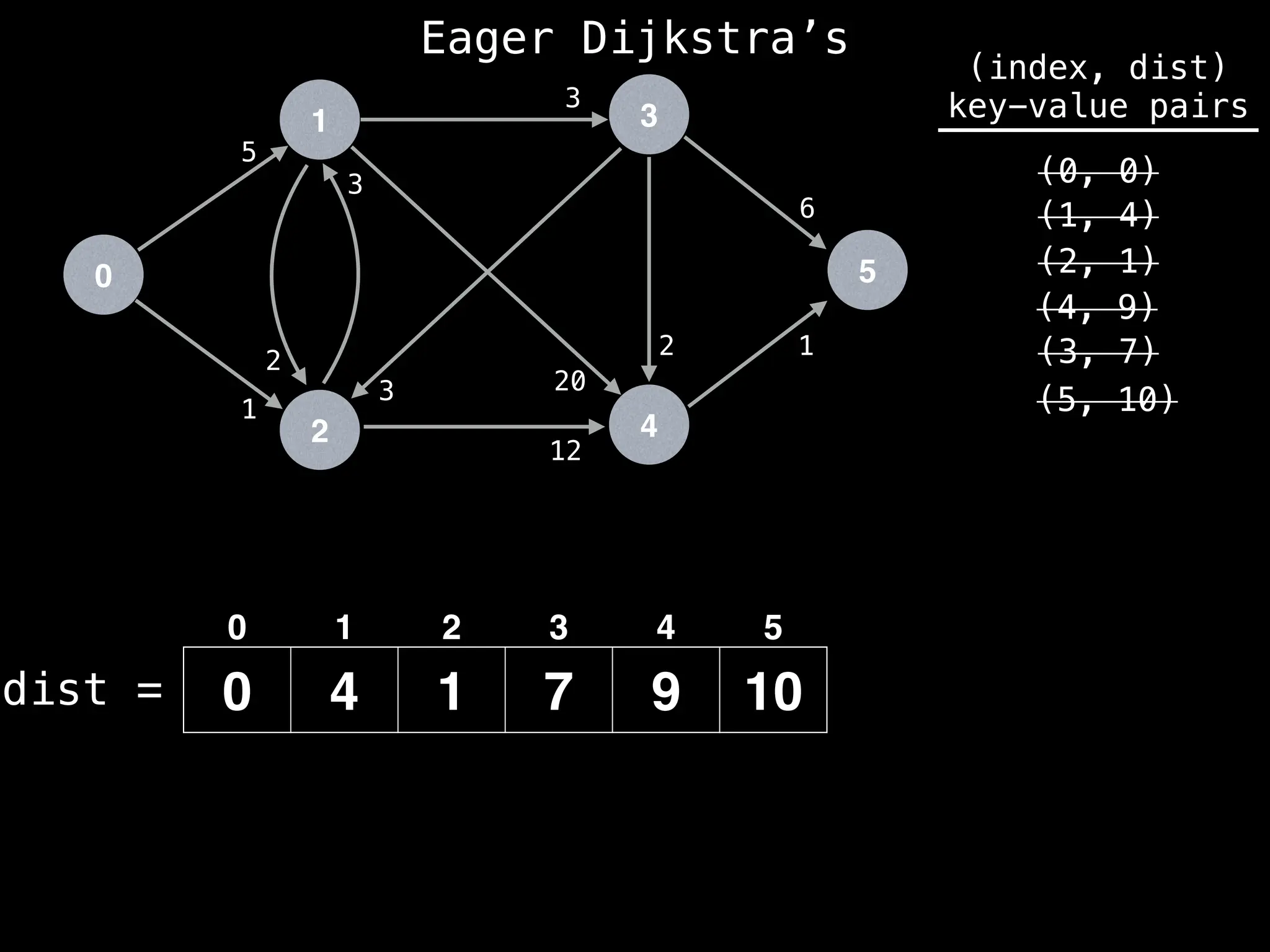
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
ipq = empty indexed priority queue
ipq.insert(s, 0)
while ipq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = ipq.poll()
vis[index] = true
if dist[index] < minValue: continue
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
if !ipq.contains(edge.to):
ipq.insert(edge.to, newDist)
else:
ipq.decreaseKey(edge.to, newDist)
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-630-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
ipq = empty indexed priority queue
ipq.insert(s, 0)
while ipq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = ipq.poll()
vis[index] = true
if dist[index] < minValue: continue
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
if !ipq.contains(edge.to):
ipq.insert(edge.to, newDist)
else:
ipq.decreaseKey(edge.to, newDist)
return dist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-631-2048.jpg)
![# Runs Dijkstra’s algorithm and returns an array that contains
# the shortest distance to every node from the start node s.
# g - adjacency list of weighted graph
# n - the number of nodes in the graph
# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function dijkstra(g, n, s):
vis = [false, false, … , false] # size n
dist = [∞, ∞, … ∞, ∞] # size n
dist[s] = 0
ipq = empty indexed priority queue
ipq.insert(s, 0)
while ipq.size() != 0:
index, minValue = ipq.poll()
vis[index] = true
if dist[index] < minValue: continue
for (edge : g[index]):
if vis[edge.to]: continue
newDist = dist[index] + edge.cost
if newDist < dist[edge.to]:
dist[edge.to] = newDist
if !ipq.contains(edge.to):
ipq.insert(edge.to, newDist)
else:
ipq.decreaseKey(edge.to, newDist)
return dist
The main advantage to using decreaseKey is to prevent
duplicate node indexes to be present in the PQ.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-632-2048.jpg)

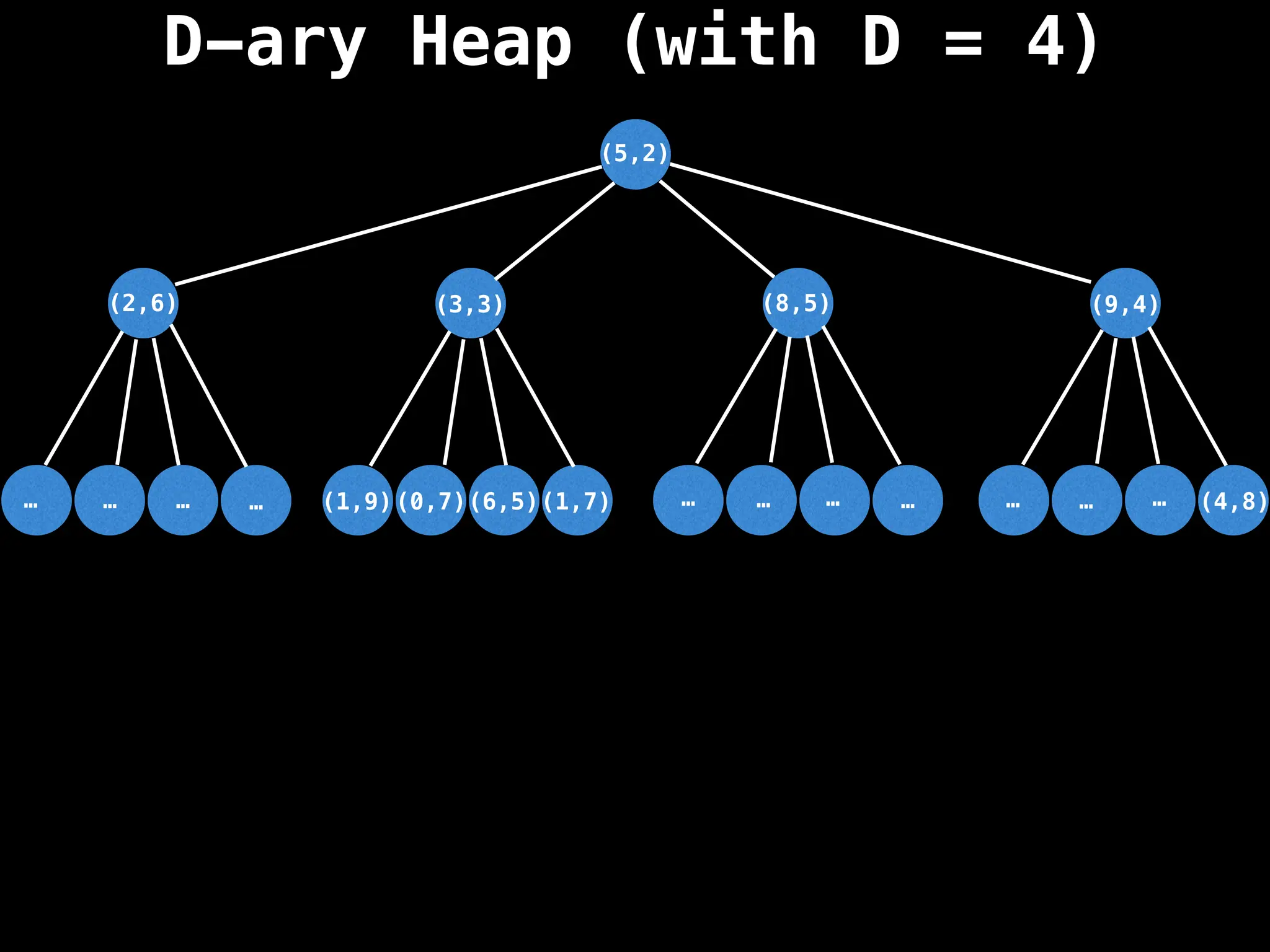
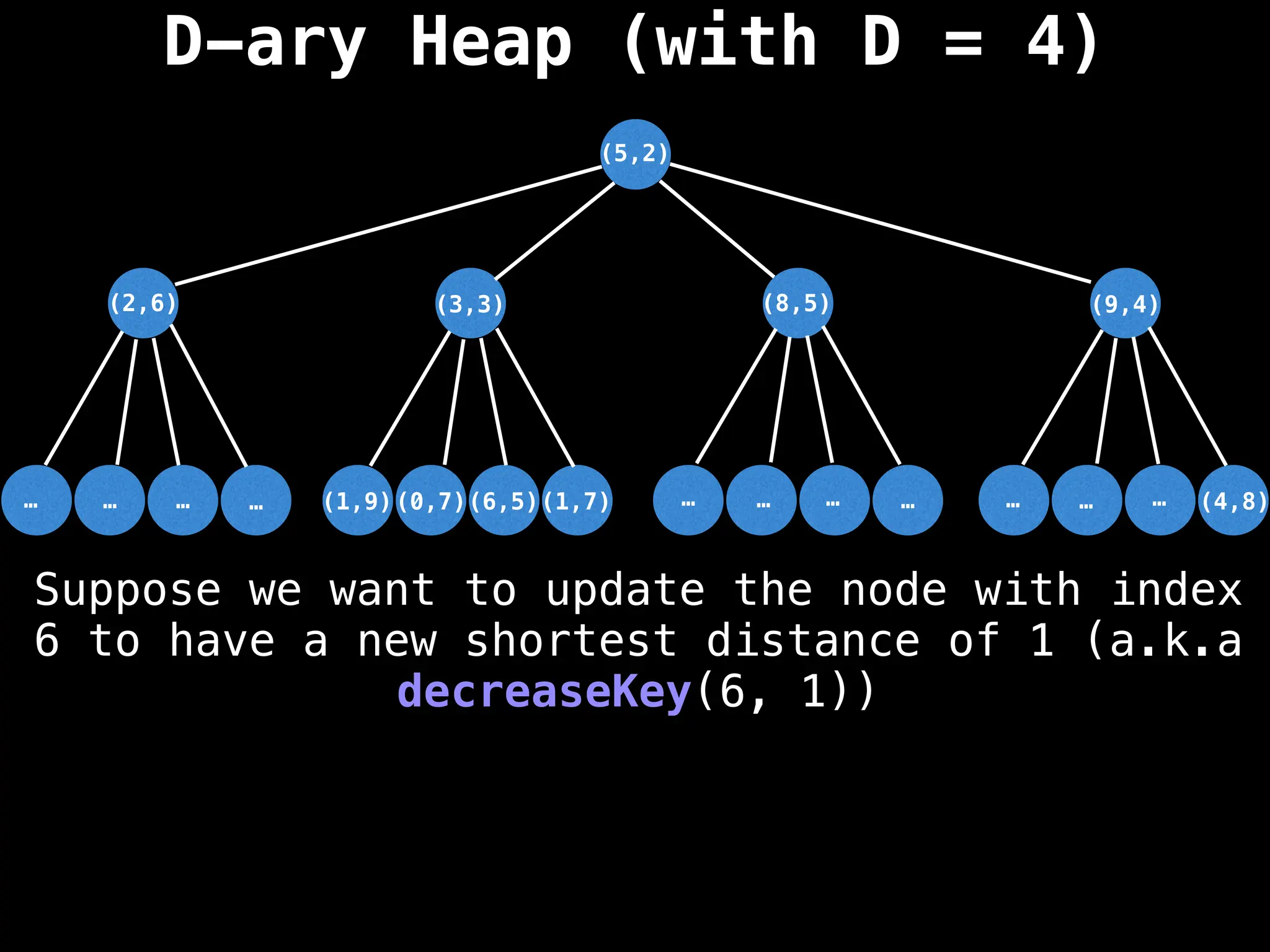
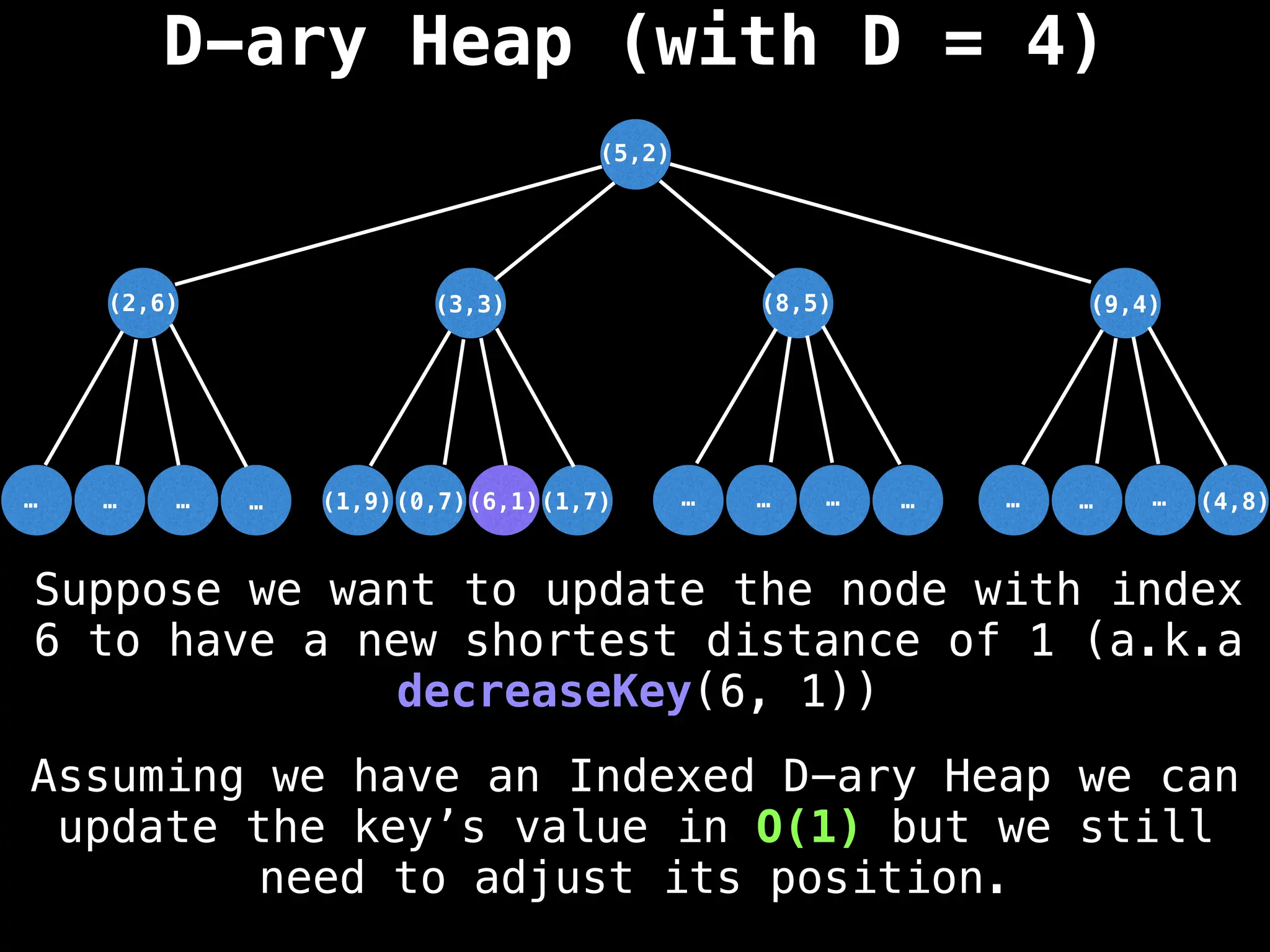
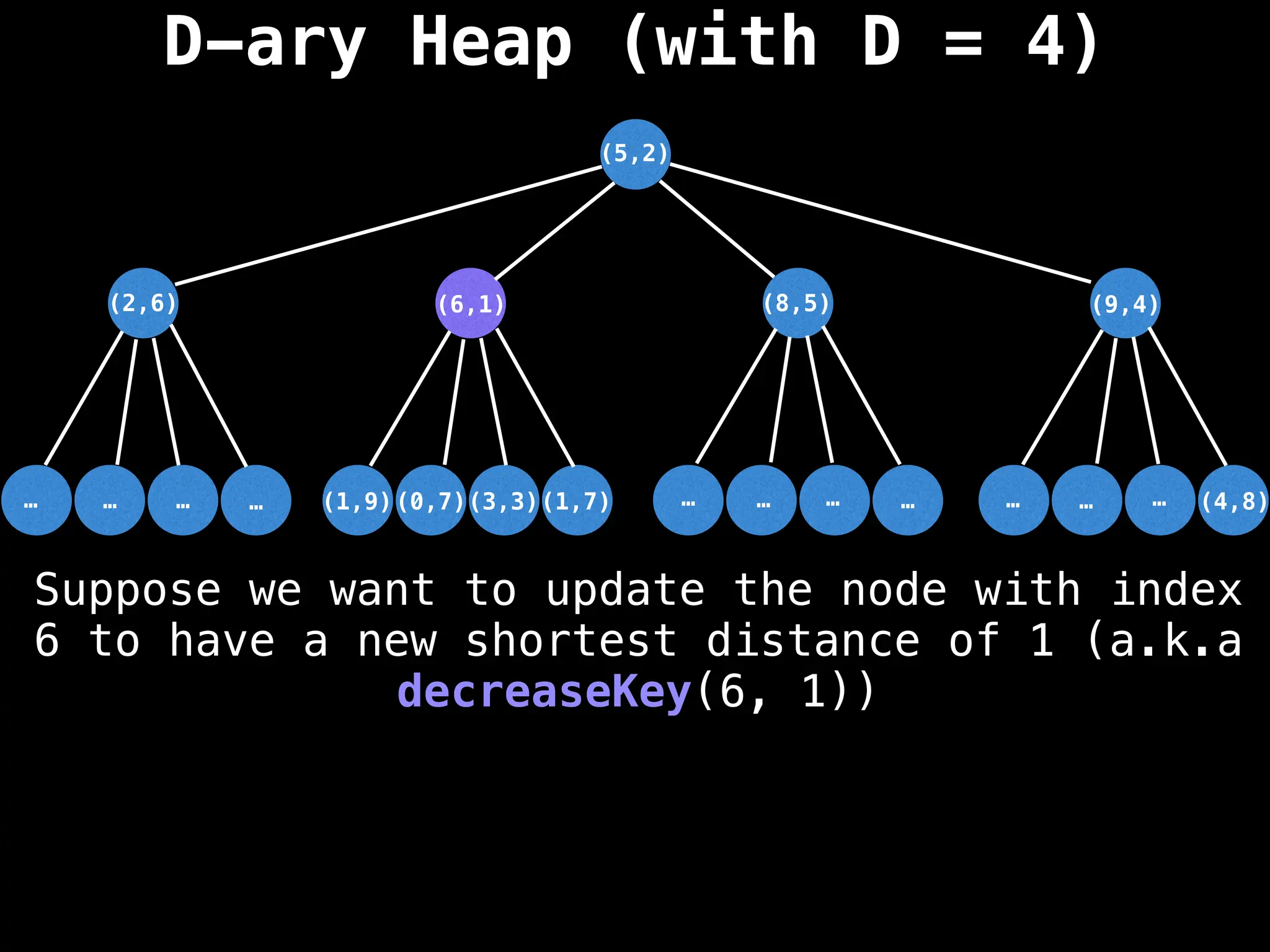
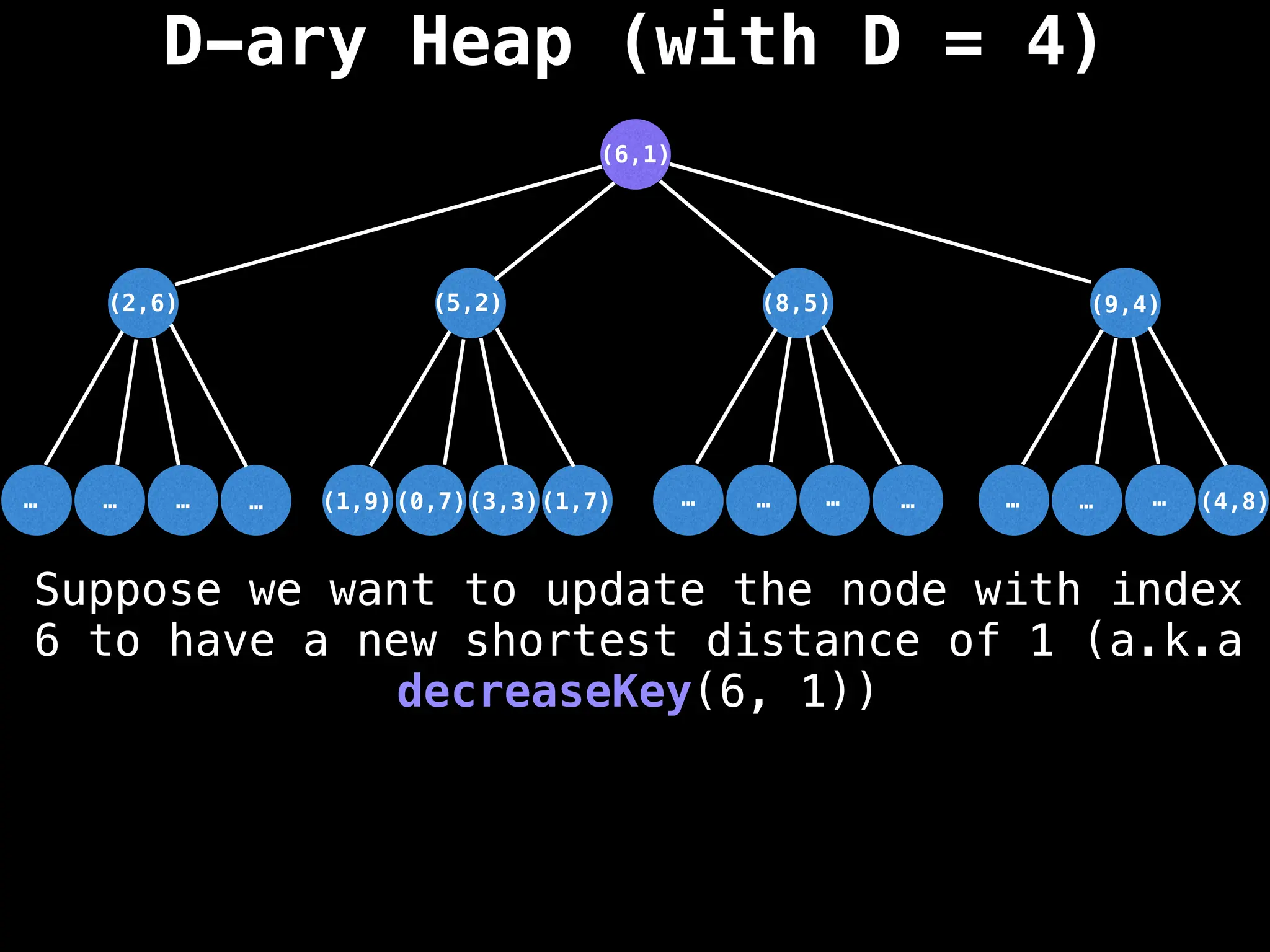
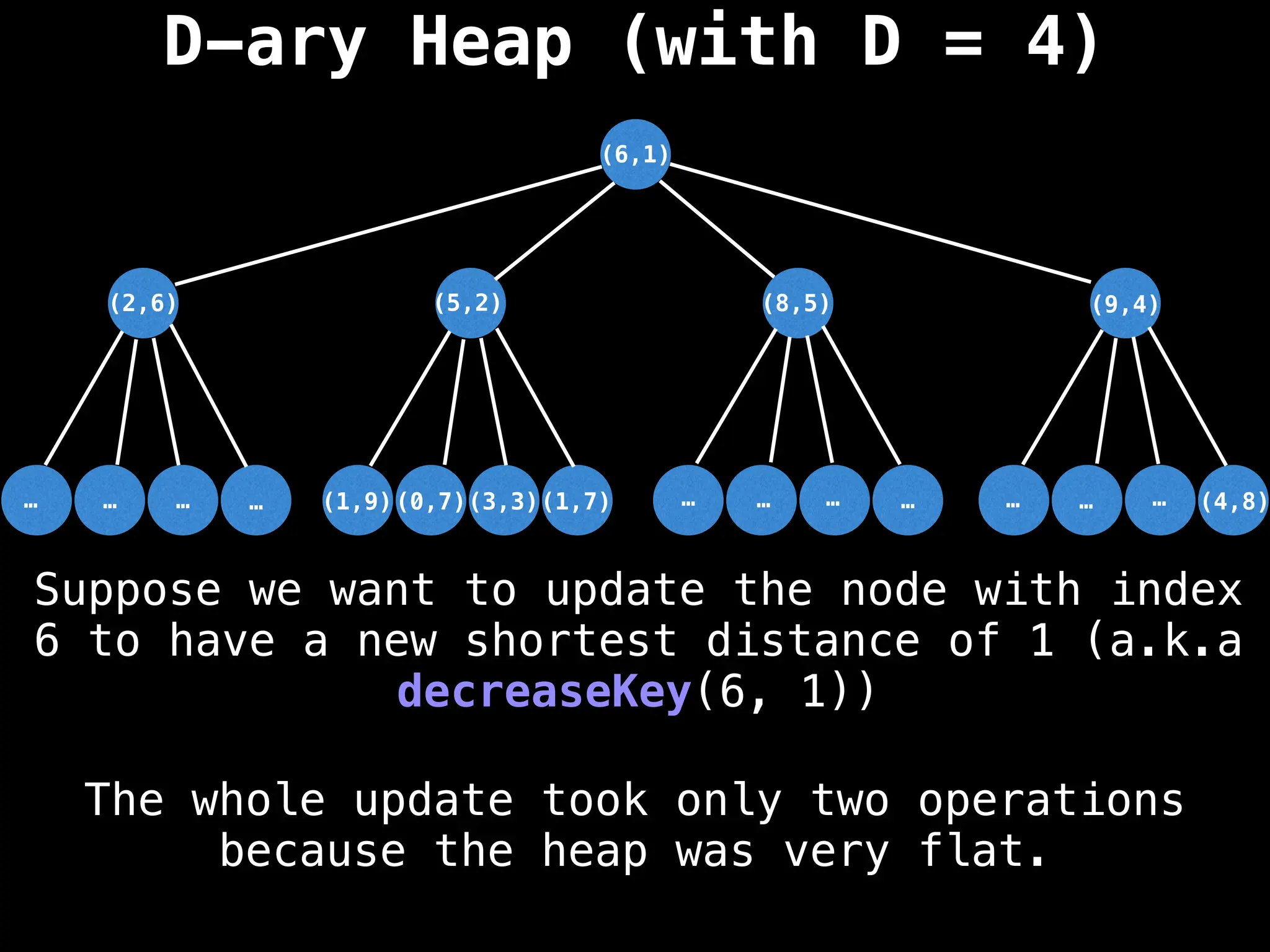
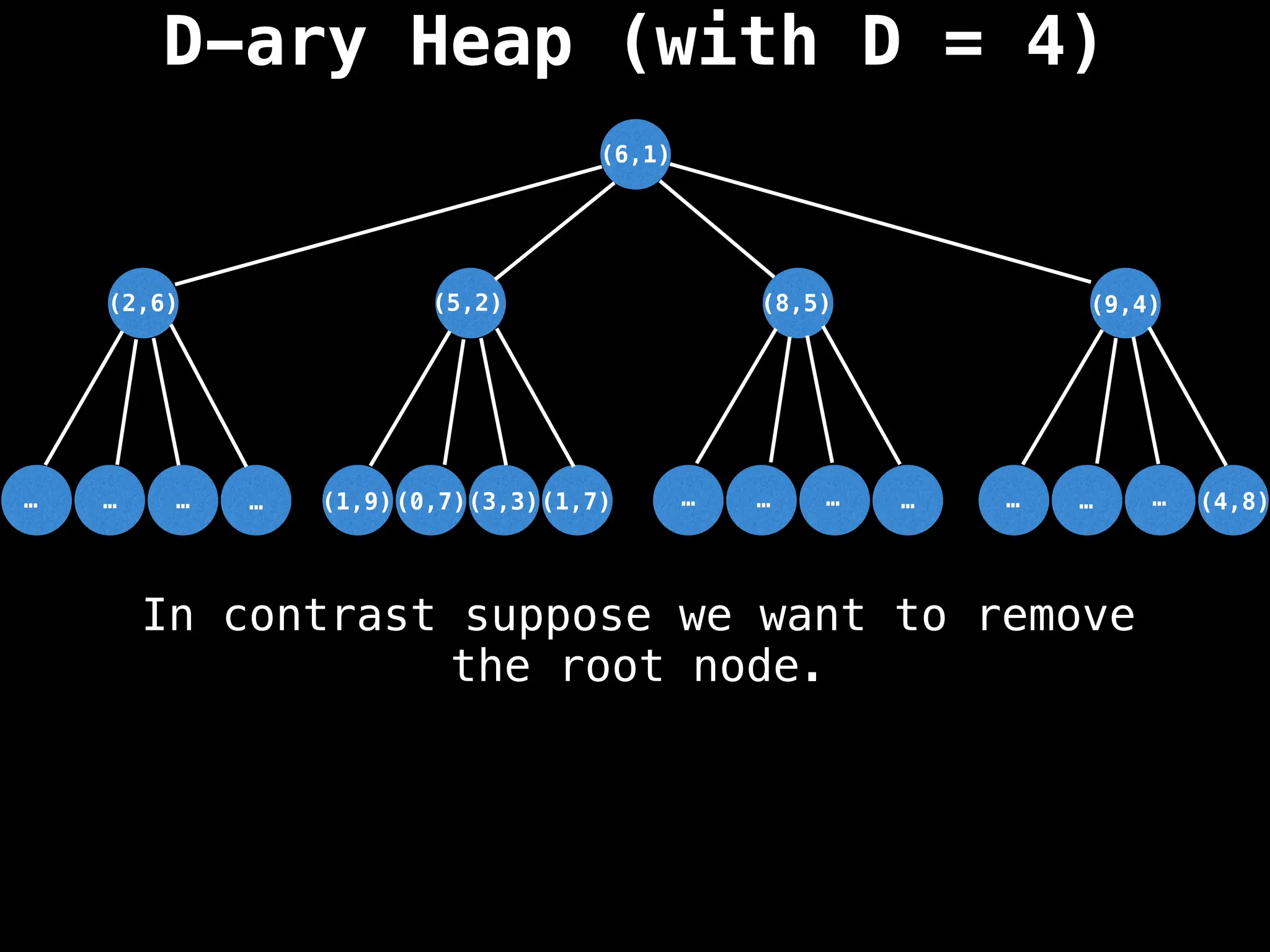
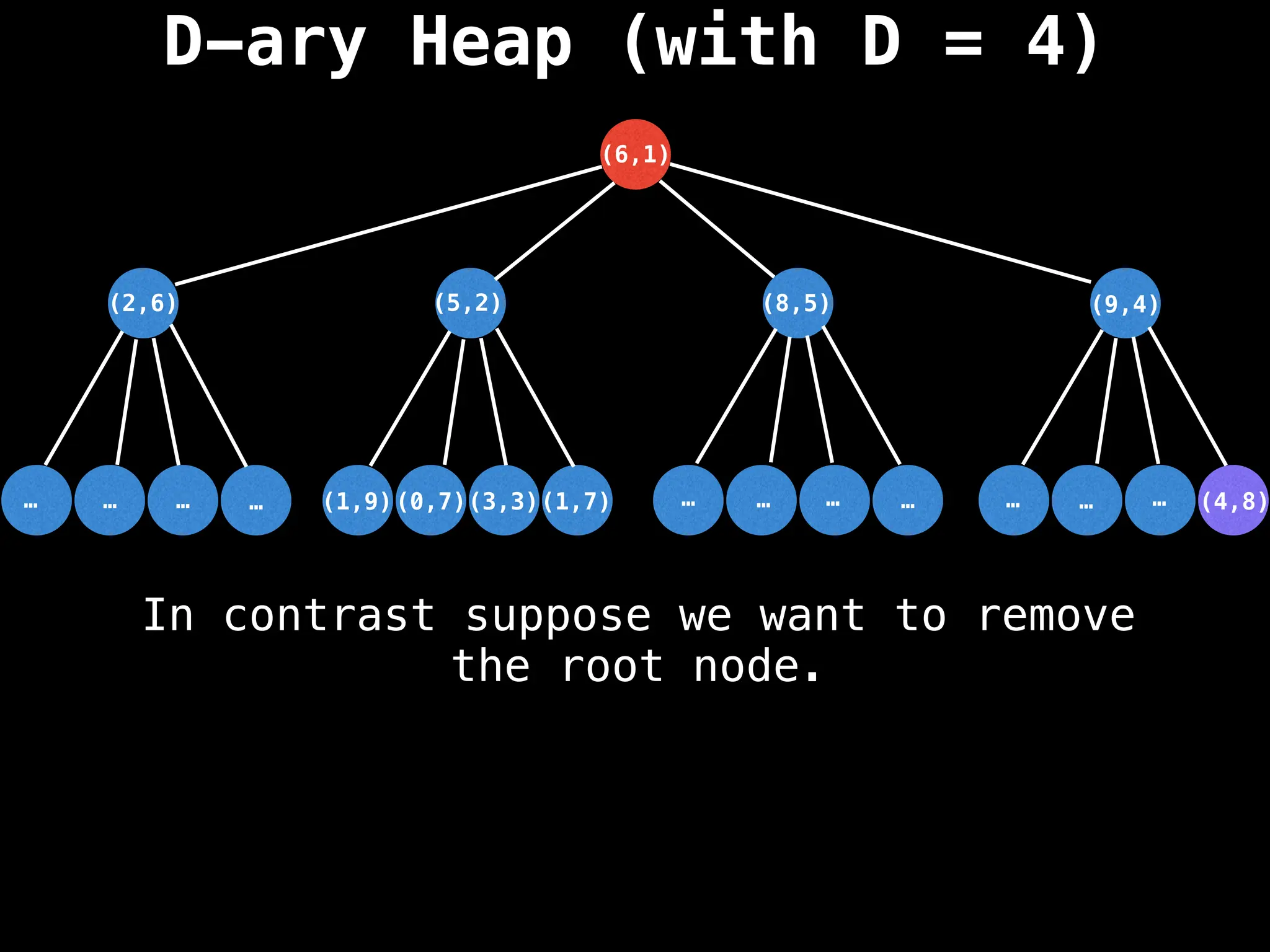
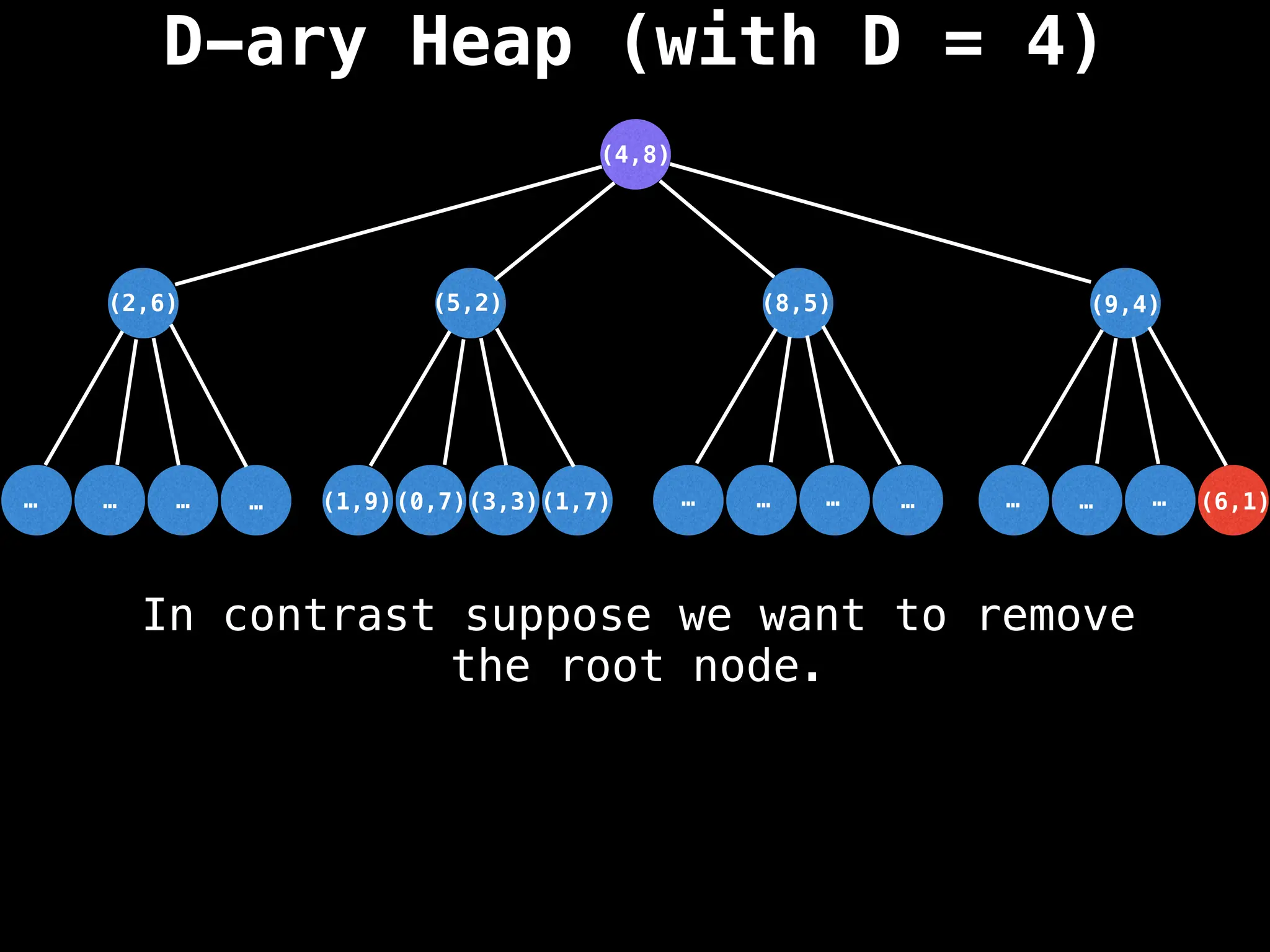
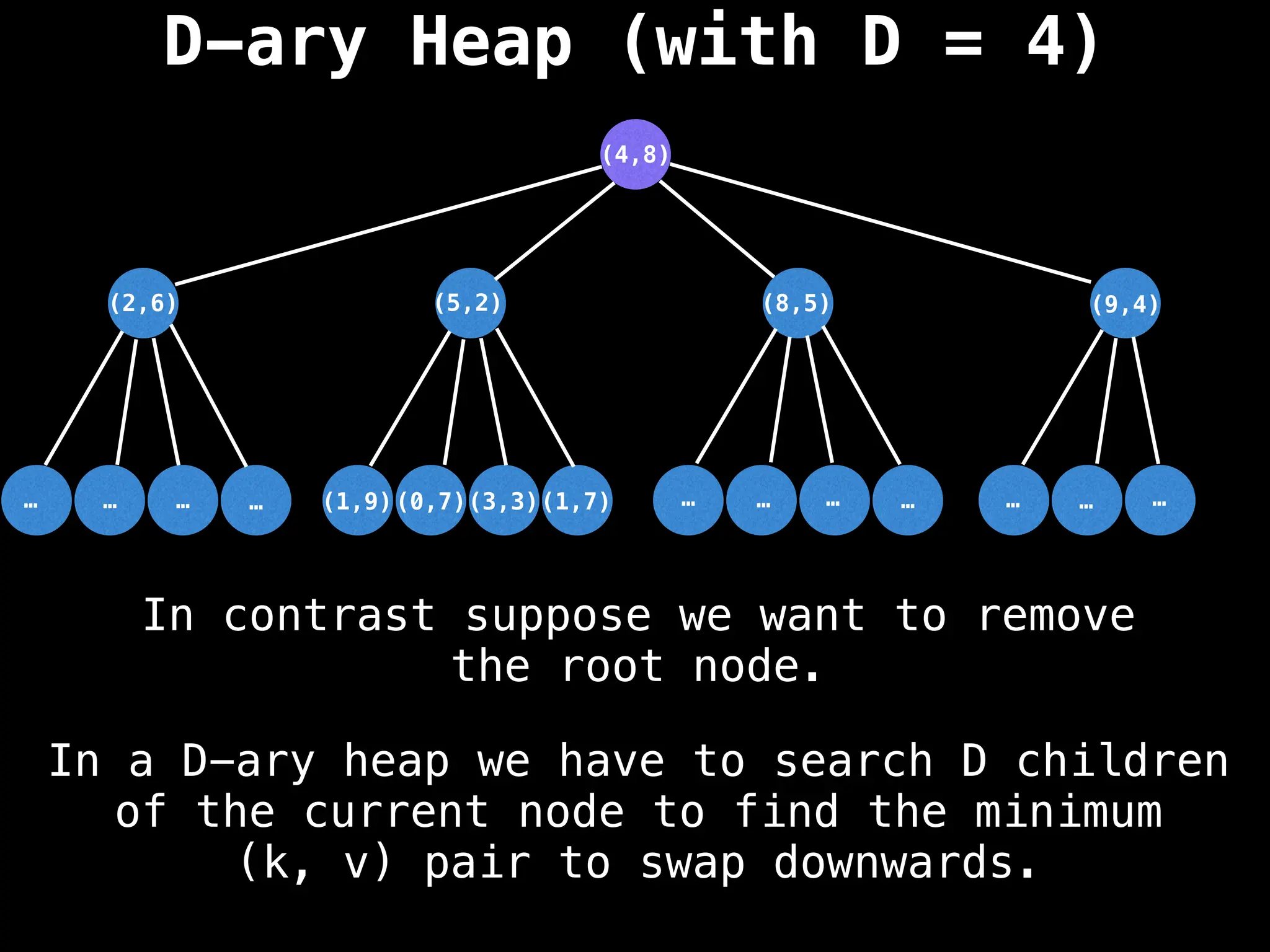
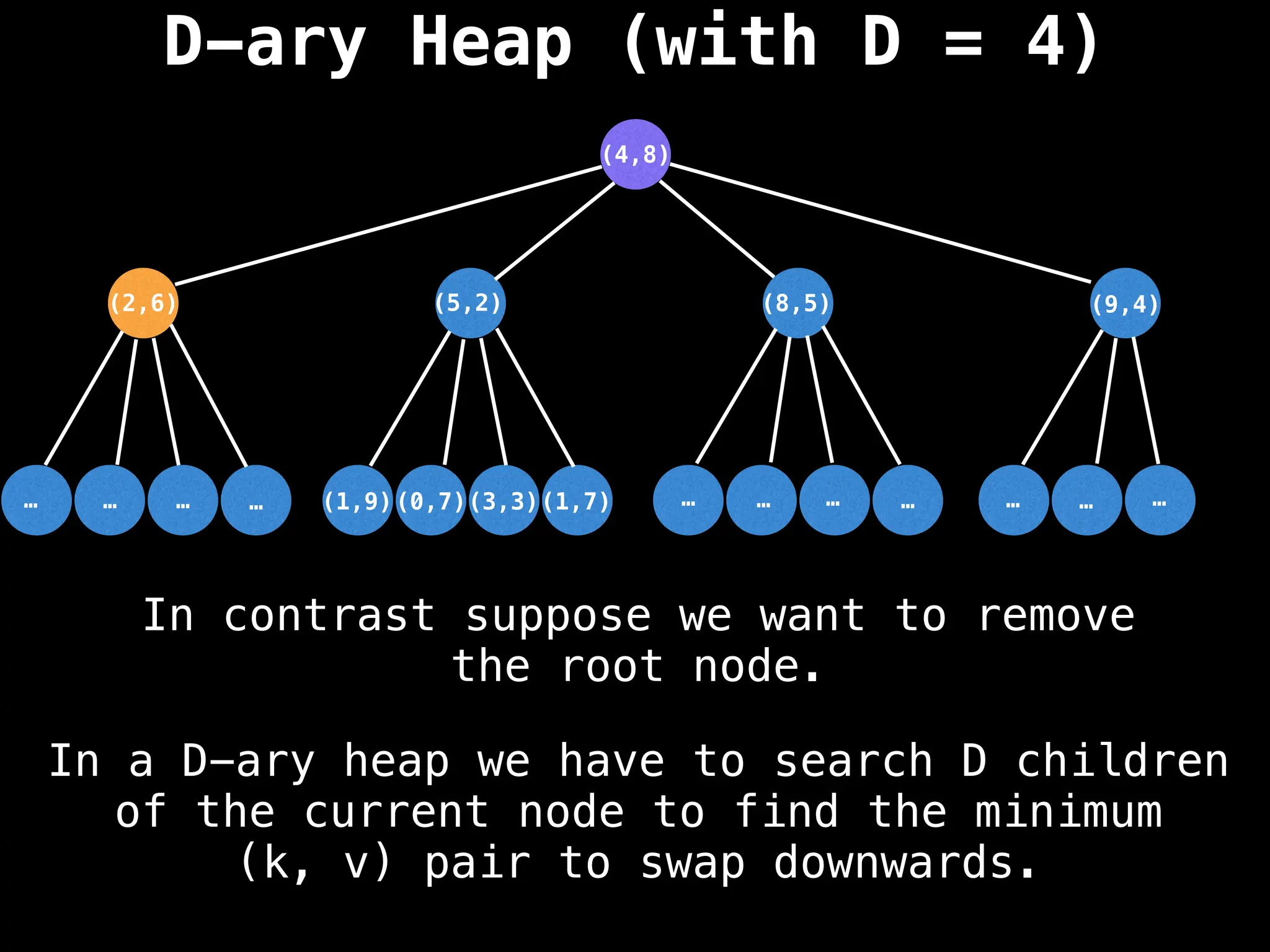
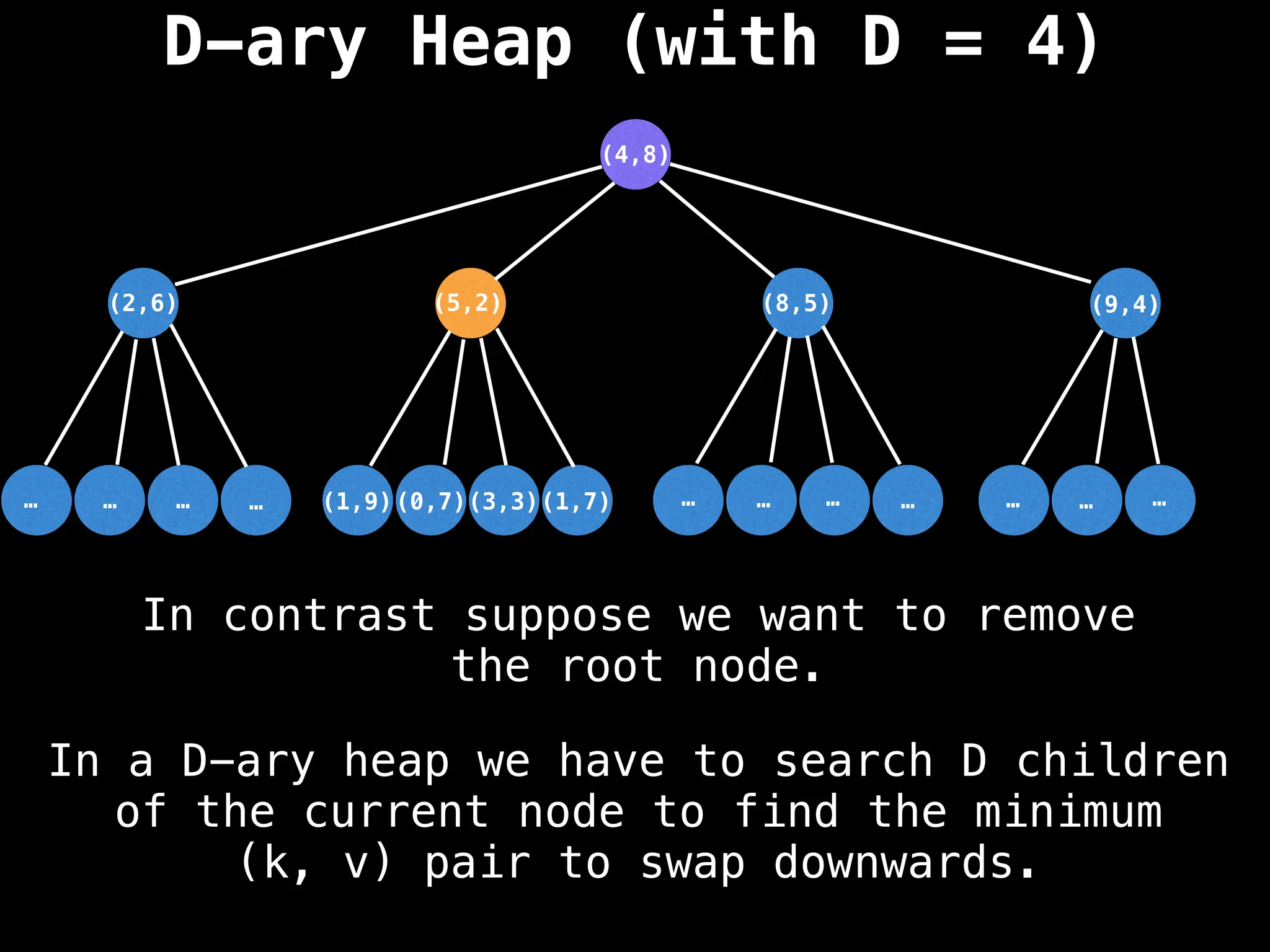
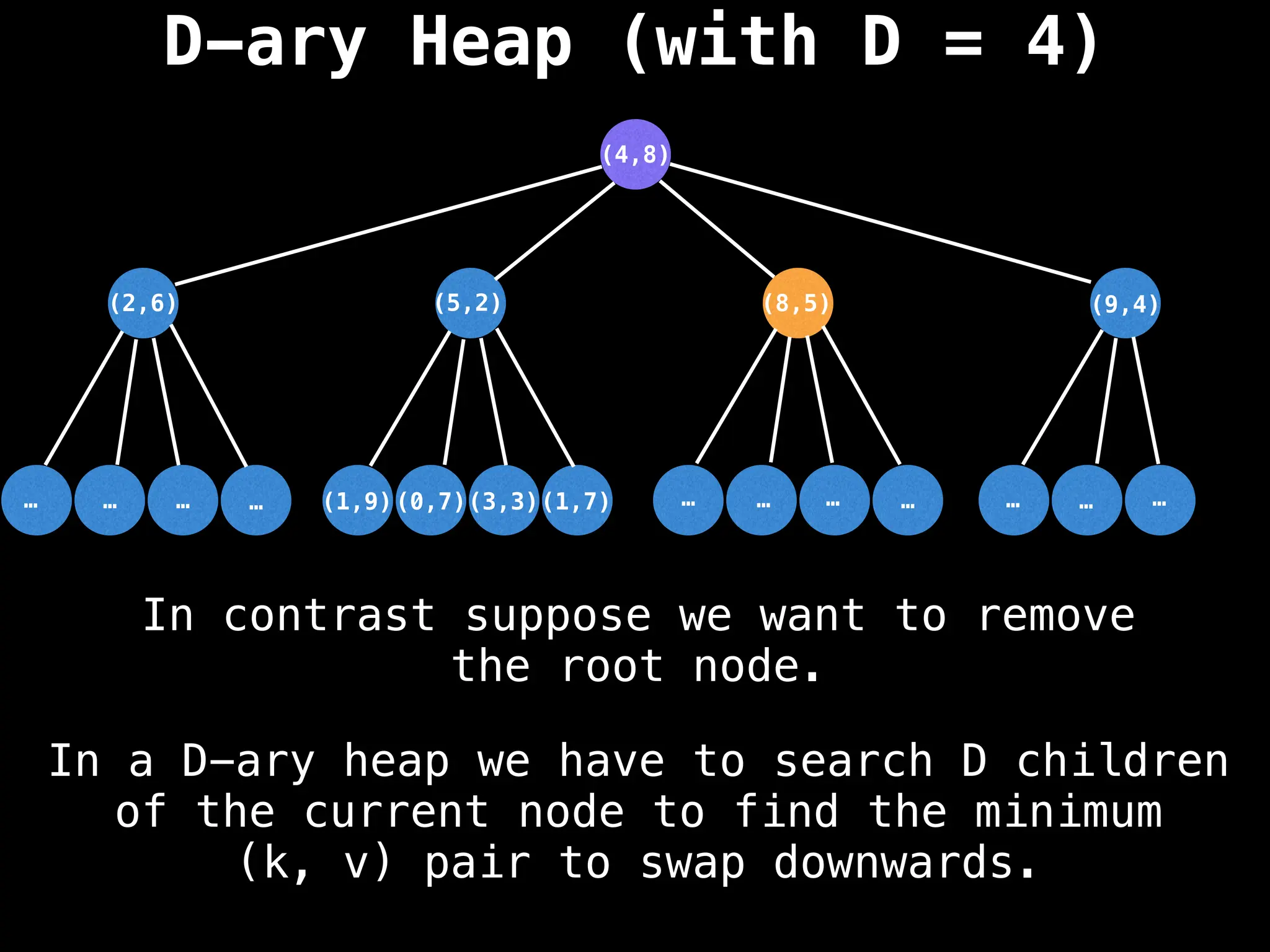
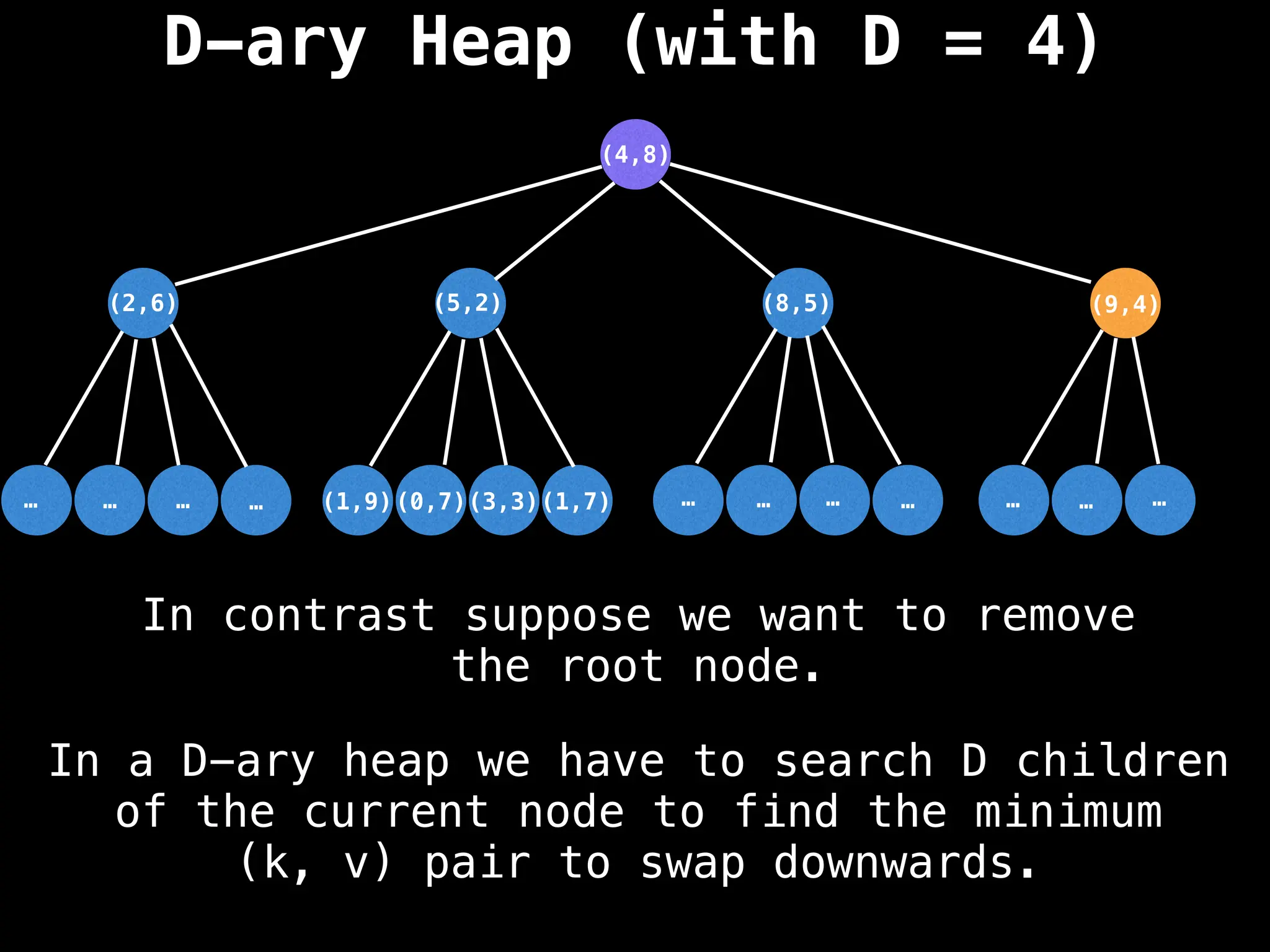
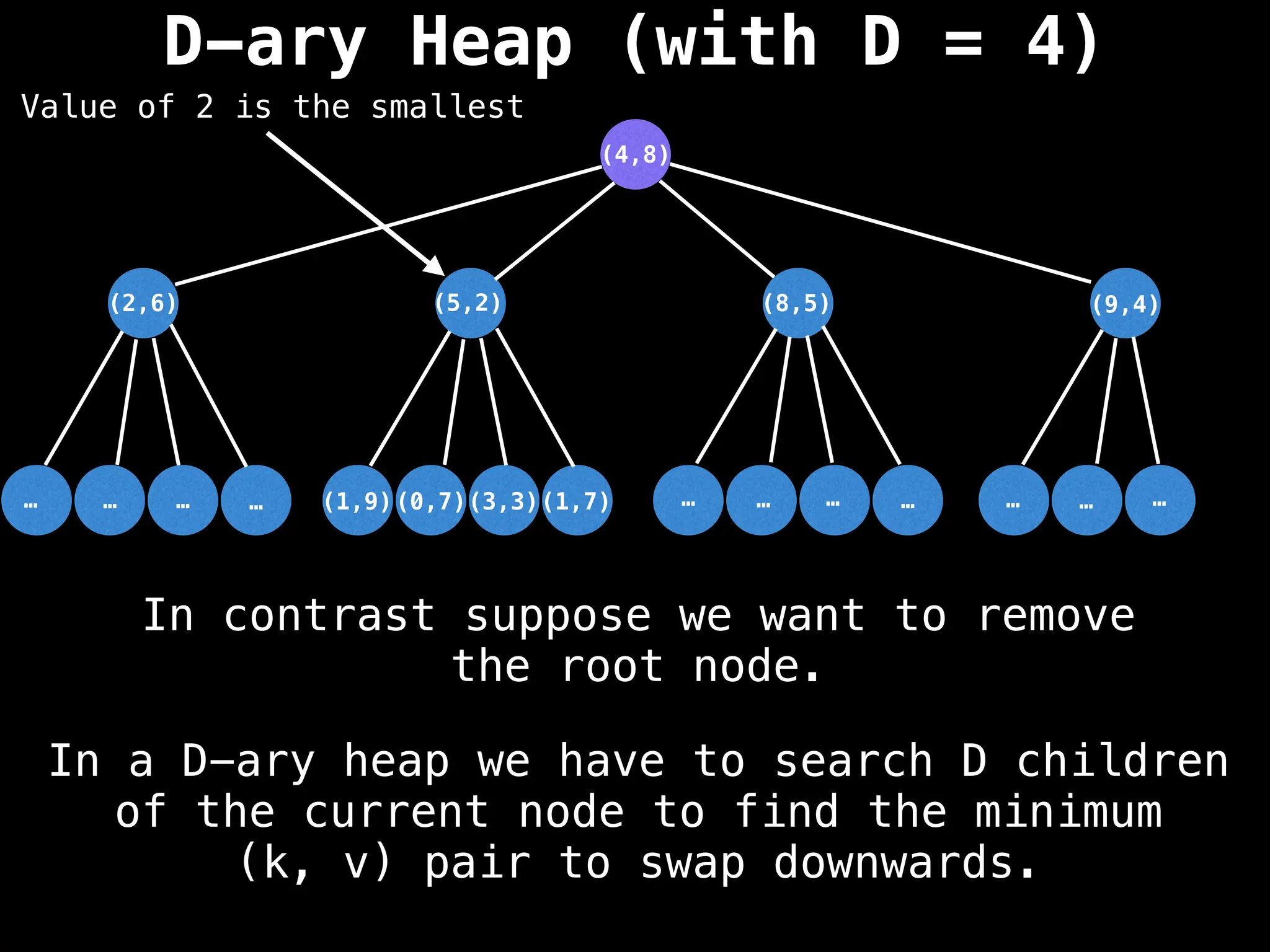
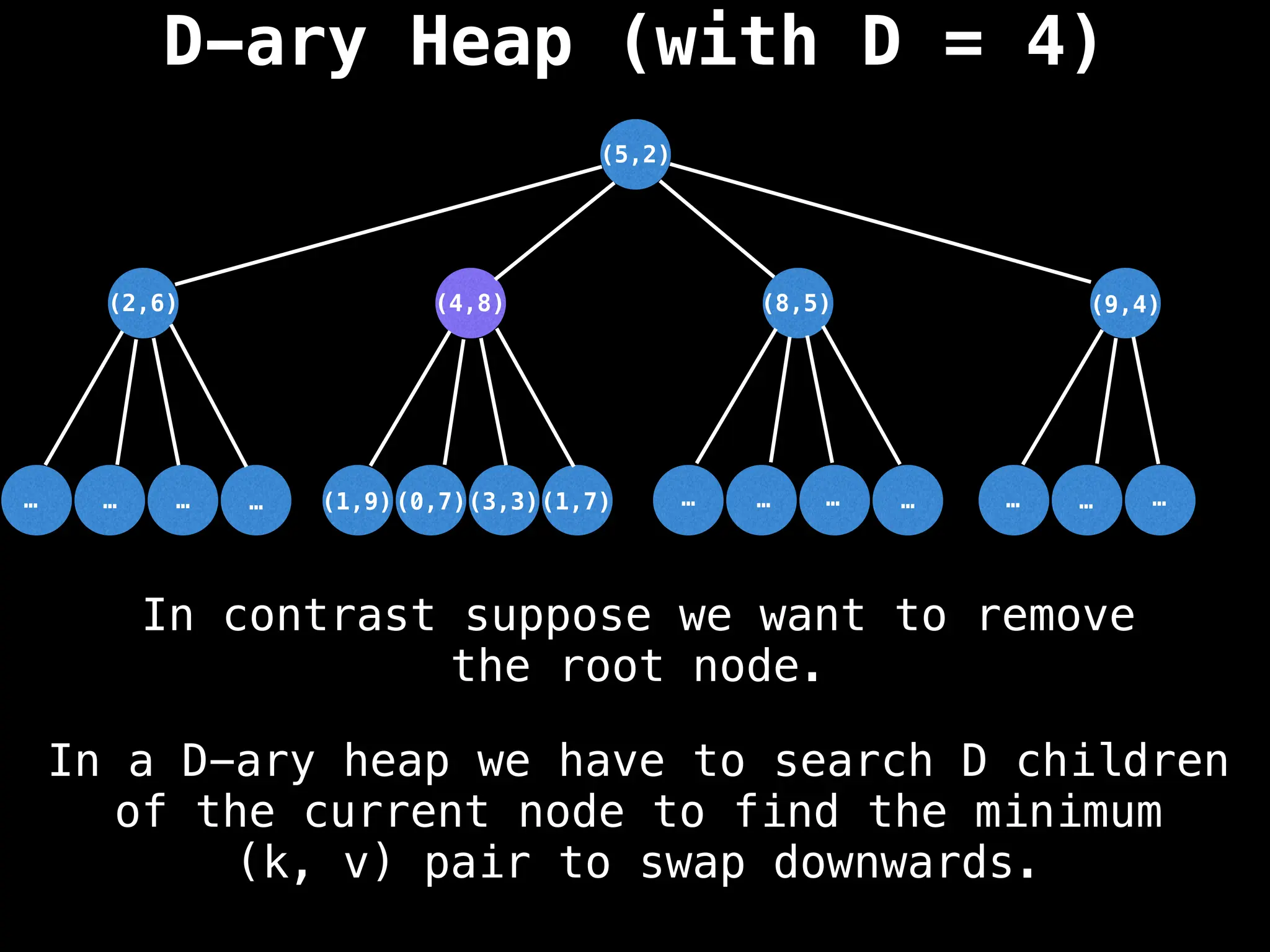
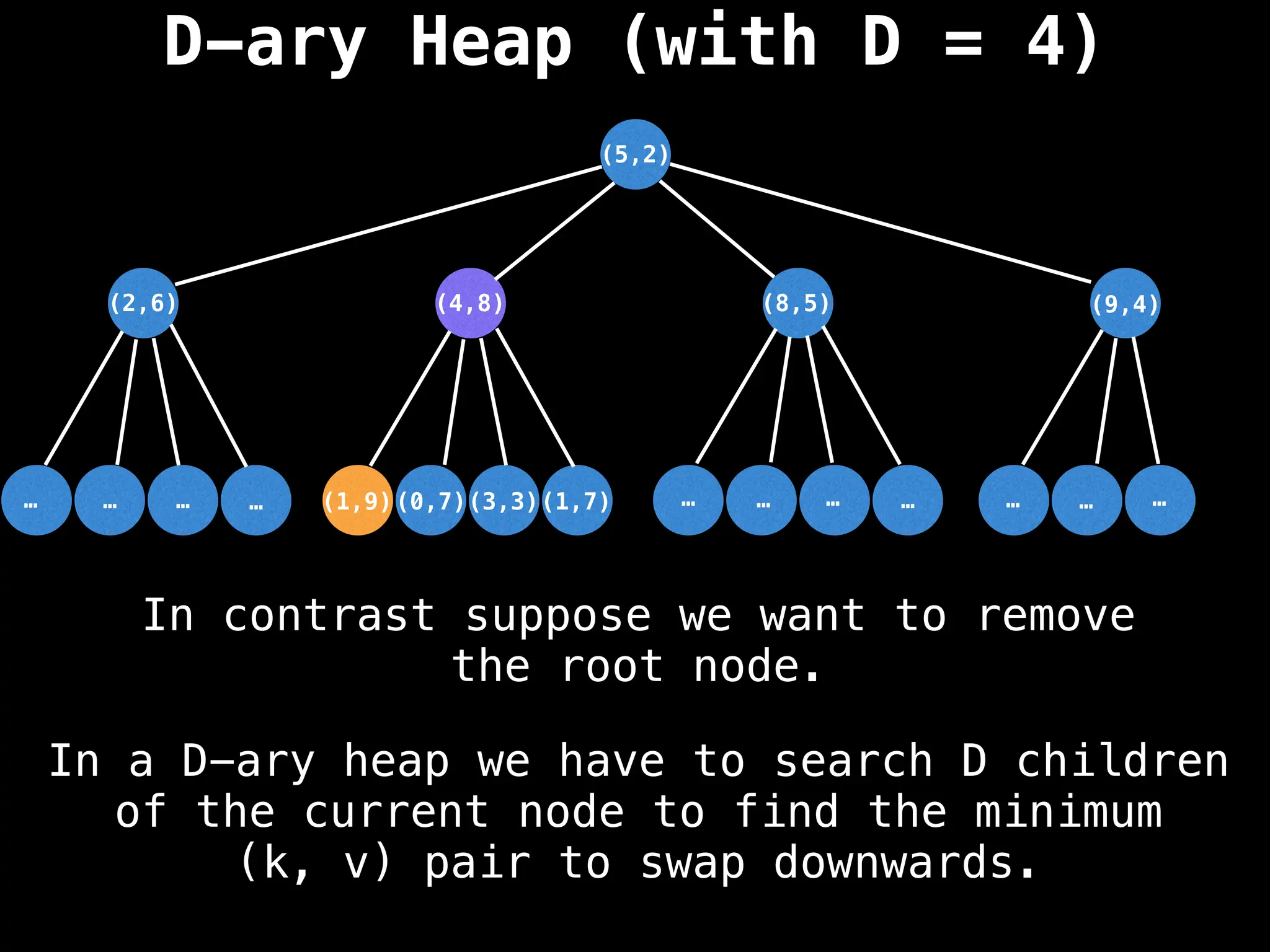
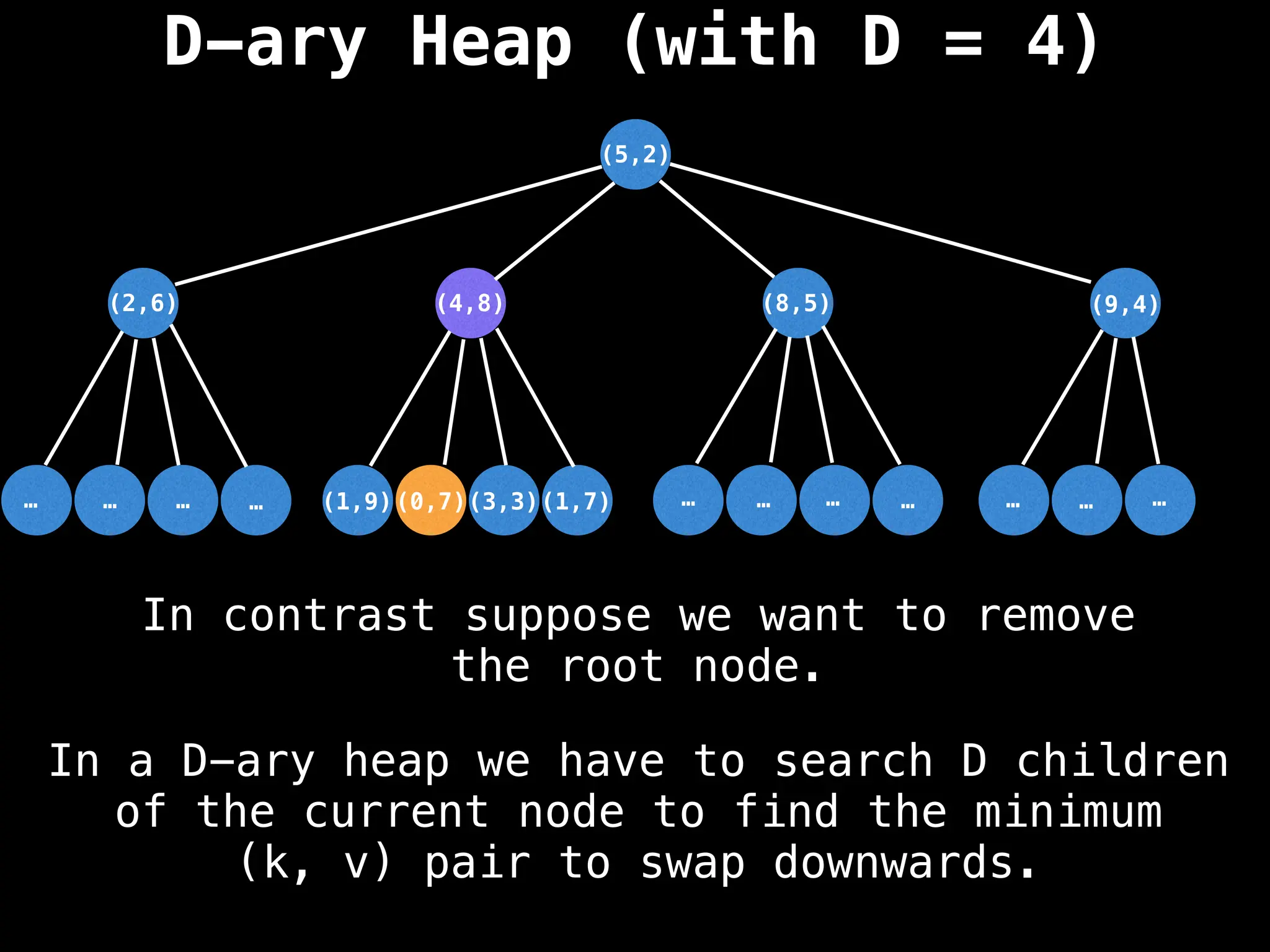
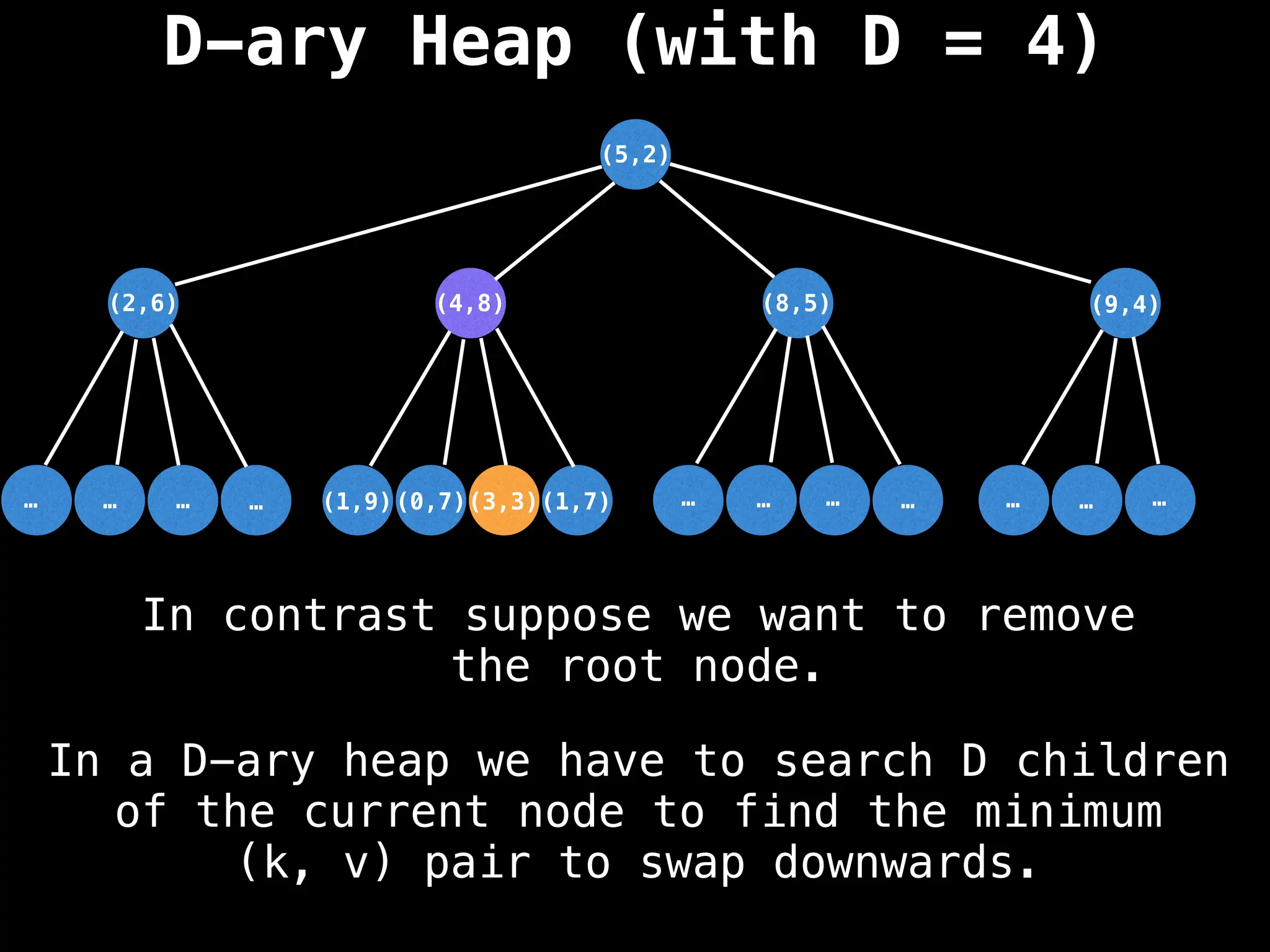
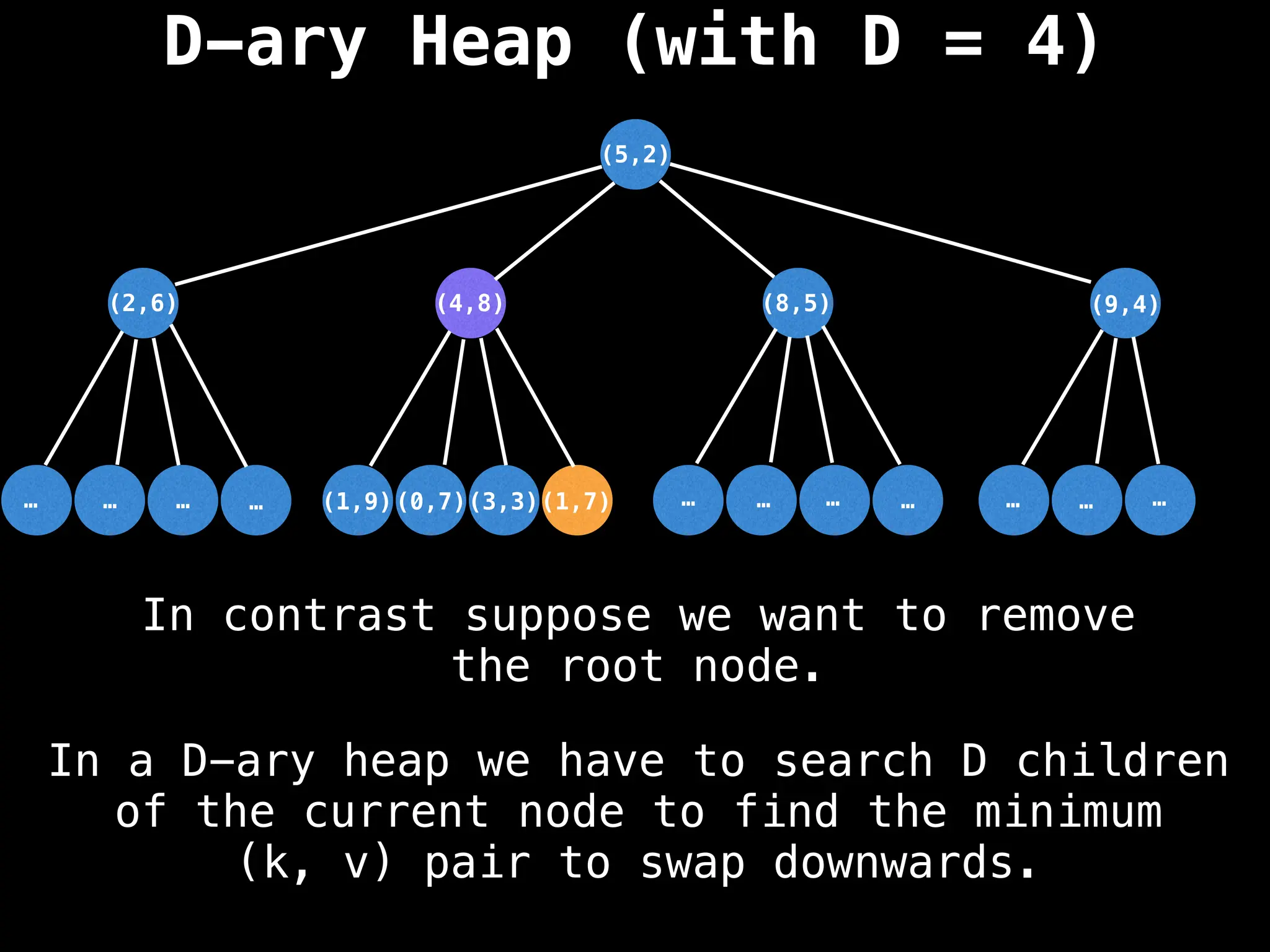
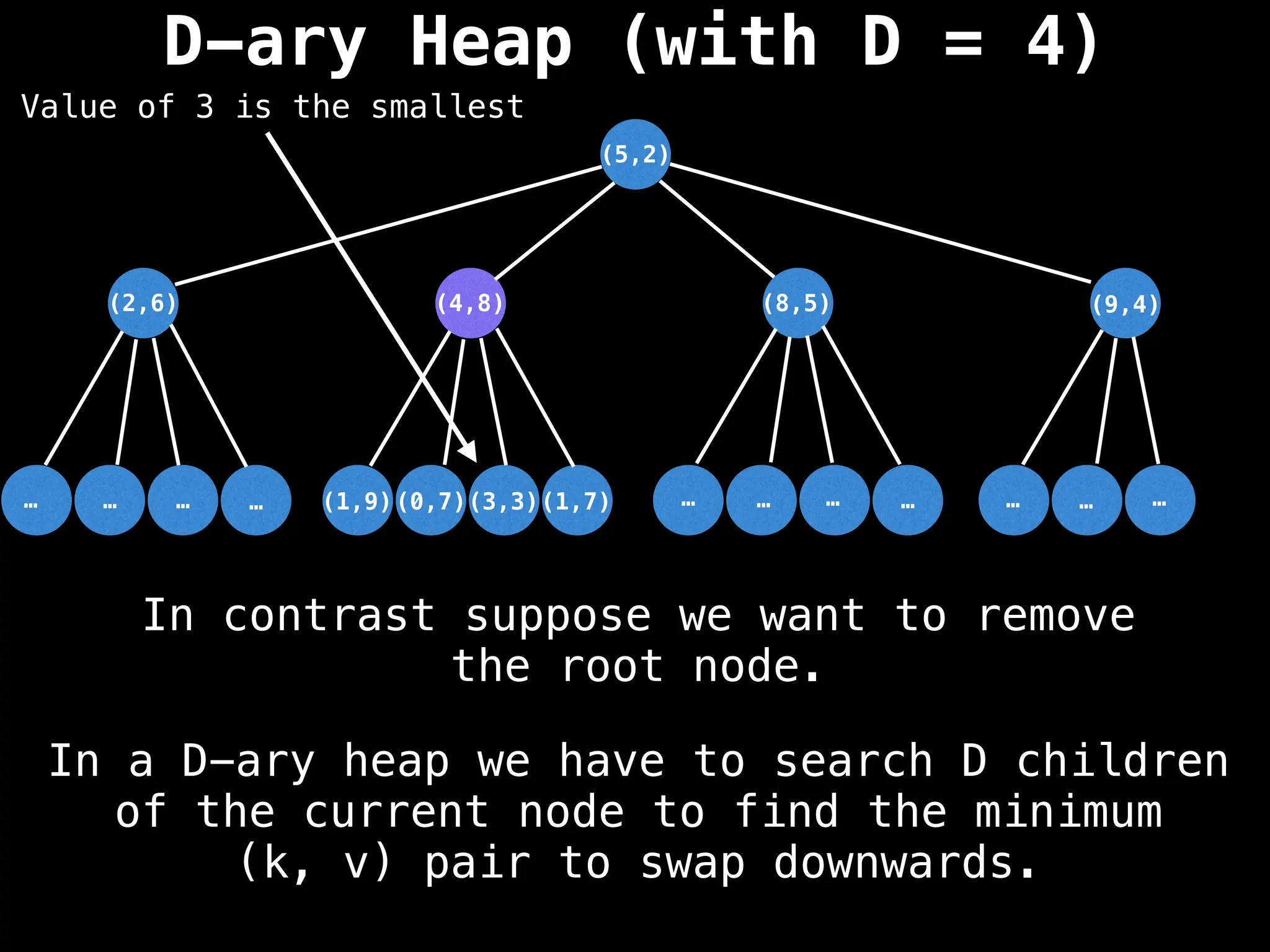
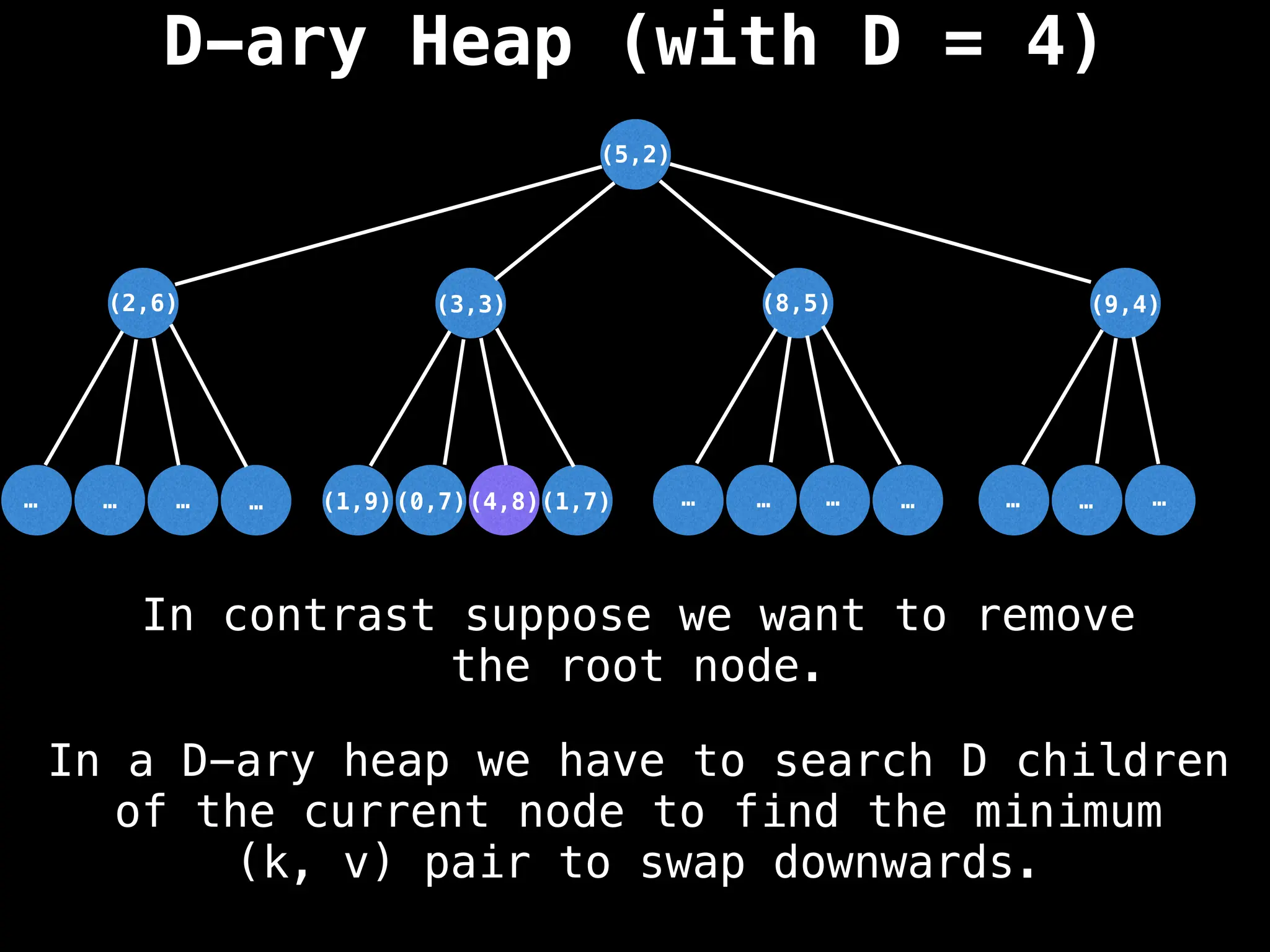
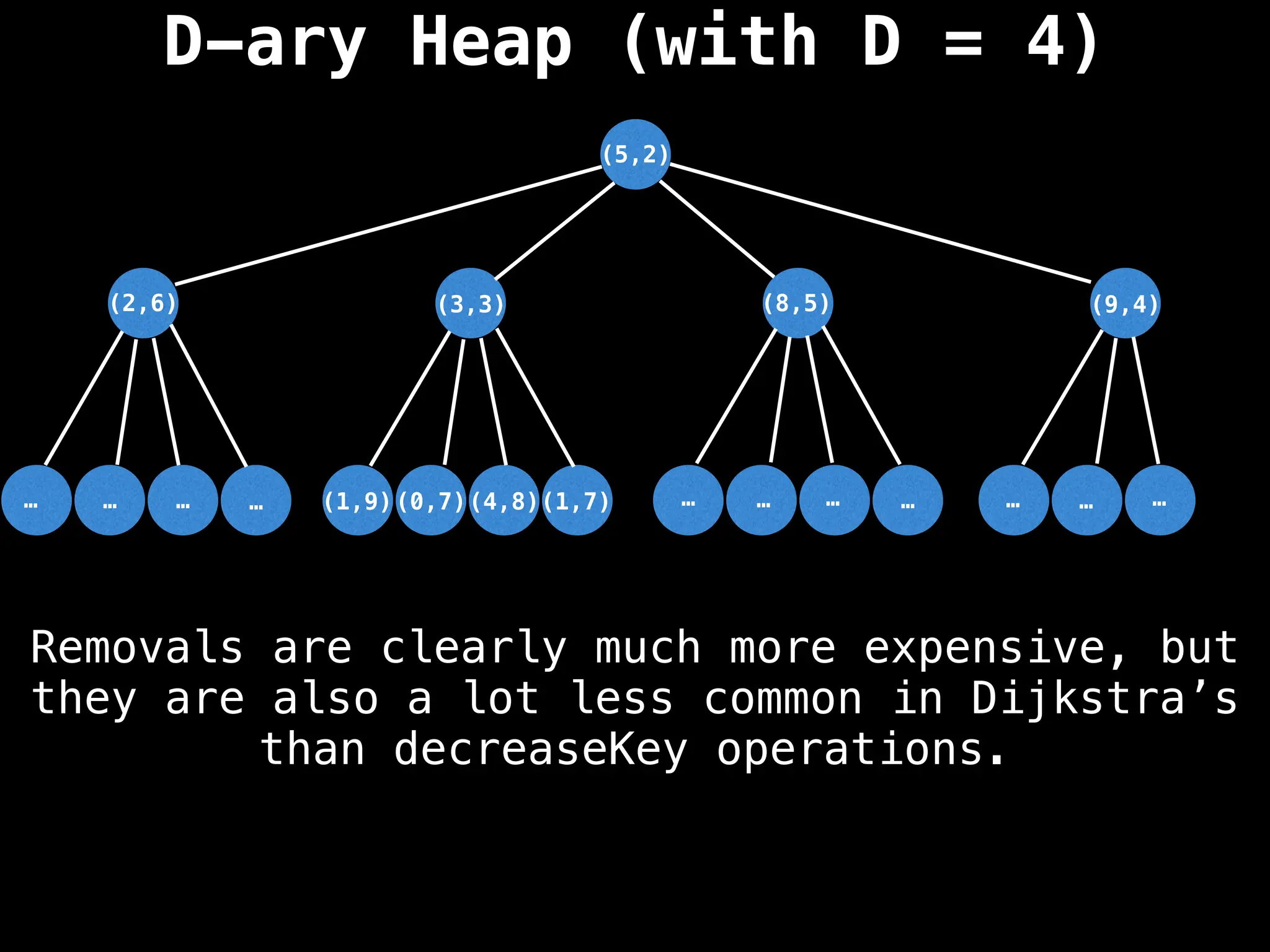
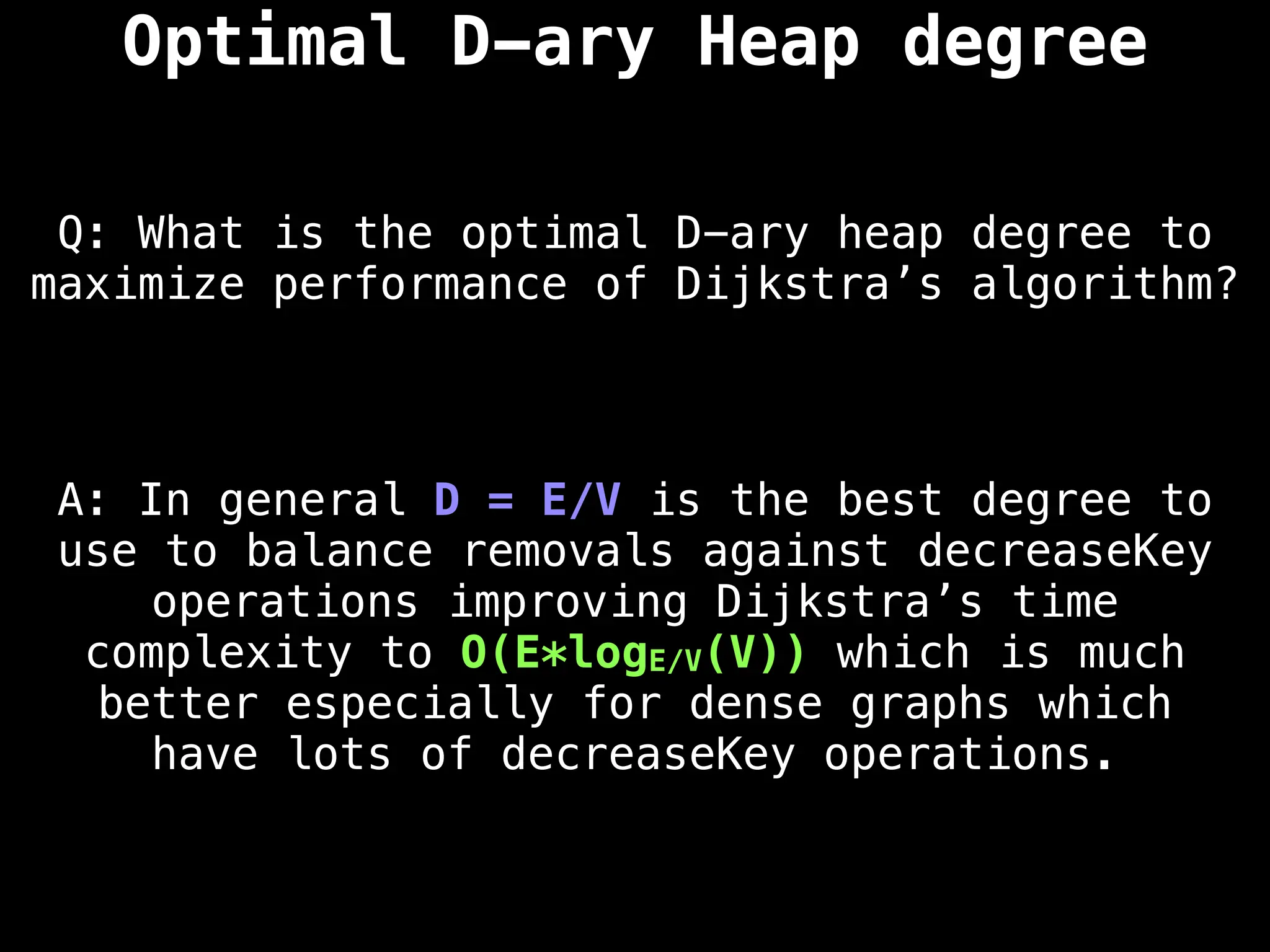



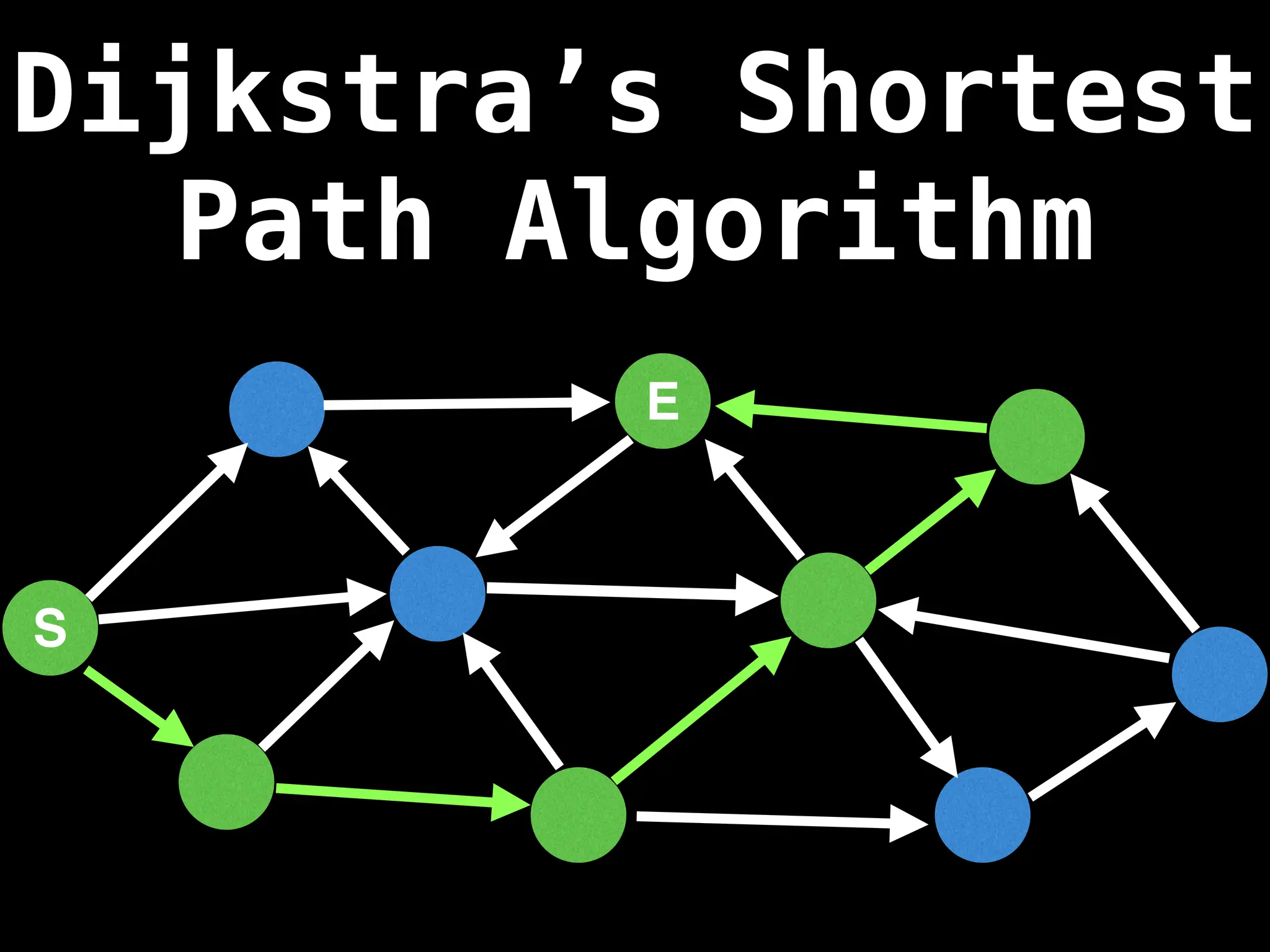



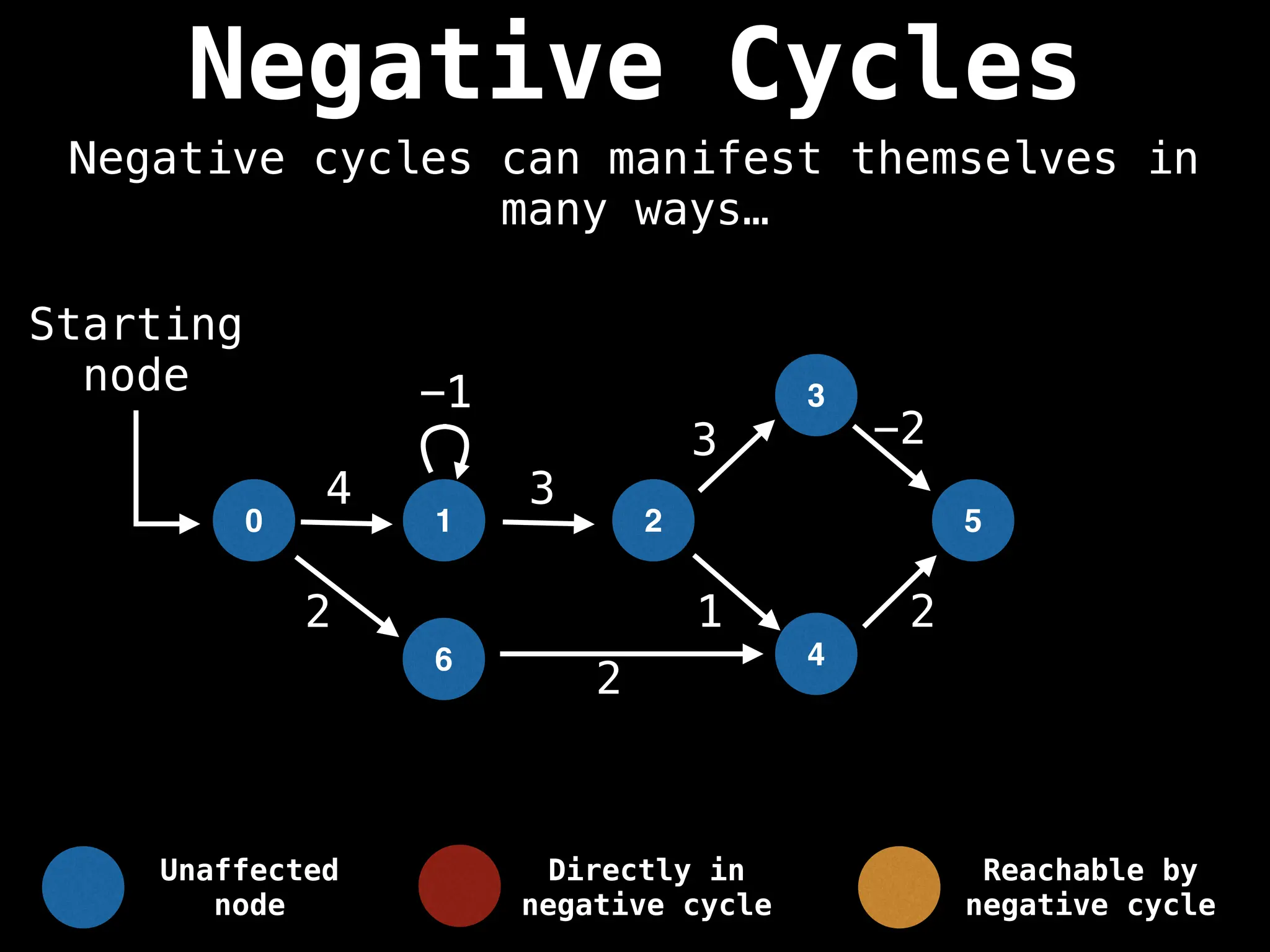
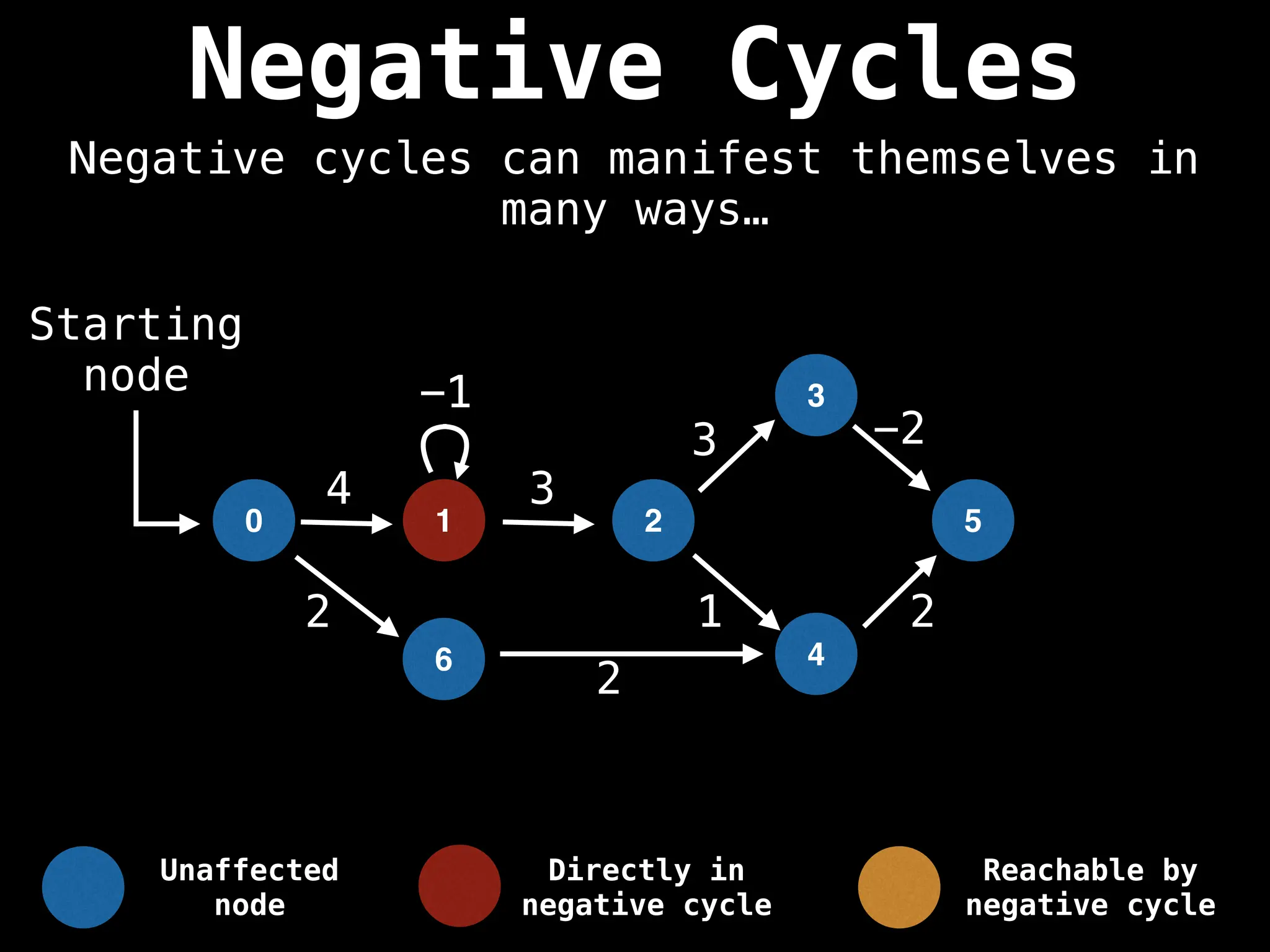
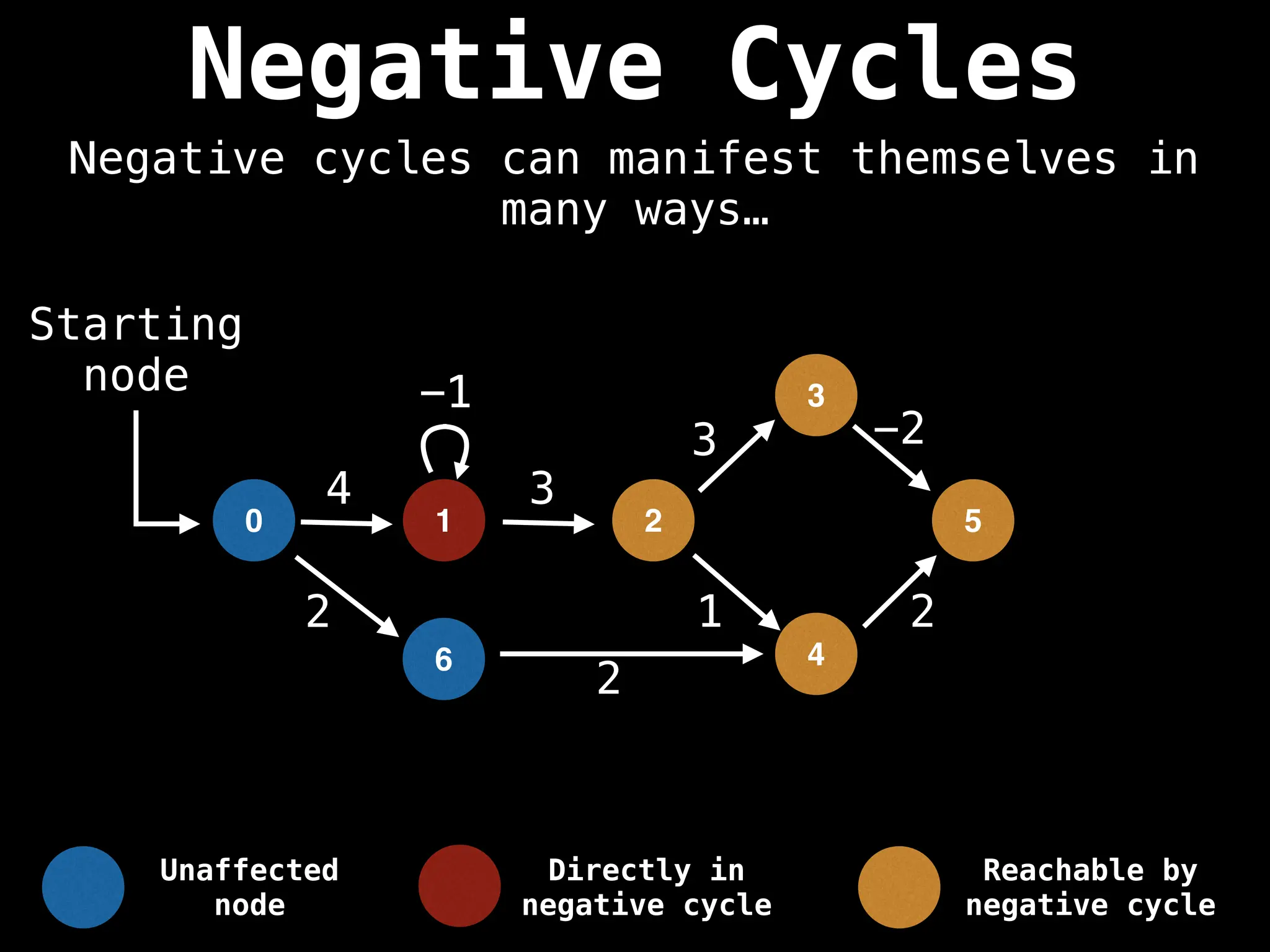
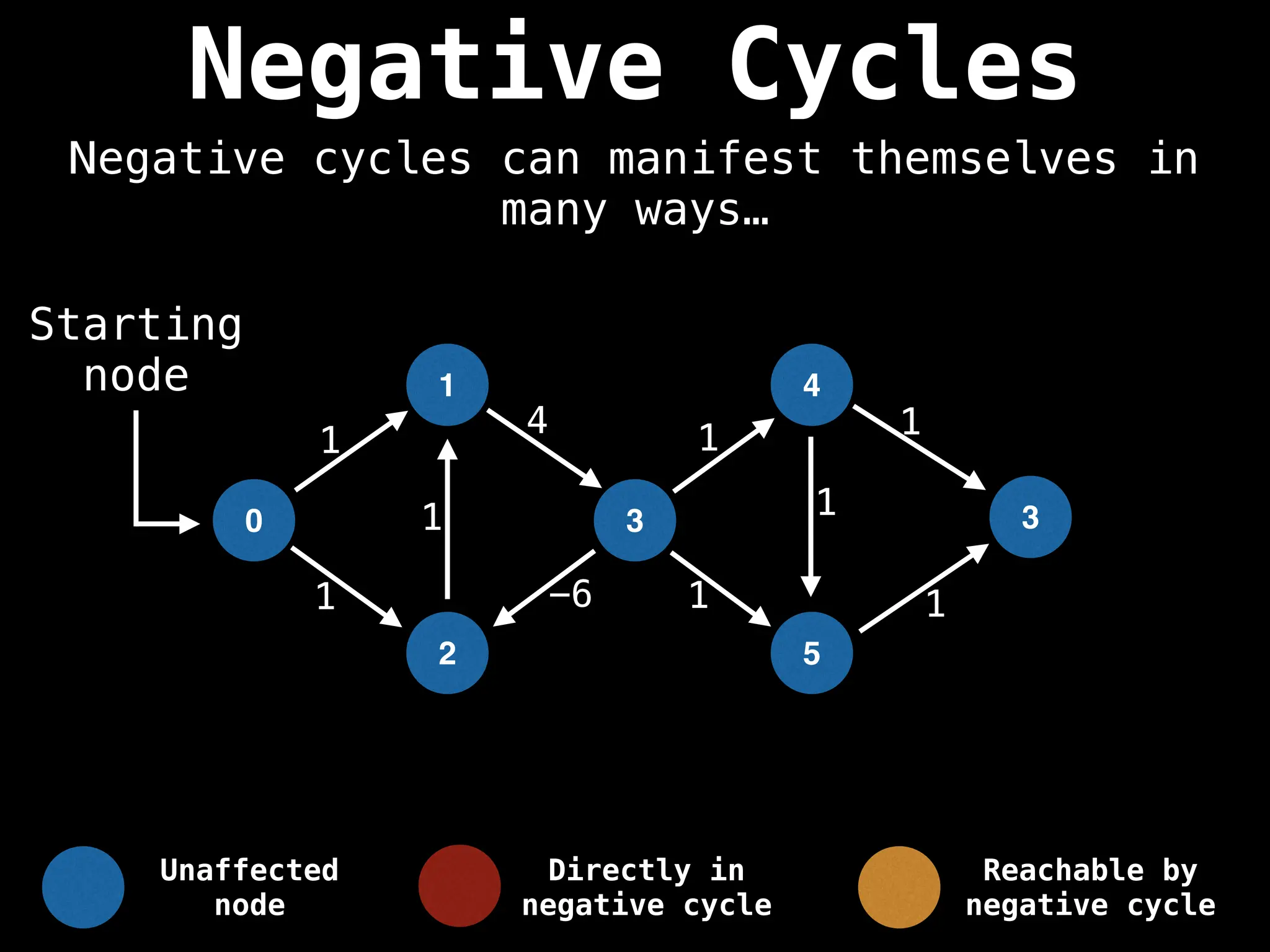
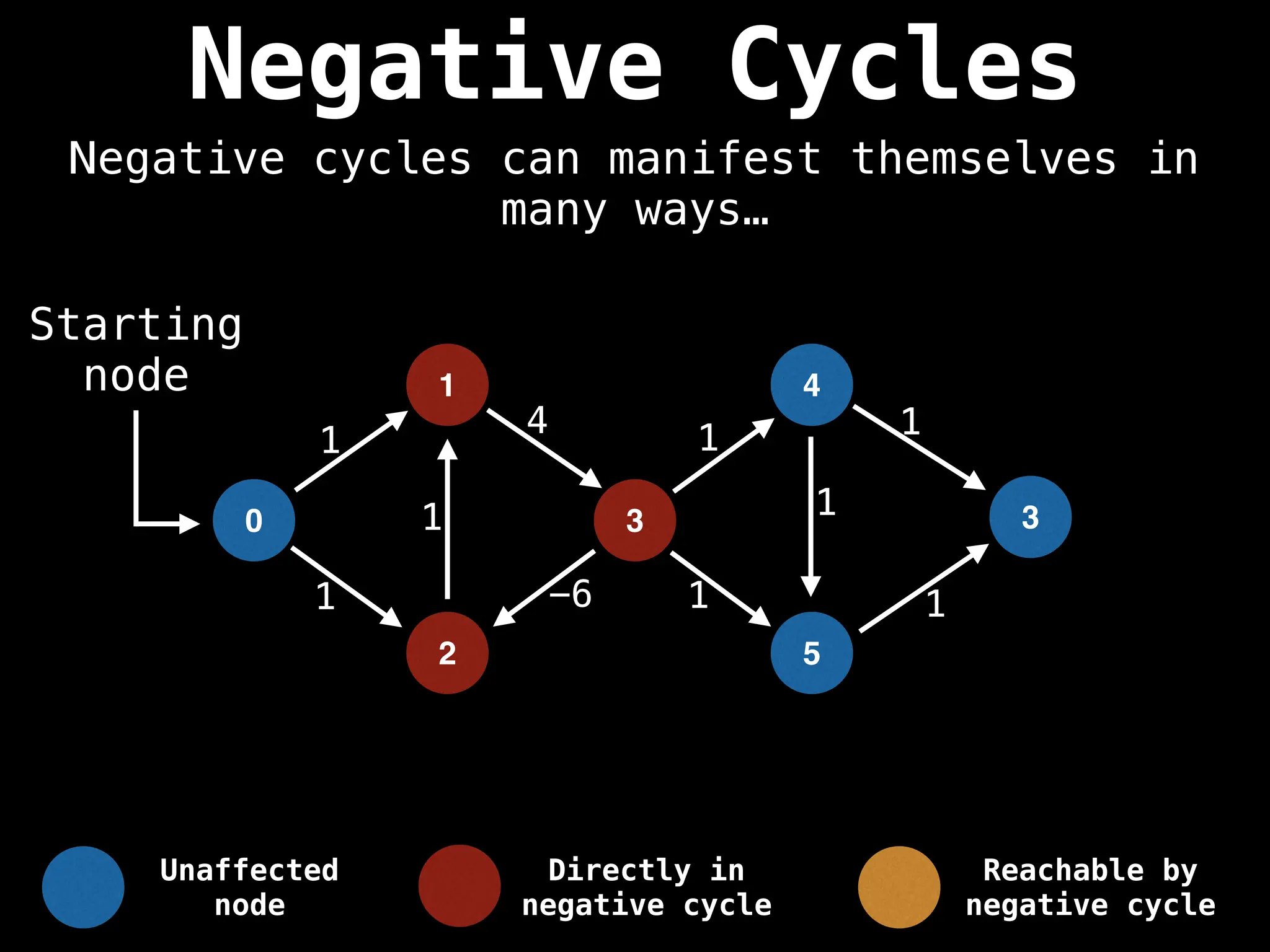
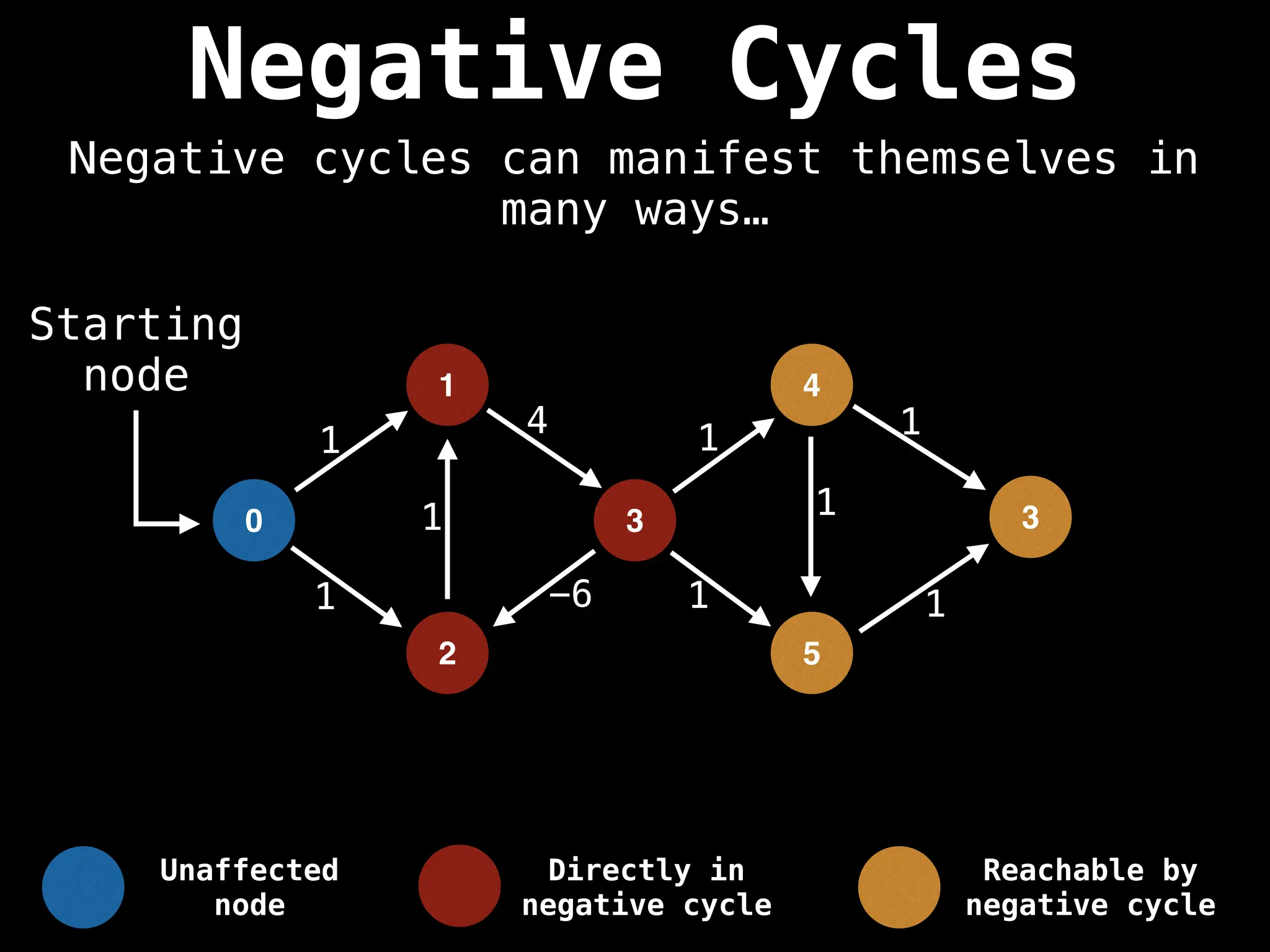

![BF Algorithm Steps
1) Set every entry in D to +∞
2) Set D[S] = 0
3) Relax each edge V-1 times:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-676-2048.jpg)
![BF Algorithm Steps
1) Set every entry in D to +∞
2) Set D[S] = 0
3) Relax each edge V-1 times:
for (i = 0; i < V-1; i = i + 1):
for edge in graph.edges:
// Relax edge (update D with shorter path)
if (D[edge.from] + edge.cost < D[edge.to])
D[edge.to] = D[edge.from] + edge.cost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-677-2048.jpg)
![BF Algorithm Steps
1) Set every entry in D to +∞
2) Set D[S] = 0
3) Relax each edge V-1 times:
for (i = 0; i < V-1; i = i + 1):
for edge in graph.edges:
// Relax edge (update D with shorter path)
if (D[edge.from] + edge.cost < D[edge.to])
D[edge.to] = D[edge.from] + edge.cost
// Repeat to find nodes caught in a negative cycle
for (i = 0; i < V-1; i = i + 1):
for edge in graph.edges:
if (D[edge.from] + edge.cost < D[edge.to])
D[edge.to] = -∞](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-678-2048.jpg)
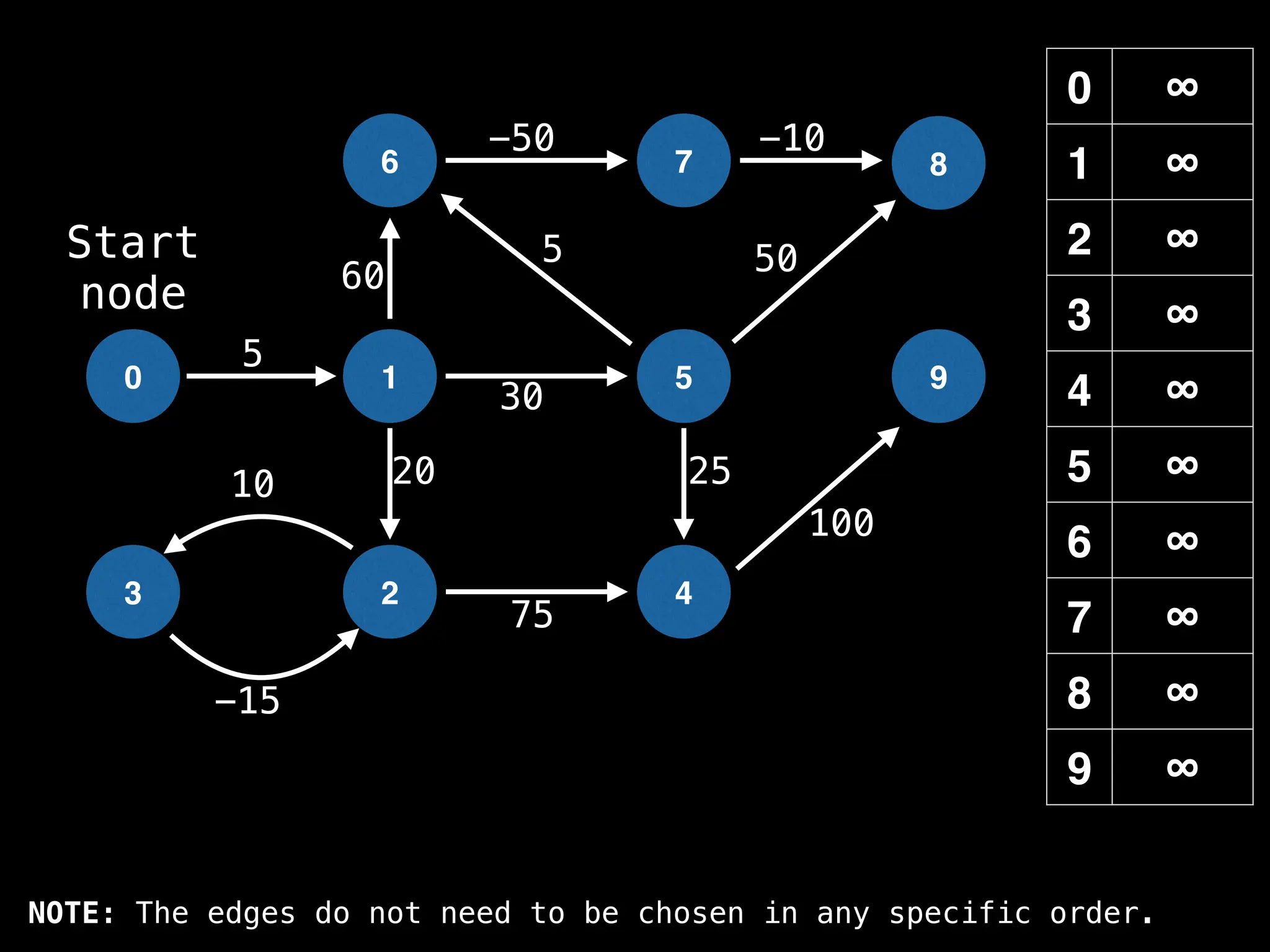
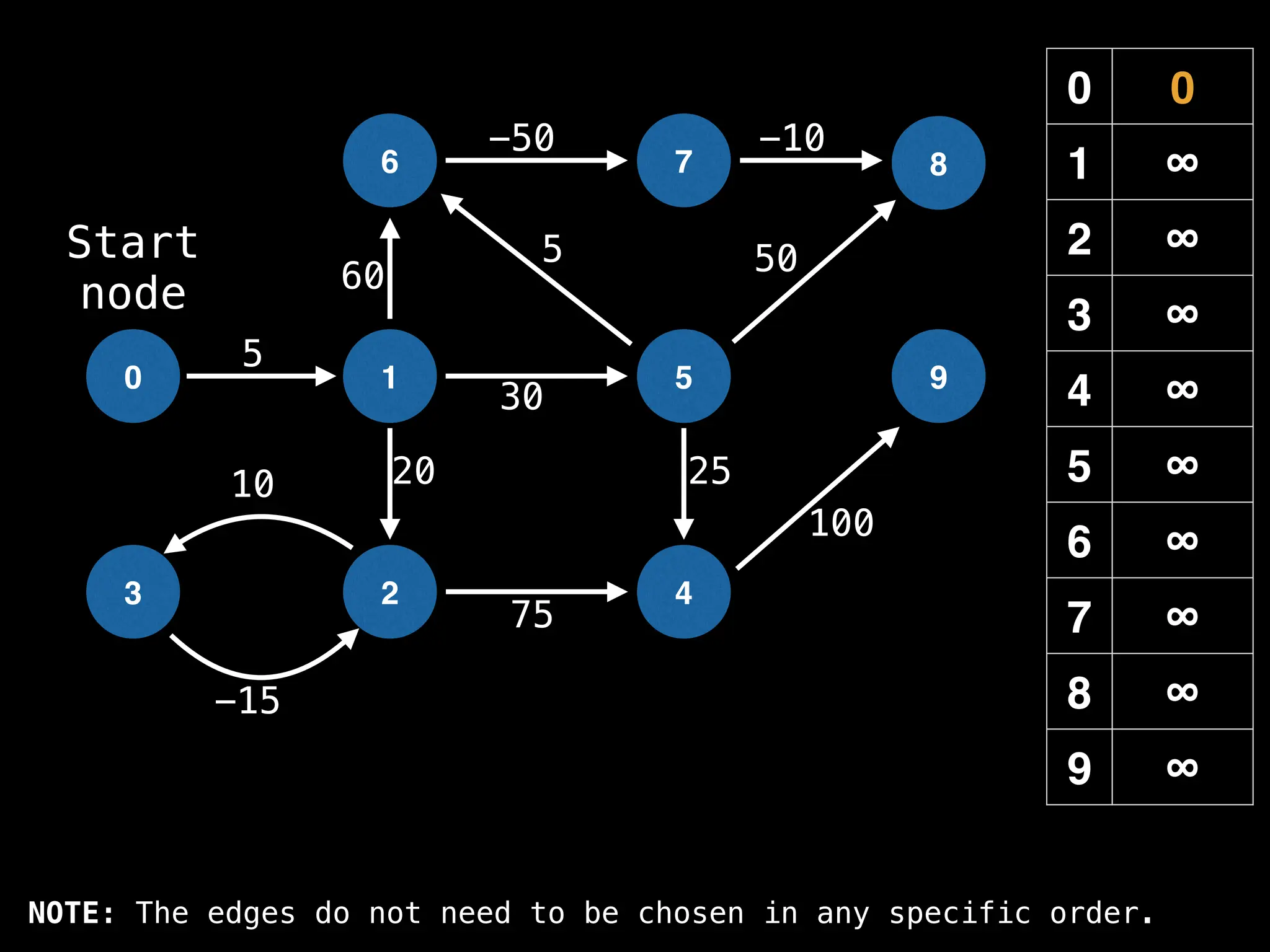
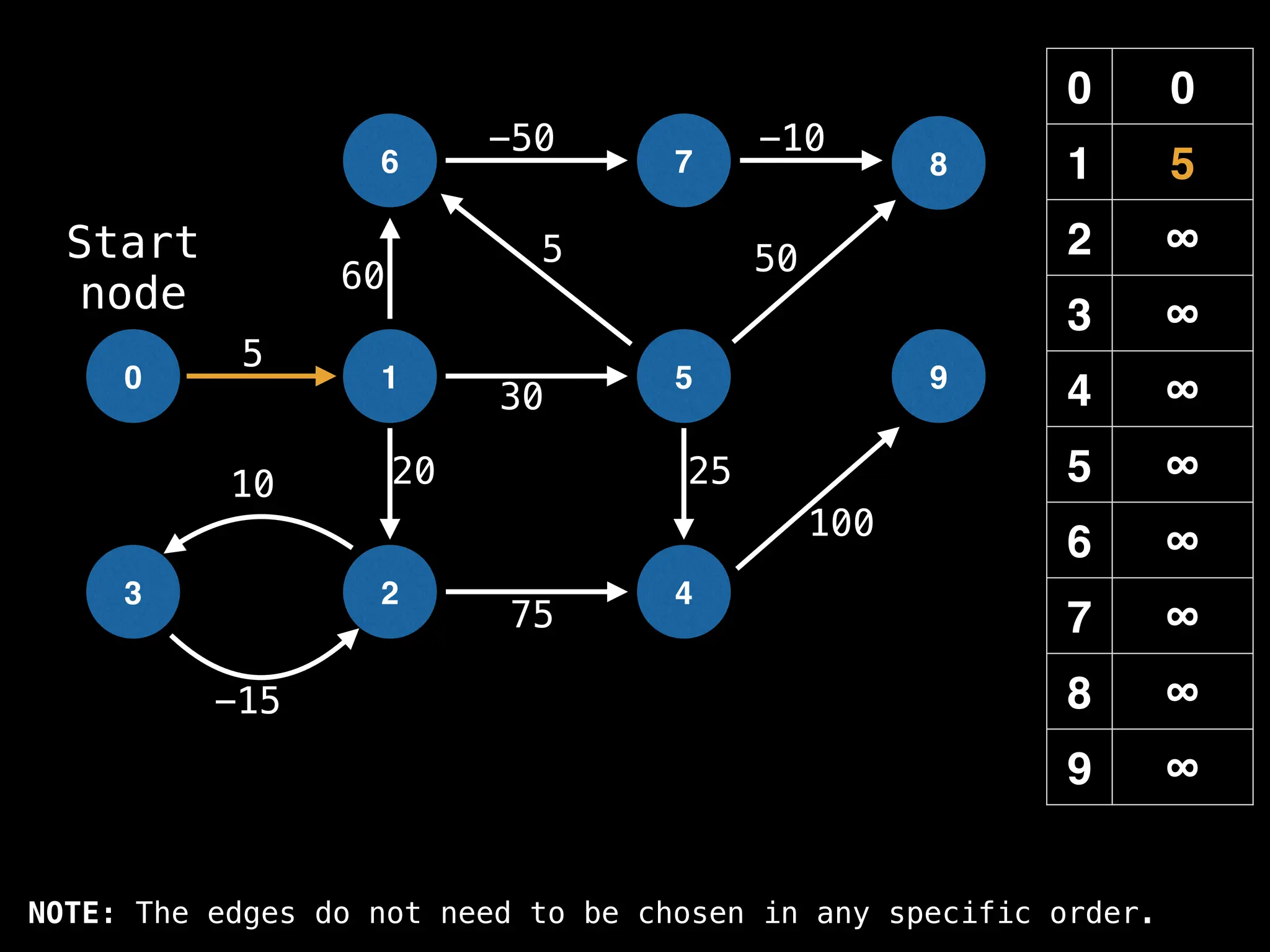
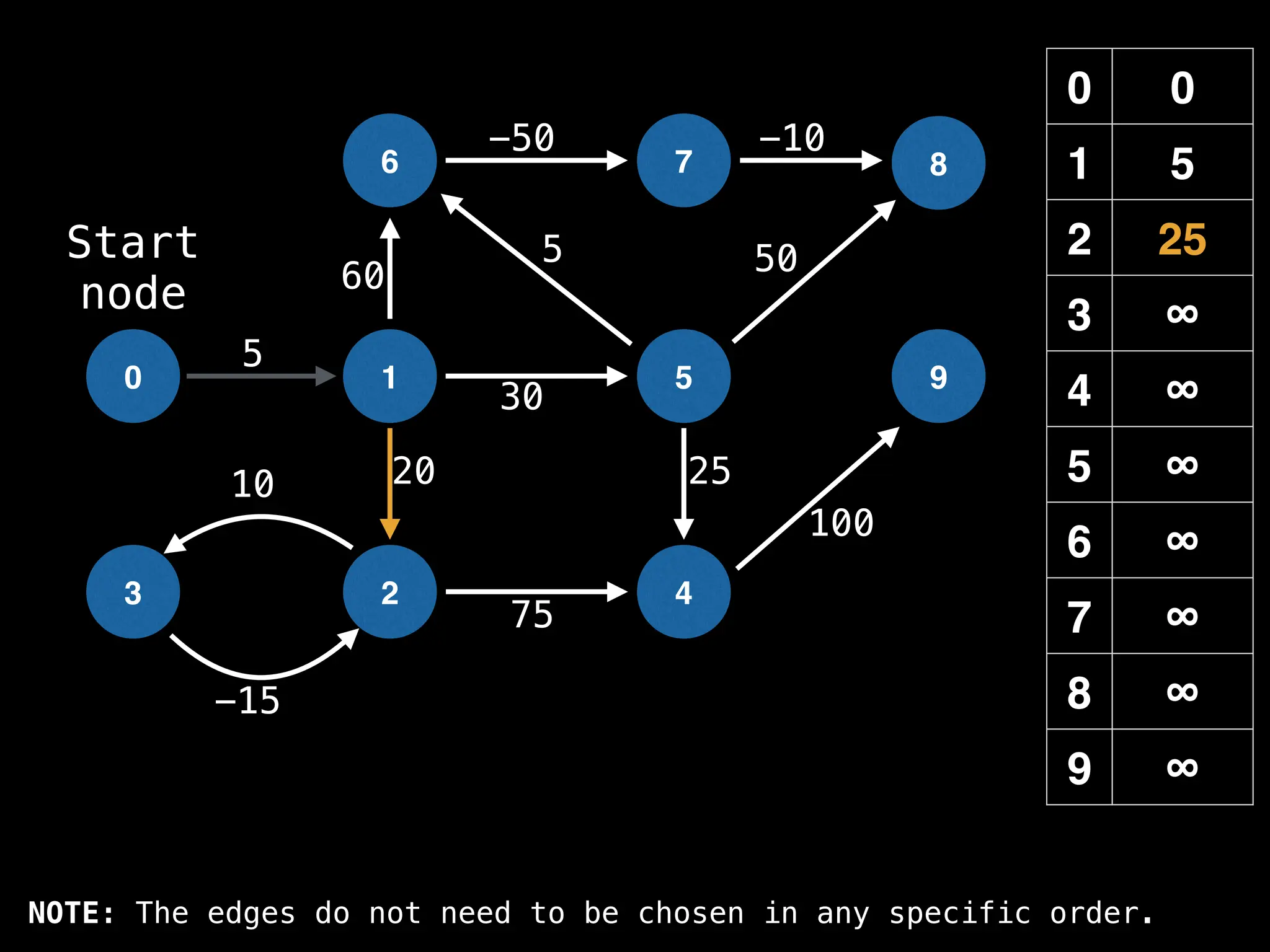
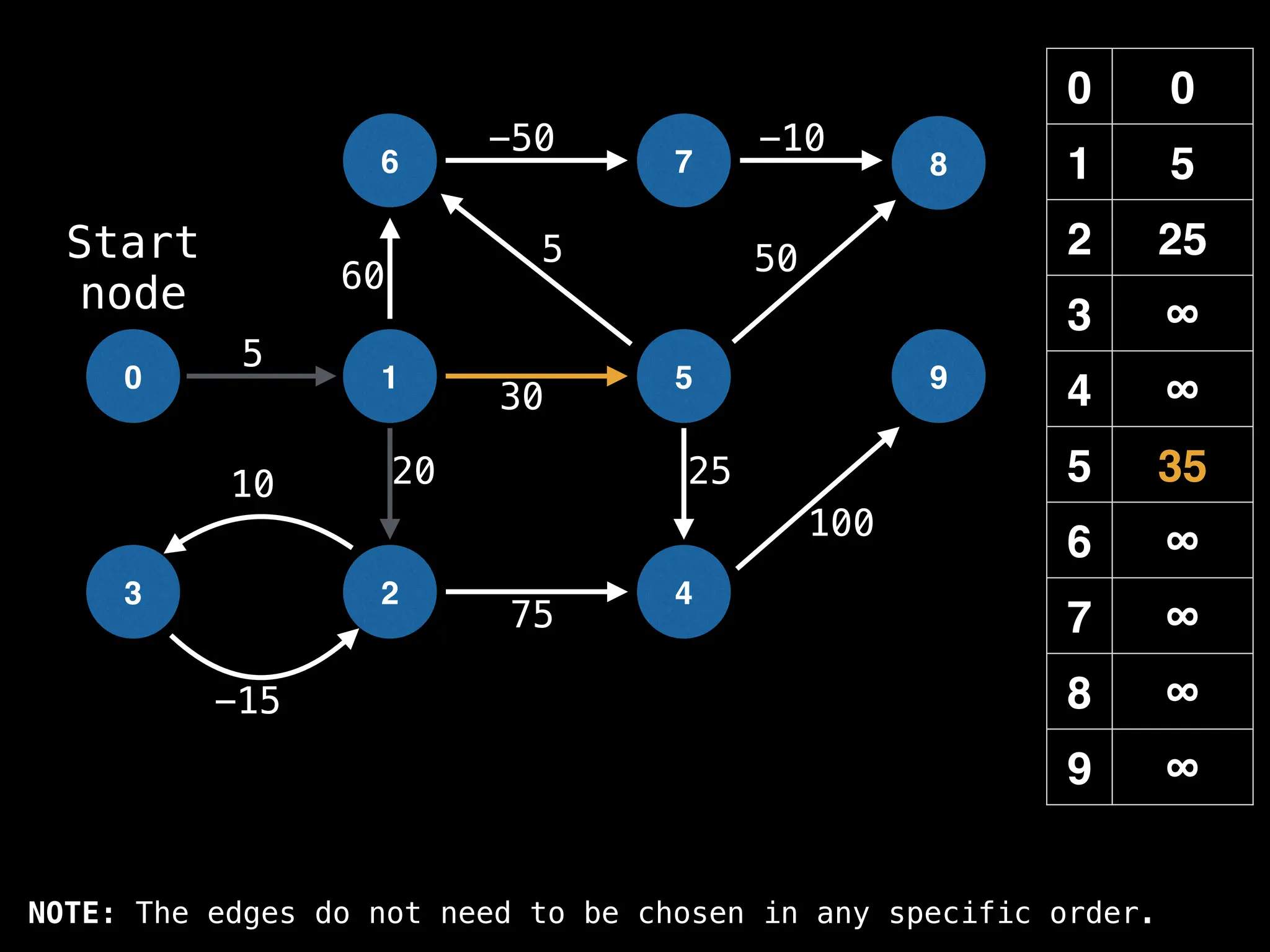
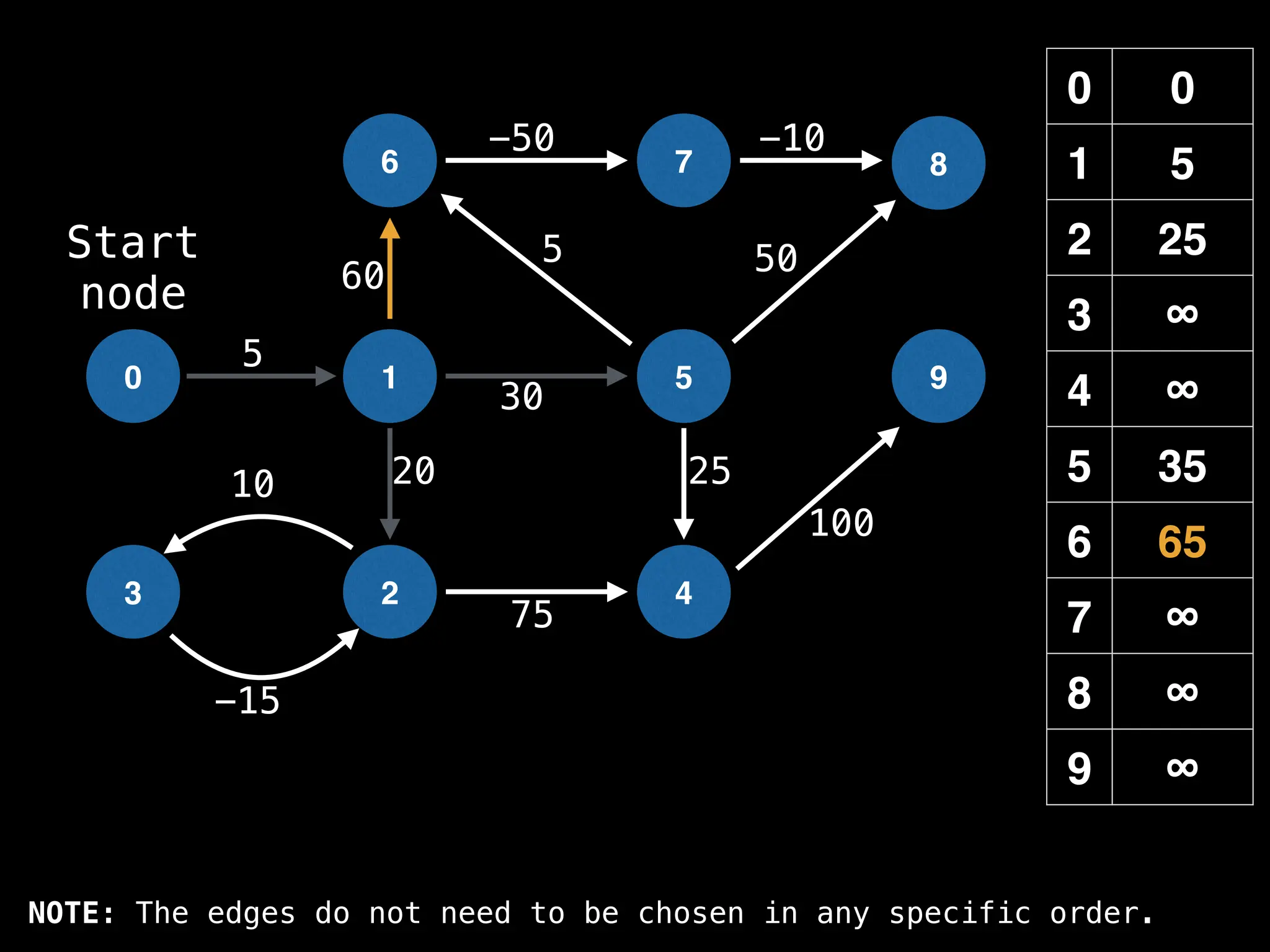
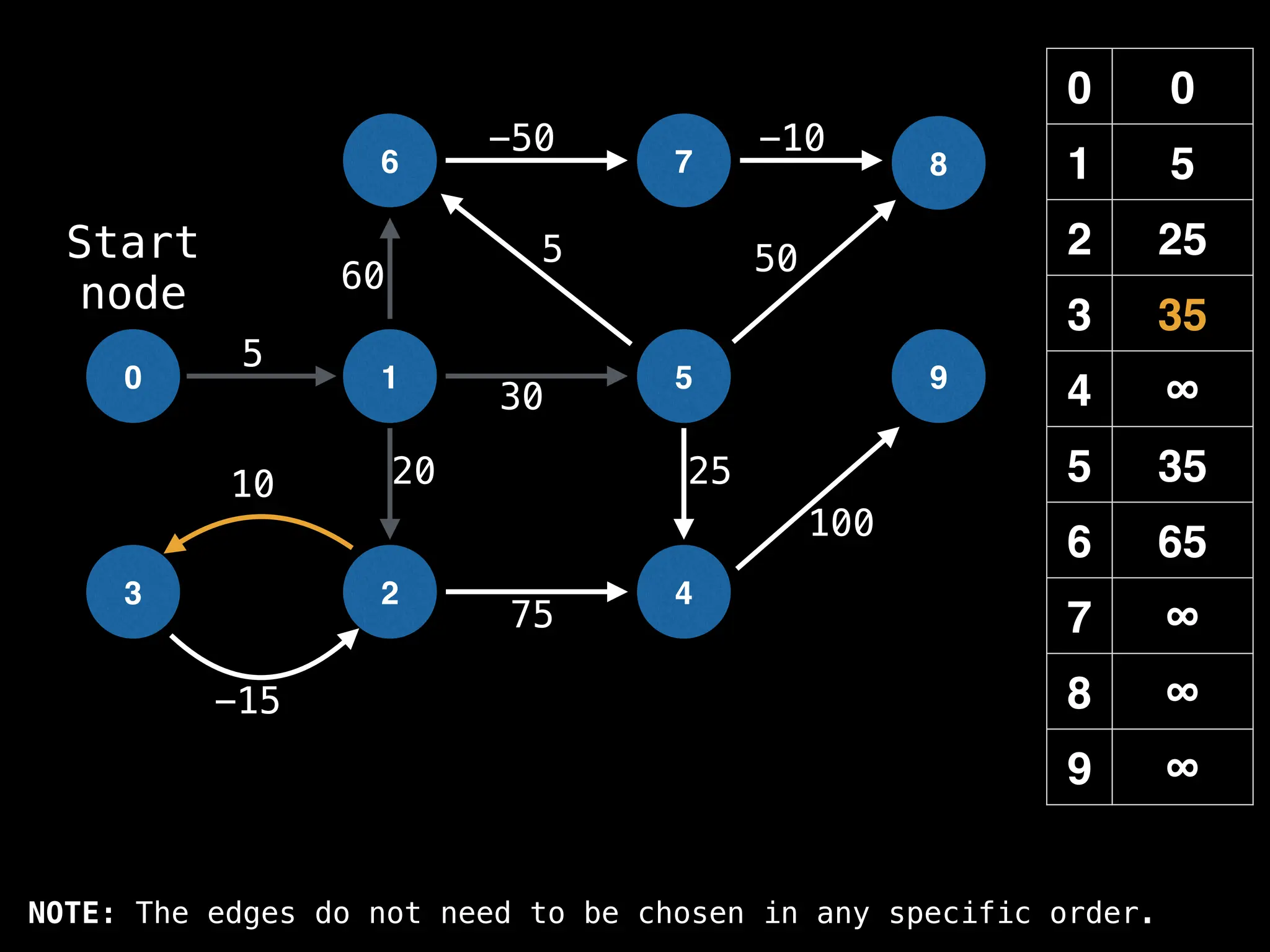
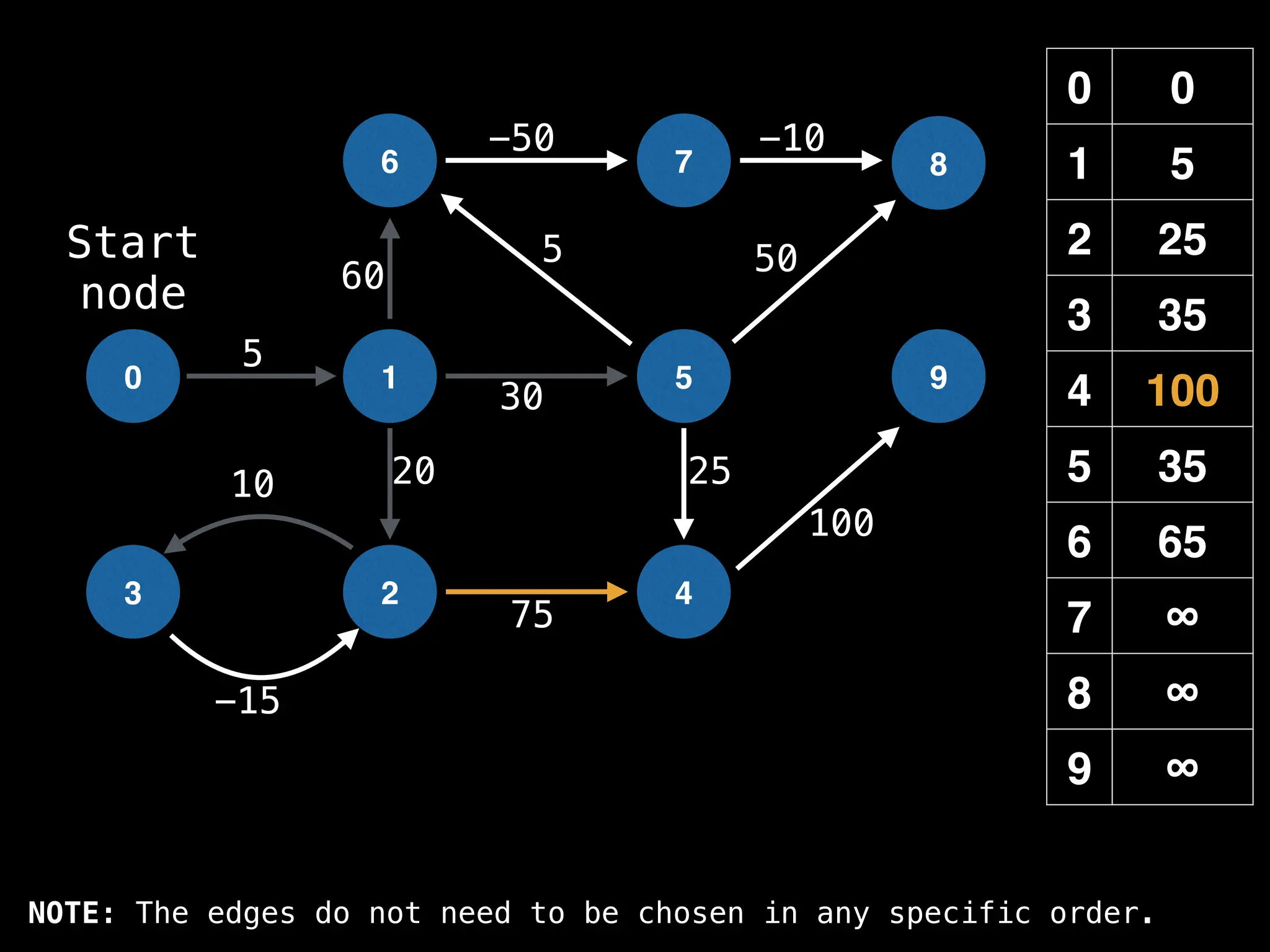
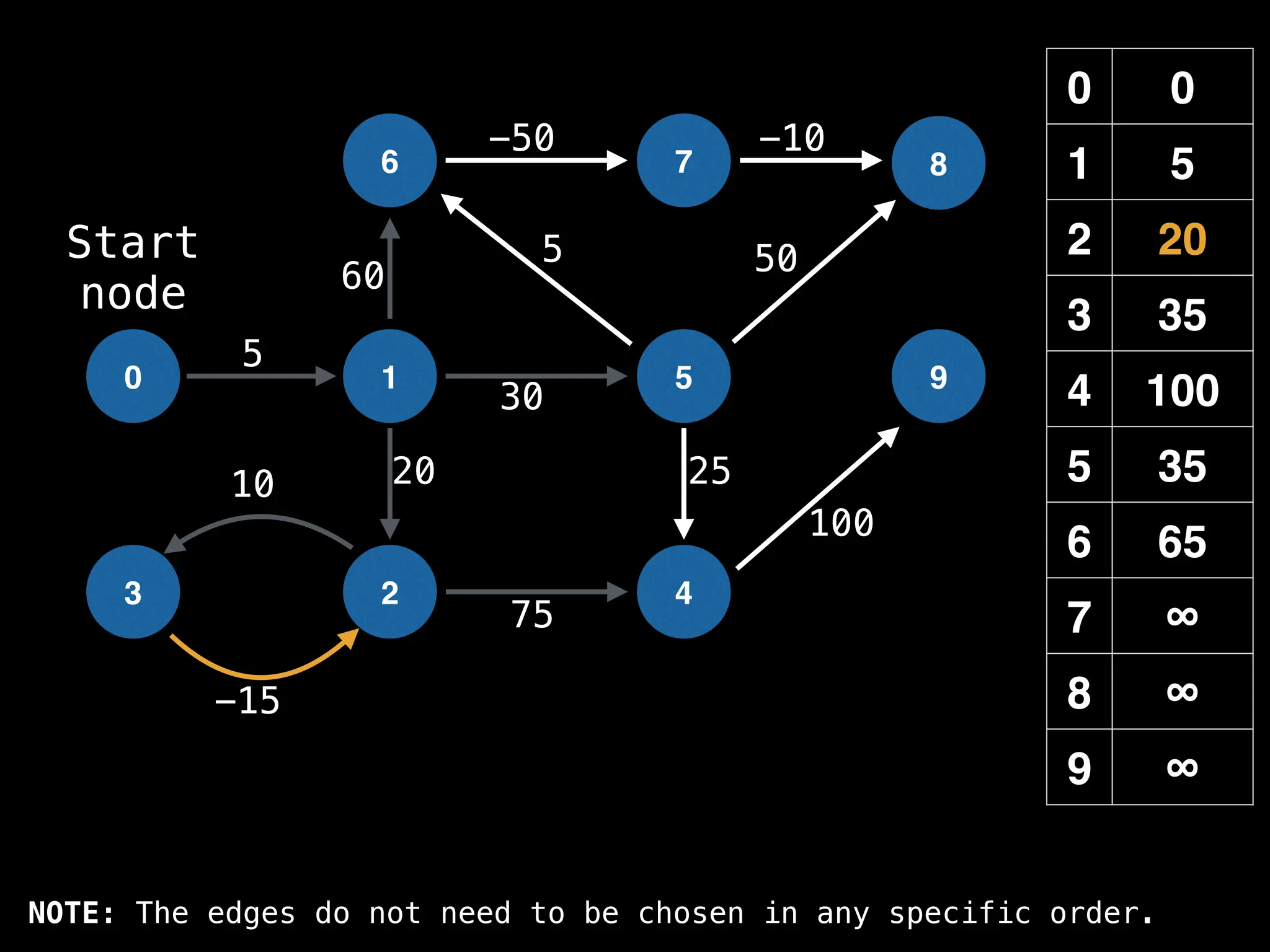
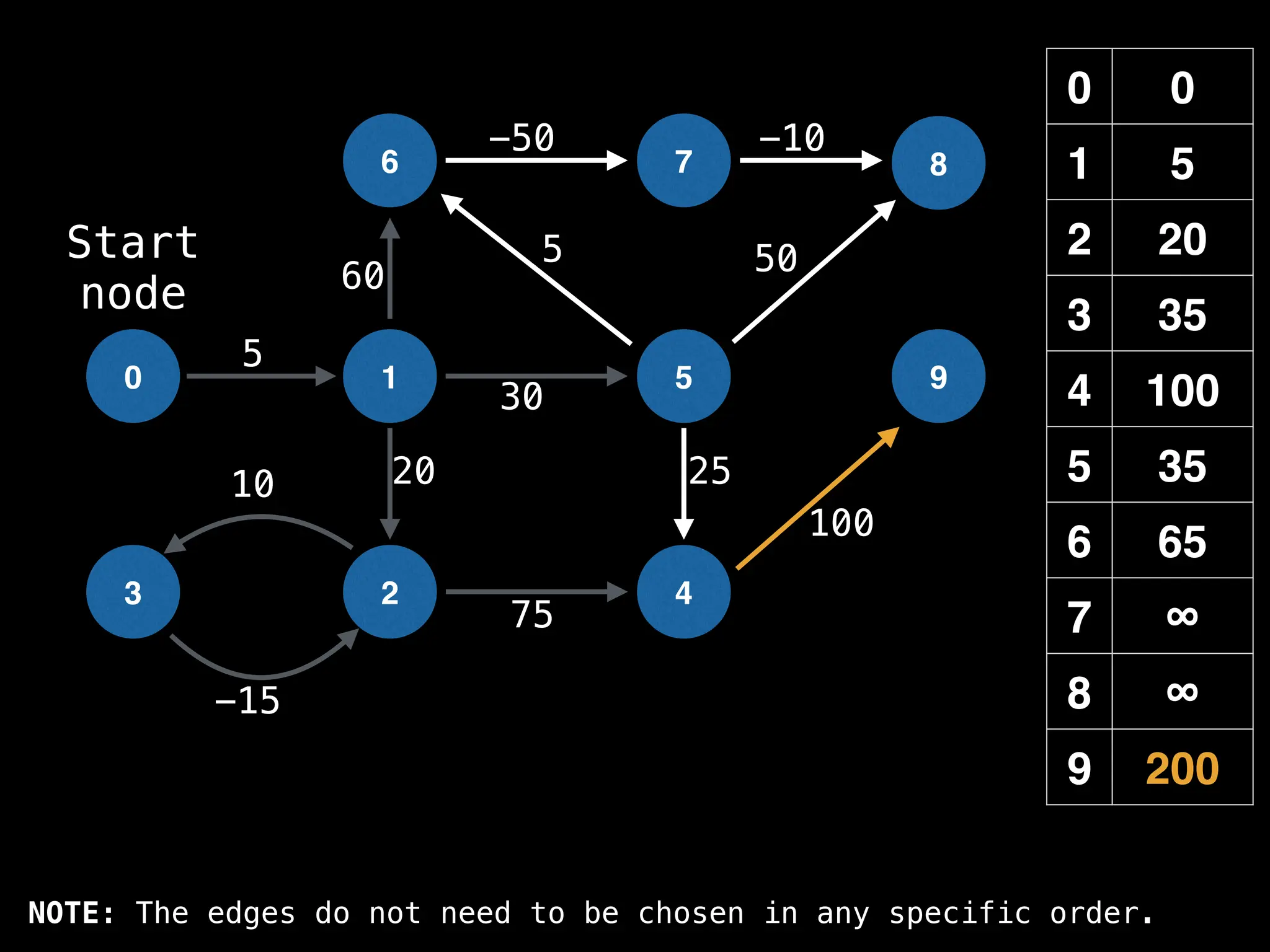
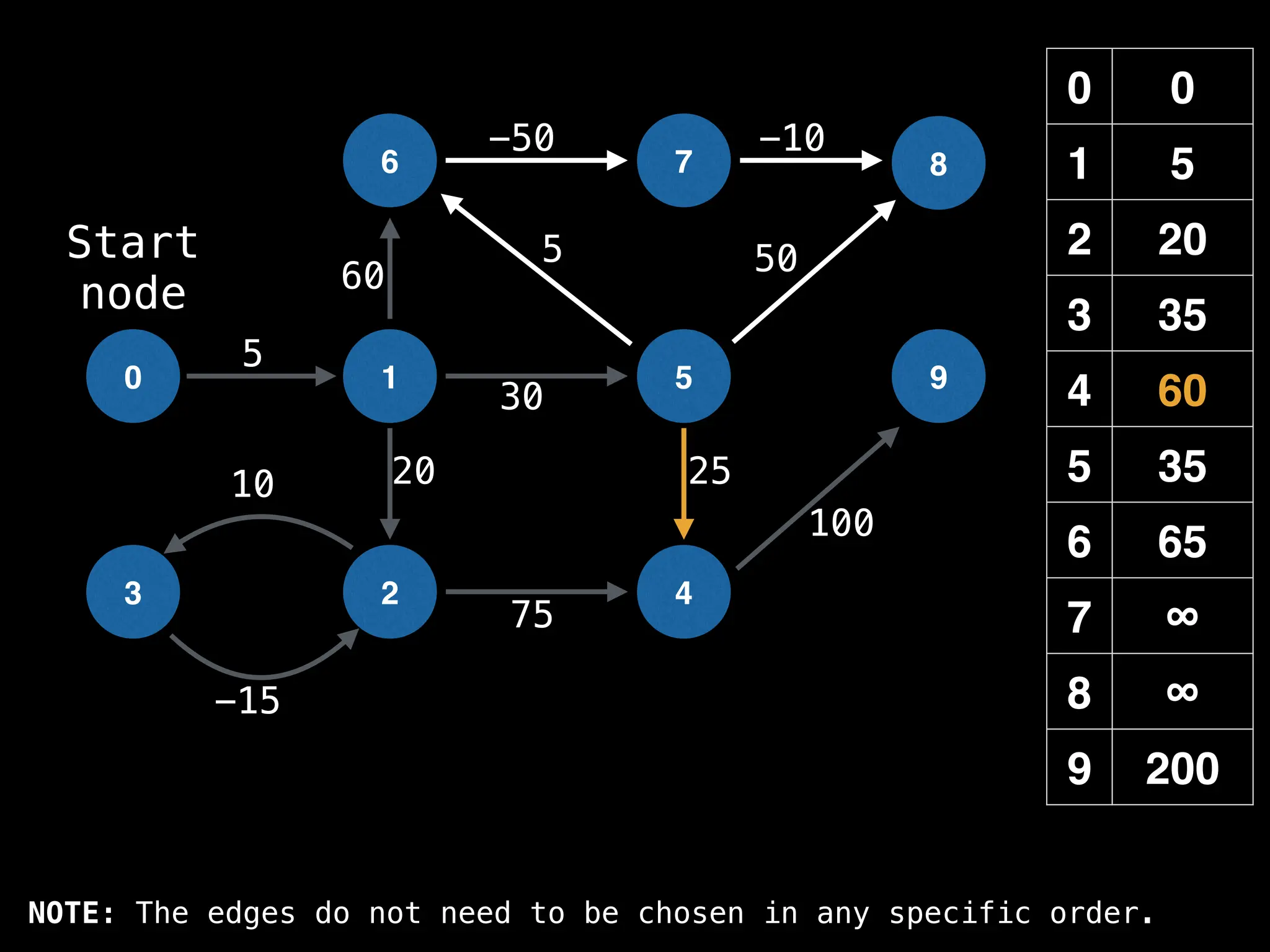
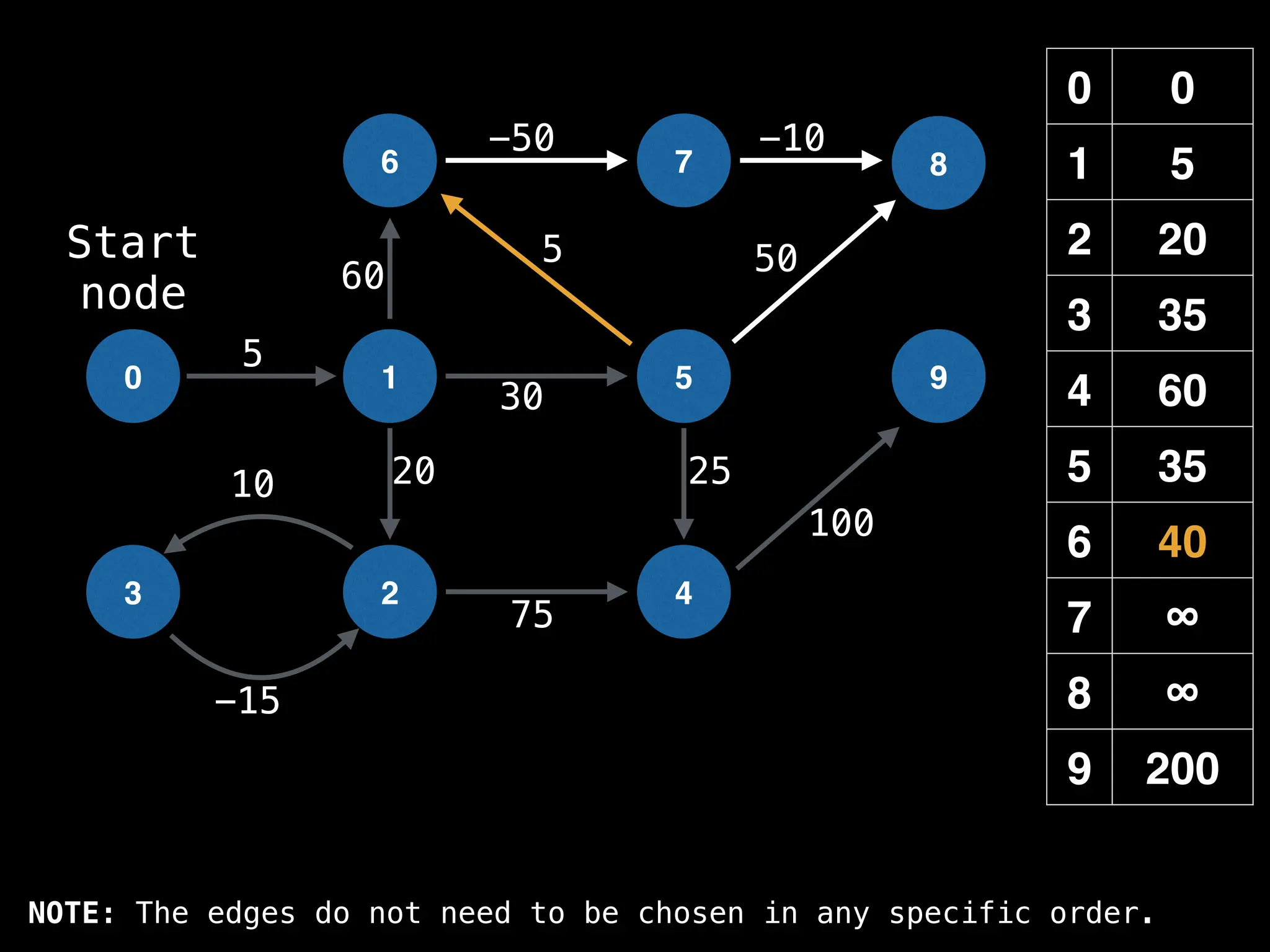
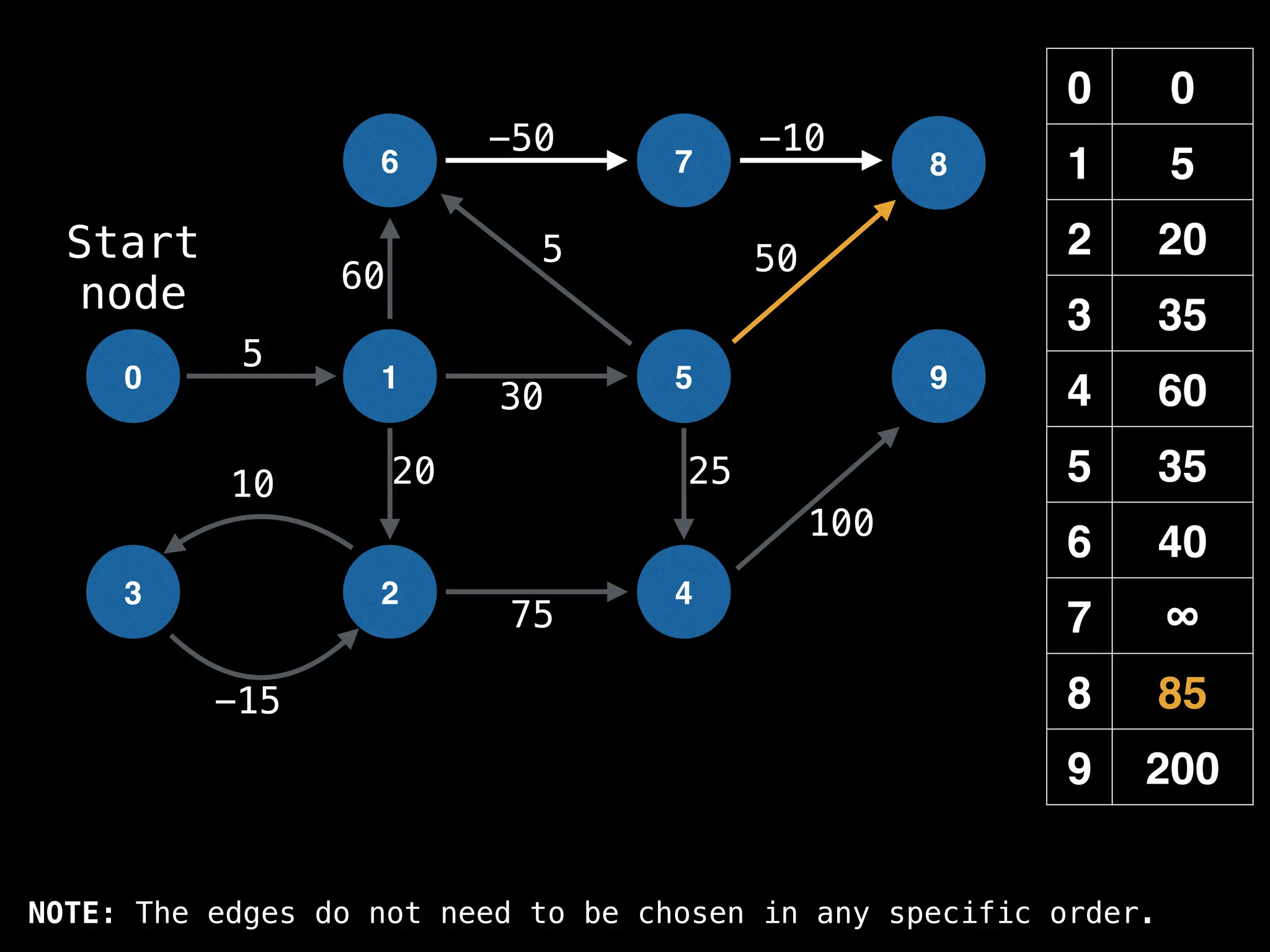
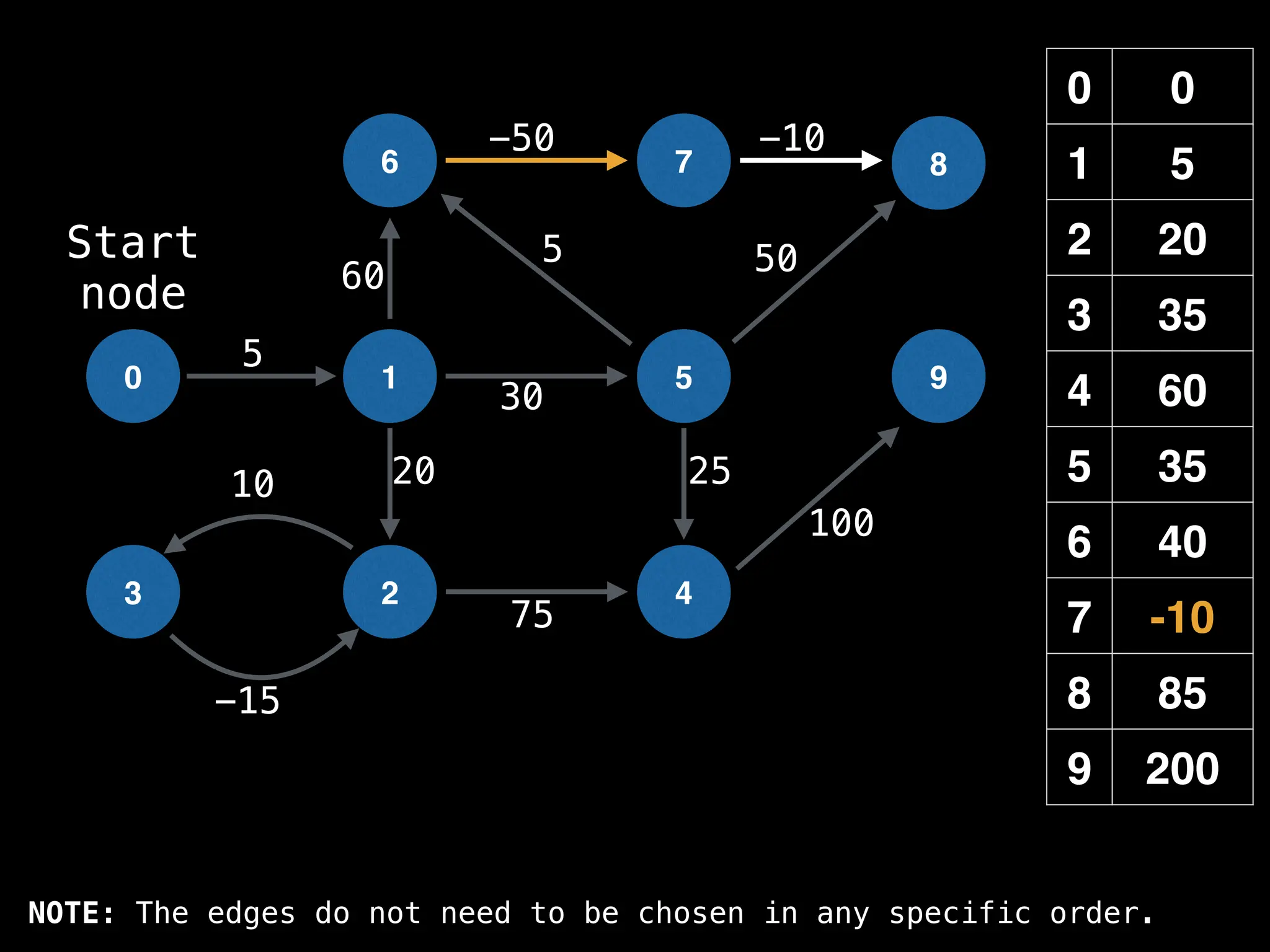
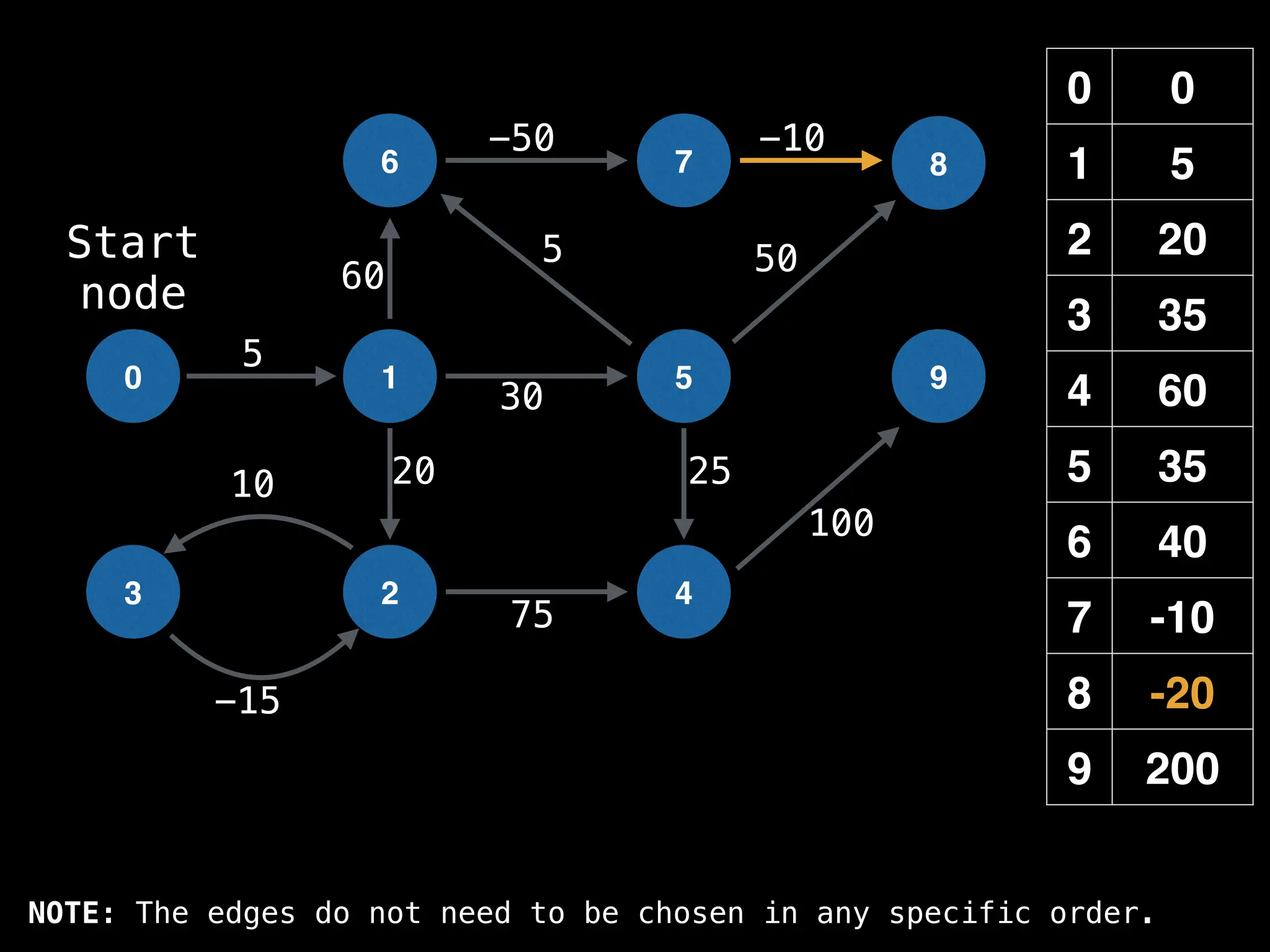
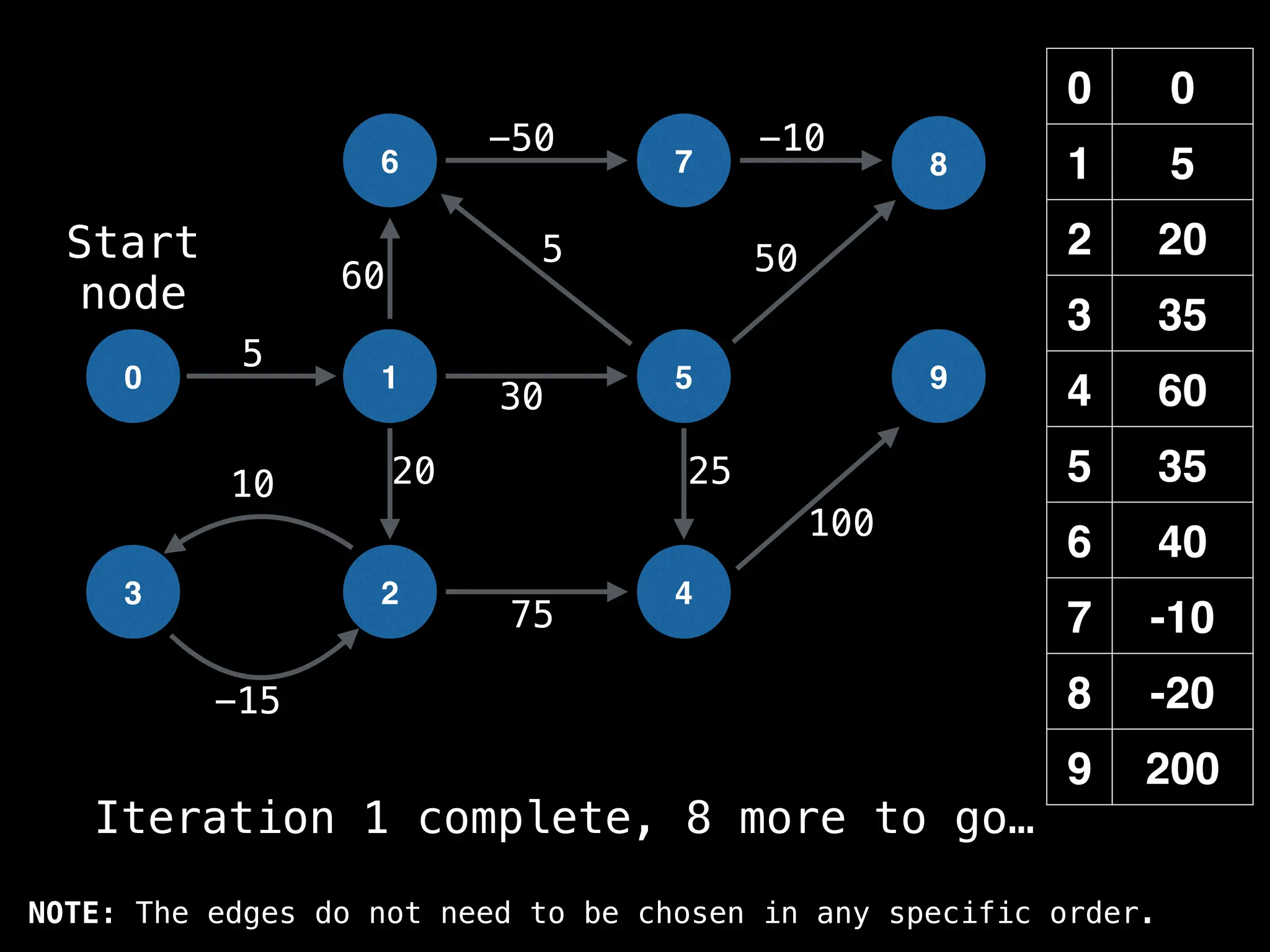
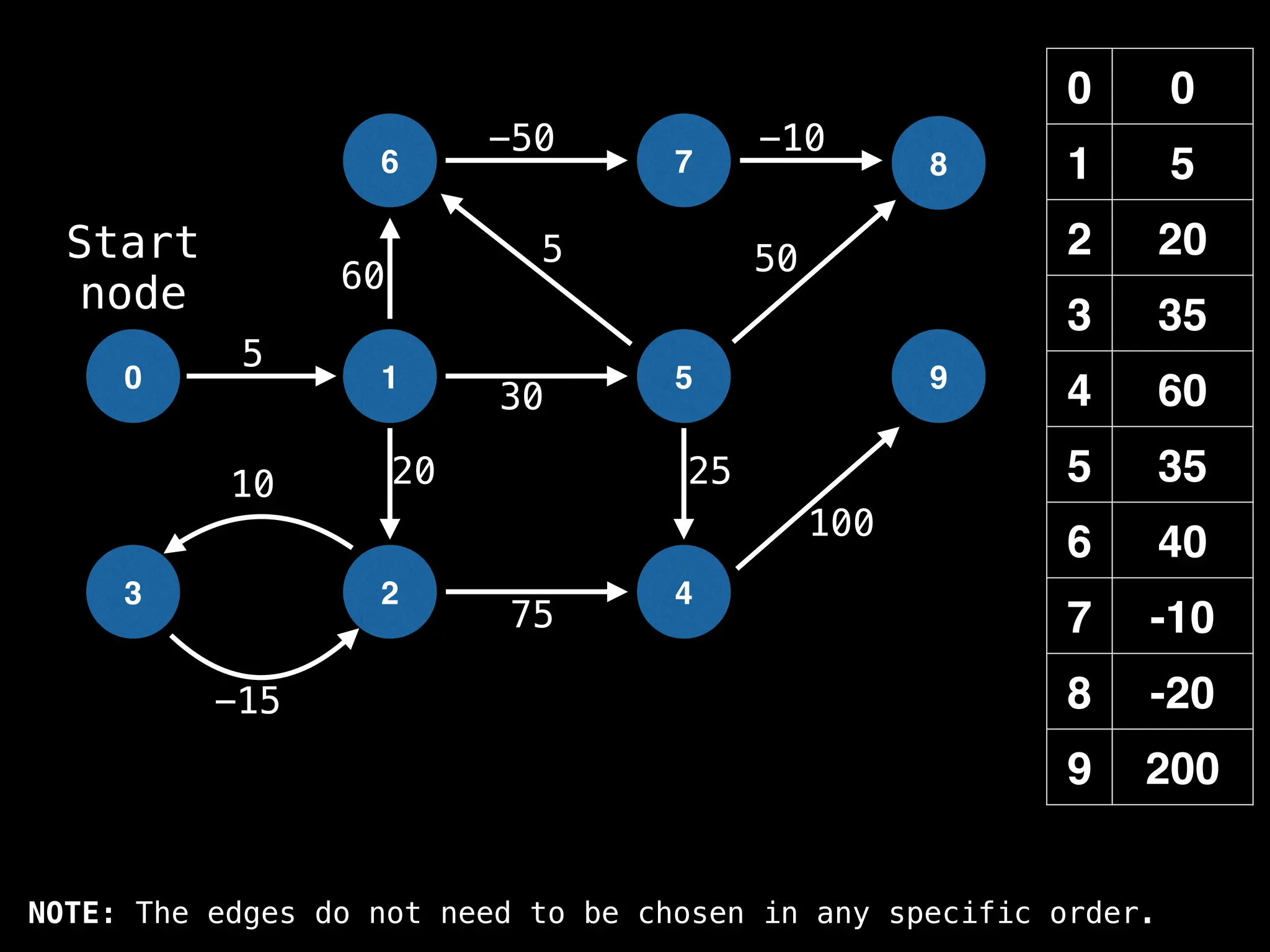
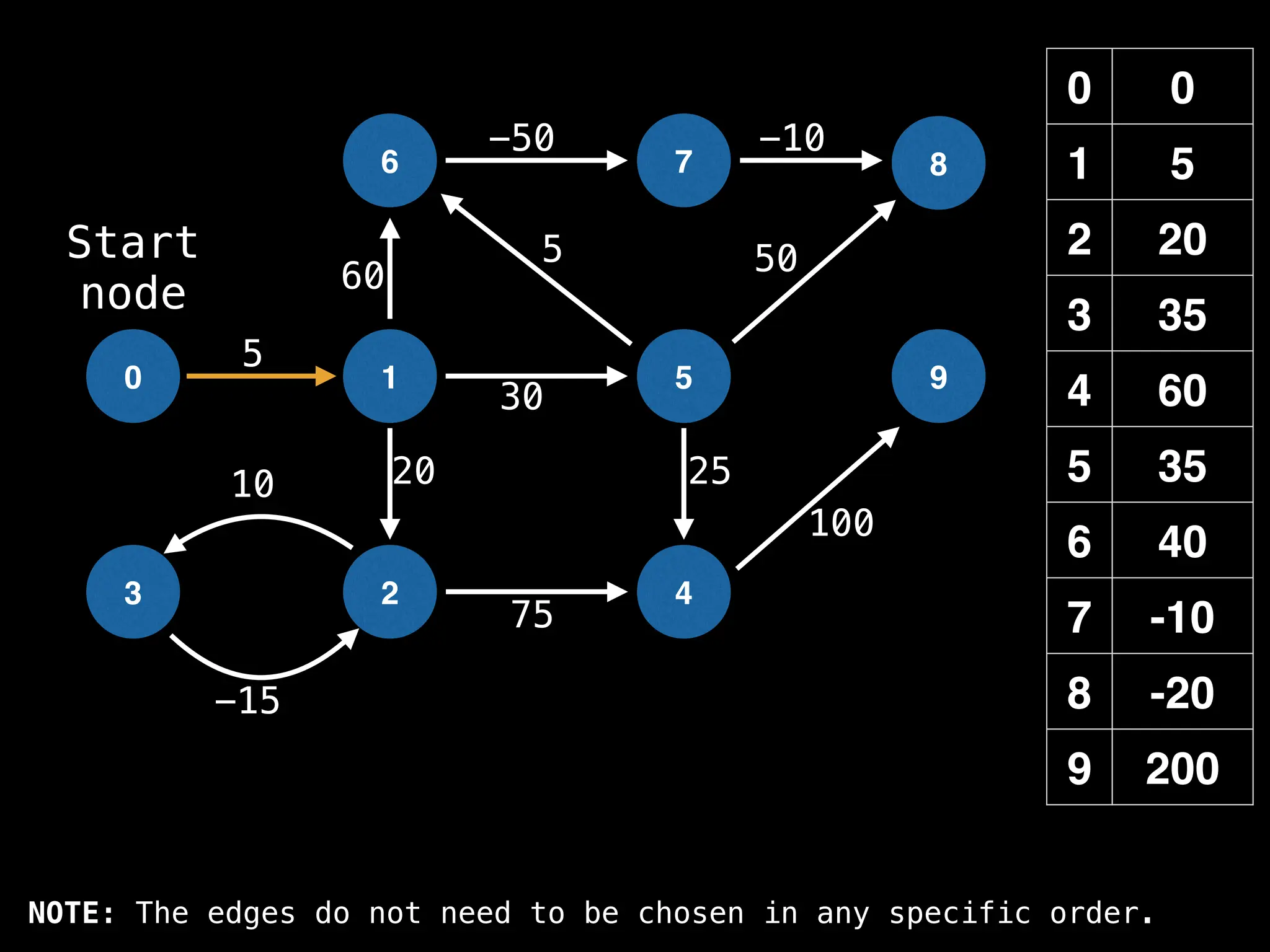
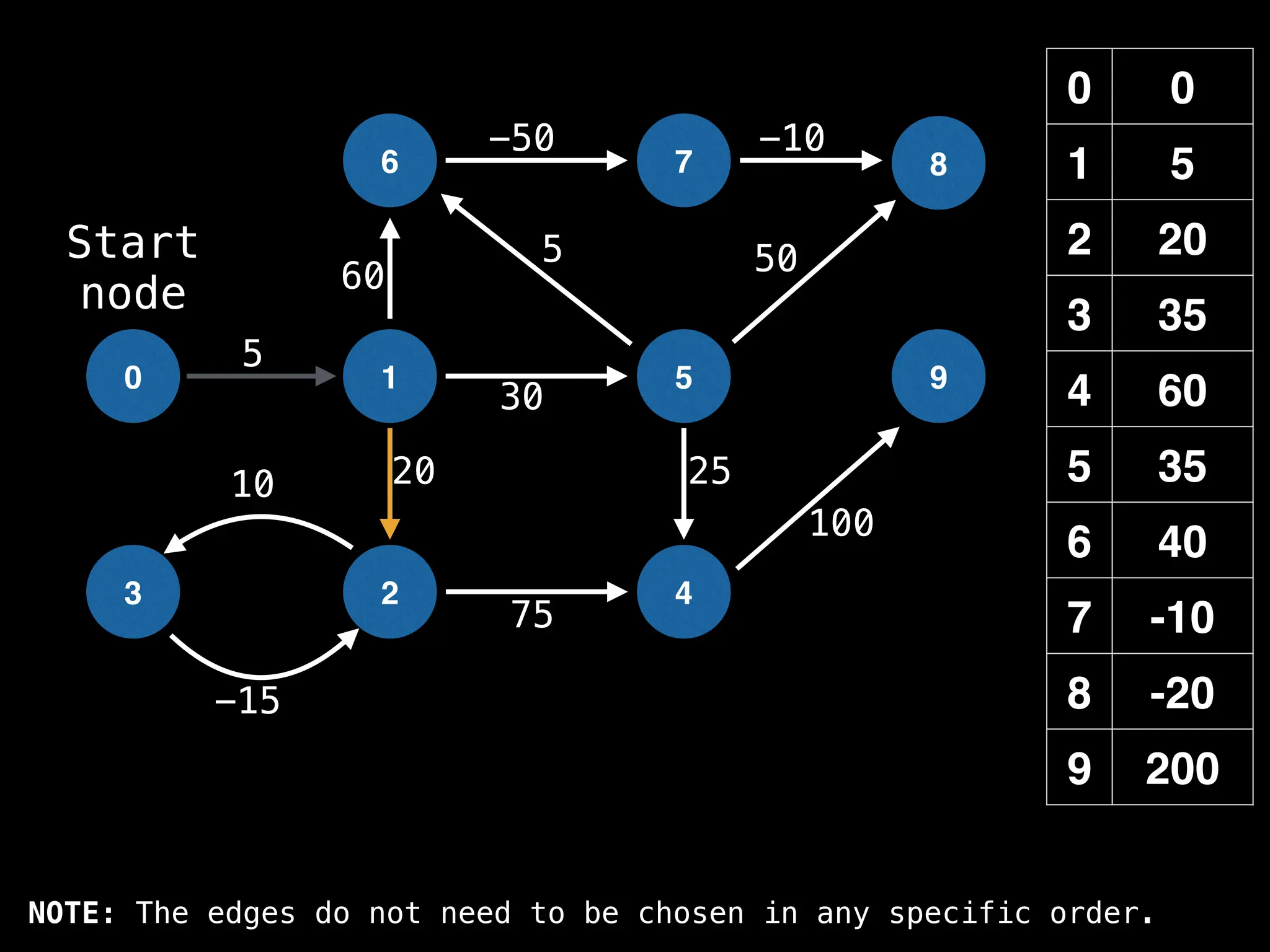
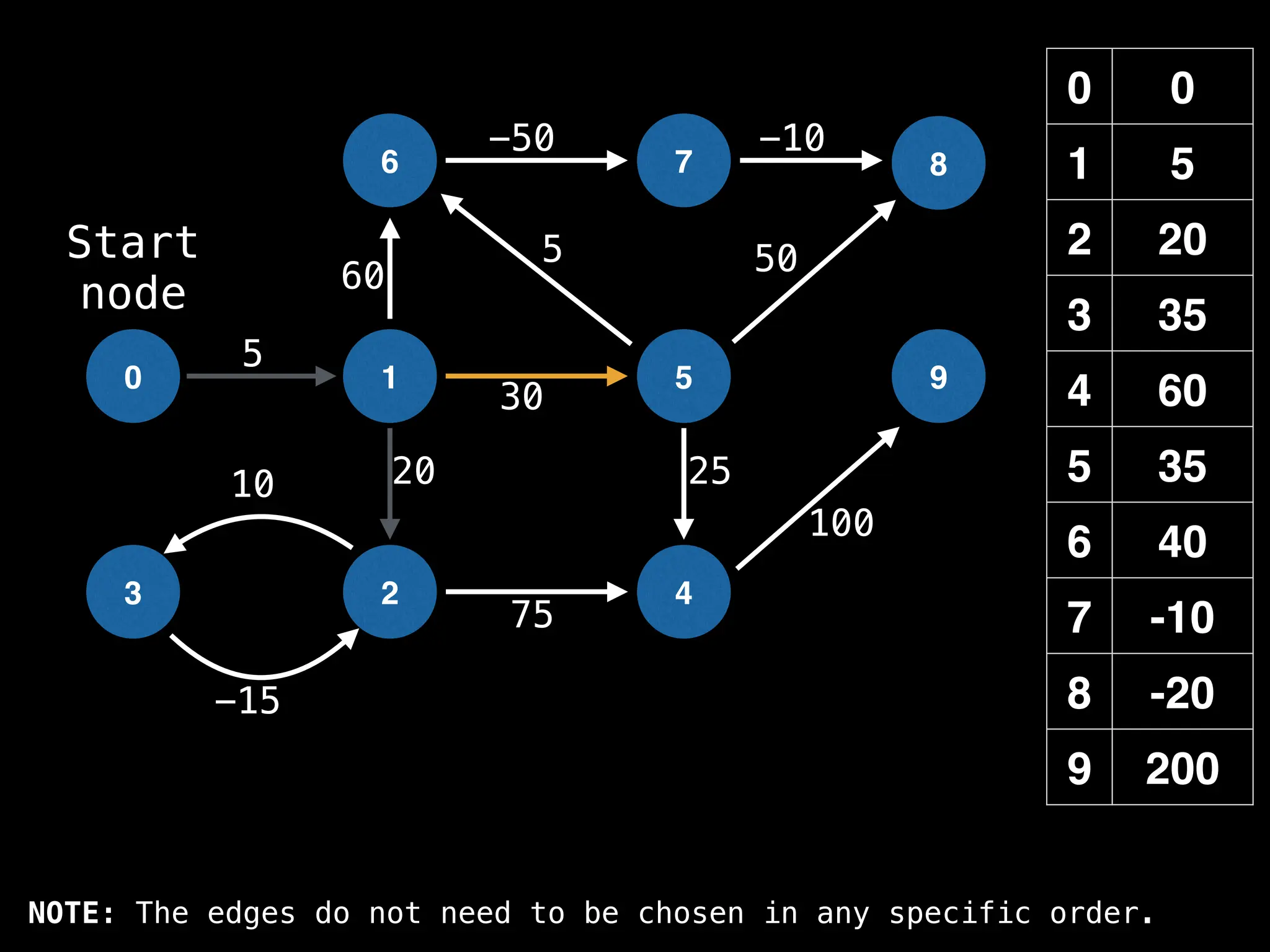
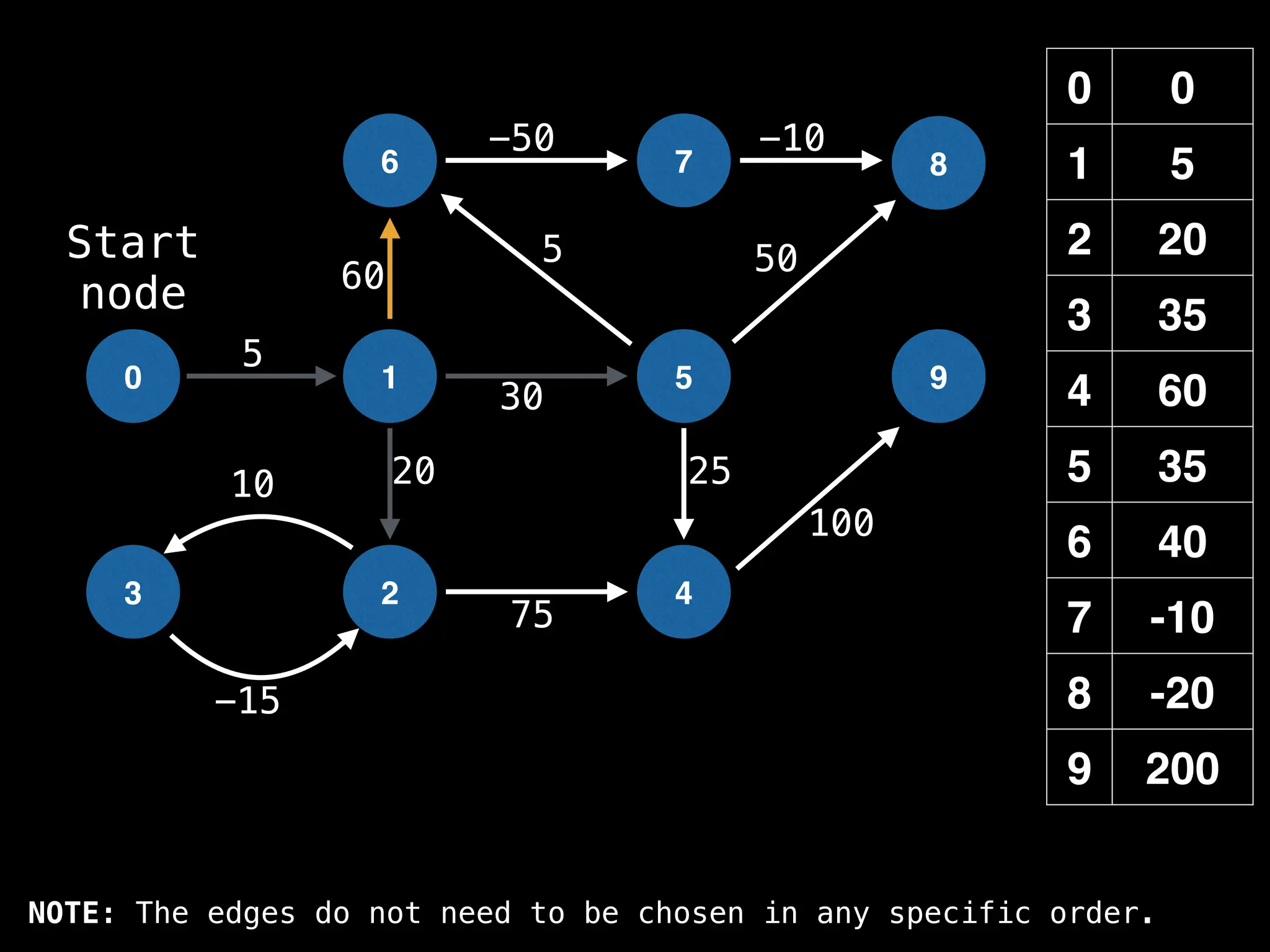
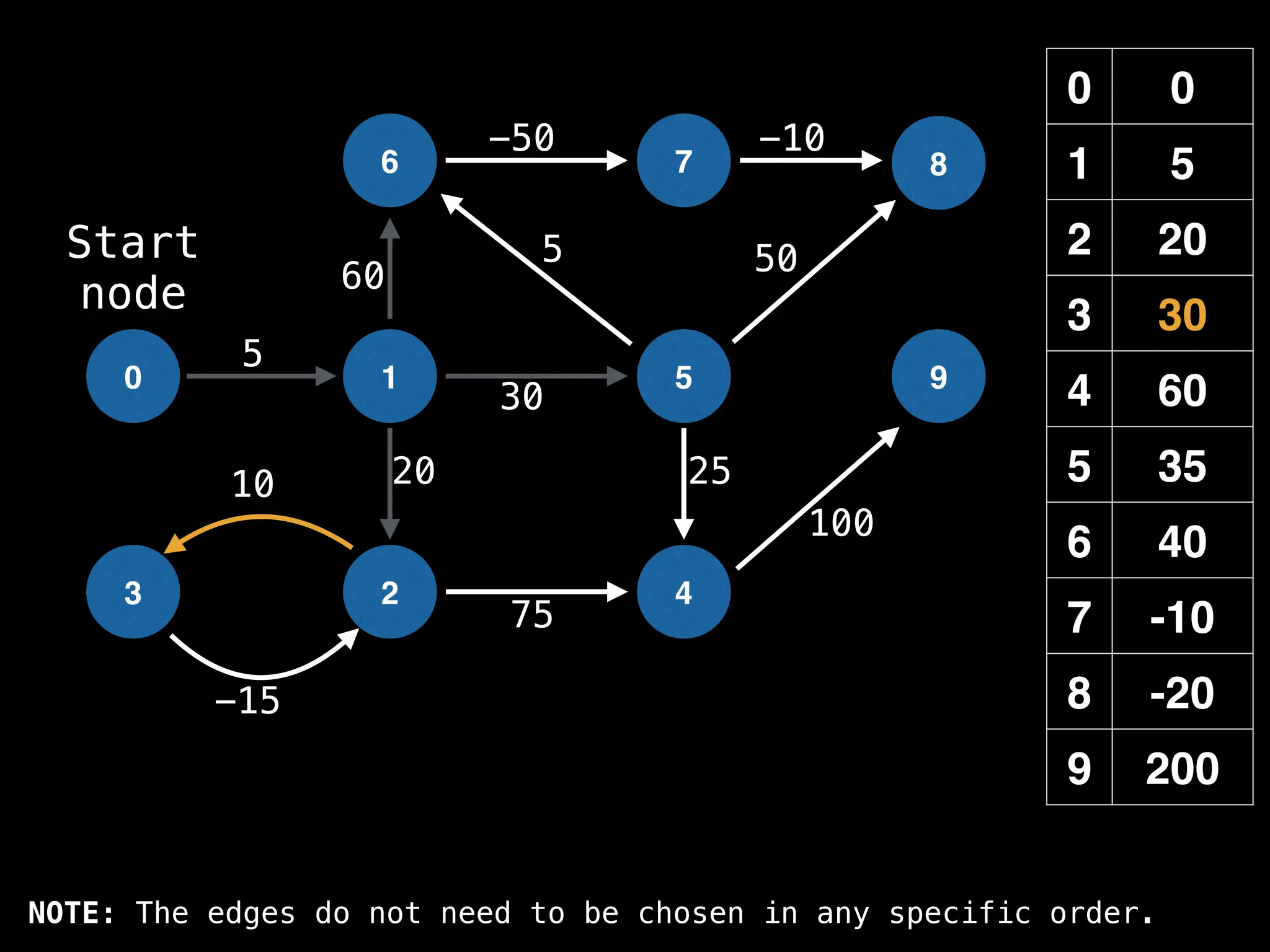
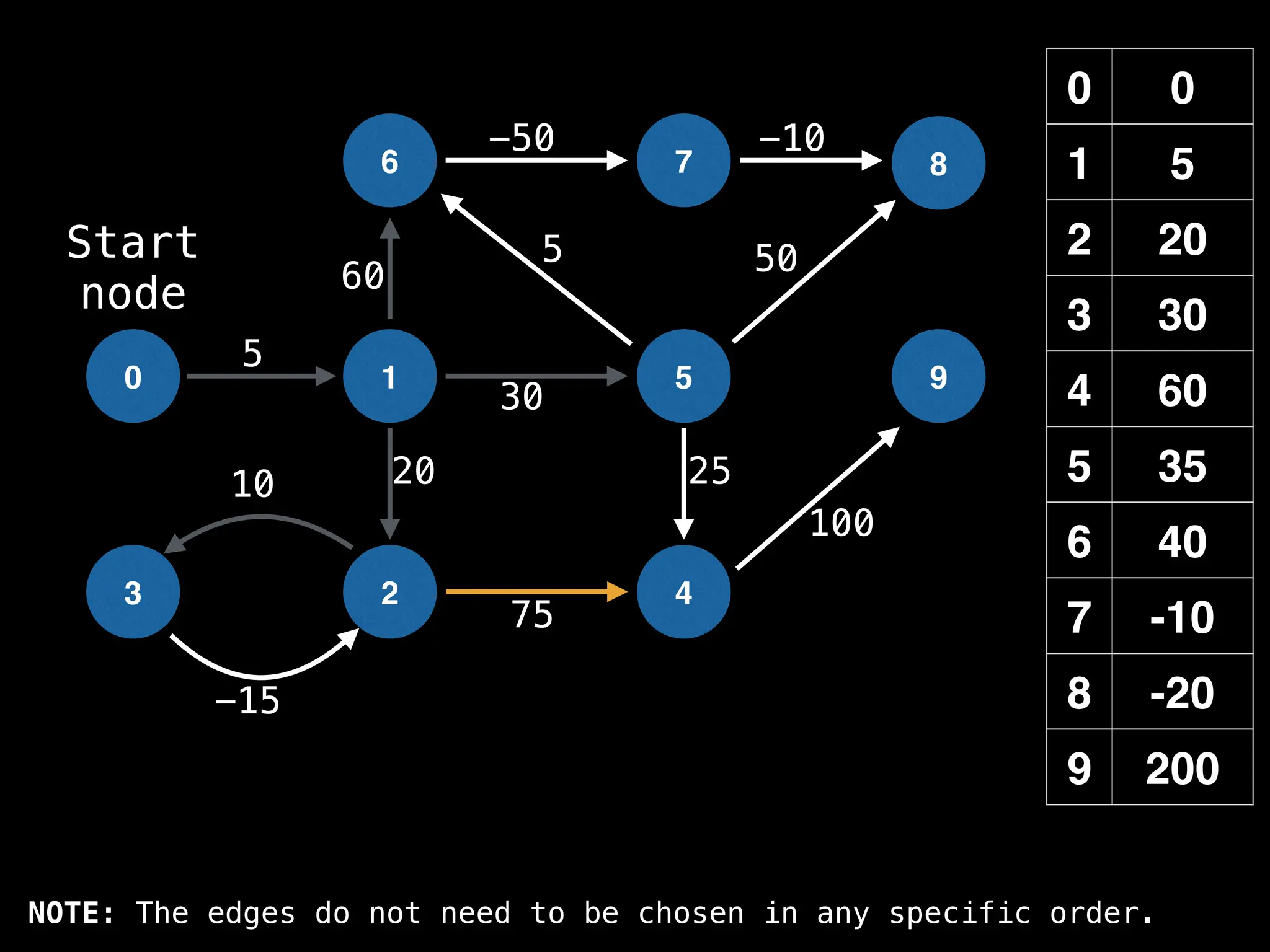
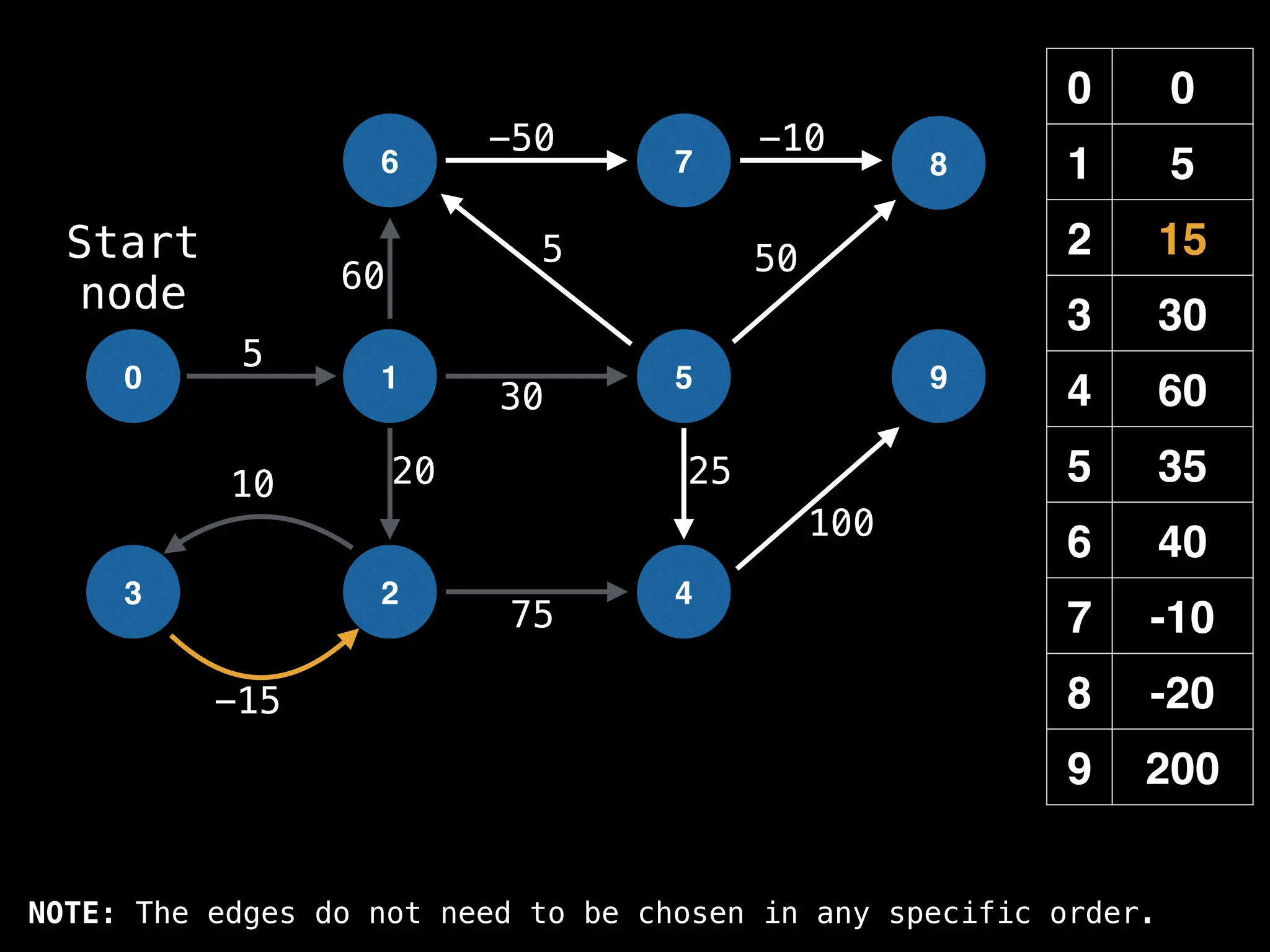
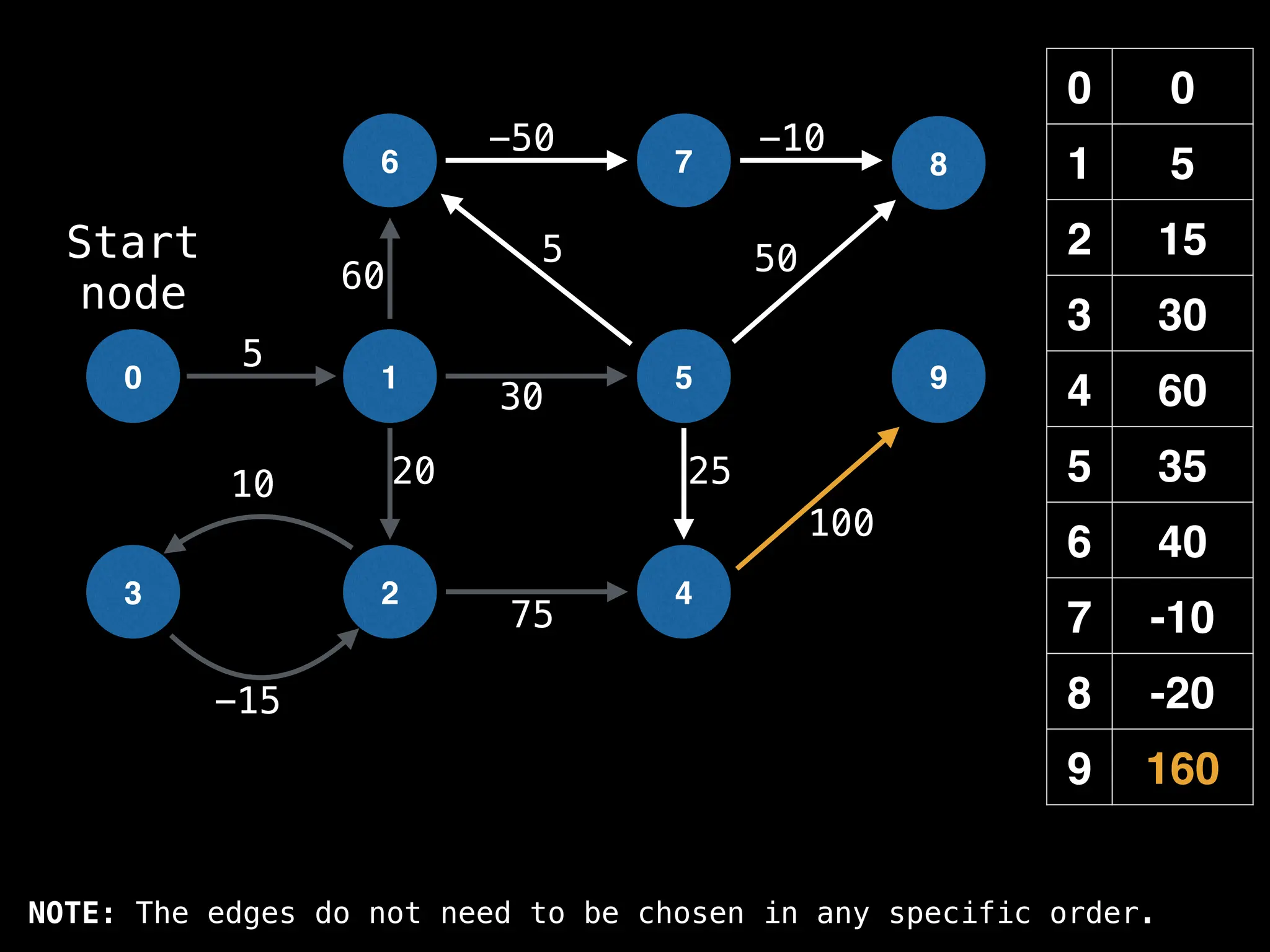
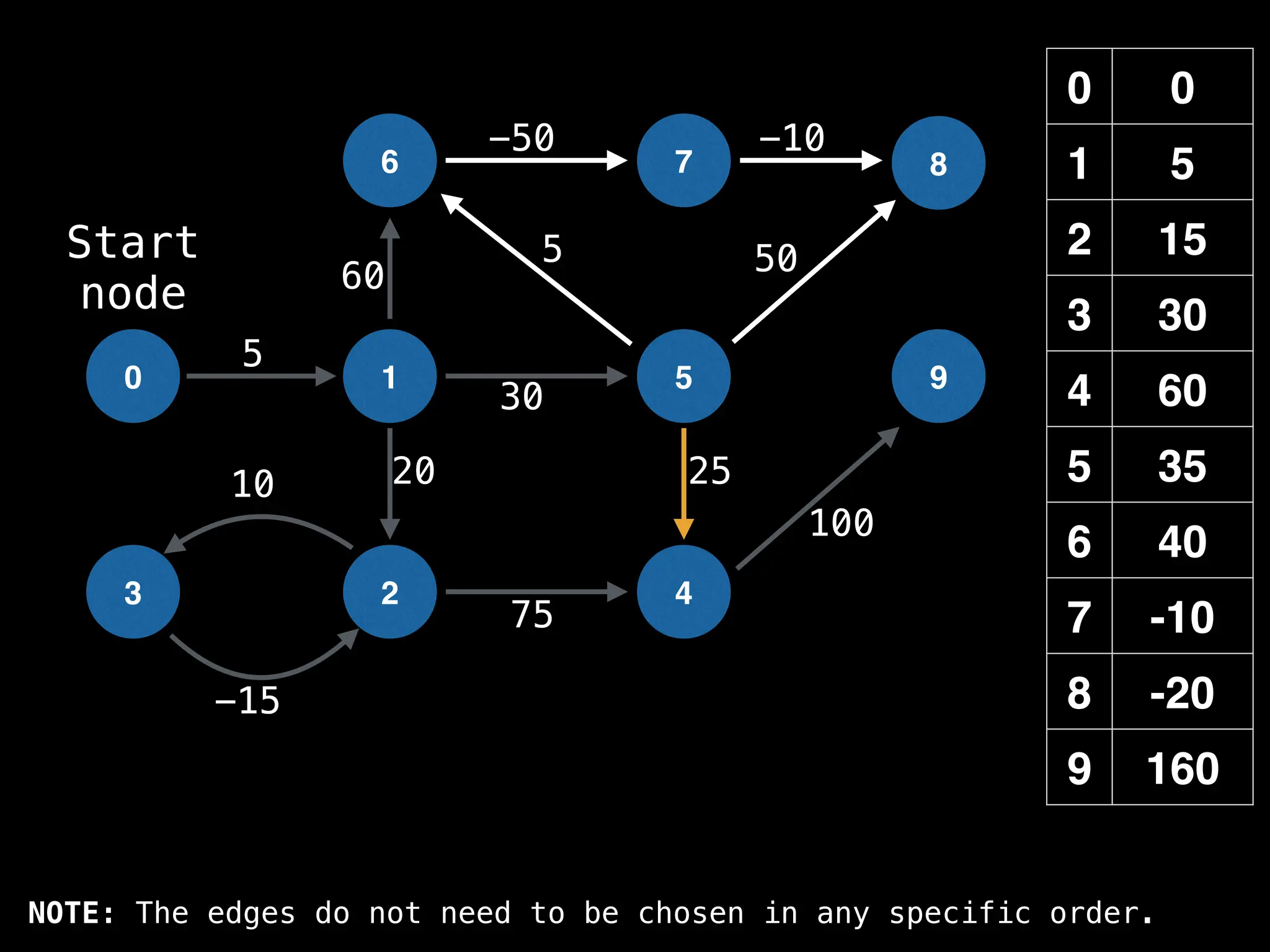
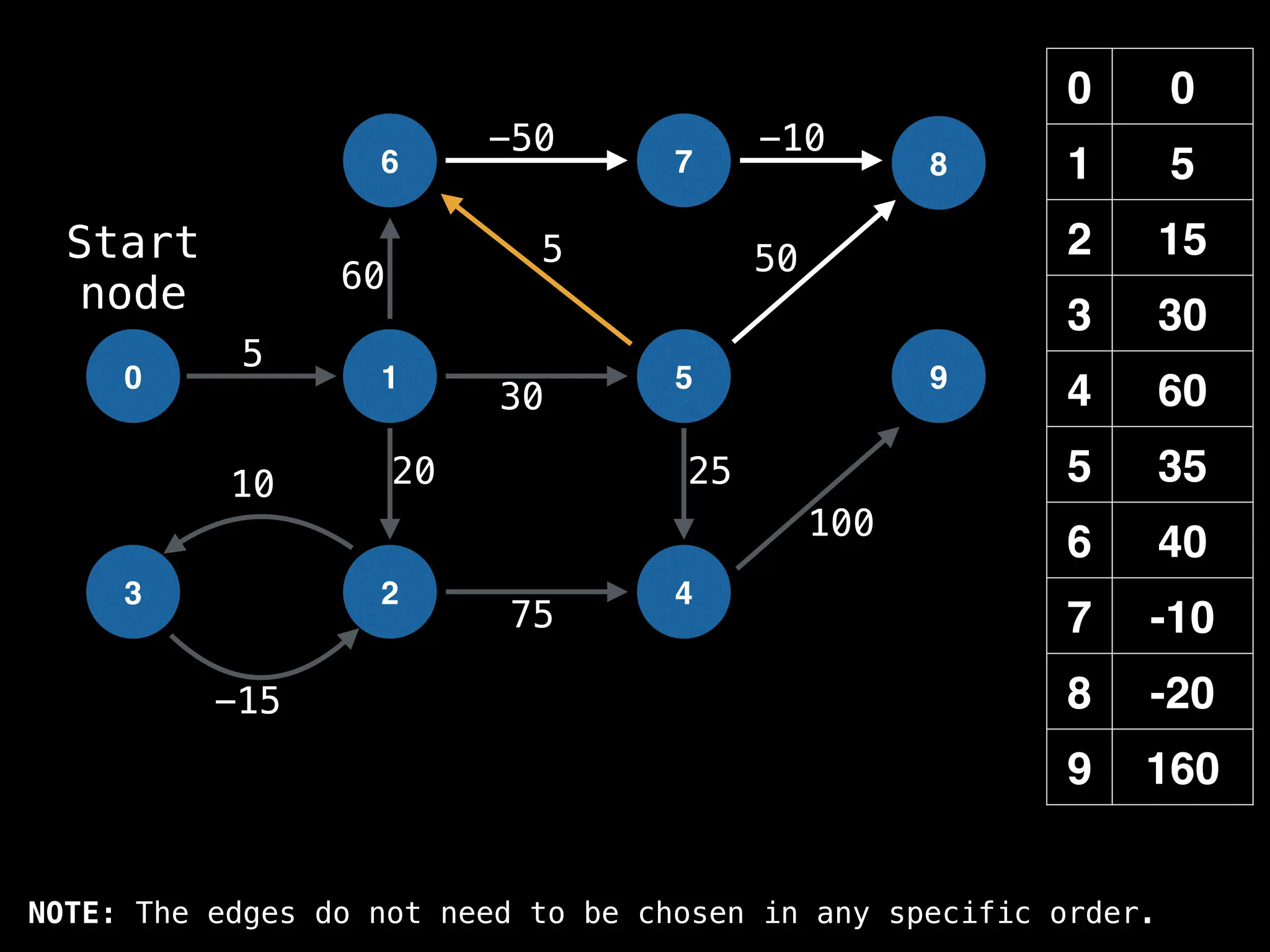
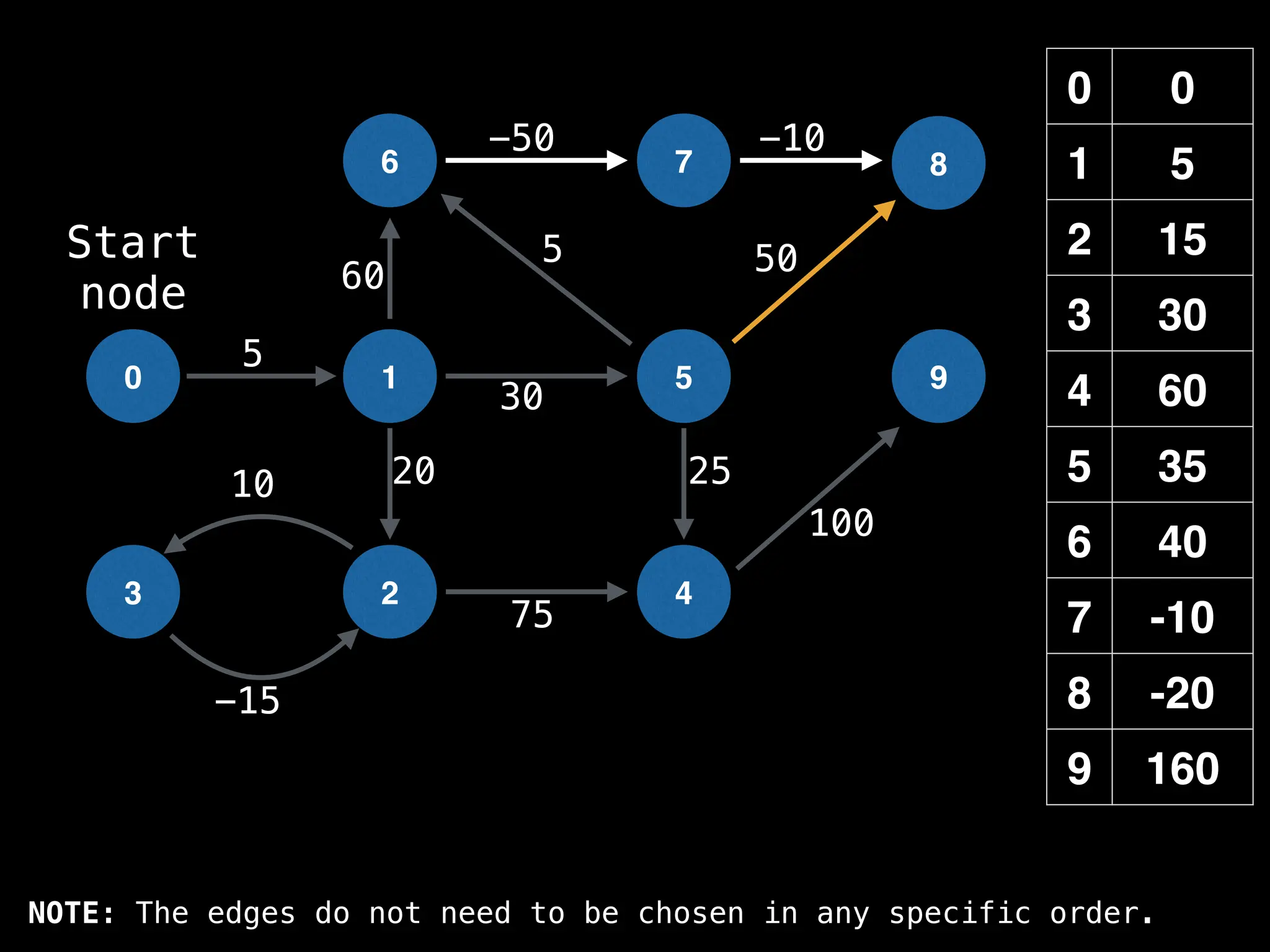
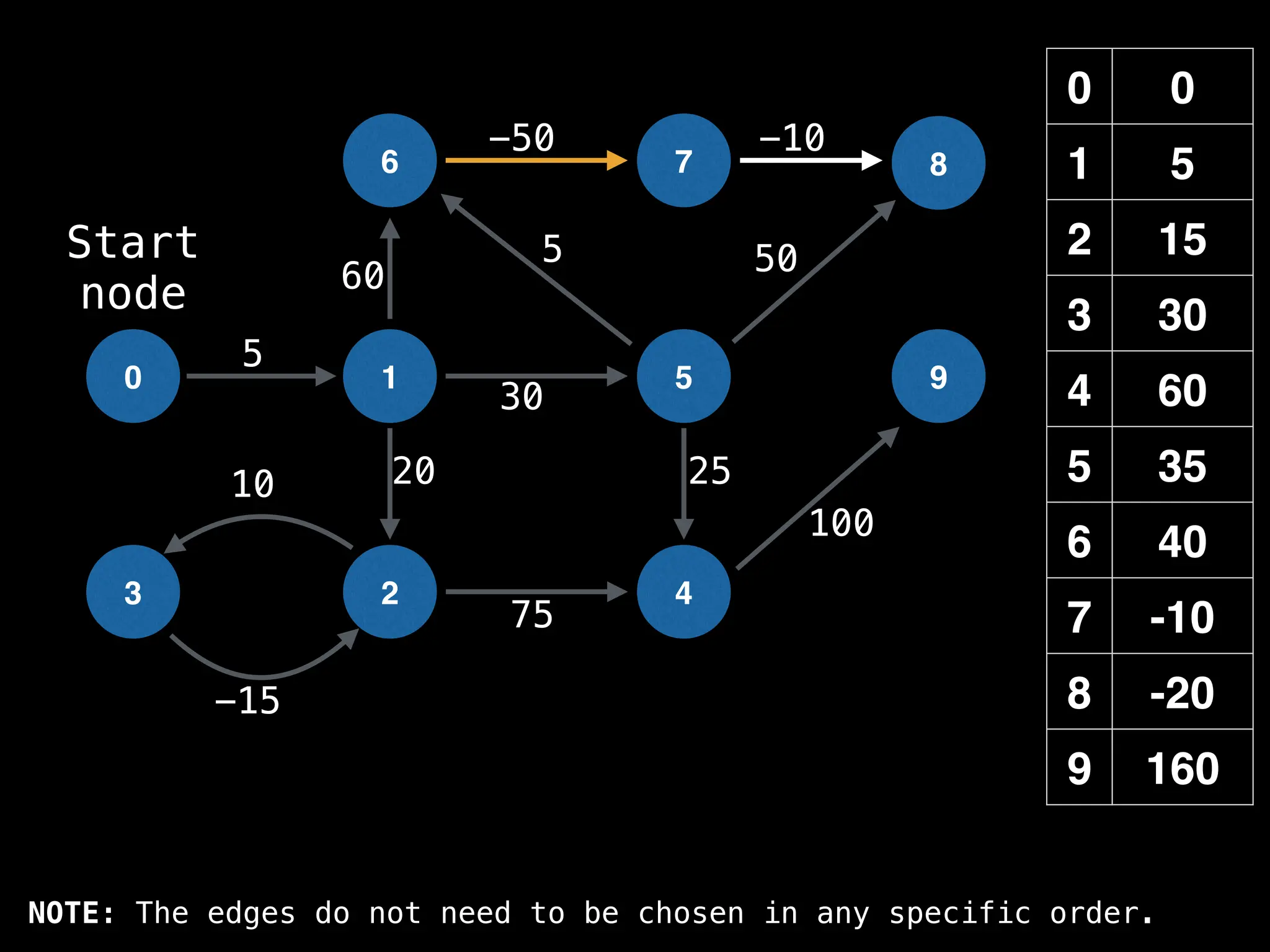
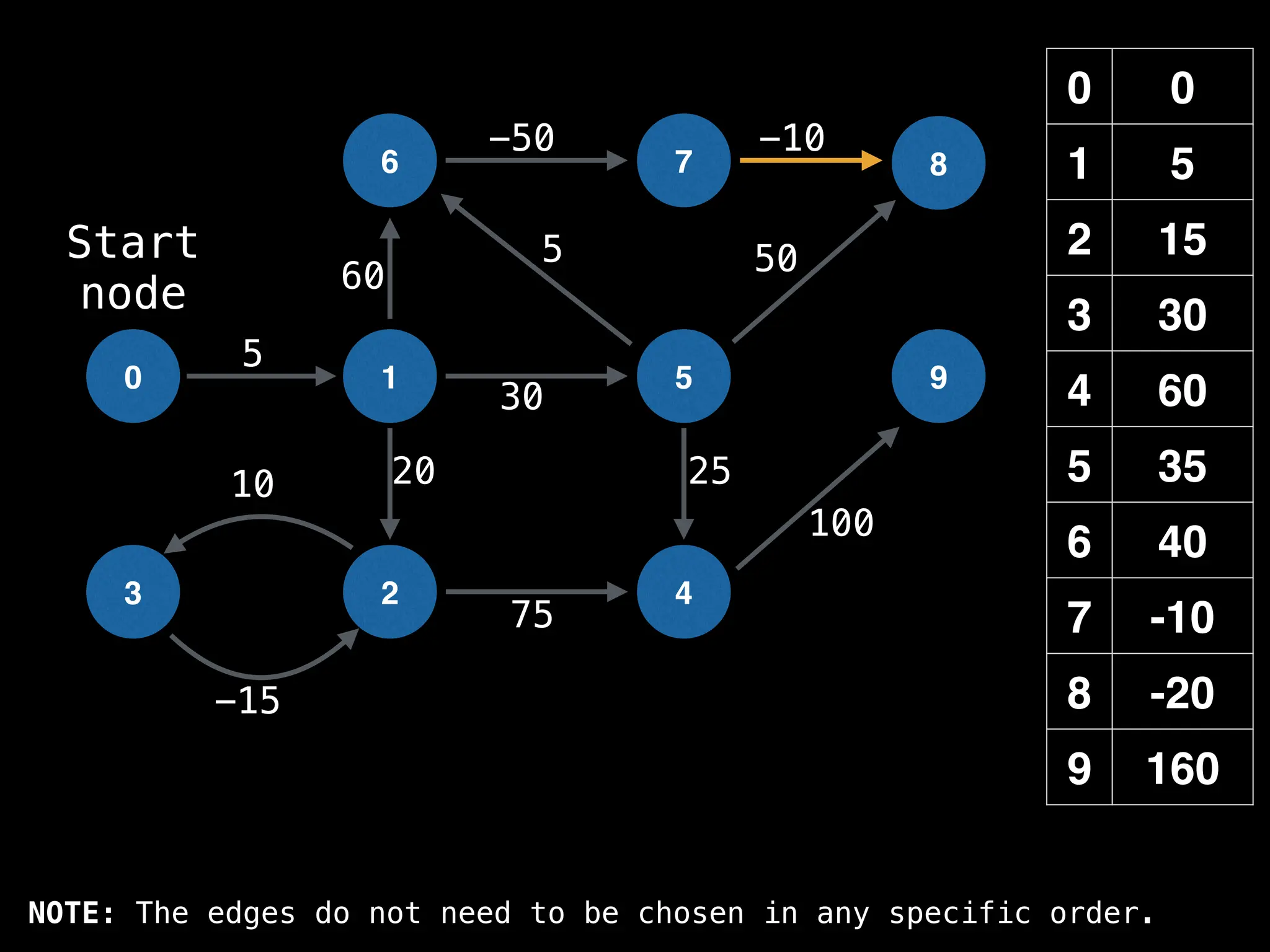
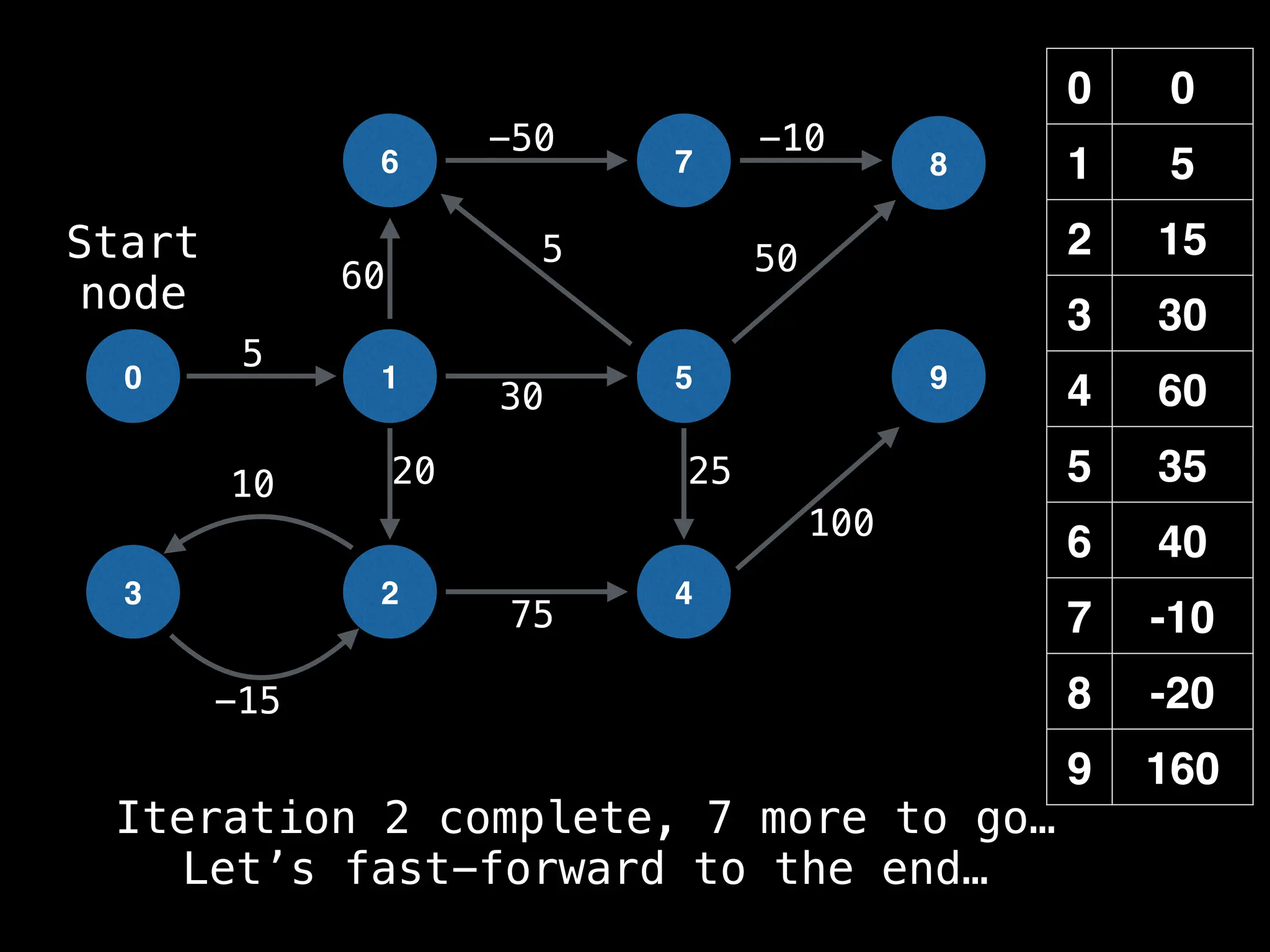
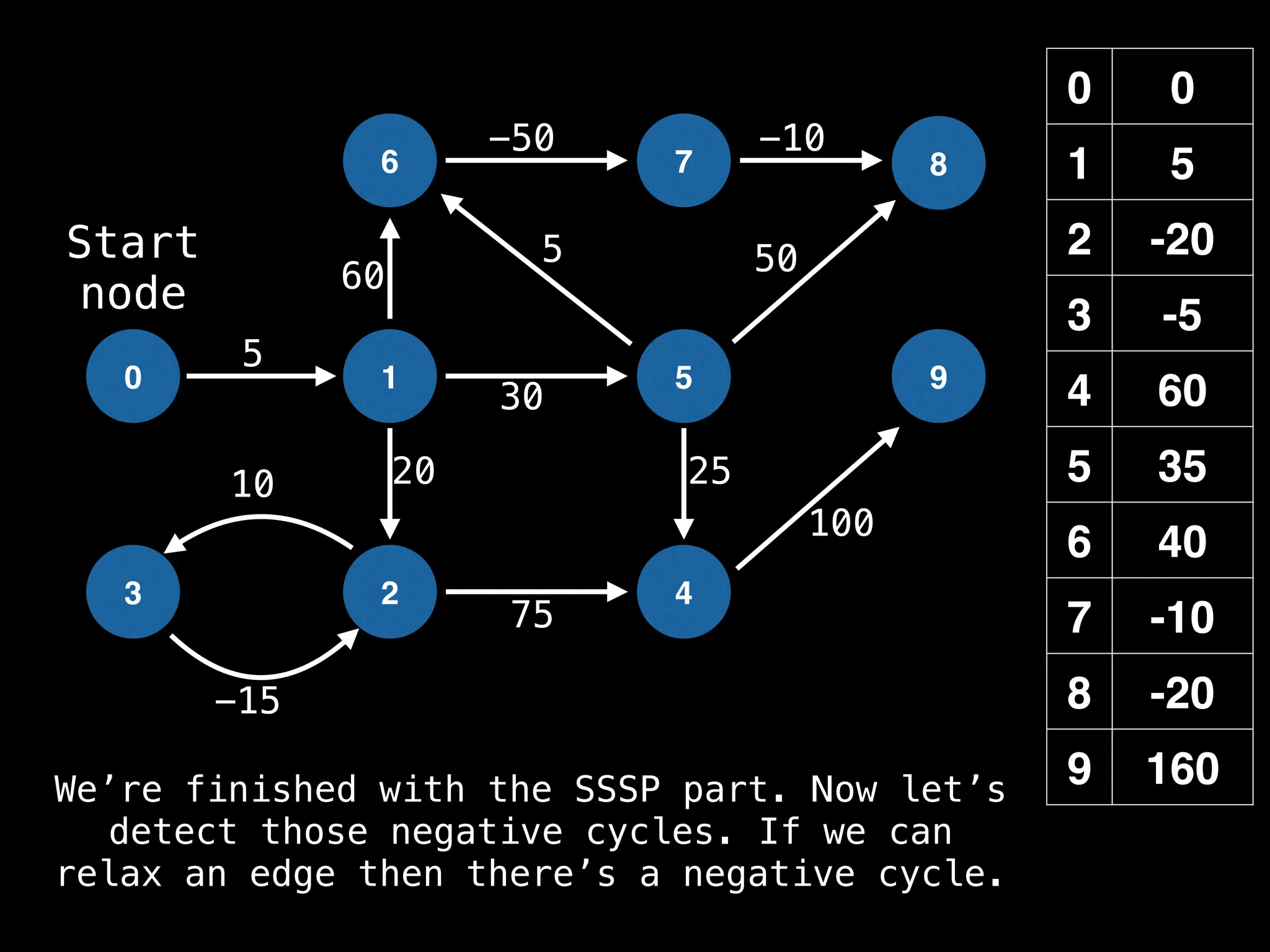
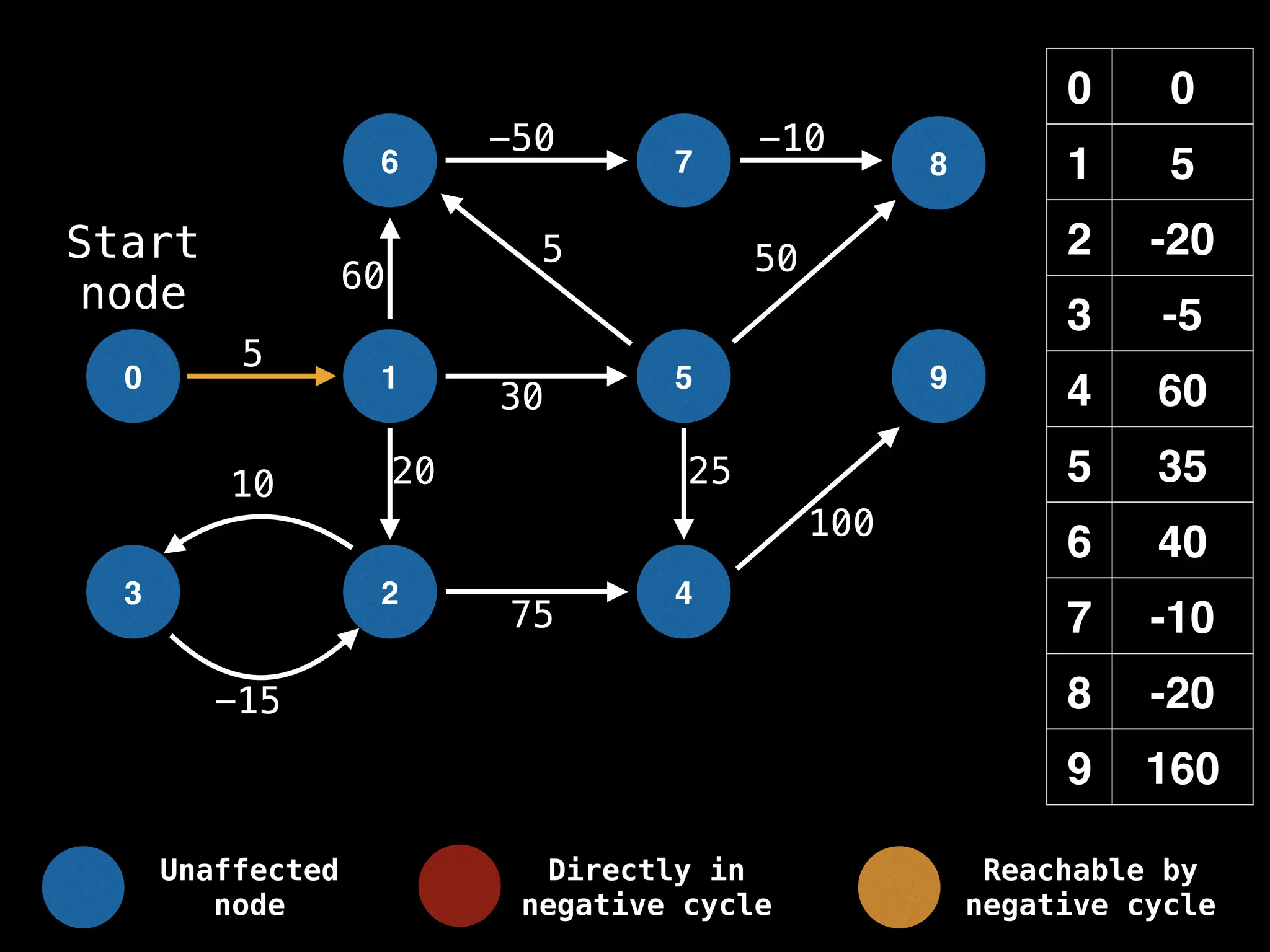
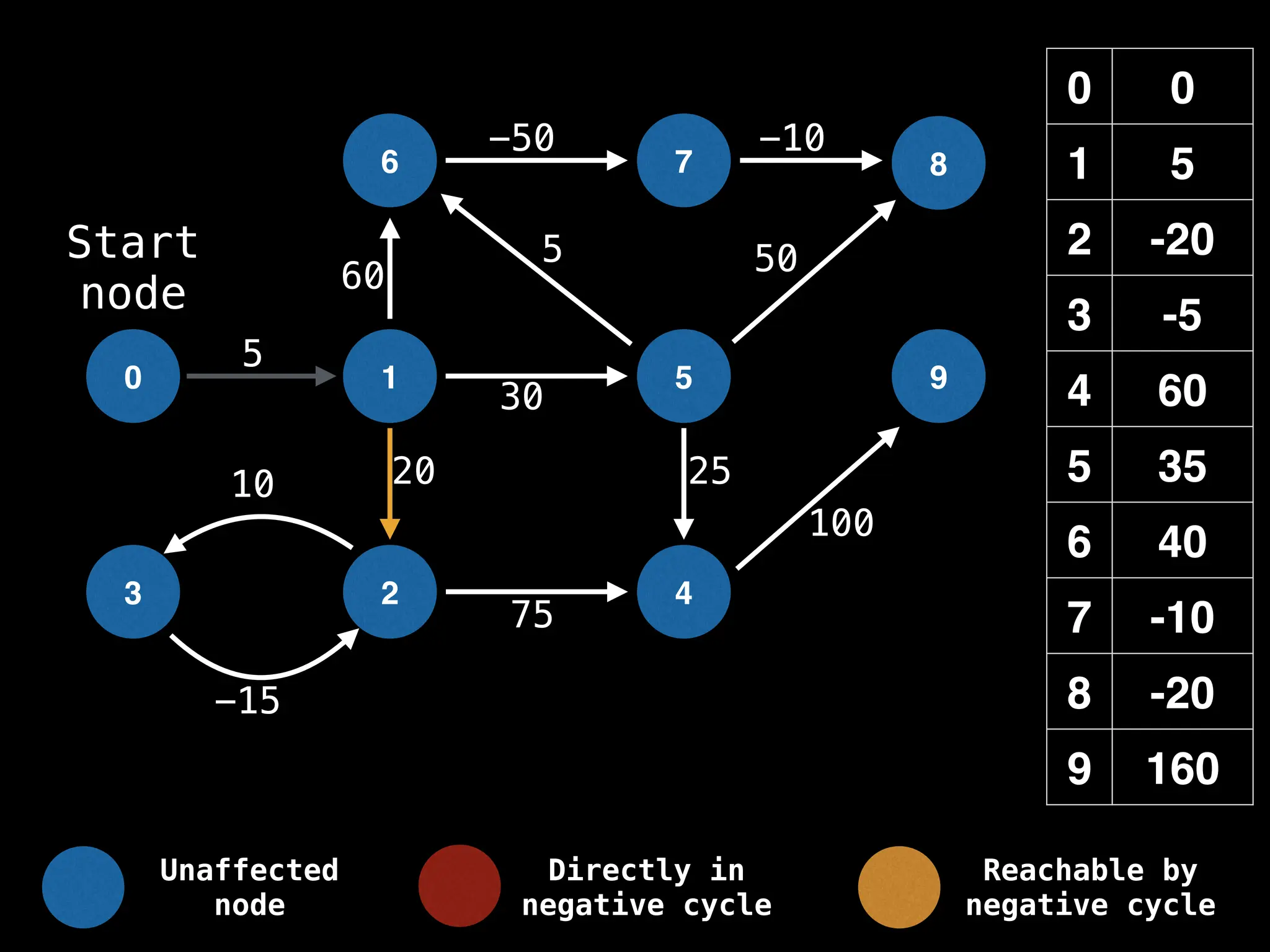
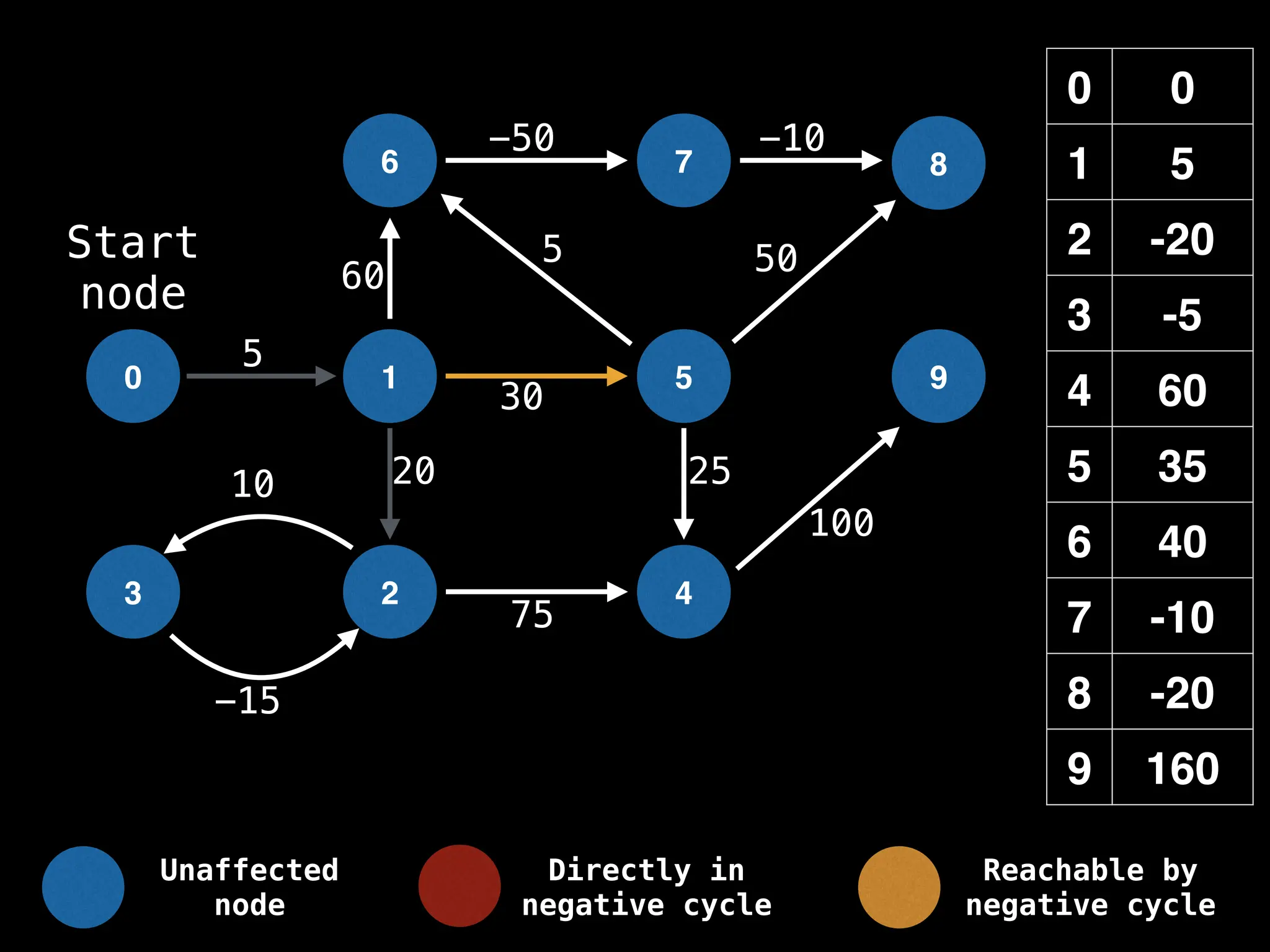
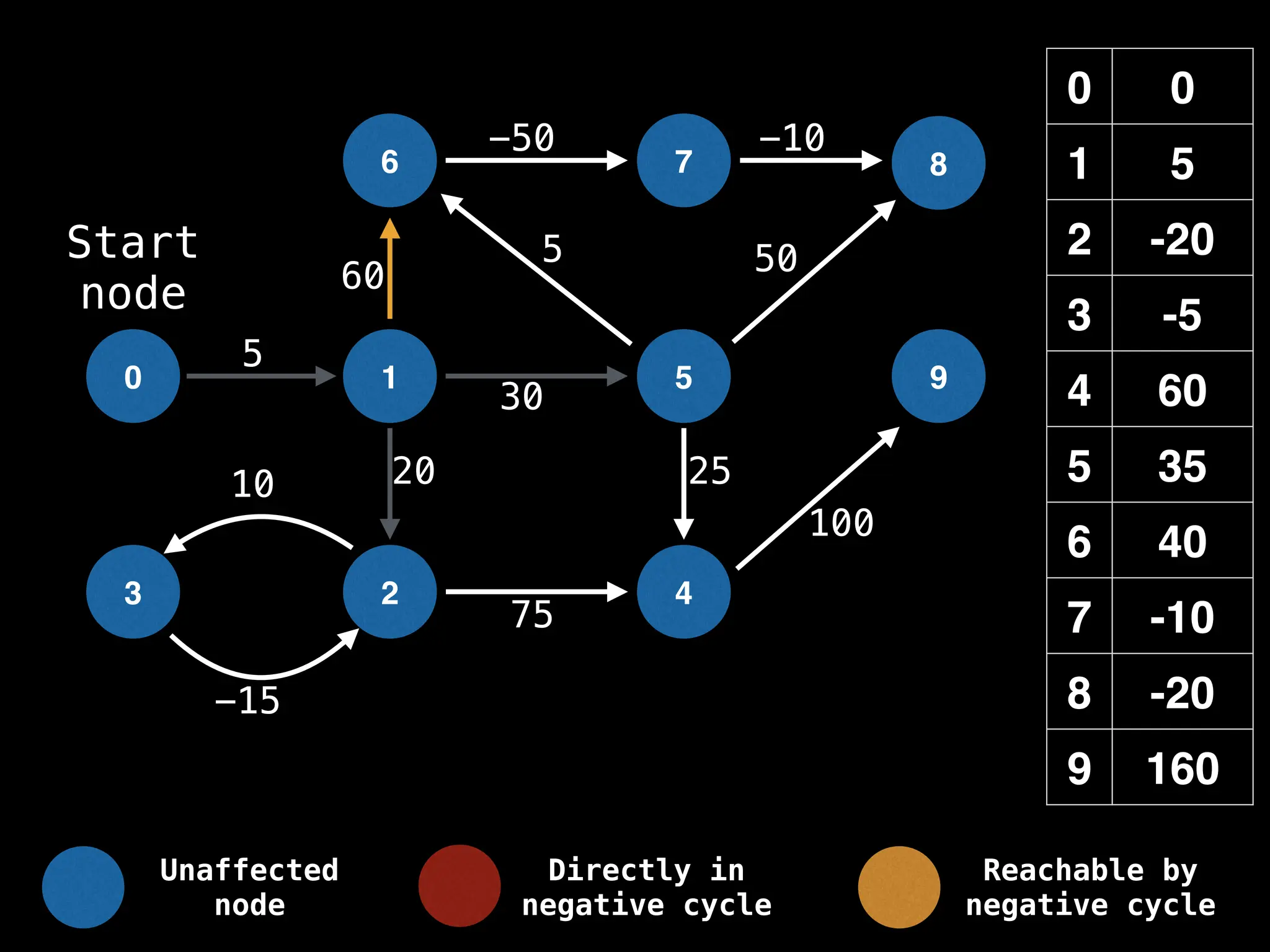
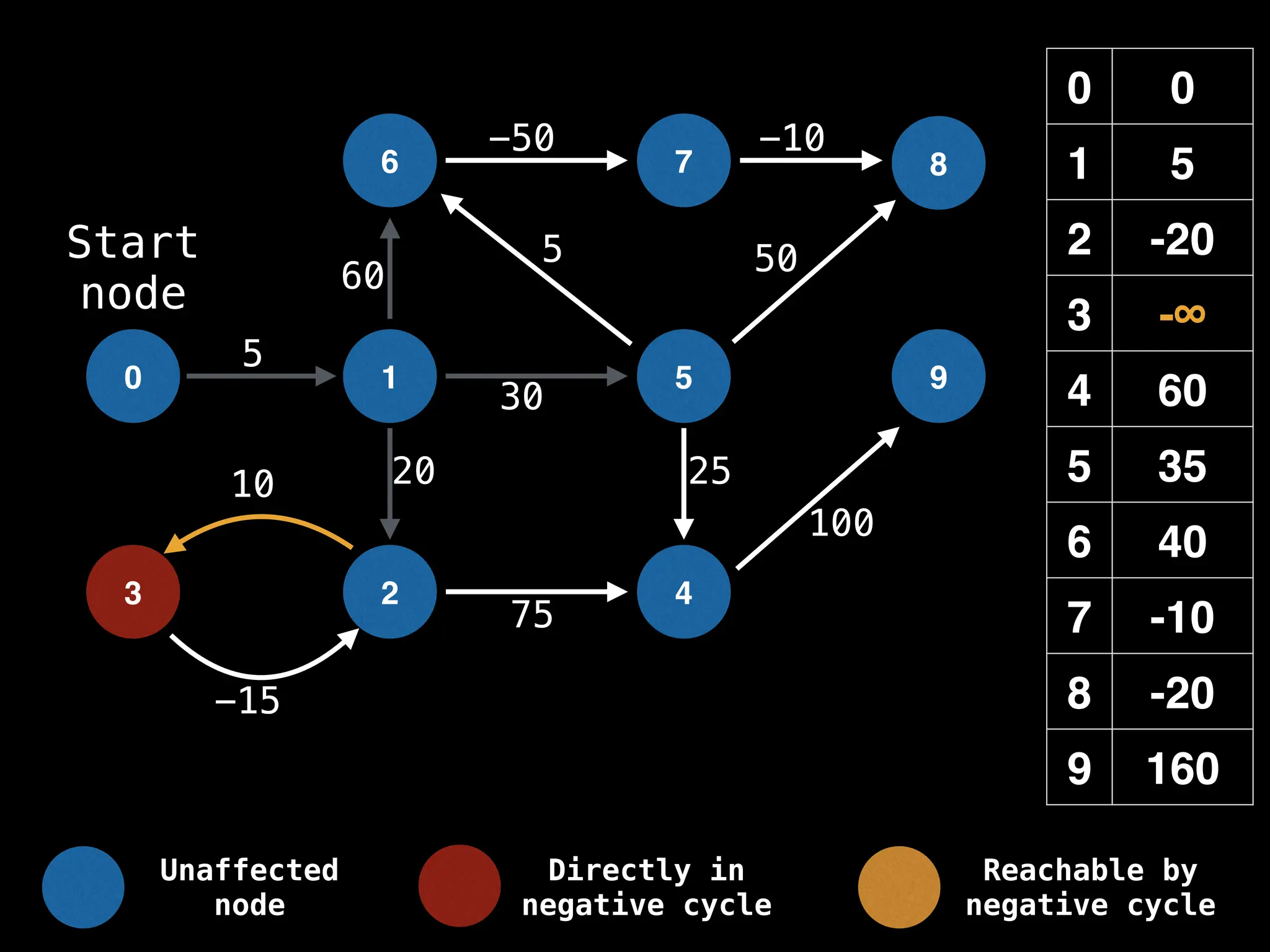
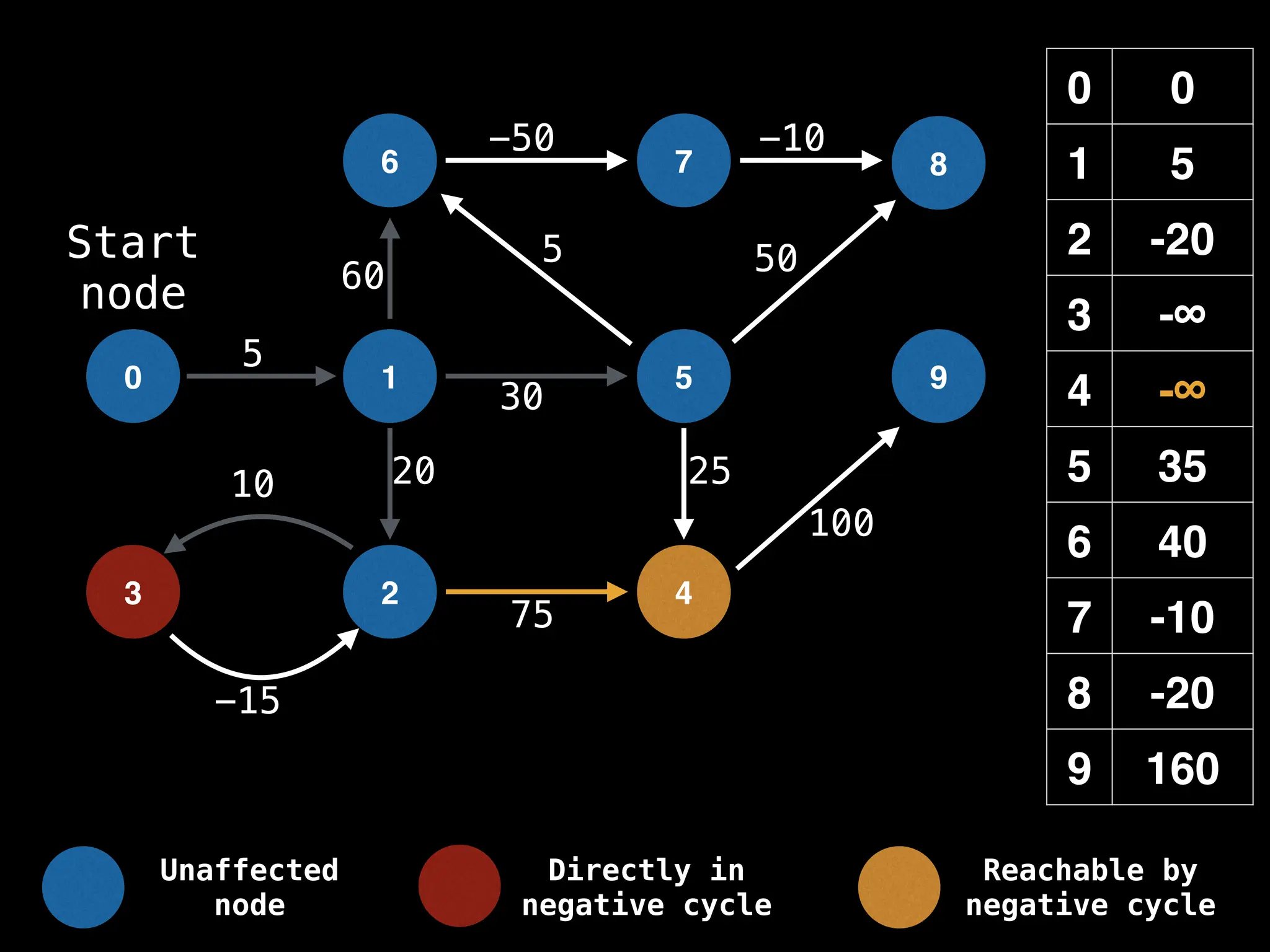
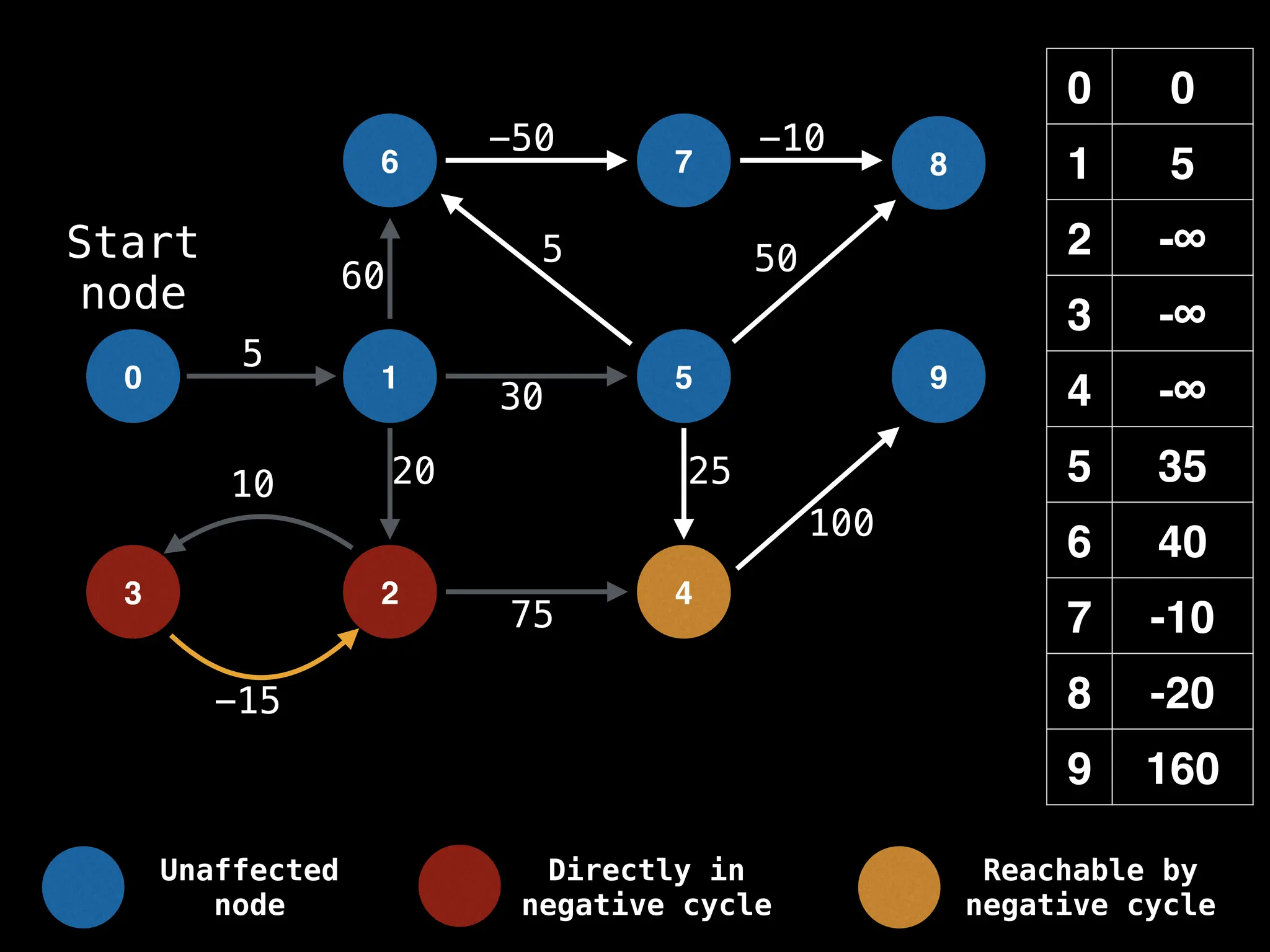
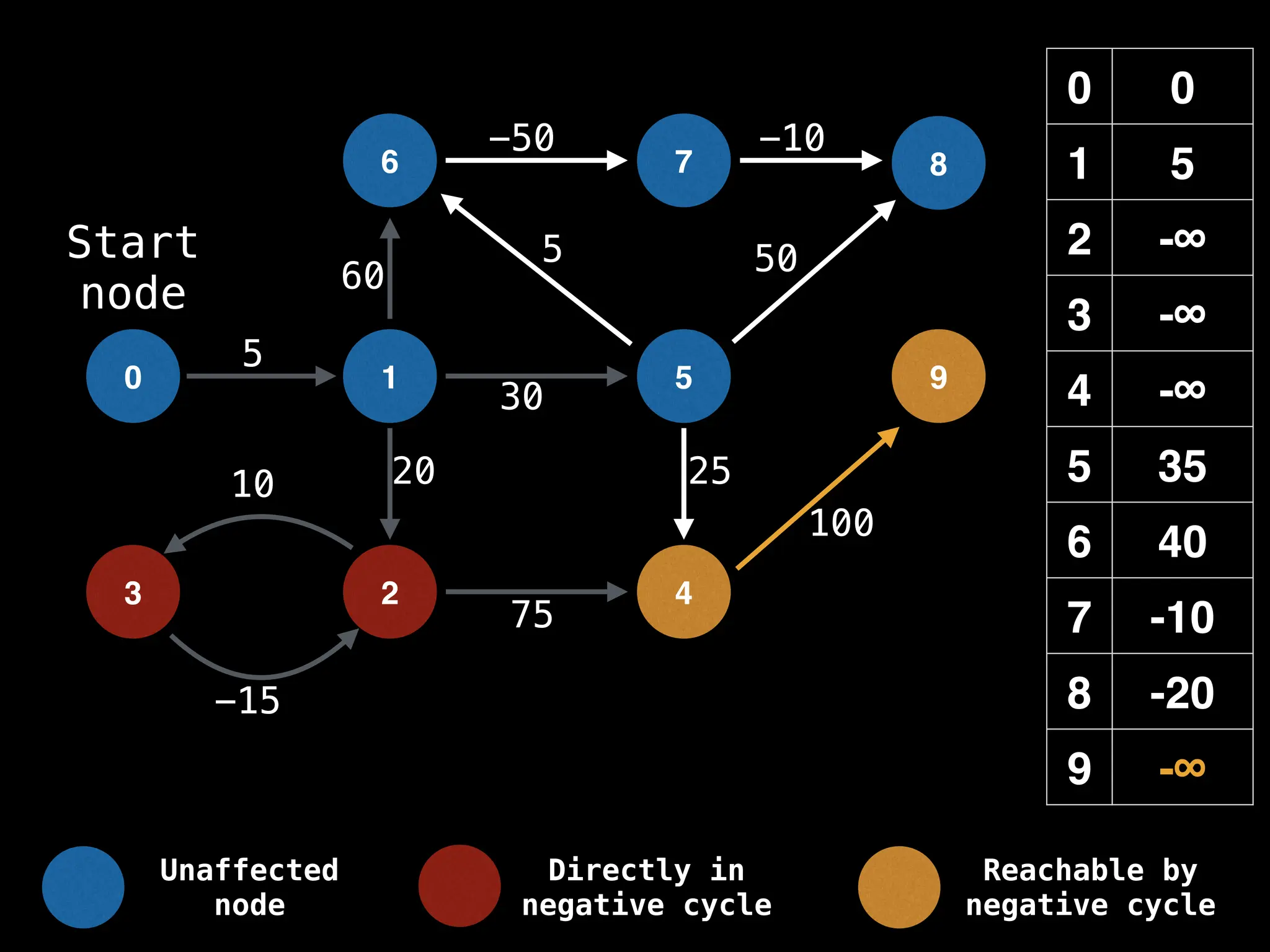
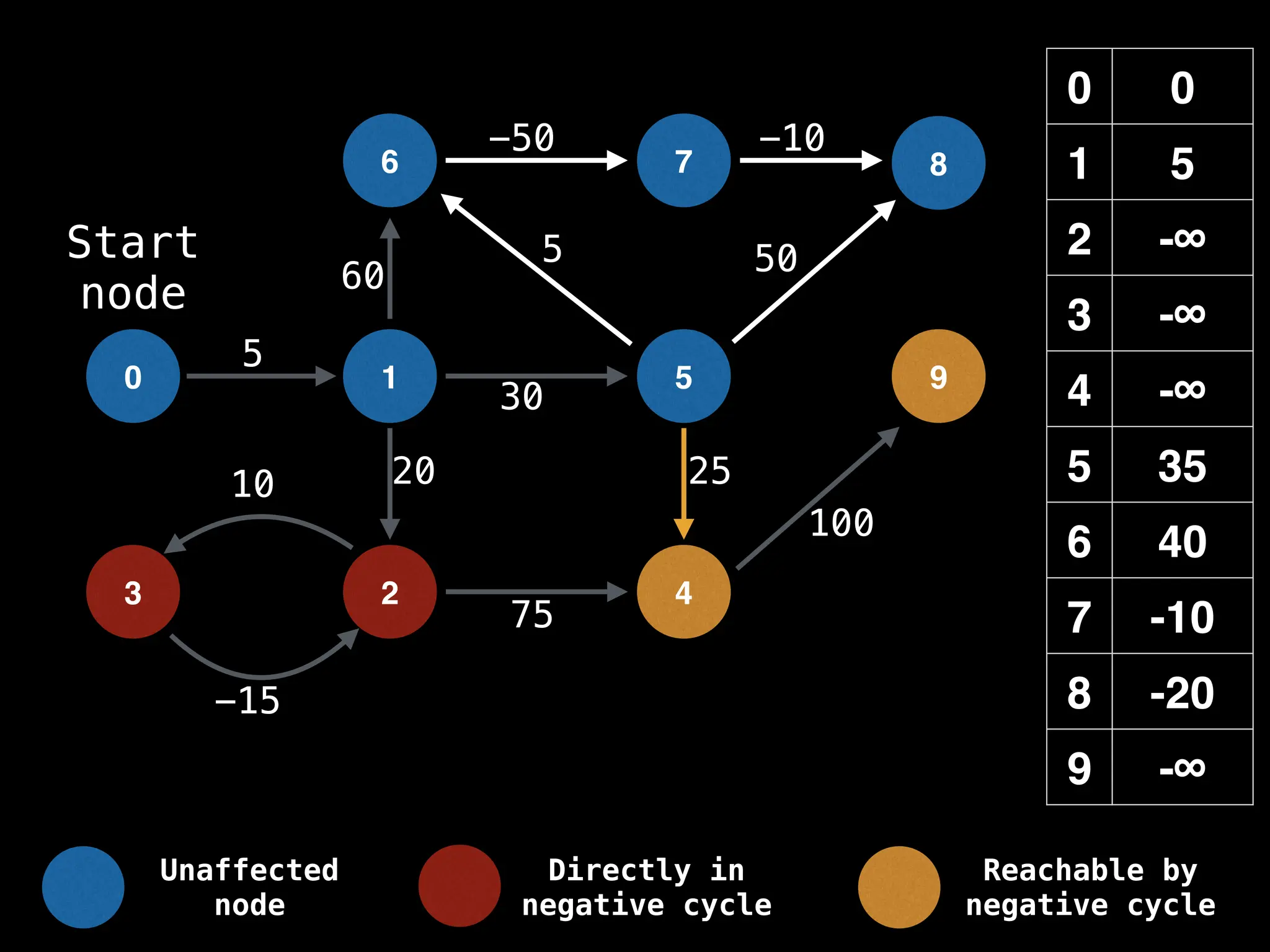
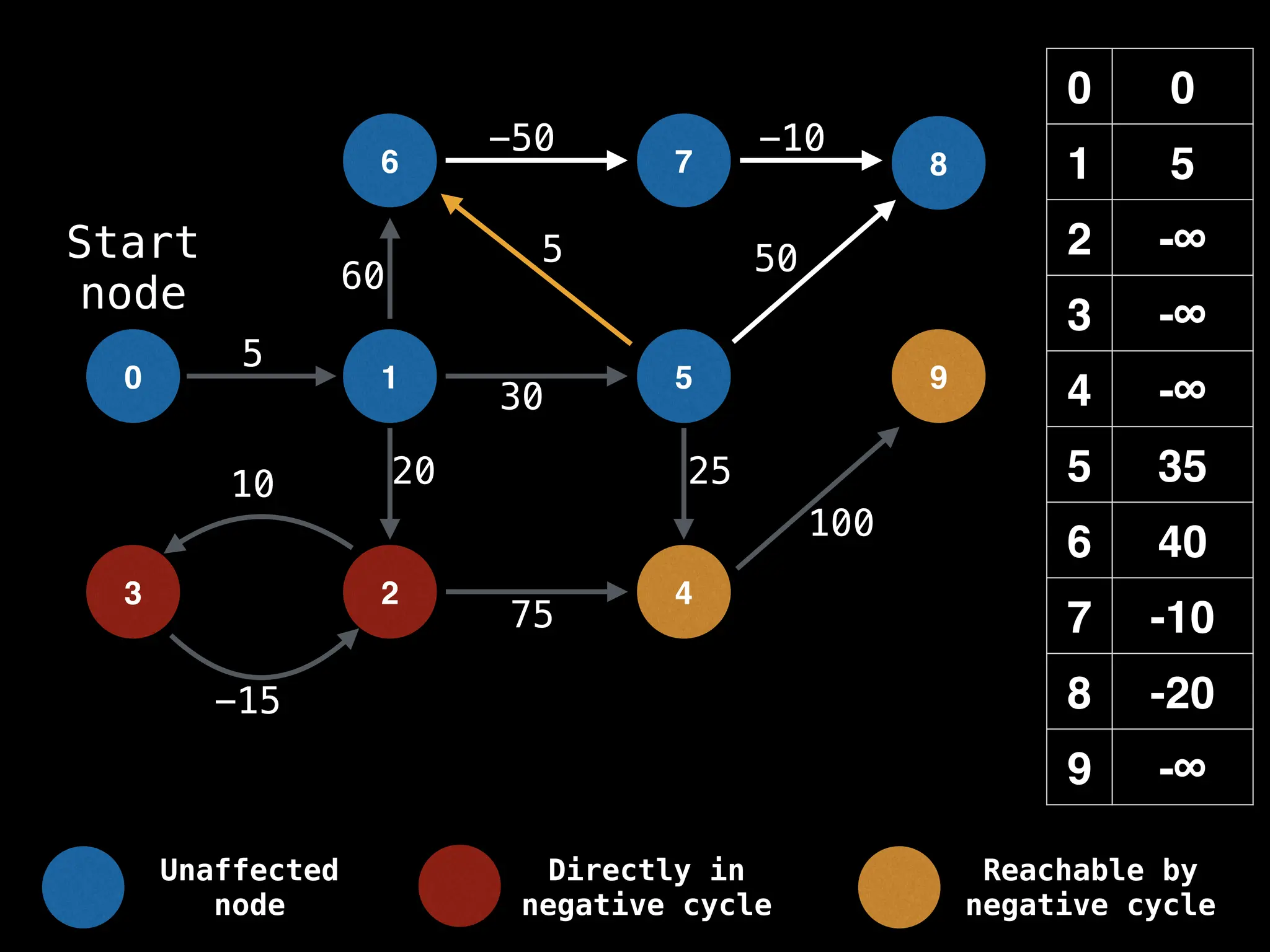
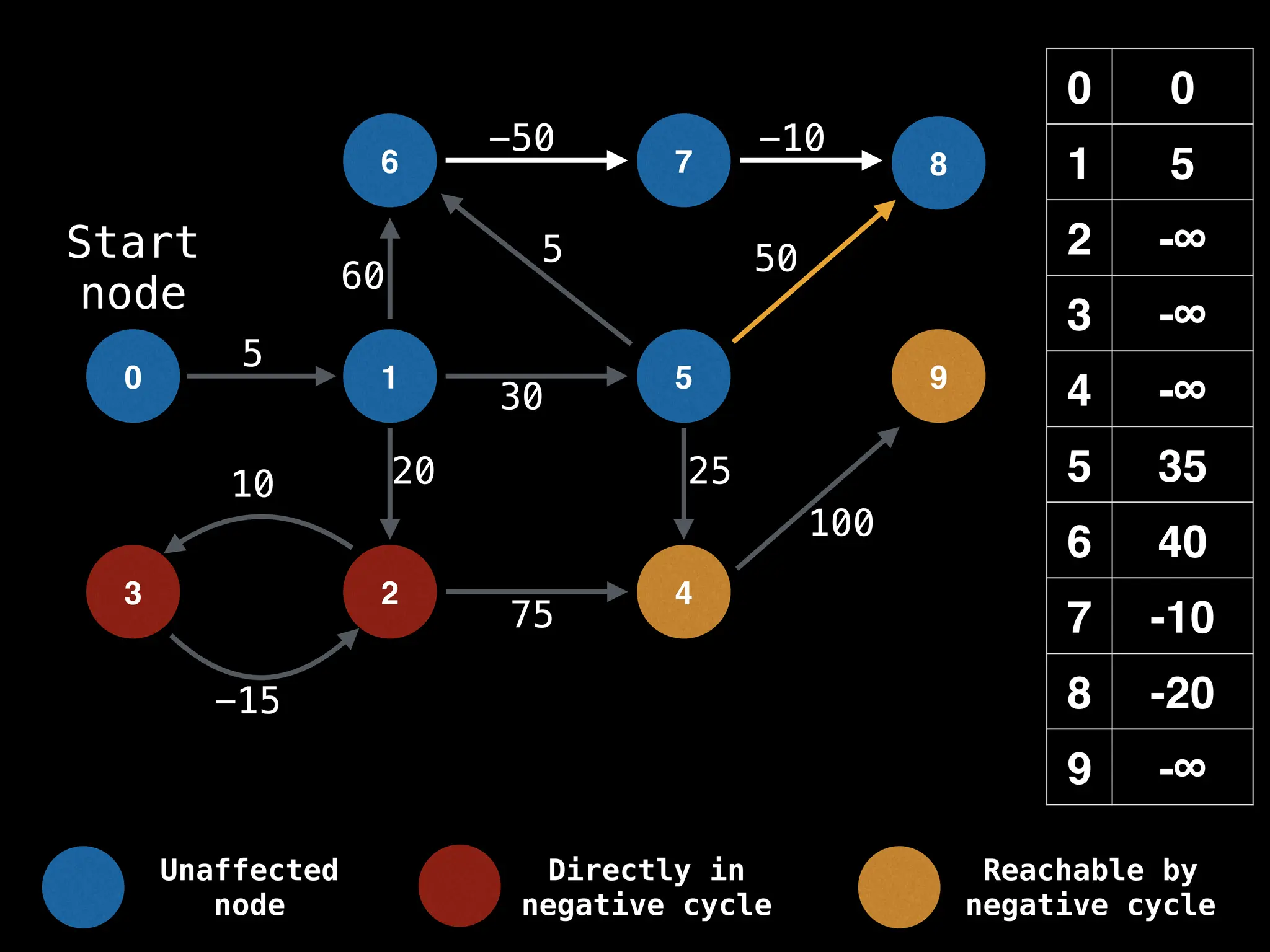
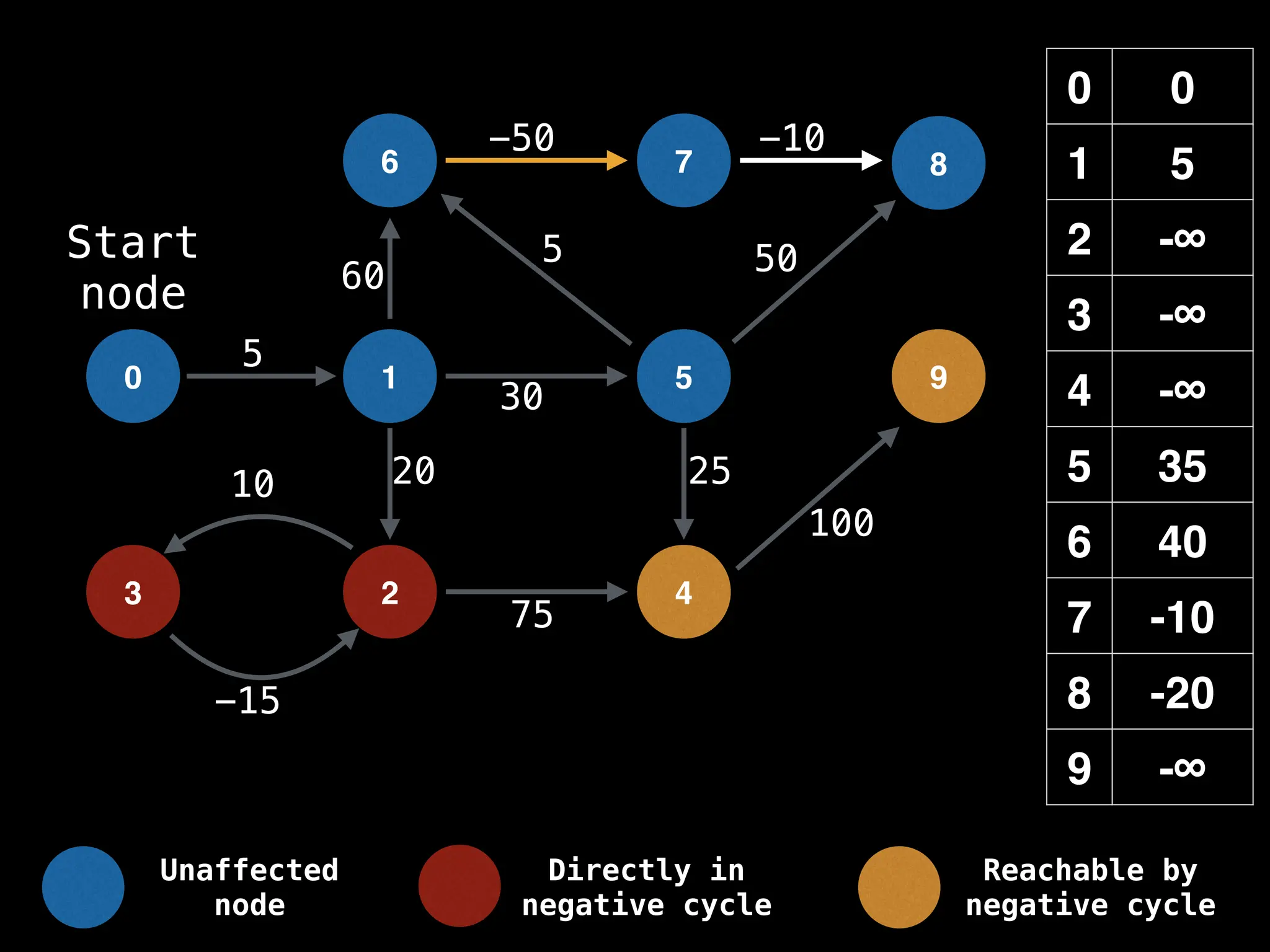
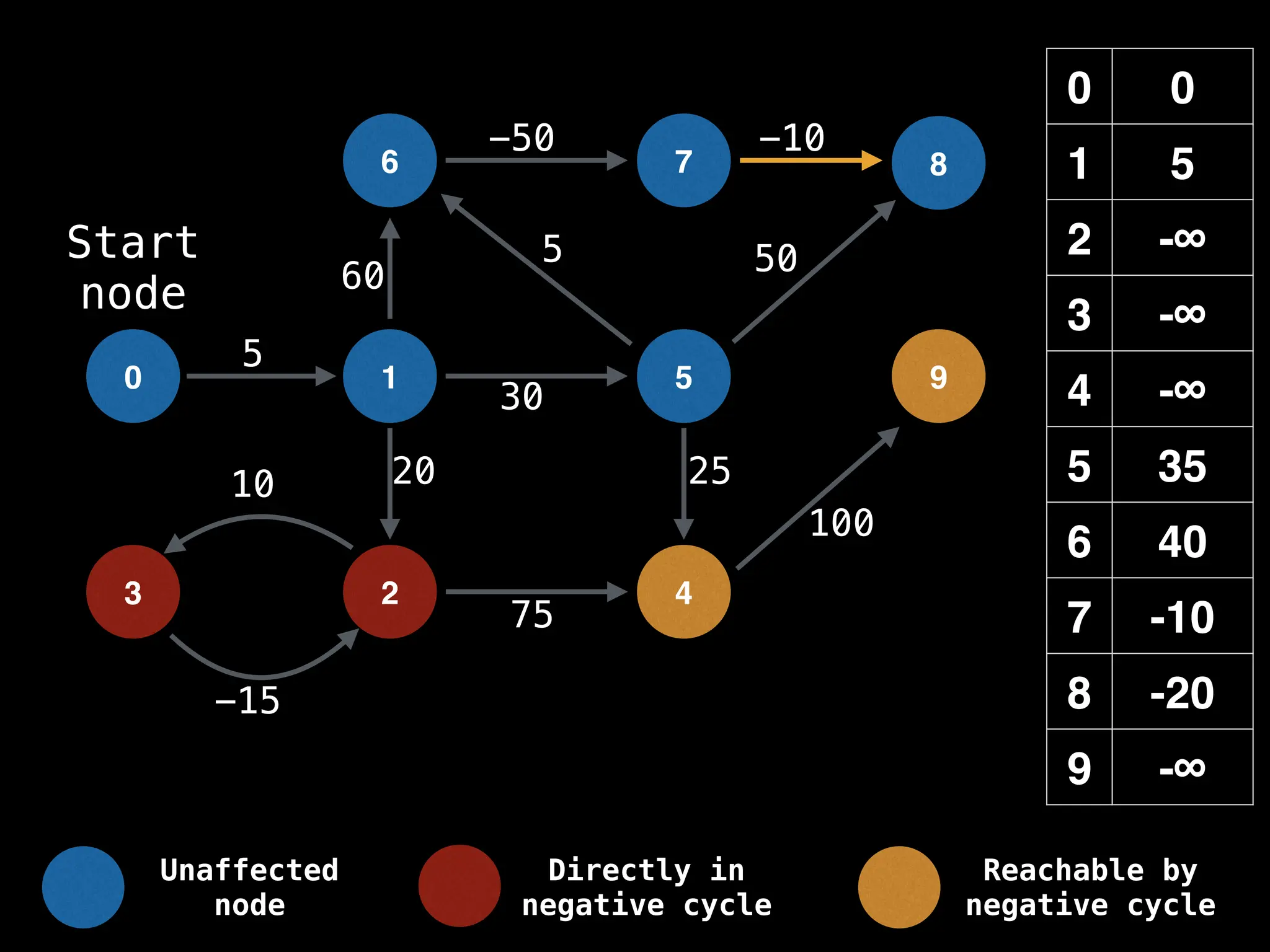
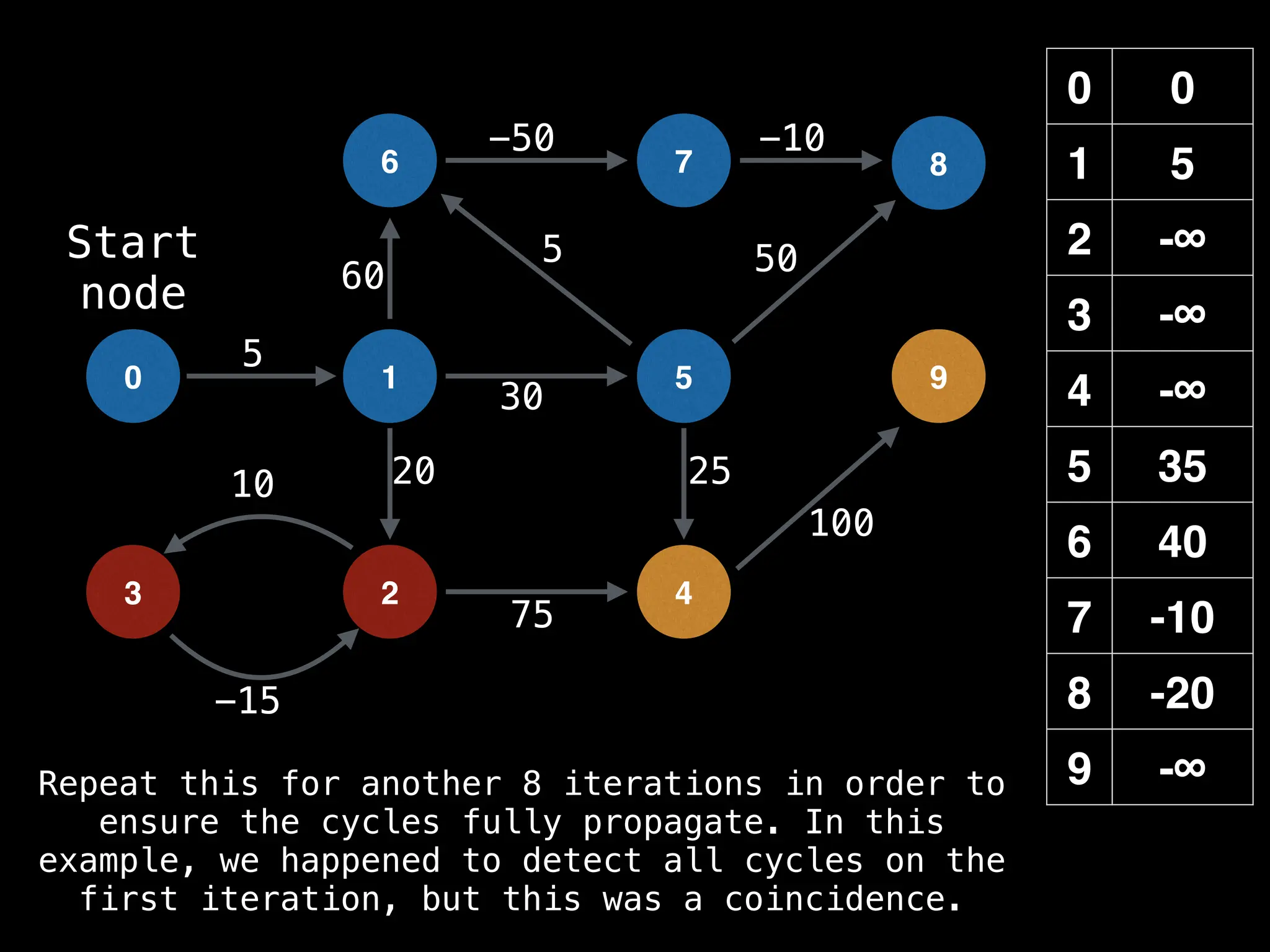

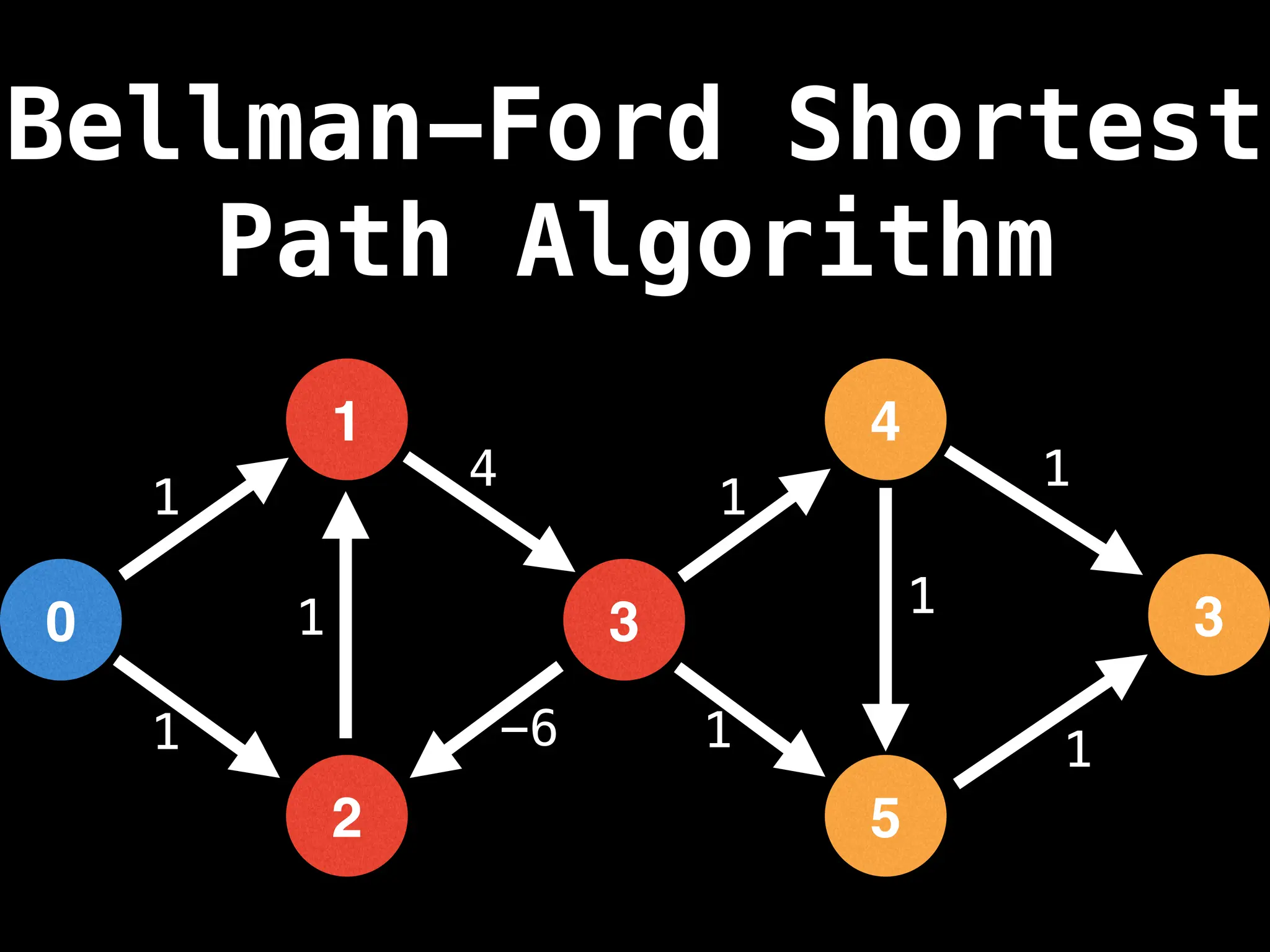


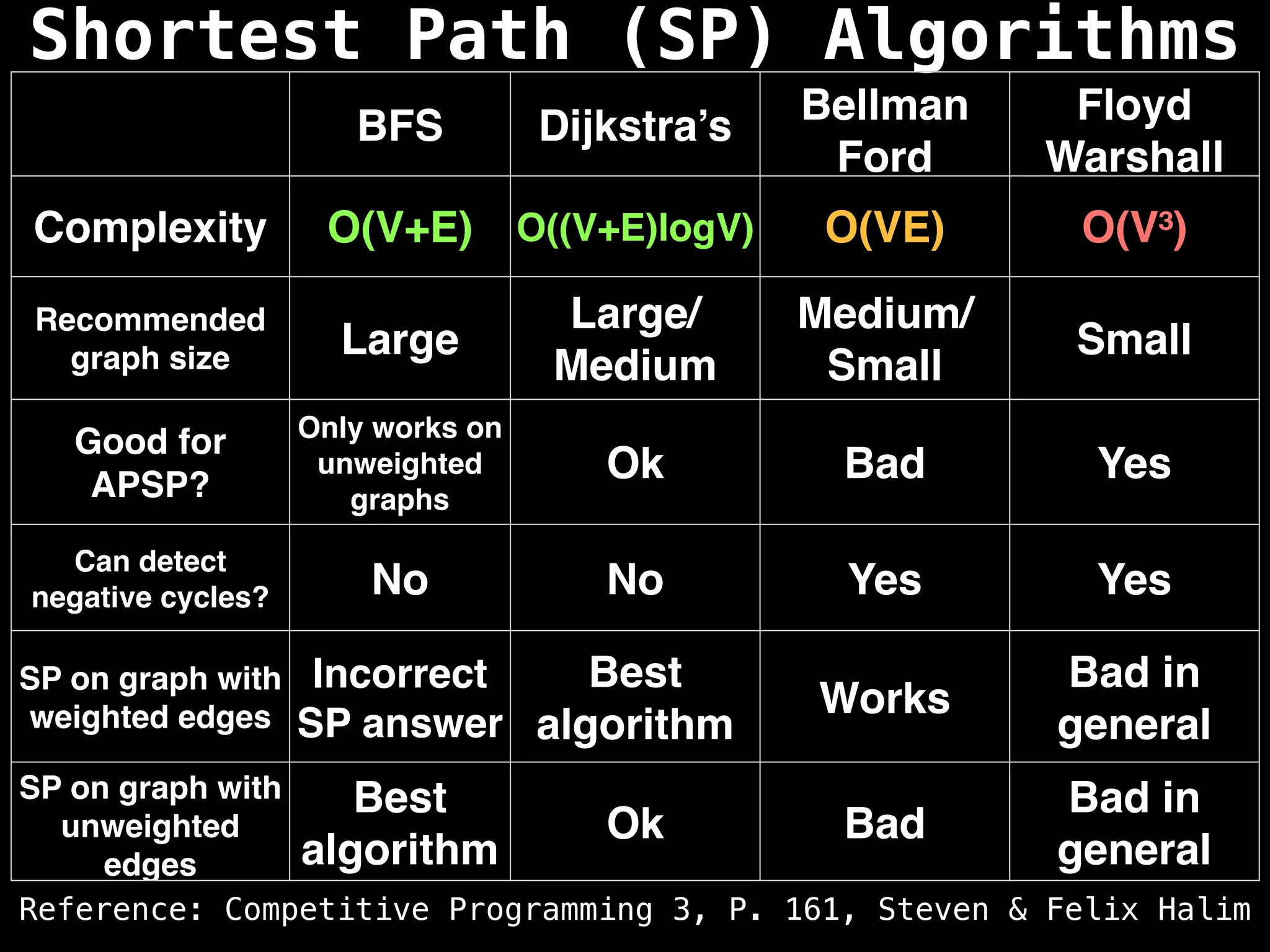
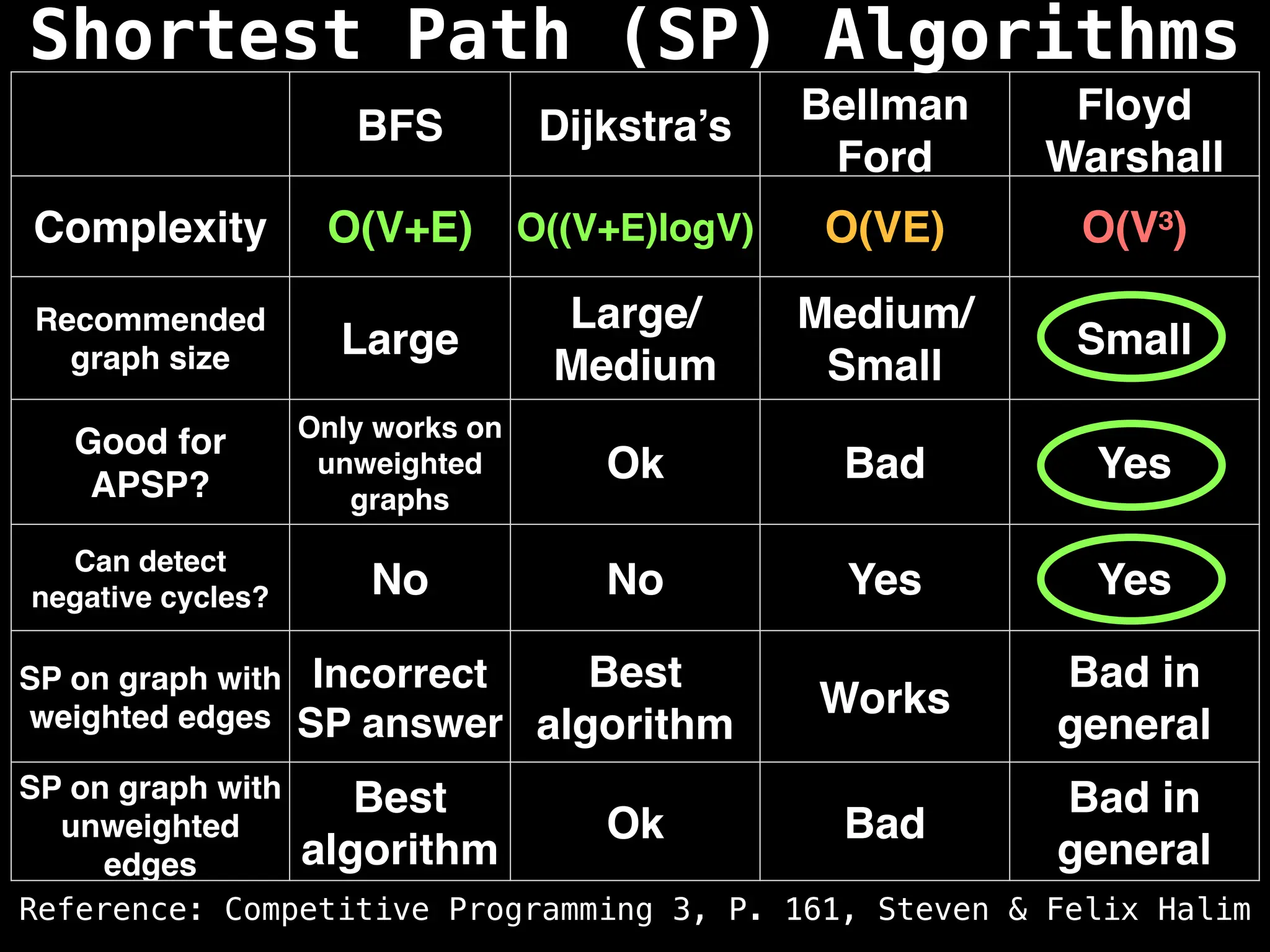
![Graph setup
With FW, the optimal way to represent our graph
is with a 2D adjacency matrix m where cell
m[i][j] represents the edge weight of going
from node i to node j.
0 4 1 9
3 0 6 11
4 1 0 2
6 5 -4 0
A B C D
A
B
C
D
A
C
B
D
4
9
1
3
6 11
4 1
2
6
5
-4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-732-2048.jpg)
![Graph setup
0 4 1 9
3 0 6 11
4 1 0 2
6 5 -4 0
A B C D
A
B
C
D
A
C
B
D
4
9
1
3
6 11
4 1
2
6
5
-4
NOTE: In the graph above, it is assumed that
the distance from a node to itself is zero.
This is why the diagonal is all zeros.
With FW, the optimal way to represent our graph
is with a 2D adjacency matrix m where cell
m[i][j] represents the edge weight of going
from node i to node j.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-733-2048.jpg)
![Graph setup
If there is no edge from node i to node j
then set the edge value for m[i][j] to be
positive infinity.
0 4 1 ∞
∞ 0 6 ∞
4 1 0 2
∞ ∞ ∞ 0
A B C D
A
B
C
D
A
C
B
D
4
1 6
4 1
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-734-2048.jpg)
![Graph setup
0 4 1 ∞
∞ 0 6 ∞
4 1 0 2
∞ ∞ ∞ 0
A B C D
A
B
C
D
A
C
B
D
4
1 6
4 1
2
IMPORTANT: If your programming language does not
support a special constant for +∞ such that ∞ + ∞ = ∞
and x + ∞ = ∞ then avoid using 231-1 as infinity!
This will cause integer overflow; prefer to use a
large constant such as 107 instead.
If there is no edge from node i to node j
then set the edge value for m[i][j] to be
positive infinity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-735-2048.jpg)
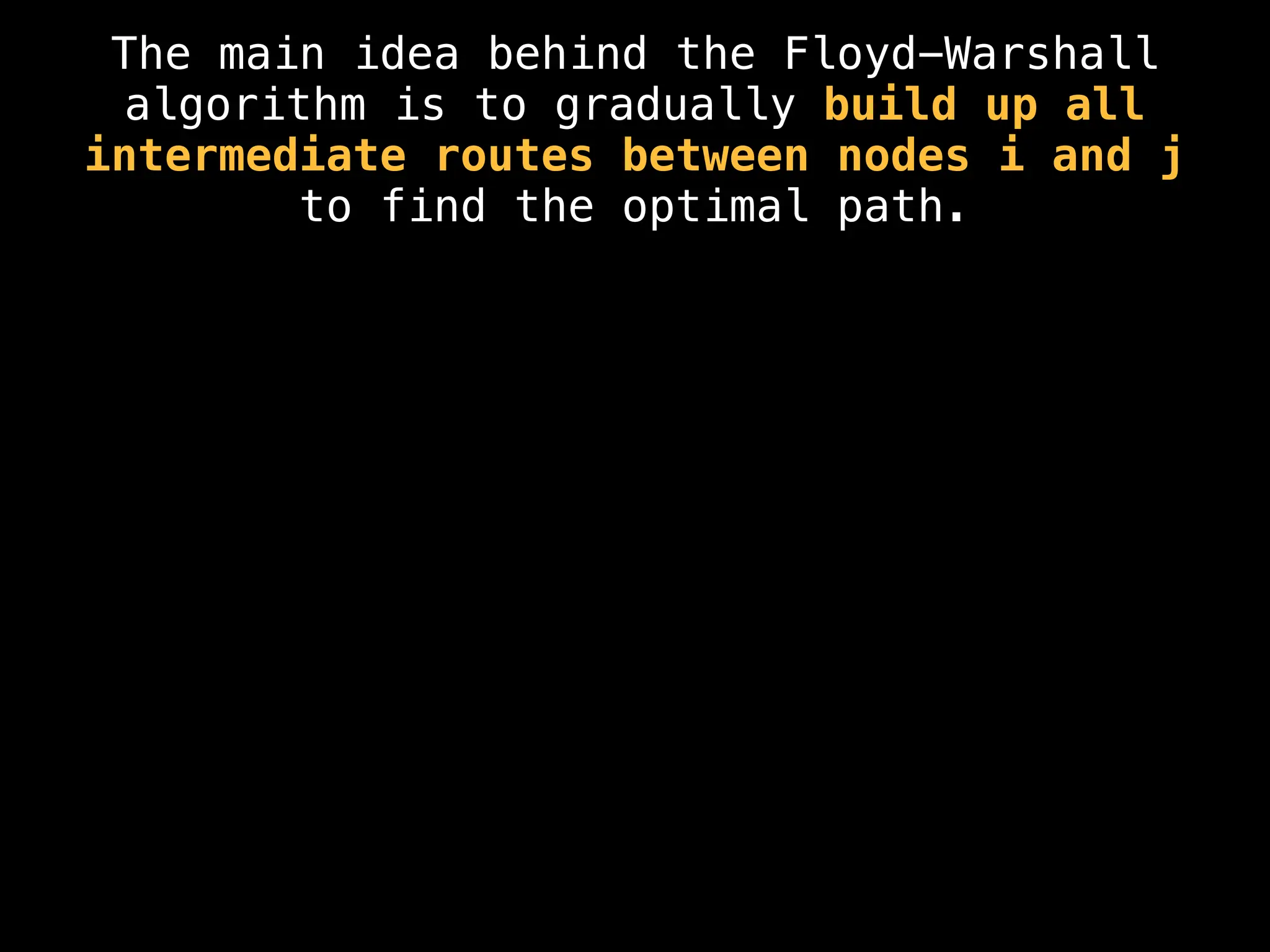
![Suppose our adjacency matrix tells us that
the distance from a to b is: m[a][b] = 11
The main idea behind the Floyd-Warshall
algorithm is to gradually build up all
intermediate routes between nodes i and j
to find the optimal path.
a b
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-737-2048.jpg)
![The main idea behind the Floyd-Warshall
algorithm is to gradually build up all
intermediate routes between nodes i and j
to find the optimal path.
a b
11
c
5 5
Suppose there exists a third node, c. If
m[a][c] + m[c][b] < m[a][b] then it’s better
to route through c!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-738-2048.jpg)
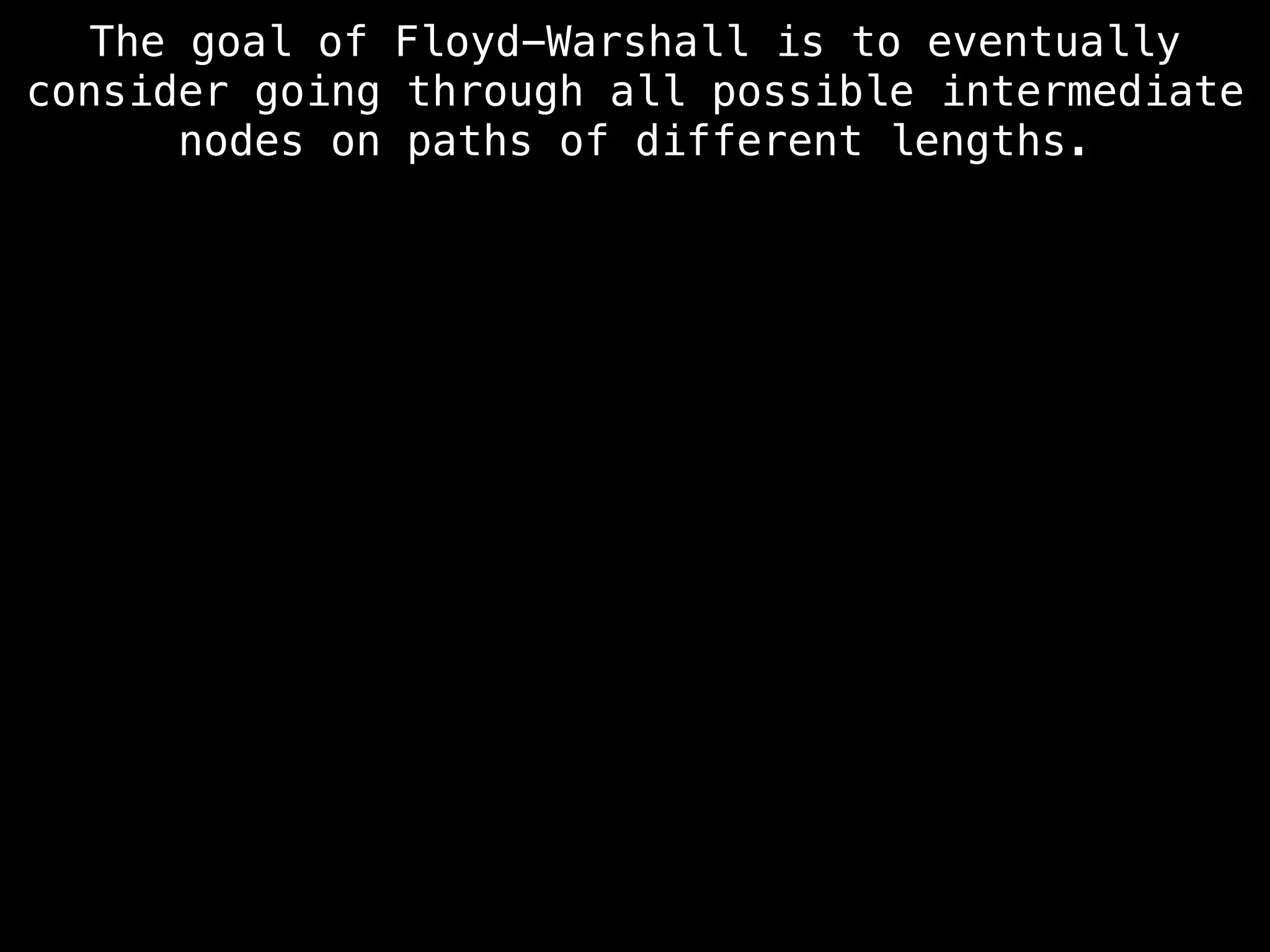
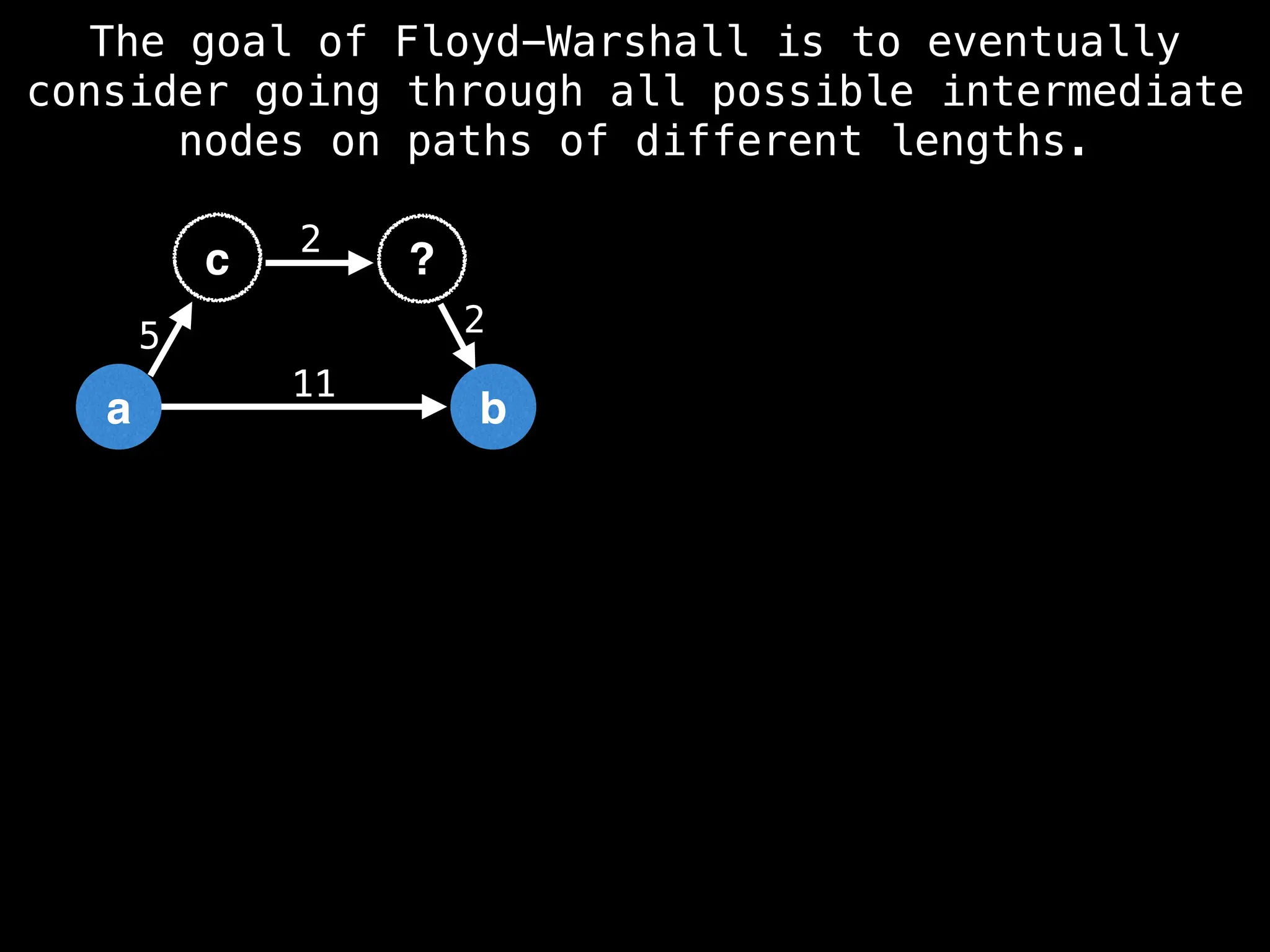
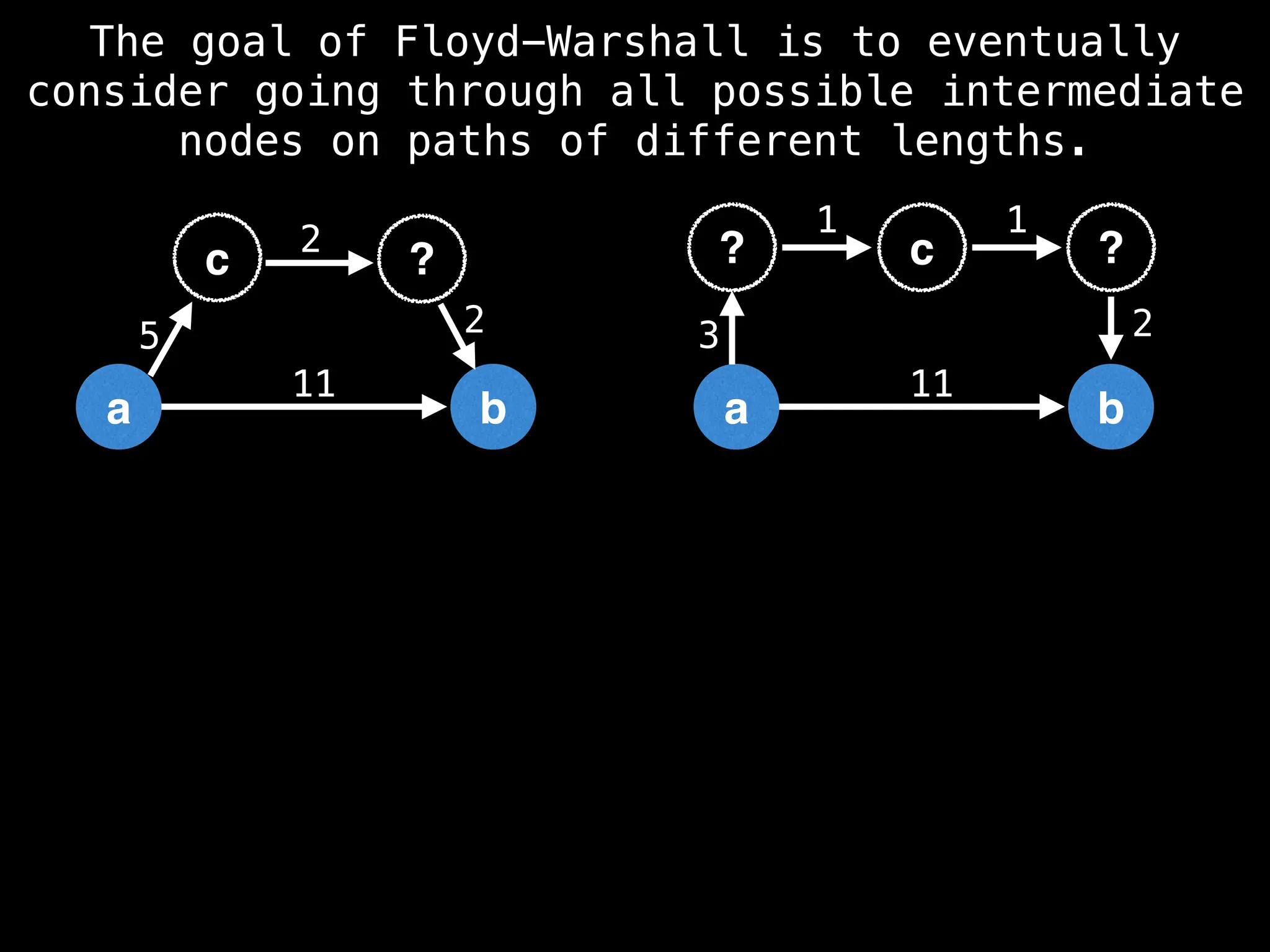
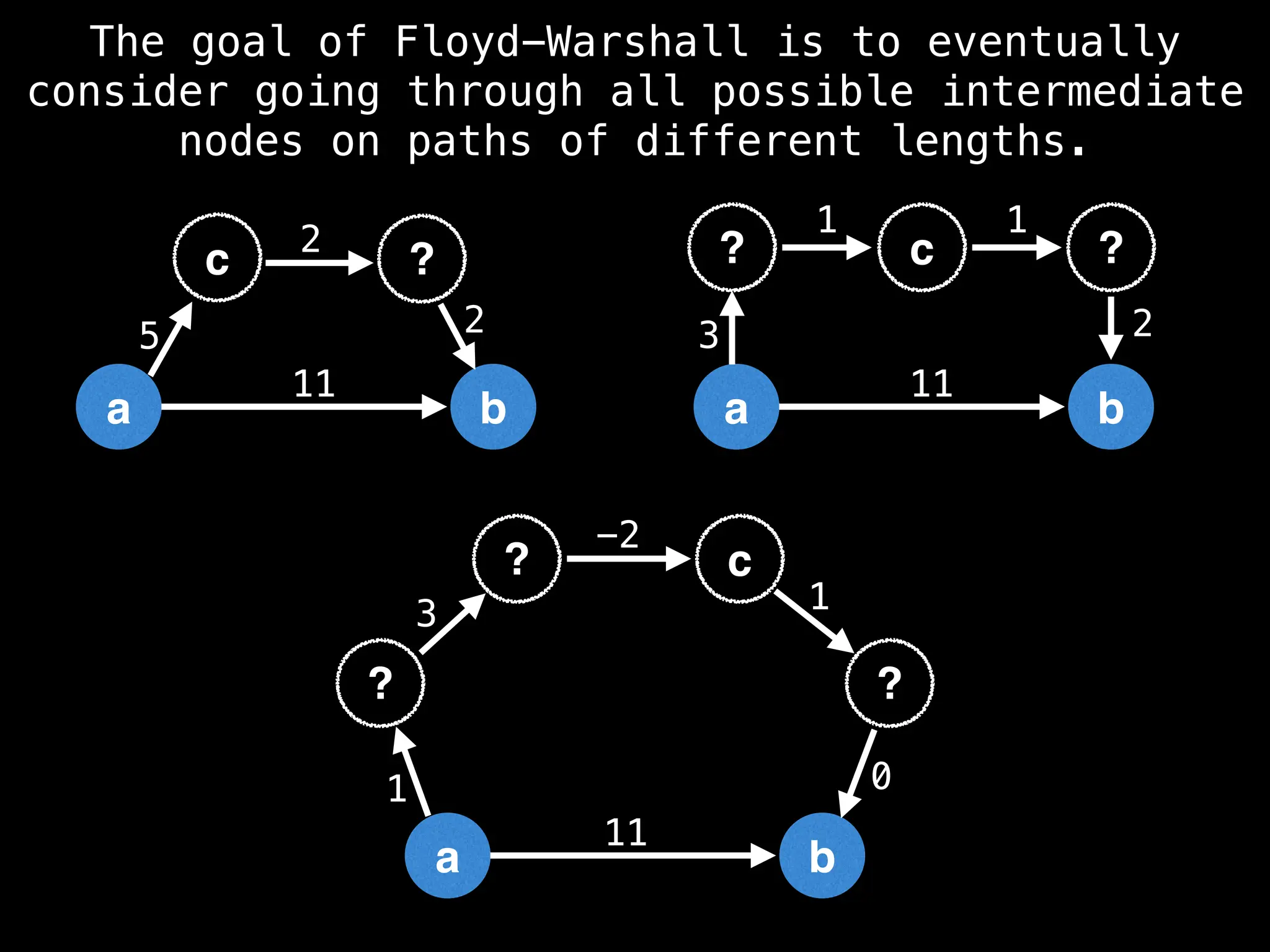
![dp[k][i][j] = shortest path from i to j
routing through nodes {0,1,…,k-1,k}
Start with k = 0, then k = 1, then k = 2, …
This gradually builds up the optimal solution
routing through 0, then all optimal solutions
routing through 0 and 1, then all optimal
solutions routing through 0, 1, 2, etc… up
until n-1 which stores to APSP solution.
Let ‘dp’ (short for Dynamic Programming) be a
3D matrix of size n x n x n that acts as a
memo table.
The Memo Table
Specifically dp[n-1] is the 2D matrix
solution we’re after.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-743-2048.jpg)
![In the beginning the optimal solution from i to j is
simply the distance in the adjacency matrix.
dp[k][i][j] = m[i][j] if k = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-744-2048.jpg)
![In the beginning the optimal solution from i to j is
simply the distance in the adjacency matrix.
dp[k][i][j] = m[i][j] if k = 0
otherwise:
dp[k][i][j] = min(dp[k-1][i][j], dp[k-1][i][k]+dp[k-1][k][j])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-745-2048.jpg)
![Reuse the best distance from i to j with
values routing through nodes {0,1,…,k-1}
In the beginning the optimal solution from i to j is
simply the distance in the adjacency matrix.
dp[k][i][j] = m[i][j] if k = 0
otherwise:
dp[k][i][j] = min(dp[k-1][i][j], dp[k-1][i][k]+dp[k-1][k][j])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-746-2048.jpg)
![dp[k][i][j] = min(dp[k-1][i][j], dp[k-1][i][k]+dp[k-1][k][j])
Find the best distance from i to j through
node k reusing best solutions from {0,1,…,k-1}
In the beginning the optimal solution from i to j is
simply the distance in the adjacency matrix.
dp[k][i][j] = m[i][j] if k = 0
otherwise:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-747-2048.jpg)
![dp[k][i][j] = min(dp[k-1][i][j], dp[k-1][i][k]+dp[k-1][k][j])
The right side of the min function in
english essentially says: “go from i to k”
and then “go from k to j”
In the beginning the optimal solution from i to j is
simply the distance in the adjacency matrix.
dp[k][i][j] = m[i][j] if k = 0
otherwise:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-748-2048.jpg)
![dp[k][i][j] = min(dp[k-1][i][j], dp[k-1][i][k]+dp[k-1][k][j])
k
i j
Visually this looks like:
dp[k-1][i][j]
dp[k-1][i][k] dp[k-1][k][j]
In the beginning the optimal solution from i to j is
simply the distance in the adjacency matrix.
dp[k][i][j] = m[i][j] if k = 0
otherwise:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-749-2048.jpg)
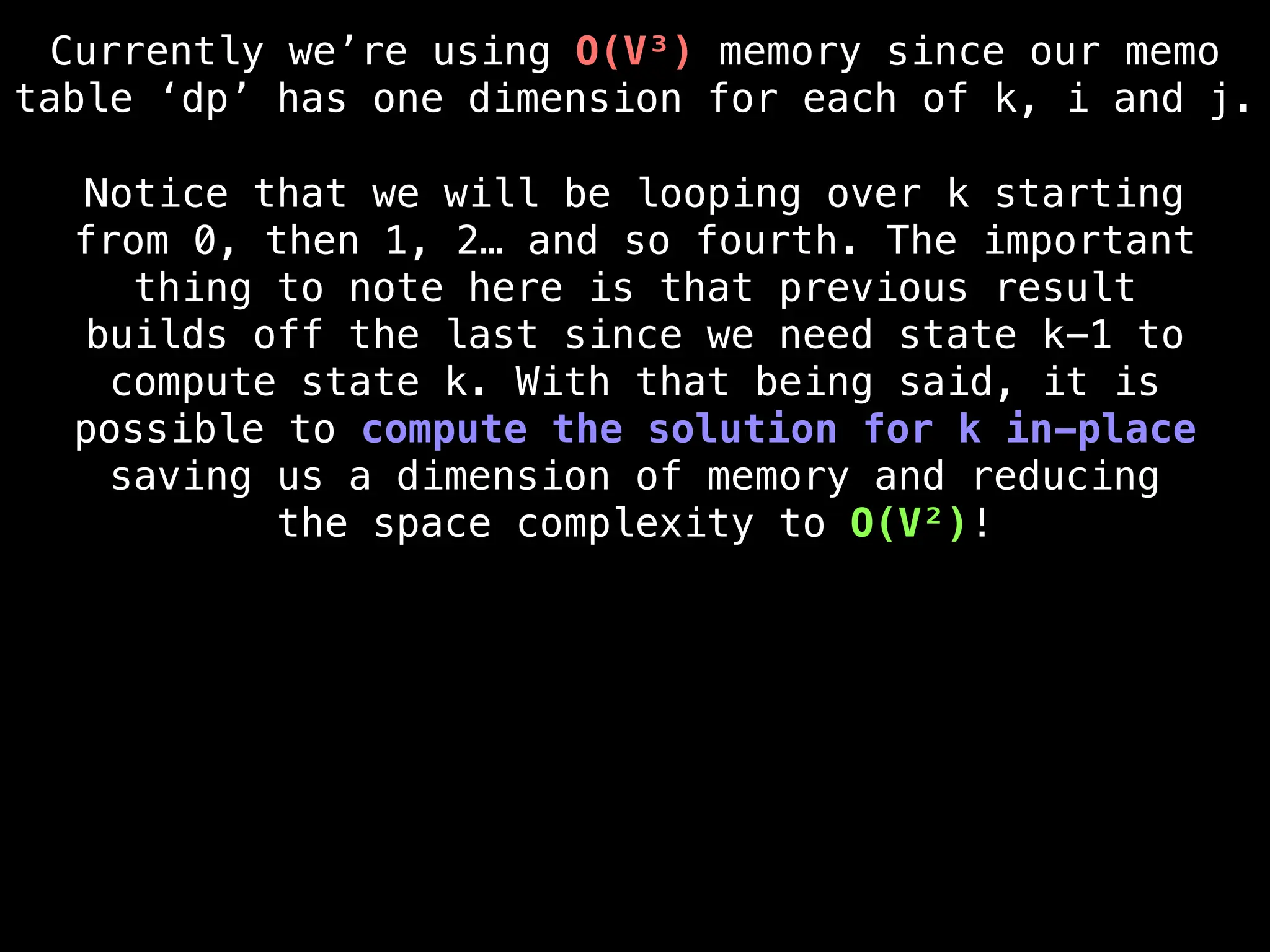
![dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i][k]+dp[k][j])
otherwise:
The new recurrence relation is:
dp[i][j] = m[i][j] if k = 0
Currently we’re using O(V³) memory since our memo
table ‘dp’ has one dimension for each of k, i and j.
Notice that we will be looping over k starting
from 0, then 1, 2… and so fourth. The important
thing to note here is that previous result
builds off the last since we need state k-1 to
compute state k. With that being said, it is
possible to compute the solution for k in-place
saving us a dimension of memory and reducing
the space complexity to O(V²)!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-751-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-752-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-753-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-754-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-755-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-756-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-757-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-758-2048.jpg)
![function setup(m):
dp = empty matrix of size n x n
# Should contain null values by default
next = empty integer matrix of size n x n
# Do a deep copy of the input matrix and setup
# the 'next' matrix for path reconstruction.
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
dp[i][j] = m[i][j]
if m[i][j] != +∞:
next[i][j] = j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-759-2048.jpg)
![function setup(m):
dp = empty matrix of size n x n
# Should contain null values by default
next = empty integer matrix of size n x n
# Do a deep copy of the input matrix and setup
# the 'next' matrix for path reconstruction.
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
dp[i][j] = m[i][j]
if m[i][j] != +∞:
next[i][j] = j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-760-2048.jpg)
![function setup(m):
dp = empty matrix of size n x n
# Should contain null values by default
next = empty integer matrix of size n x n
# Do a deep copy of the input matrix and setup
# the 'next' matrix for path reconstruction.
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
dp[i][j] = m[i][j]
if m[i][j] != +∞:
next[i][j] = j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-761-2048.jpg)
![function setup(m):
dp = empty matrix of size n x n
# Should contain null values by default
next = empty integer matrix of size n x n
# Do a deep copy of the input matrix and setup
# the 'next' matrix for path reconstruction.
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
dp[i][j] = m[i][j]
if m[i][j] != +∞:
next[i][j] = j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-762-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-763-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-764-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-765-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-766-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-767-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-768-2048.jpg)

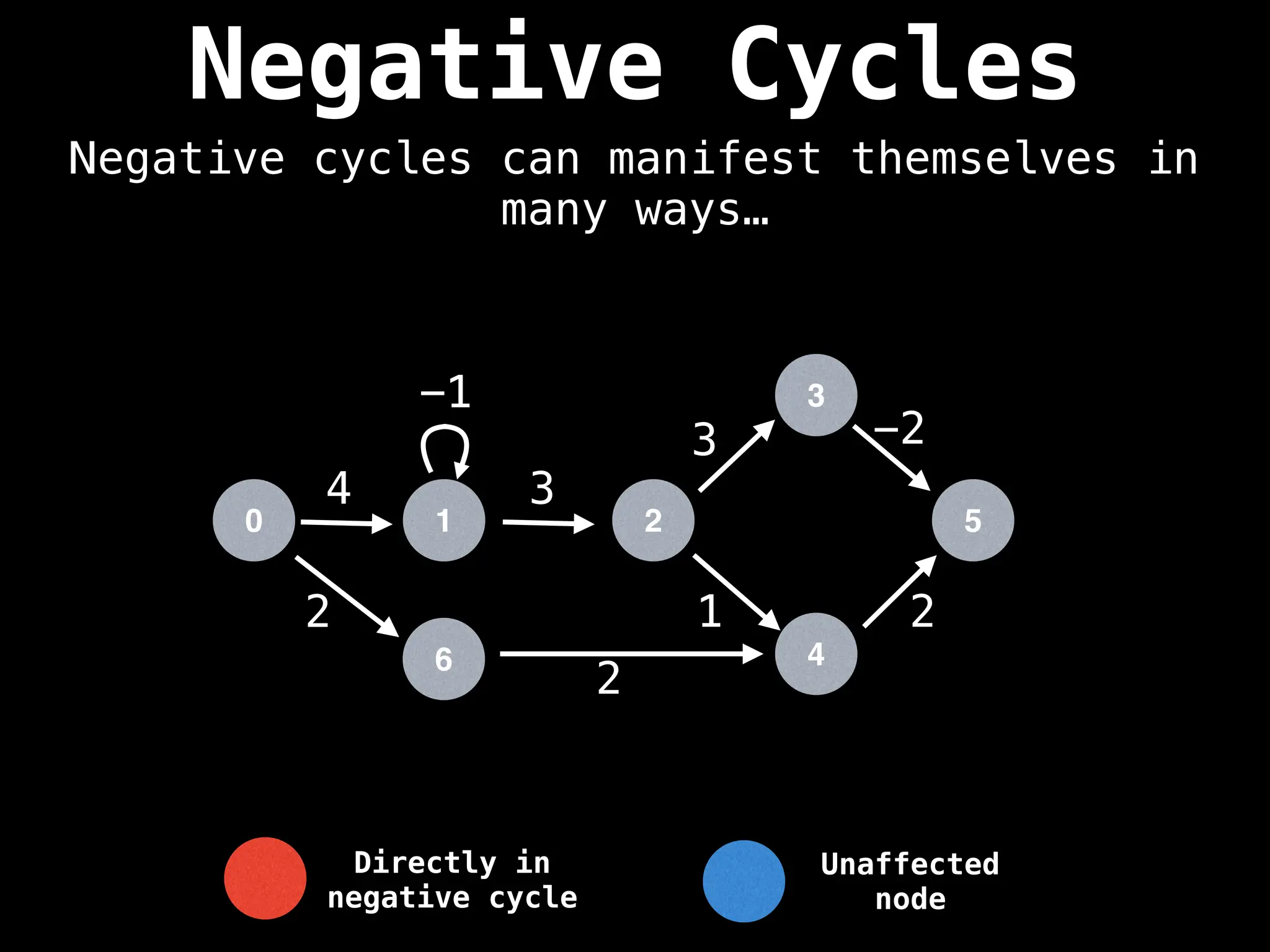
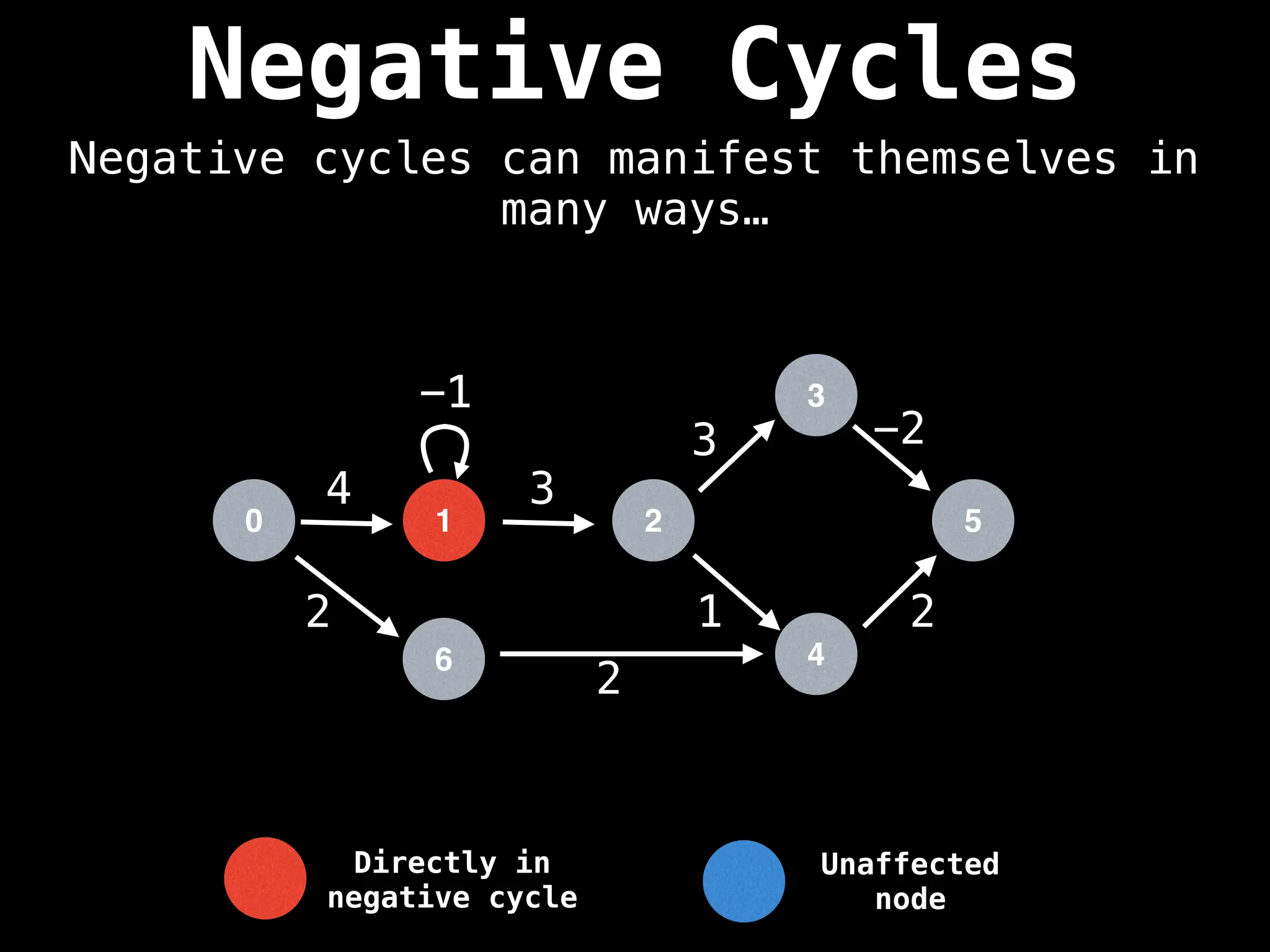
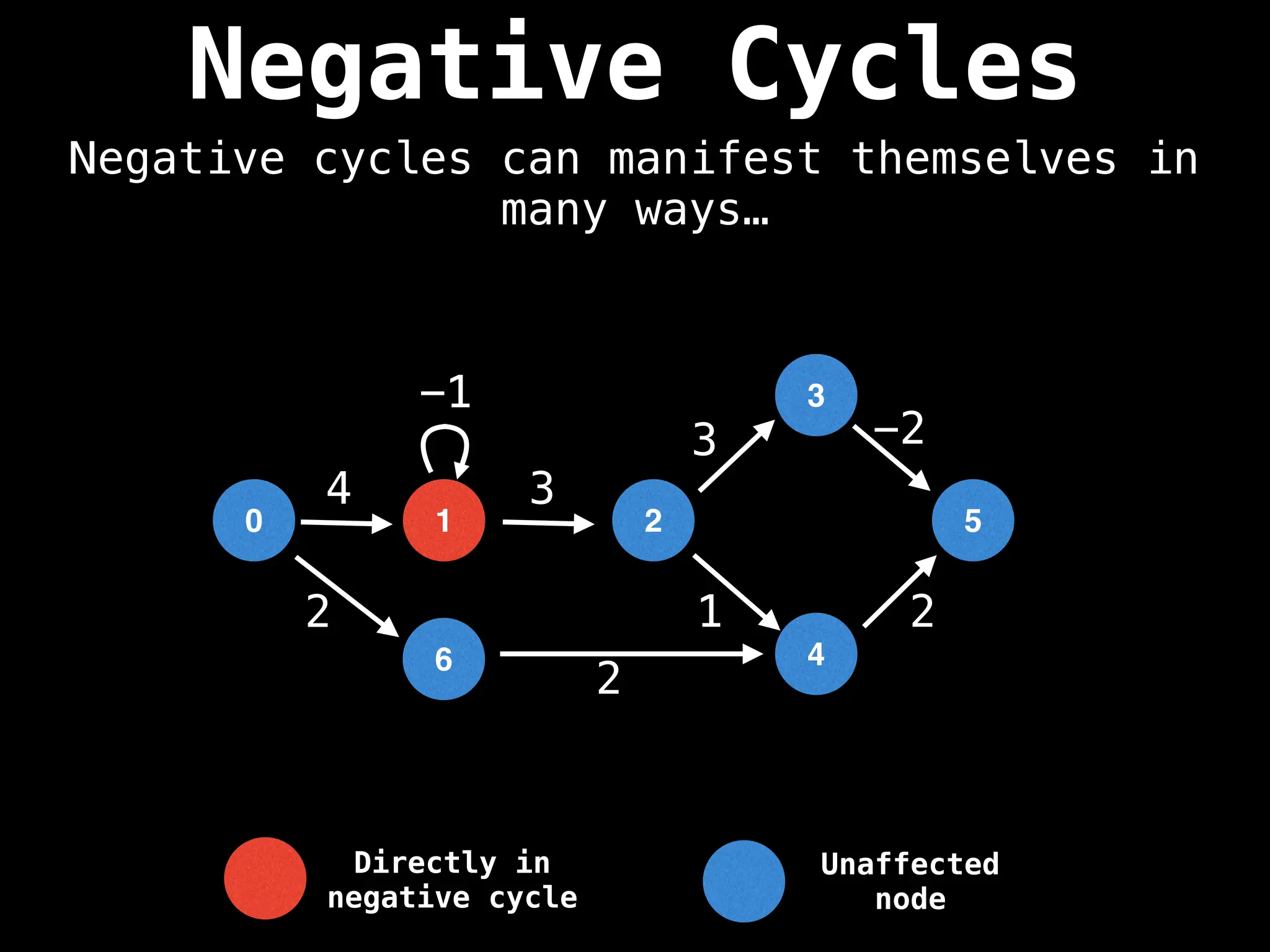
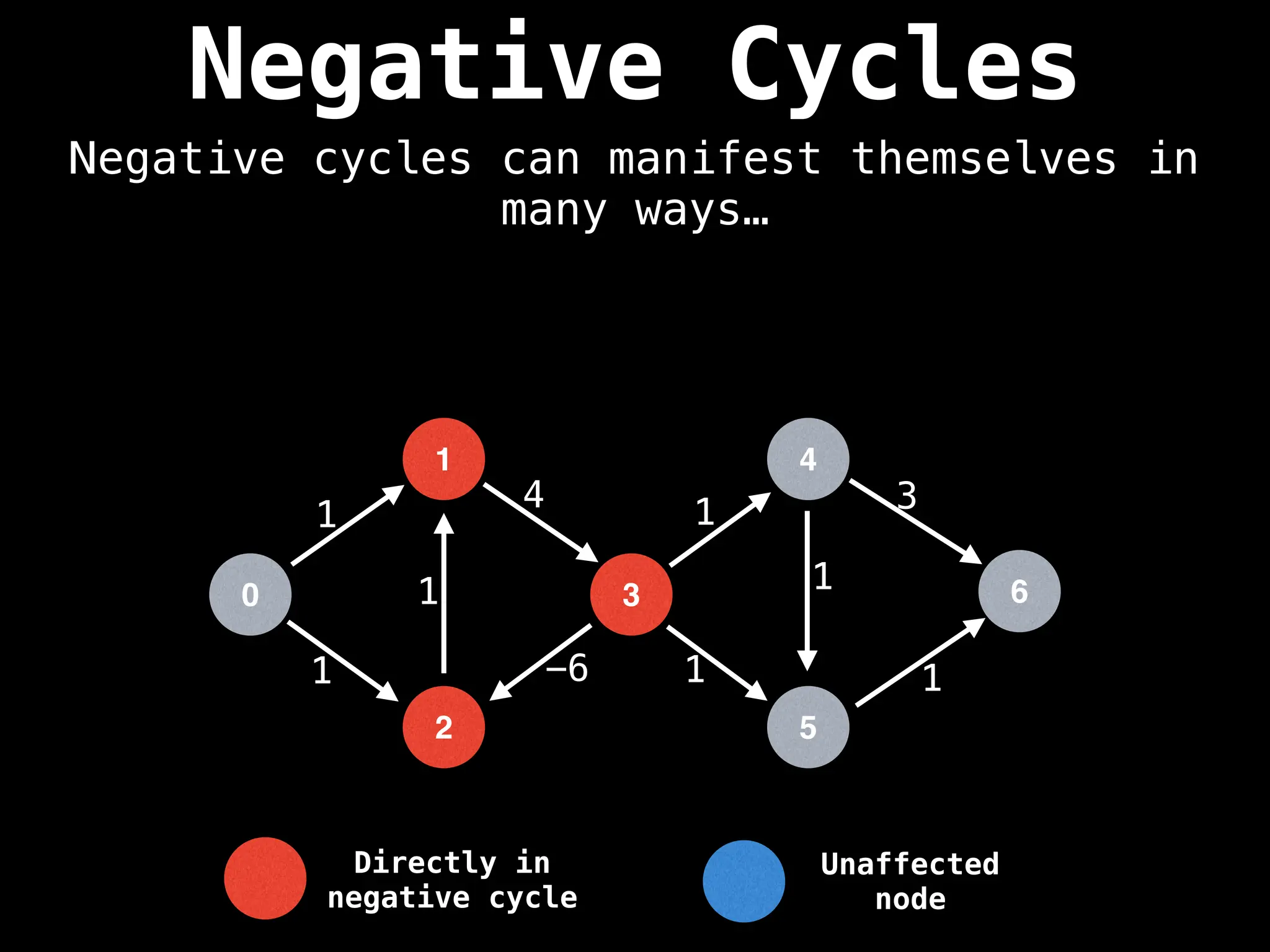
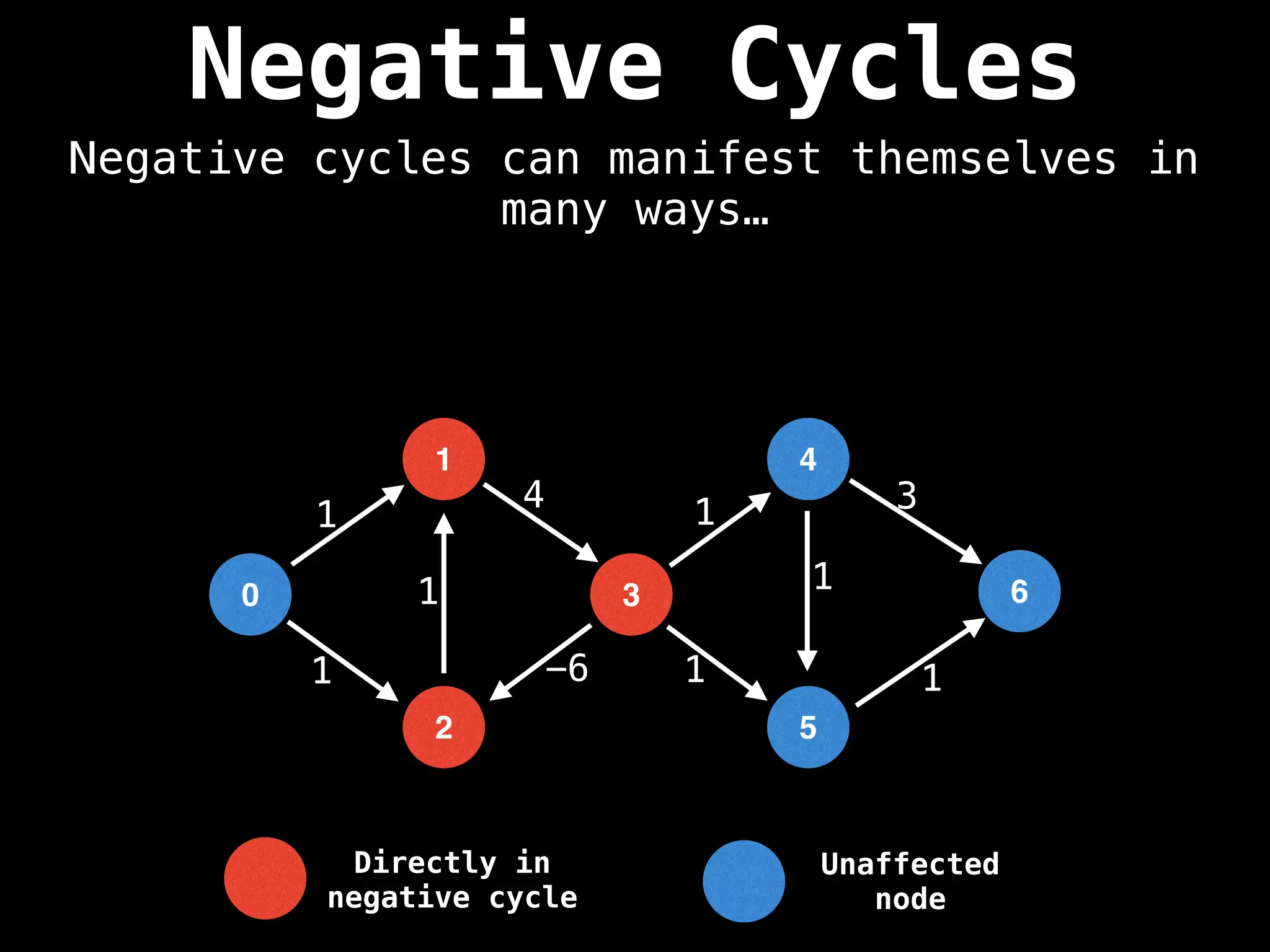
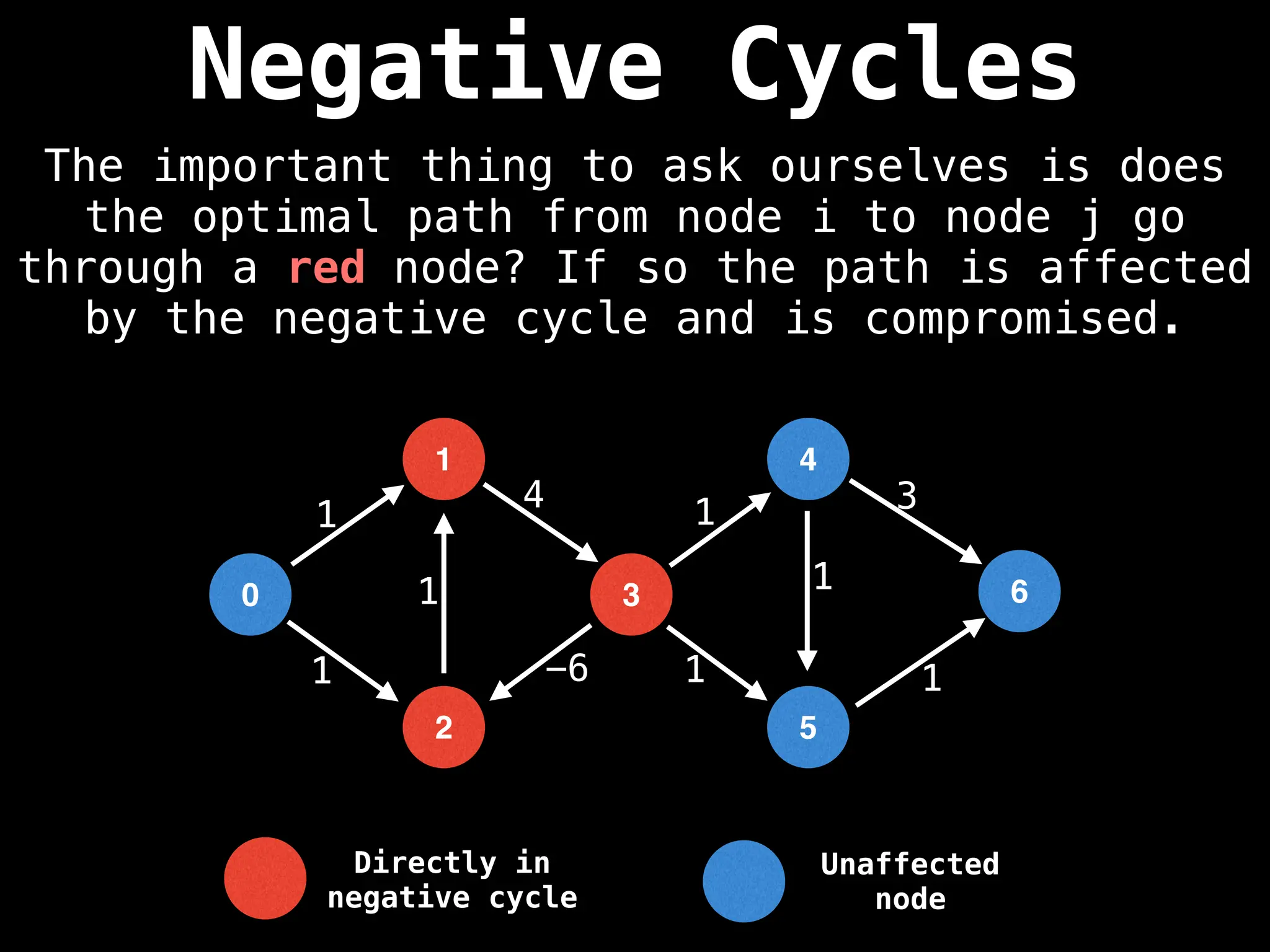
![function propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n):
# Execute FW APSP algorithm a second time but
# this time if the distance can be improved
# set the optimal distance to be -∞.
# Every edge (i, j) marked with -∞ is either
# part of or reaches into a negative cycle.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = -∞
next[i][j] = -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-776-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = size of the adjacency matrix
dp = the memo table that will contain APSP soln
next = matrix used to reconstruct shortest paths
function floydWarshall(m):
setup(m)
# Execute FW all pairs shortest path algorithm.
for(k := 0; k < n; k++):
for(i := 0; i < n; i++):
for(j := 0; j < n; j++):
if(dp[i][k] + dp[k][j] < dp[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][k] + dp[k][j]
next[i][j] = next[i][k]
# Detect and propagate negative cycles.
propagateNegativeCycles(dp, n)
# Return APSP matrix
return dp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-777-2048.jpg)
![# Reconstructs the shortest path between nodes
# ’start’ and ‘end’. You must run the
# floydWarshall solver before calling this method.
# Returns null if path if affected by negative cycle.
function reconstructPath(start, end):
path = []
# Check if there exists a path between
# the start and the end node.
if dp[start][end] == +∞: return path
at := start
# Reconstruct path from next matrix
for(;at != end; at = next[at][end]):
if at == -1: return null
path.add(at)
if next[at][end] == -1: return null
path.add(end)
return path](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-778-2048.jpg)

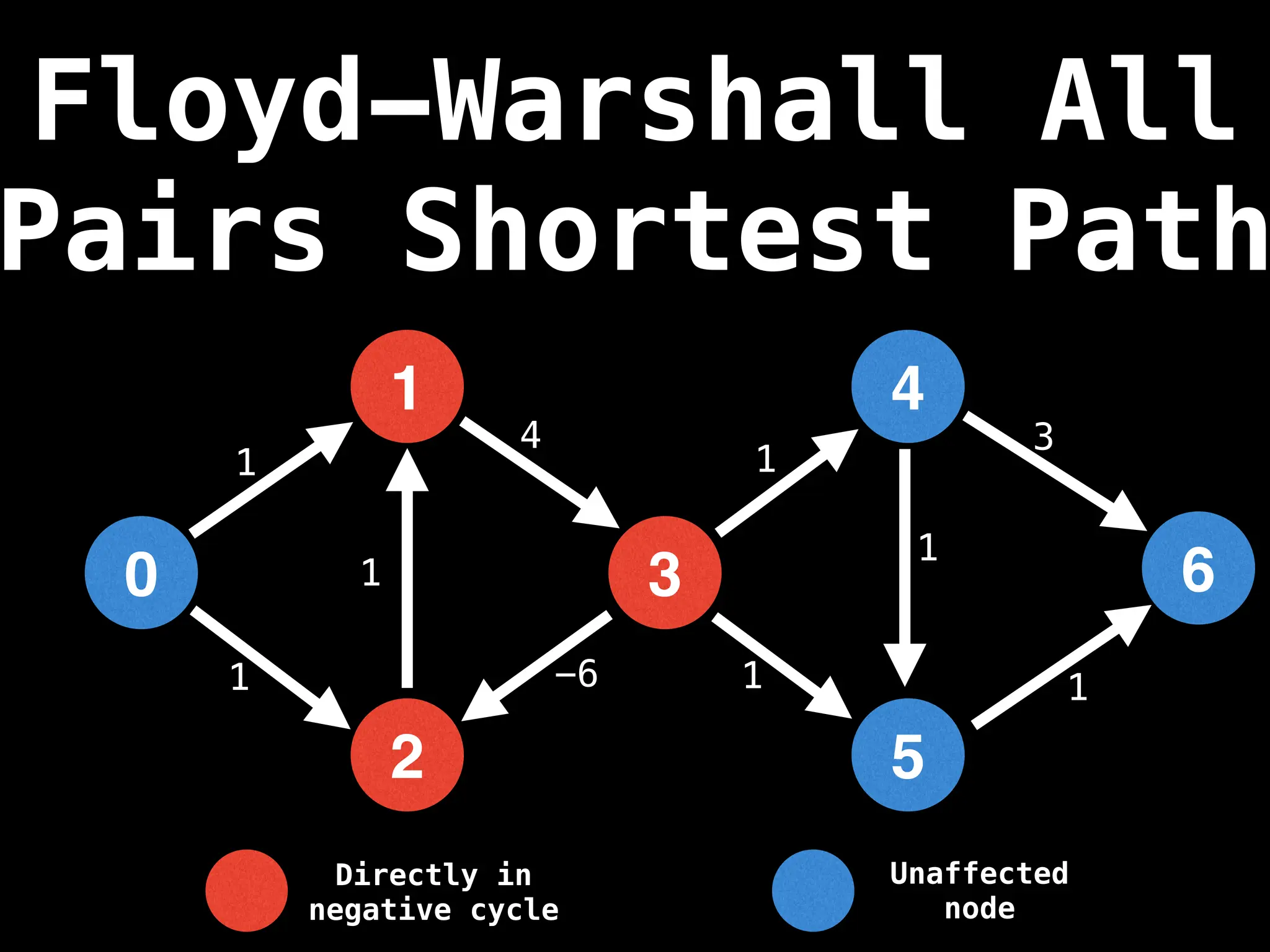

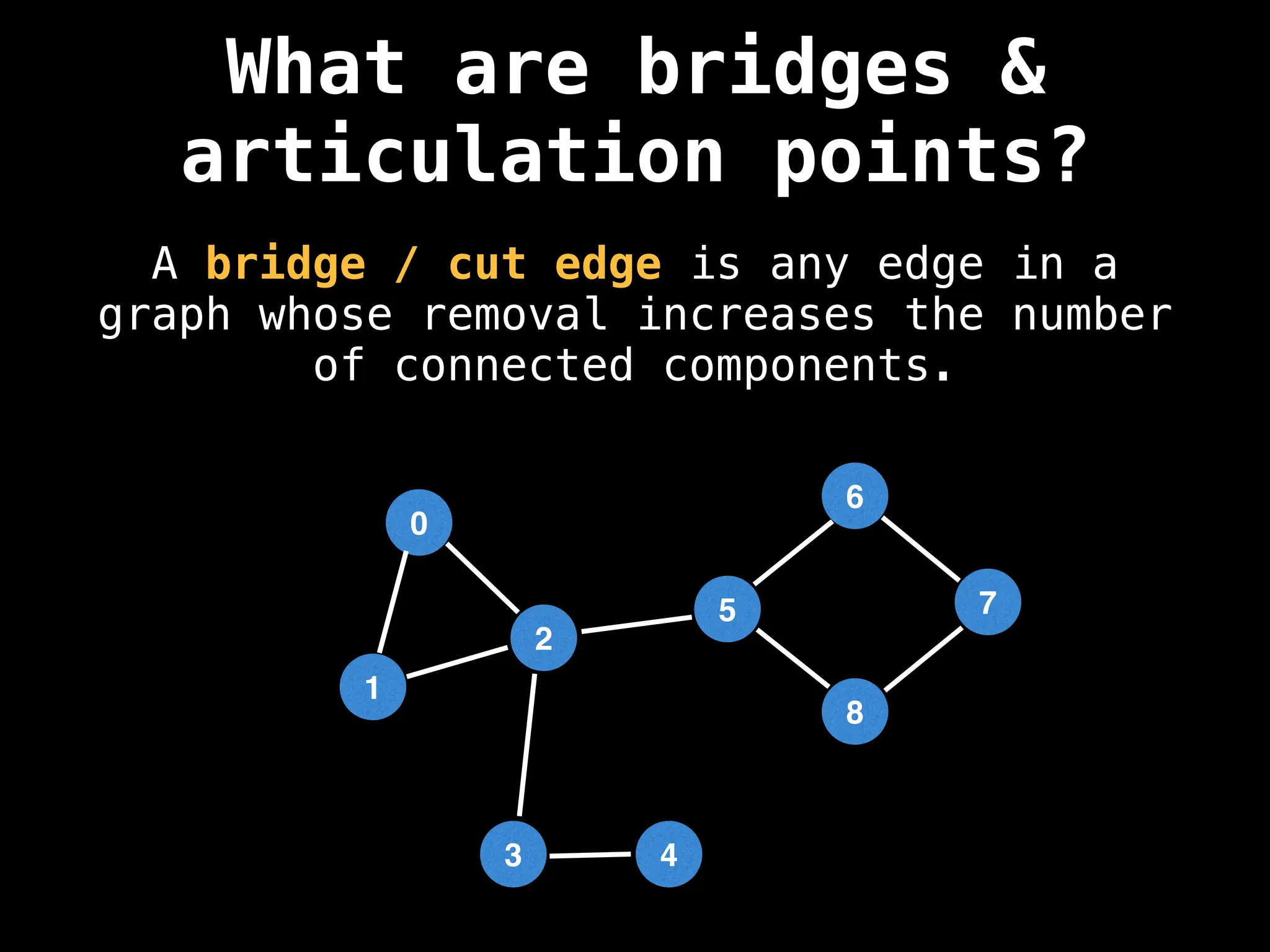
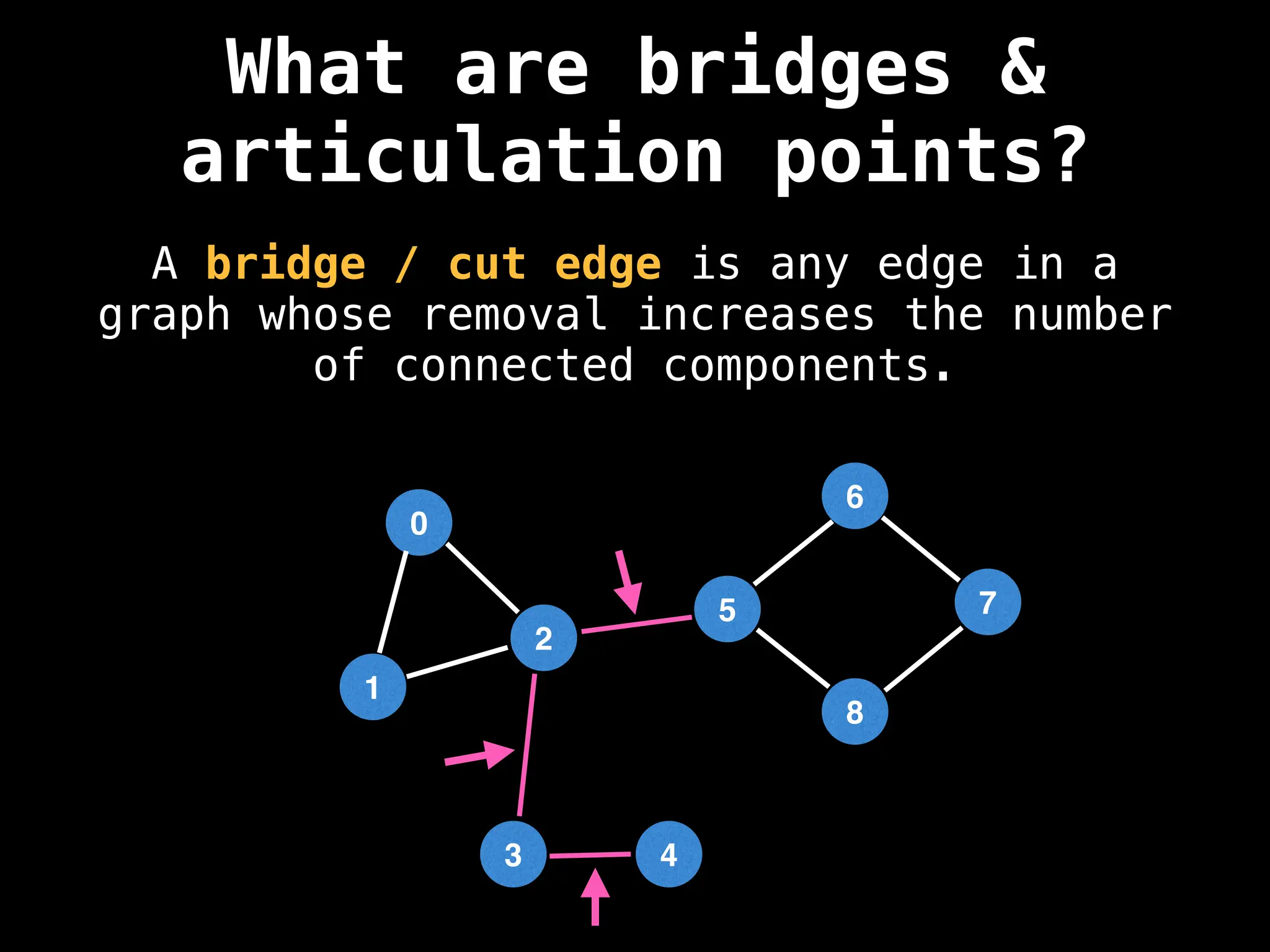
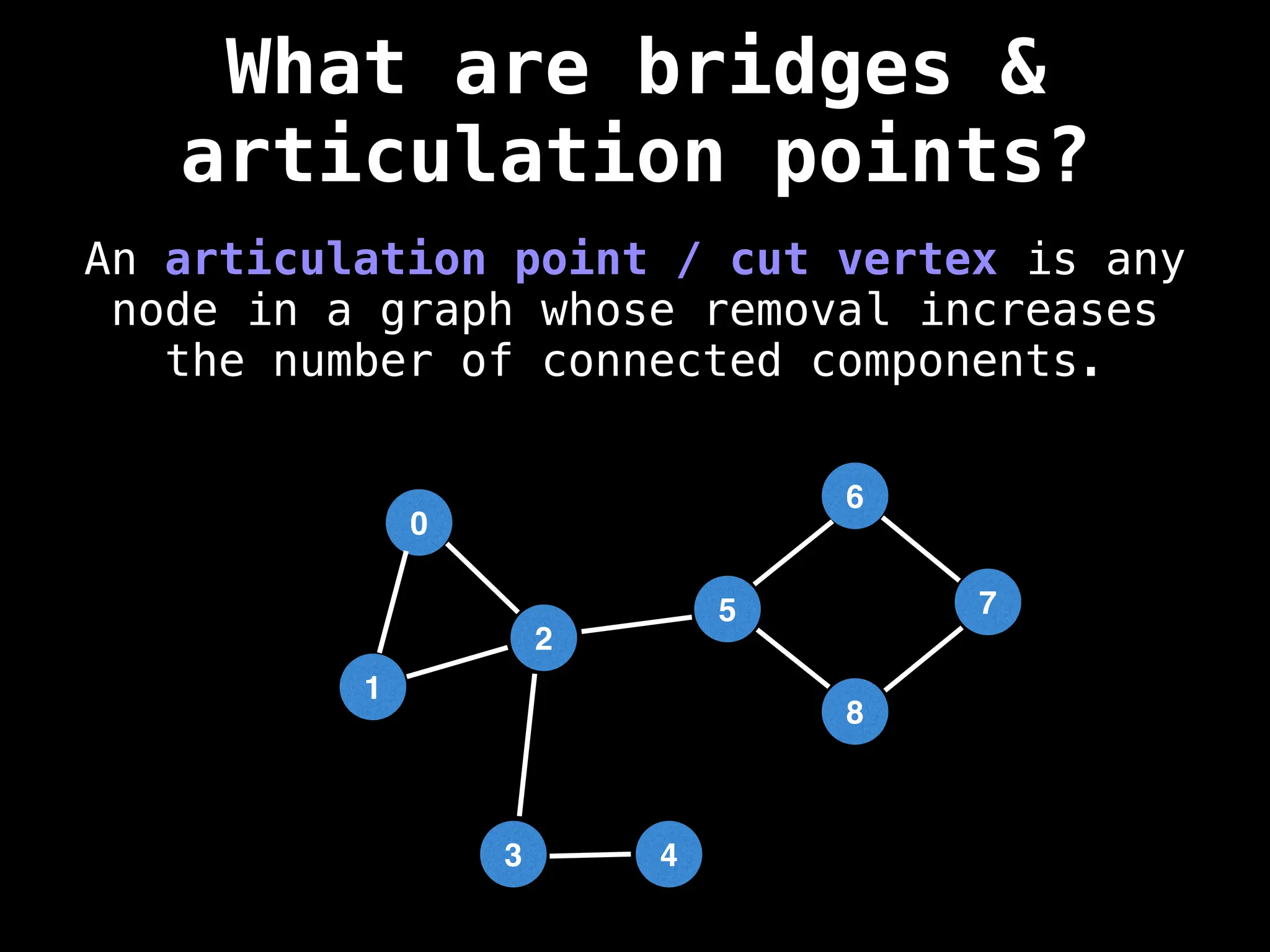
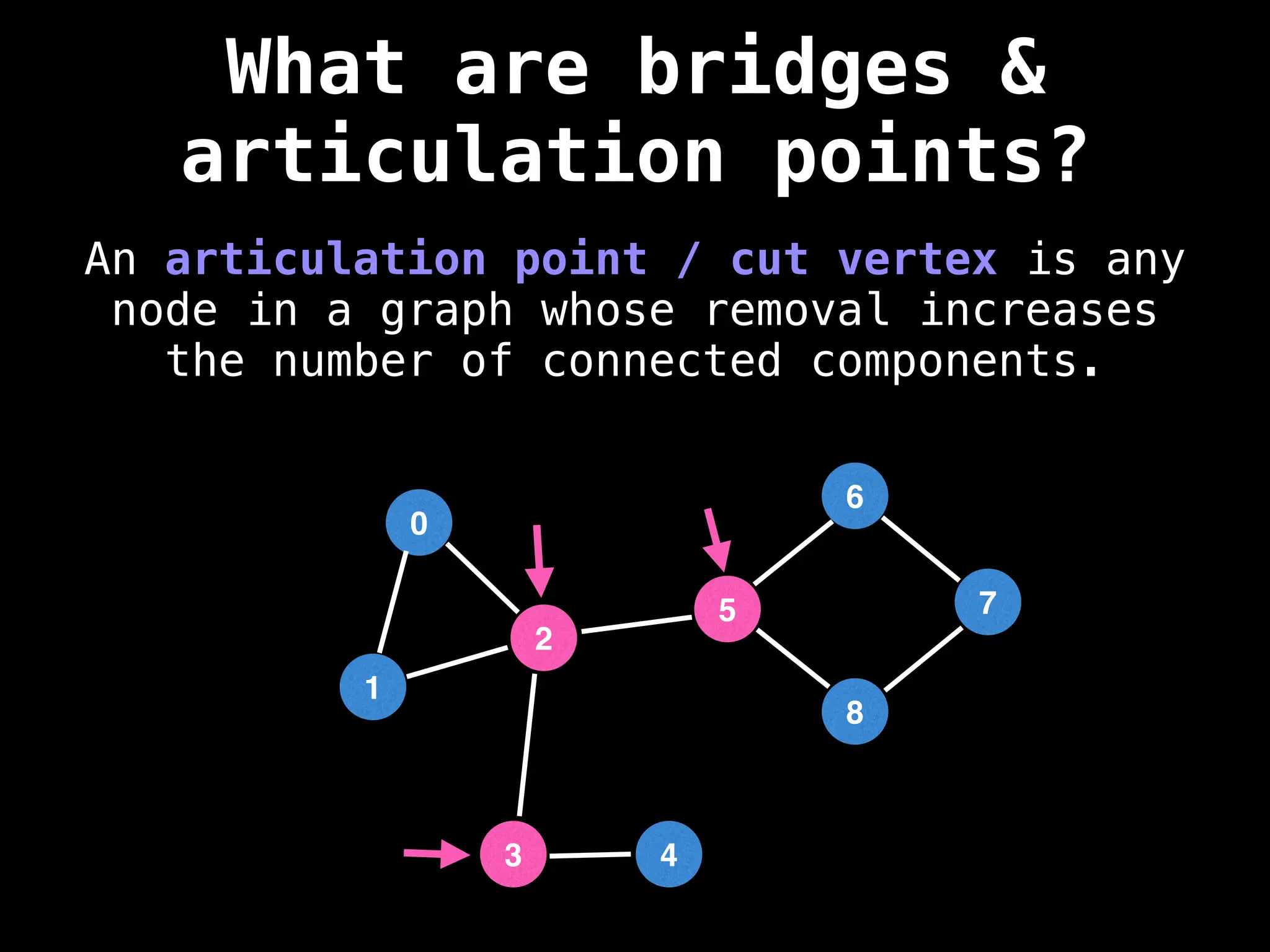
![Bridges algorithm
Start at any node and do a Depth First
Search (DFS) traversal labeling nodes with
an increasing id value as you go. Keep track
the id of each node and the smallest low-
link value. During the DFS, bridges will be
found where the id of the node your edge is
coming from is less than the low link value
of the node your edge is going to.
NOTE: The low-link value of a node is
defined as the smallest [lowest] id
reachable from that node when doing a DFS
(including itself).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-790-2048.jpg)
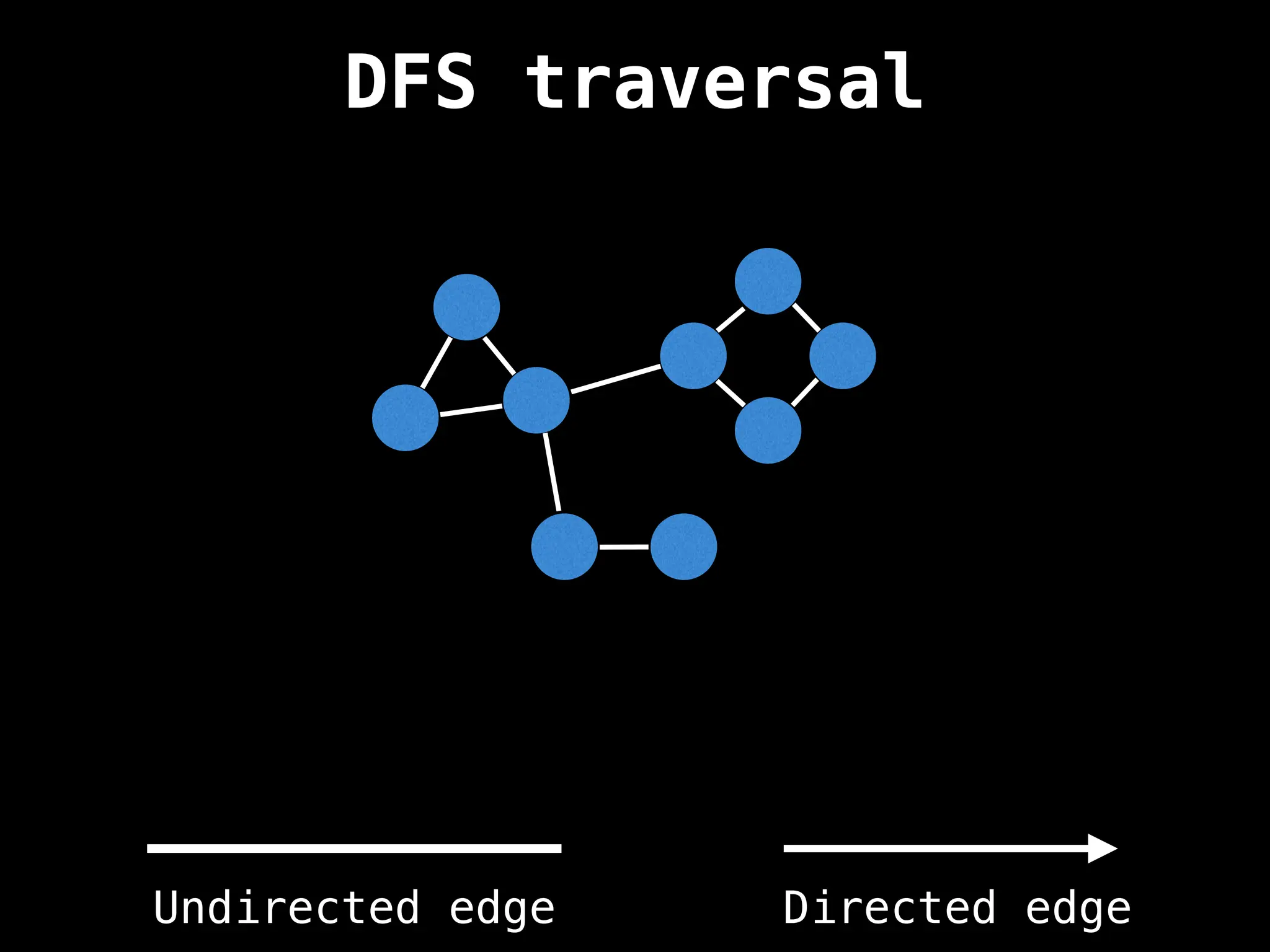
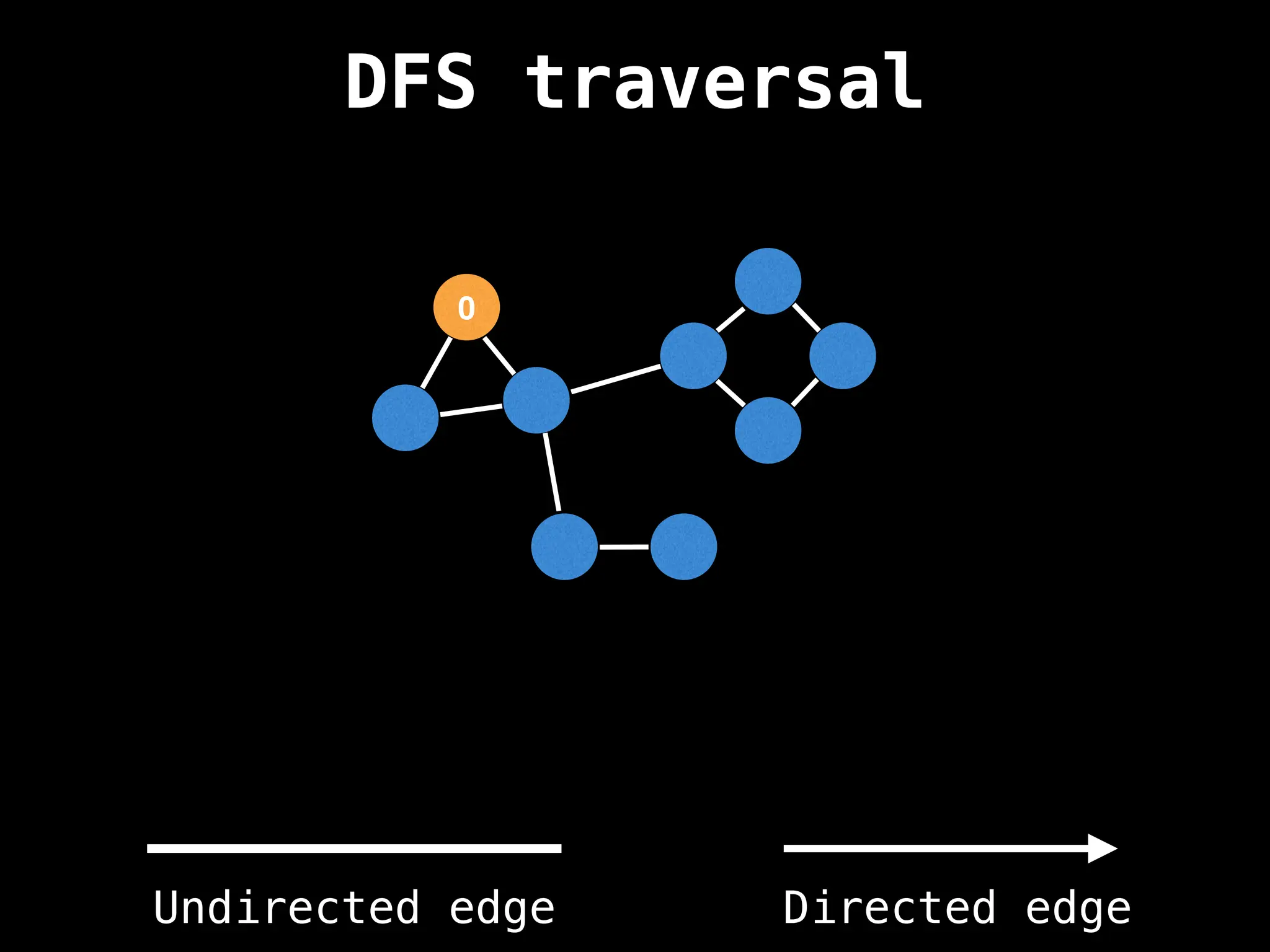
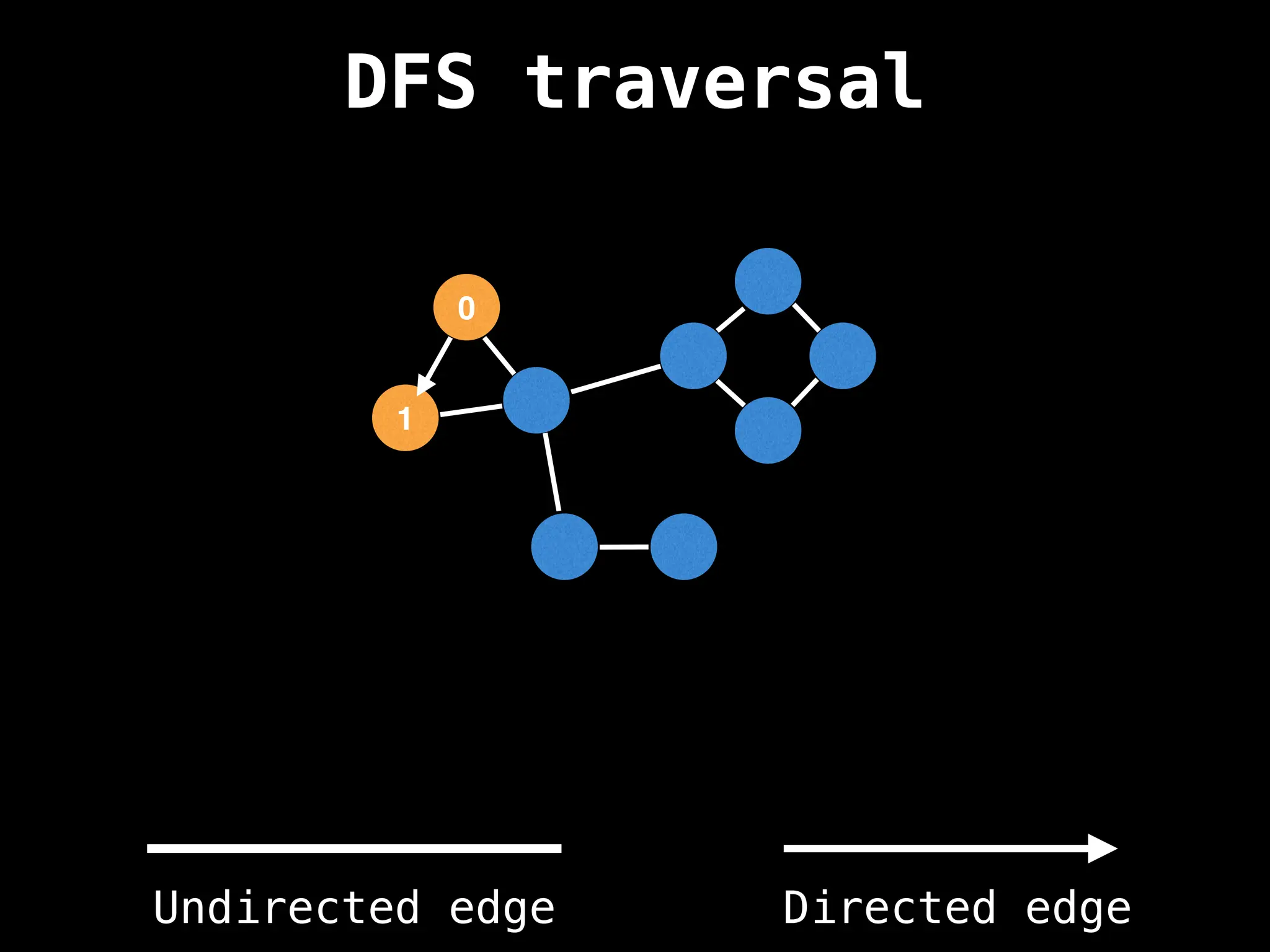
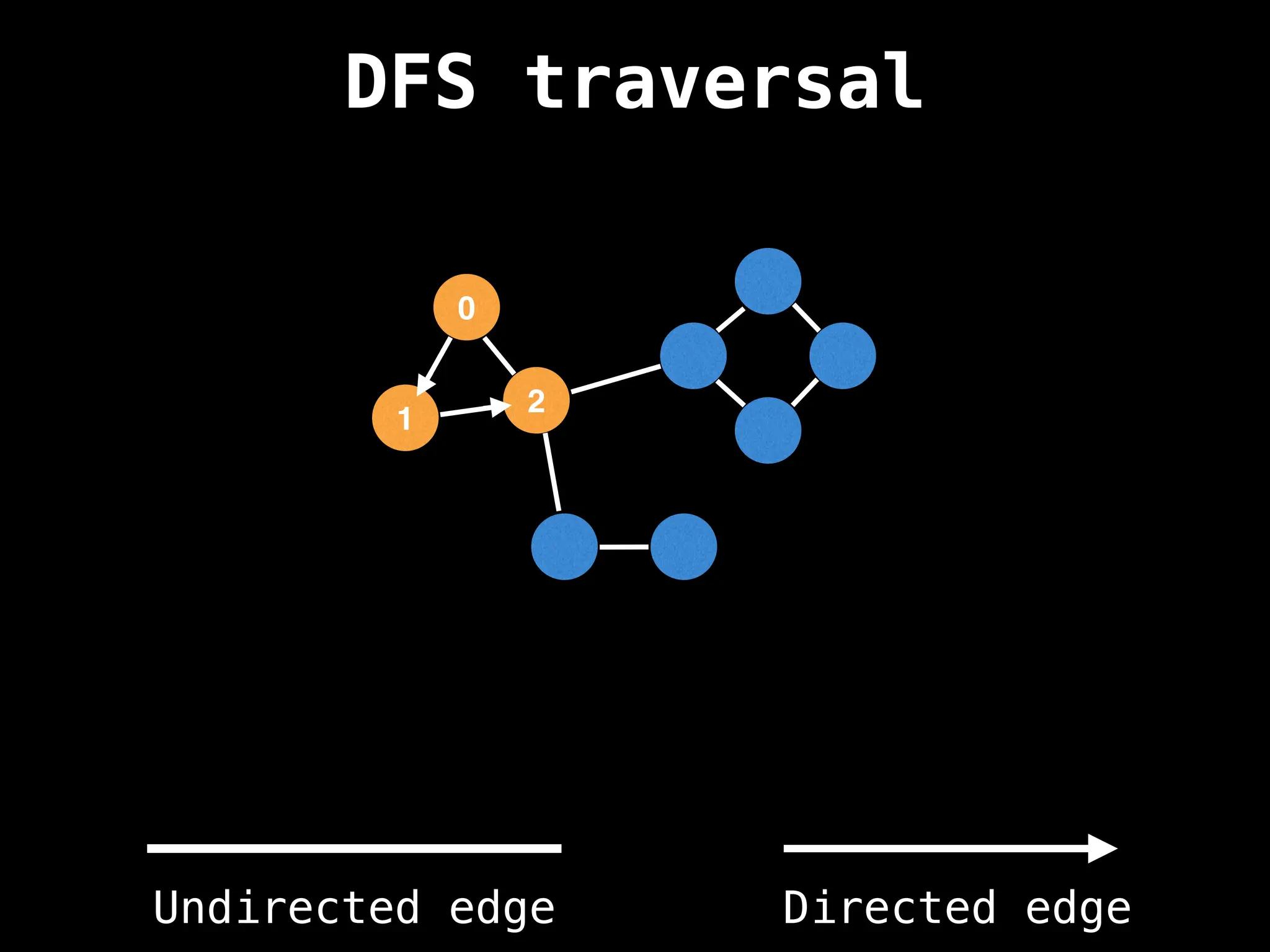
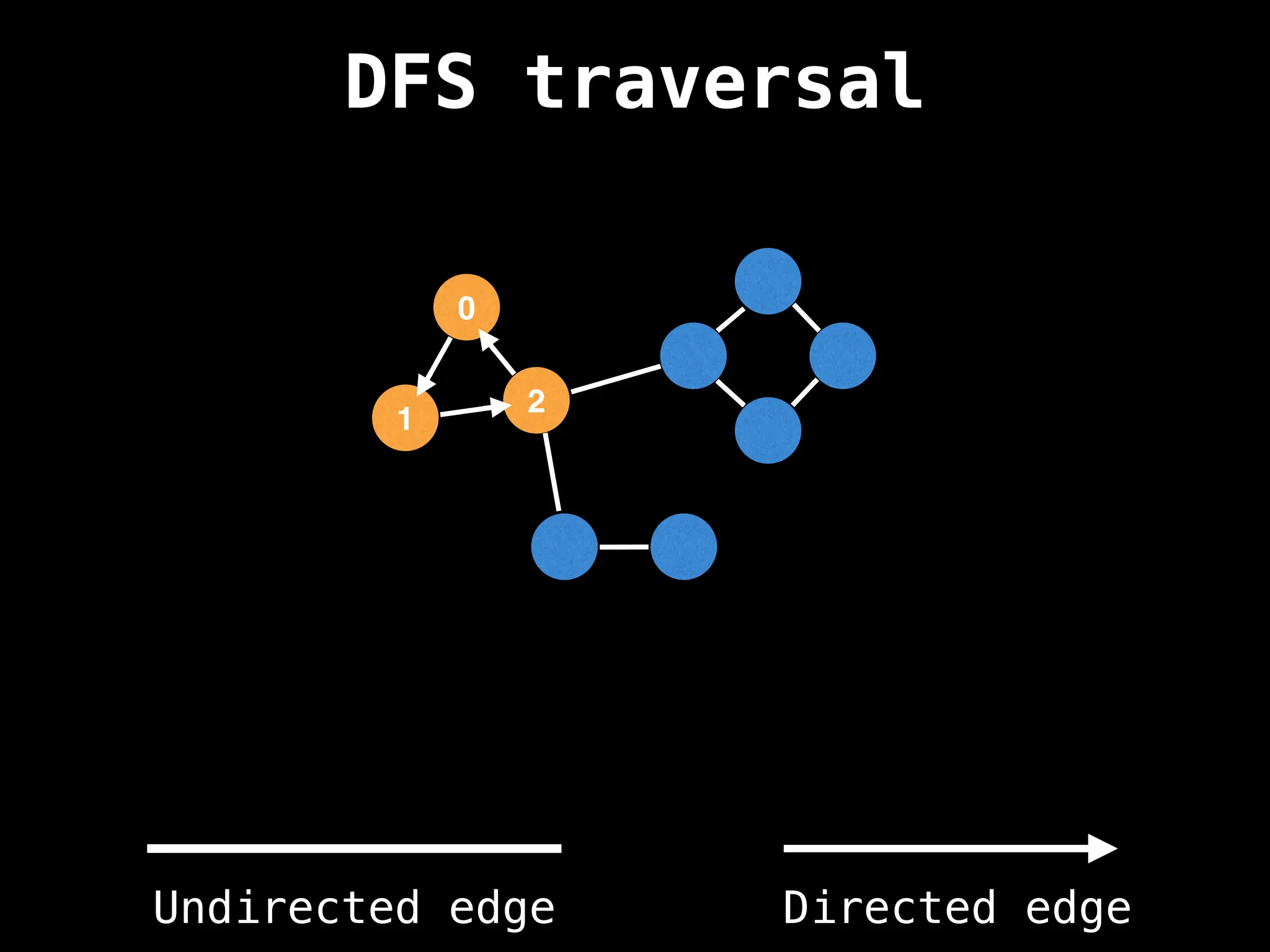
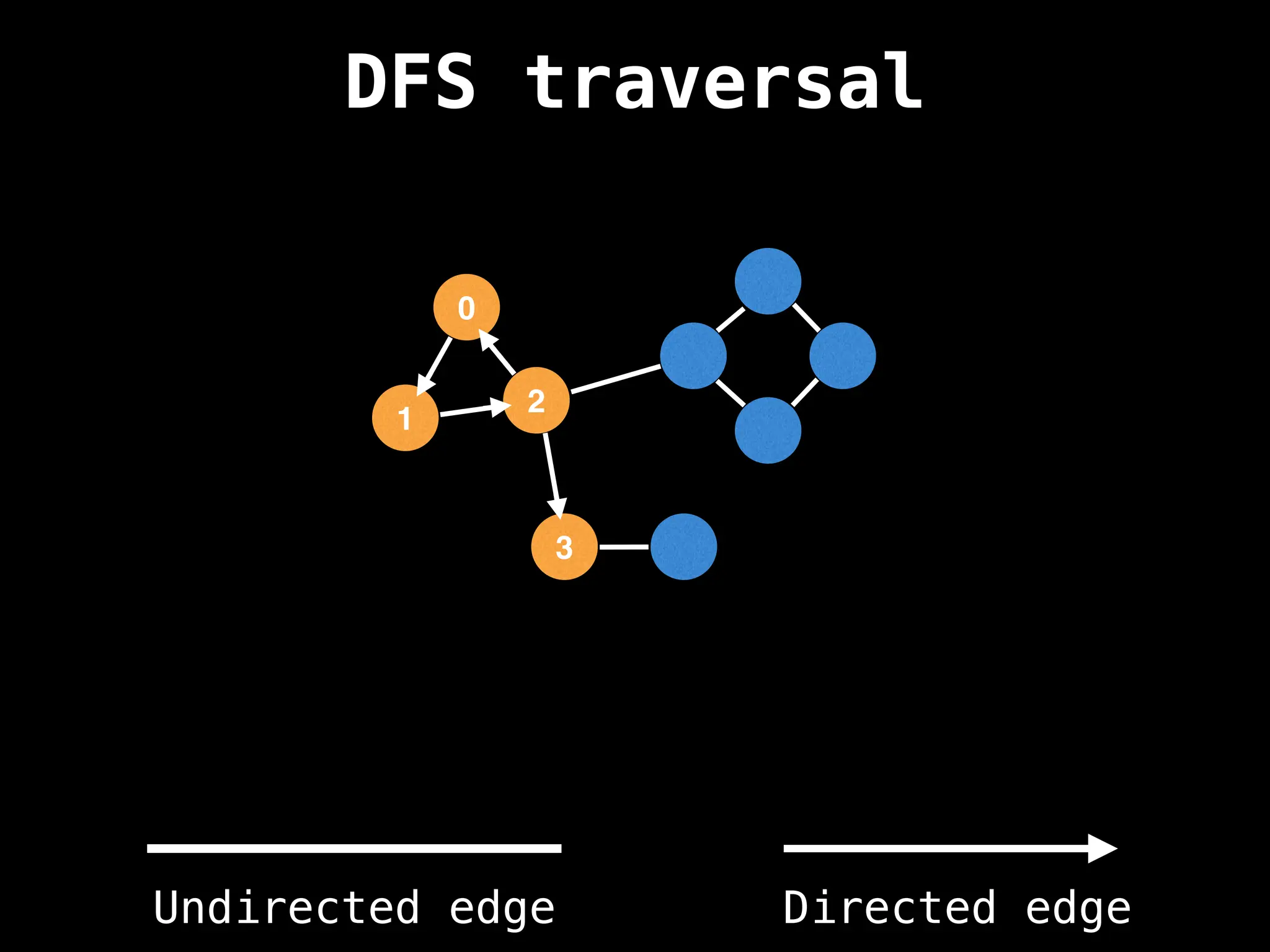
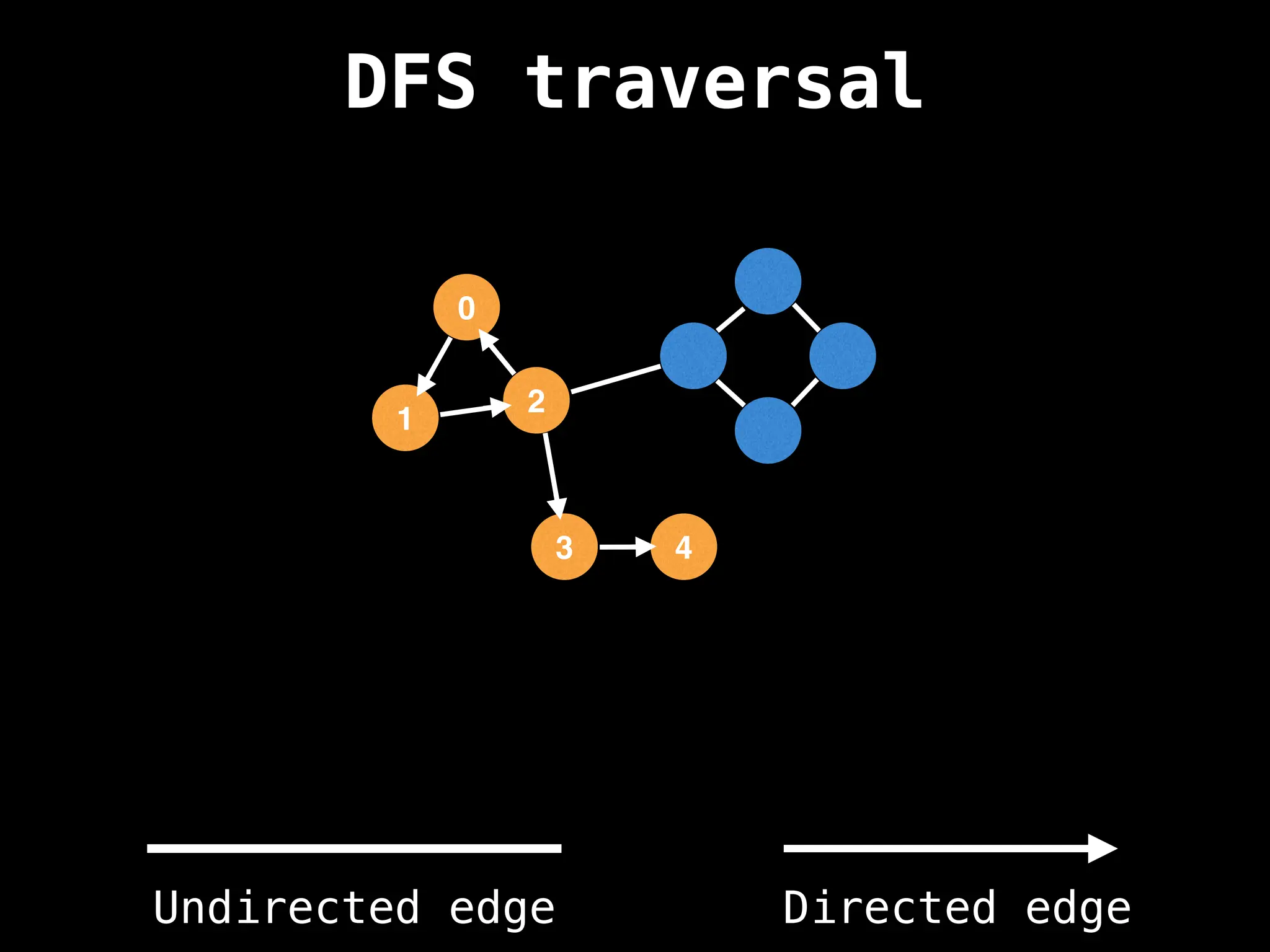
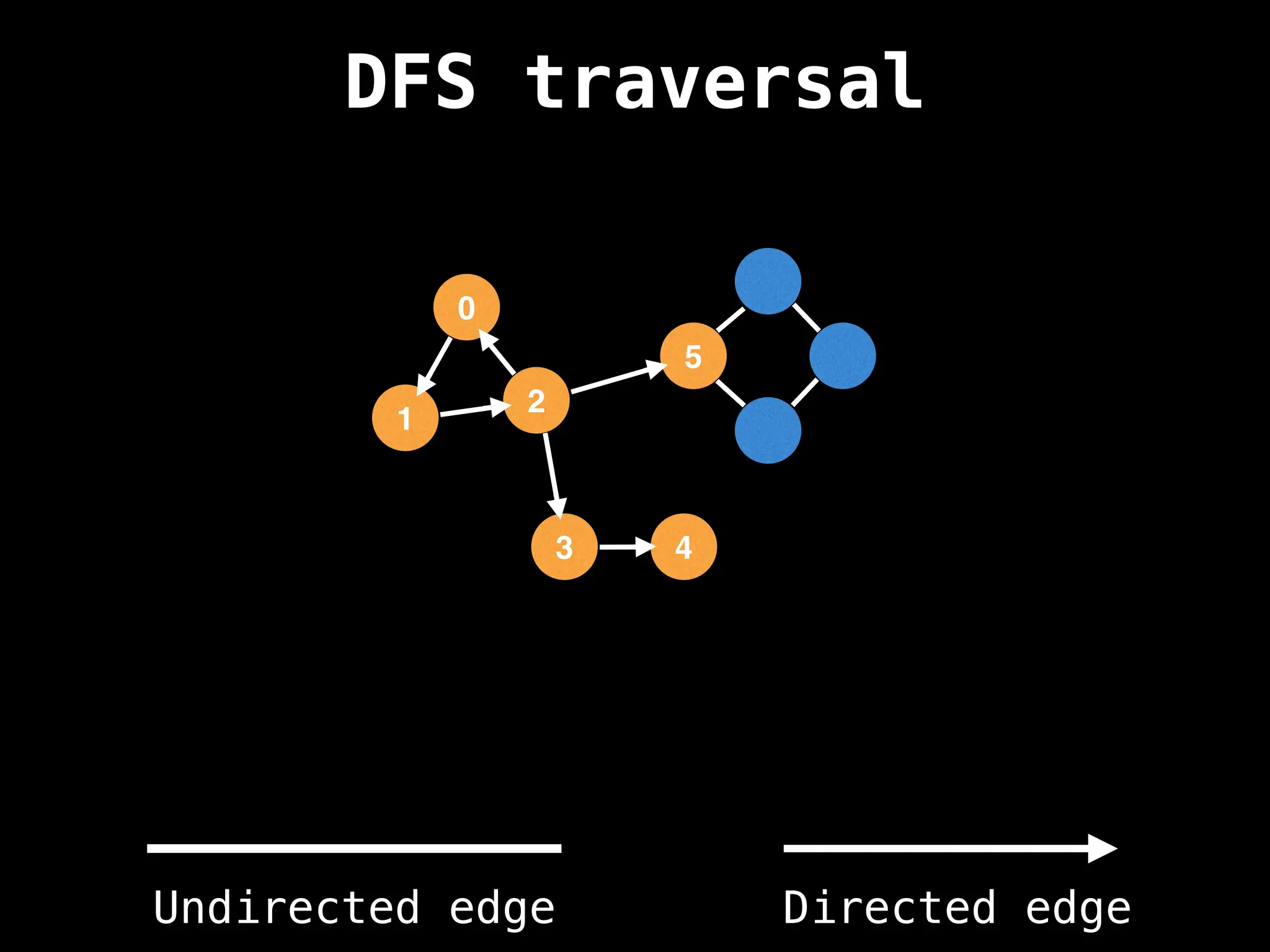
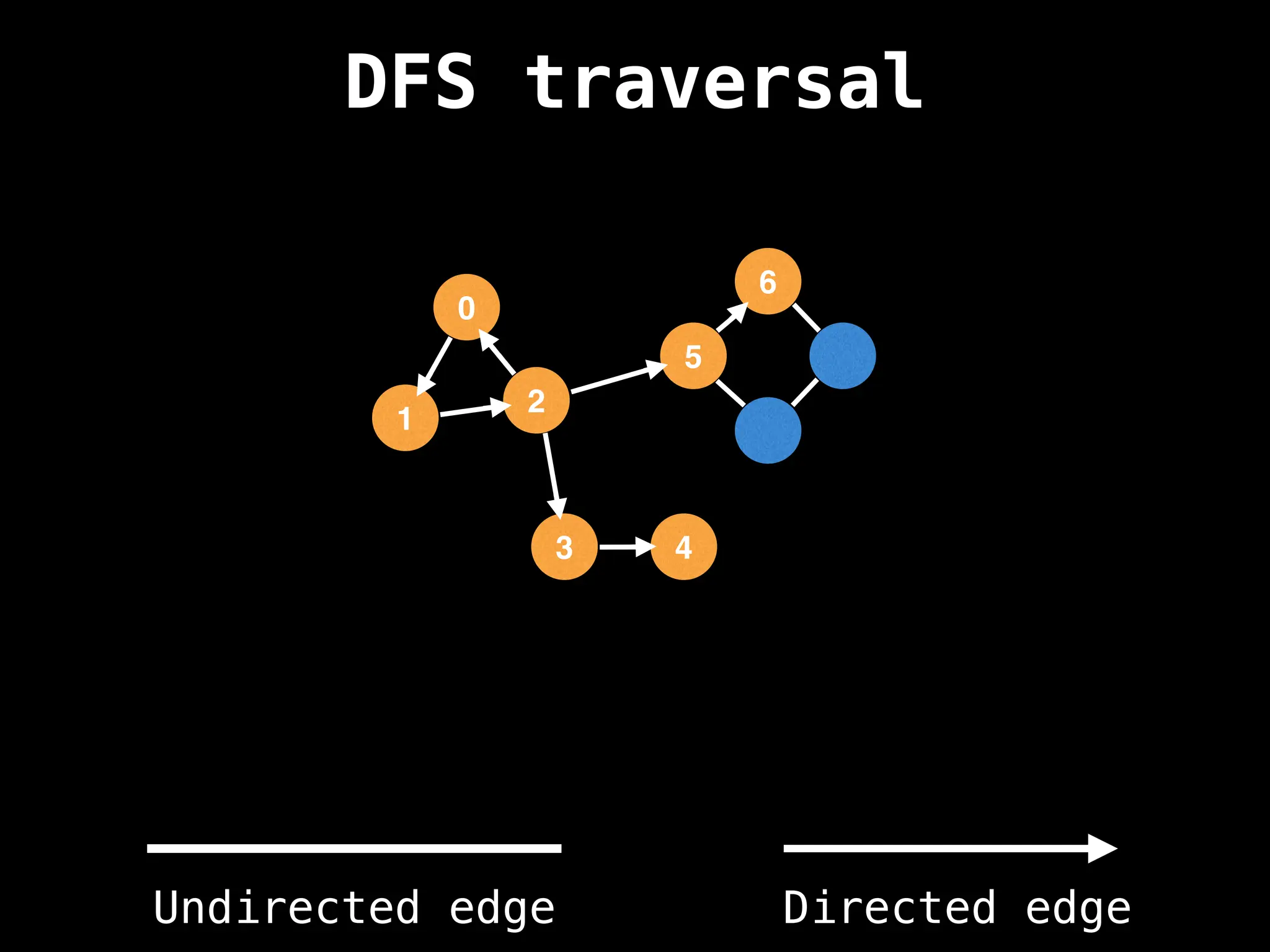
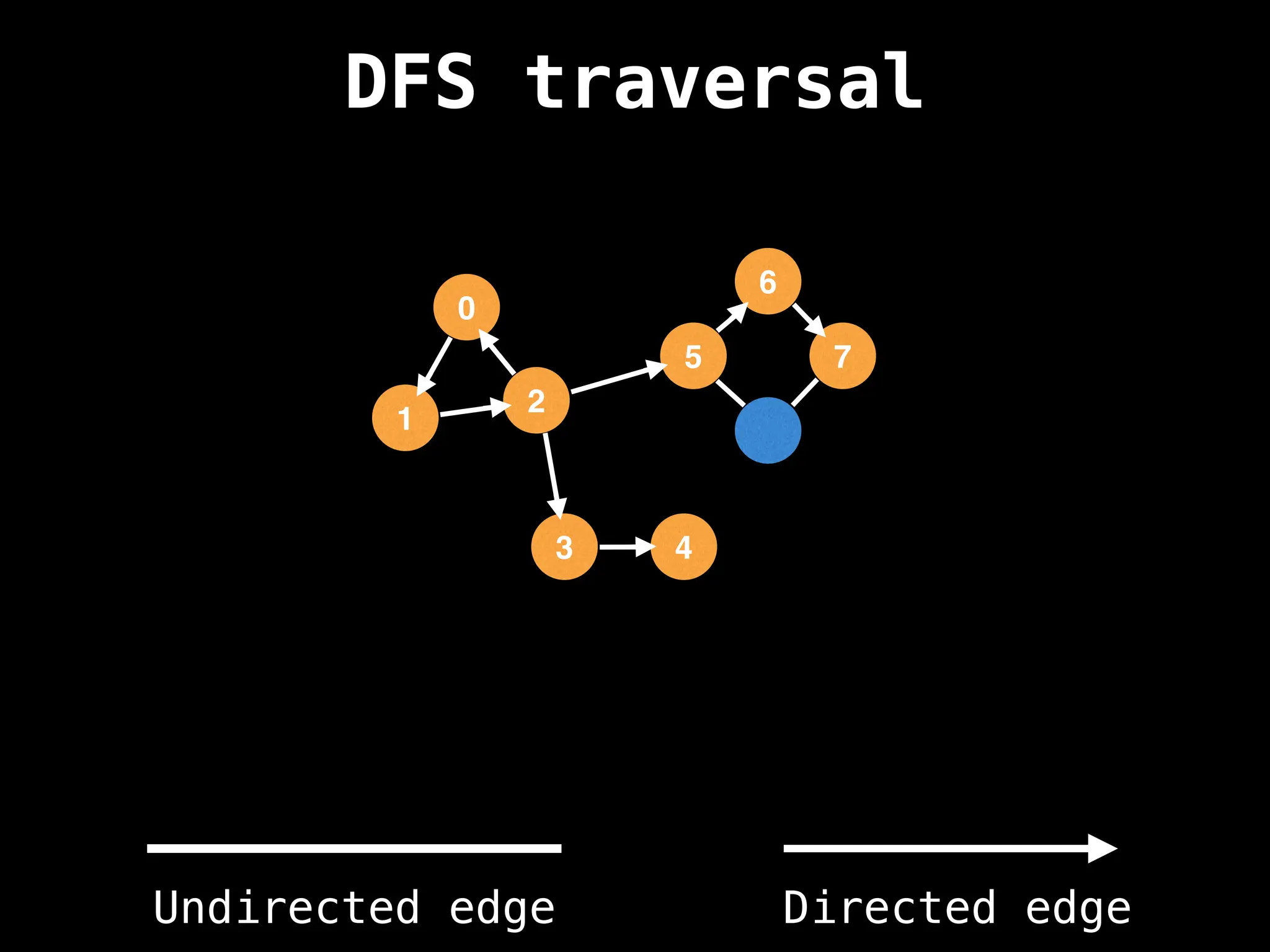
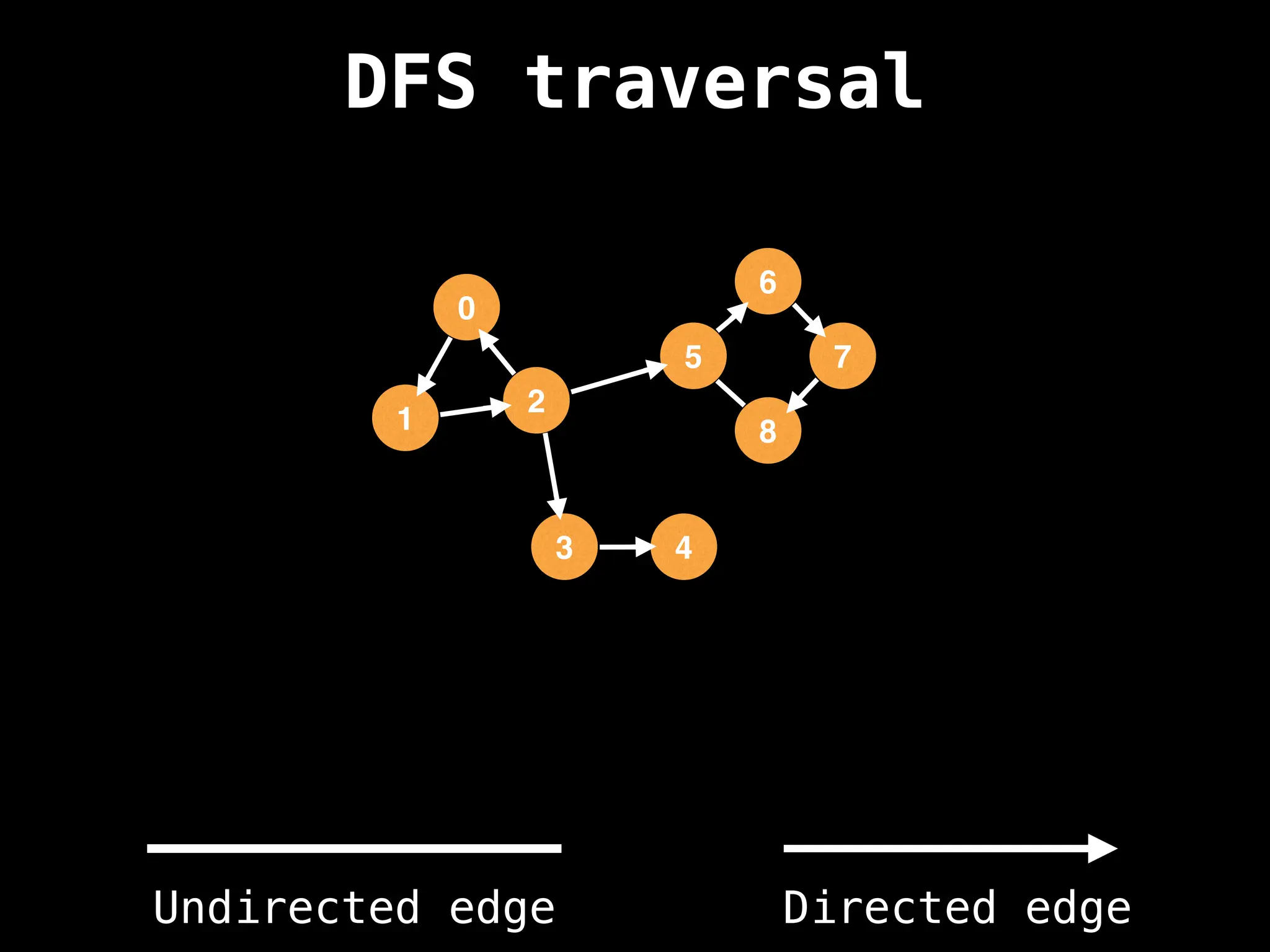
![0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-802-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
Initially all low-link values can be
initialized to the node ids.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-803-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 1 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 1.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-804-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 1 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 1.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-805-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 1 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 1.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-806-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 1 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 1.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-807-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 1 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 1.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-808-2048.jpg)
![0
1
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 1 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 1.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-809-2048.jpg)
![0
0
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 1 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 1.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-810-2048.jpg)
![0
0
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 2 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 2.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-811-2048.jpg)
![0
0
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 2 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 2.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-812-2048.jpg)
![0
0
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 2 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 2.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-813-2048.jpg)
![0
0
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of node 2 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 2.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-814-2048.jpg)
![0
0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
The low-link value of node 2 is 0 since
node 0 is reachable from node 2.
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-815-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Cannot update low-link values for nodes
3, 4 and 5.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-816-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-817-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-818-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-819-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-820-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-821-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-822-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-823-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
6
7
8
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
0
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-824-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
5
7
8
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-825-2048.jpg)
![0
0
3 4
5
5
5
5
The low-link value of a node is defined as the
smallest [lowest] id reachable from that node
using forward and backward edges.
0
0
1
2
5
3
6
4
8
7
Node 6’s low-link value can be updated to 5
since node 5 is reachable from node 6.
Undirected edge Directed edge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-826-2048.jpg)
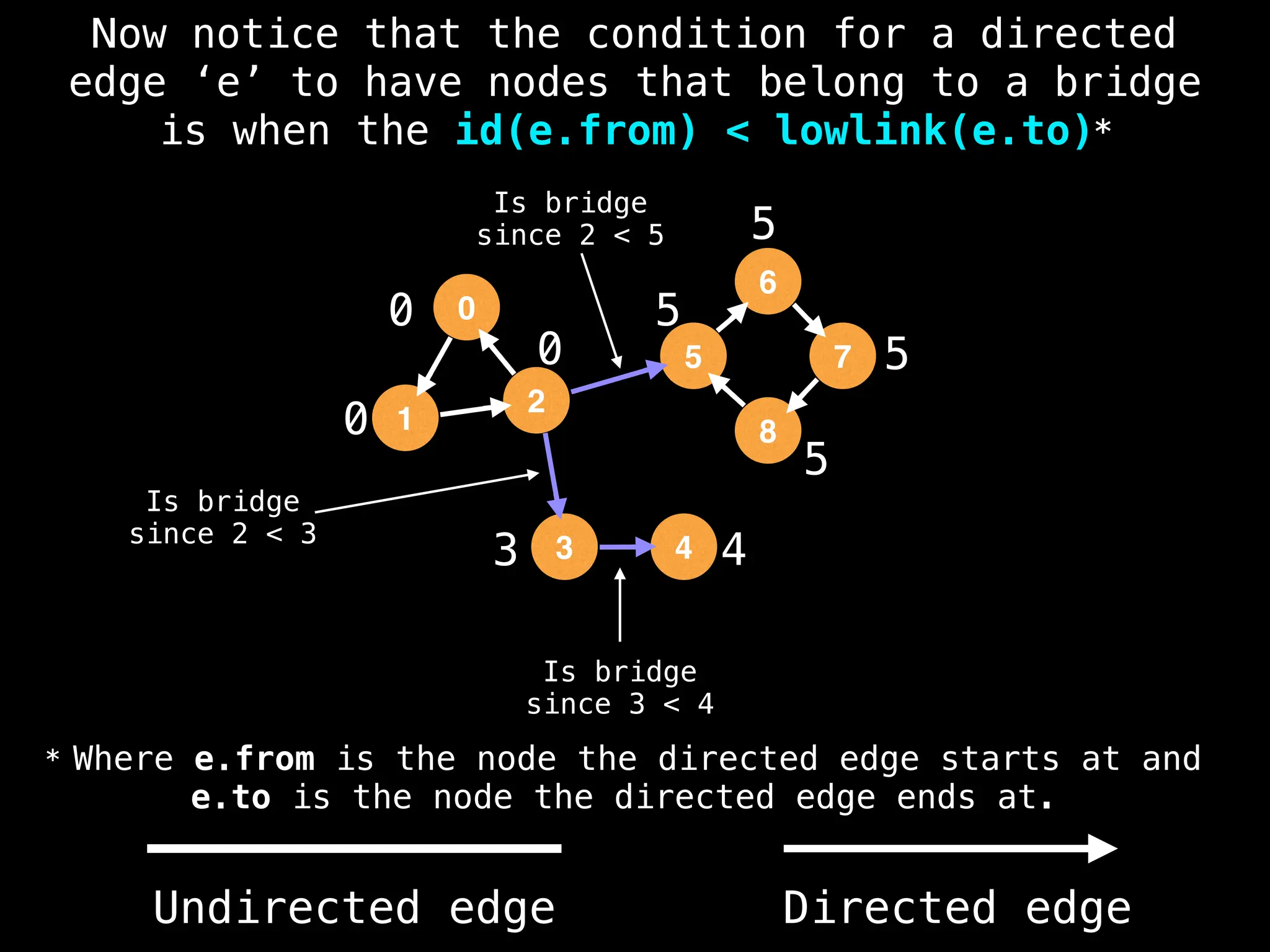
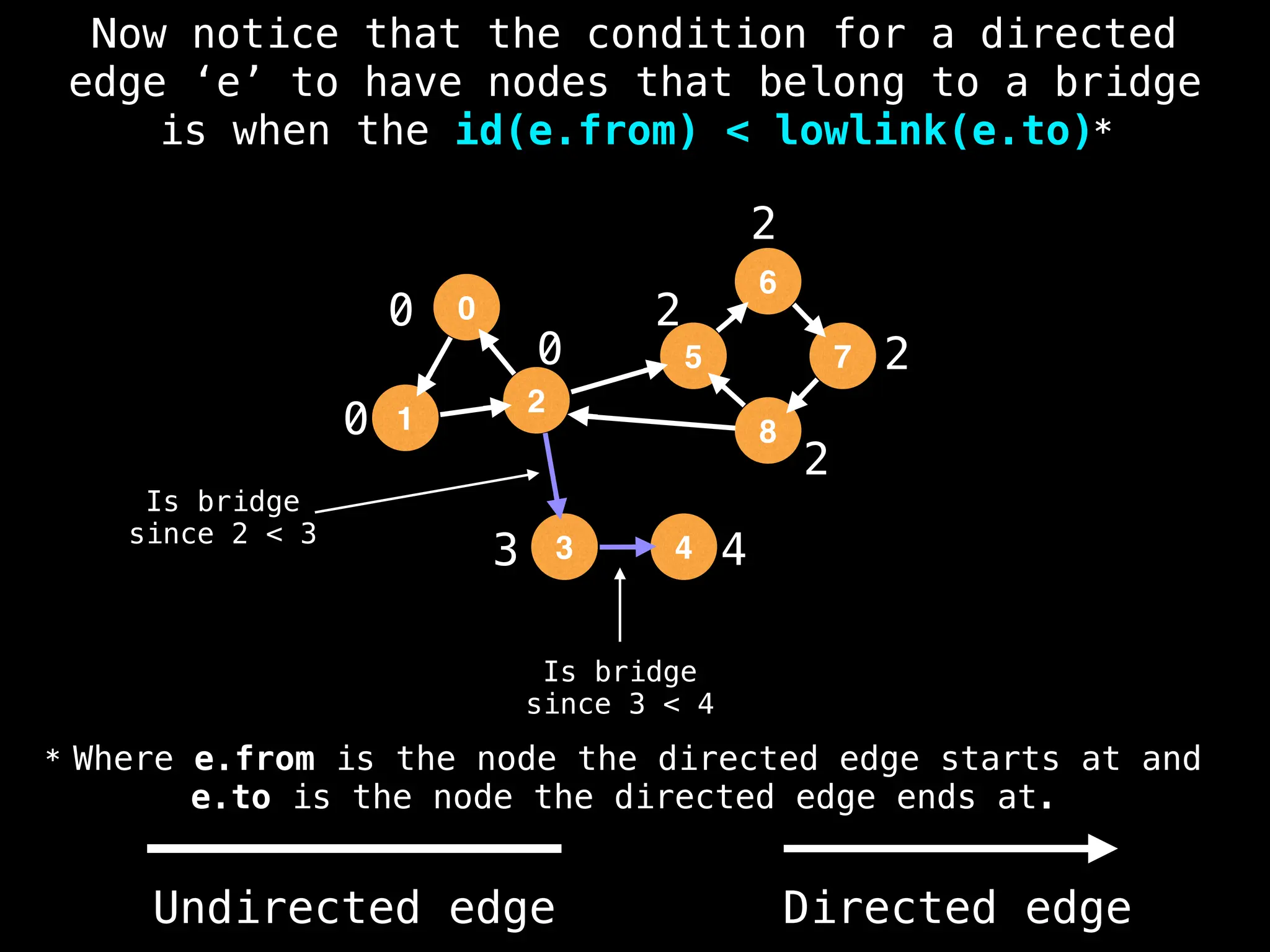

![id = 0
g = adjacency list with undirected edges
n = size of the graph
# In these arrays index i represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
visited = [false, …, false] # Length n
function findBridges():
bridges = []
# Finds all bridges in the graph across
# various connected components.
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
if (!visited[i]):
dfs(i, -1, bridges)
return bridges](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-830-2048.jpg)
![id = 0
g = adjacency list with undirected edges
n = size of the graph
# In these arrays index i represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
visited = [false, …, false] # Length n
function findBridges():
bridges = []
# Finds all bridges in the graph across
# various connected components.
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
if (!visited[i]):
dfs(i, -1, bridges)
return bridges](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-831-2048.jpg)
![# Perform Depth First Search (DFS) to find bridges.
# at = current node, parent = previous node. The
# bridges list is always of even length and indexes
# (2*i, 2*i+1) form a bridge. For example, nodes at
# indexes (0, 1) are a bridge, (2, 3) is another etc...
function dfs(at, parent, bridges):
visited[at] = true
id = id + 1
low[at] = ids[at] = id
# For each edge from node ‘at’ to node ‘to’
for (to : g[at]):
if to == parent: continue
if (!visited[to]):
dfs(to, at, bridges)
low[at] = min(low[at], low[to])
if (ids[at] < low[to]):
bridges.add(at)
bridges.add(to)
else:
low[at] = min(low[at], ids[to])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-832-2048.jpg)
![# Perform Depth First Search (DFS) to find bridges.
# at = current node, parent = previous node. The
# bridges list is always of even length and indexes
# (2*i, 2*i+1) form a bridge. For example, nodes at
# indexes (0, 1) are a bridge, (2, 3) is another etc...
function dfs(at, parent, bridges):
visited[at] = true
id = id + 1
low[at] = ids[at] = id
# For each edge from node ‘at’ to node ‘to’
for (to : g[at]):
if to == parent: continue
if (!visited[to]):
dfs(to, at, bridges)
low[at] = min(low[at], low[to])
if (ids[at] < low[to]):
bridges.add(at)
bridges.add(to)
else:
low[at] = min(low[at], ids[to])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-833-2048.jpg)
![# Perform Depth First Search (DFS) to find bridges.
# at = current node, parent = previous node. The
# bridges list is always of even length and indexes
# (2*i, 2*i+1) form a bridge. For example, nodes at
# indexes (0, 1) are a bridge, (2, 3) is another etc...
function dfs(at, parent, bridges):
visited[at] = true
id = id + 1
low[at] = ids[at] = id
# For each edge from node ‘at’ to node ‘to’
for (to : g[at]):
if to == parent: continue
if (!visited[to]):
dfs(to, at, bridges)
low[at] = min(low[at], low[to])
if (ids[at] < low[to]):
bridges.add(at)
bridges.add(to)
else:
low[at] = min(low[at], ids[to])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-834-2048.jpg)
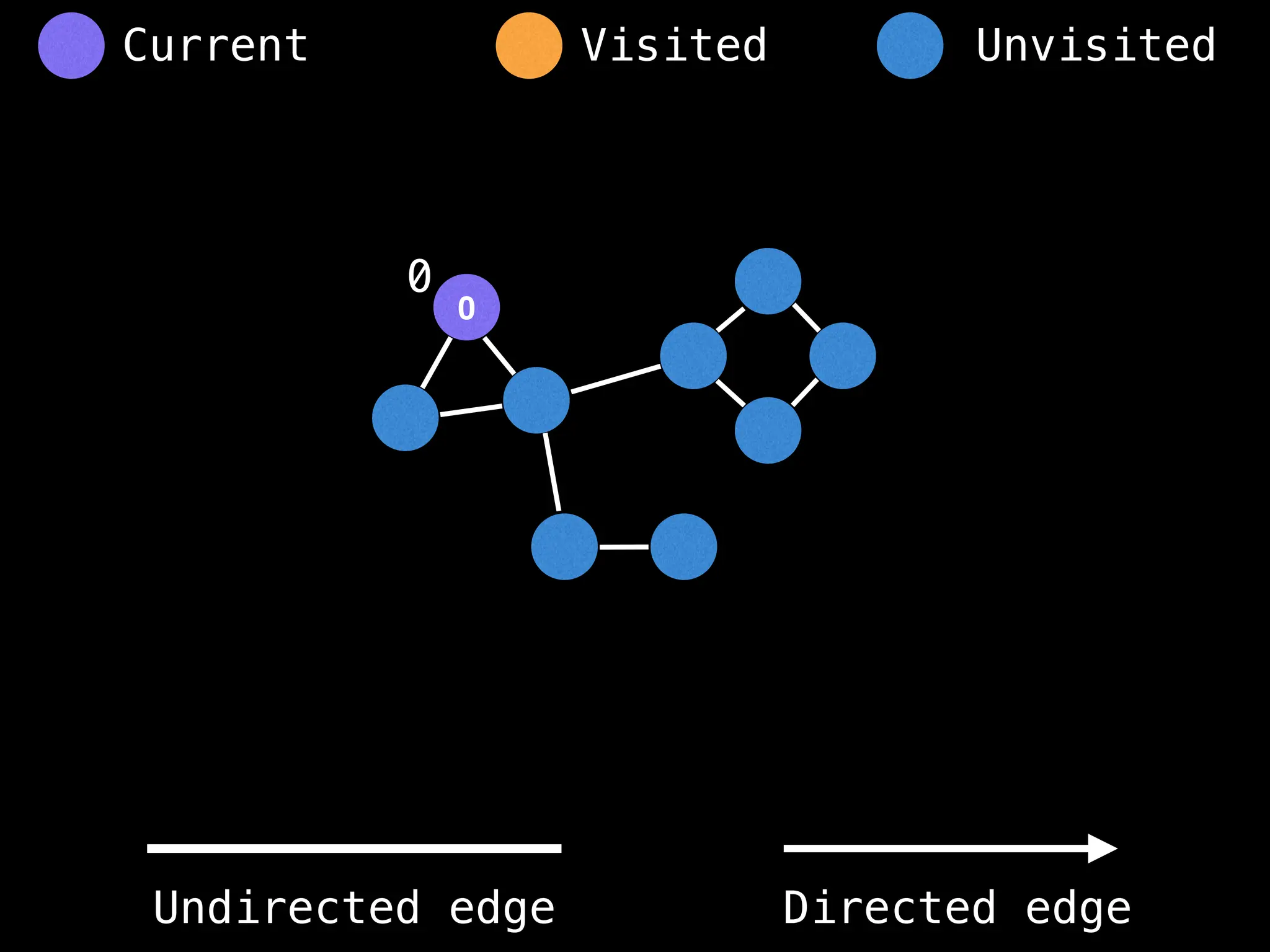
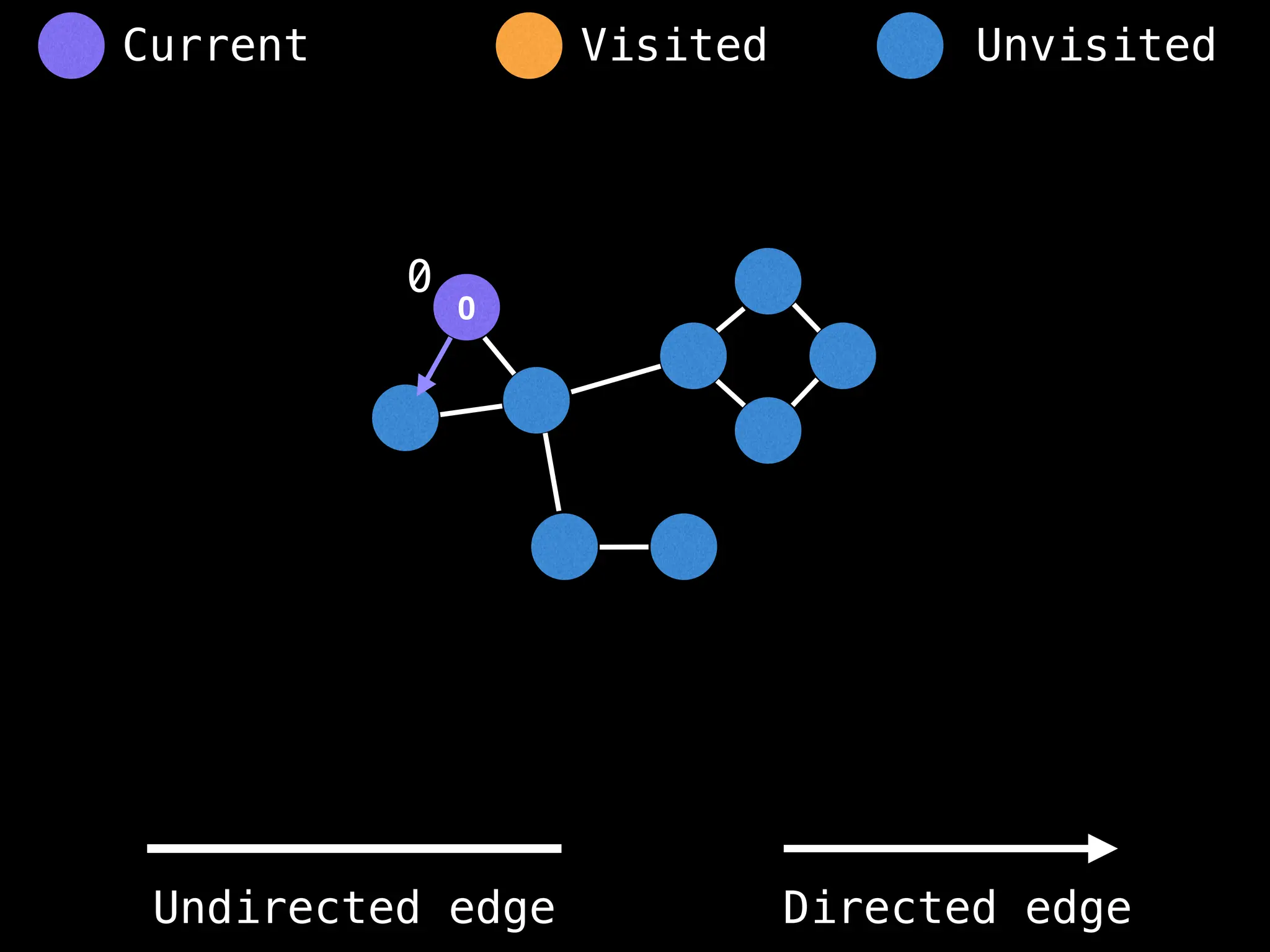
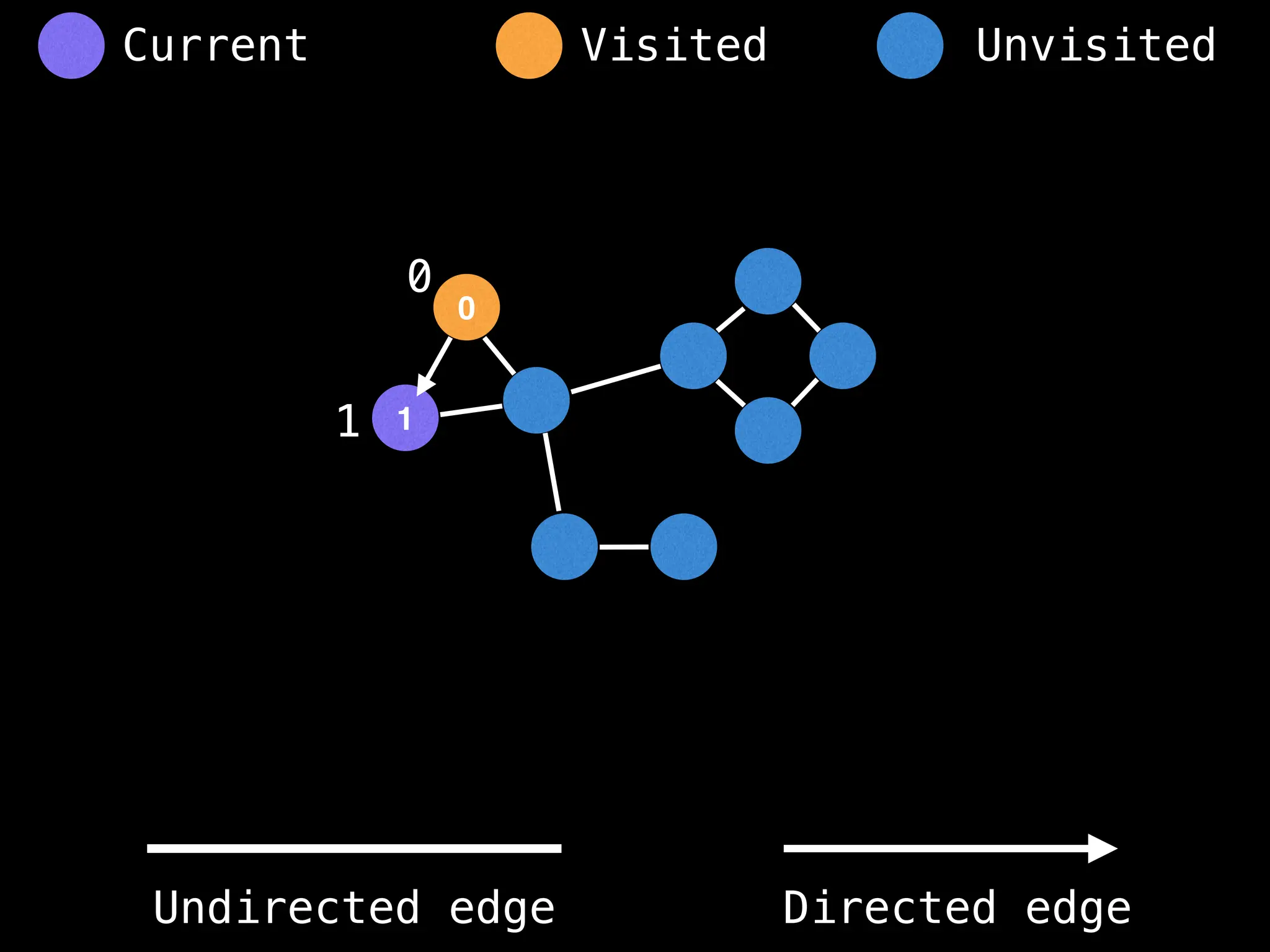
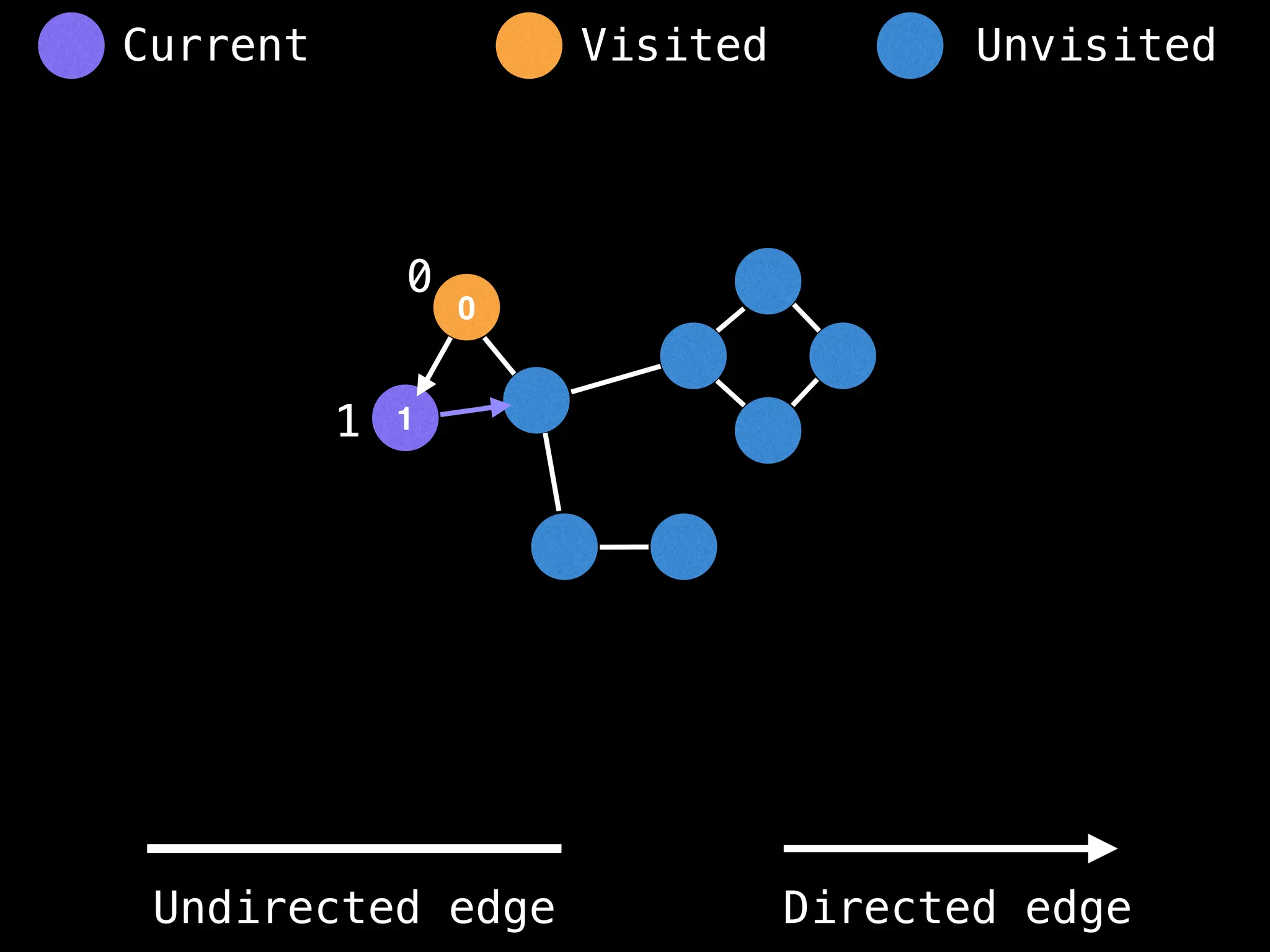
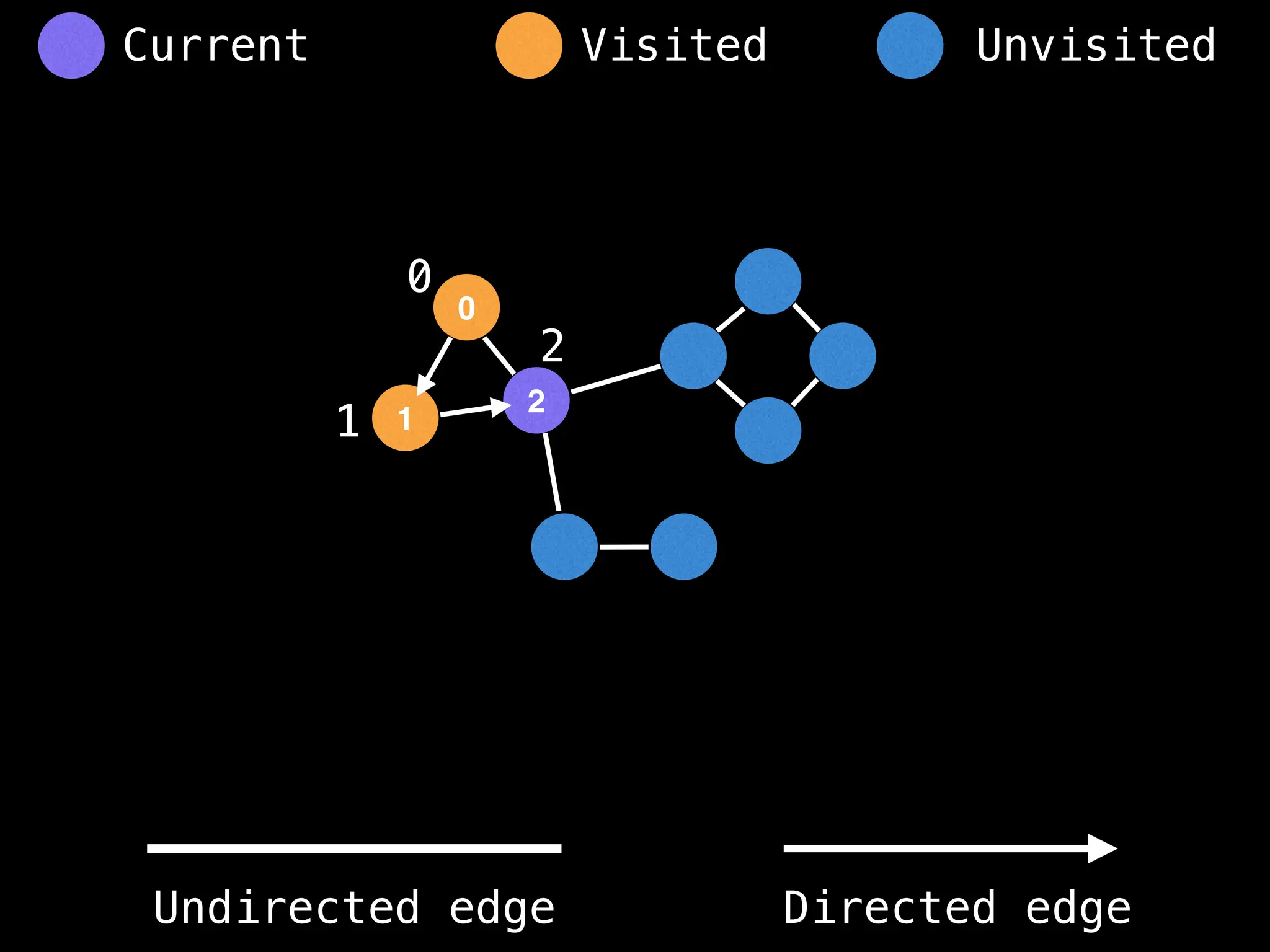
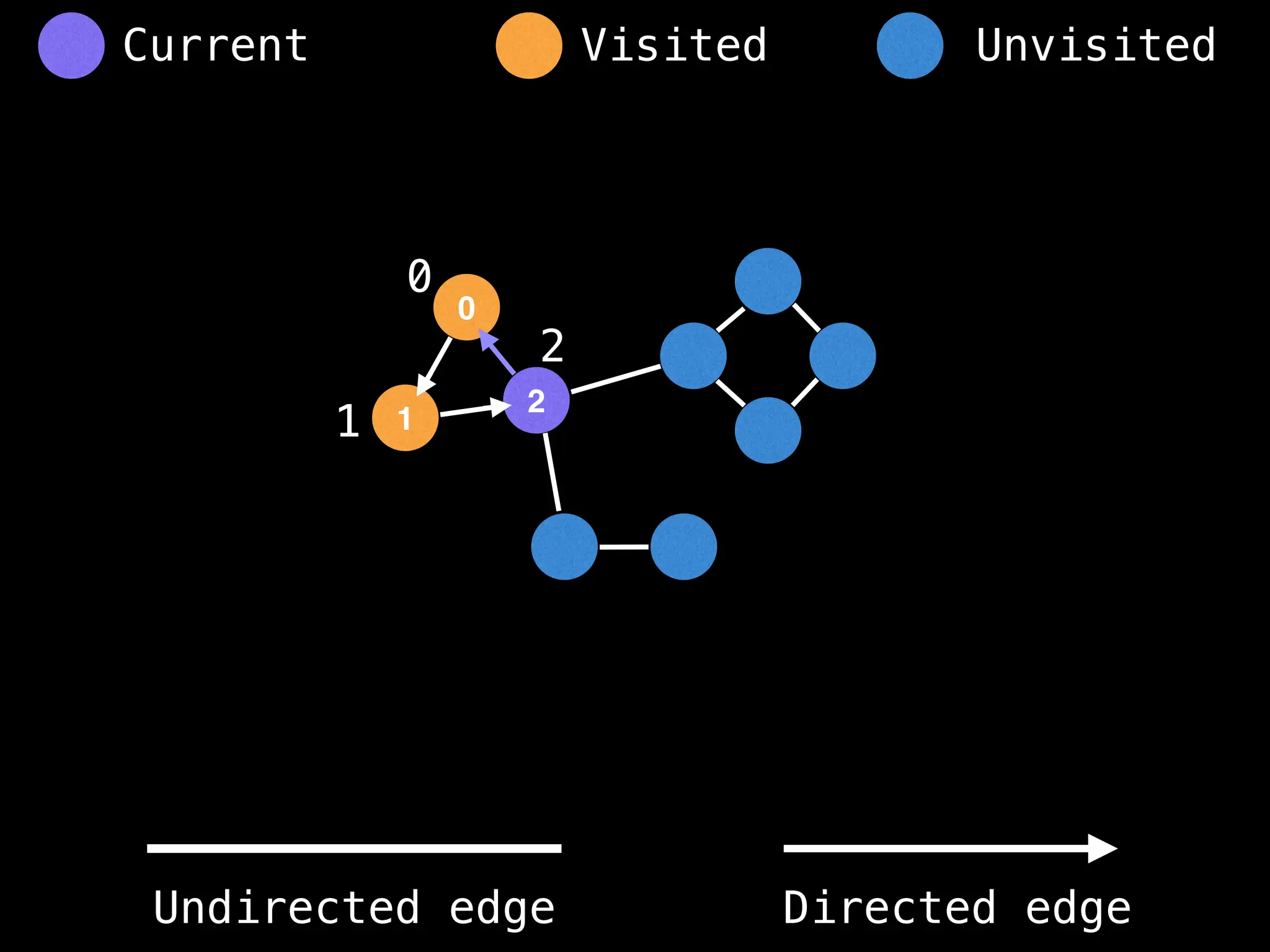
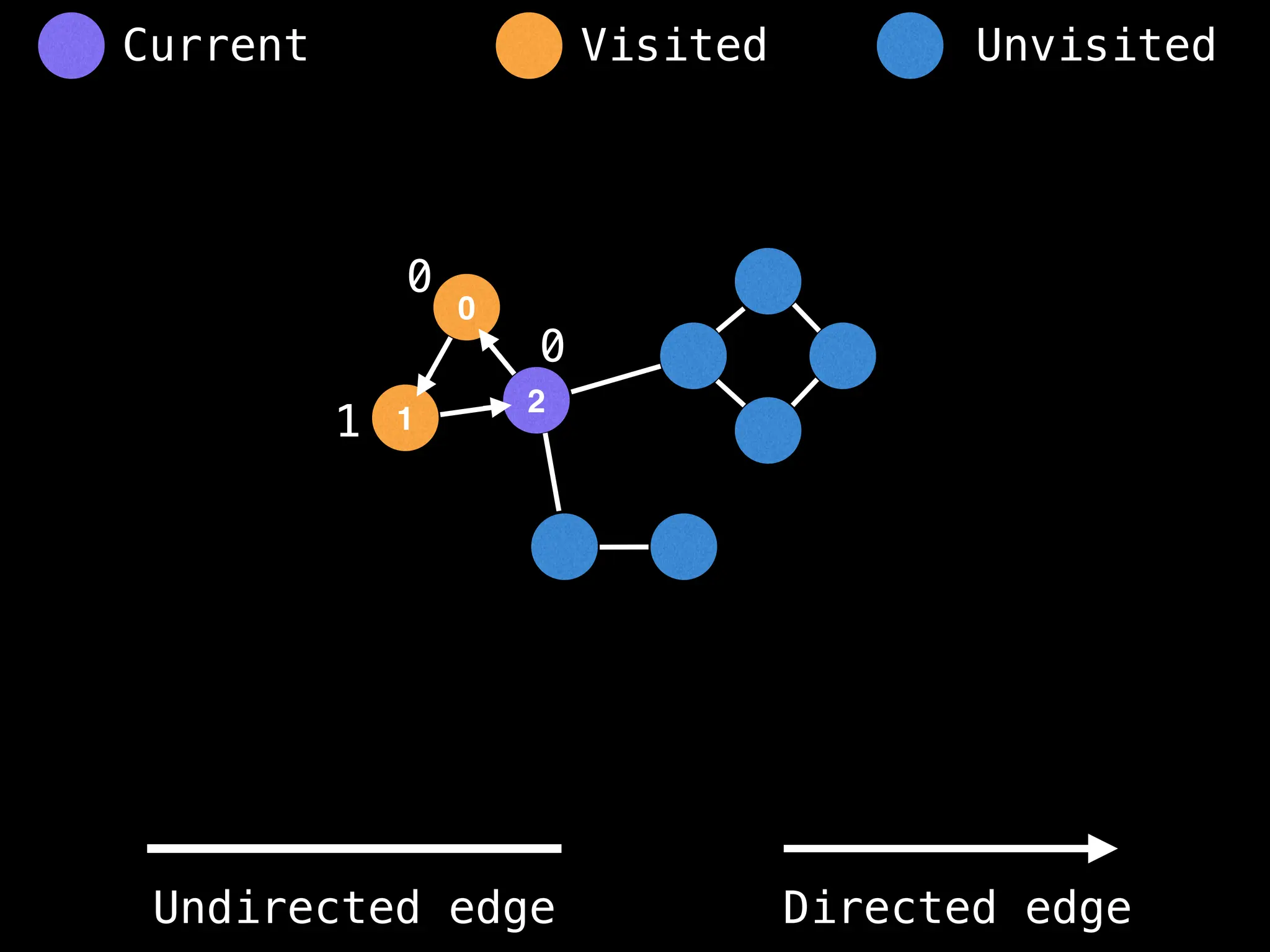
![# Perform Depth First Search (DFS) to find bridges.
# at = current node, parent = previous node. The
# bridges list is always of even length and indexes
# (2*i, 2*i+1) form a bridge. For example, nodes at
# indexes (0, 1) are a bridge, (2, 3) is another etc...
function dfs(at, parent, bridges):
visited[at] = true
id = id + 1
low[at] = ids[at] = id
# For each edge from node ‘at’ to node ‘to’
for (to : g[at]):
if to == parent: continue
if (!visited[to]):
dfs(to, at, bridges)
low[at] = min(low[at], low[to])
if (ids[at] < low[to]):
bridges.add(at)
bridges.add(to)
else:
low[at] = min(low[at], ids[to])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-843-2048.jpg)
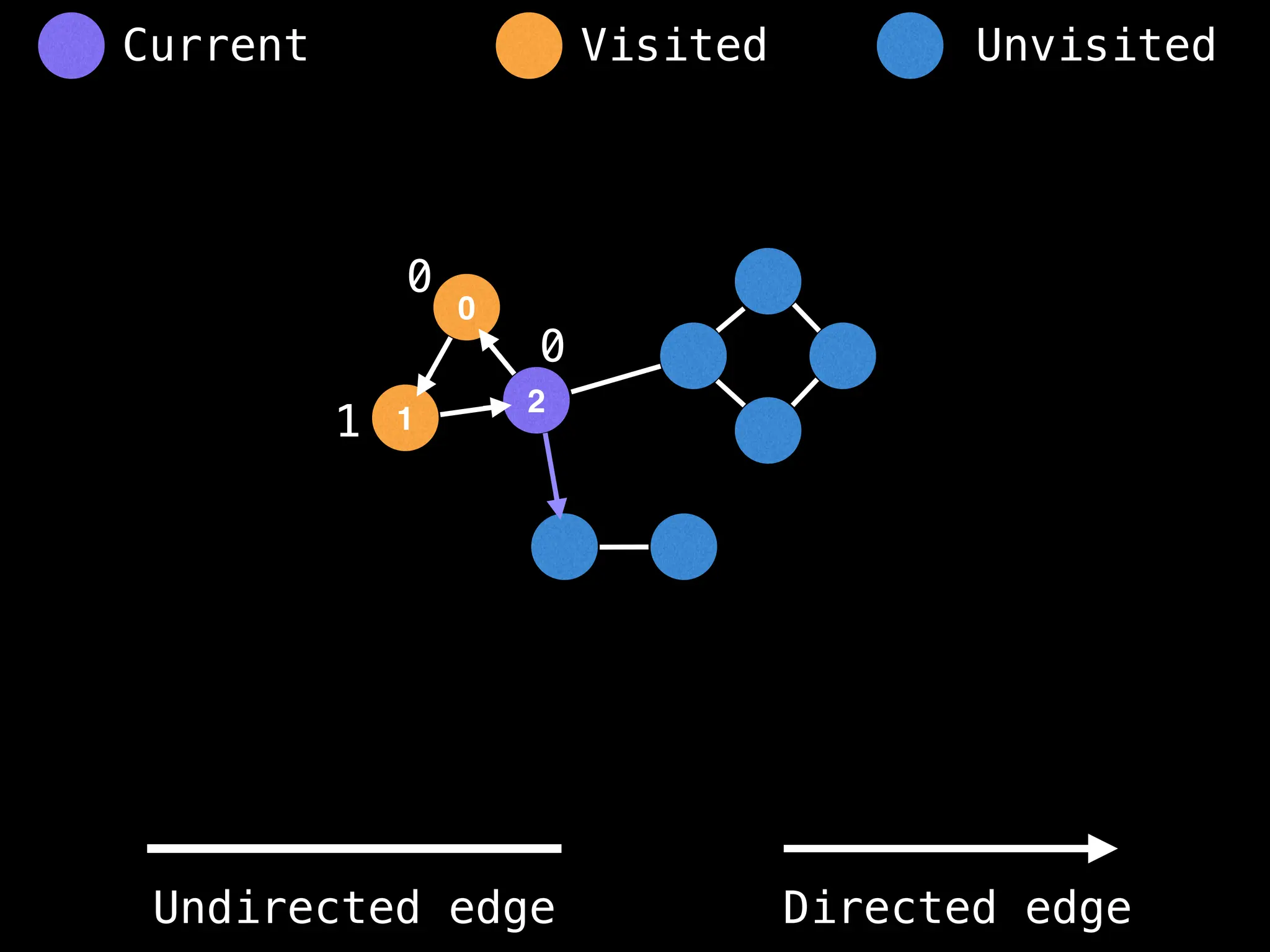
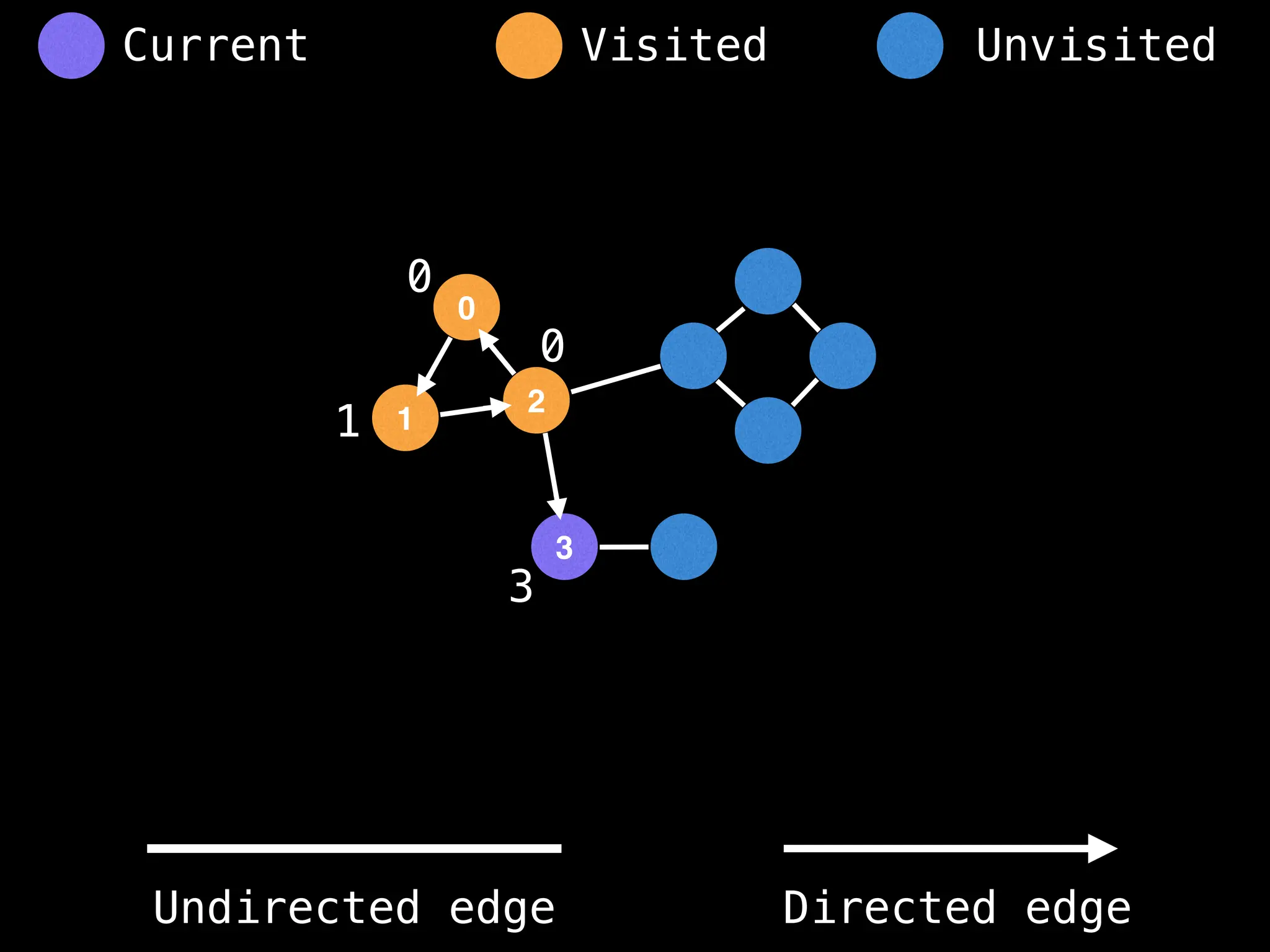
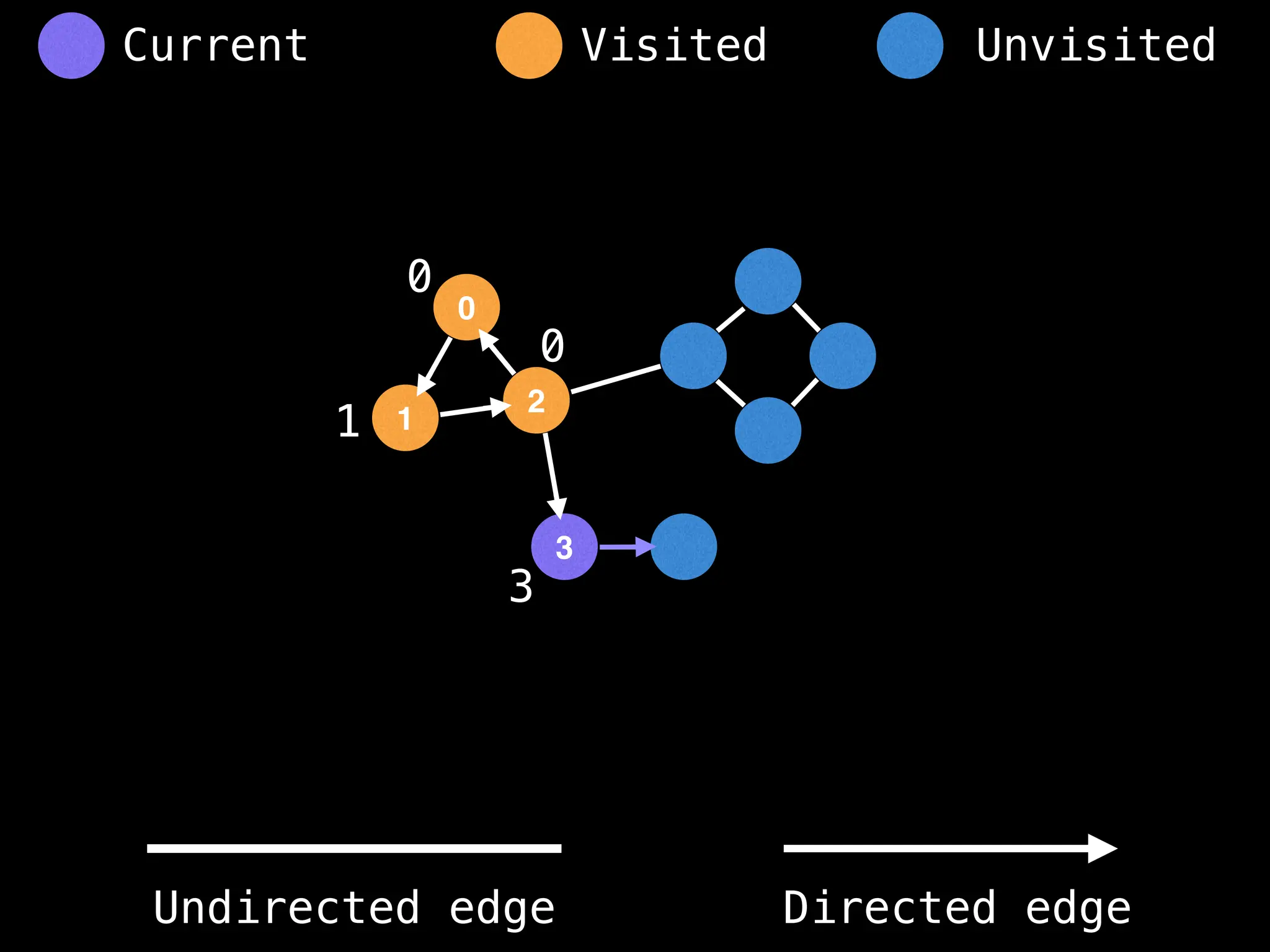
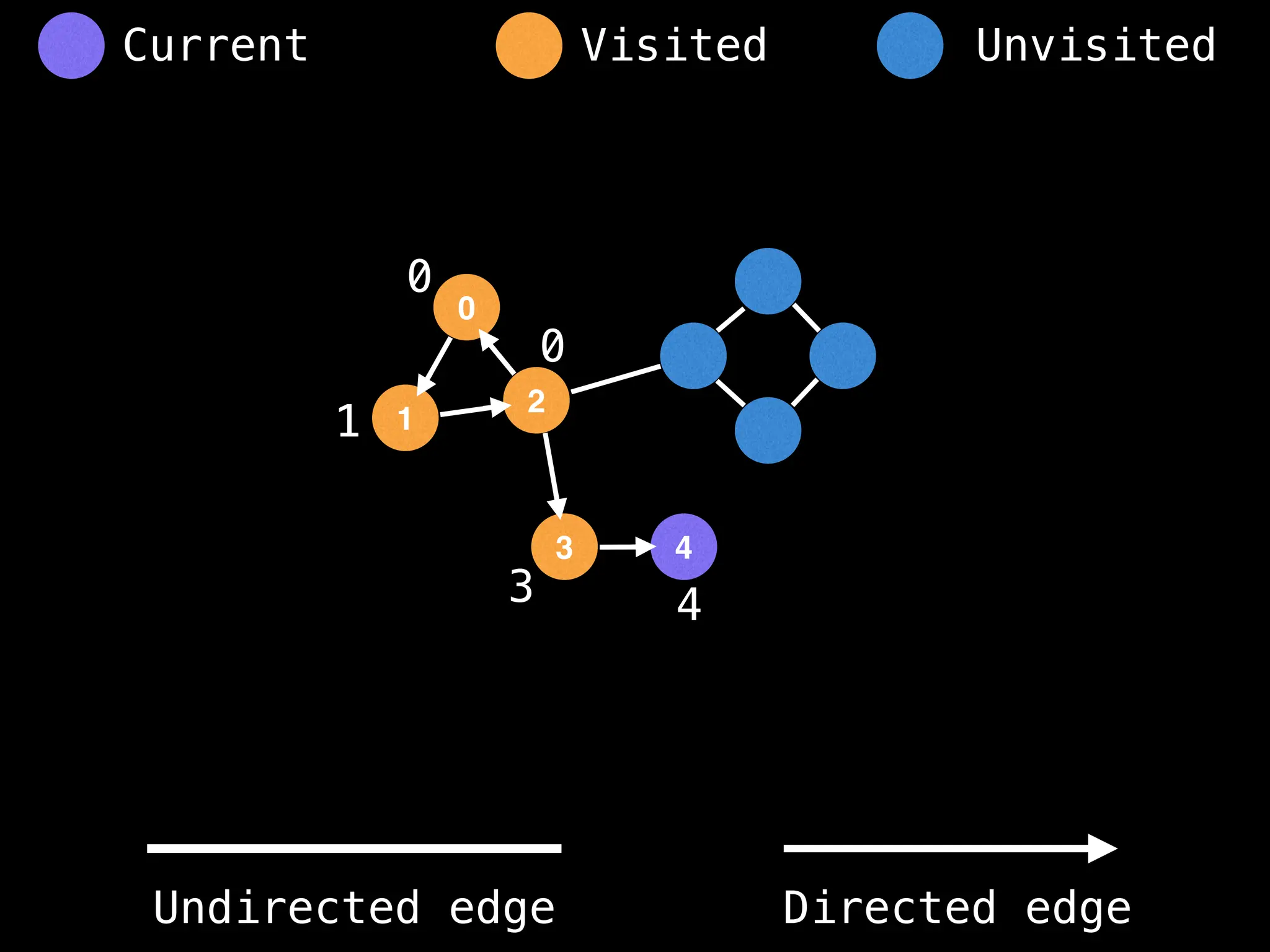
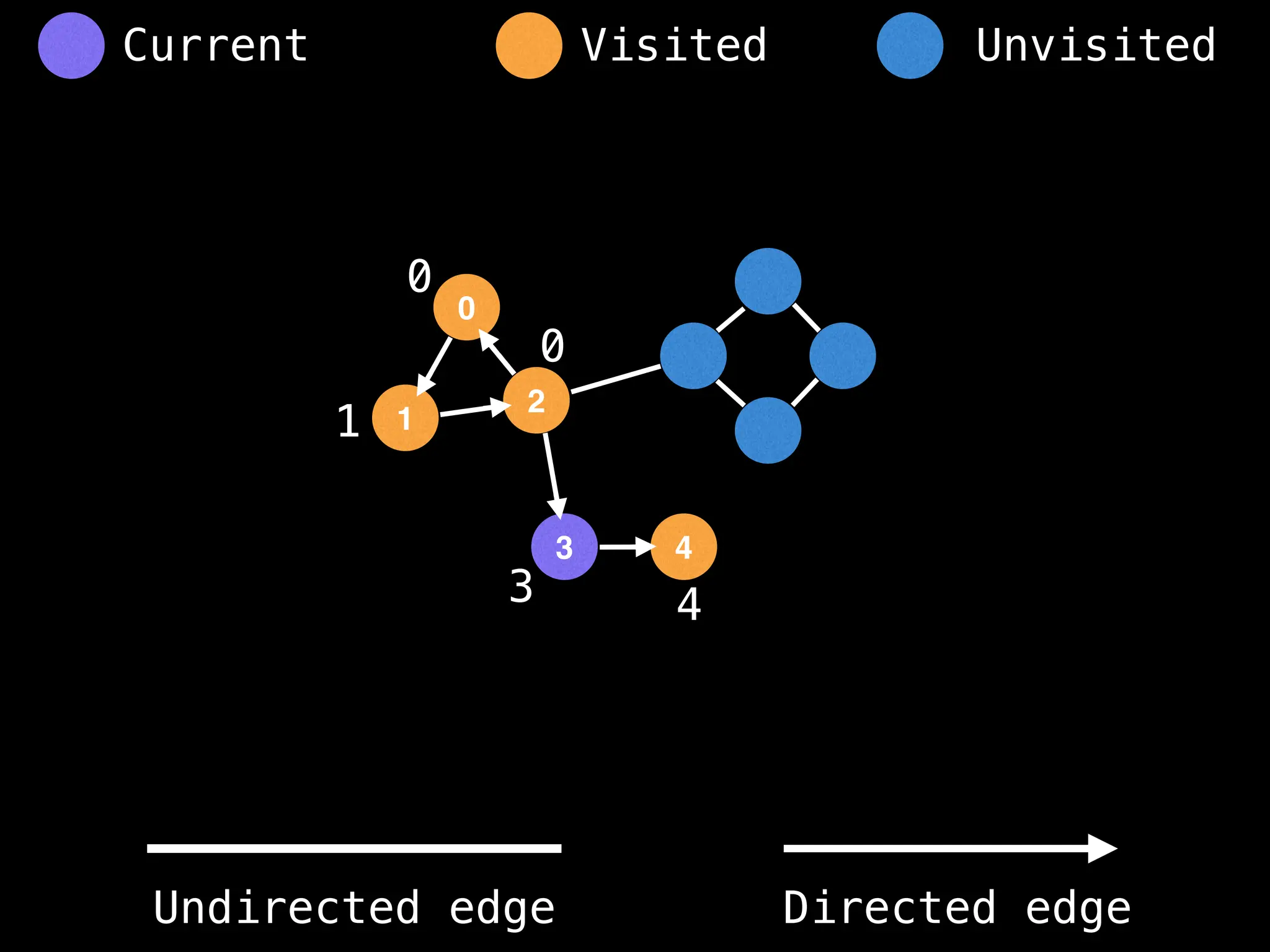
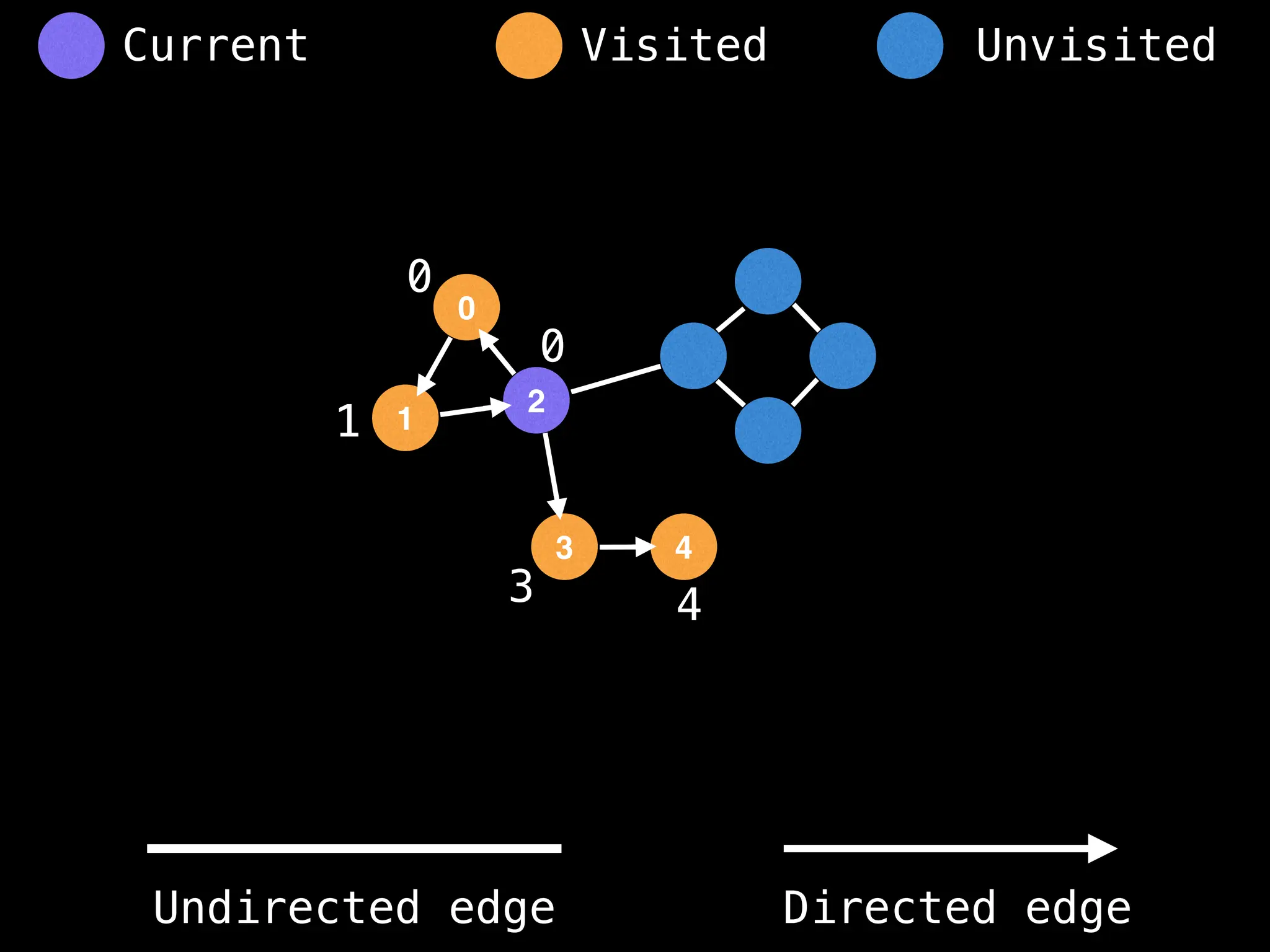
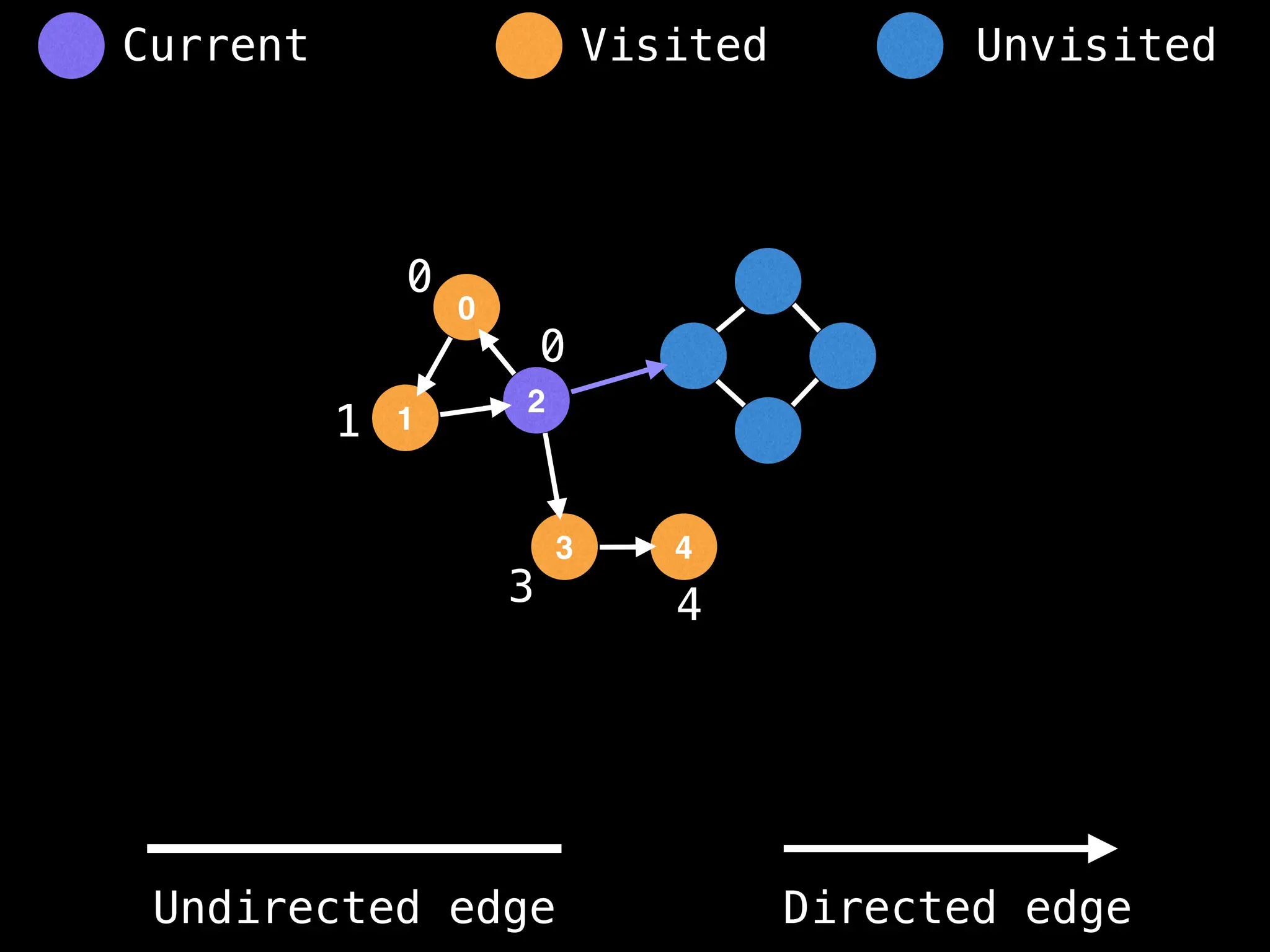
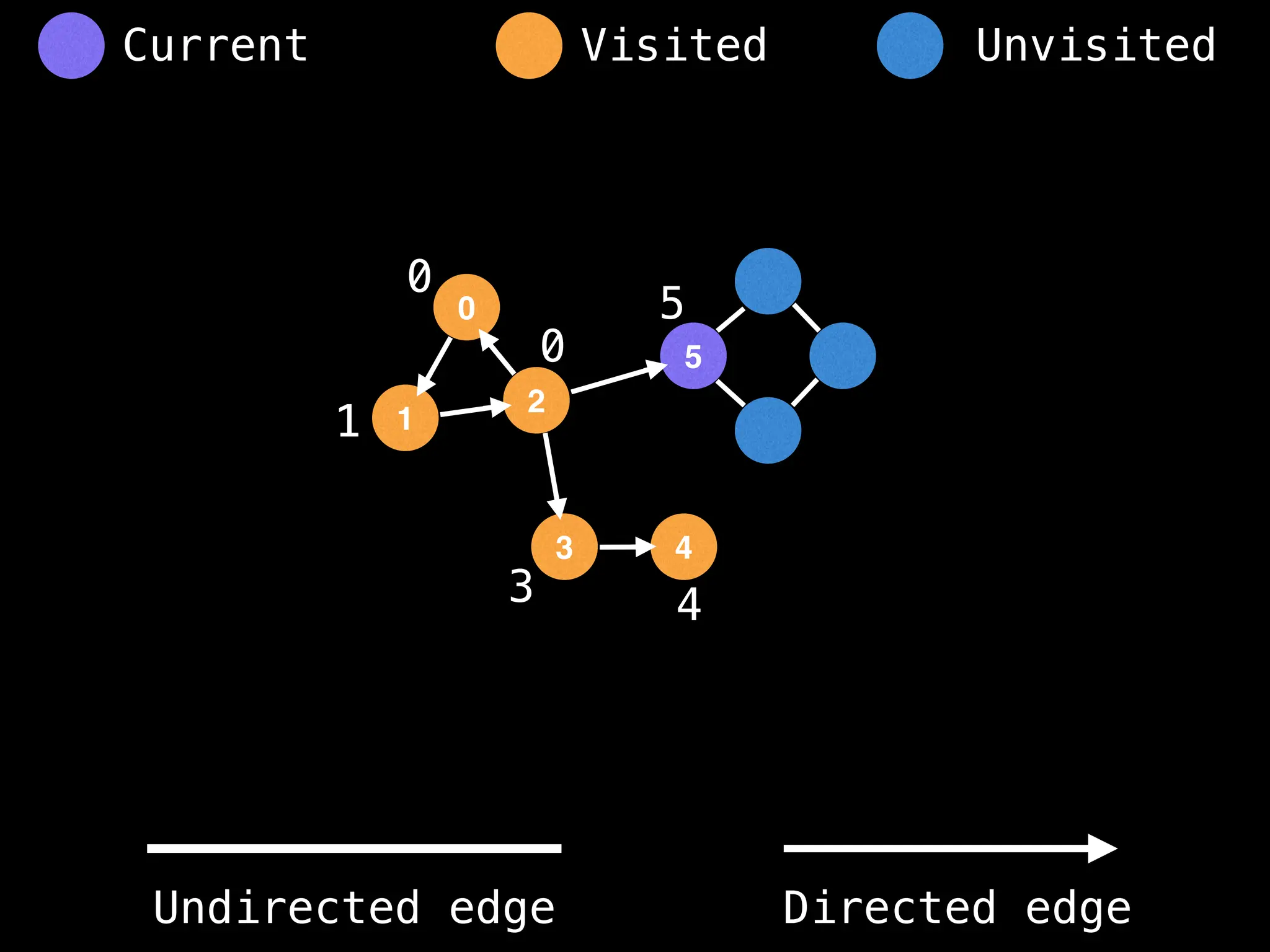
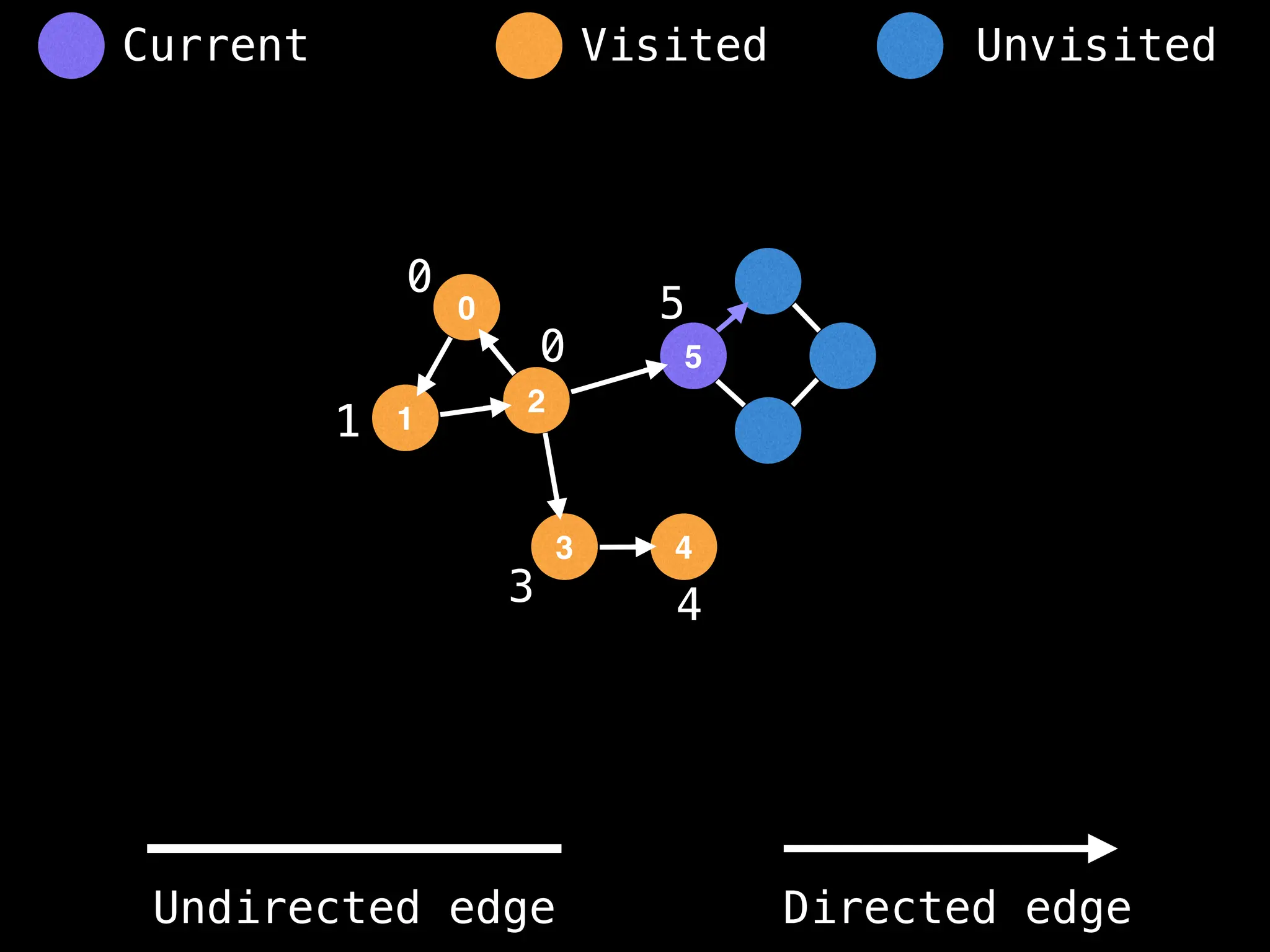
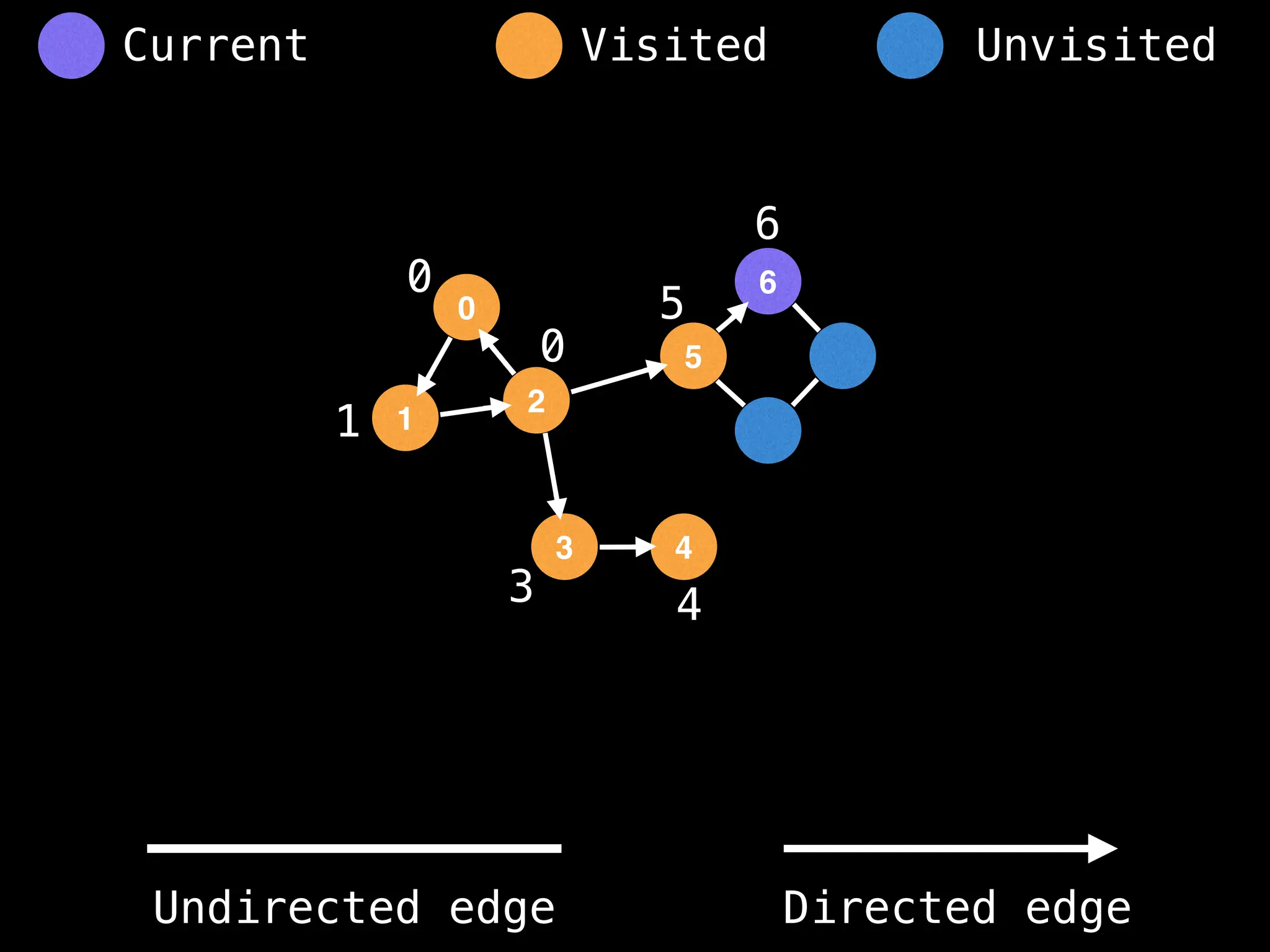
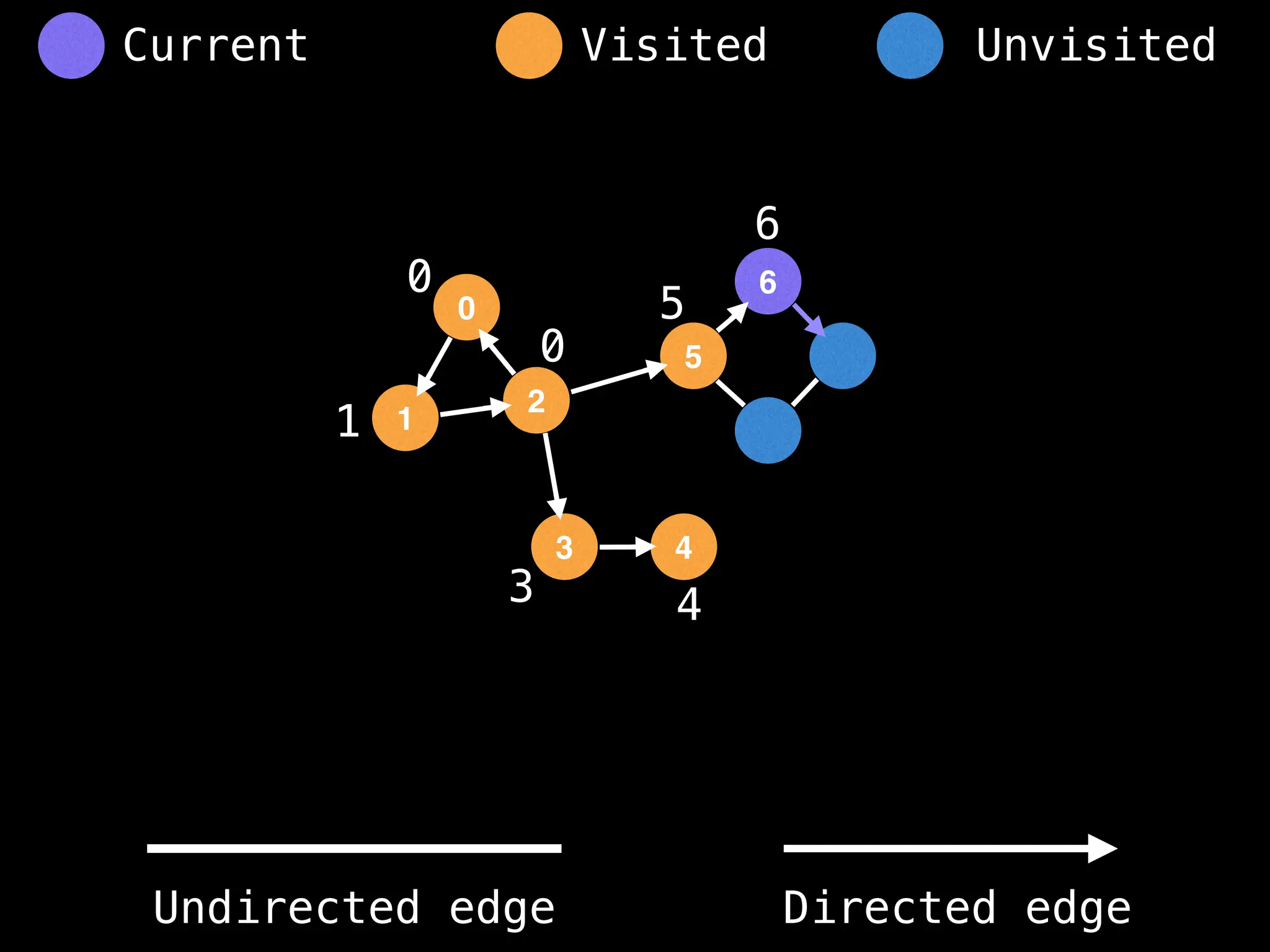
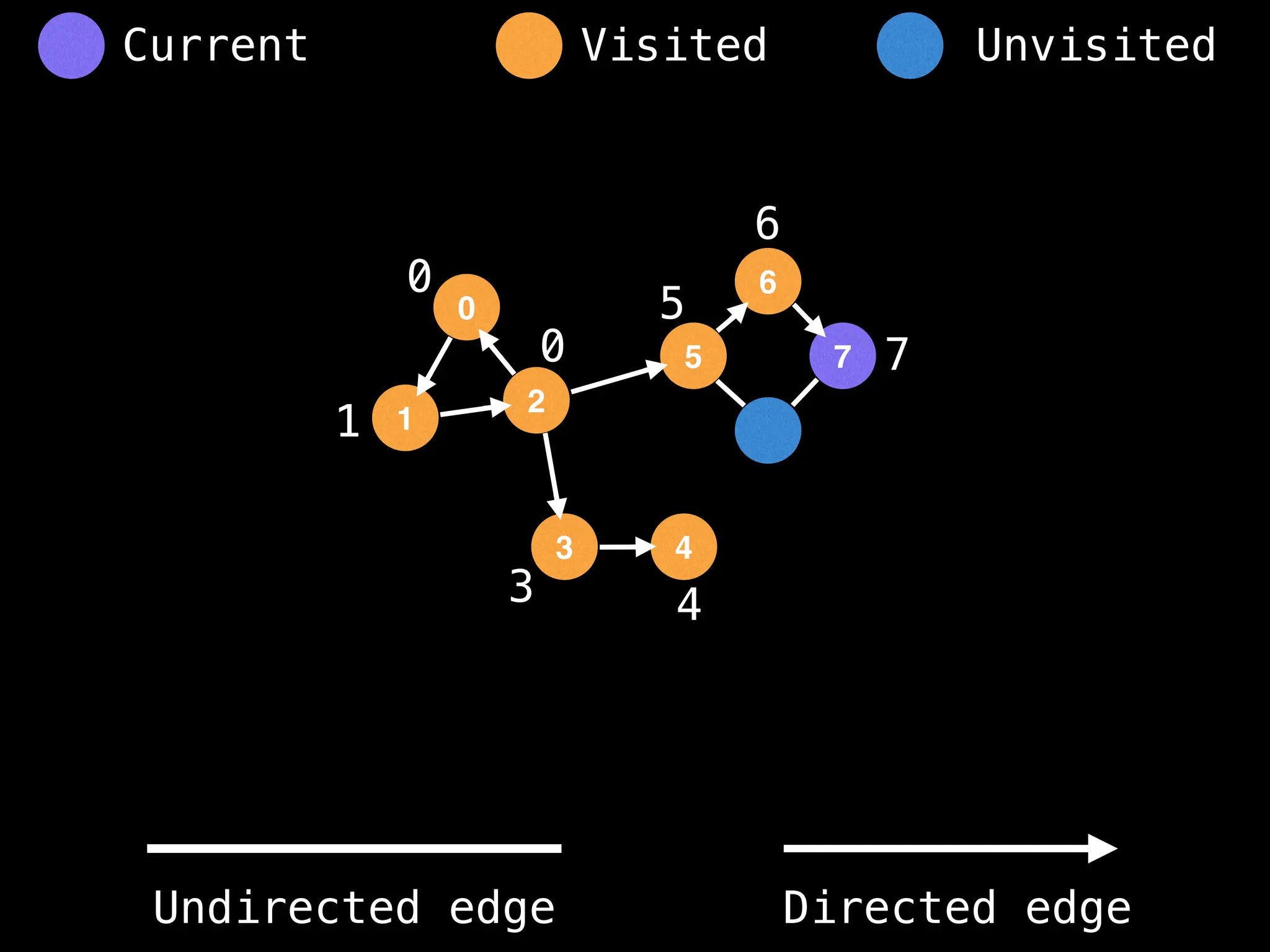
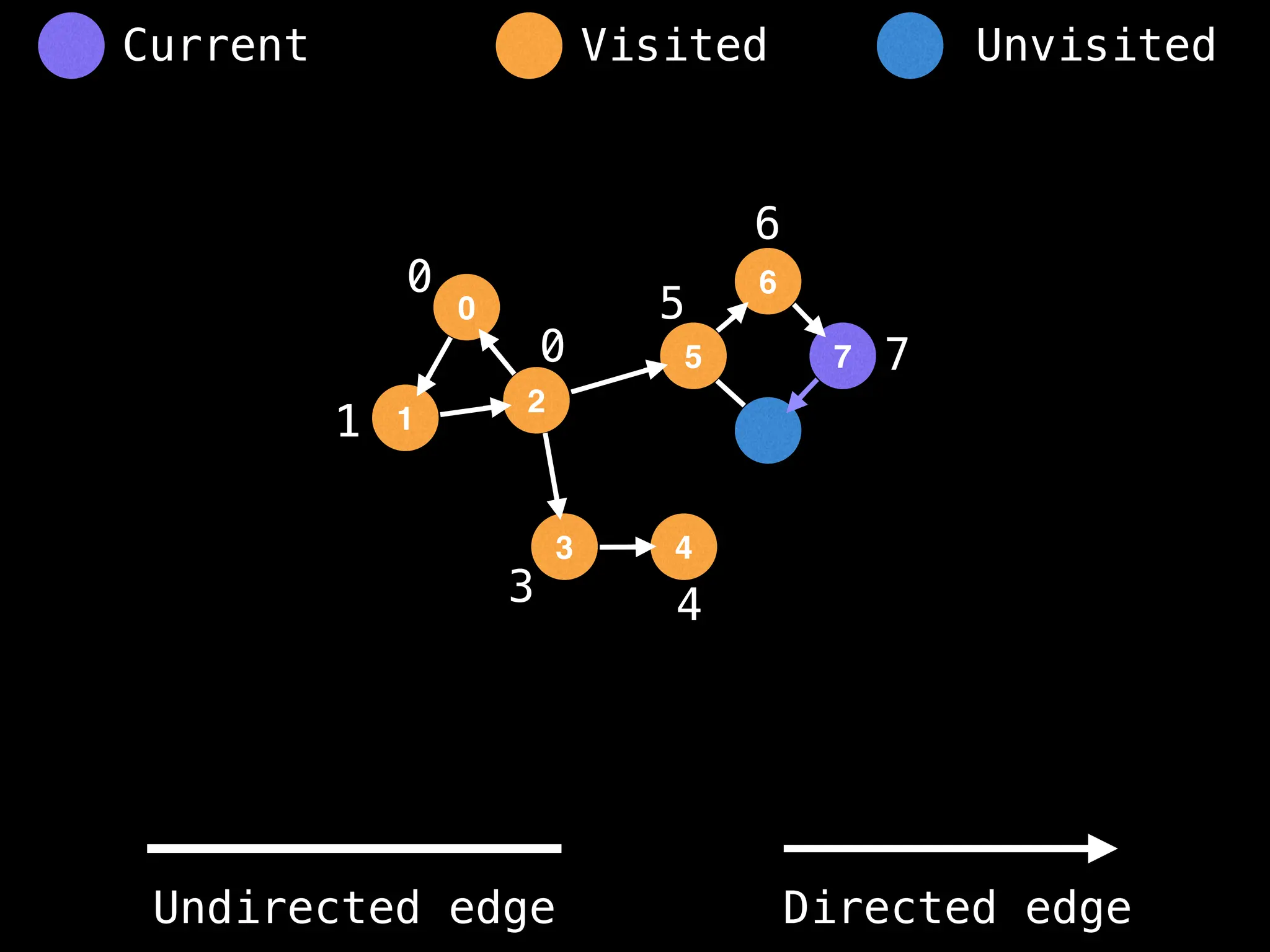
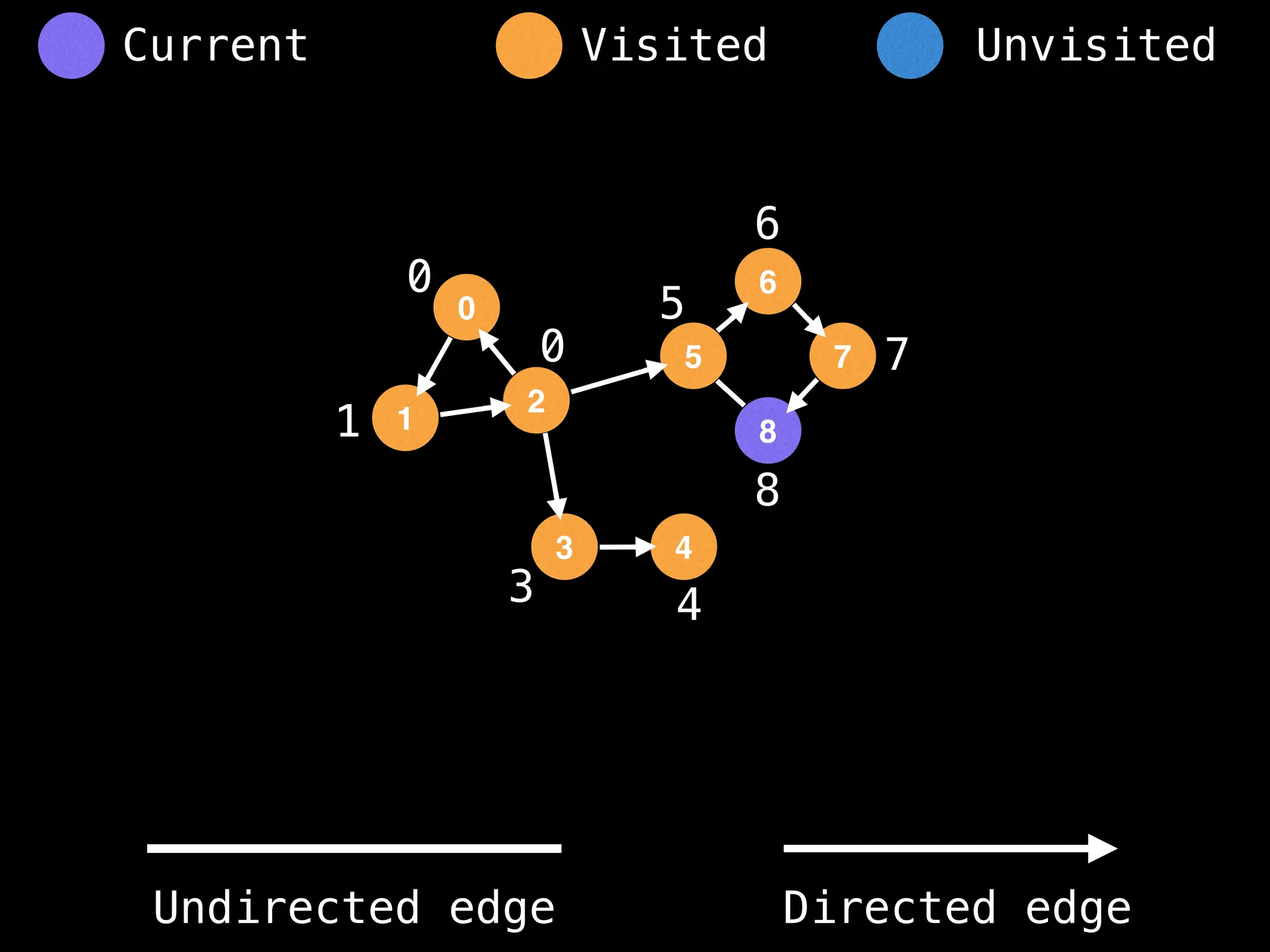
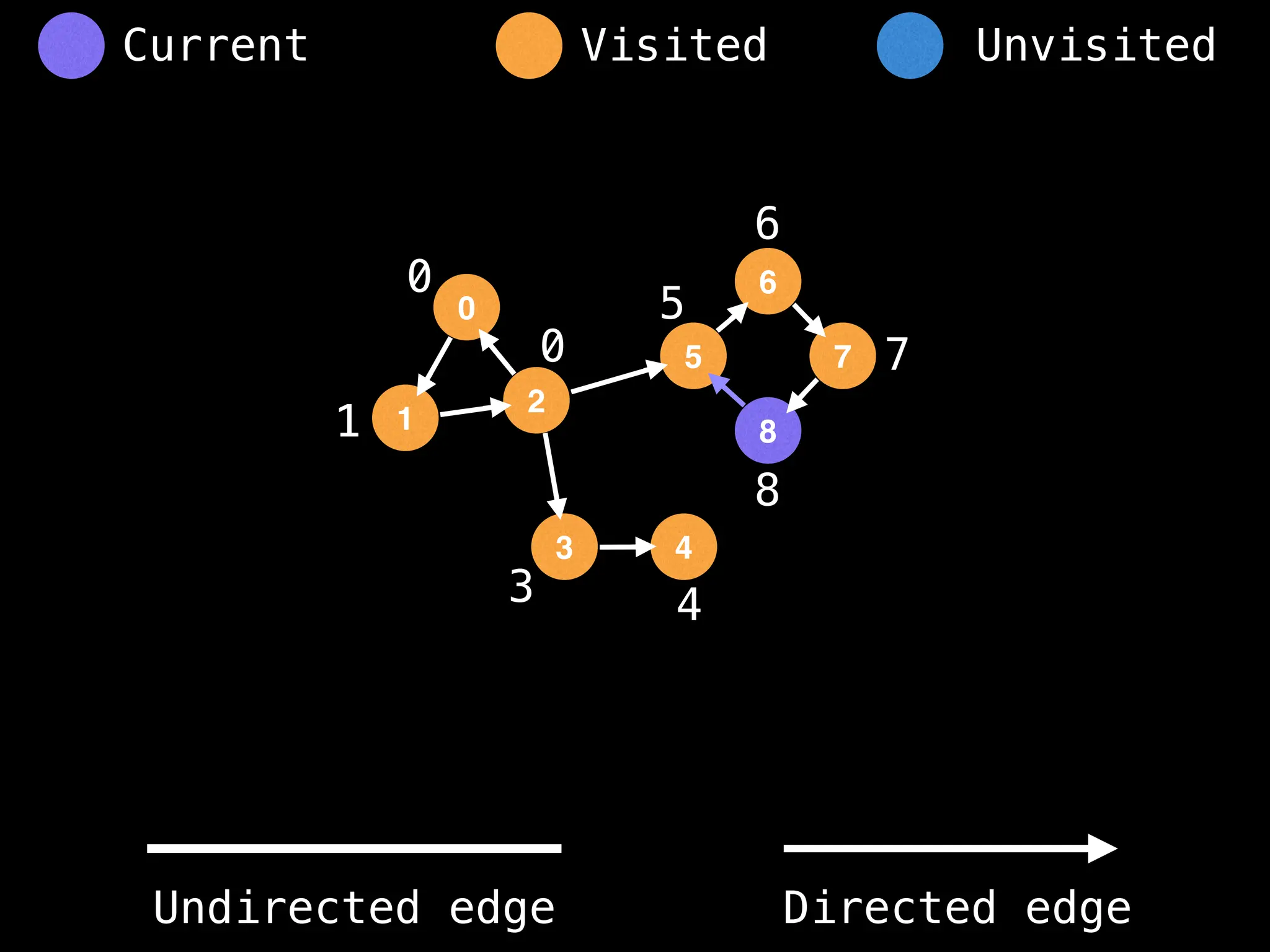
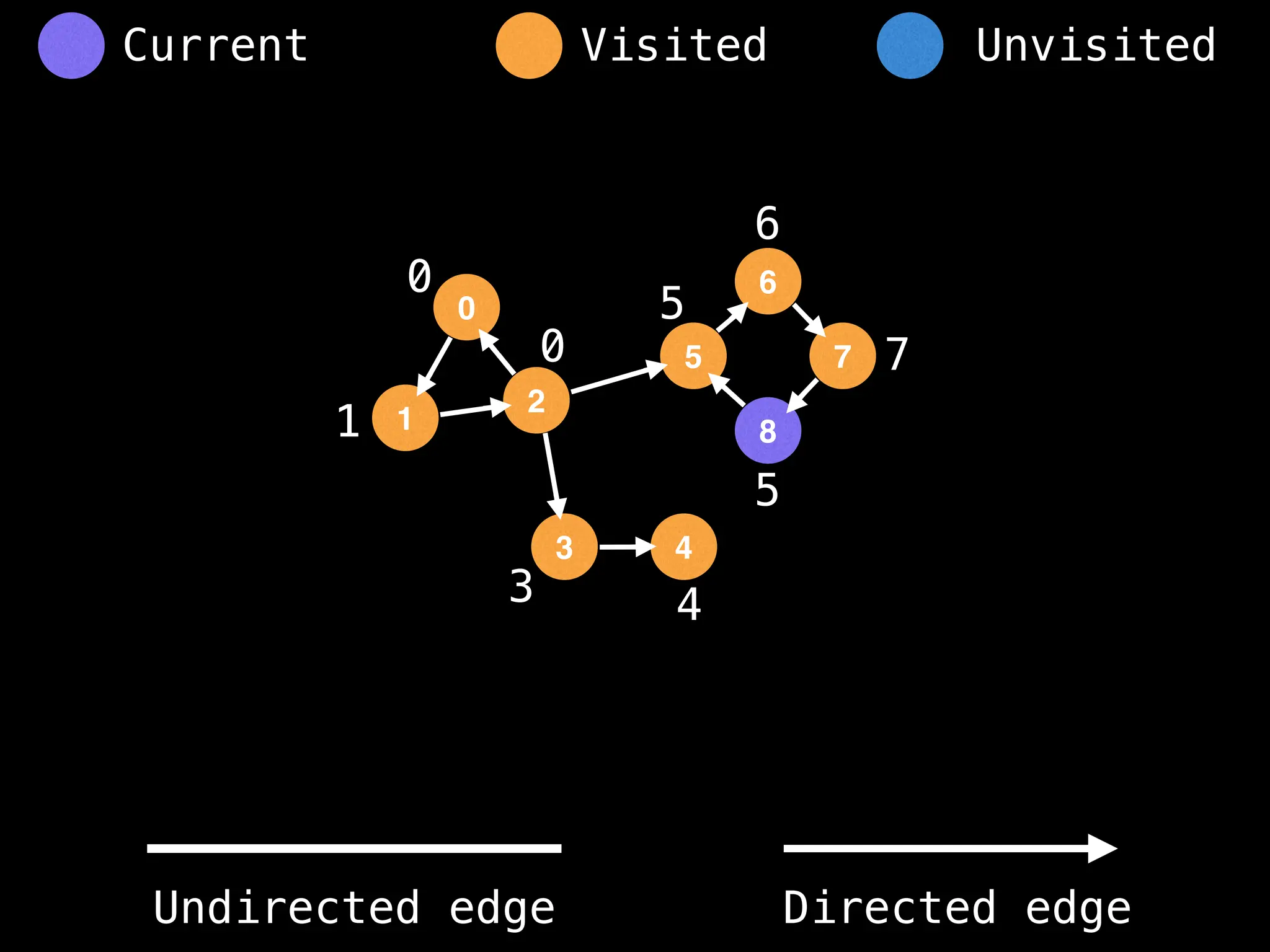
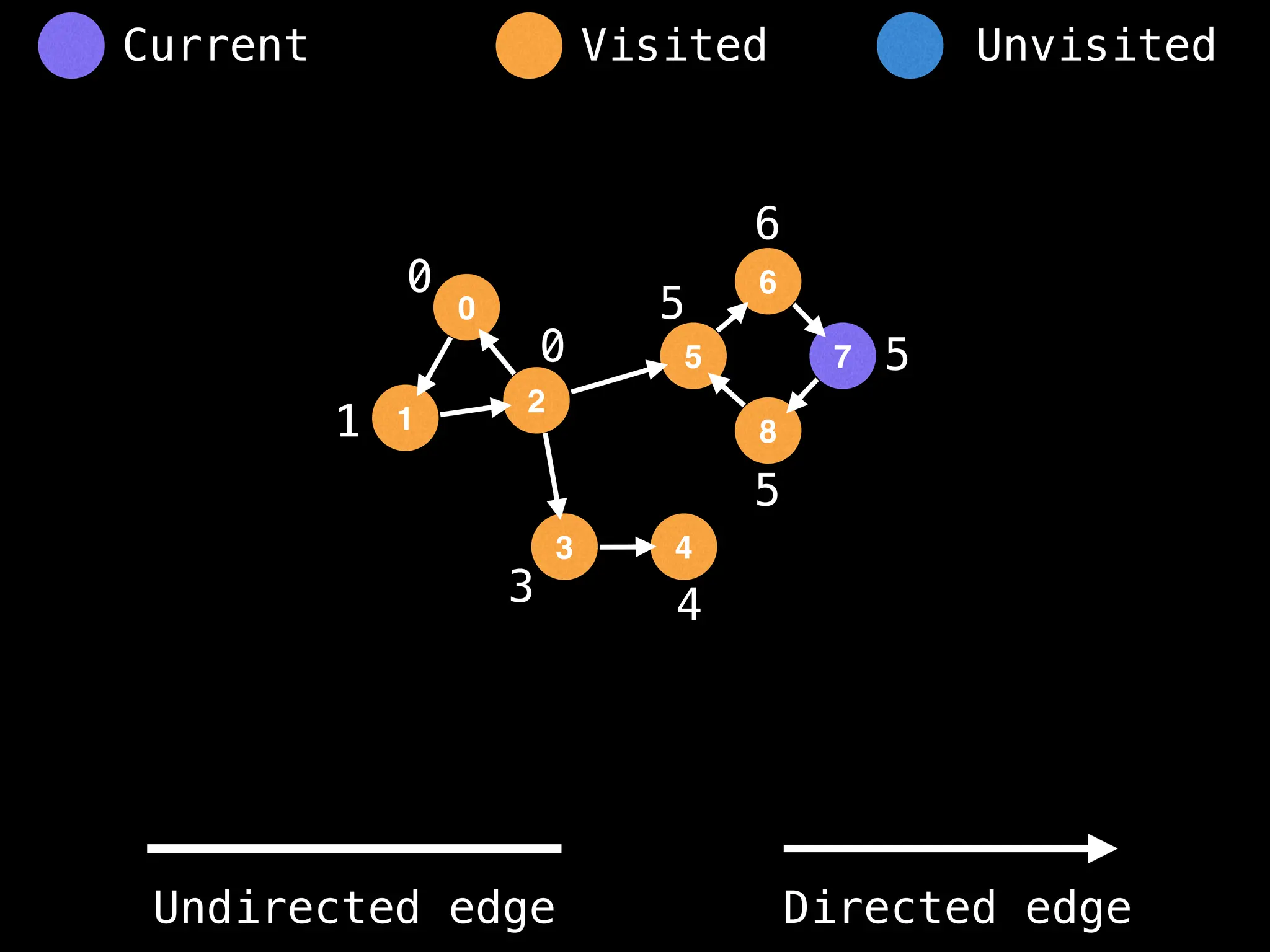
![# Perform Depth First Search (DFS) to find bridges.
# at = current node, parent = previous node. The
# bridges list is always of even length and indexes
# (2*i, 2*i+1) form a bridge. For example, nodes at
# indexes (0, 1) are a bridge, (2, 3) is another etc...
function dfs(at, parent, bridges):
visited[at] = true
id = id + 1
low[at] = ids[at] = id
# For each edge from node ‘at’ to node ‘to’
for (to : g[at]):
if to == parent: continue
if (!visited[to]):
dfs(to, at, bridges)
low[at] = min(low[at], low[to])
if (ids[at] < low[to]):
bridges.add(at)
bridges.add(to)
else:
low[at] = min(low[at], ids[to])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-861-2048.jpg)
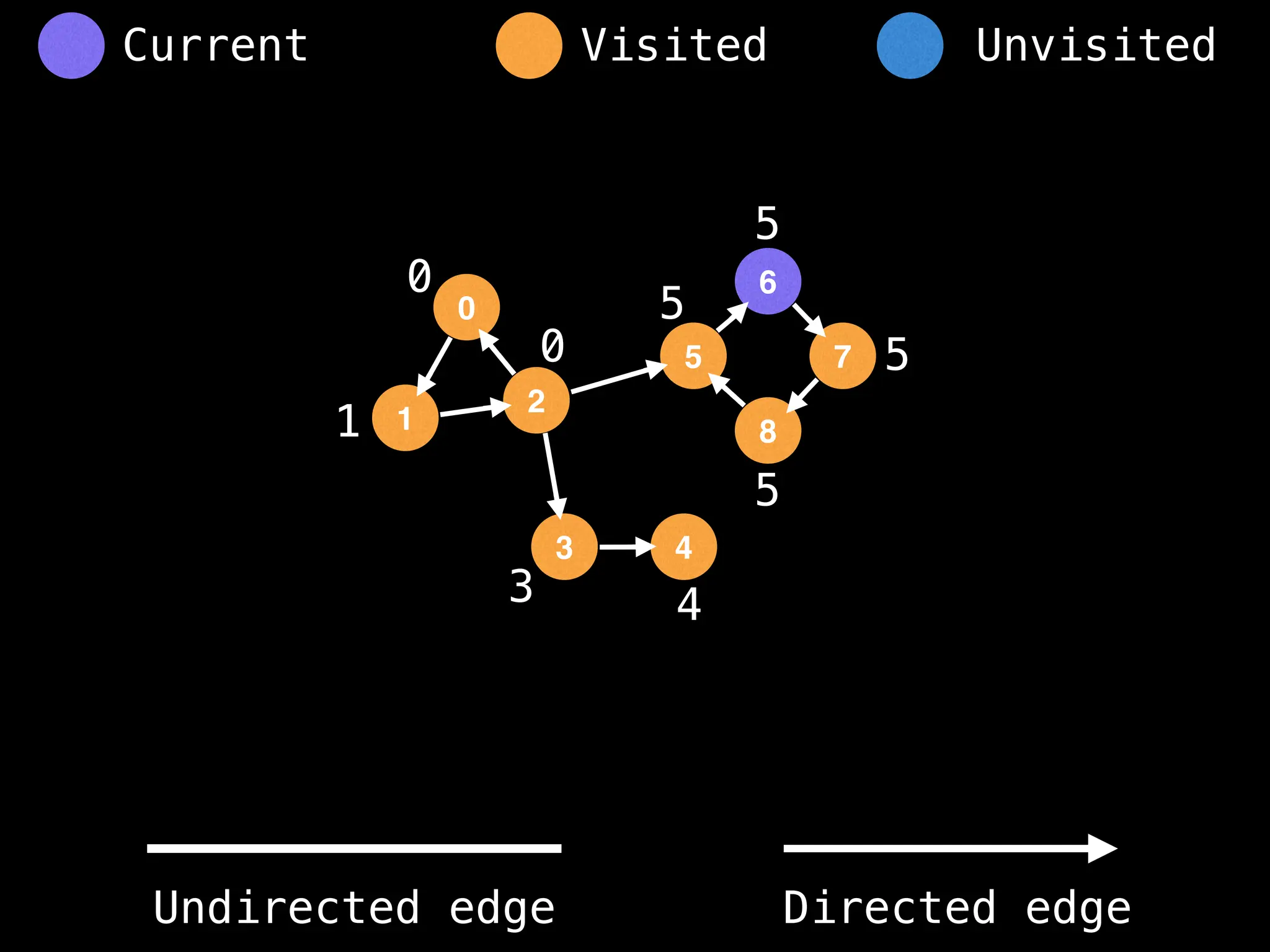
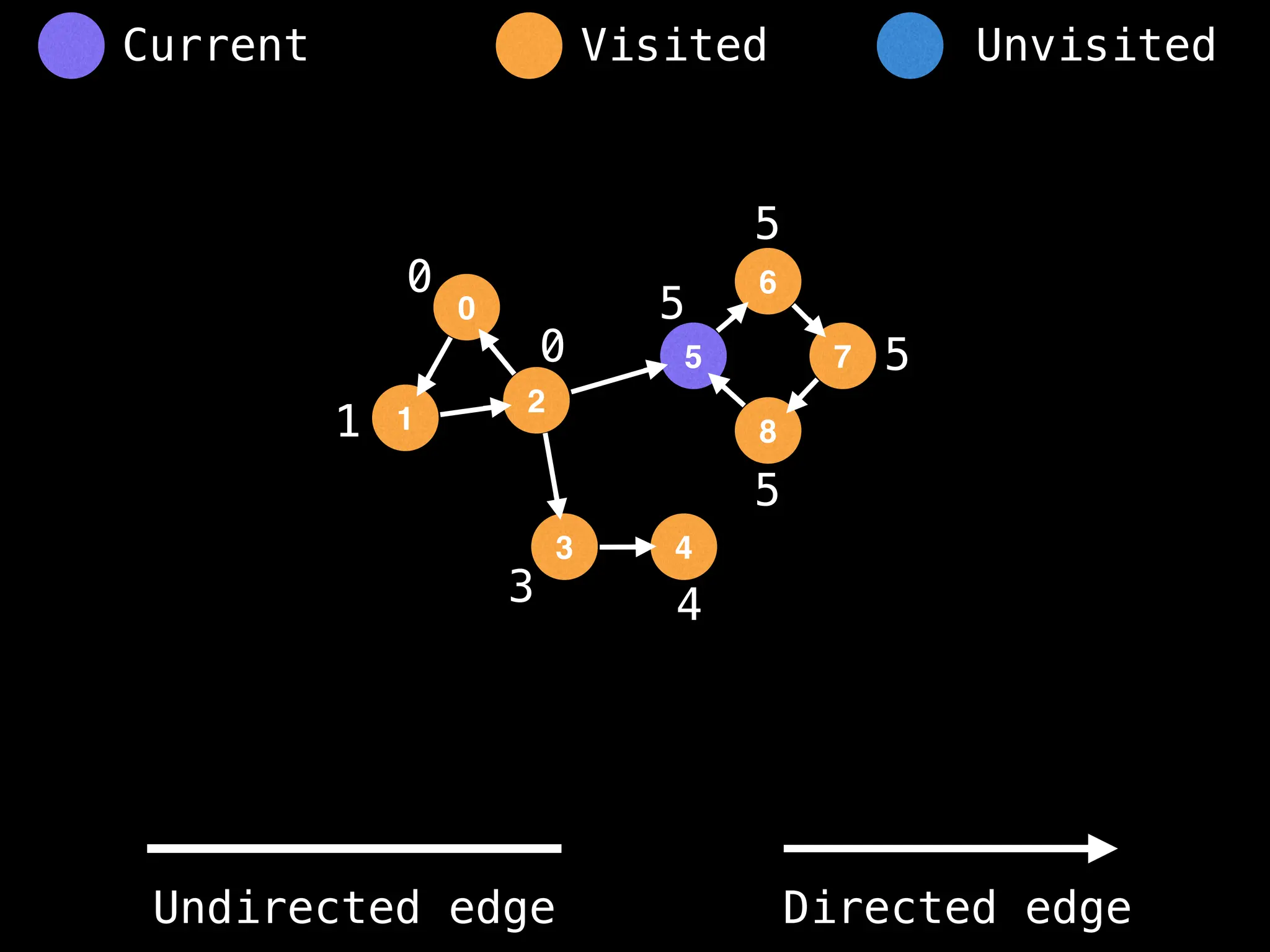
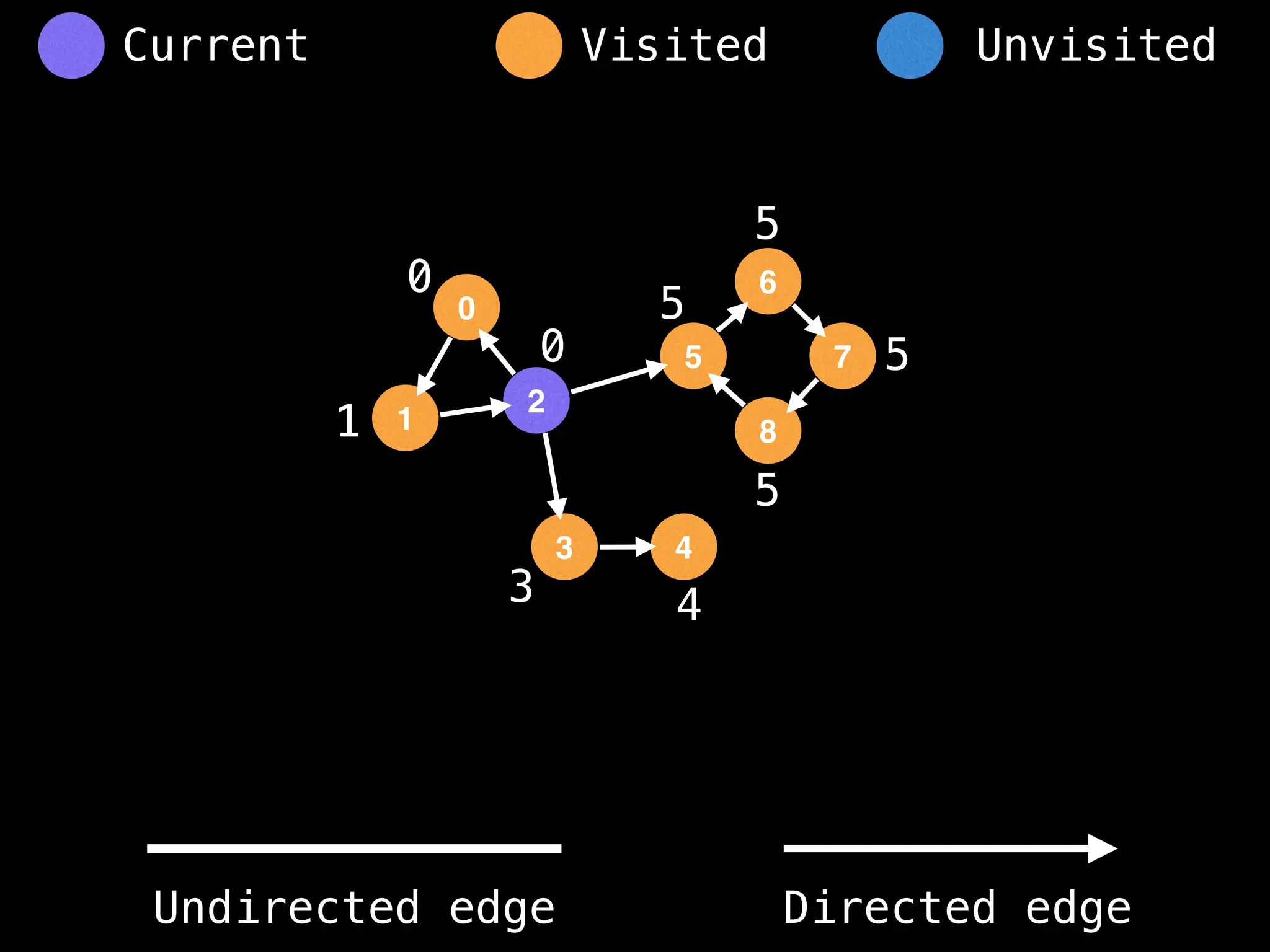
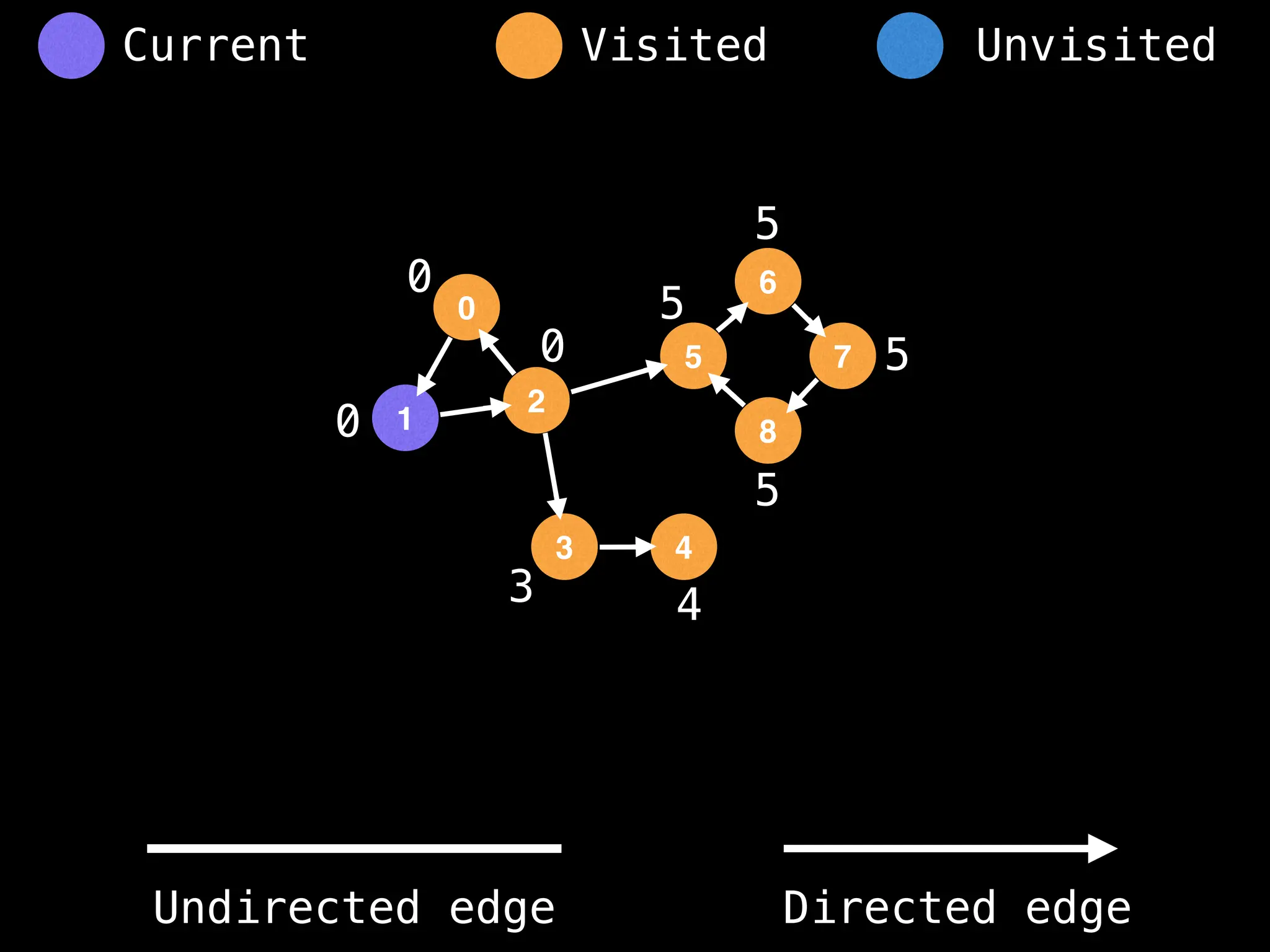
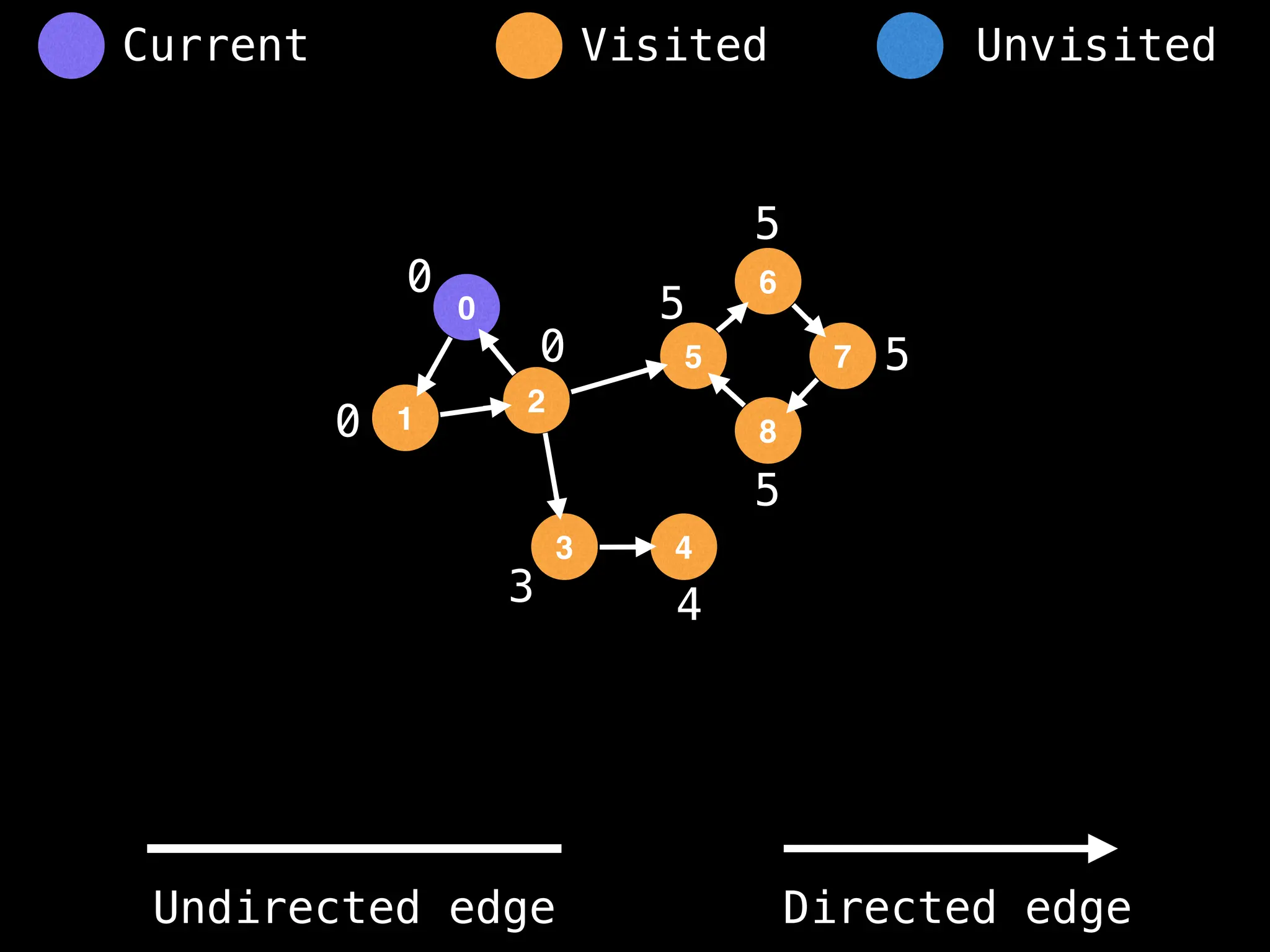
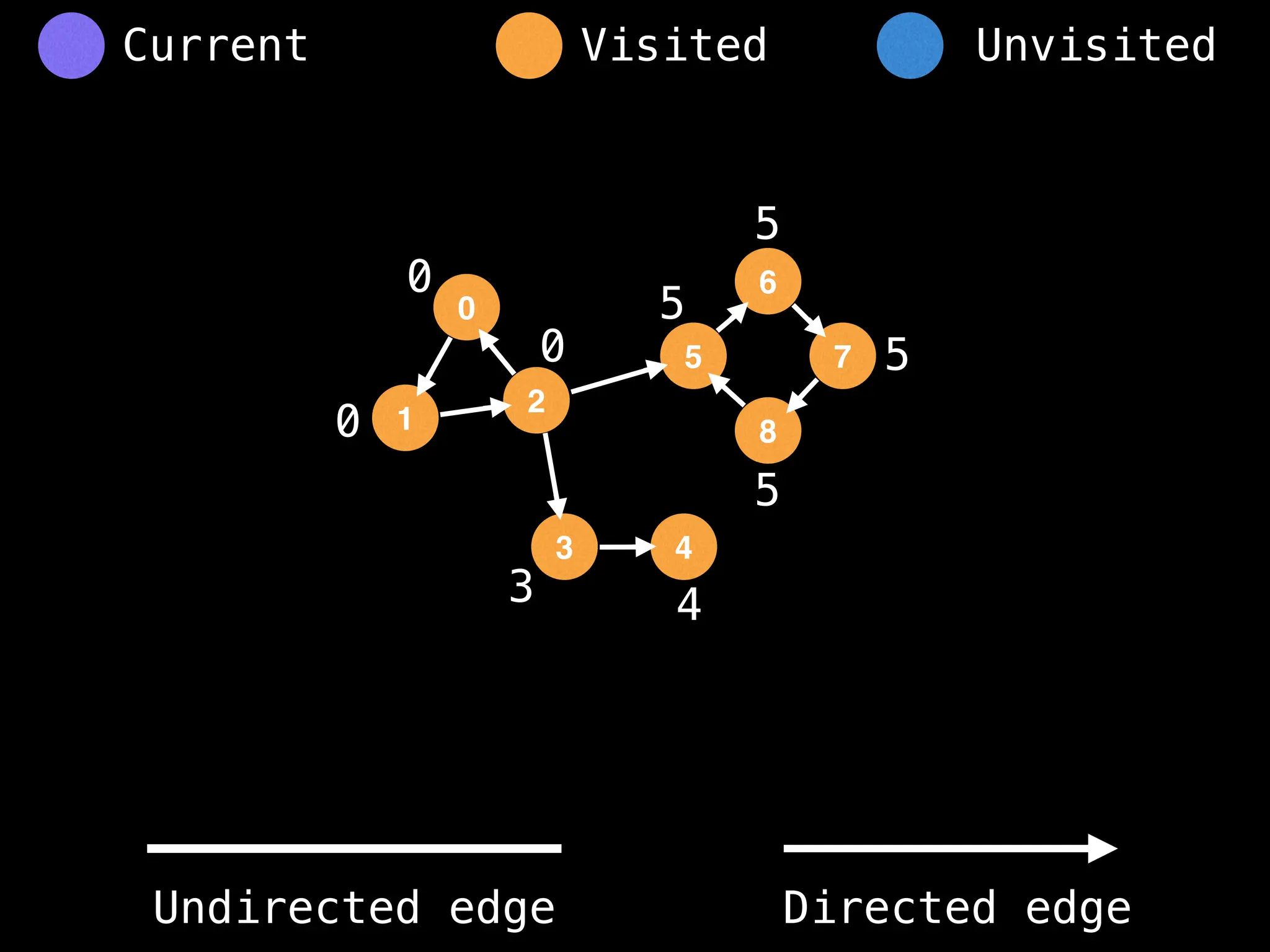
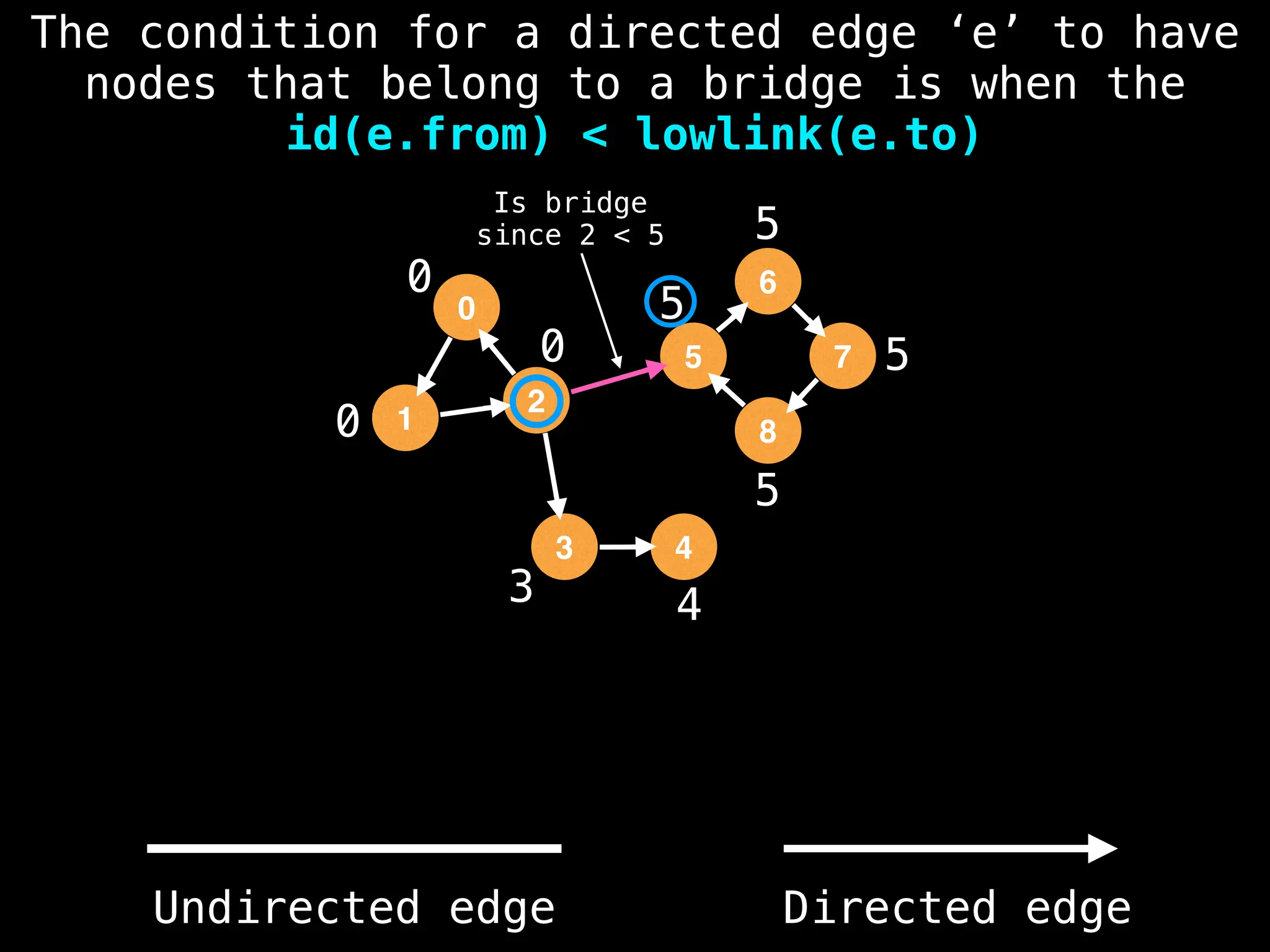
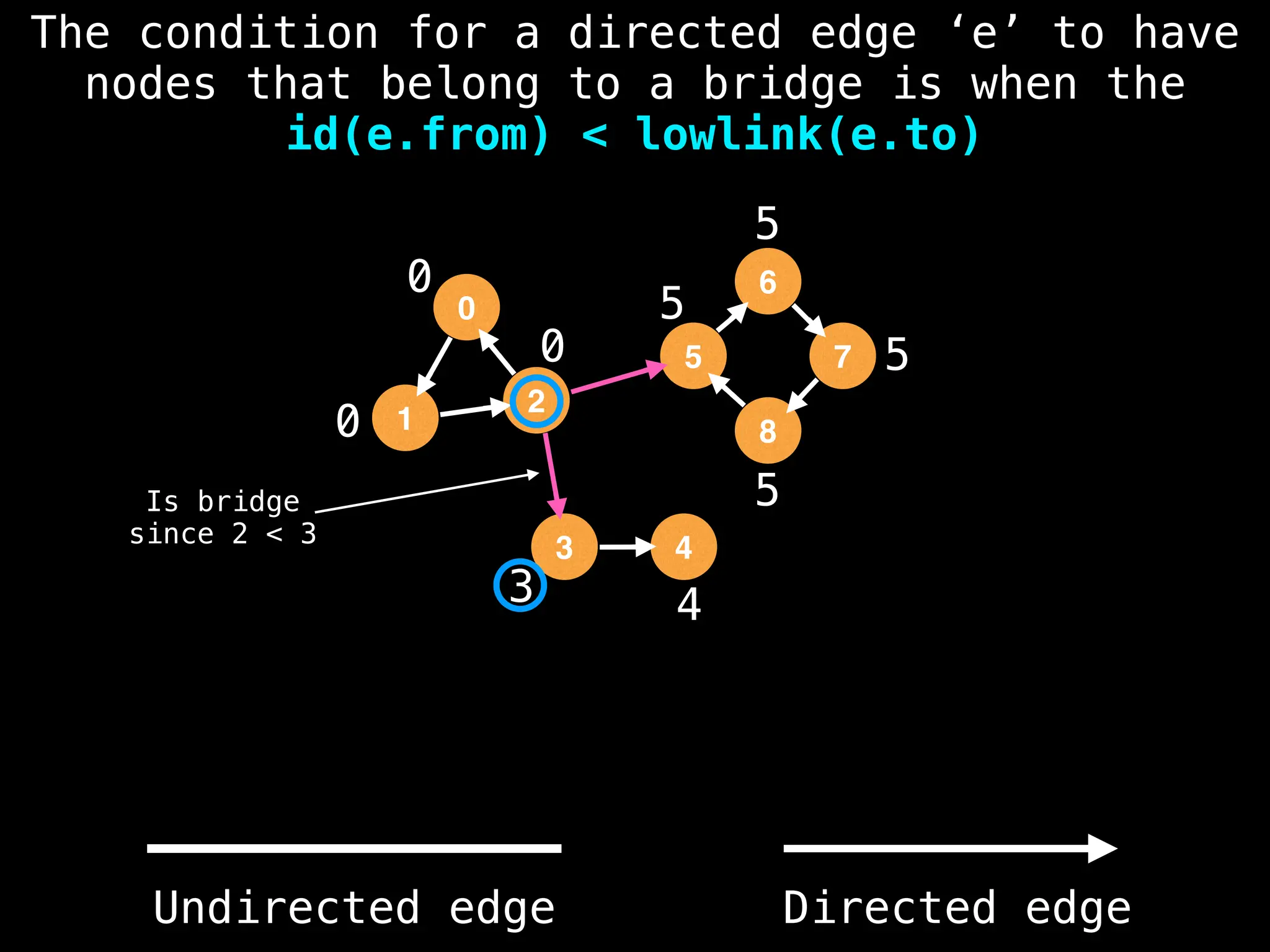
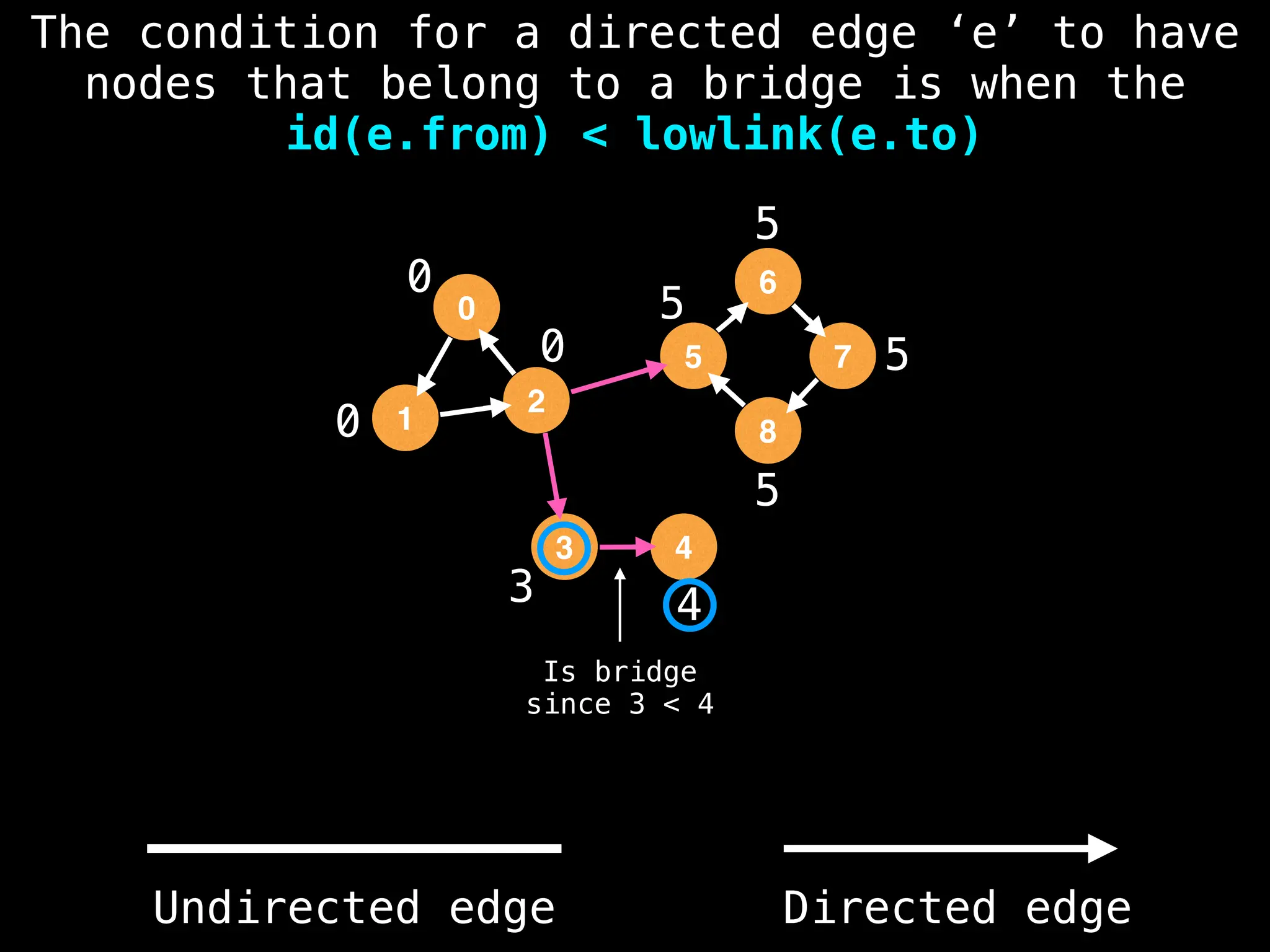
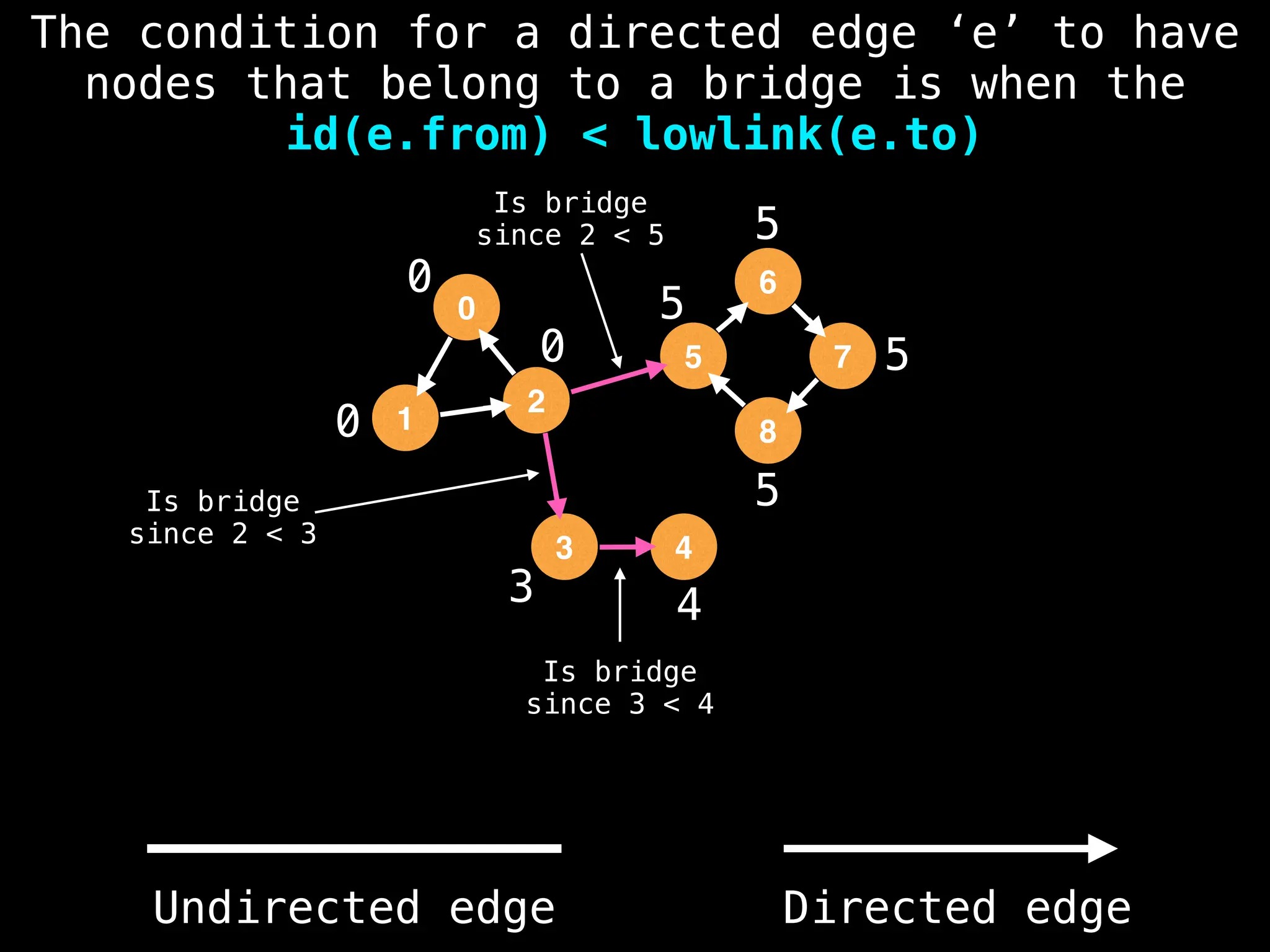


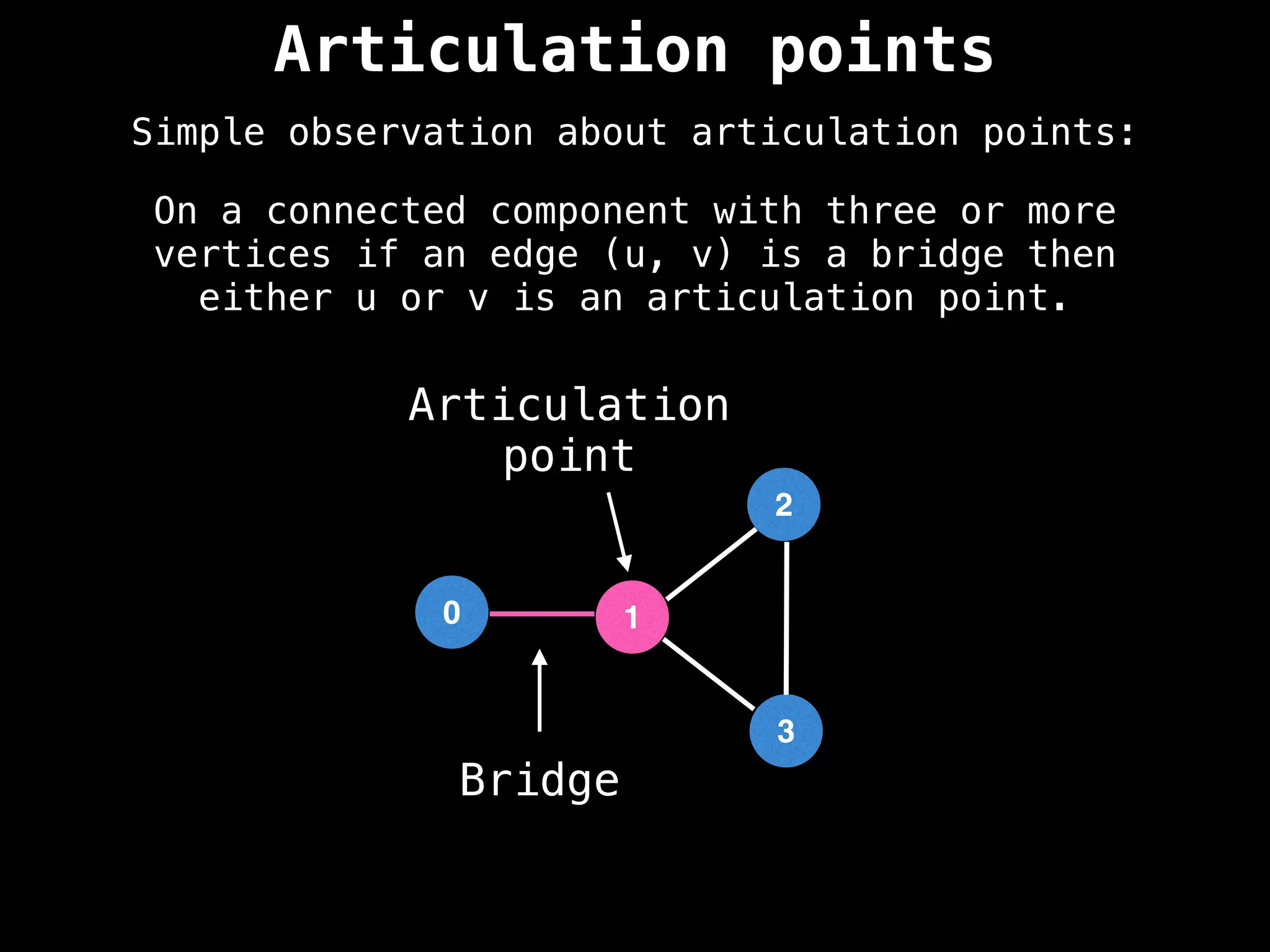
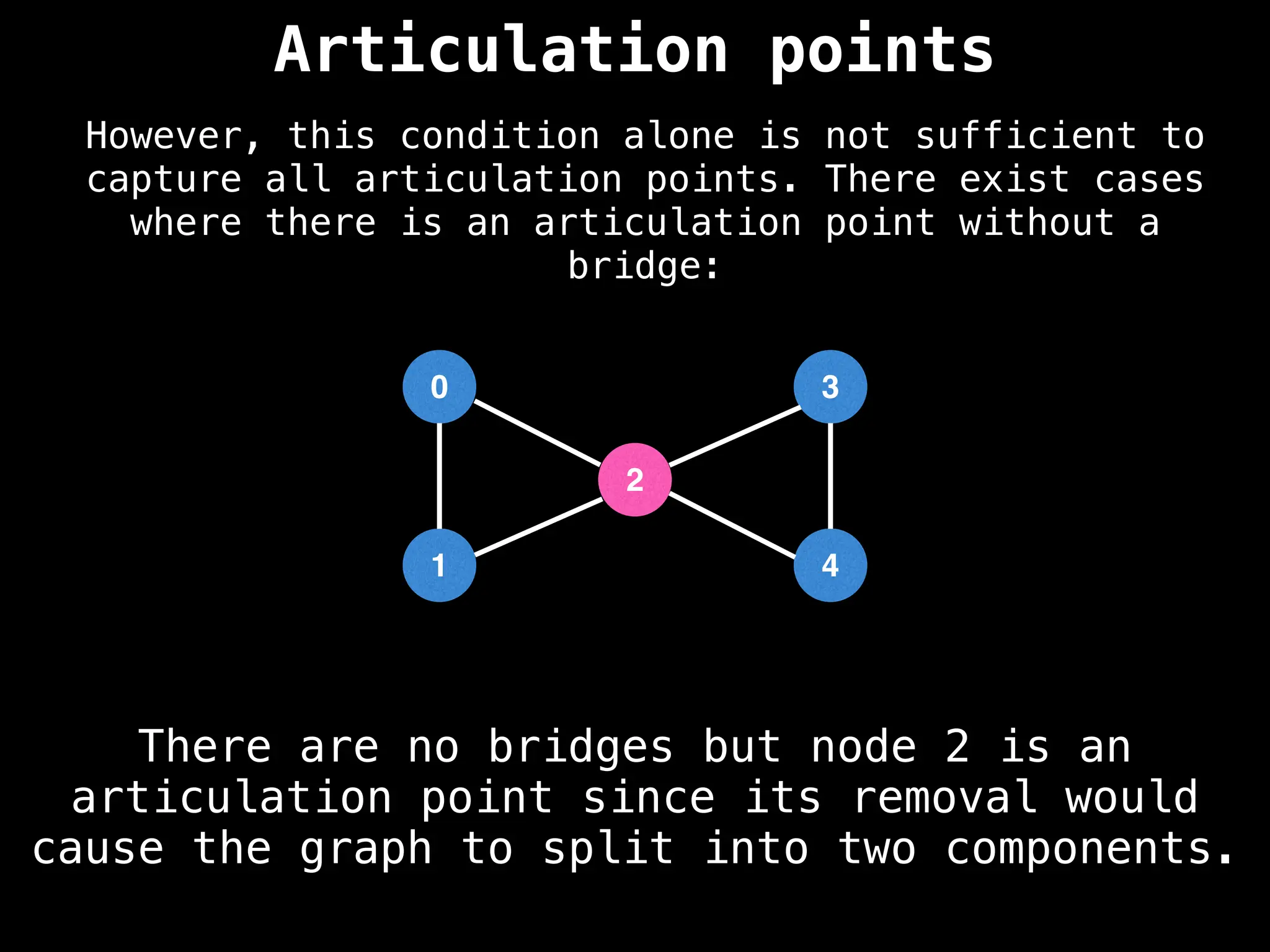
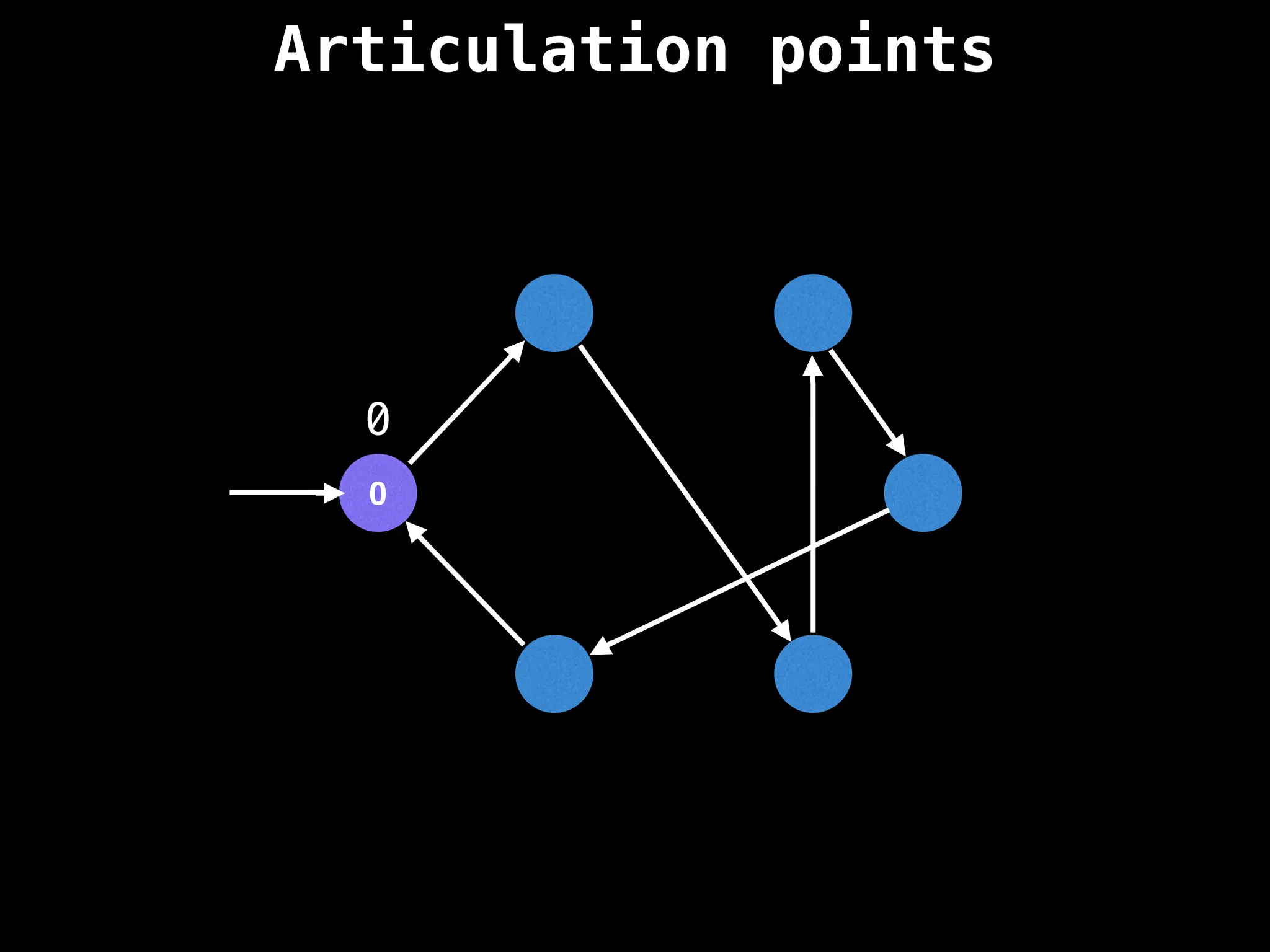
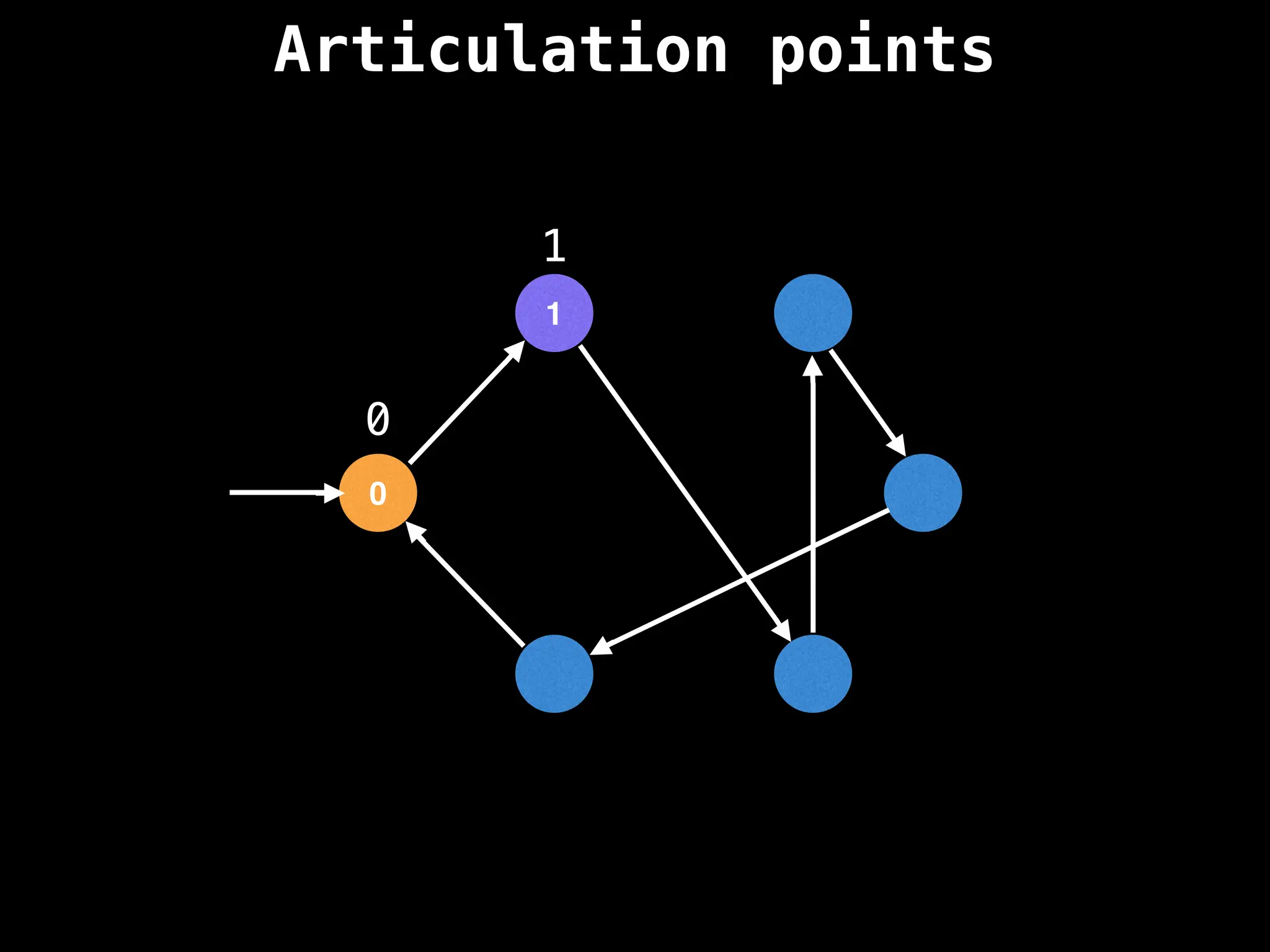
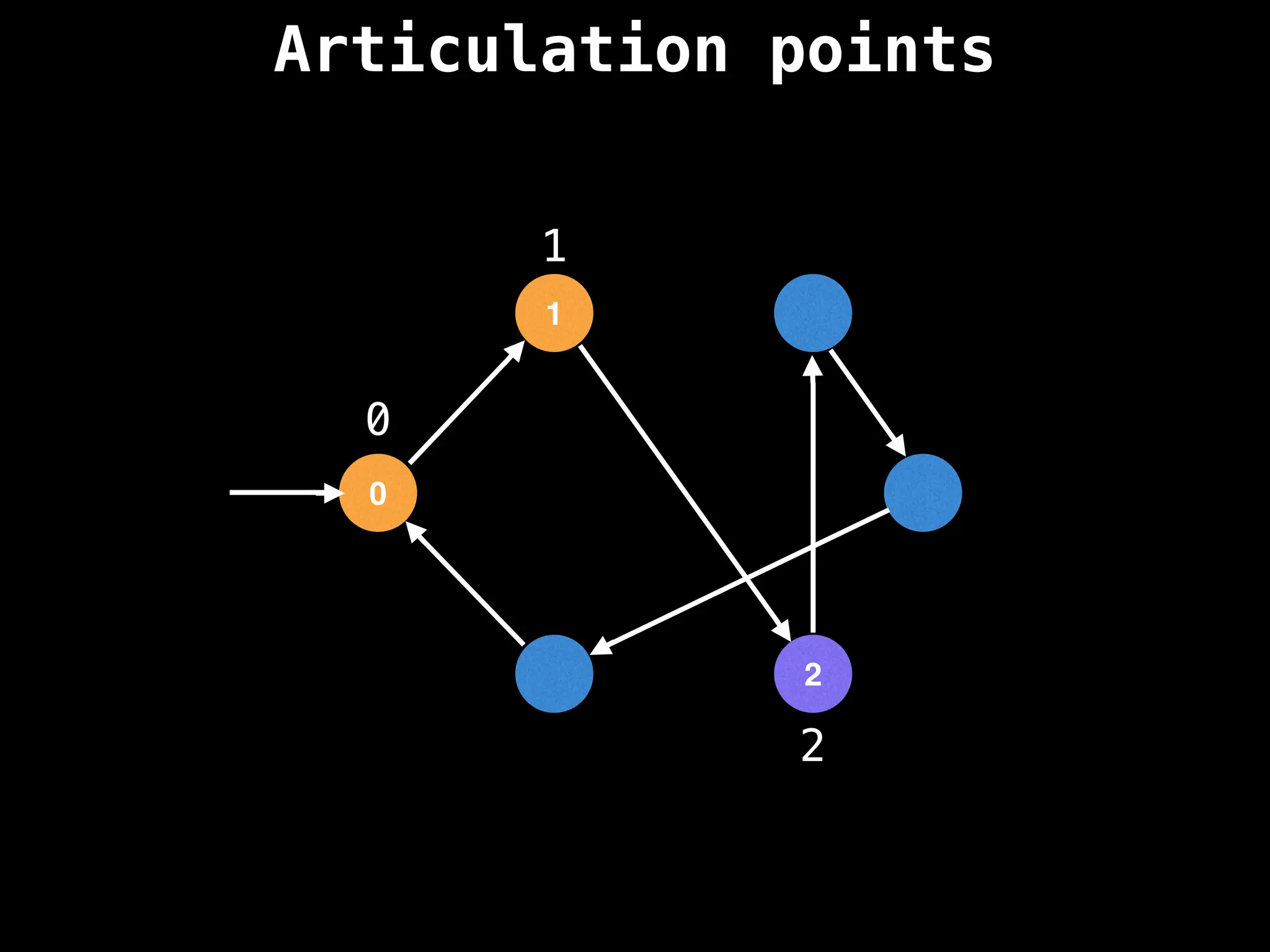
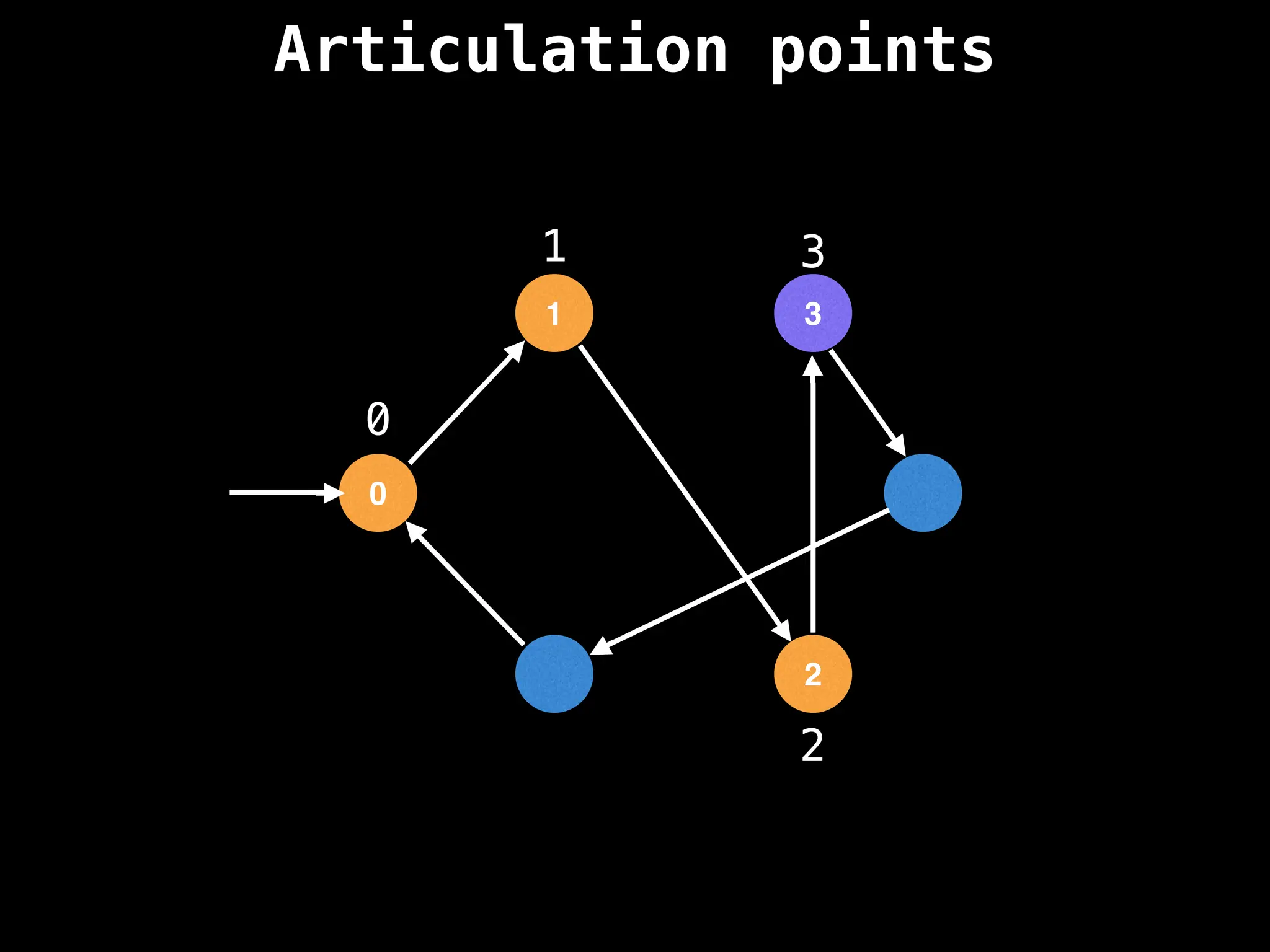
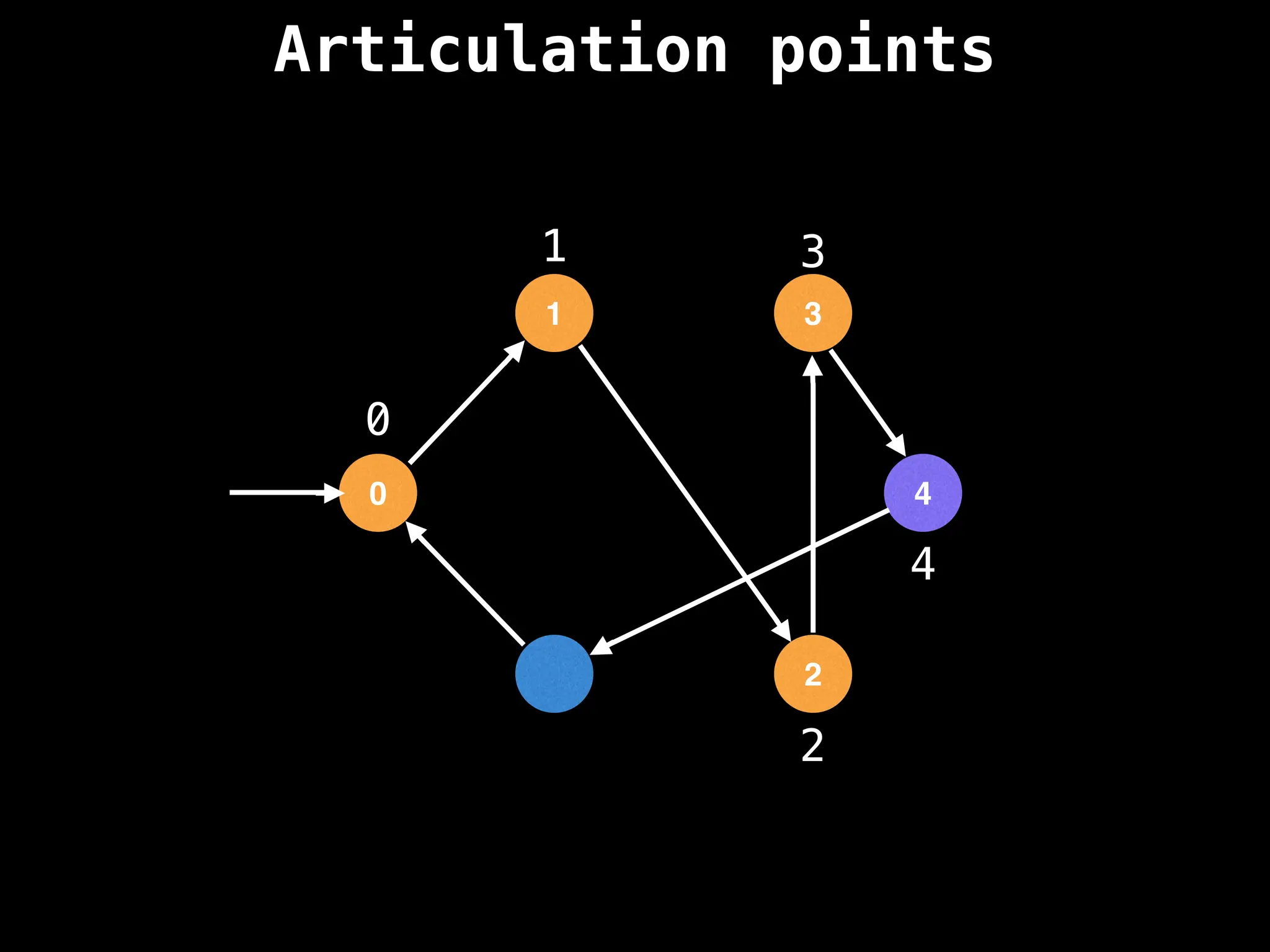
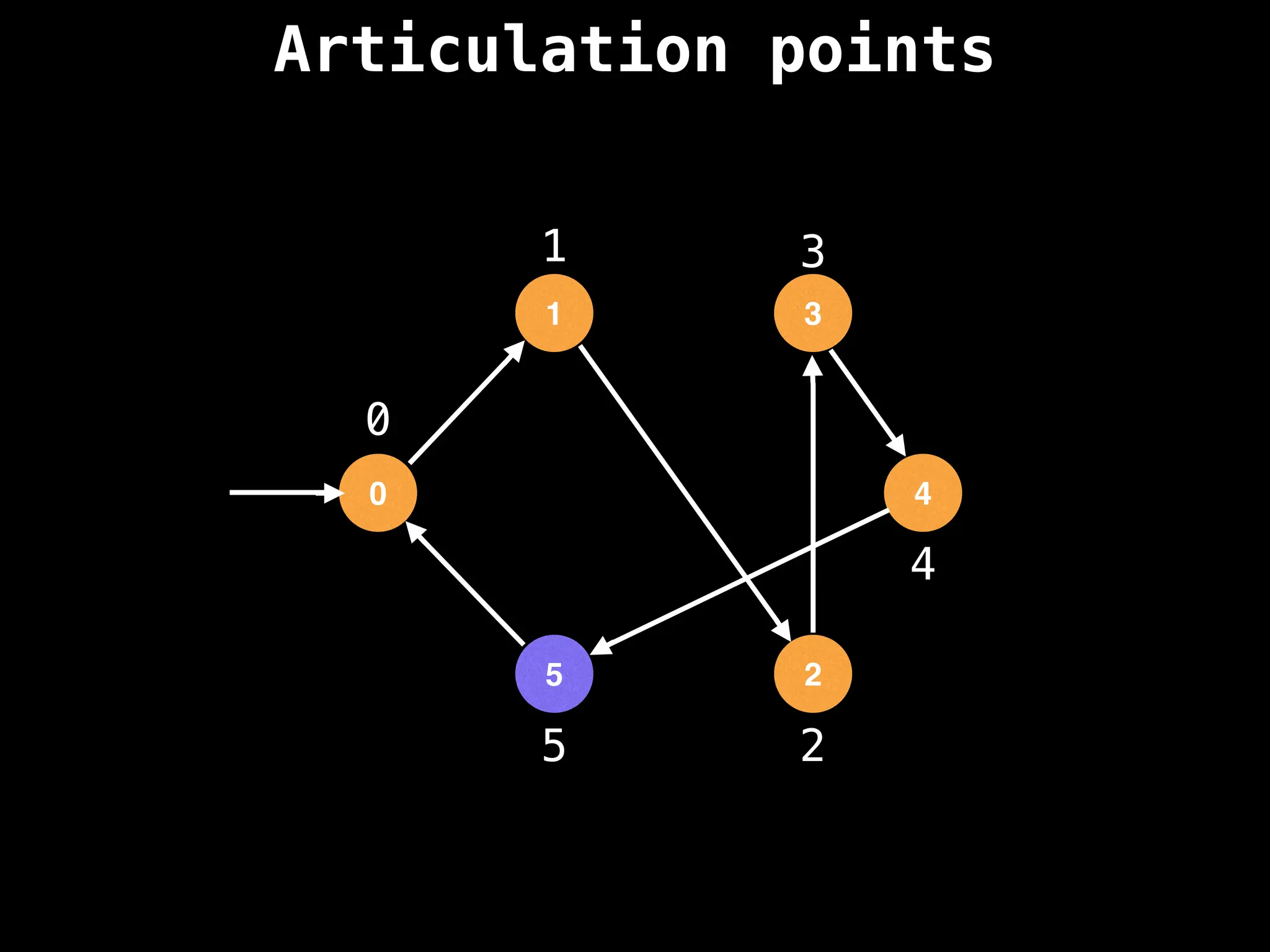
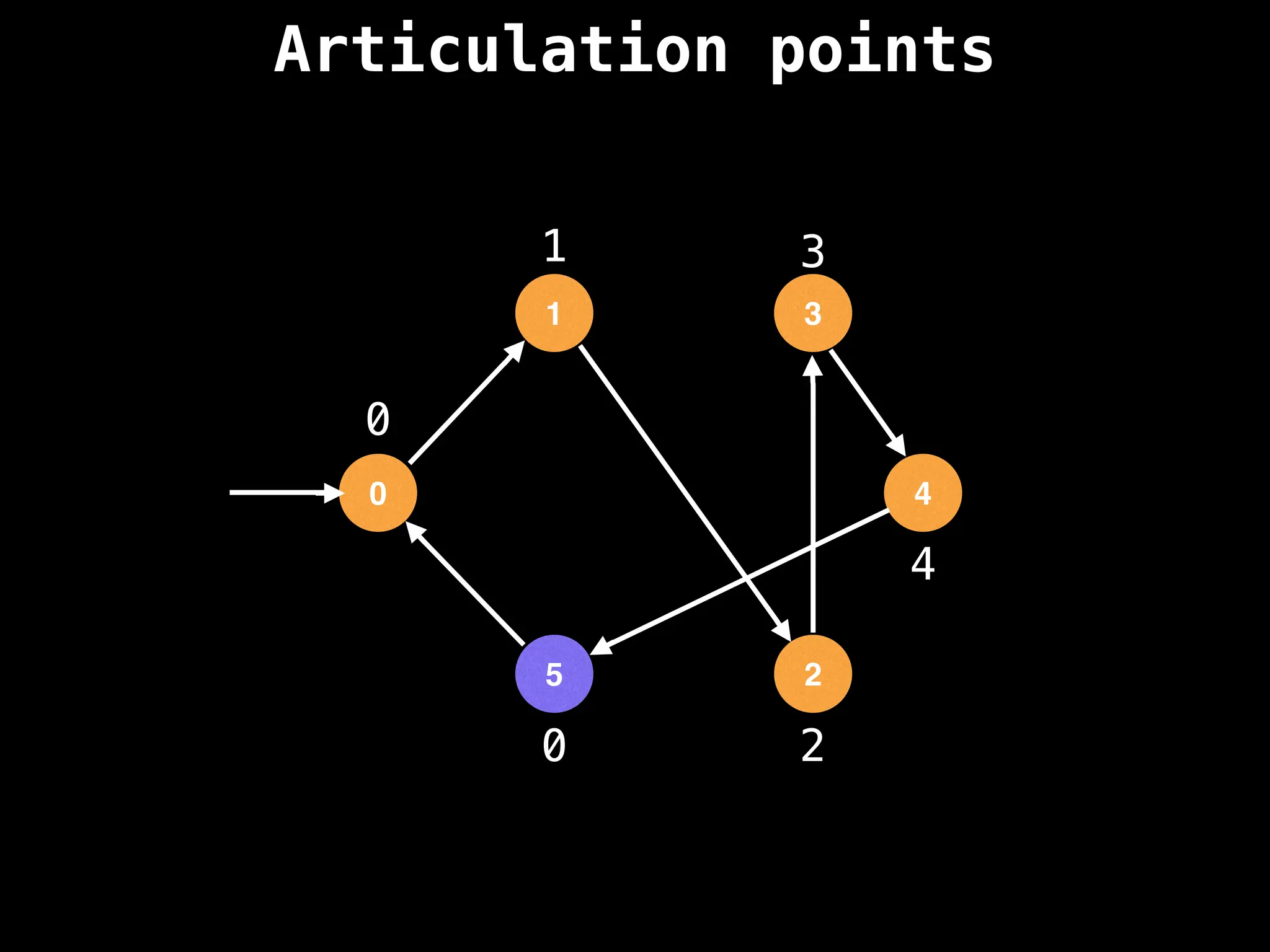
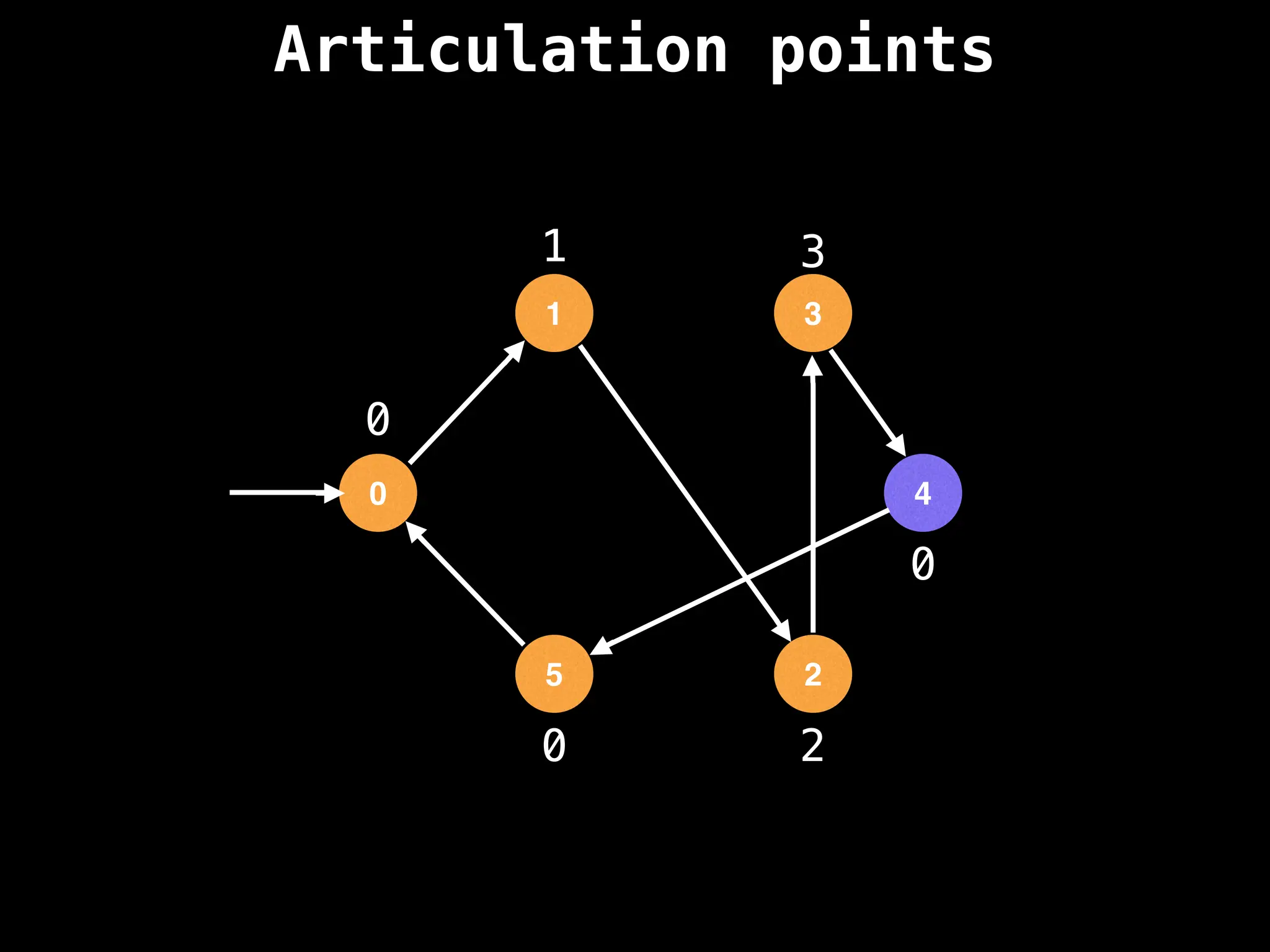
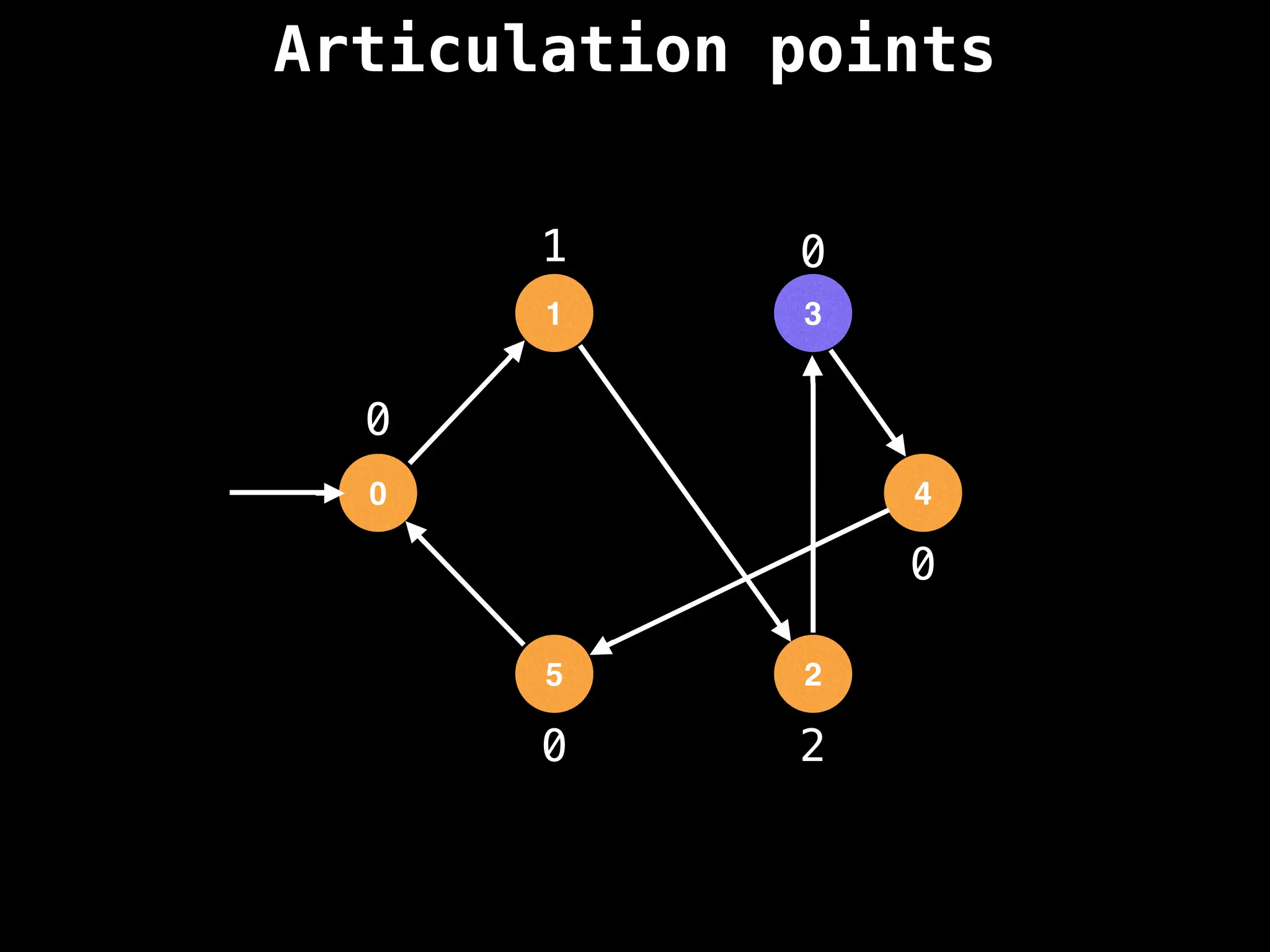
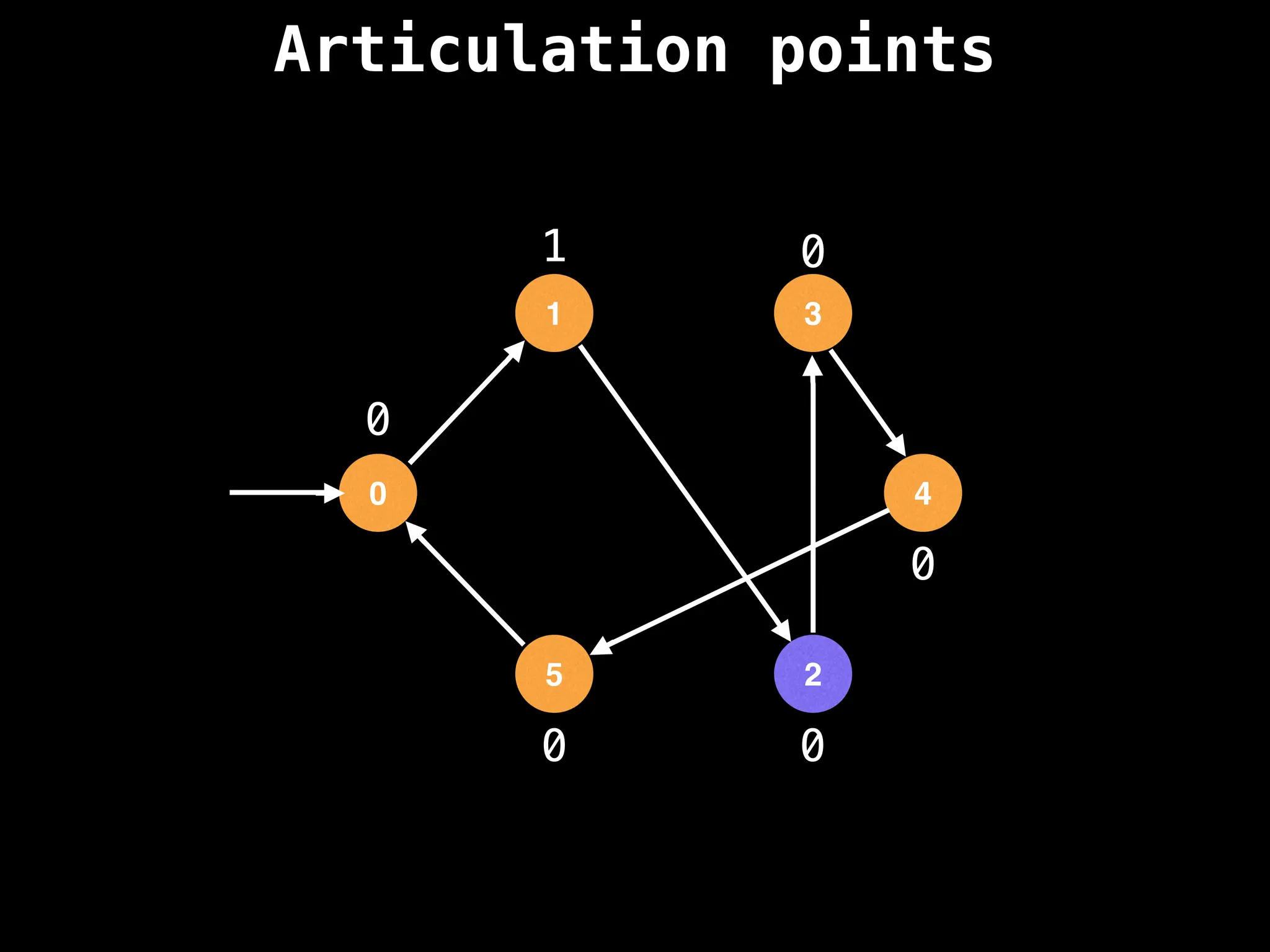
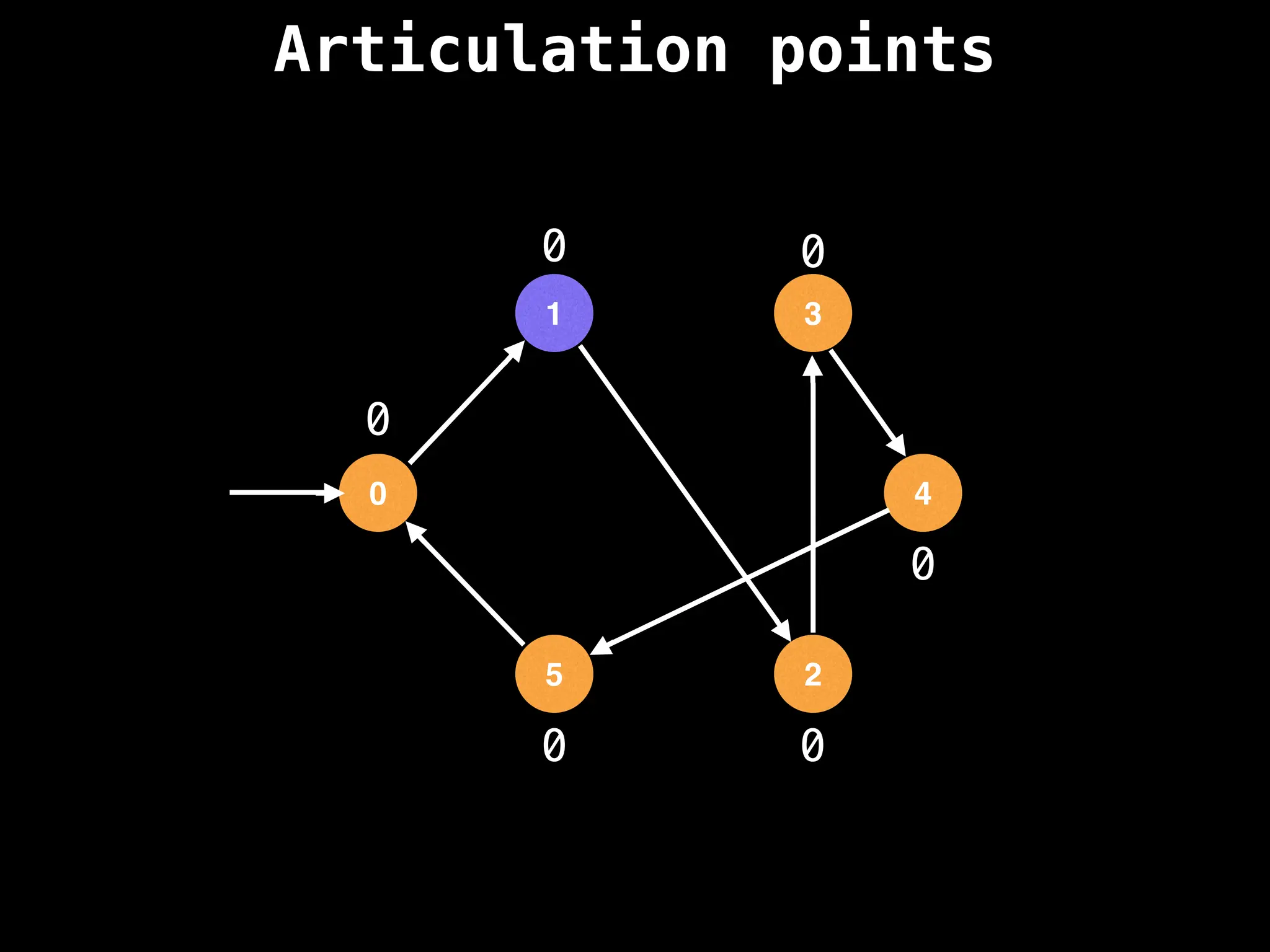
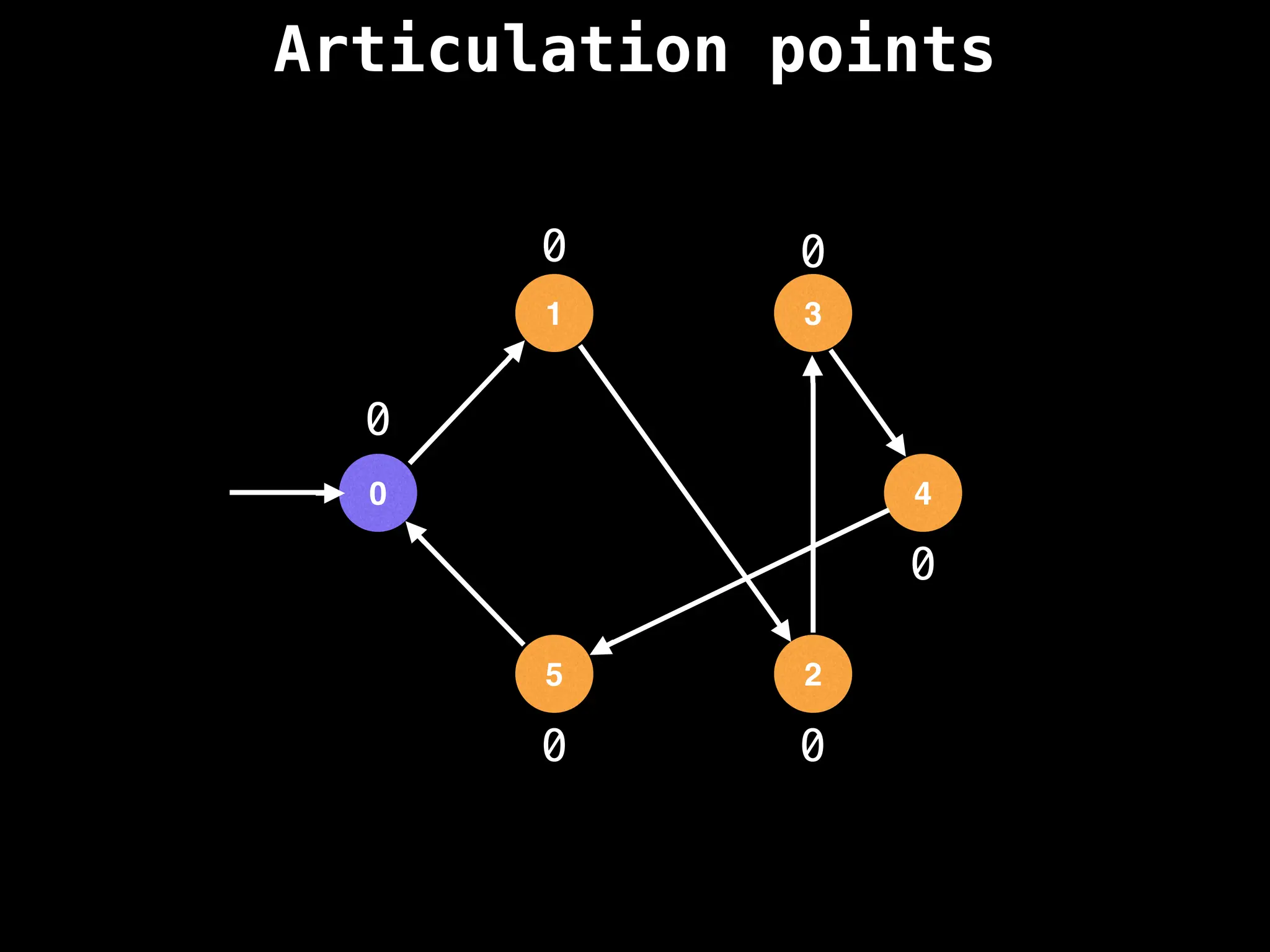
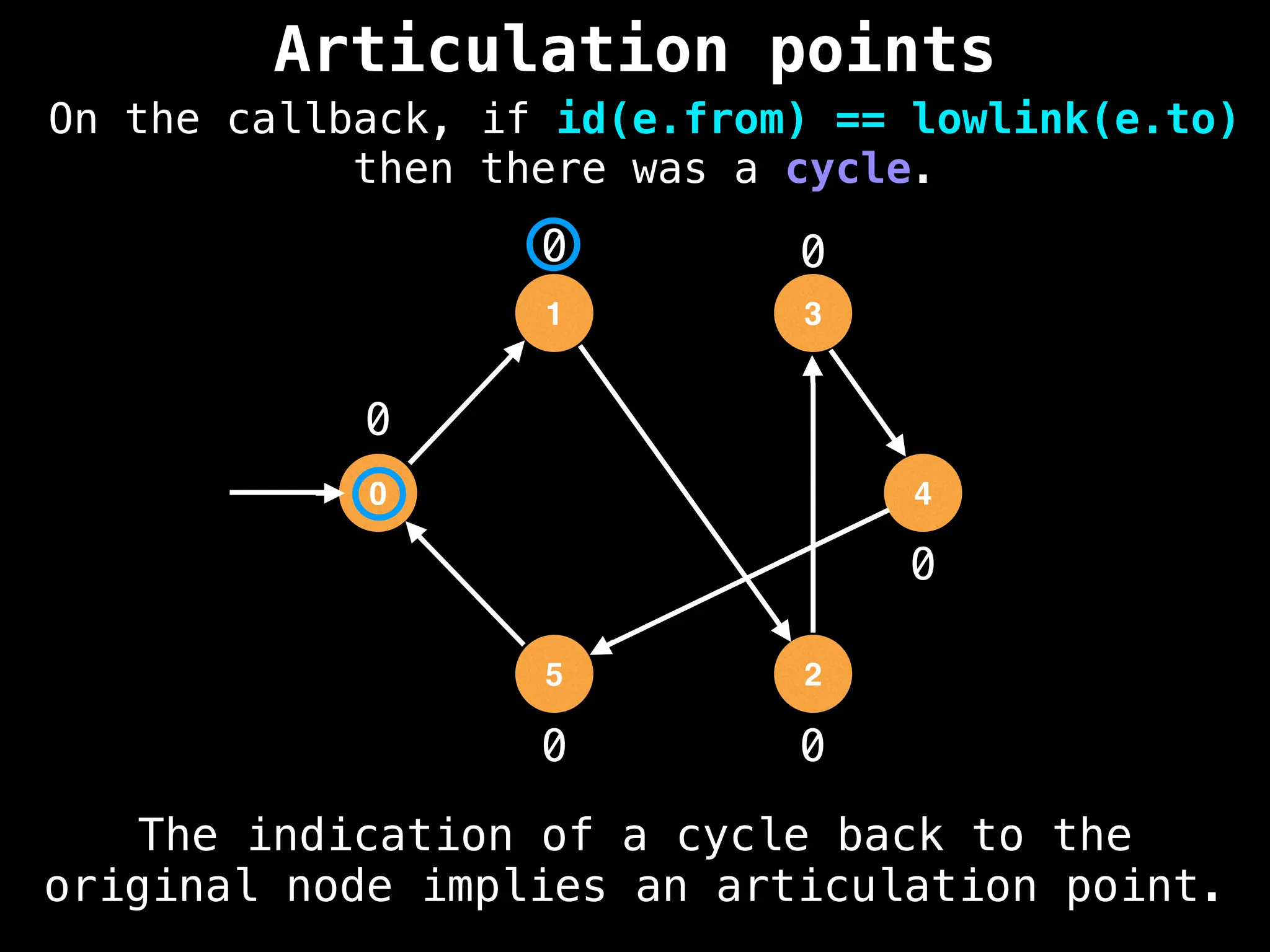
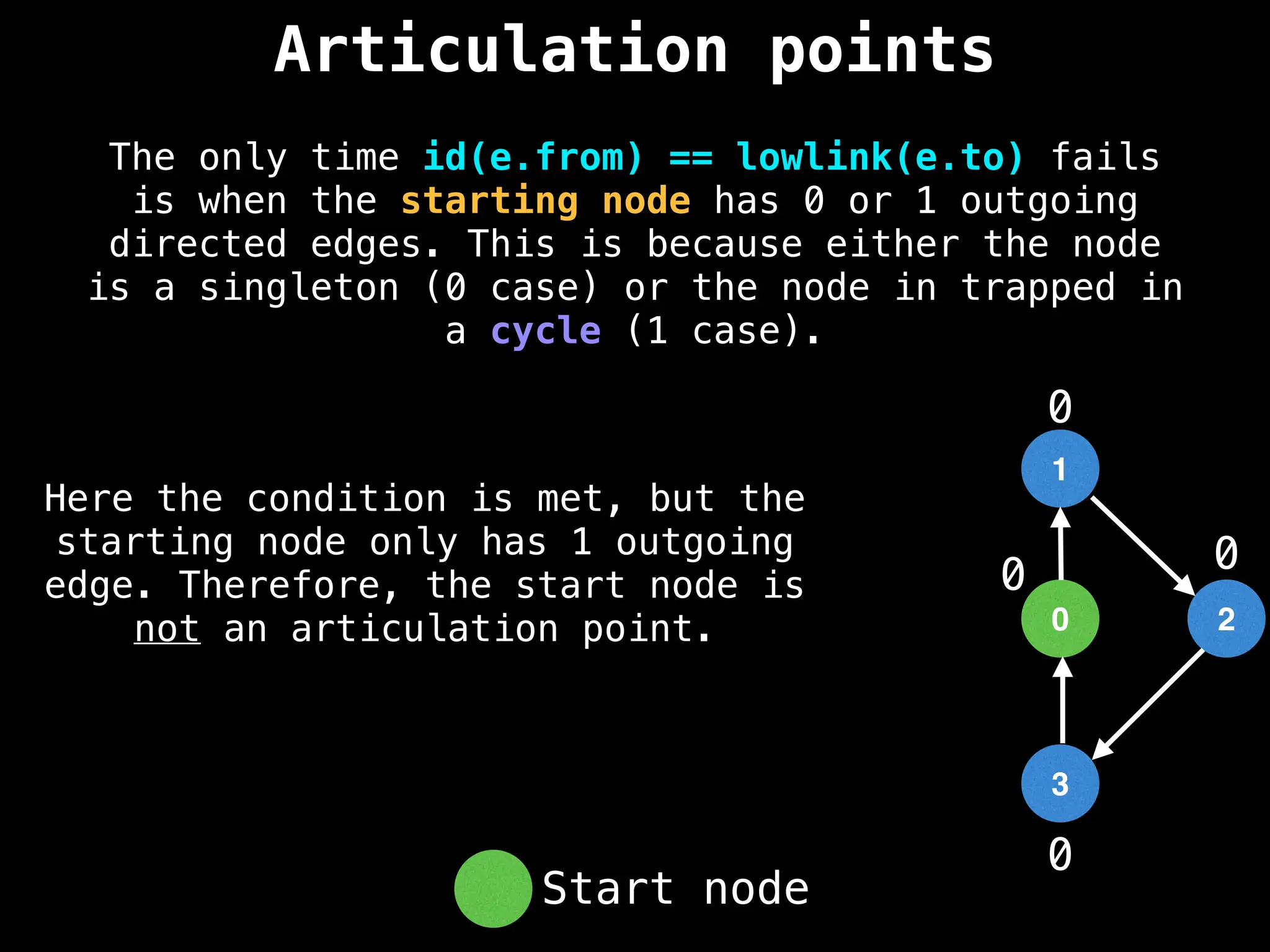
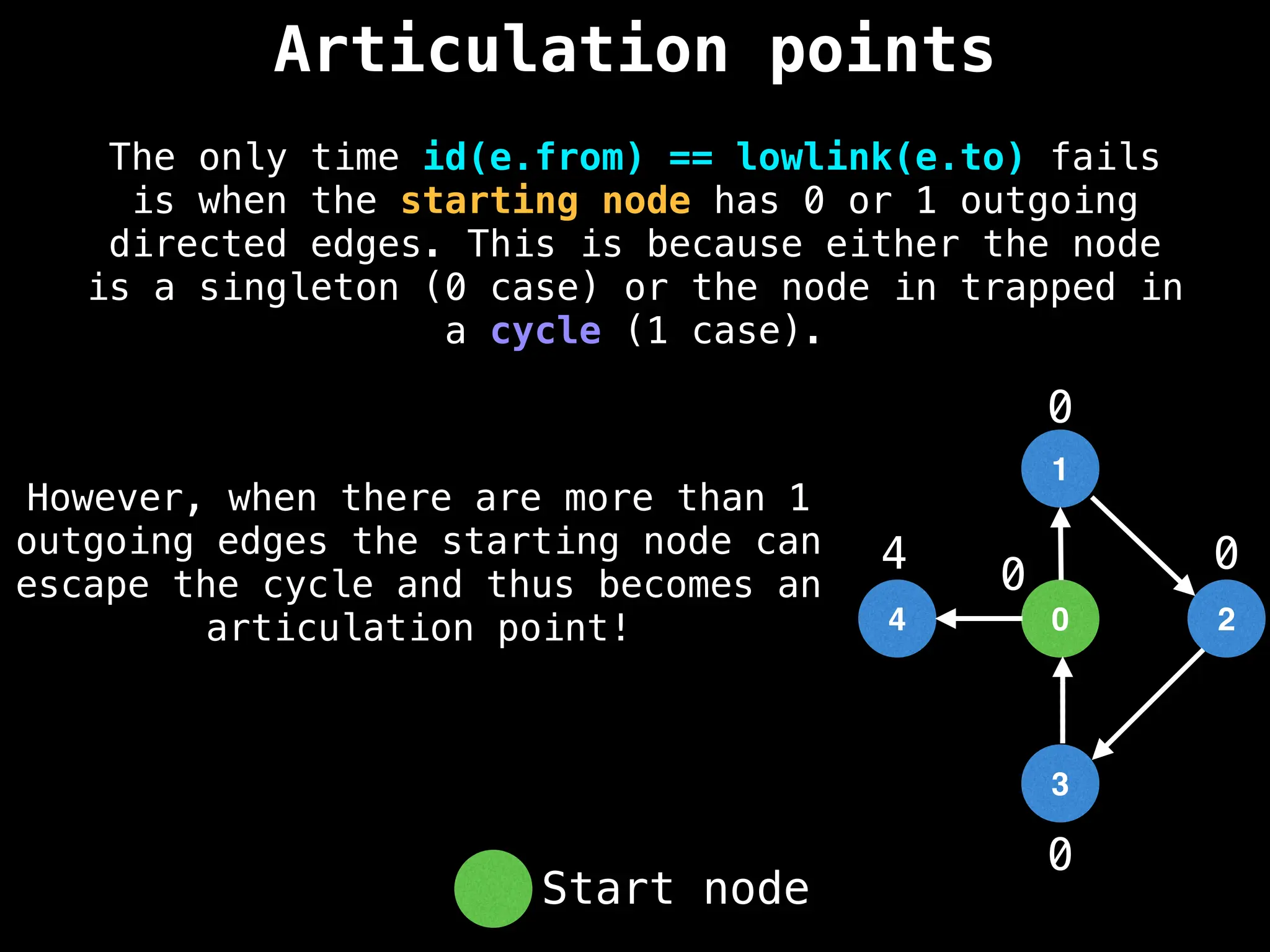
![id = 0
g = adjacency list with undirected edges
n = size of the graph
outEdgeCount = 0
# In these arrays index i represents node i
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
visited = [false, …, false] # Length n
isArt = [false, …, false] # Length n
function findArtPoints():
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
if (!visited[i]):
outEdgeCount = 0 # Reset edge count
dfs(i, i, -1)
isArt[i] = (outEdgeCount > 1)
return isArt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-891-2048.jpg)
![# Perform DFS to find articulation points.
function dfs(root, at, parent):
if (parent == root): outEdgeCount++
visited[at] = true
id = id + 1
low[at] = ids[at] = id
# For each edge from node ‘at’ to node ‘to’
for (to : g[at]):
if to == parent: continue
if (!visited[to]):
dfs(root, to, at)
low[at] = min(low[at], low[to])
# Articulation point found via bridge
if (ids[at] < low[to]):
isArt[at] = true
# Articulation point found via cycle
if (ids[at] == low[to]):
isArt[at] = true
else:
low[at] = min(low[at], ids[to])
Being explicit here.
However, this could just
be a <= clause.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-892-2048.jpg)

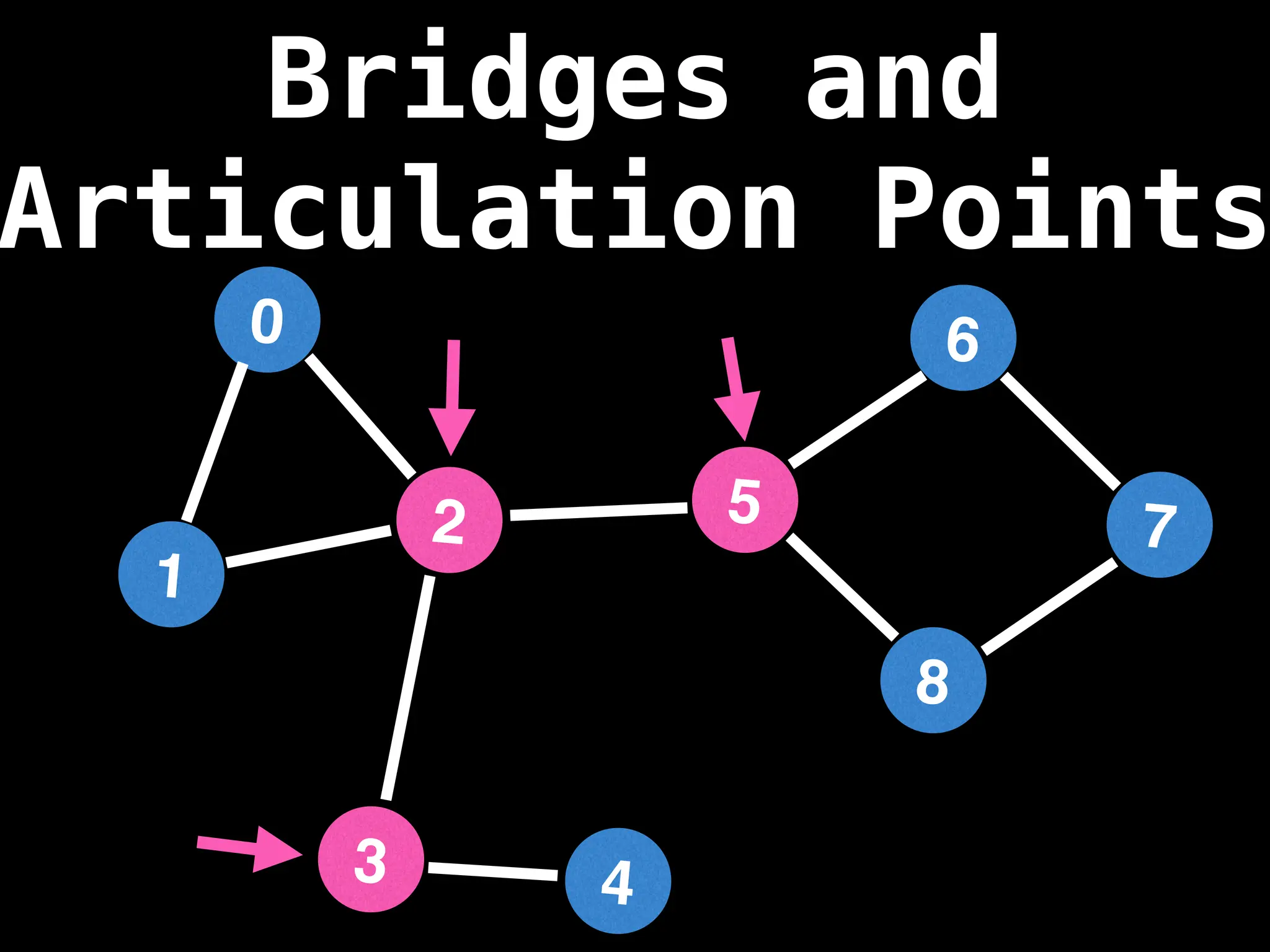


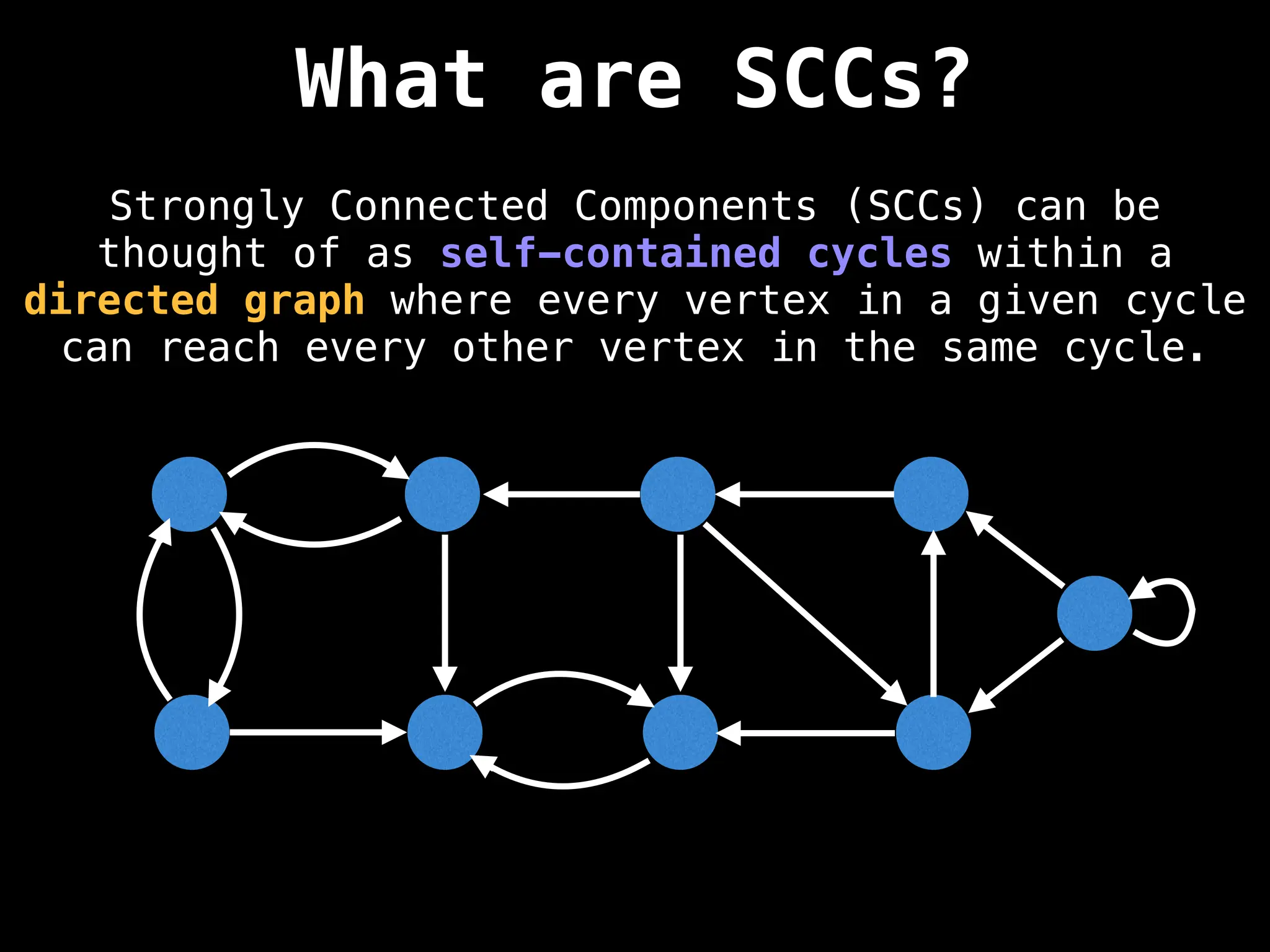
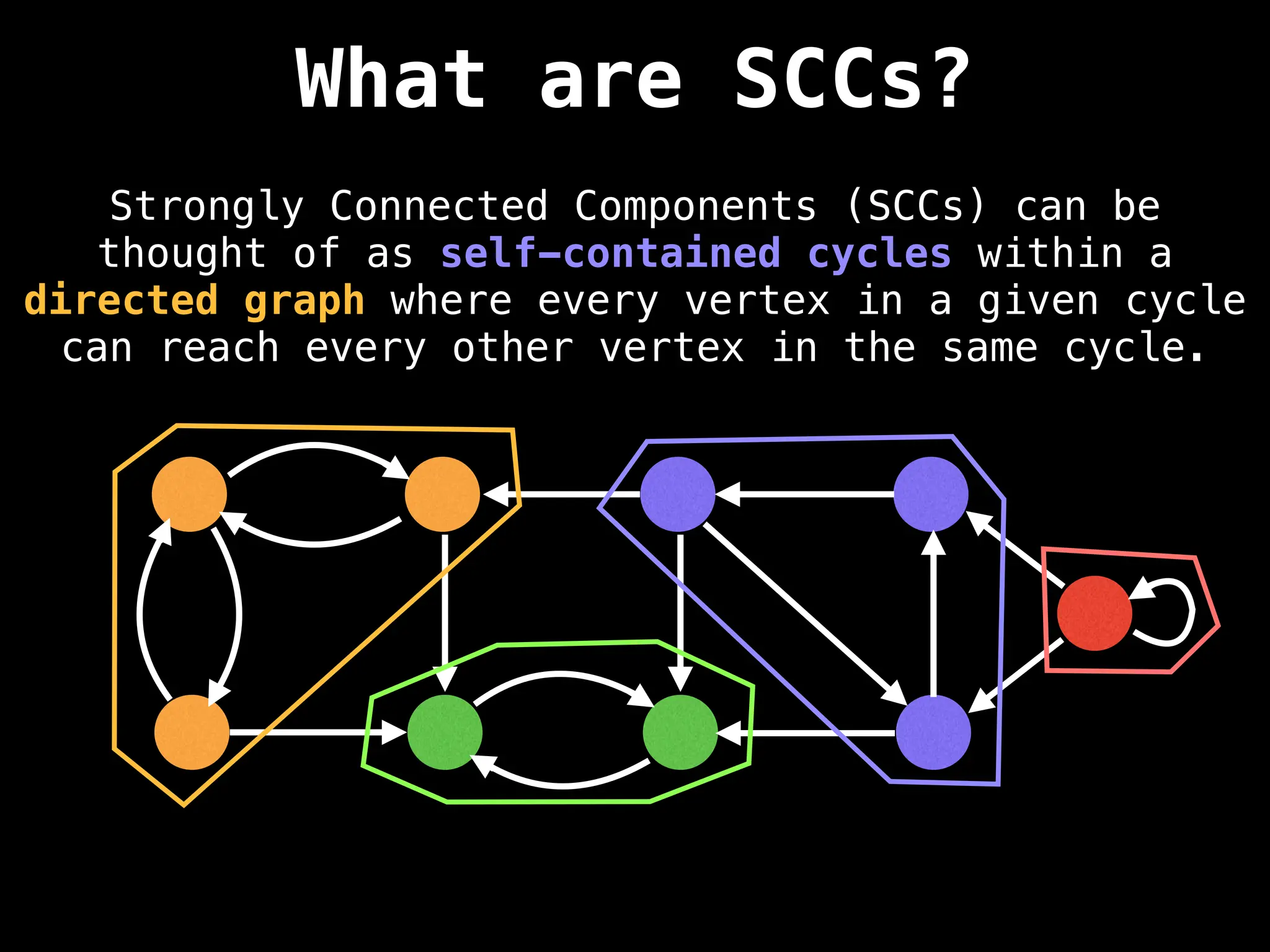
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-901-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-902-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-903-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-904-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0
2 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-905-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-906-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-907-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-908-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-909-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-910-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-911-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-912-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-913-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-914-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-915-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-916-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-917-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-918-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-919-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-920-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-921-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-922-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-923-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-924-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-925-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-926-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-927-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-928-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-929-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-930-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-931-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-932-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-933-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-934-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5
0
The low-link of node 1 is 0, since node 0 is
node with the lowest id reachable from node 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-935-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
The low-link of node 3 is 2, since node 2 is
node with the lowest id reachable from node 3
1
0 4
2
6 3
5
0 0
0 2 2
4
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-936-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5
0 0
0 2 2
4
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-937-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
1
0 4
2
6 3
5
0 0
0 2 2
4
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-938-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-939-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
4
6 1
3
5 2
0
Started DFS on the rightmost node, resumed DFS
on node 2, and then resumed DFS on node 4 to
finish labelling all nodes in the graph.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-940-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
4
6 1
3
5 2
0
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-941-2048.jpg)
![Low-Link Values
The low-link value of a node is the smallest
[lowest] node id reachable from that node when
doing a DFS (including itself).
All low link values
are the same, but
there are multiple
SCCs!
4
6 1
3
5 2
0
IMPORTANT: Depending on where the DFS starts, and the order
in which nodes/edges are visited, the low-link values for
identifying SCCs could be wrong. In the context of Tarjan’s
SCC algorithm, we maintain an invariant that prevents SCCs
to interfere with the low link value of other SCCs.
0 0 0
0
0
0
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-942-2048.jpg)
![The Stack Invariant
To cope with the random traversal order of
the DFS, Tarjan’s algorithm maintains a set
(often as a stack) of valid nodes from which
to update low-link values from.
Nodes are added to the stack [set] of valid
nodes as they’re explored for the first time.
Nodes are removed from the stack [set] each
time a complete SCC is found.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-943-2048.jpg)
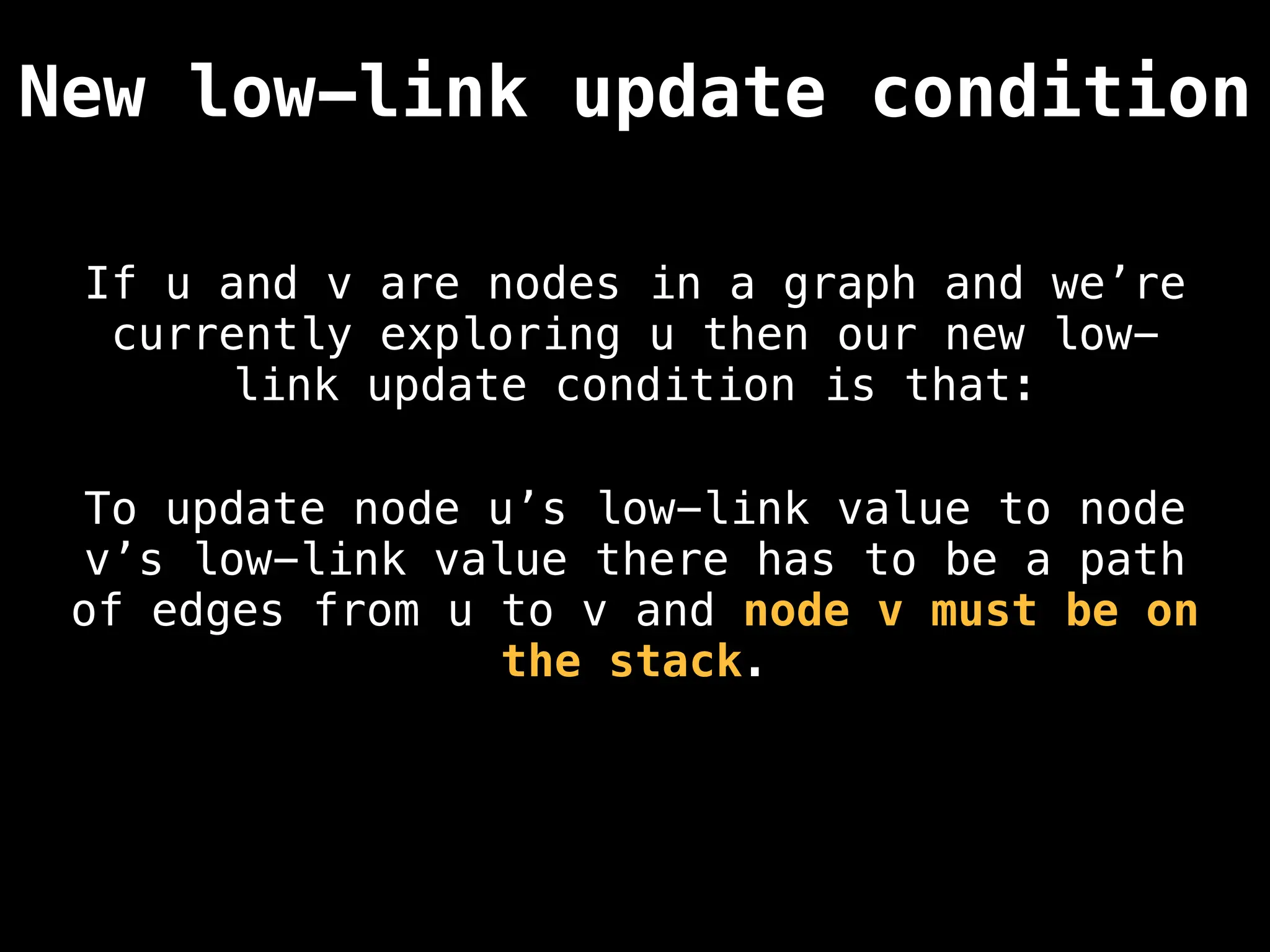

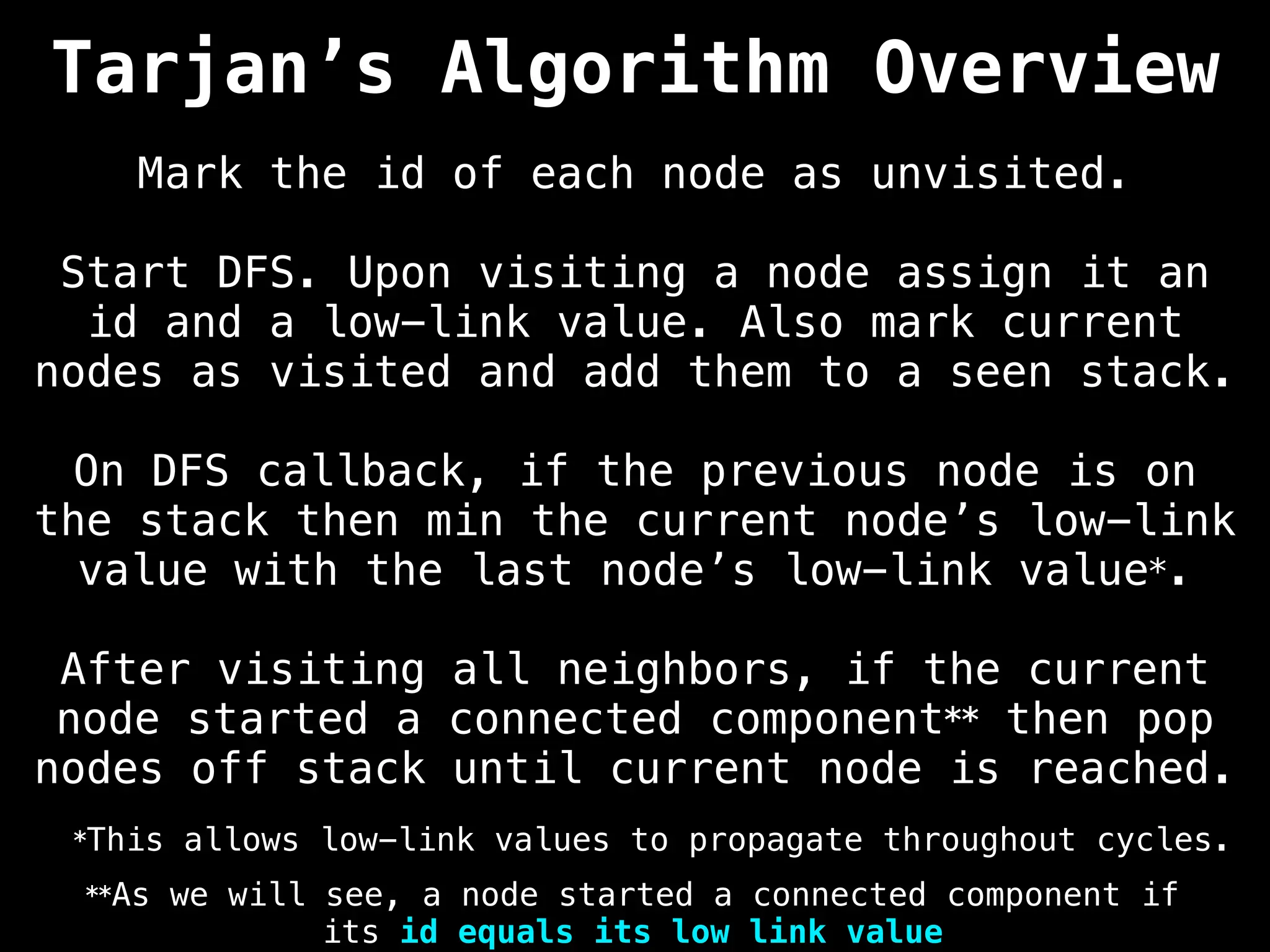
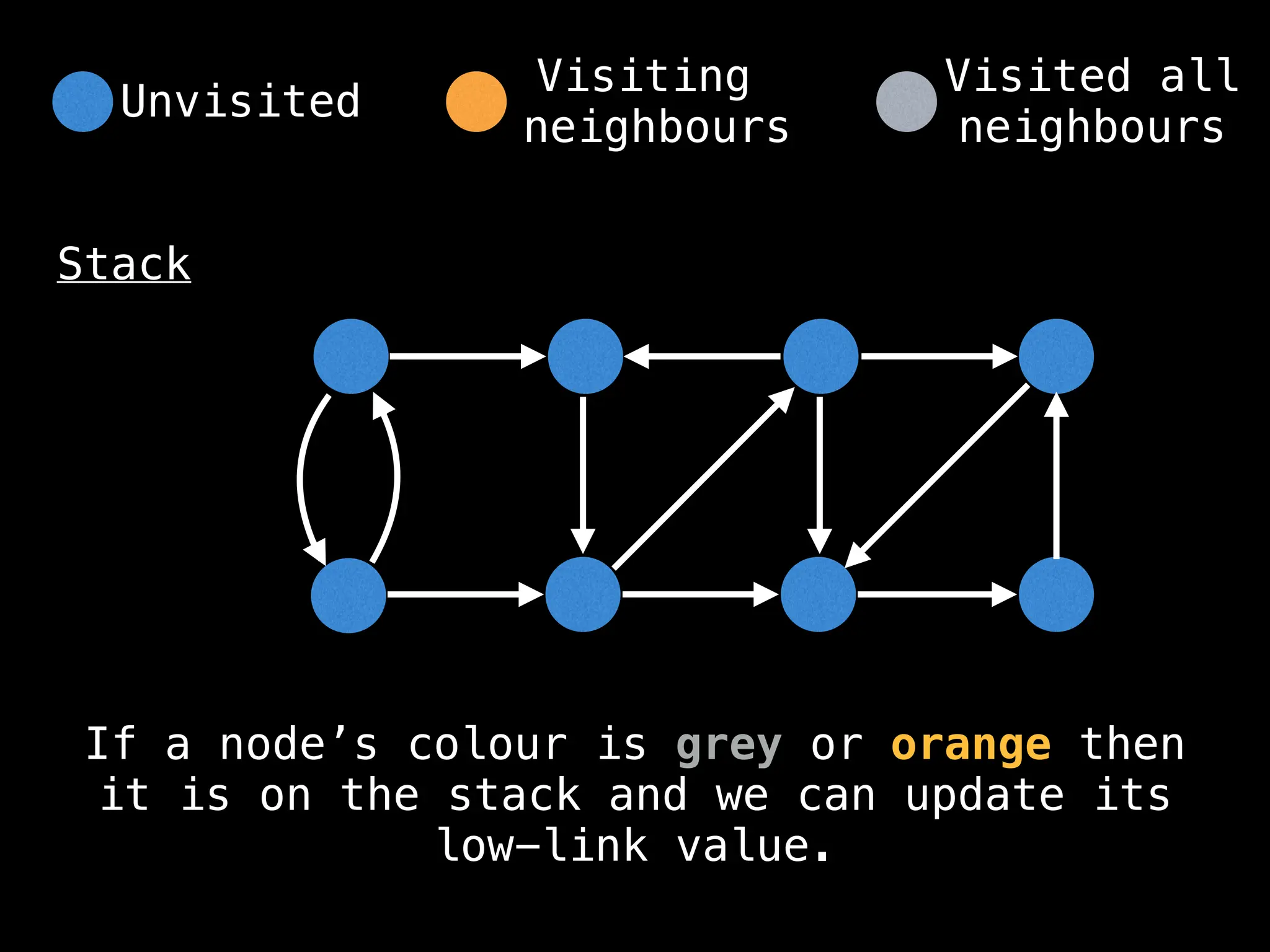
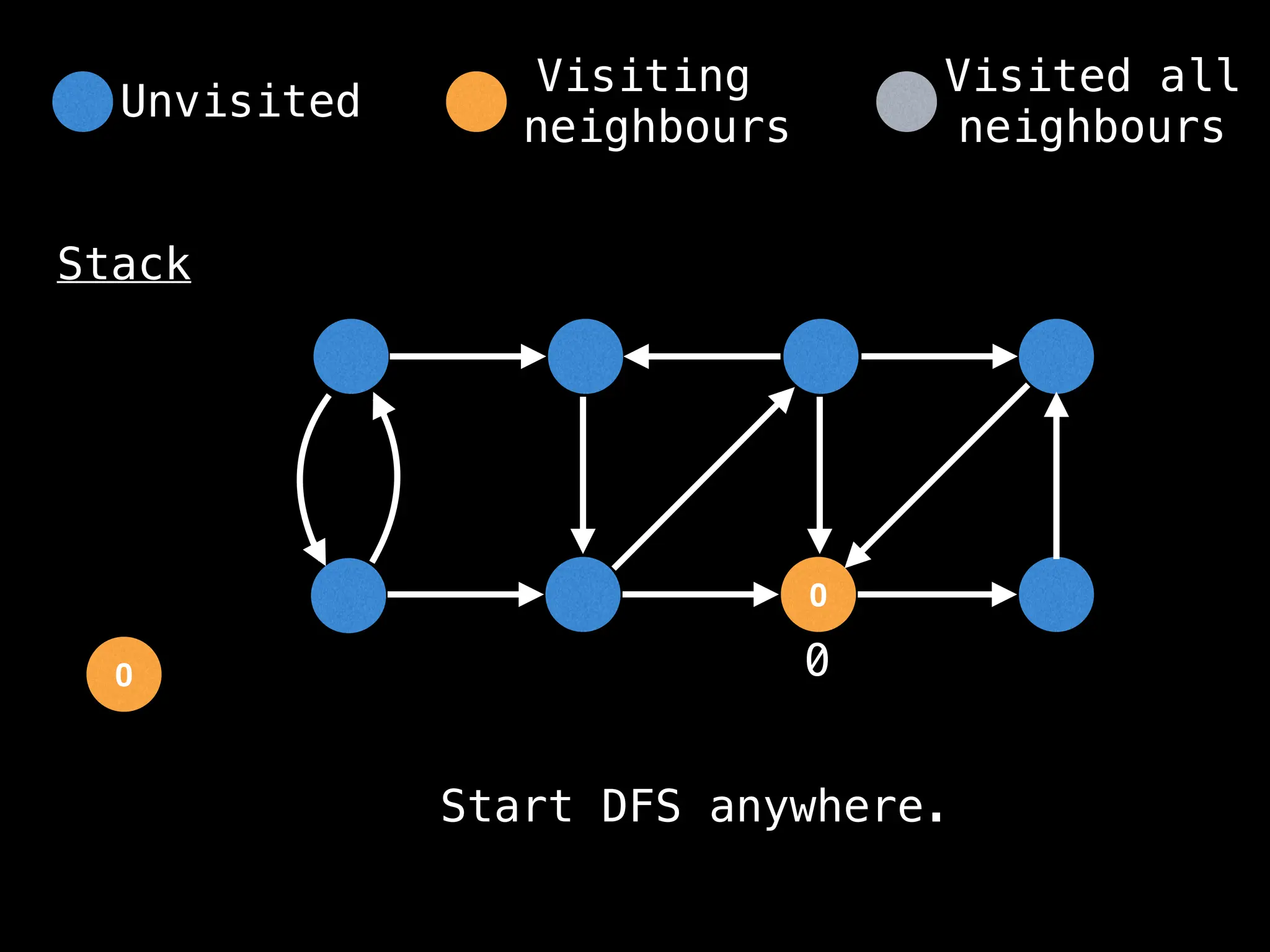
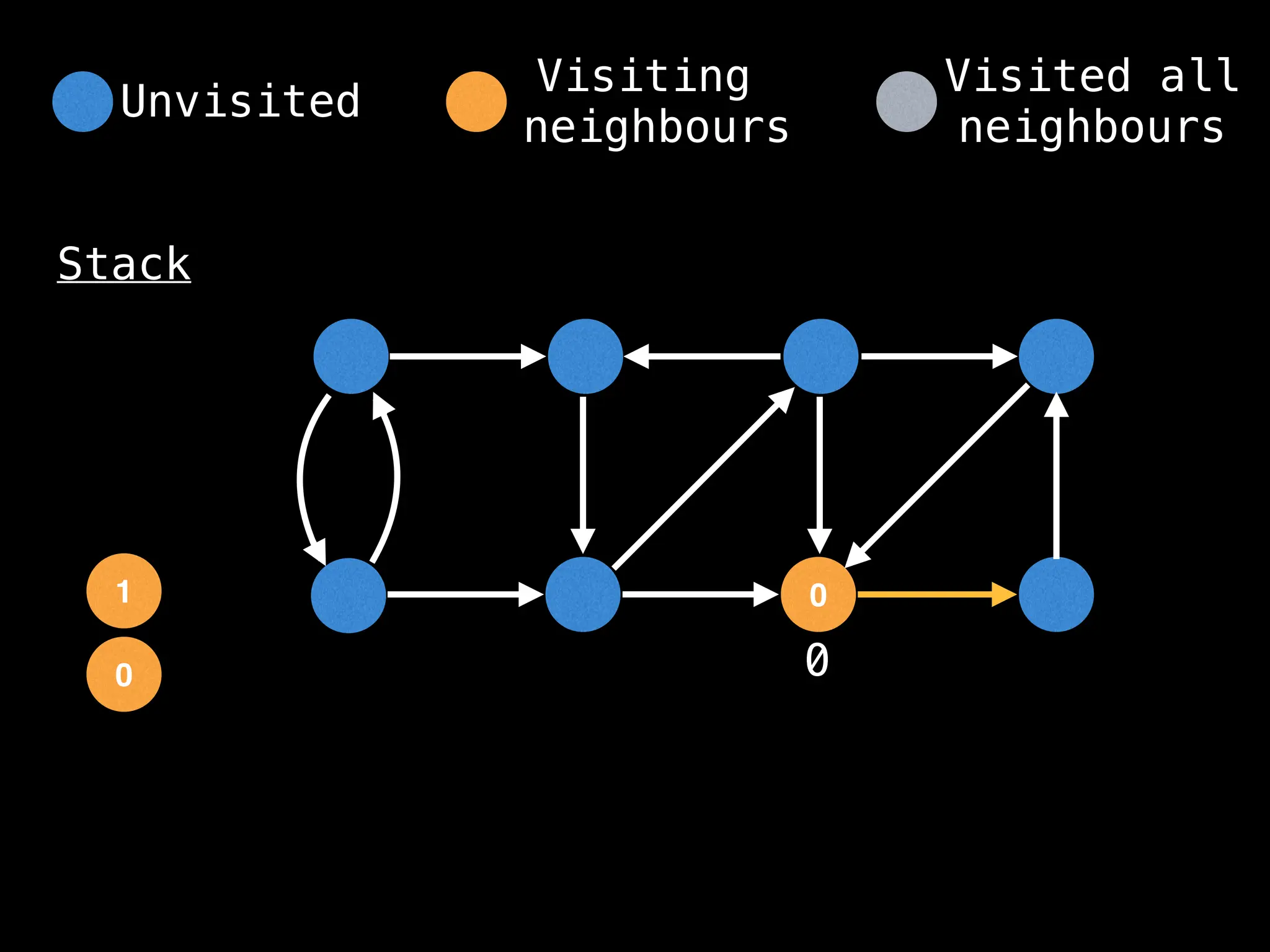
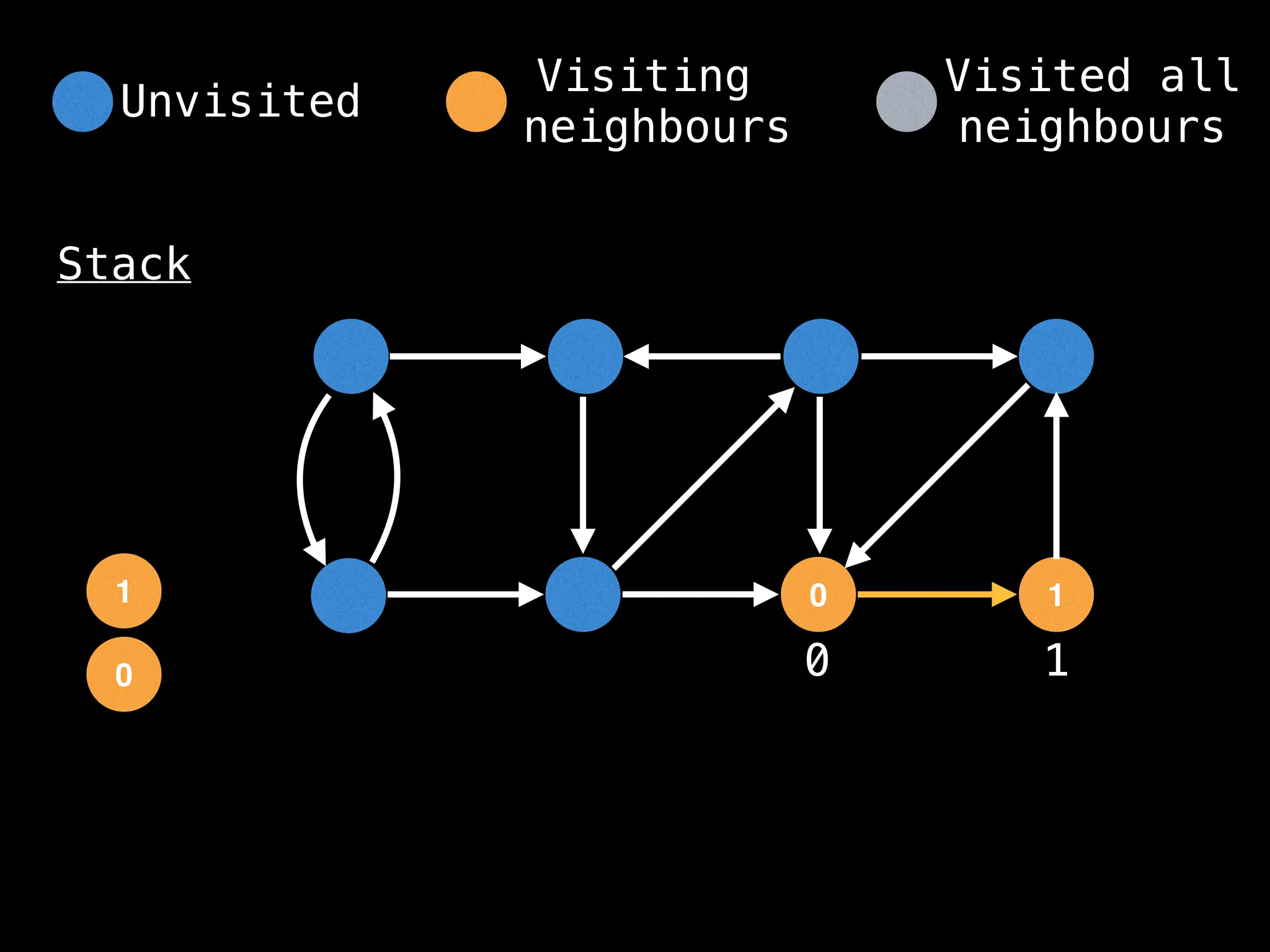
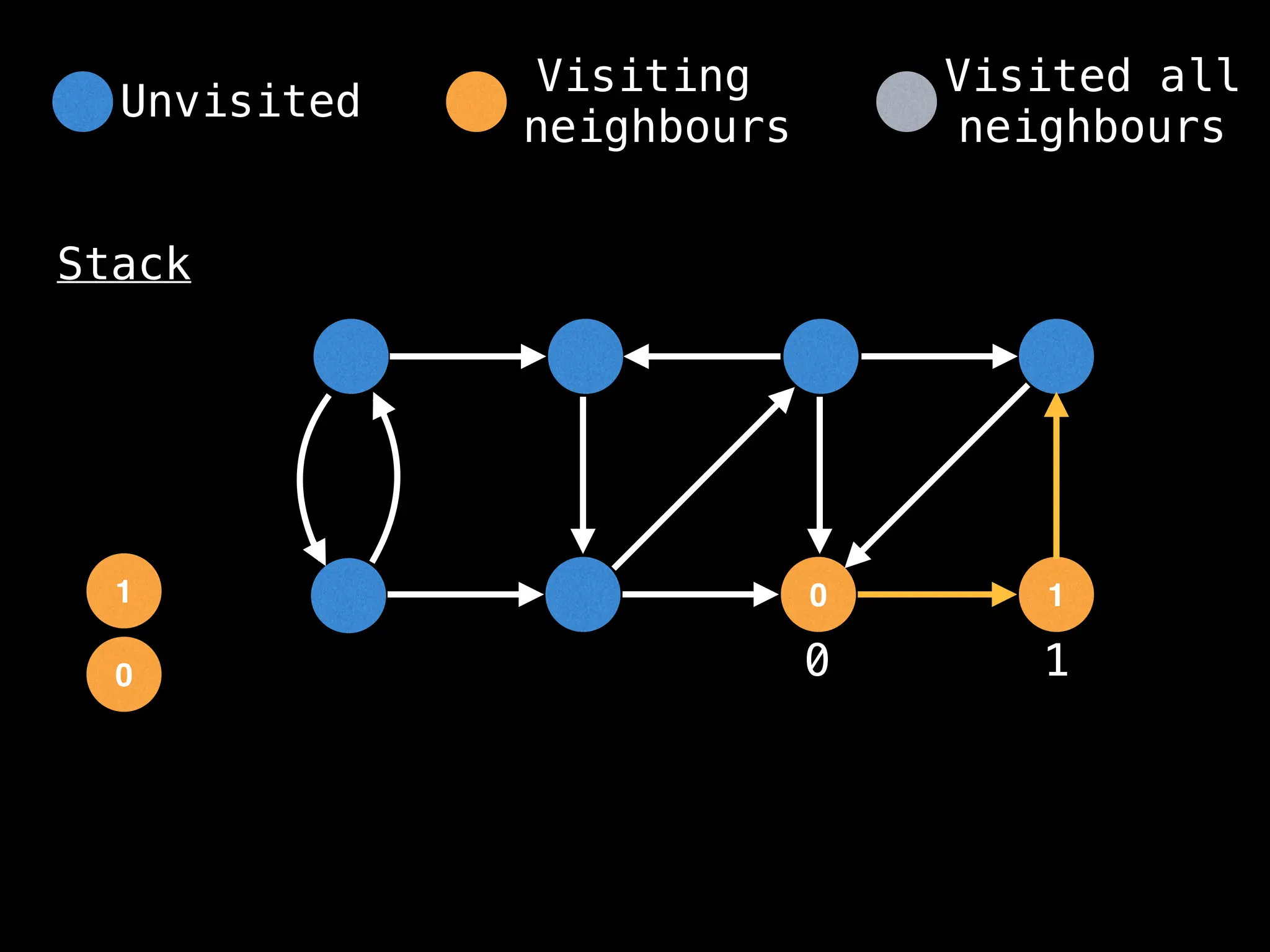
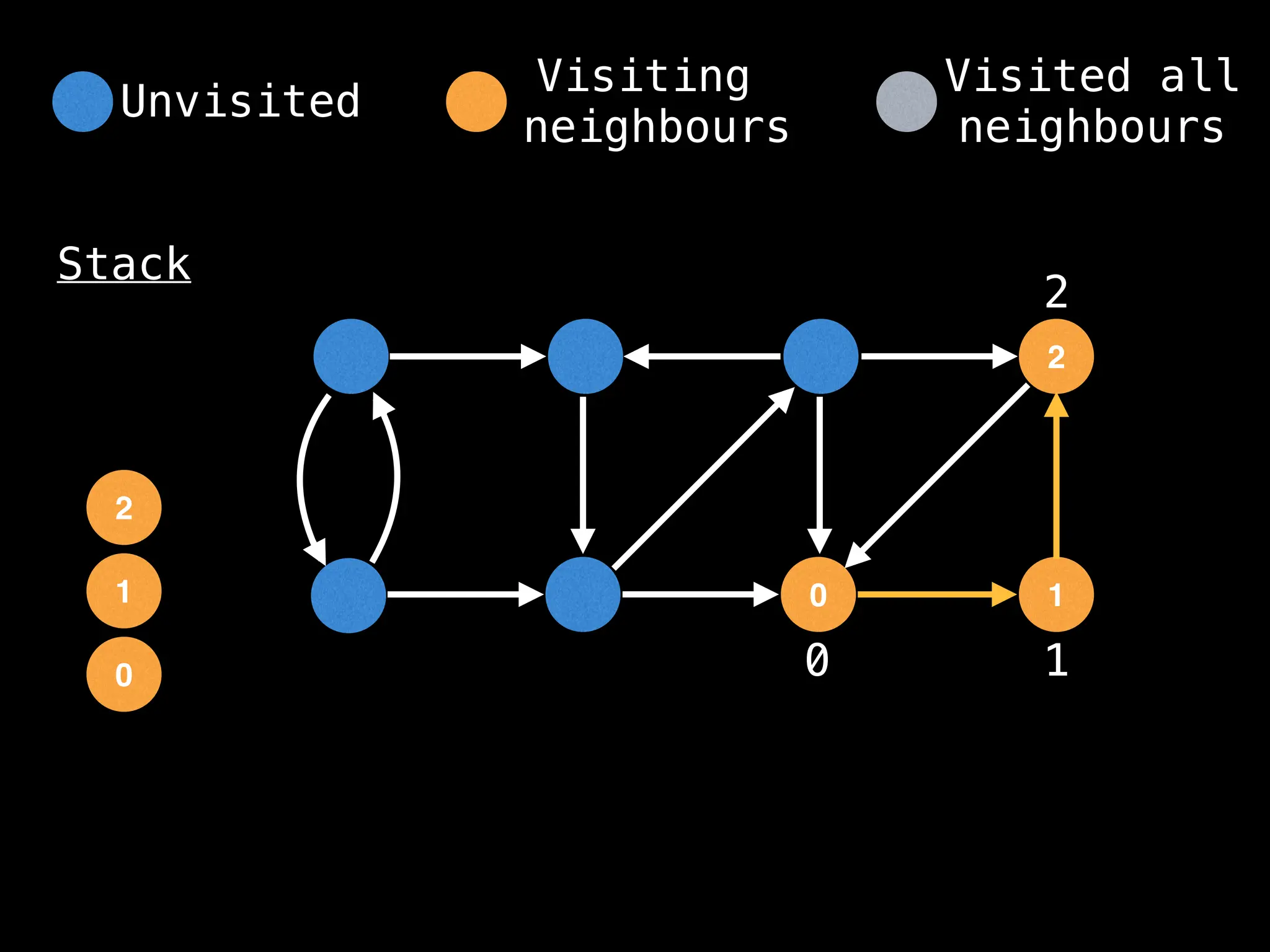
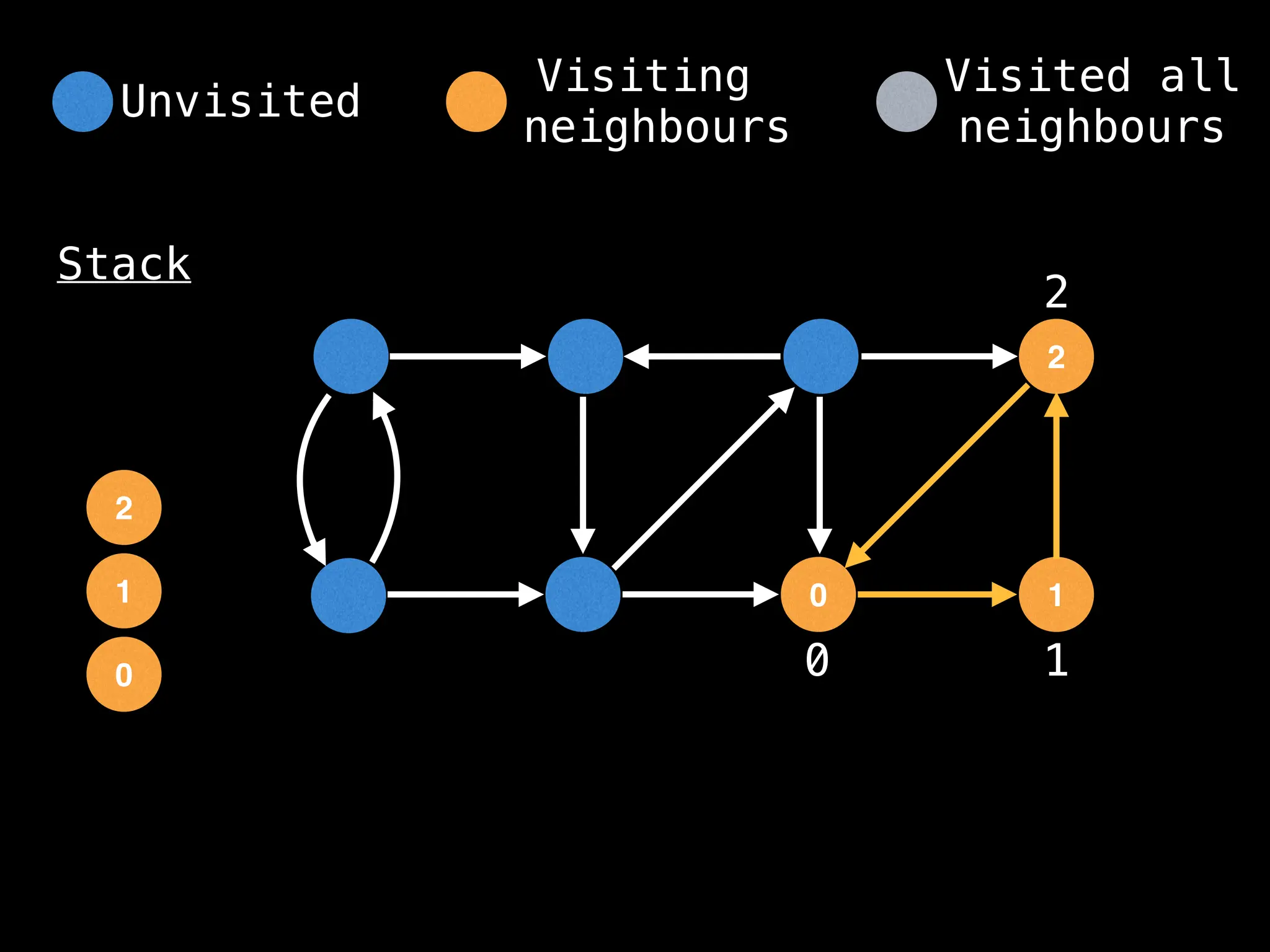
![0
2
1
0
Stack
1
2
0 1
0
lowlink[2] = min(lowlink[2], lowlink[0])
= 0
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-954-2048.jpg)
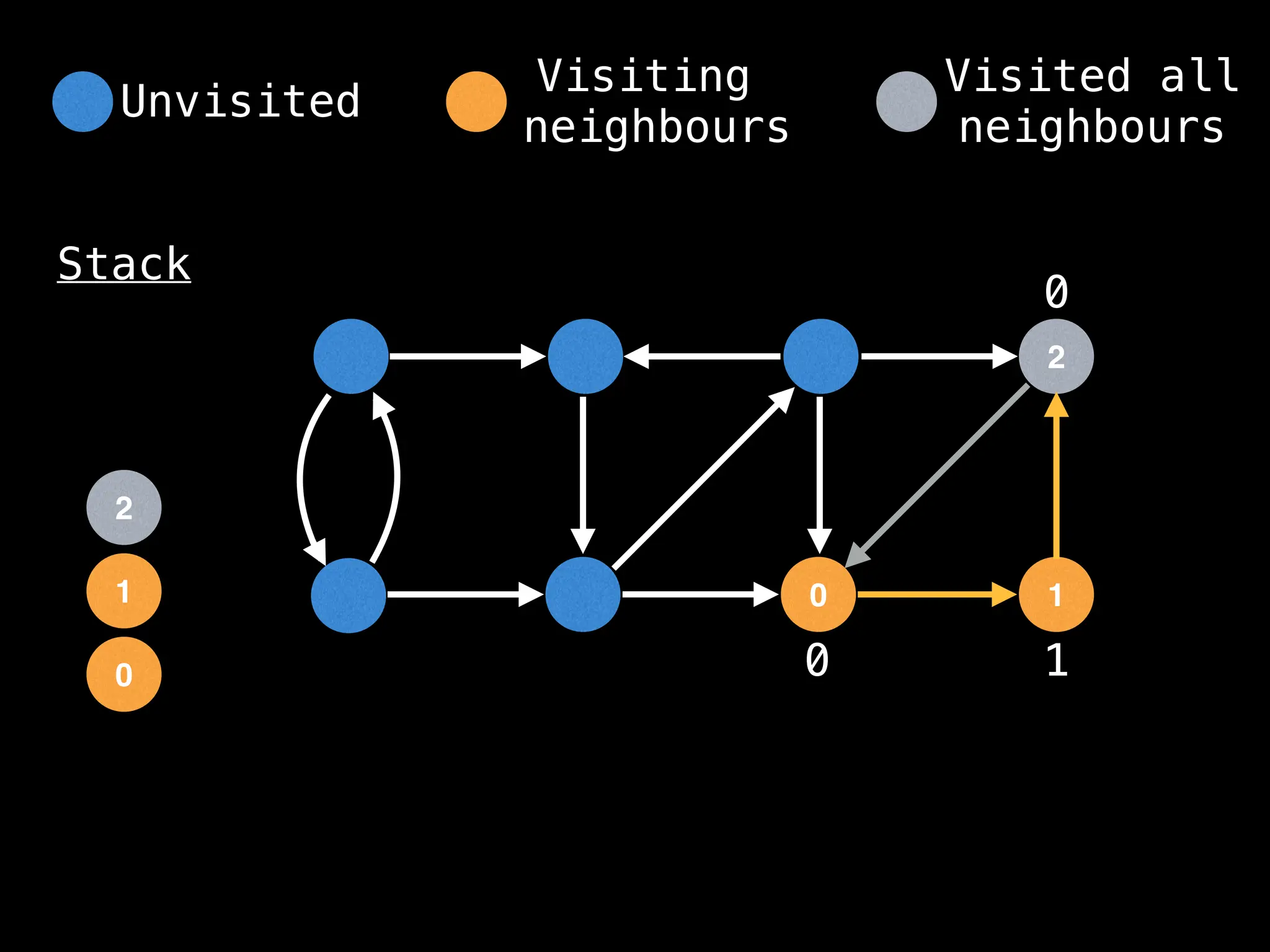
![0
2
1
0
Stack
1
2
0 0
0
lowlink[1] = min(lowlink[1], lowlink[2])
= 0
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-956-2048.jpg)
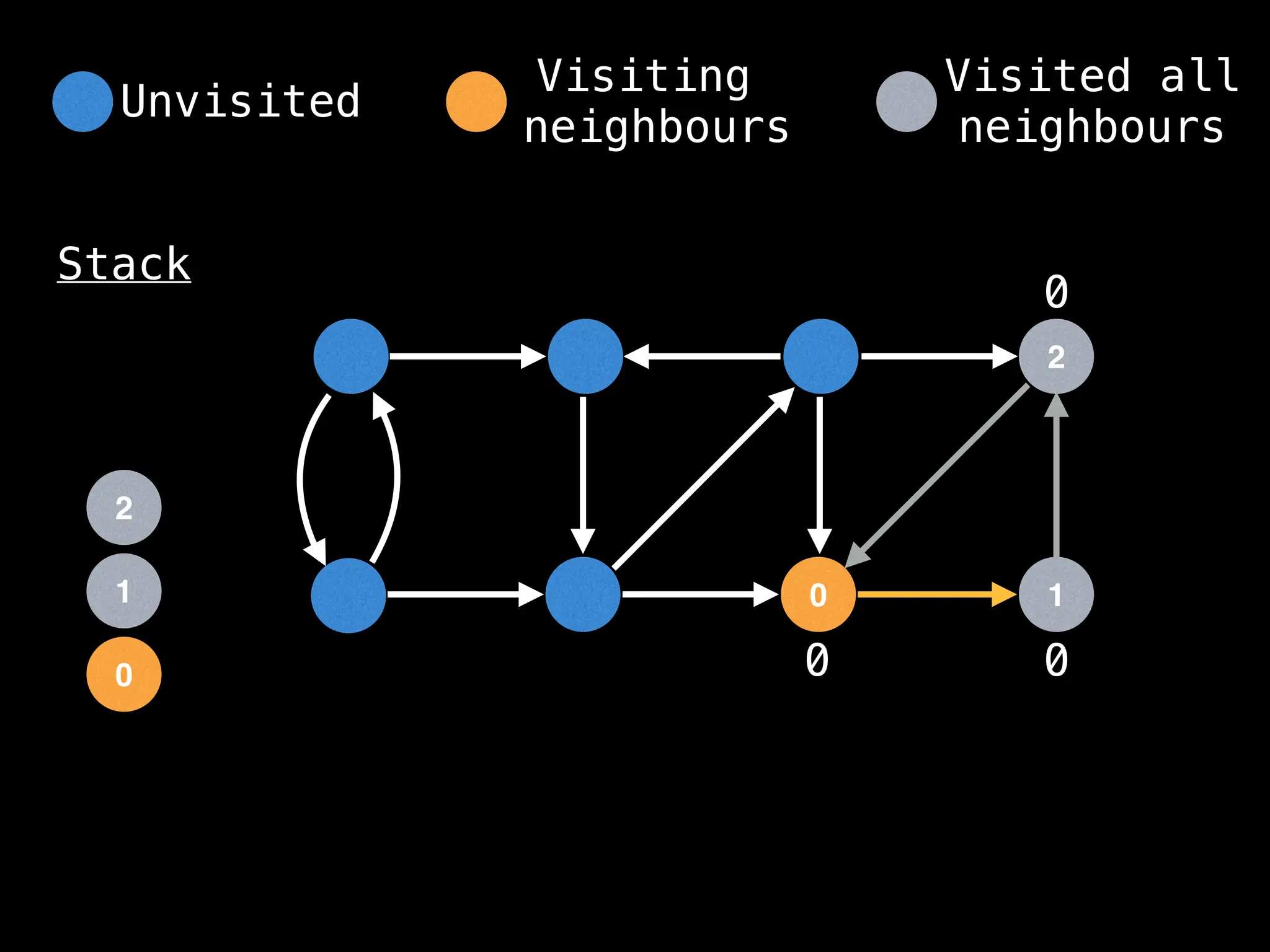
![0
2
1
0
Stack
1
2
0 0
0
lowlink[0] = min(lowlink[0], lowlink[1])
= 0
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-958-2048.jpg)
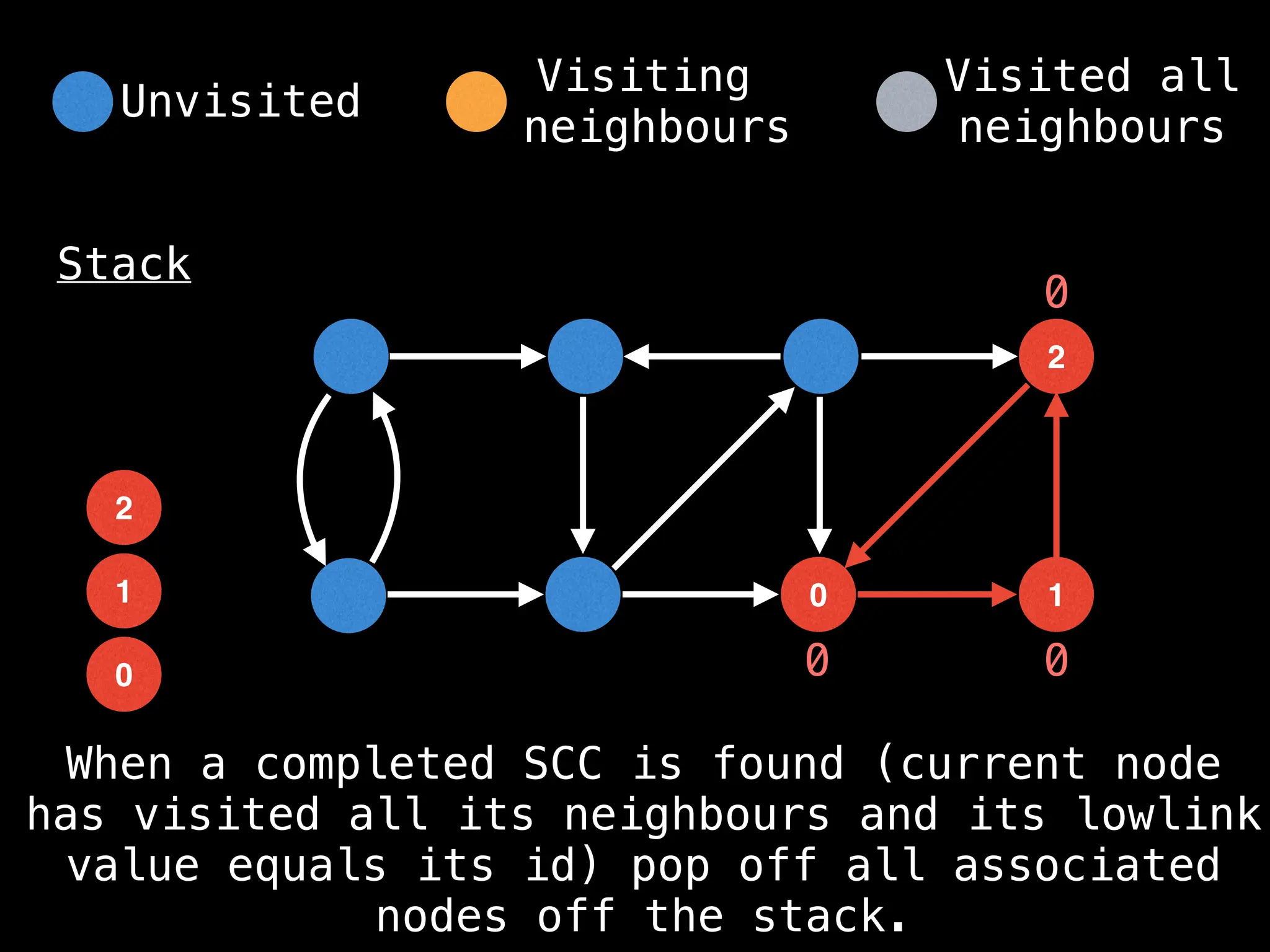
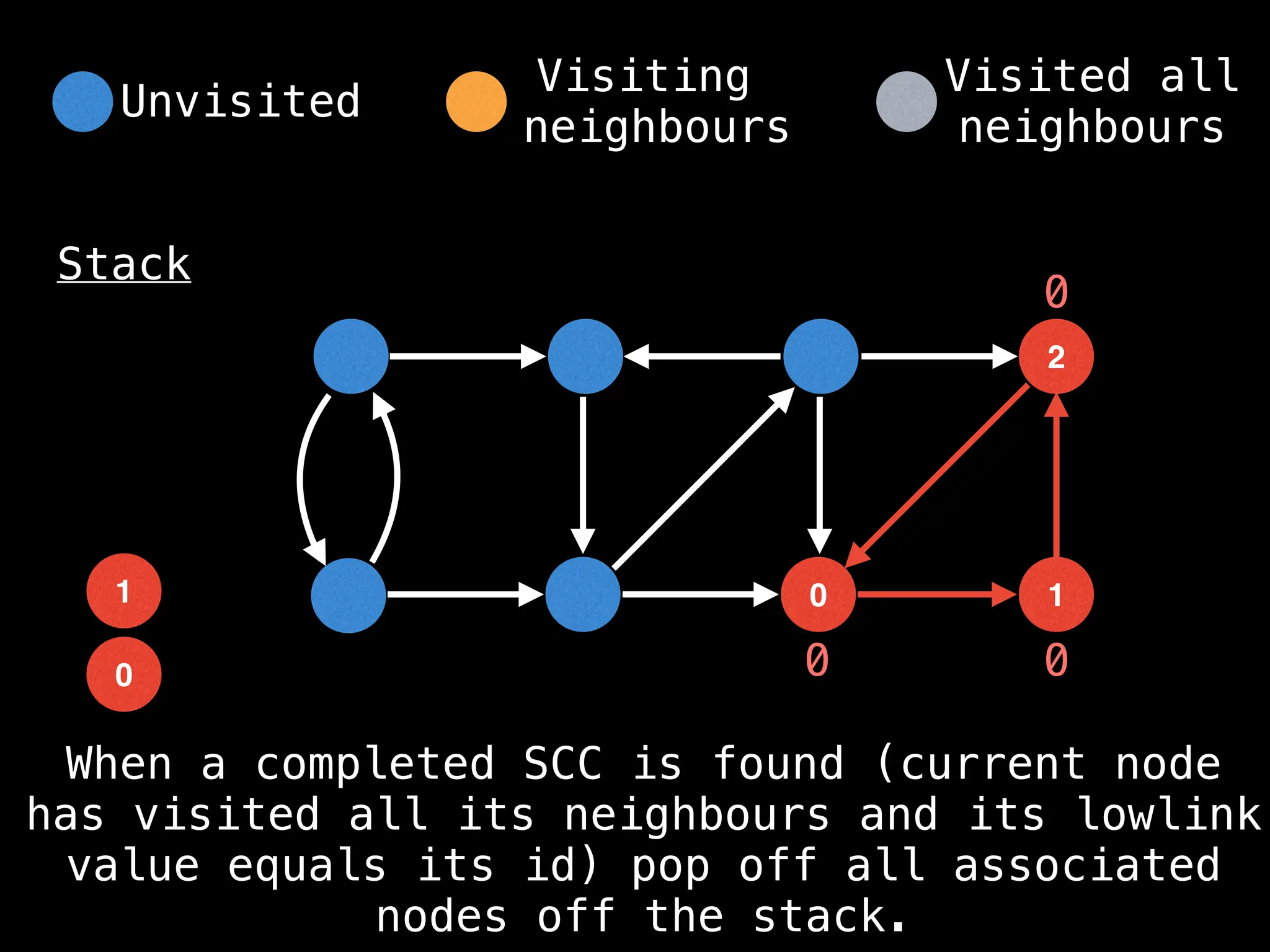
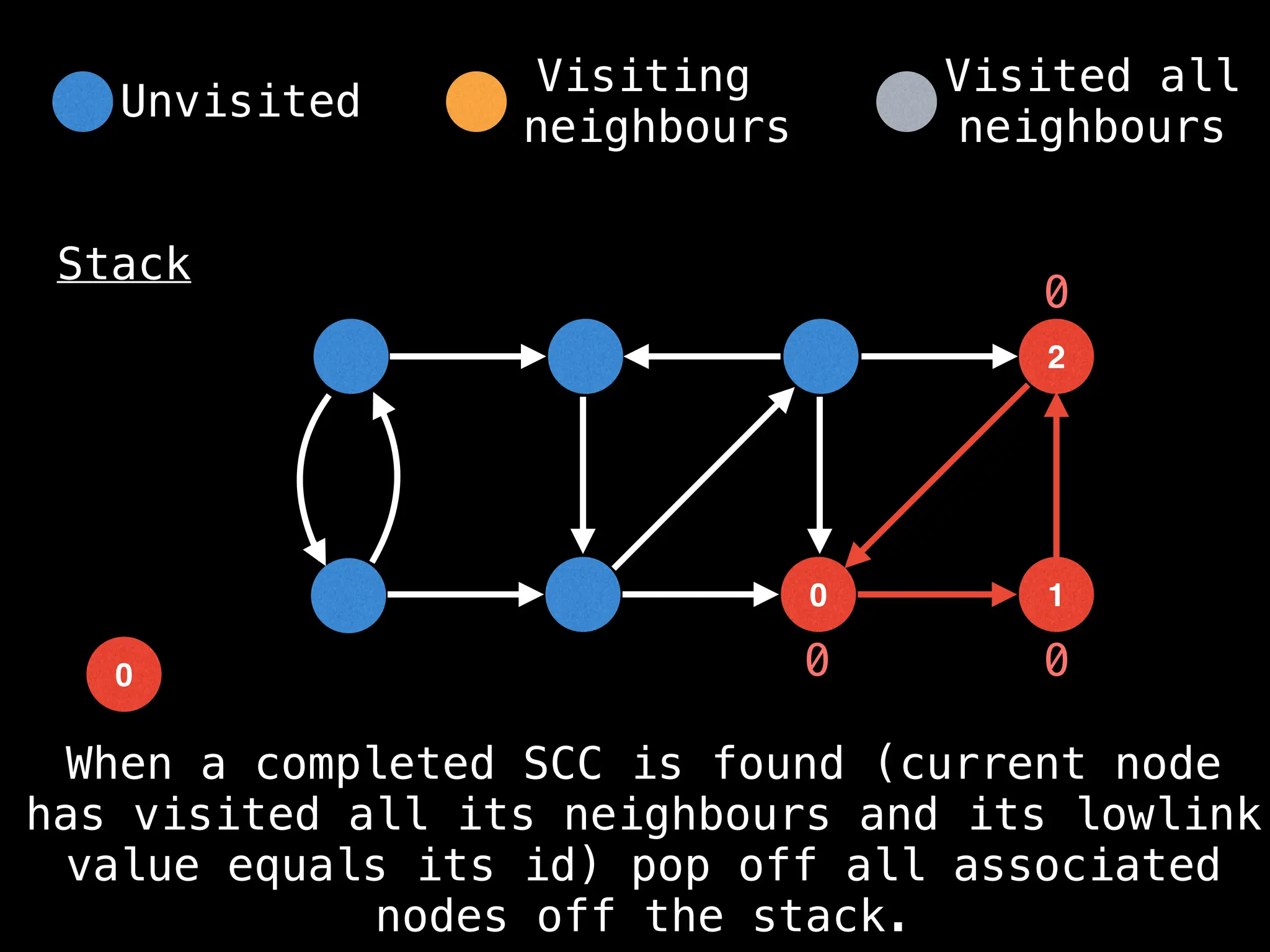
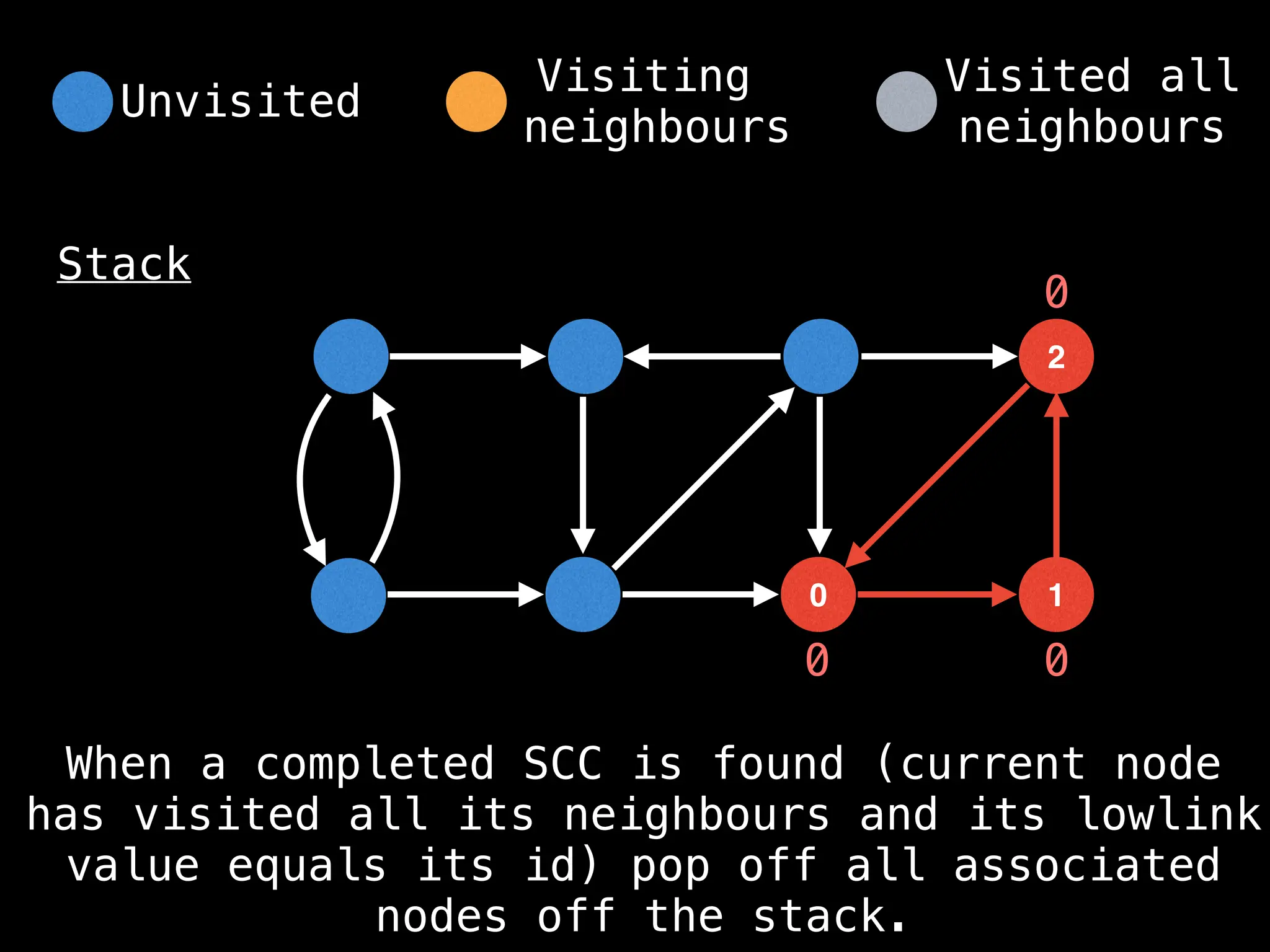
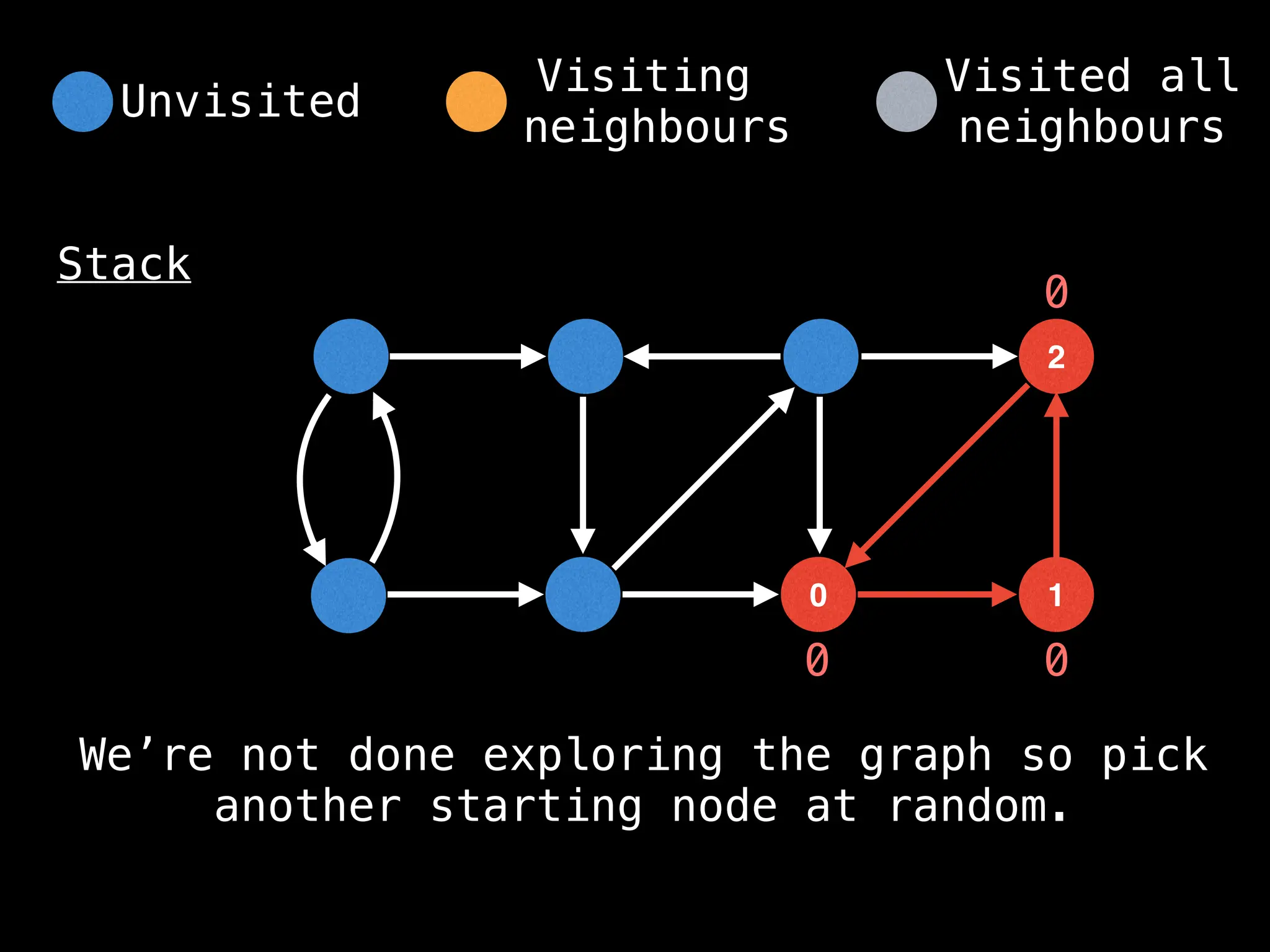
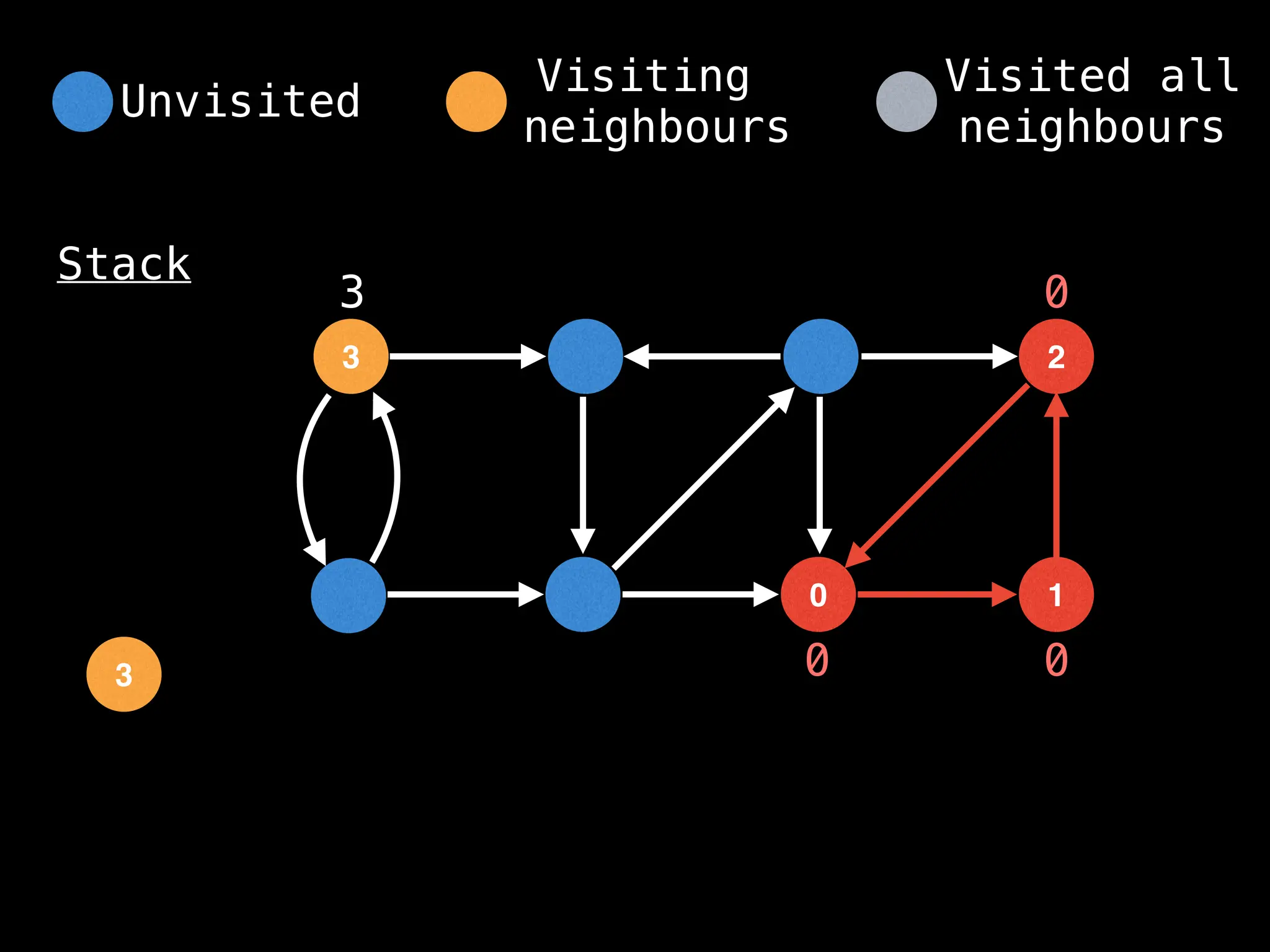
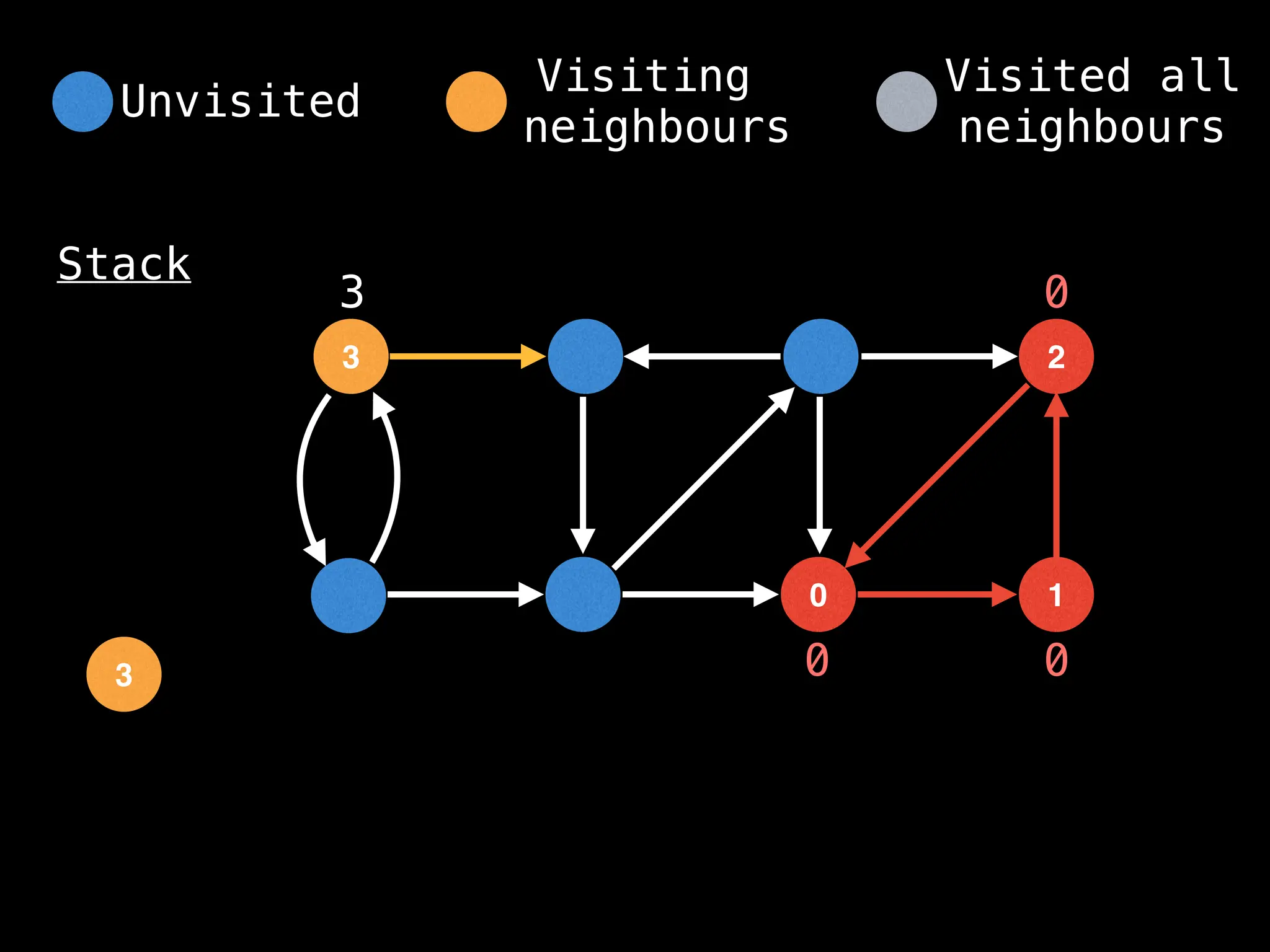
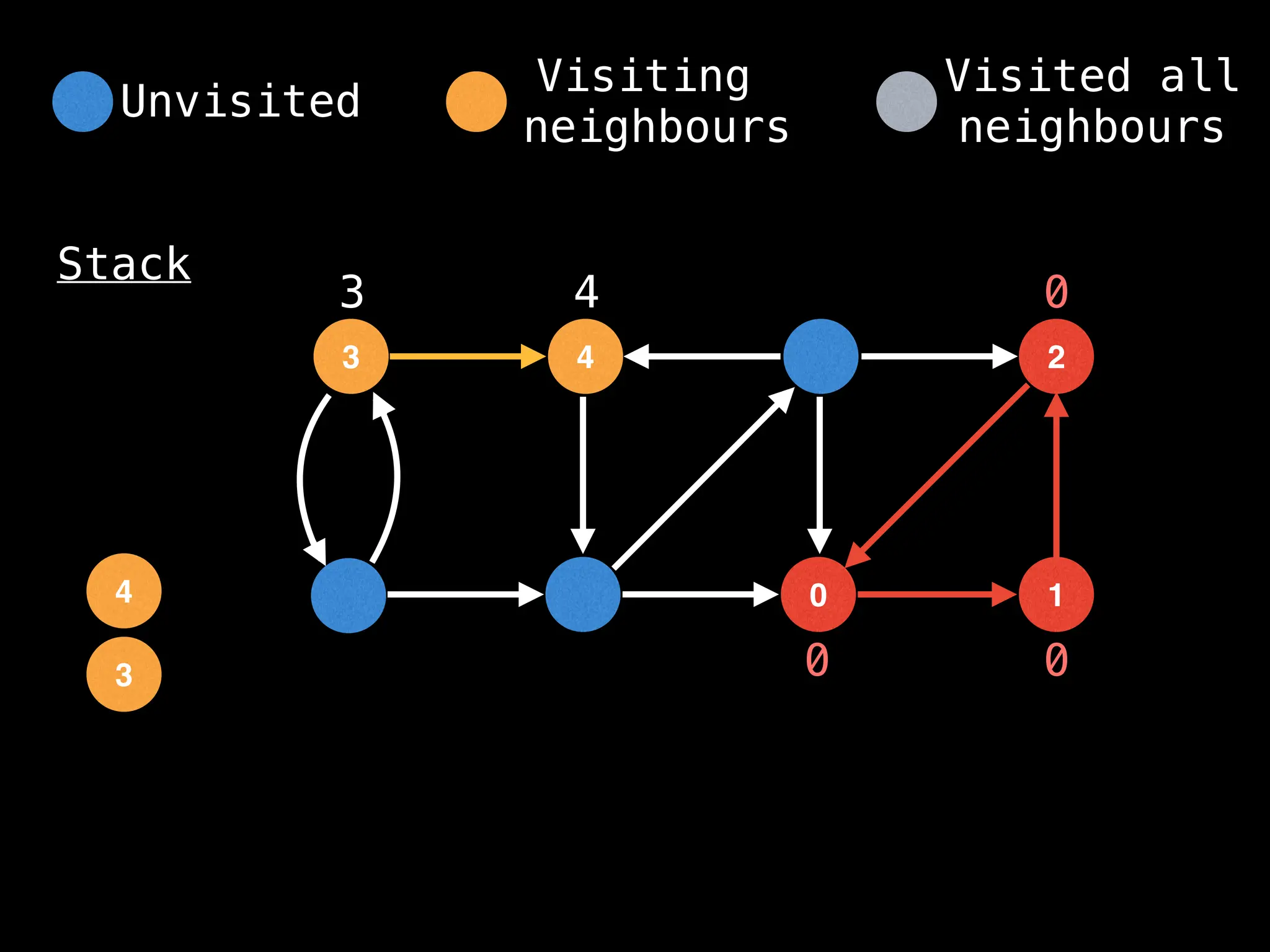
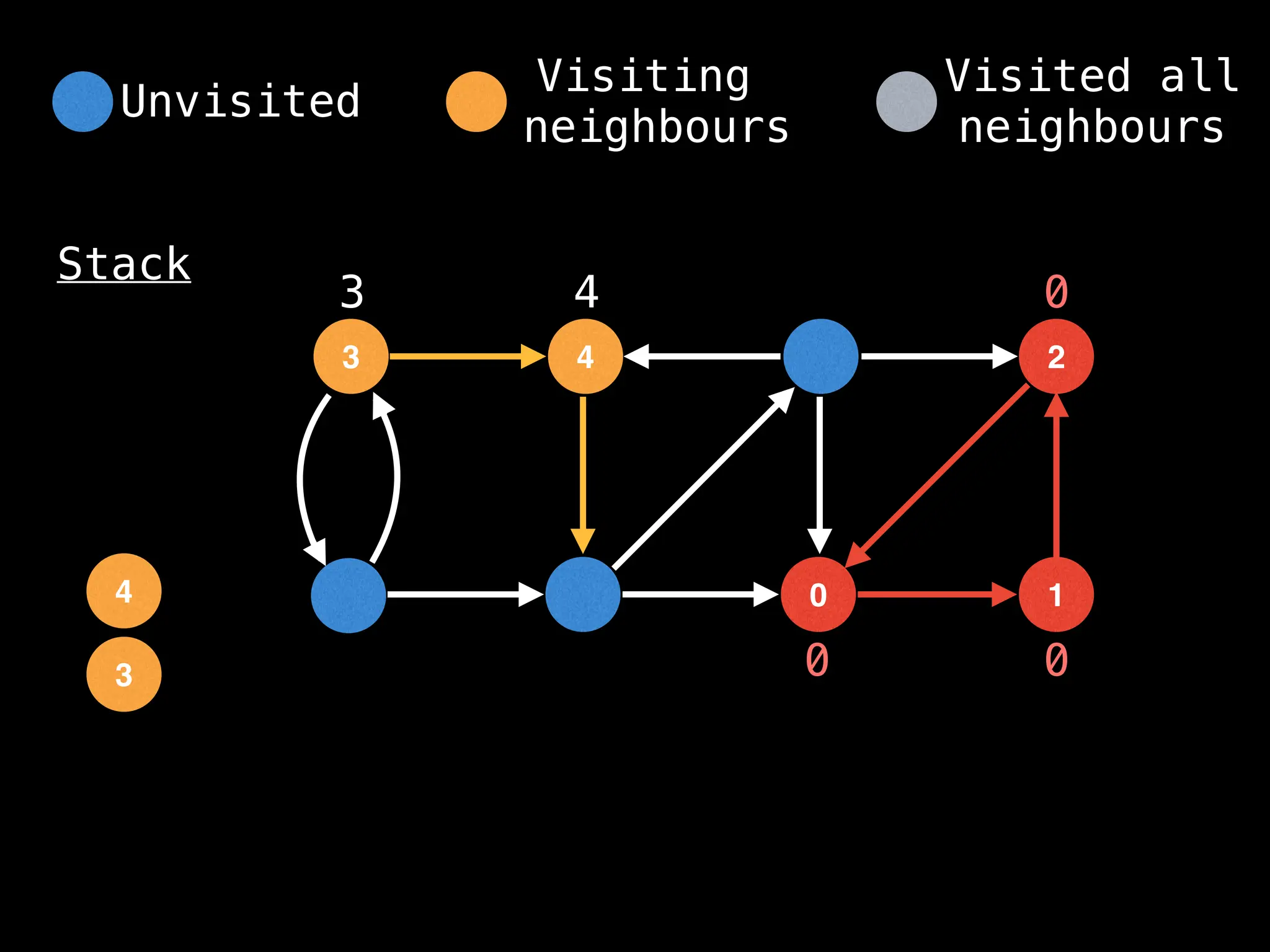
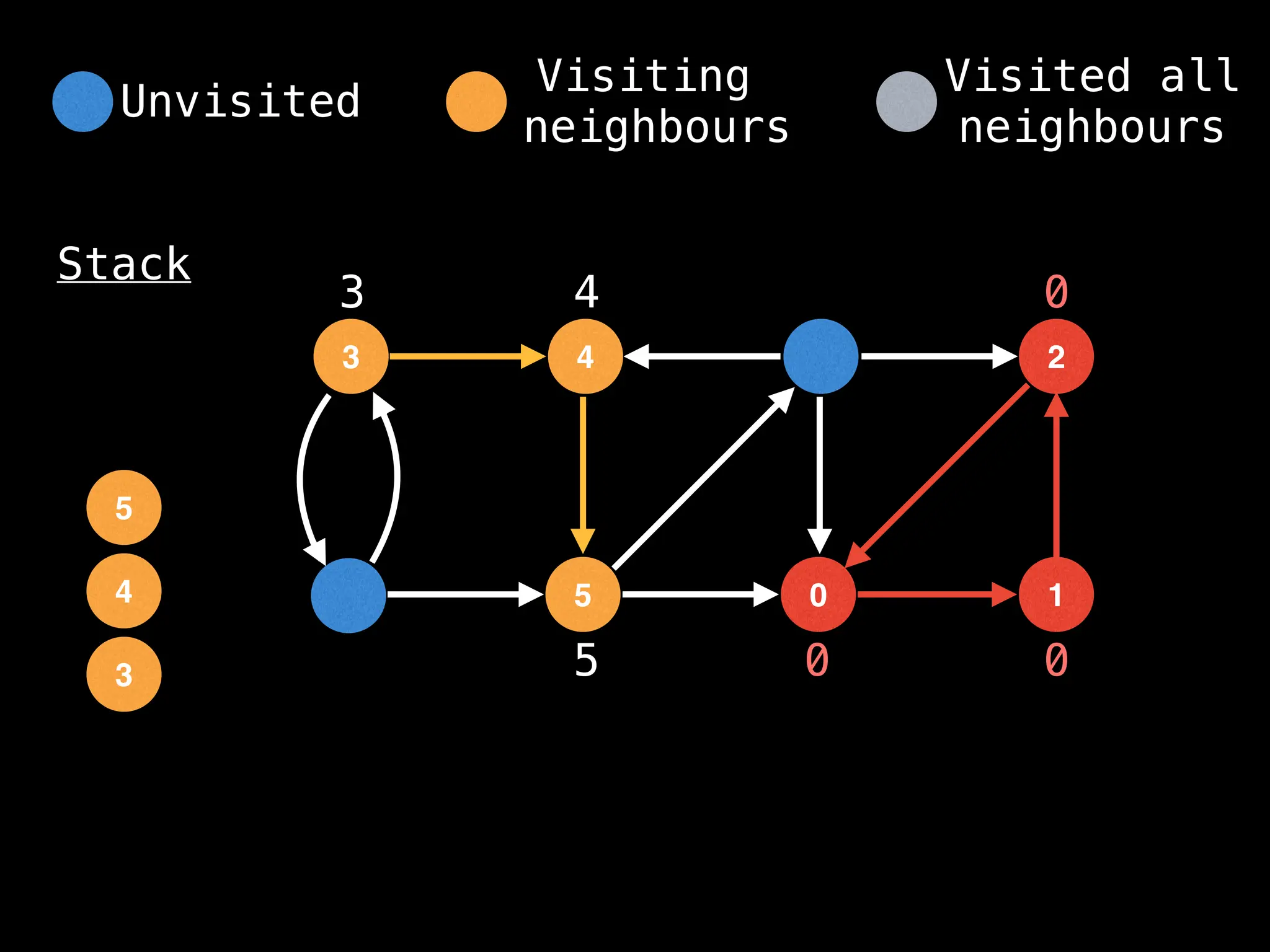
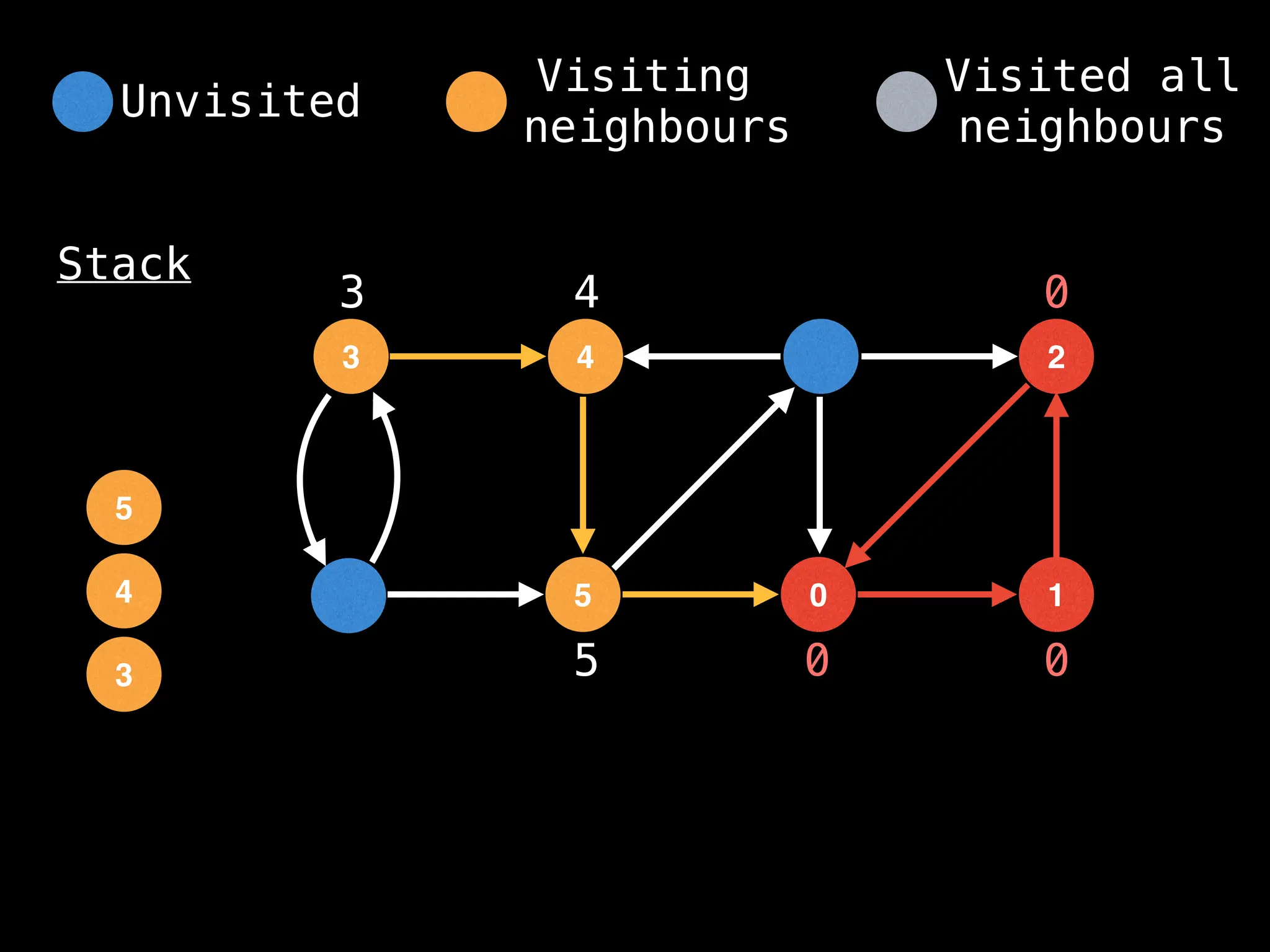
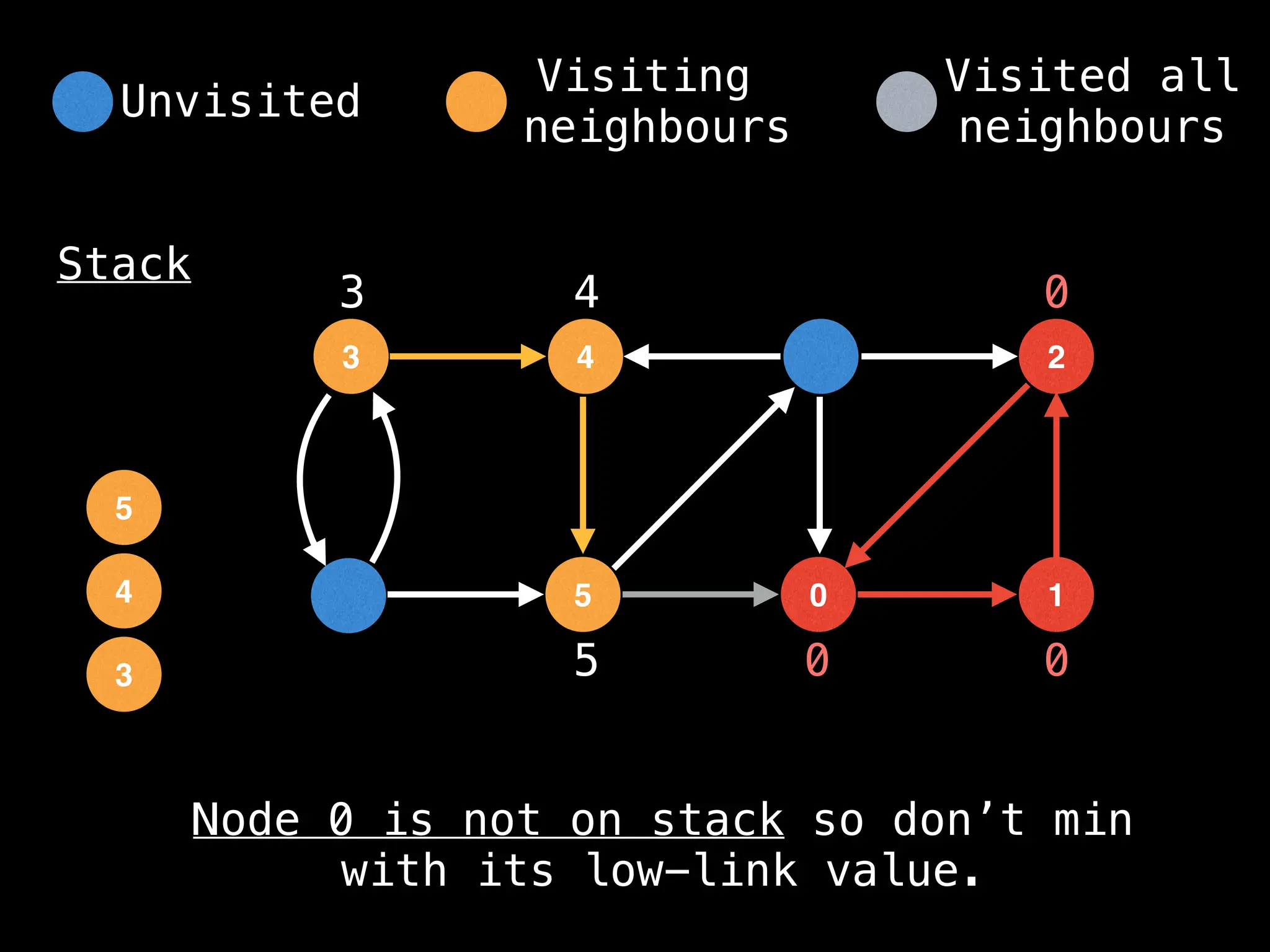
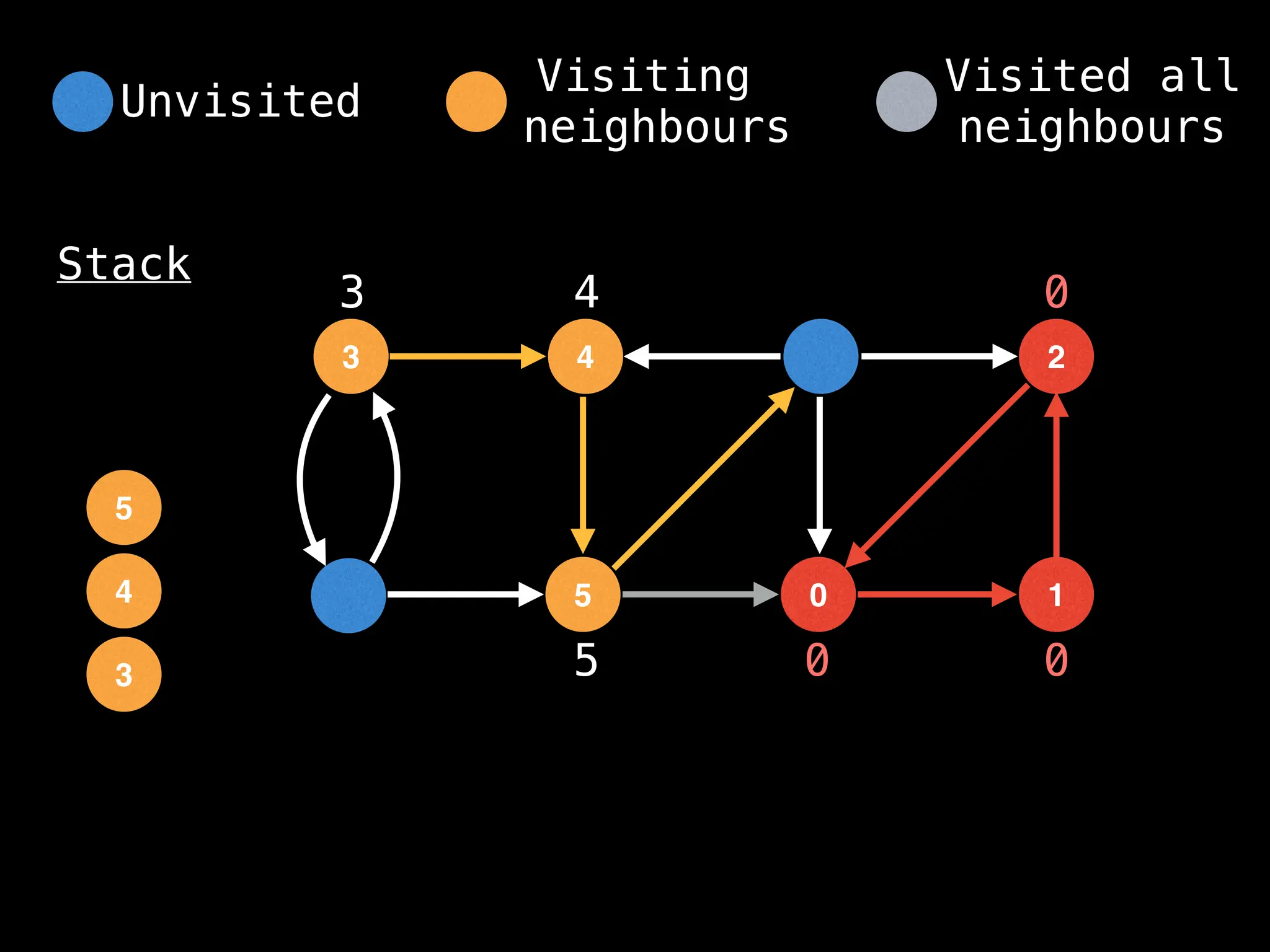
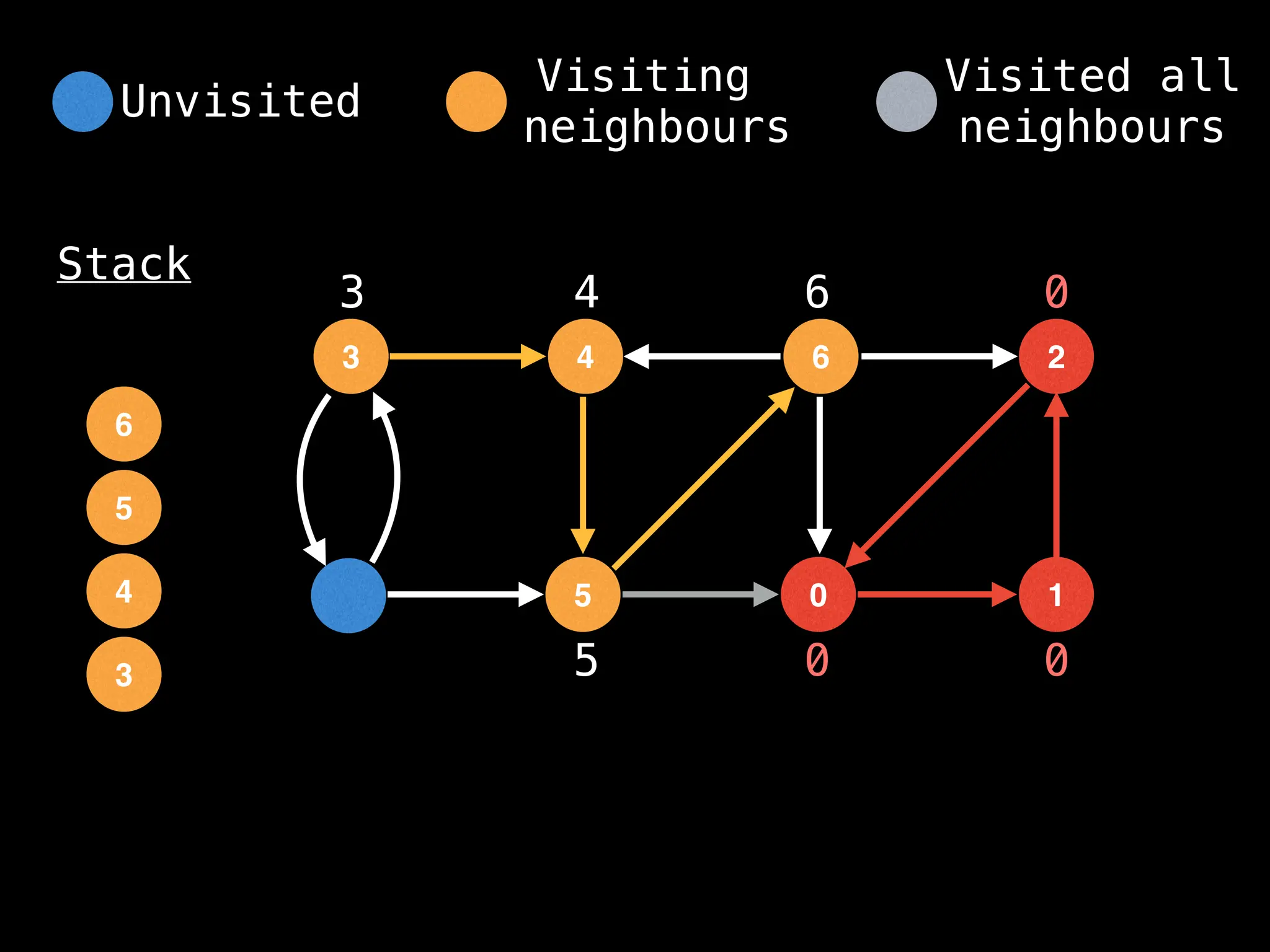
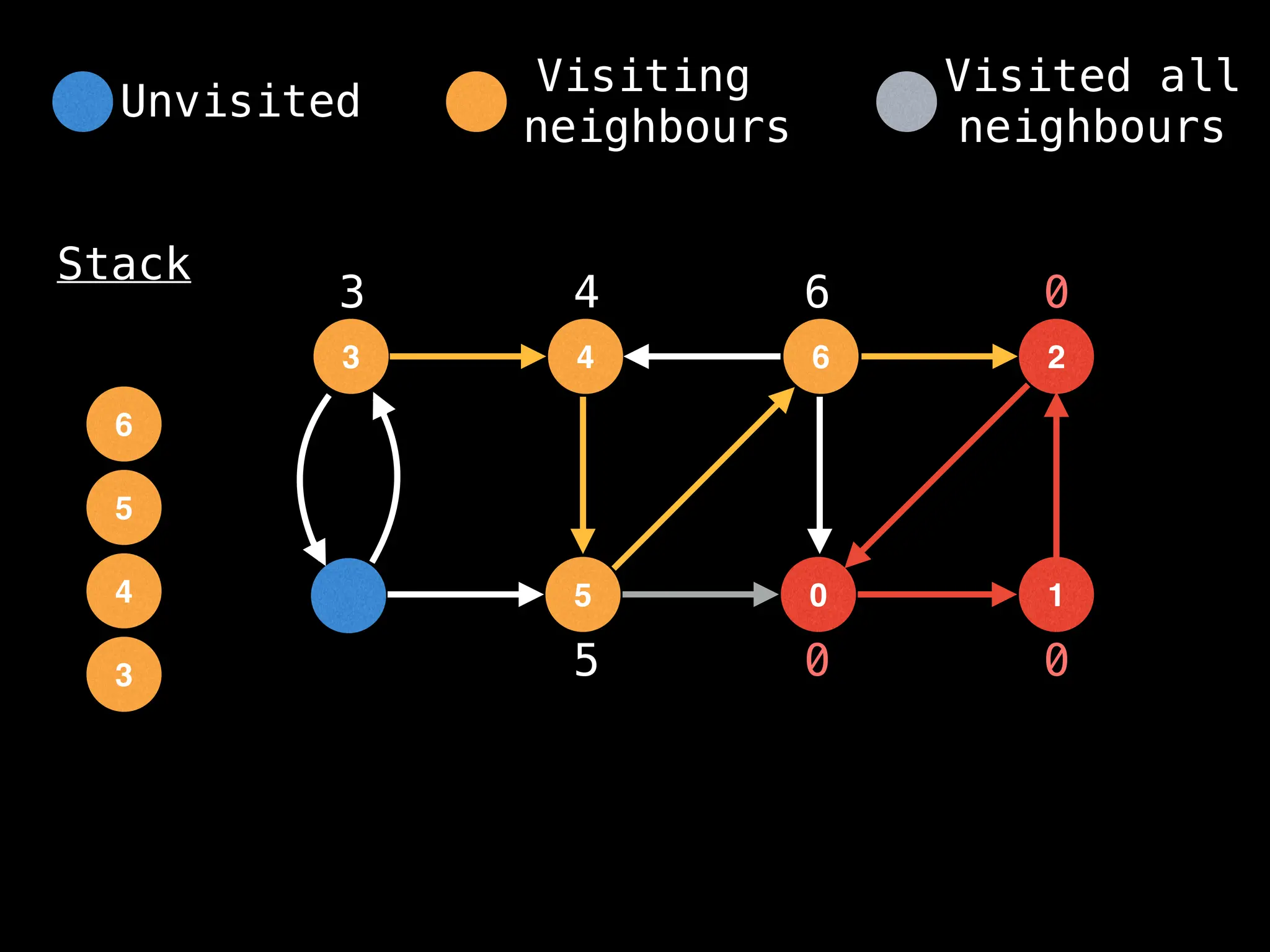
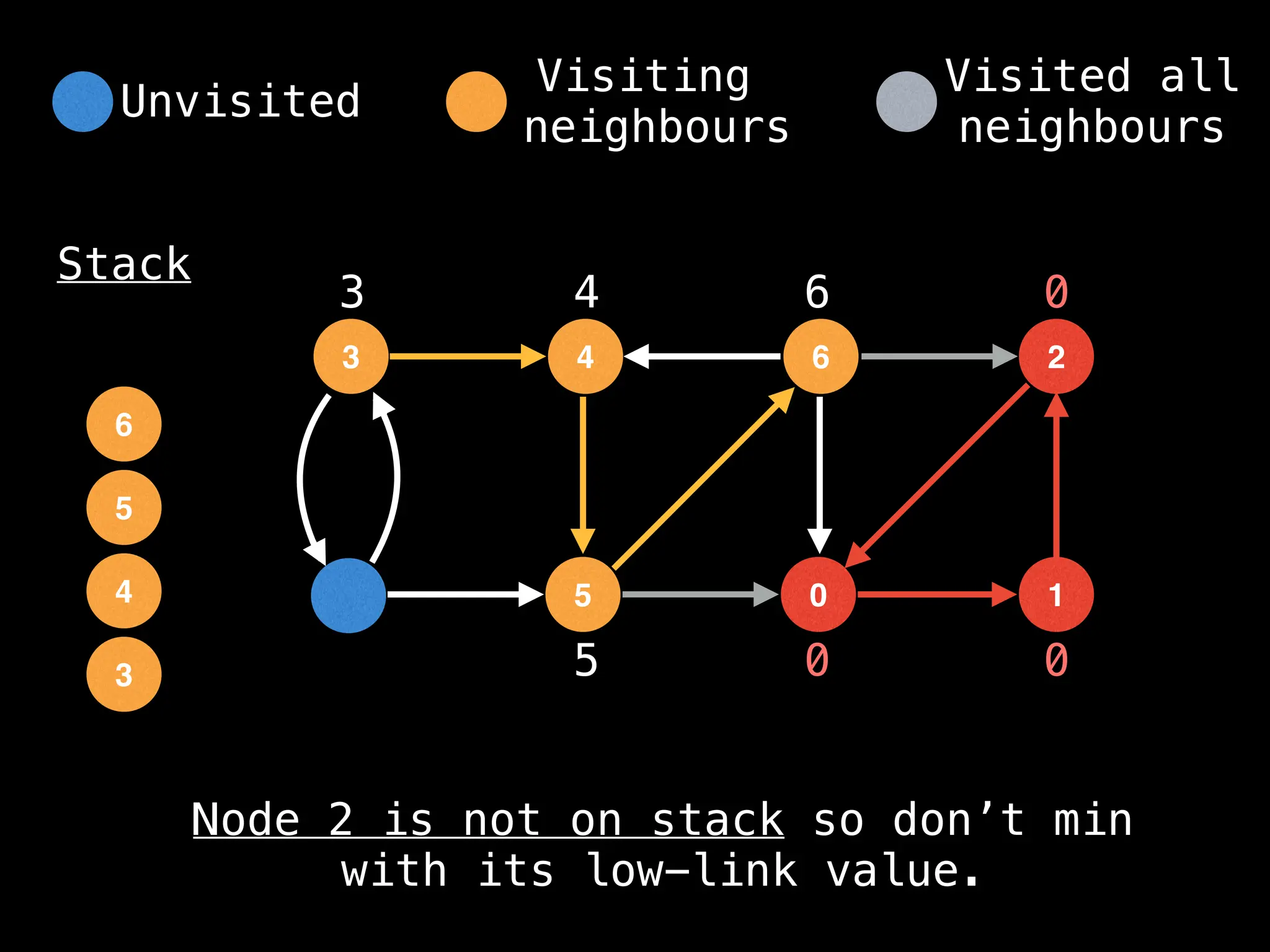
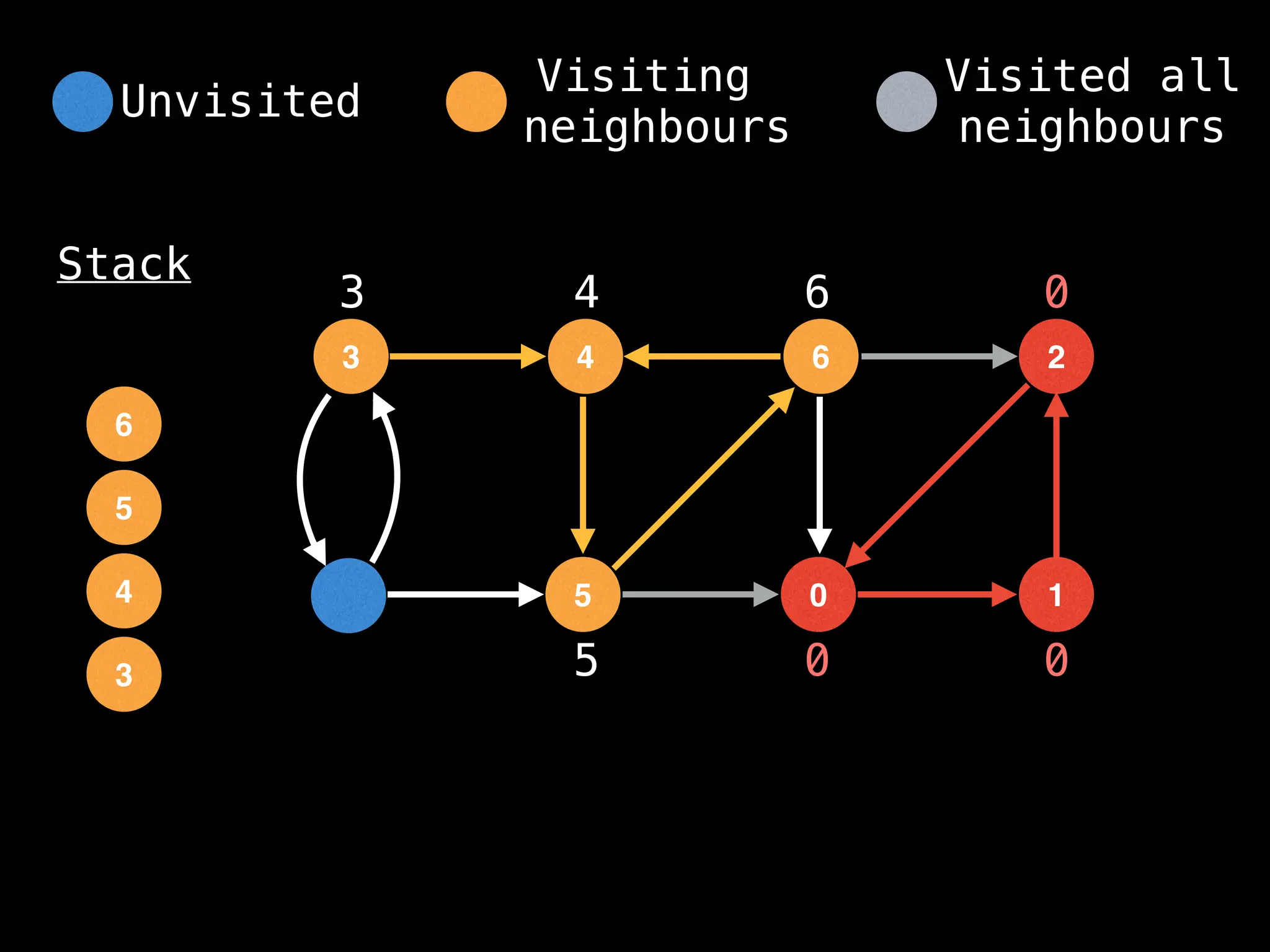
![4
3 6
5 0
2
1
Stack
0 0
0
3
3
4
4
5
5
4
6
lowlink[6] = min(lowlink[6], lowlink[4])
= 4
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-976-2048.jpg)
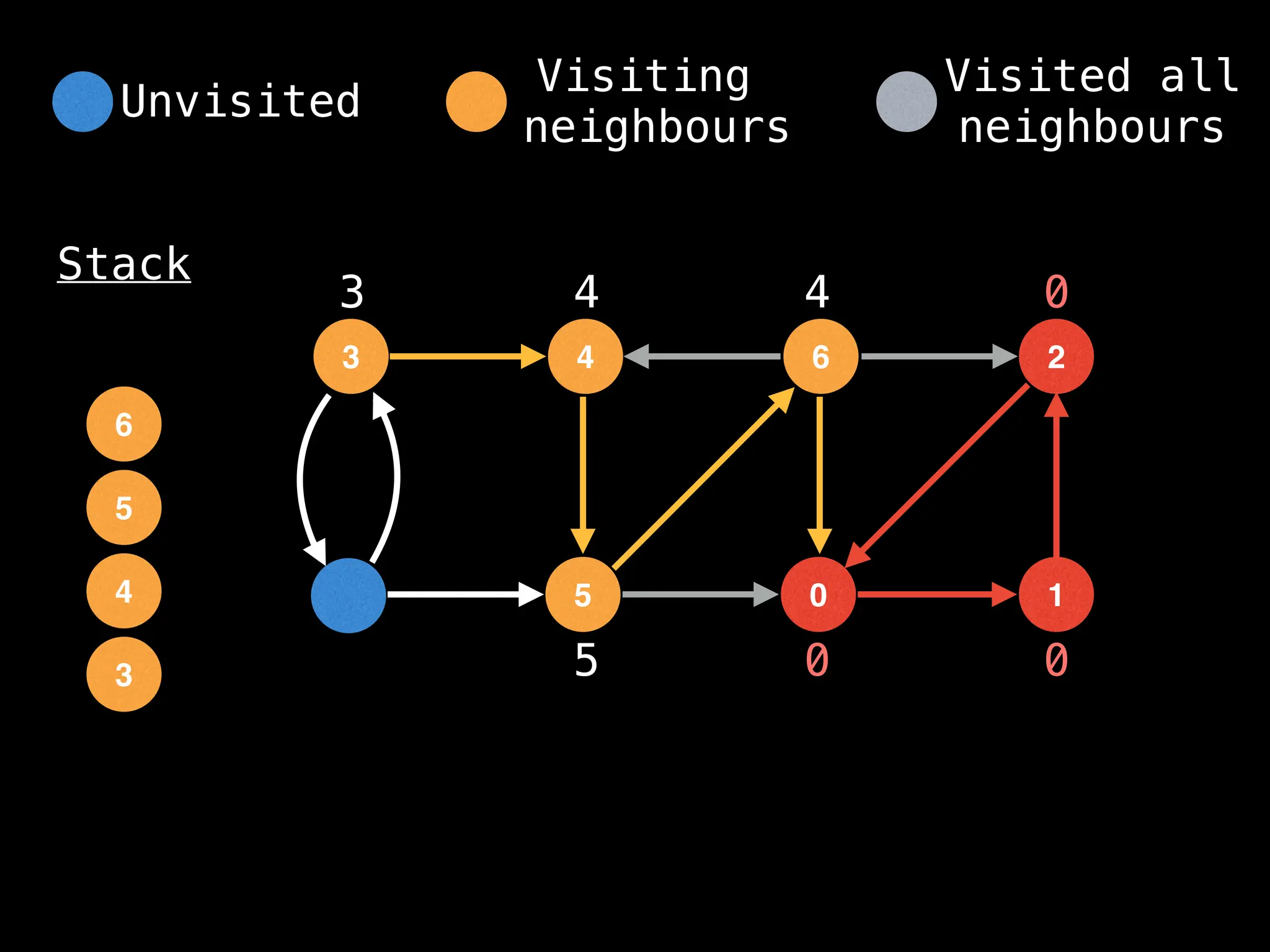
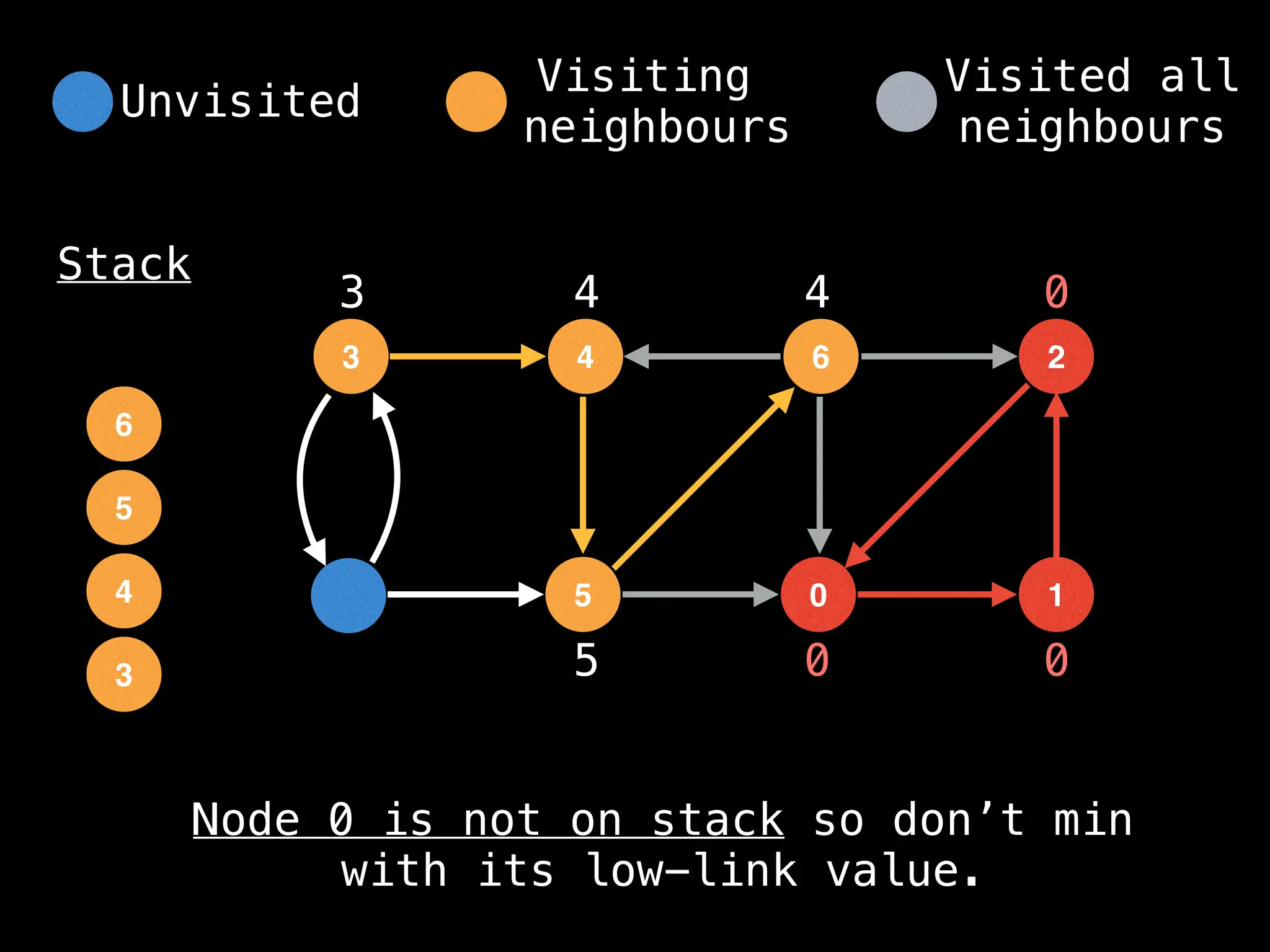
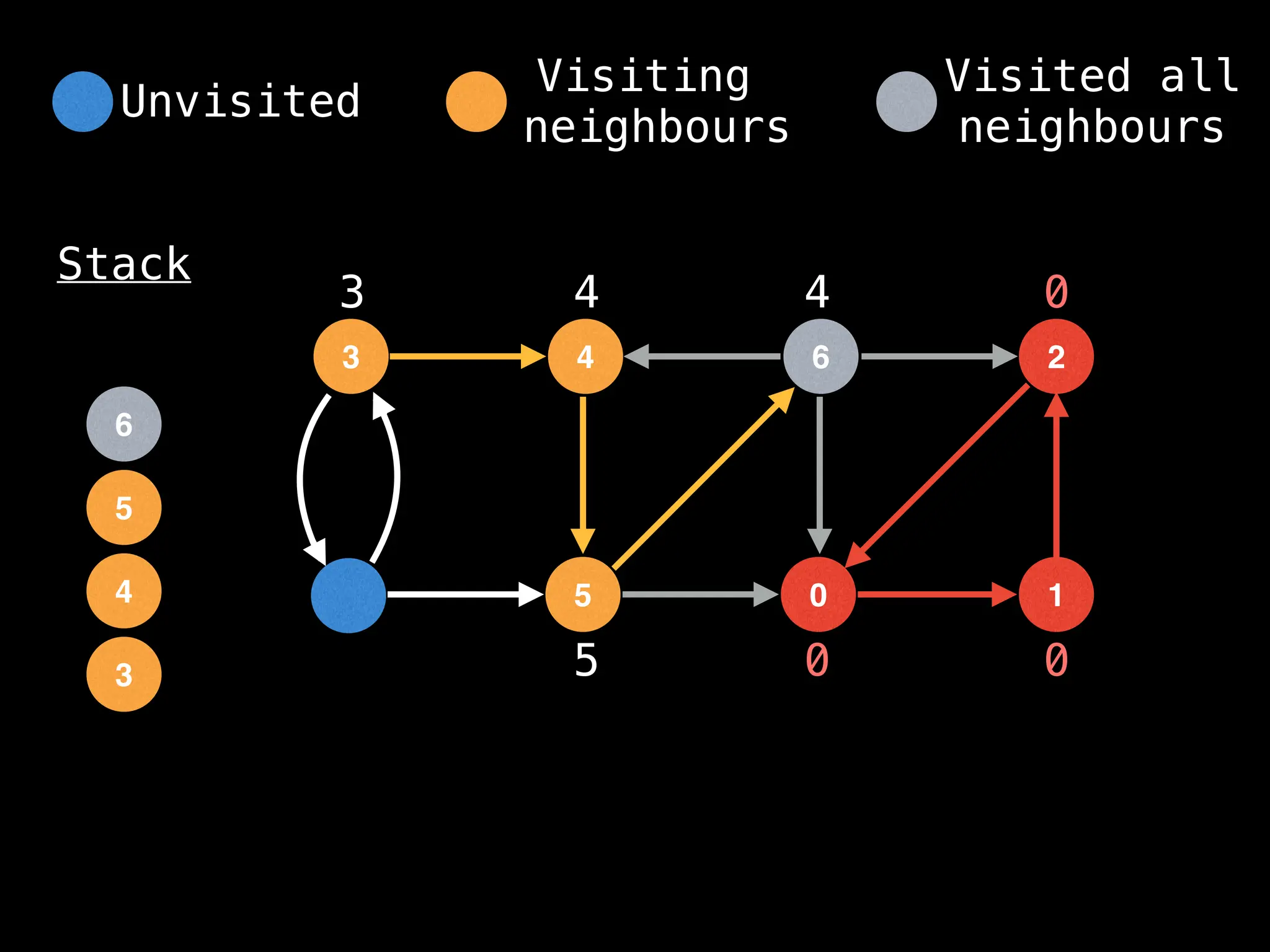
![4
3 6
5 0
2
1
Stack
0 0
0
3
3
4
4
5
4
4
6
lowlink[5] = min(lowlink[5], lowlink[6])
= 4
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-980-2048.jpg)
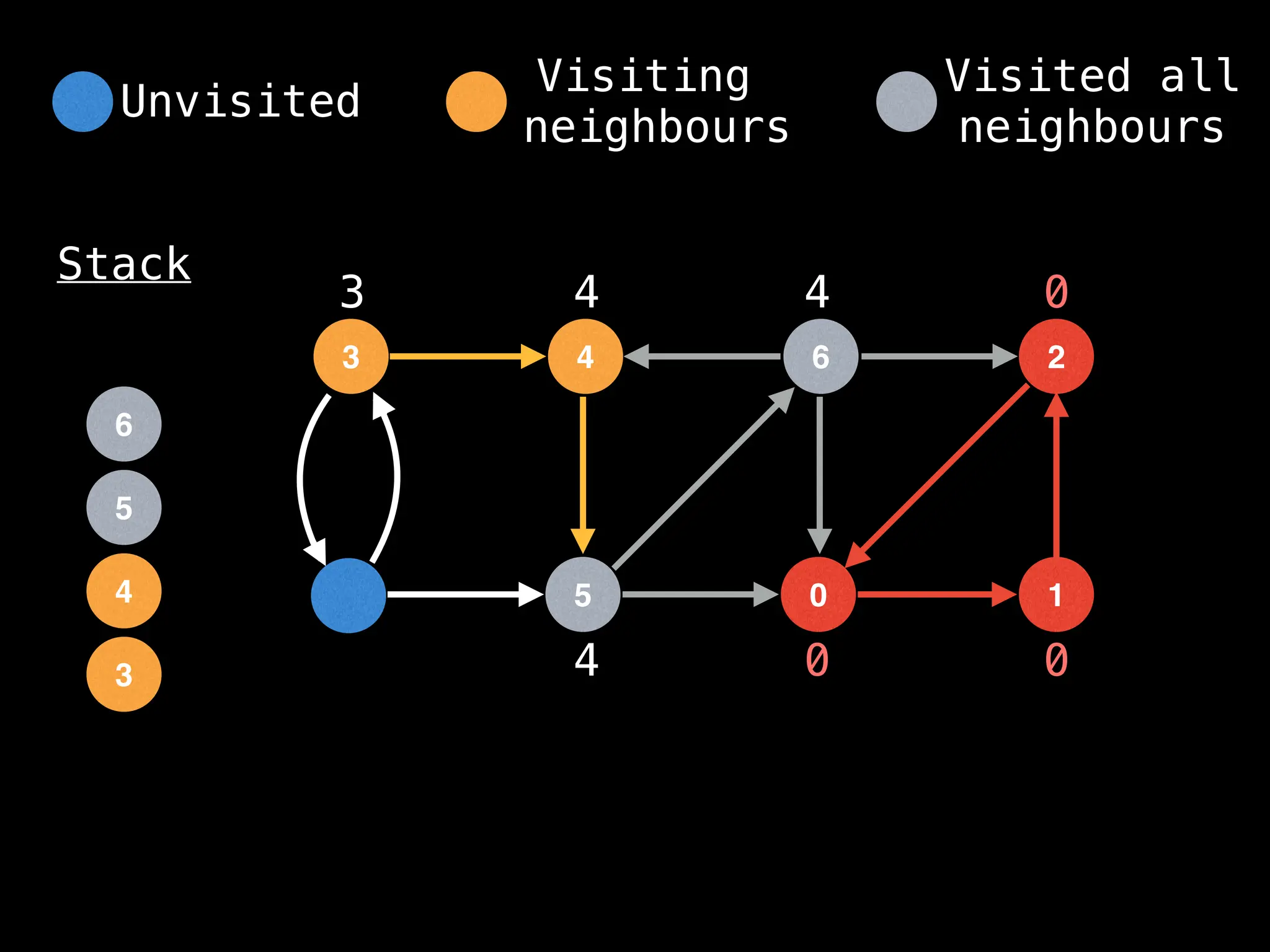
![4
3 6
5 0
2
1
Stack
0 0
0
3
3
4
4
5
4
4
6
lowlink[4] = min(lowlink[4], lowlink[5])
= 4
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-982-2048.jpg)
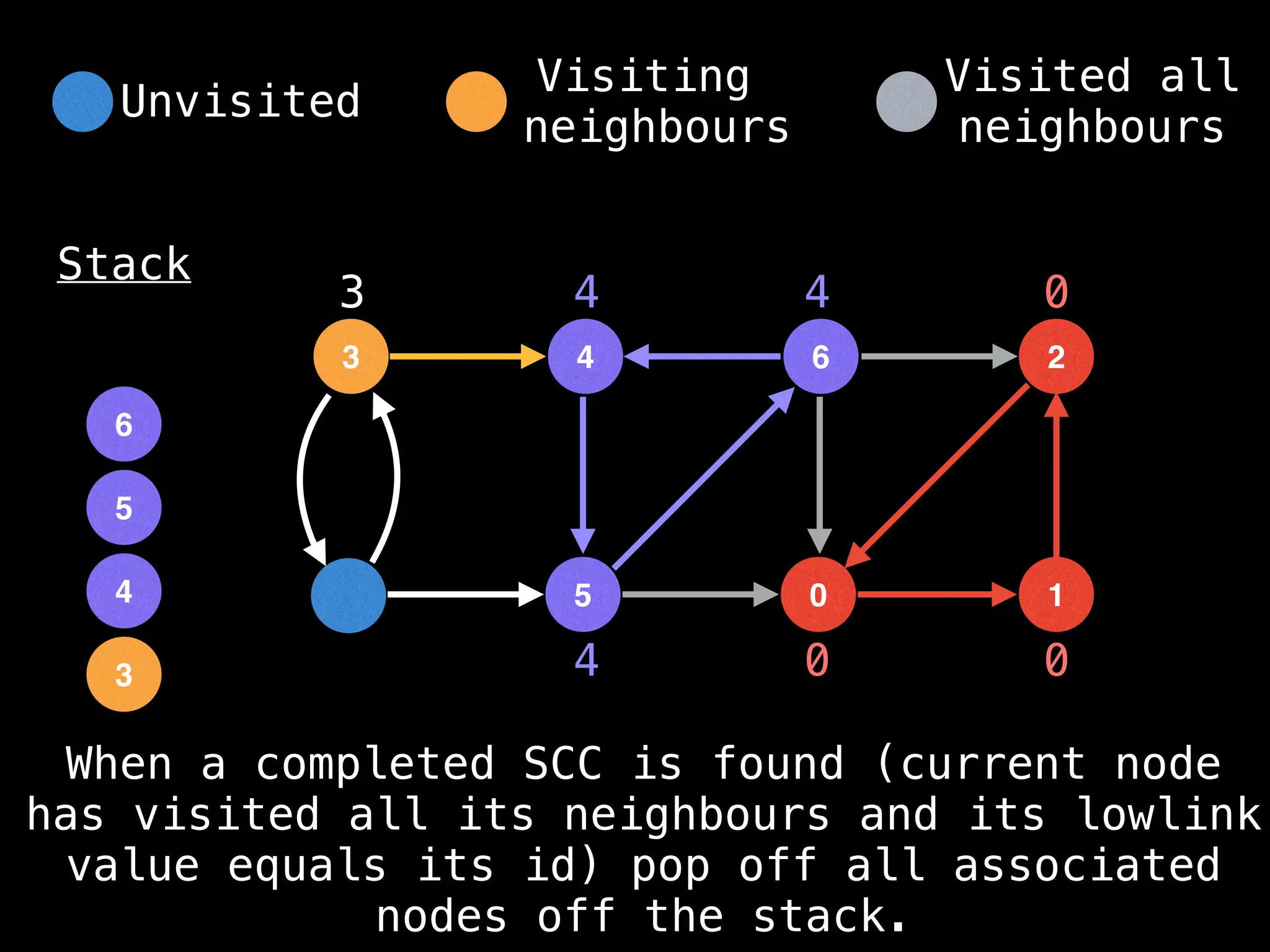
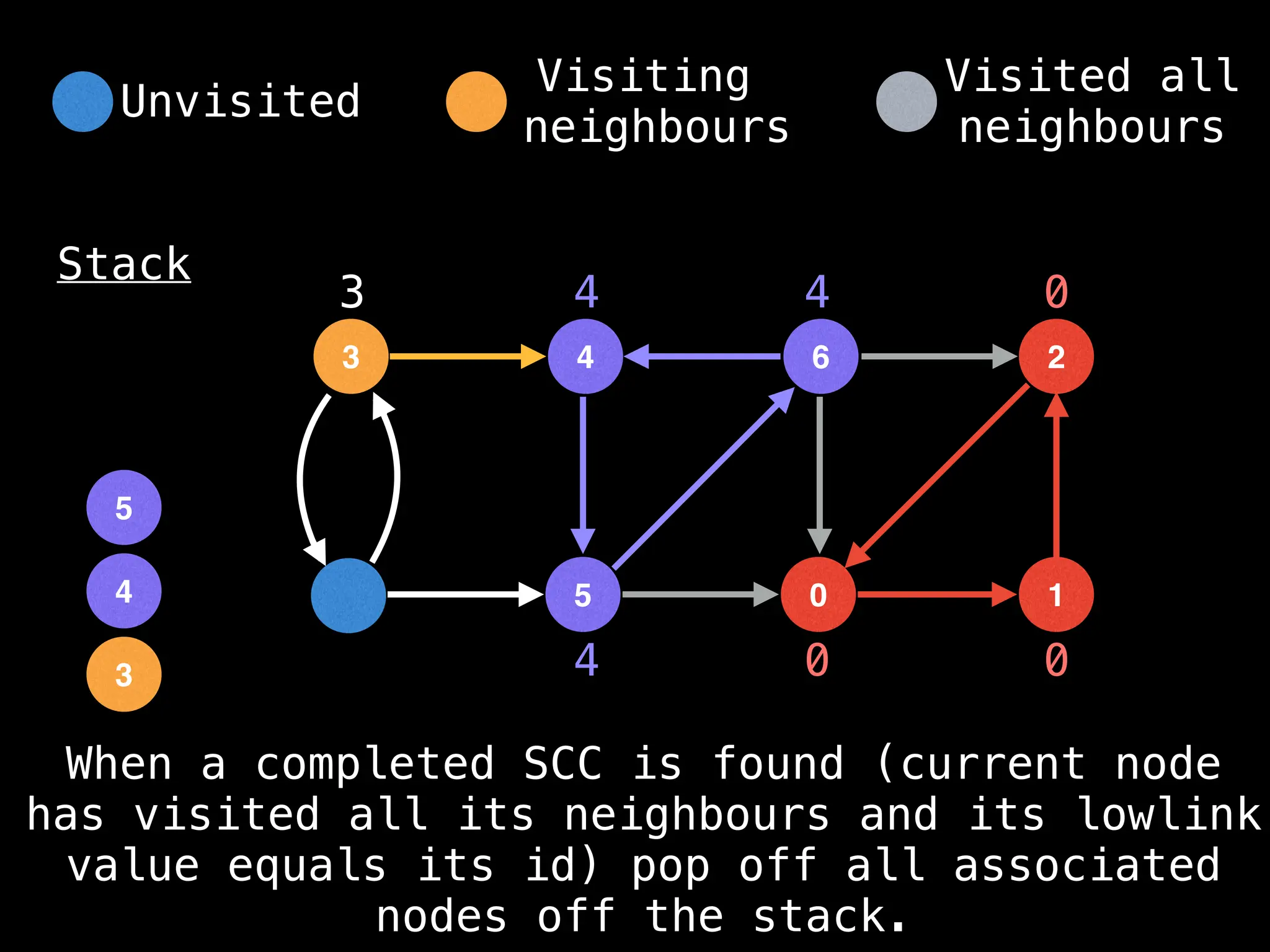
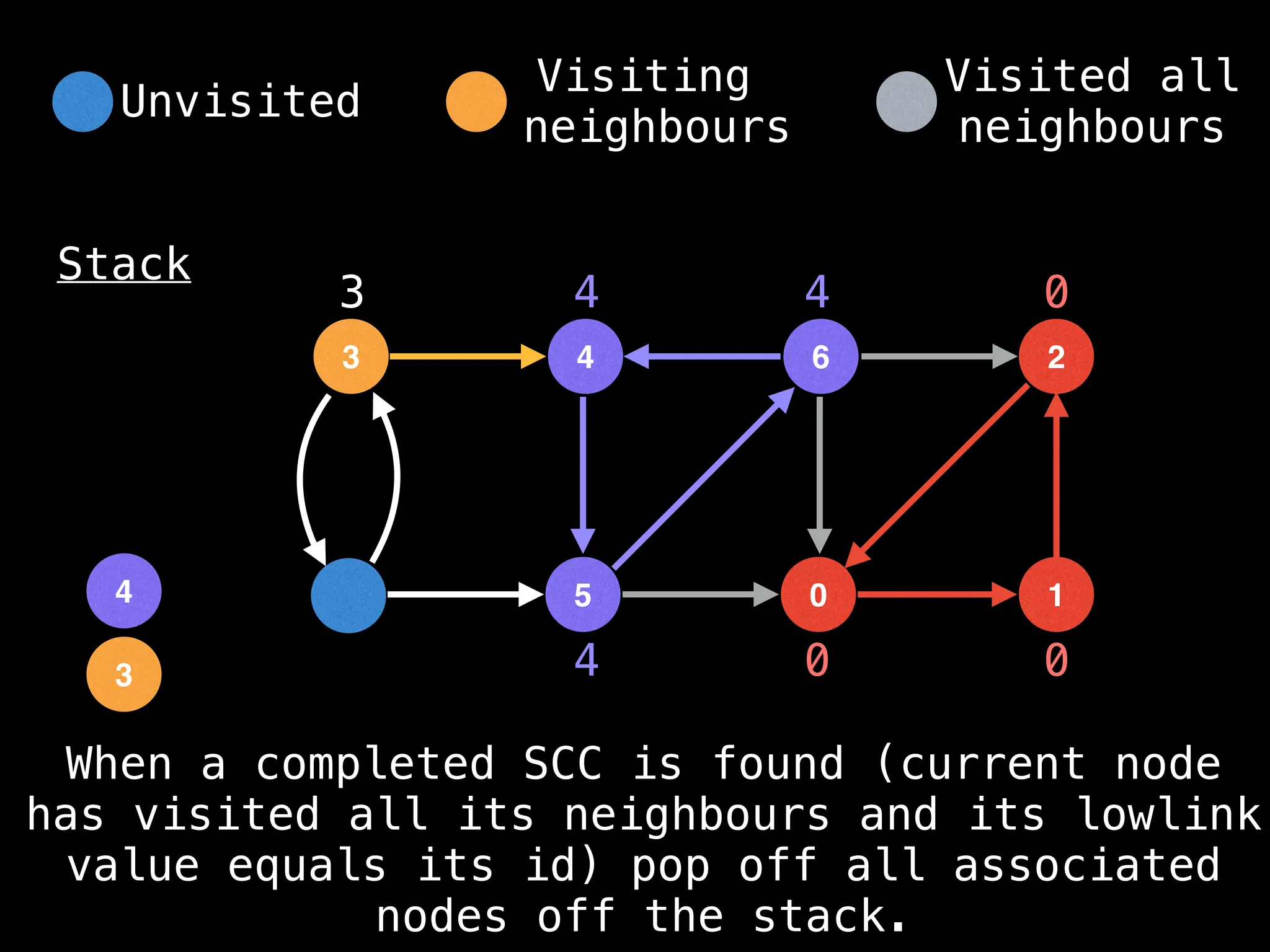
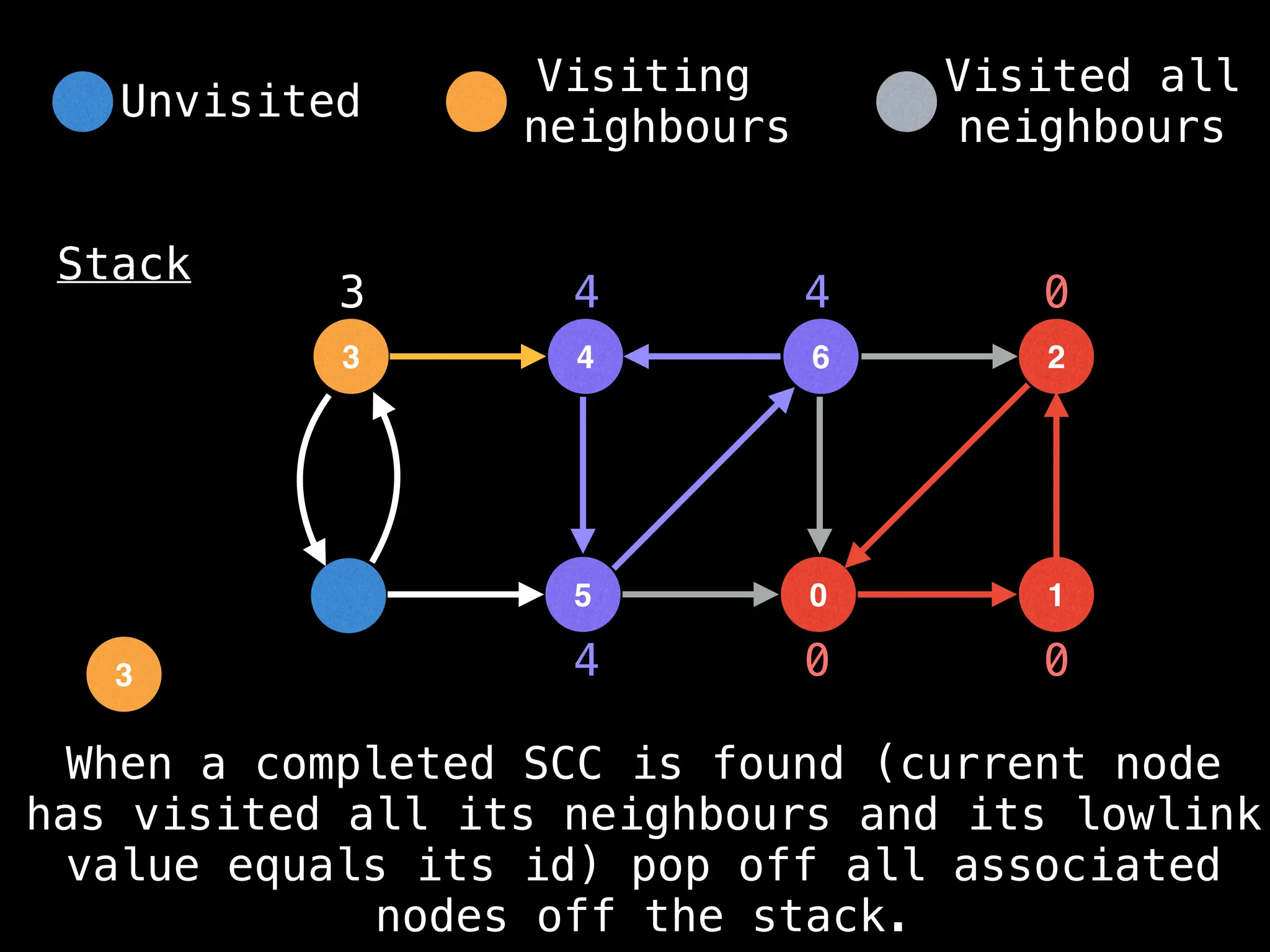
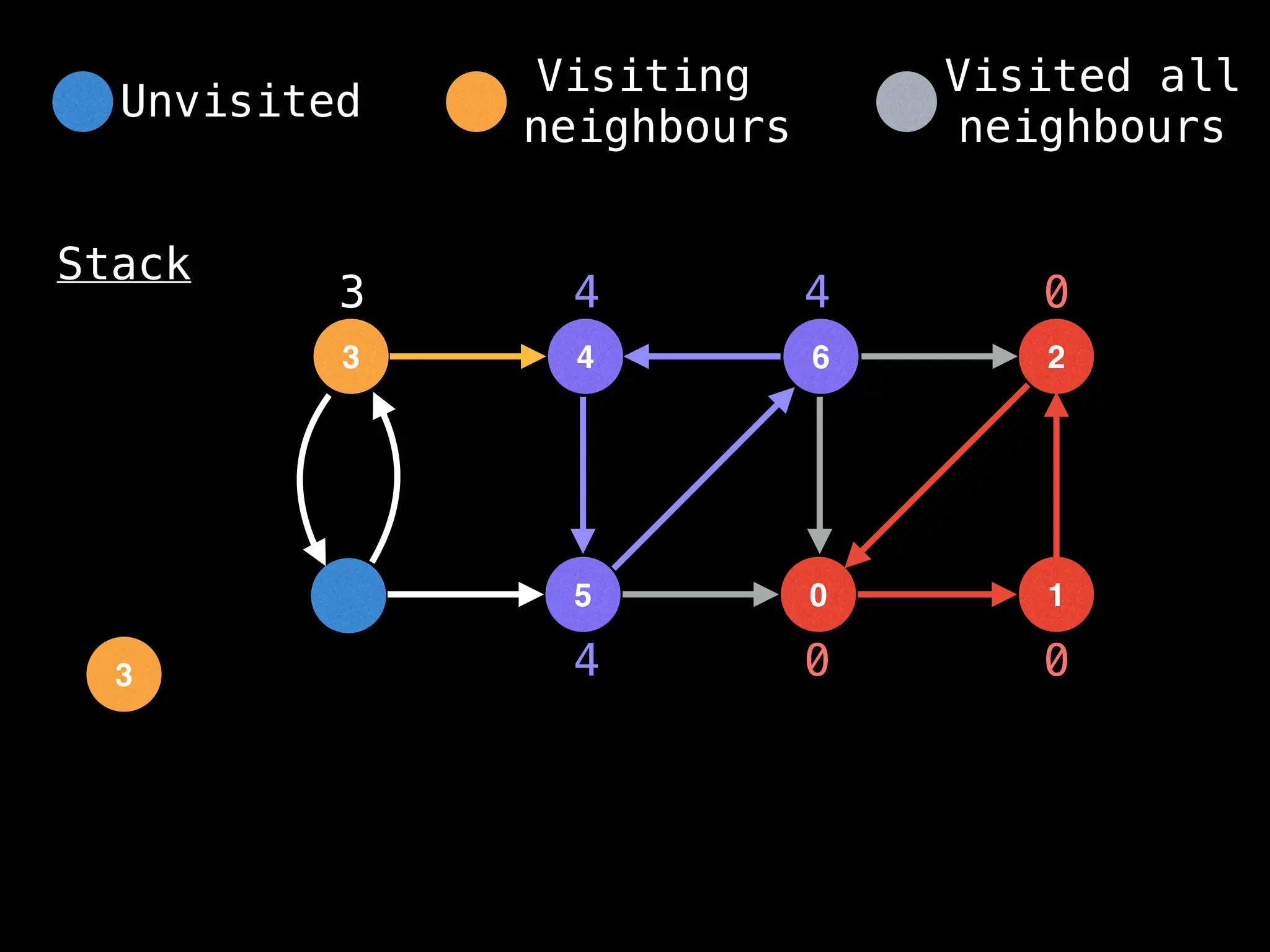
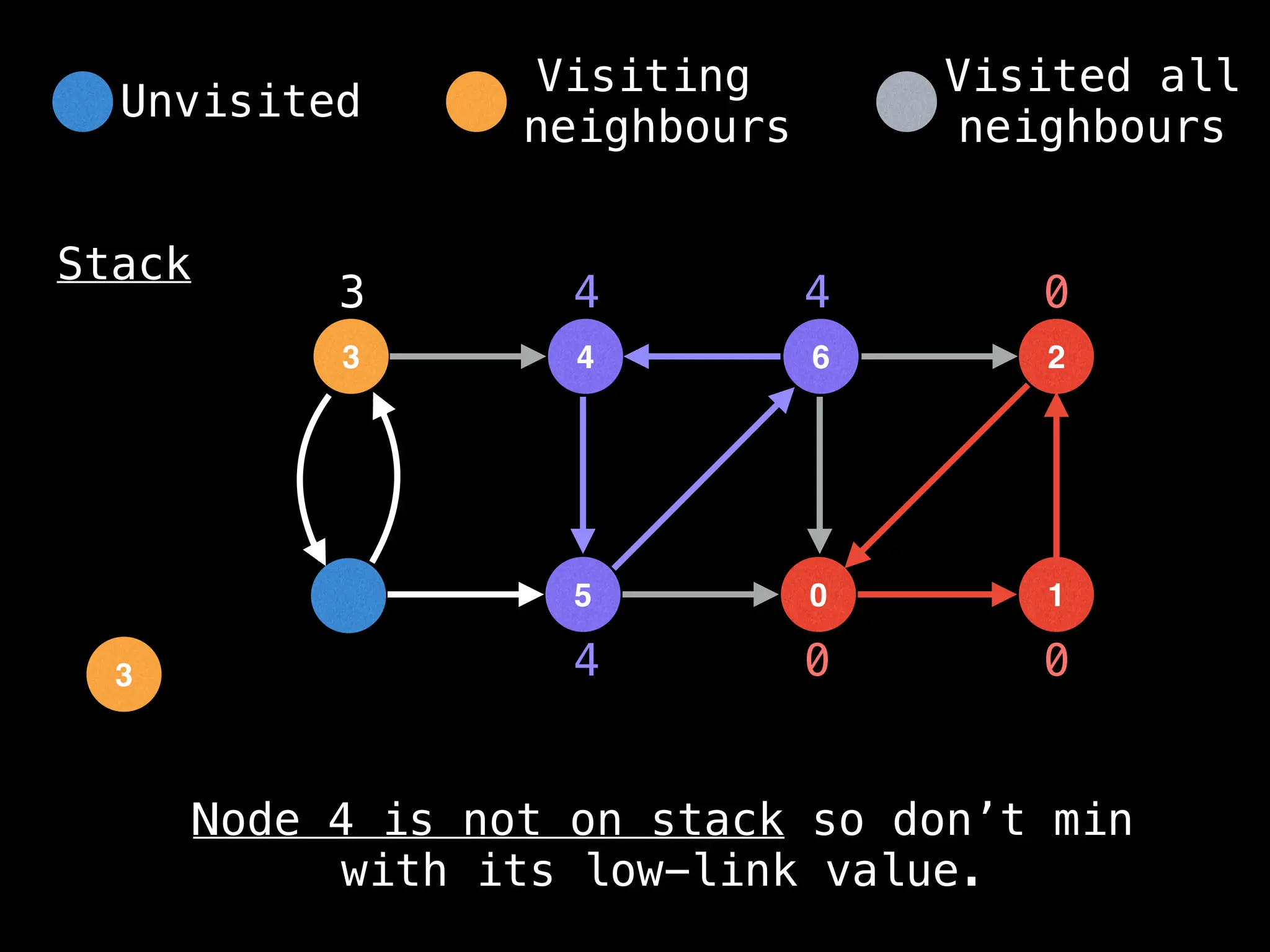
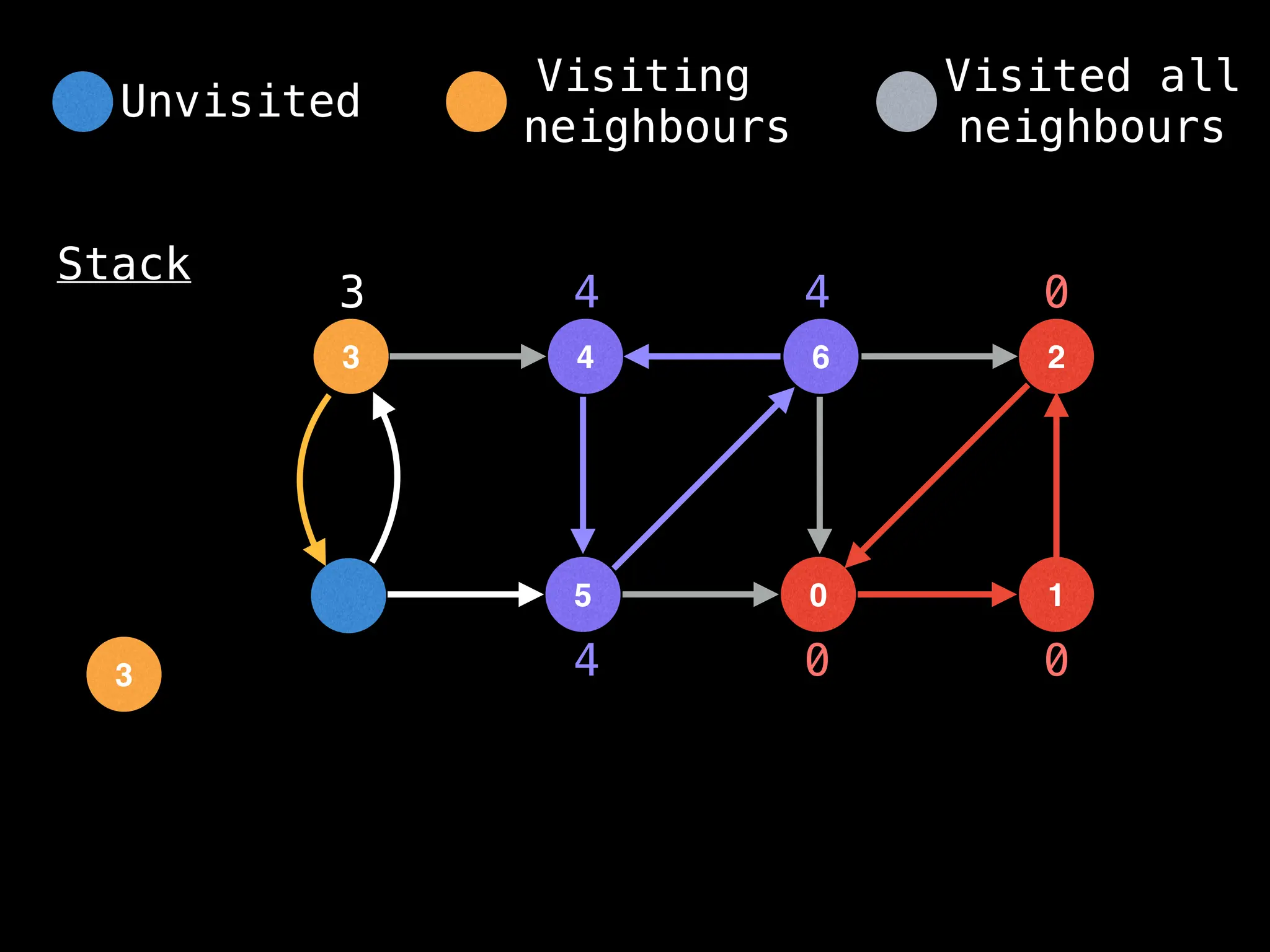
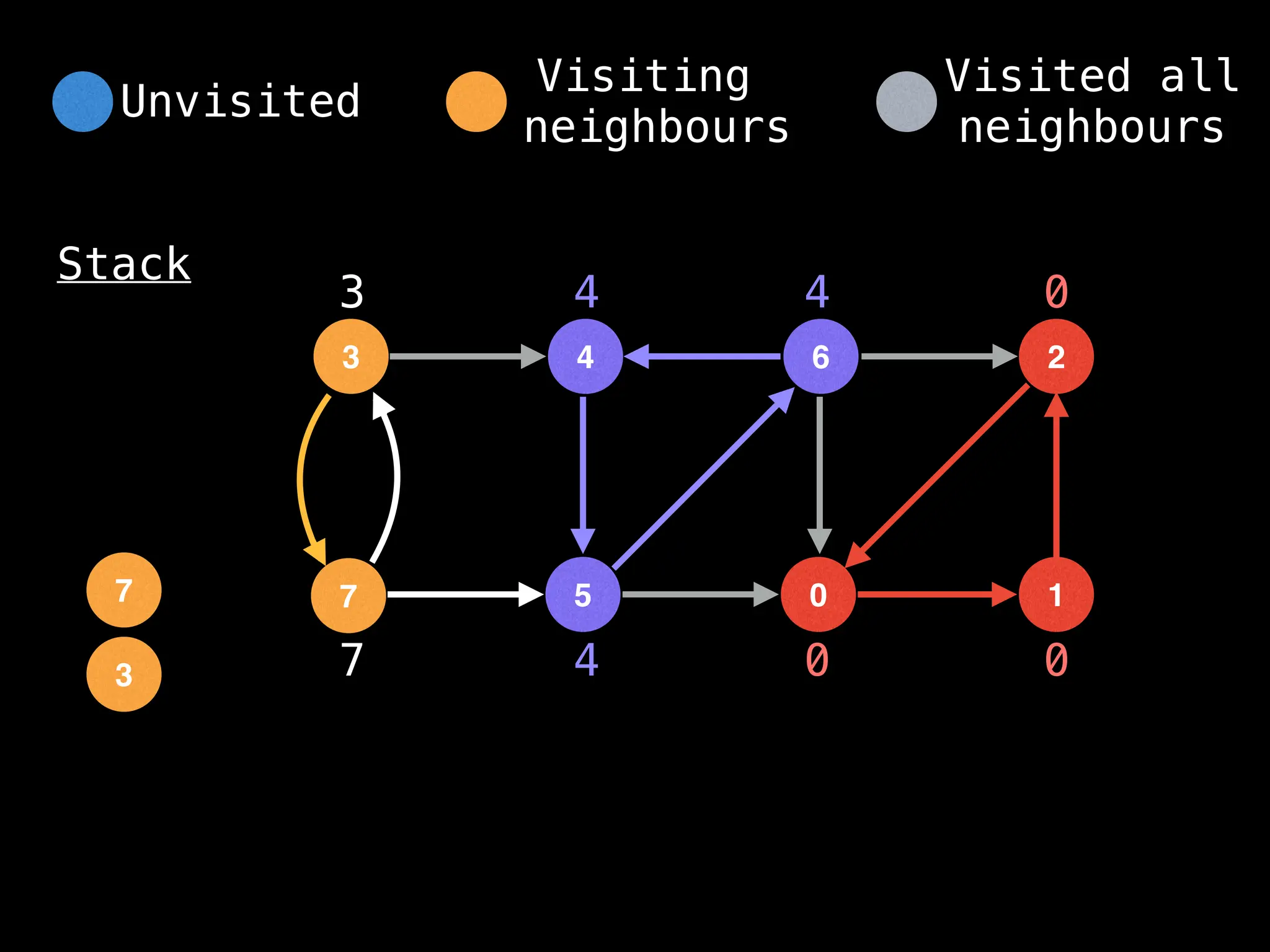
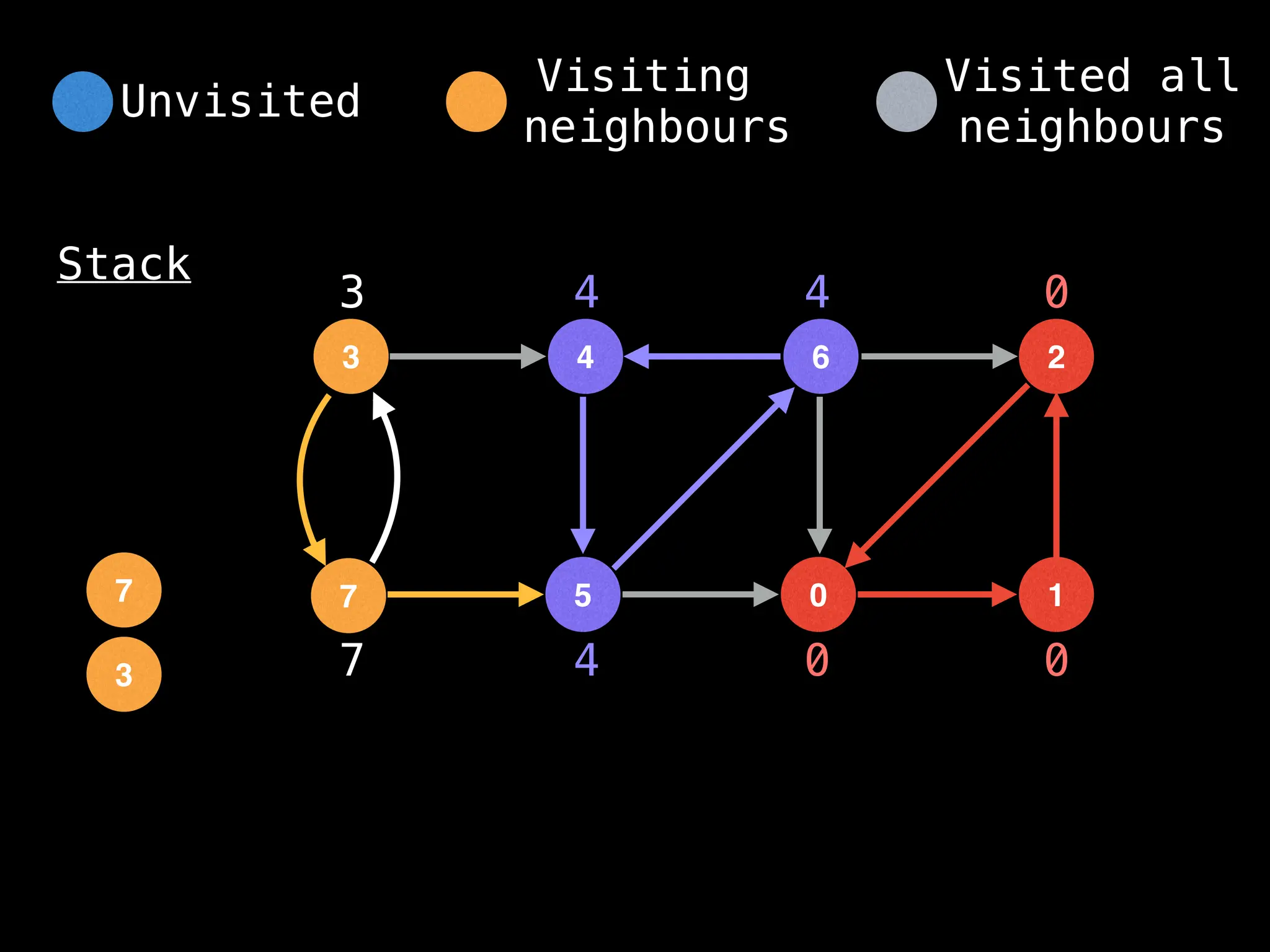
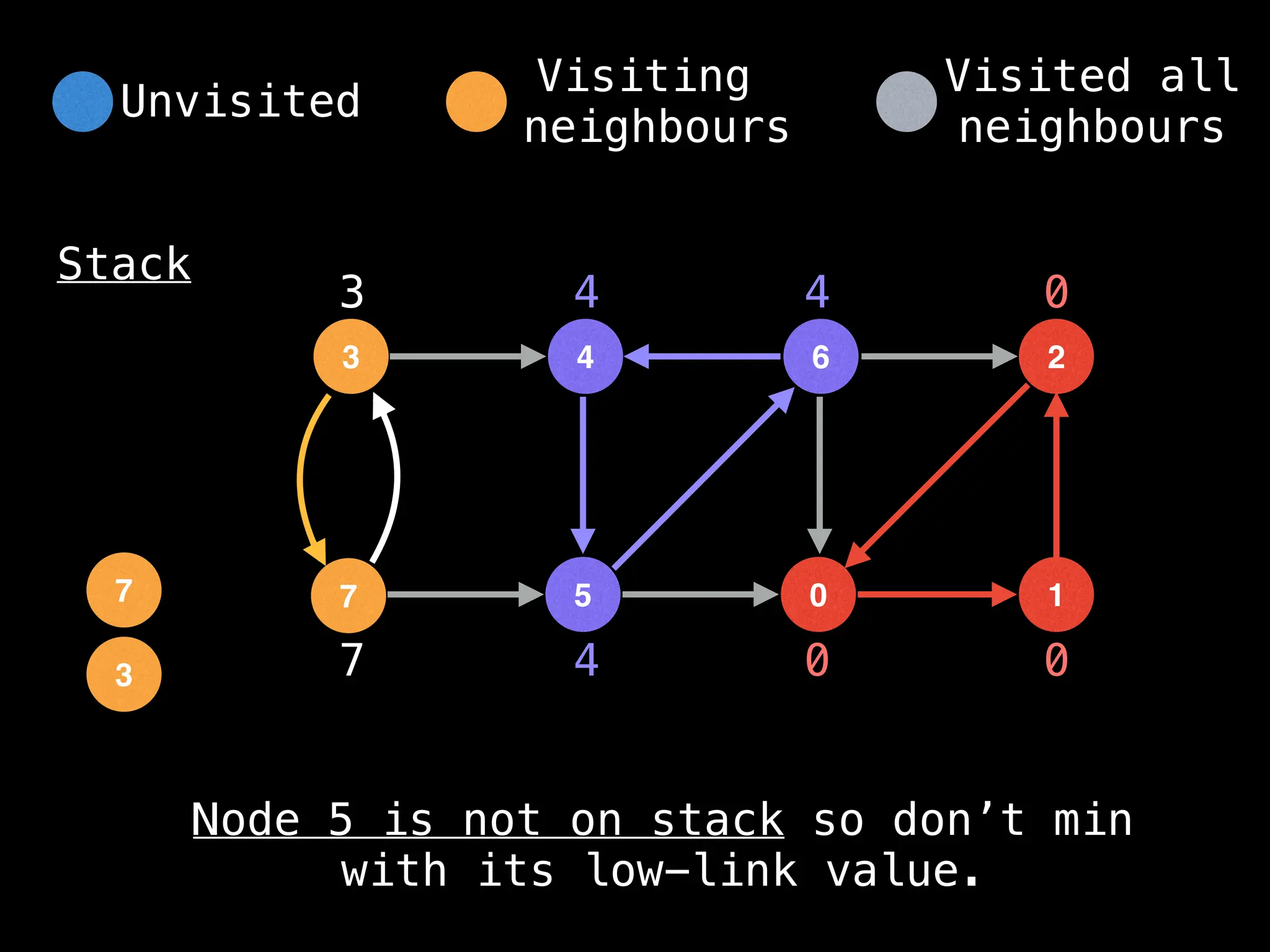
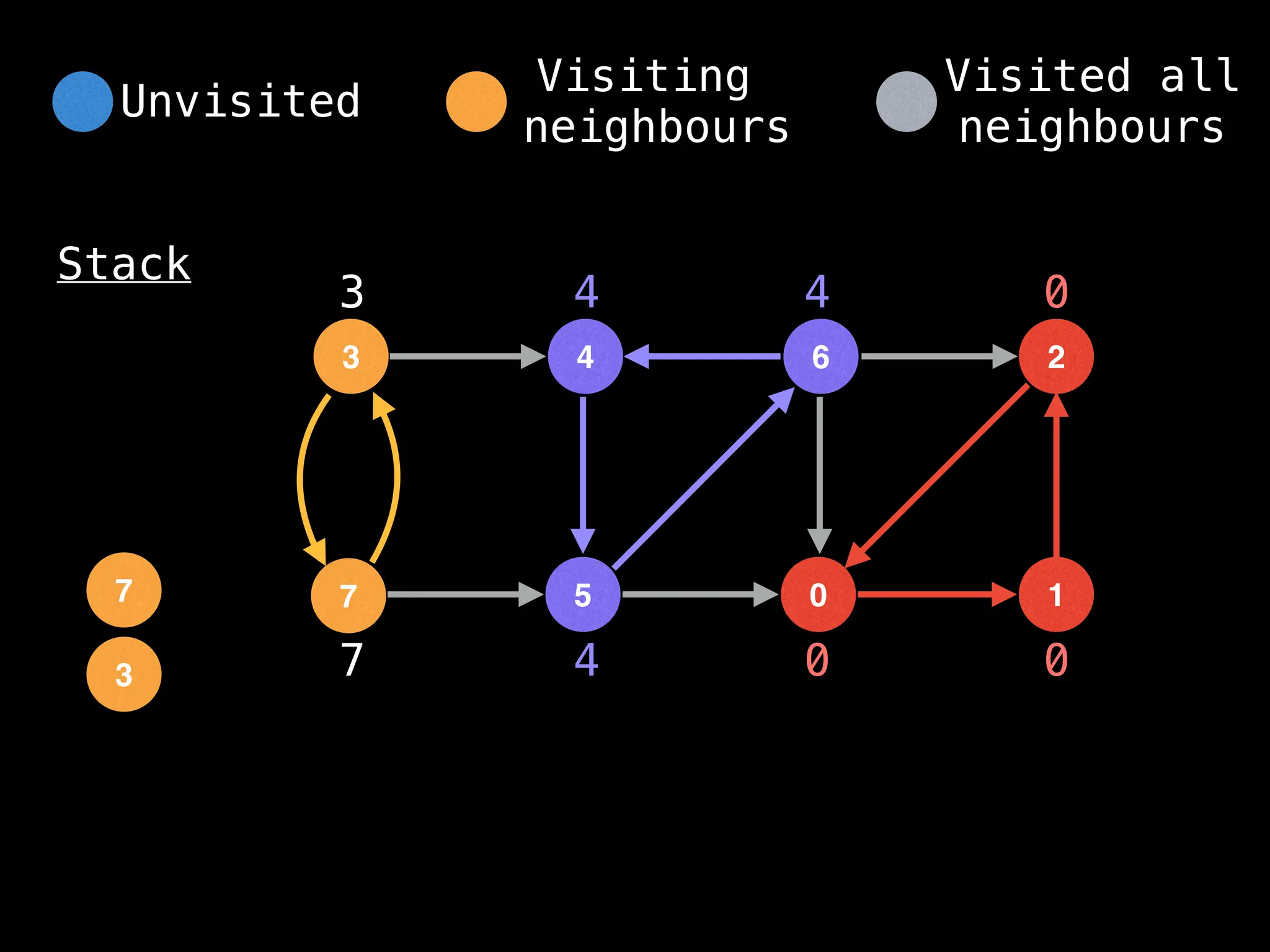
![4
3 6
5
7 0
2
1
Stack
0 0
0
3
3
4
4
4
3
7
lowlink[6] = min(lowlink[6], lowlink[3])
= 3
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-994-2048.jpg)
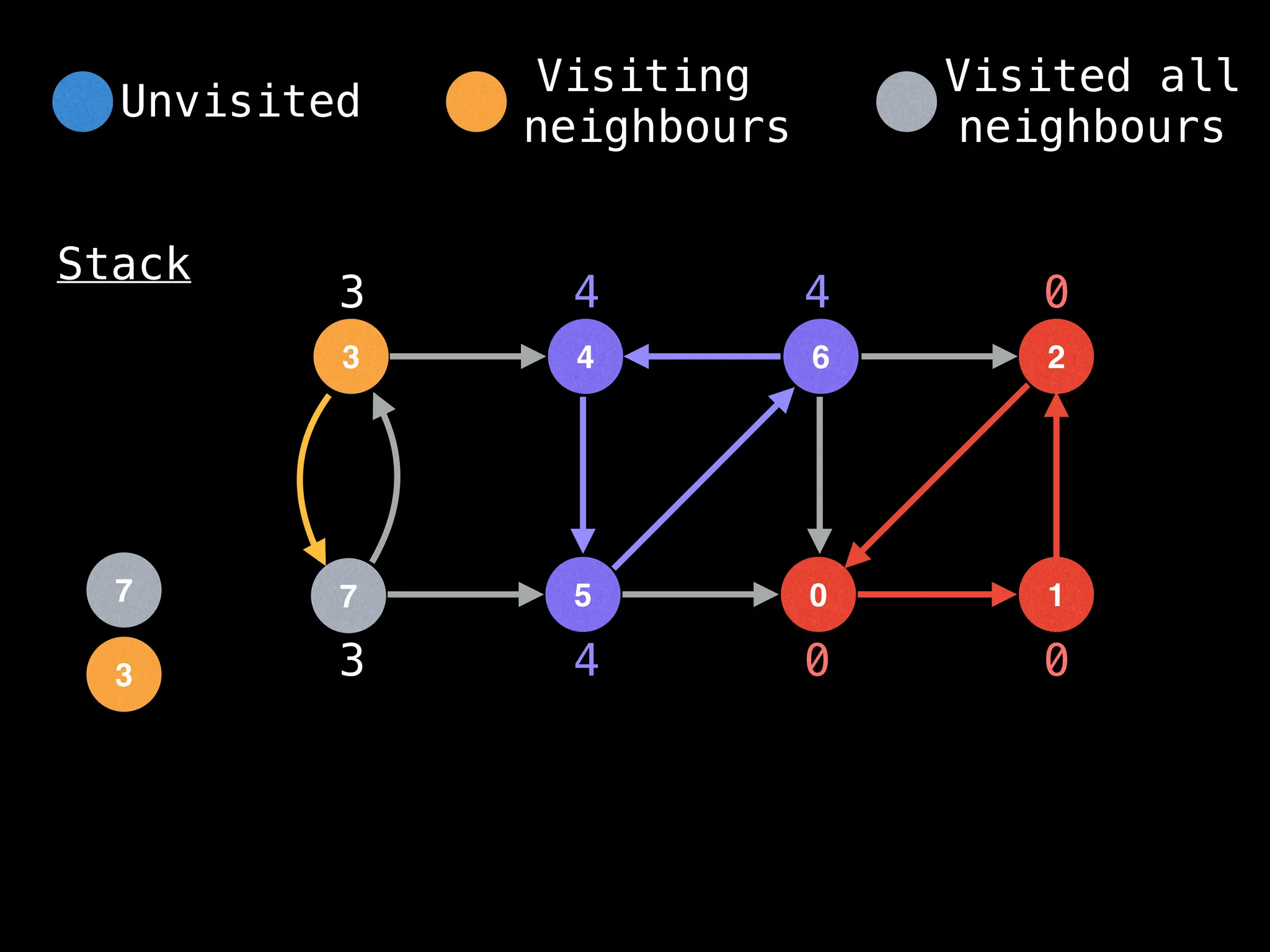
![4
3 6
5
7 0
2
1
Stack
0 0
0
3
3
4
4
4
3
lowlink[3] = min(lowlink[3], lowlink[6])
= 3
Unvisited
Visiting
neighbours
Visited all
neighbours
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-996-2048.jpg)
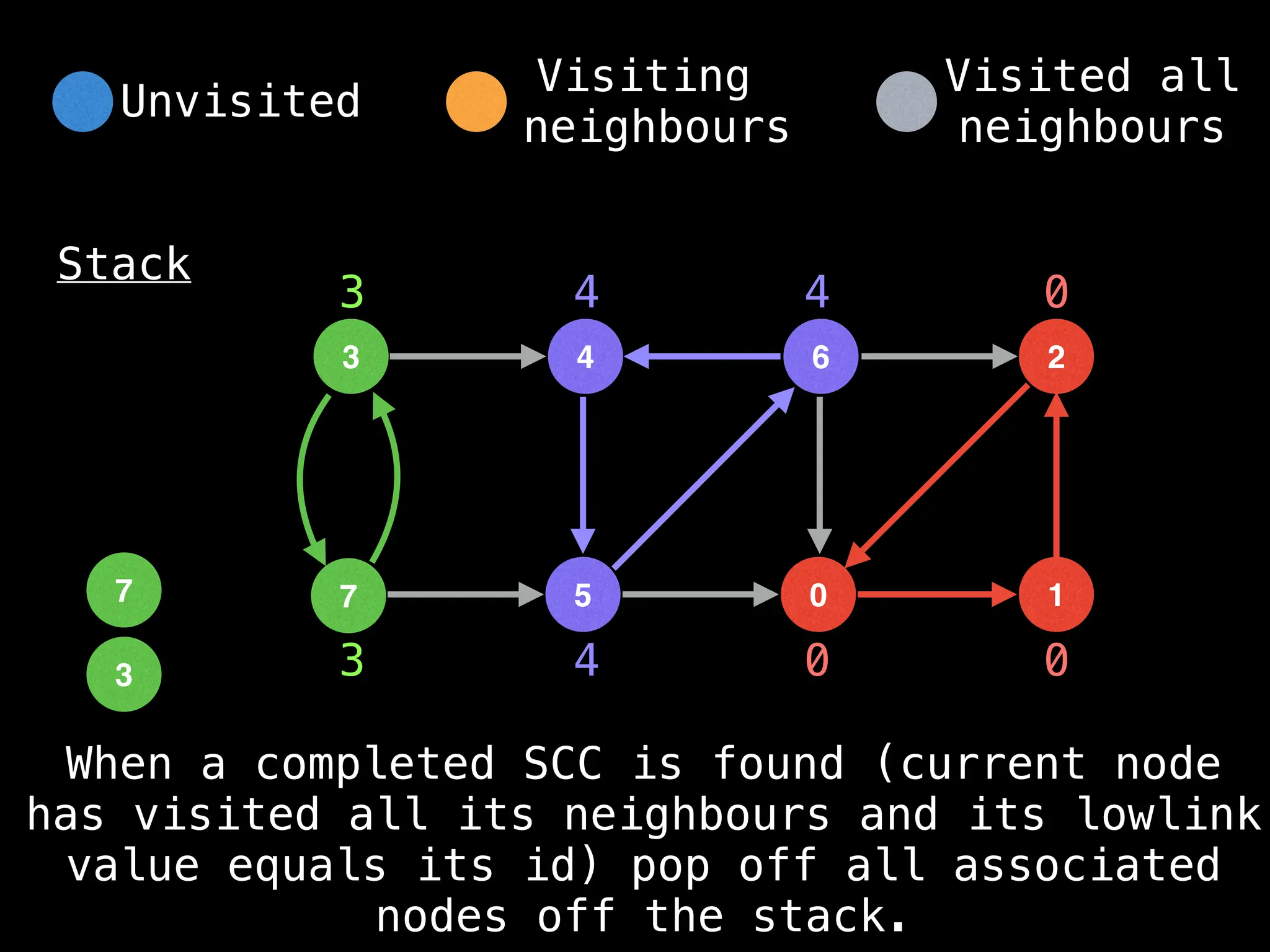
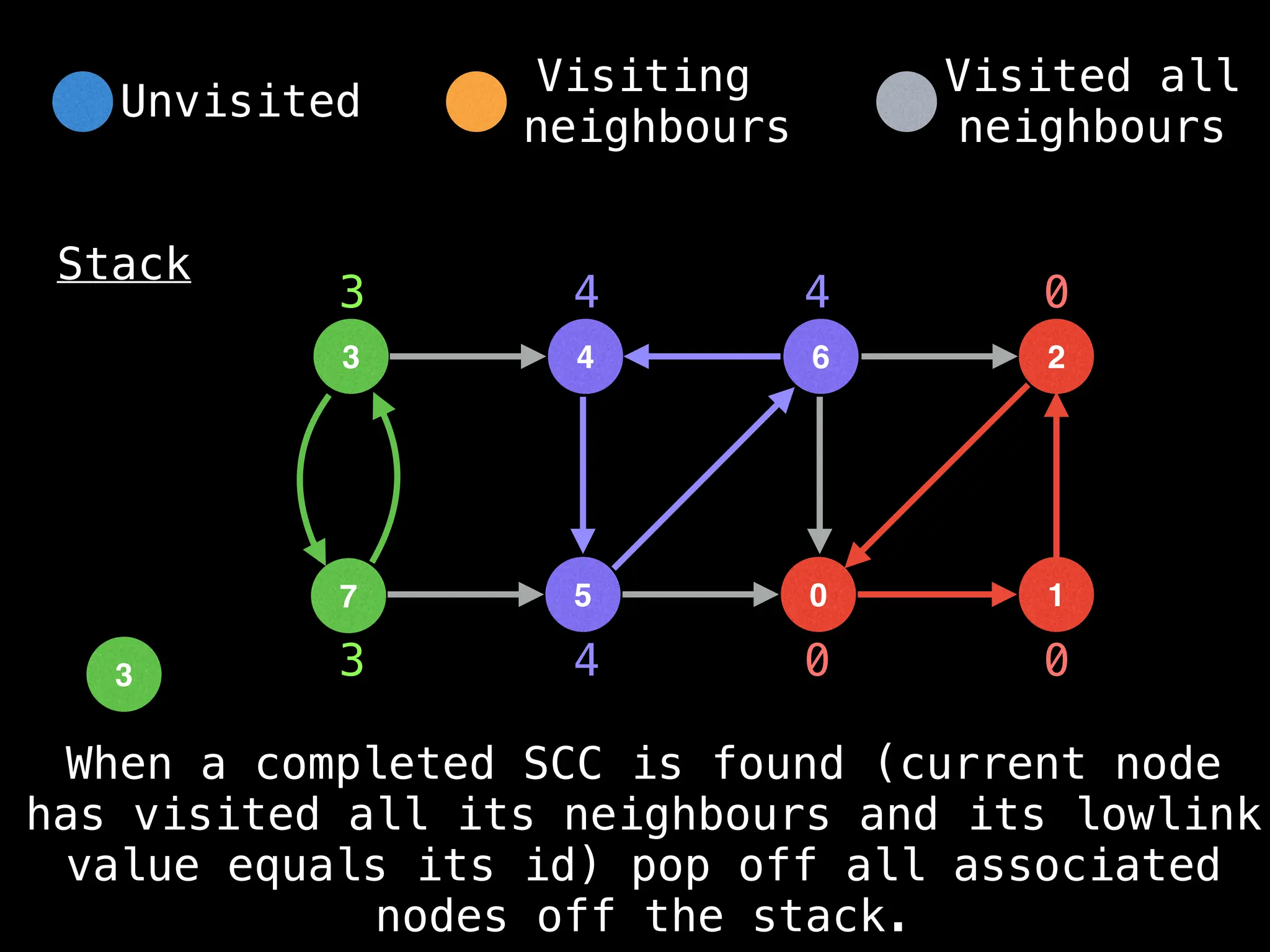
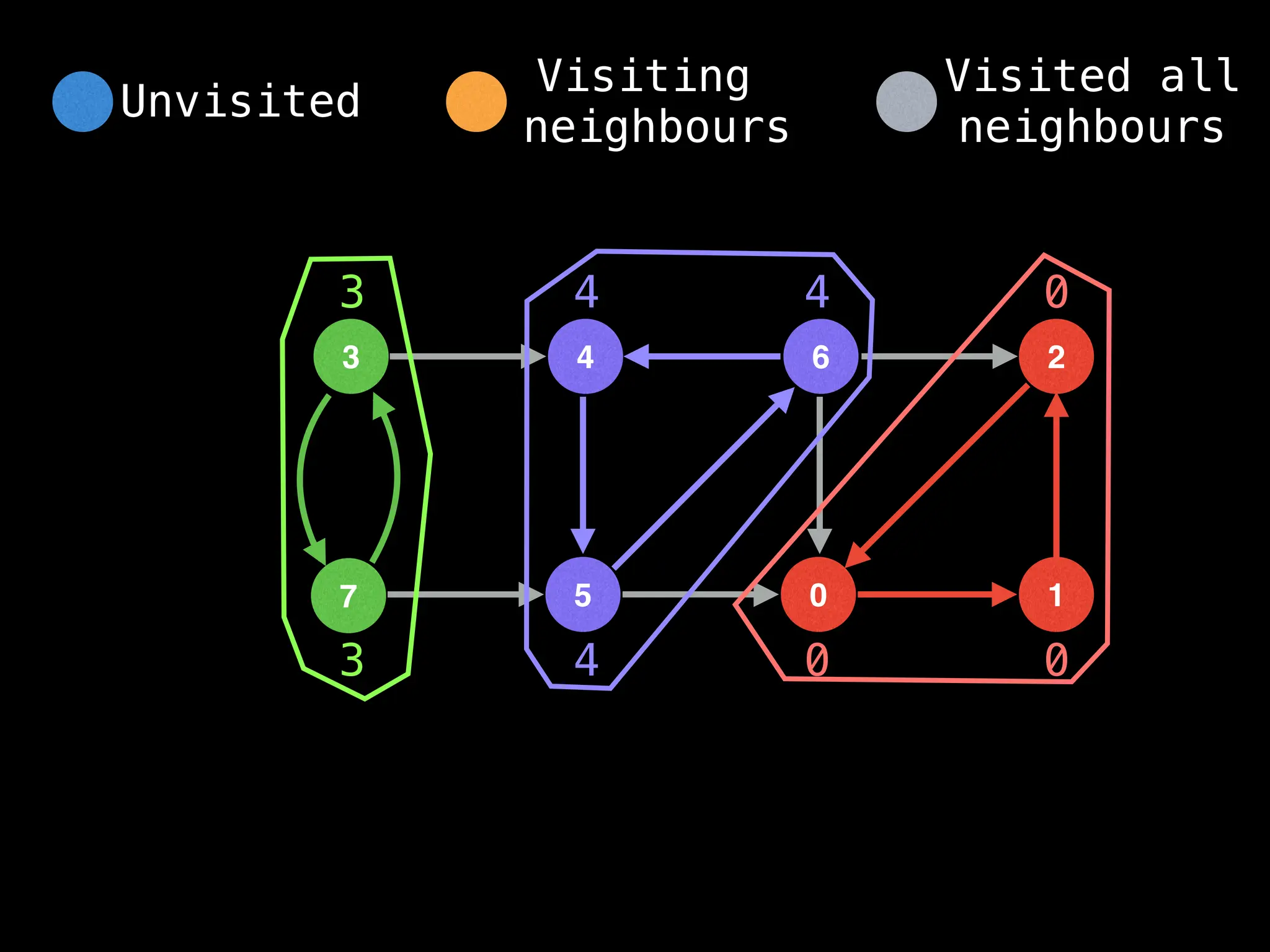
![UNVISITED = -1
n = number of nodes in graph
g = adjacency list with directed edges
id = 0 # Used to give each node an id
sccCount = 0 # Used to count number of SCCs found
# Index i in these arrays represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
onStack = [false, false, …, false] # Length n
stack = an empty stack data structure
function findSccs():
for(i = 0; i < n; i++): ids[i] = UNVISITED
for(i = 0; i < n; i++):
if(ids[i] == UNVISITED):
dfs(i)
return low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1000-2048.jpg)
![UNVISITED = -1
n = number of nodes in graph
g = adjacency list with directed edges
id = 0 # Used to give each node an id
sccCount = 0 # Used to count number of SCCs found
# Index i in these arrays represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
onStack = [false, false, …, false] # Length n
stack = an empty stack data structure
function findSccs():
for(i = 0; i < n; i++): ids[i] = UNVISITED
for(i = 0; i < n; i++):
if(ids[i] == UNVISITED):
dfs(i)
return low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1001-2048.jpg)
![UNVISITED = -1
n = number of nodes in graph
g = adjacency list with directed edges
id = 0 # Used to give each node an id
sccCount = 0 # Used to count number of SCCs found
# Index i in these arrays represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
onStack = [false, false, …, false] # Length n
stack = an empty stack data structure
function findSccs():
for(i = 0; i < n; i++): ids[i] = UNVISITED
for(i = 0; i < n; i++):
if(ids[i] == UNVISITED):
dfs(i)
return low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1002-2048.jpg)
![UNVISITED = -1
n = number of nodes in graph
g = adjacency list with directed edges
id = 0 # Used to give each node an id
sccCount = 0 # Used to count number of SCCs found
# Index i in these arrays represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
onStack = [false, false, …, false] # Length n
stack = an empty stack data structure
function findSccs():
for(i = 0; i < n; i++): ids[i] = UNVISITED
for(i = 0; i < n; i++):
if(ids[i] == UNVISITED):
dfs(i)
return low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1003-2048.jpg)
![UNVISITED = -1
n = number of nodes in graph
g = adjacency list with directed edges
id = 0 # Used to give each node an id
sccCount = 0 # Used to count number of SCCs found
# Index i in these arrays represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
onStack = [false, false, …, false] # Length n
stack = an empty stack data structure
function findSccs():
for(i = 0; i < n; i++): ids[i] = UNVISITED
for(i = 0; i < n; i++):
if(ids[i] == UNVISITED):
dfs(i)
return low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1004-2048.jpg)
![UNVISITED = -1
n = number of nodes in graph
g = adjacency list with directed edges
id = 0 # Used to give each node an id
sccCount = 0 # Used to count number of SCCs found
# Index i in these arrays represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
onStack = [false, false, …, false] # Length n
stack = an empty stack data structure
function findSccs():
for(i = 0; i < n; i++): ids[i] = UNVISITED
for(i = 0; i < n; i++):
if(ids[i] == UNVISITED):
dfs(i)
return low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1005-2048.jpg)
![UNVISITED = -1
n = number of nodes in graph
g = adjacency list with directed edges
id = 0 # Used to give each node an id
sccCount = 0 # Used to count number of SCCs found
# Index i in these arrays represents node i
ids = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
low = [0, 0, … 0, 0] # Length n
onStack = [false, false, …, false] # Length n
stack = an empty stack data structure
function findSccs():
for(i = 0; i < n; i++): ids[i] = UNVISITED
for(i = 0; i < n; i++):
if(ids[i] == UNVISITED):
dfs(i)
return low](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1006-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1007-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1008-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1009-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1010-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1011-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1012-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1013-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1014-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
stack.push(at)
onStack[at] = true
ids[at] = low[at] = id++
# Visit all neighbours & min low-link on callback
for(to : g[at]):
if(ids[to] == UNVISITED): dfs(to)
if(onStack[to]): low[at] = min(low[at],low[to])
# After having visited all the neighbours of ‘at’
# if we're at the start of a SCC empty the seen
# stack until we’re back to the start of the SCC.
if(ids[at] == low[at]):
for(node = stack.pop();;node = stack.pop()):
onStack[node] = false
low[node] = ids[at]
if(node == at): break
sccCount++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1015-2048.jpg)



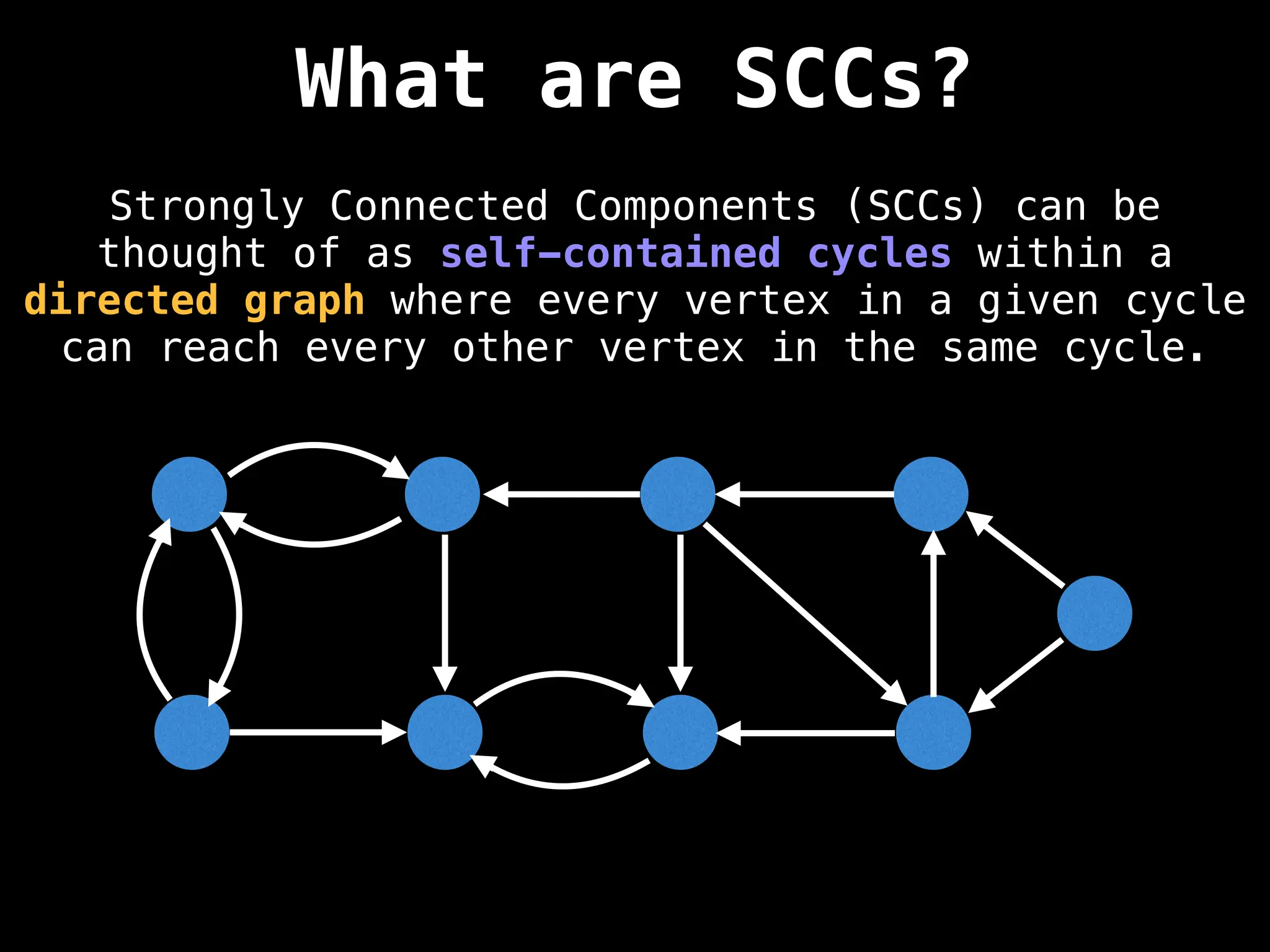
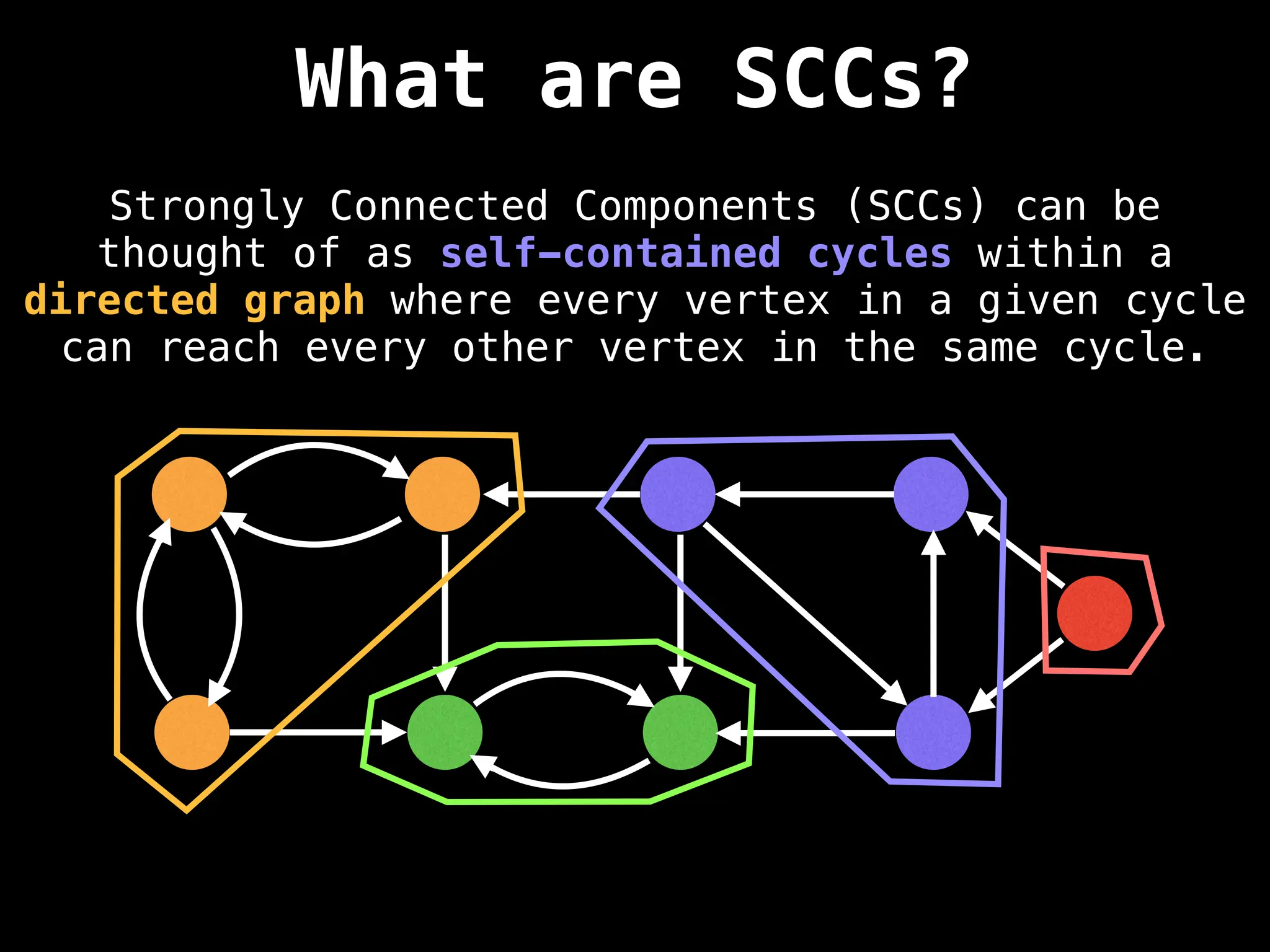
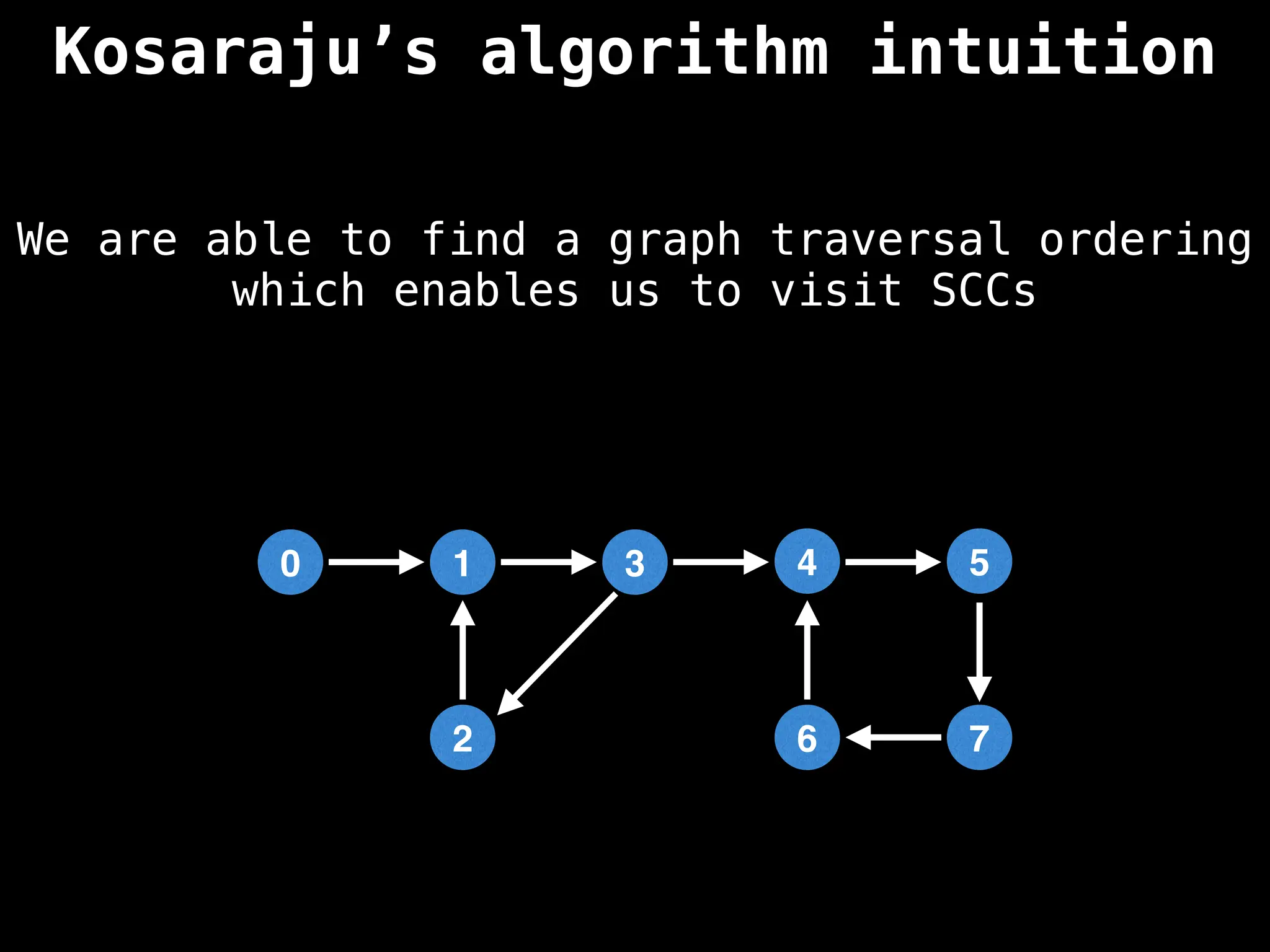
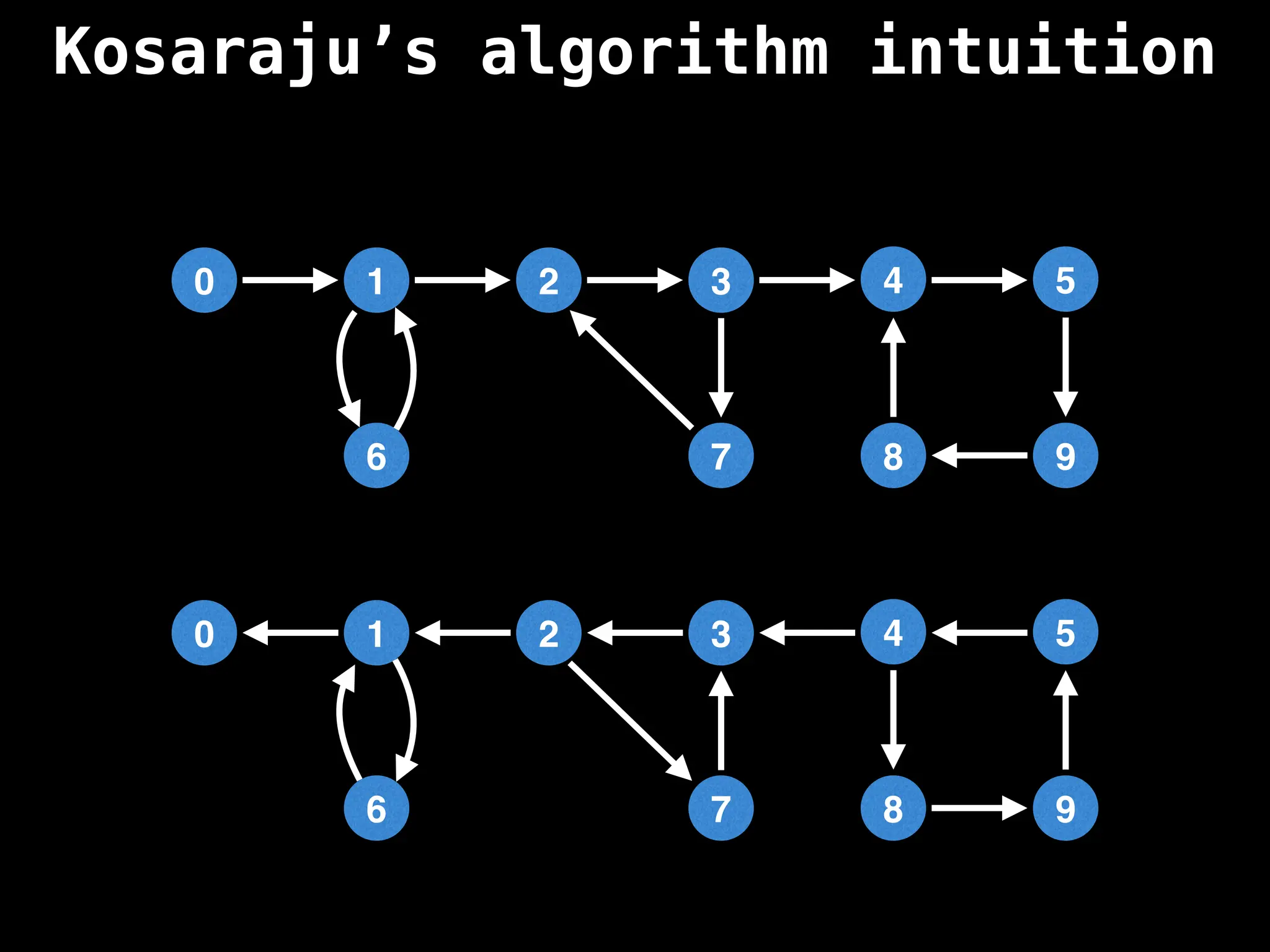
![Kosaraju’s algorithm intuition
0 1
6
2 3
7 8
4 5
9
0 1
6
2 3
7 8
4 5
9
[0, 1, 6, 2, 3, 7, 4, 5, 9, 8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1025-2048.jpg)
![Kosaraju’s algorithm intuition
1 0 2
4
5
3
[1, 3, 0, 5, 2, 4]
1 0 2
4
5
3
Nodes than can reach](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1026-2048.jpg)
![Kosaraju’s algorithm intuition
0 2 1
7
4
3
6
5
[0, 3, 2, 1, 7, 6, 5, 4]
0 2 1
7
4
3
6
5
The reverse post order ordering presents the nodes in a
order in which the node(s) which leak the most appear
first. In G^T, these nodes will be those which are part
the "smallest SCC", that is the SCC which leak the least](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1027-2048.jpg)
![Kosaraju’s algorithm intuition
[0, 3, 2, 1, 7, 6, 5, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1028-2048.jpg)


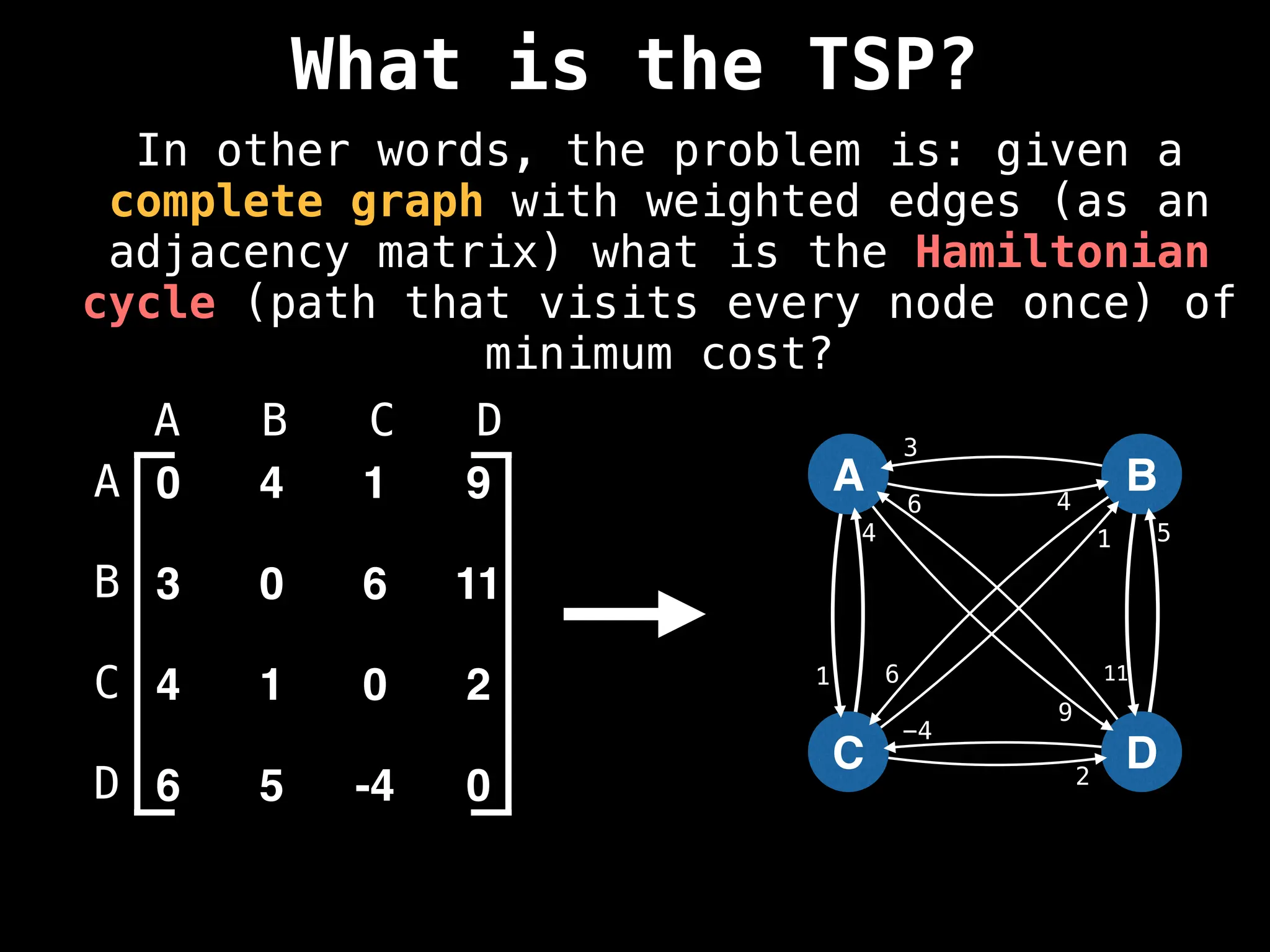
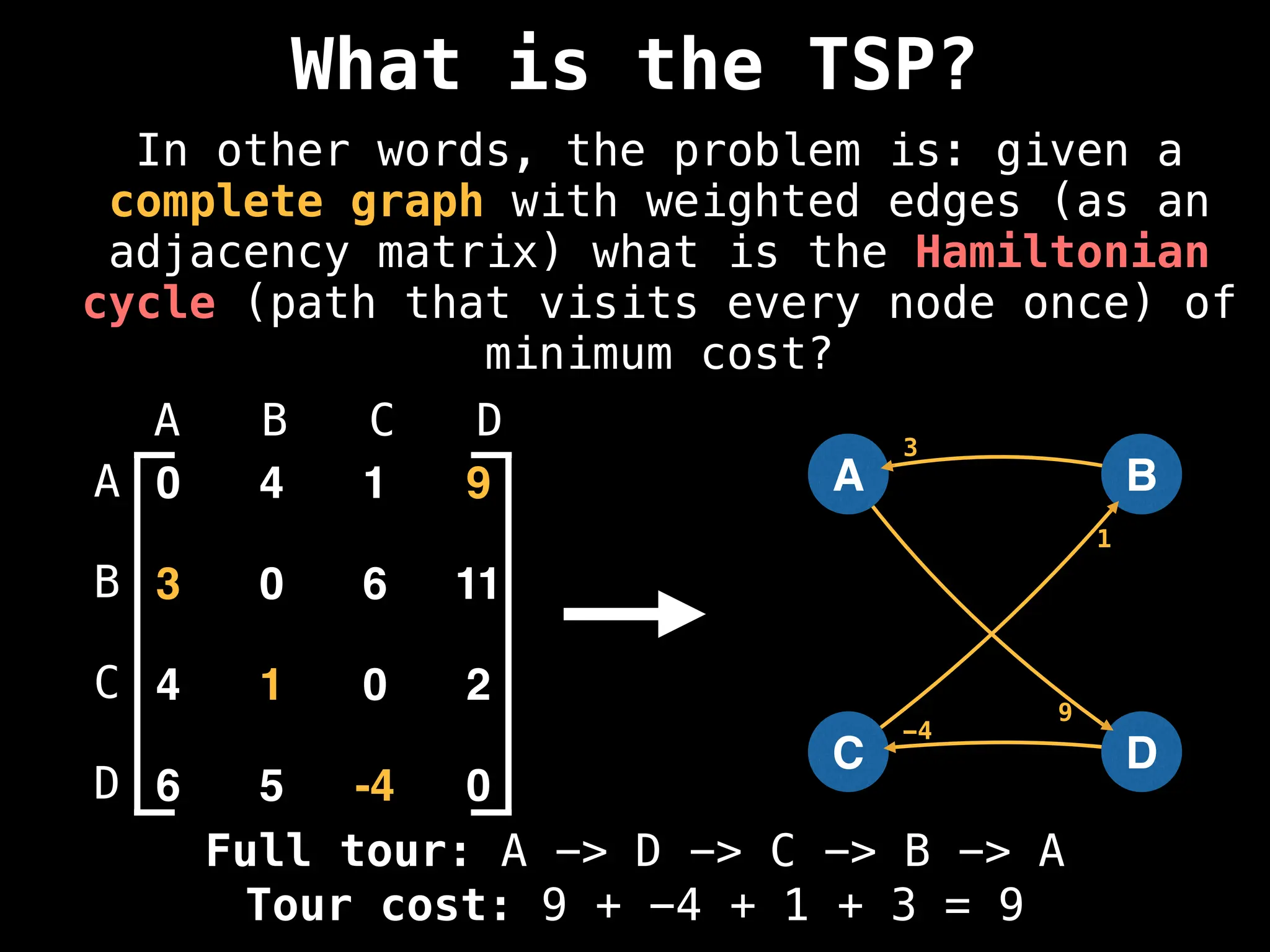
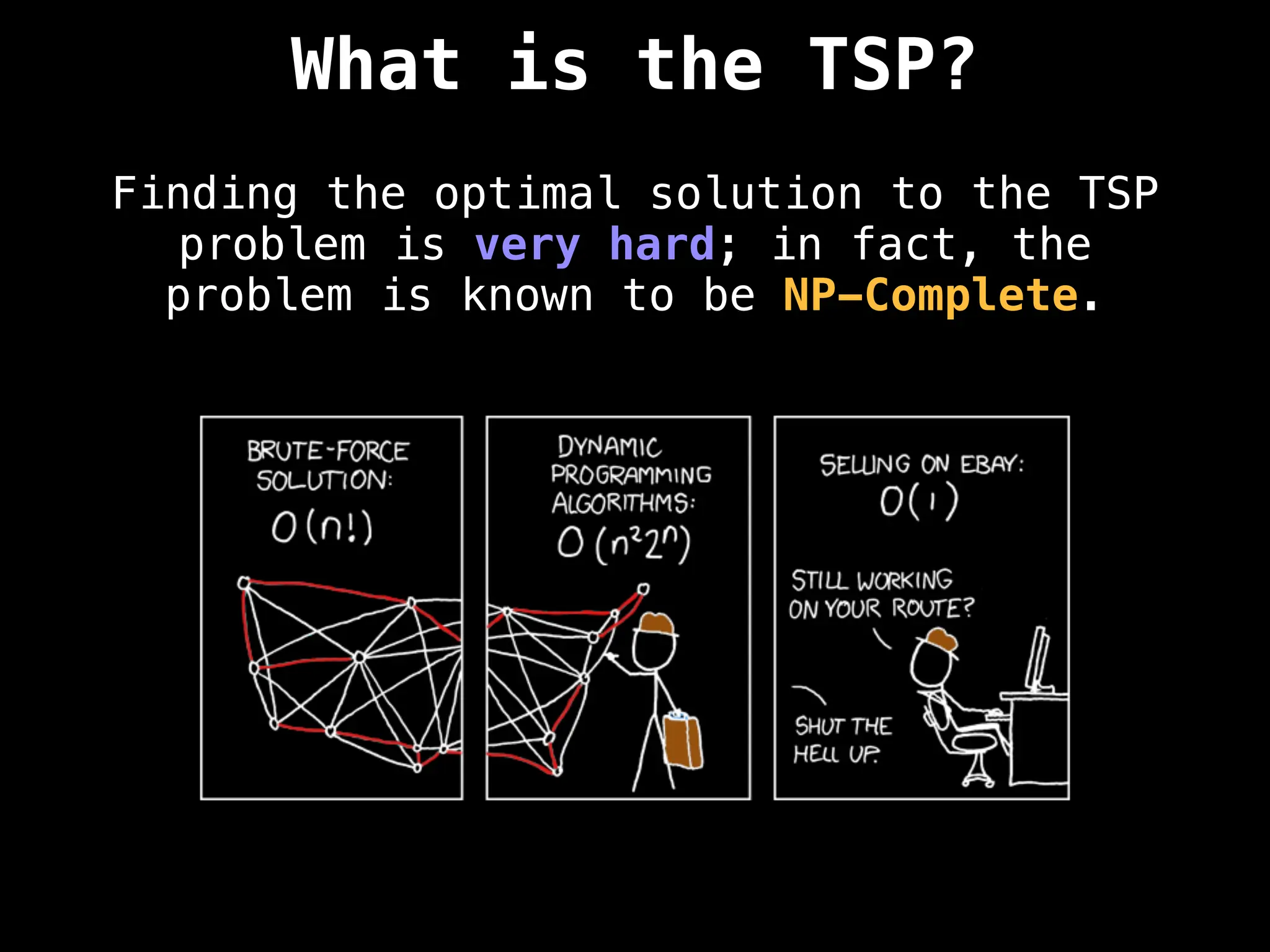
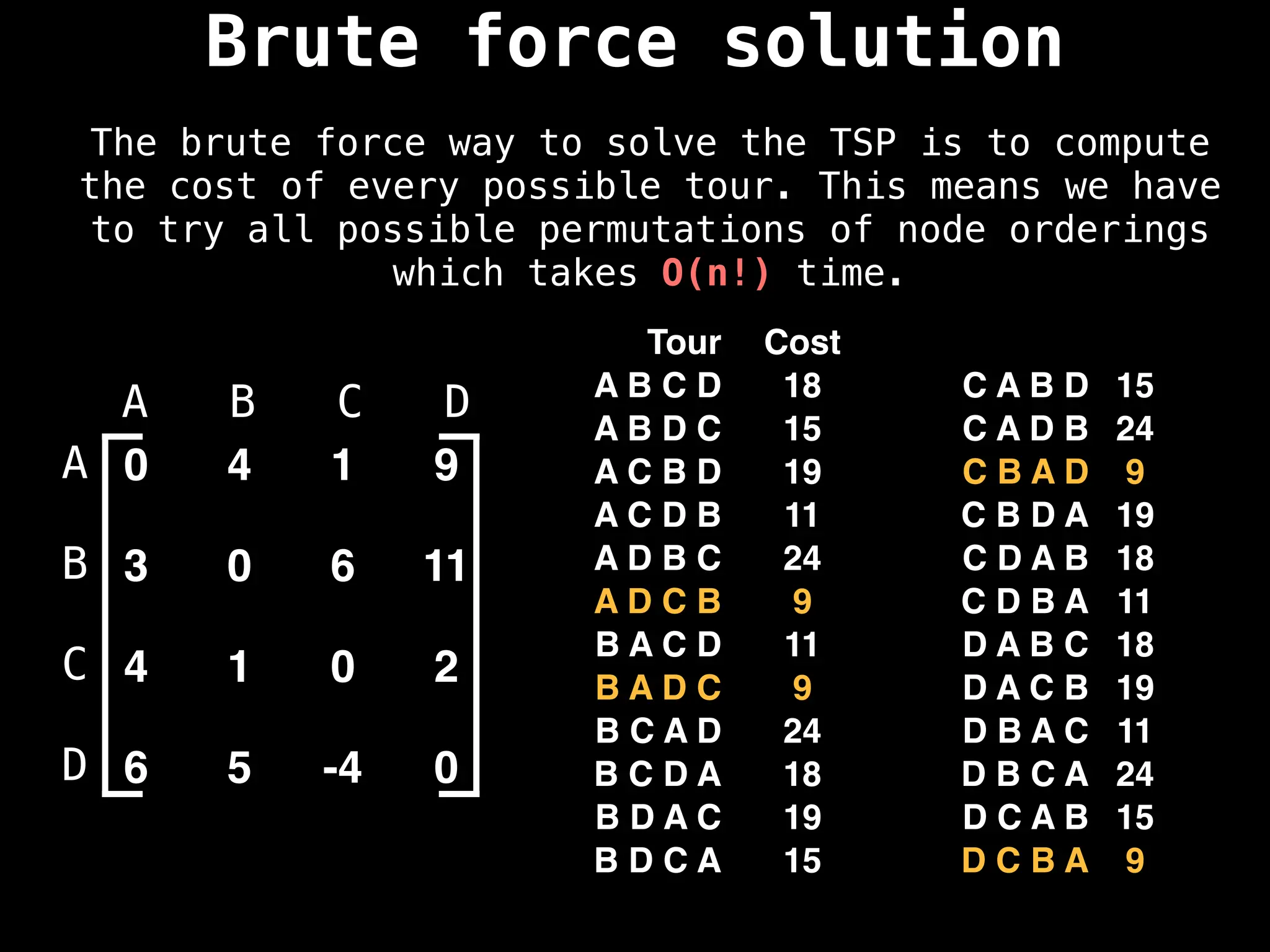
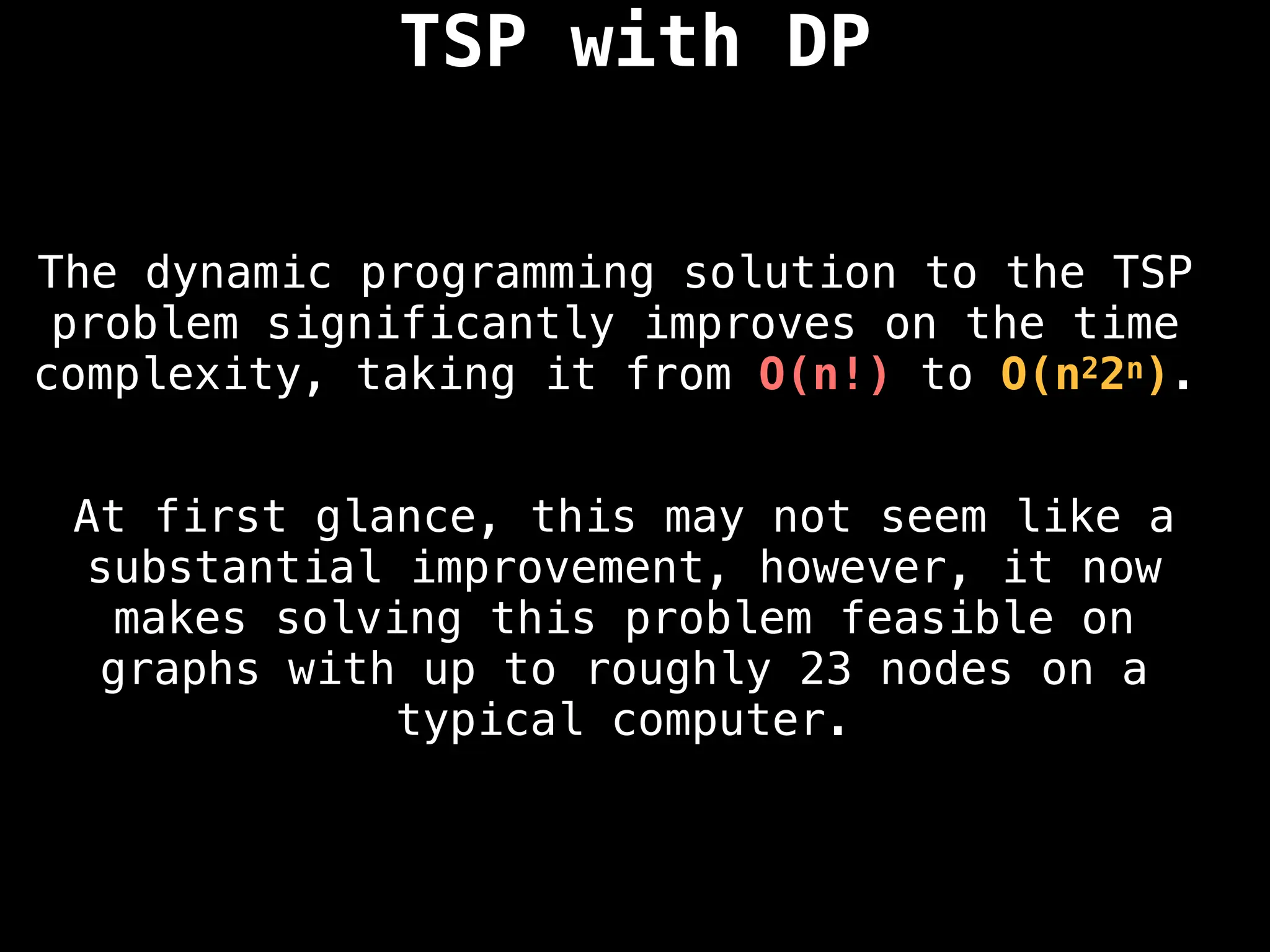
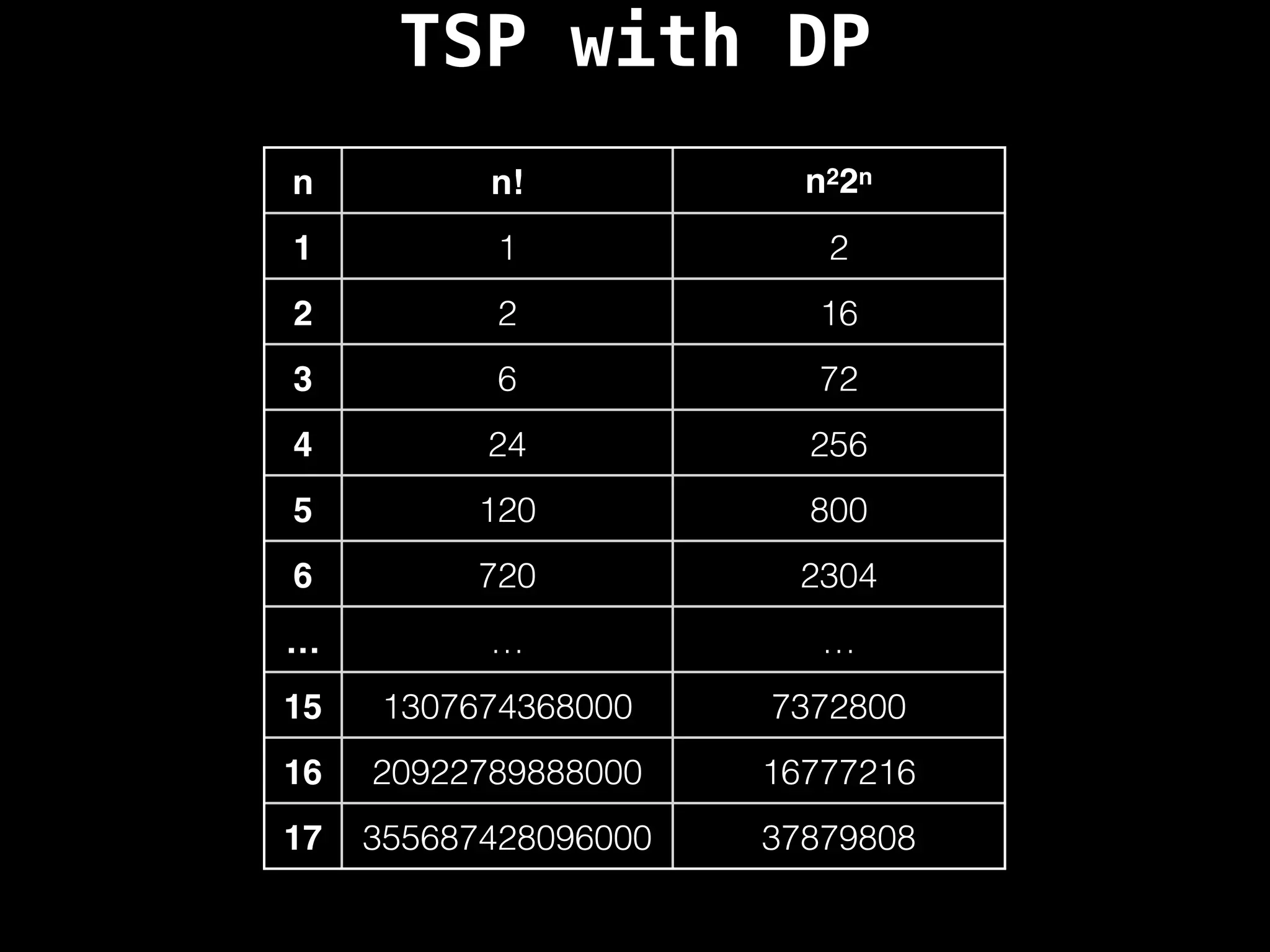
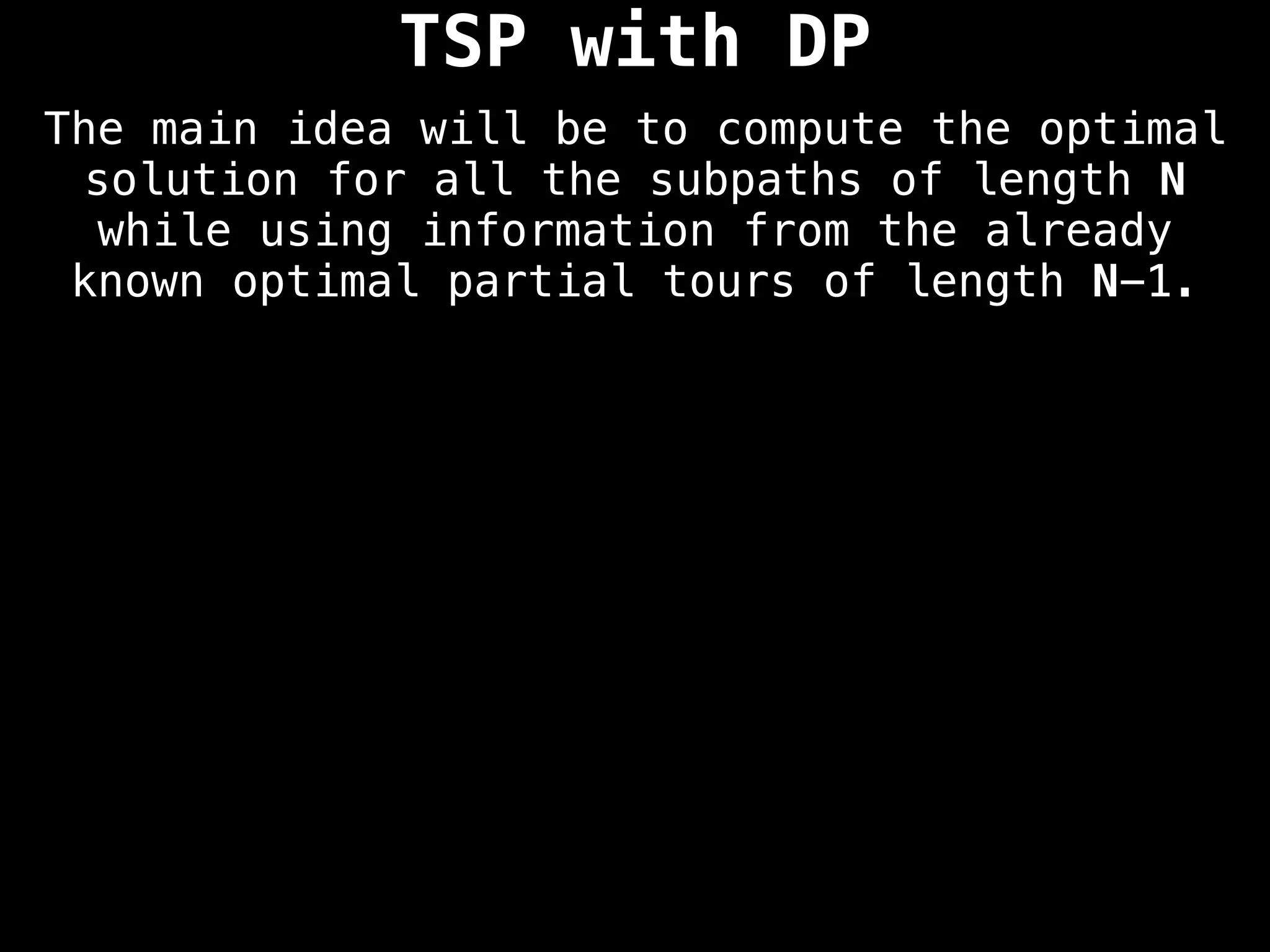
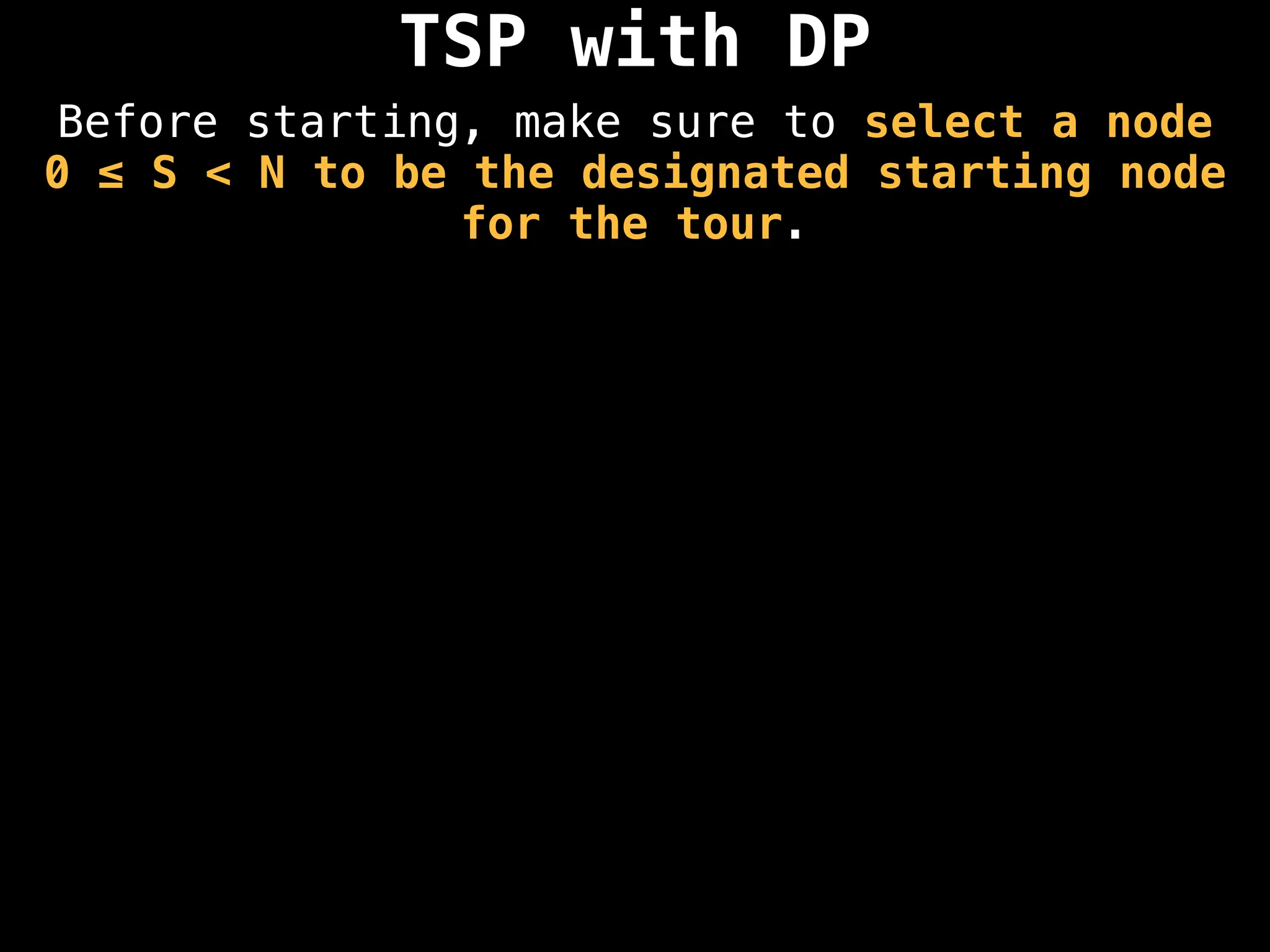
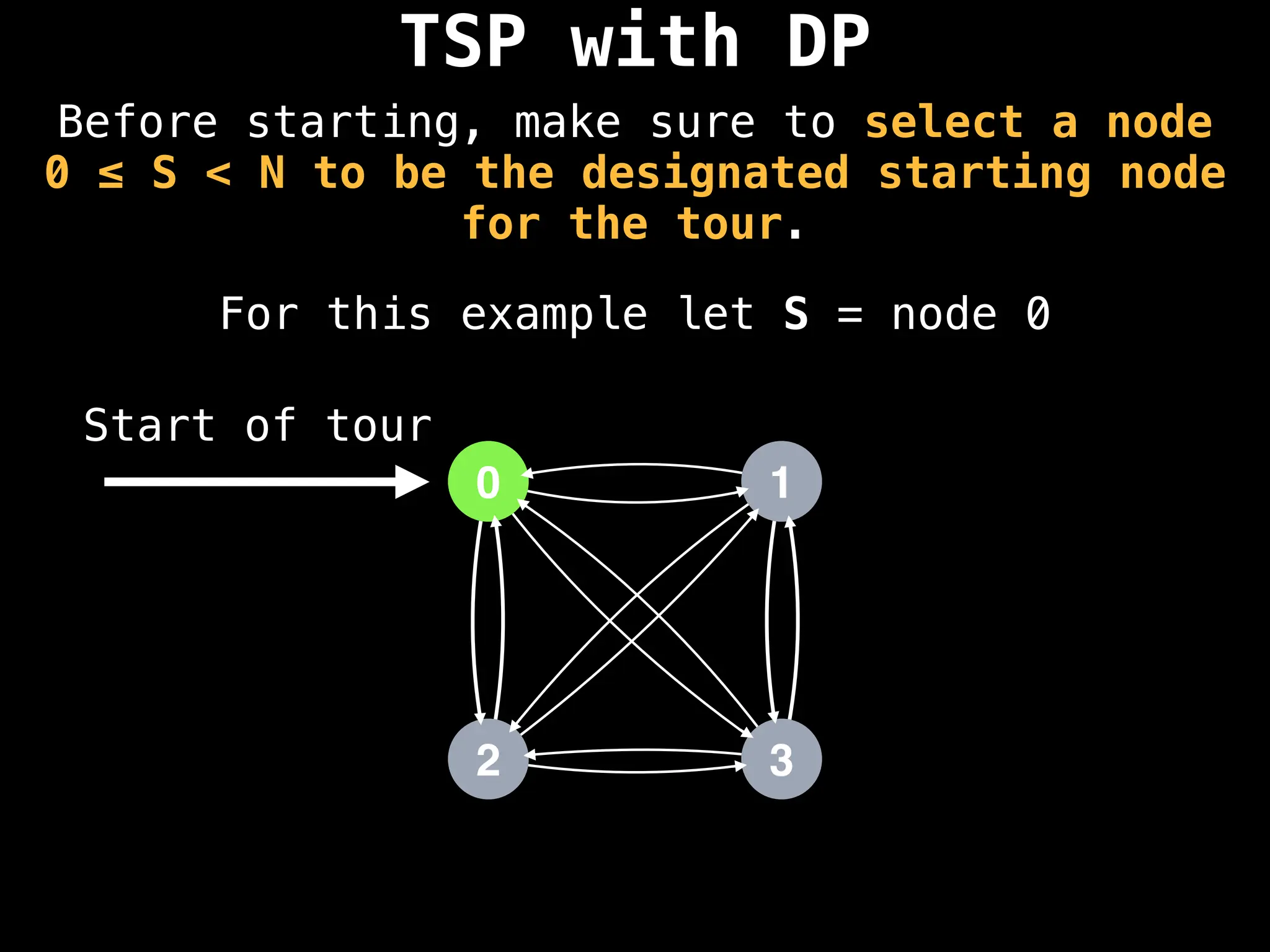
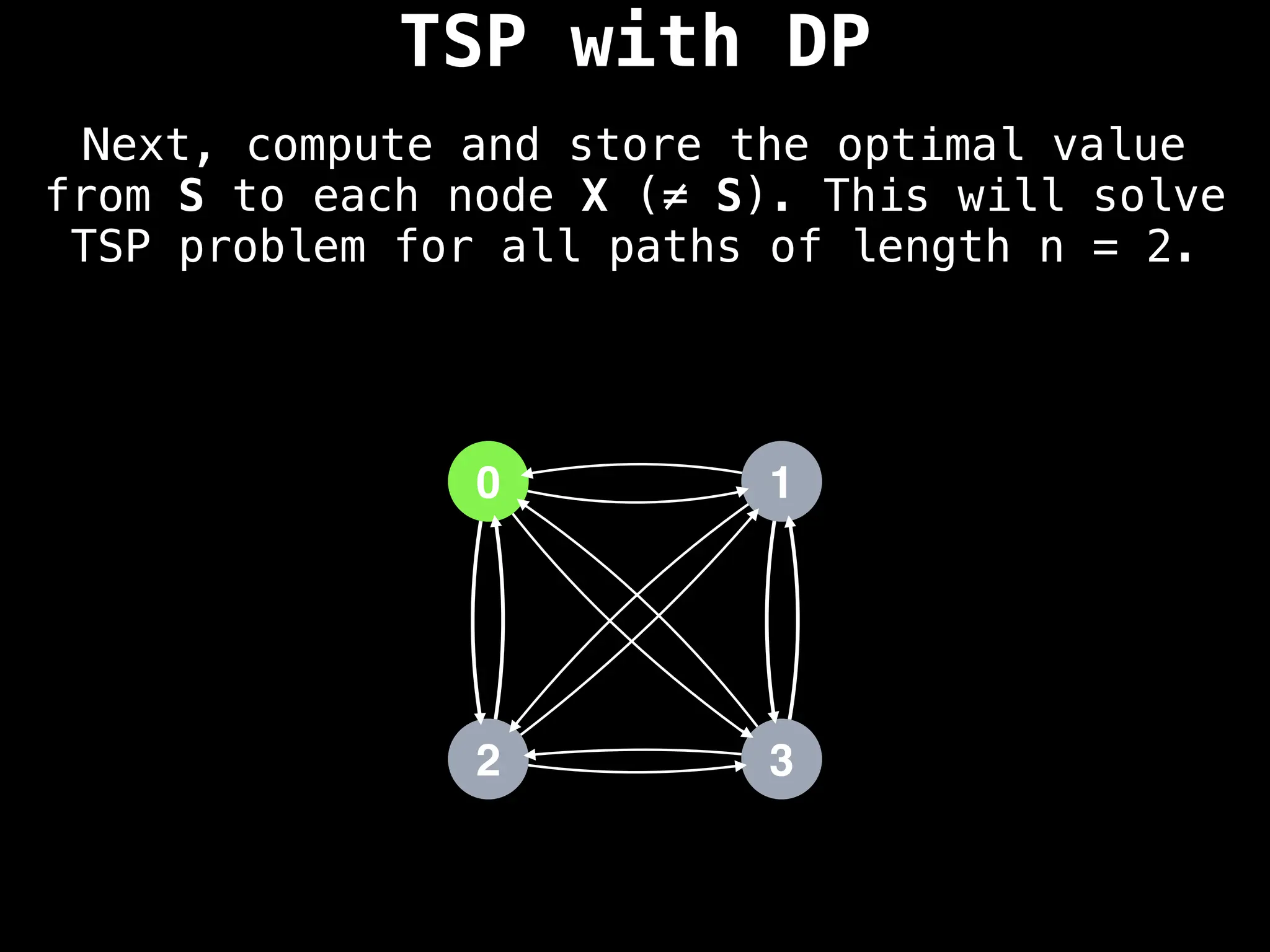
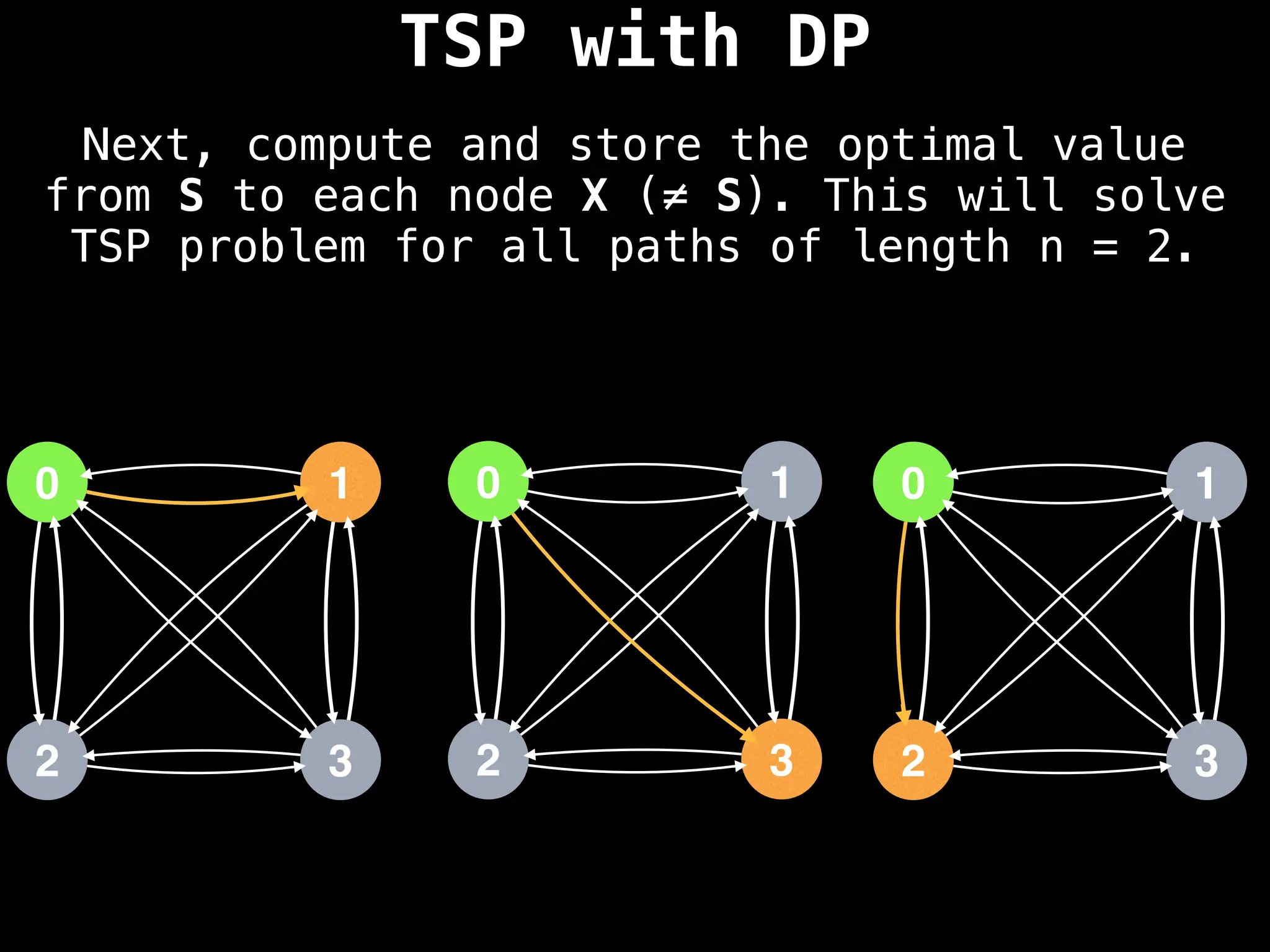
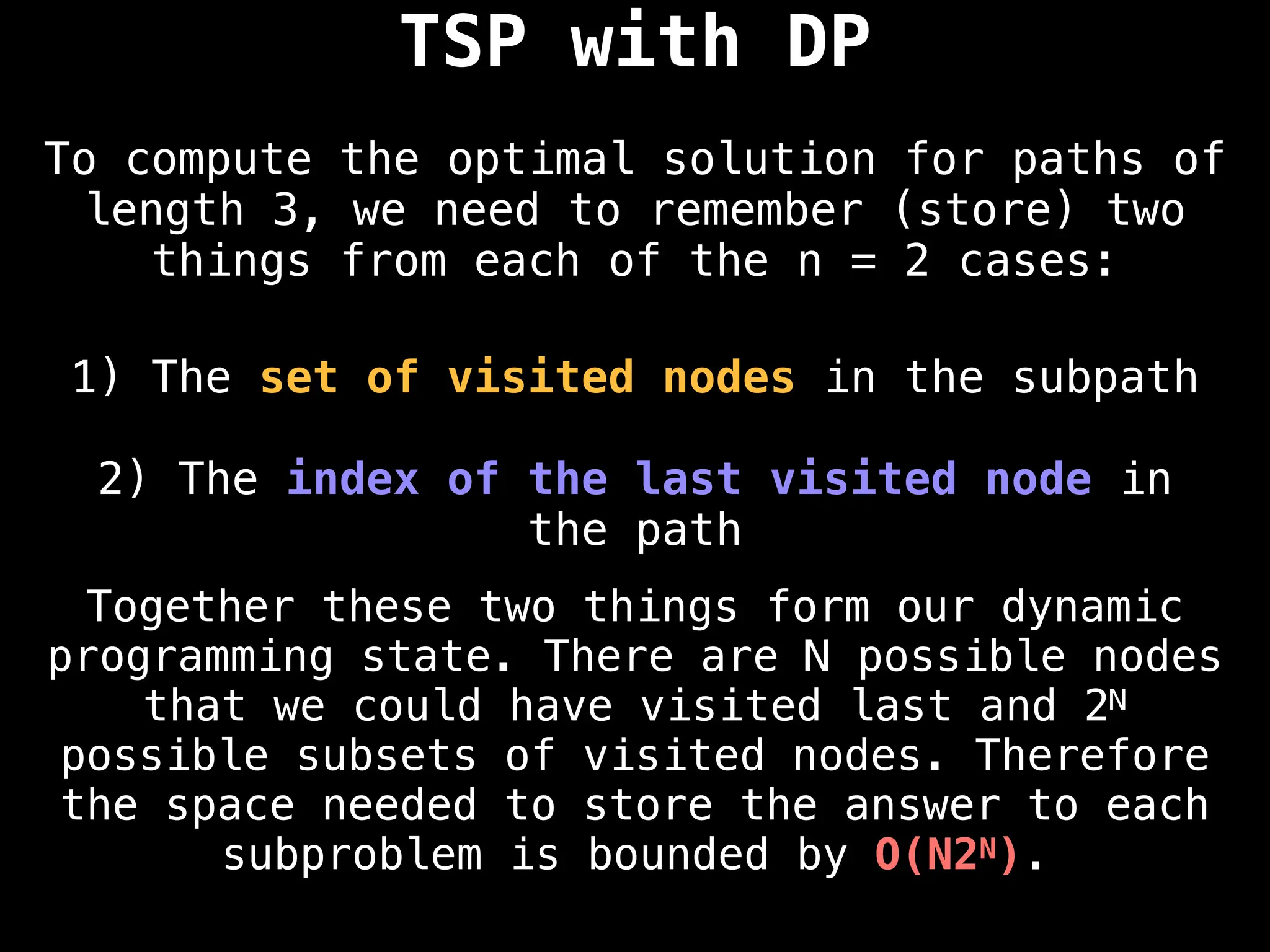
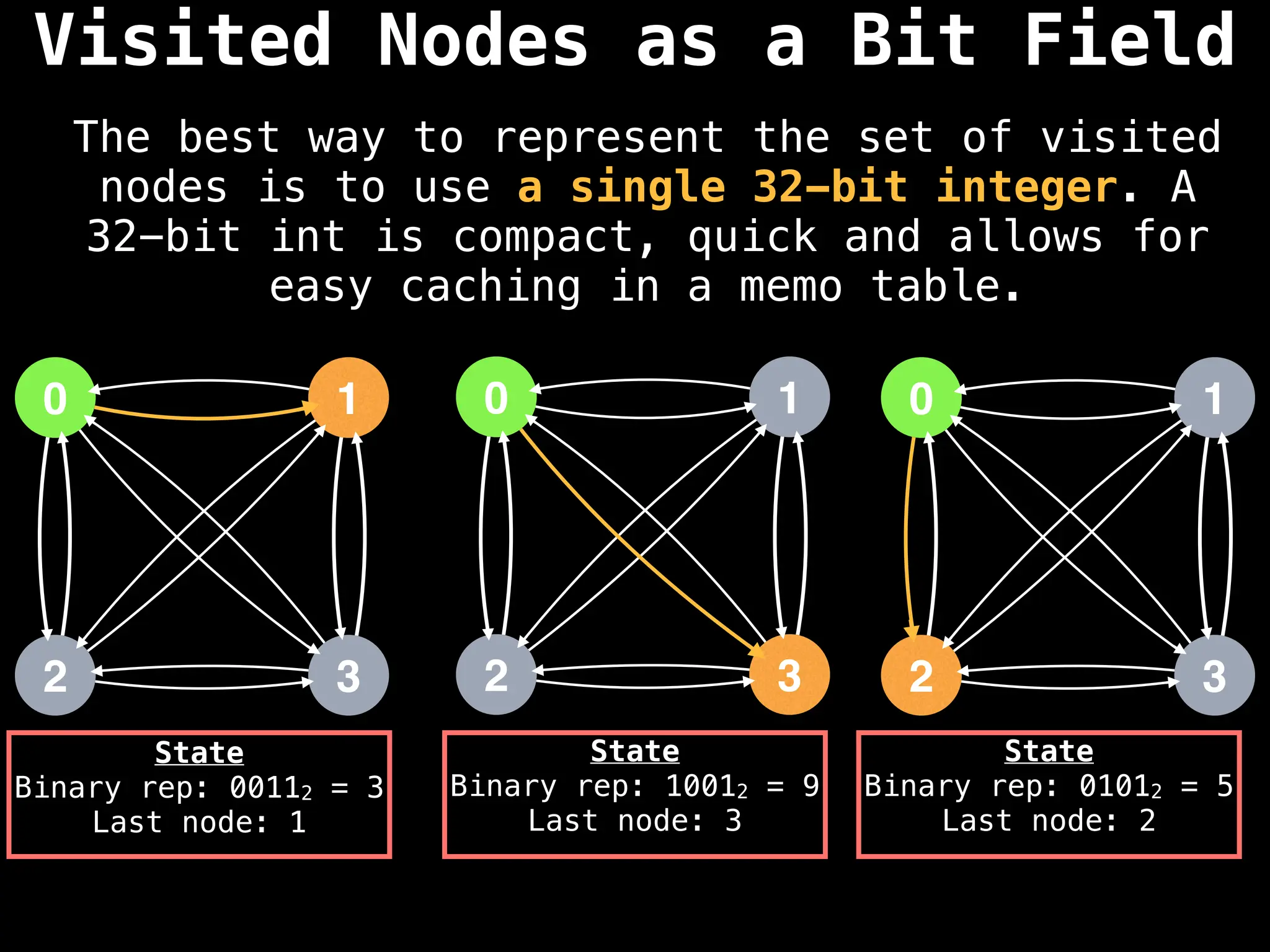
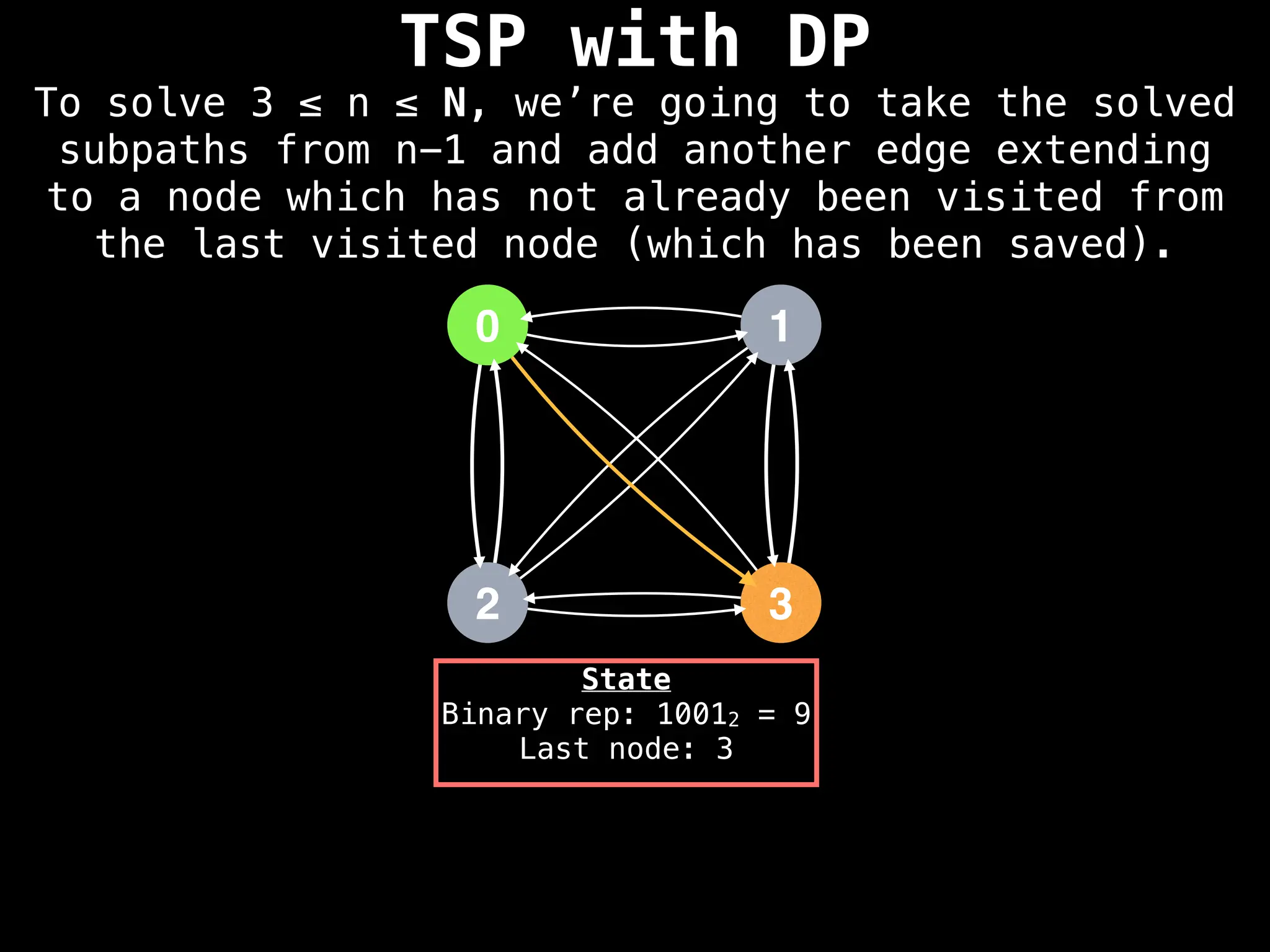
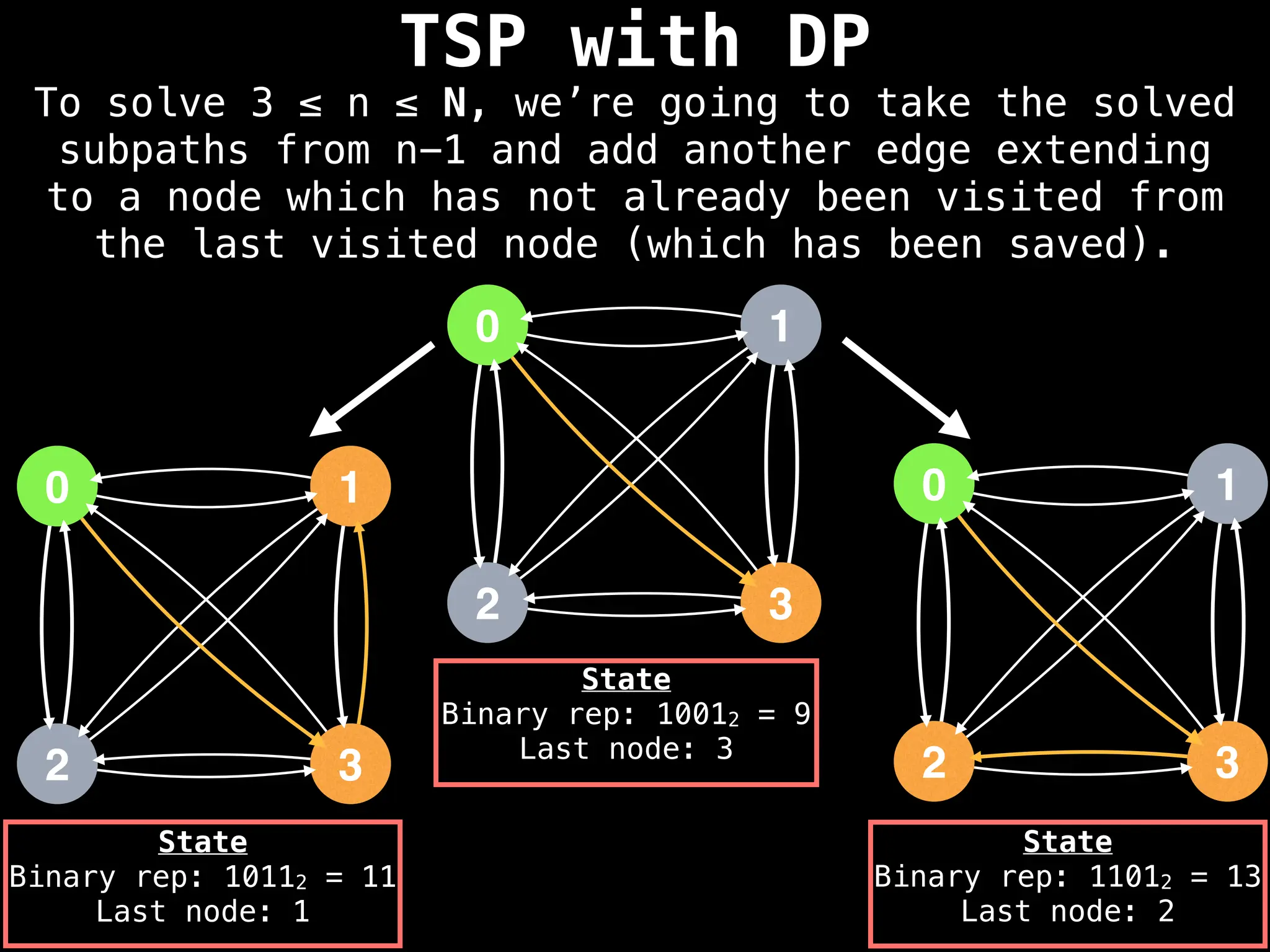


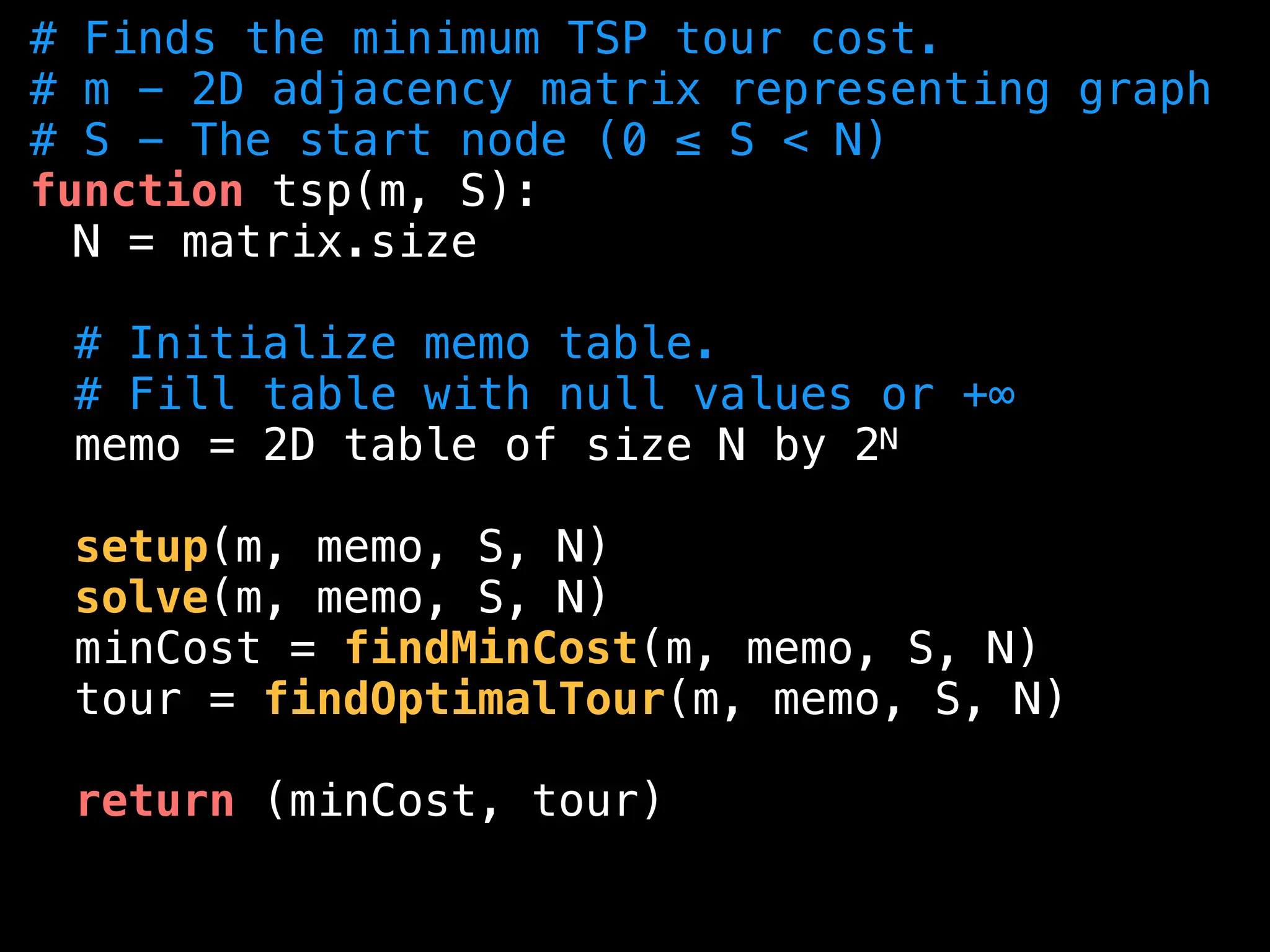
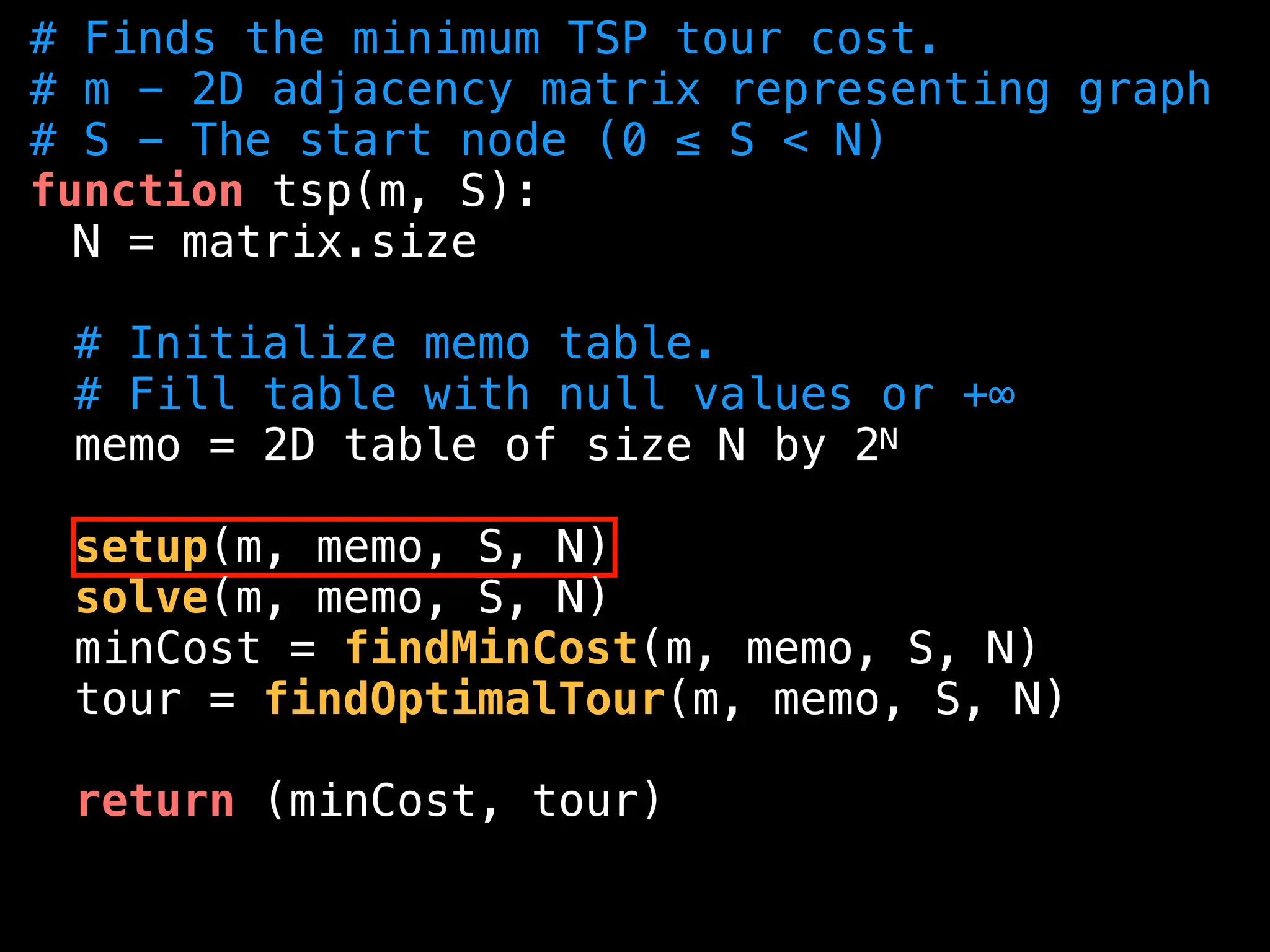
![# Initializes the memo table by caching
# the optimal solution from the start
# node to every other node.
function setup(m, memo, S, N):
for (i = 0; i < N; i = i + 1):
if i == S: continue
# Store the optimal value from node S
# to each node i (this is given as input
# in the adjacency matrix m).
memo[i][1 << S | 1 << i] = m[S][i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1052-2048.jpg)
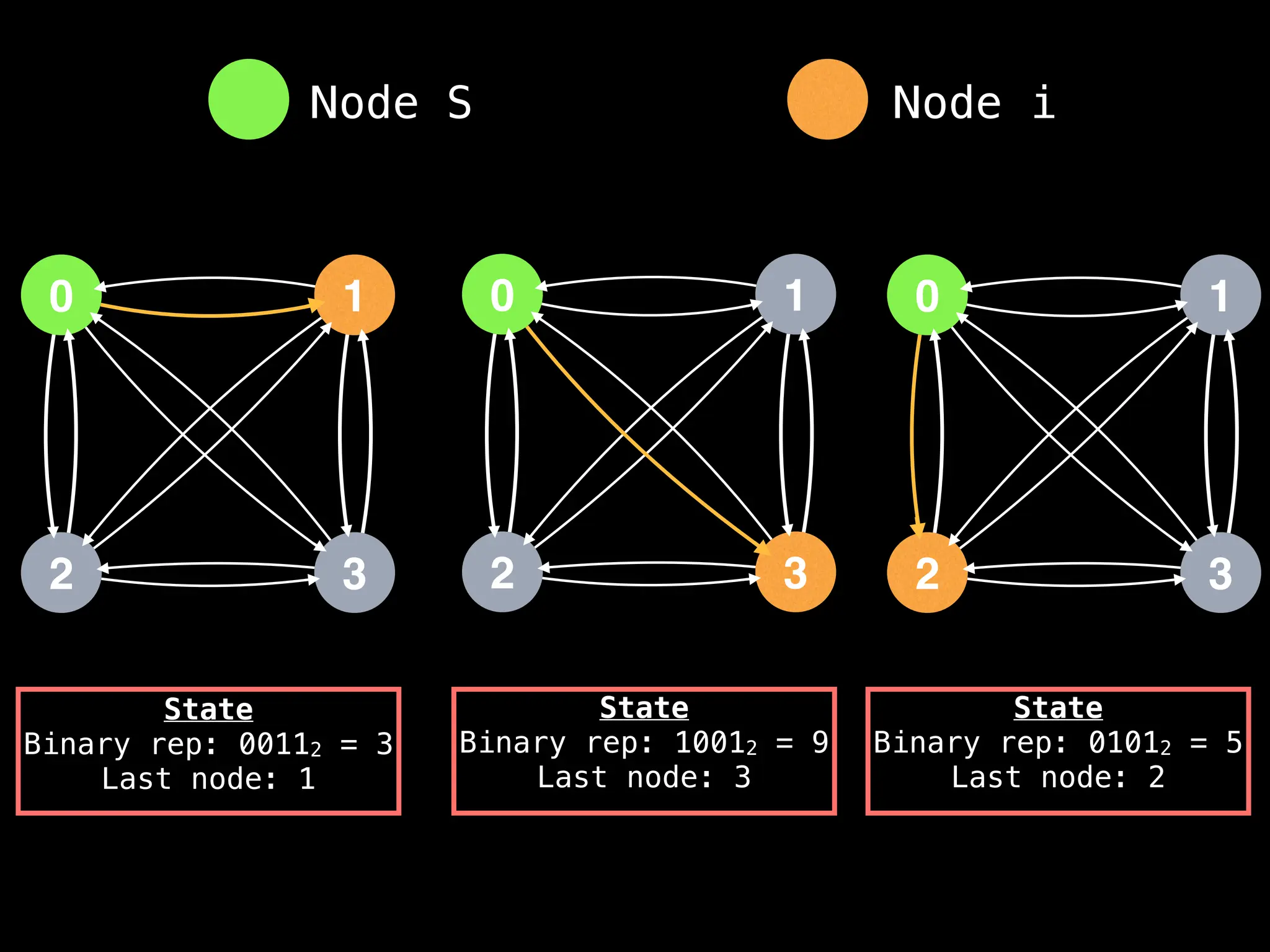
![# Initializes the memo table by caching
# the optimal solution from the start
# node to every other node.
function setup(m, memo, S, N):
for (i = 0; i < N; i = i + 1):
if i == S: continue
# Store the optimal value from node S
# to each node i (this is given as input
# in the adjacency matrix m).
memo[i][1 << S | 1 << i] = m[S][i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1054-2048.jpg)
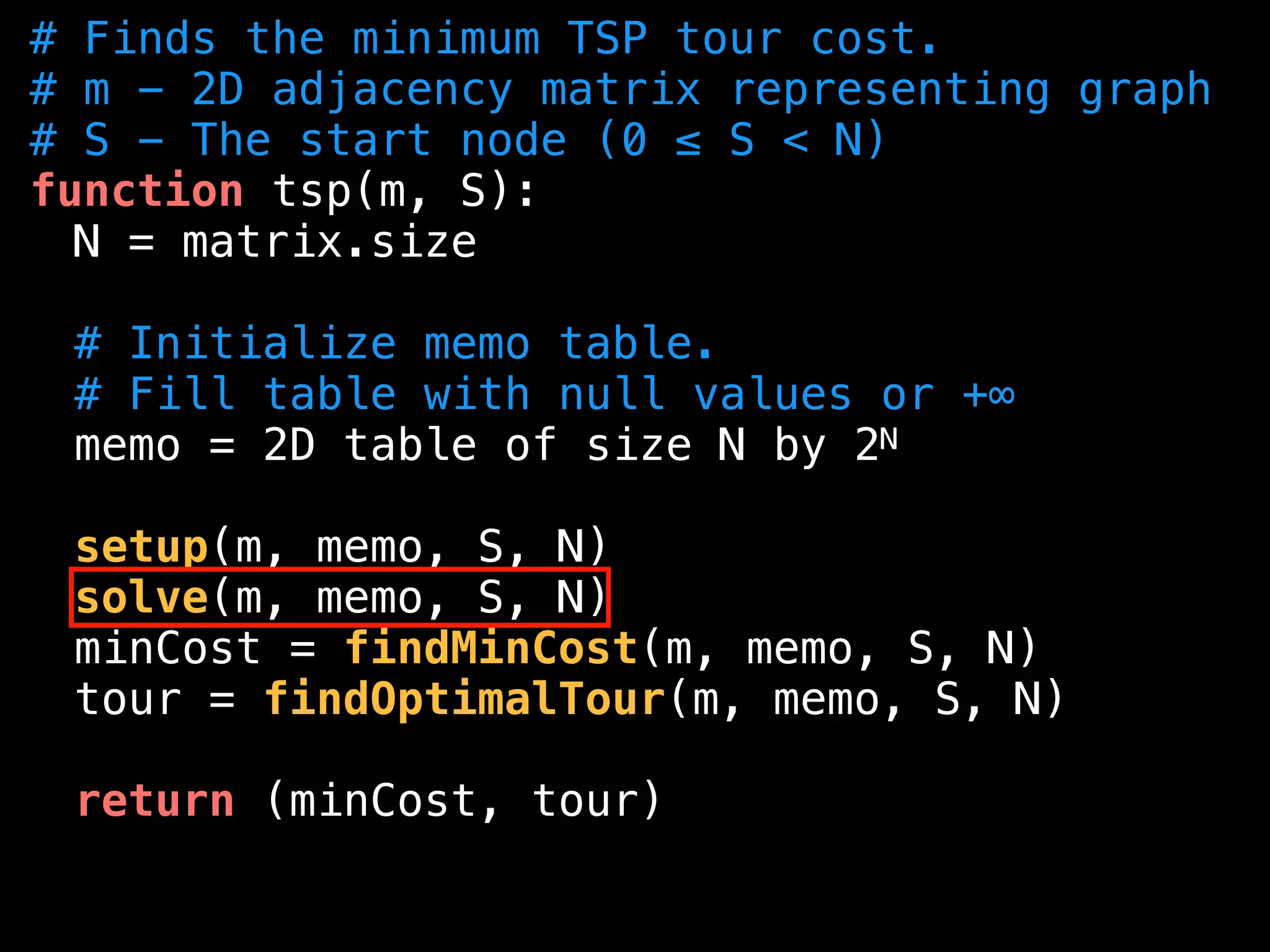
![function solve(m, memo, S, N):
for (r = 3; r <= N; r++):
# The combinations function generates all bit sets
# of size N with r bits set to 1. For example,
# combinations(3, 4) = {01112, 10112, 11012, 11102}
for subset in combinations(r, N):
if notIn(S, subset): continue
for (next = 0; next < N; next = next + 1):
if next == S || notIn(next, subset): continue
# The subset state without the next node
state = subset ^ (1 << next)
minDist = +∞
# ‘e’ is short for end node.
for (e = 0; e < N; e = e + 1):
if e == S || e == next || notIn(e, subset)):
continue
newDistance = memo[e][state] + m[e][next]
if (newDistance < minDist): minDist = newDistance
memo[next][subset] = minDist
# Returns true if the ith bit in ‘subset’ is not set
function notIn(i, subset):
return ((1 << i) & subset) == 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1056-2048.jpg)
![function solve(m, memo, S, N):
for (r = 3; r <= N; r++):
# The combinations function generates all bit sets
# of size N with r bits set to 1. For example,
# combinations(3, 4) = {01112, 10112, 11012, 11102}
for subset in combinations(r, N):
if notIn(S, subset): continue
for (next = 0; next < N; next = next + 1):
if next == S || notIn(next, subset): continue
# The subset state without the next node
state = subset ^ (1 << next)
minDist = +∞
# ‘e’ is short for end node.
for (e = 0; e < N; e = e + 1):
if e == S || e == next || notIn(e, subset)):
continue
newDistance = memo[e][state] + m[e][next]
if (newDistance < minDist): minDist = newDistance
memo[next][subset] = minDist
# Returns true if the ith bit in ‘subset’ is not set
function notIn(i, subset):
return ((1 << i) & subset) == 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1057-2048.jpg)
![# Generate all bit sets of size n with r bits set to 1.
function combinations(r, n):
subsets = []
combinations(0, 0, r, n, subsets)
return subsets
# Recursive method to generate bit sets.
function combinations(set, at, r, n, subsets):
if r == 0:
subsets.add(set)
else:
for (i = at; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Flip on ith bit
set = set | (1 << i)
combinations(set, i + 1, r - 1, n, subsets)
# Backtrack and flip off ith bit
set = set & ~(1 << i)
NOTE: For a more detailed explanation on generating
combinations see video “Backtracking tutorial: power set”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1058-2048.jpg)
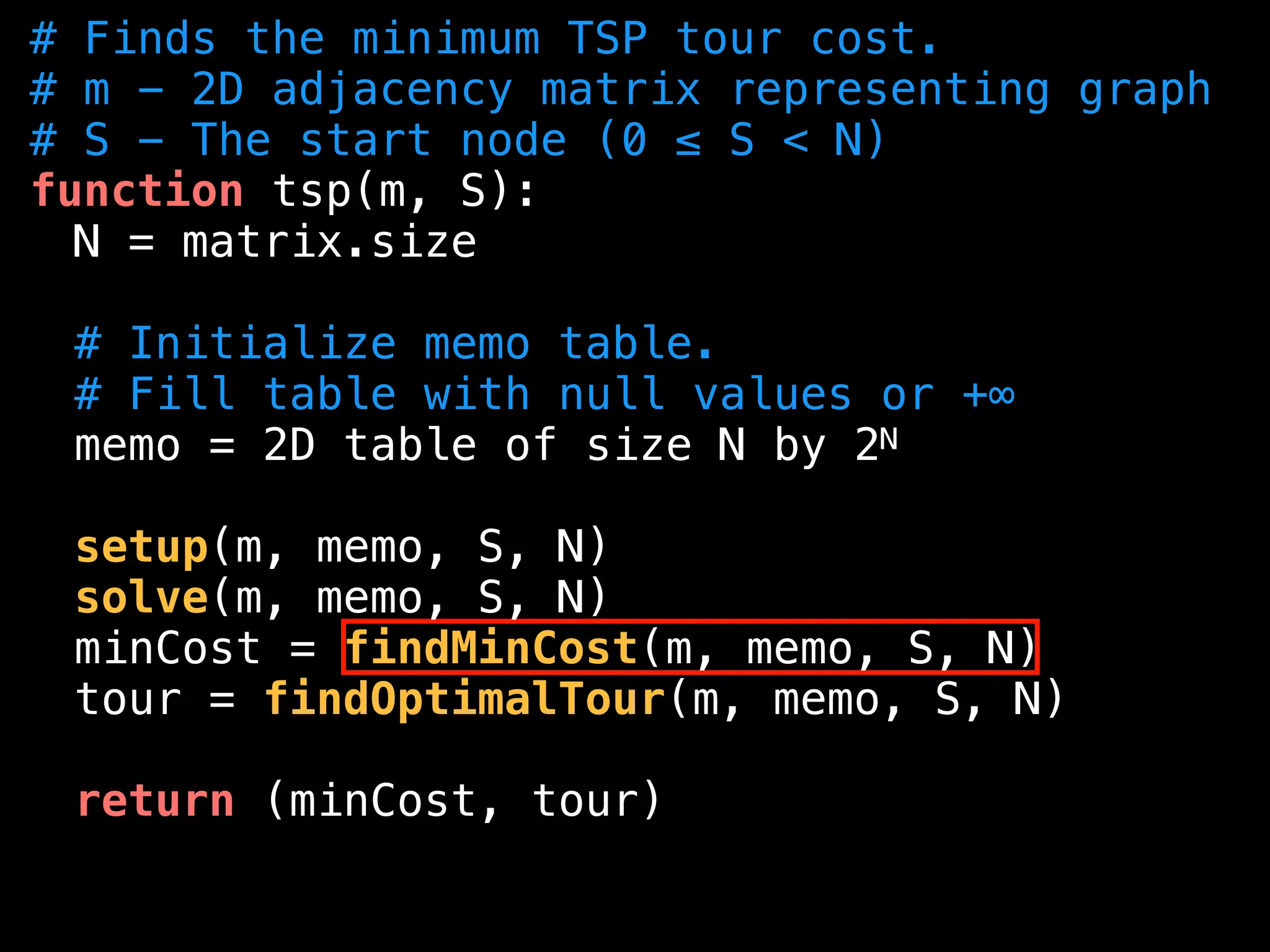
![function findMinCost(m, memo, S, N):
# The end state is the bit mask with
# N bits set to 1 (equivalently 2N - 1)
END_STATE = (1 << N) - 1
minTourCost = +∞
for (e = 0; e < N; e = e + 1):
if e == S: continue
tourCost = memo[e][END_STATE] + m[e][S]
if tourCost < minTourCost:
minTourCost = tourCost
return minTourCost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1060-2048.jpg)
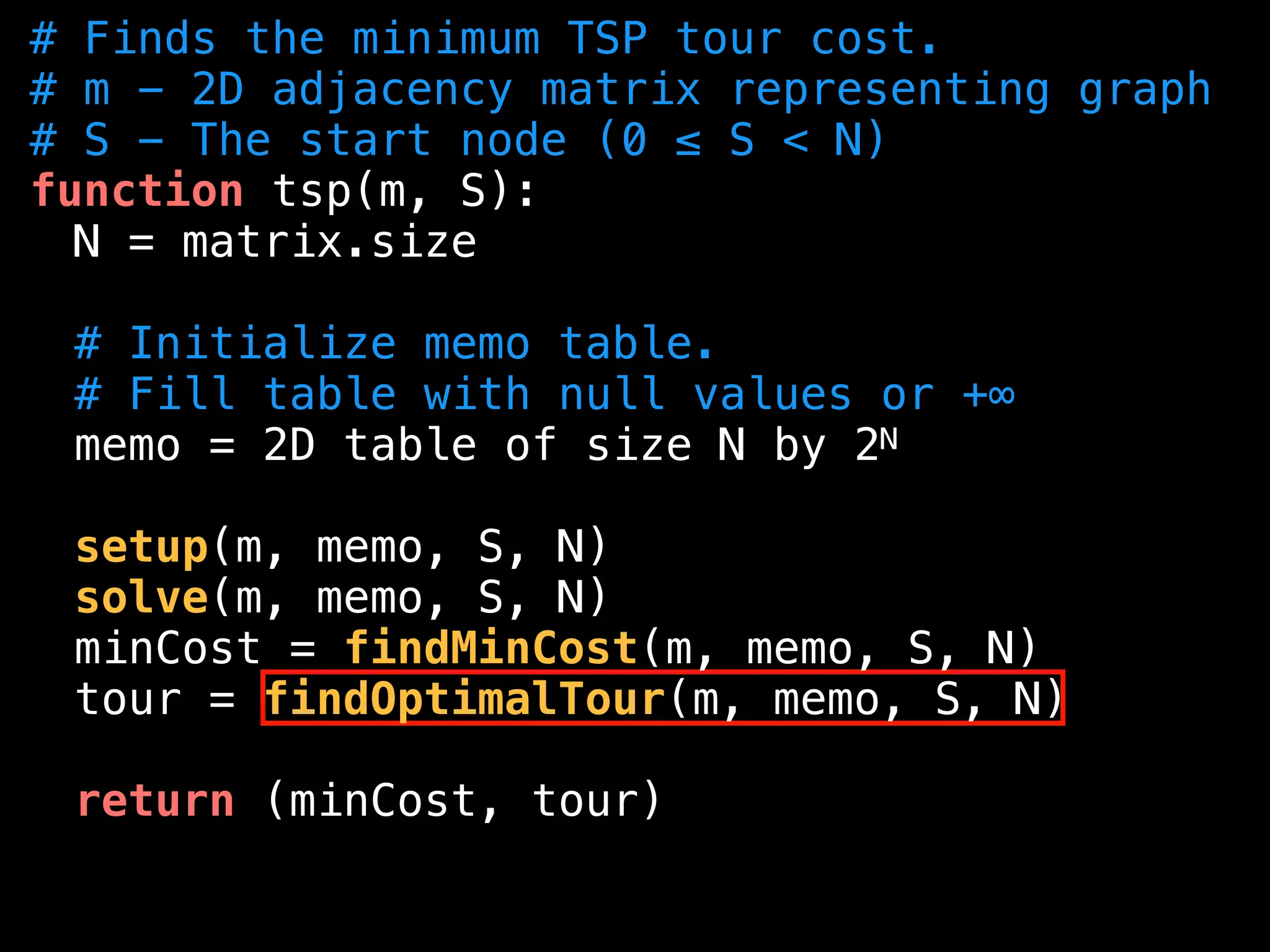
![function findOptimalTour(m, memo, S, N):
lastIndex = S
state = (1 << N) - 1; # End state
tour = array of size N+1
for (i = N-1; i >= 1; i--):
index = -1
for (j = 0; j < N; j++):
if j == S || notIn(j, state): continue
if (index == -1) index = j
prevDist = memo[index][state] + m[index]lastIndex]
newDist = memo[j][state] + m[j][lastIndex];
if (newDist < prevDist) index = j
tour[i] = index
state = state ^ (1 << index)
lastIndex = index
tour[0] = tour[N] = S
return tour](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1062-2048.jpg)
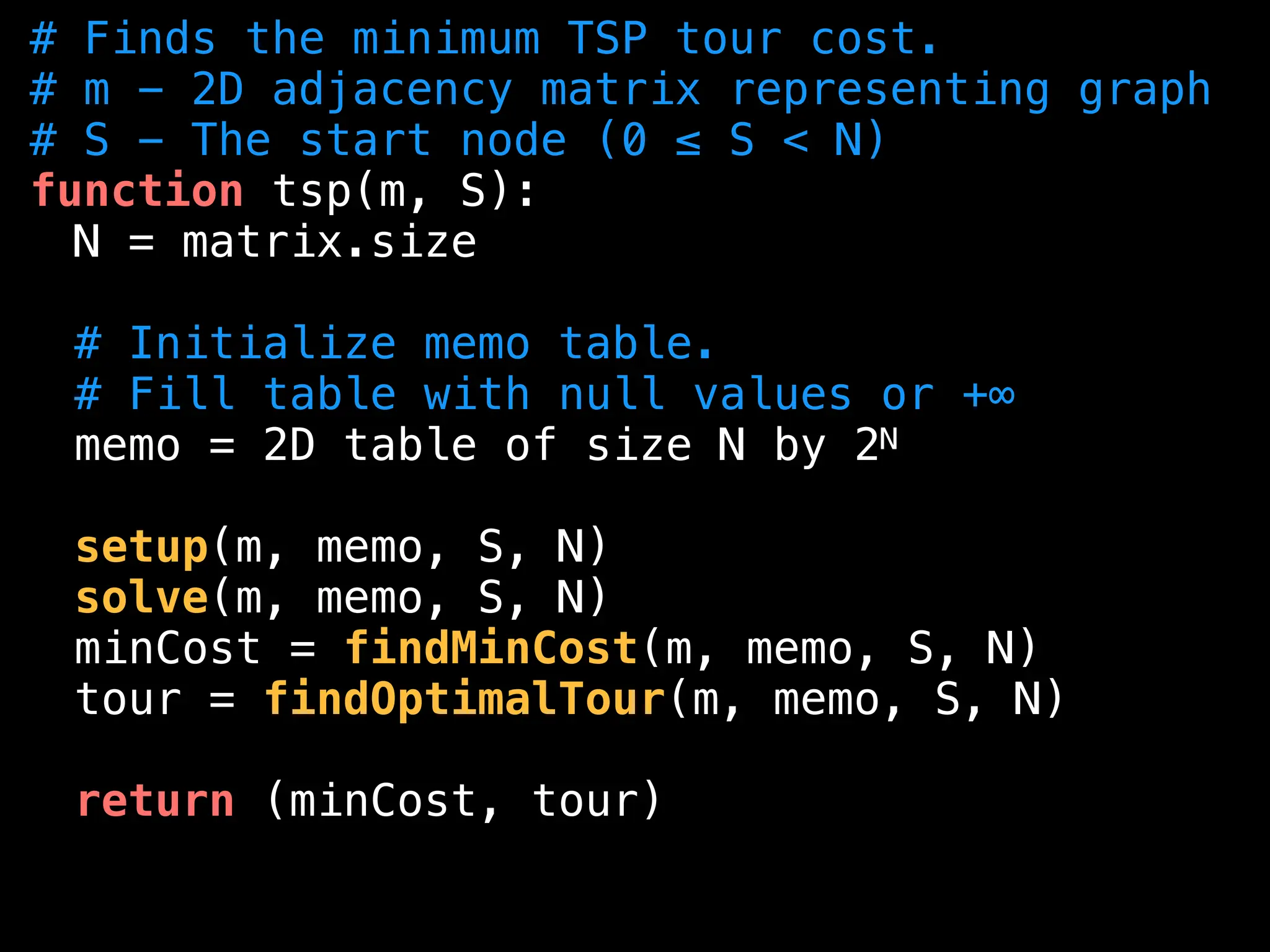

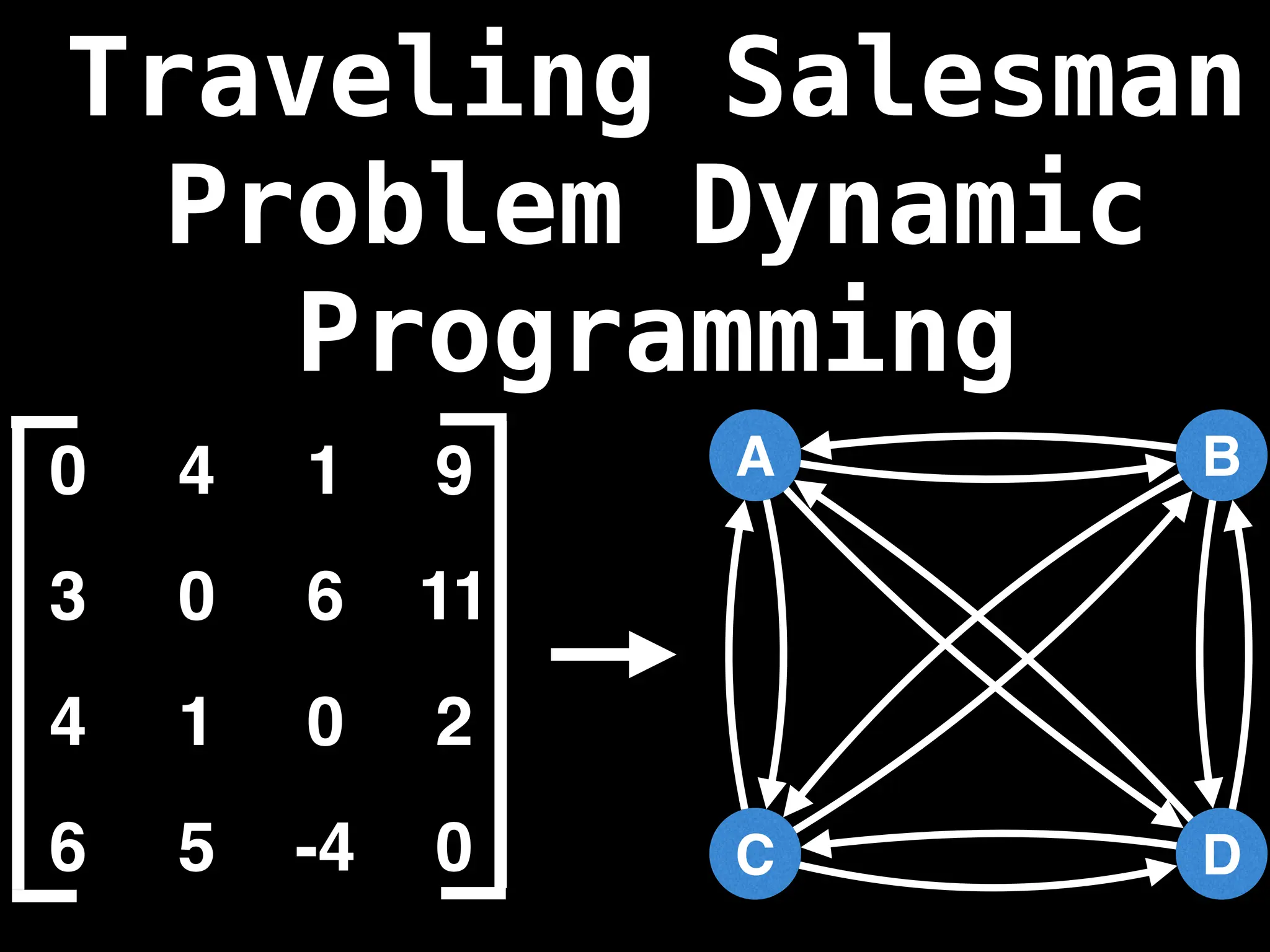



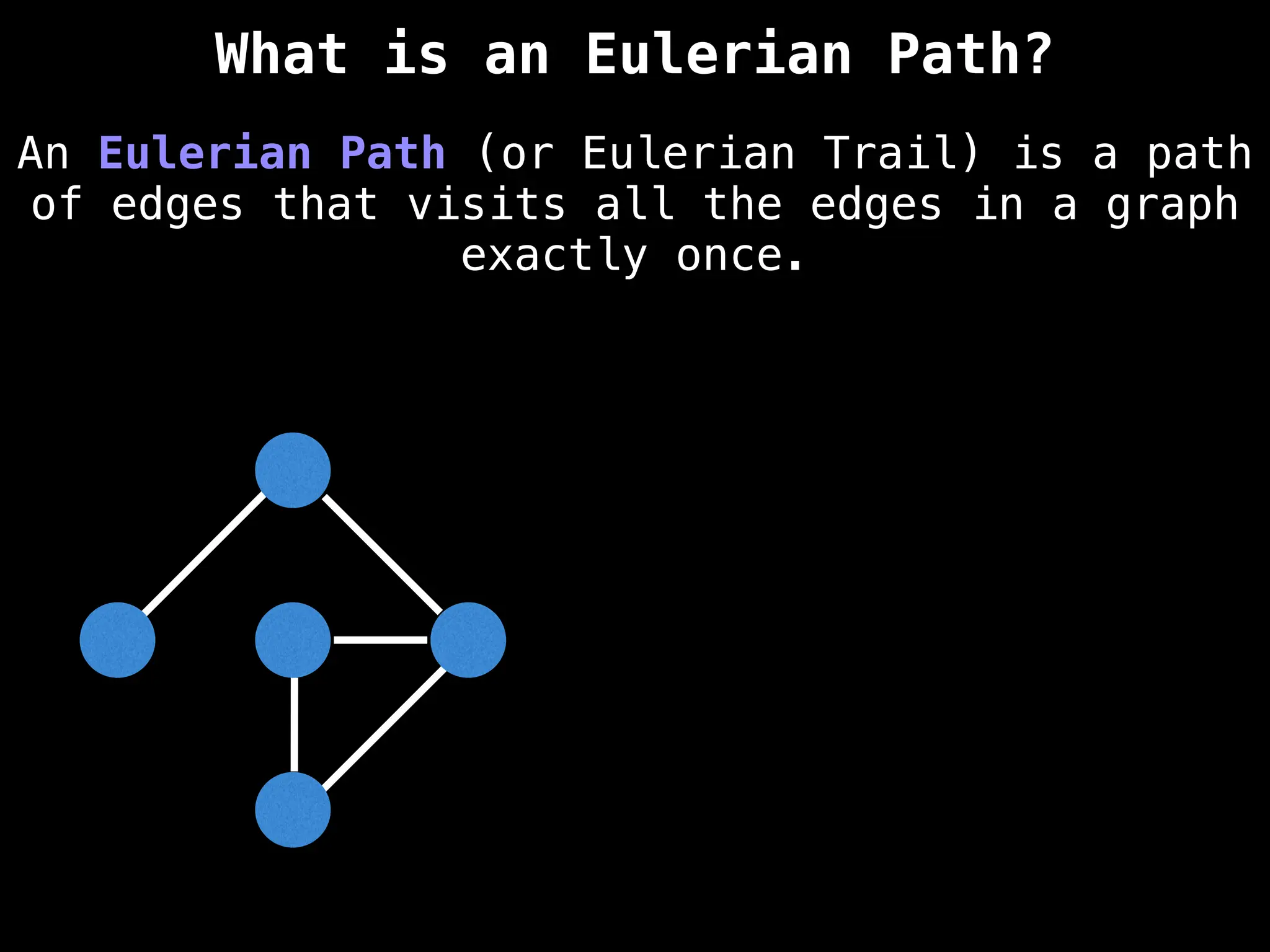
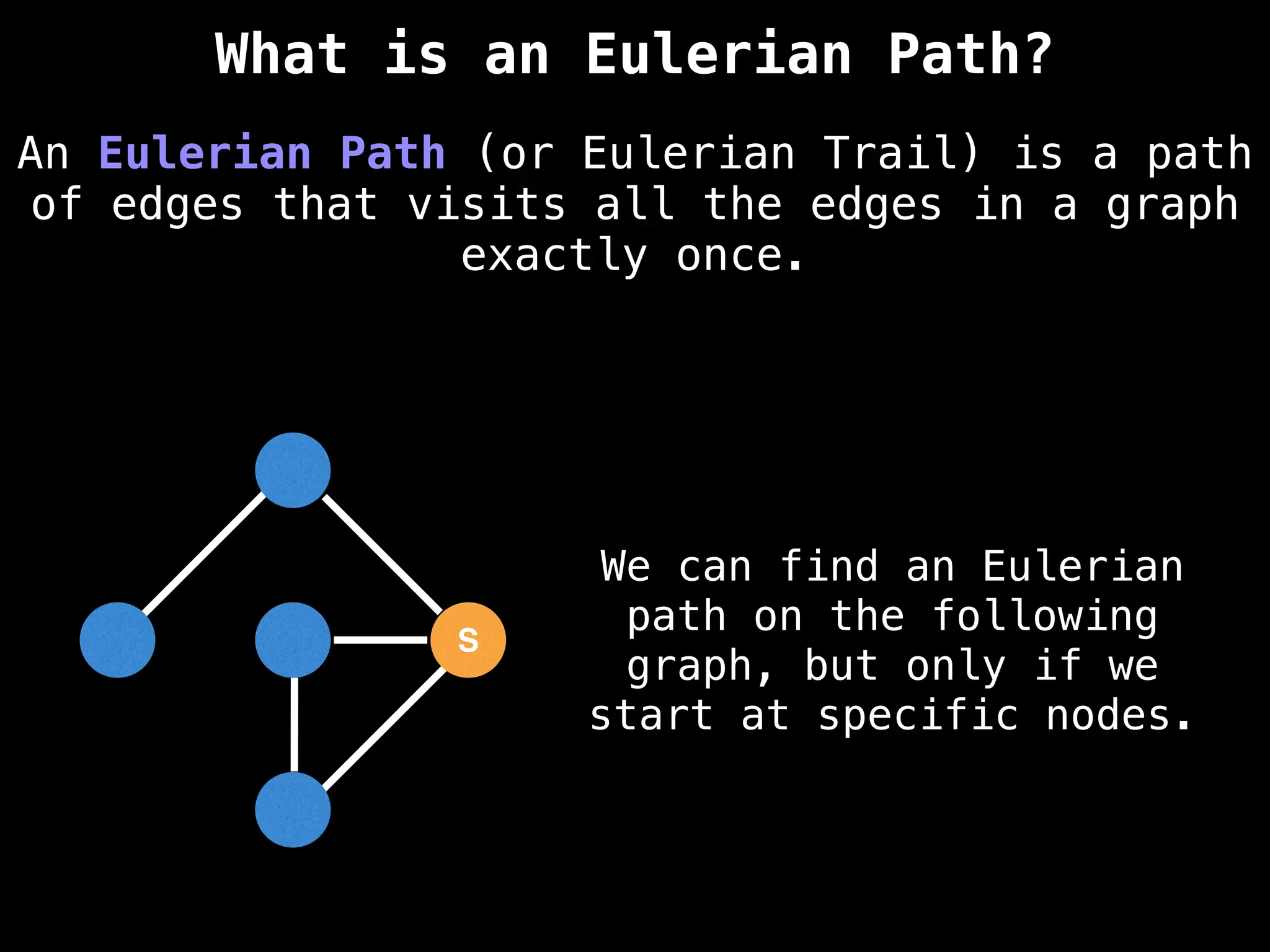
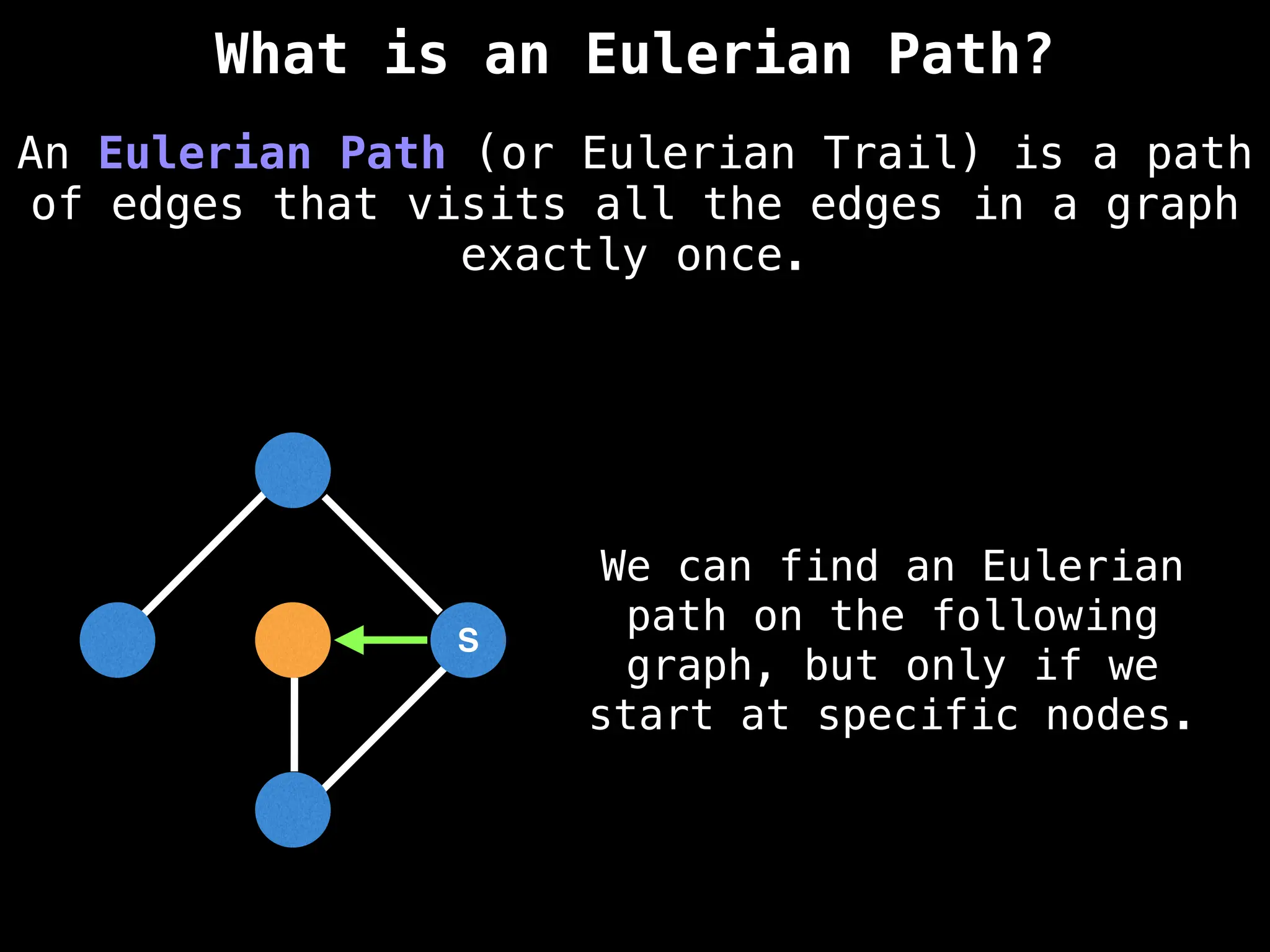
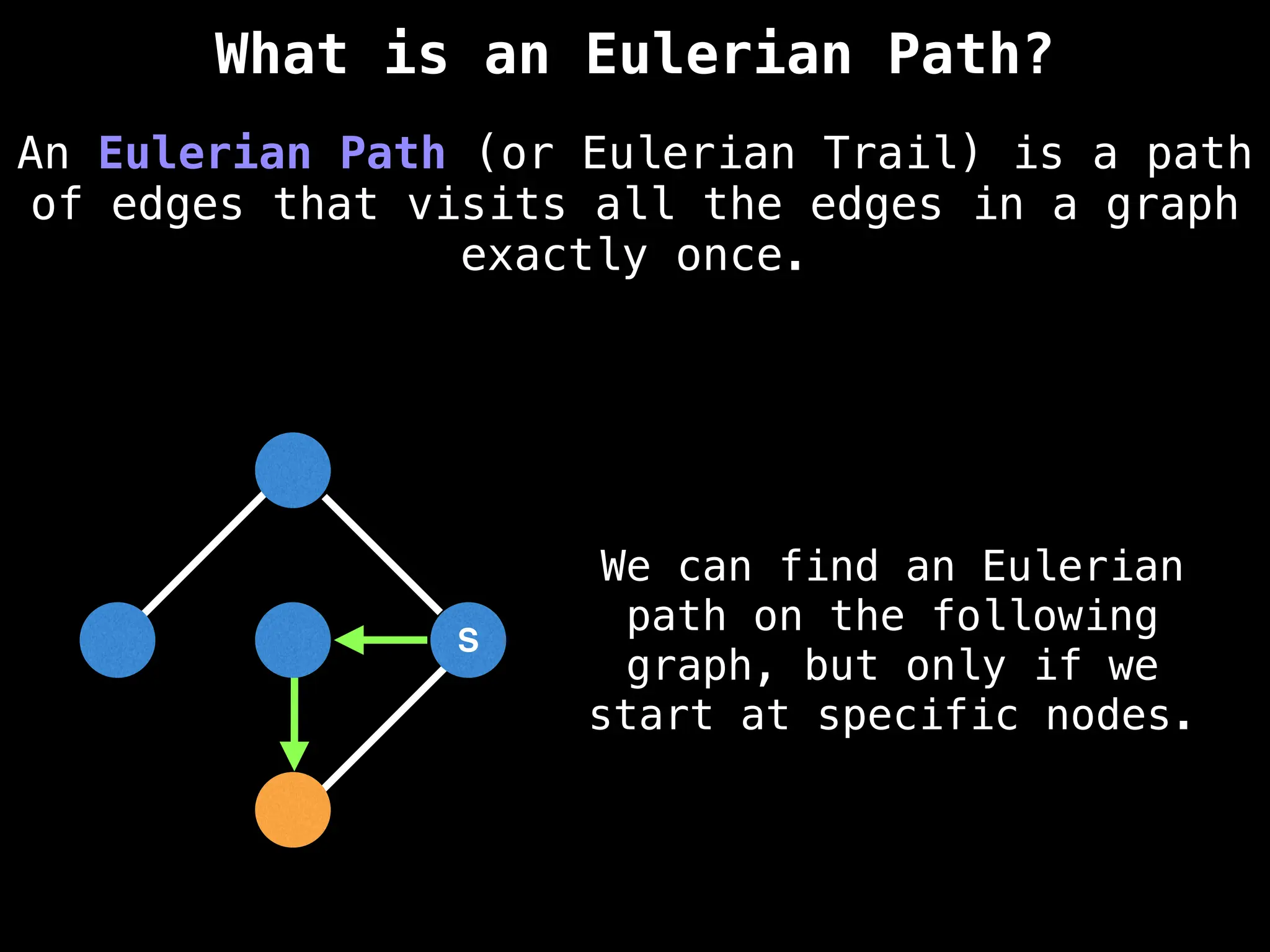
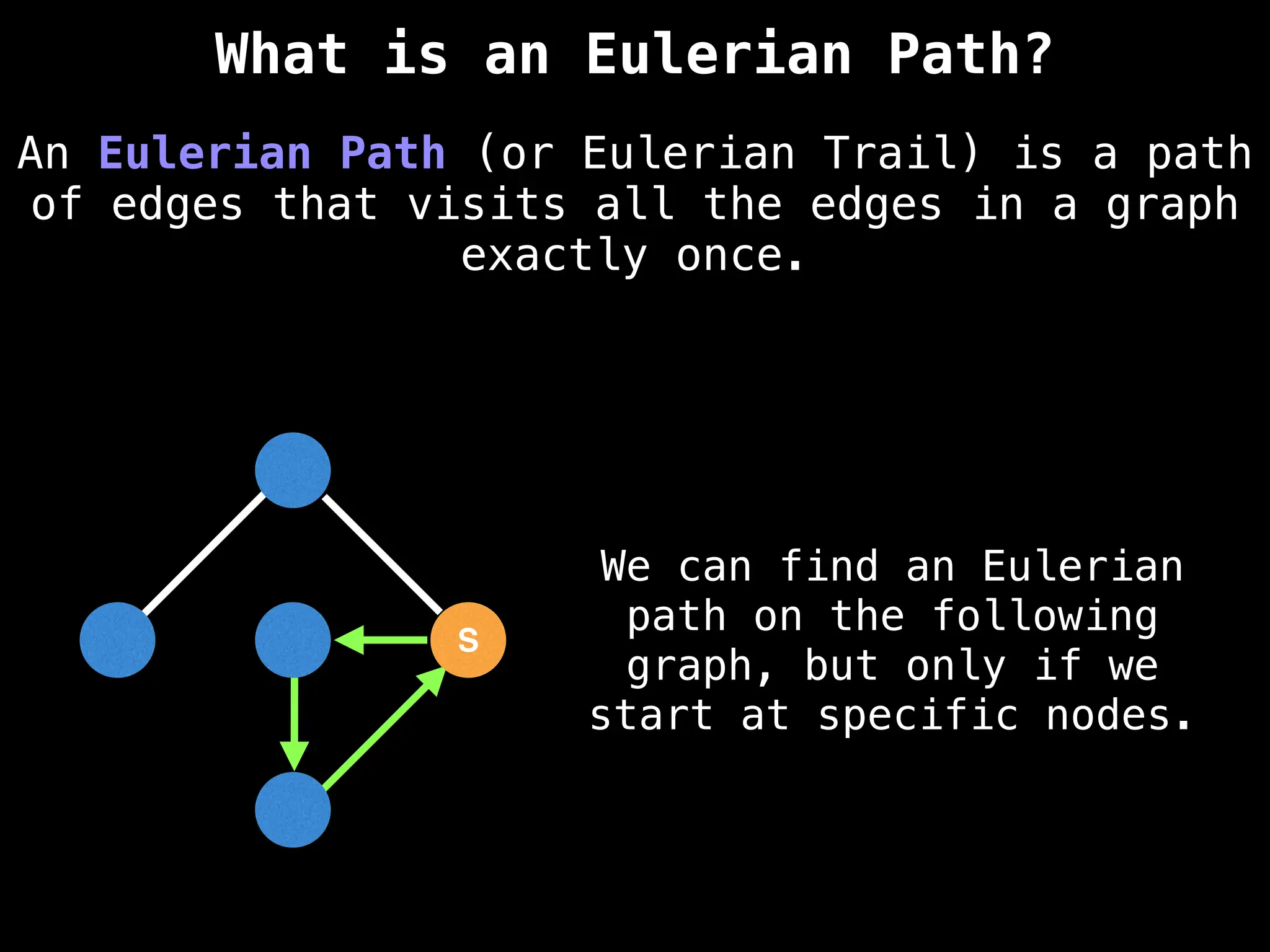
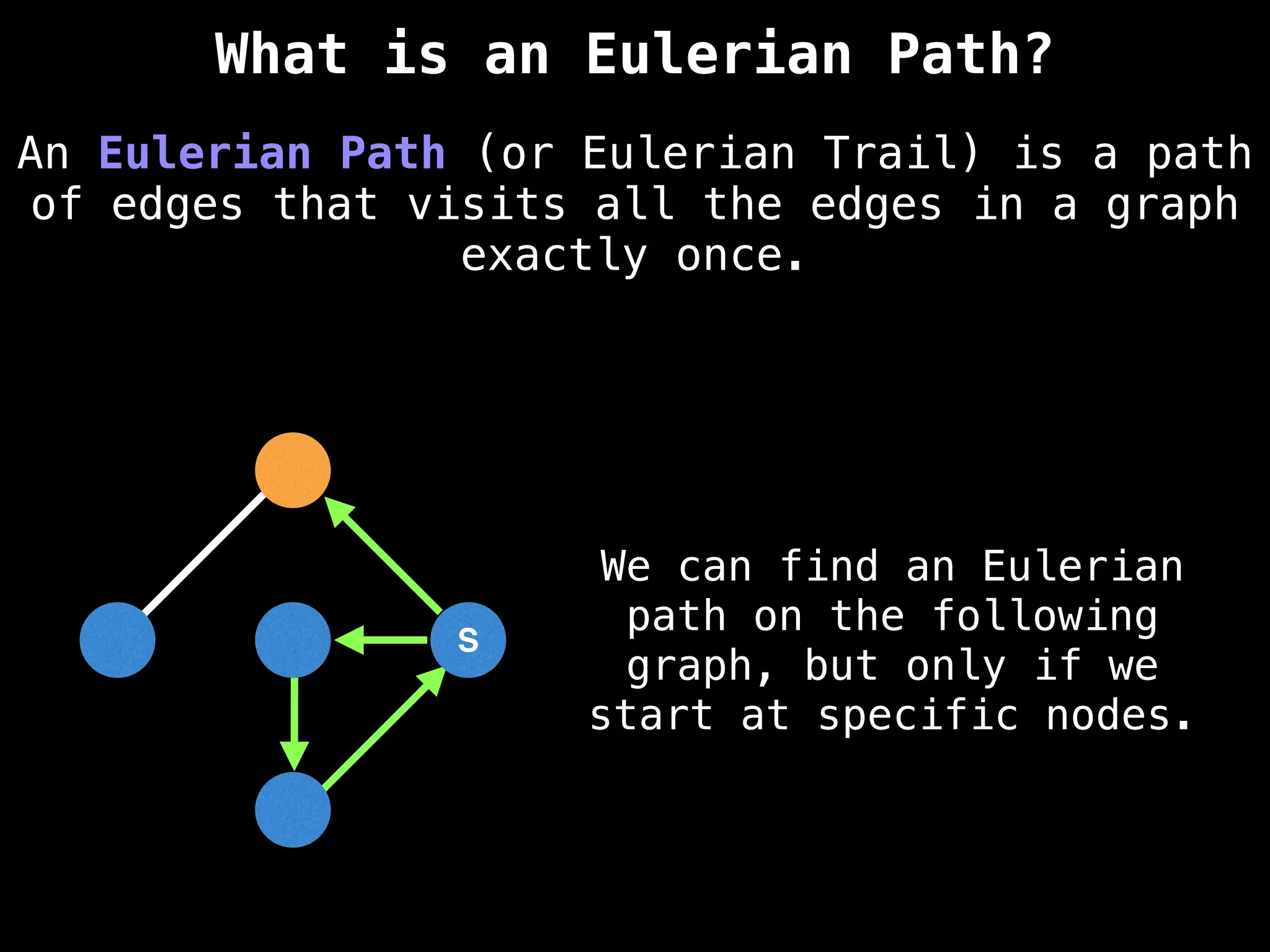
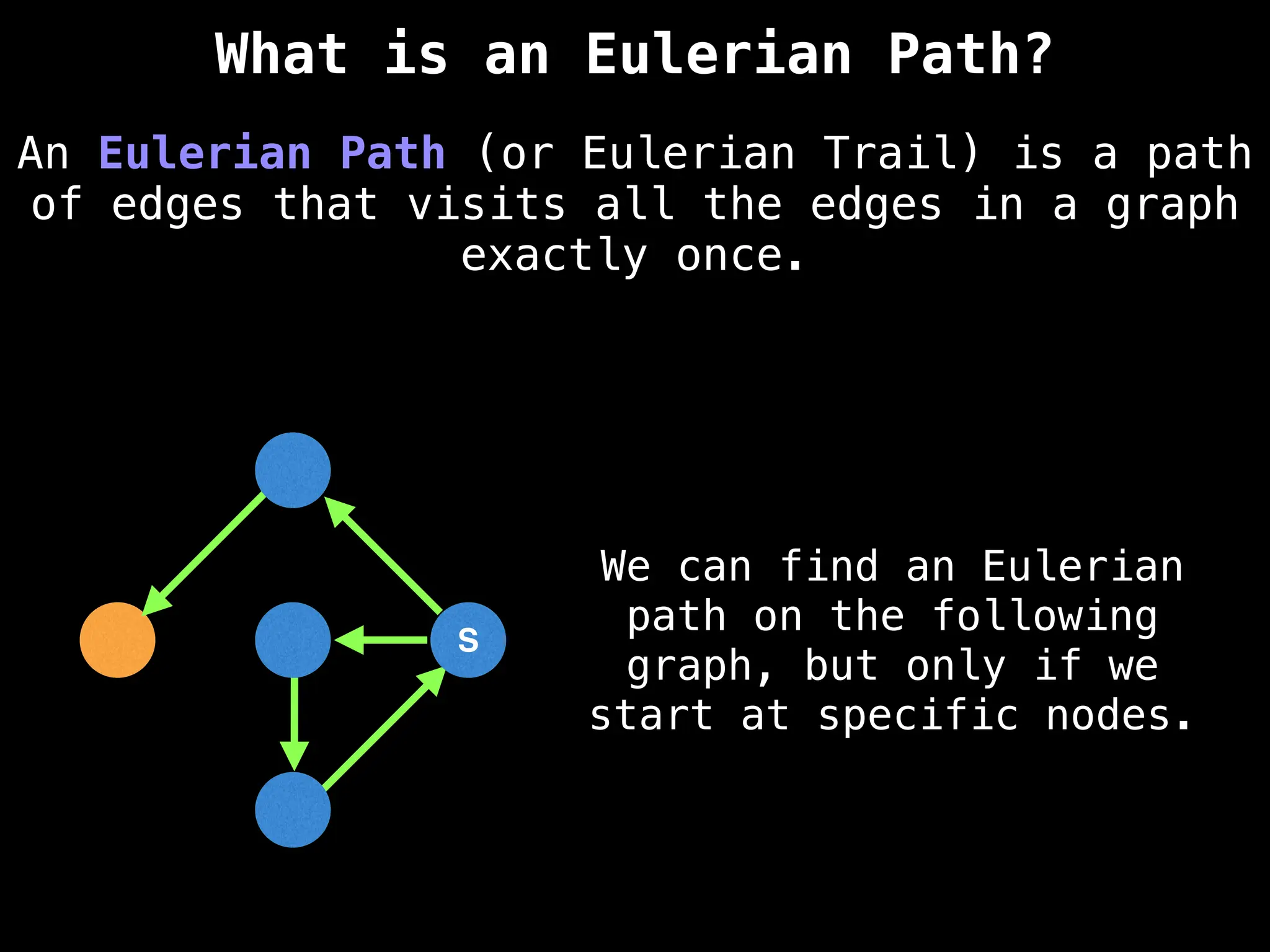
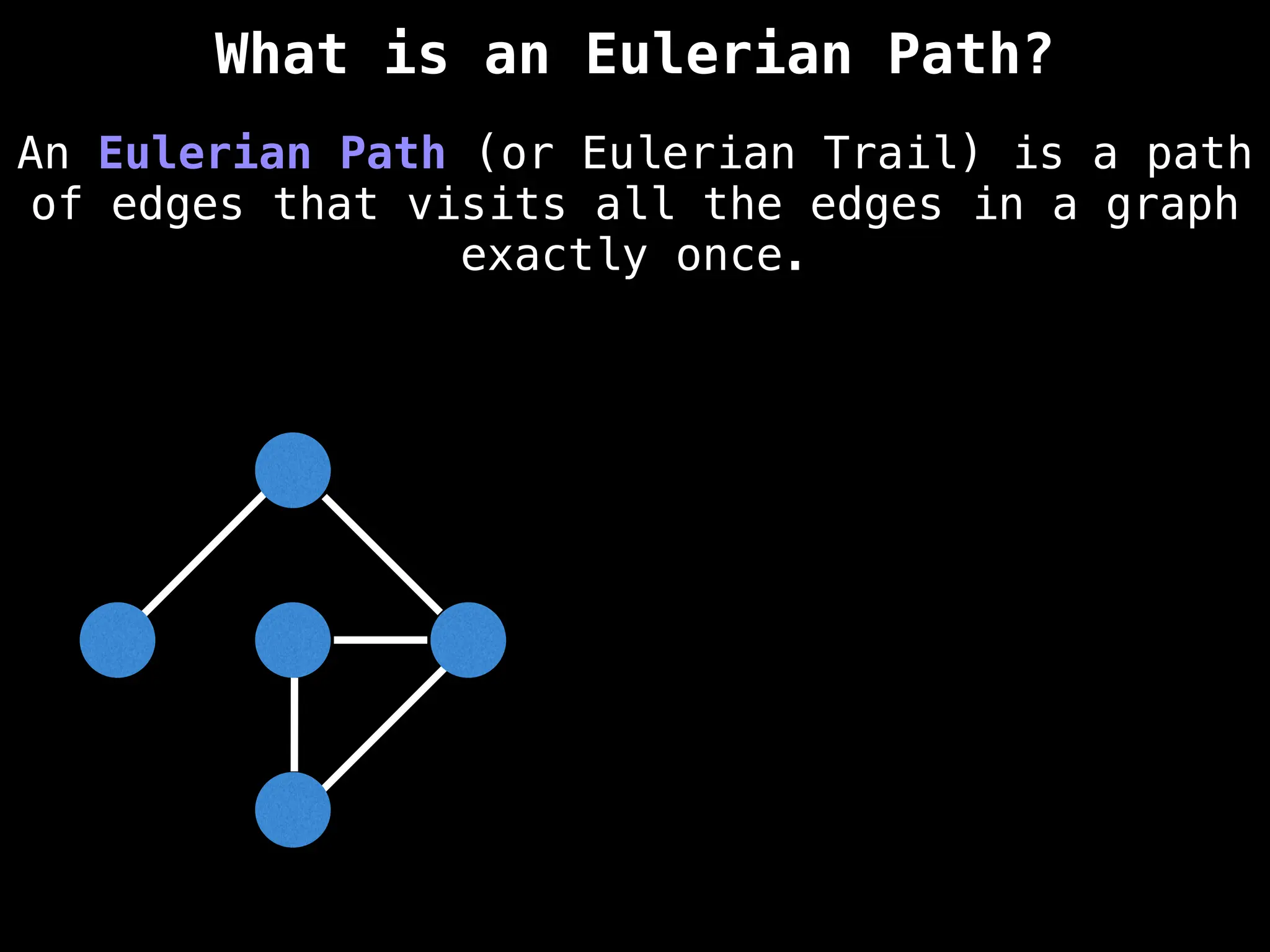
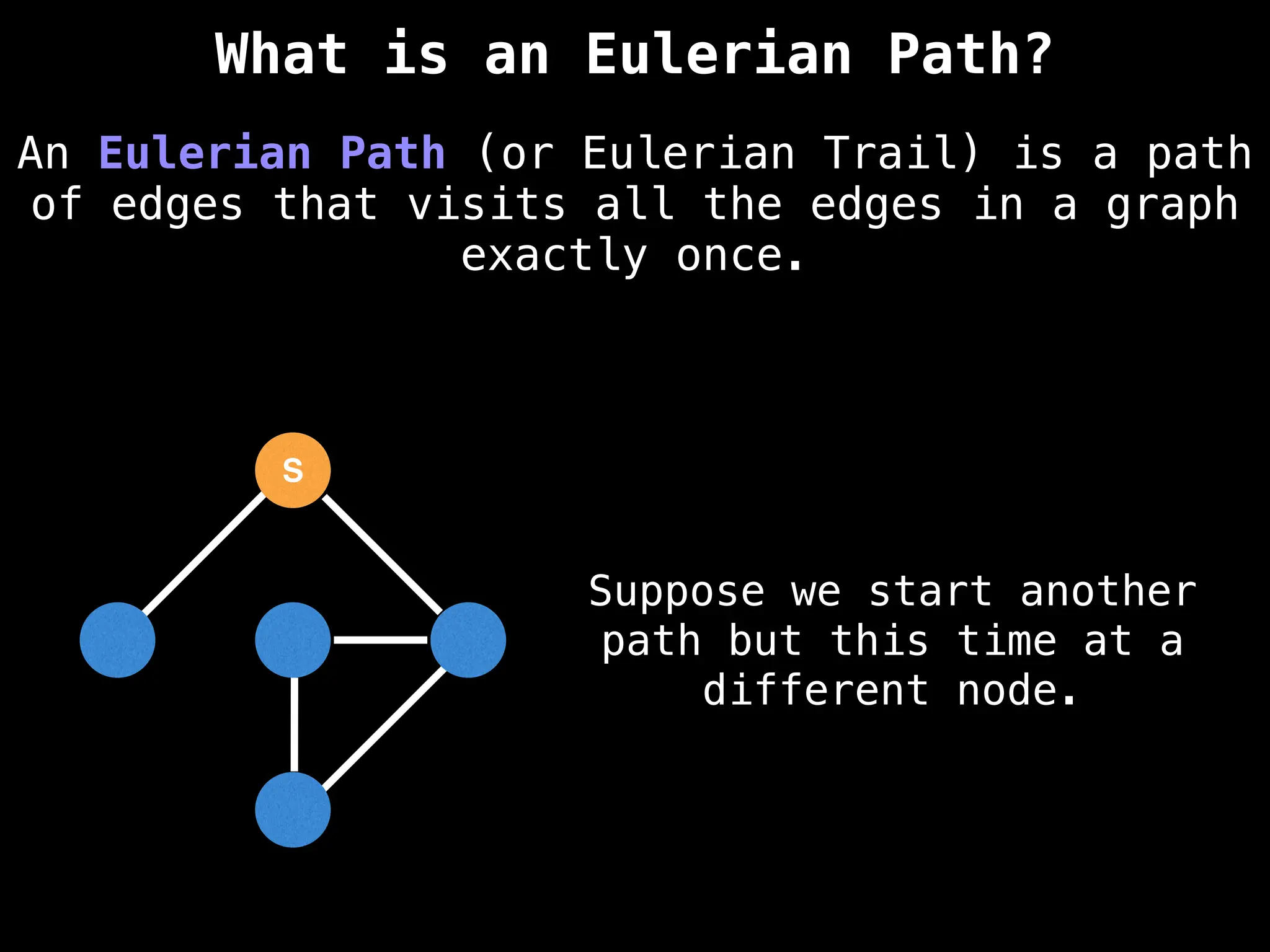
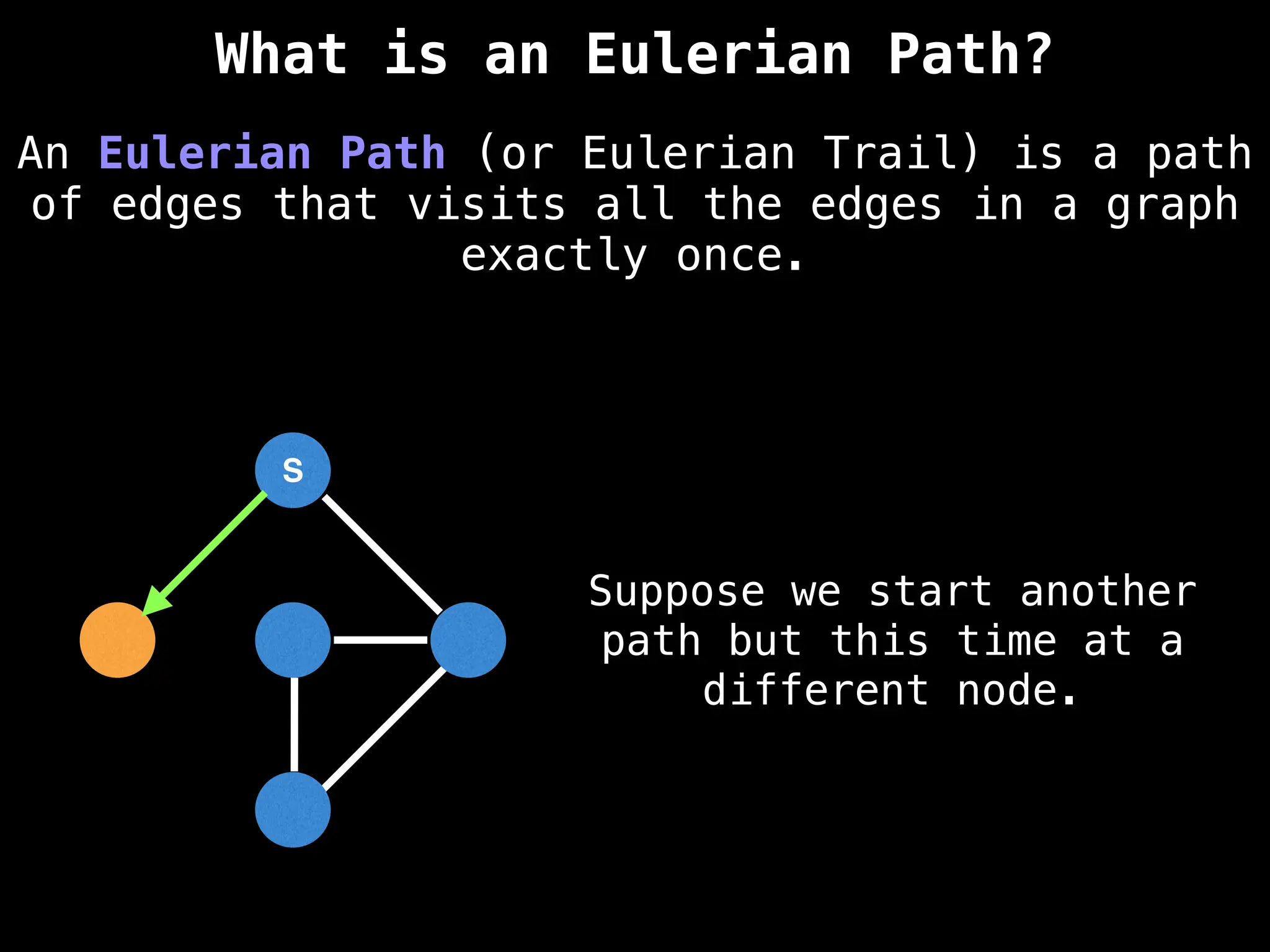
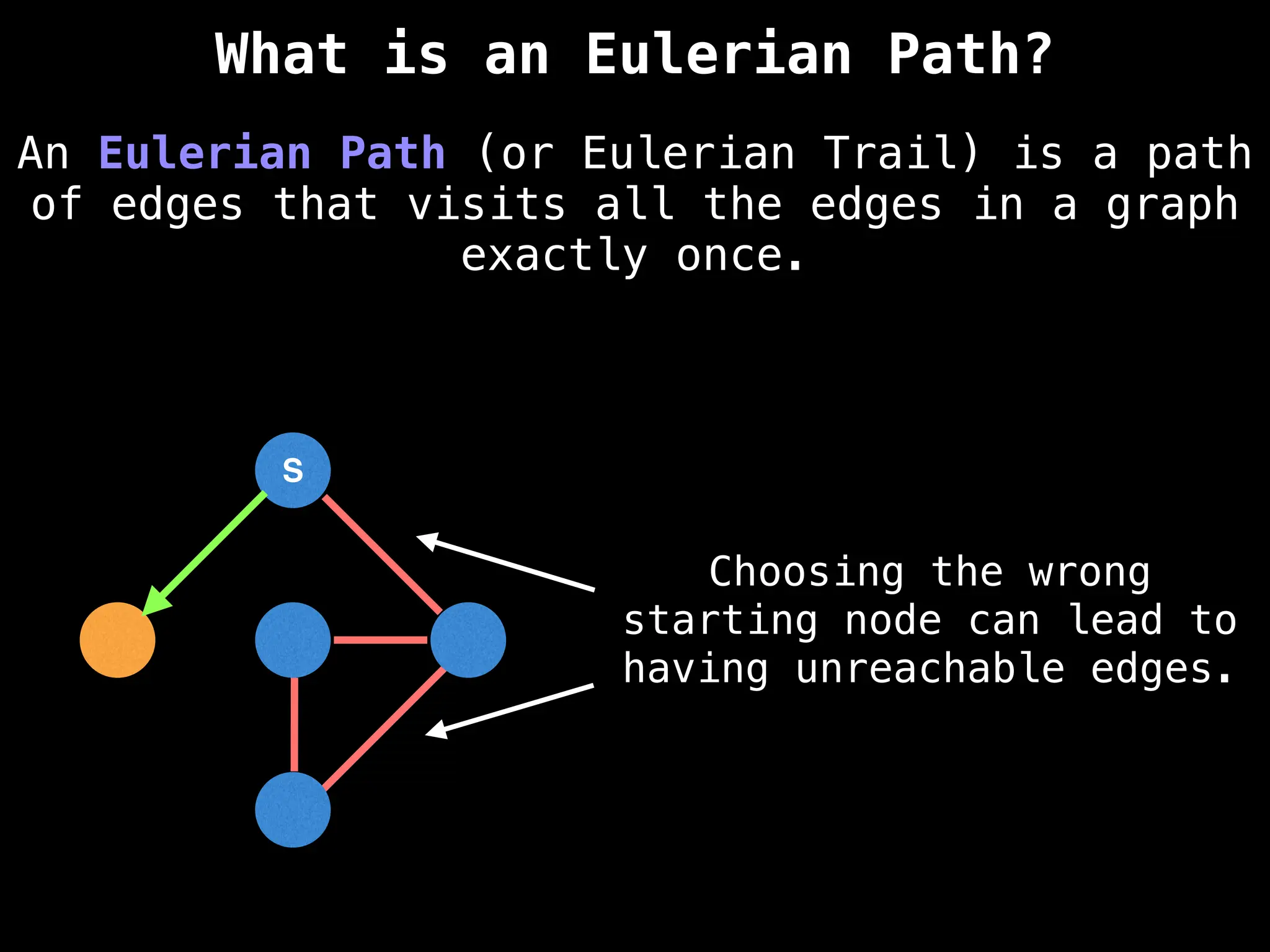
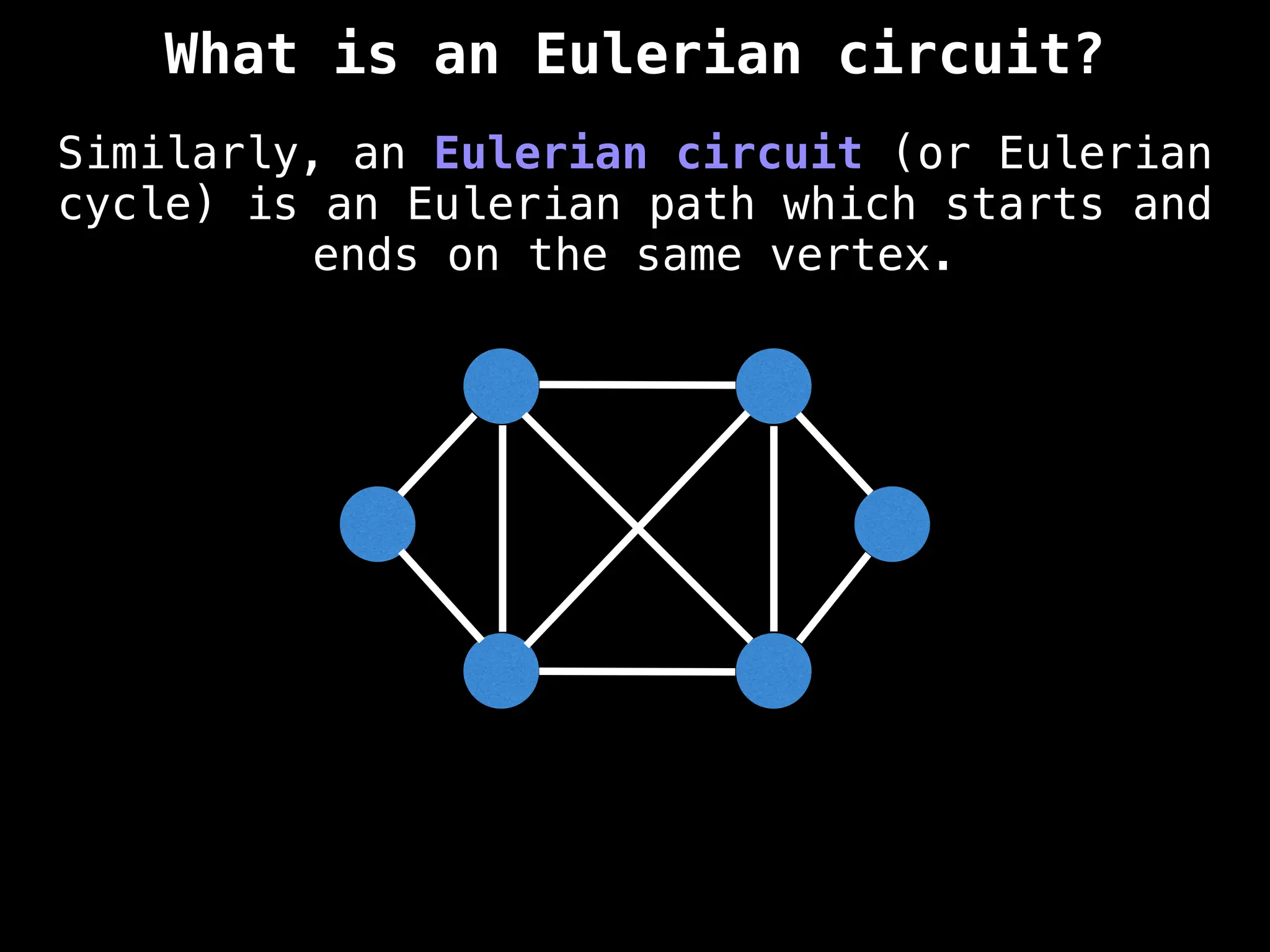
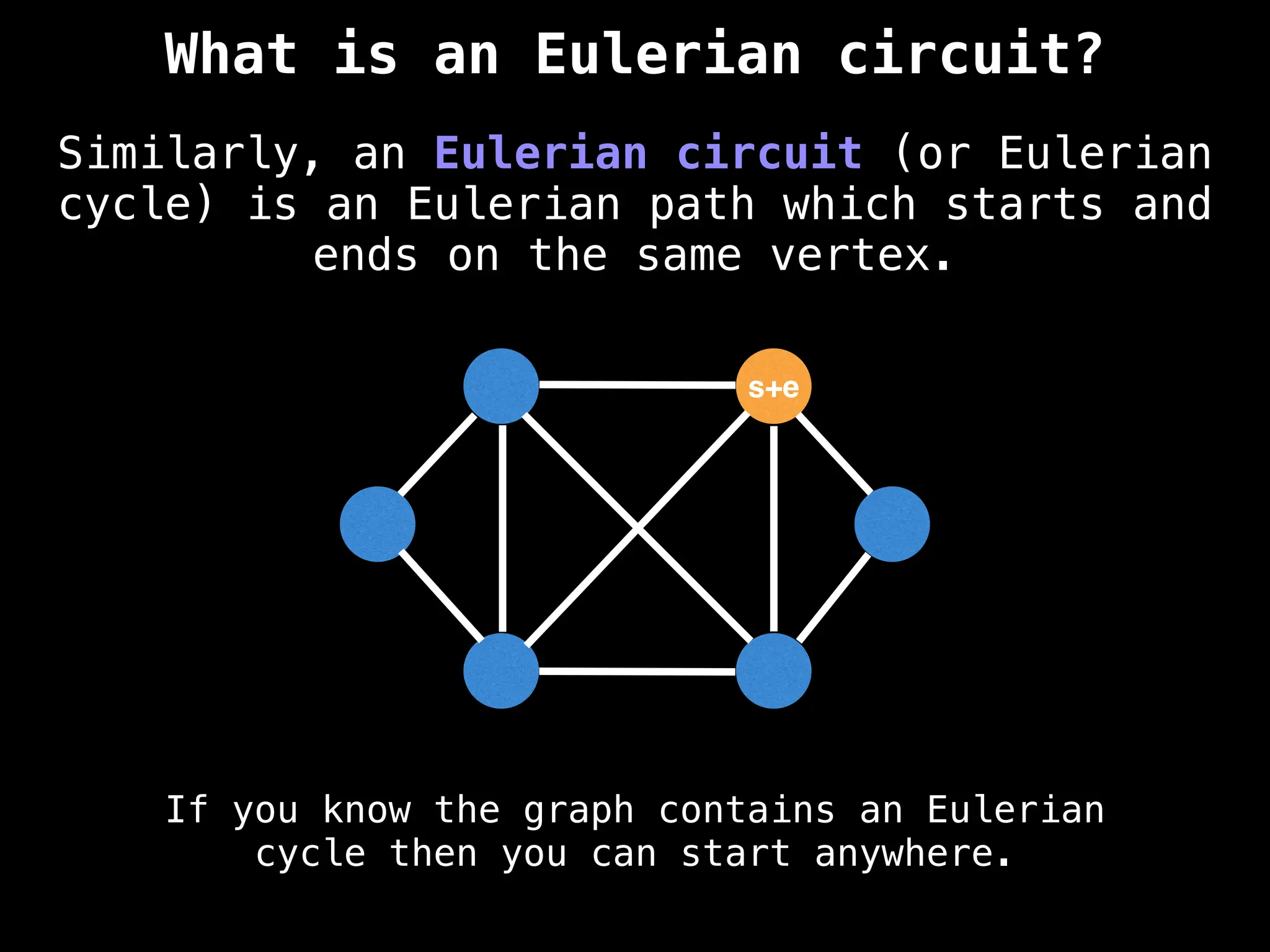
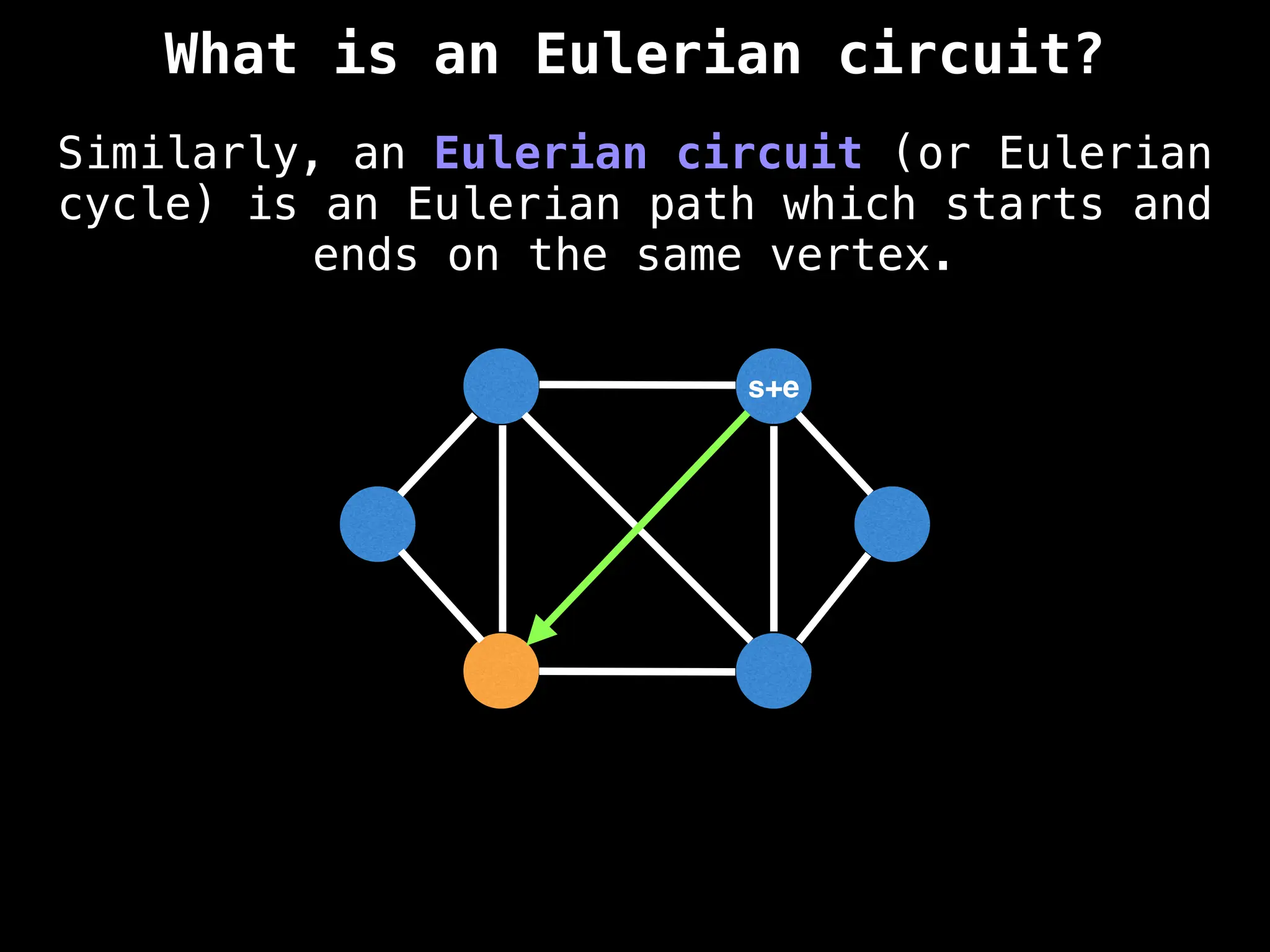
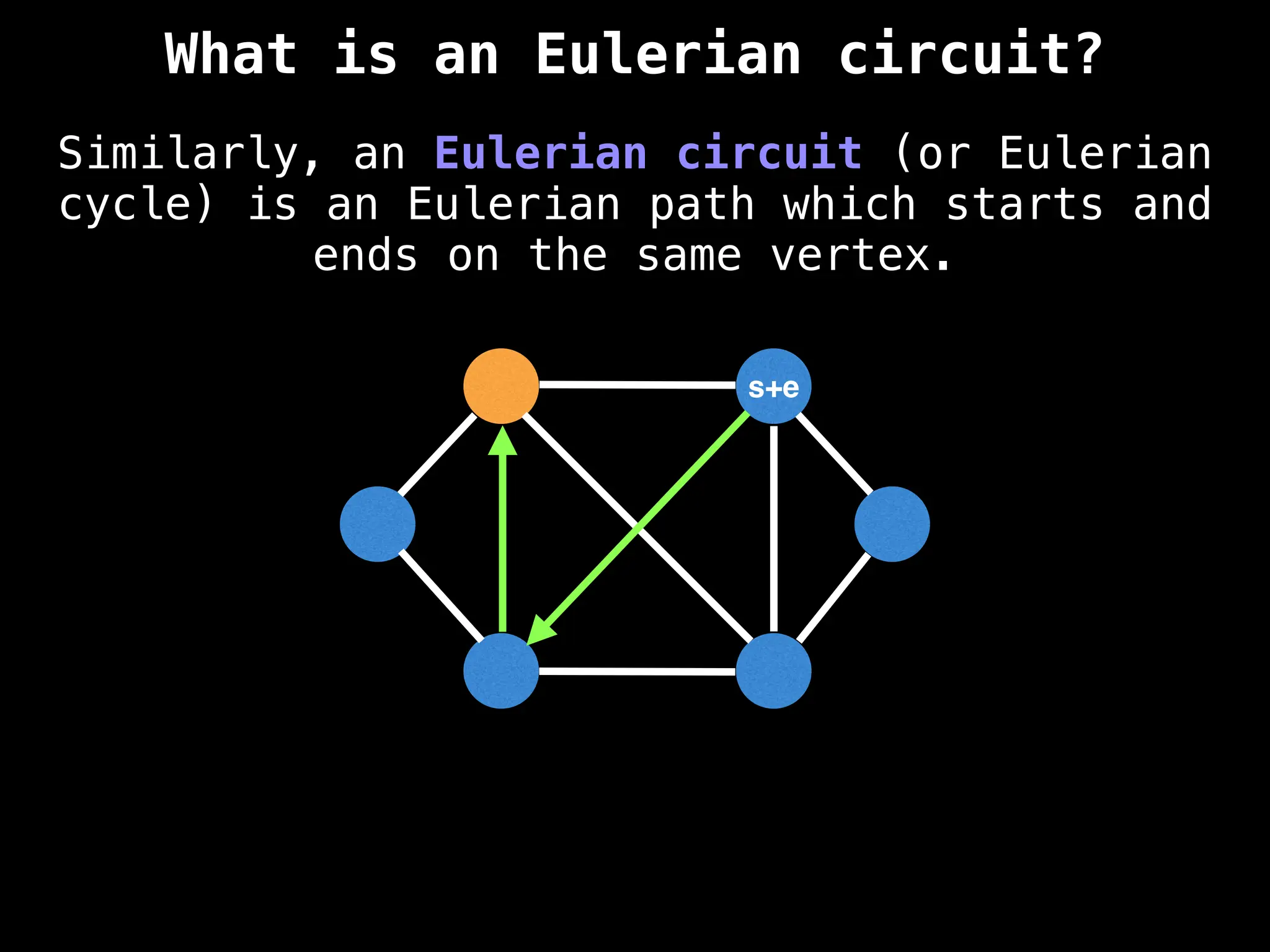
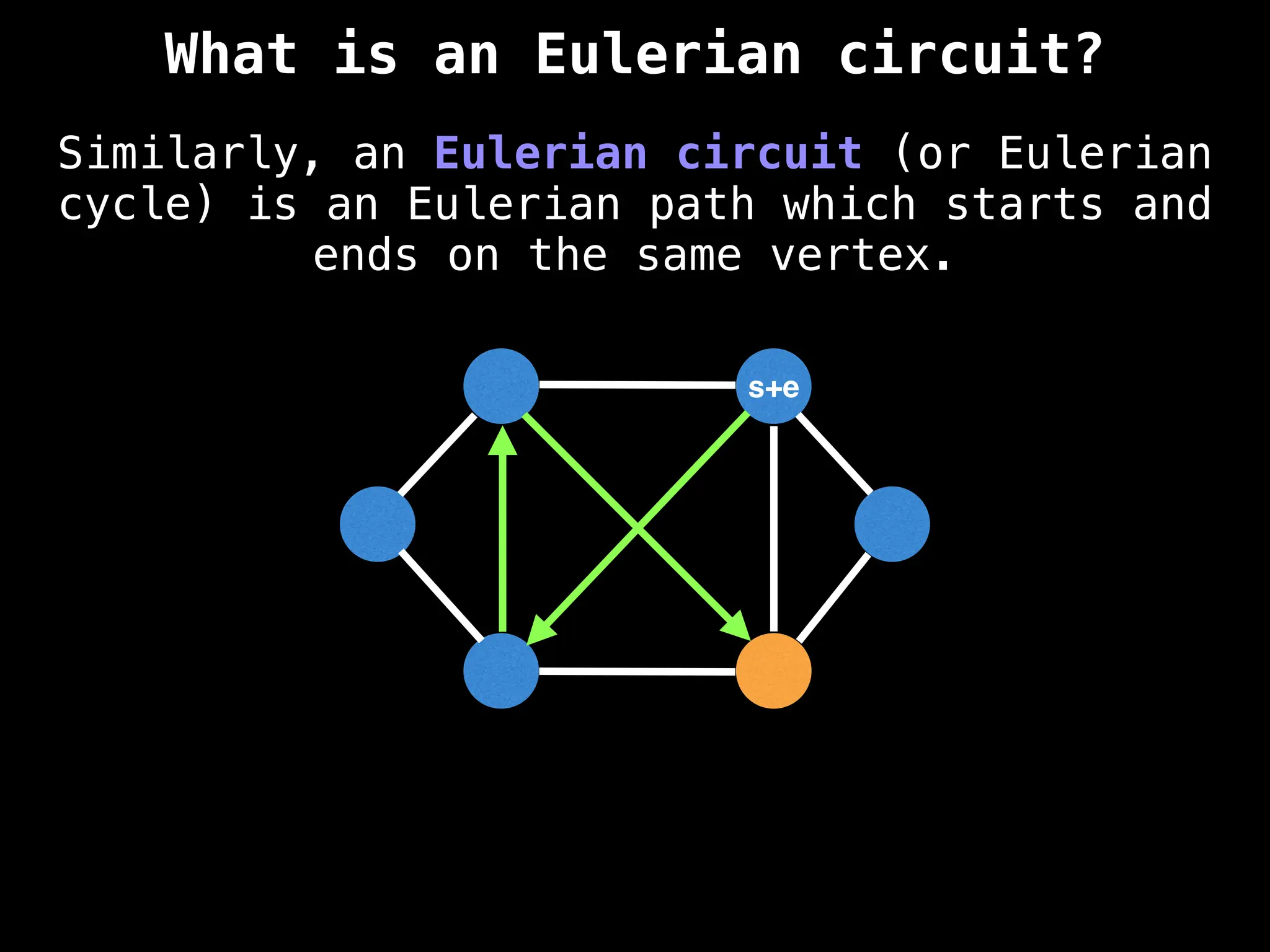
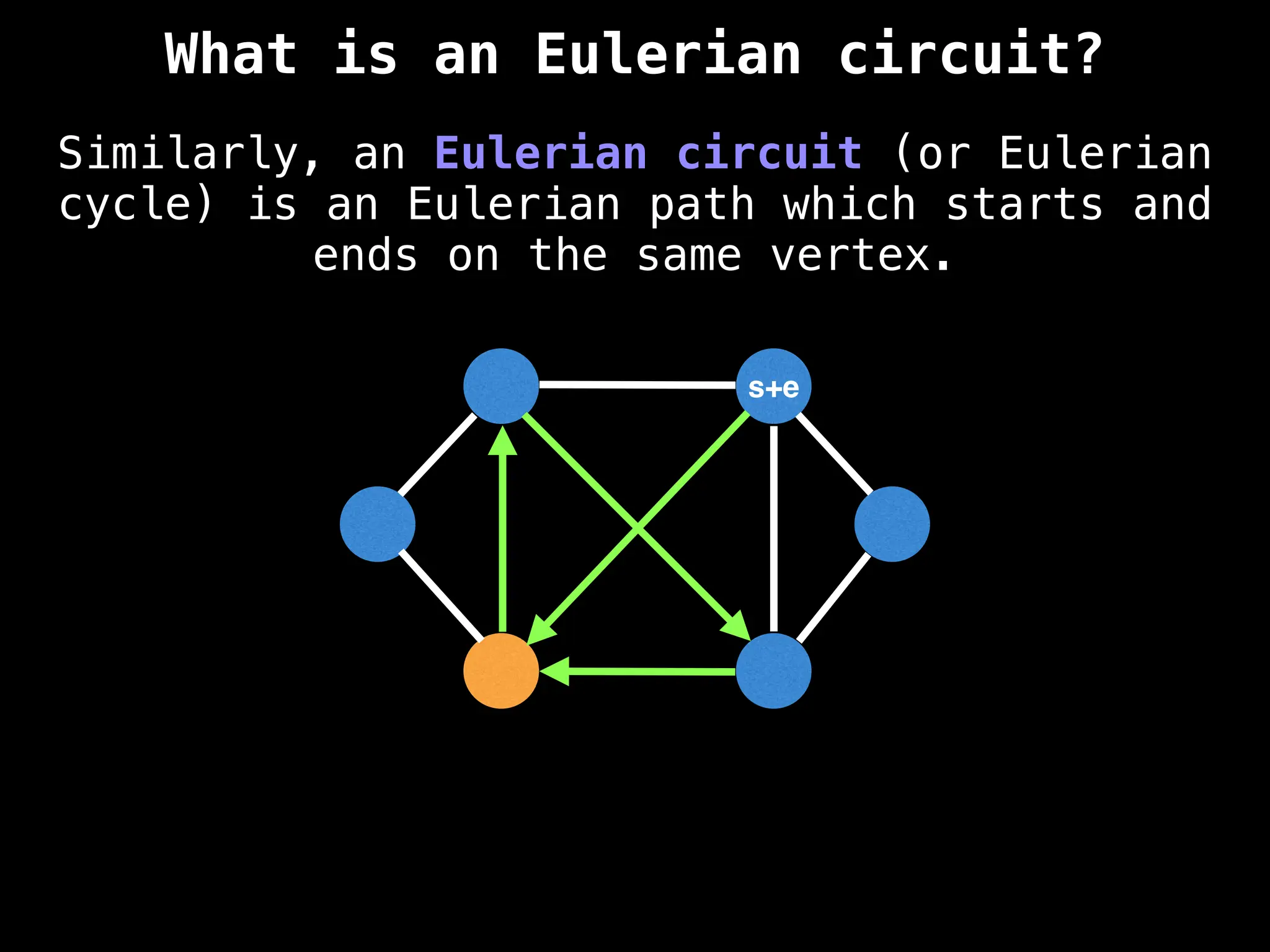
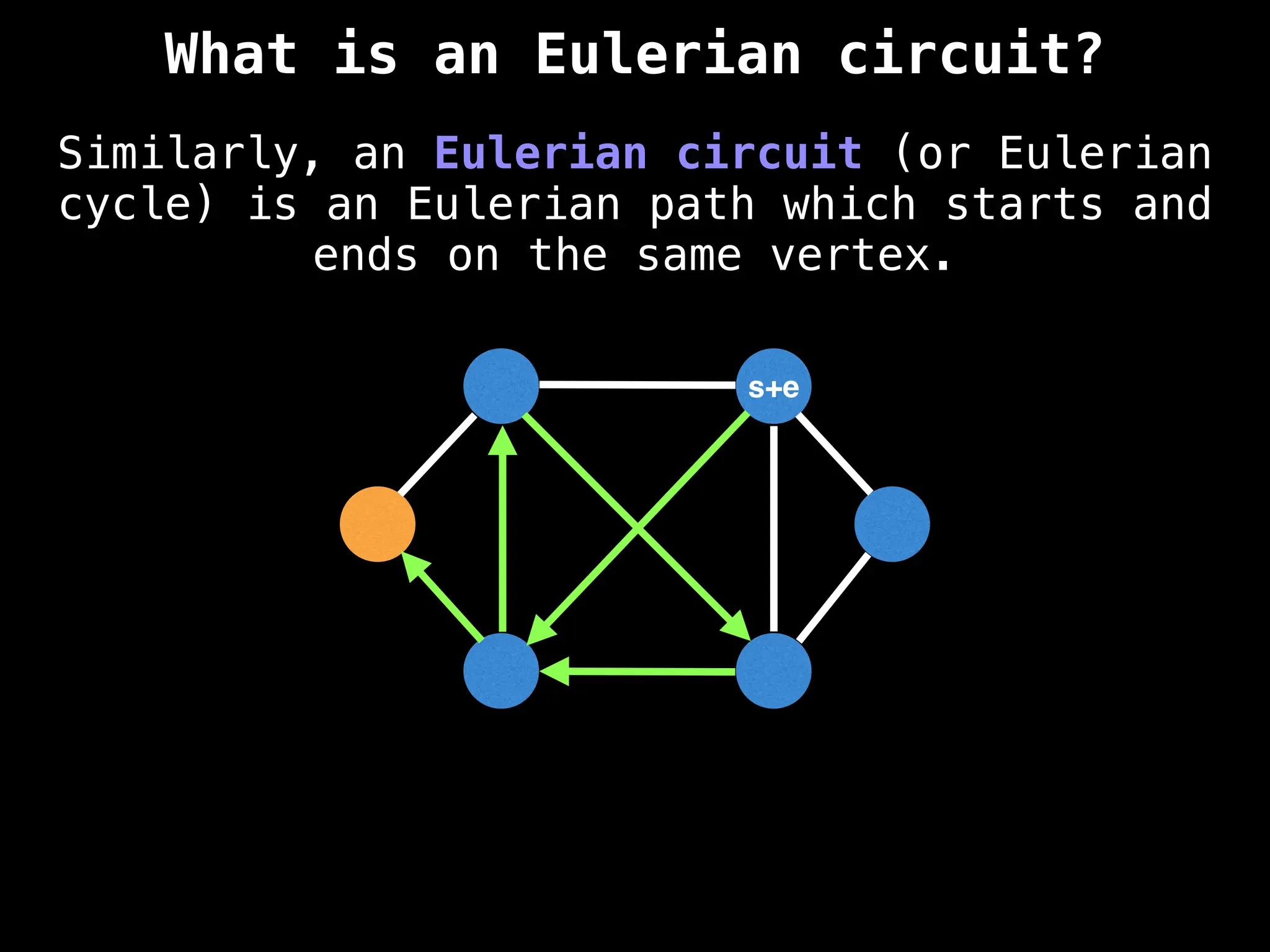
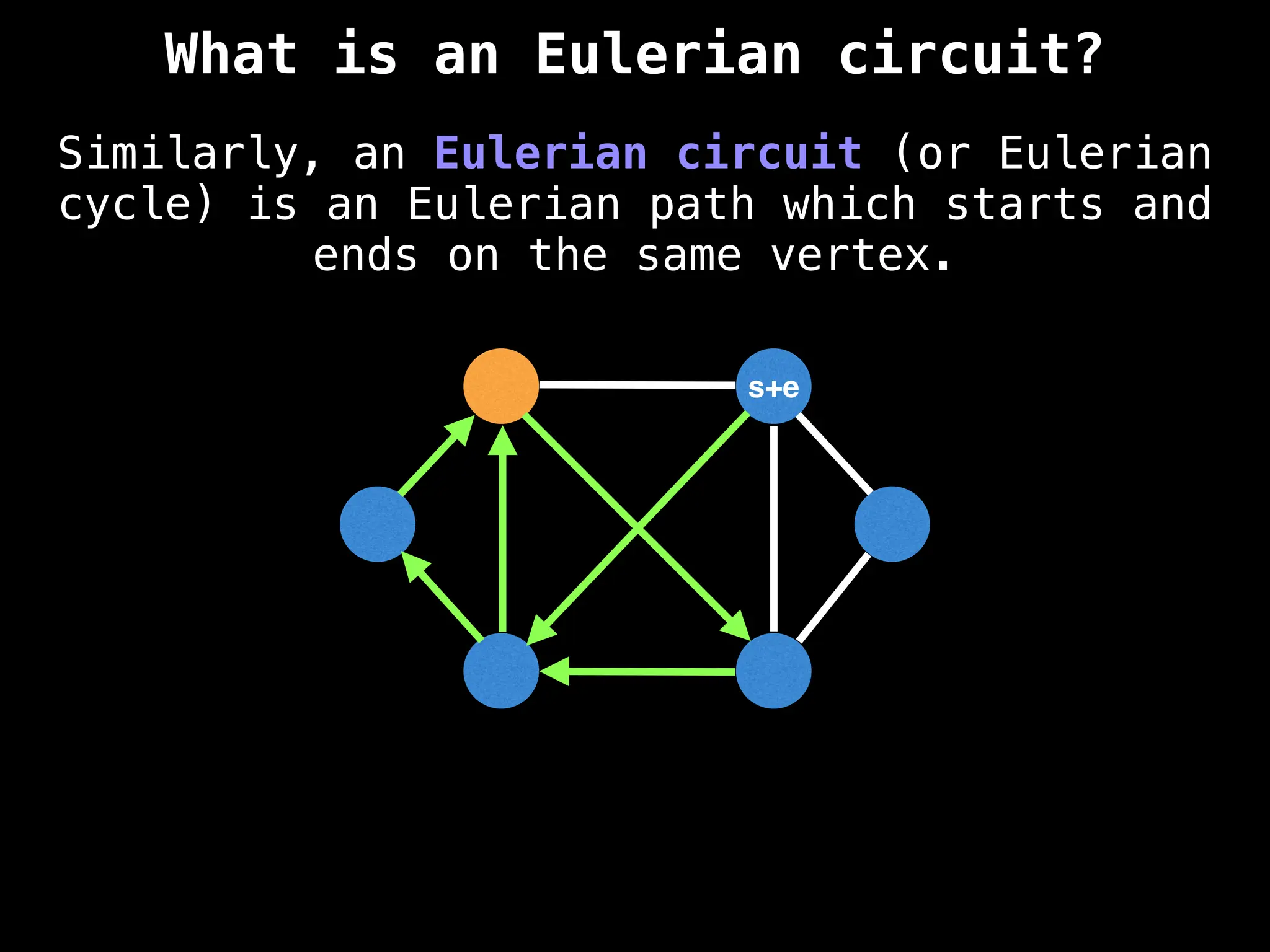
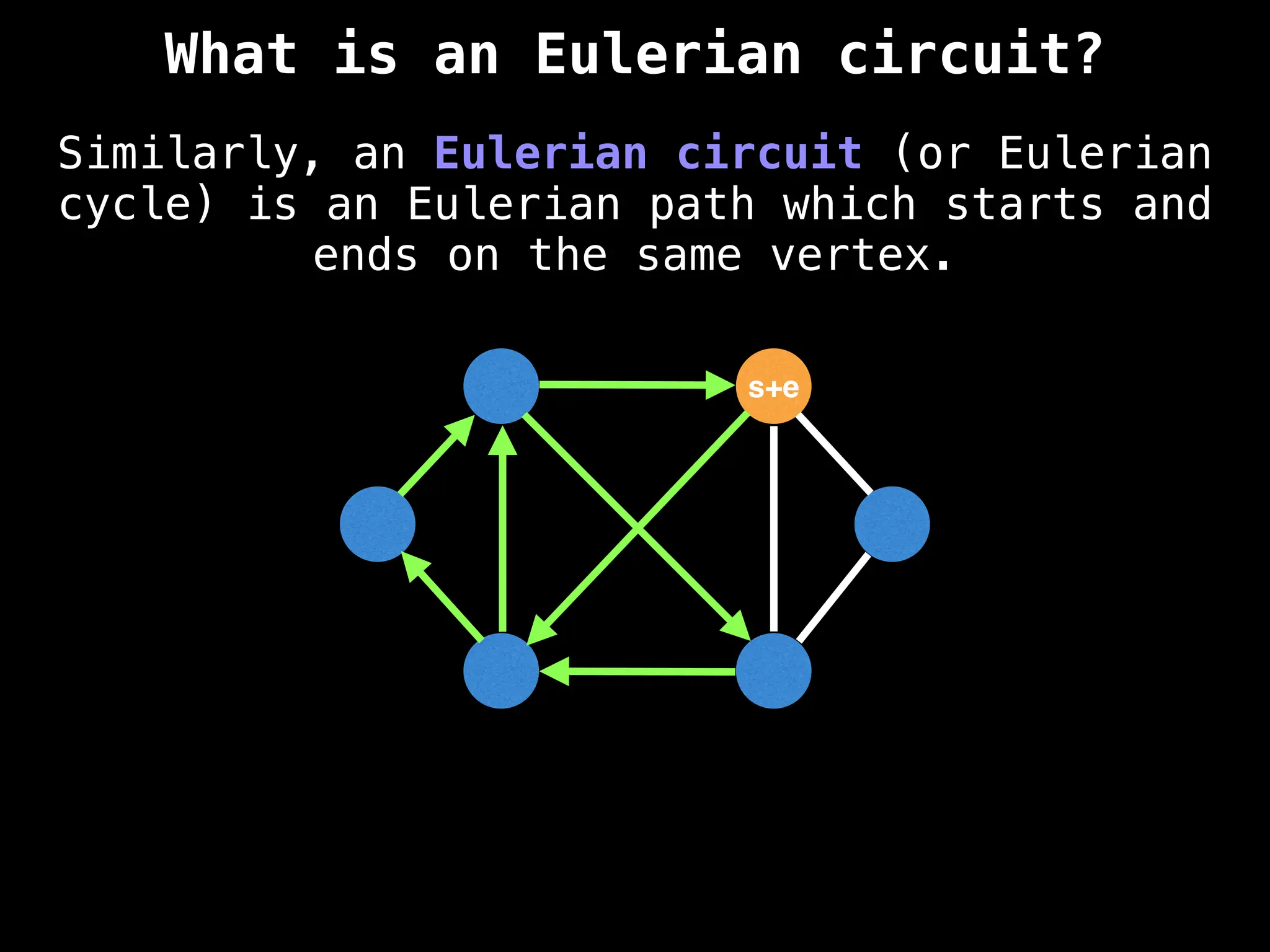
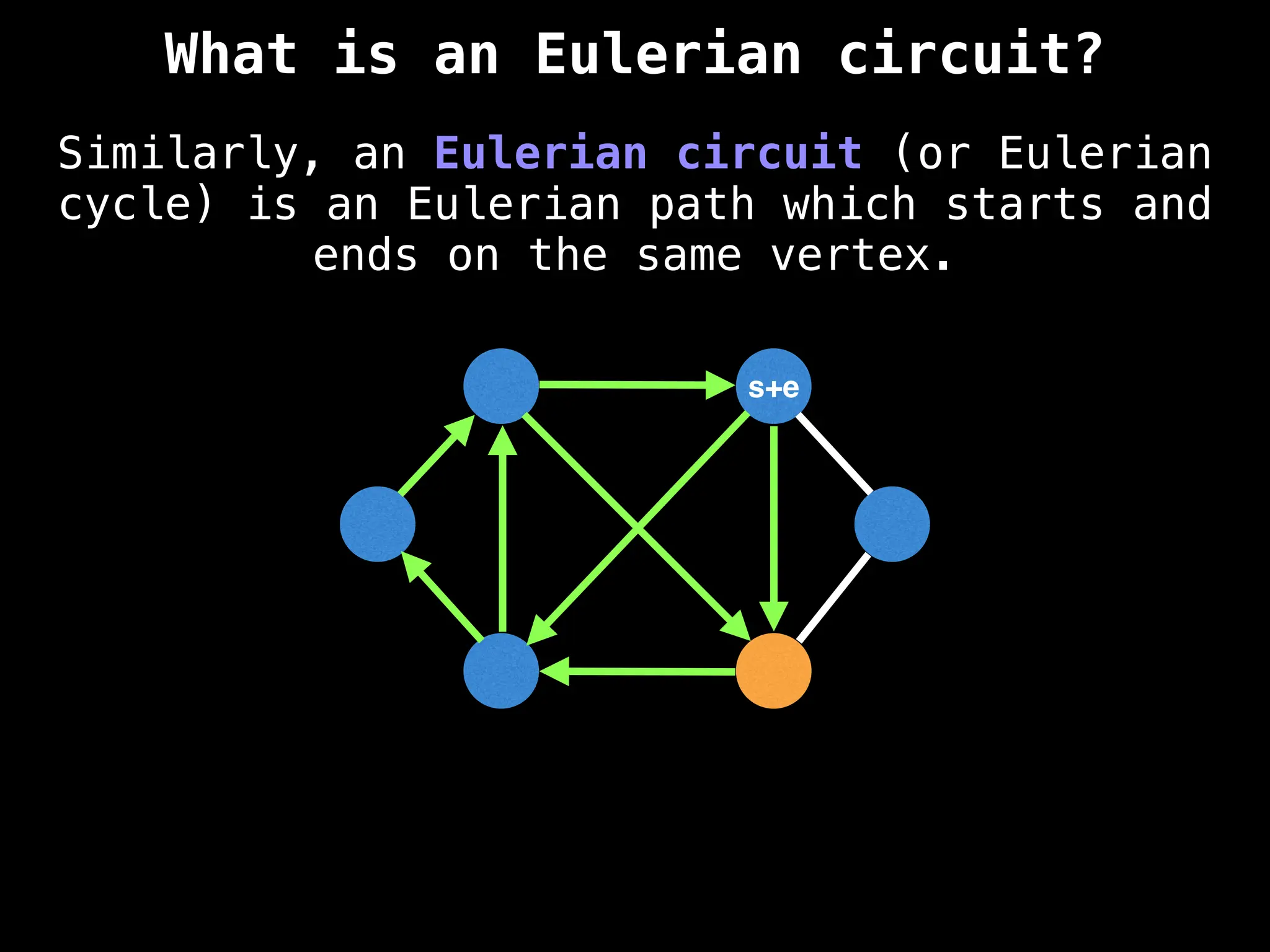
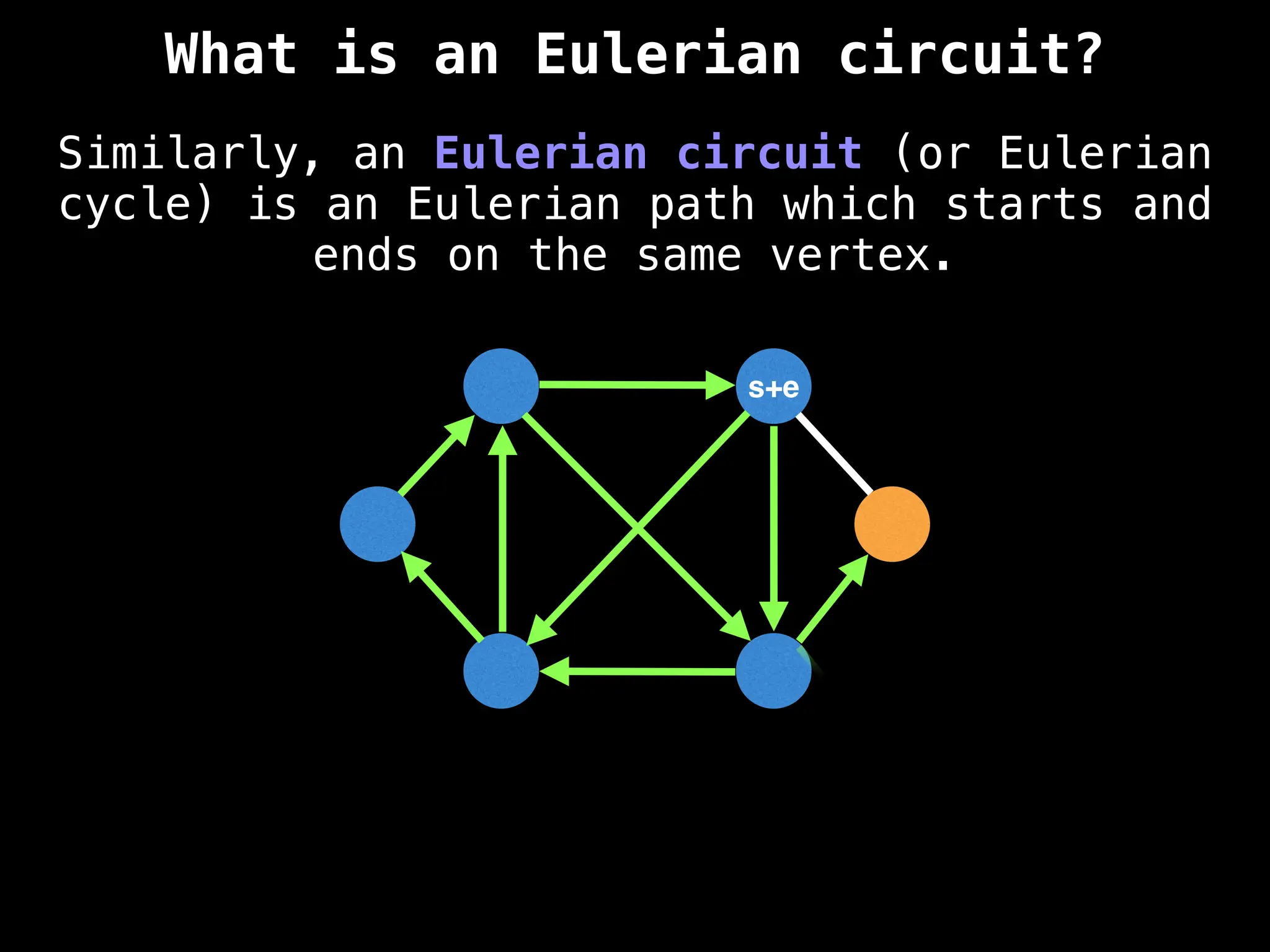
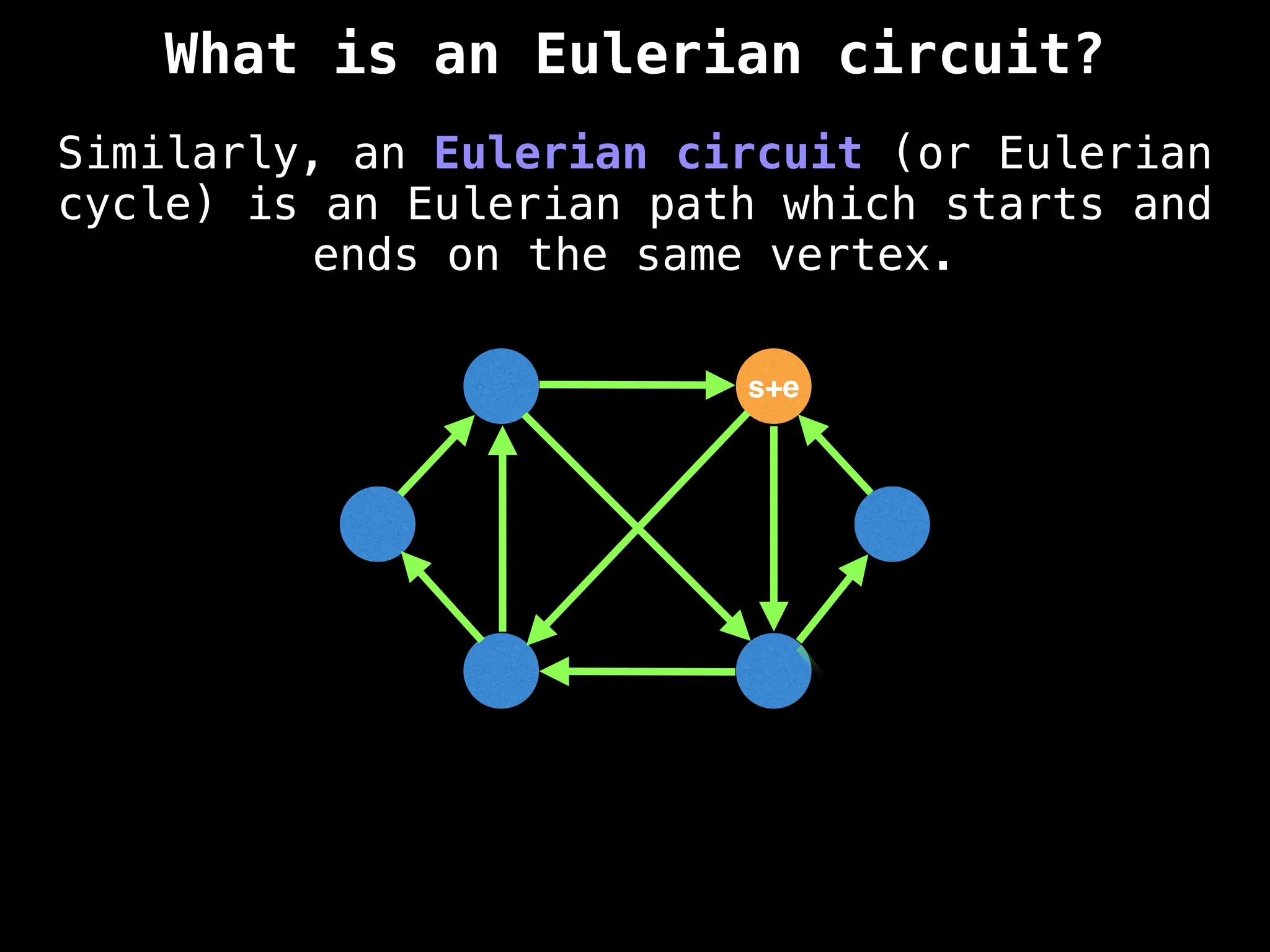
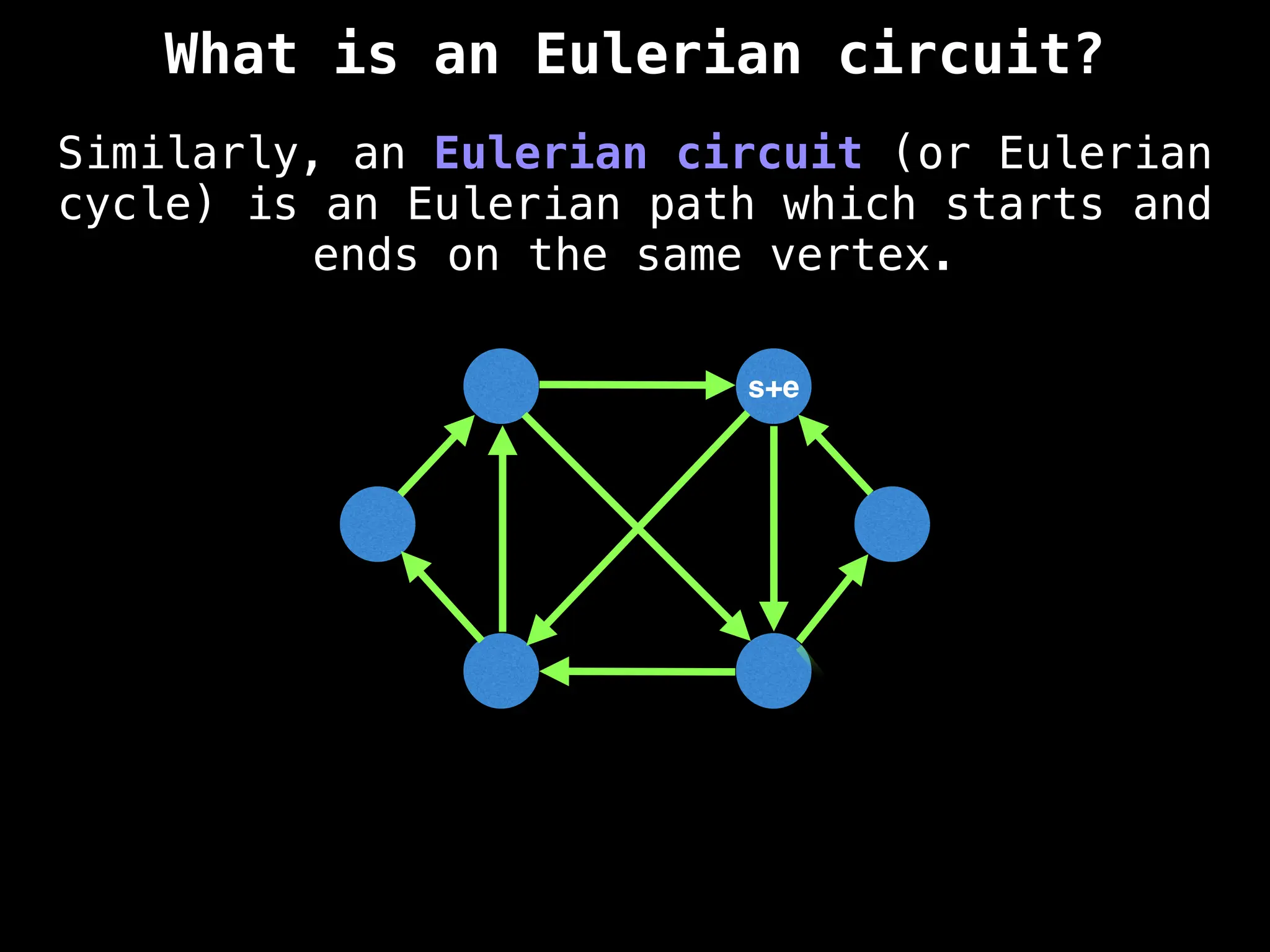
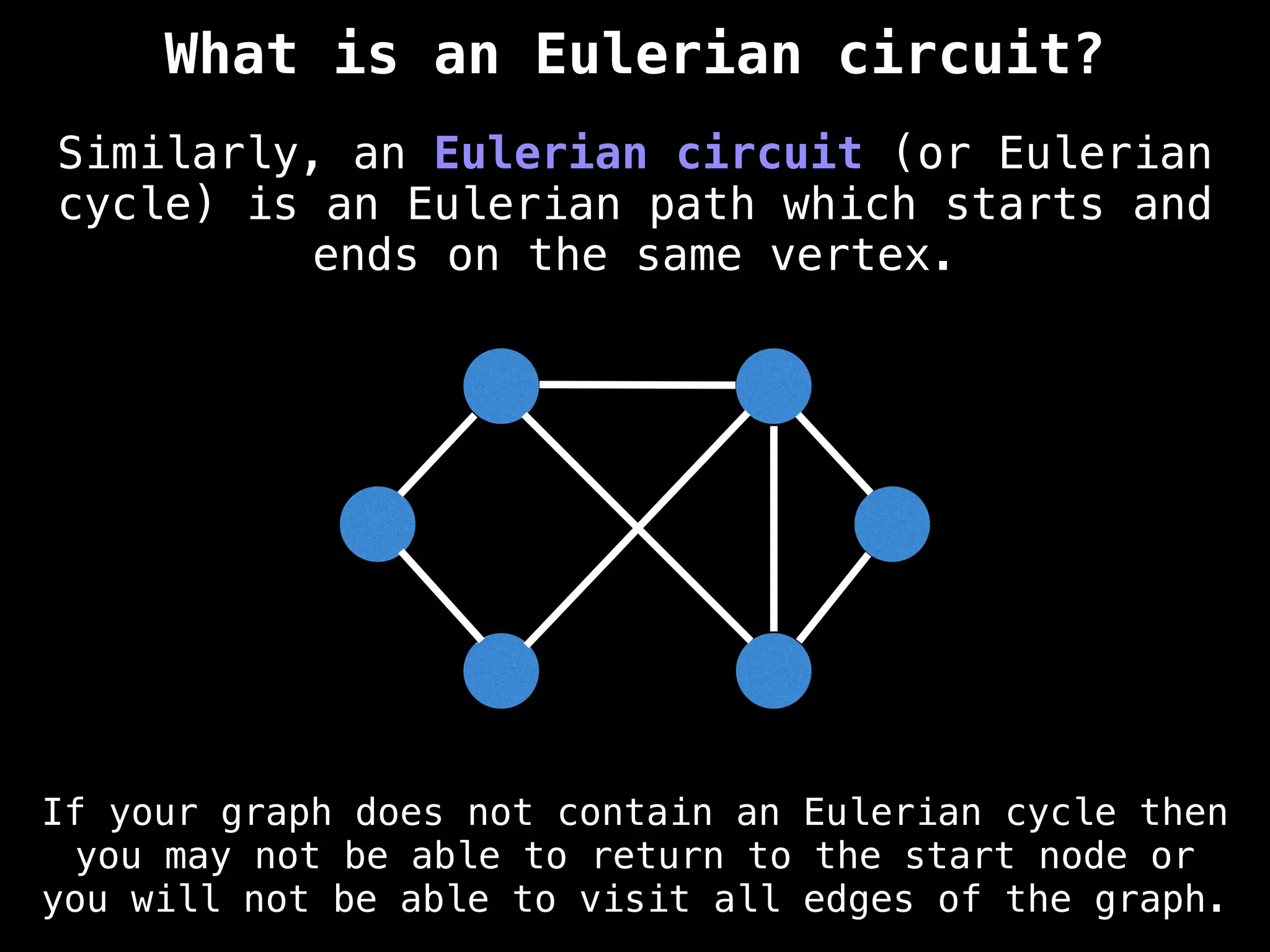
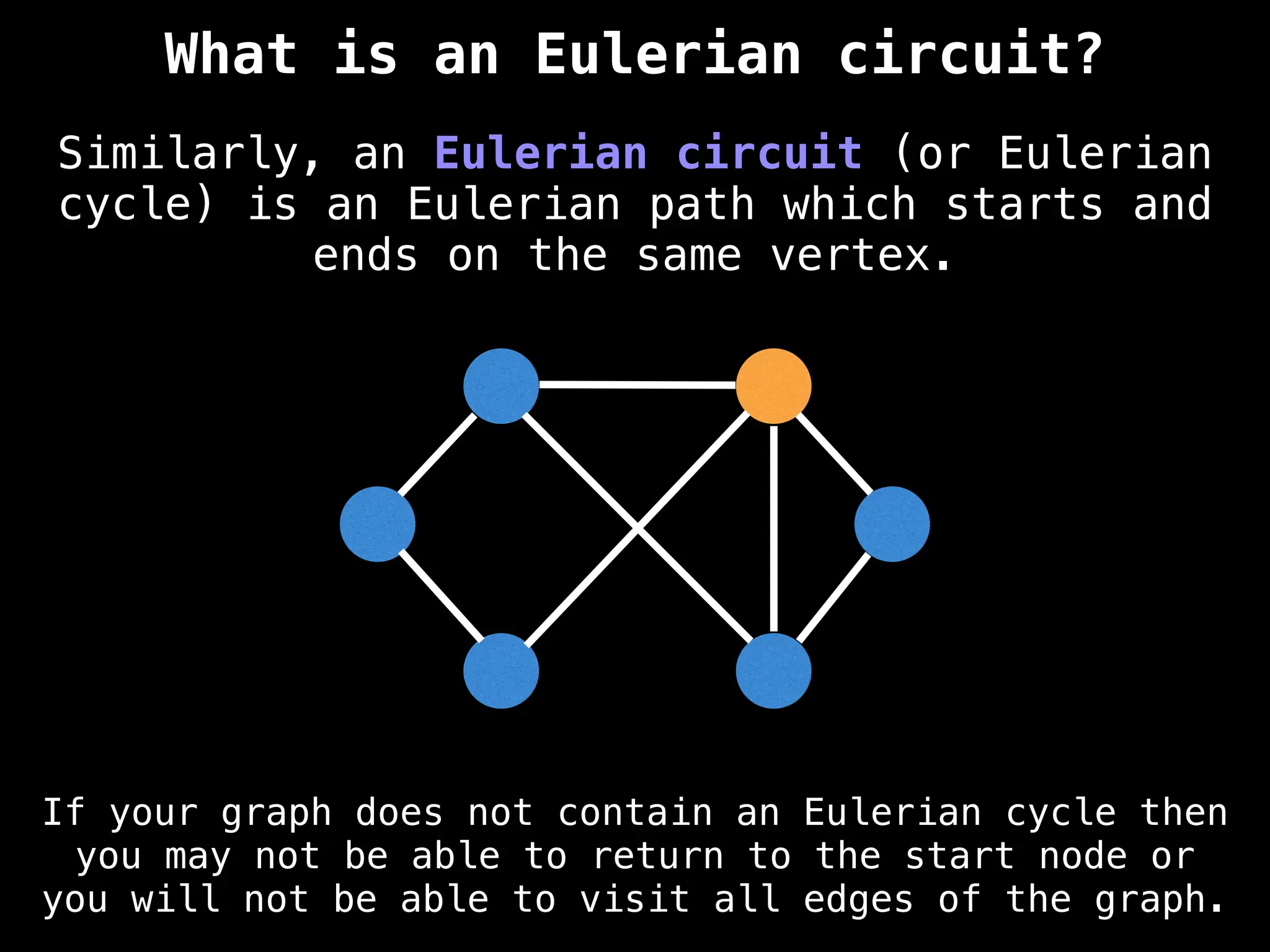
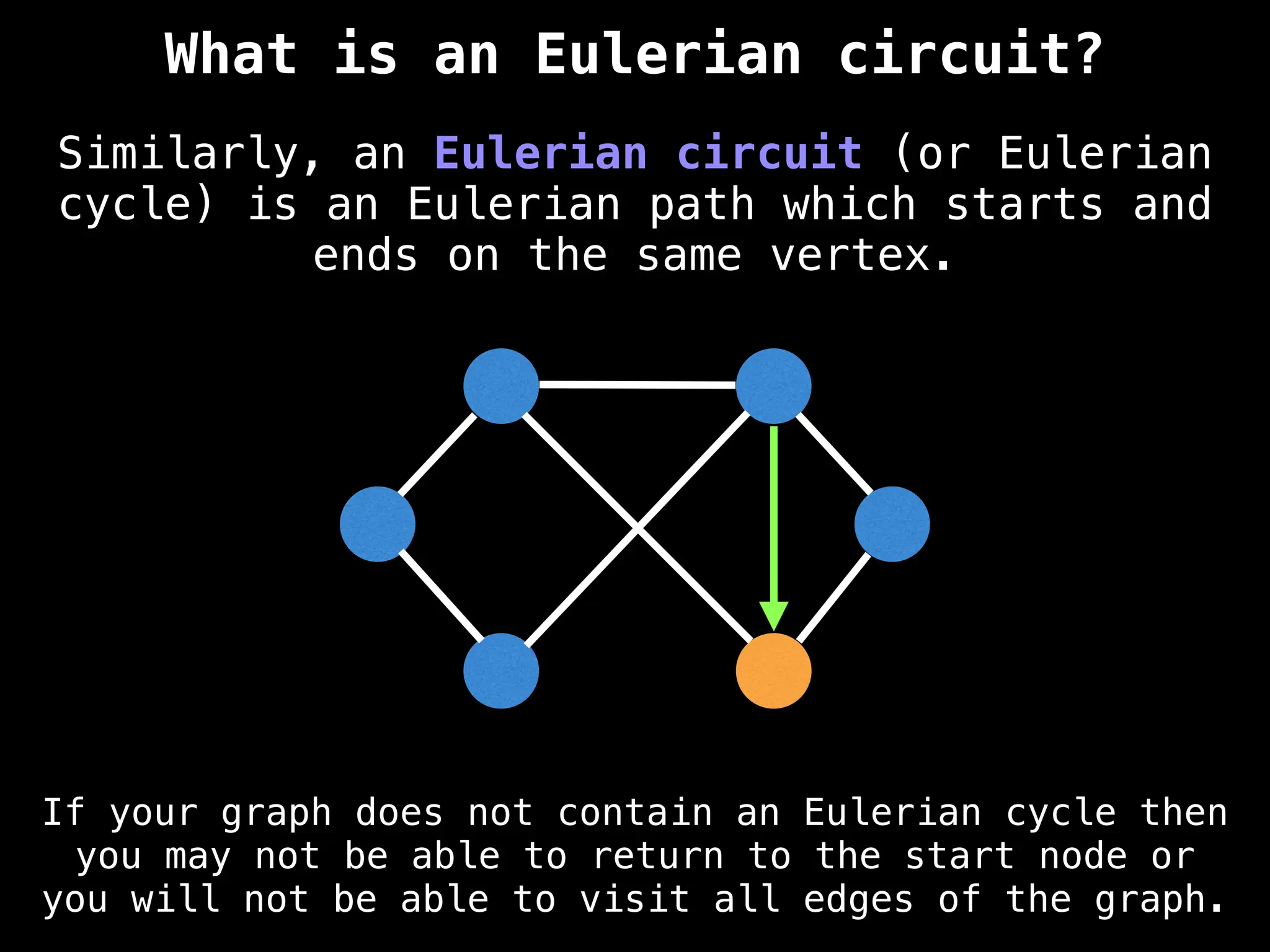
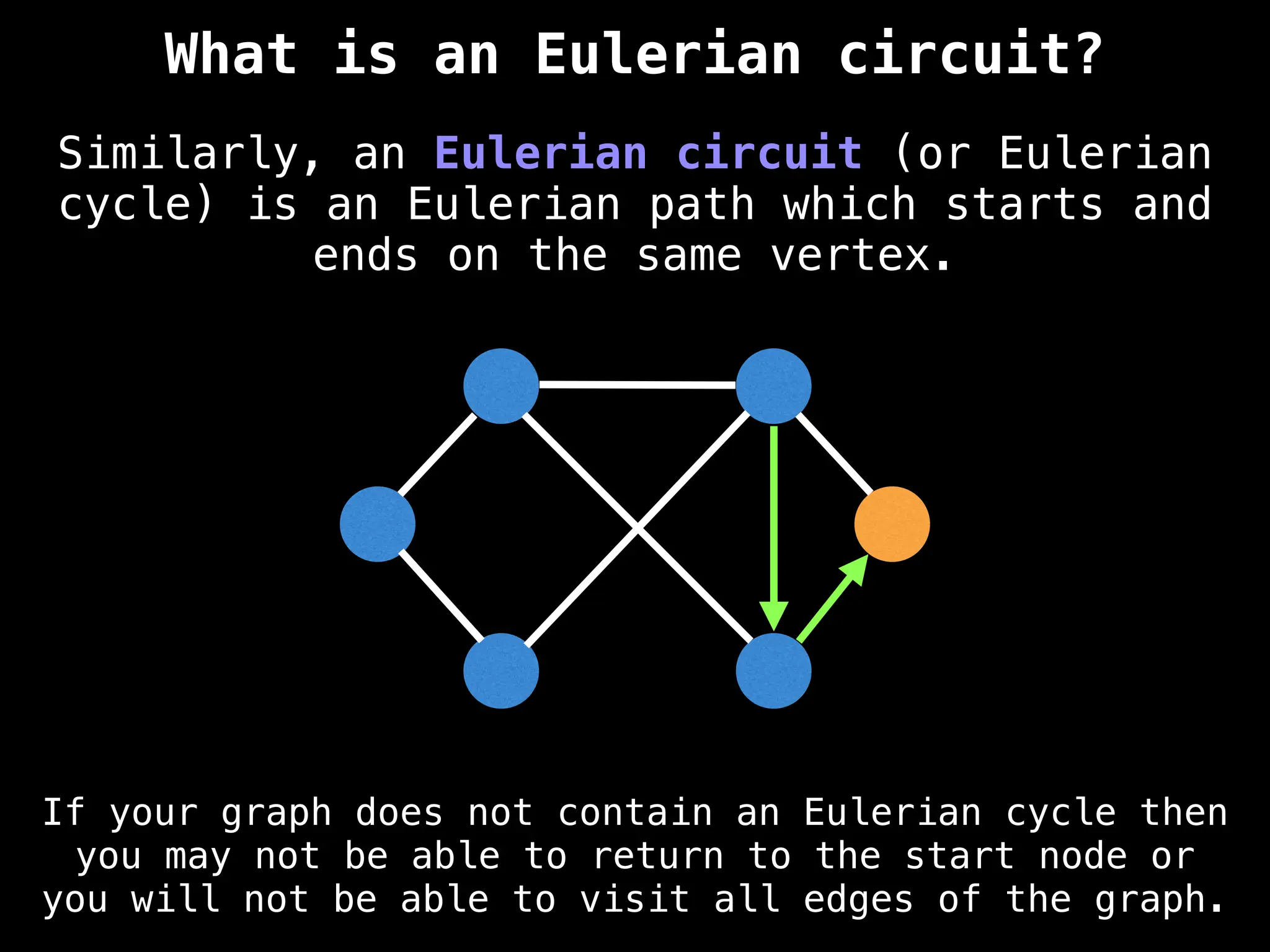
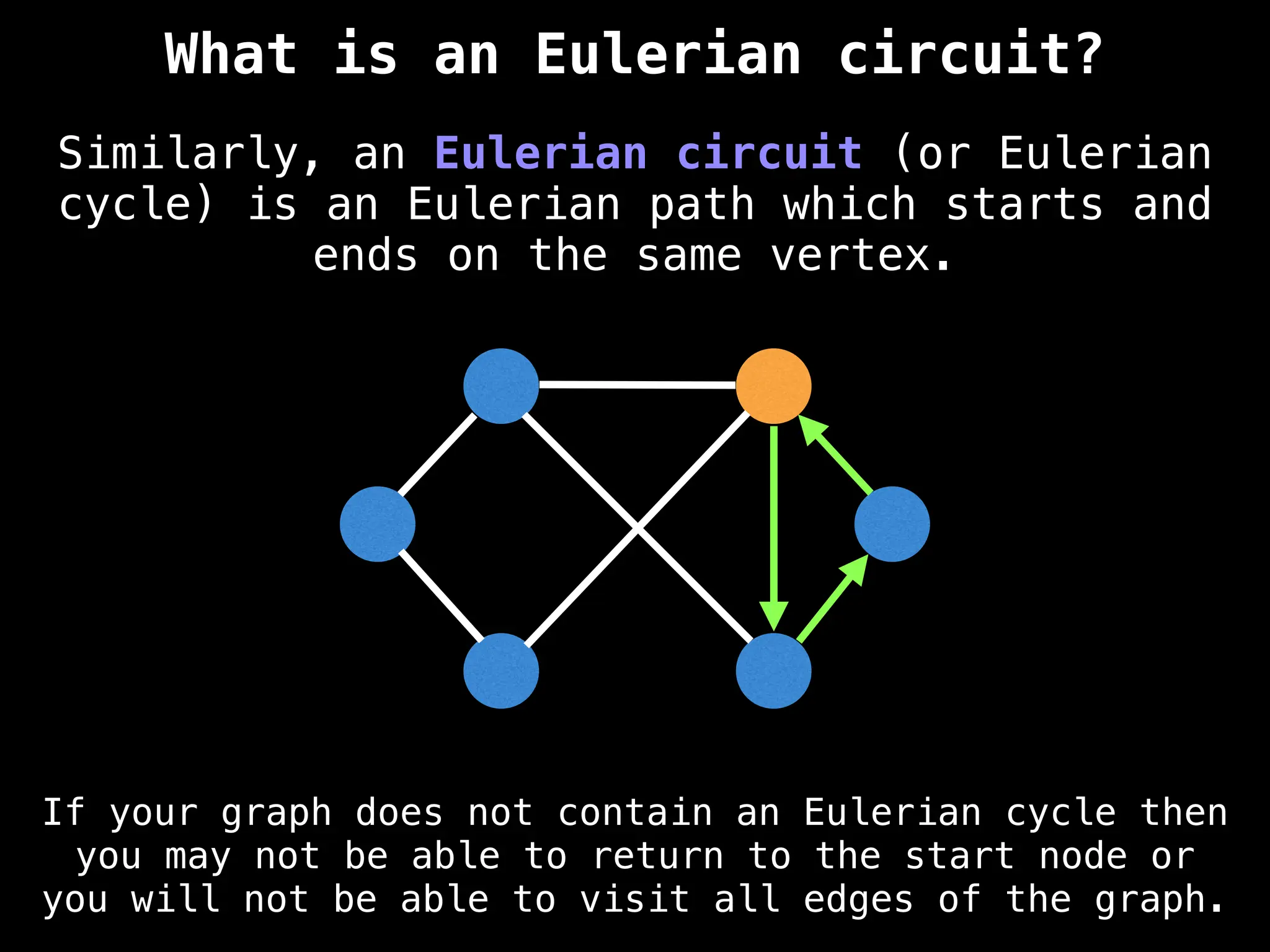
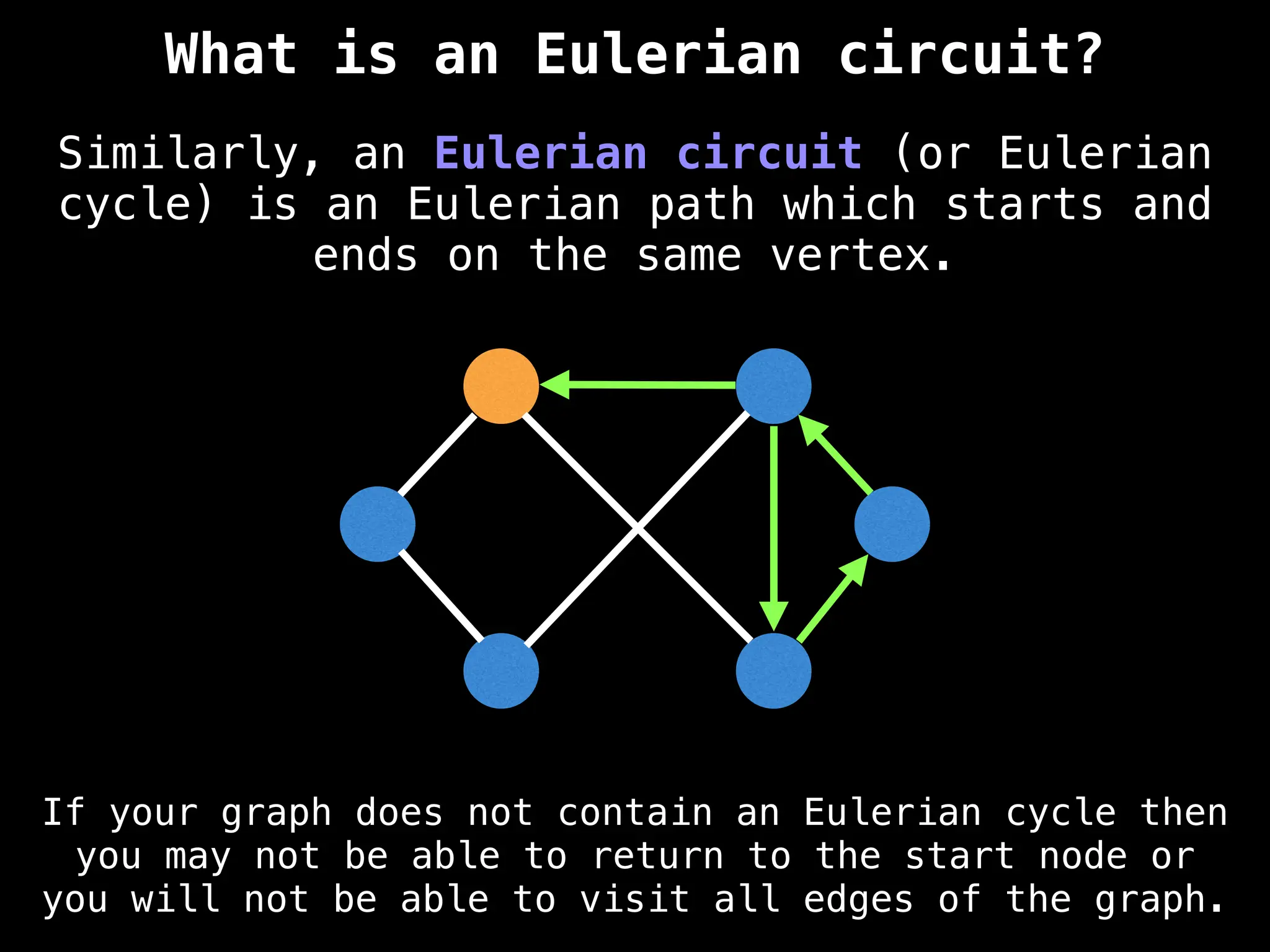
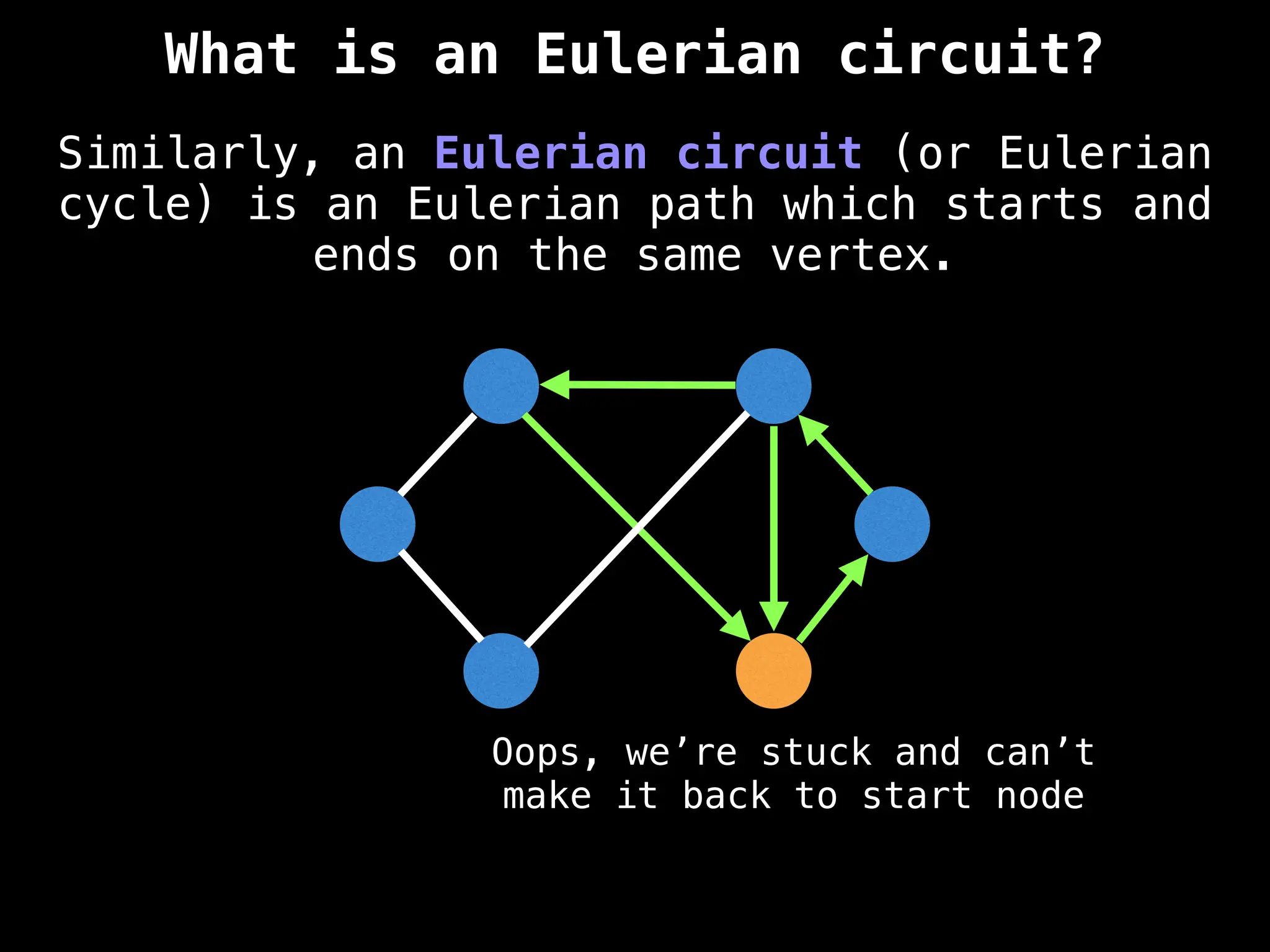
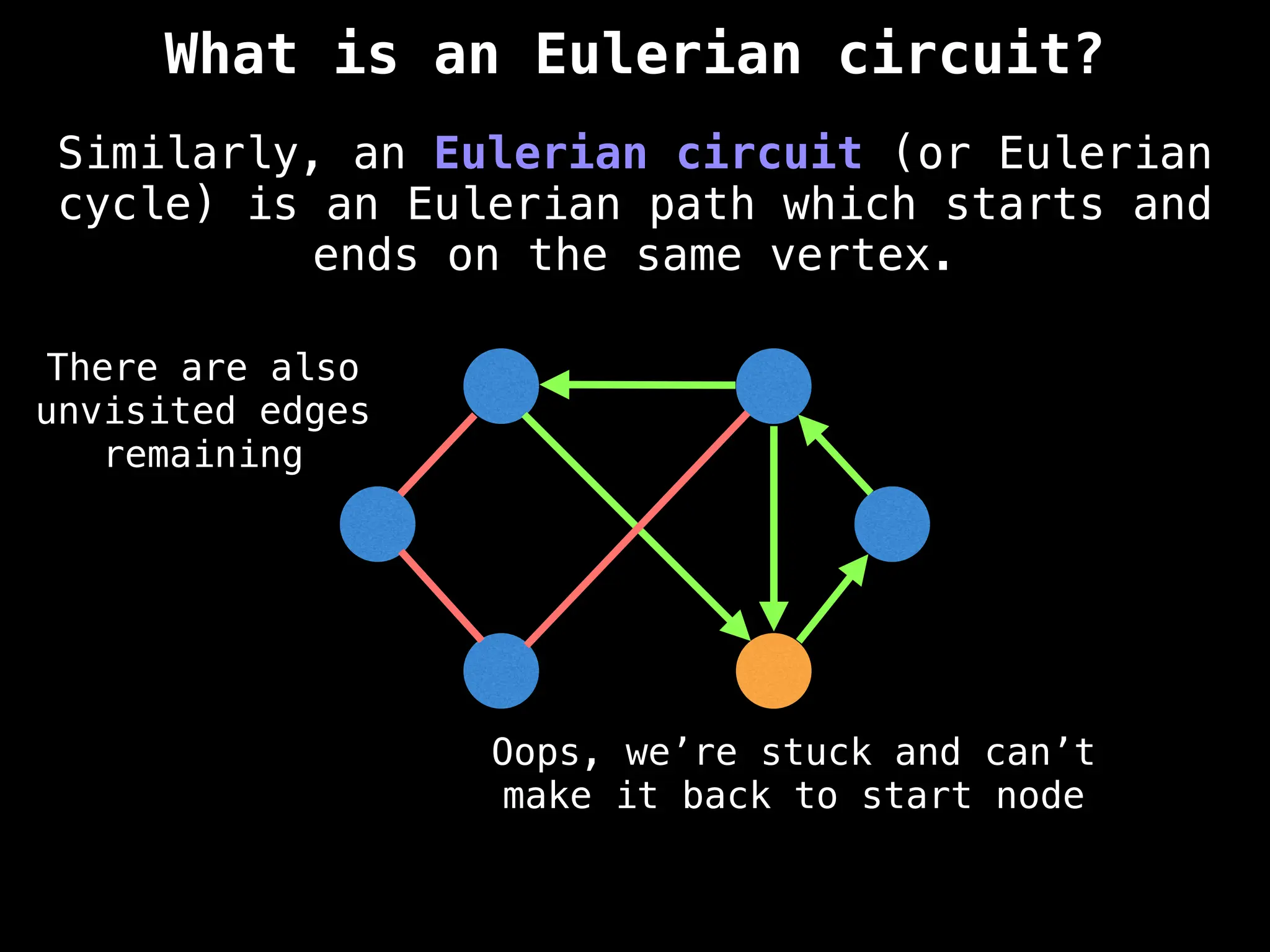

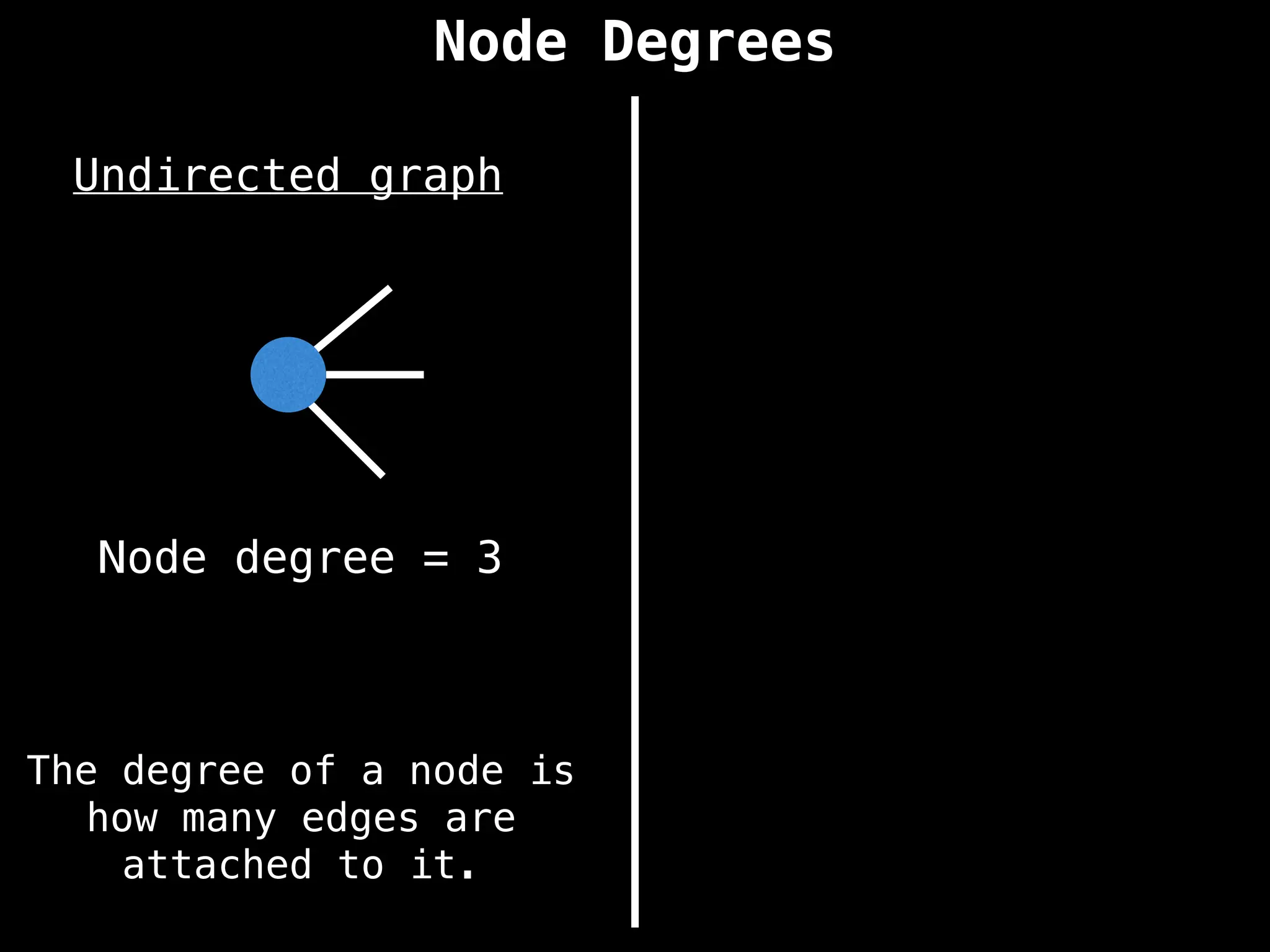
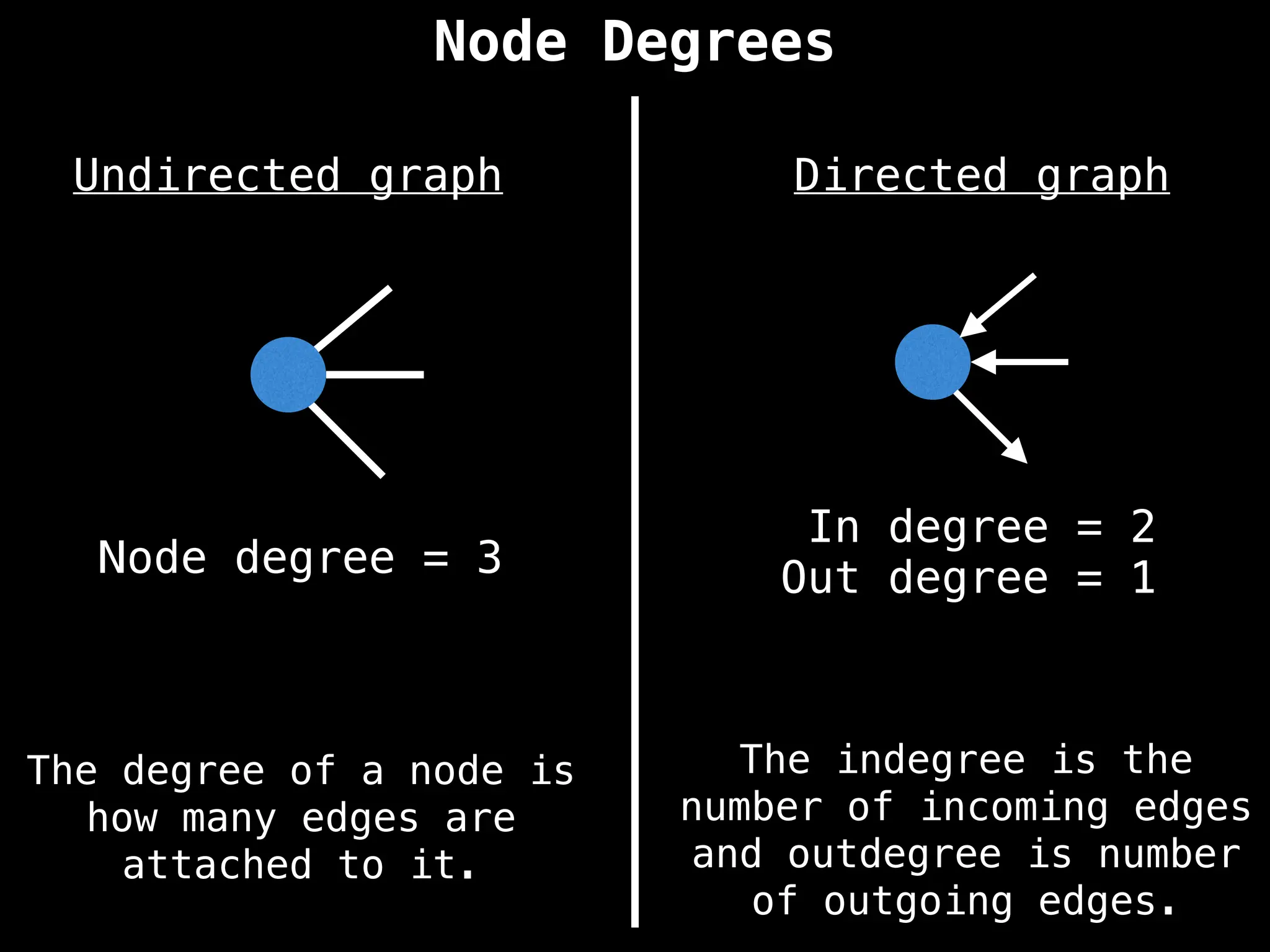





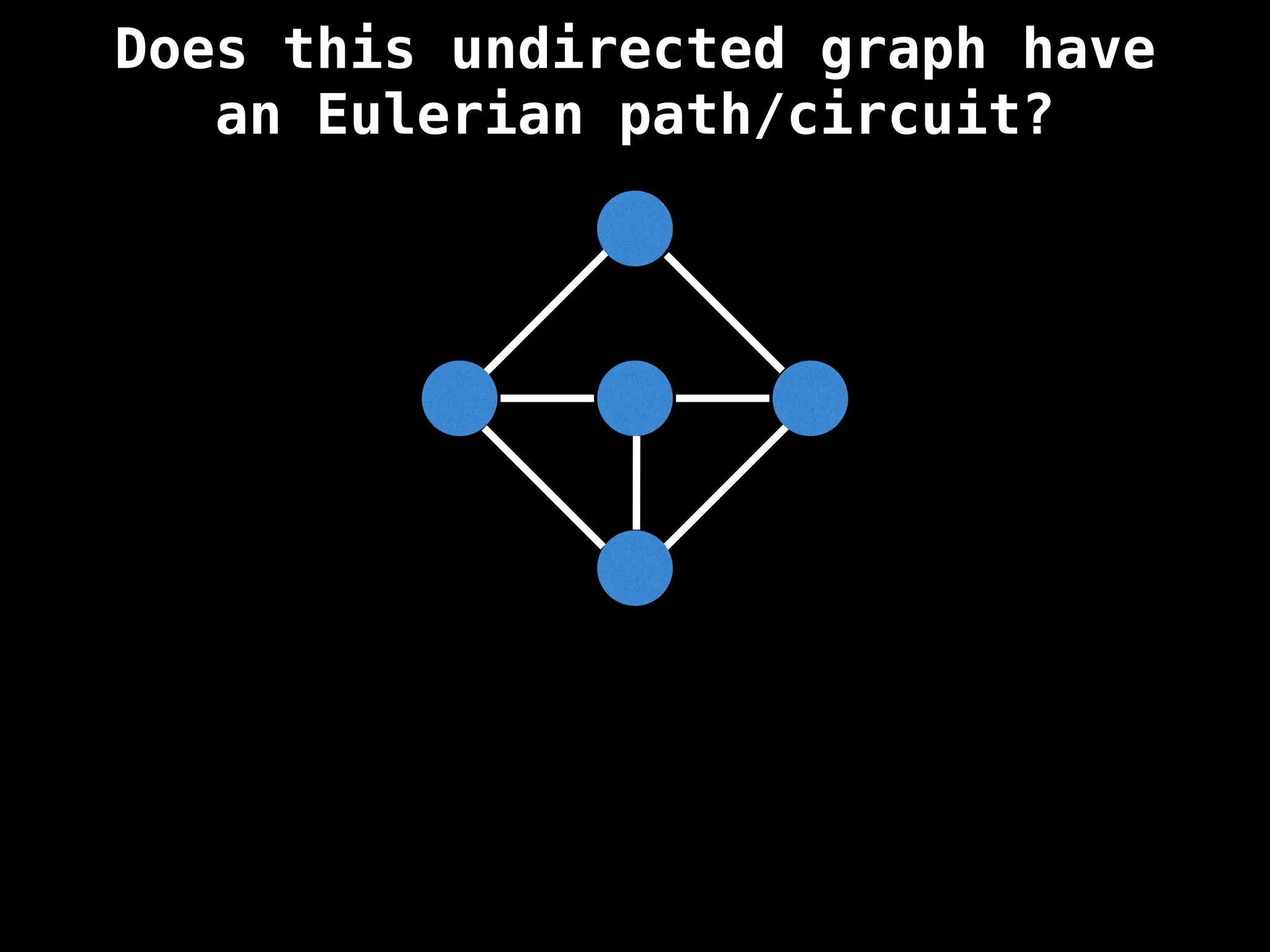
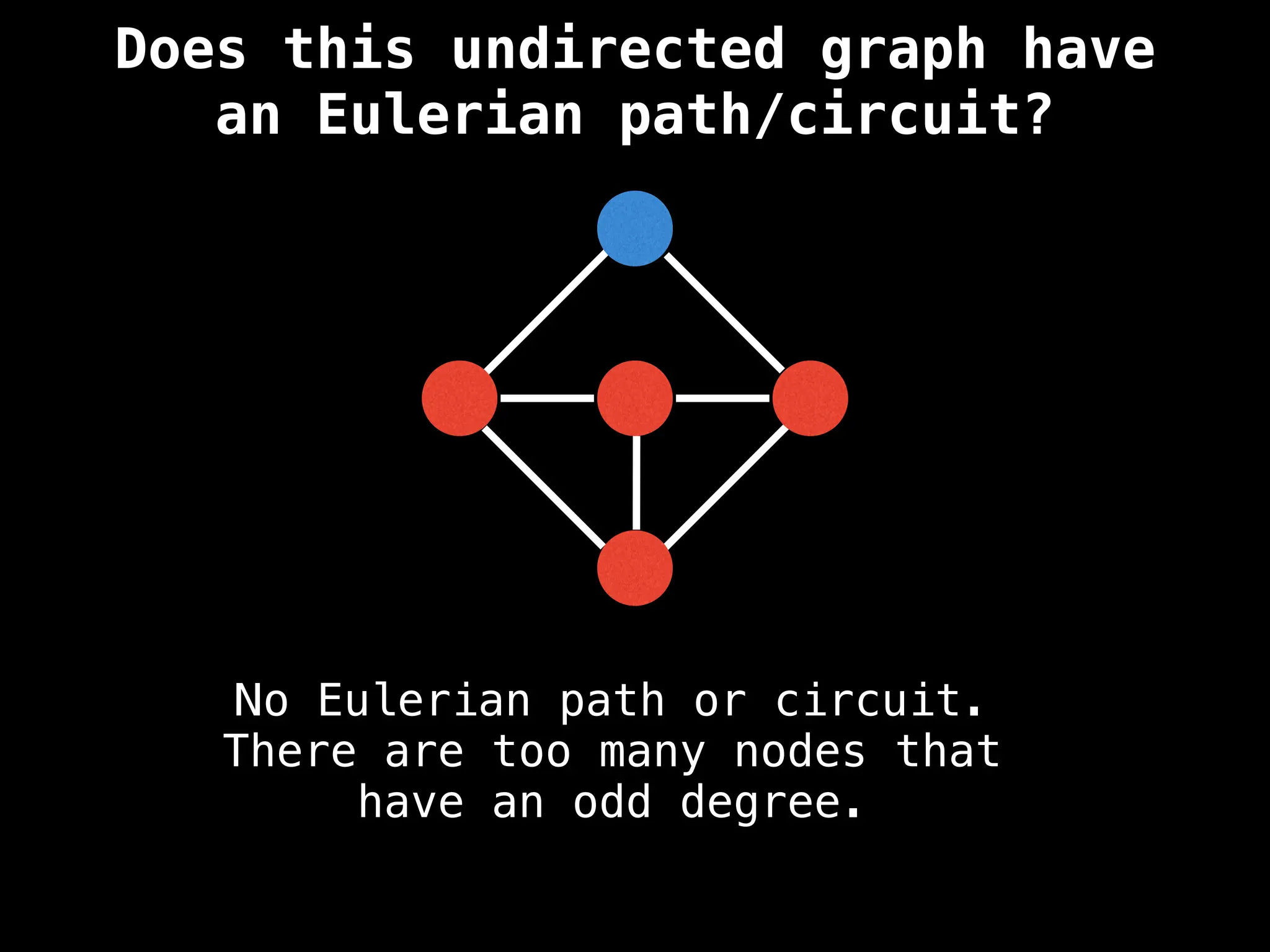
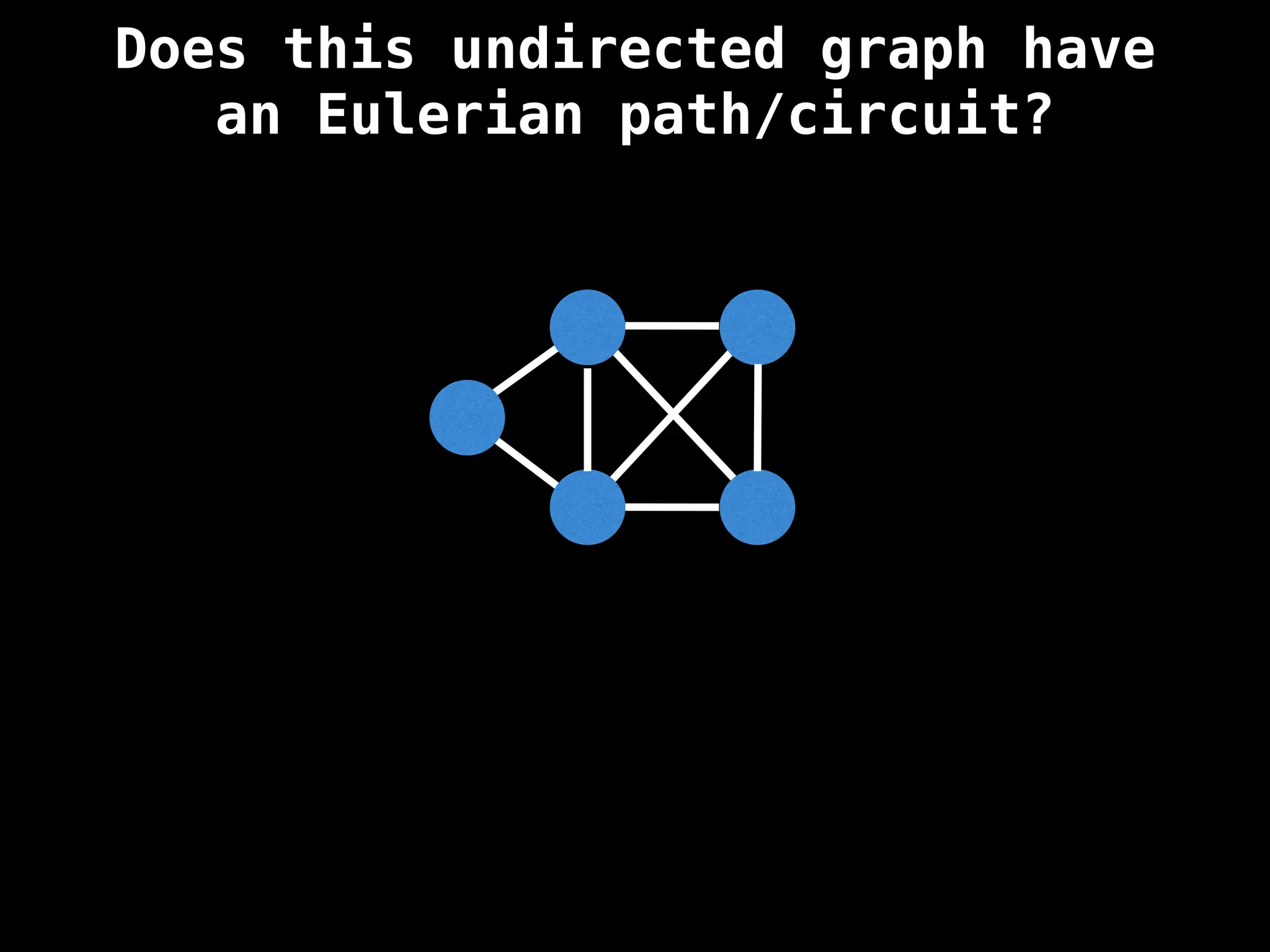
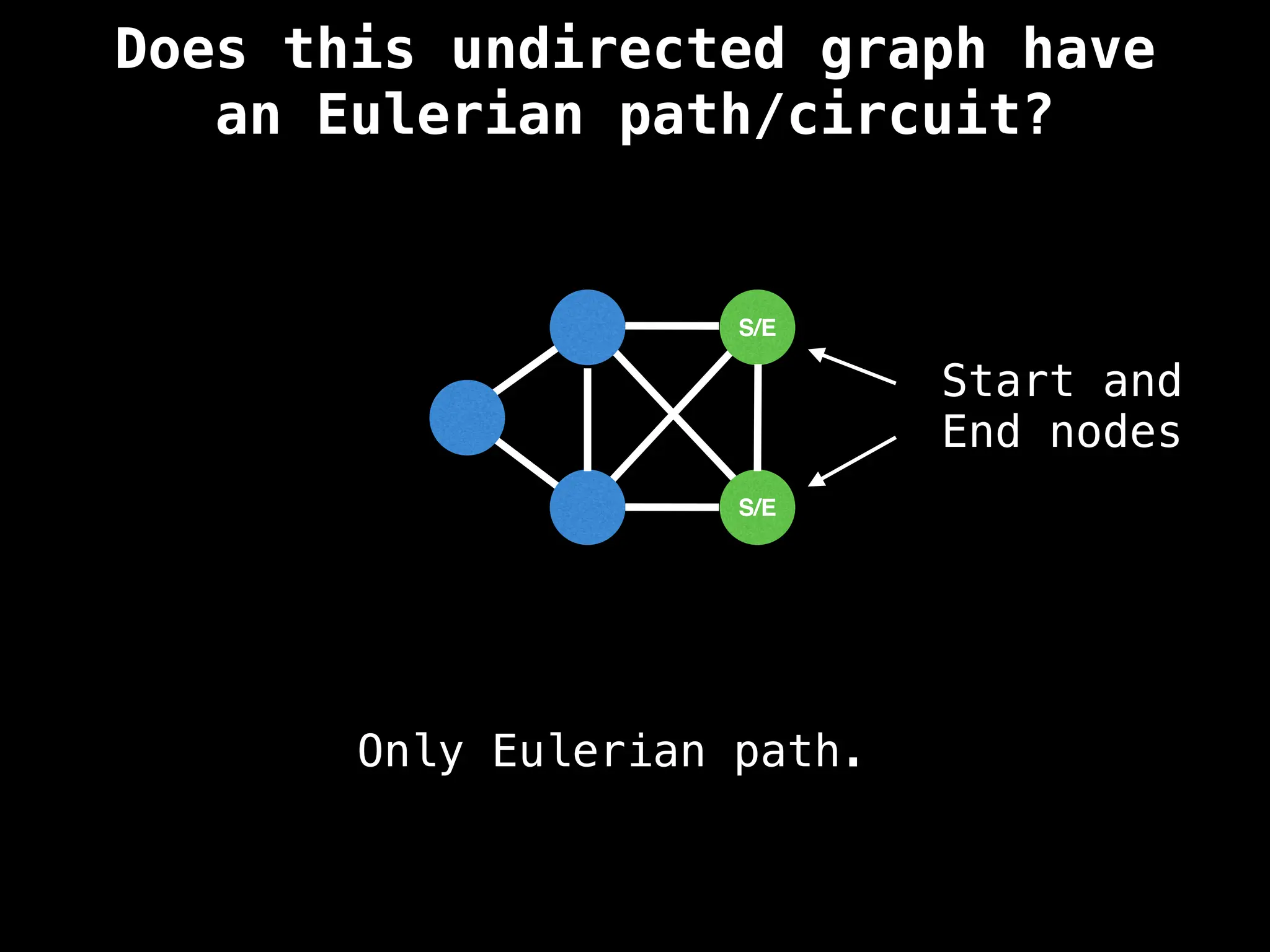
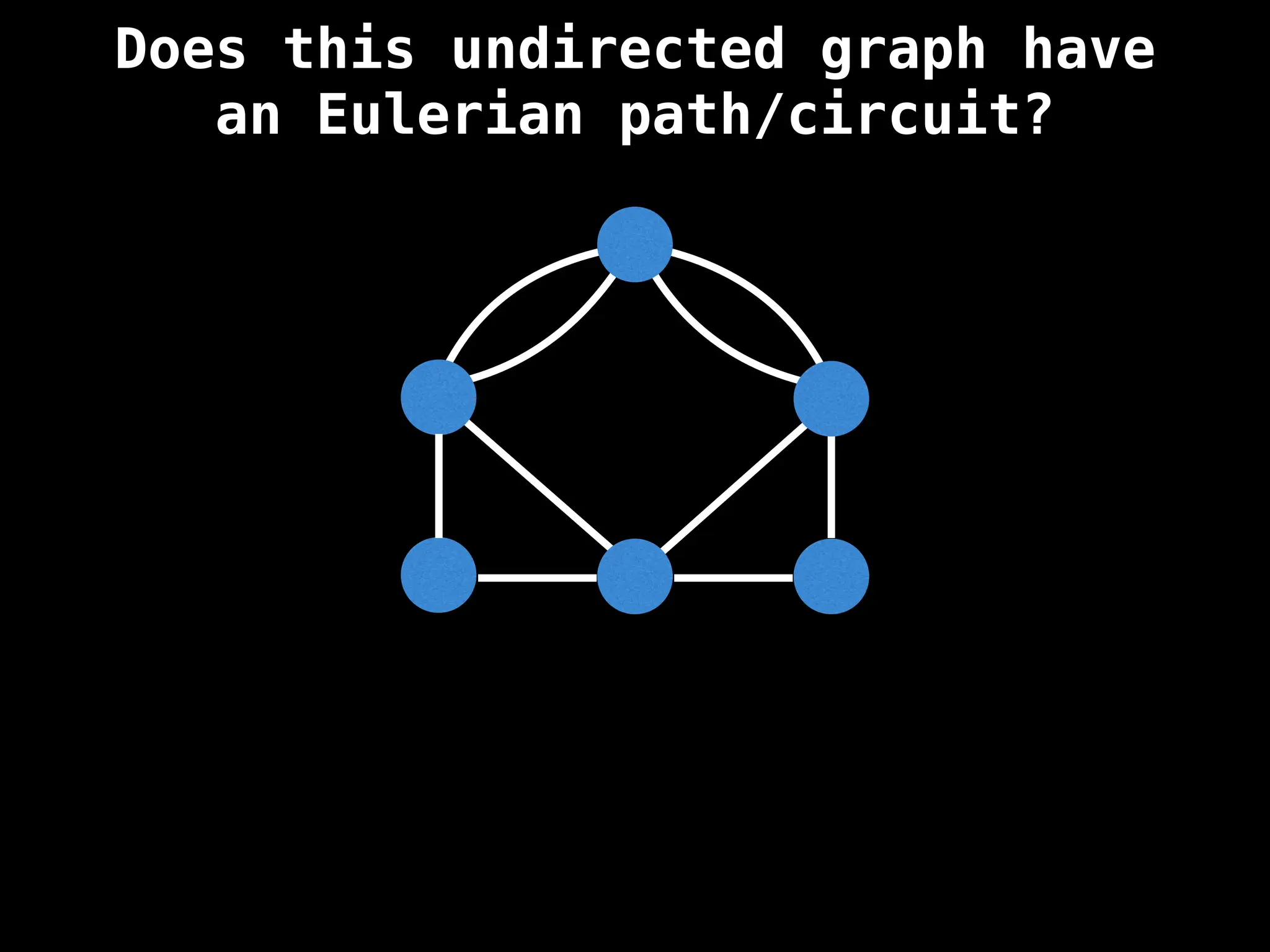
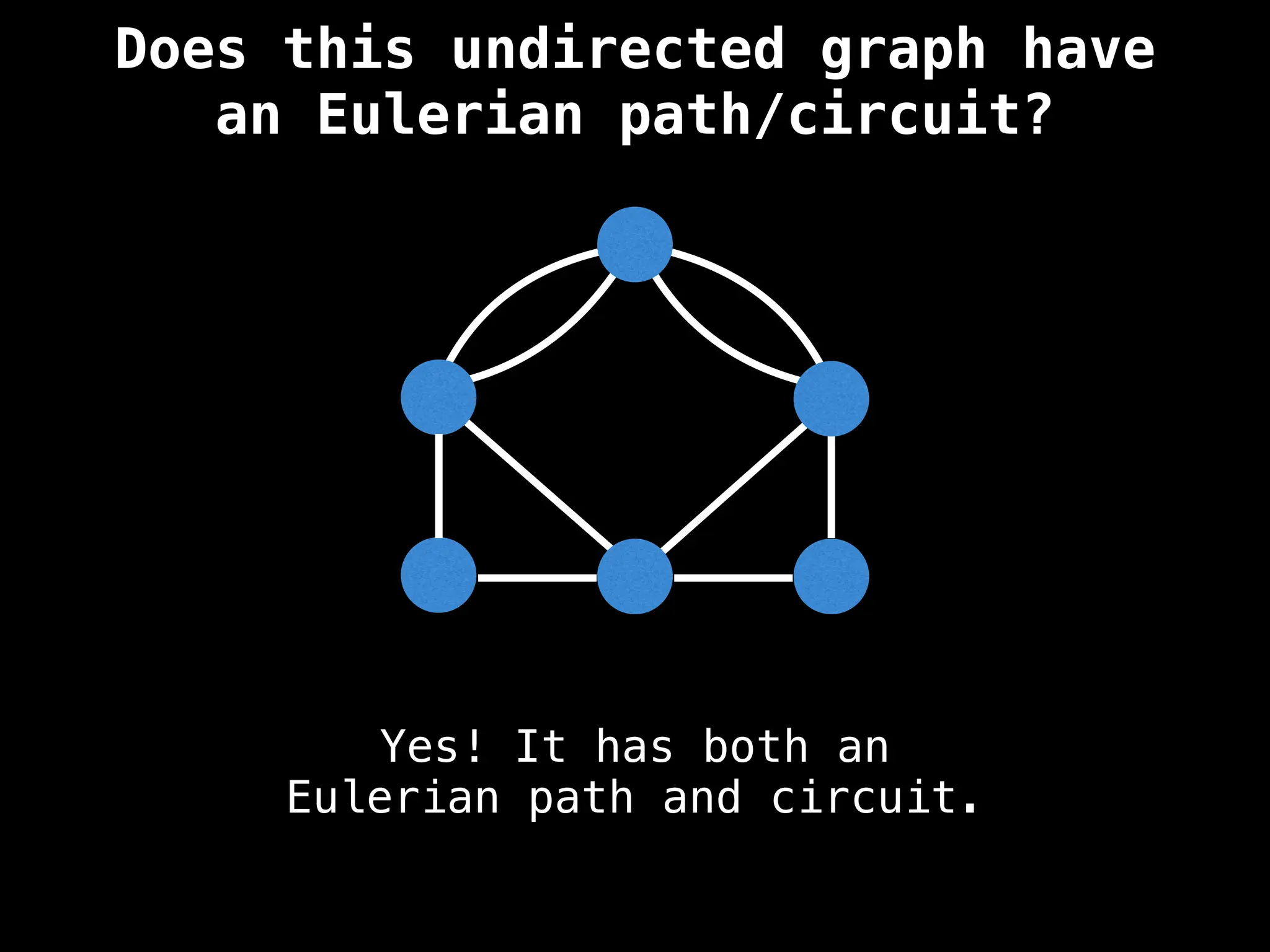
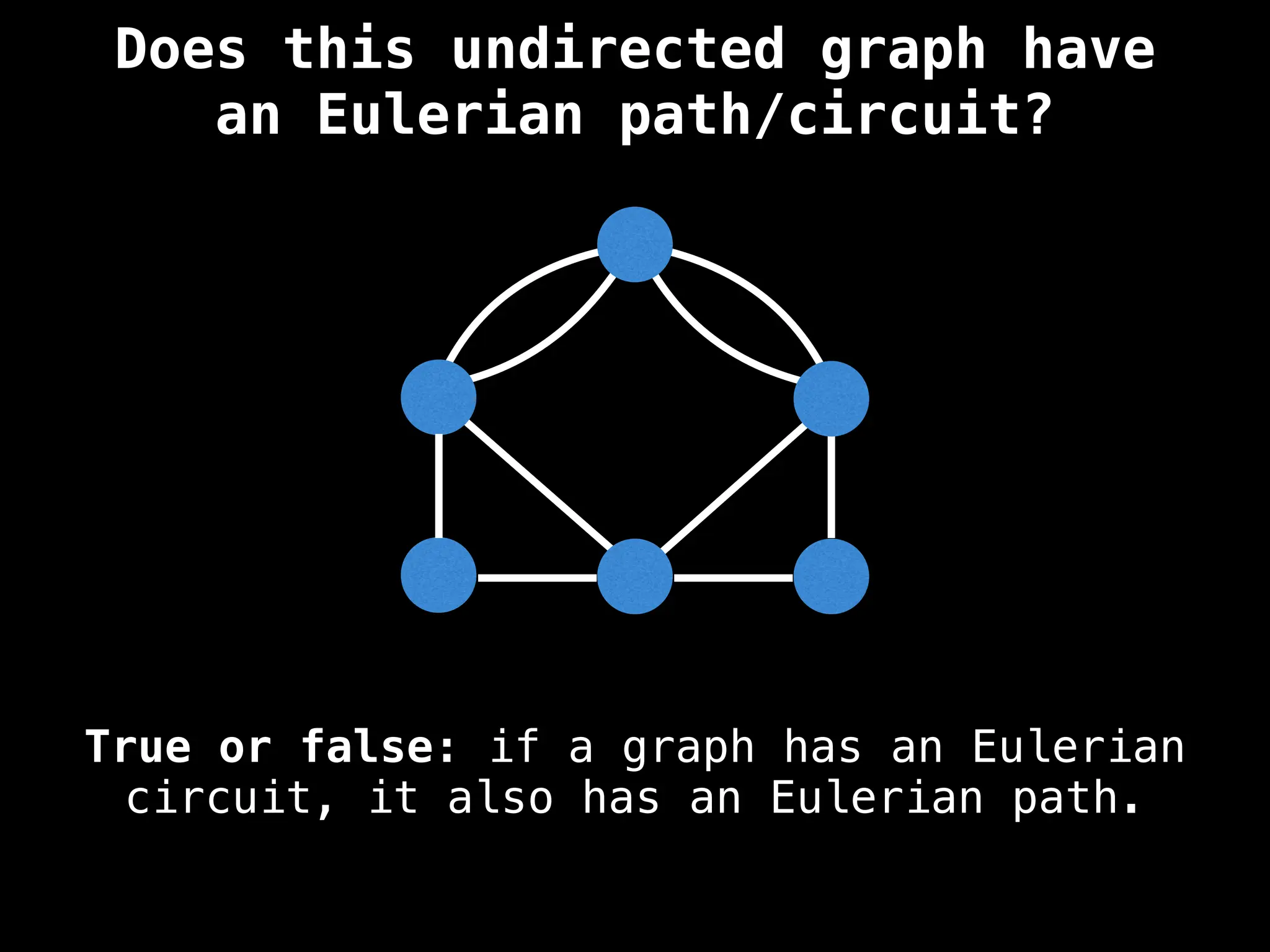
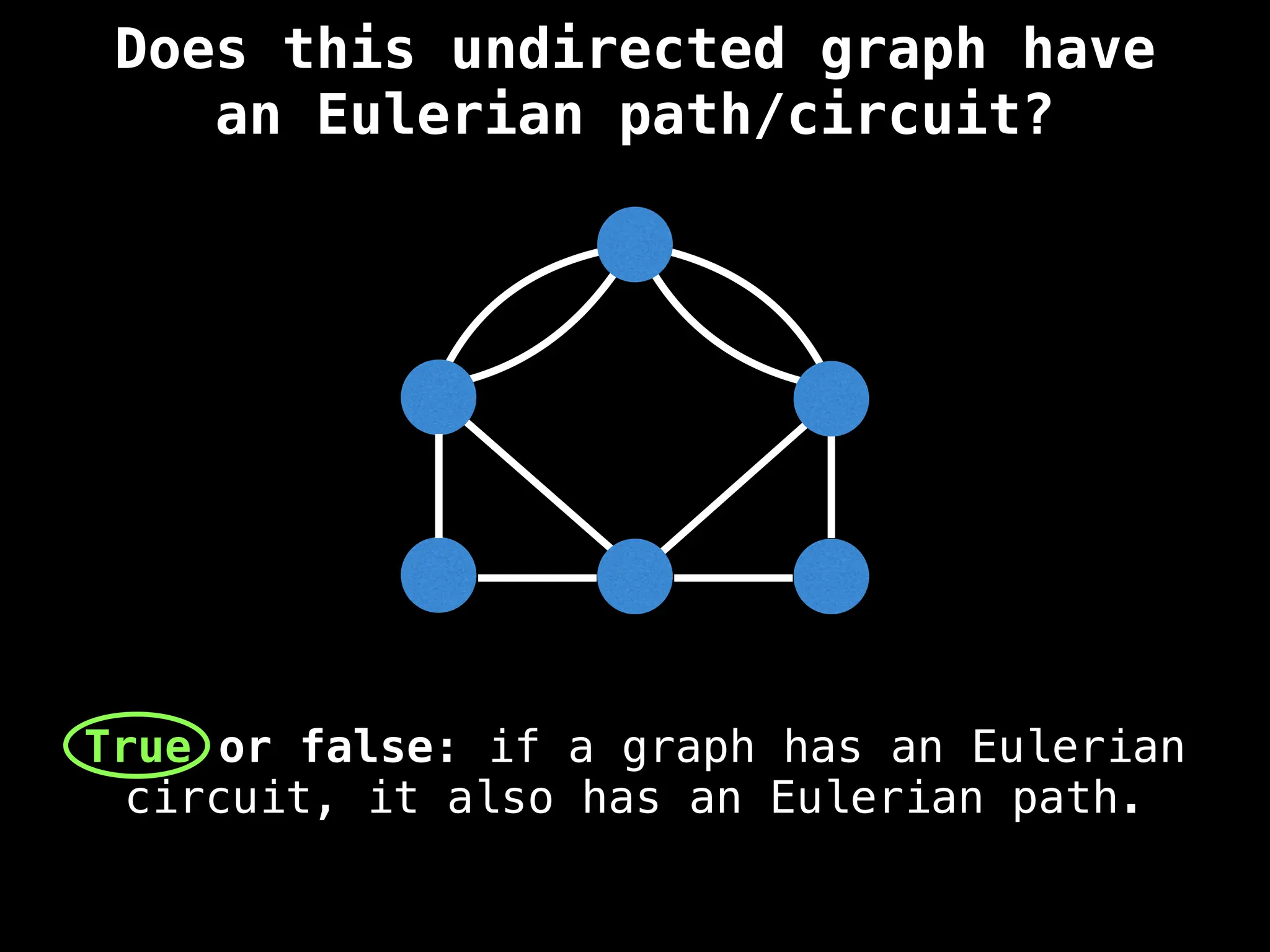
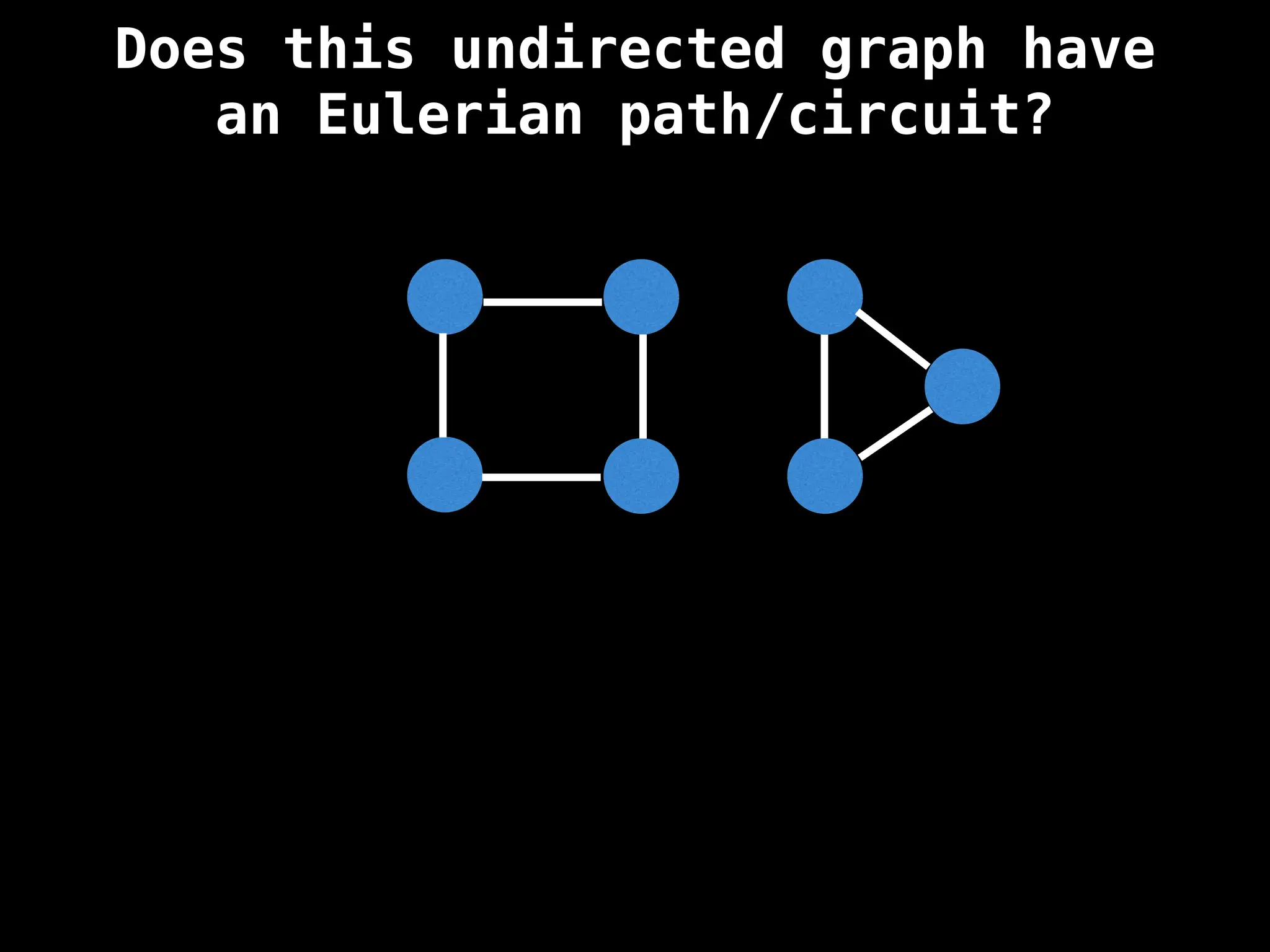
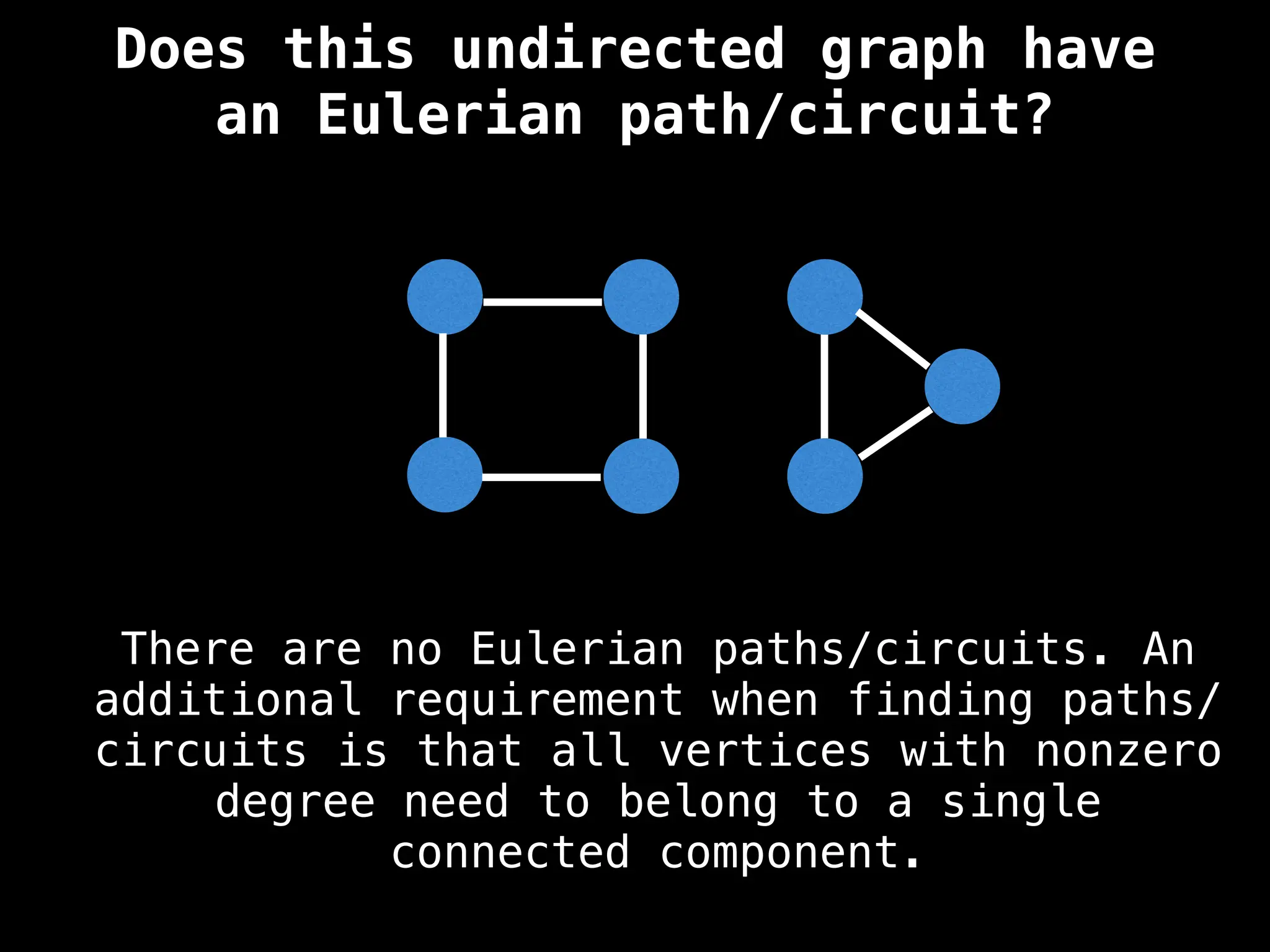
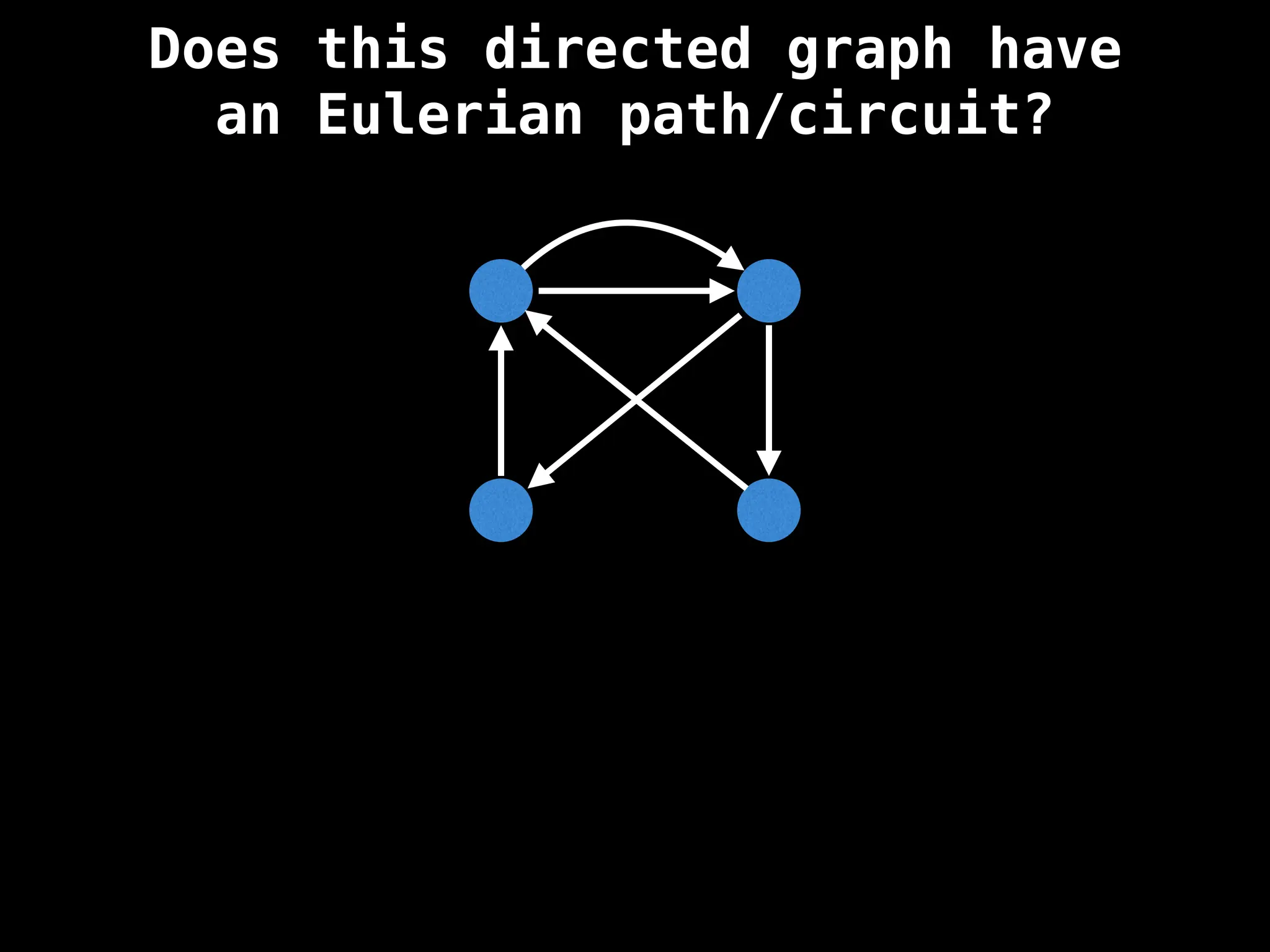

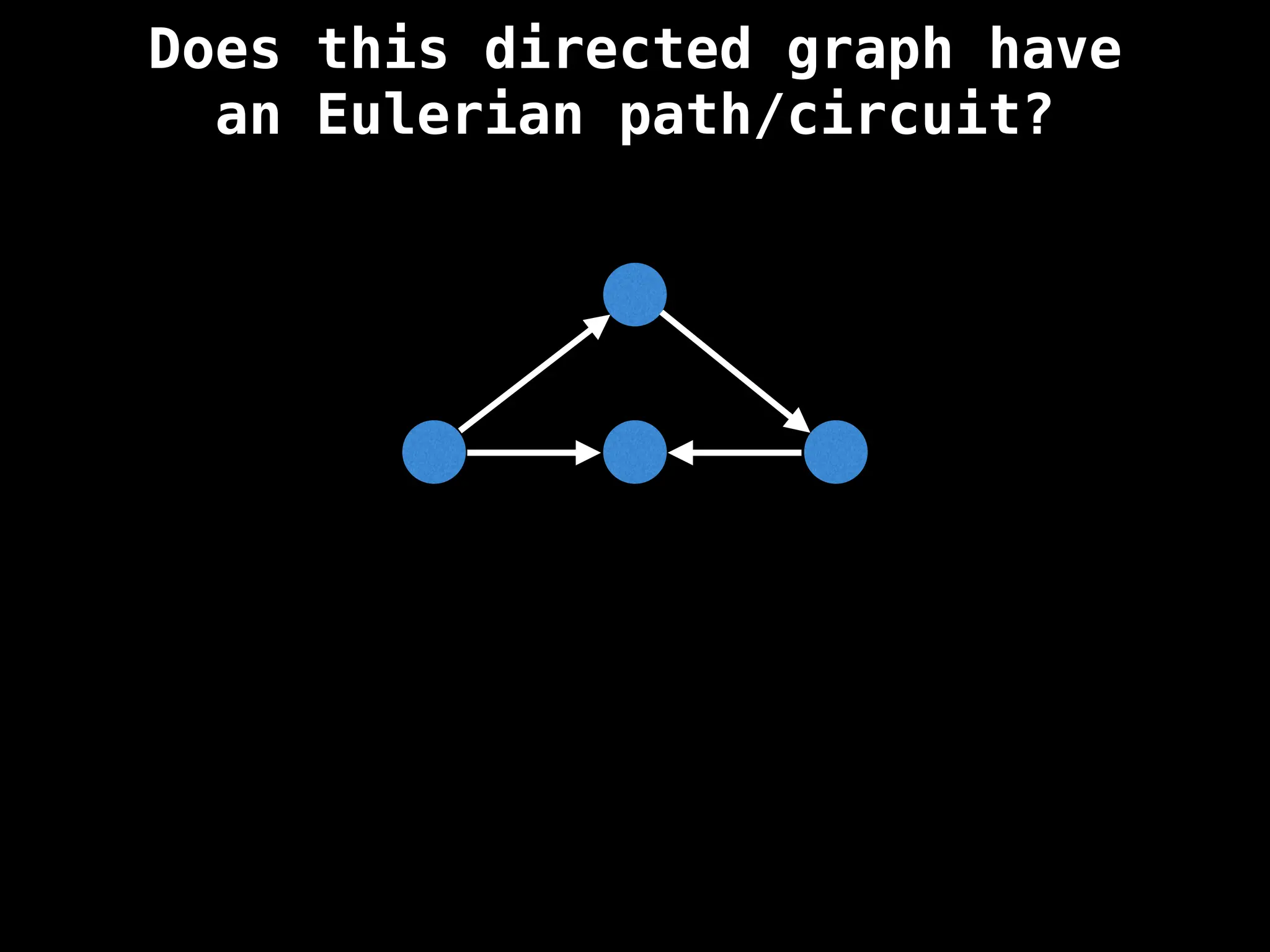
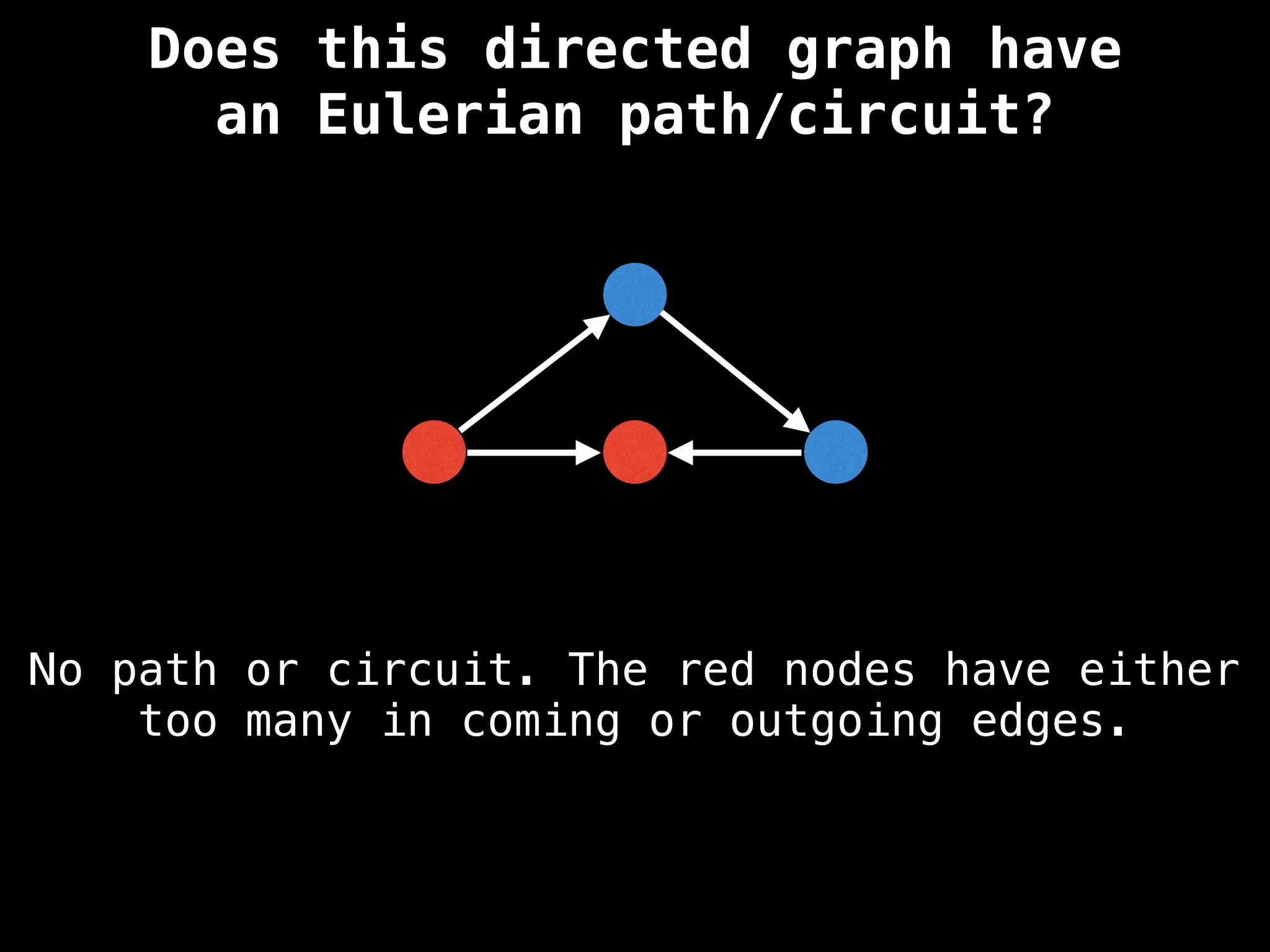
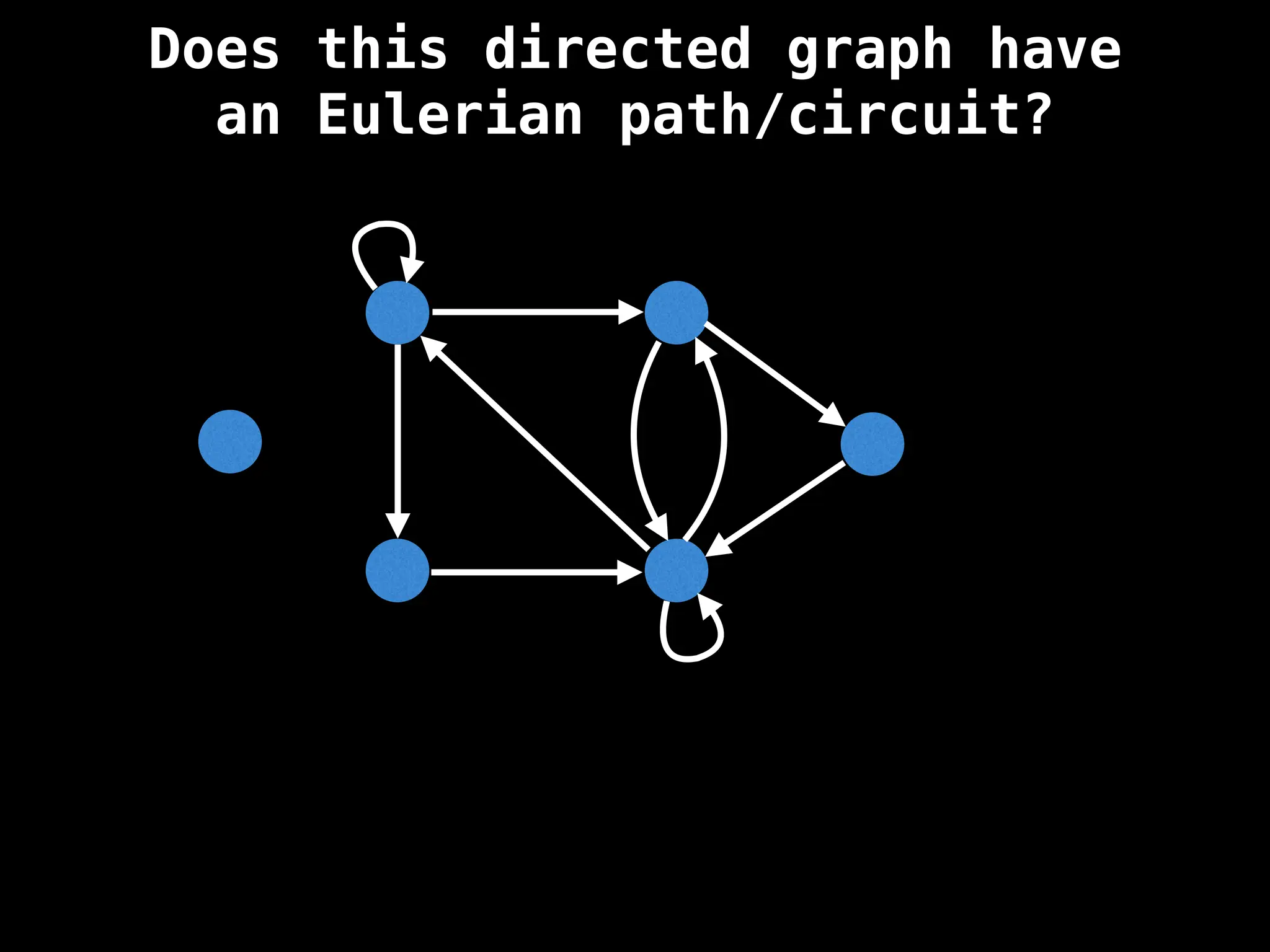
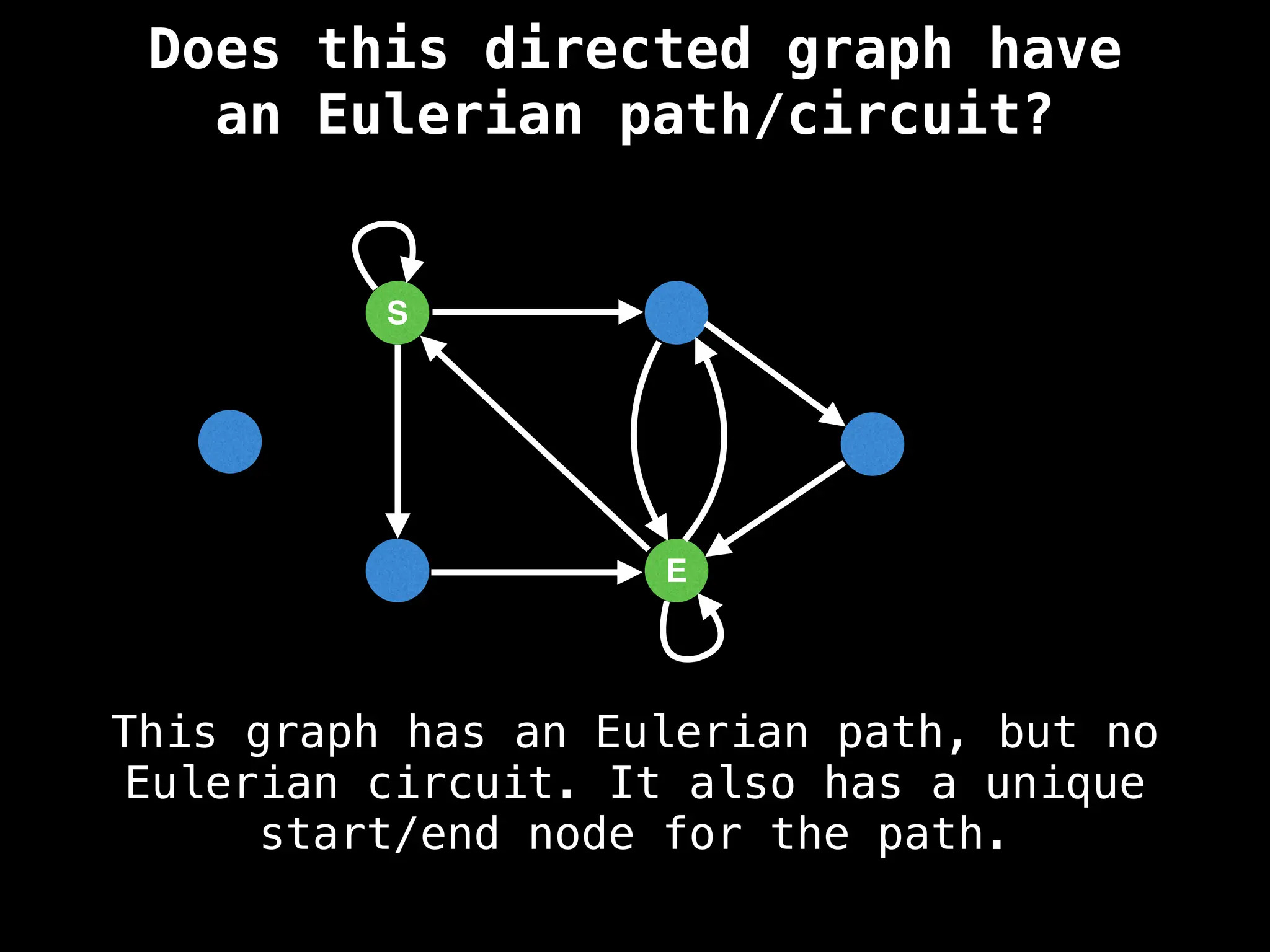
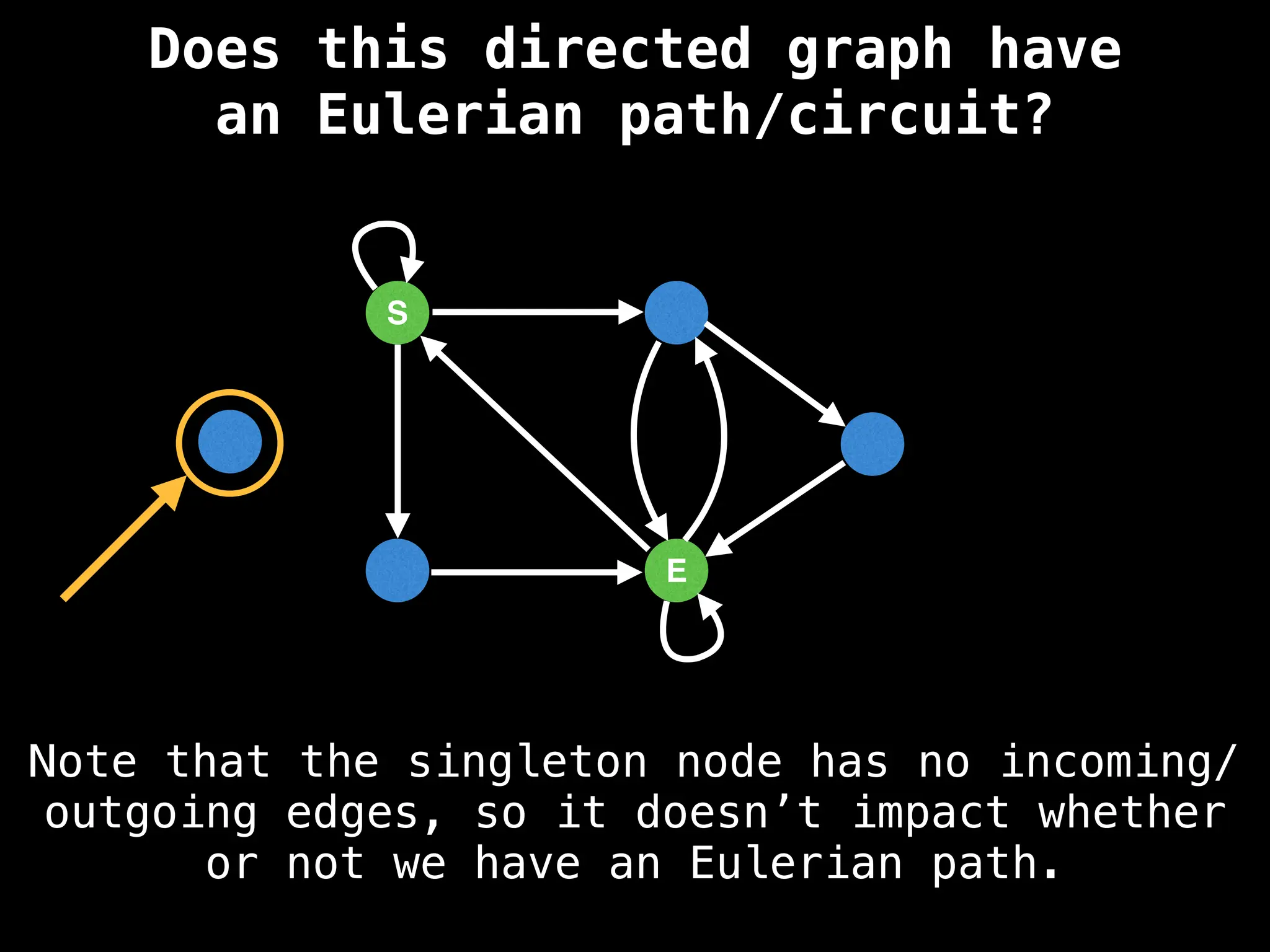

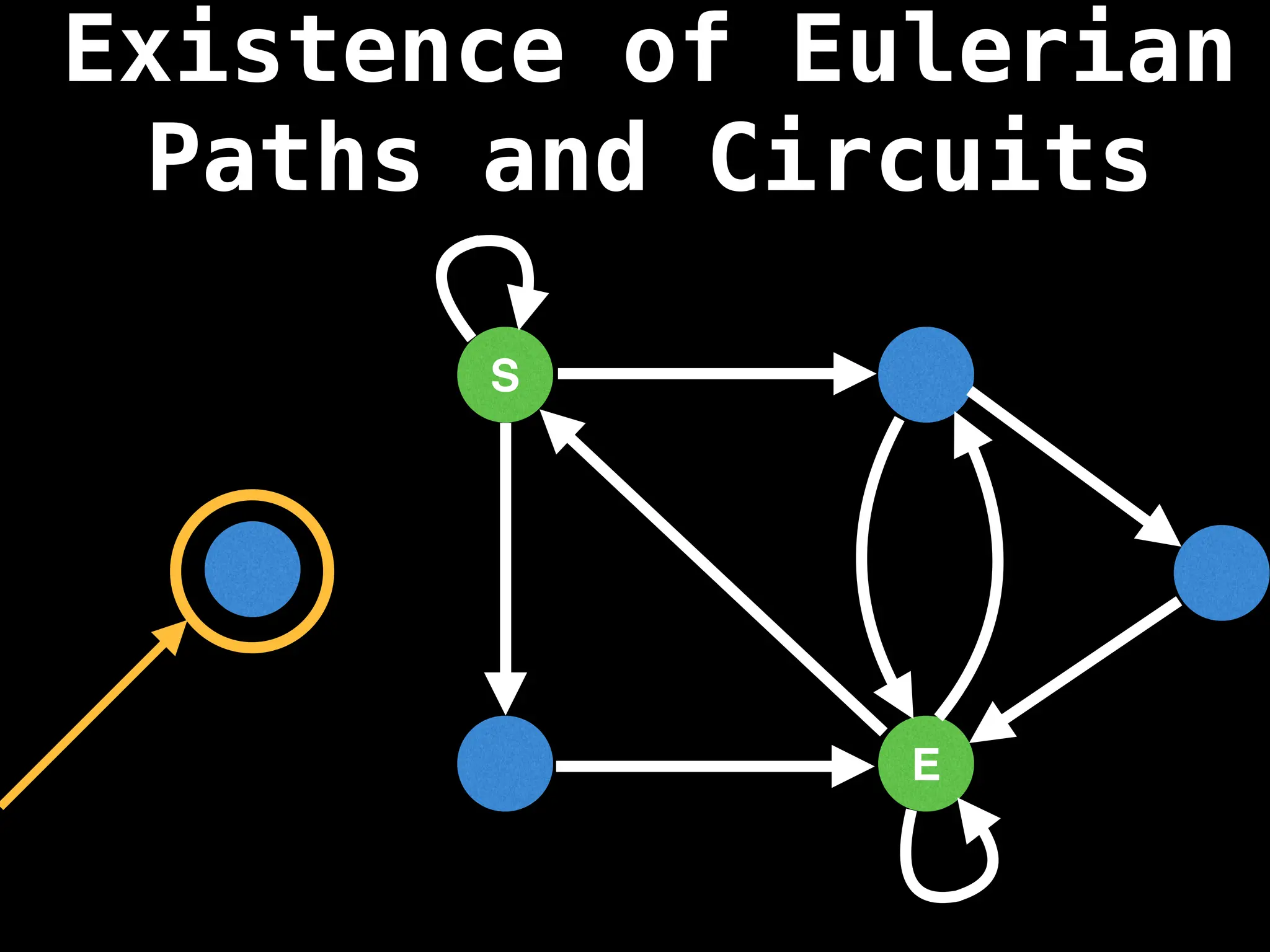


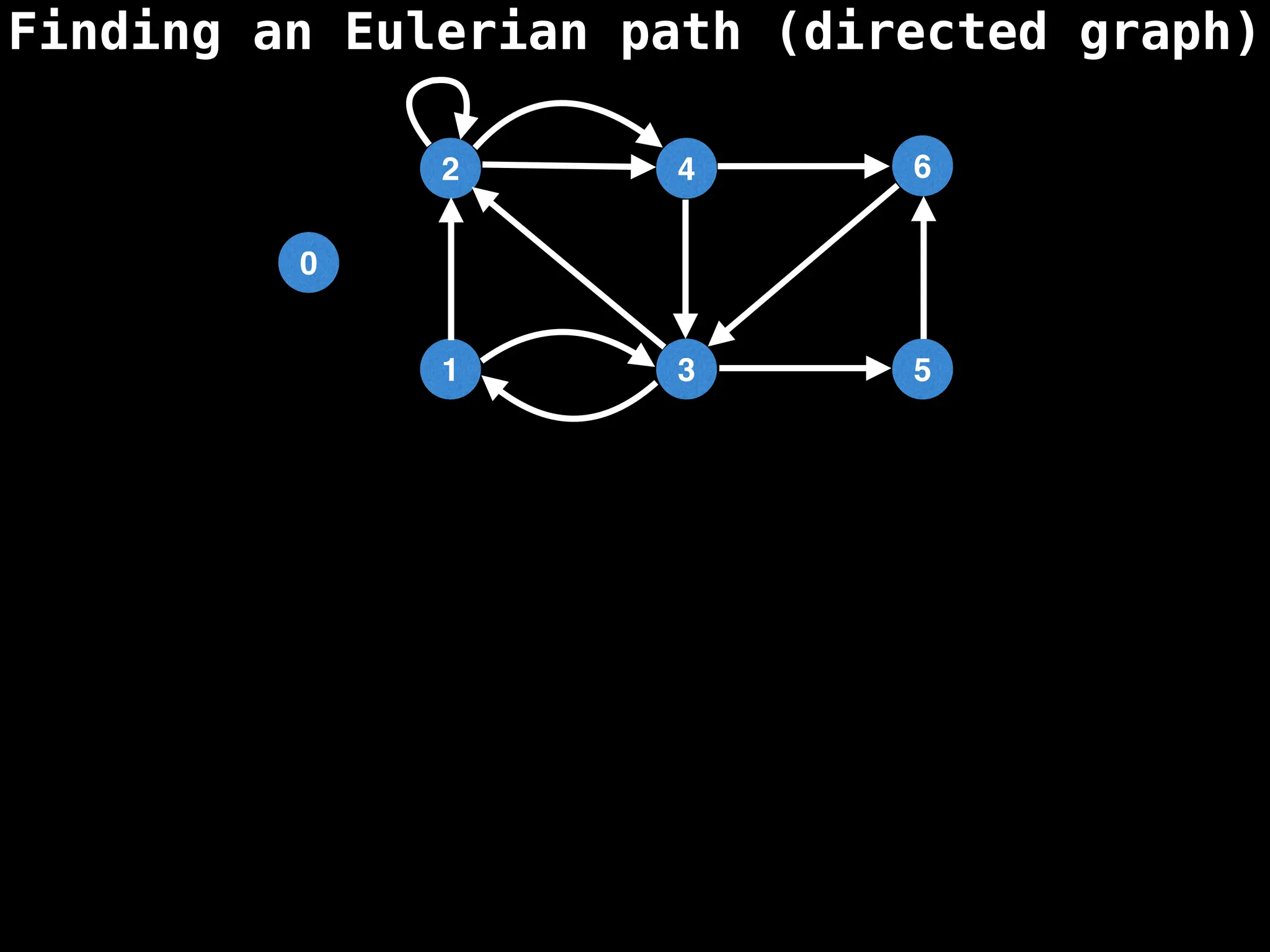
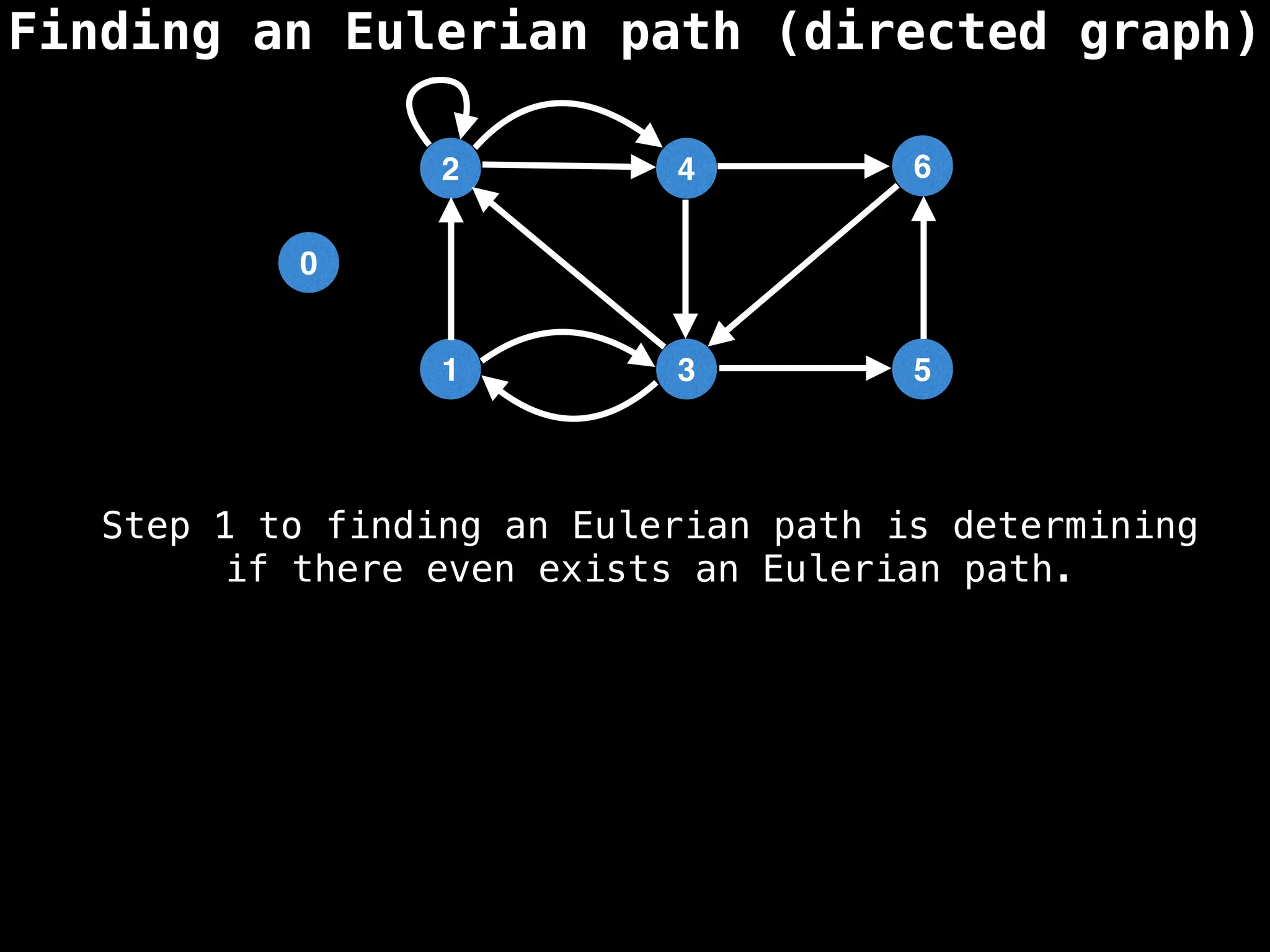
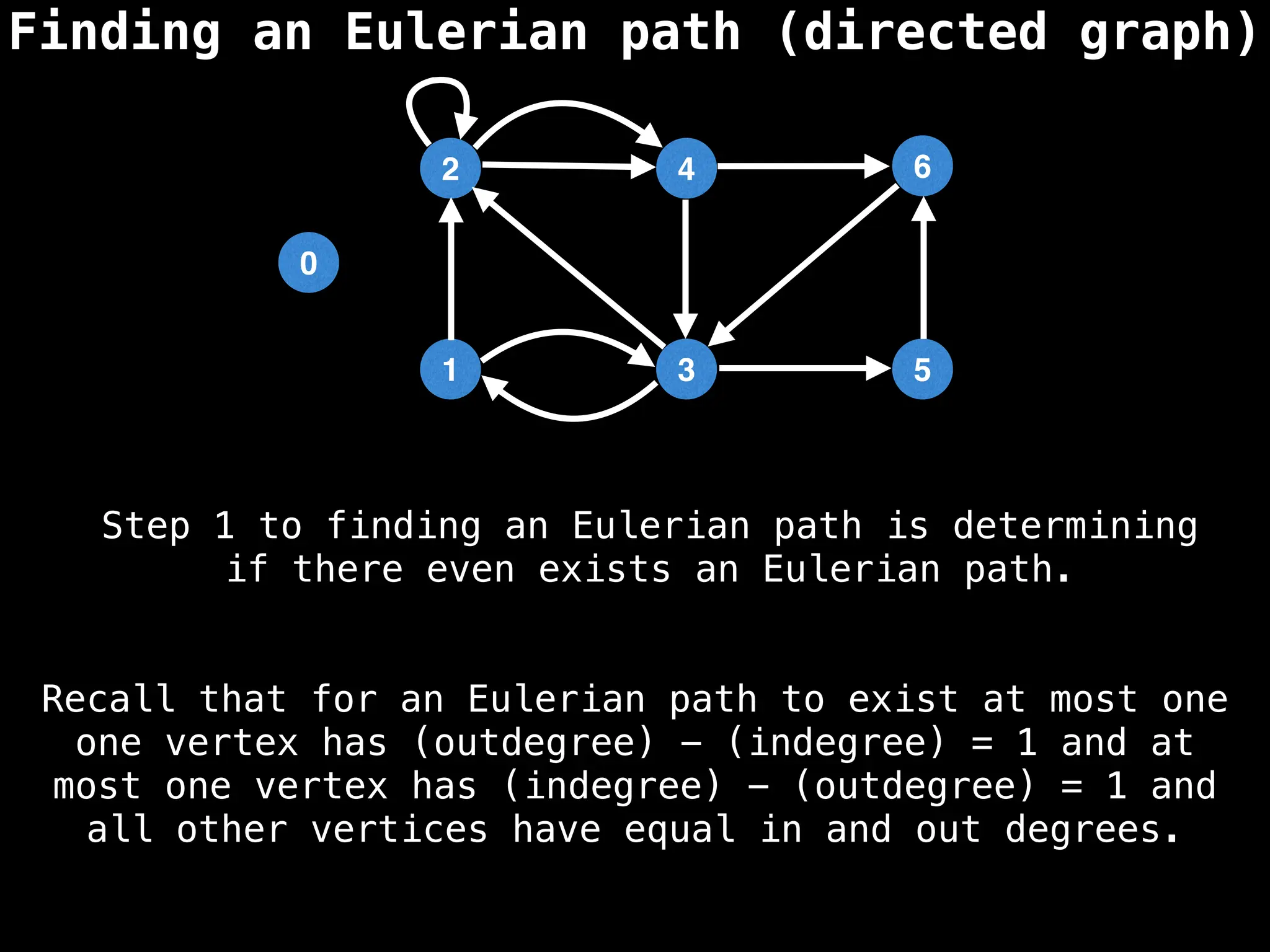
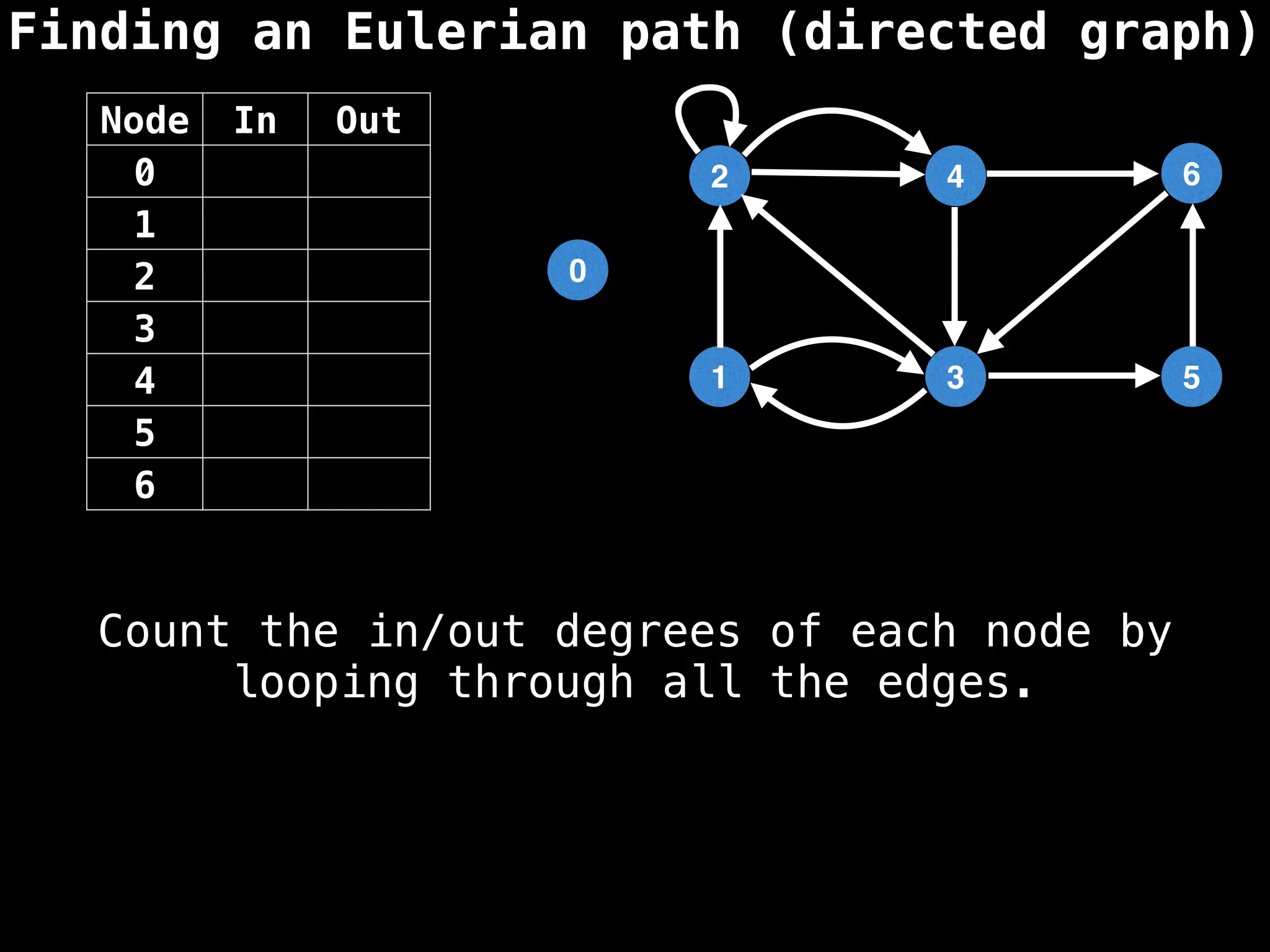
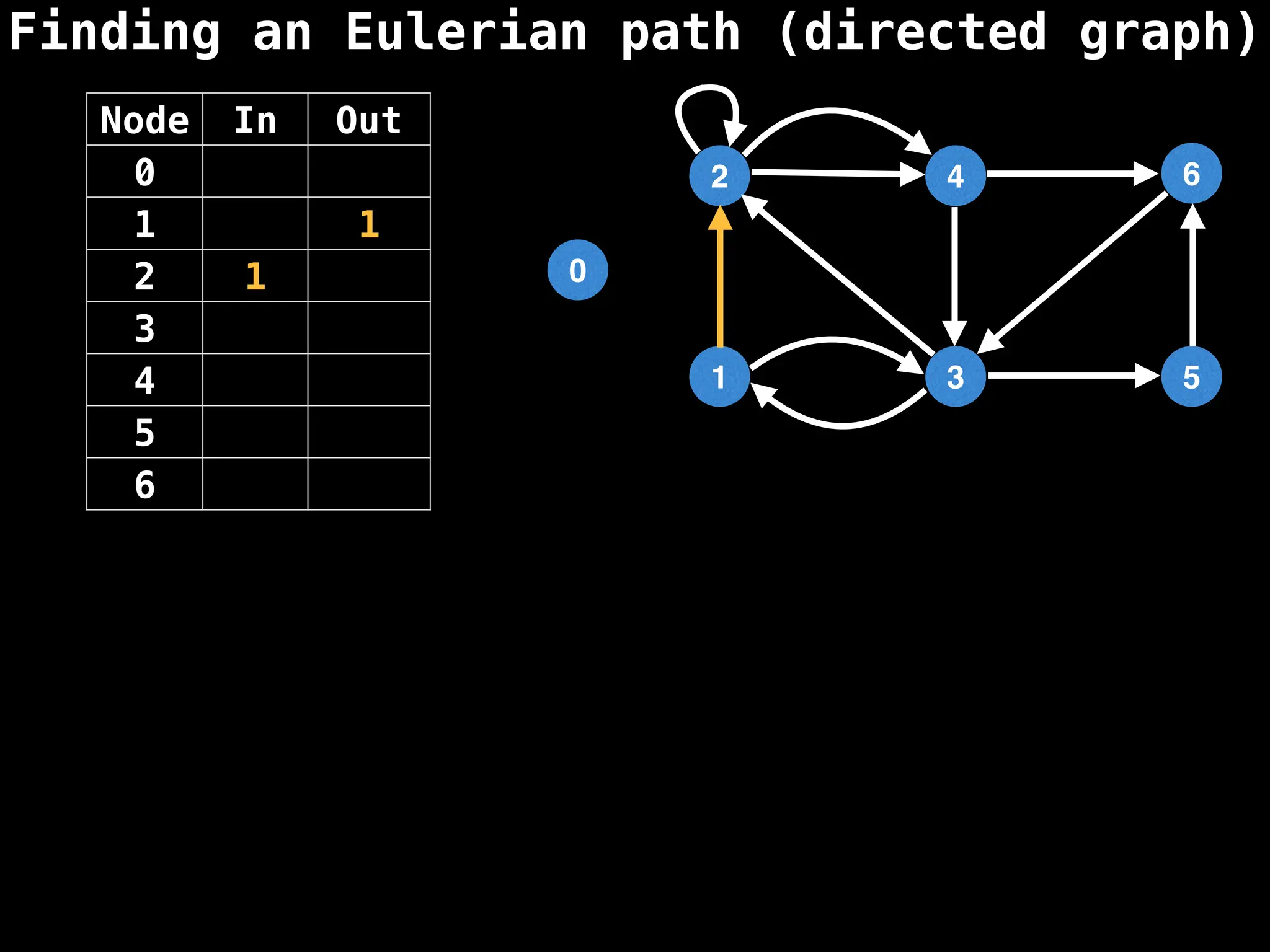
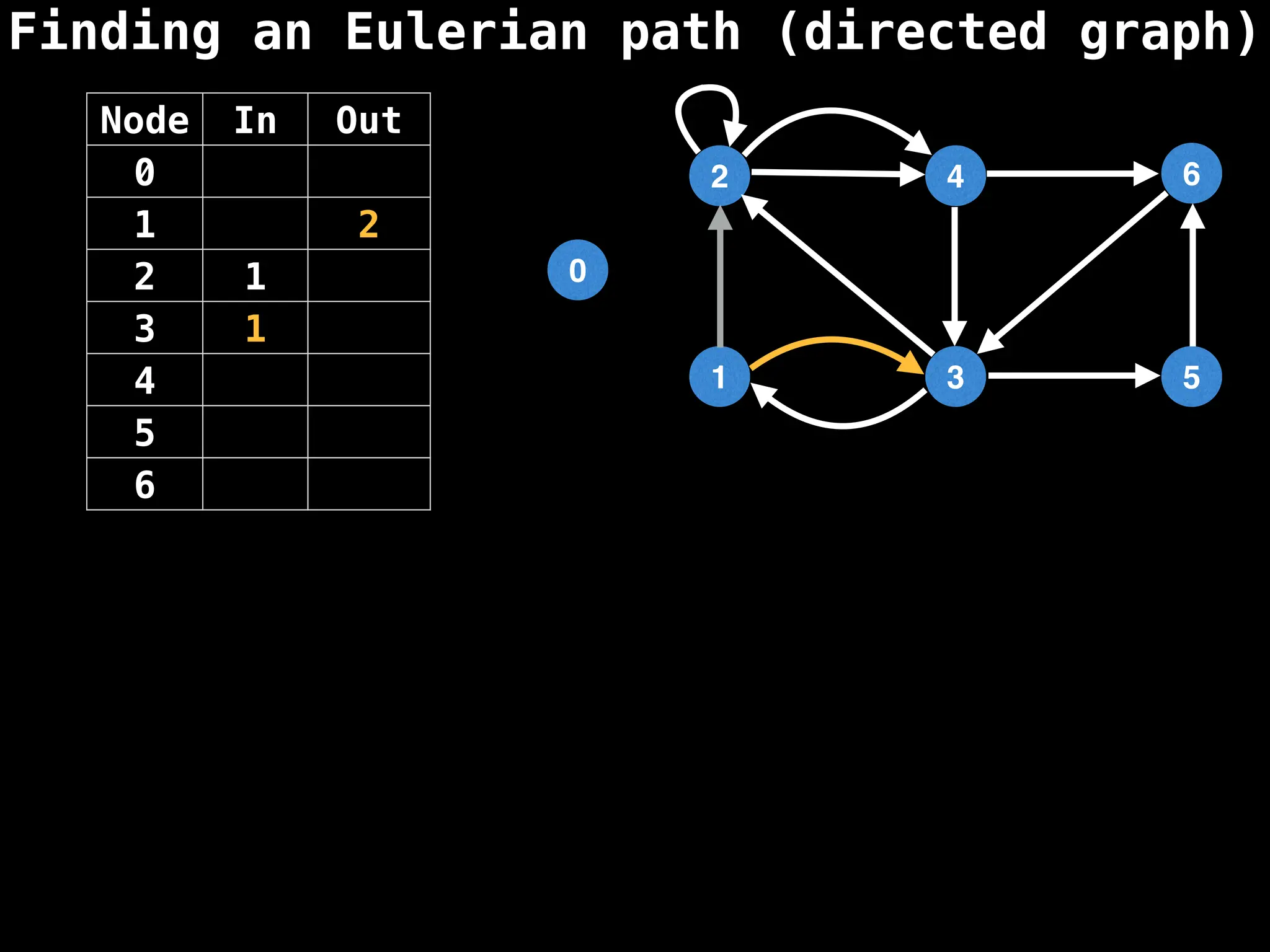
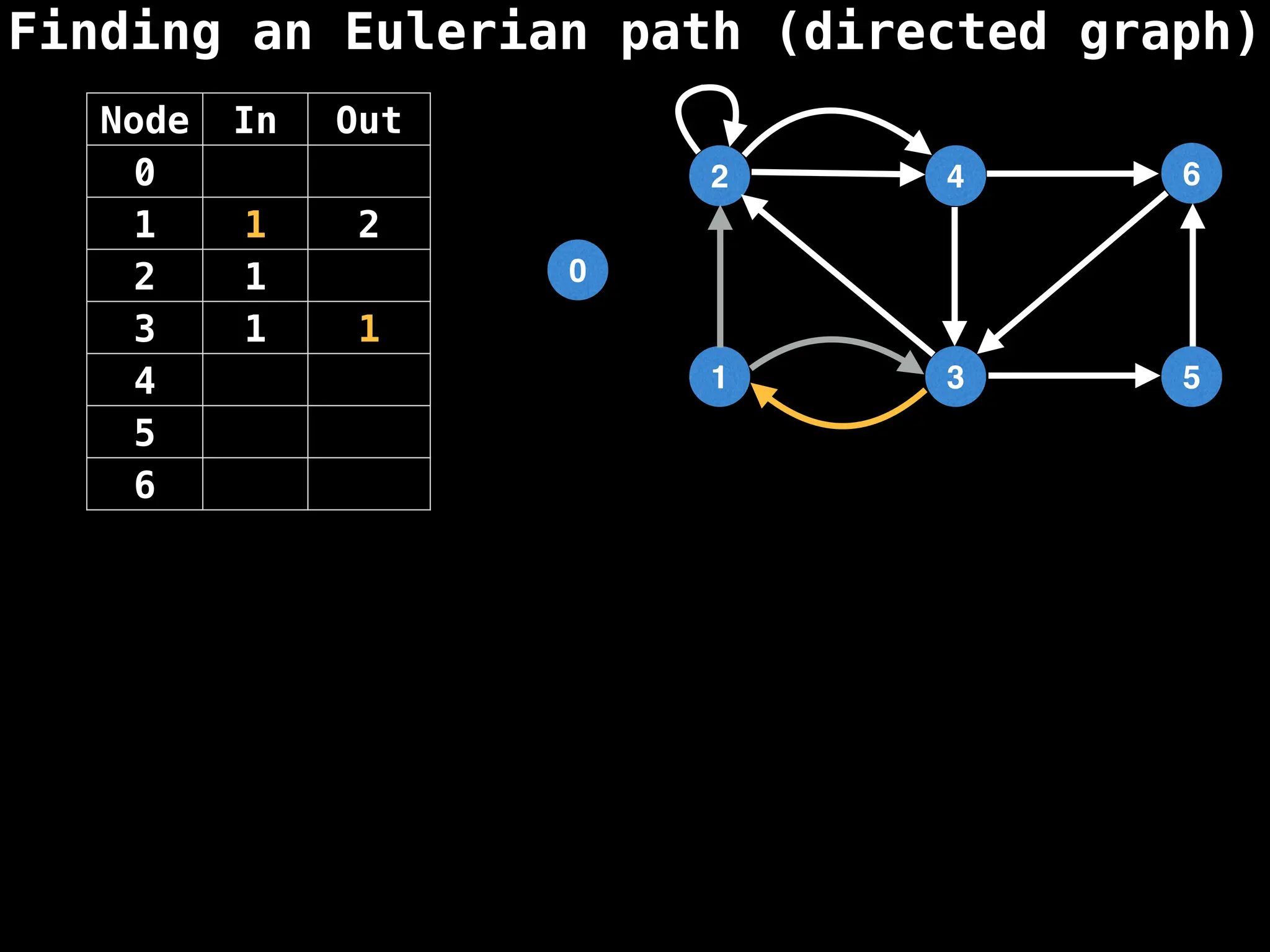
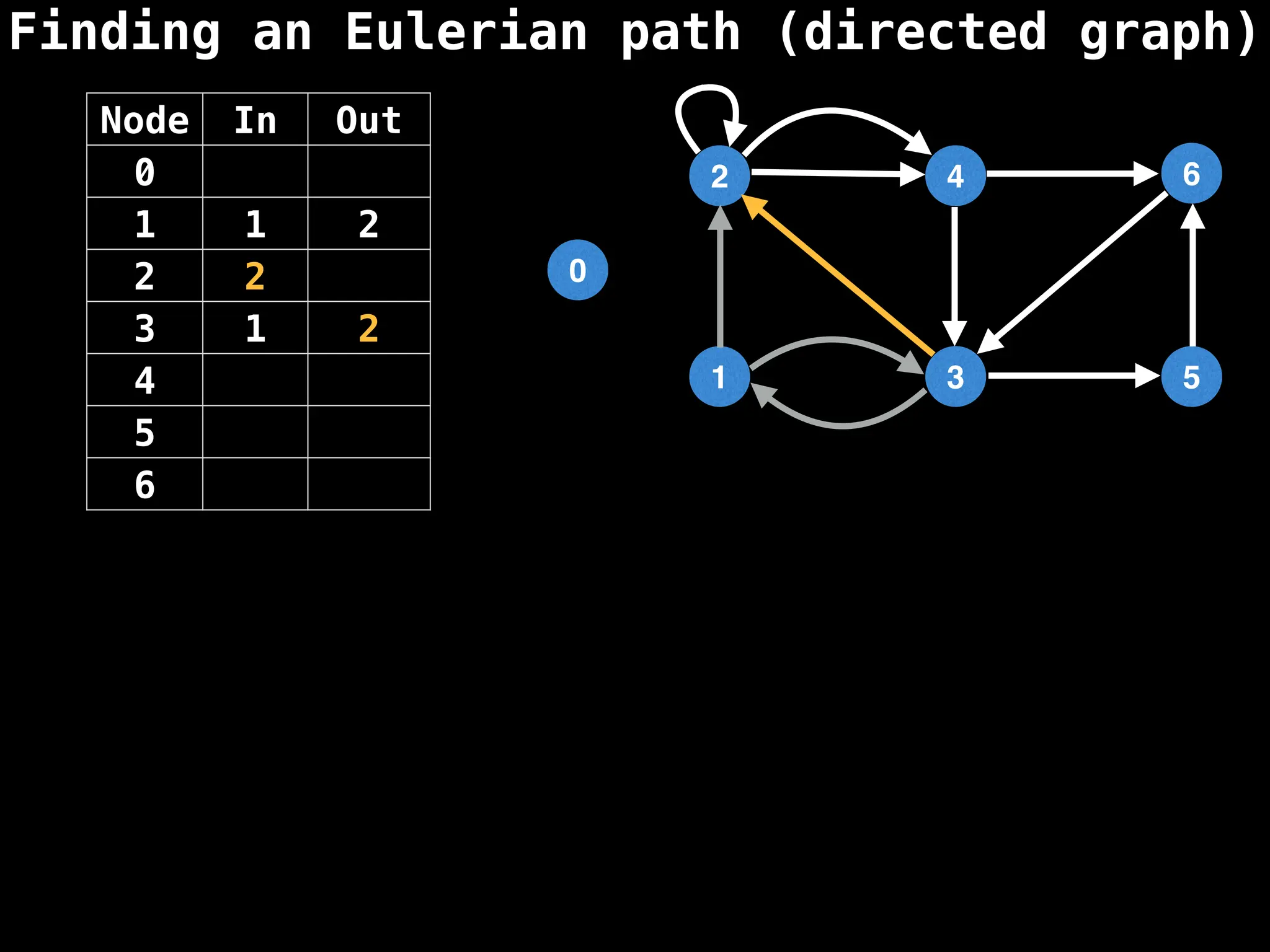
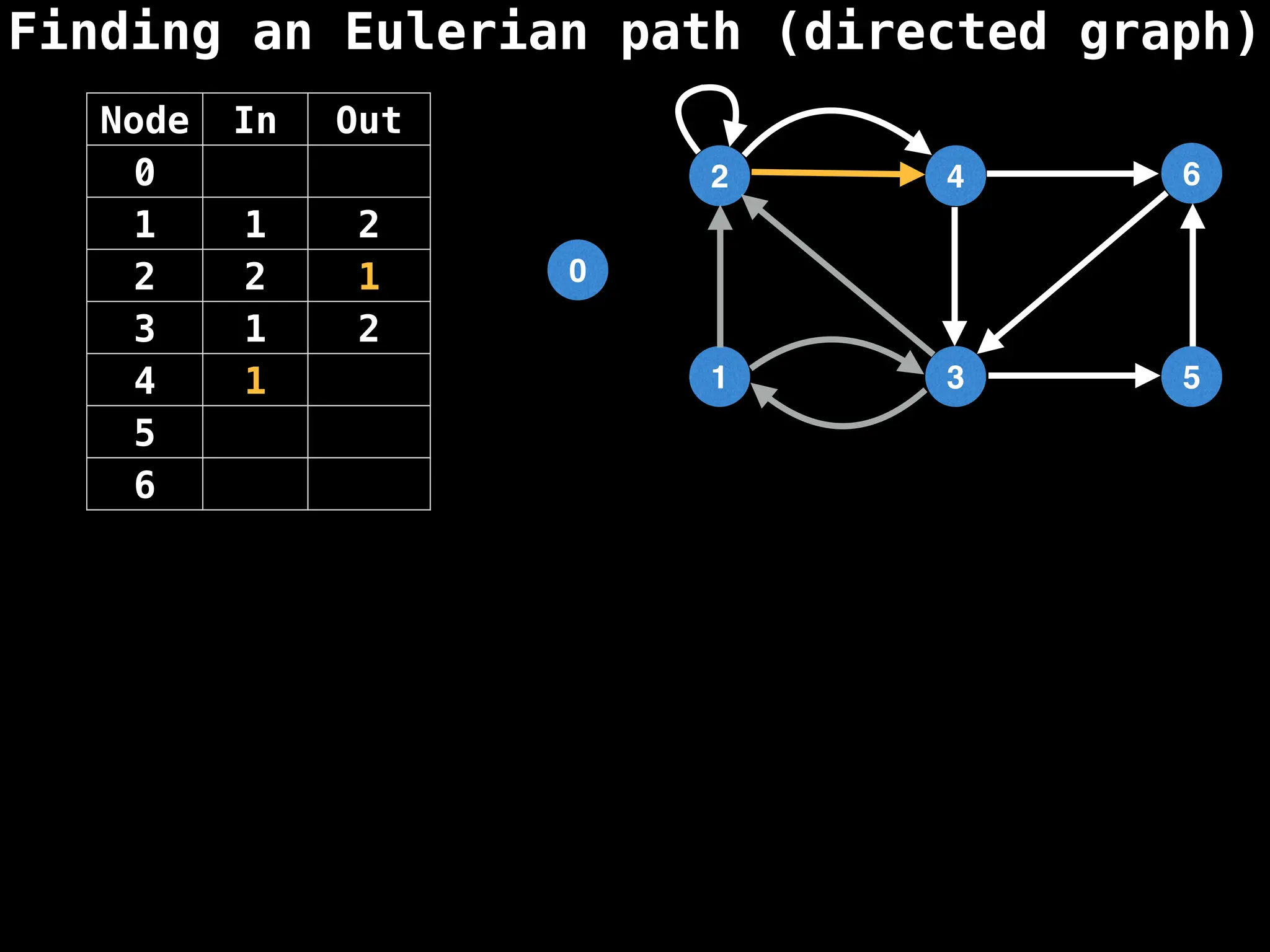
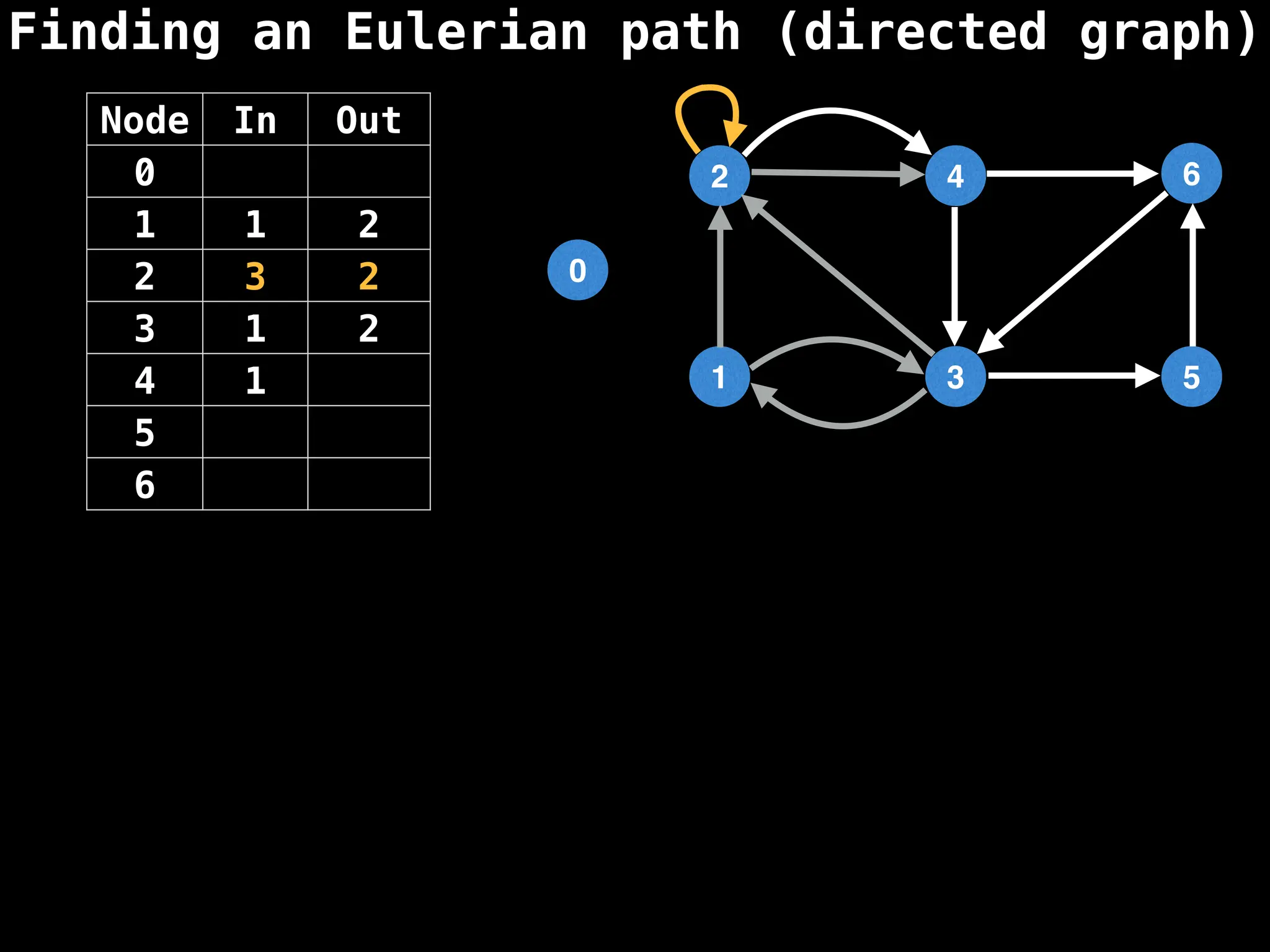
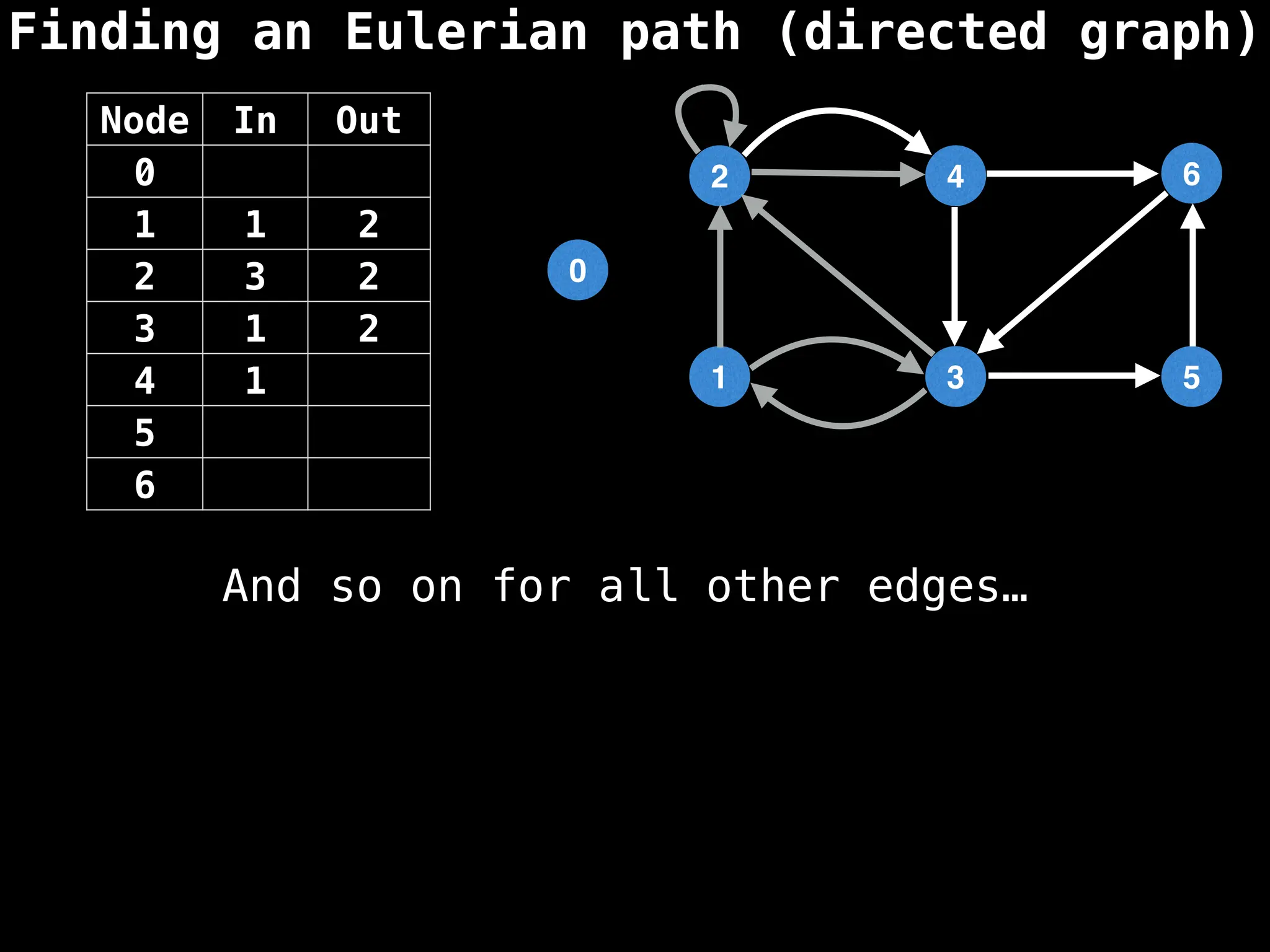
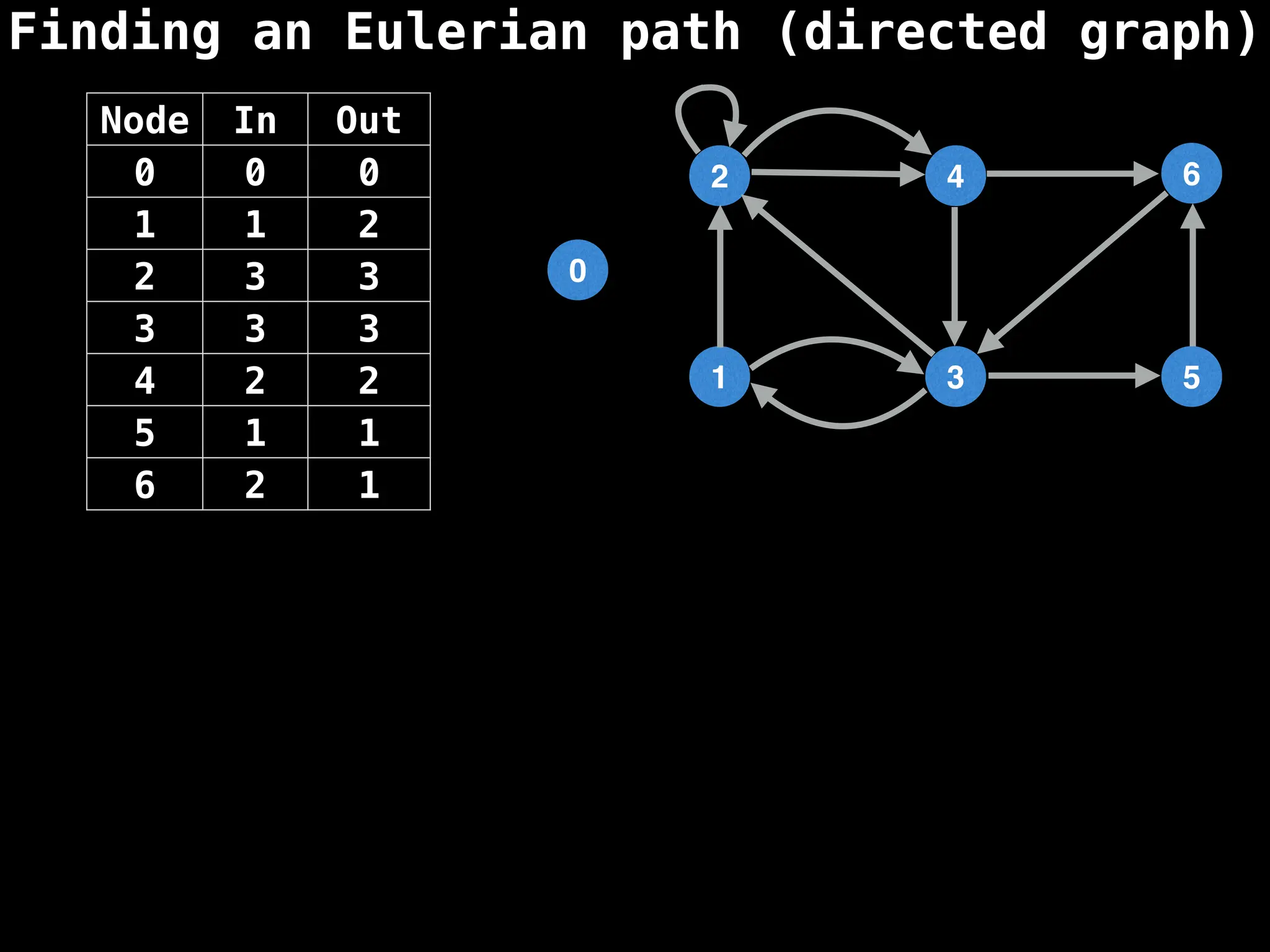
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node In Out
0 0 0
1 1 2
2 3 3
3 3 3
4 2 2
5 1 1
6 2 1
Once we’ve verified that no node has too many
outgoing edges (out[i] - in[i] > 1) or incoming
edges (in[i] - out[i] > 1) and there are just
the right amount of start/end nodes we can be
certain that an Eulerian path exists.
The next step is to find a valid starting node.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1148-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node In Out
0 0 0
1 1 2
2 3 3
3 3 3
4 2 2
5 1 1
6 2 1
Node 1 is the only node with exactly one extra outgoing
edge, so it’s our only valid start node. Similarly,
node 6 is the only node with exactly one extra incoming
edge, so it will end up being the end node.
out[1] - in[1] = 2 - 1 = 1
in[6] - out[6] = 2 - 1 = 1
Start node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1149-2048.jpg)
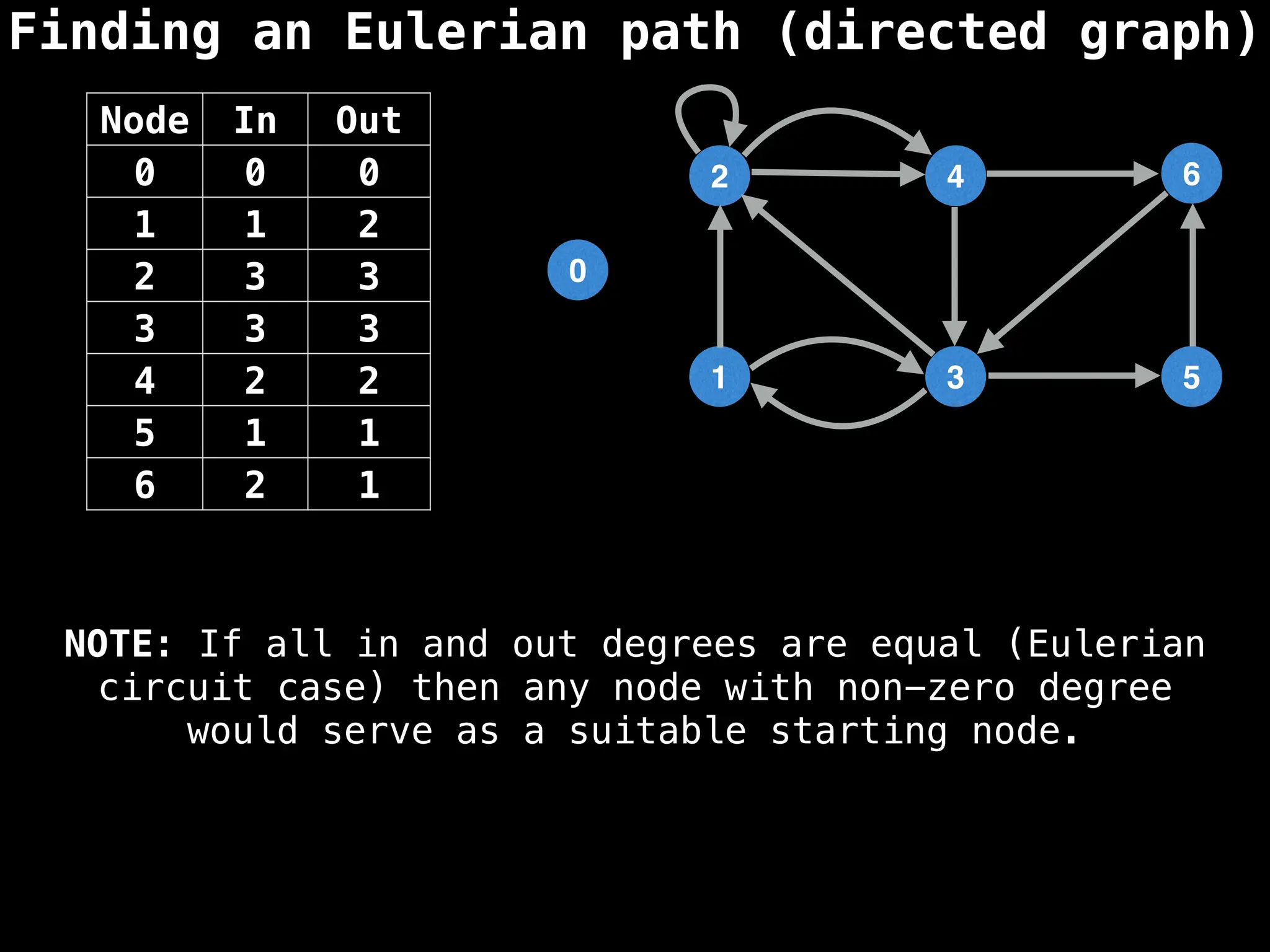
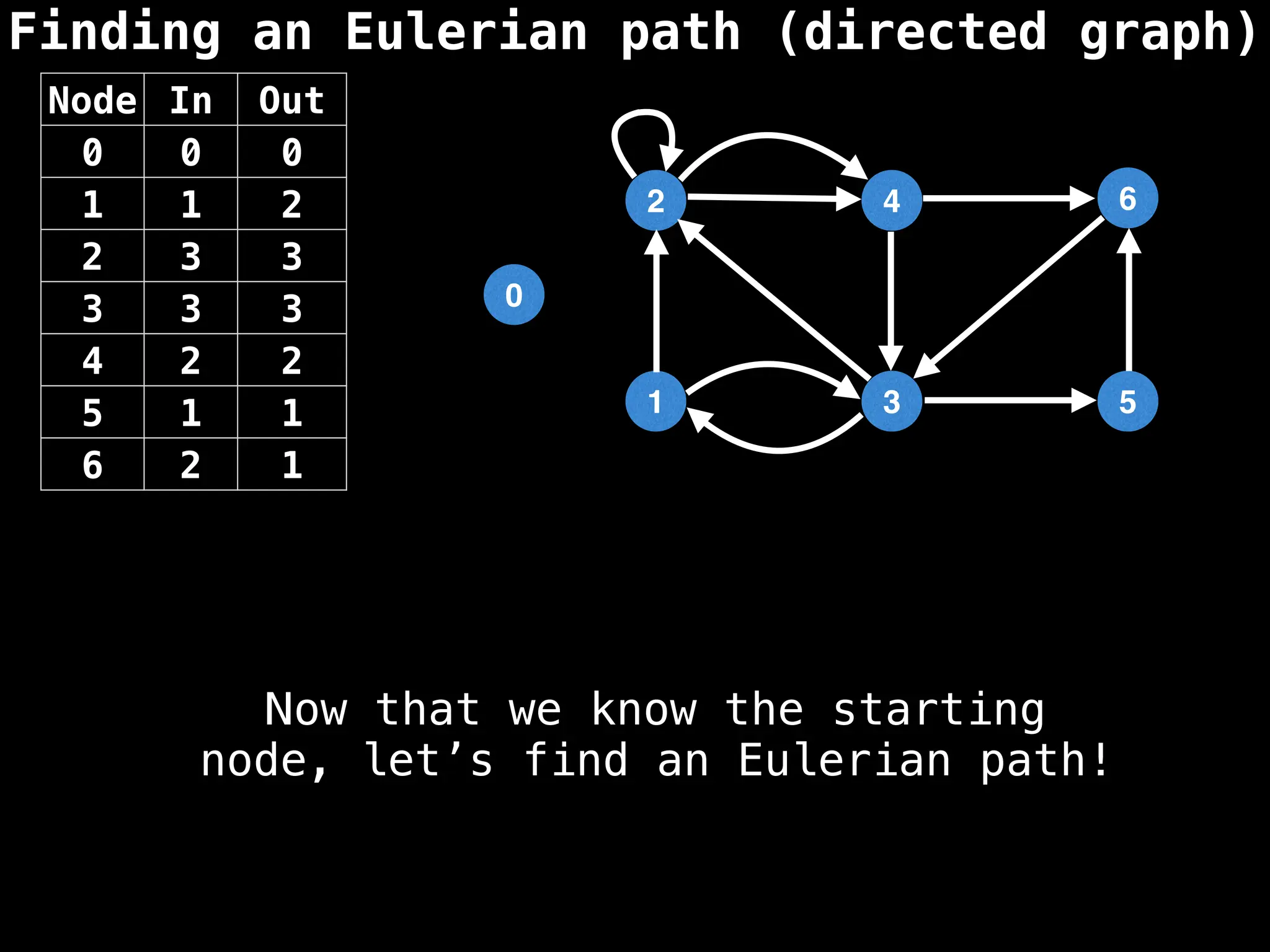
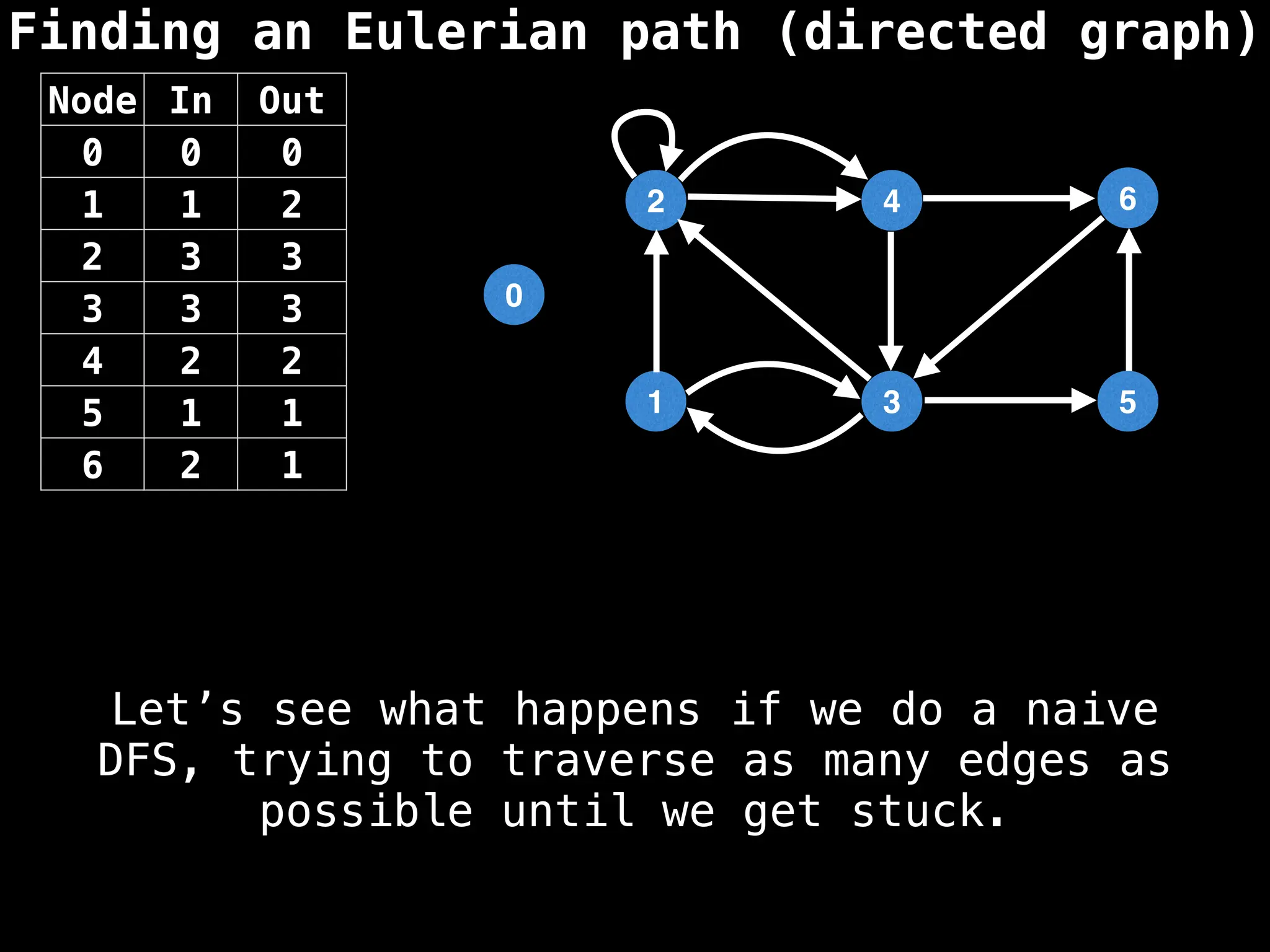
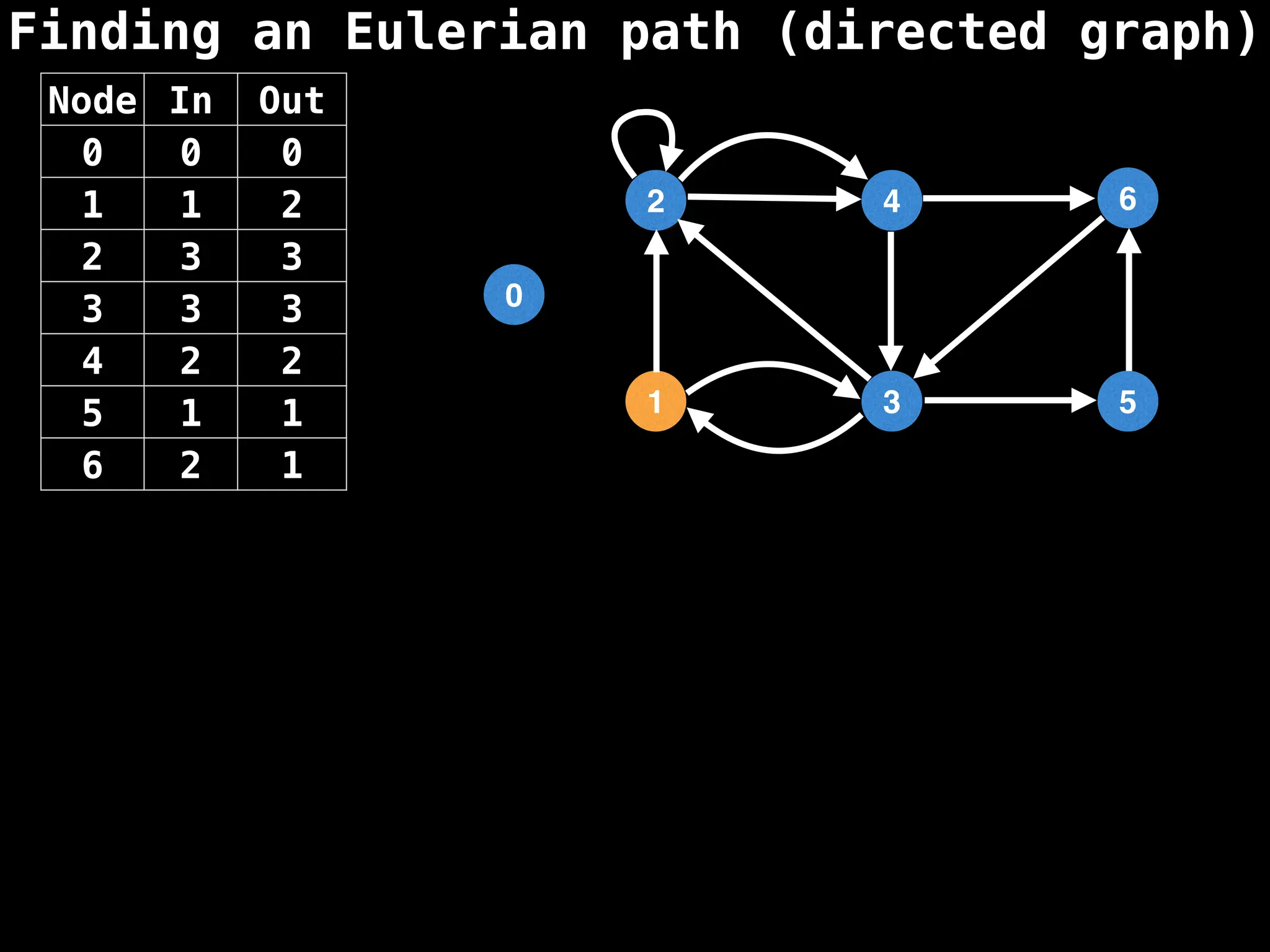
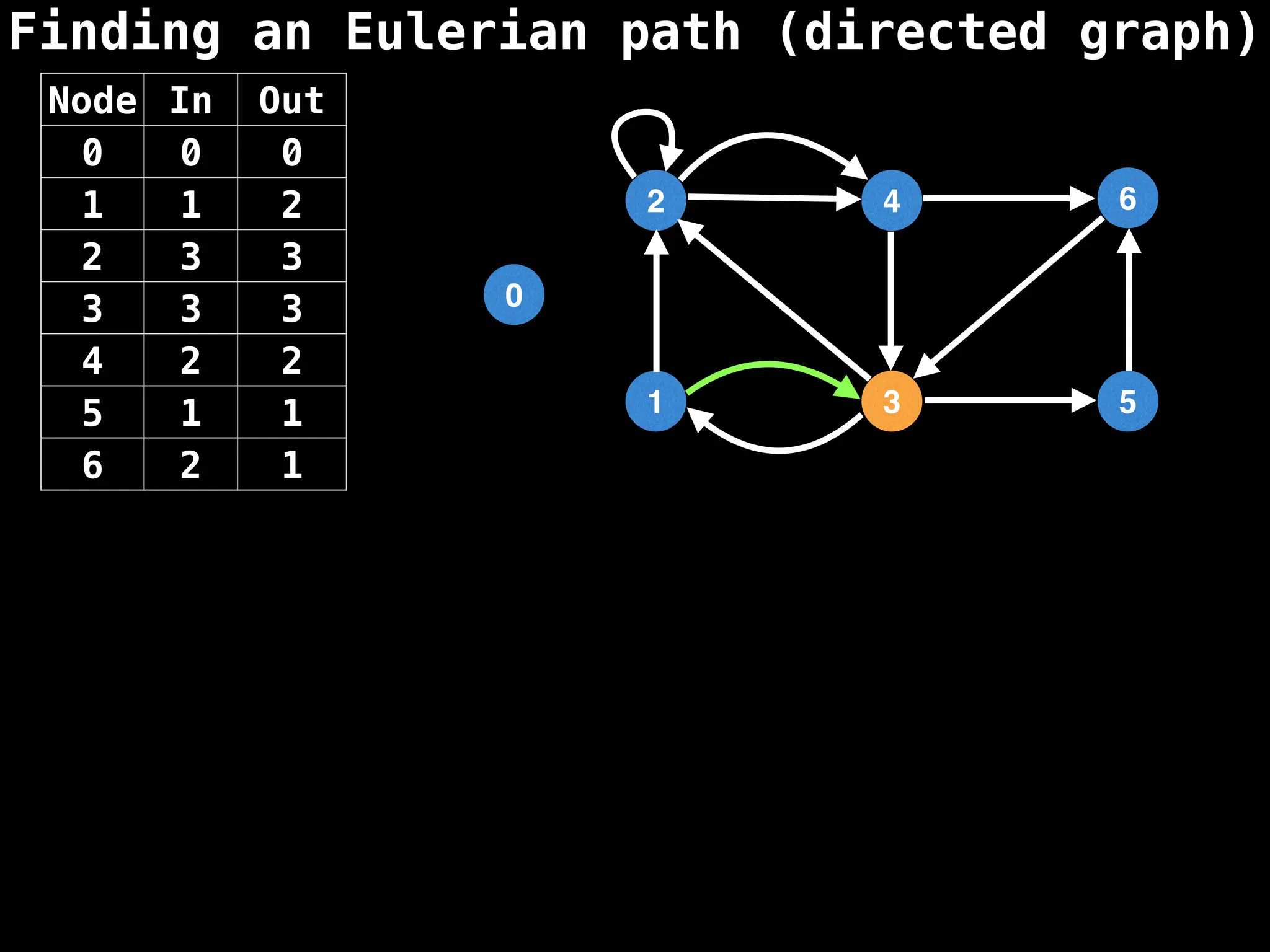
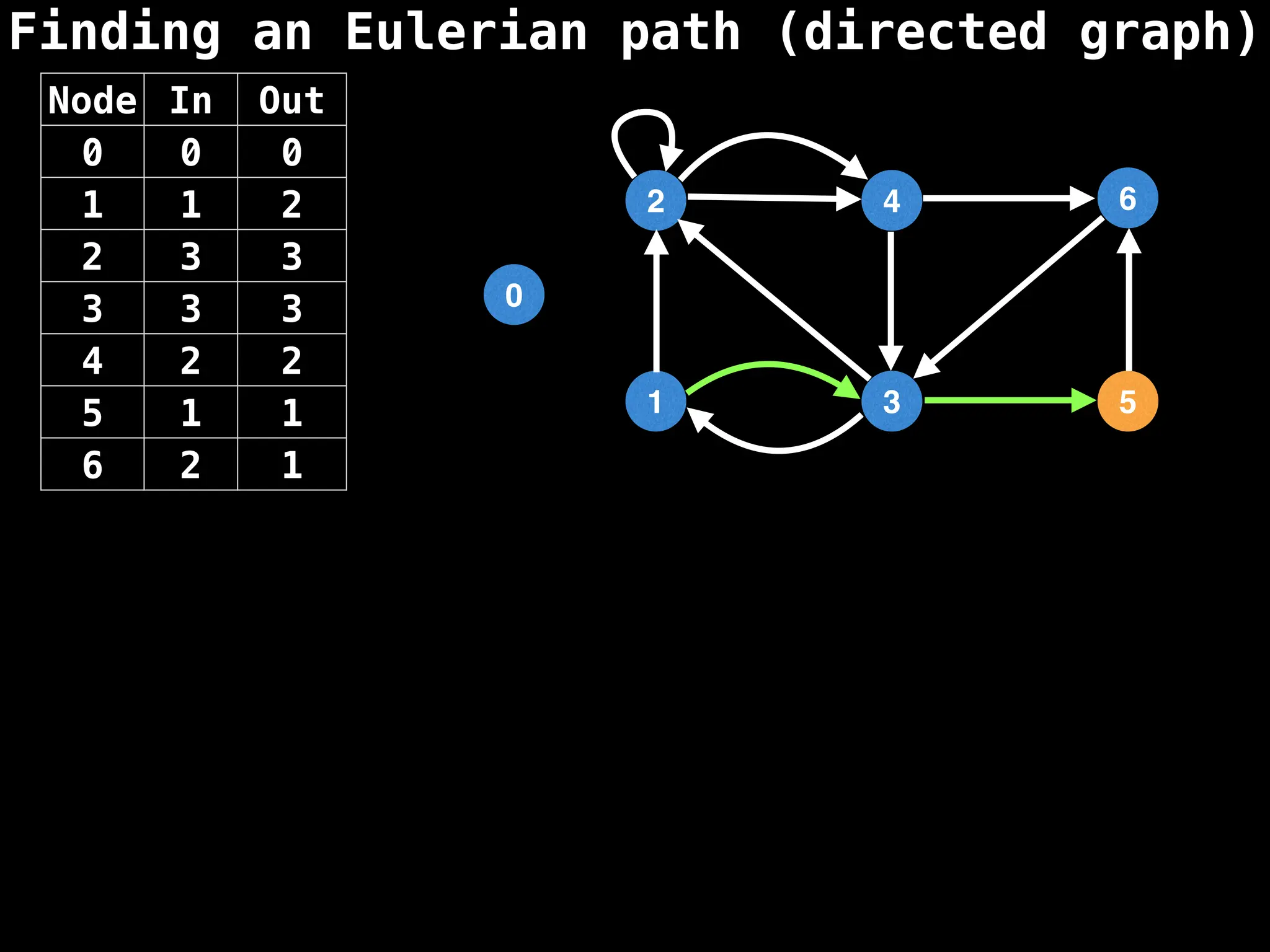
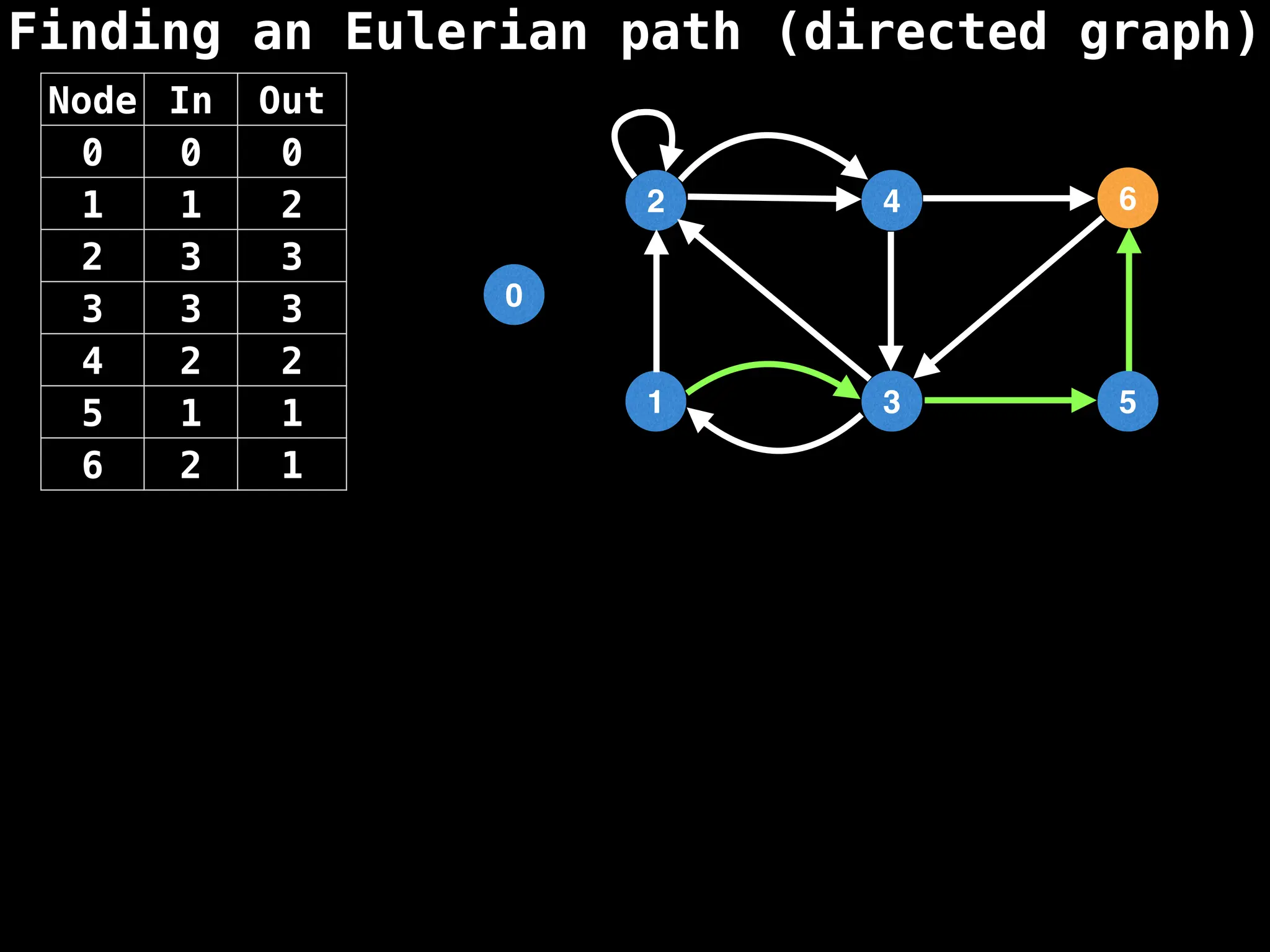
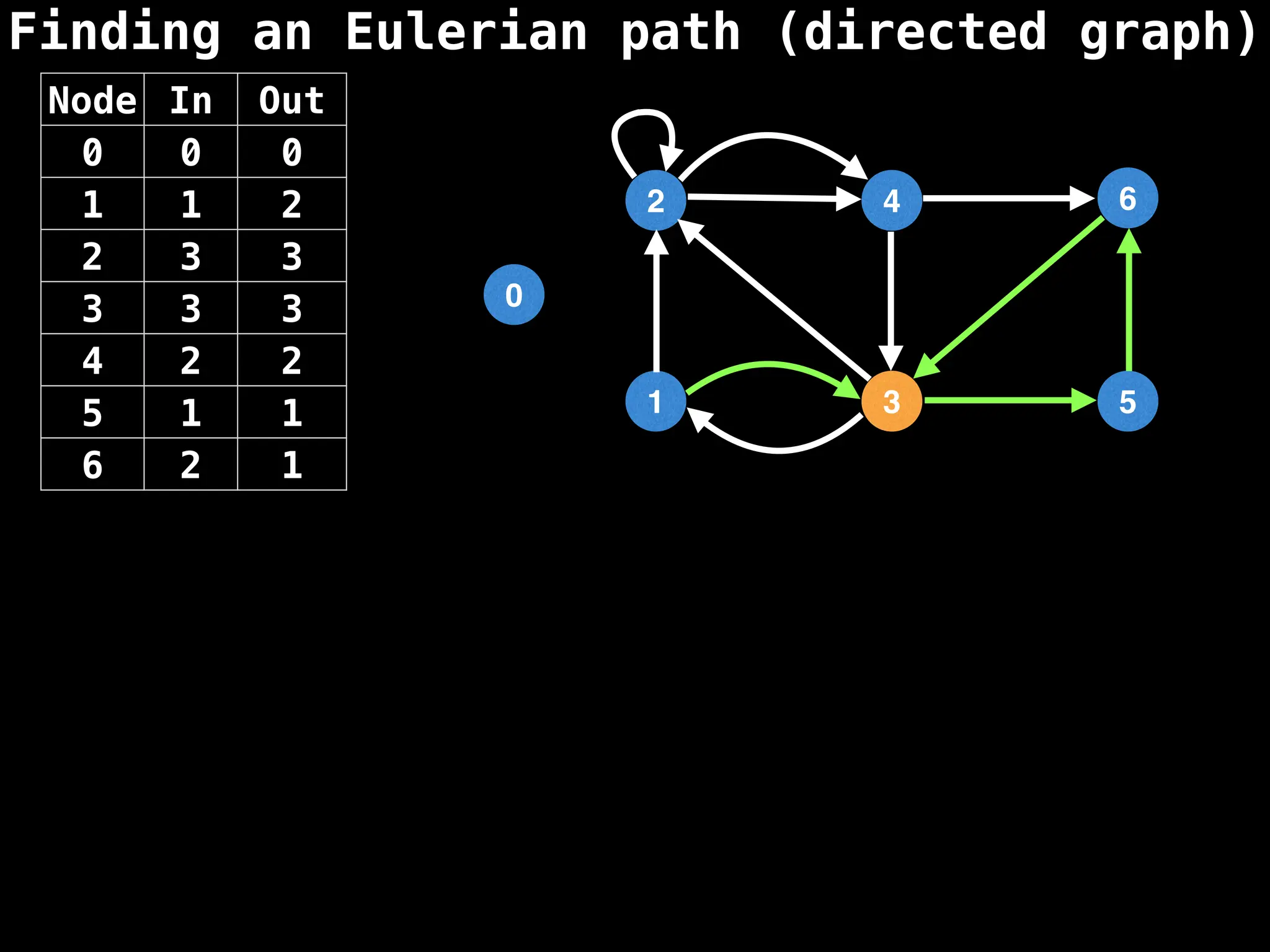
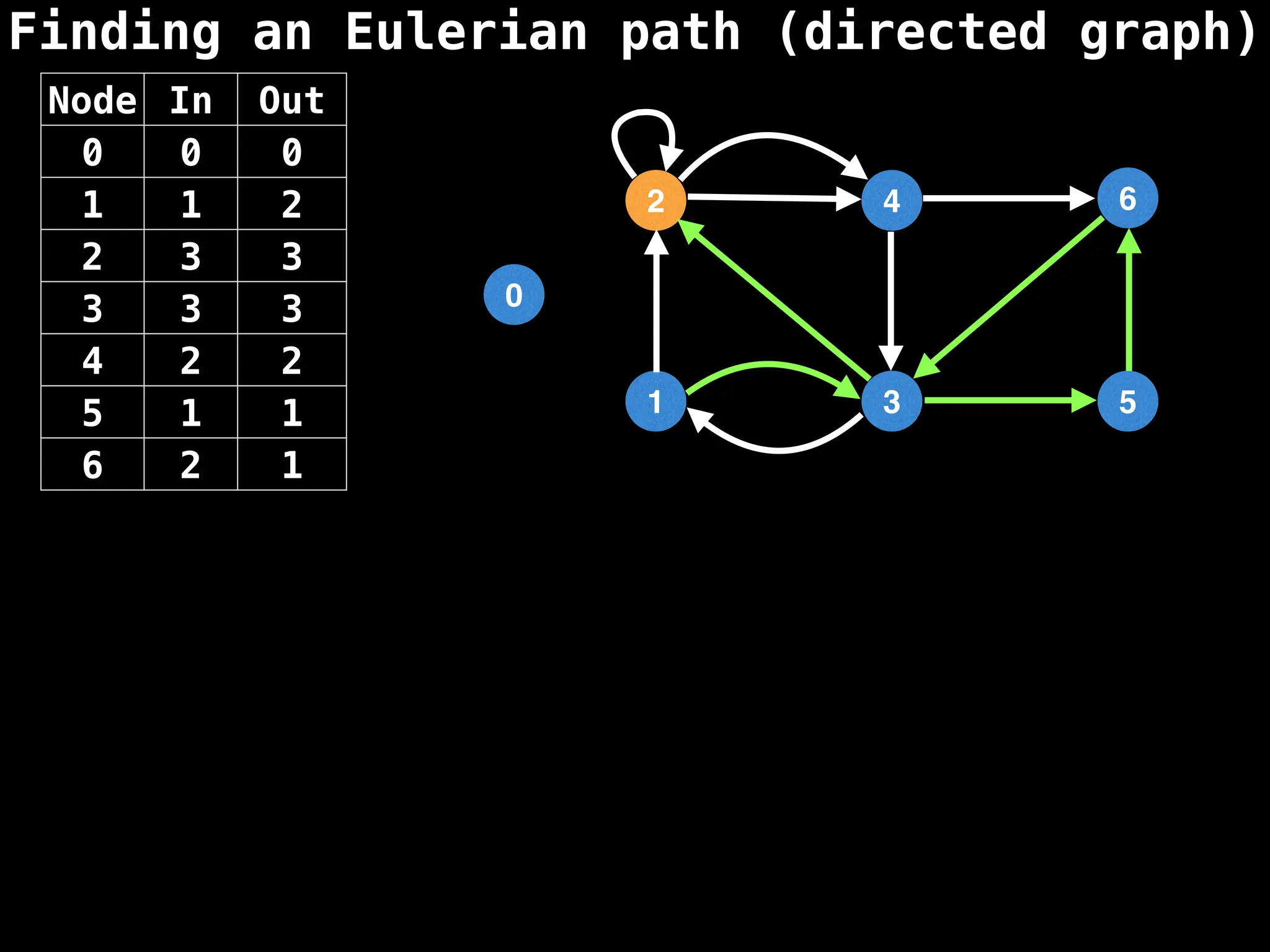
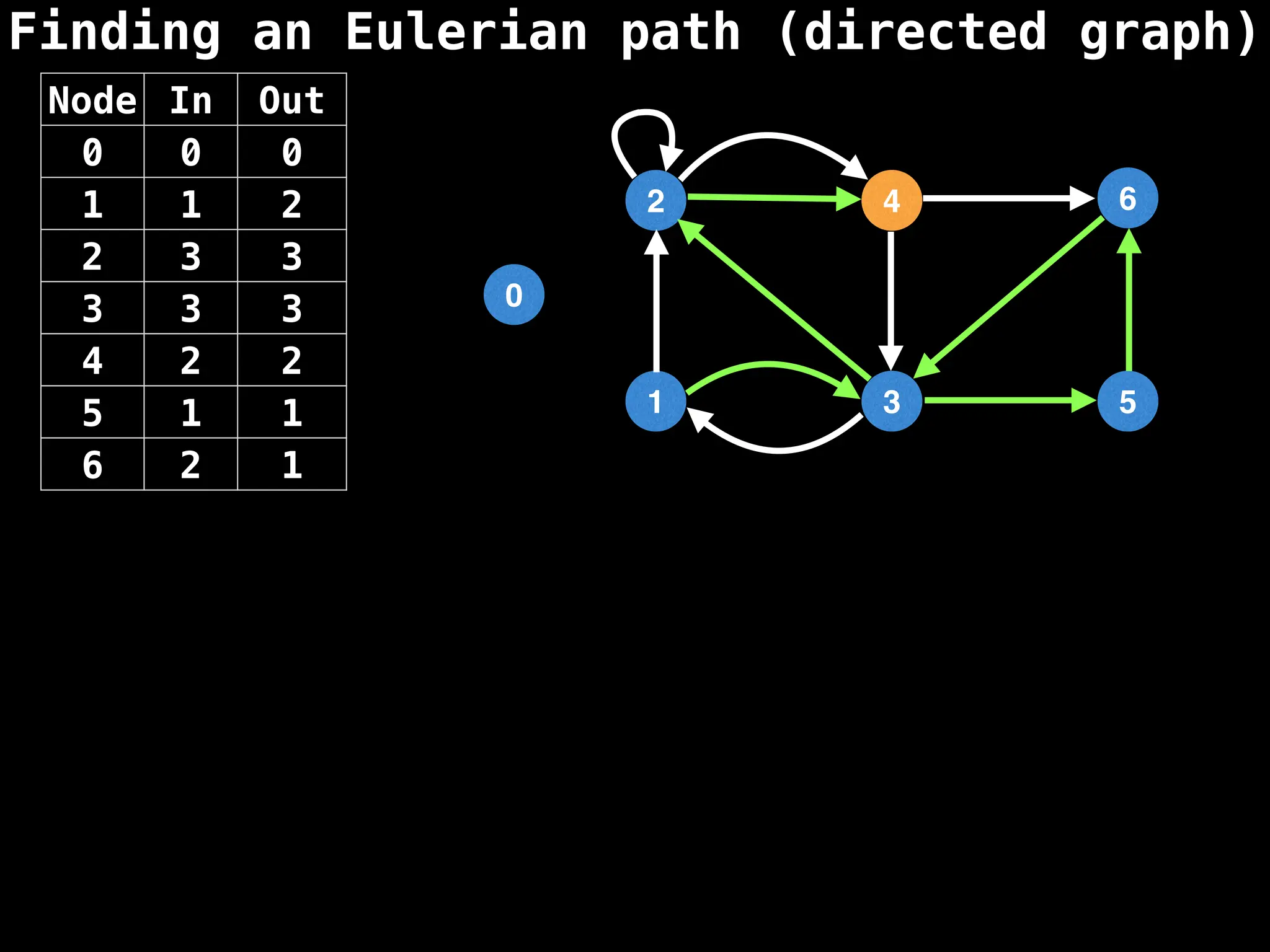
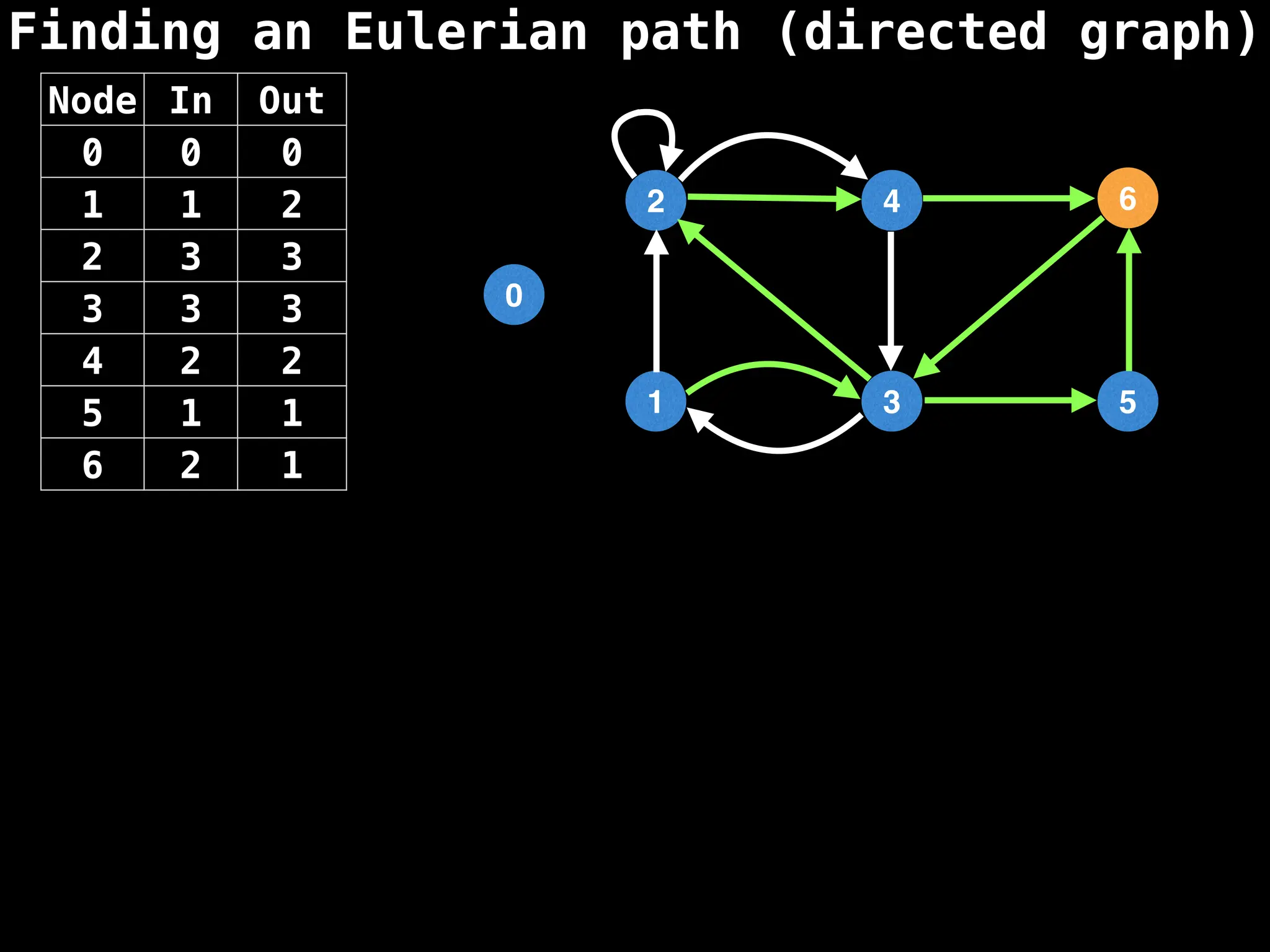
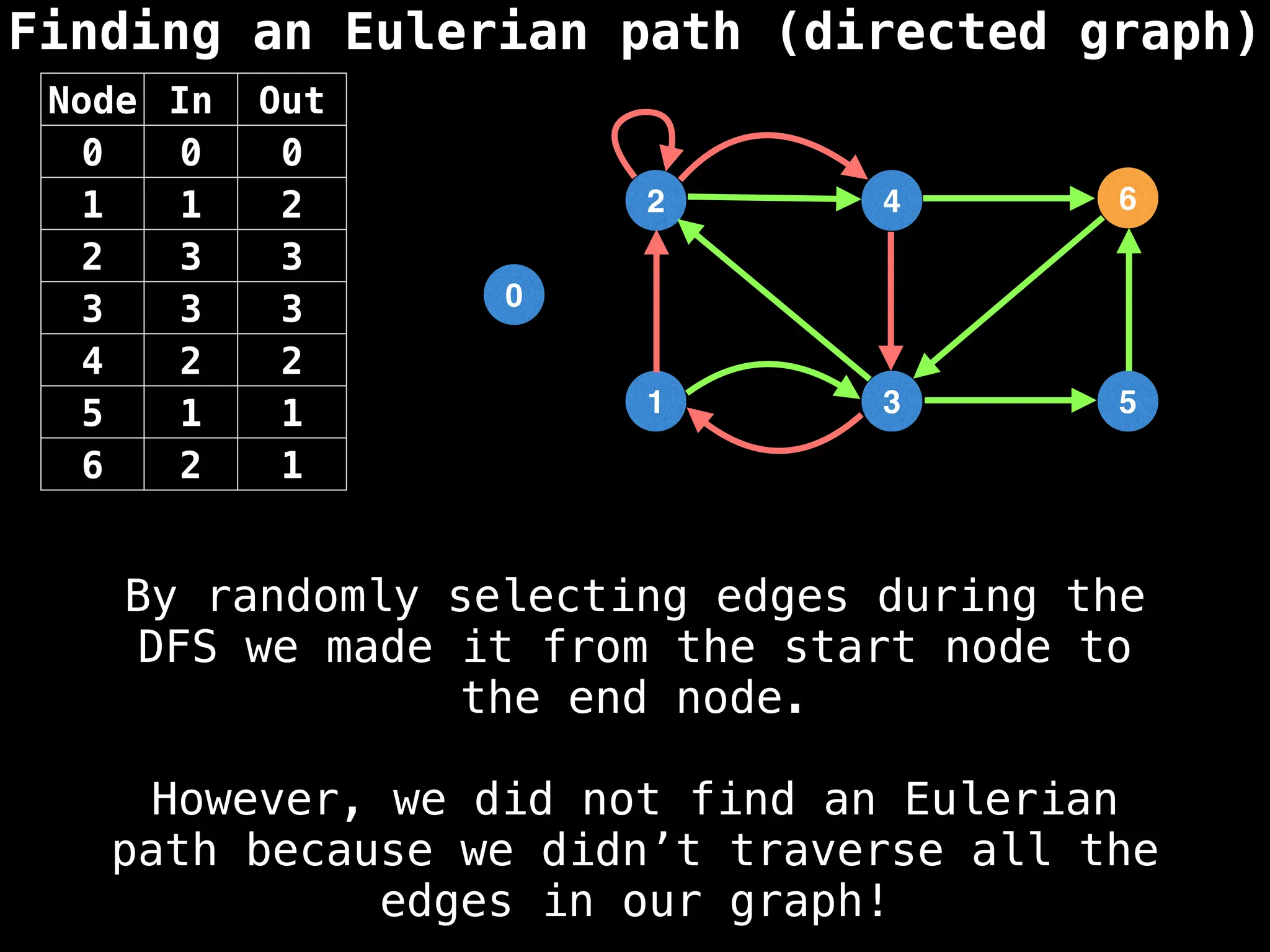
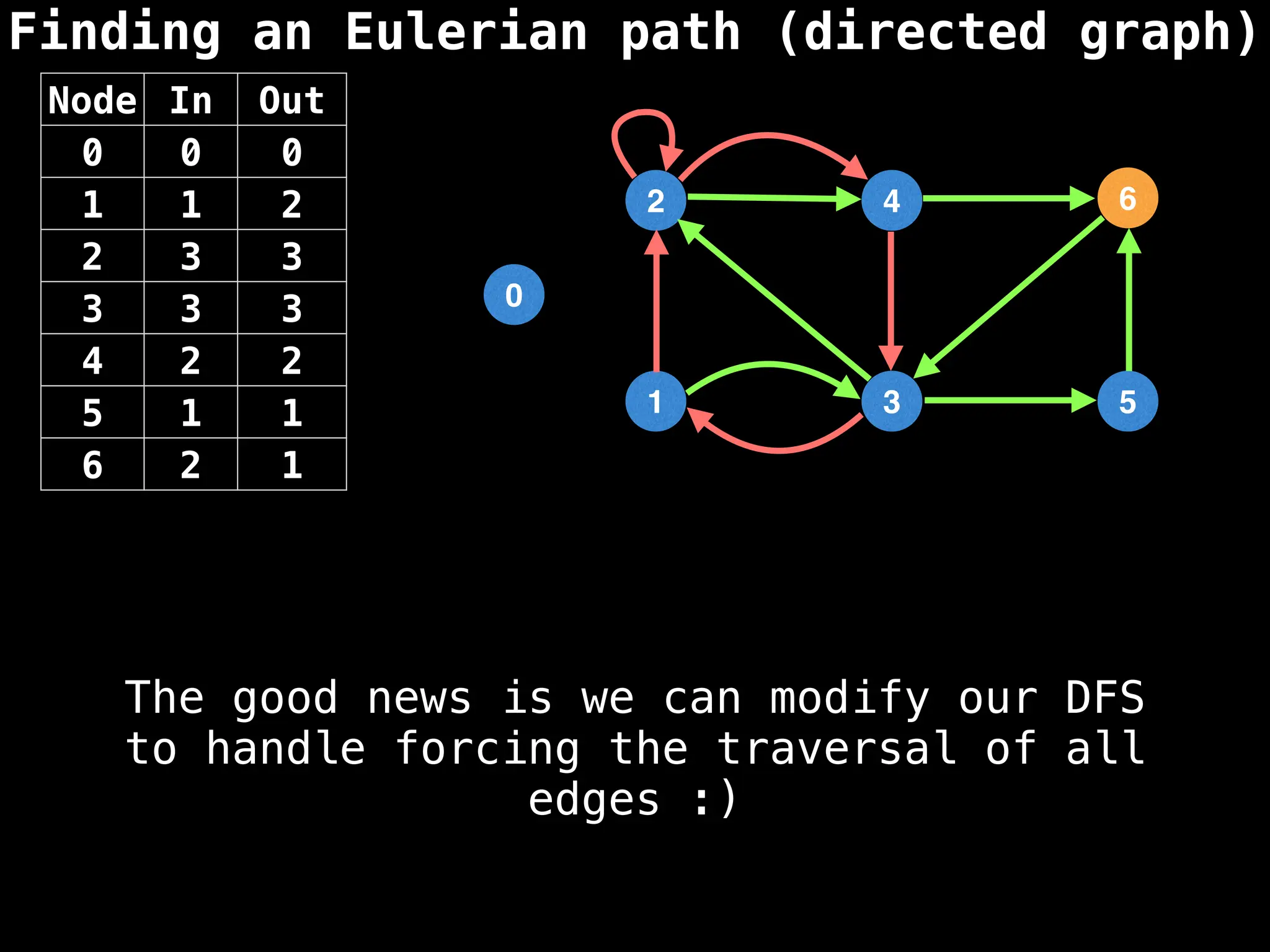
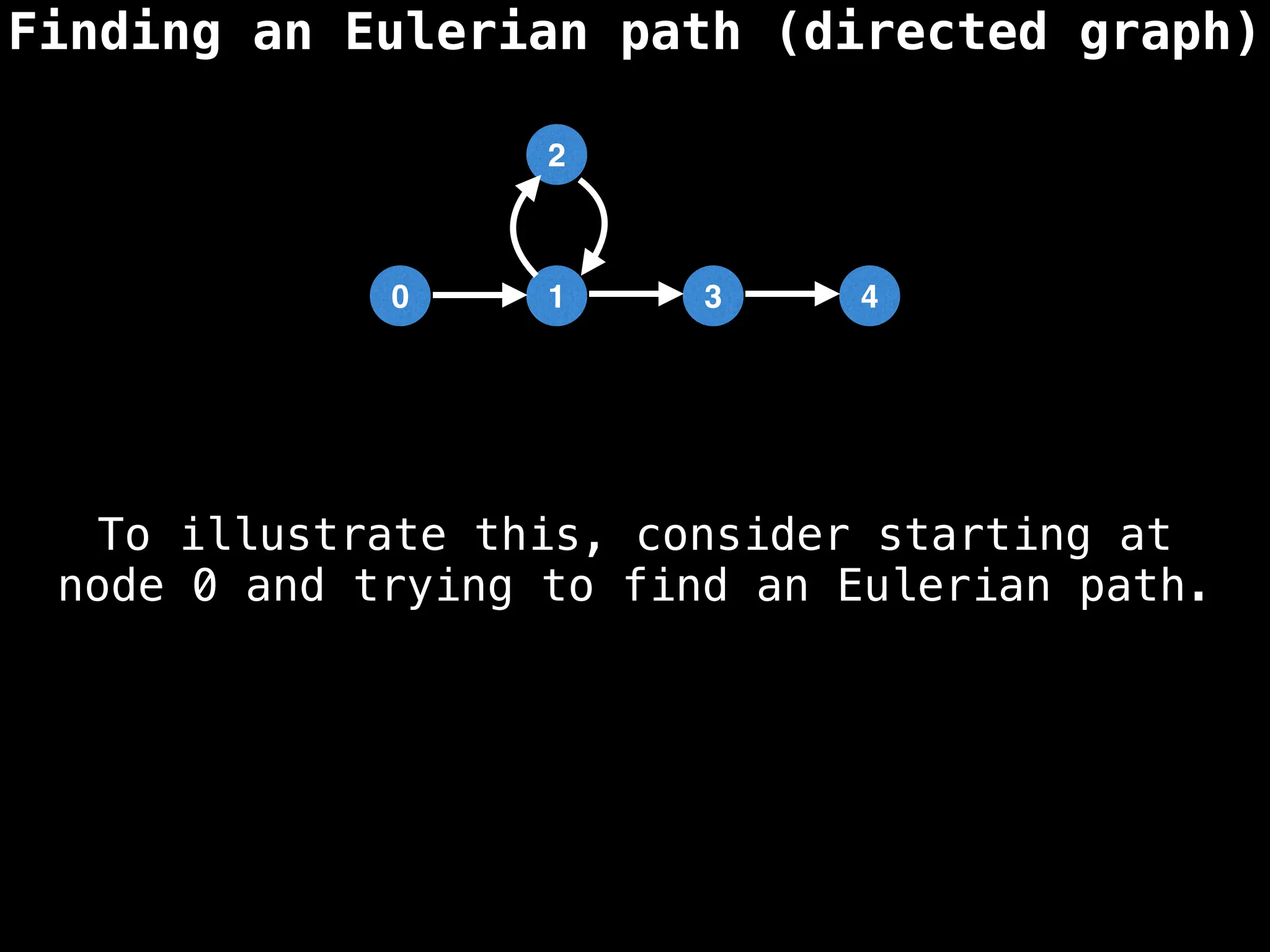
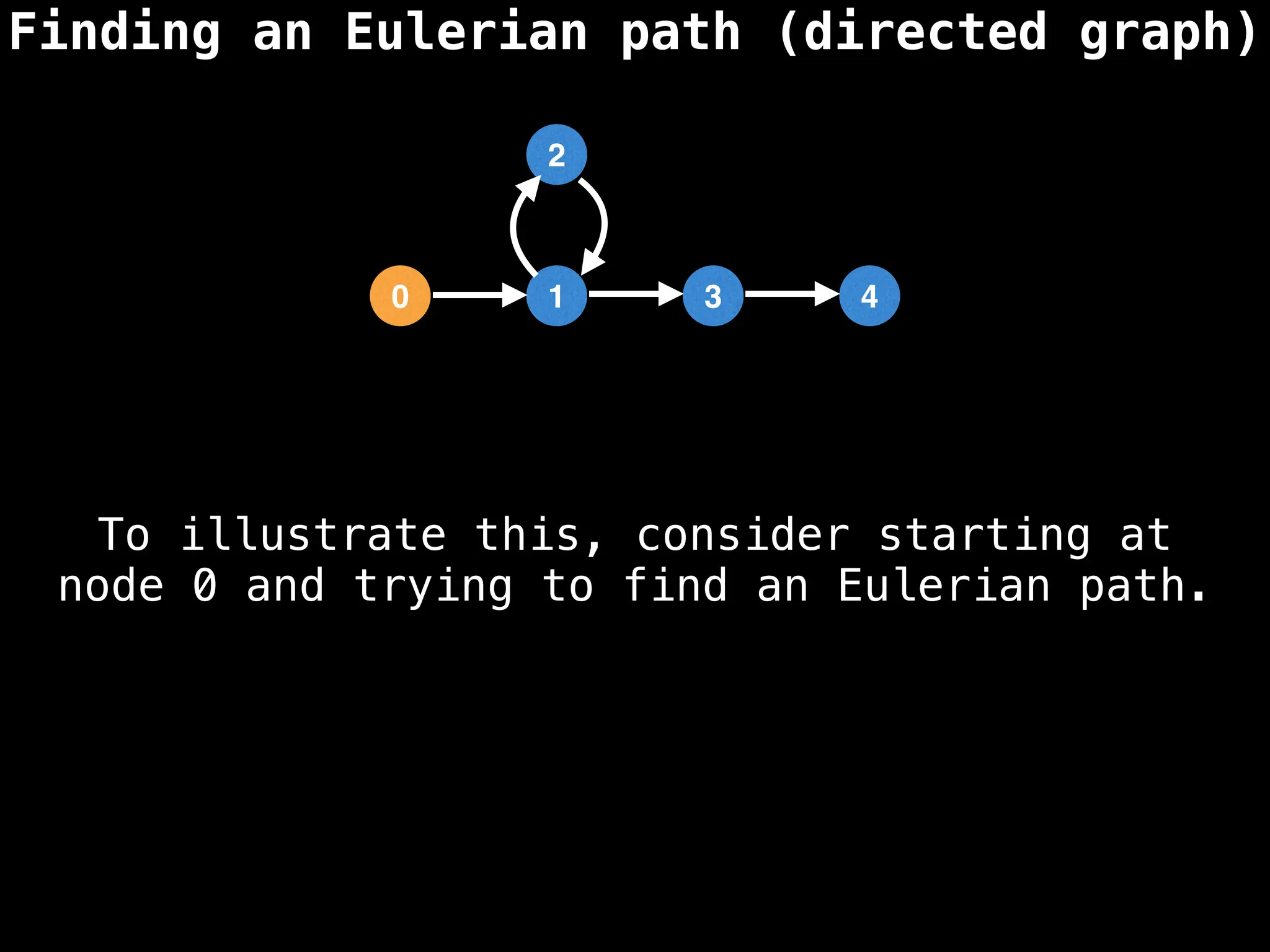
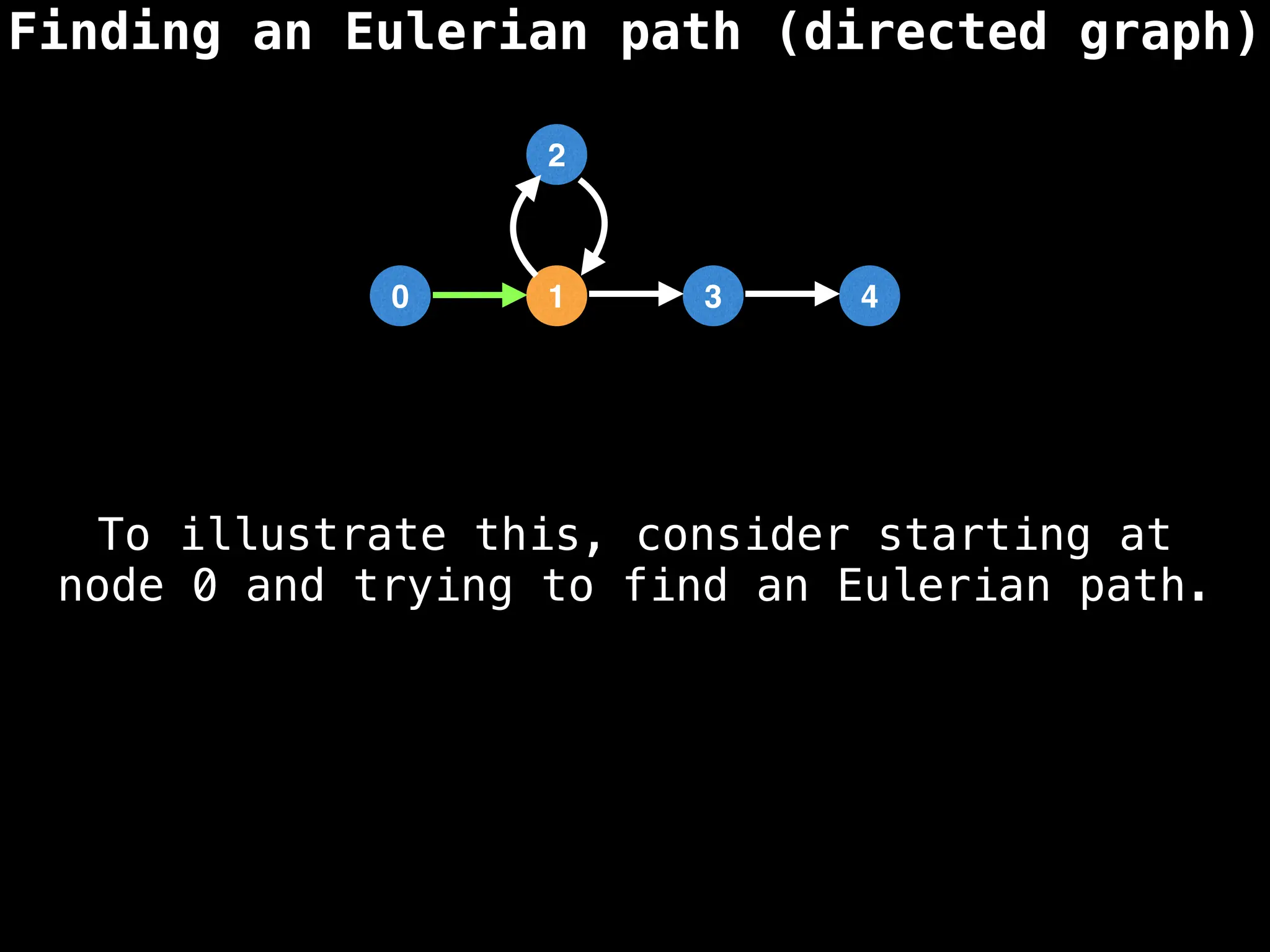
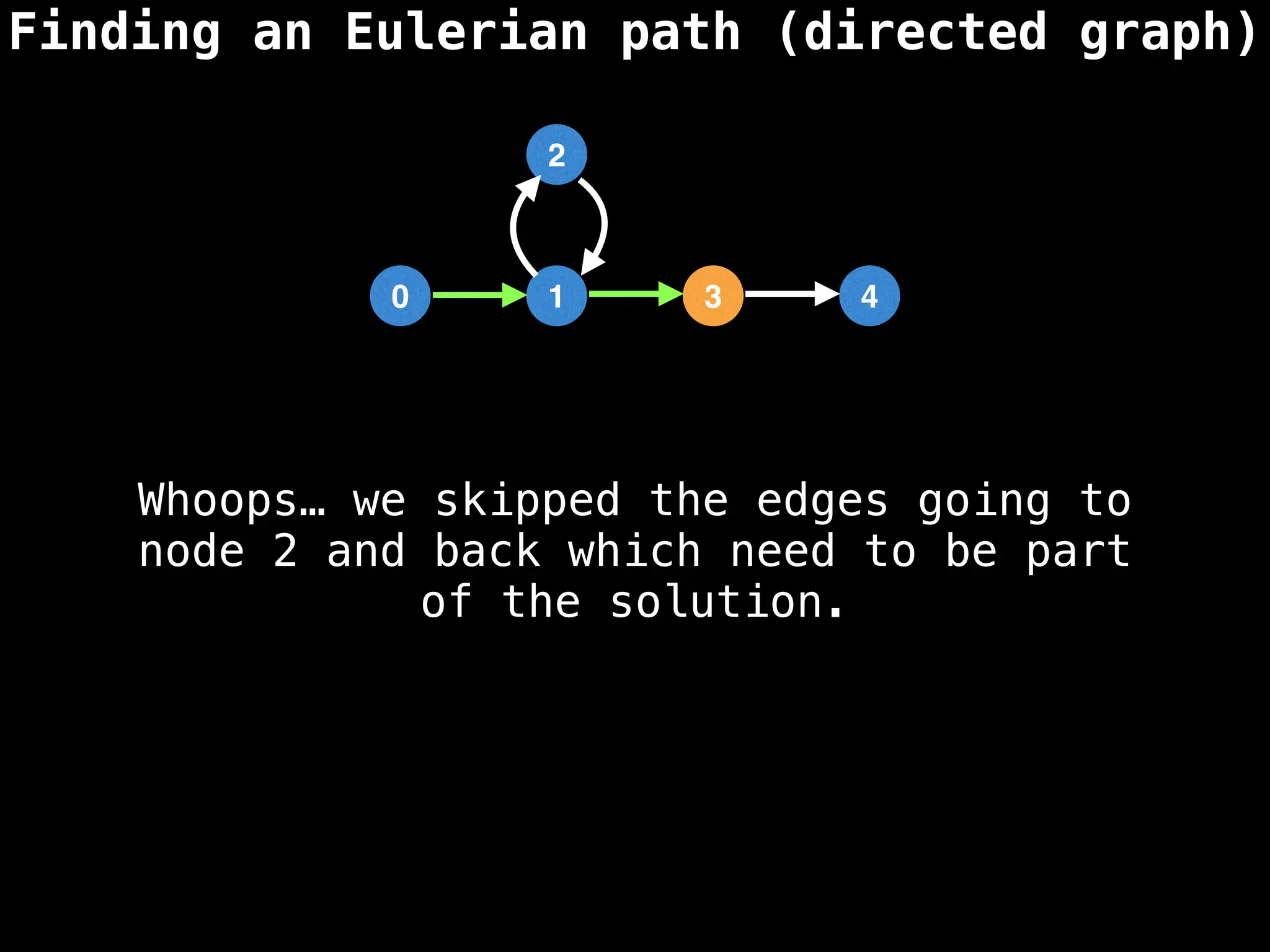

![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [4]
Once we get stuck (meaning the current
node has no unvisited outgoing edges),
we backtrack and add the current node to
the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1168-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [3, 4]
When backtracking, if the current node has
any remaining unvisited edges (white edges)
we follow any of them calling our DFS method
recursively to extend the Eulerian path.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1169-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [3, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1170-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [3, 4]
Once we get stuck (meaning the current
node has no unvisited outgoing edges),
we backtrack and add the current node to
the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1171-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [1, 3, 4]
Once we get stuck (meaning the current
node has no unvisited outgoing edges),
we backtrack and add the current node to
the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1172-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [2, 1, 3, 4]
Once we get stuck (meaning the current
node has no unvisited outgoing edges),
we backtrack and add the current node to
the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1173-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [1, 2, 1, 3, 4]
Once we get stuck (meaning the current
node has no unvisited outgoing edges),
we backtrack and add the current node to
the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1174-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0 1 3 4
2
Solution: [0, 1, 2, 1, 3, 4]
Once we get stuck (meaning the current
node has no unvisited outgoing edges),
we backtrack and add the current node to
the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1175-2048.jpg)
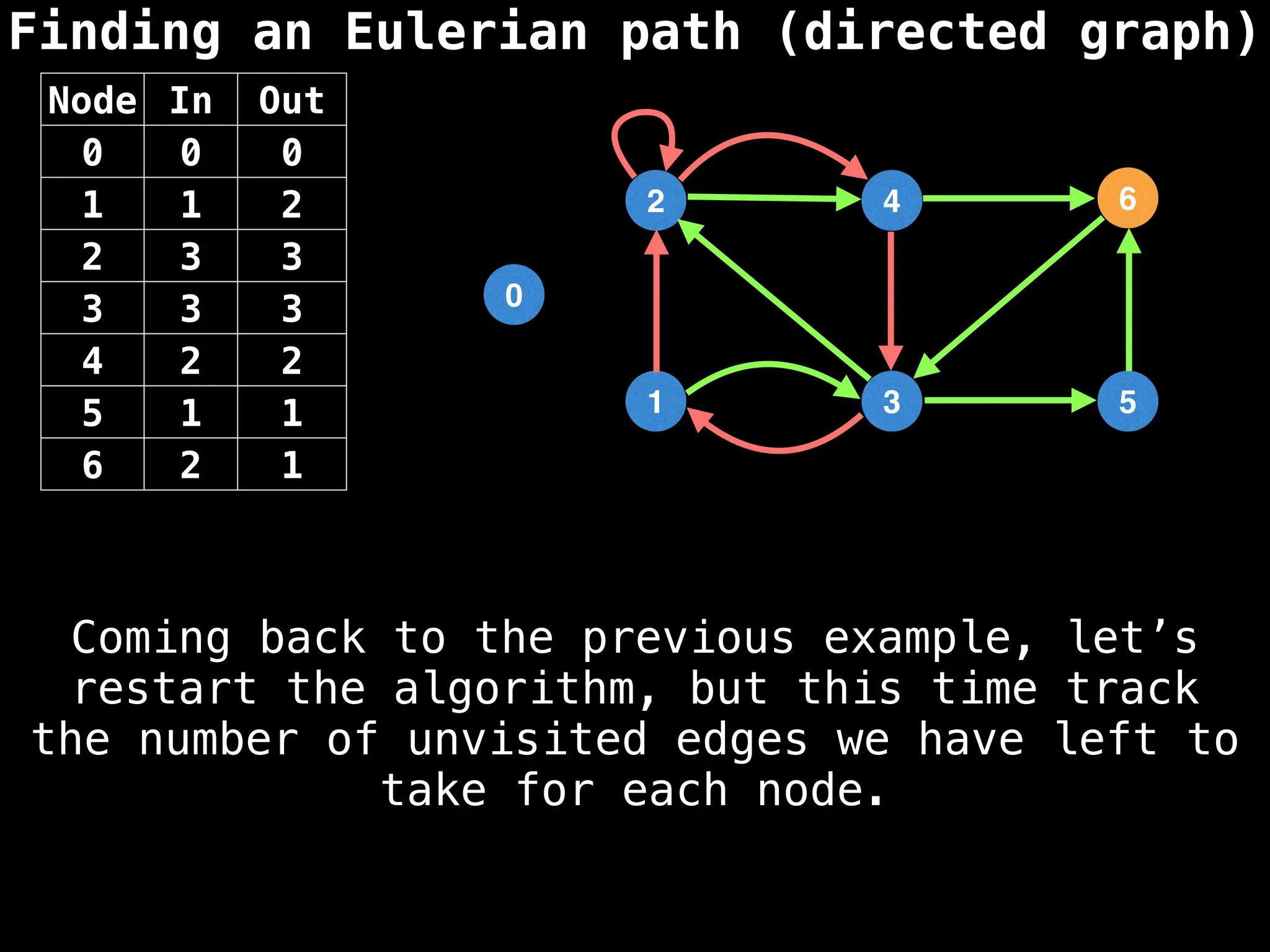
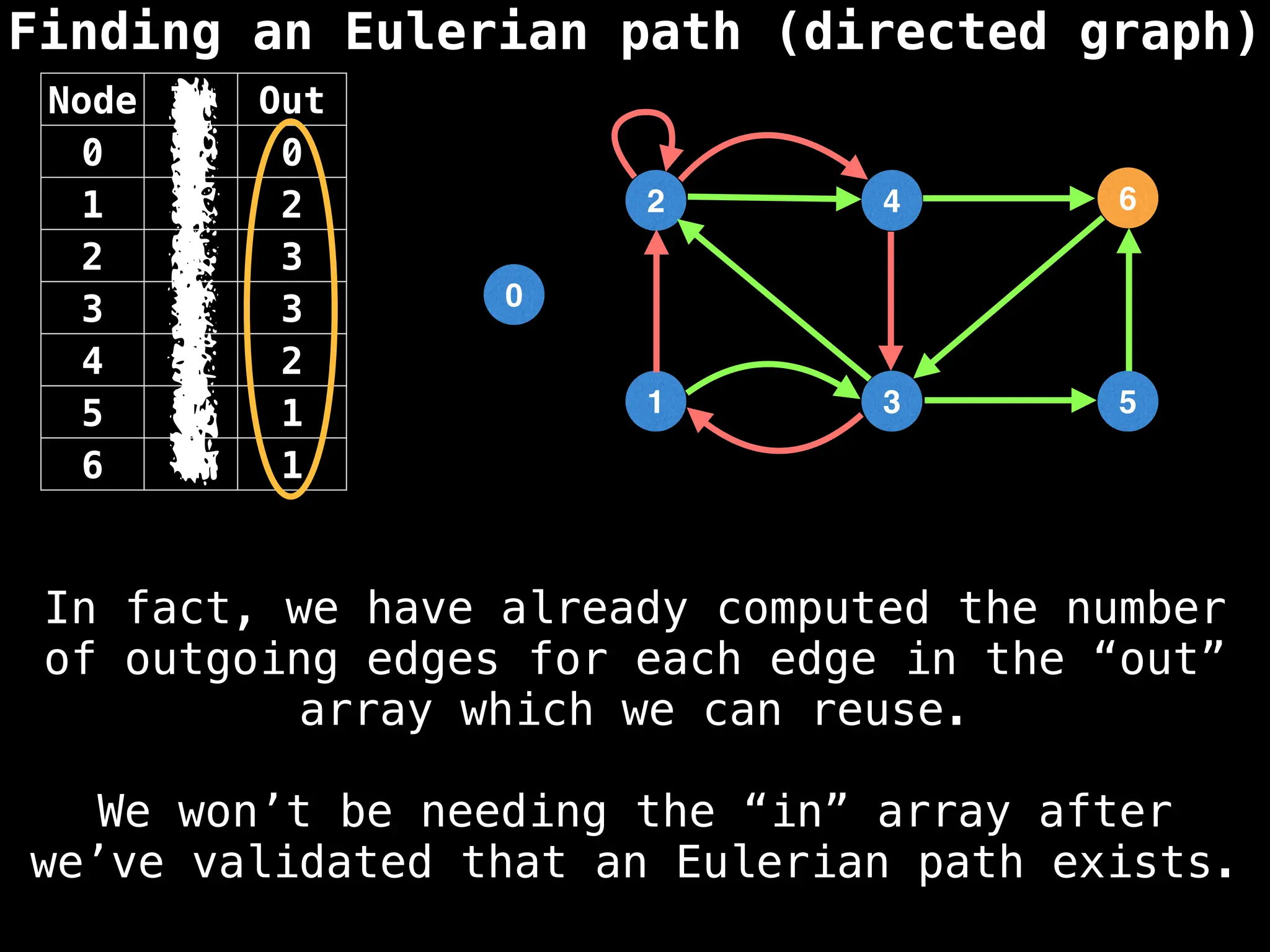
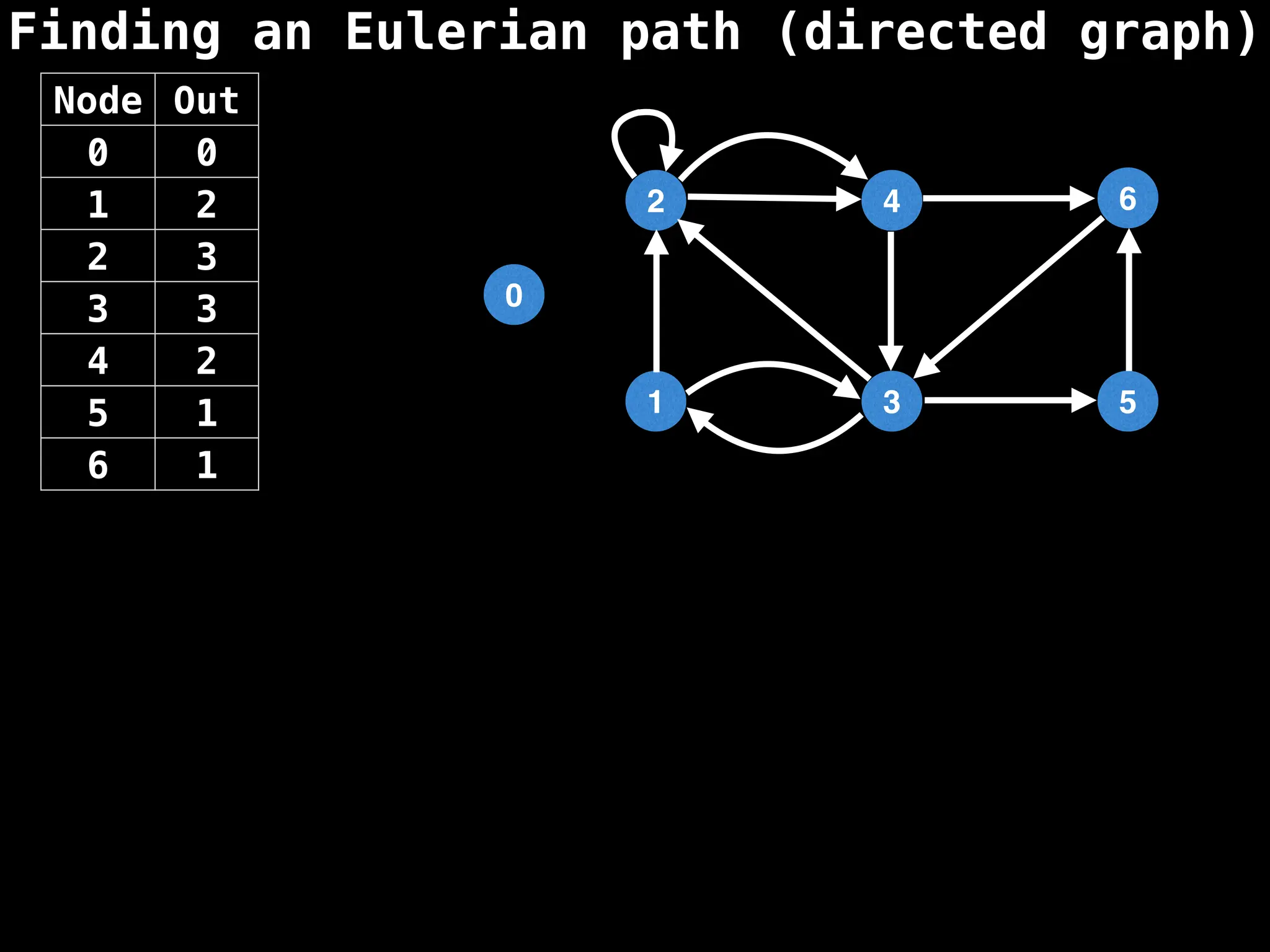
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 2
2 3
3 3
4 2
5 1
6 1
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1179-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 3
3 3
4 2
5 1
6 1
Every time an edge is taken, reduce the
outgoing edge count in the out array.
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1180-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 3
3 2
4 2
5 1
6 1
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1181-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 3
3 2
4 2
5 0
6 1
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1182-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 3
3 2
4 2
5 0
6 0
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1183-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 3
3 1
4 2
5 0
6 0
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1184-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 1
4 2
5 0
6 0
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1185-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 1
4 1
5 0
6 0
Solution = []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1186-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = []
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 1
4 1
5 0
6 0
When the DFS is stuck, meaning there are
no more outgoing edges (i.e out[i] = 0),
then we know to backtrack and add the
current node to the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1187-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [6]
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 1
4 1
5 0
6 0
When backtracking, if the current node has
any remaining unvisited edges (white edges),
we follow any of them, calling our DFS method
recursively to extend the Eulerian path. We
can verify there still are outgoing edges by
checking if out[i] != 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1188-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [6]
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 1
4 0
5 0
6 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1189-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [6]
Node Out
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1190-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [6]
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 2
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1191-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [6]
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 1
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1192-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [6]
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 1
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
When the DFS is stuck, meaning there are
no more outgoing edges (i.e out[i] = 0),
then we know to backtrack and add the
current node to the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1193-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [4,6]
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 1
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Node 2 still has an unvisited edge (since
out[i] != 0) so we need to follow that edge.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1194-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [4,6]
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
When the DFS is stuck, meaning there are
no more outgoing edges (i.e out[i] = 0),
then we know to backtrack and add the
current node to the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1195-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [2,4,6]
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1196-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Solution = [2,2,4,6]
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1197-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1198-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1199-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [4,3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1200-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [2,4,3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1201-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [3,2,4,3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1202-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [6,3,2,4,3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1203-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [5,6,3,2,4,3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1204-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [3,5,6,3,2,4,3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1205-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [1,3,5,6,3,2,4,3,1,2,2,4,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1206-2048.jpg)
![Finding an Eulerian path (directed graph)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Node Out
0 0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
Solution = [1,3,5,6,3,2,4,3,1,2,2,4,6]
The time complexity to find an eulerian
path with this algorithm is O(E). The two
calculations we’re doing: computing in/out
degrees + DFS are both linear in the
number of edges.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1207-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1208-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1209-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1210-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1211-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1212-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1213-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1214-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1215-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1216-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1217-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1218-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1219-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1220-2048.jpg)
![function countInOutDegrees():
for edges in g:
for edge in edges:
out[edge.from]++
in[edge.to]++
function graphHasEulerianPath():
start_nodes, end_nodes = 0, 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++):
if (out[i] - in[i]) > 1 or (in[i] - out[i]) > 1:
return false
else if out[i] - in[i] == 1:
start_nodes++
else if in[i] - out[i] == 1:
end_nodes++
return (end_nodes == 0 and start_nodes == 0) or
(end_nodes == 1 and start_nodes == 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1221-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1222-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1223-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1224-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1225-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1226-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1227-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1228-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)
Avoids starting DFS
at a singleton](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1229-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1230-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1231-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1232-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1233-2048.jpg)
![function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)
The out array is currently serving two purposes. One
purpose is to track whether or not there are still
outgoing edges, and the other is to index into the
adjacency list to select the next outgoing edge.
This assumes the adjacency list stores edges in a
data structure that is indexable in O(1) (e.g stored
in an array). If not (e.g a linked-list/stack/etc…),
you can use an iterator to iterate over the edges.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1234-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1235-2048.jpg)
![function findStartNode():
start = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1):
# Unique starting node
if out[i] - in[i] == 1: return i
# Start at any node with an outgoing edge
if out[i] > 0: start = i
return start
function dfs(at):
# While the current node still has outgoing edges
while (out[at] != 0):
# Select the next unvisited outgoing edge
next_edge = g[at].get(——out[at])
dfs(next_edge.to)
# Add current node to solution
path.insertFirst(at)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1236-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1237-2048.jpg)
![# Global/class scope variables
n = number of vertices in the graph
m = number of edges in the graph
g = adjacency list representing directed graph
in = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
out = [0, 0, …, 0, 0] # Length n
path = empty integer linked list data structure
function findEulerianPath():
countInOutDegrees()
if not graphHasEulerianPath(): return null
dfs(findStartNode())
# Return eulerian path if we traversed all the
# edges. The graph might be disconnected, in which
# case it’s impossible to have an euler path.
if path.size() == m+1: return path
return null](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1238-2048.jpg)


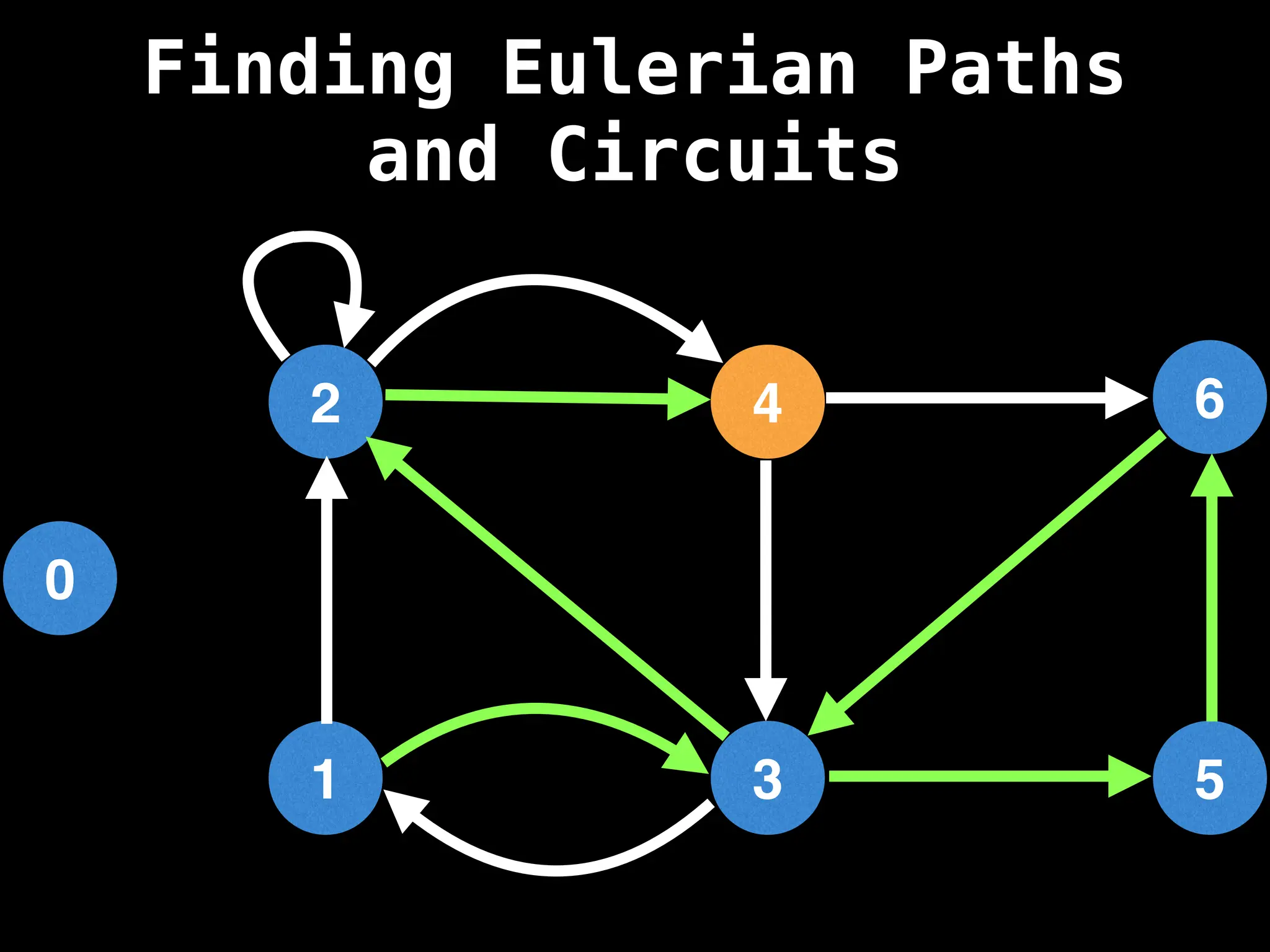

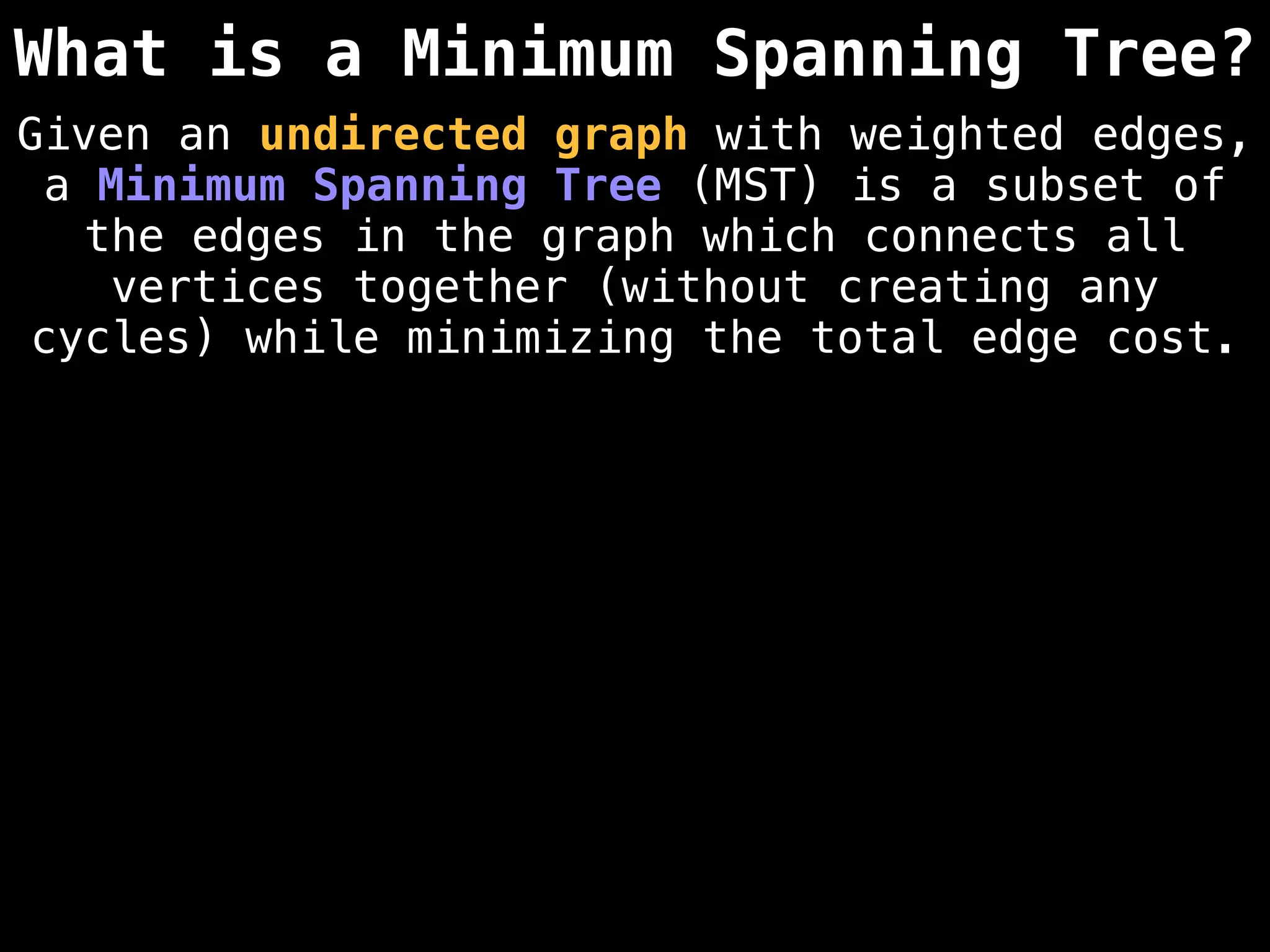
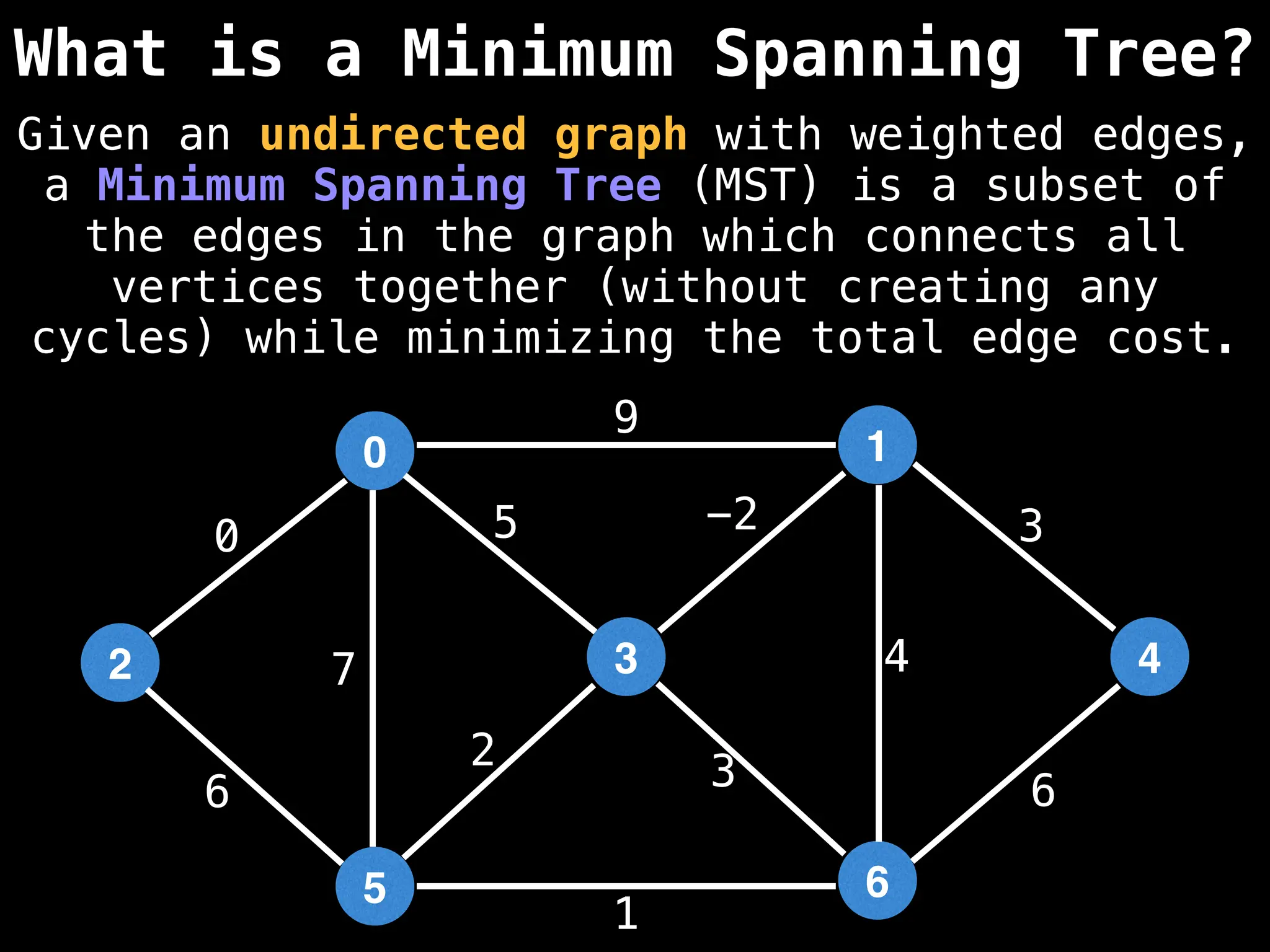
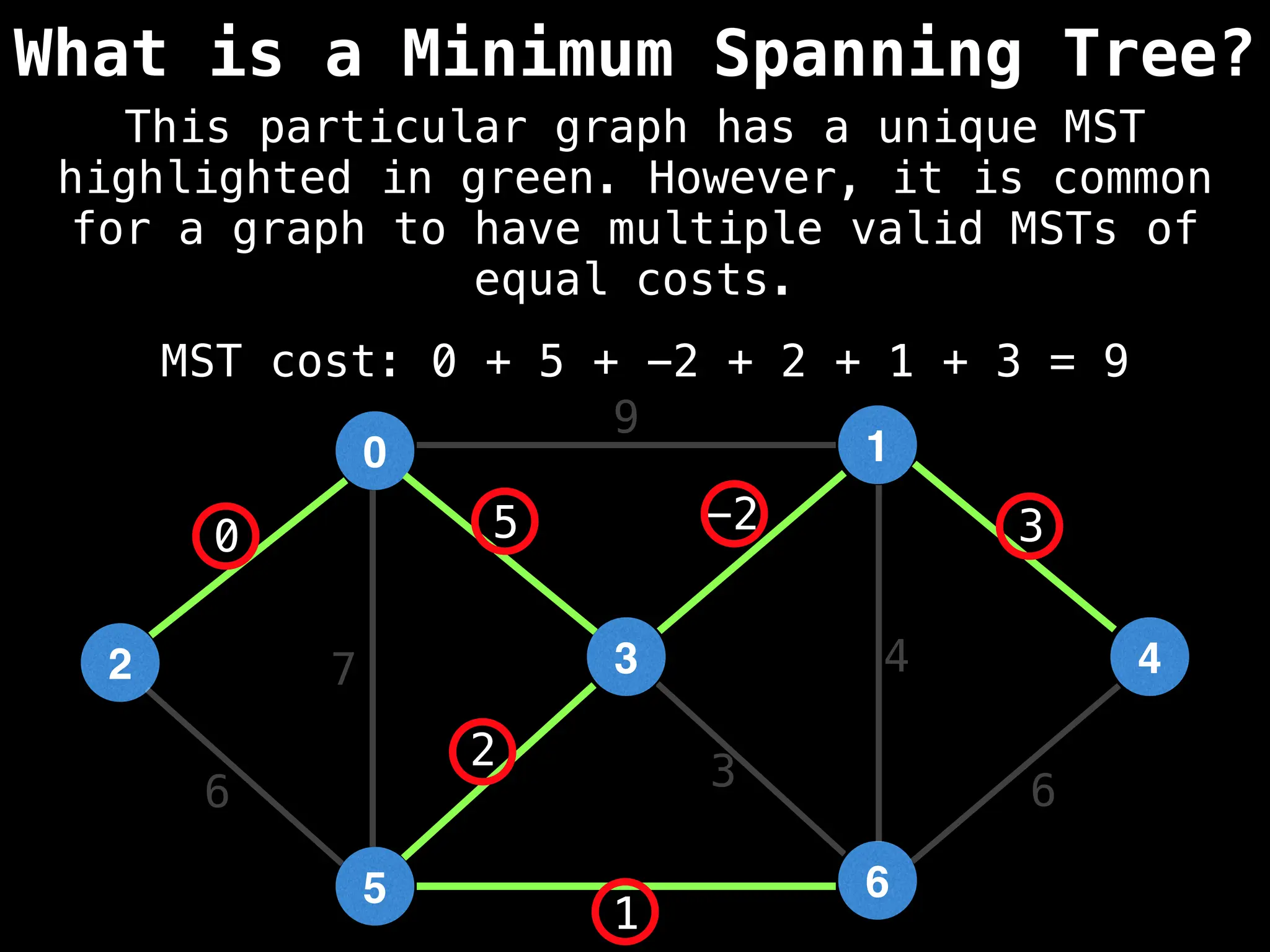
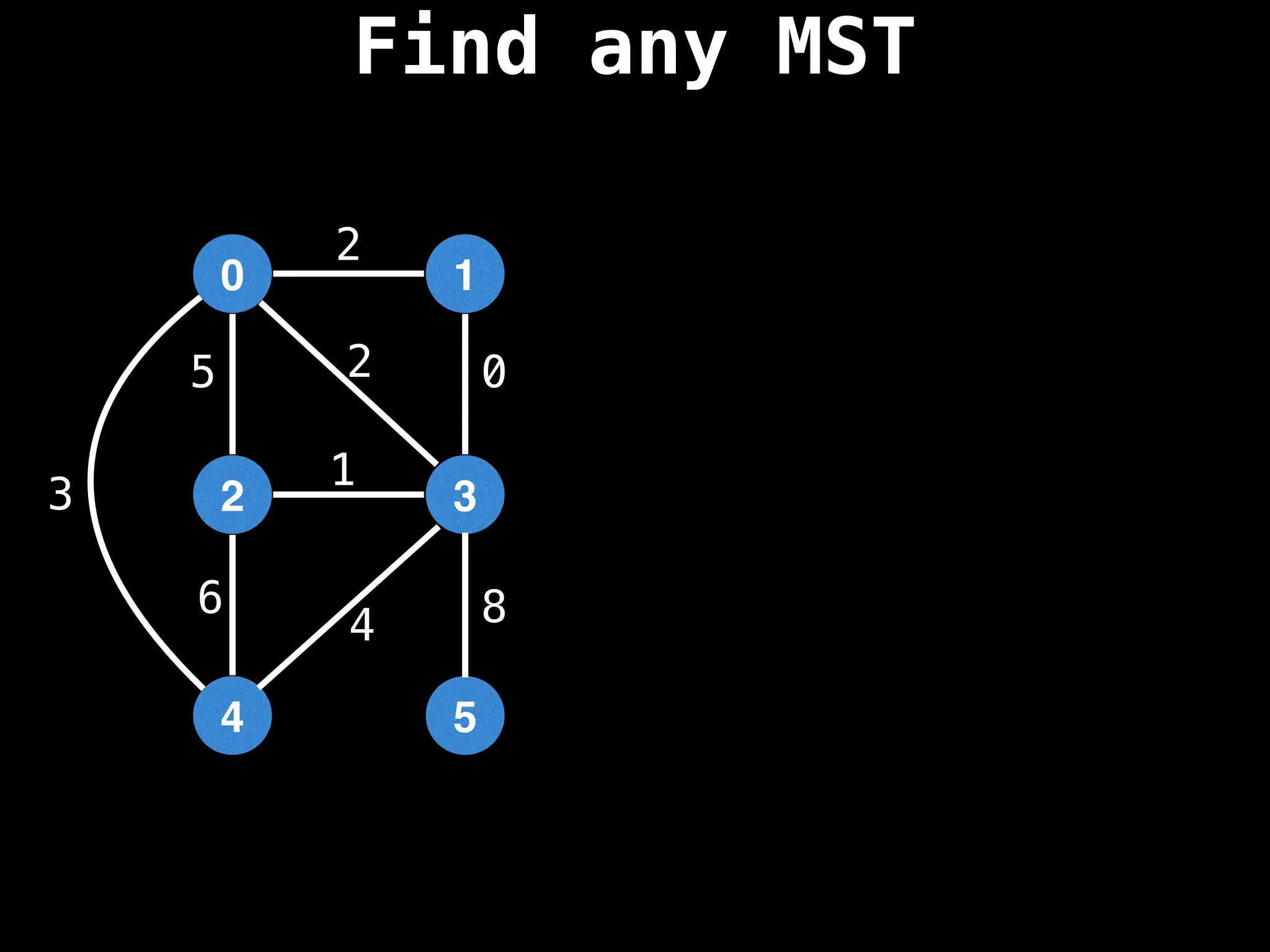
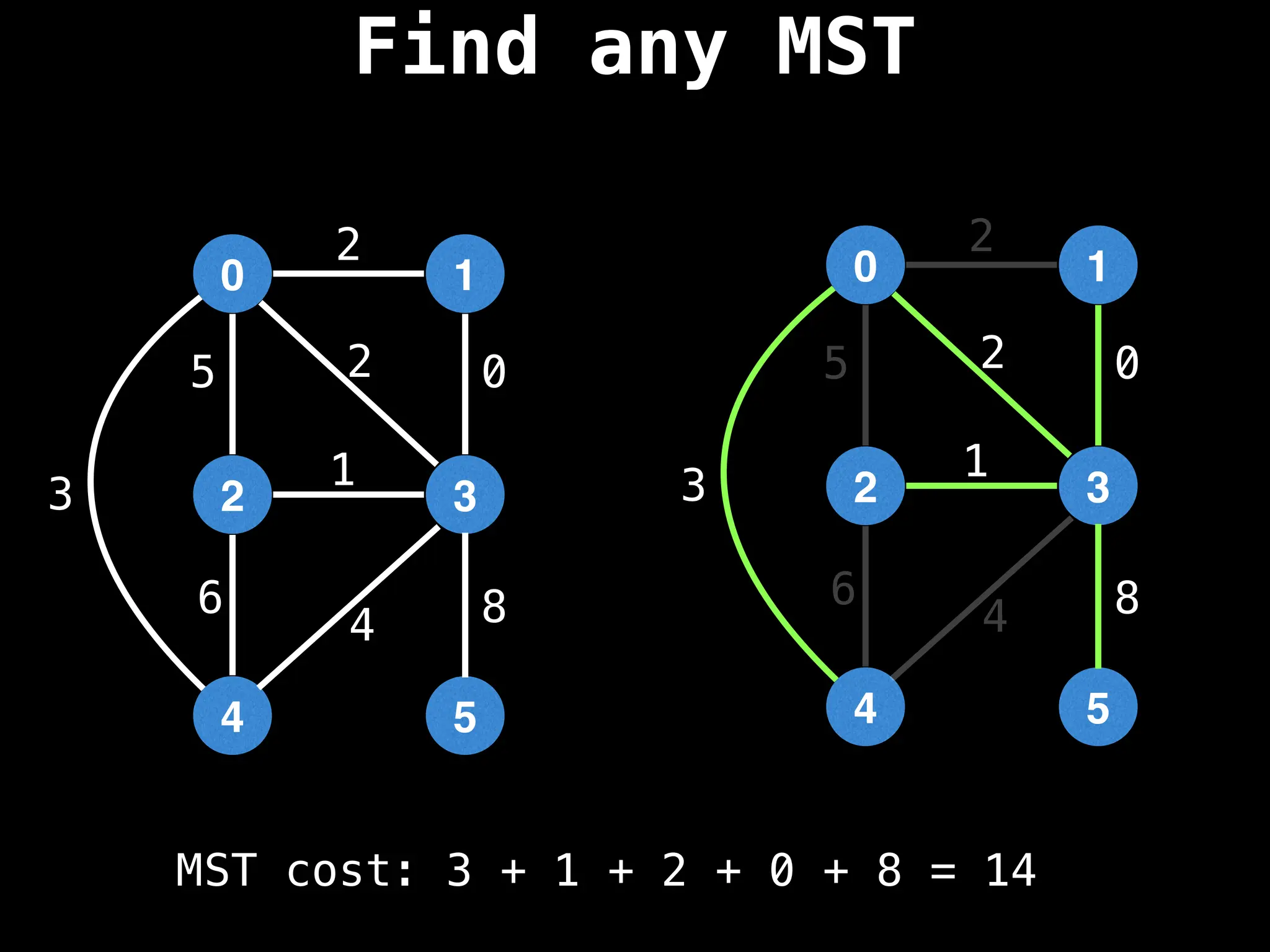
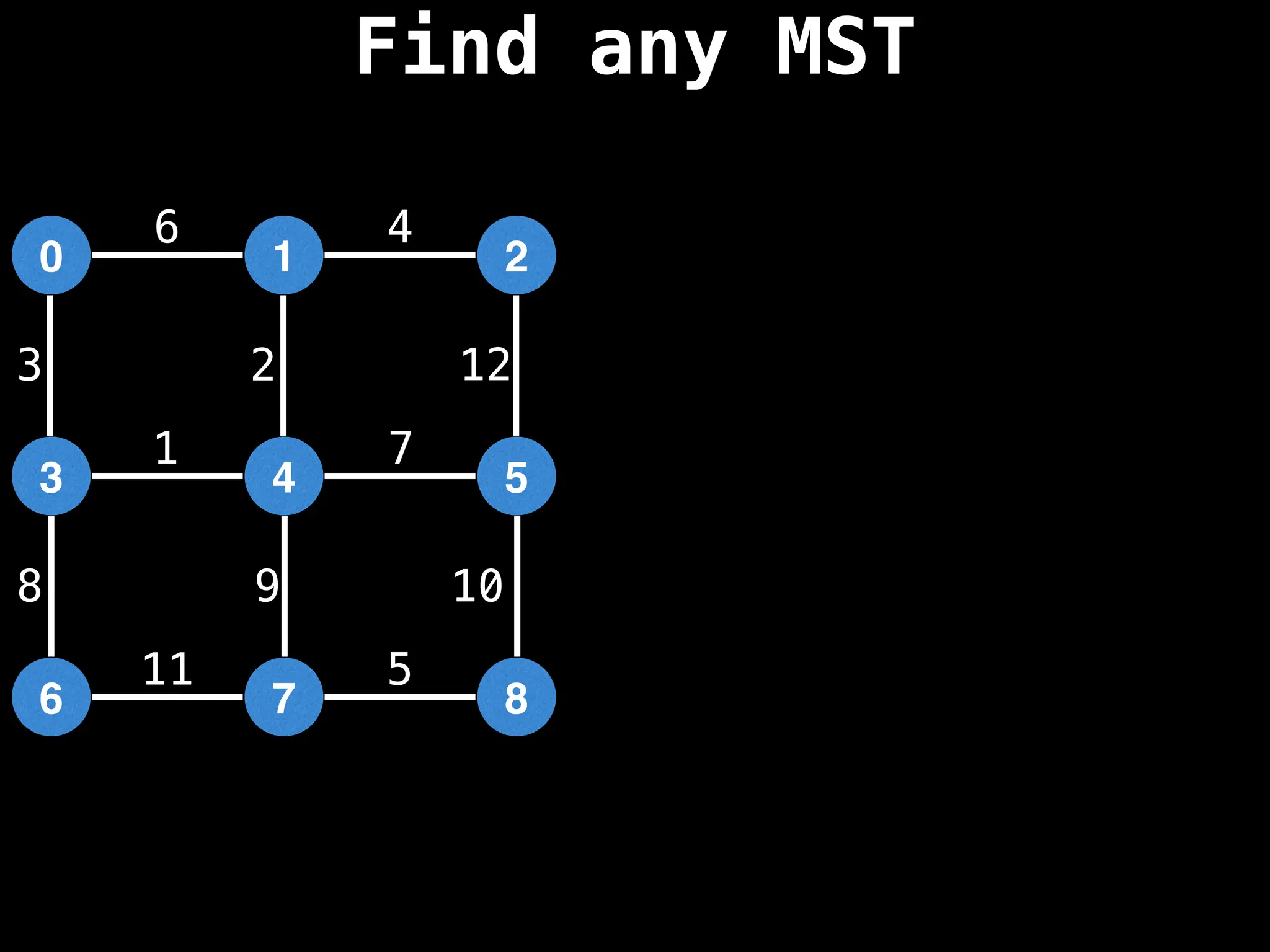
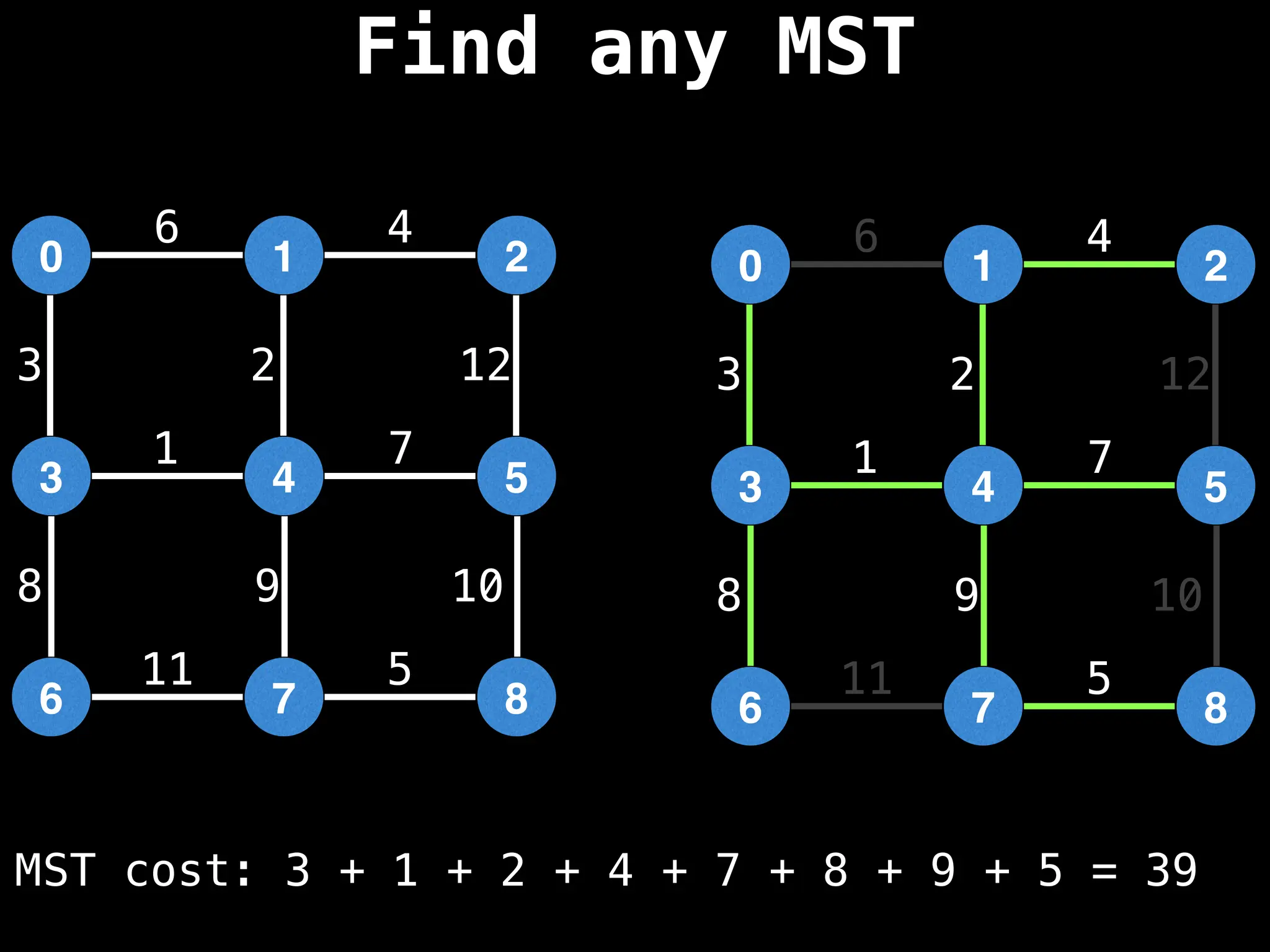
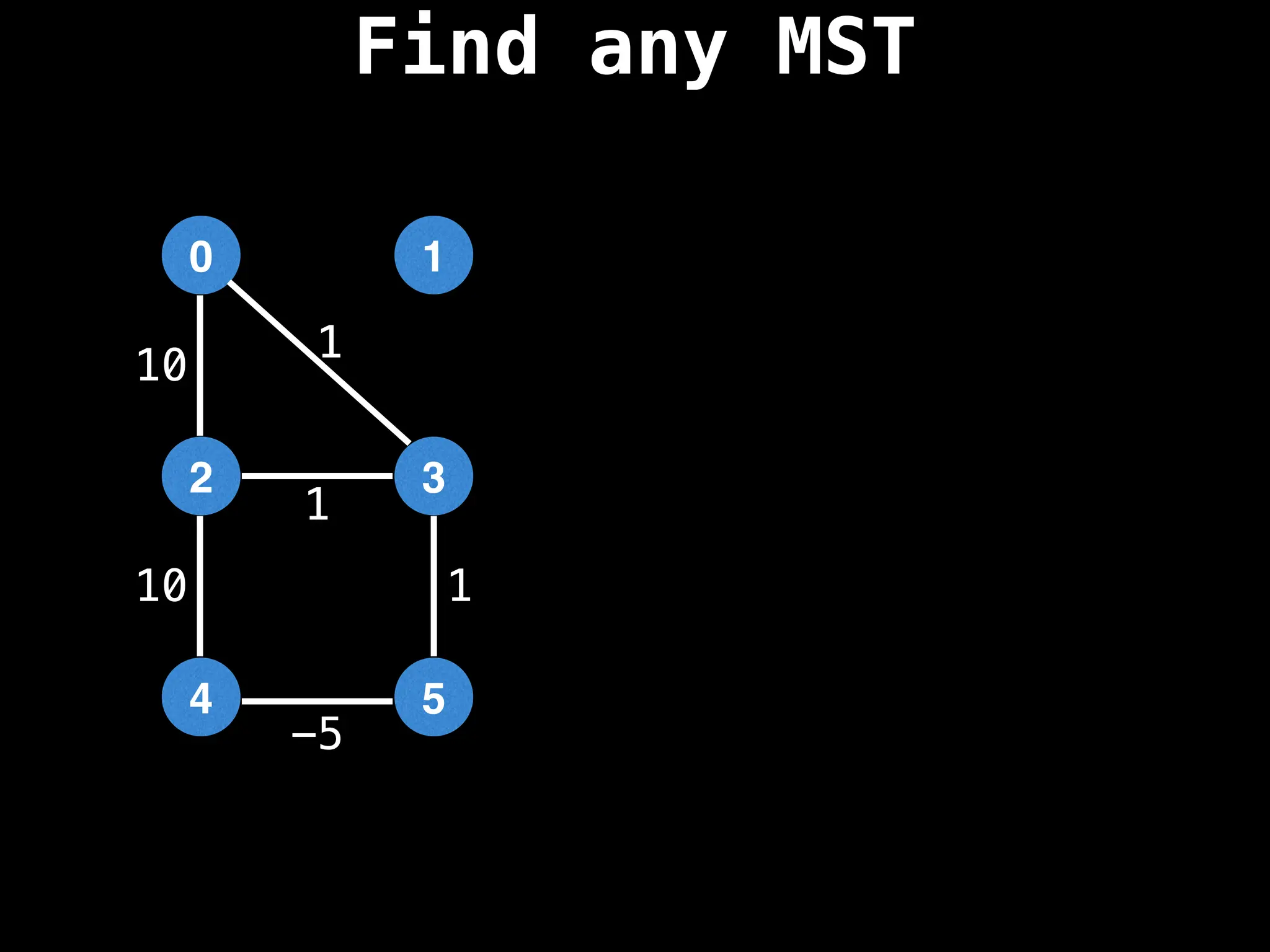
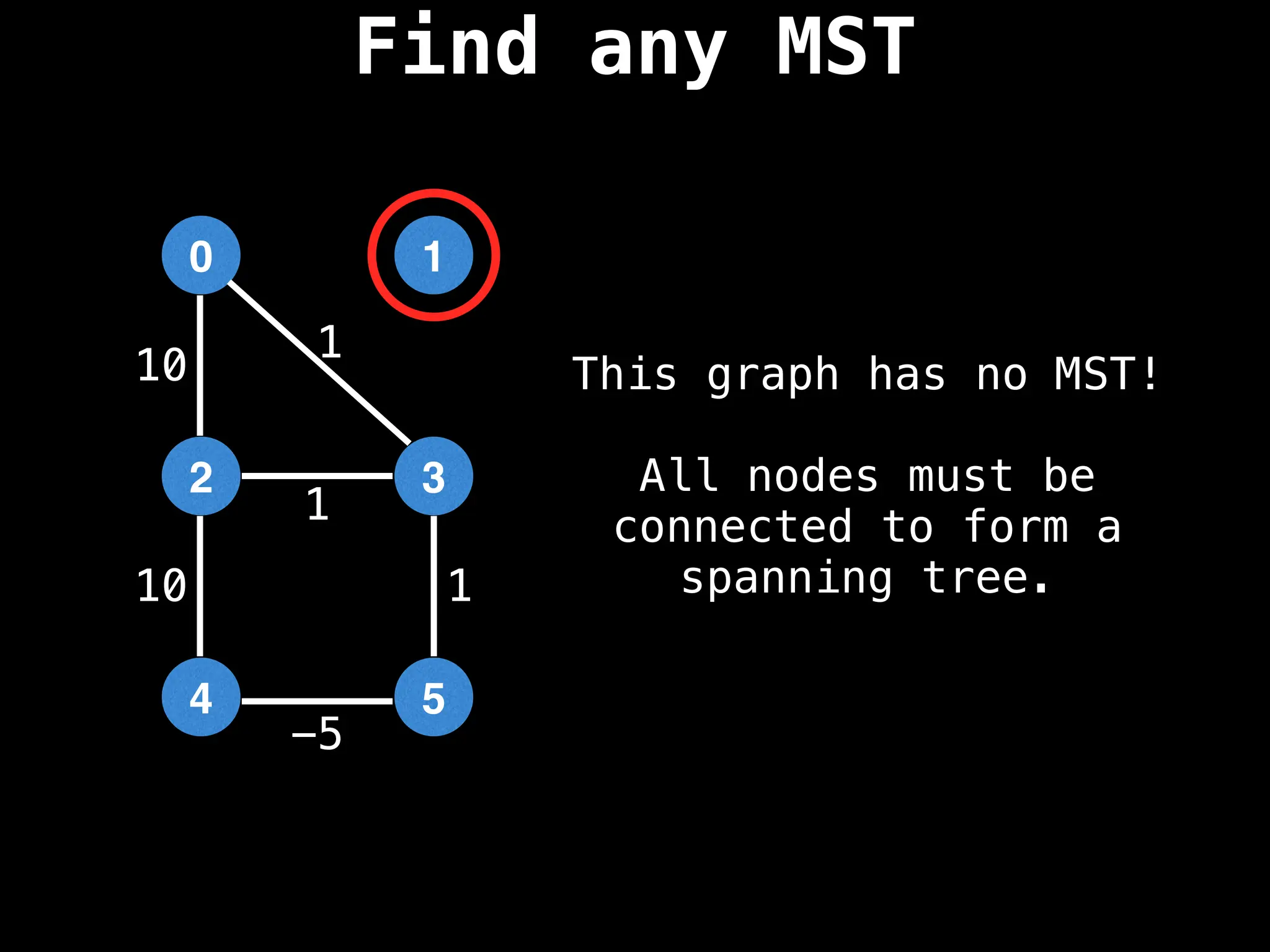
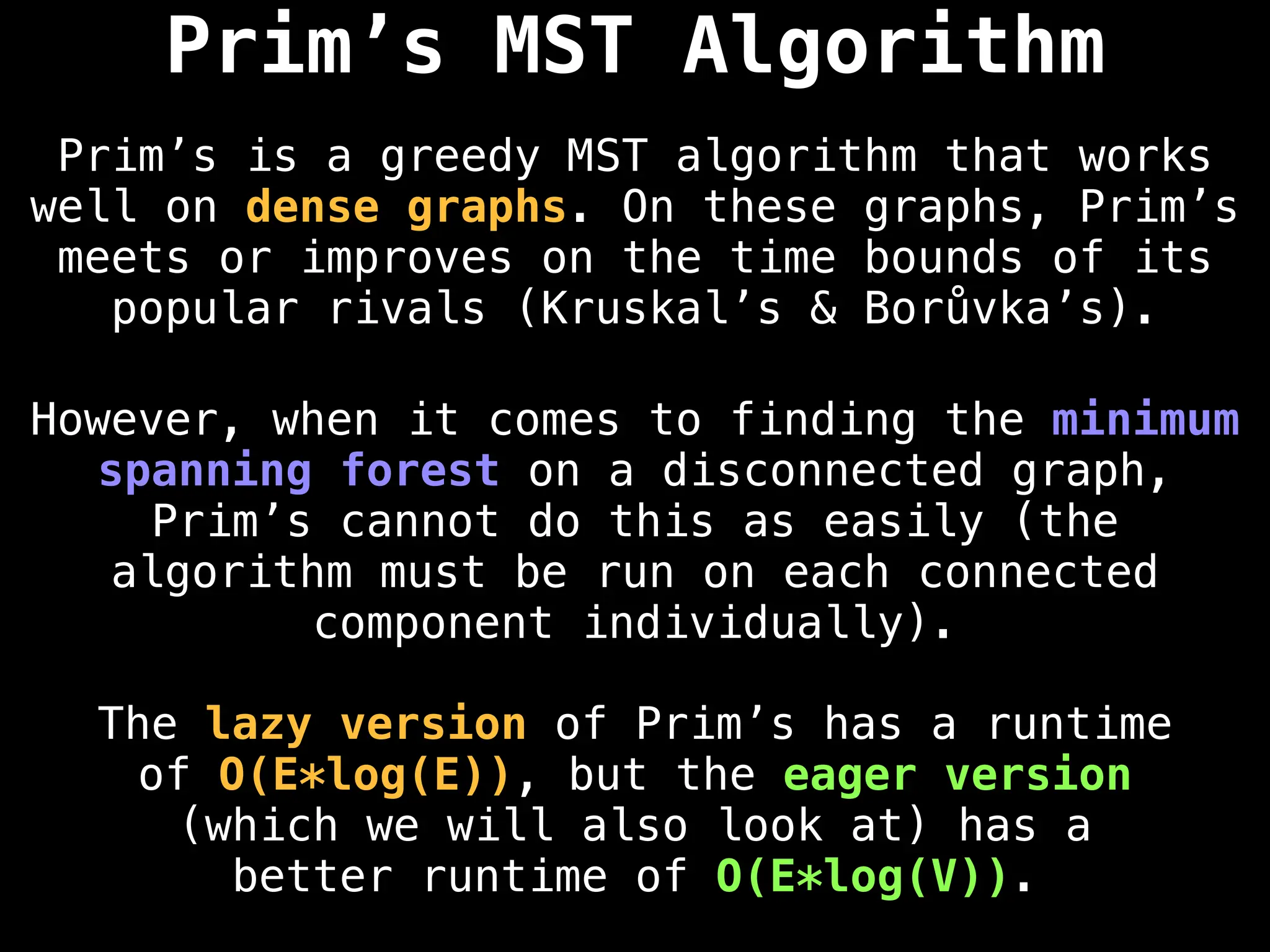
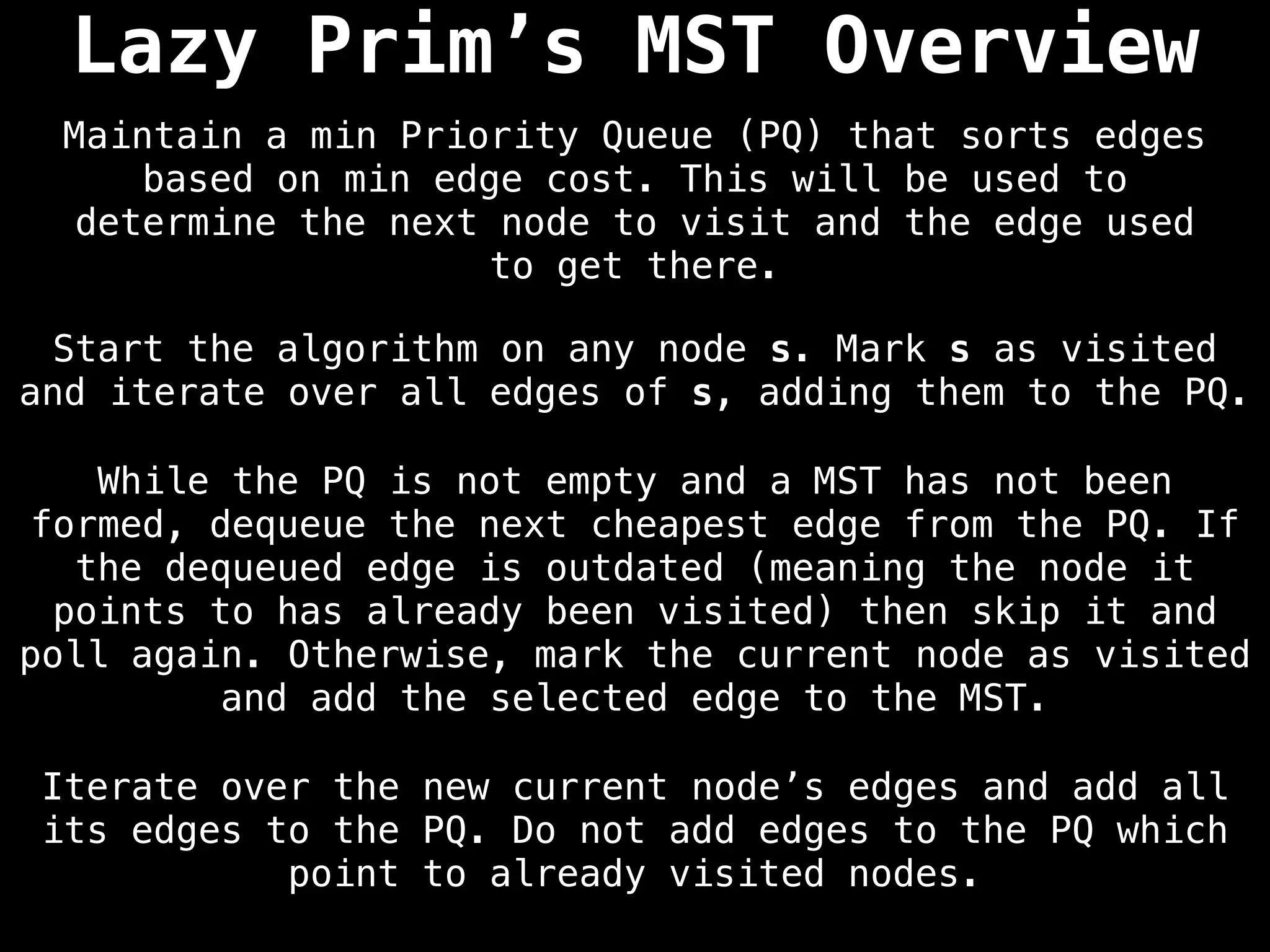
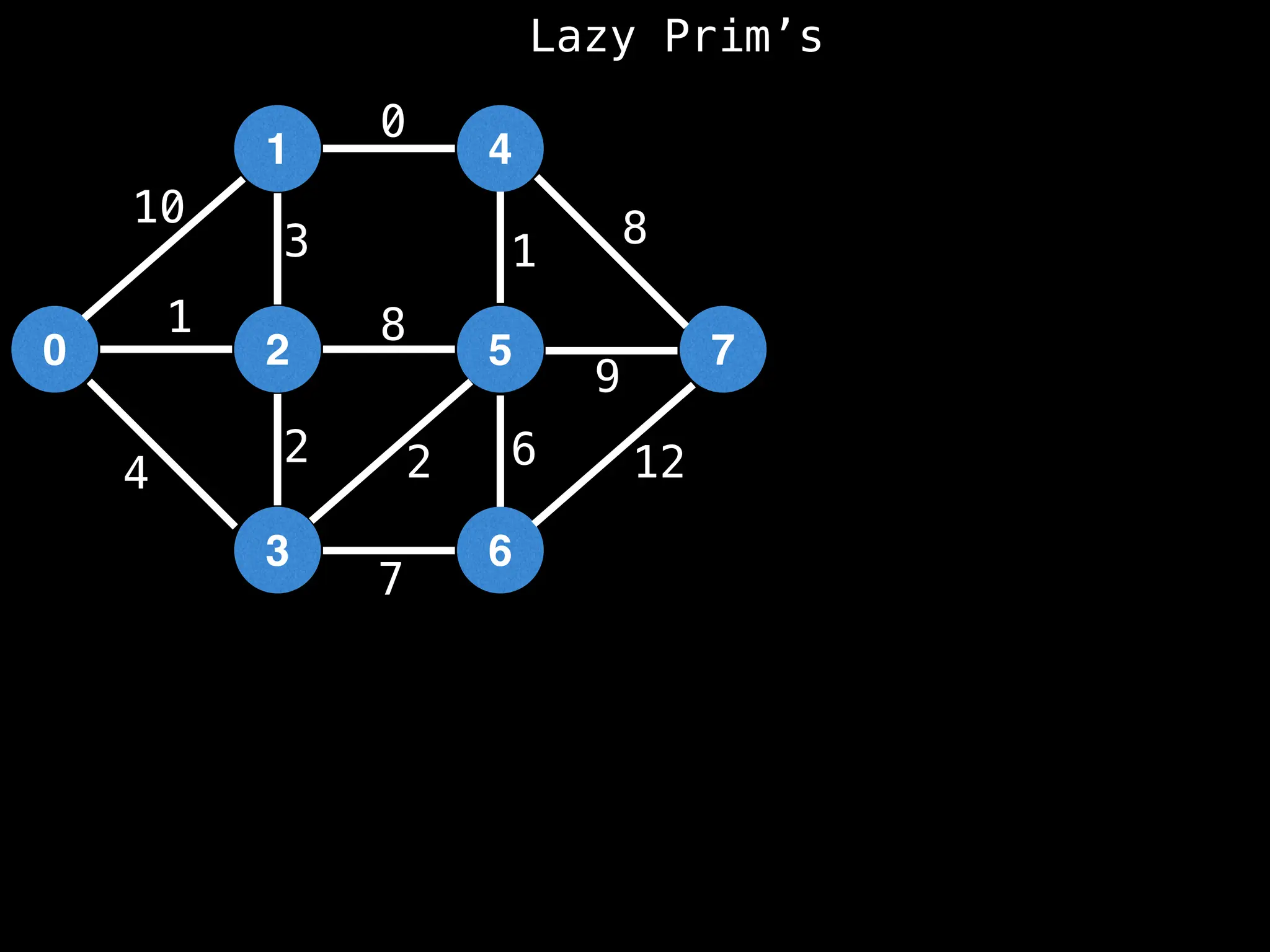
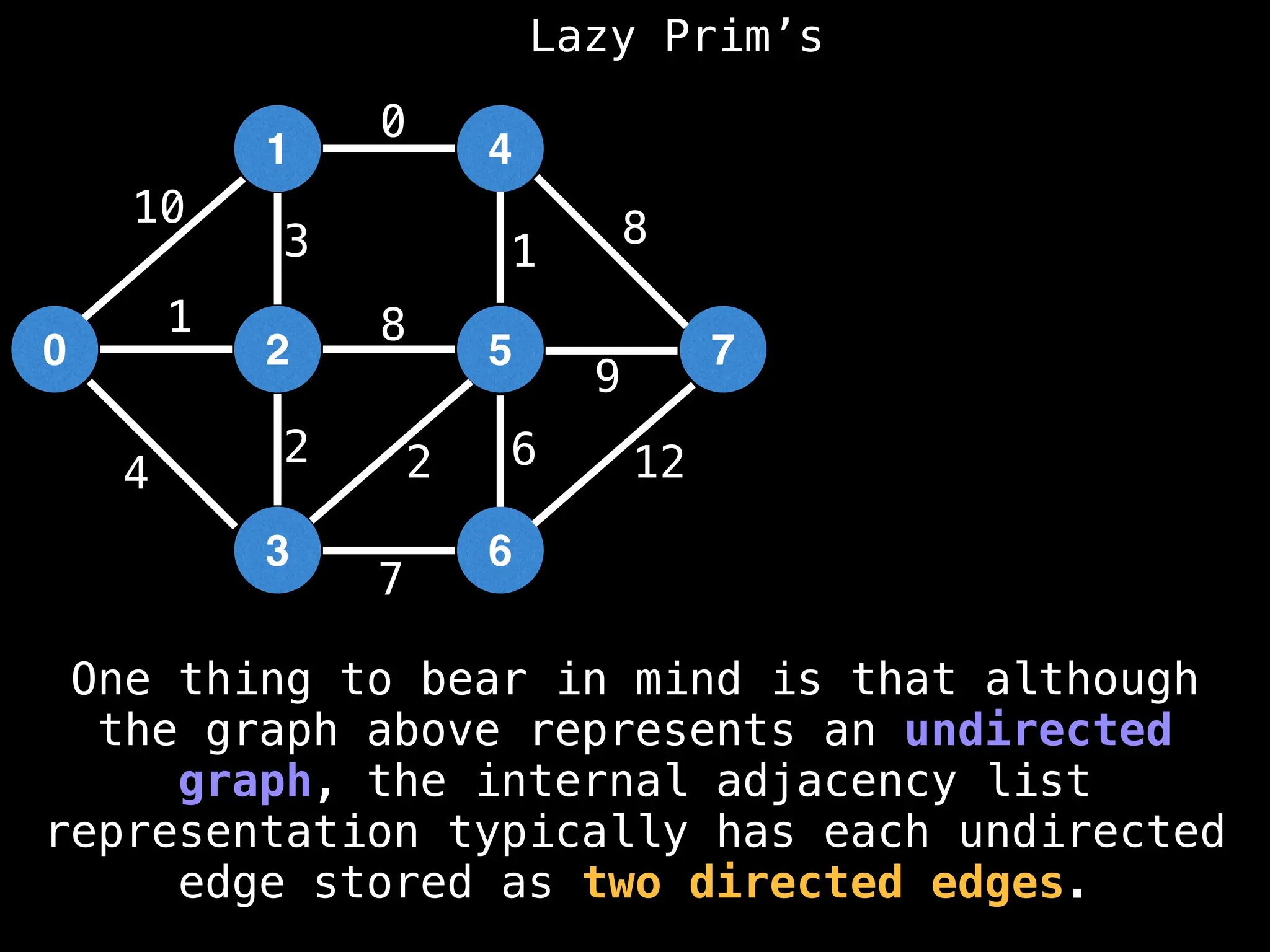
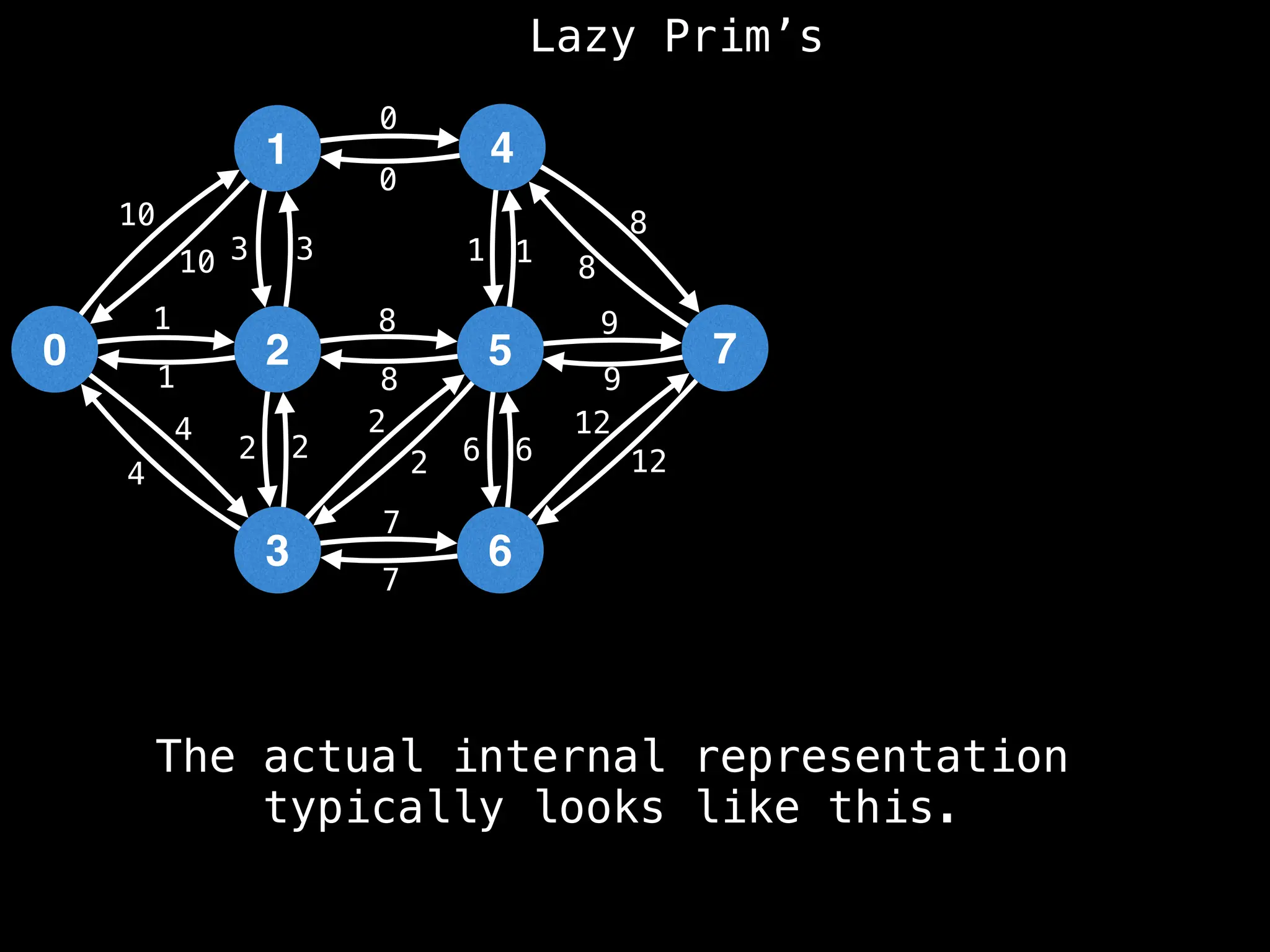
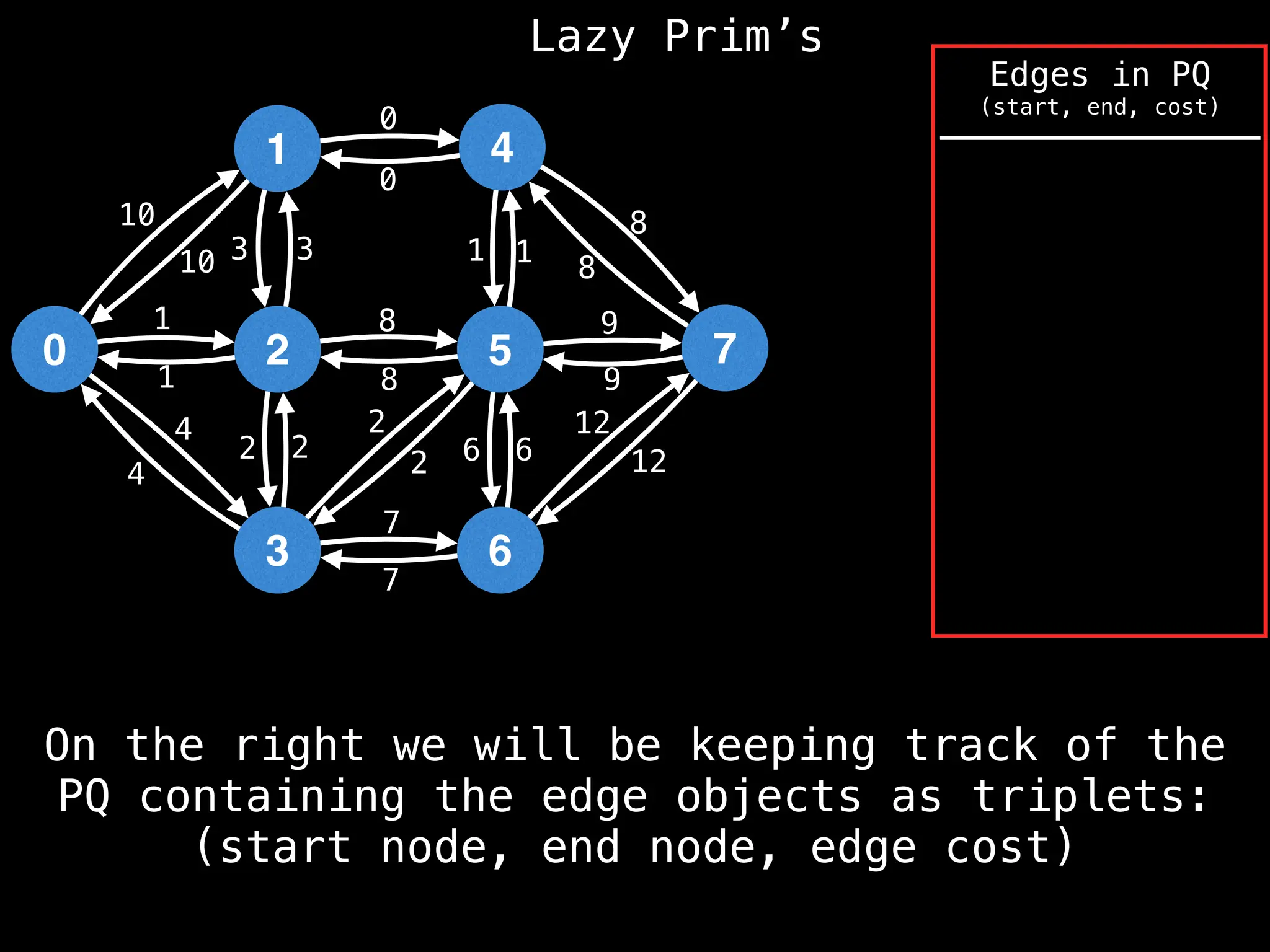
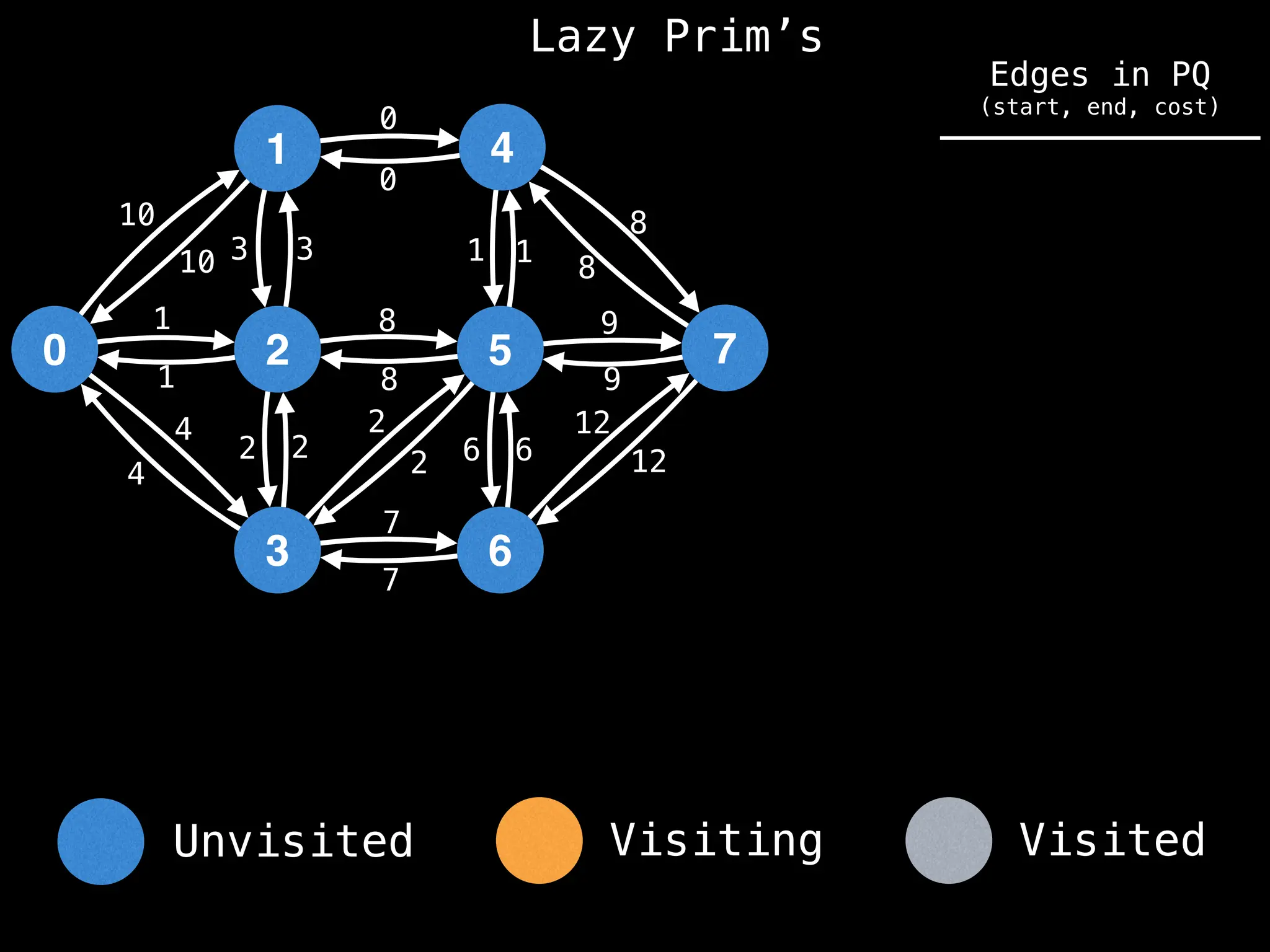
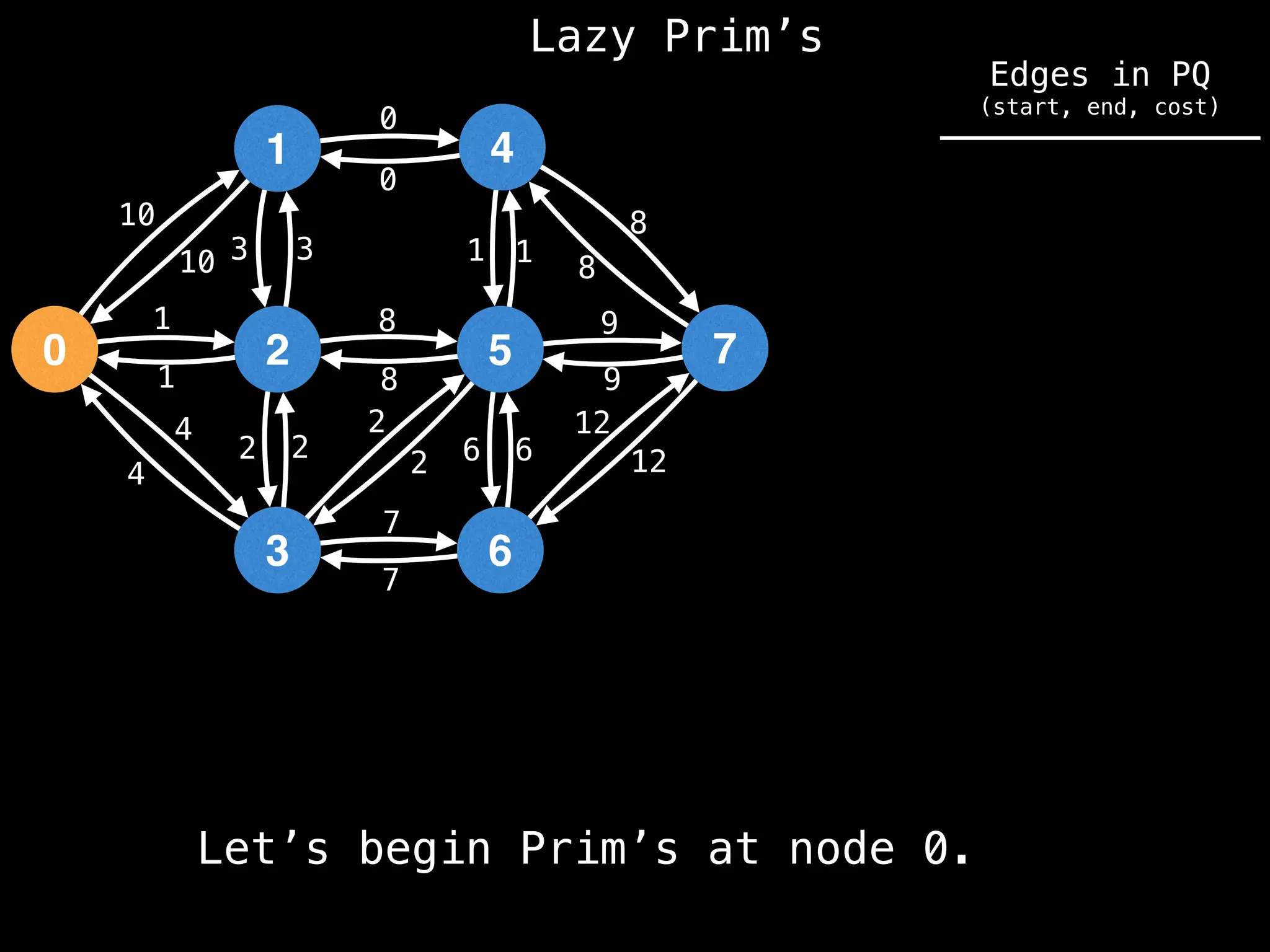
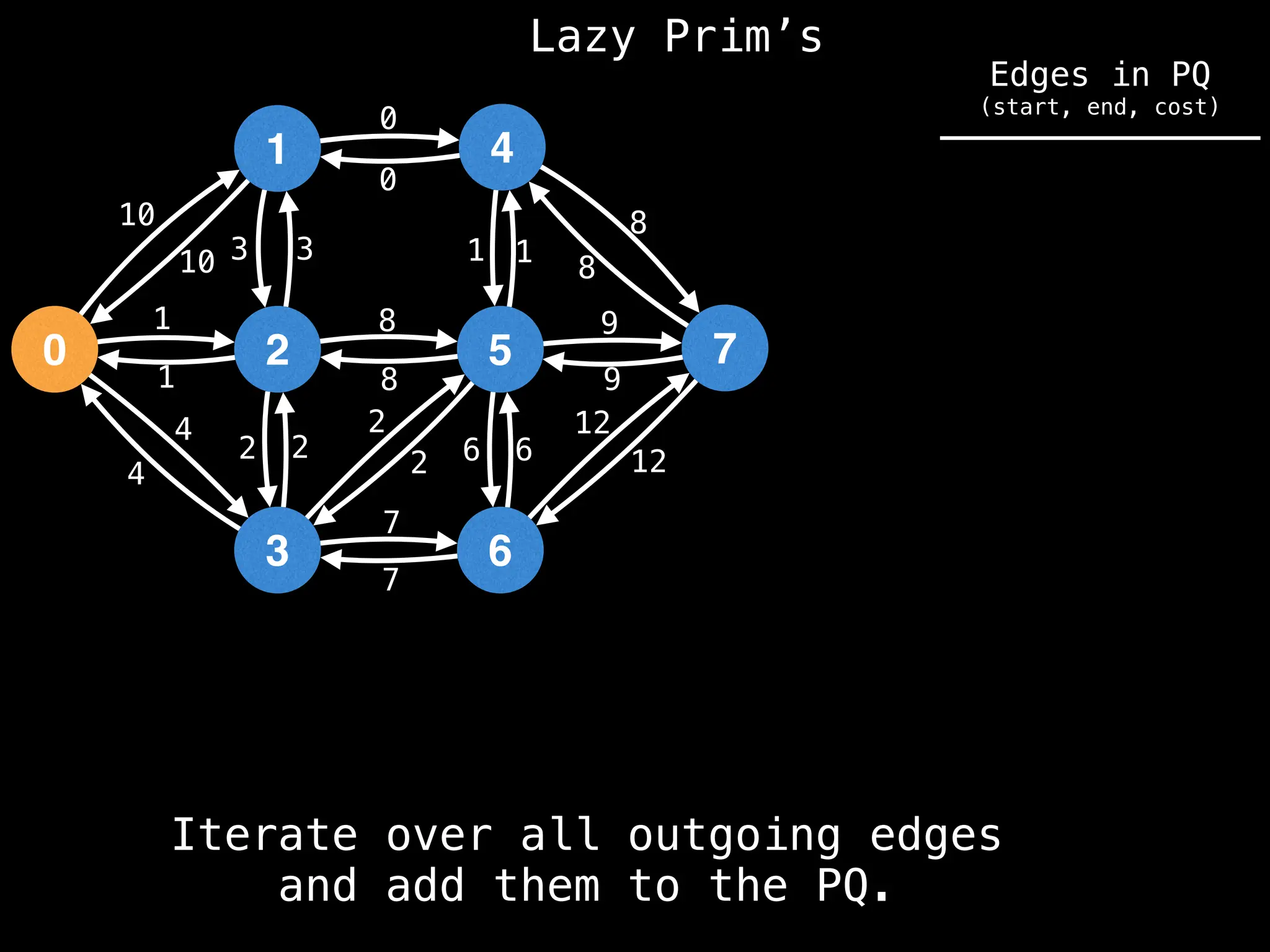
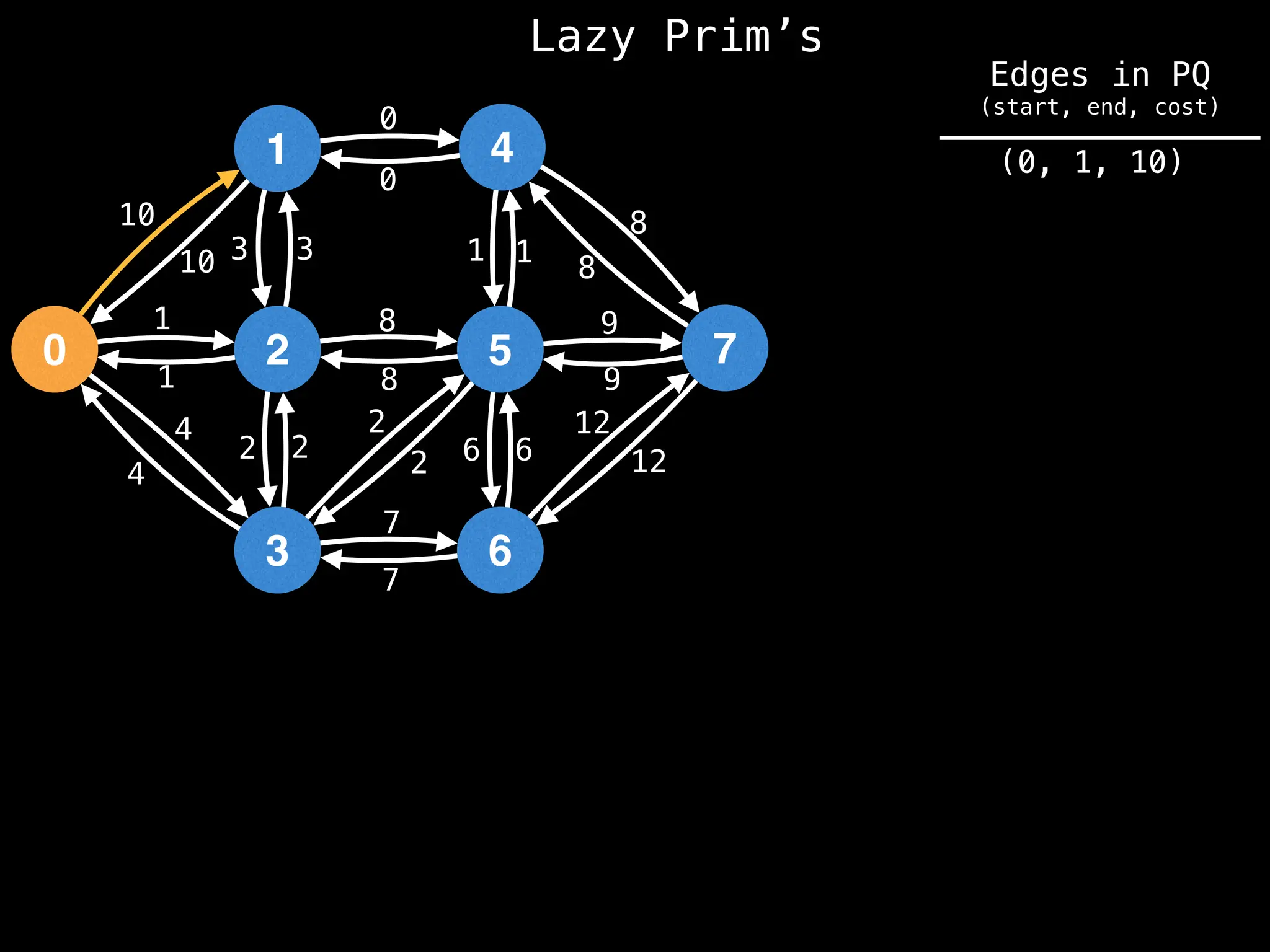
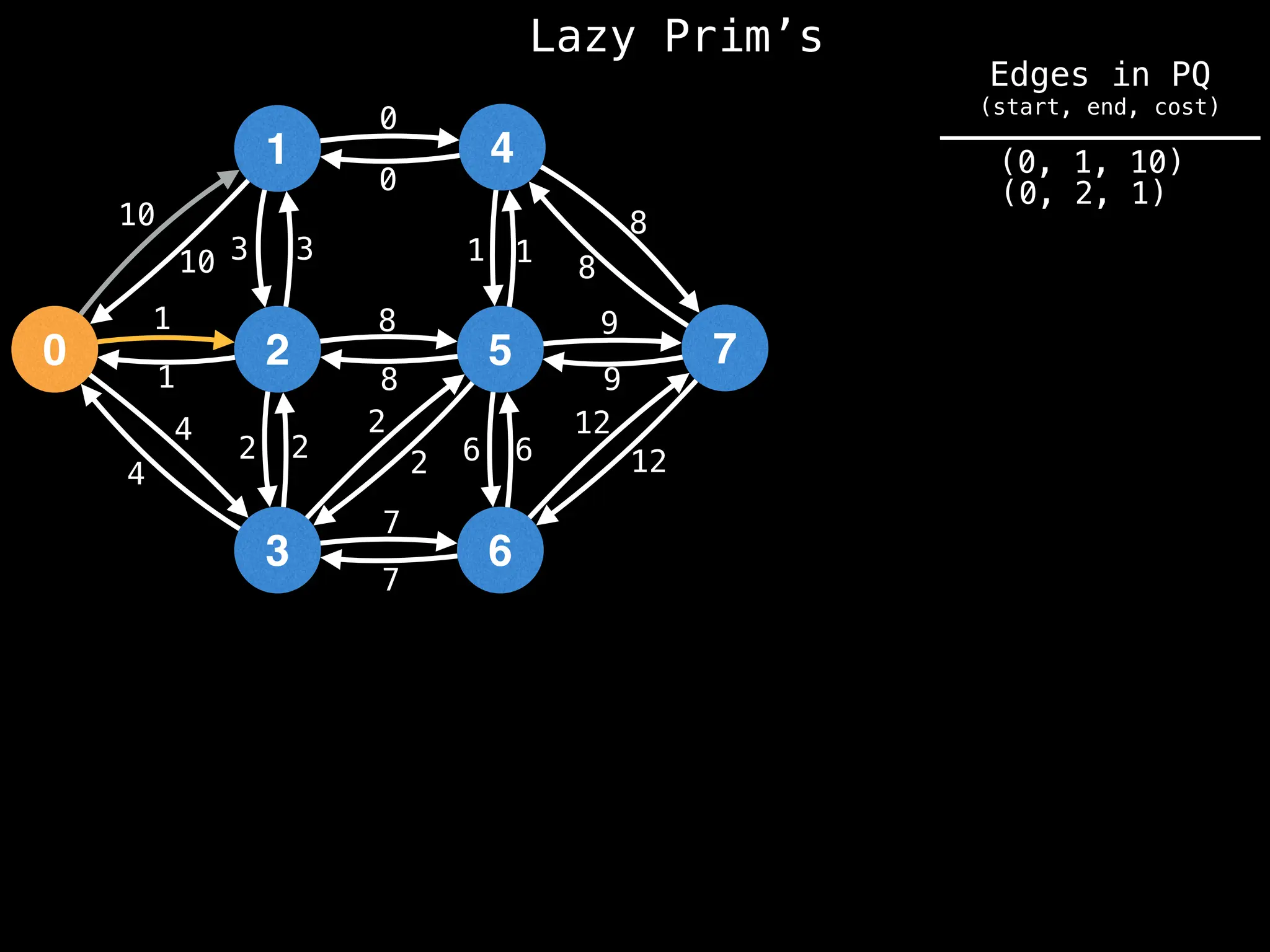
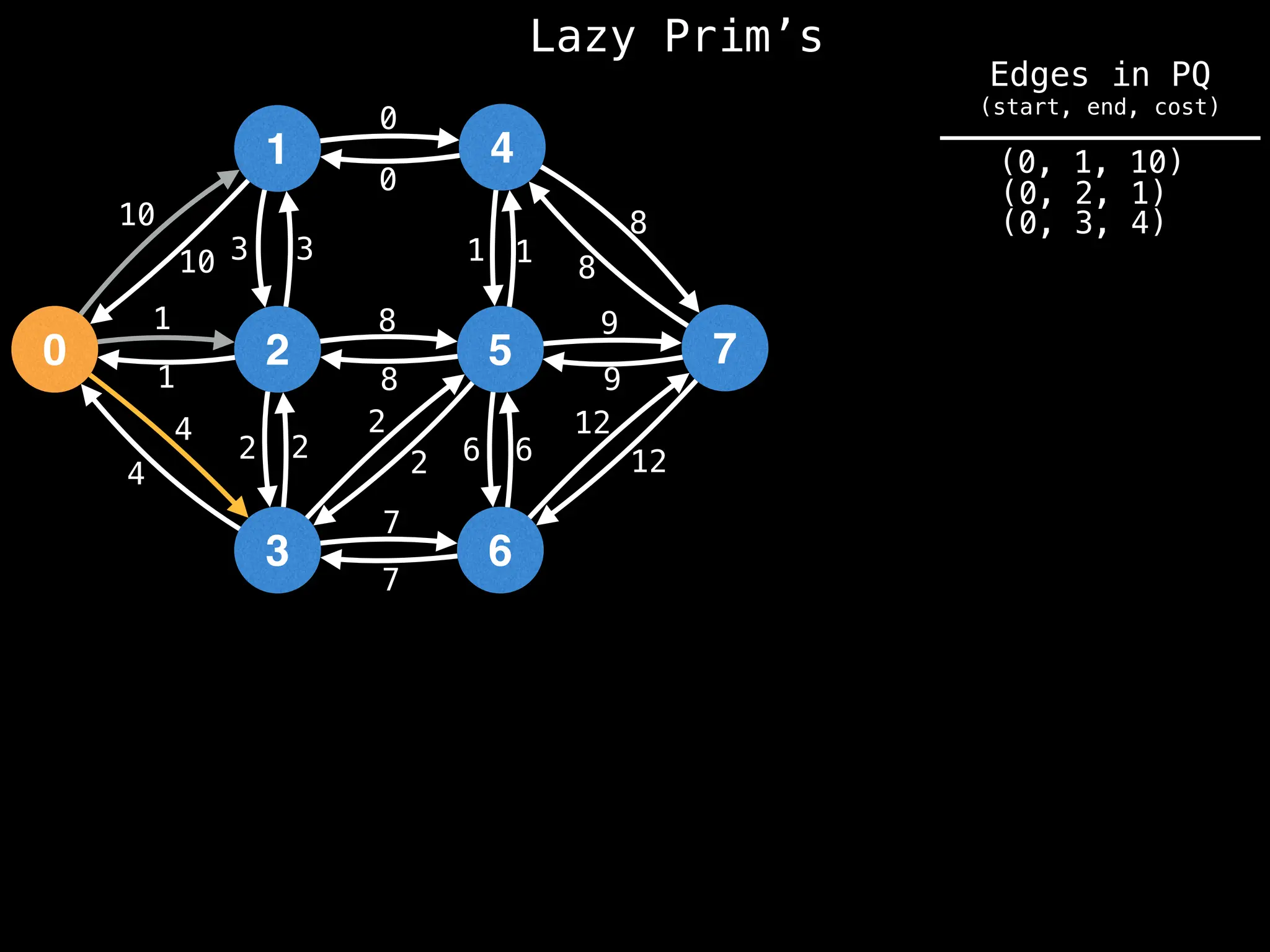
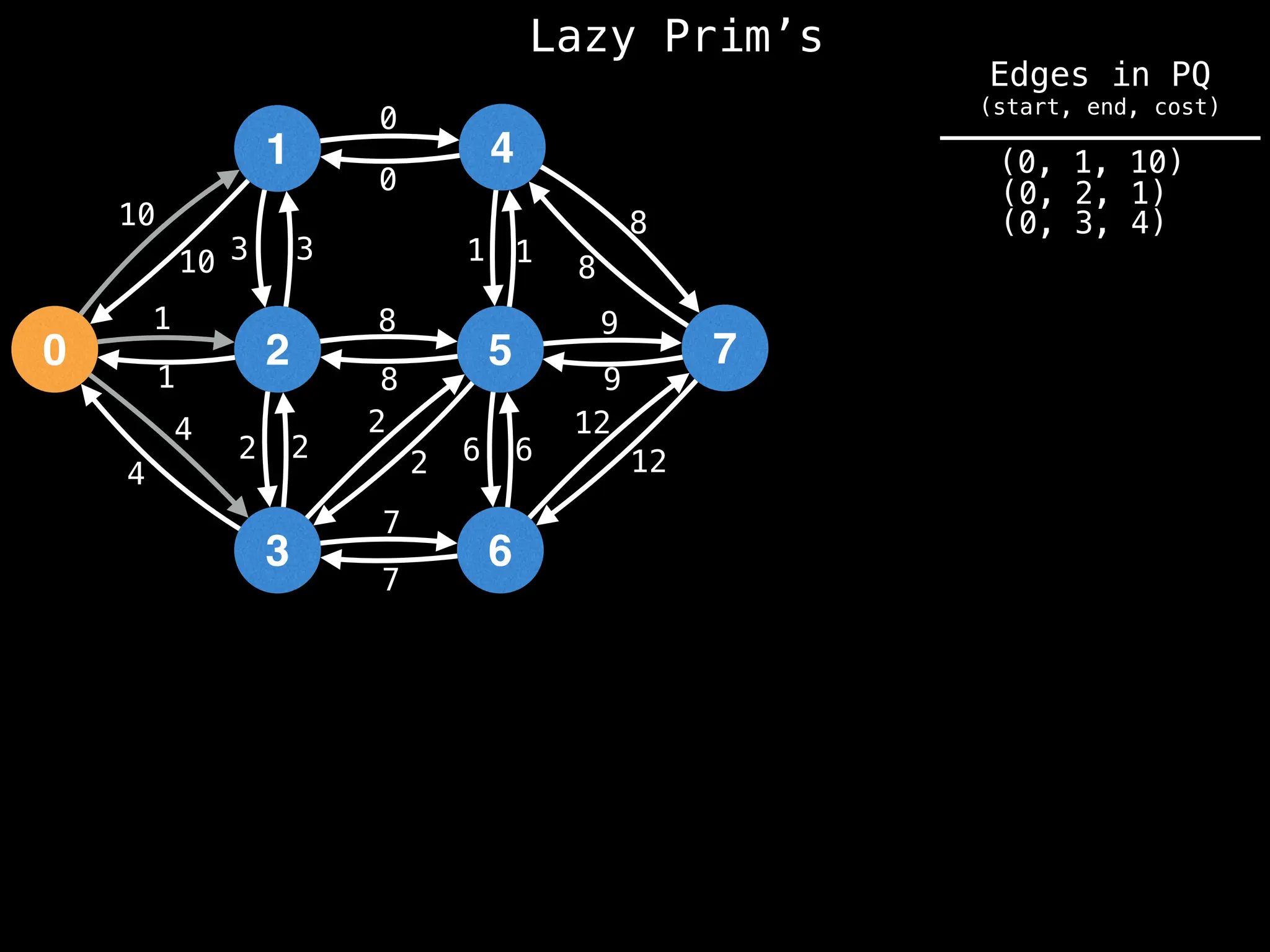
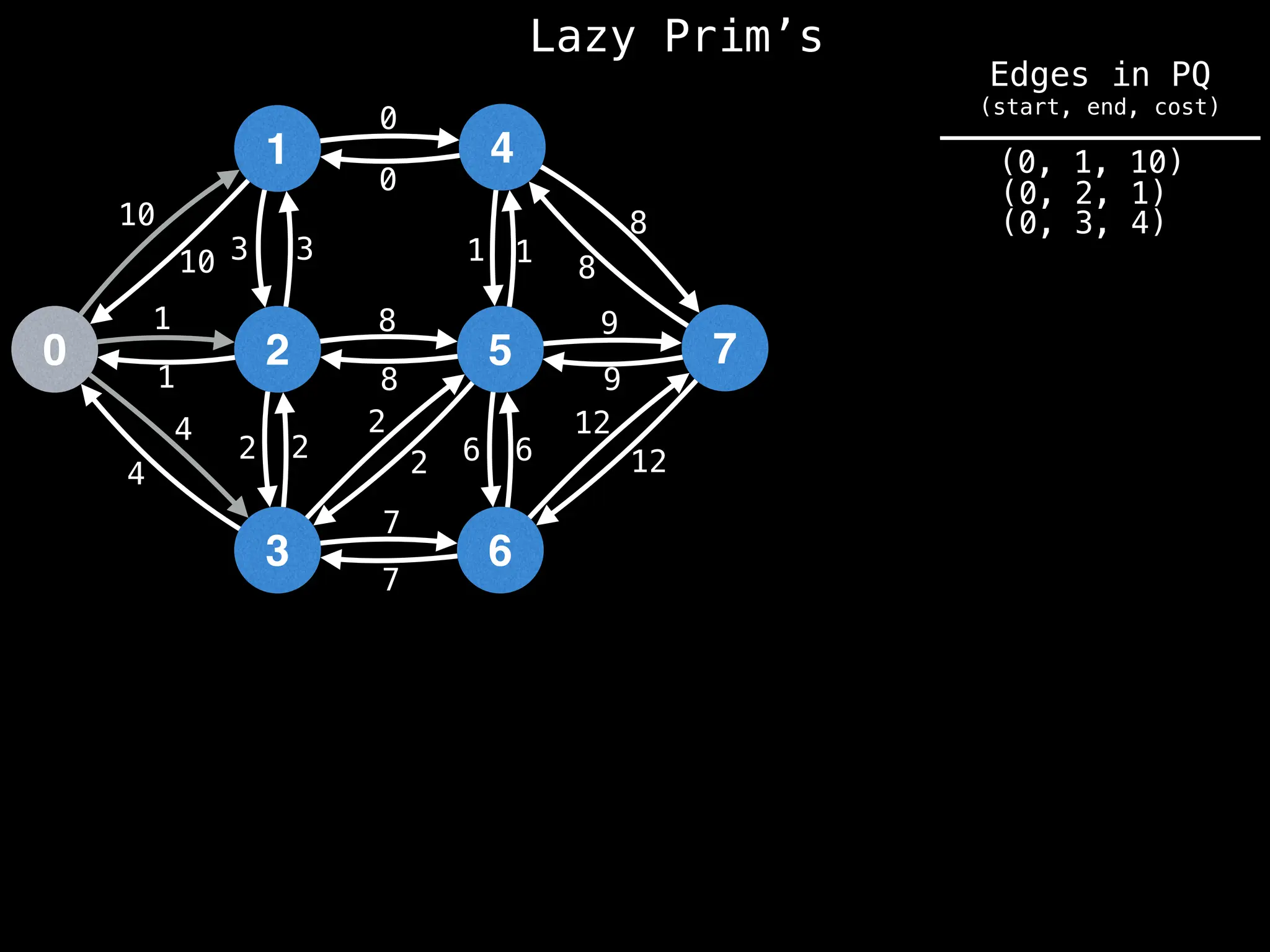
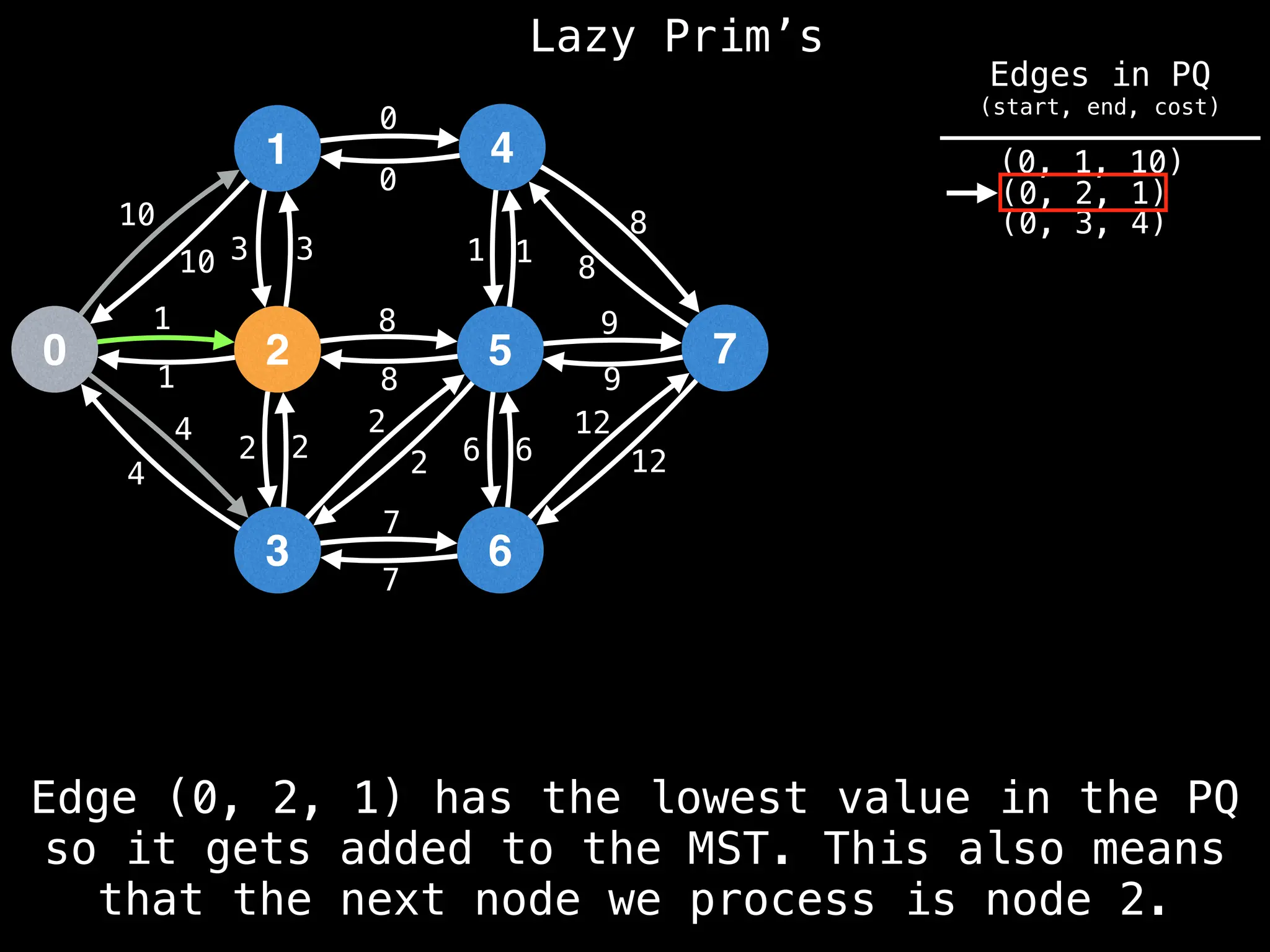
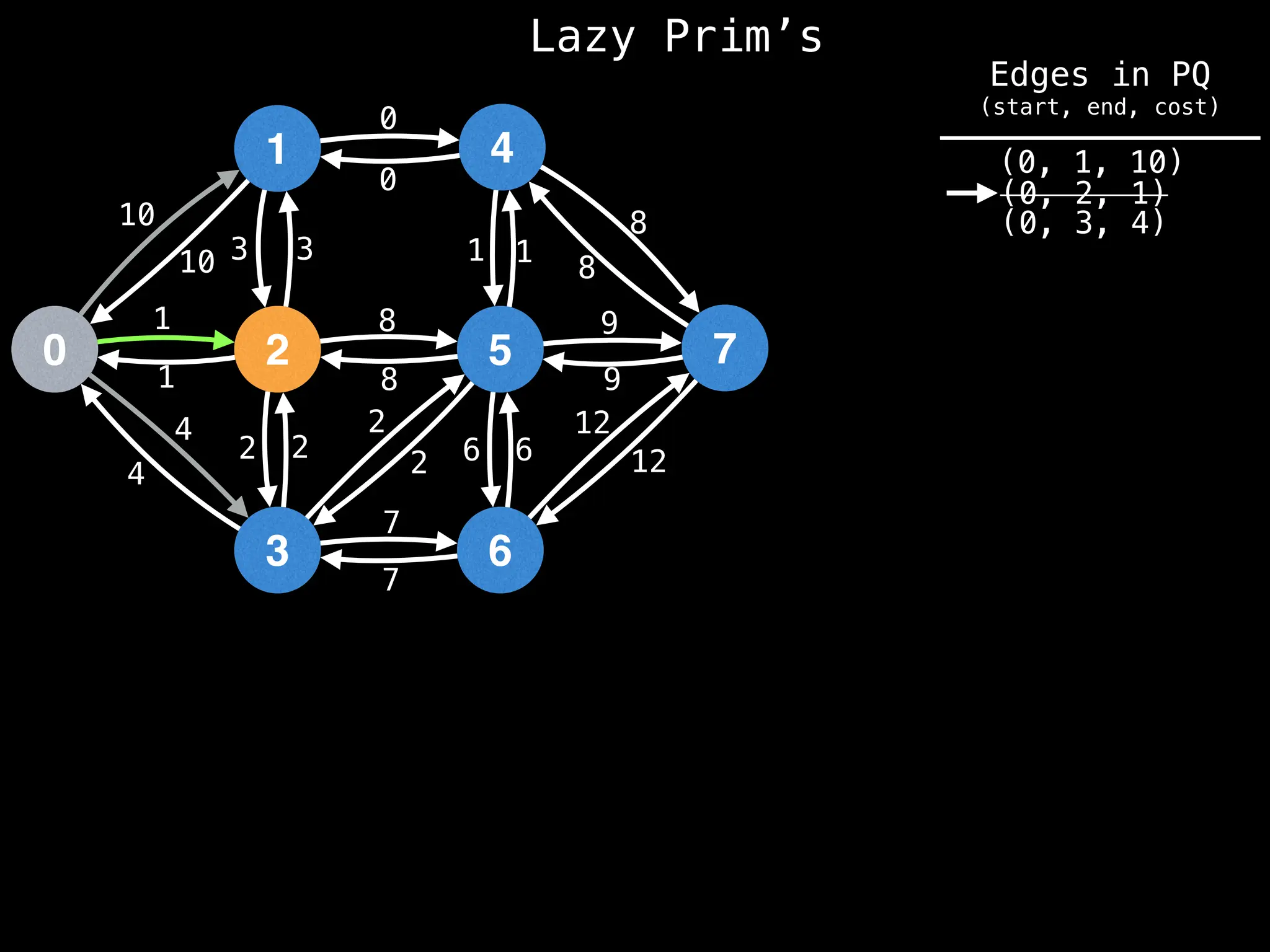
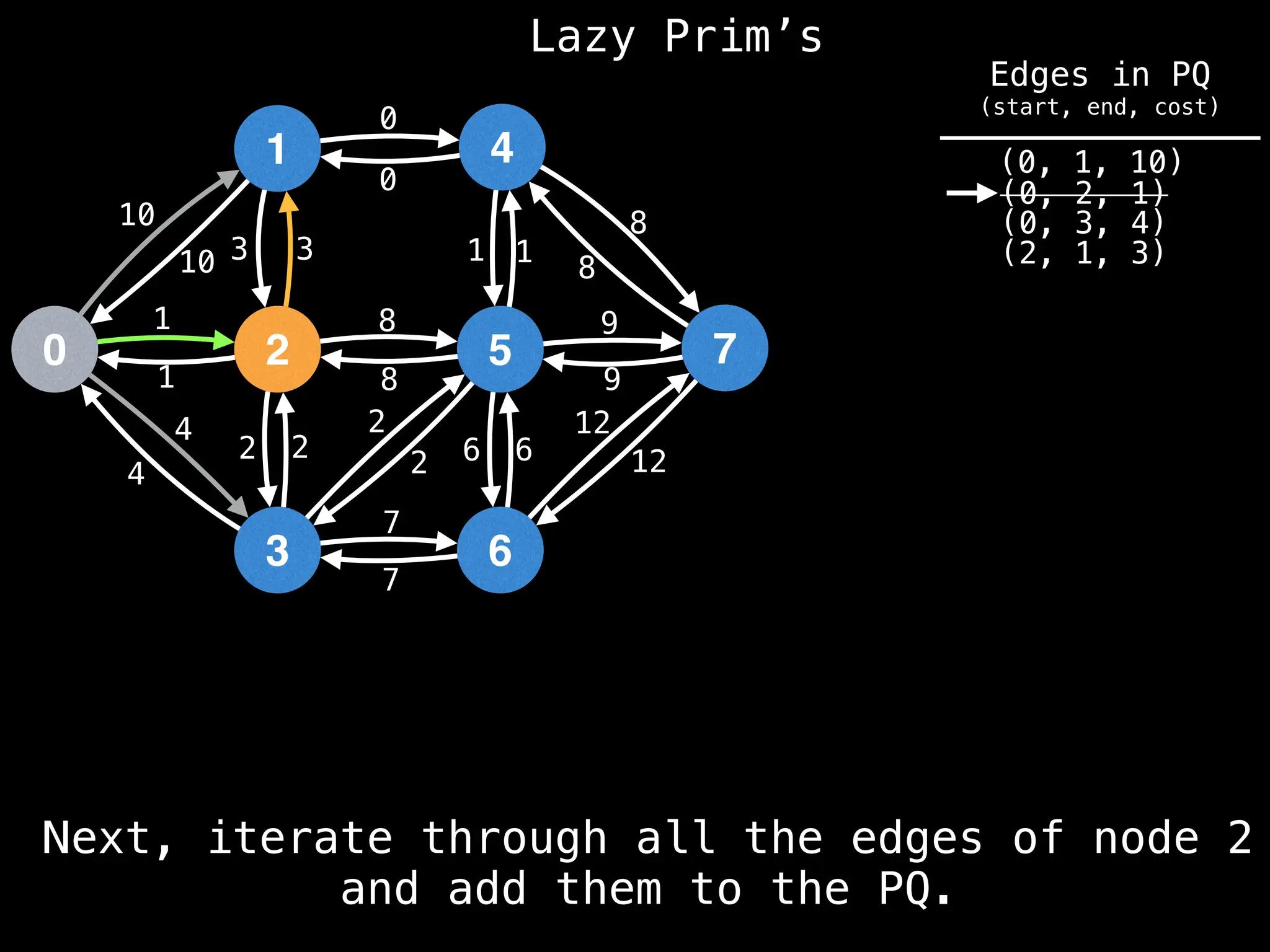
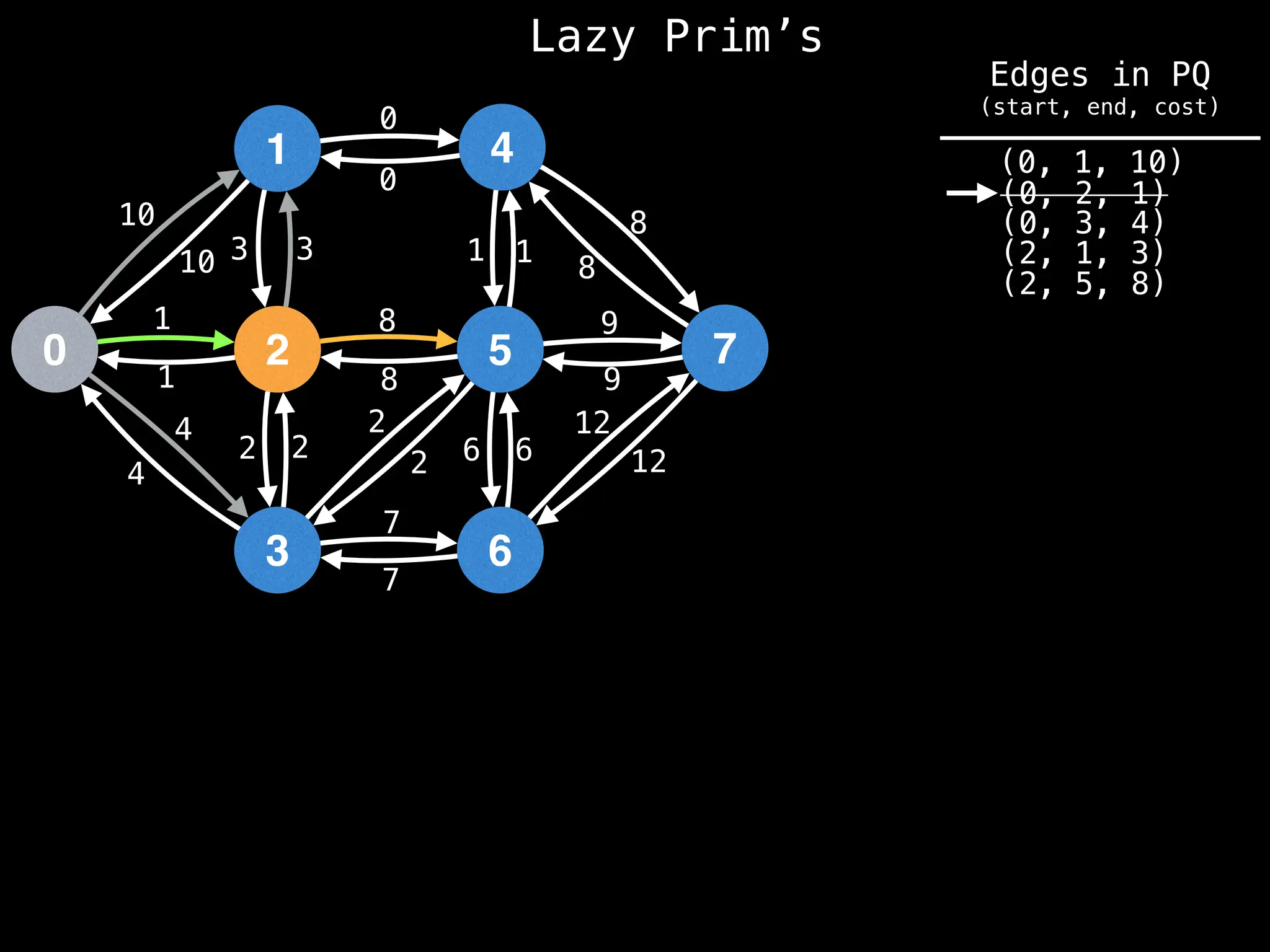
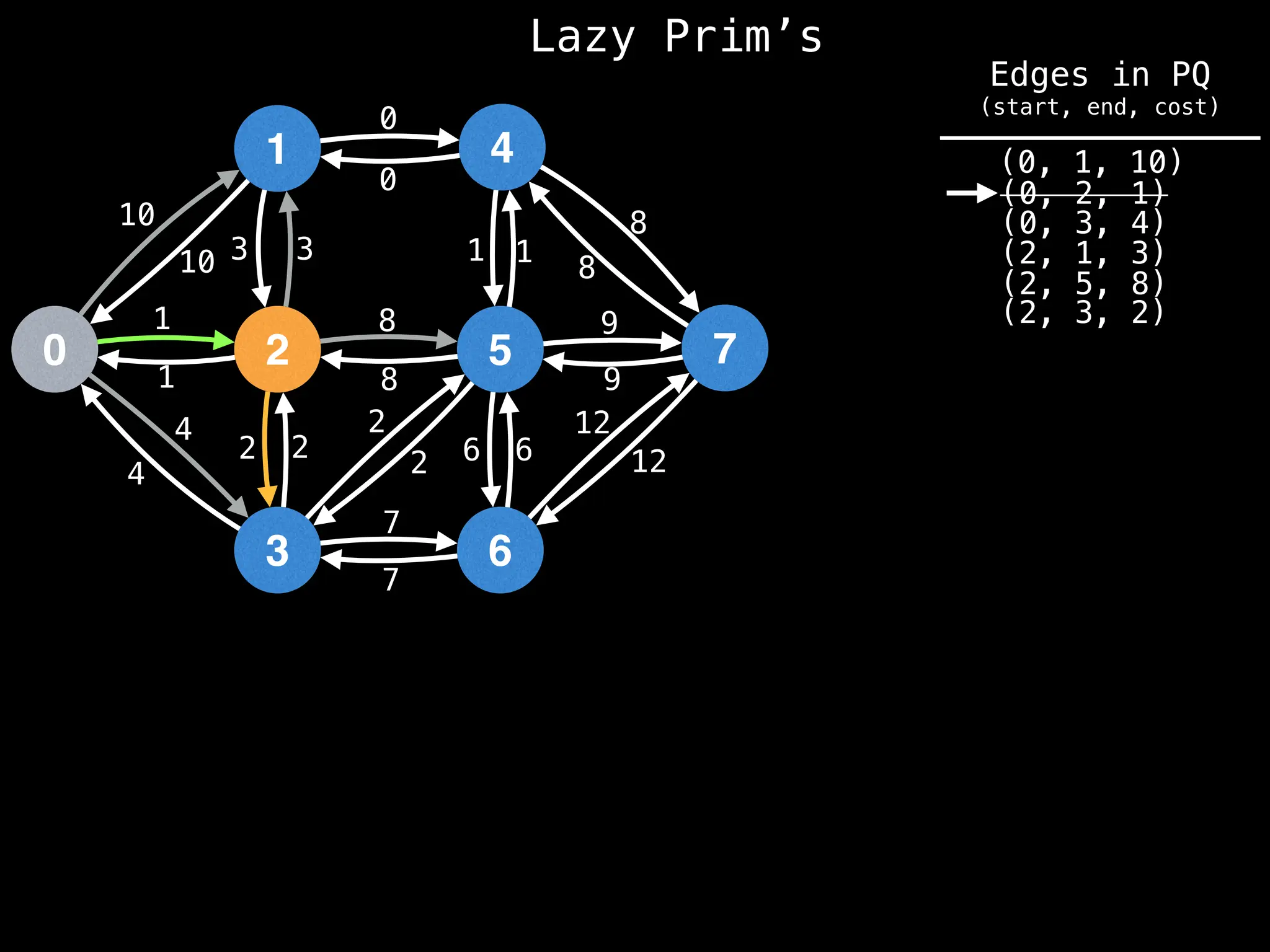
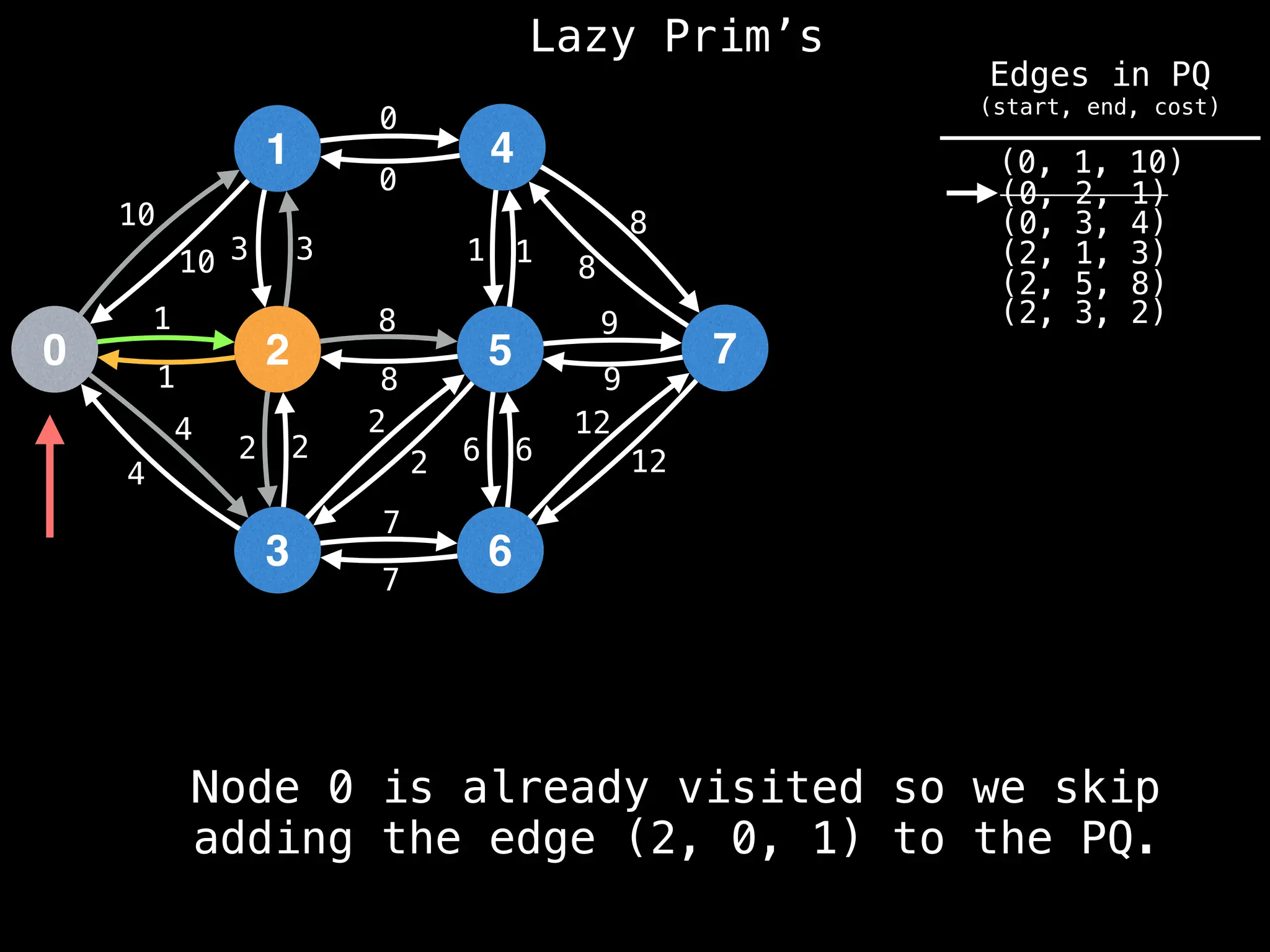
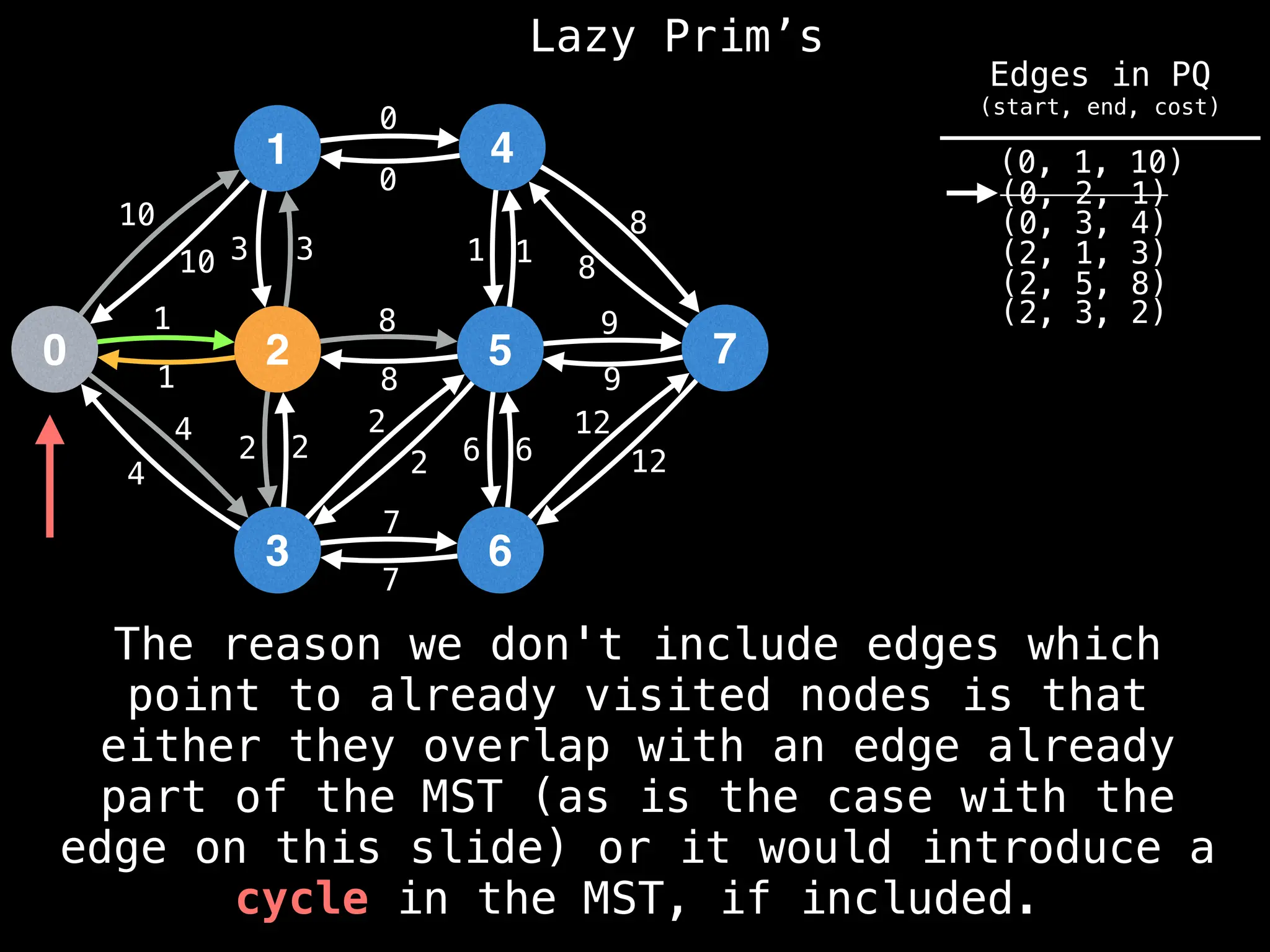
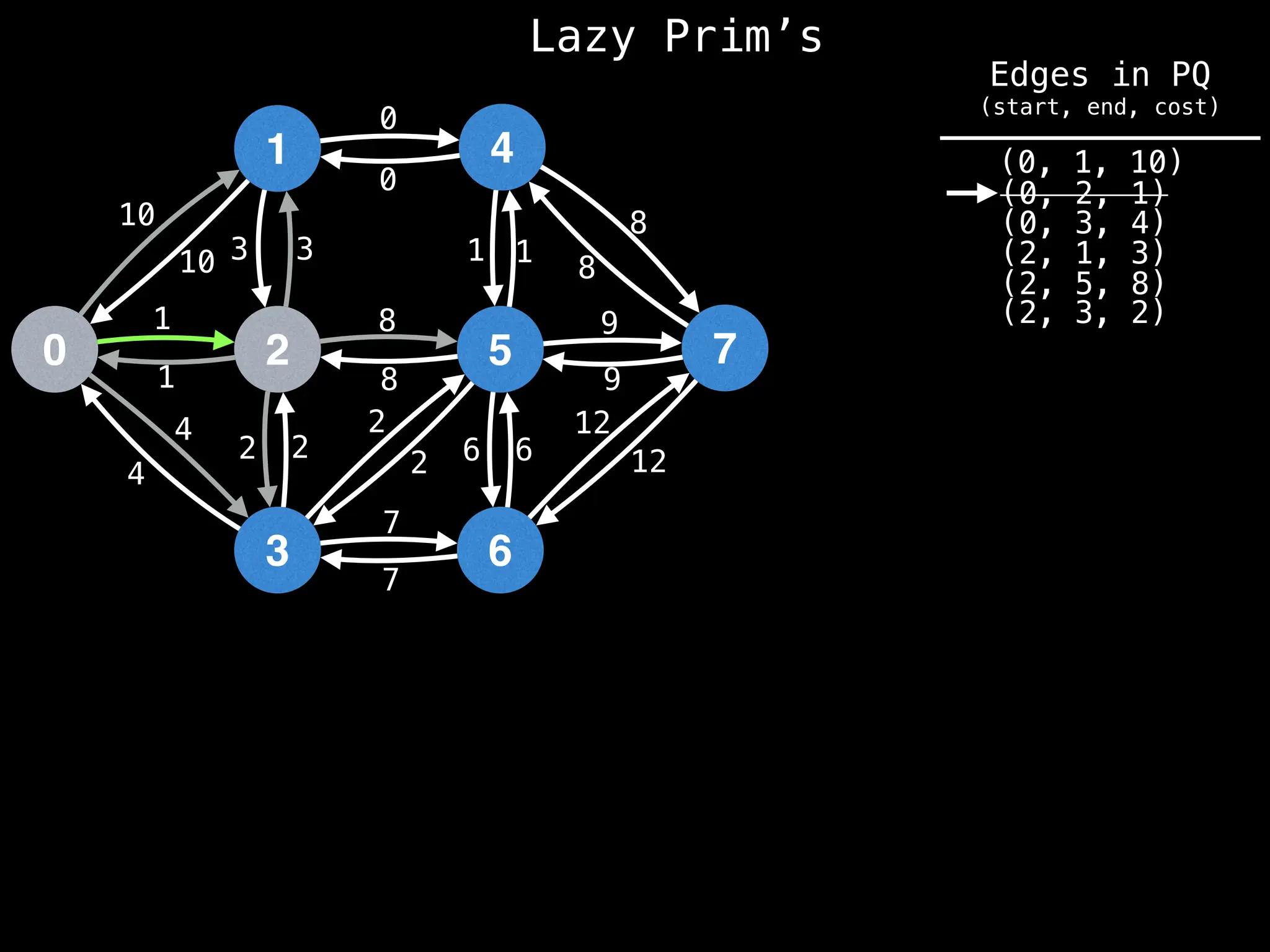
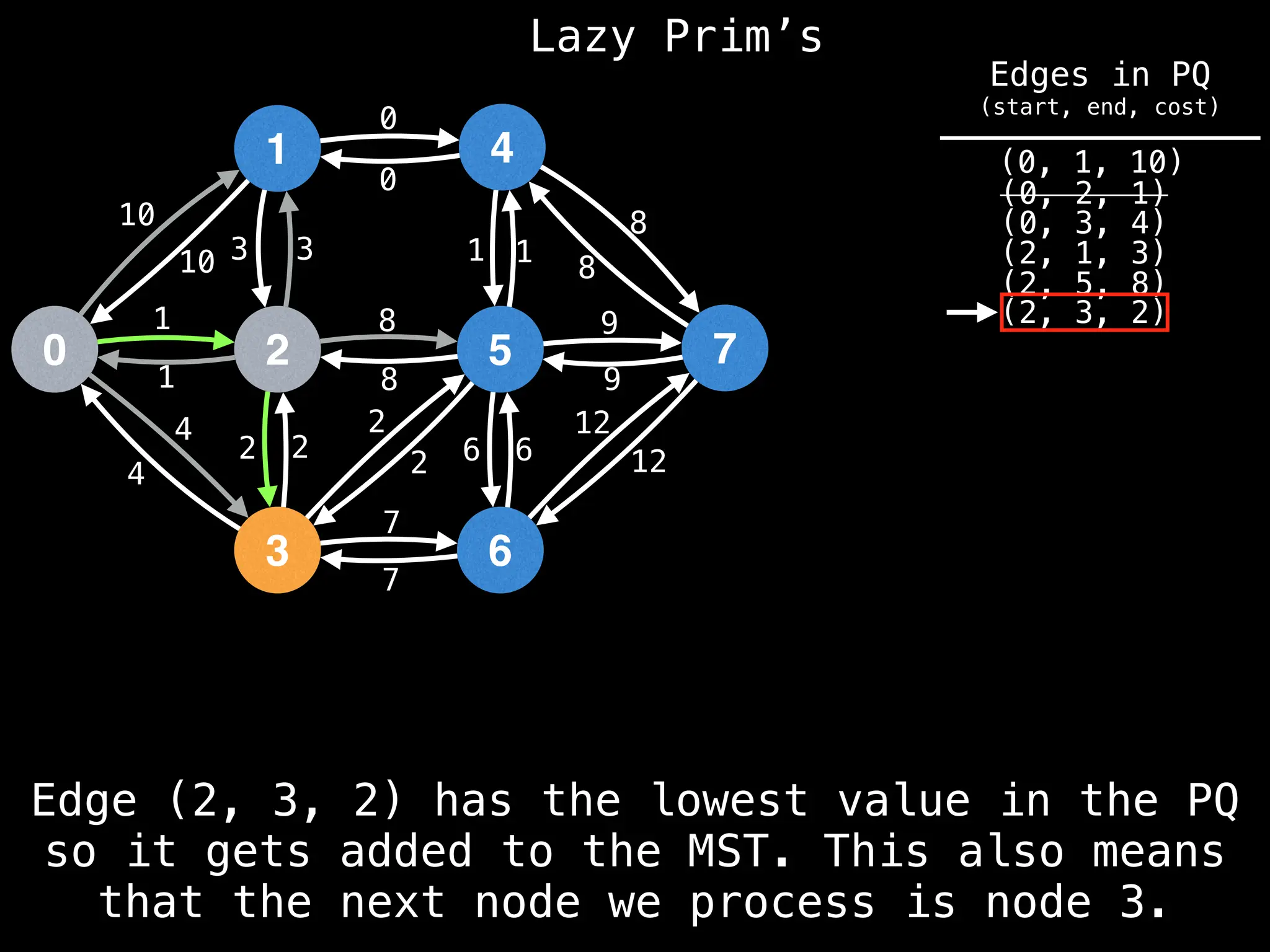
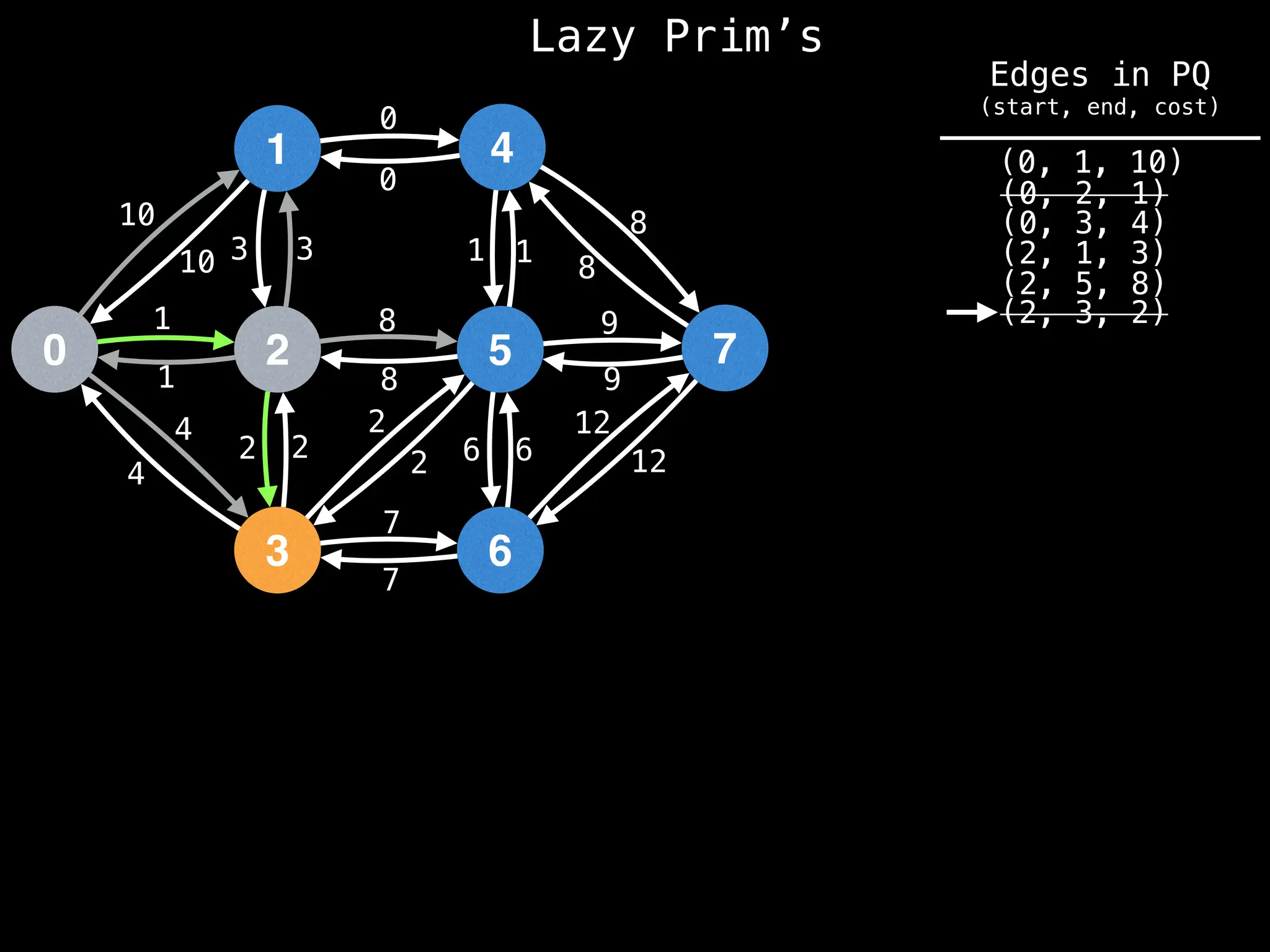
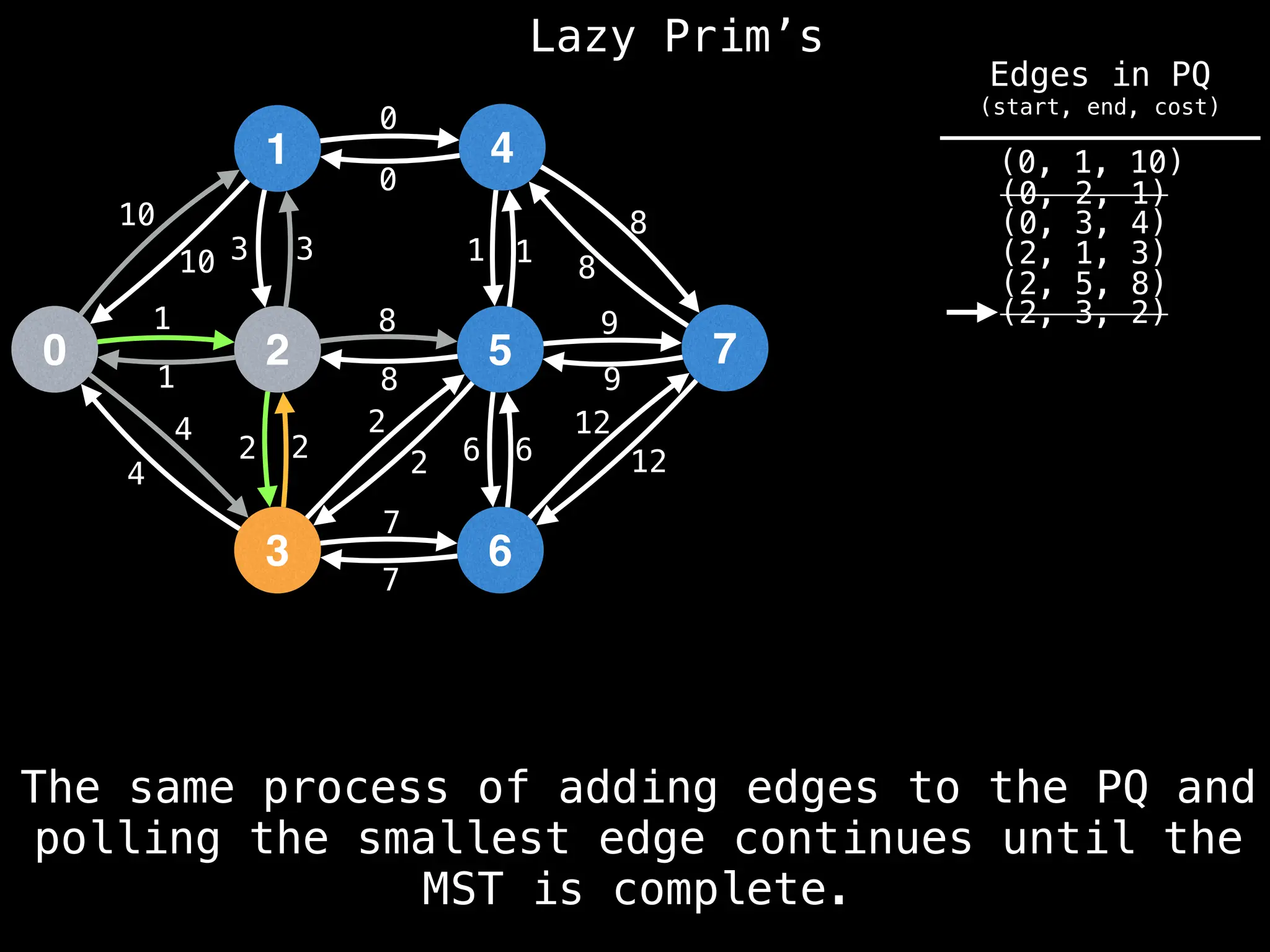
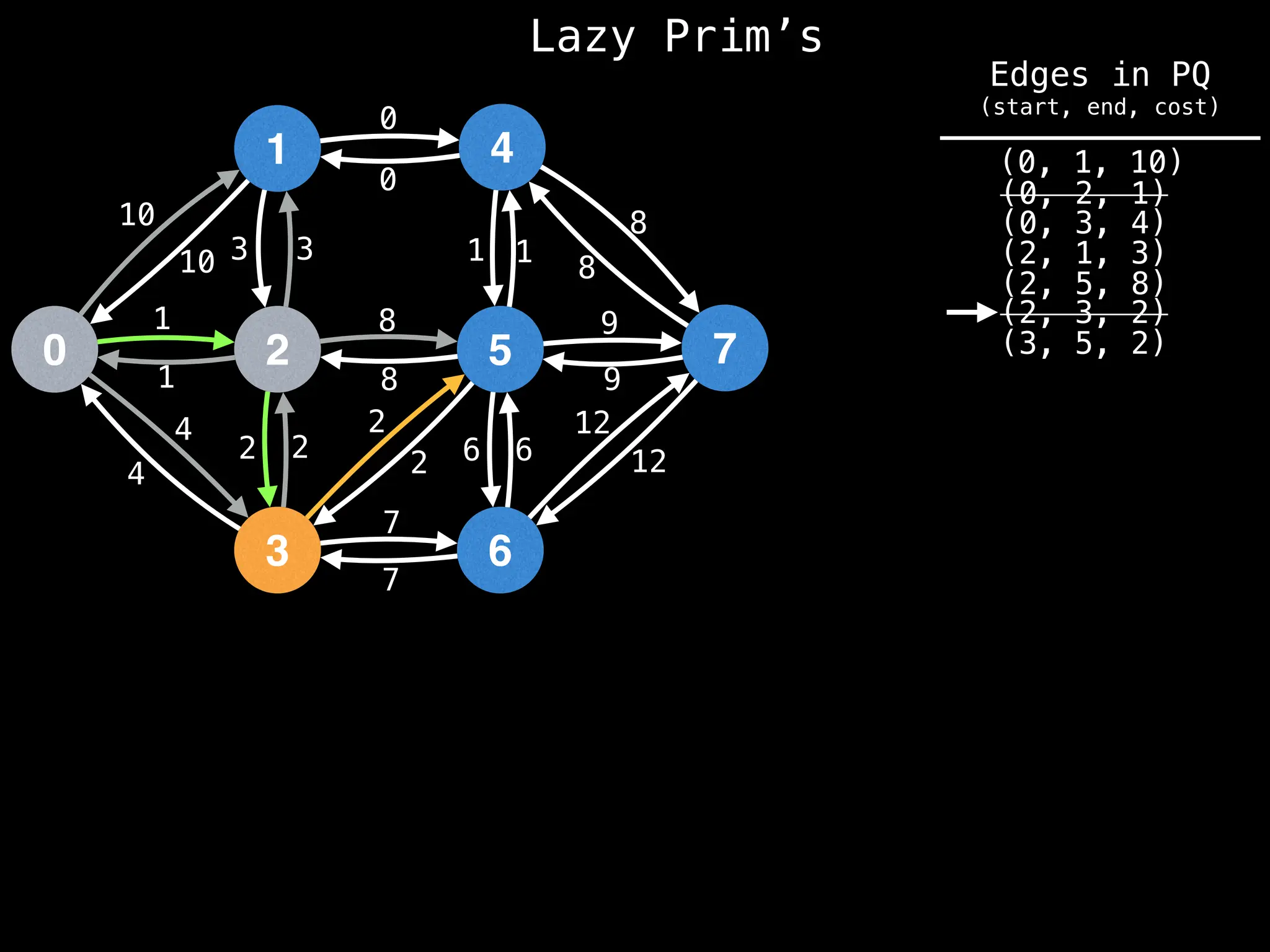
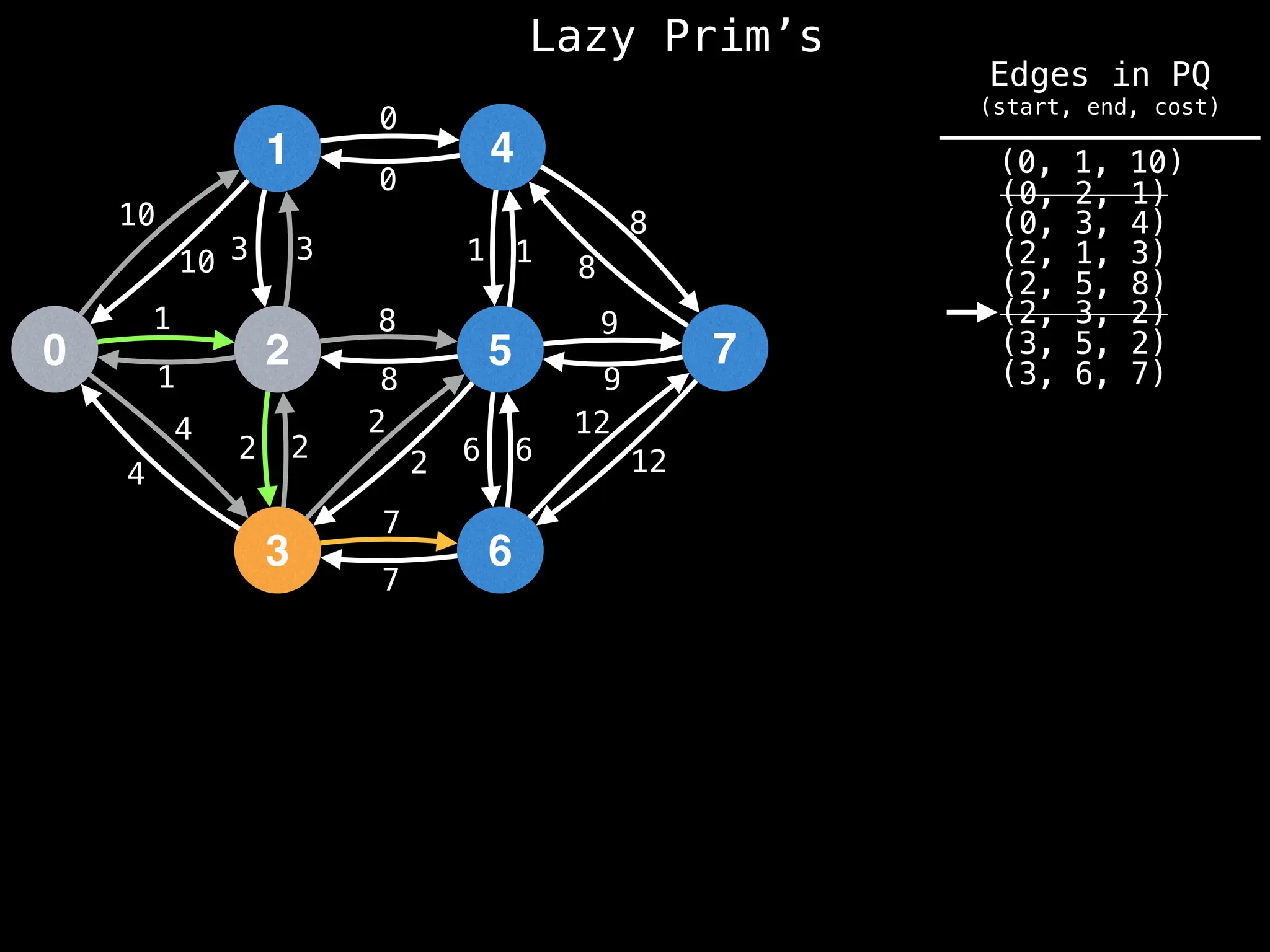
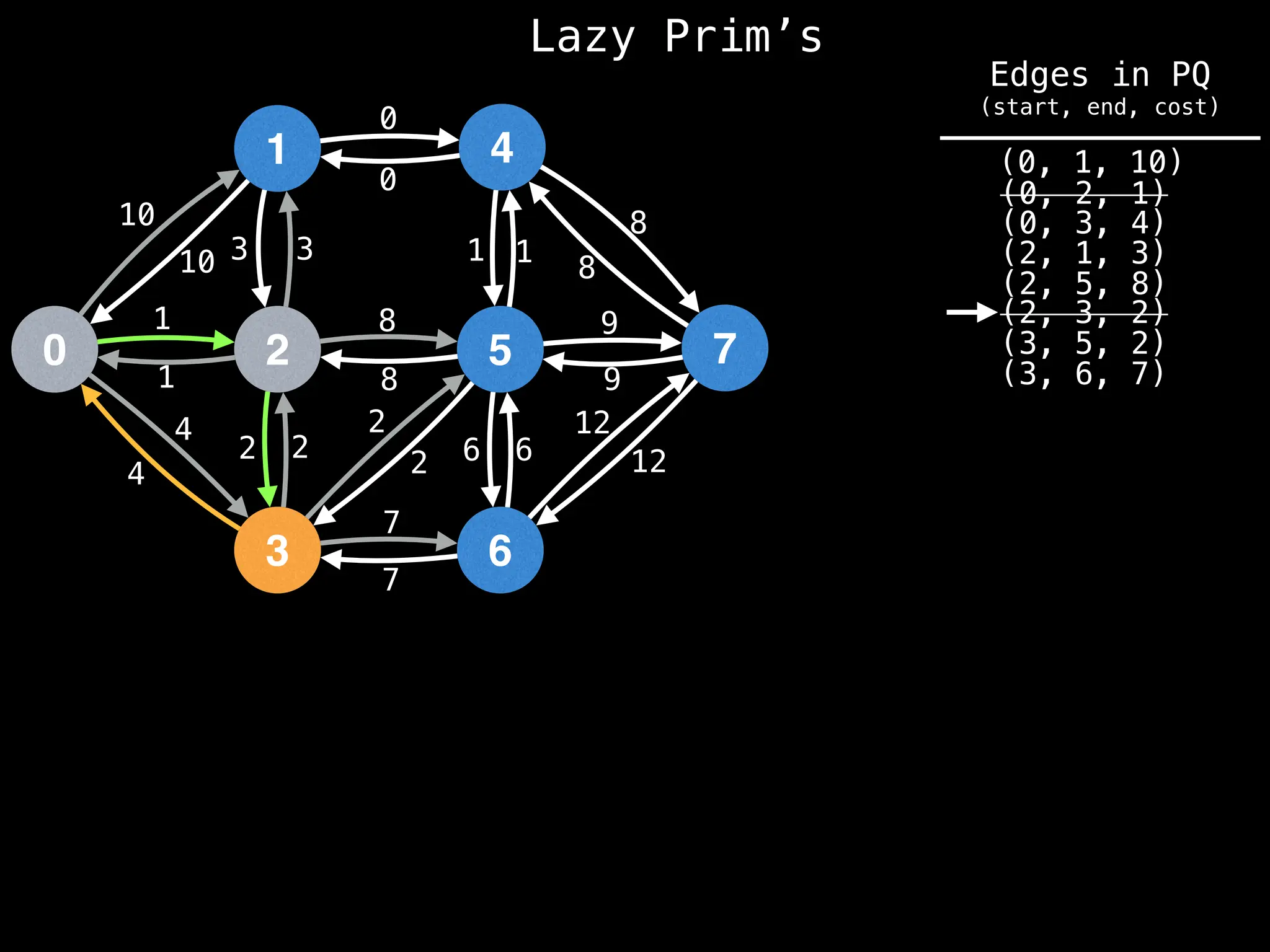
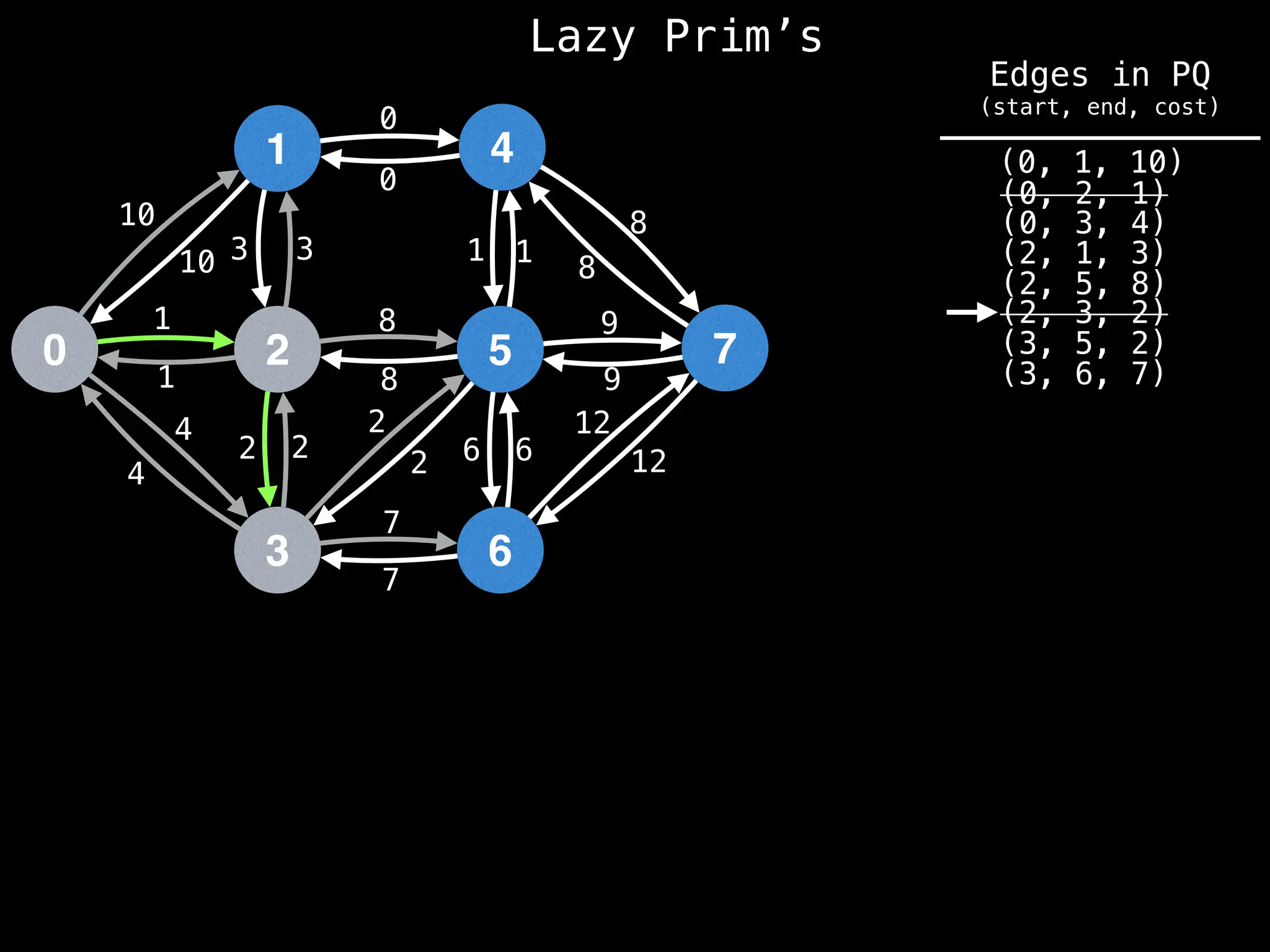
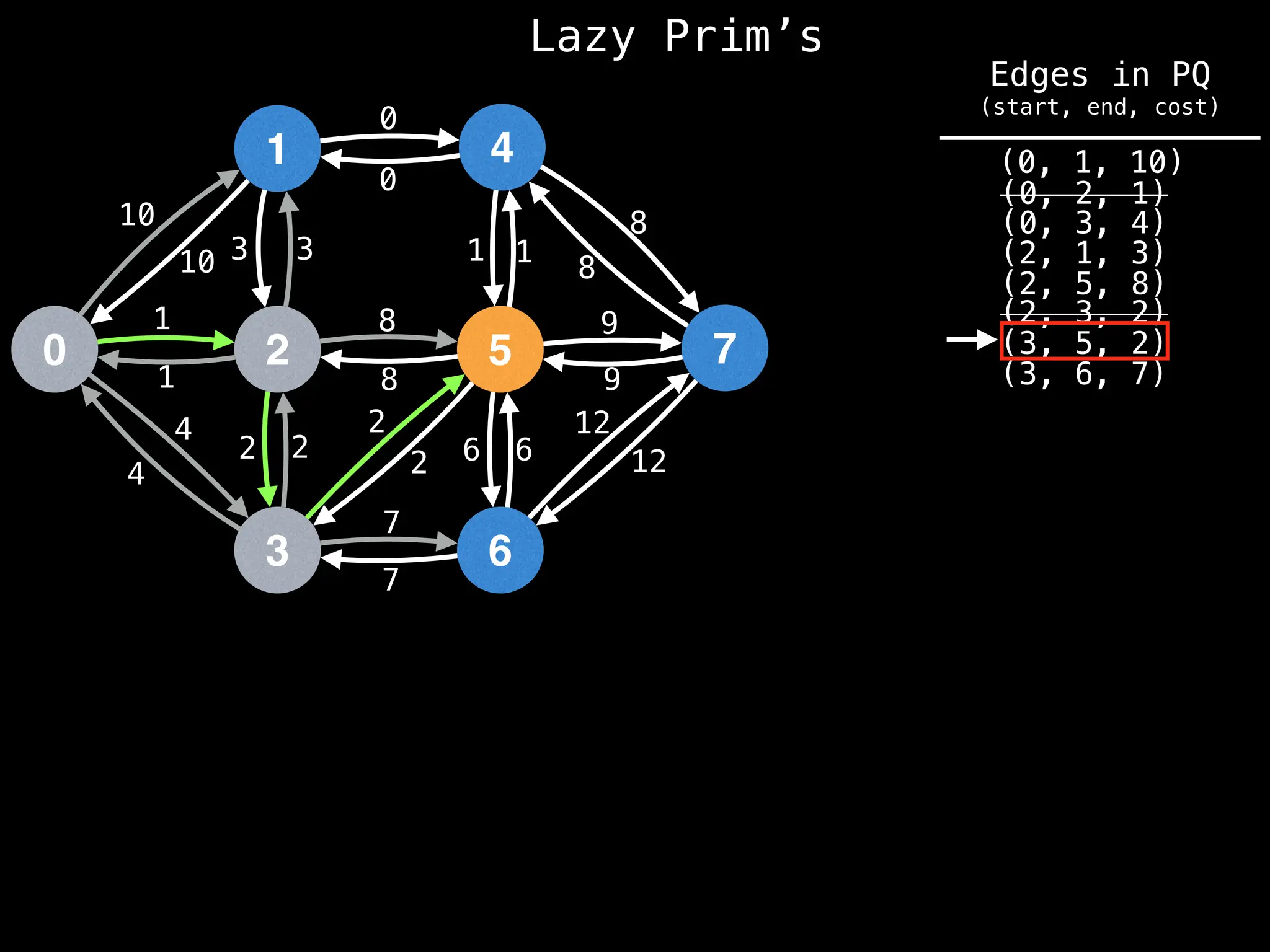
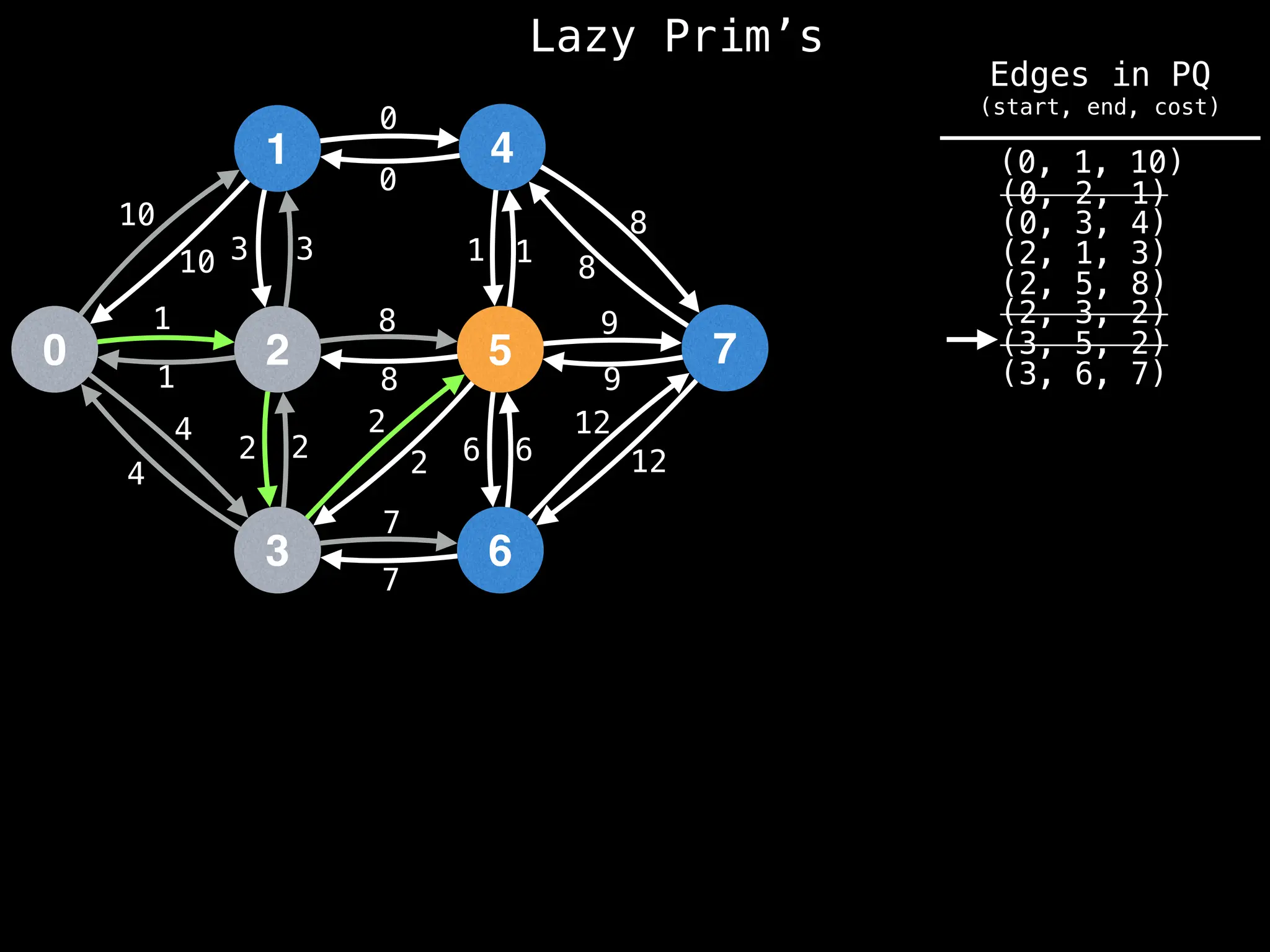
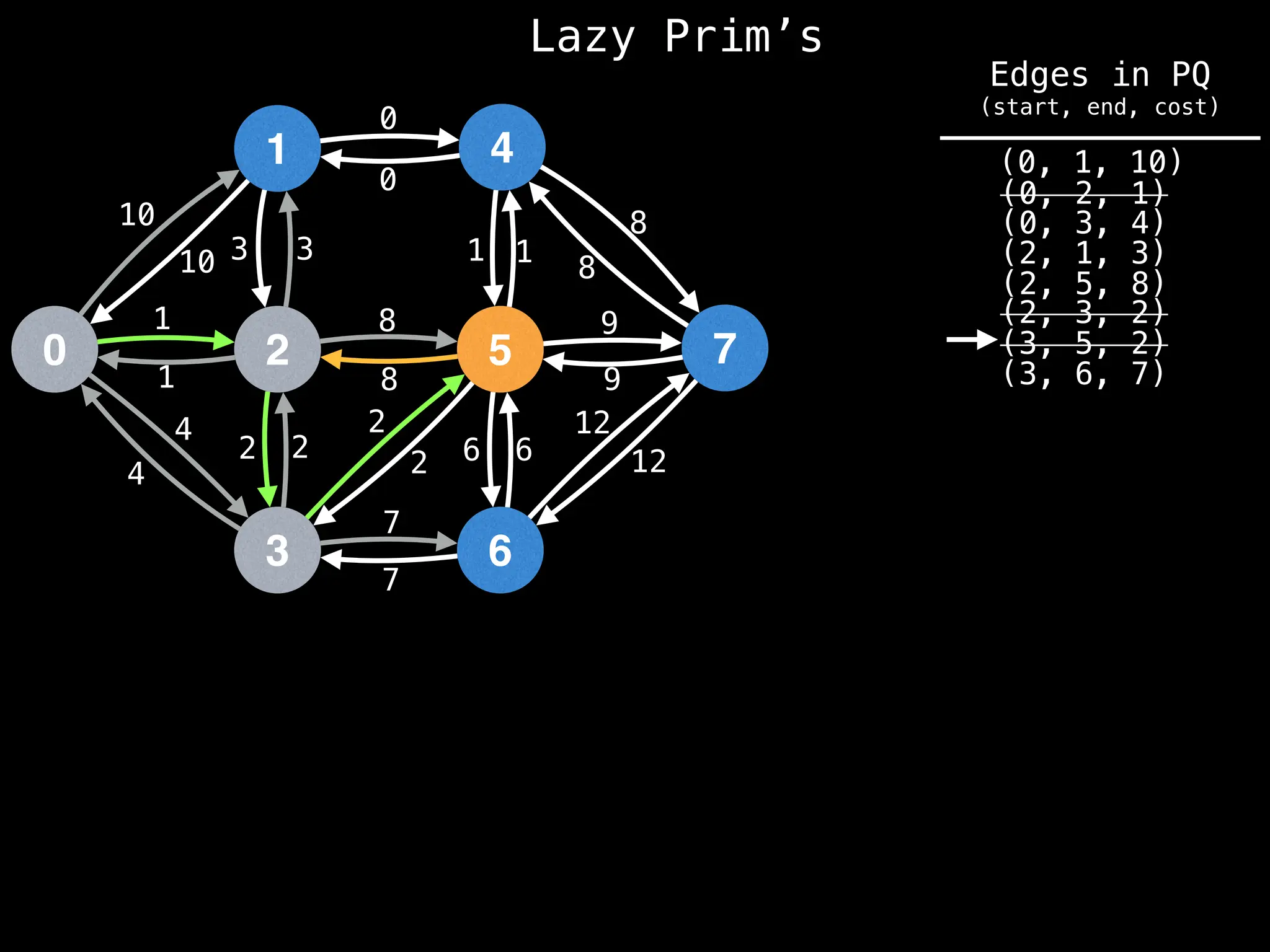
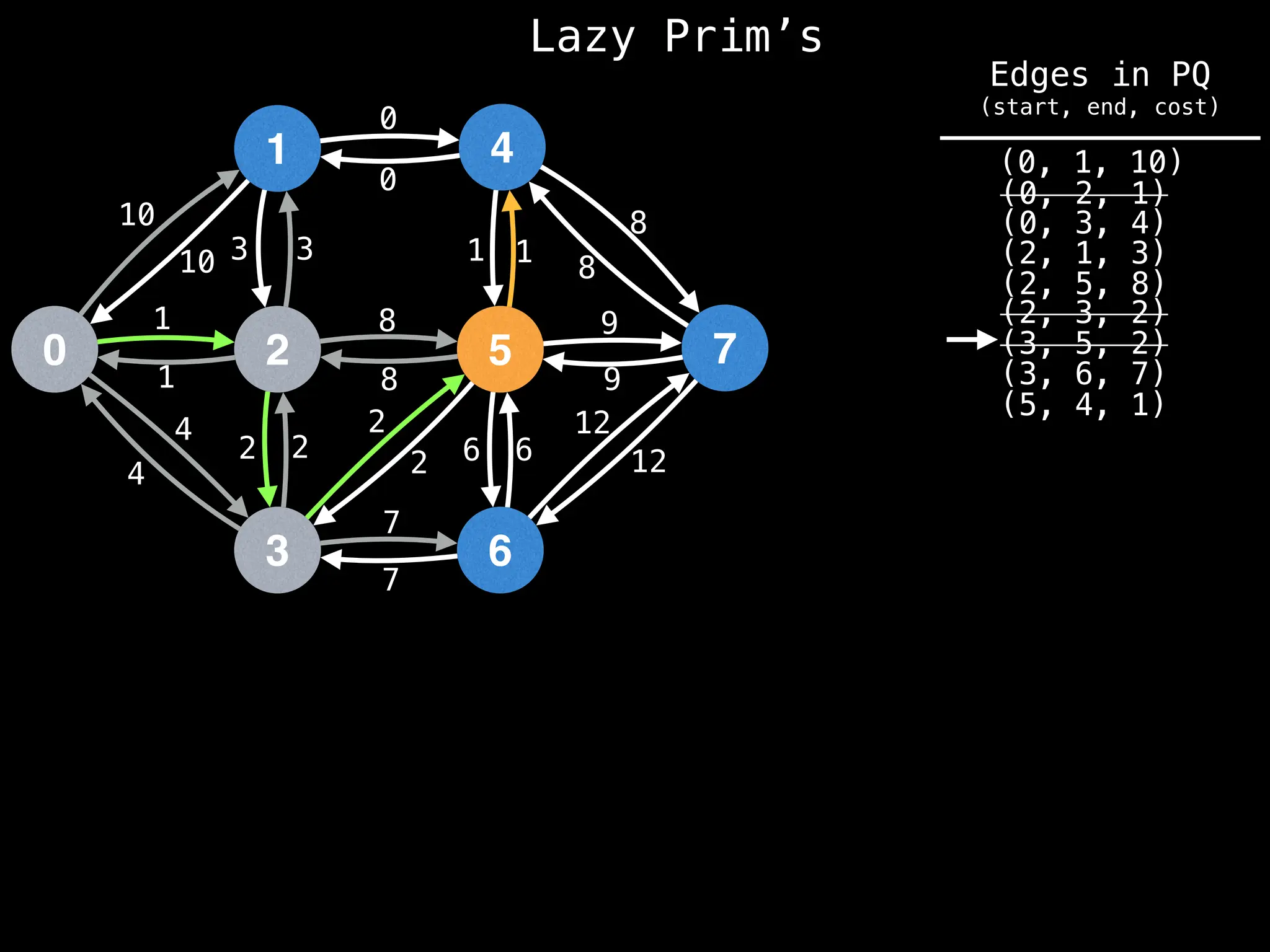
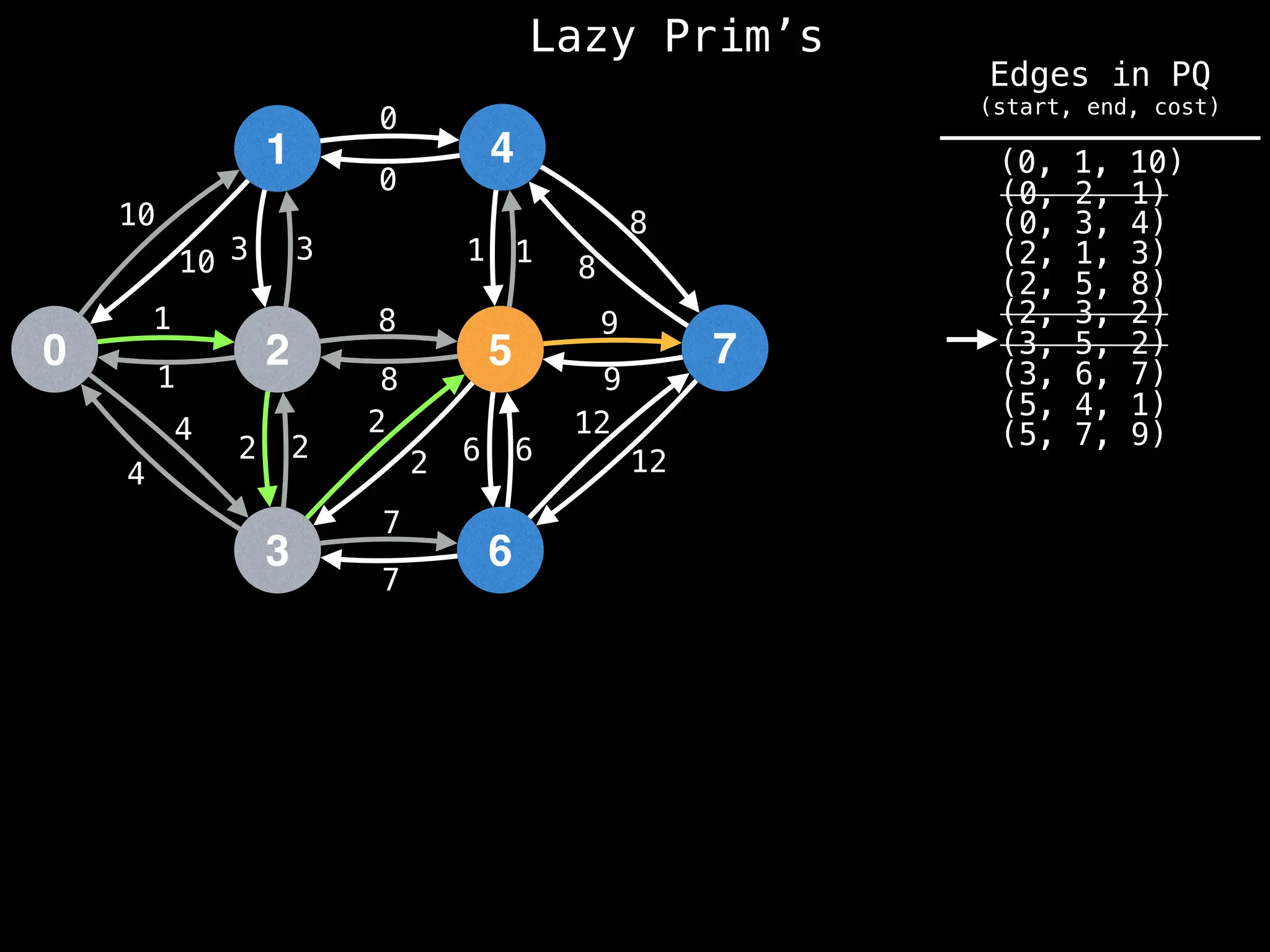
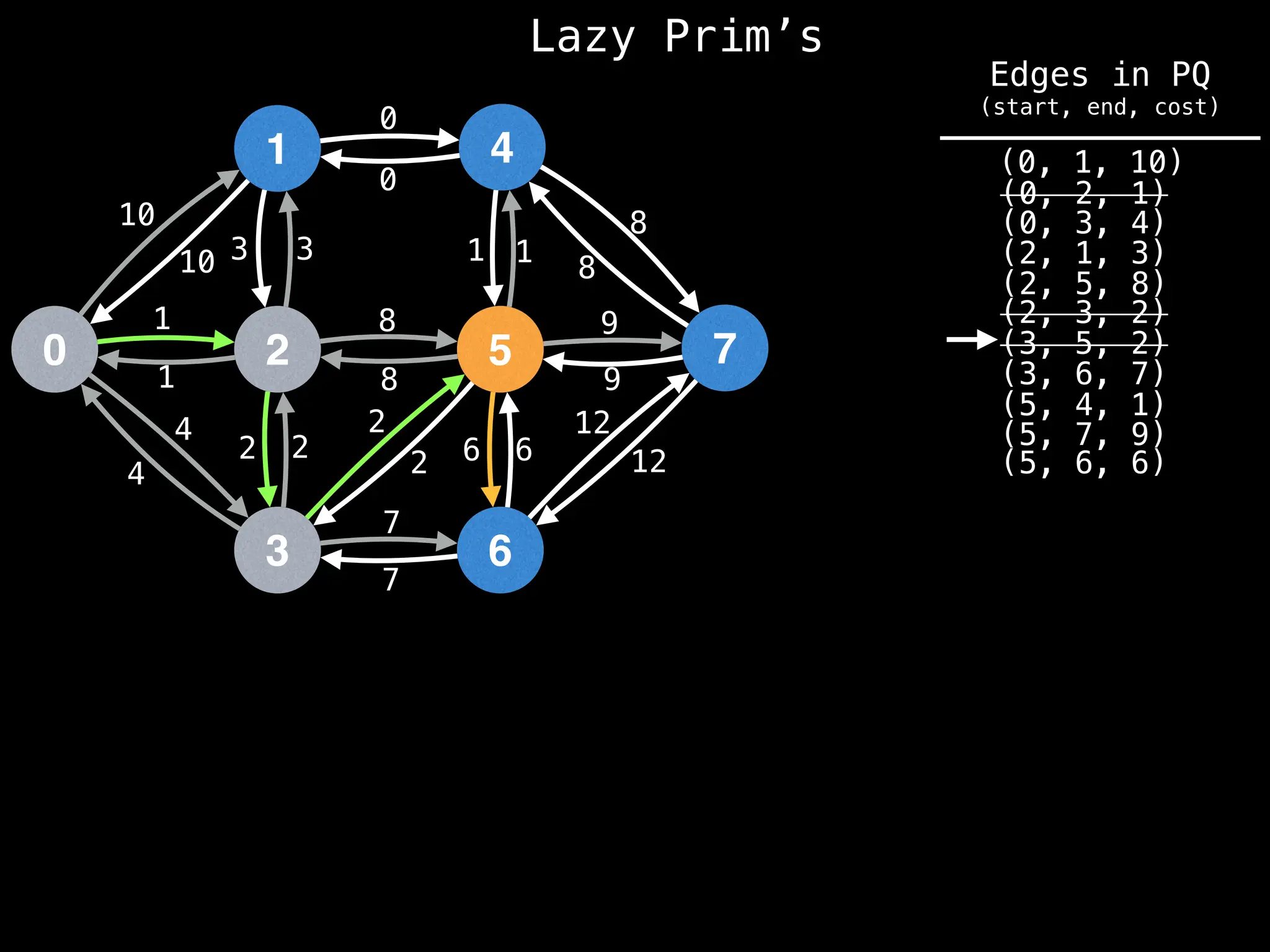
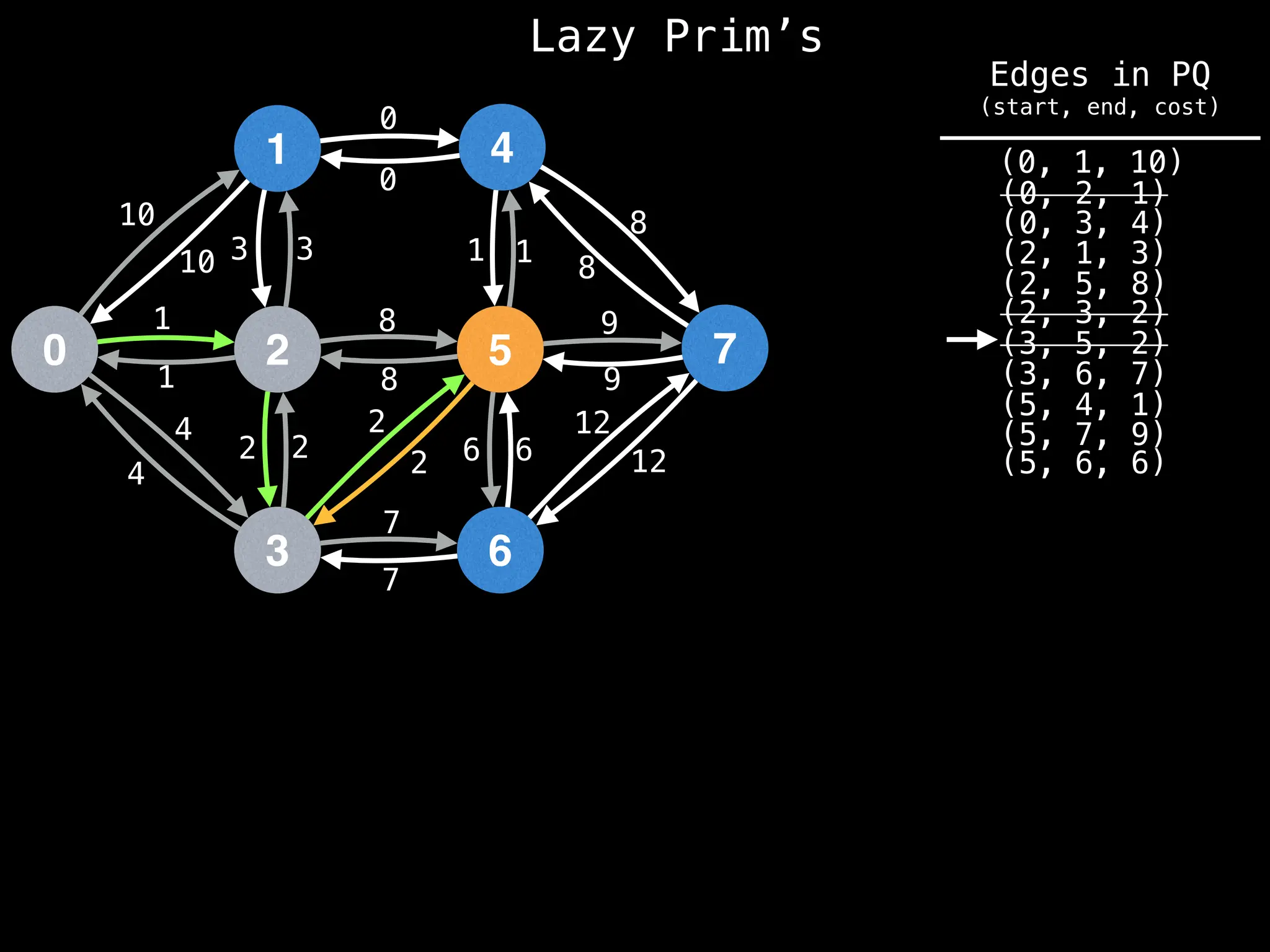
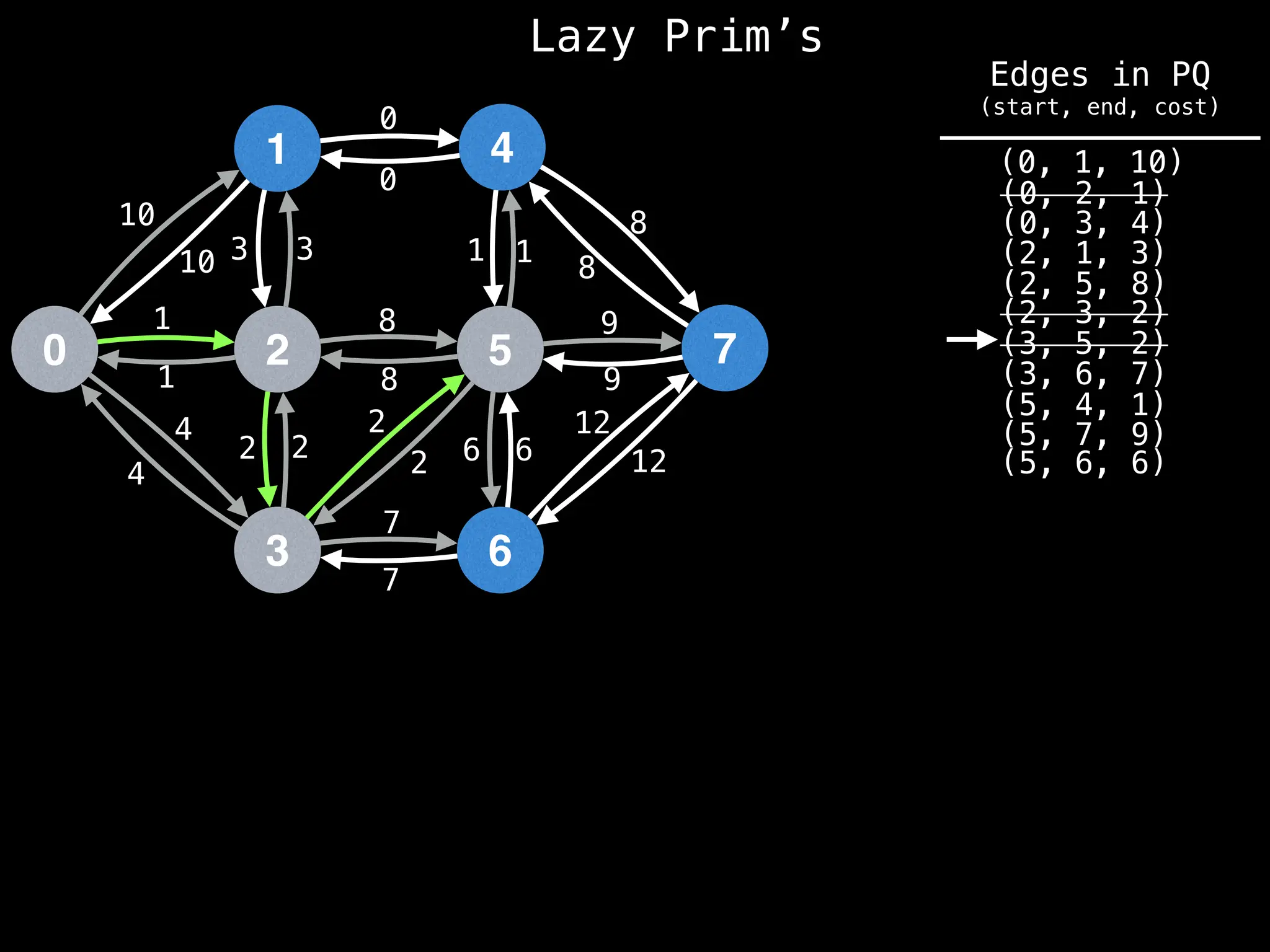
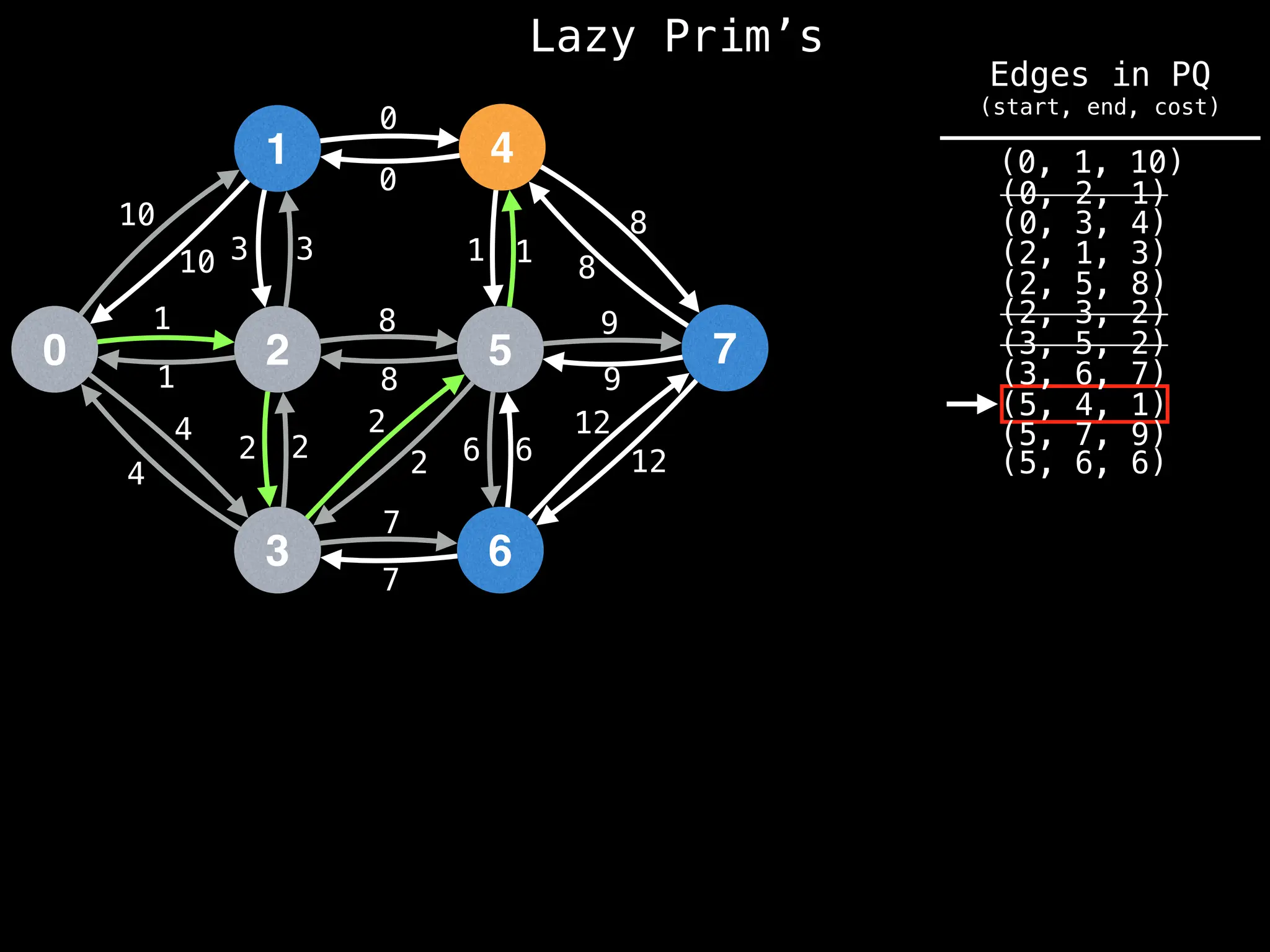
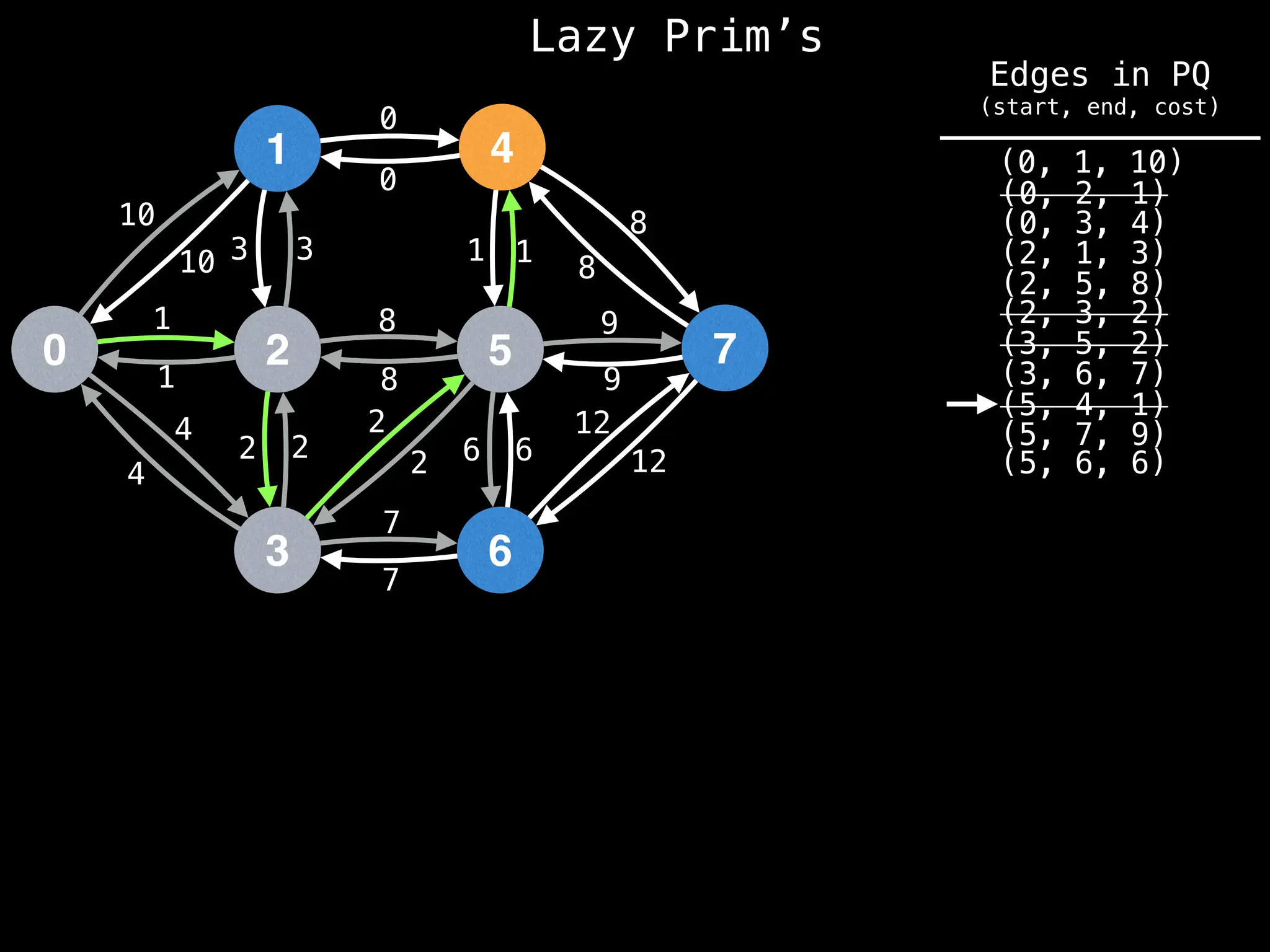
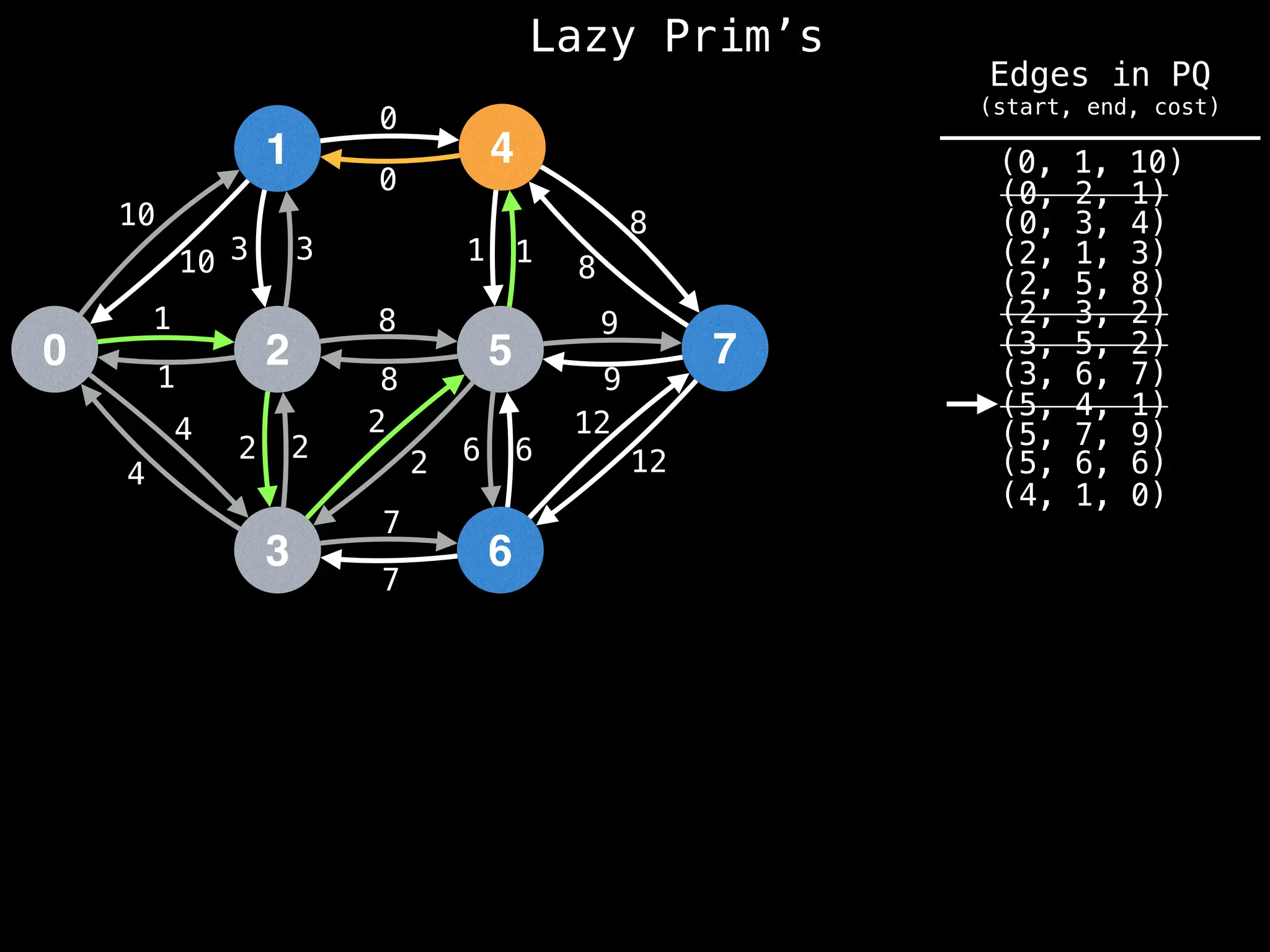
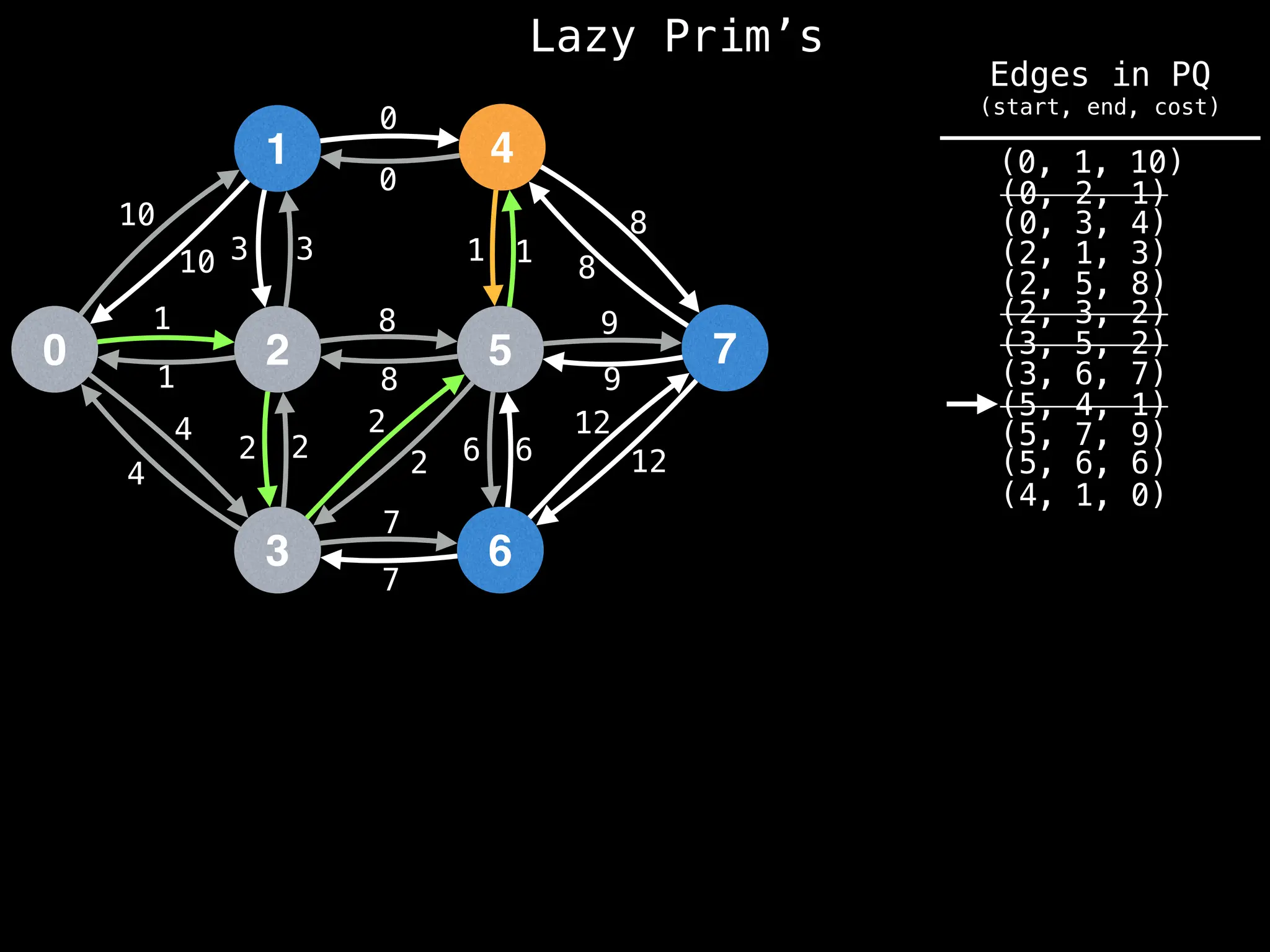
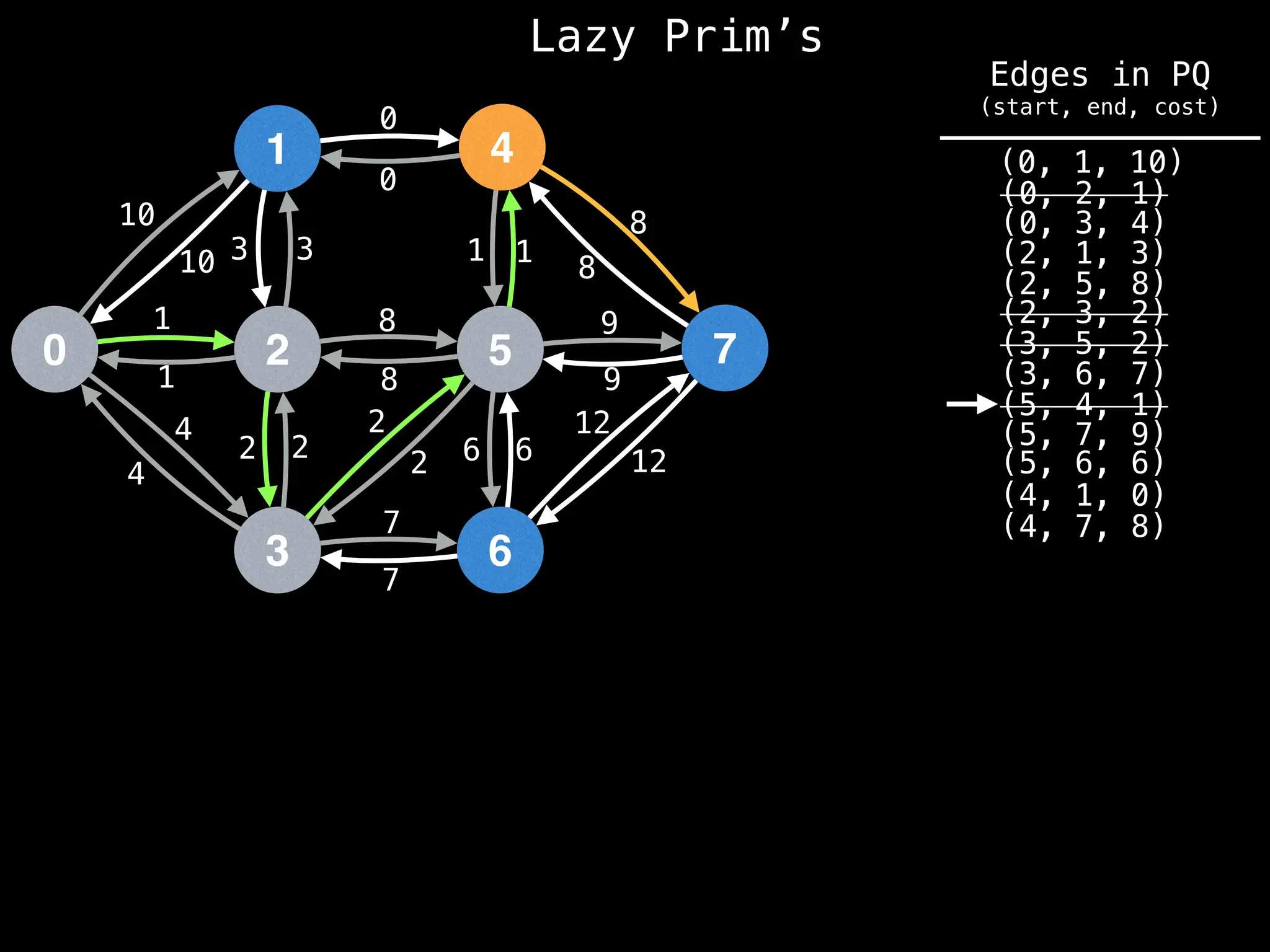
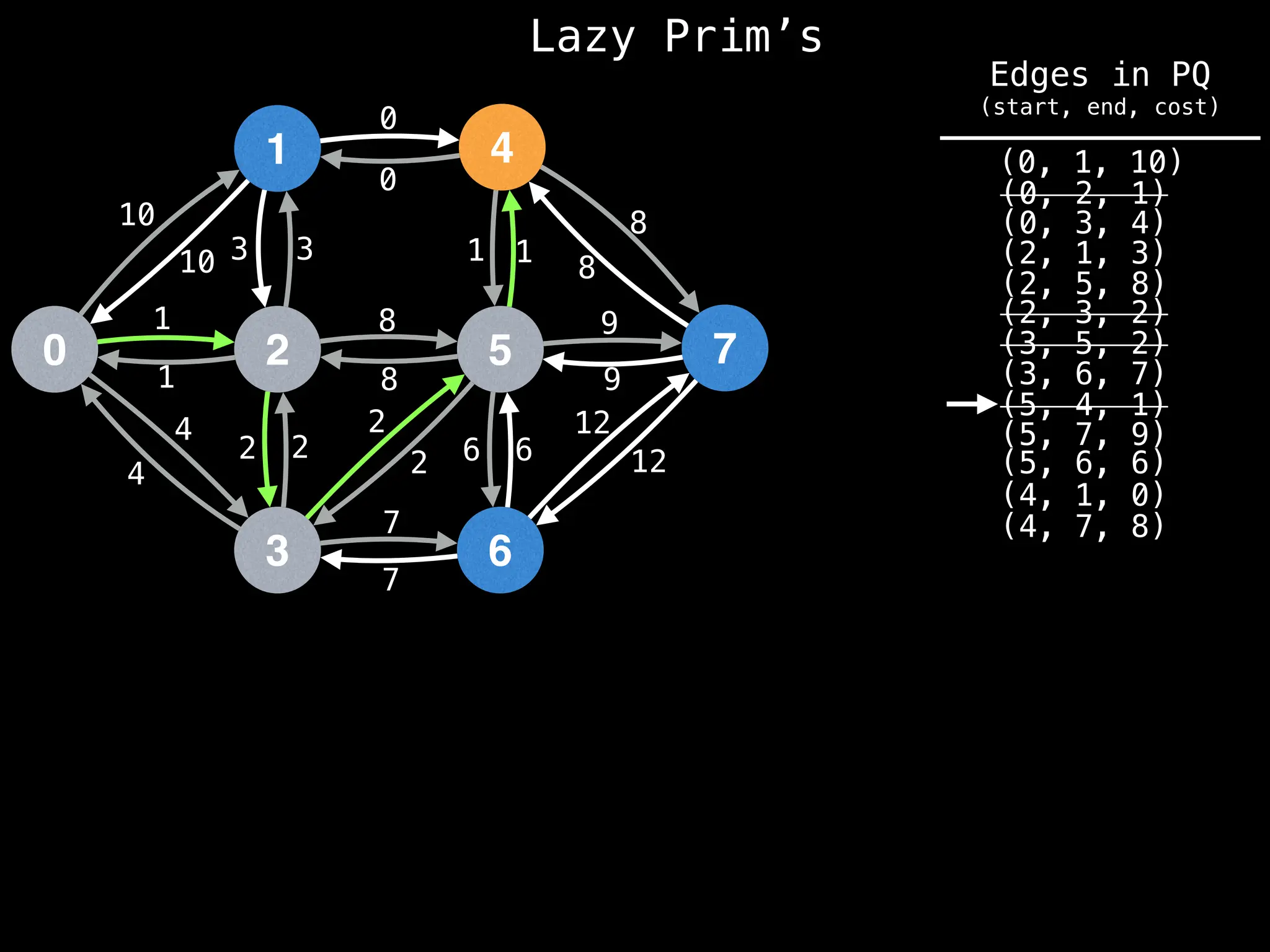
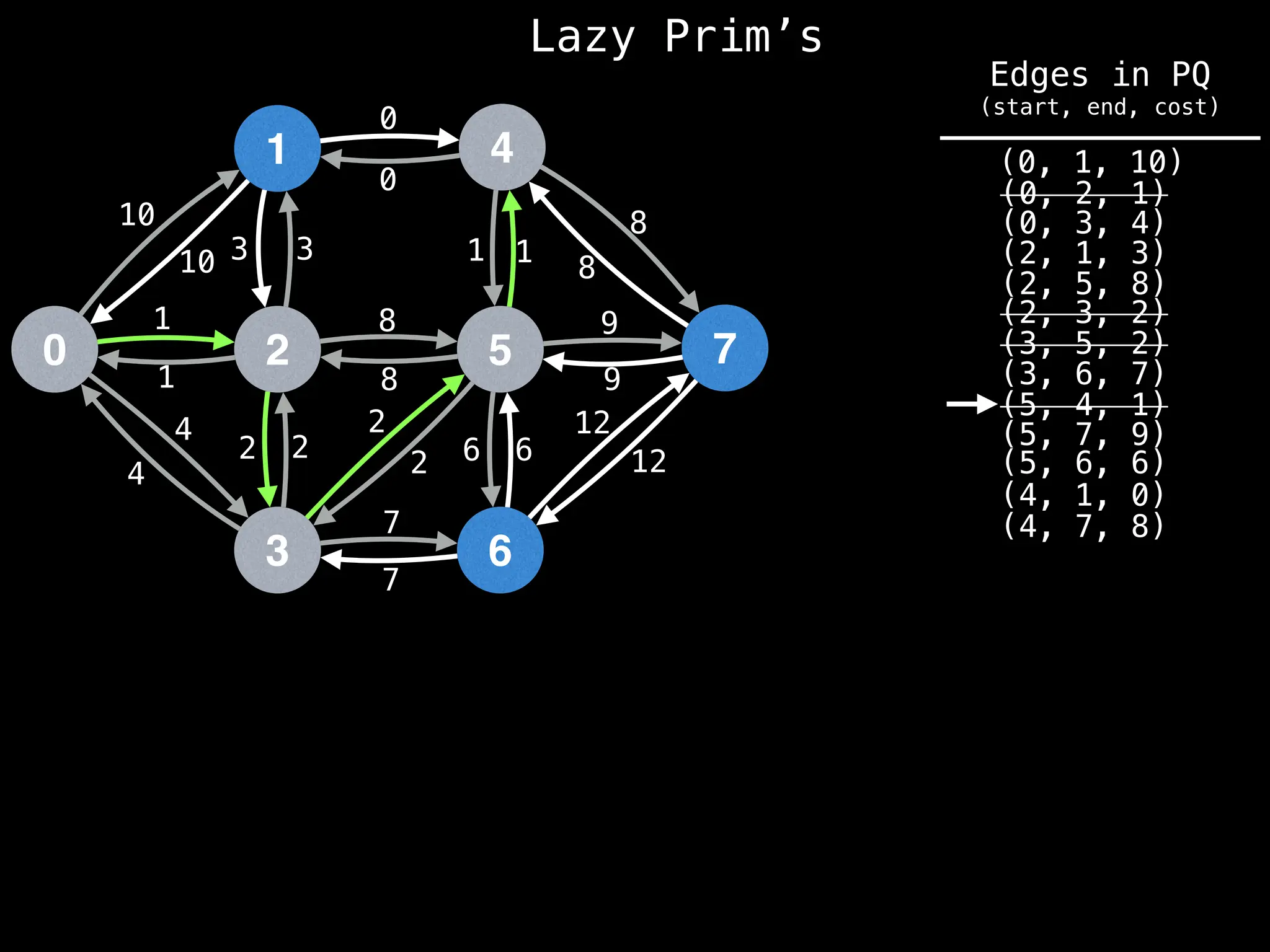
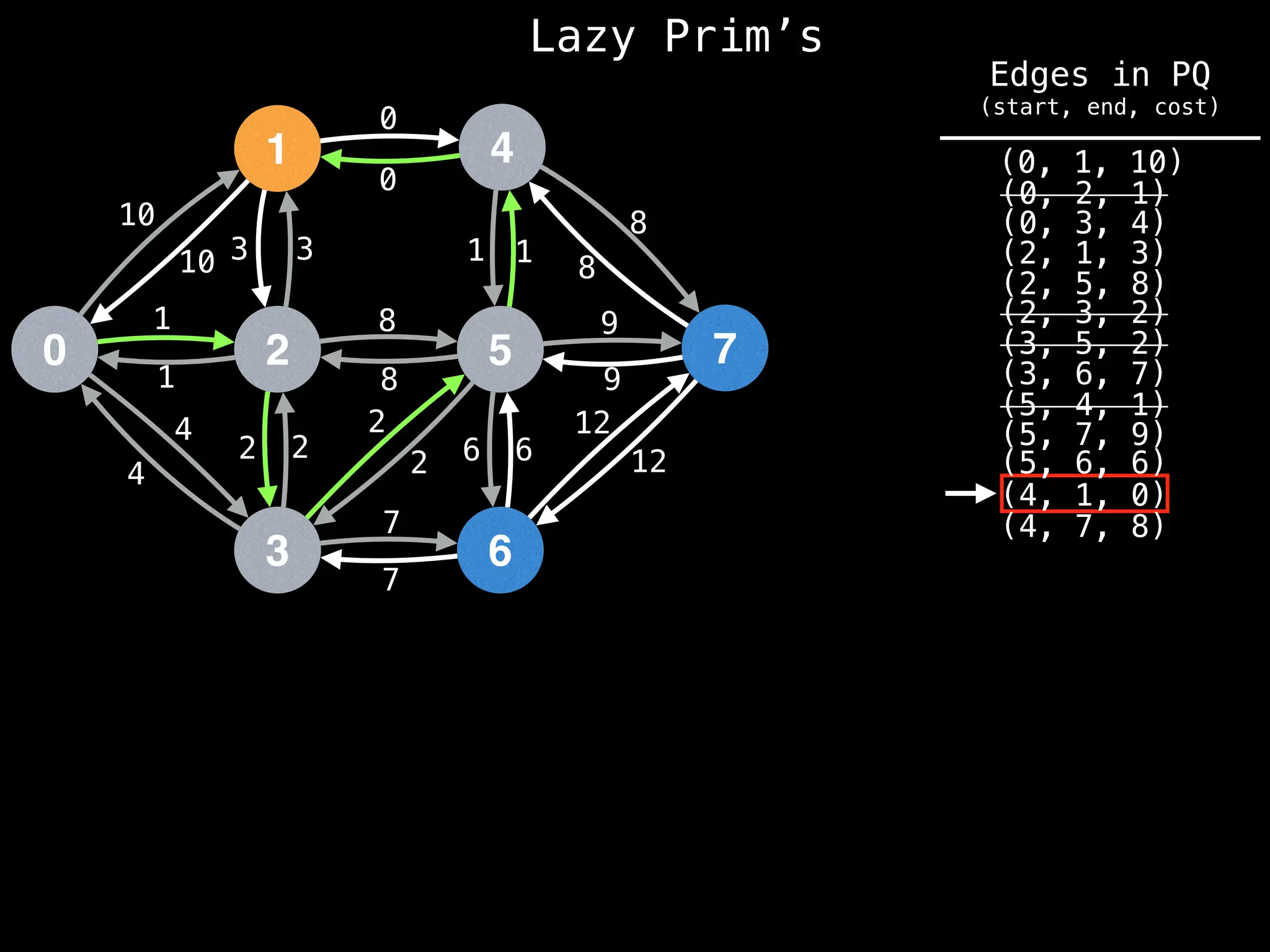
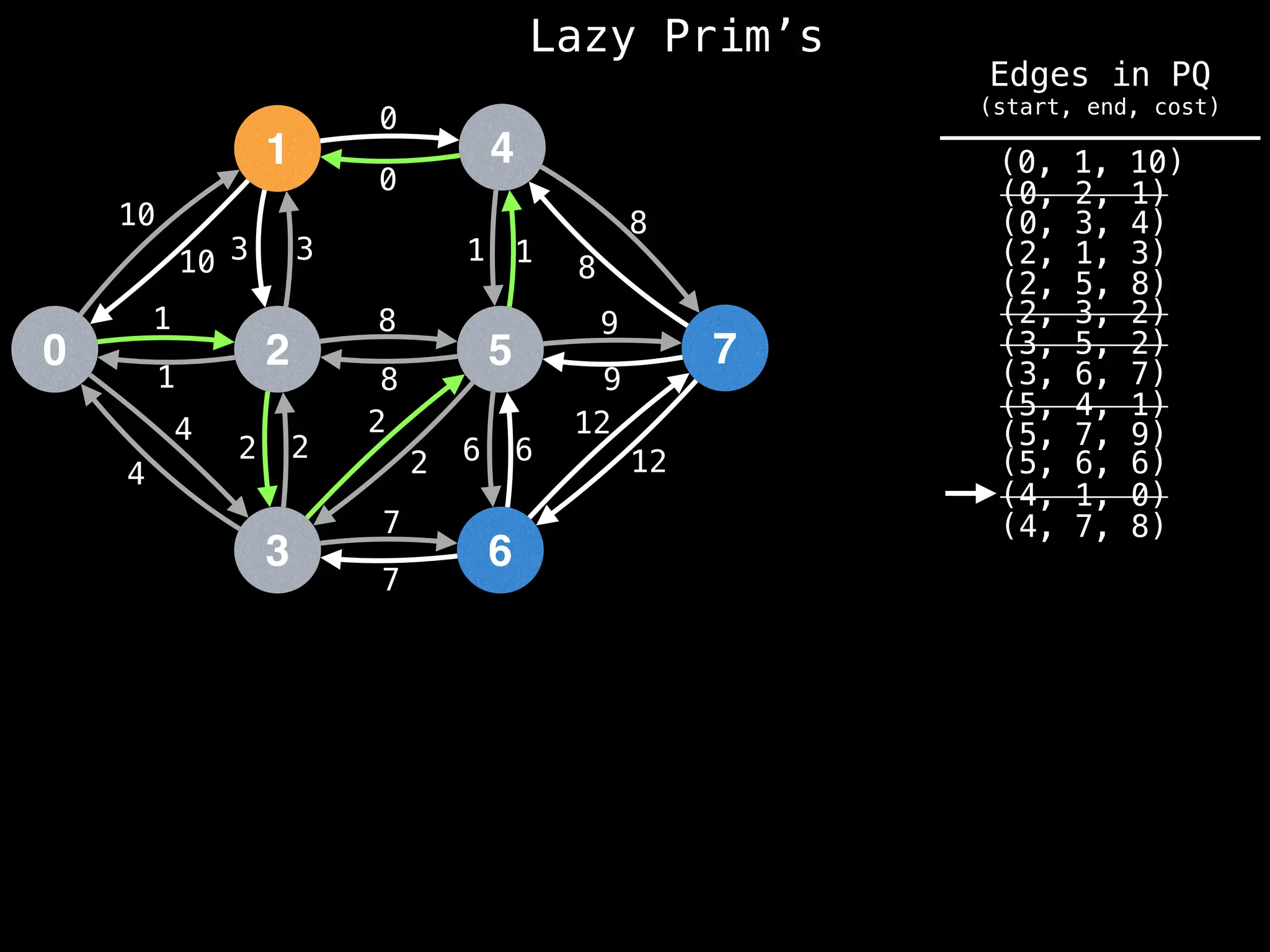
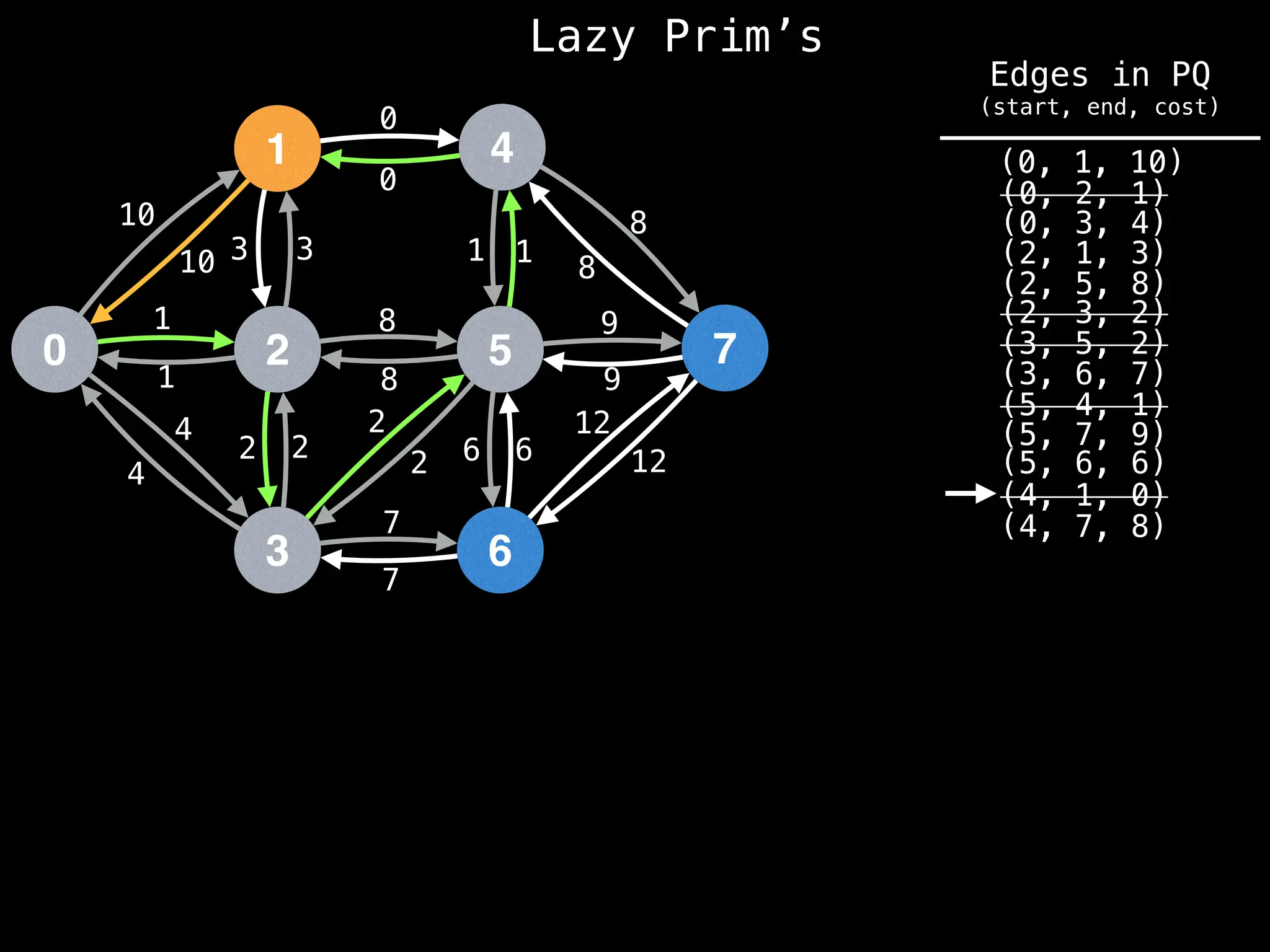
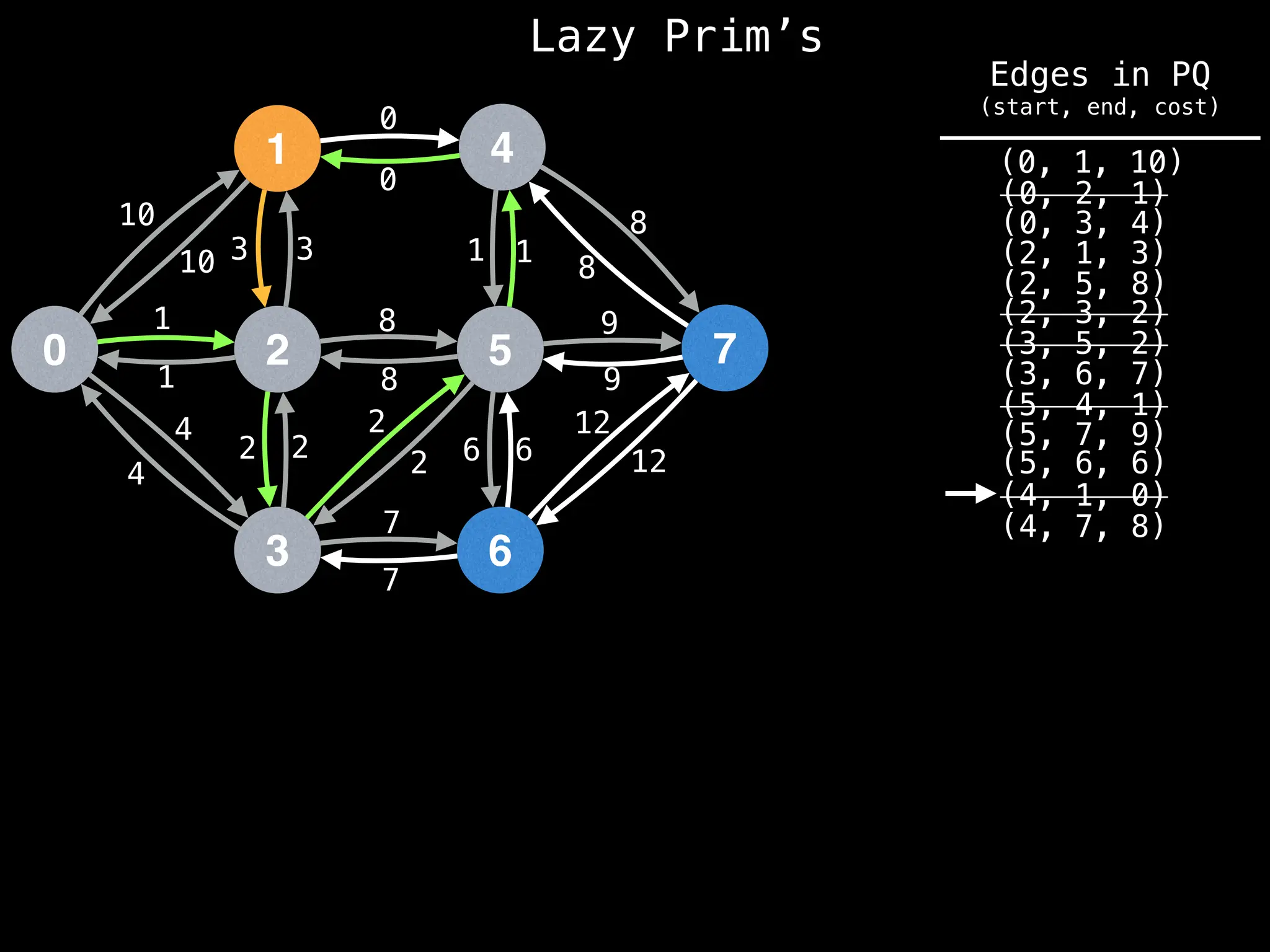
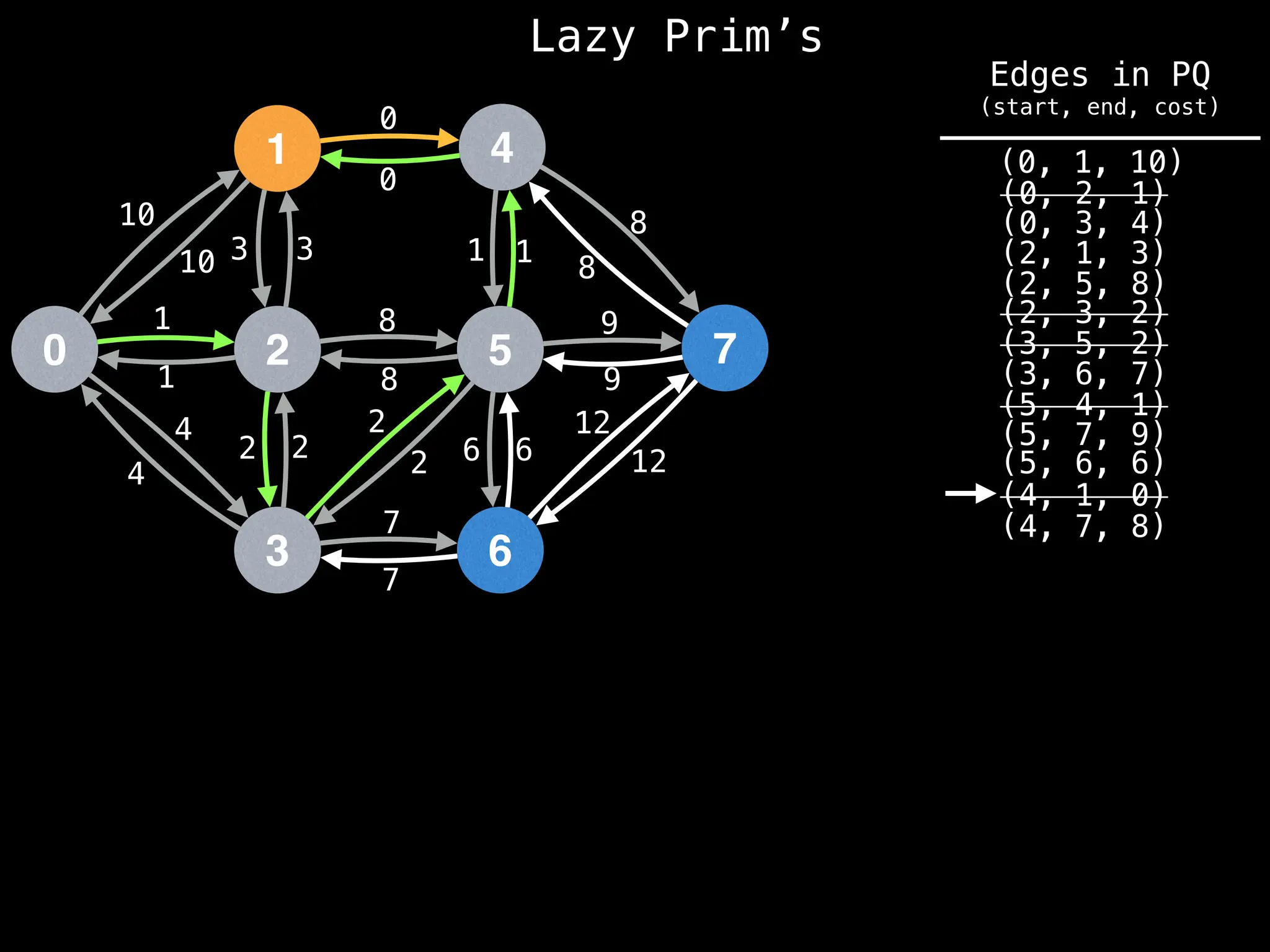
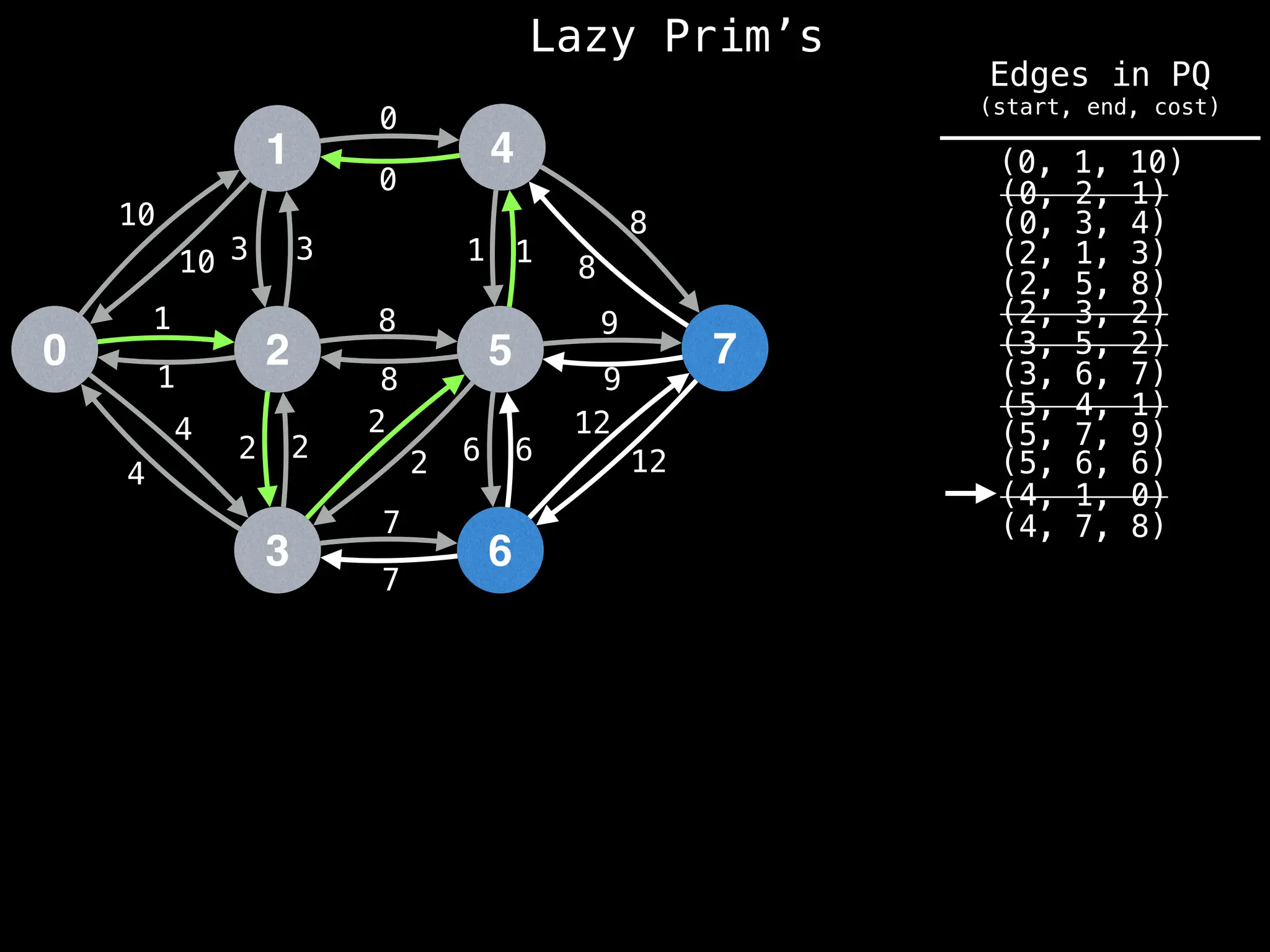
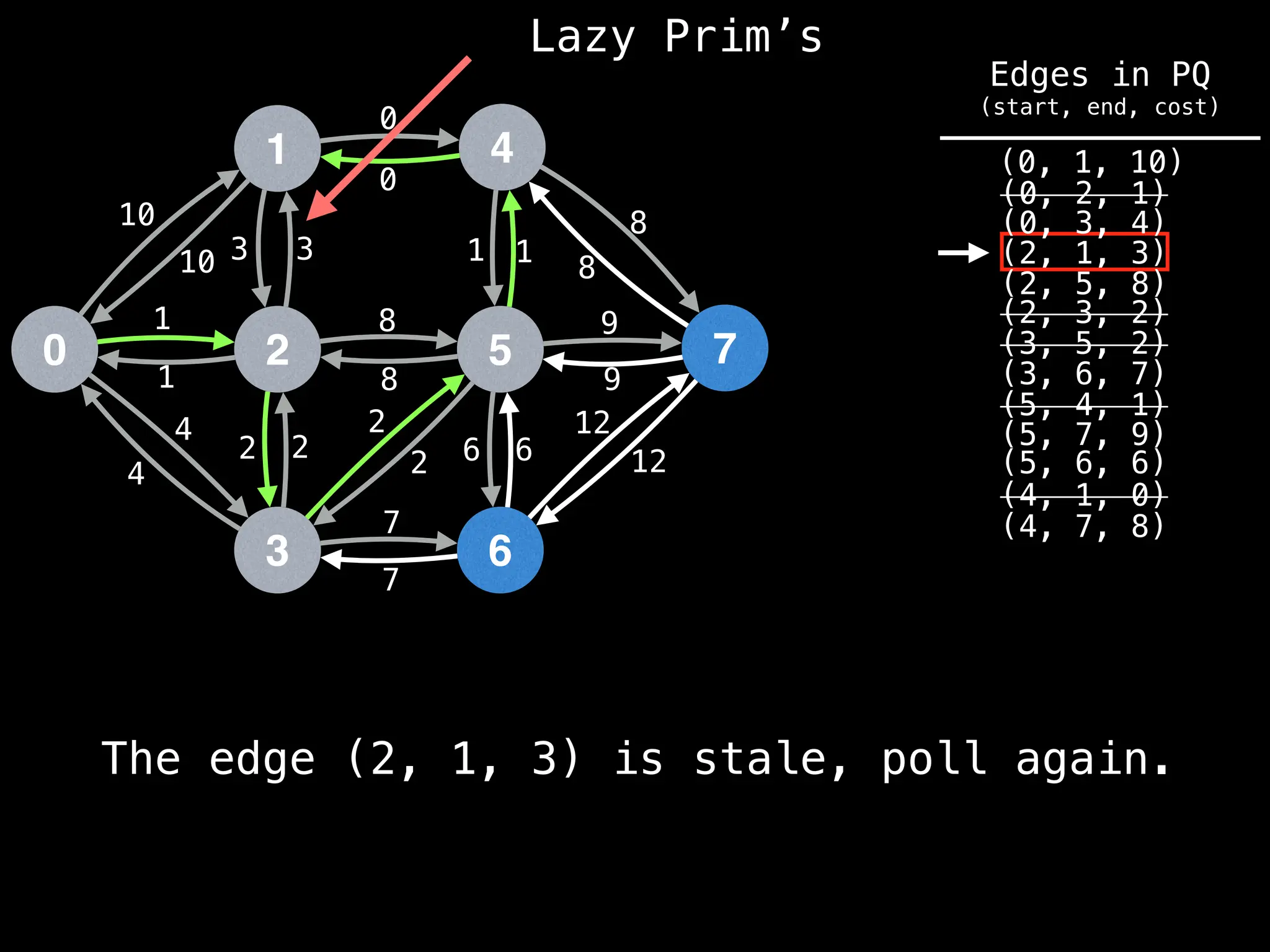
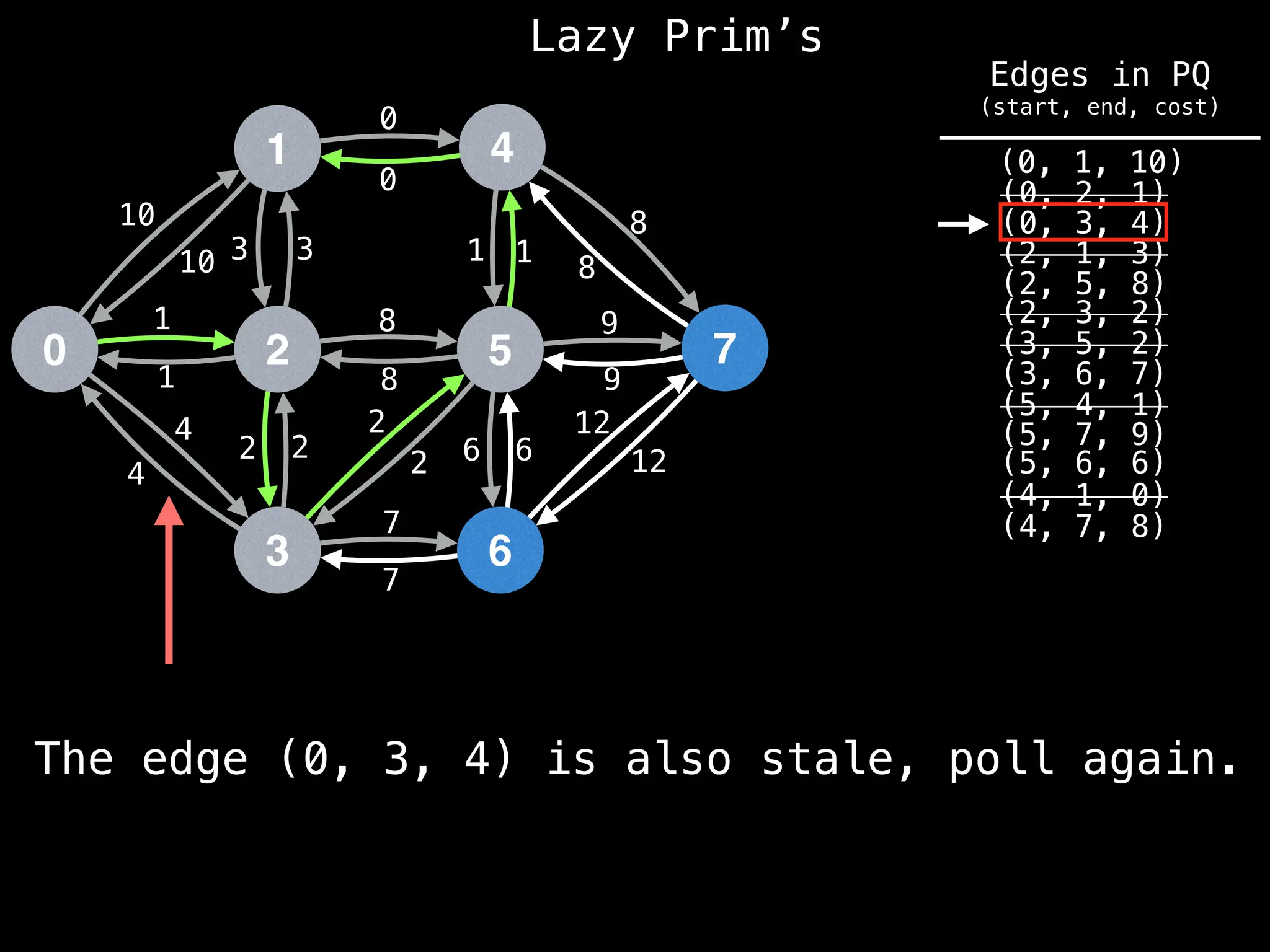
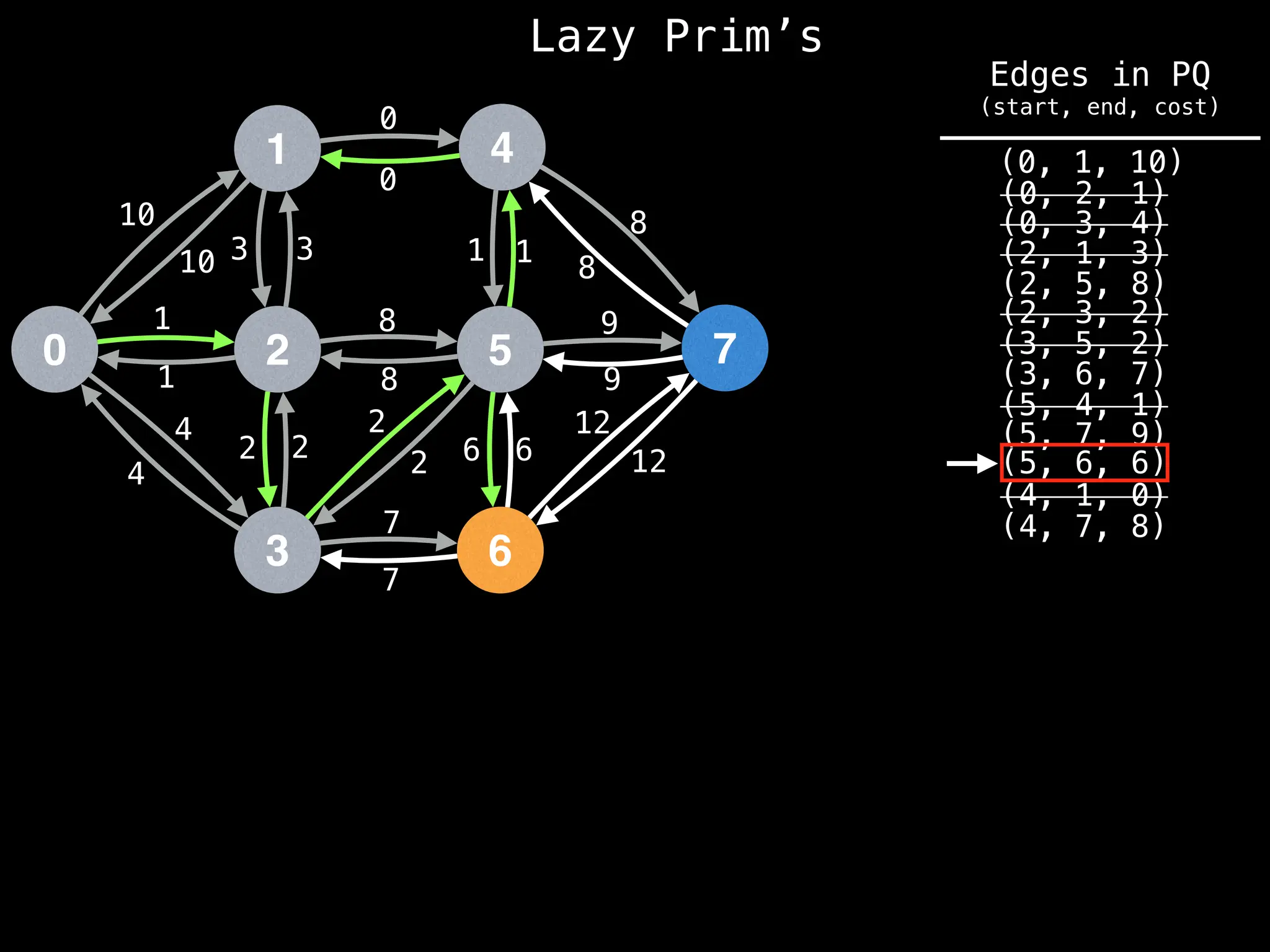
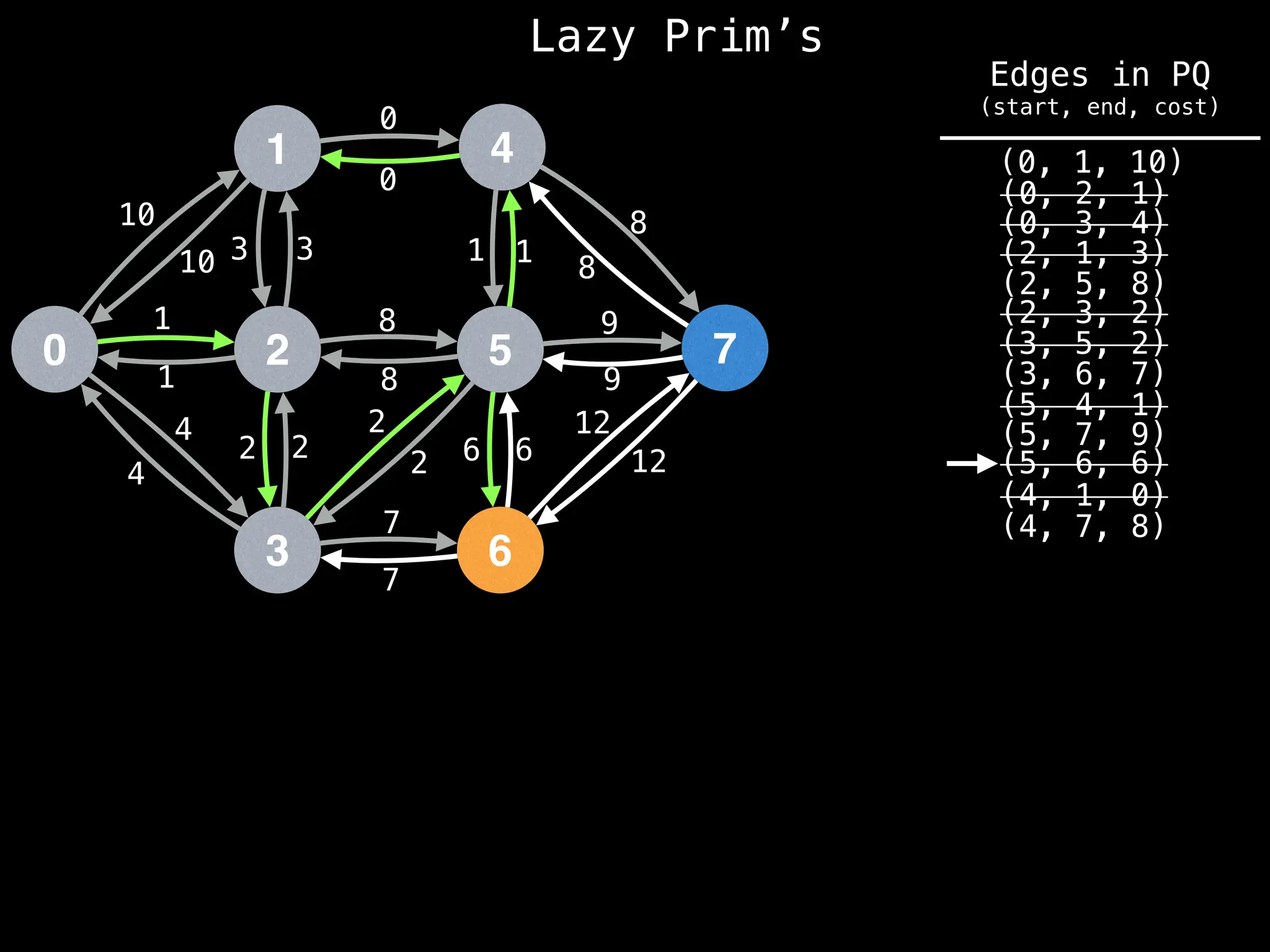
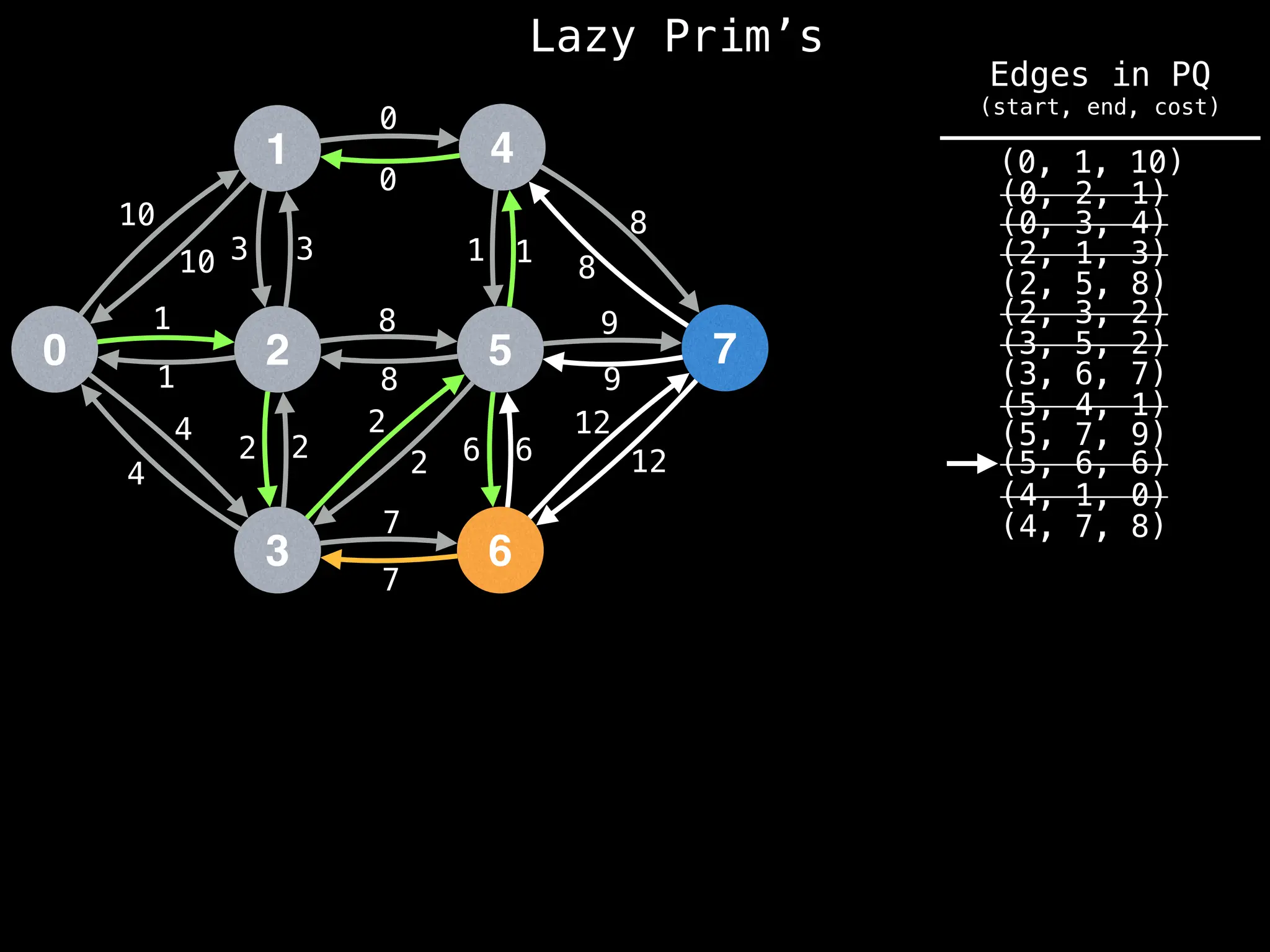
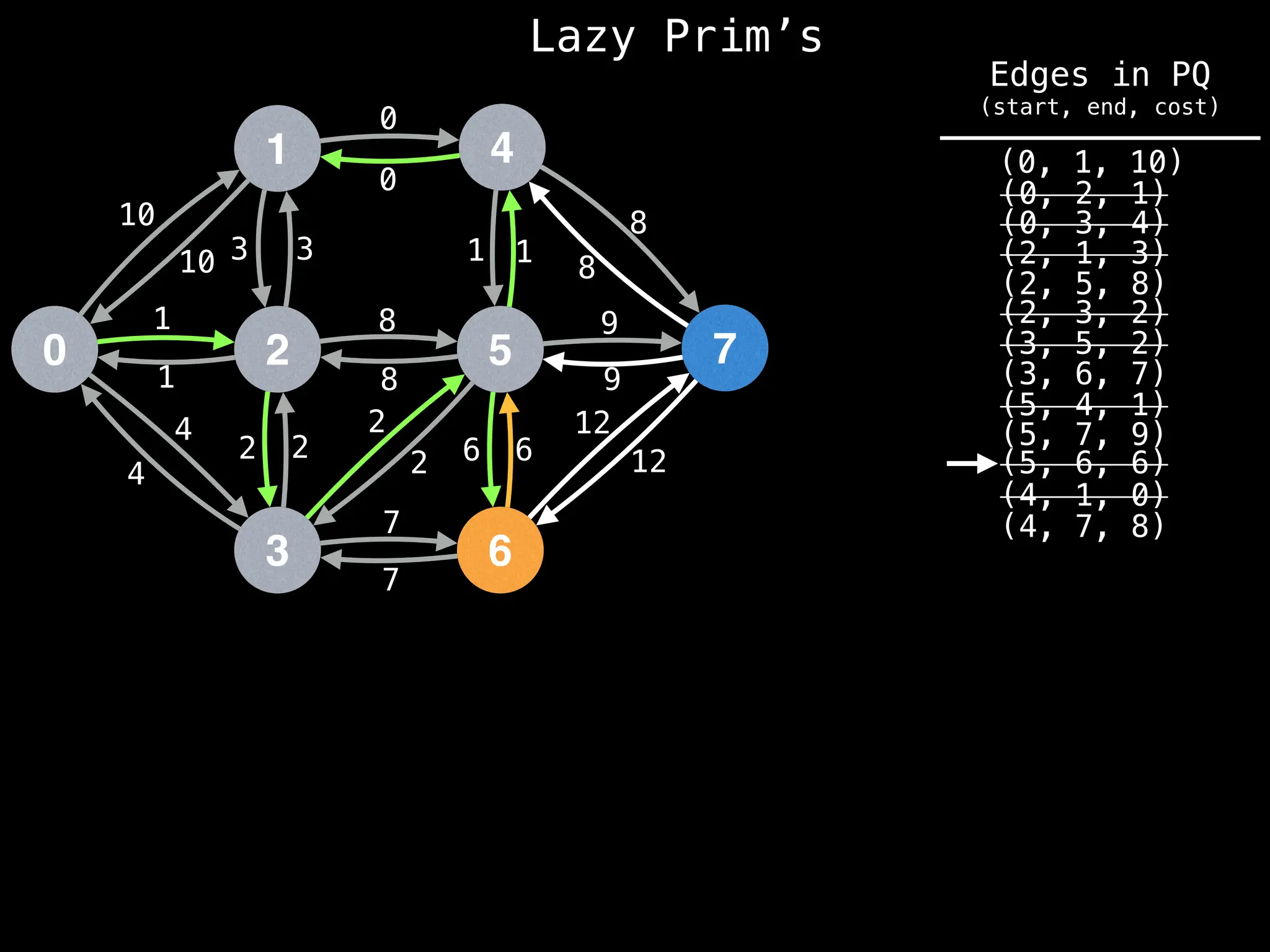
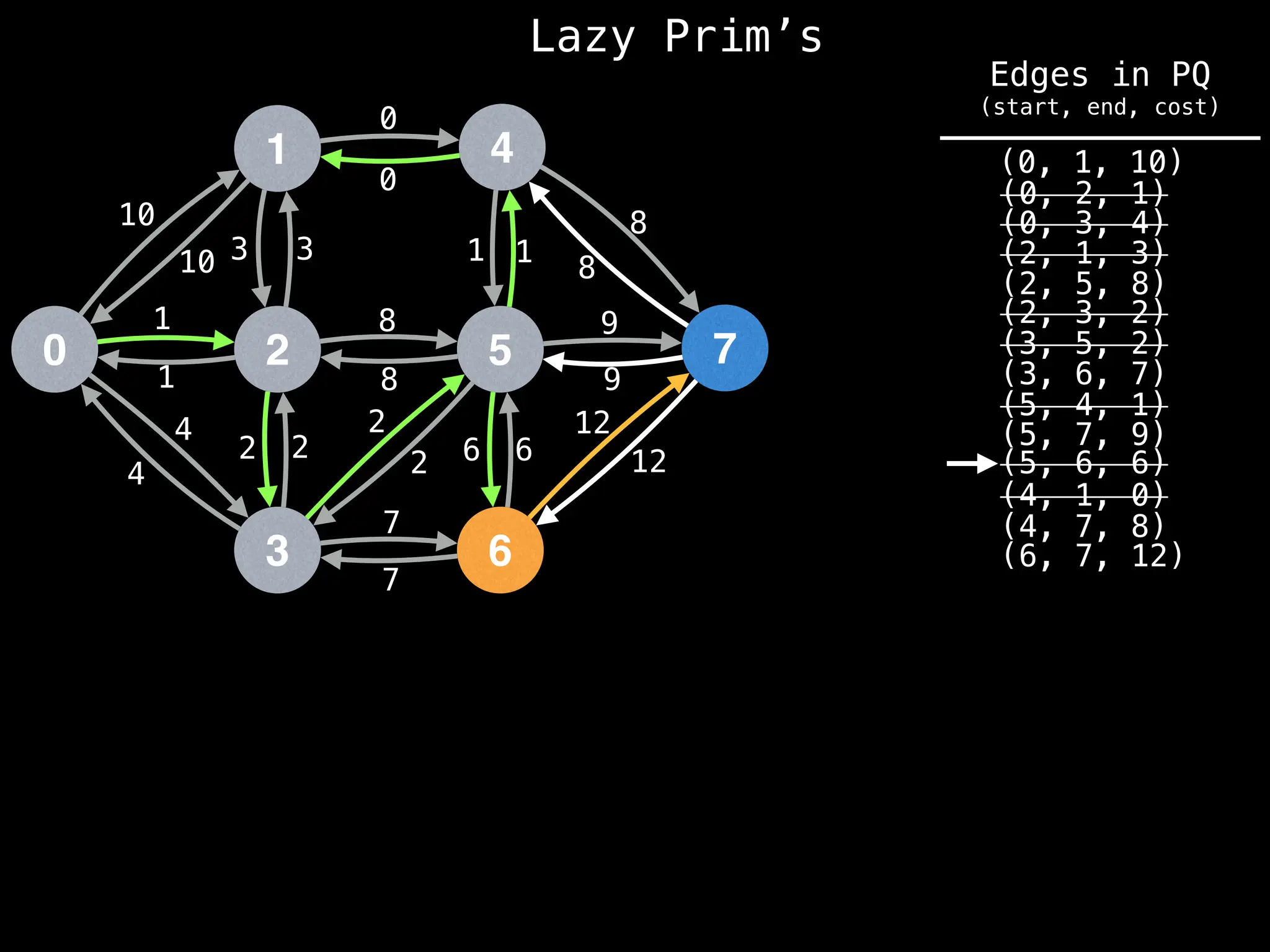
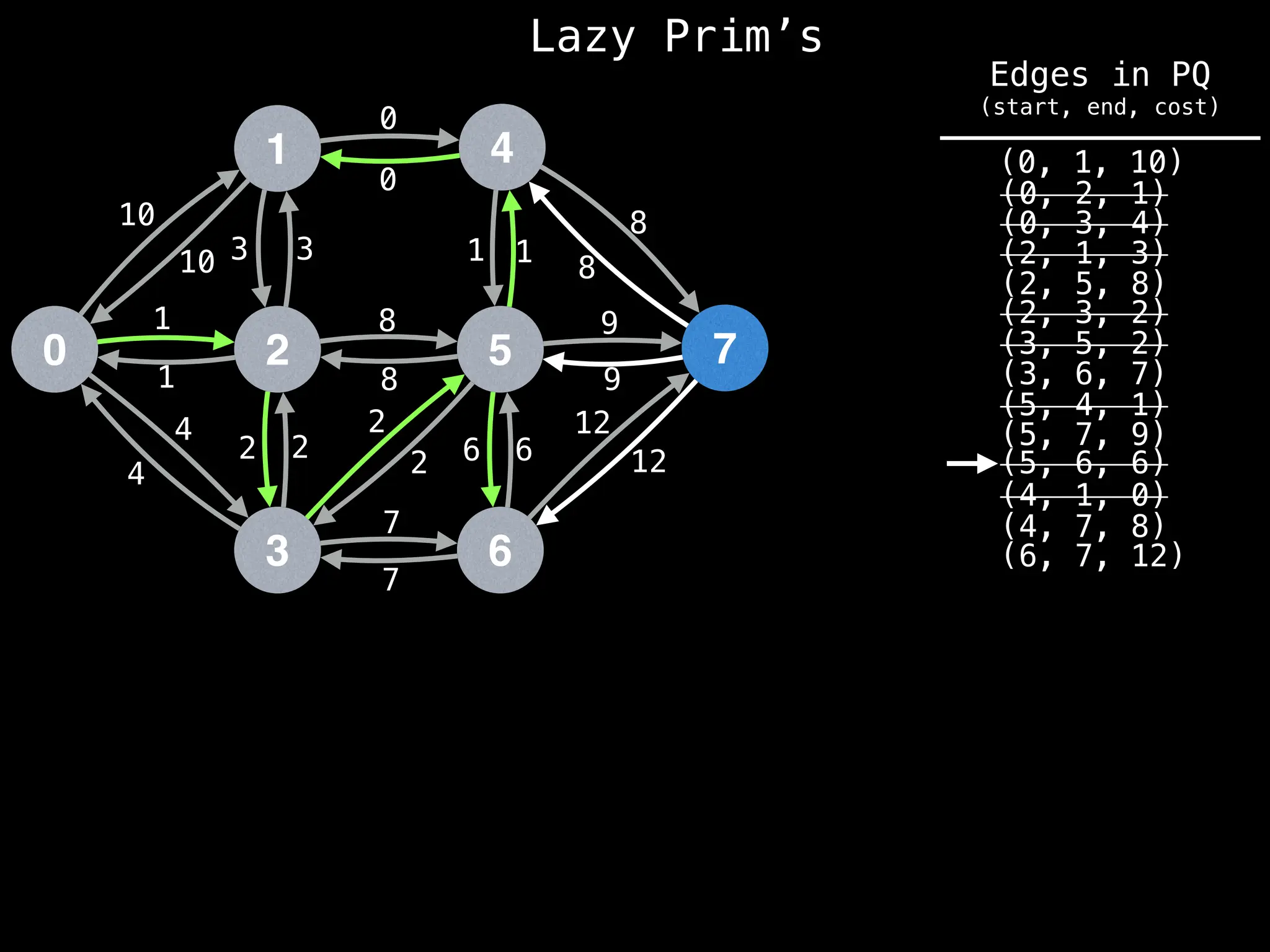
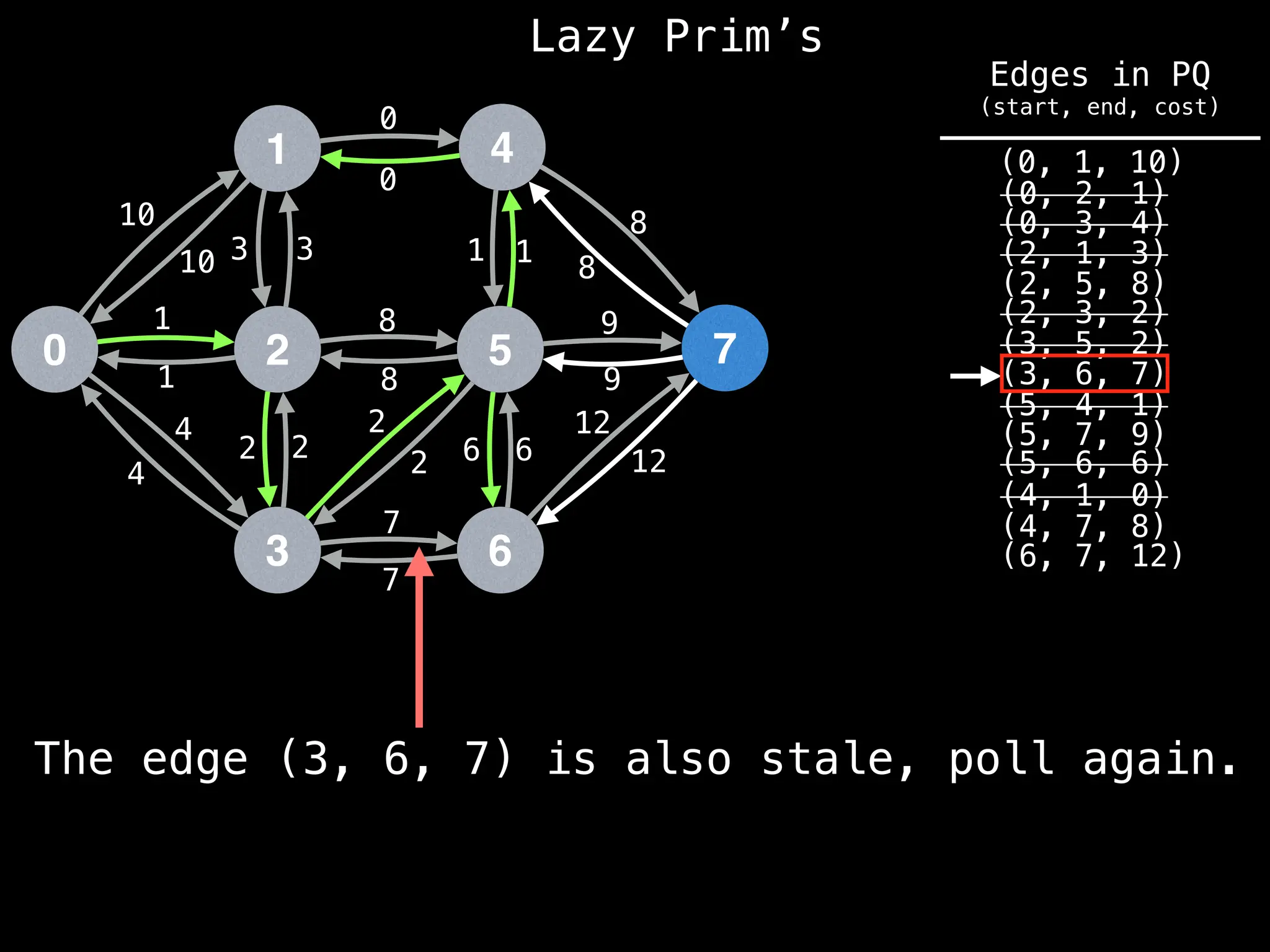
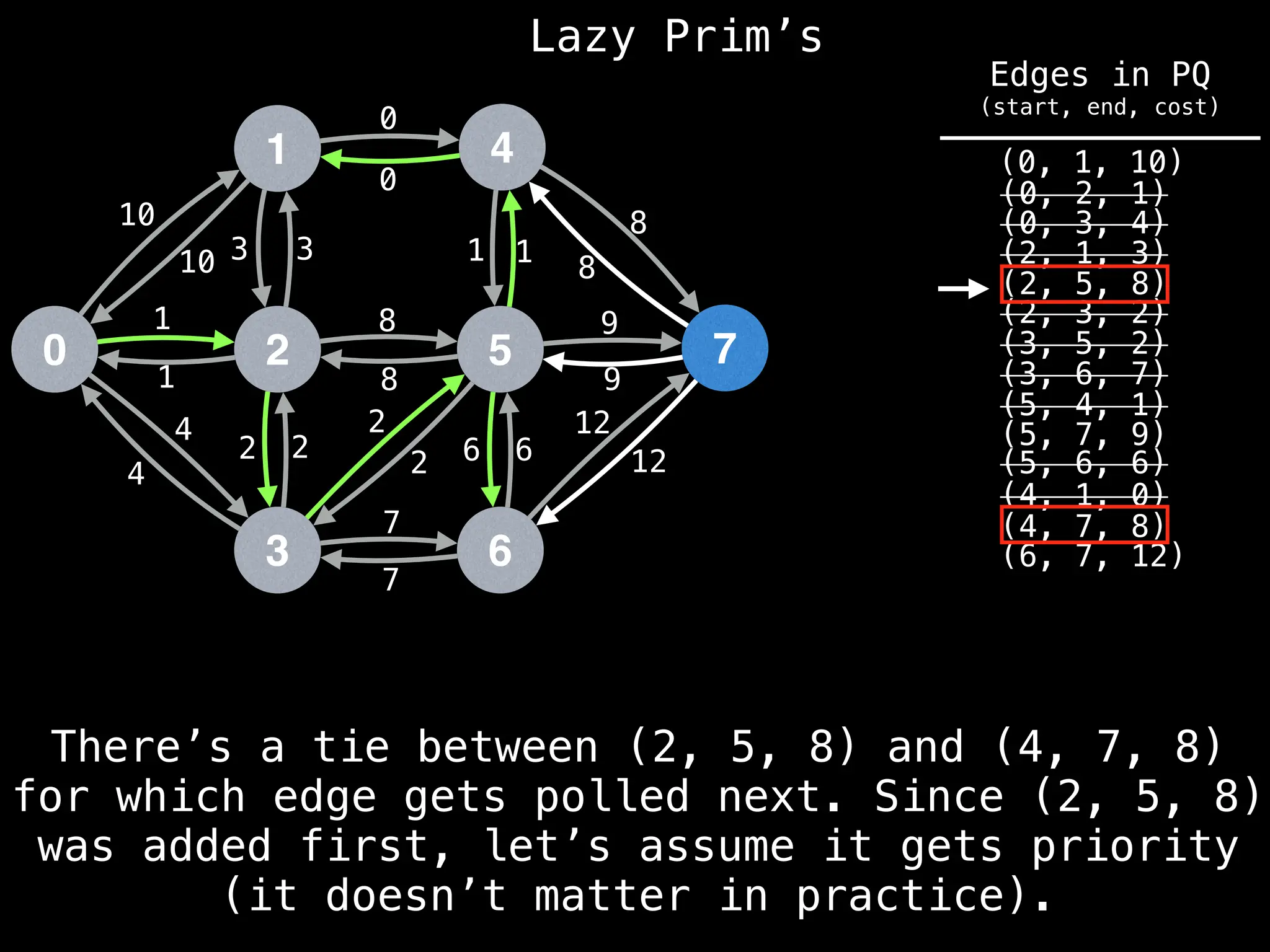
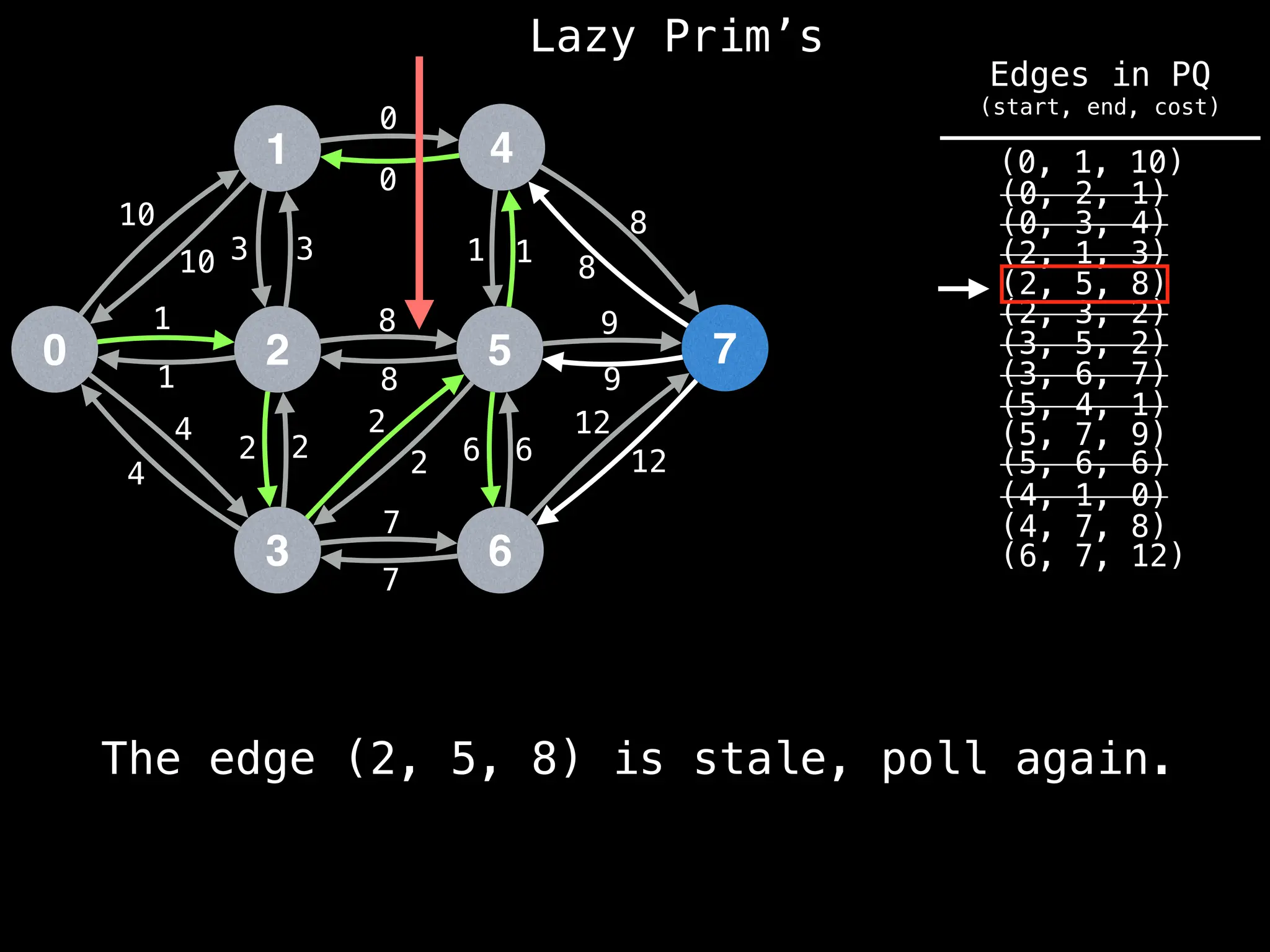
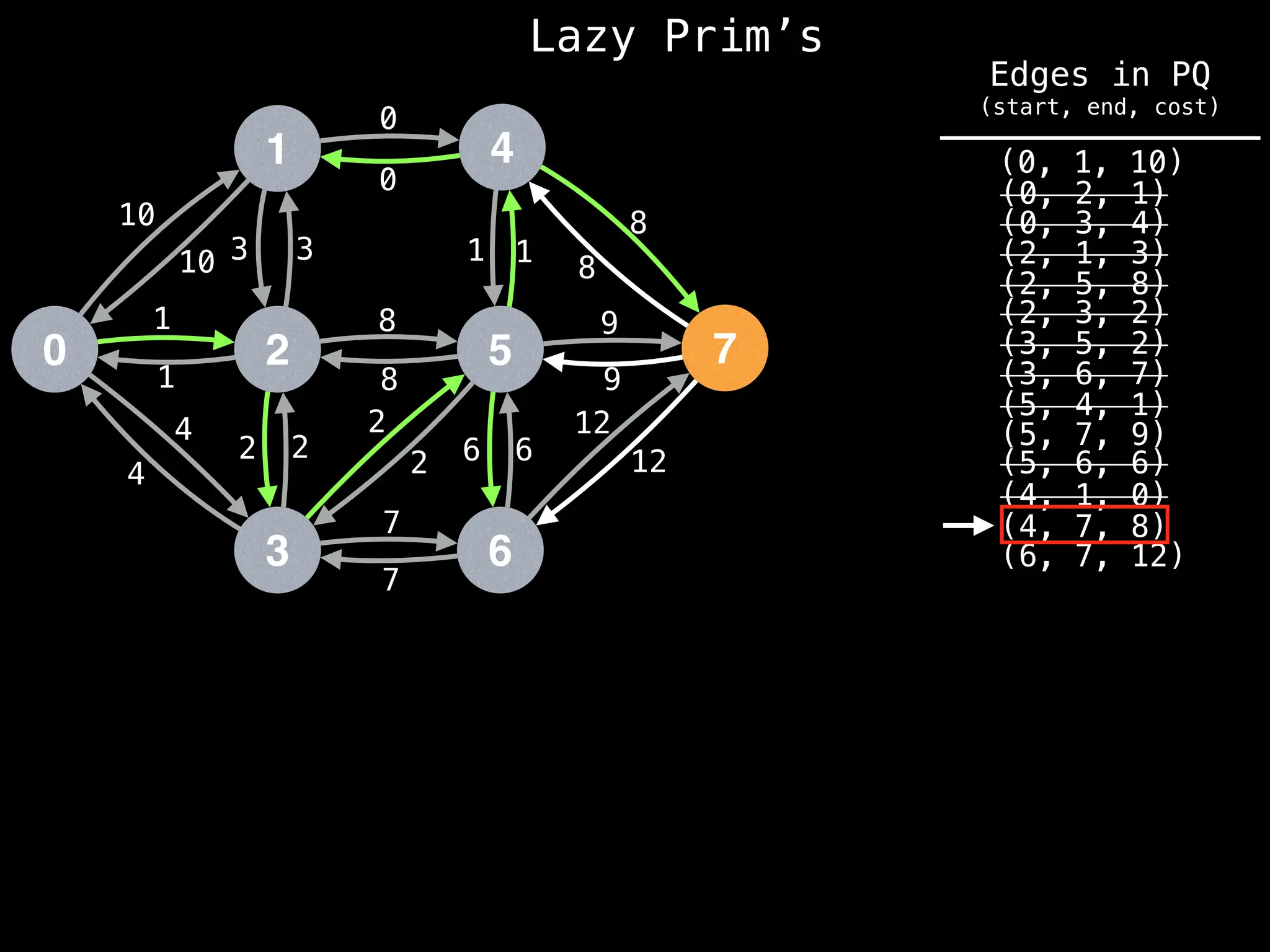
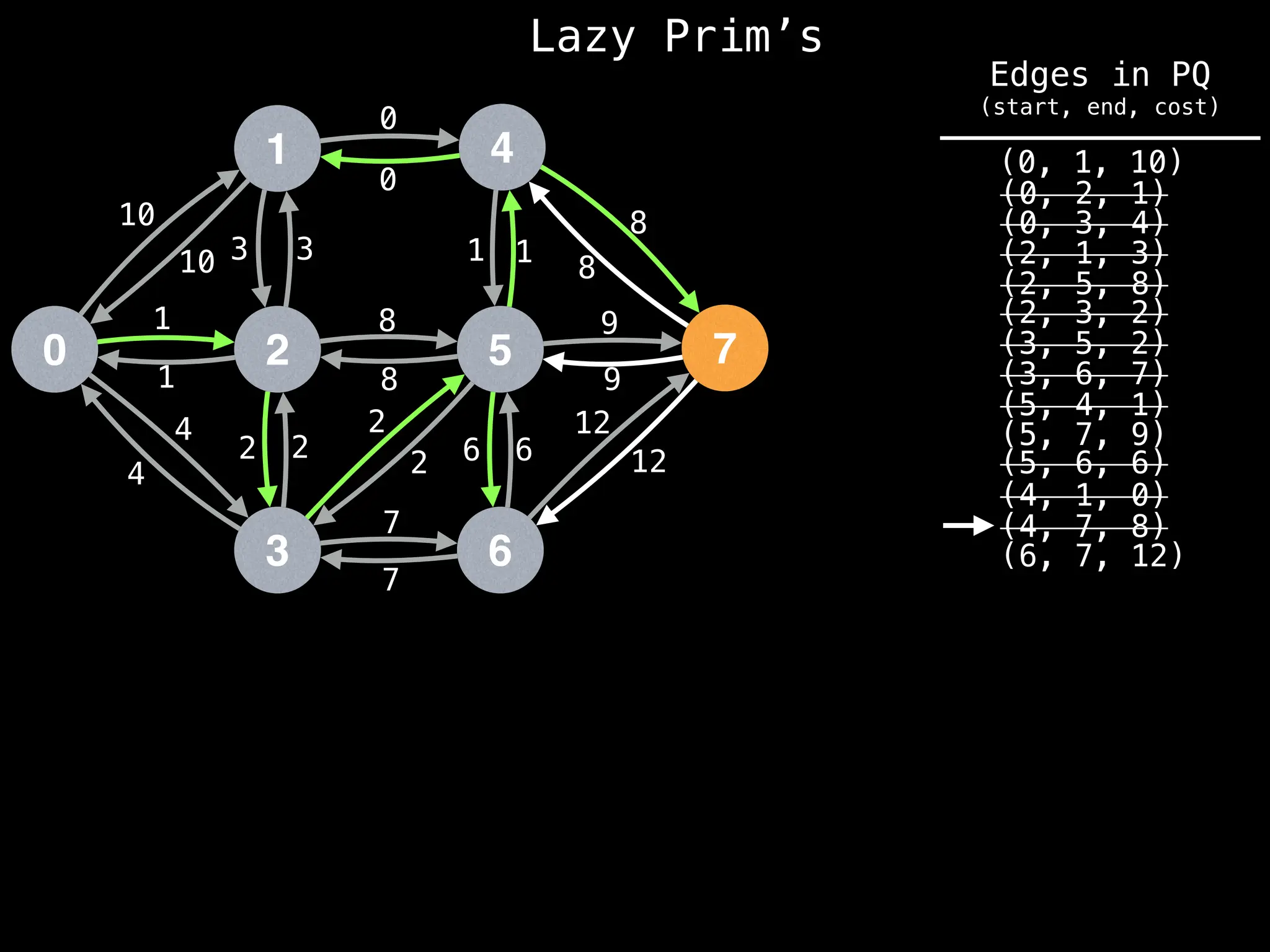
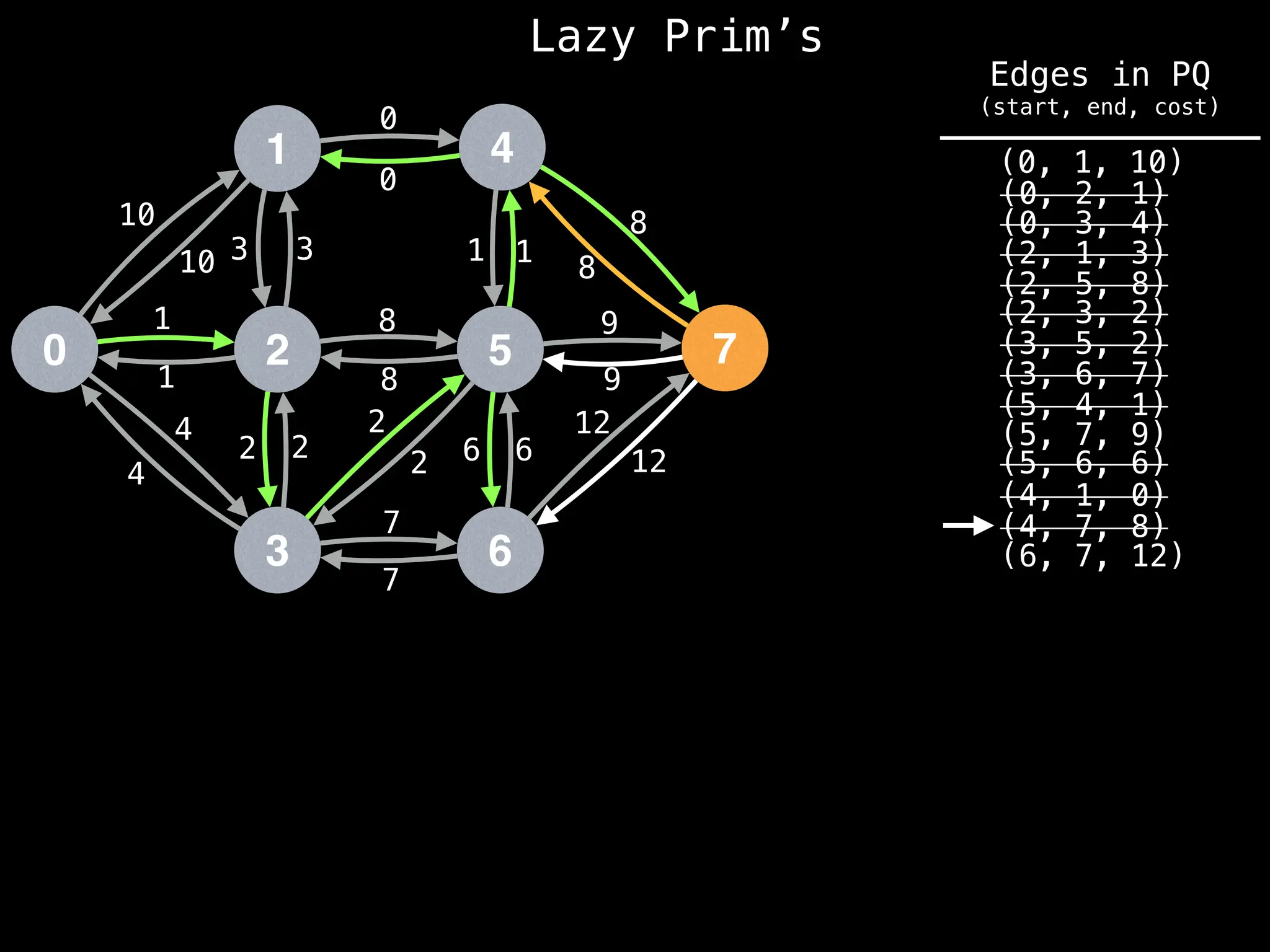
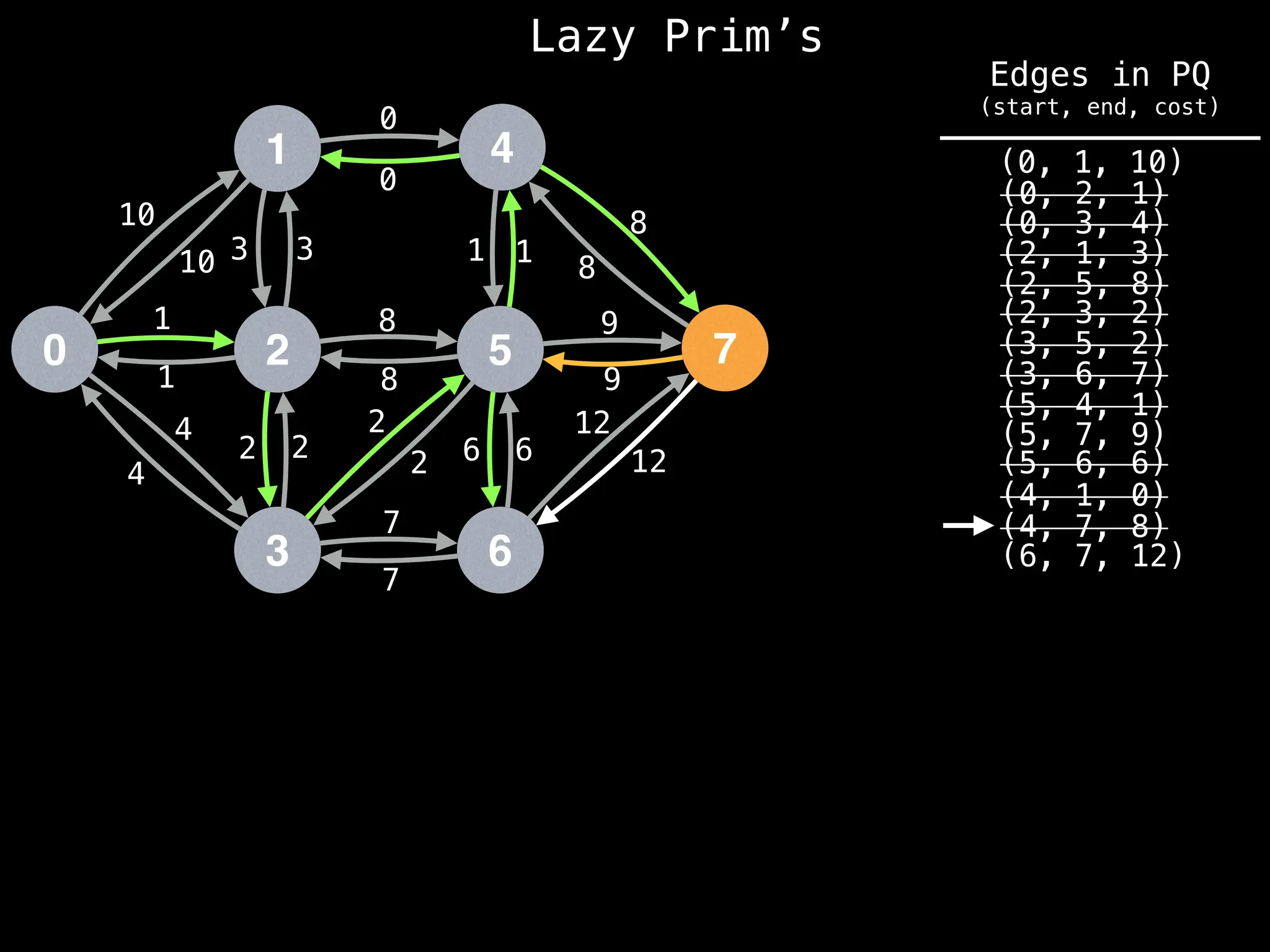
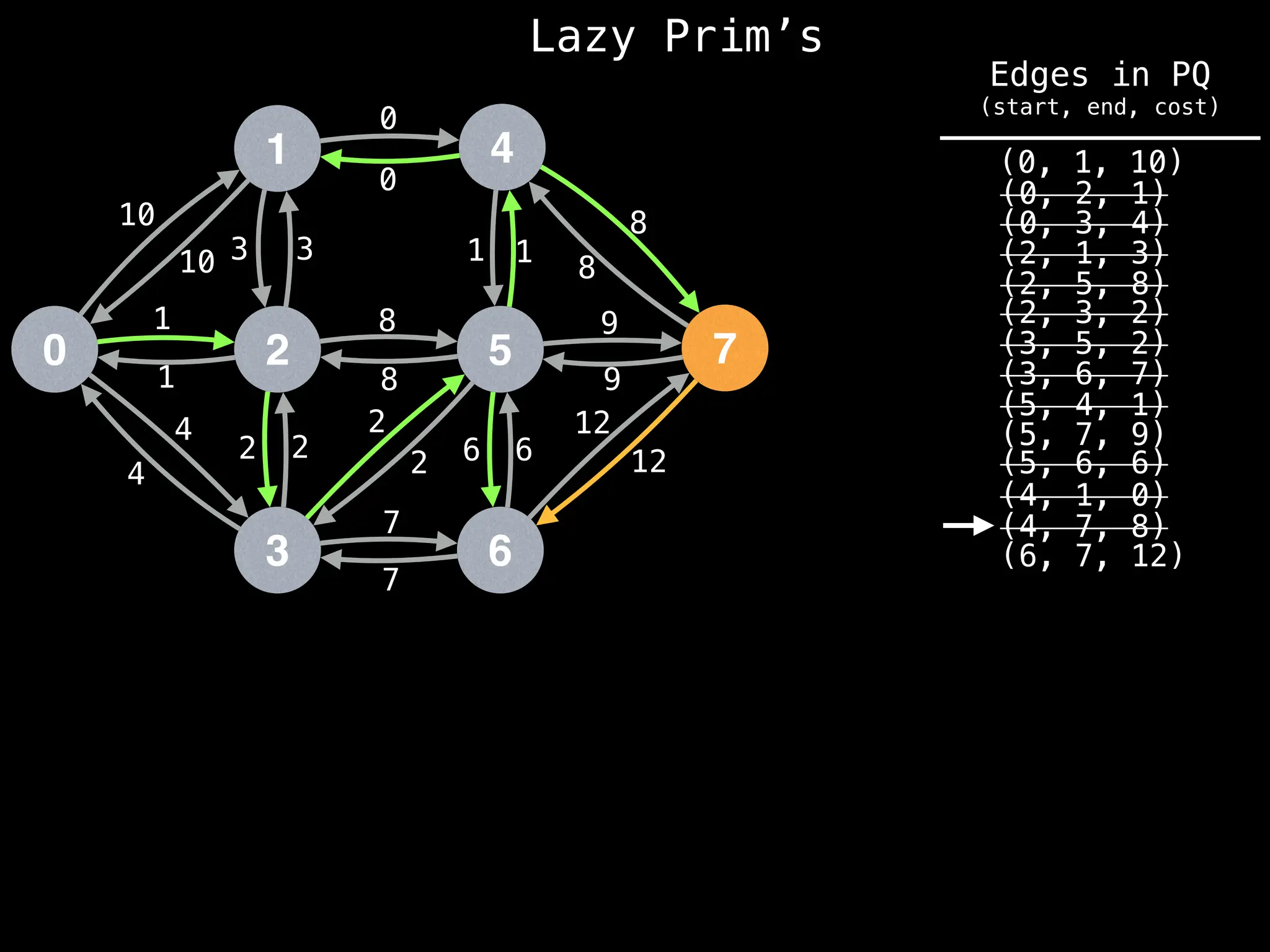
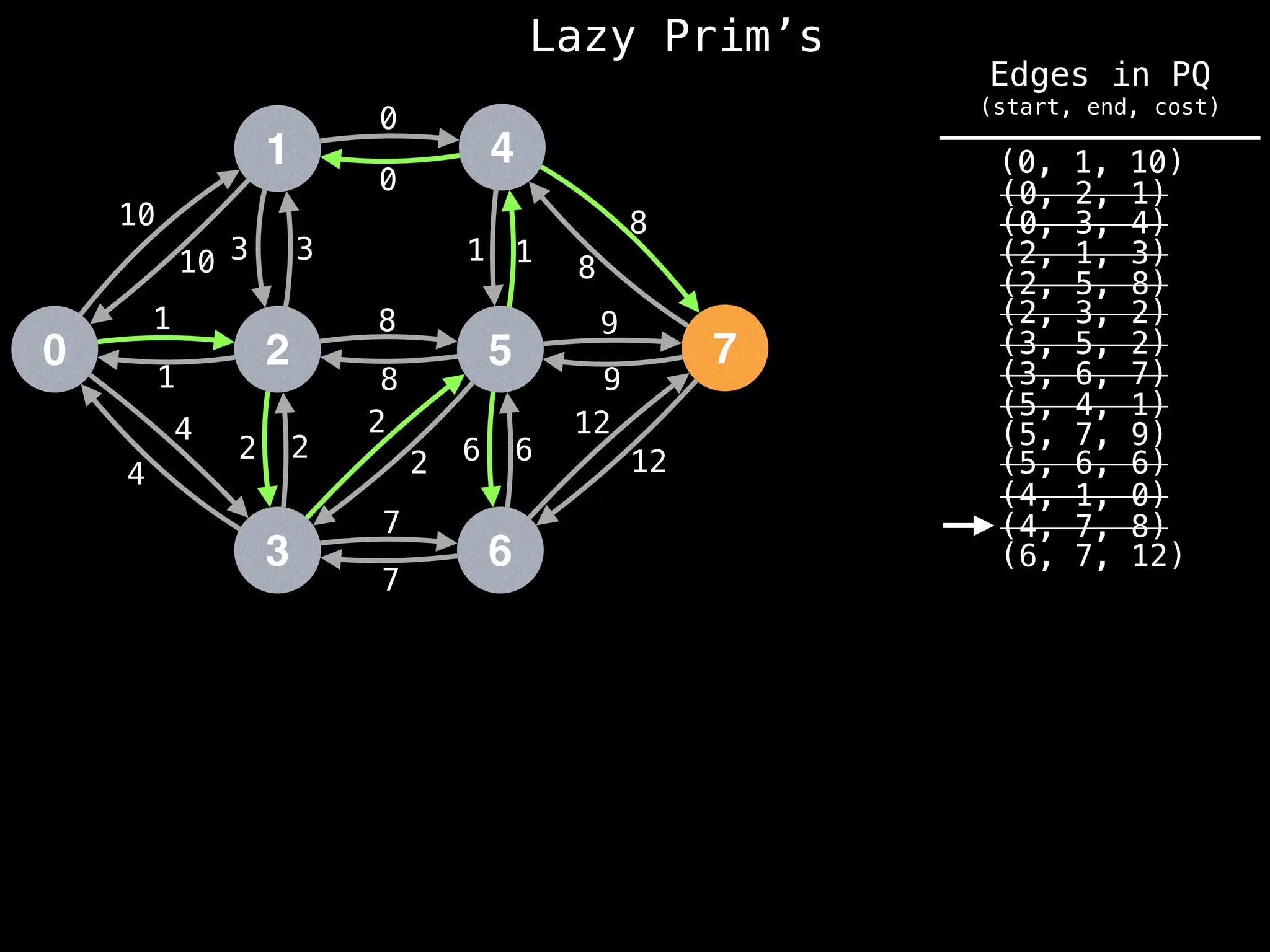
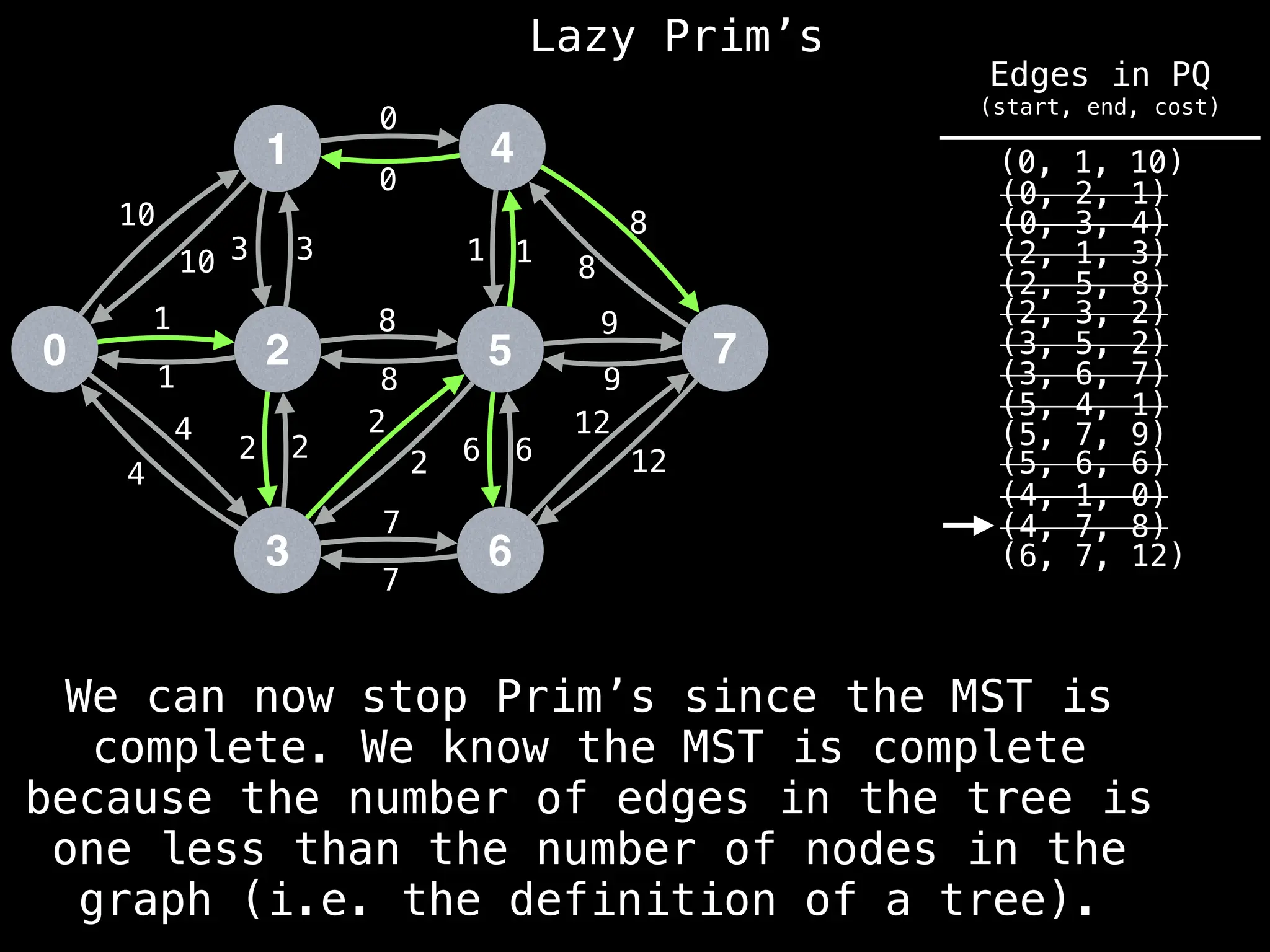
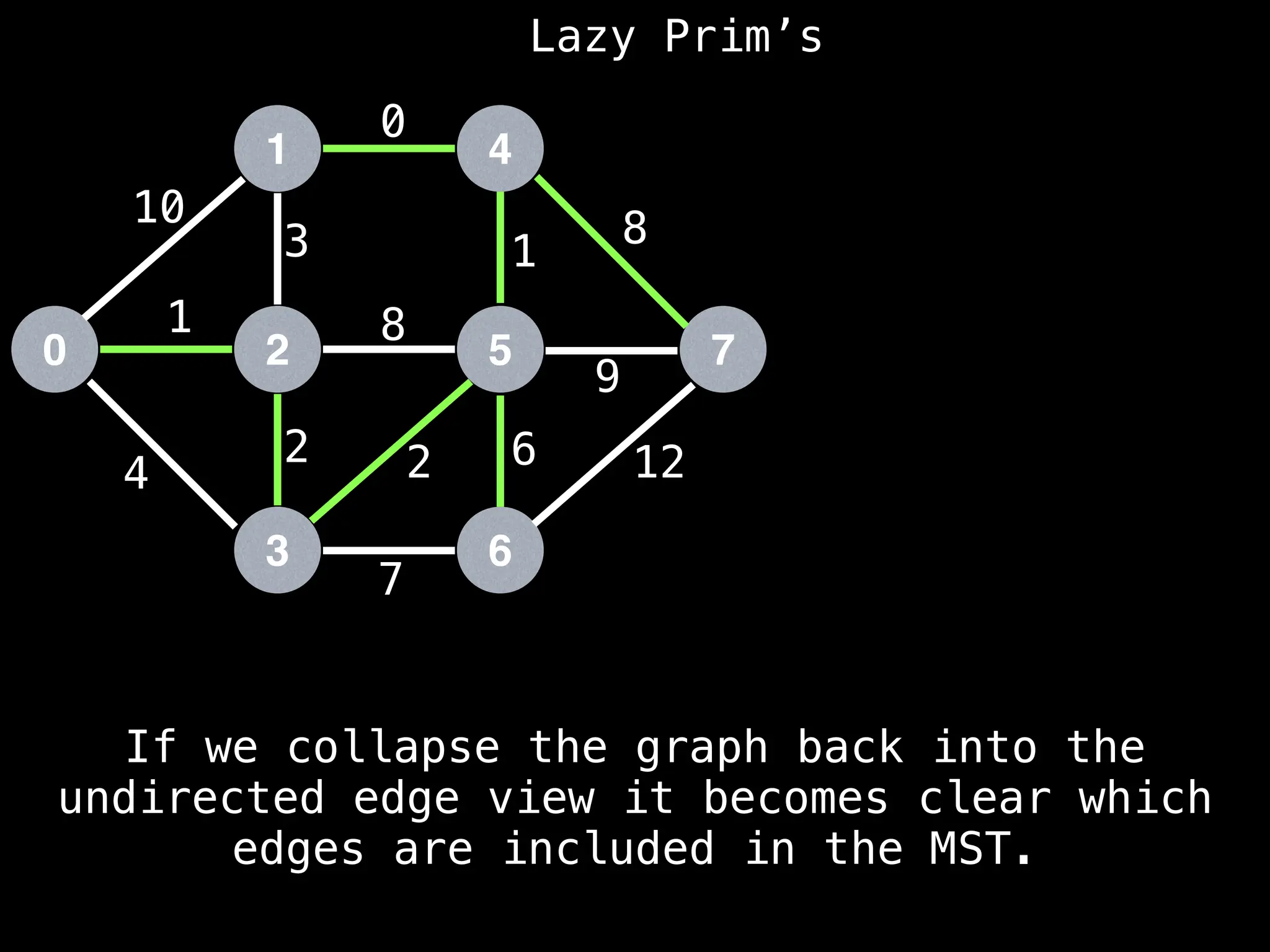
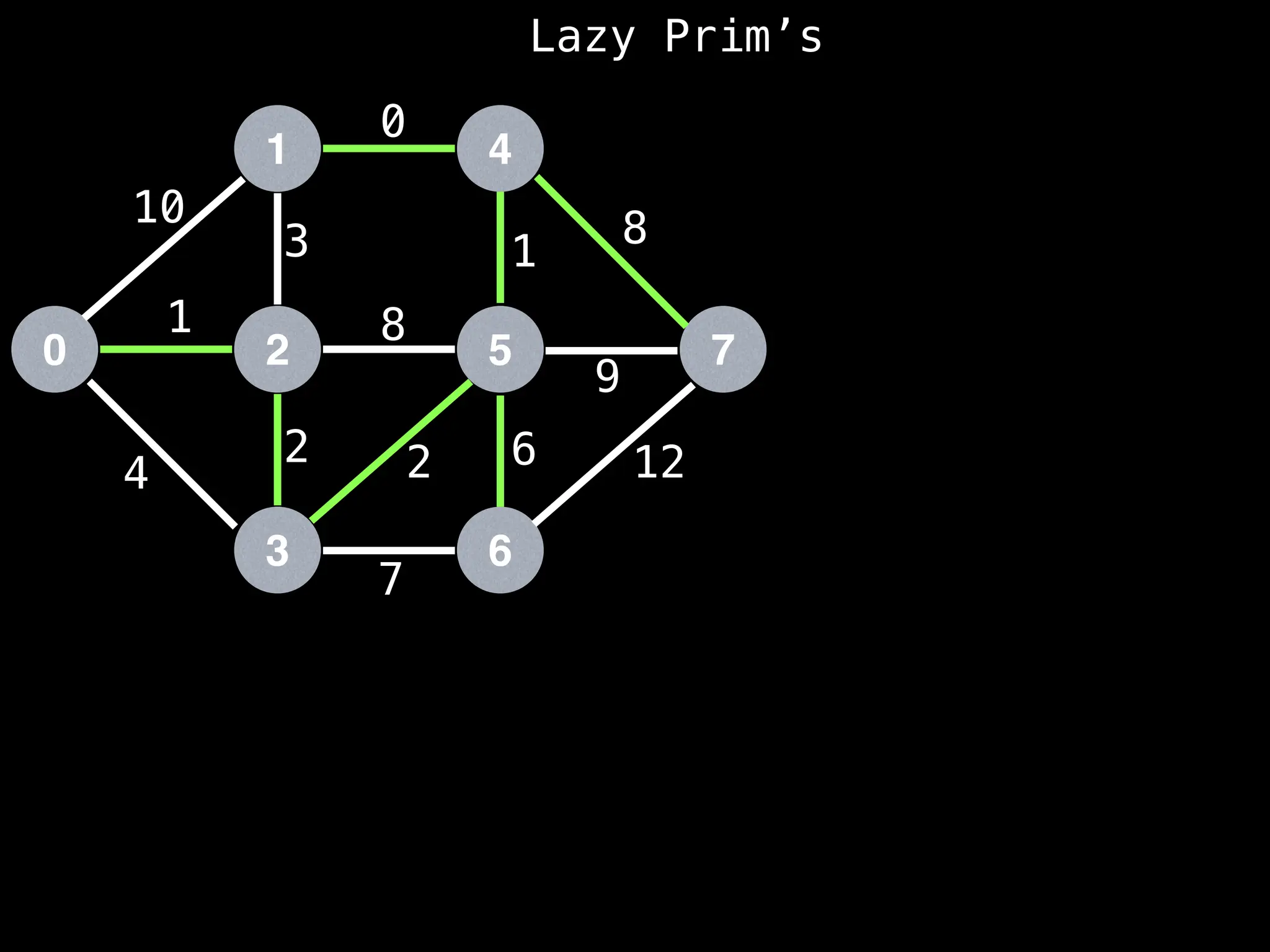
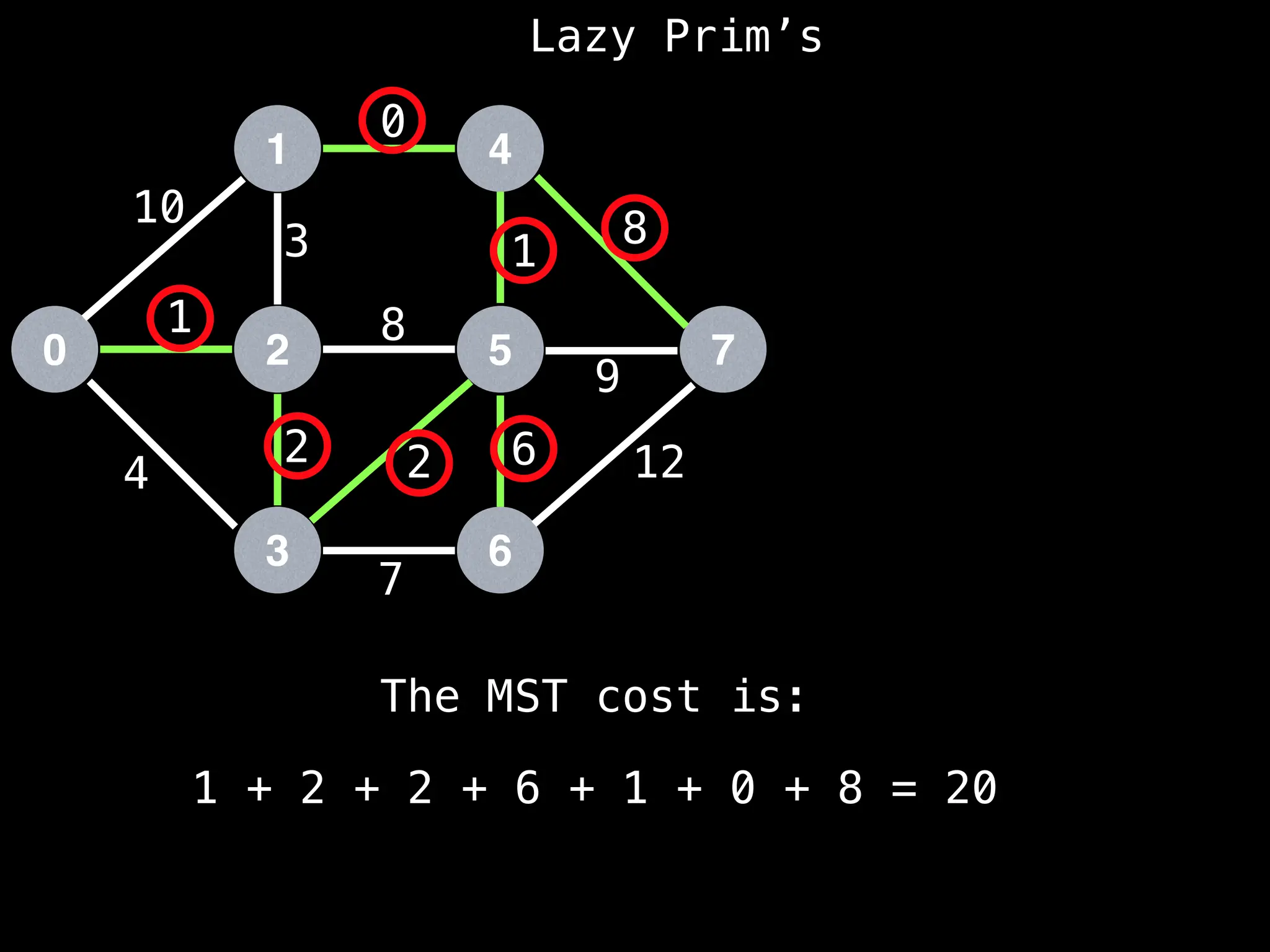
![Lazy Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
pq = … # PQ data structure; stores edge objects consisting of
# {start node, end node, edge cost} tuples. The PQ sorts
# edges based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1325-2048.jpg)
![Lazy Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
pq = … # PQ data structure; stores edge objects consisting of
# {start node, end node, edge cost} tuples. The PQ sorts
# edges based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1326-2048.jpg)
![Lazy Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
pq = … # PQ data structure; stores edge objects consisting of
# {start node, end node, edge cost} tuples. The PQ sorts
# edges based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1327-2048.jpg)
![Lazy Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
pq = … # PQ data structure; stores edge objects consisting of
# {start node, end node, edge cost} tuples. The PQ sorts
# edges based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1328-2048.jpg)
![Lazy Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
pq = … # PQ data structure; stores edge objects consisting of
# {start node, end node, edge cost} tuples. The PQ sorts
# edges based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1329-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1330-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1331-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1332-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1333-2048.jpg)
![function addEdges(nodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[nodeIndex] = true
# Iterate over all edges going outwards from the current node.
# Add edges to the PQ which point to unvisited nodes.
edges = g[nodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
if !visited[edge.to]:
pq.enqueue(edge)
Helper method to iterate over the edges of a
node and add edges to the PQ:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1334-2048.jpg)
![function addEdges(nodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[nodeIndex] = true
# Iterate over all edges going outwards from the current node.
# Add edges to the PQ which point to unvisited nodes.
edges = g[nodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
if !visited[edge.to]:
pq.enqueue(edge)
Helper method to iterate over the edges of a
node and add edges to the PQ:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1335-2048.jpg)
![function addEdges(nodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[nodeIndex] = true
# Iterate over all edges going outwards from the current node.
# Add edges to the PQ which point to unvisited nodes.
edges = g[nodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
if !visited[edge.to]:
pq.enqueue(edge)
Helper method to iterate over the edges of a
node and add edges to the PQ:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1336-2048.jpg)
![function addEdges(nodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[nodeIndex] = true
# Iterate over all edges going outwards from the current node.
# Add edges to the PQ which point to unvisited nodes.
edges = g[nodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
if !visited[edge.to]:
pq.enqueue(edge)
Helper method to iterate over the edges of a
node and add edges to the PQ:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1337-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1338-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1339-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1340-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)
Skip edge that points to
a visited node.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1341-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1342-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1343-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function lazyPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
addEdges(s)
while (!pq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
edge = pq.dequeue()
nodeIndex = edge.to
if visited[nodeIndex]:
continue
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
addEdges(nodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1344-2048.jpg)
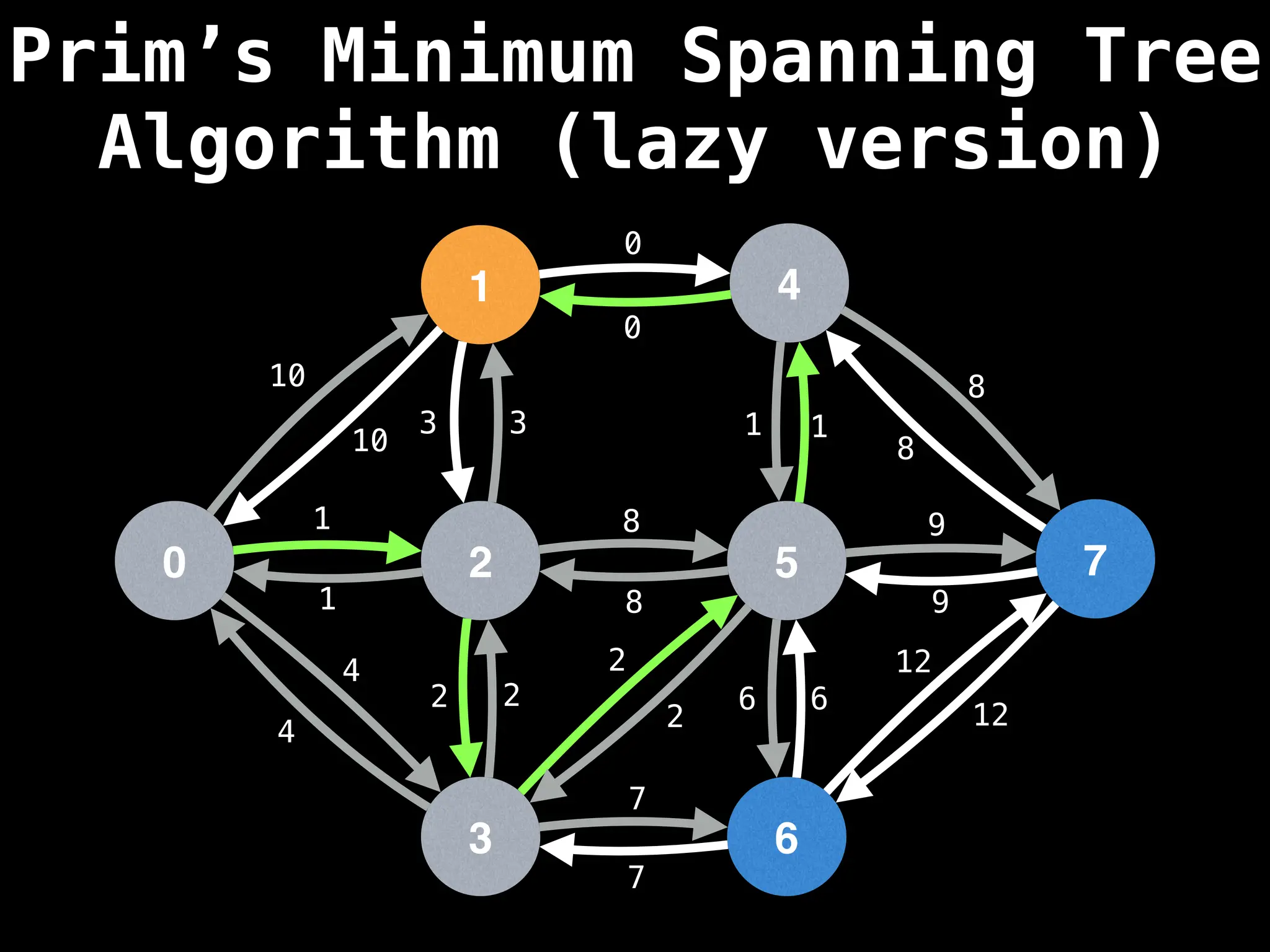

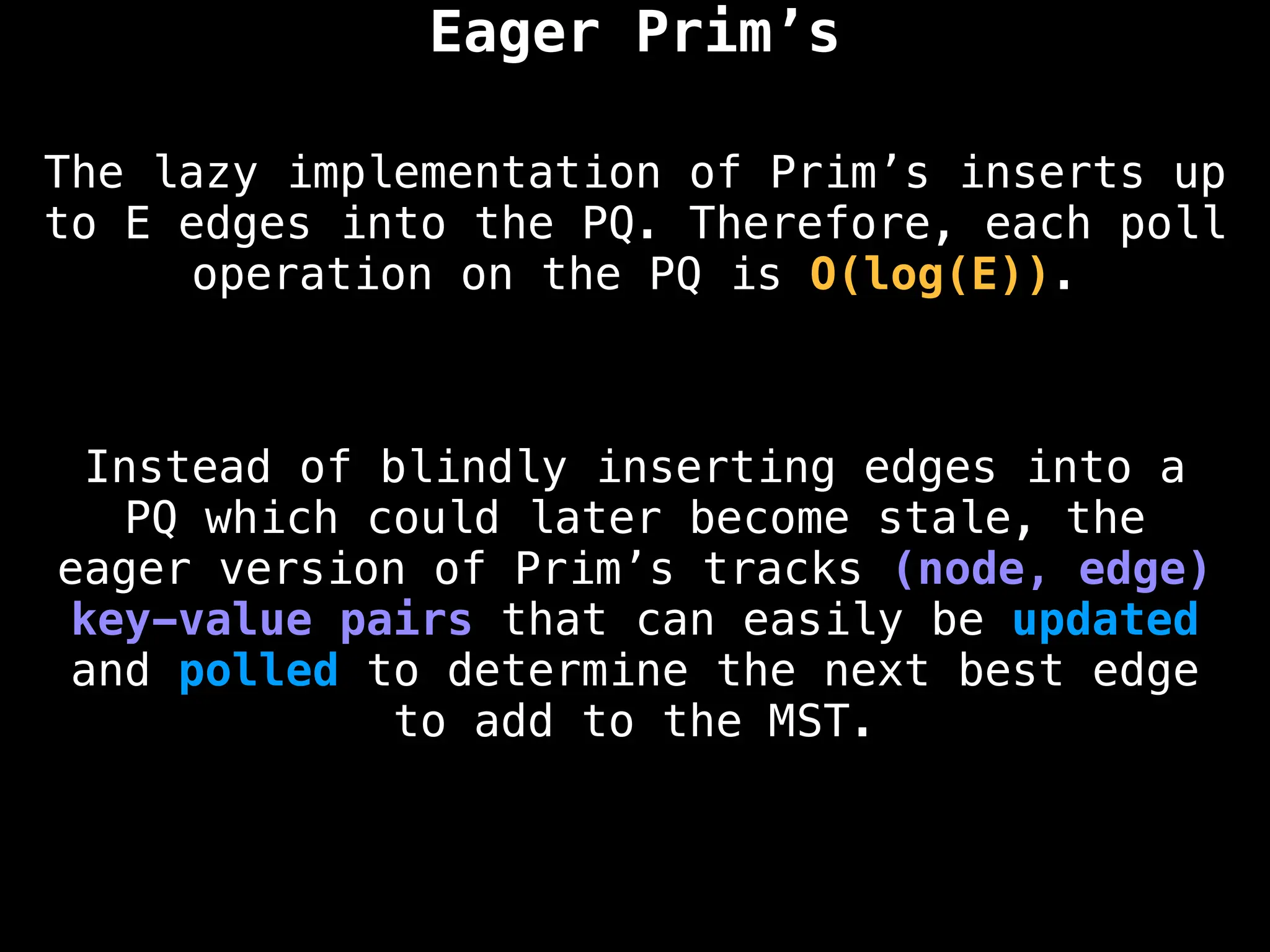

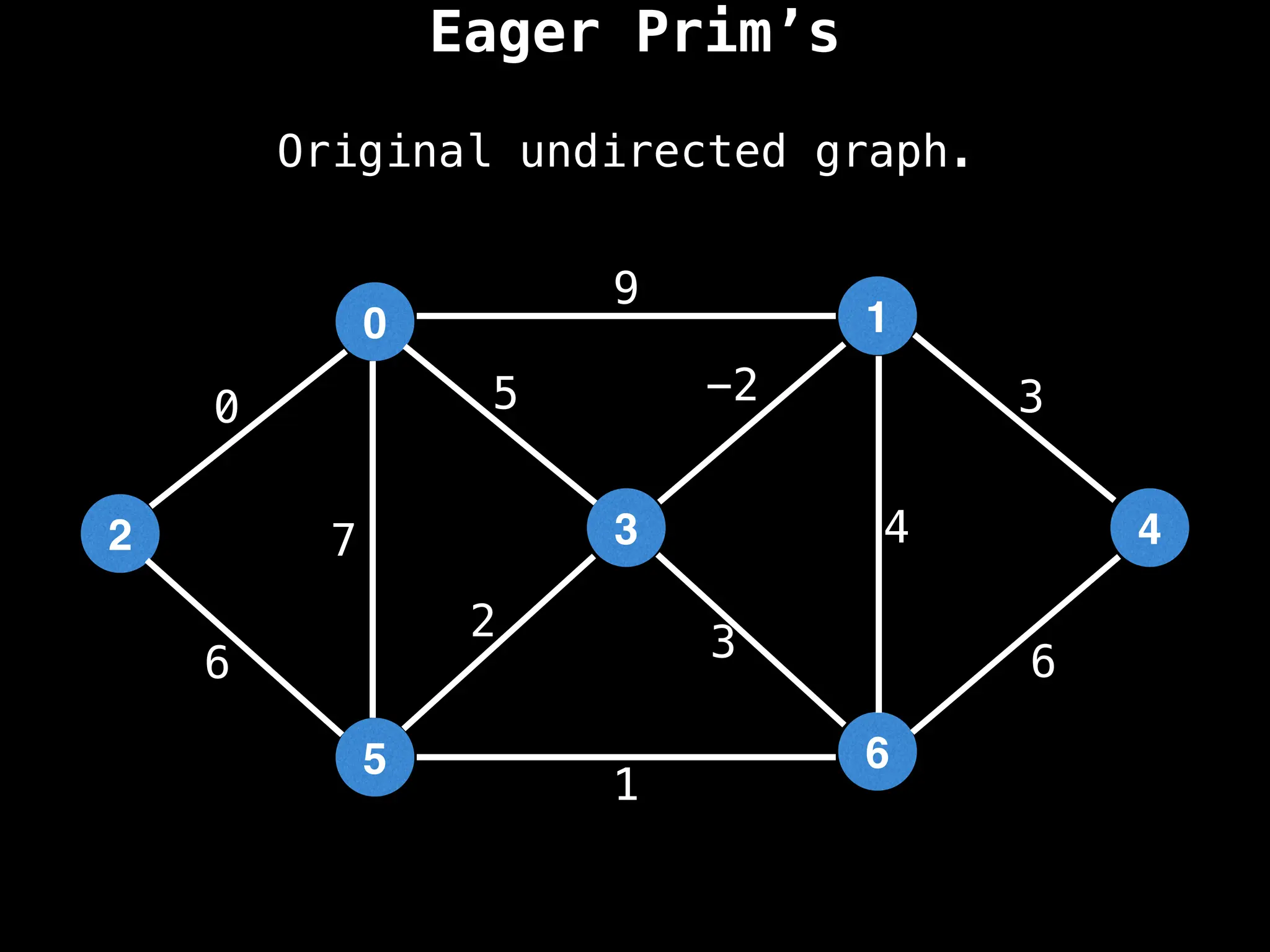
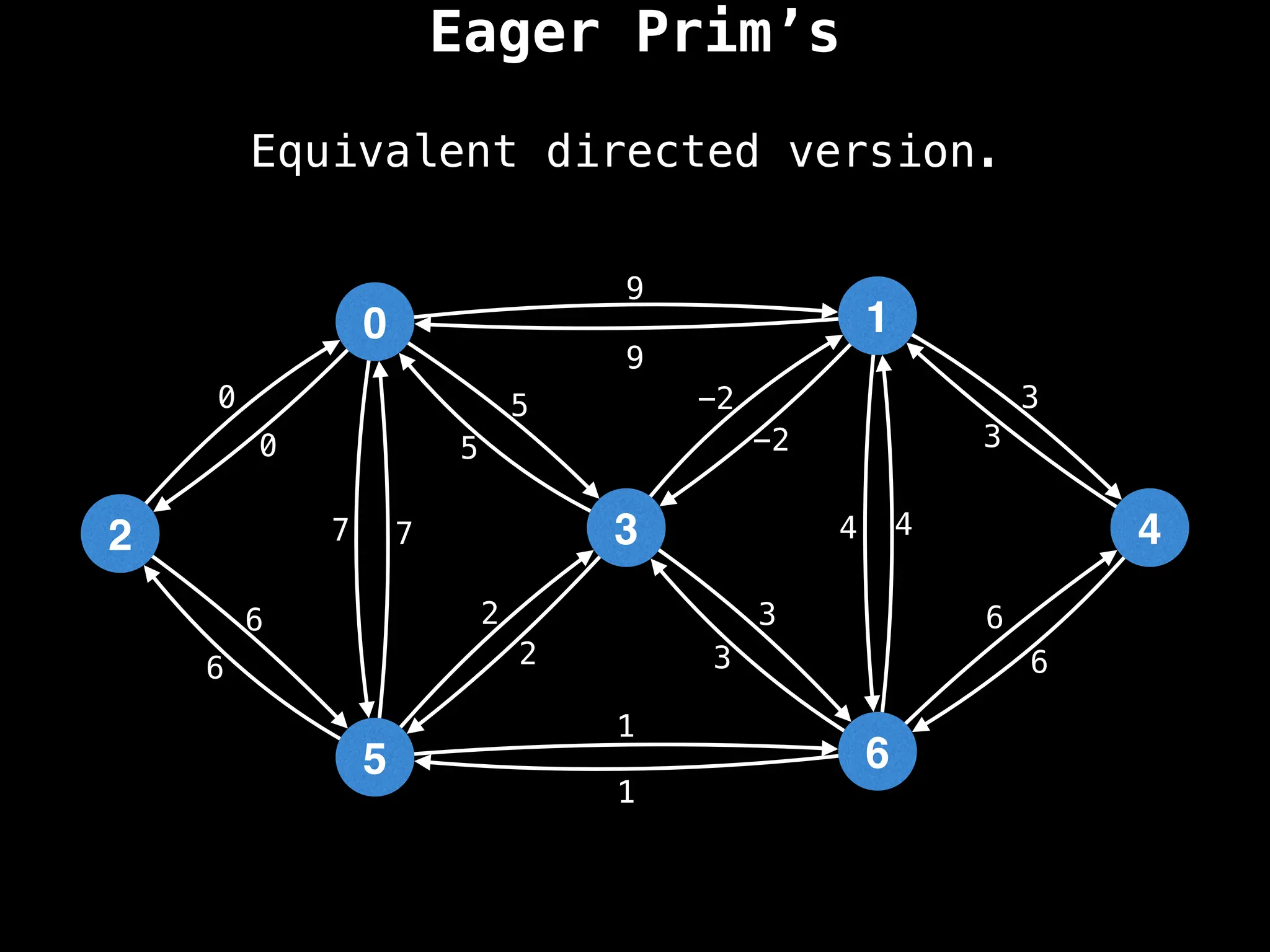
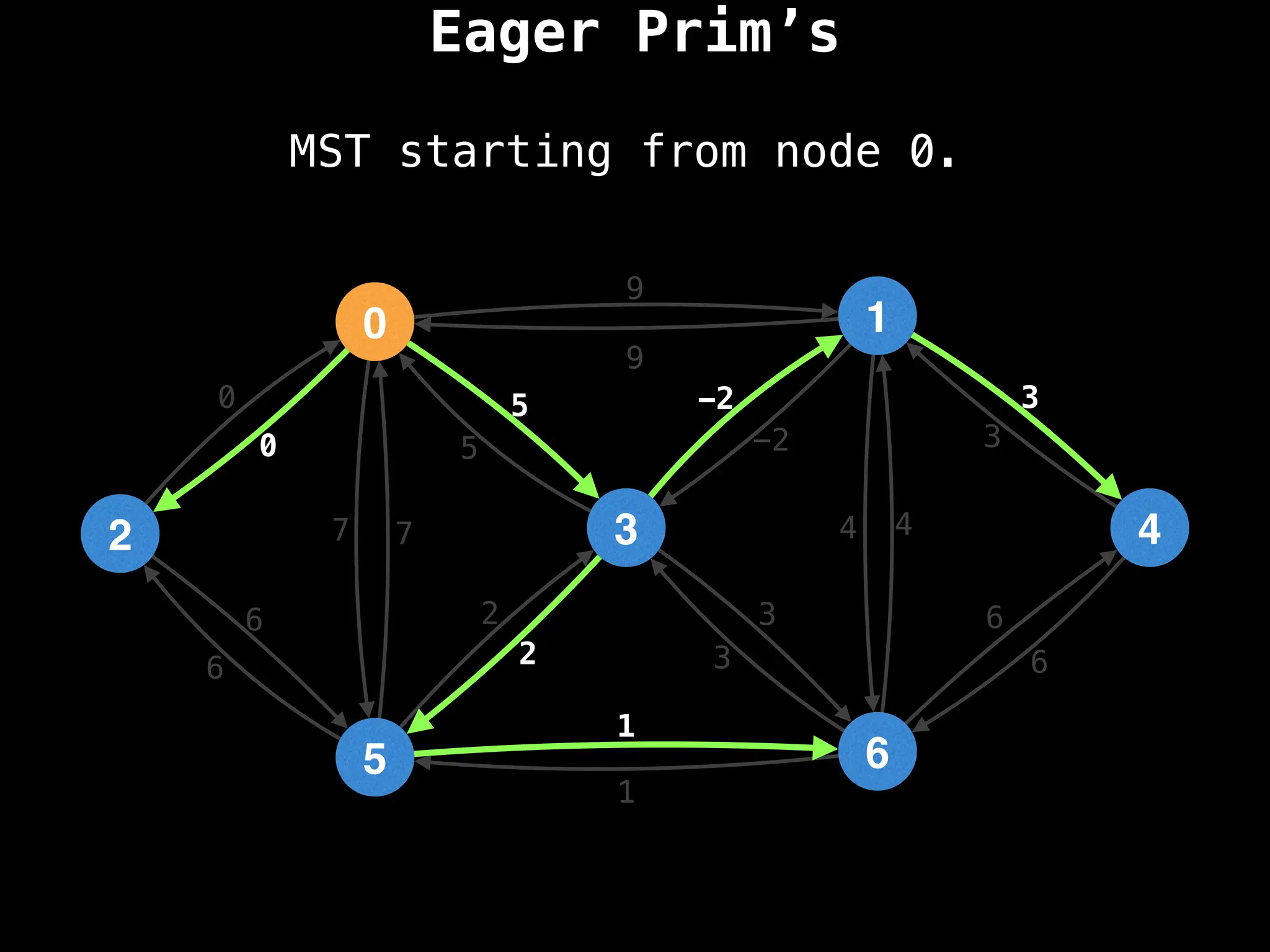
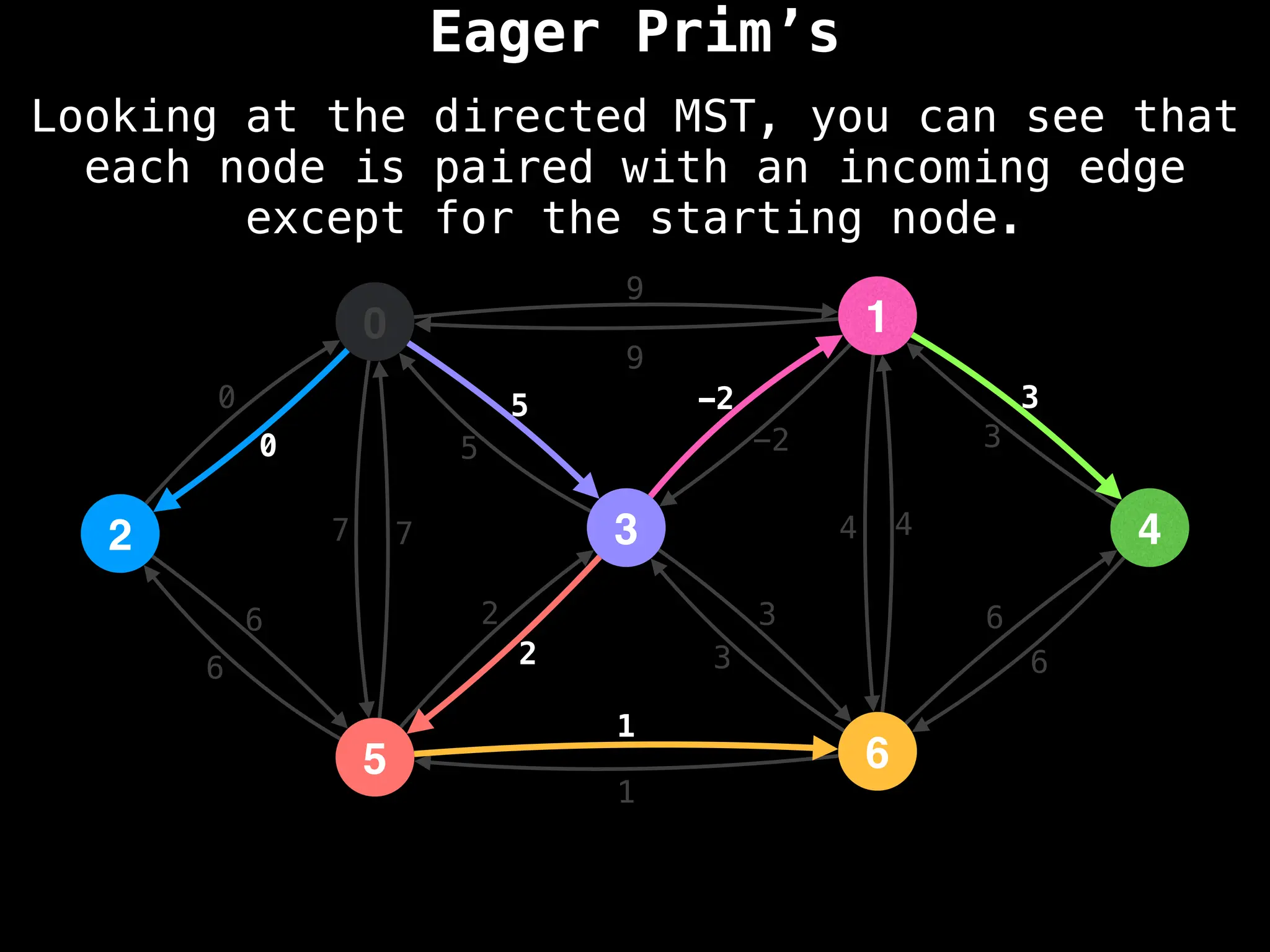
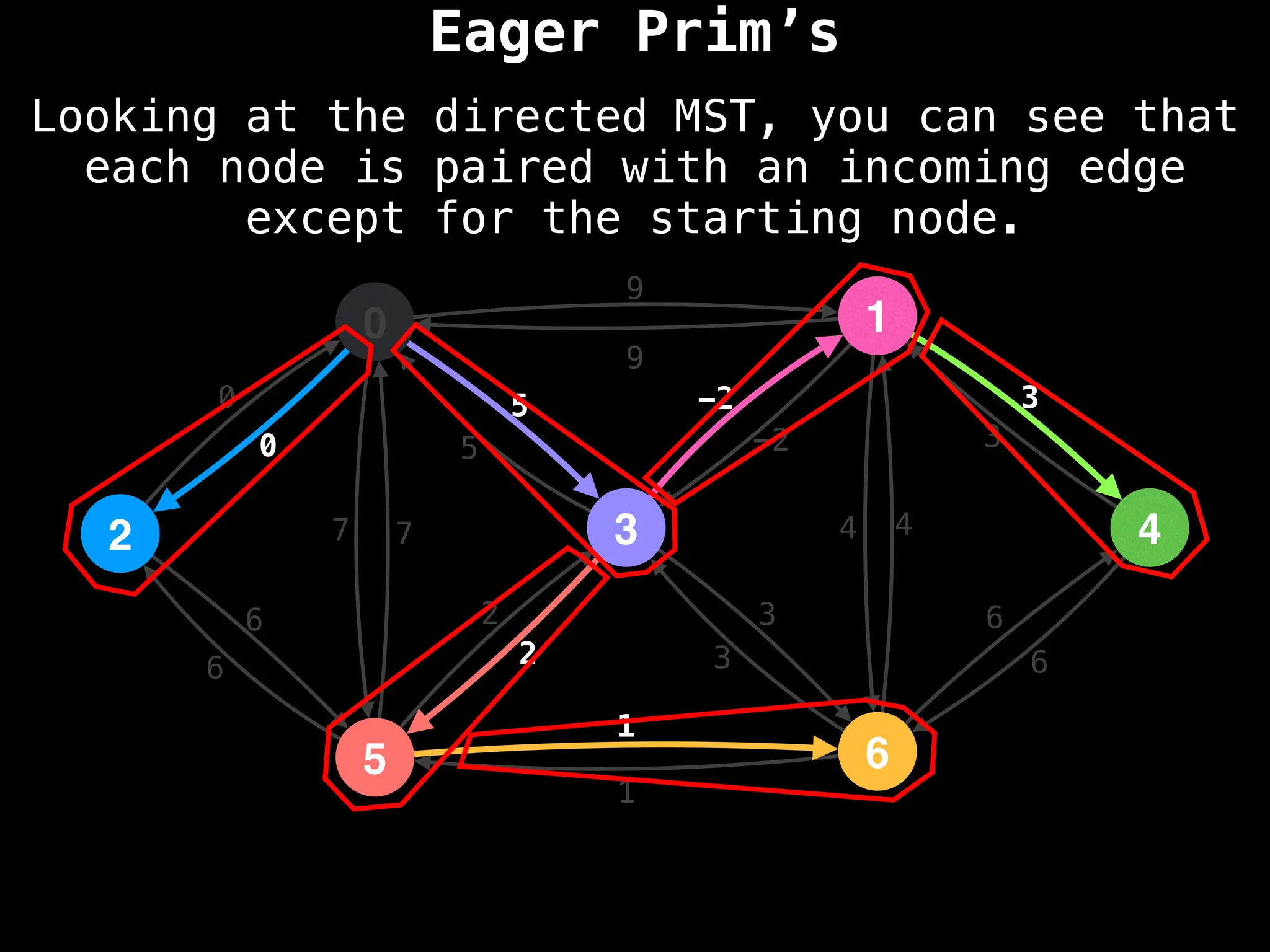
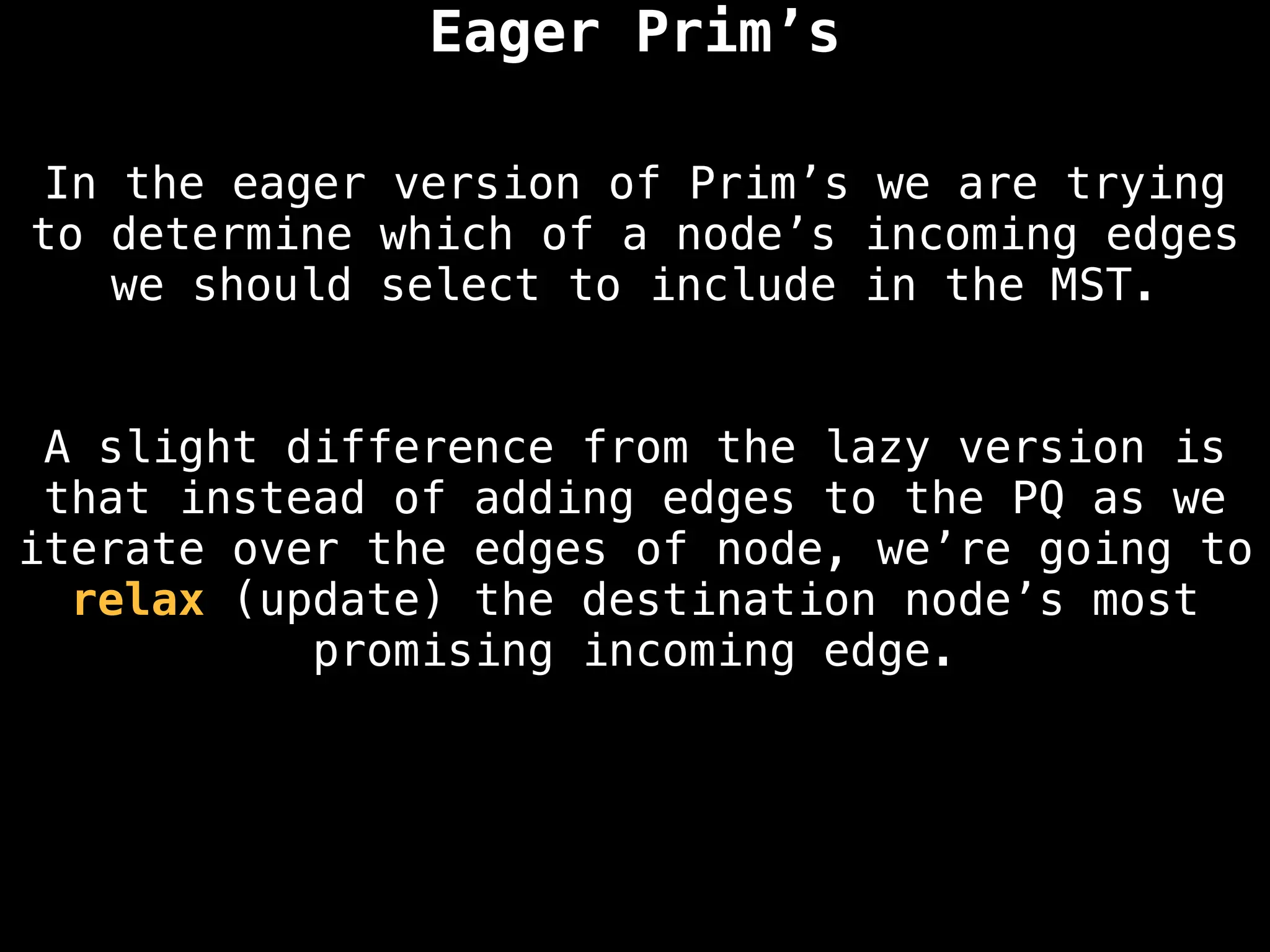
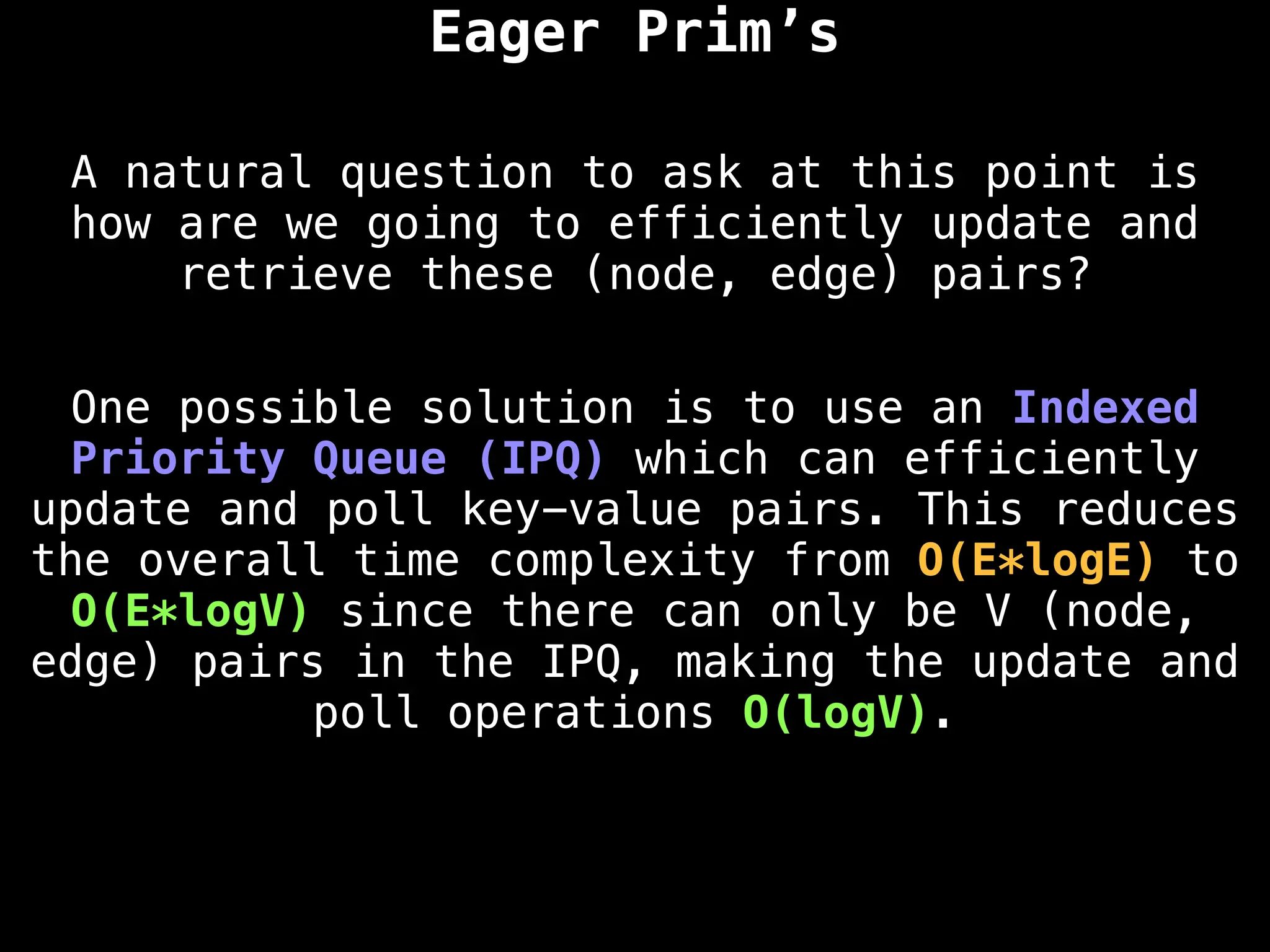
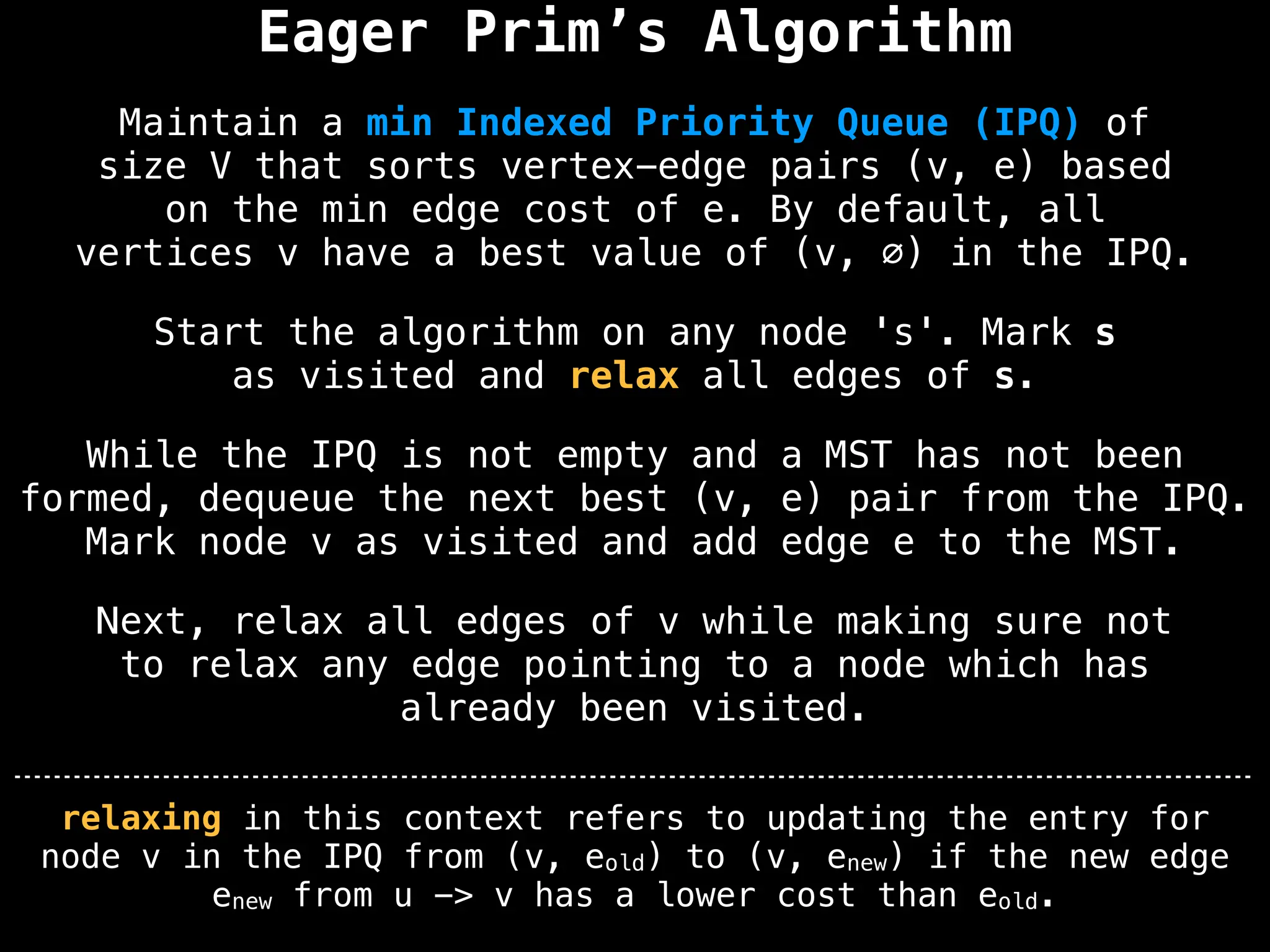
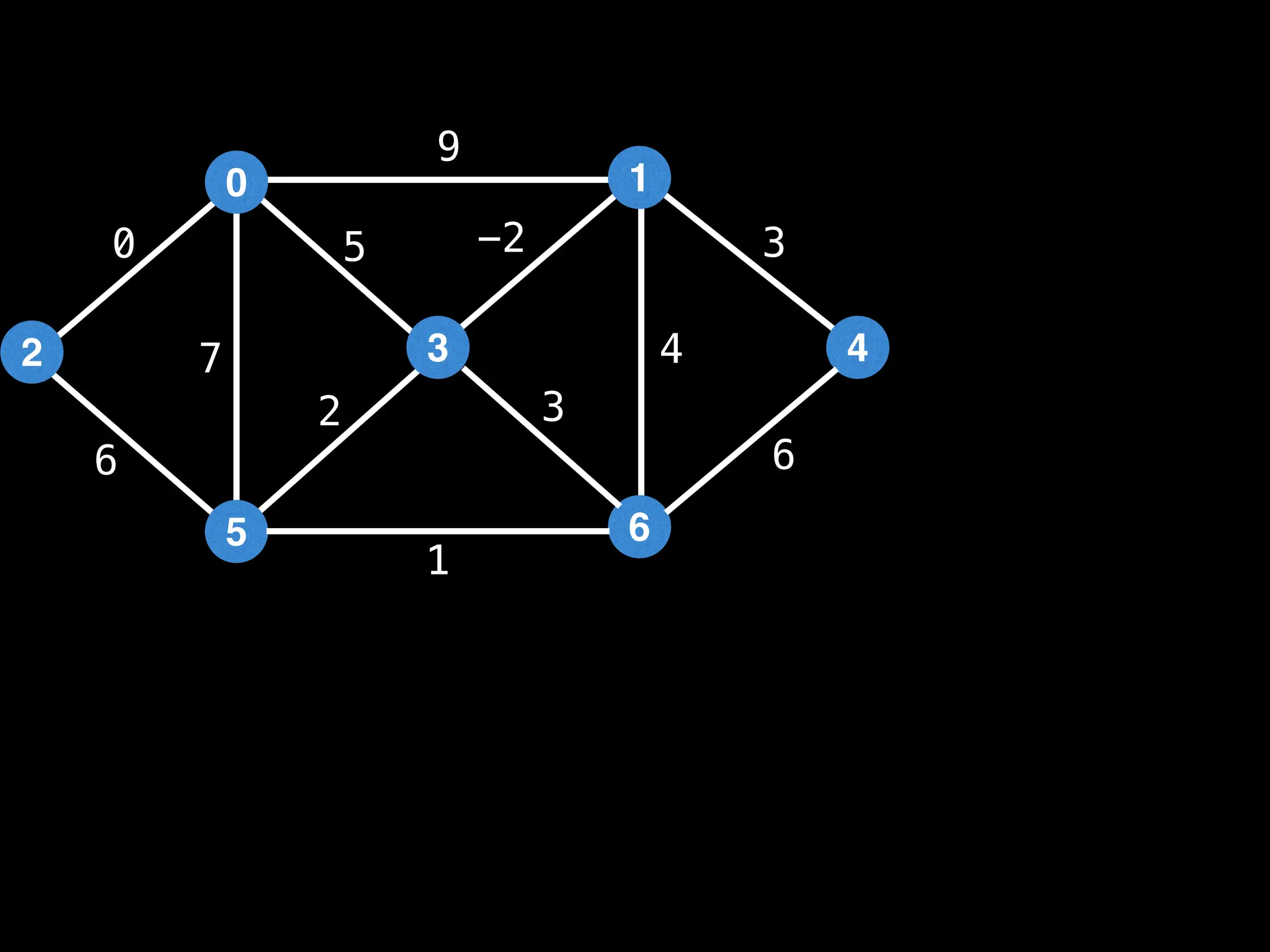
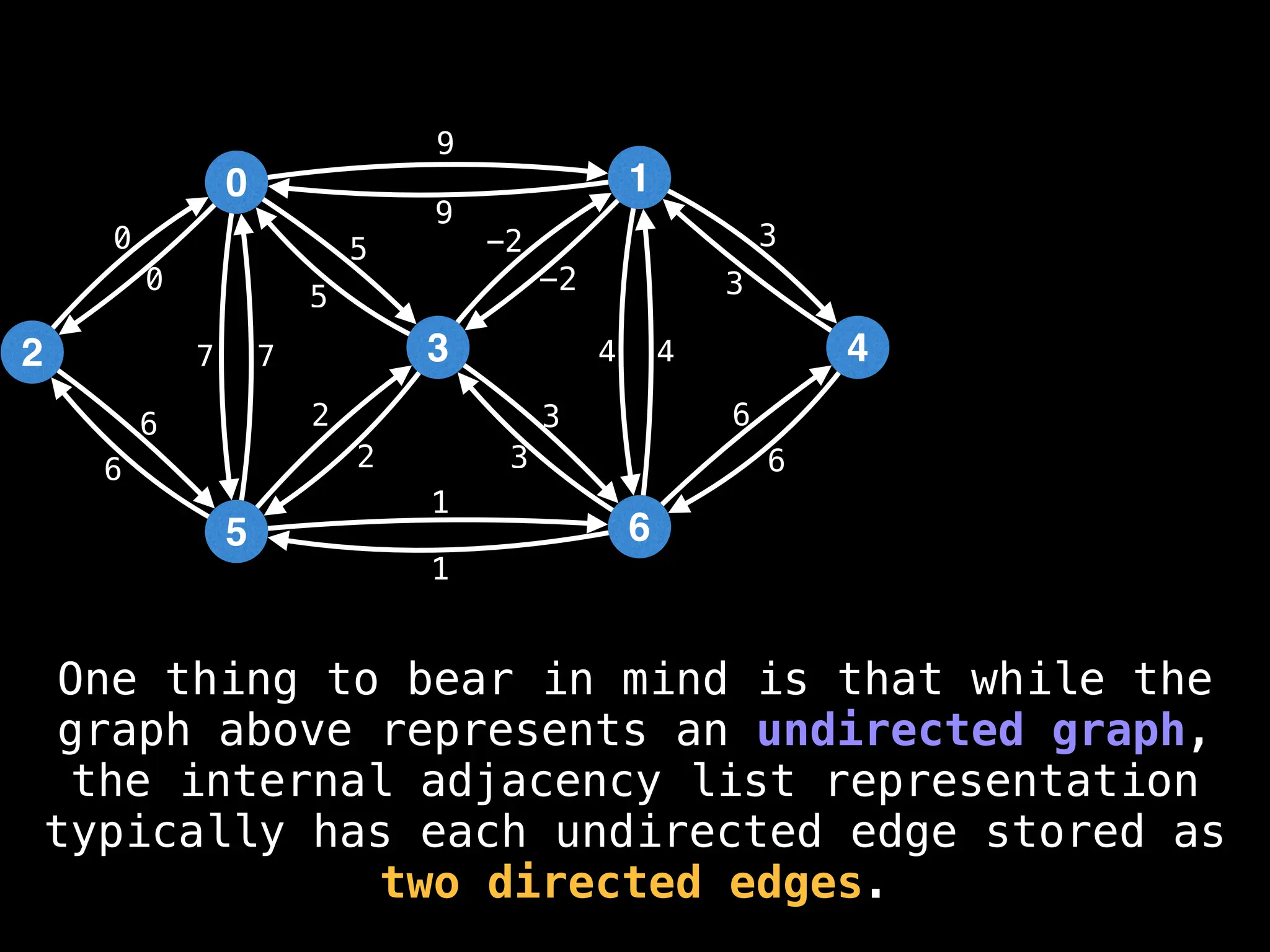
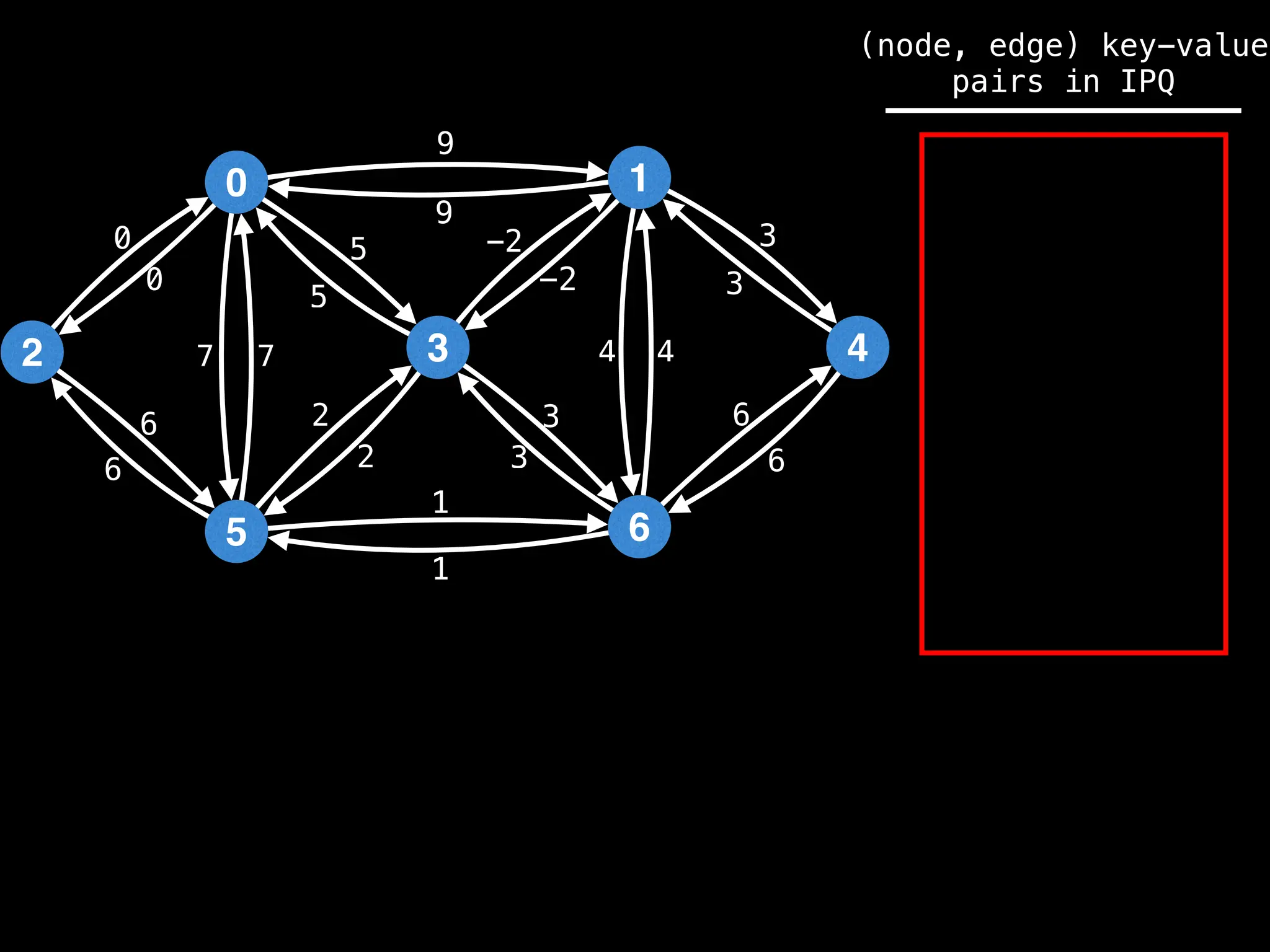
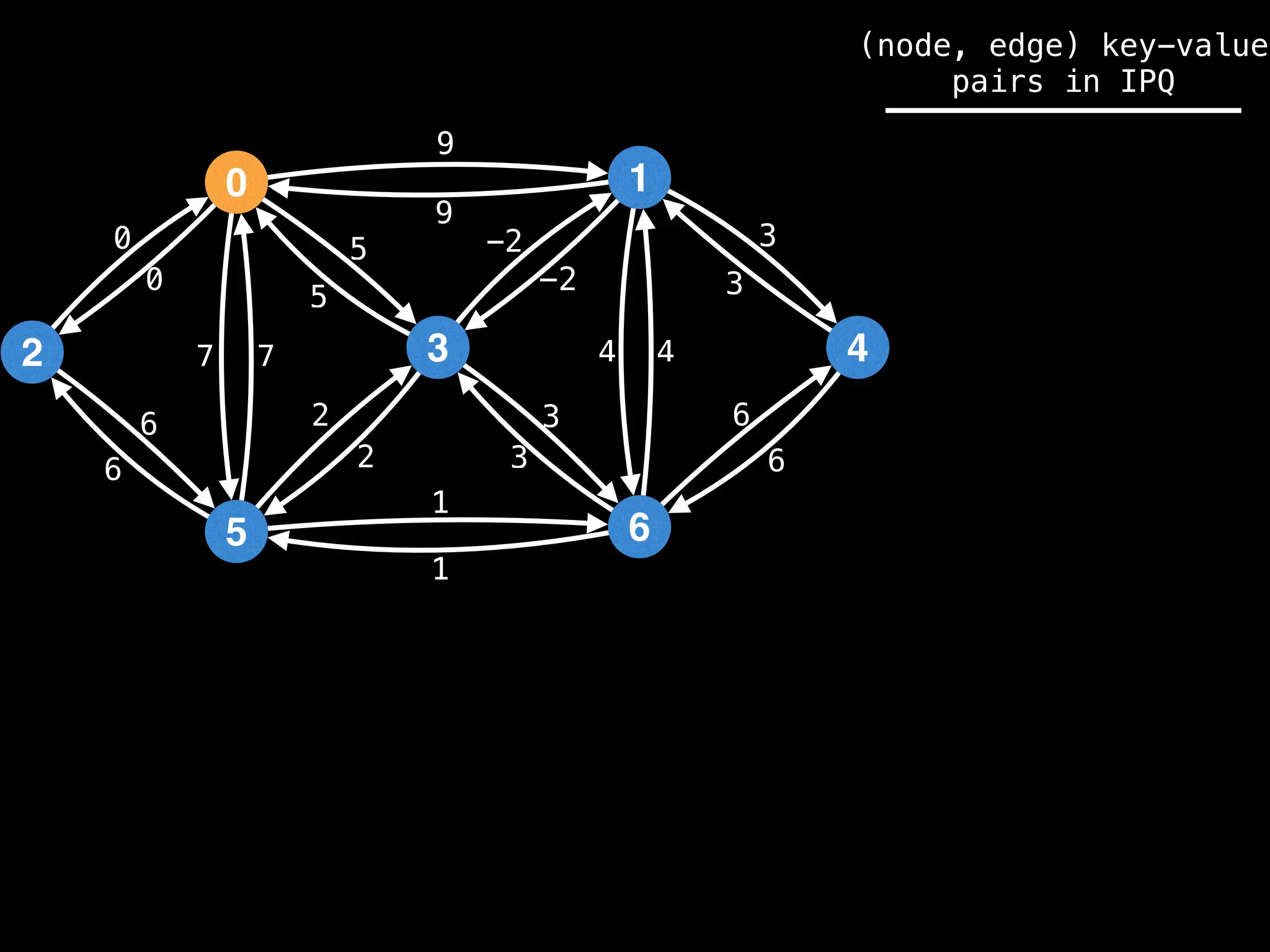
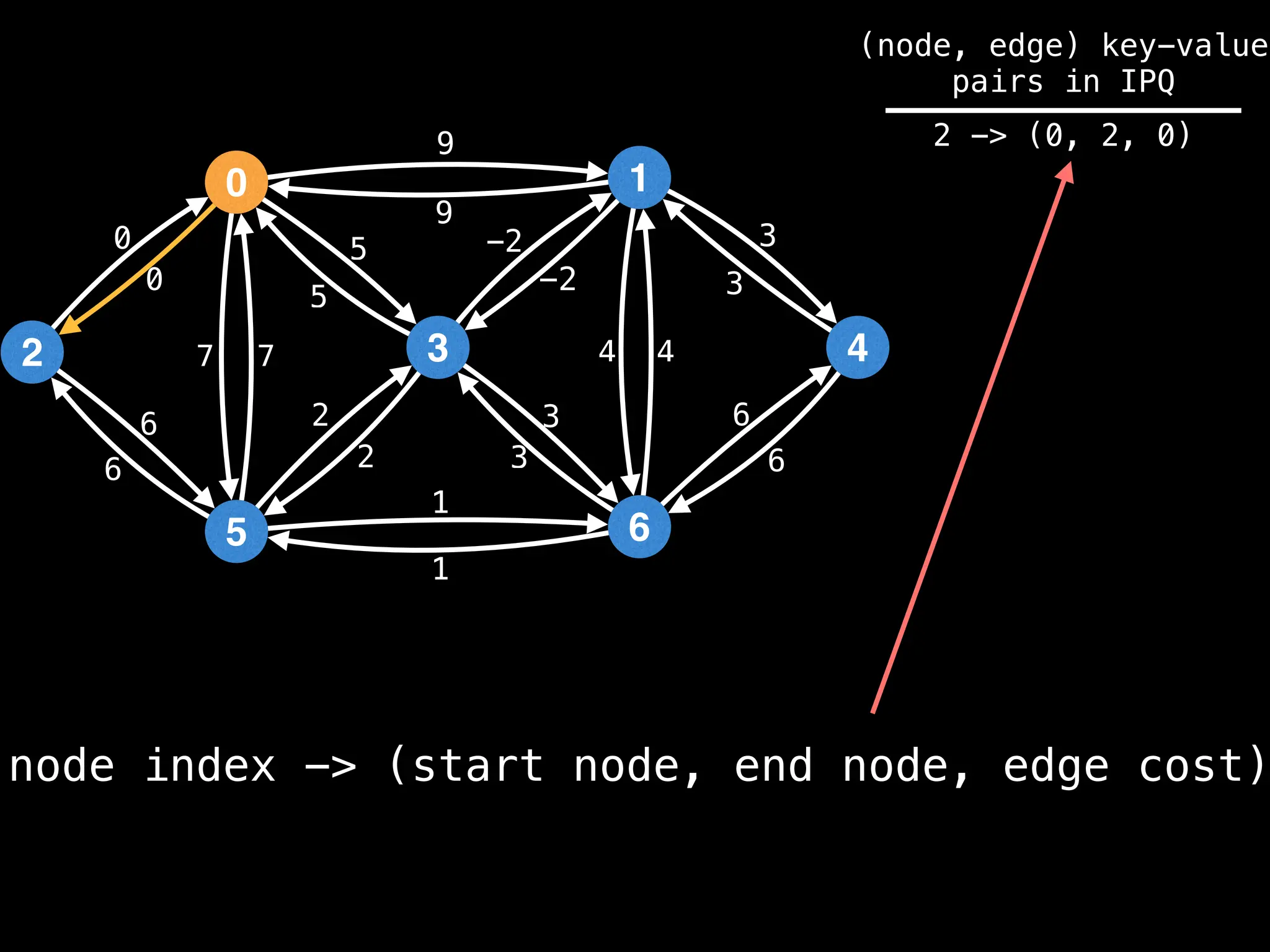
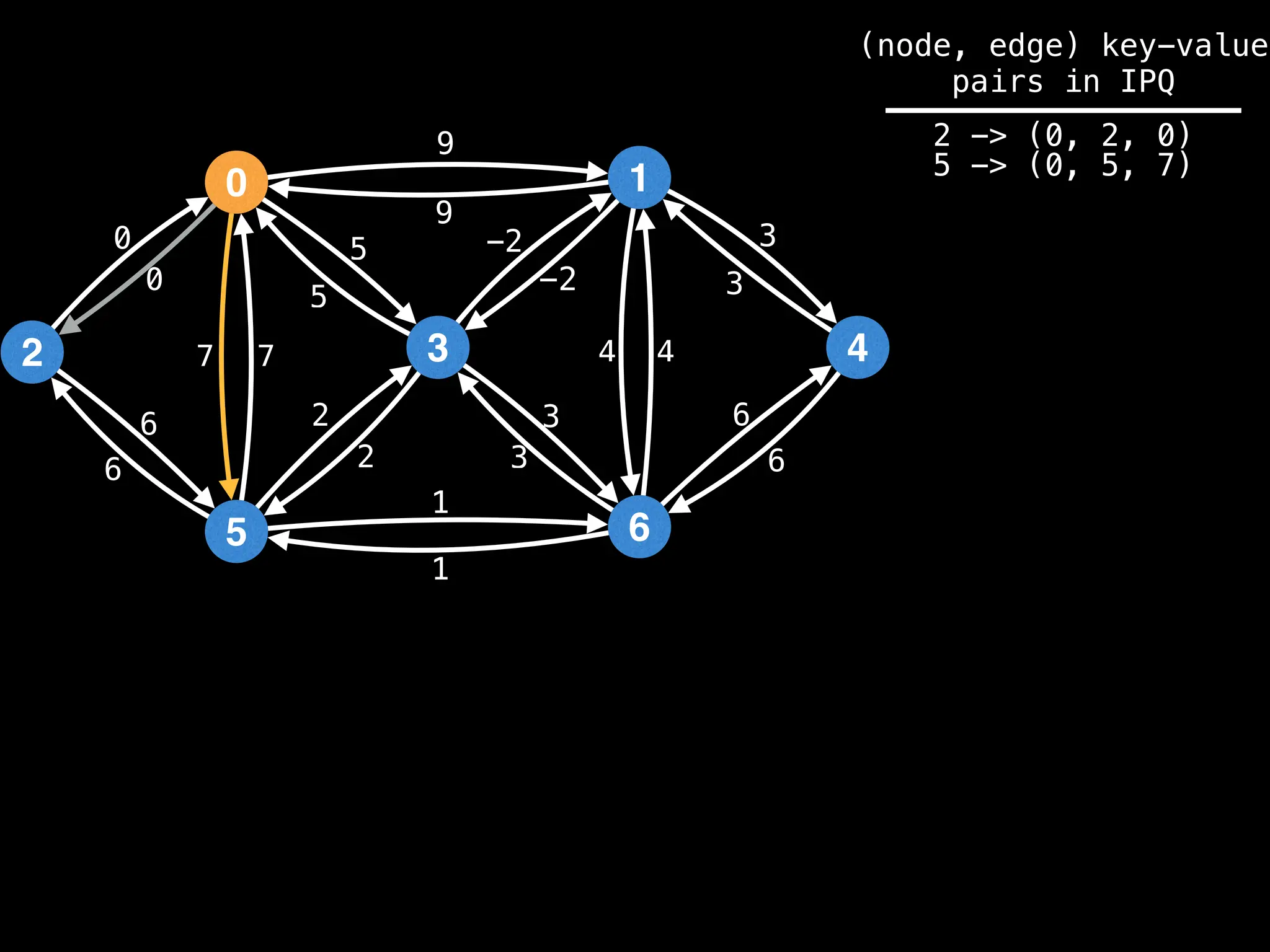
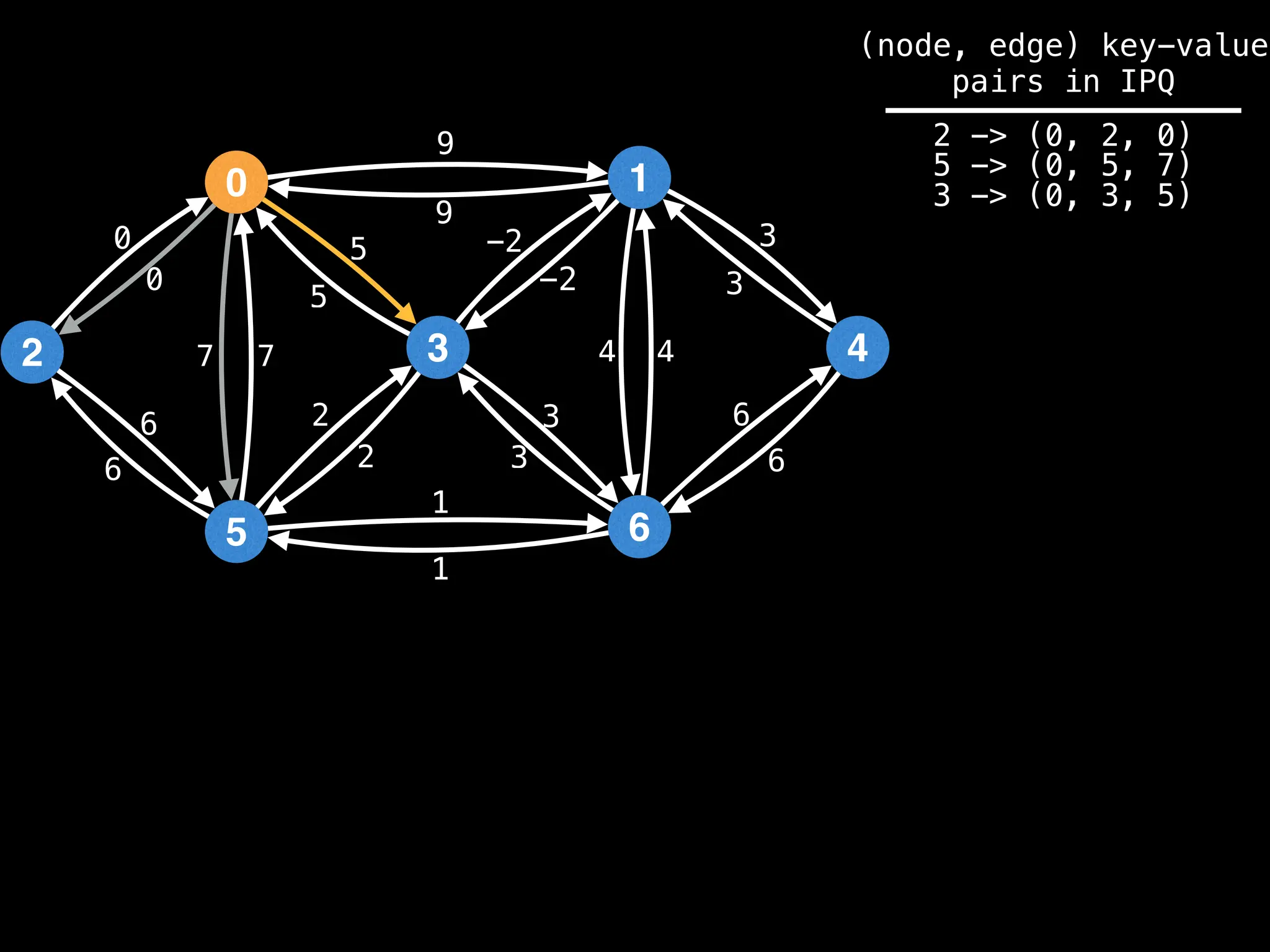
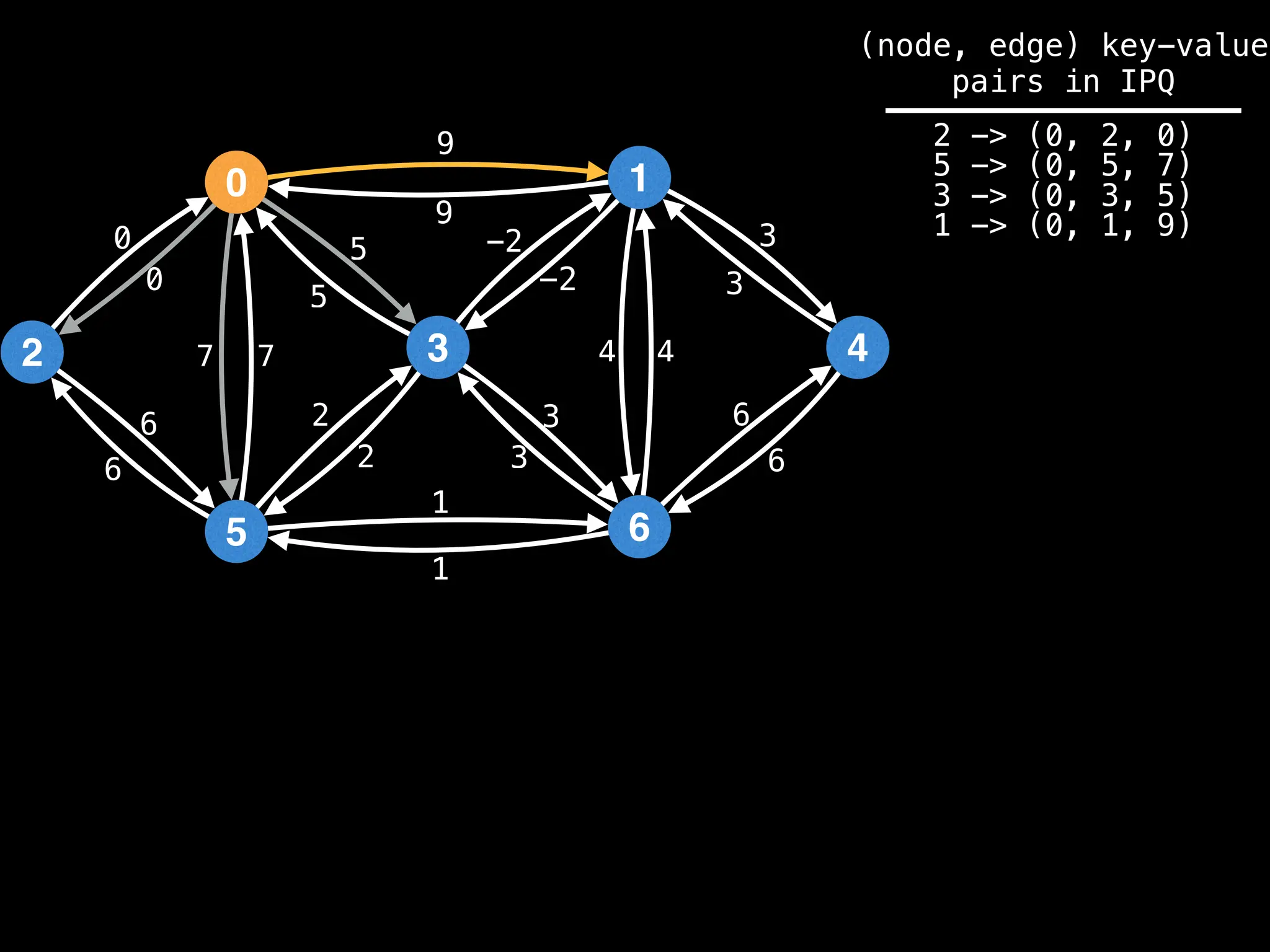
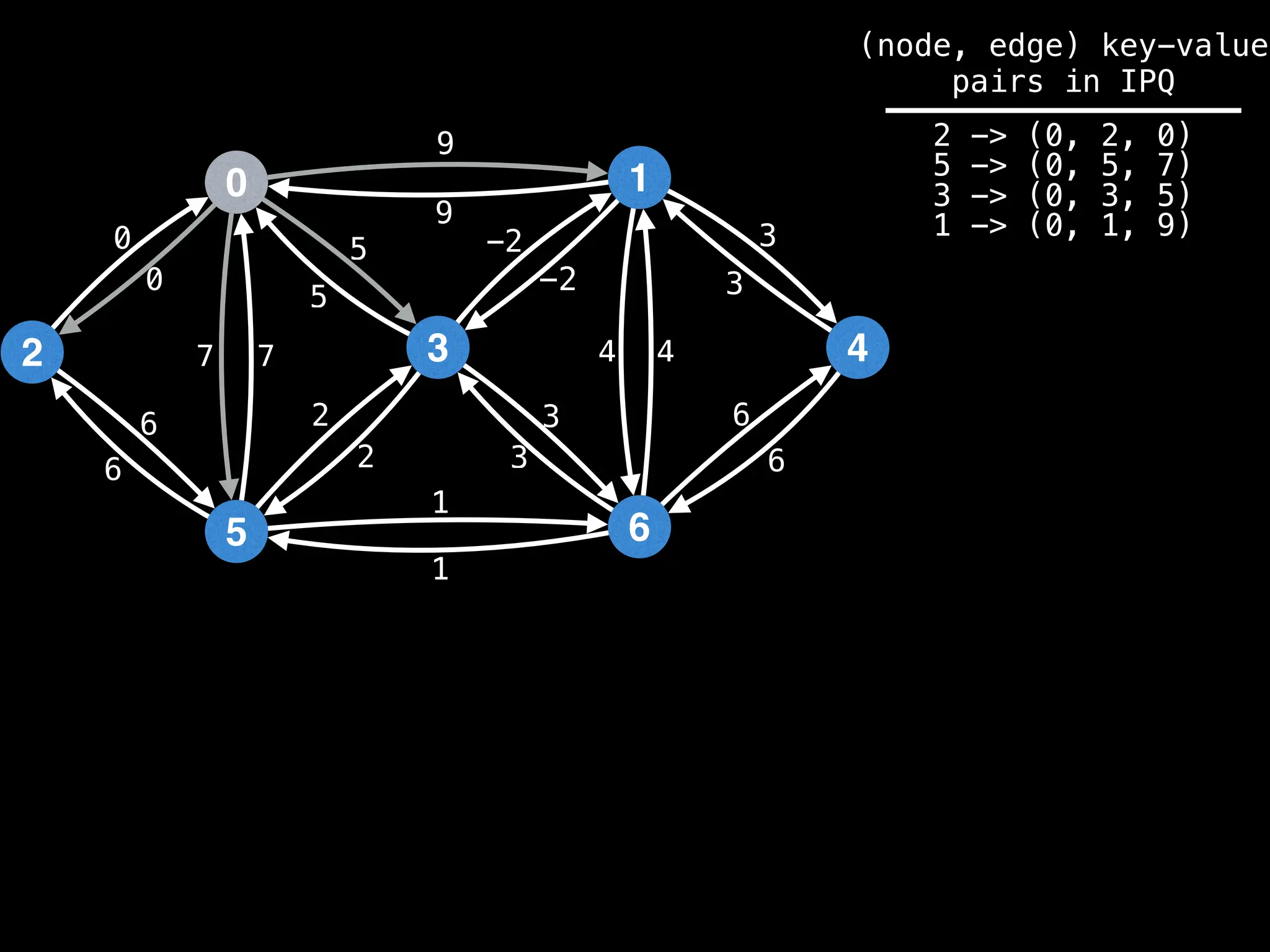
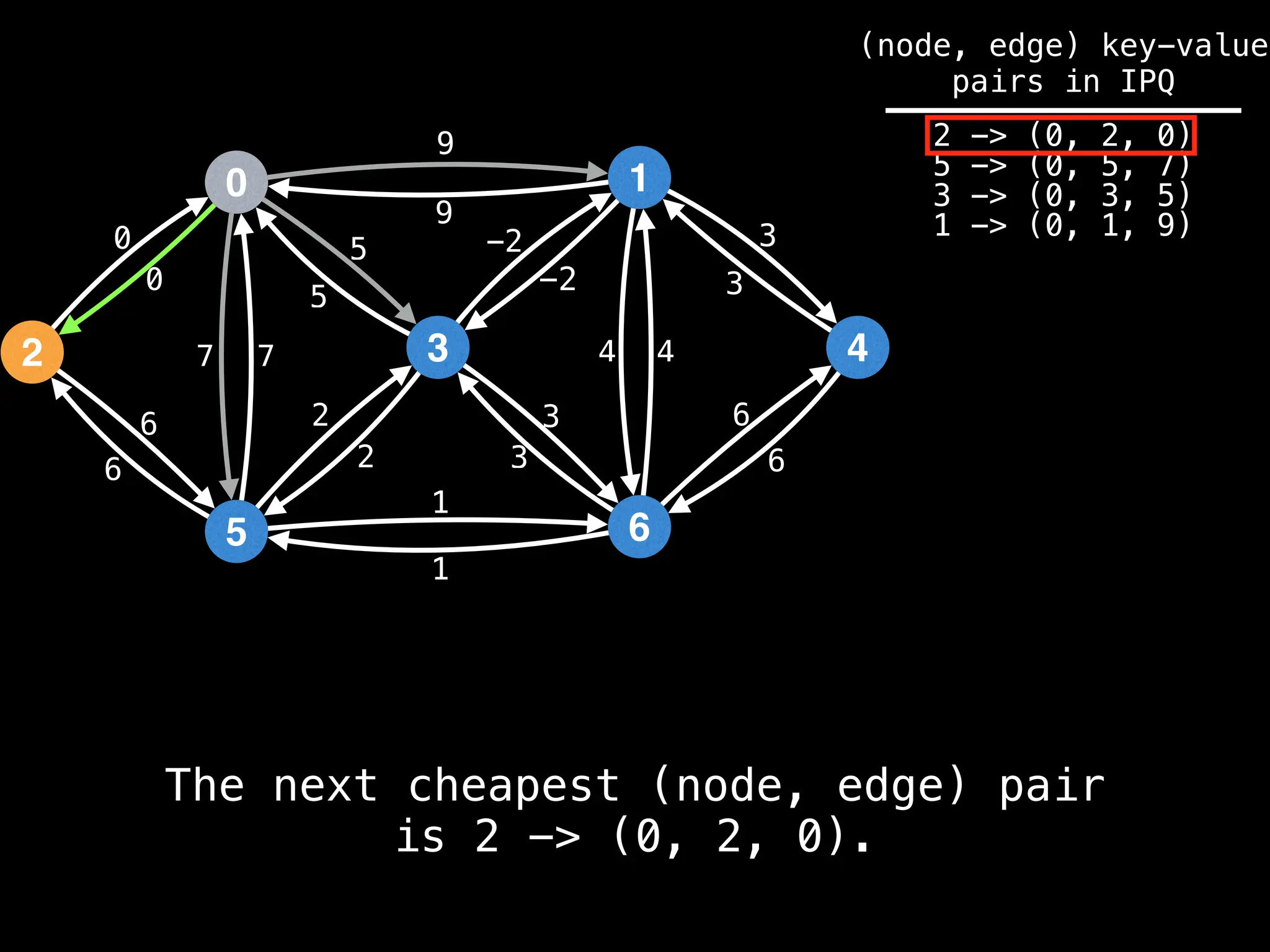
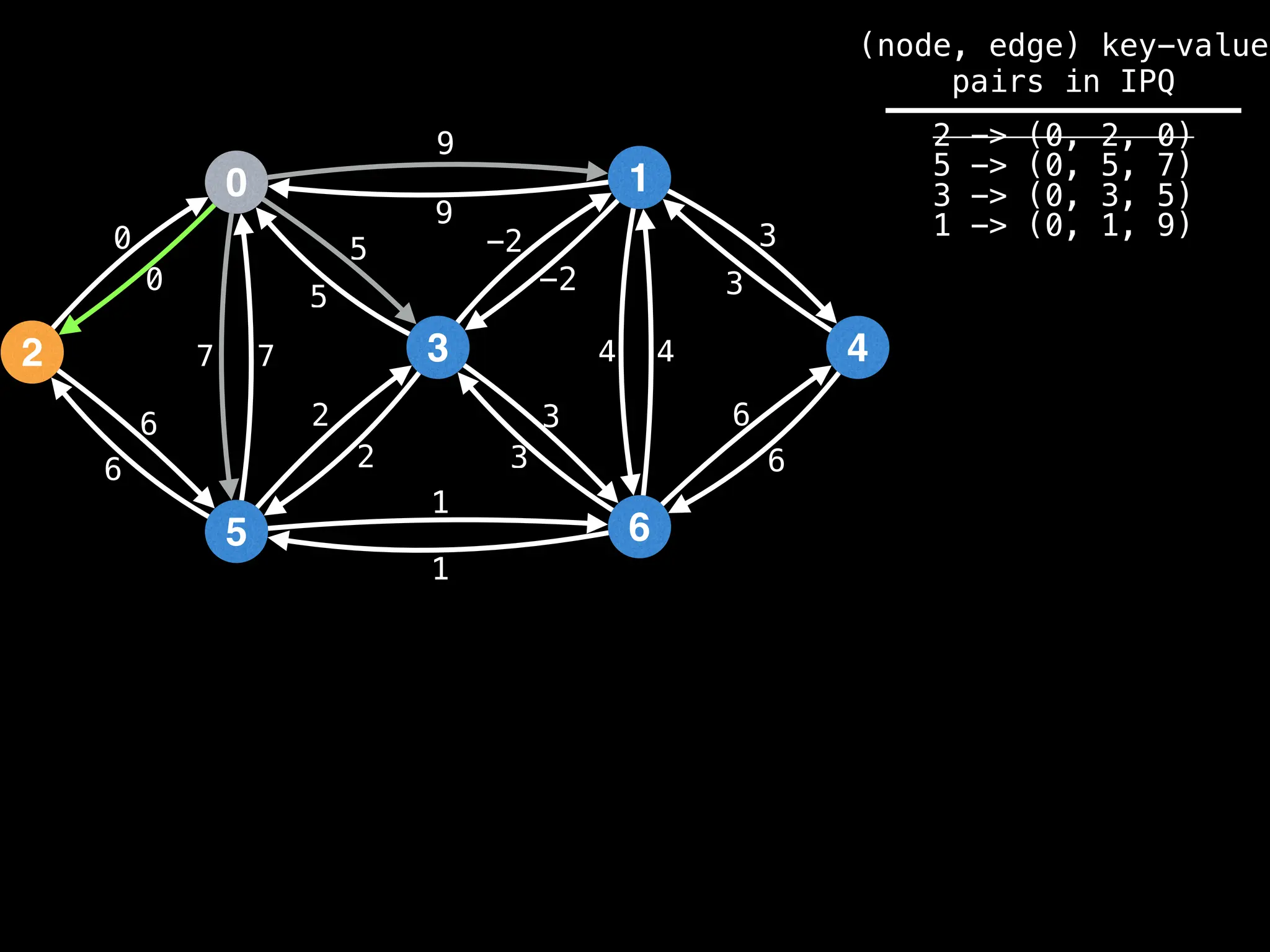
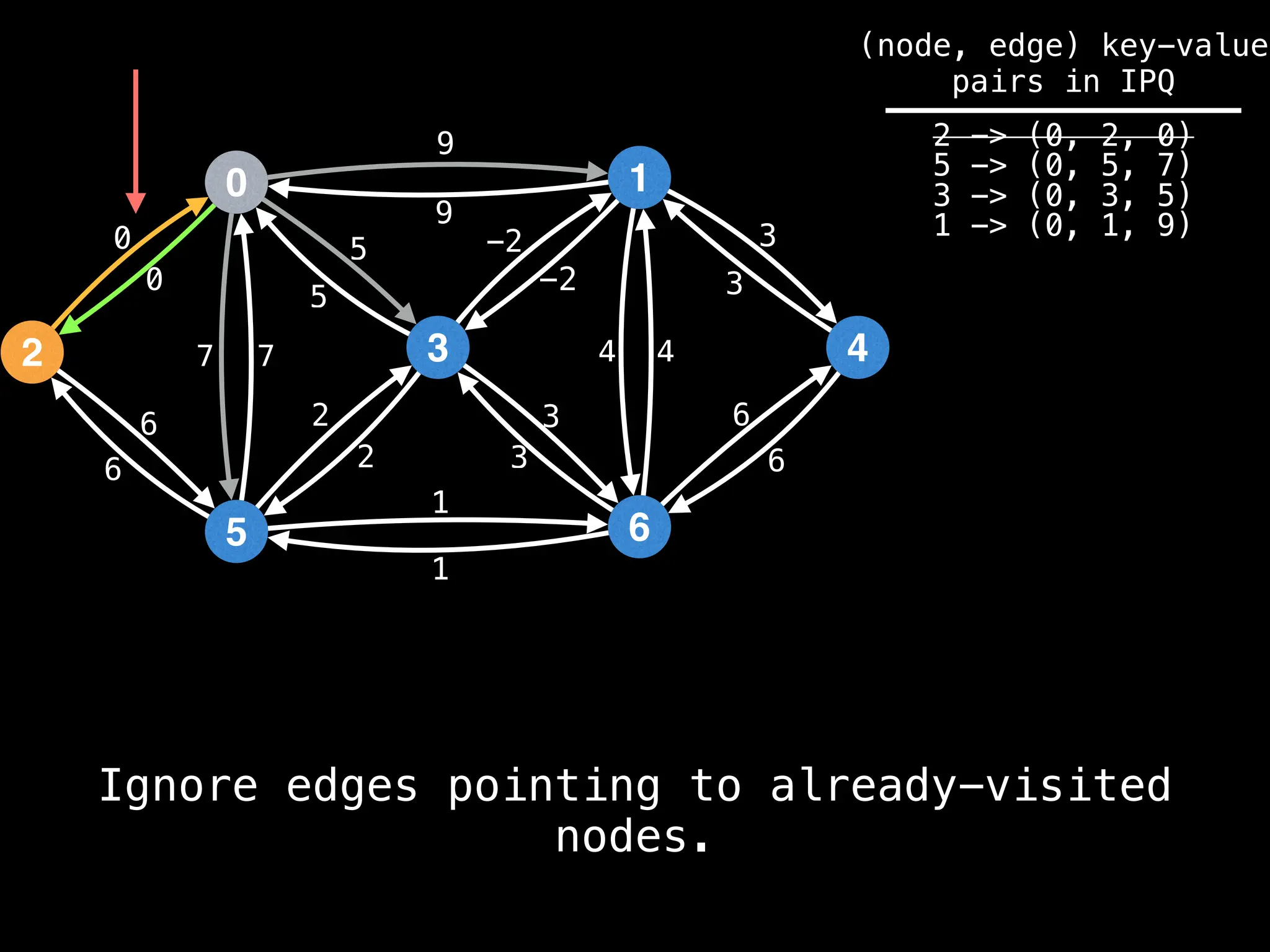
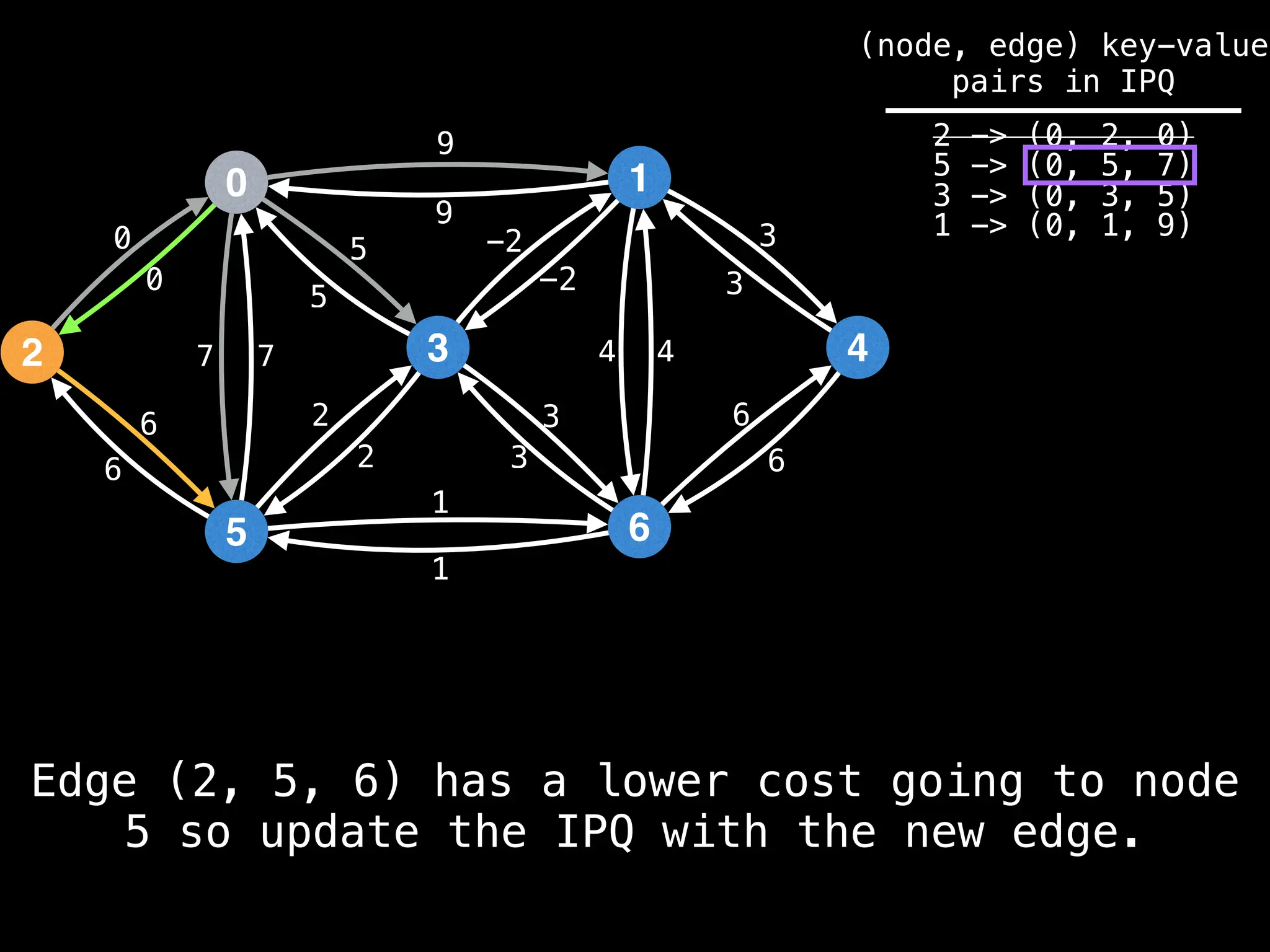
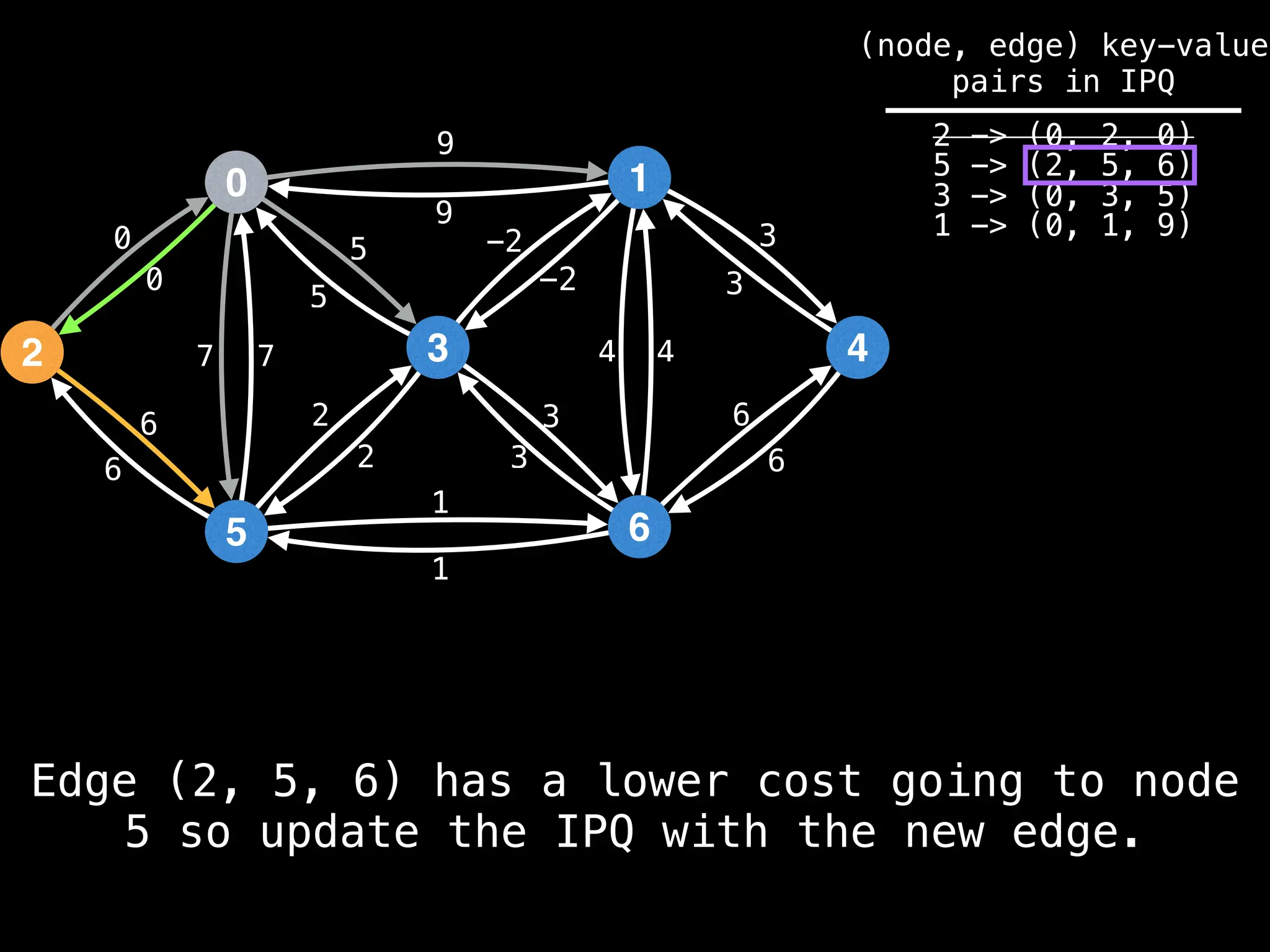
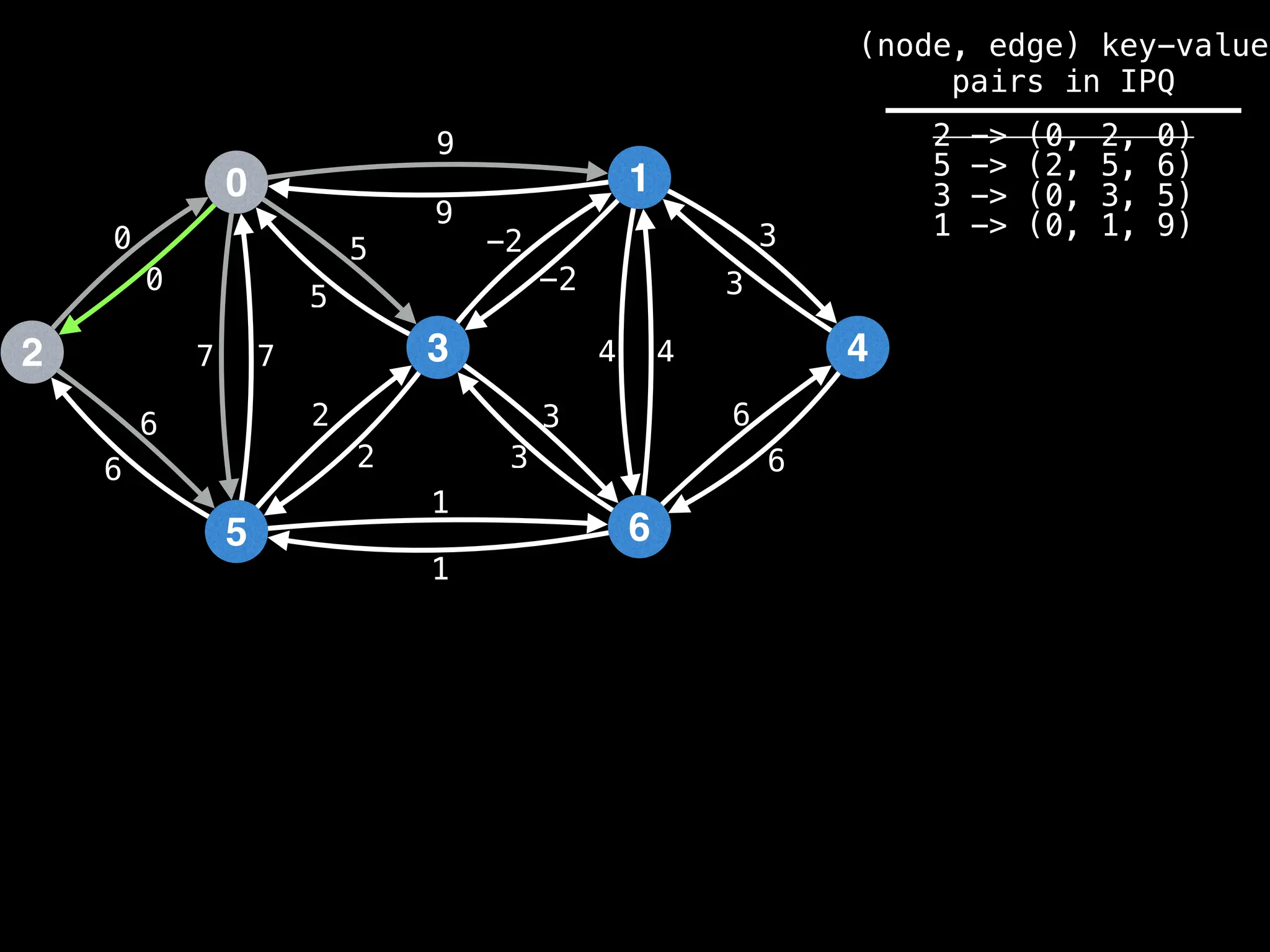
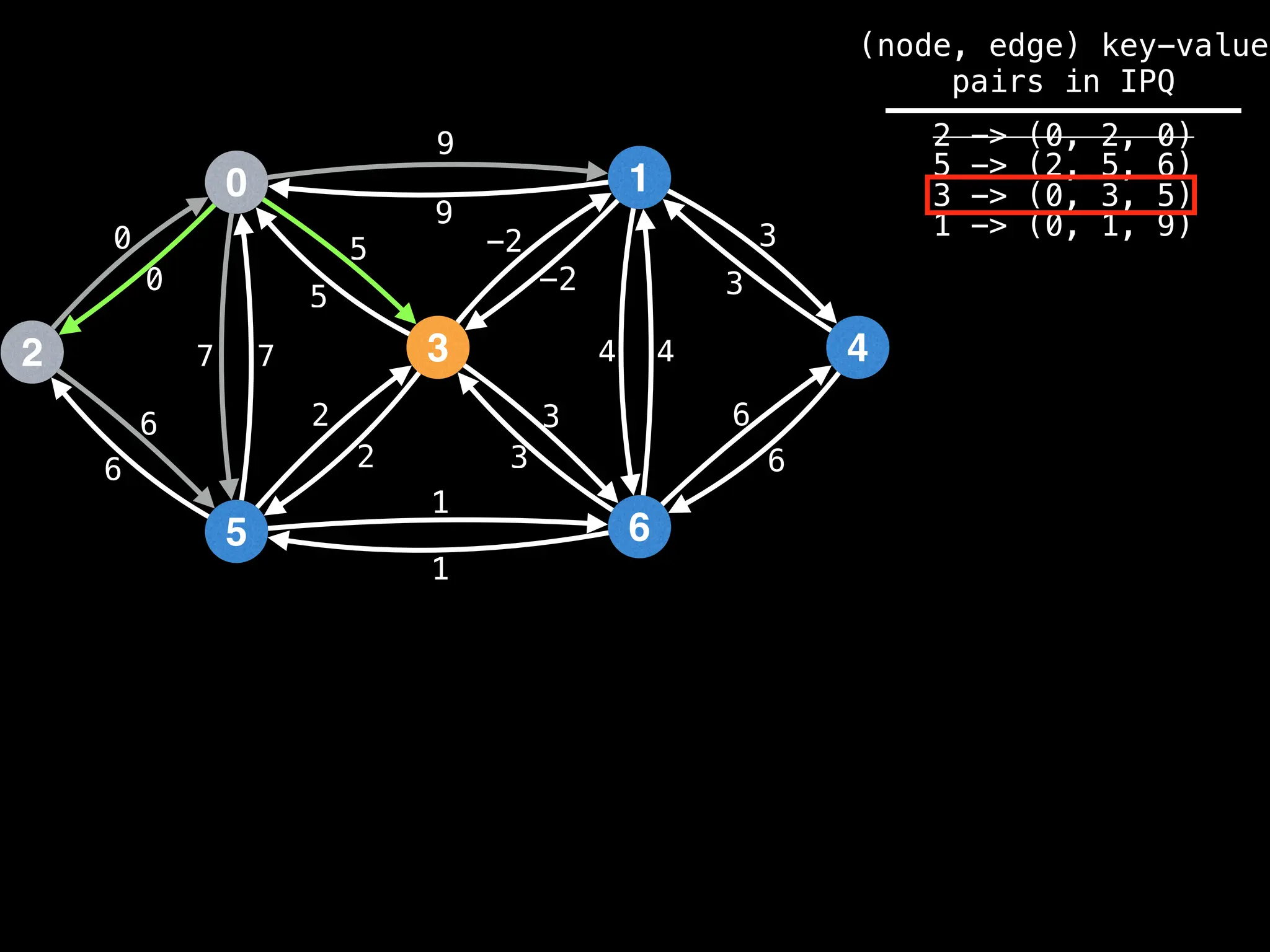
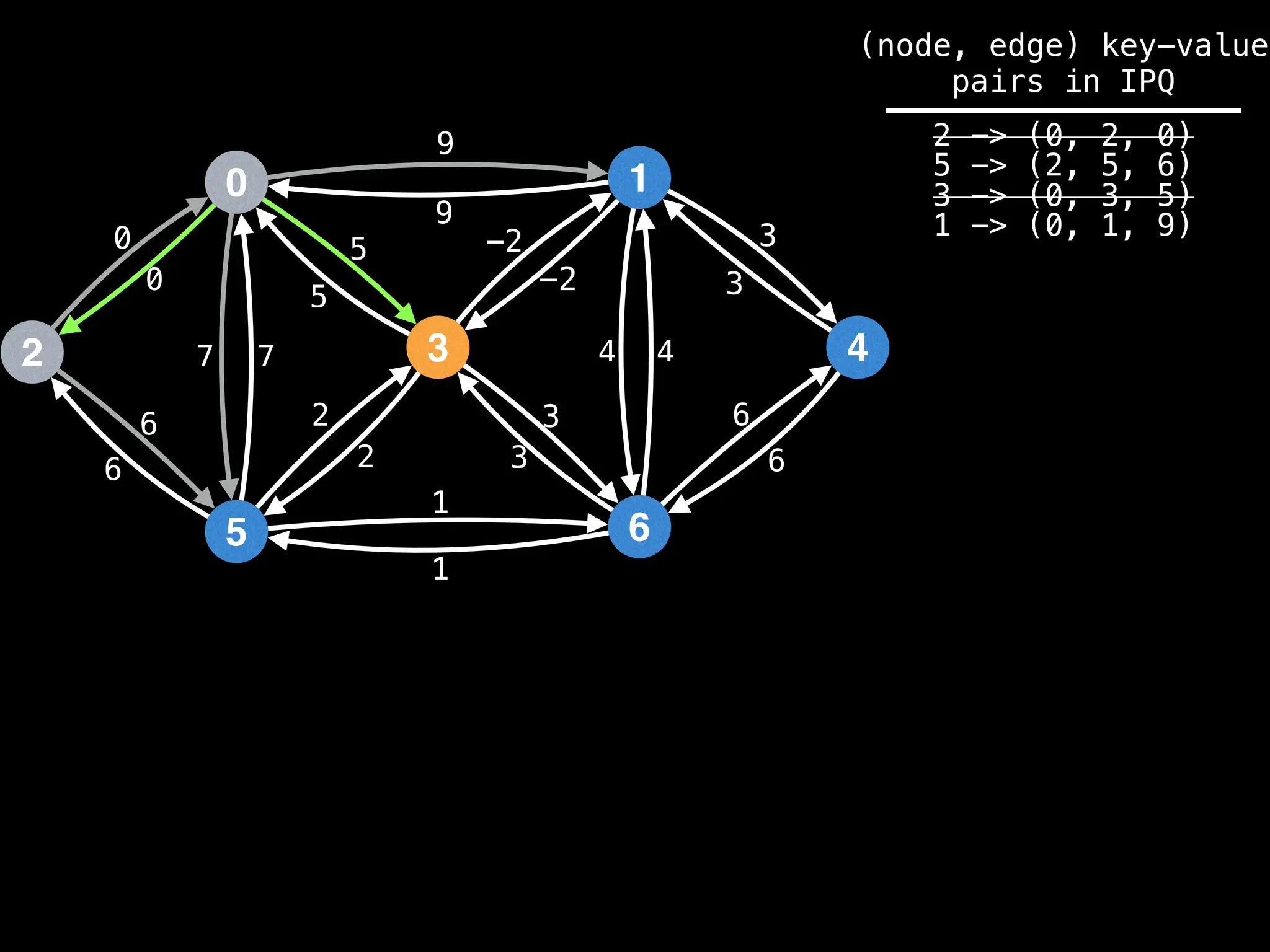
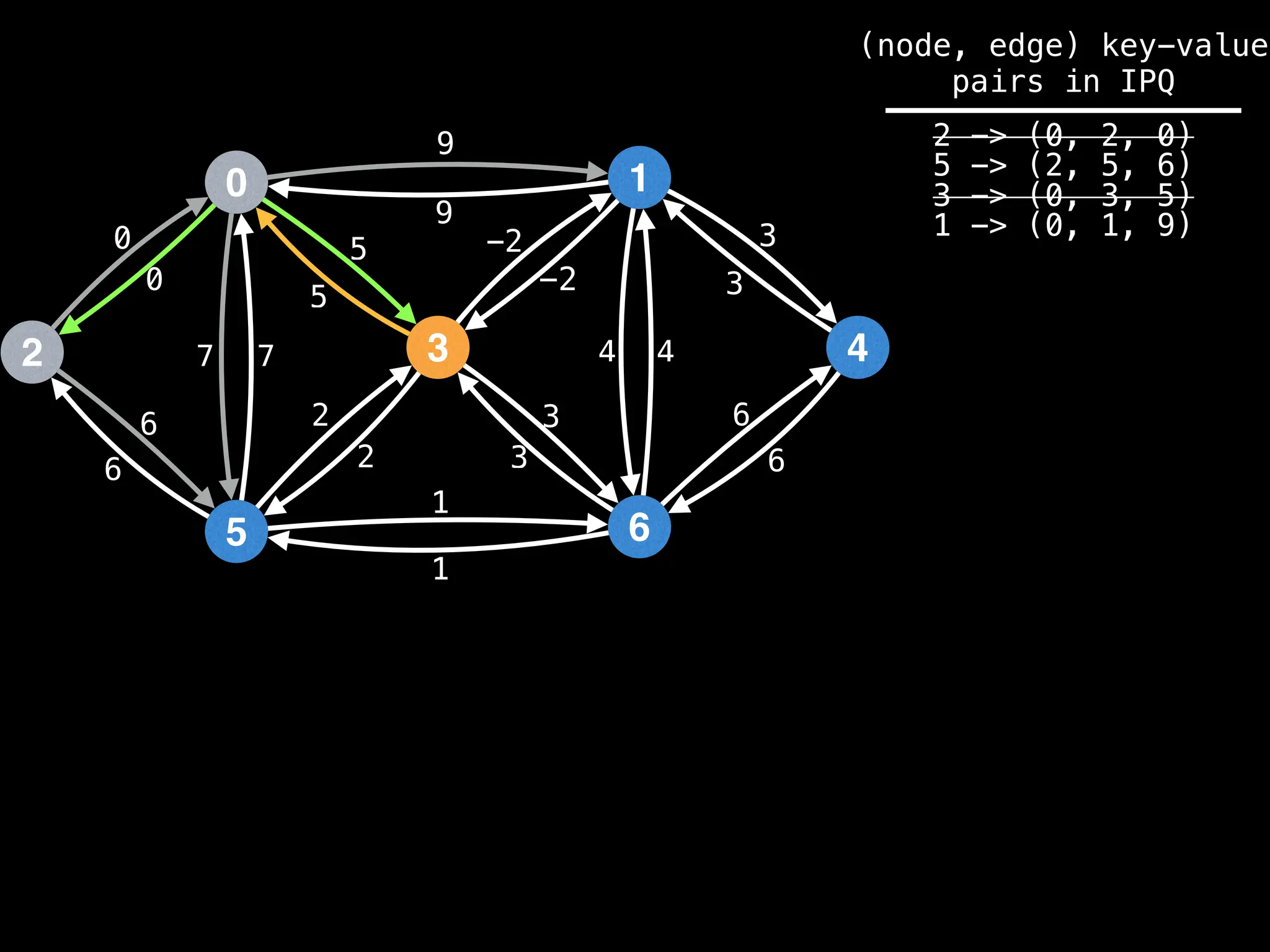
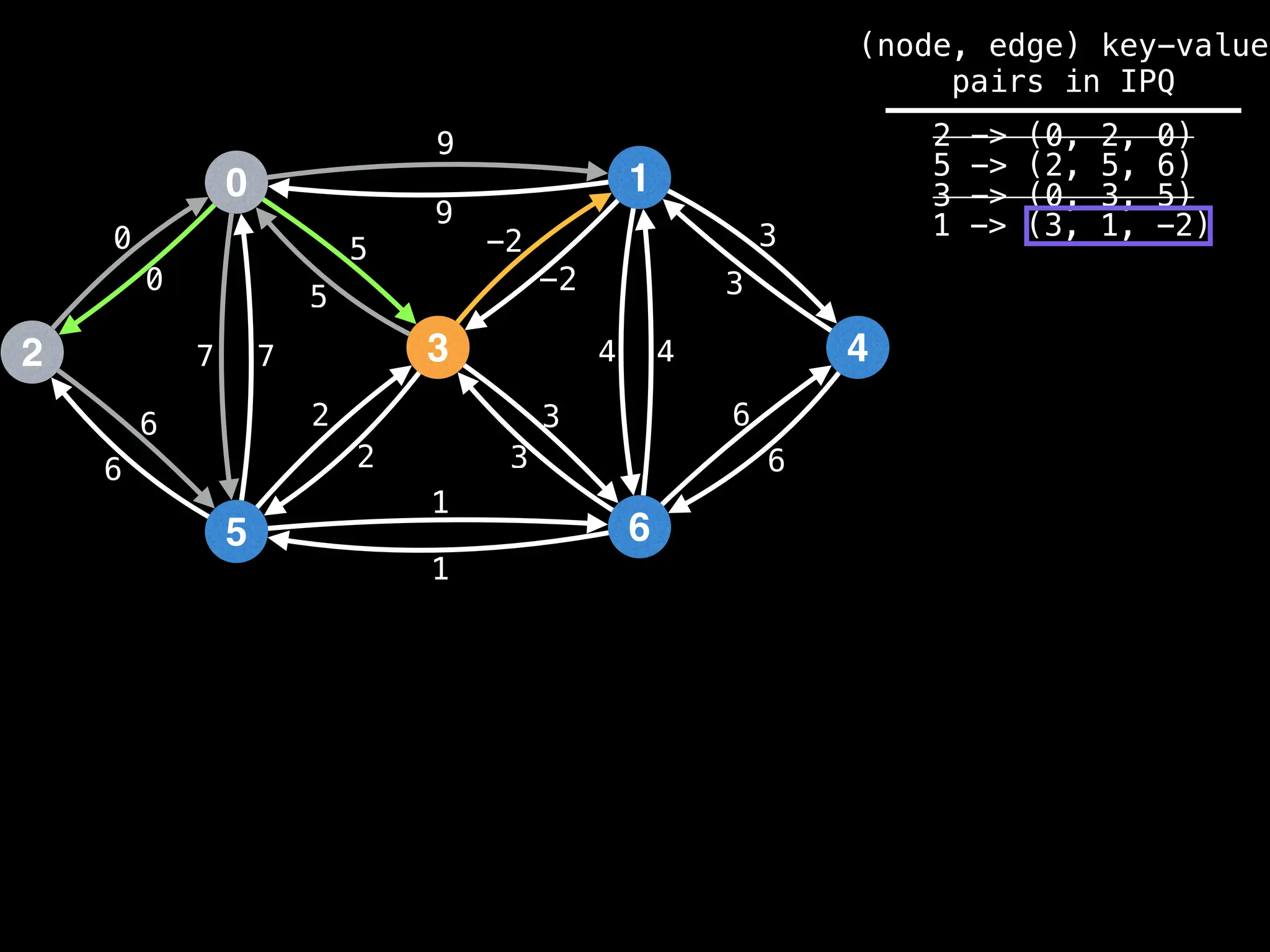
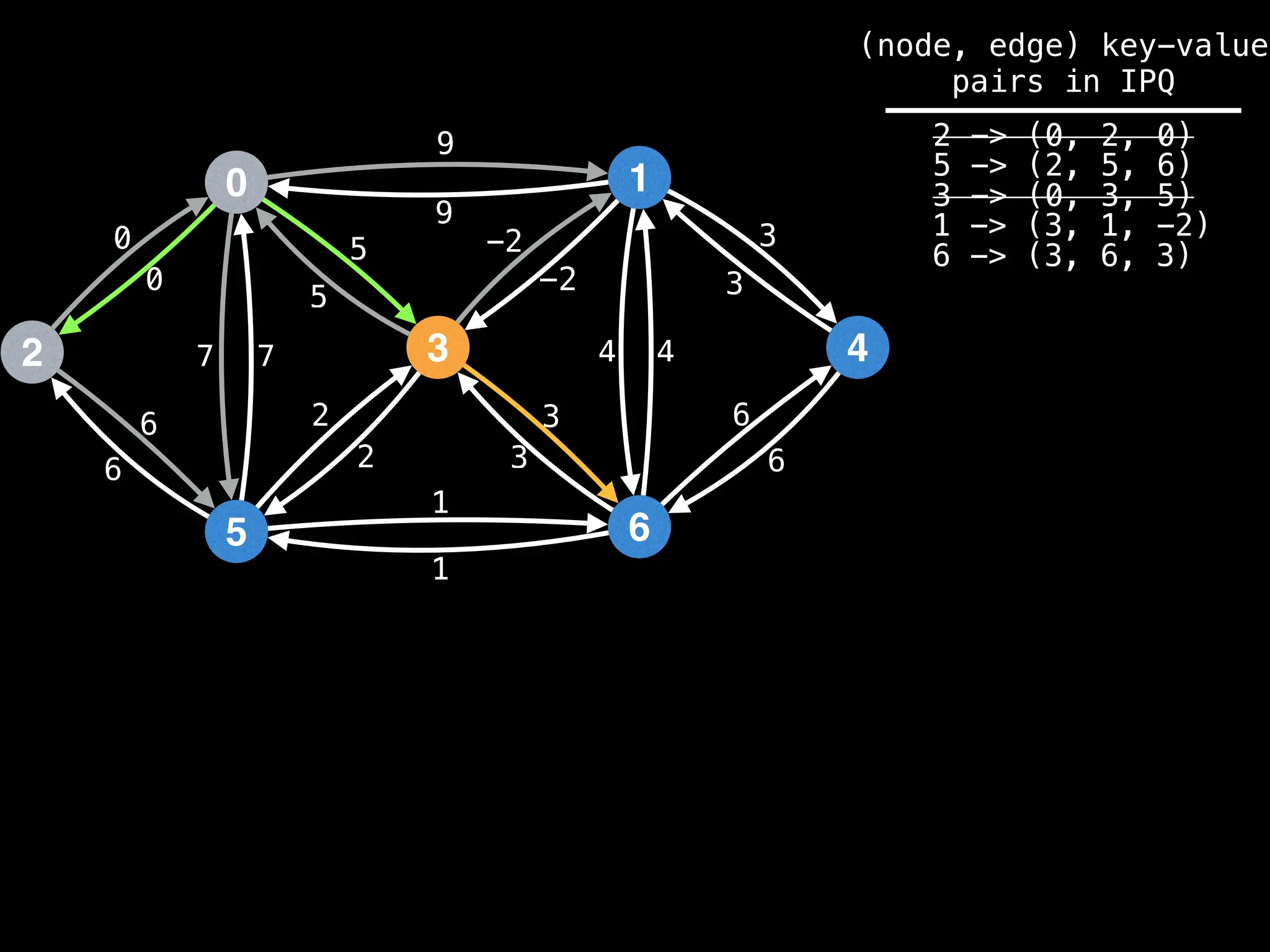
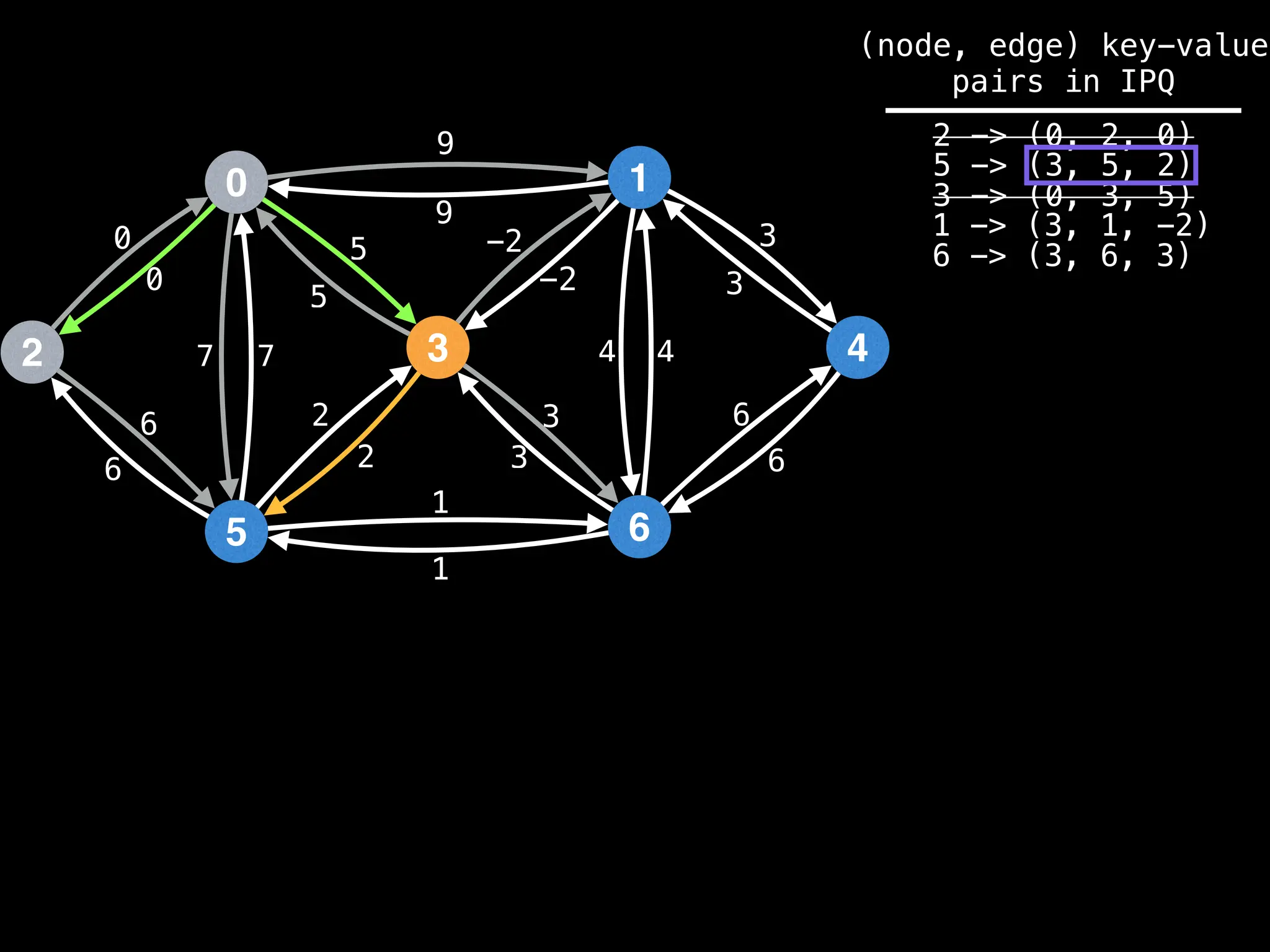
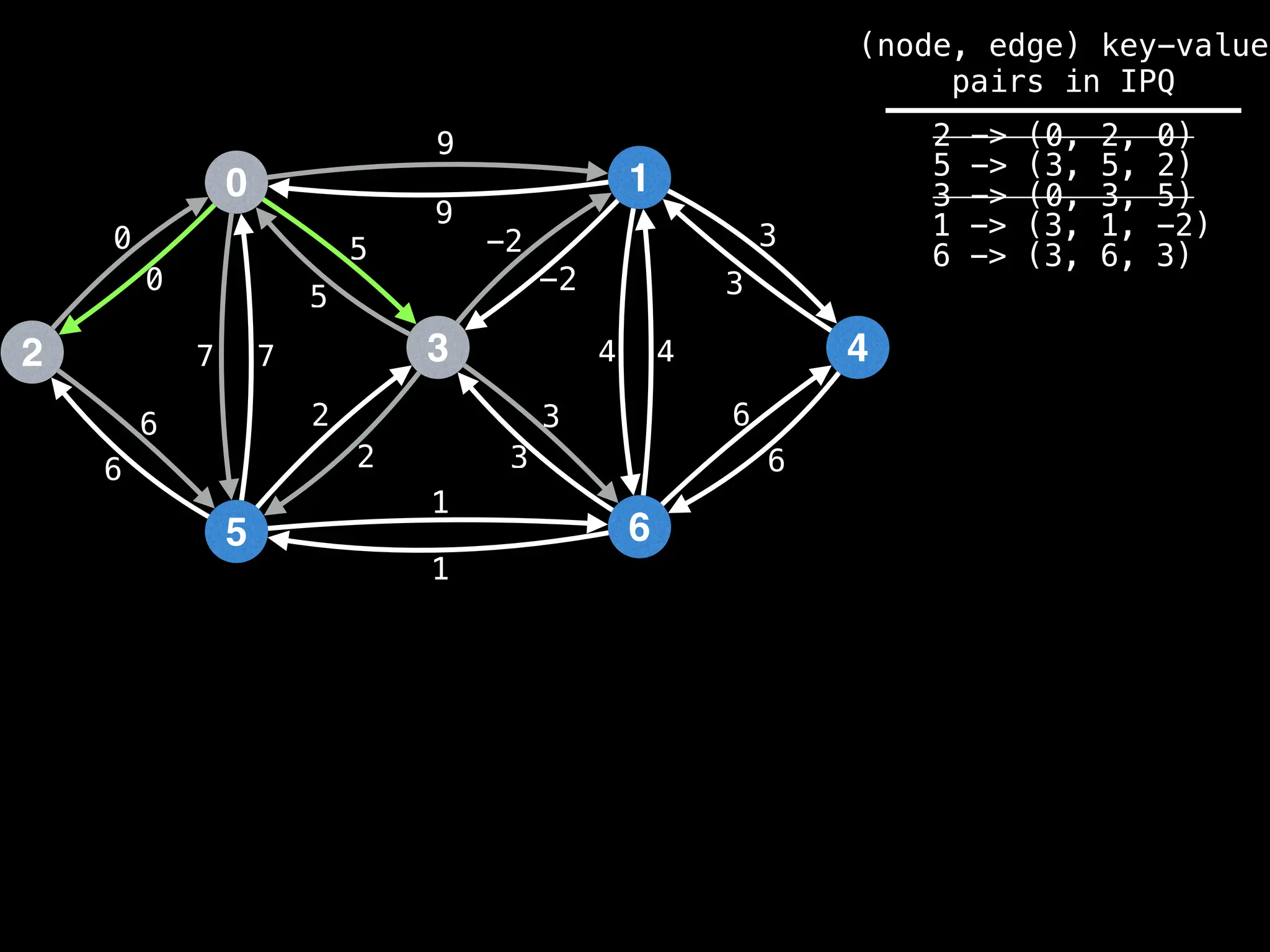
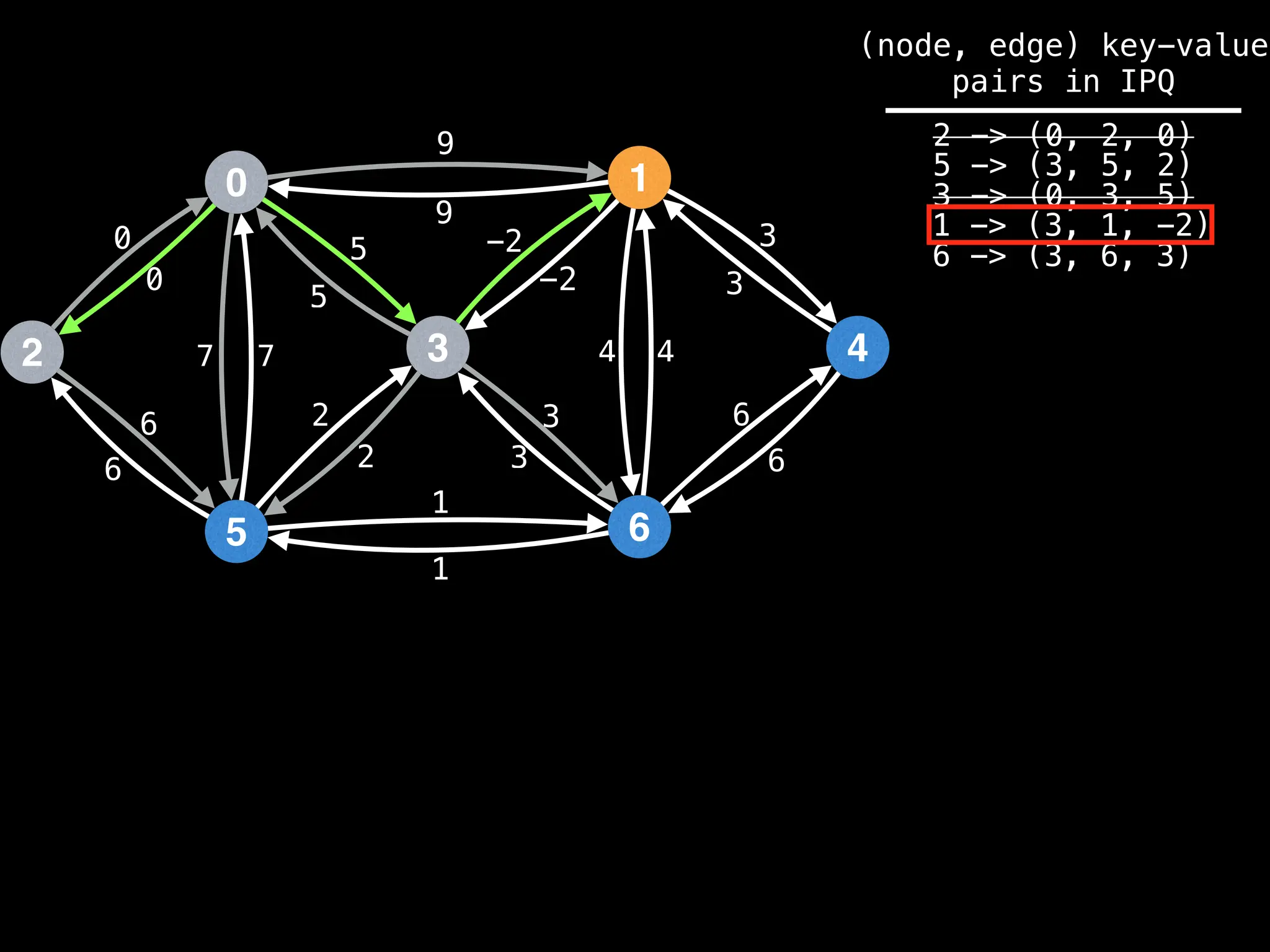
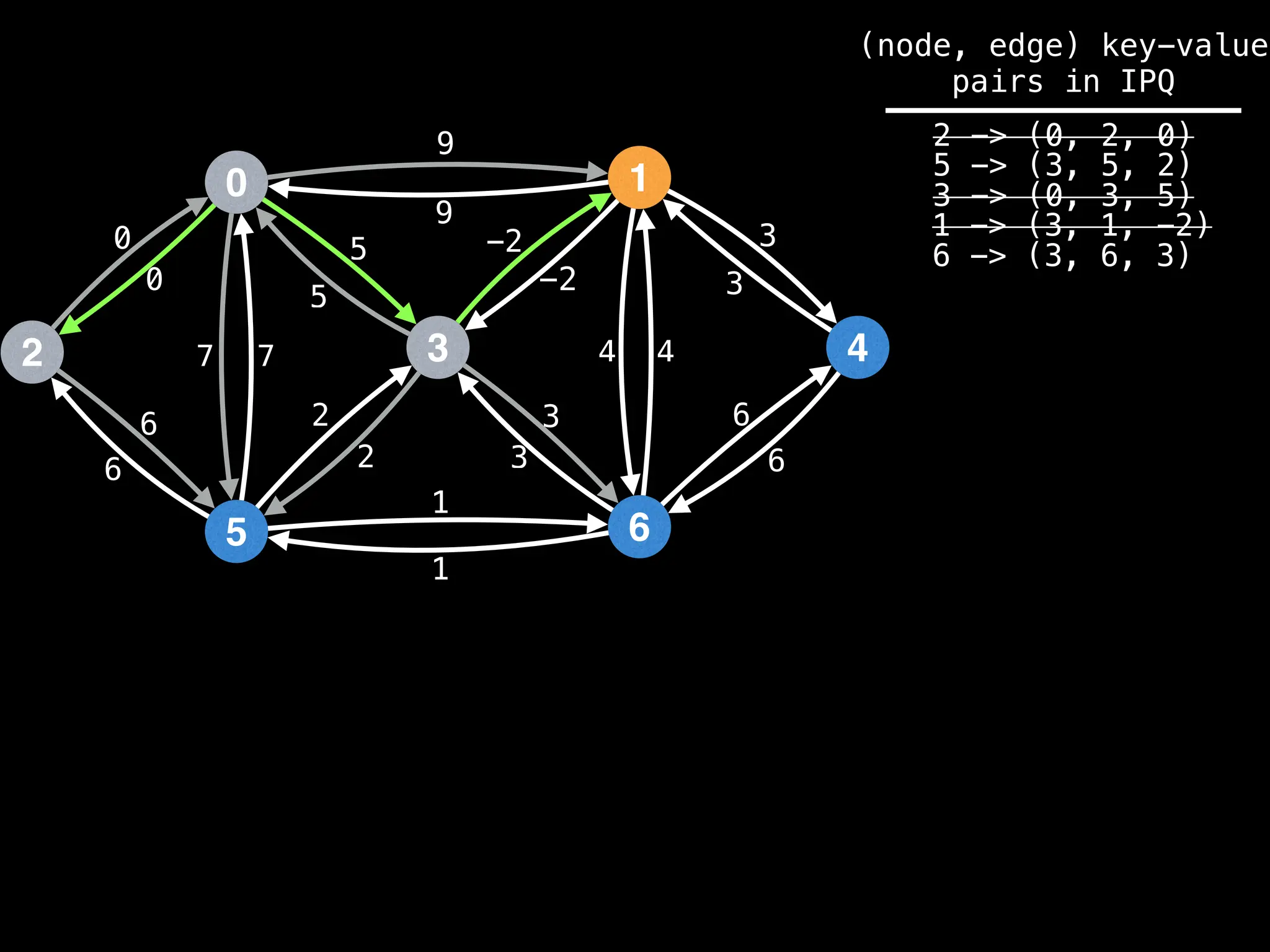
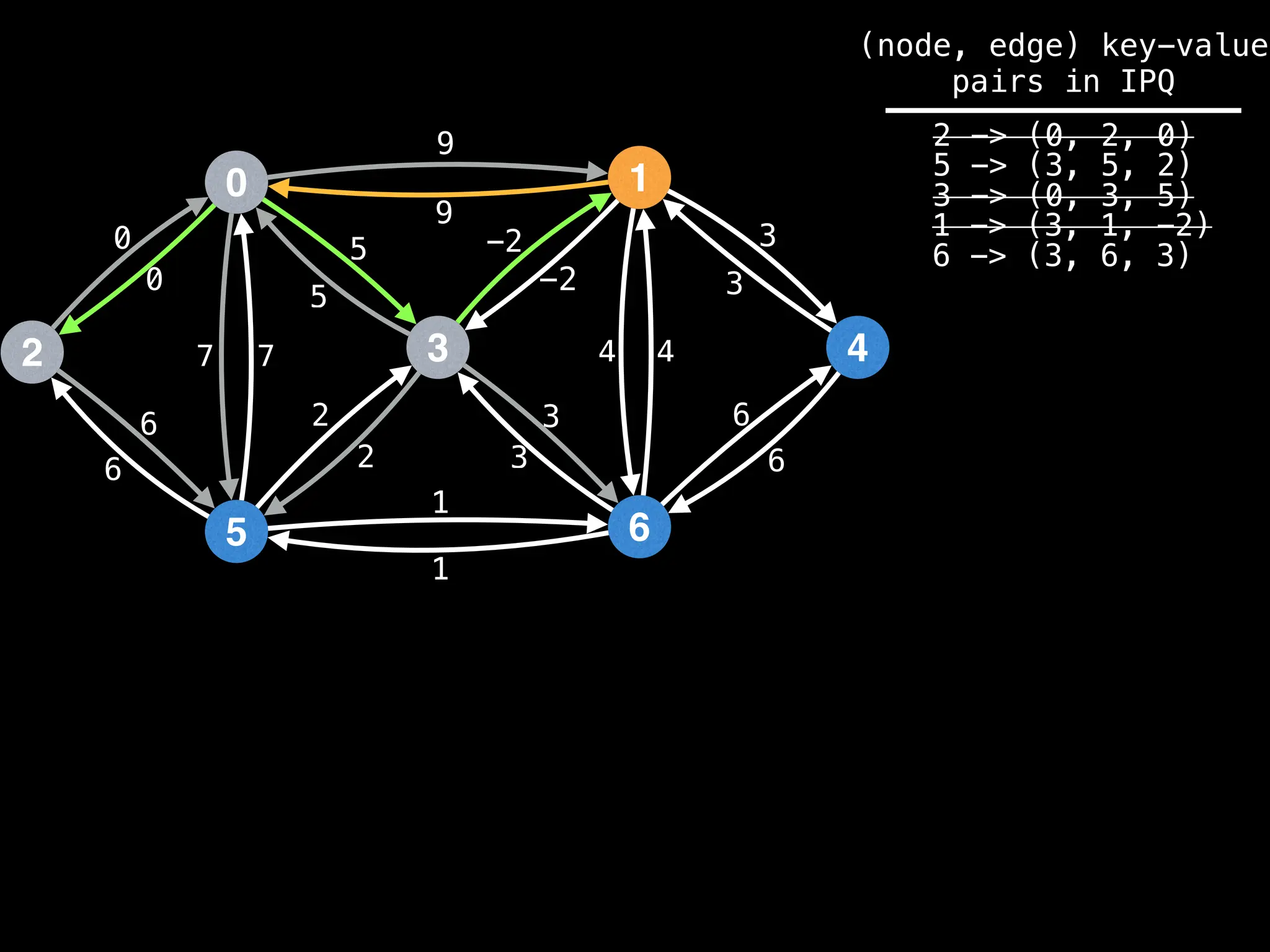
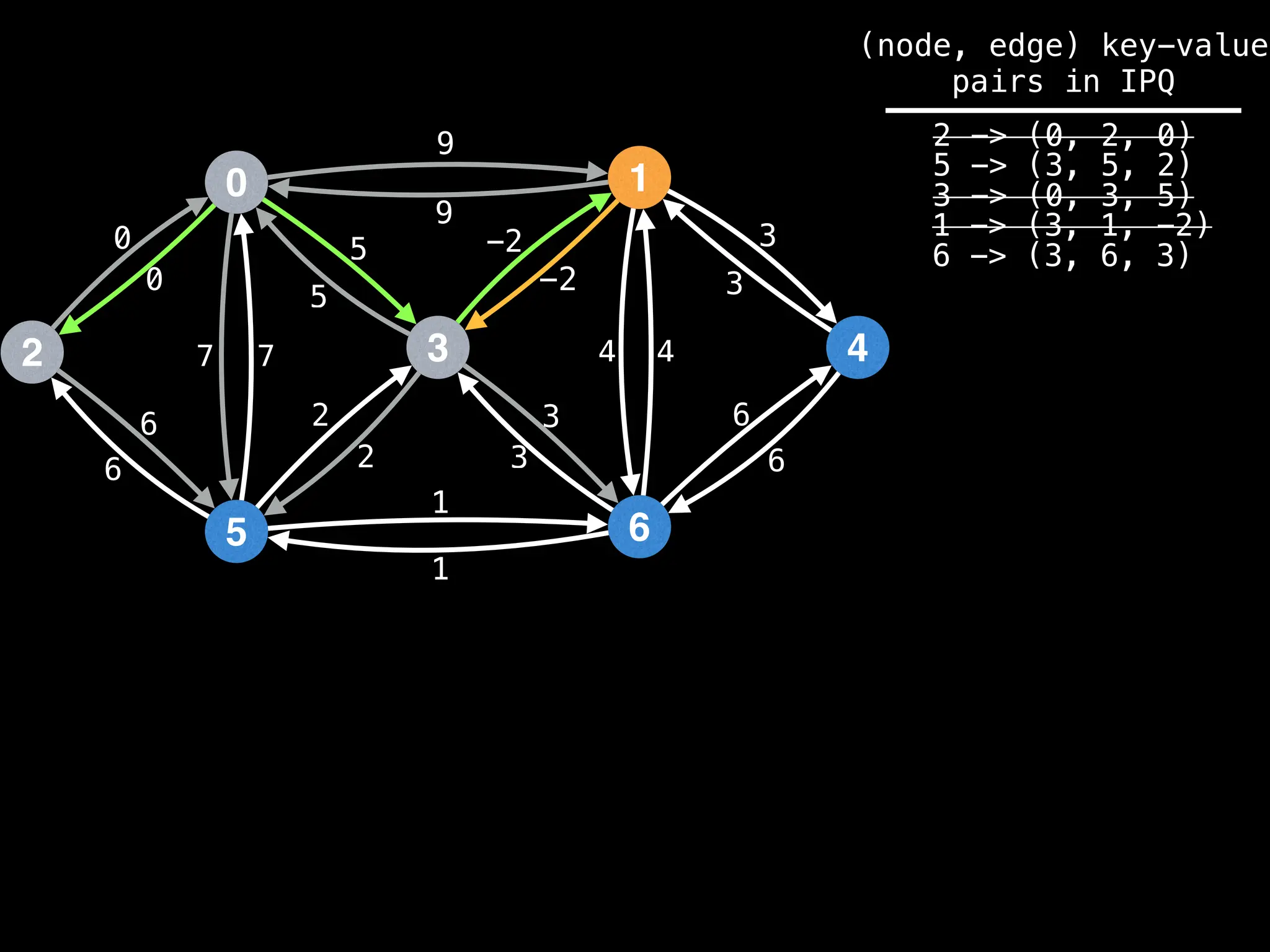
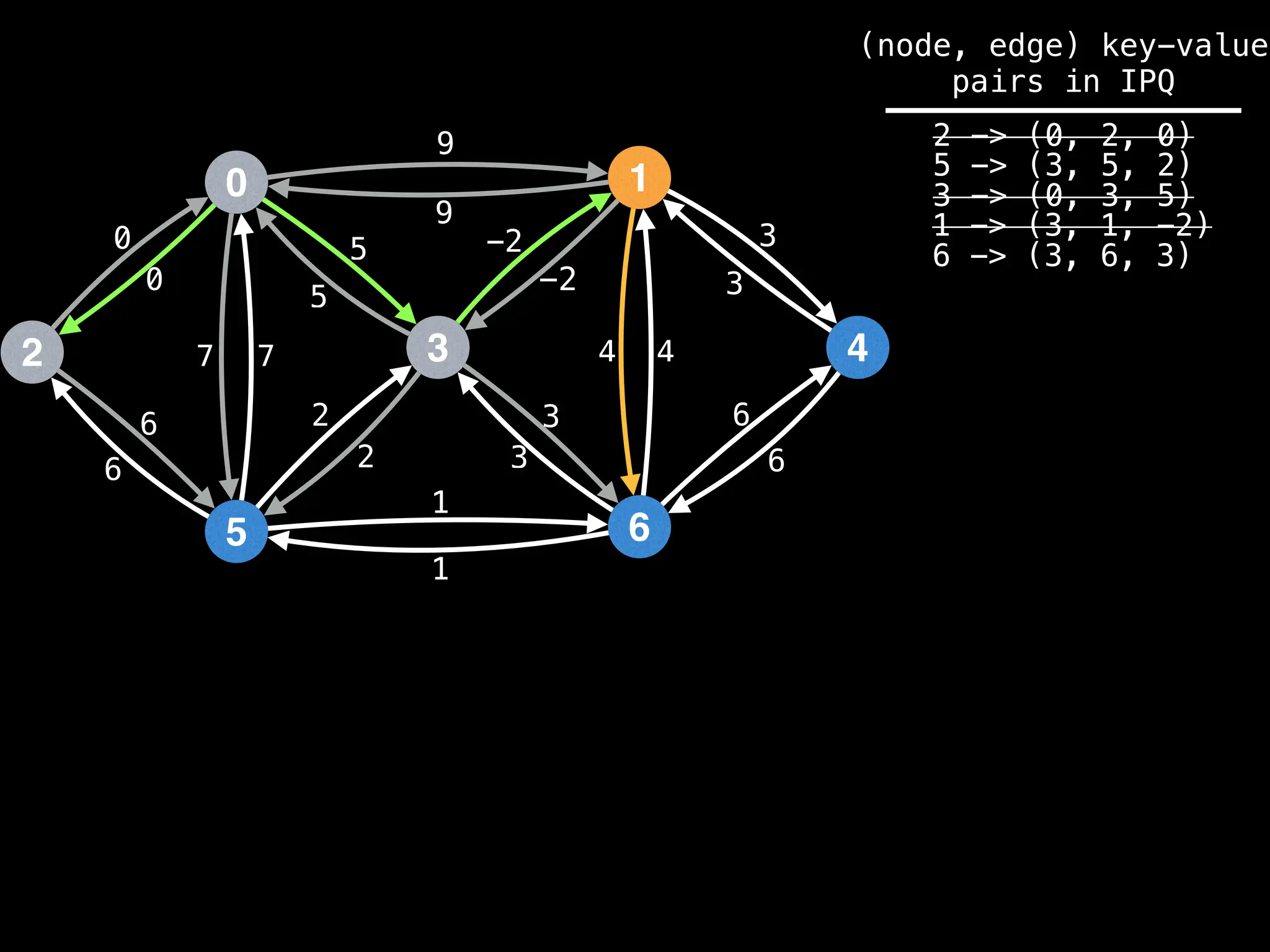
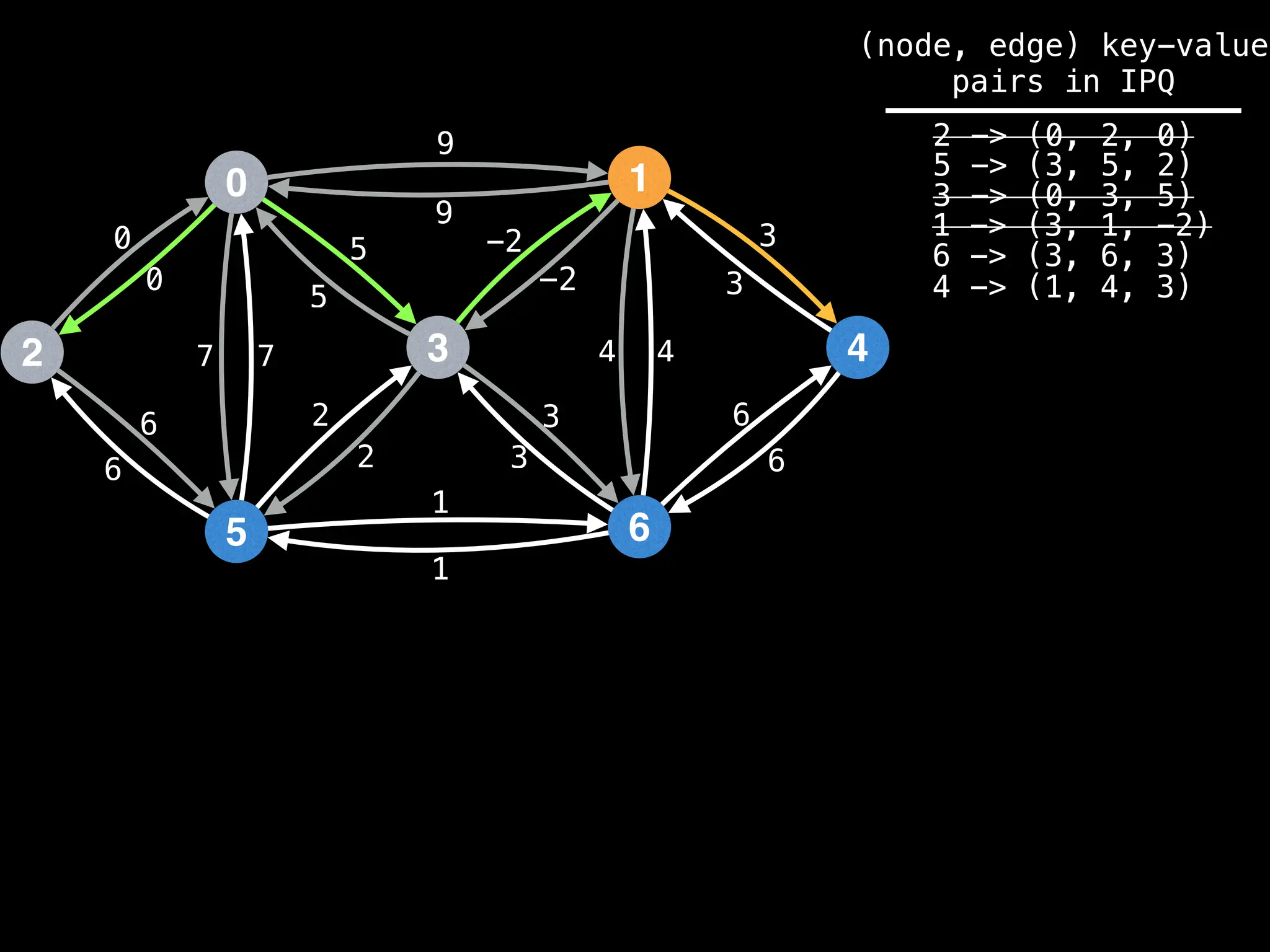
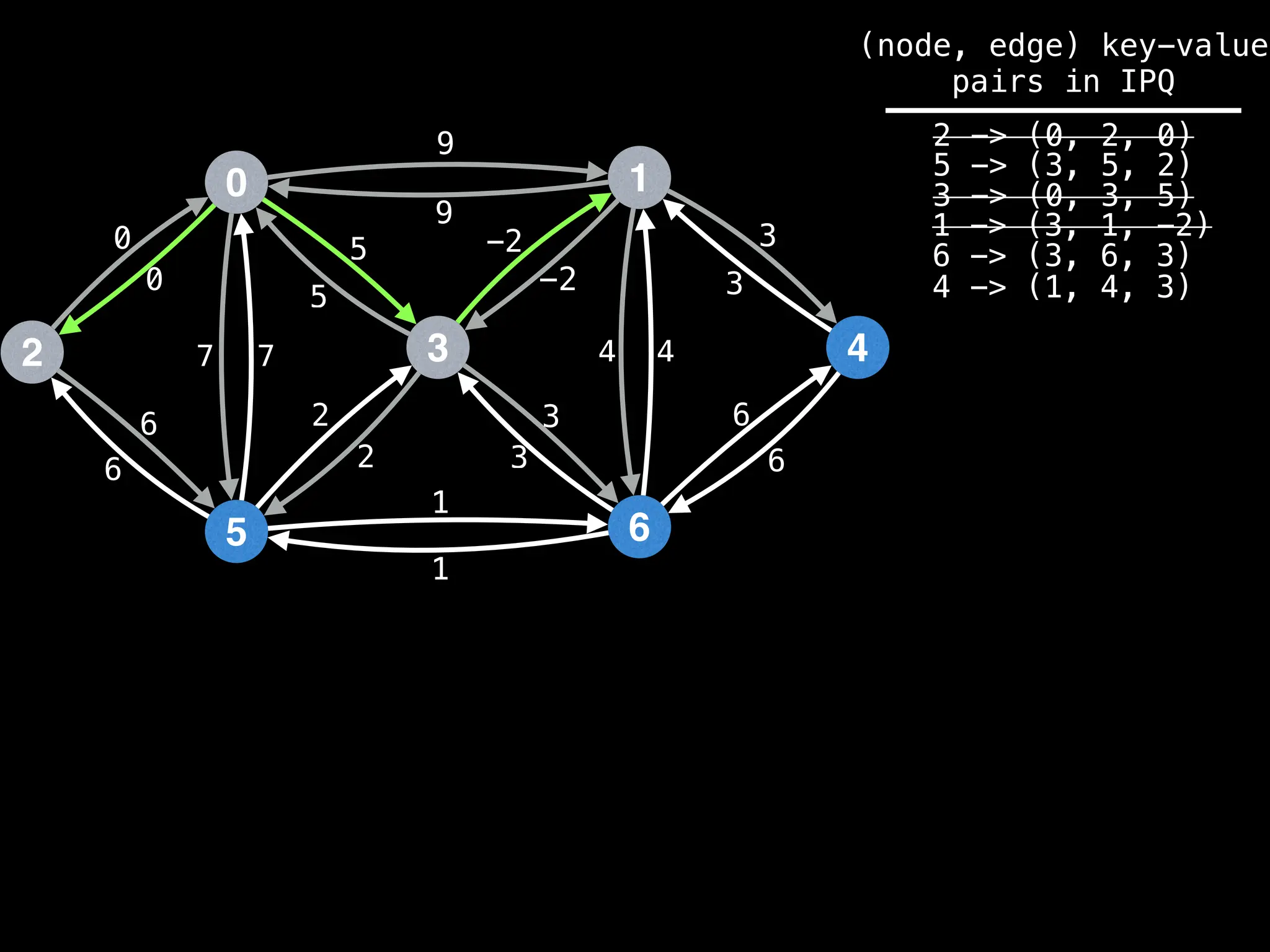
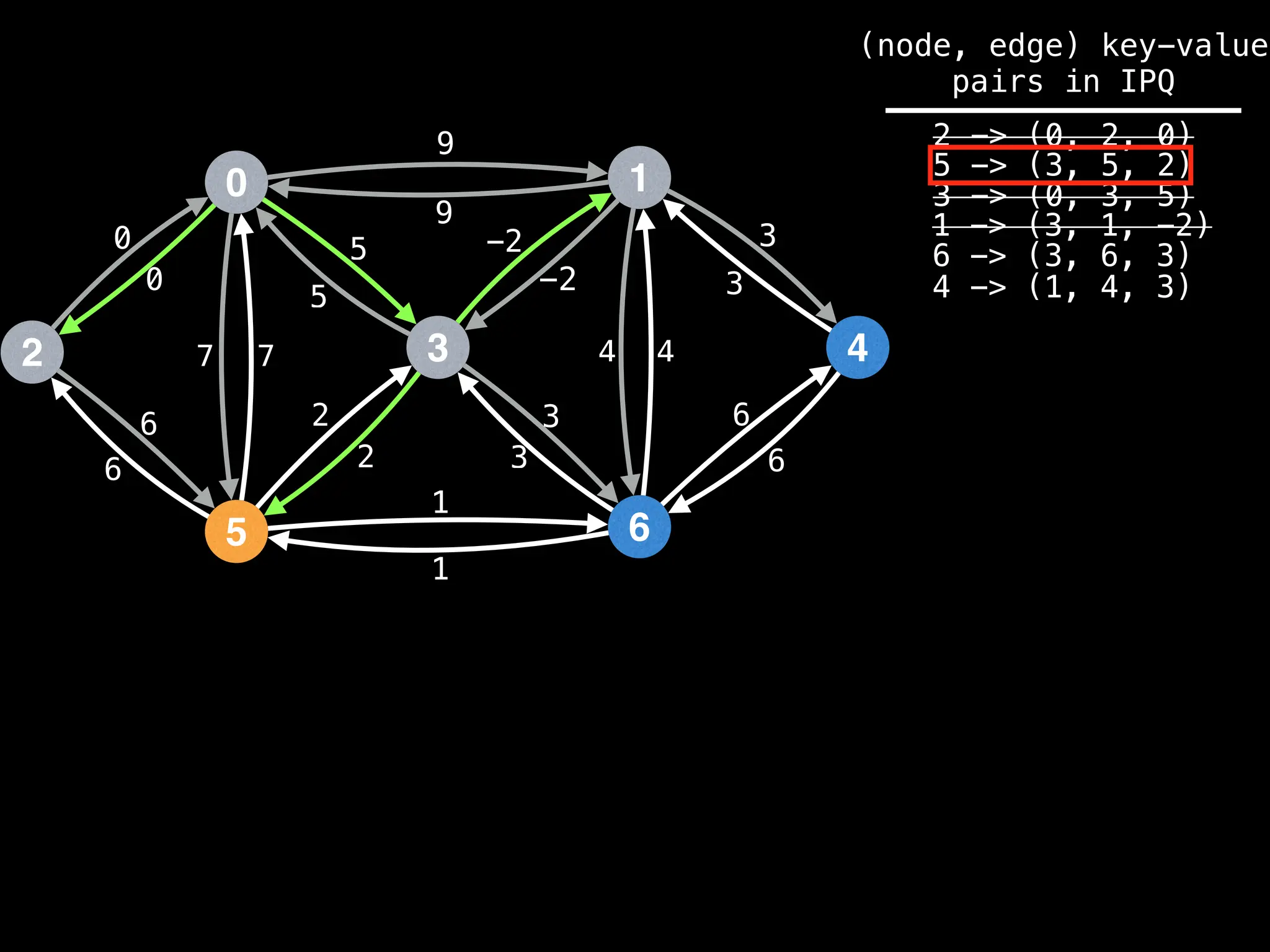
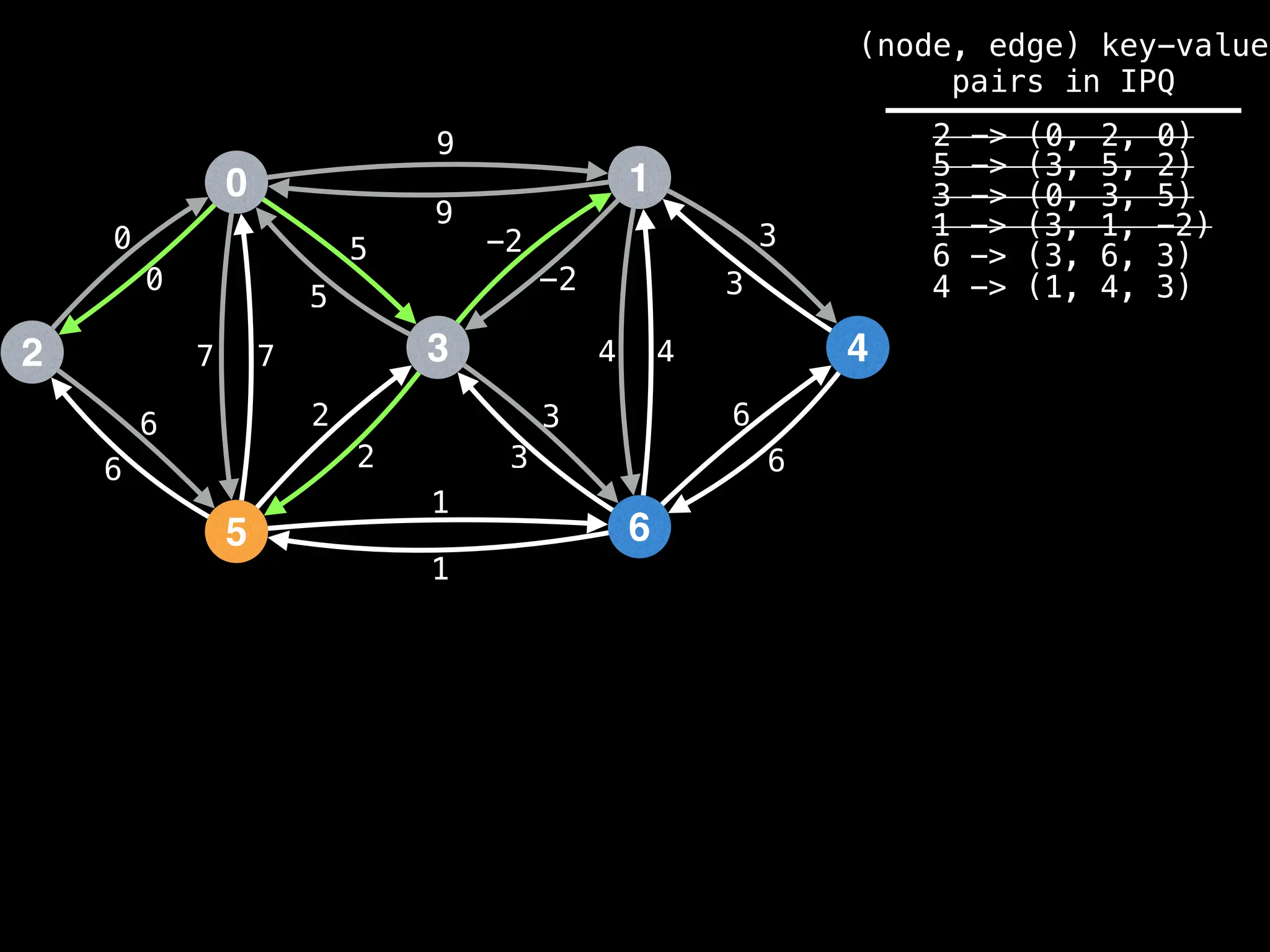
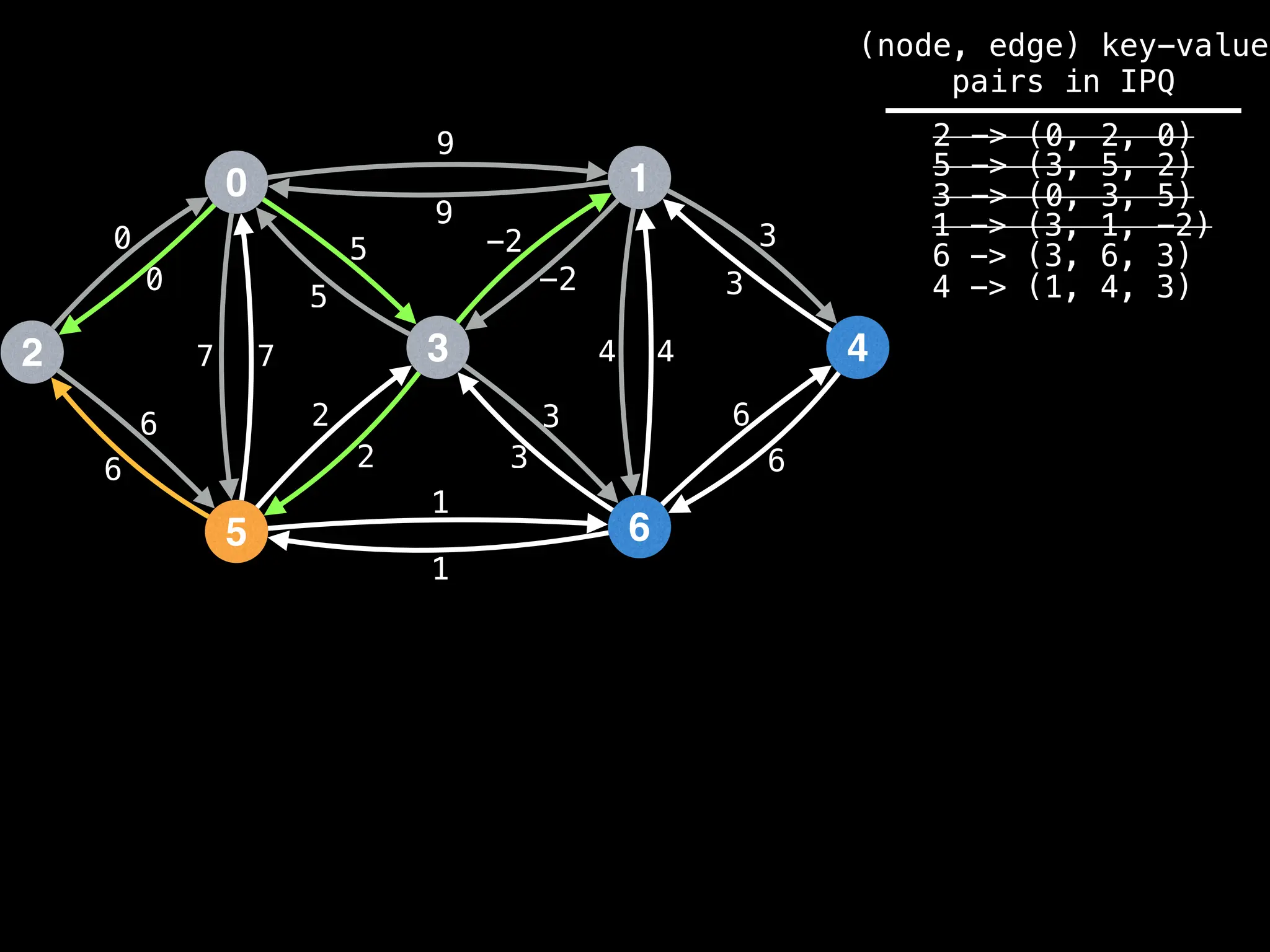
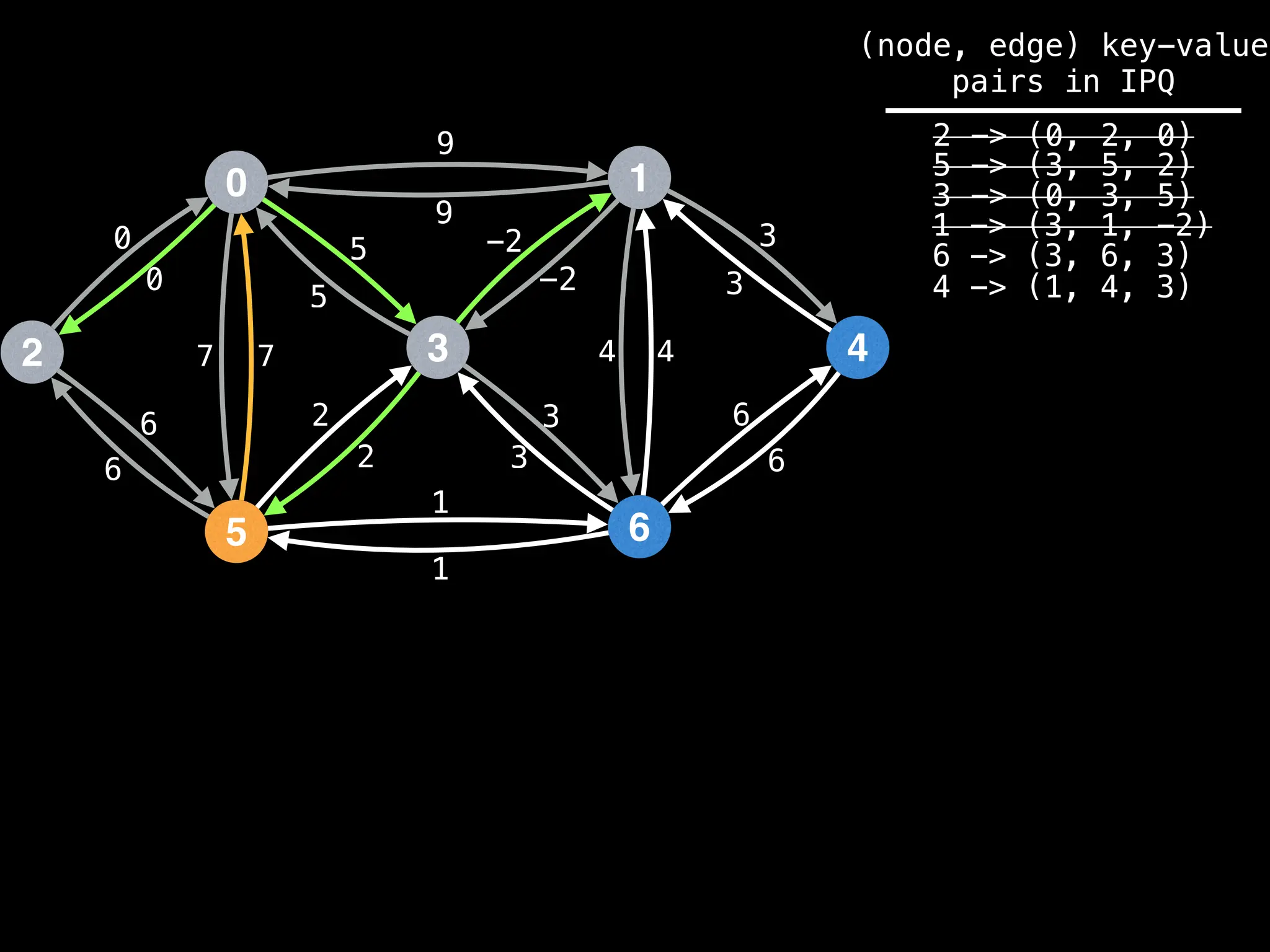
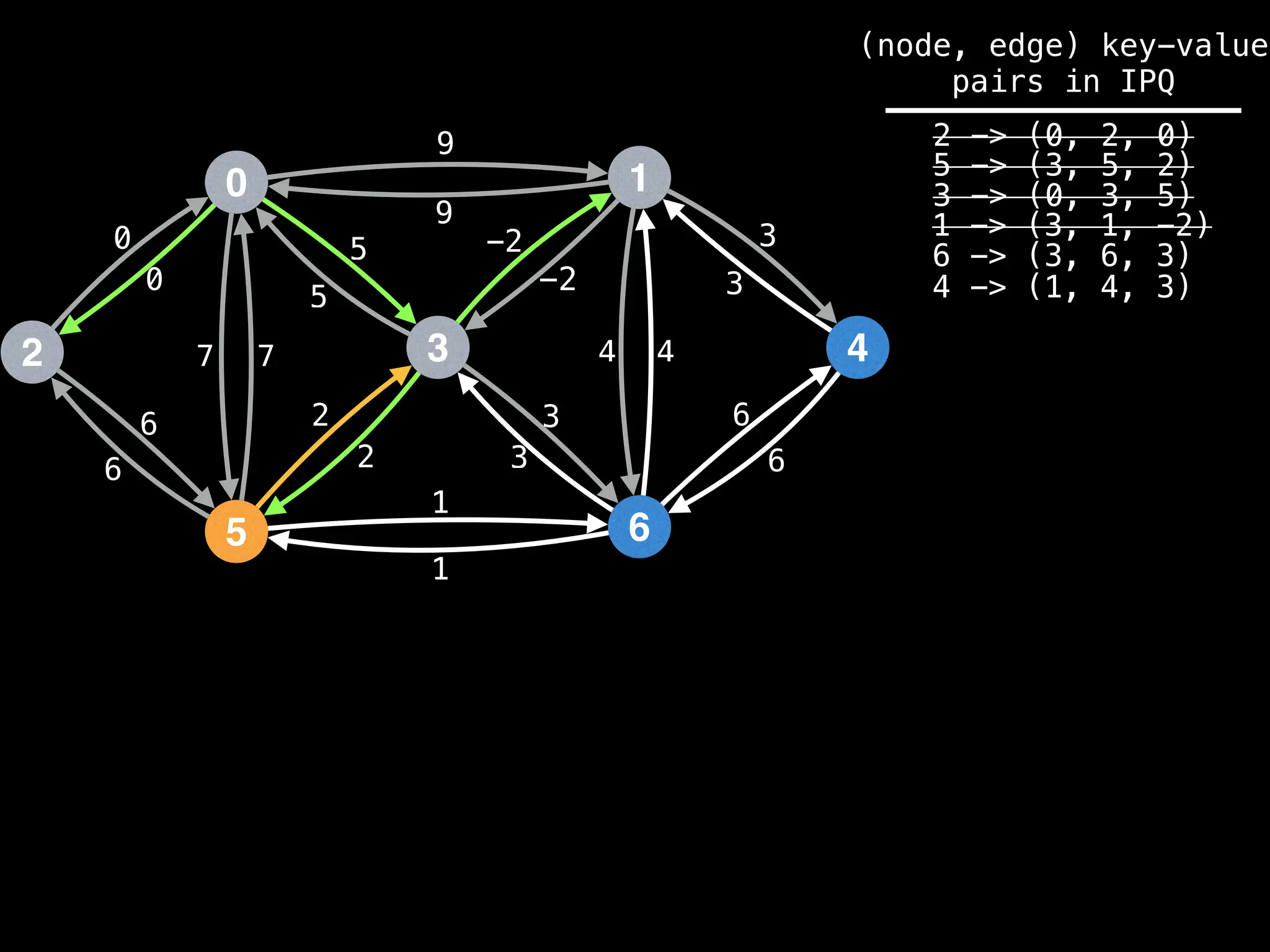
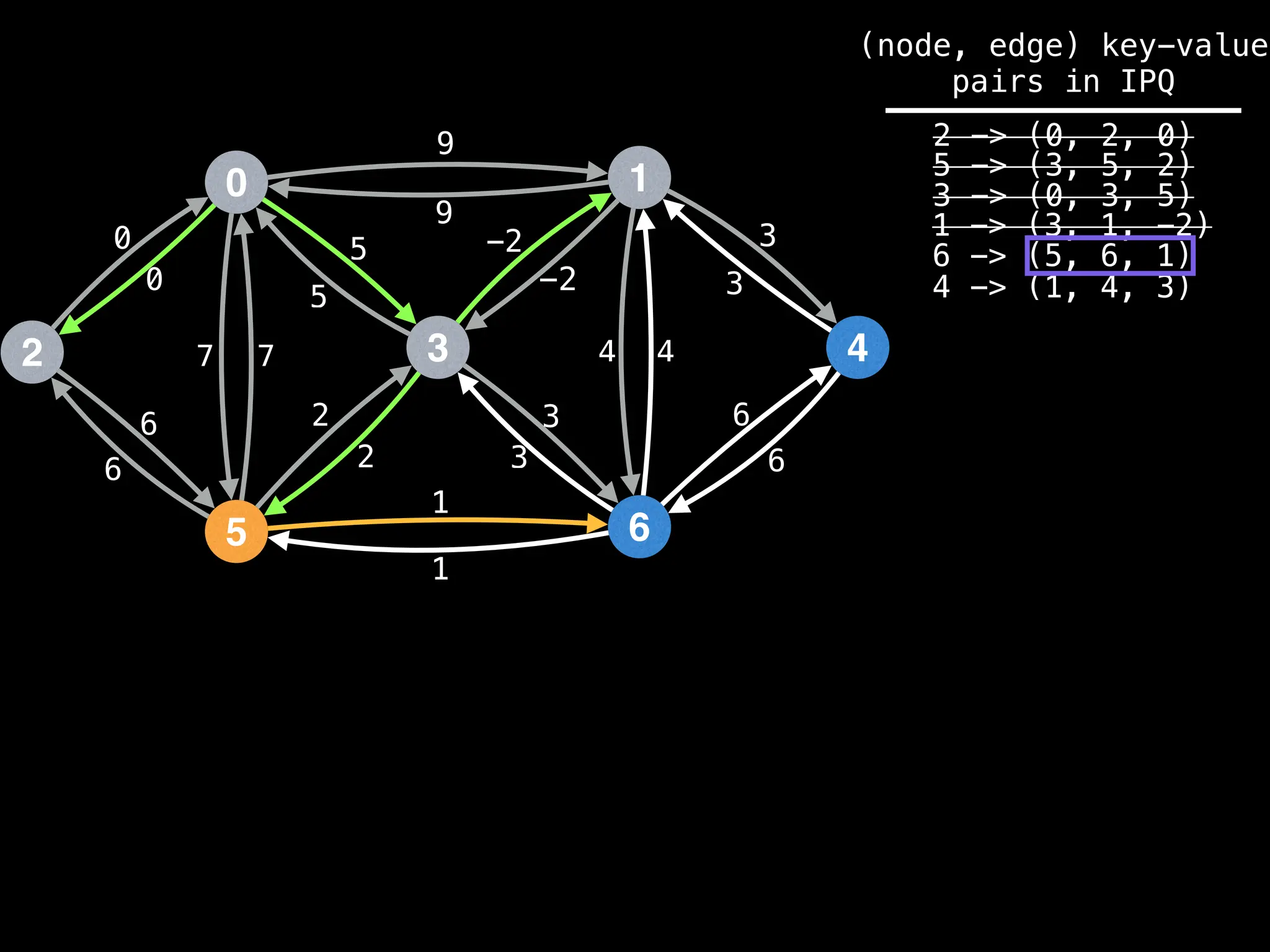
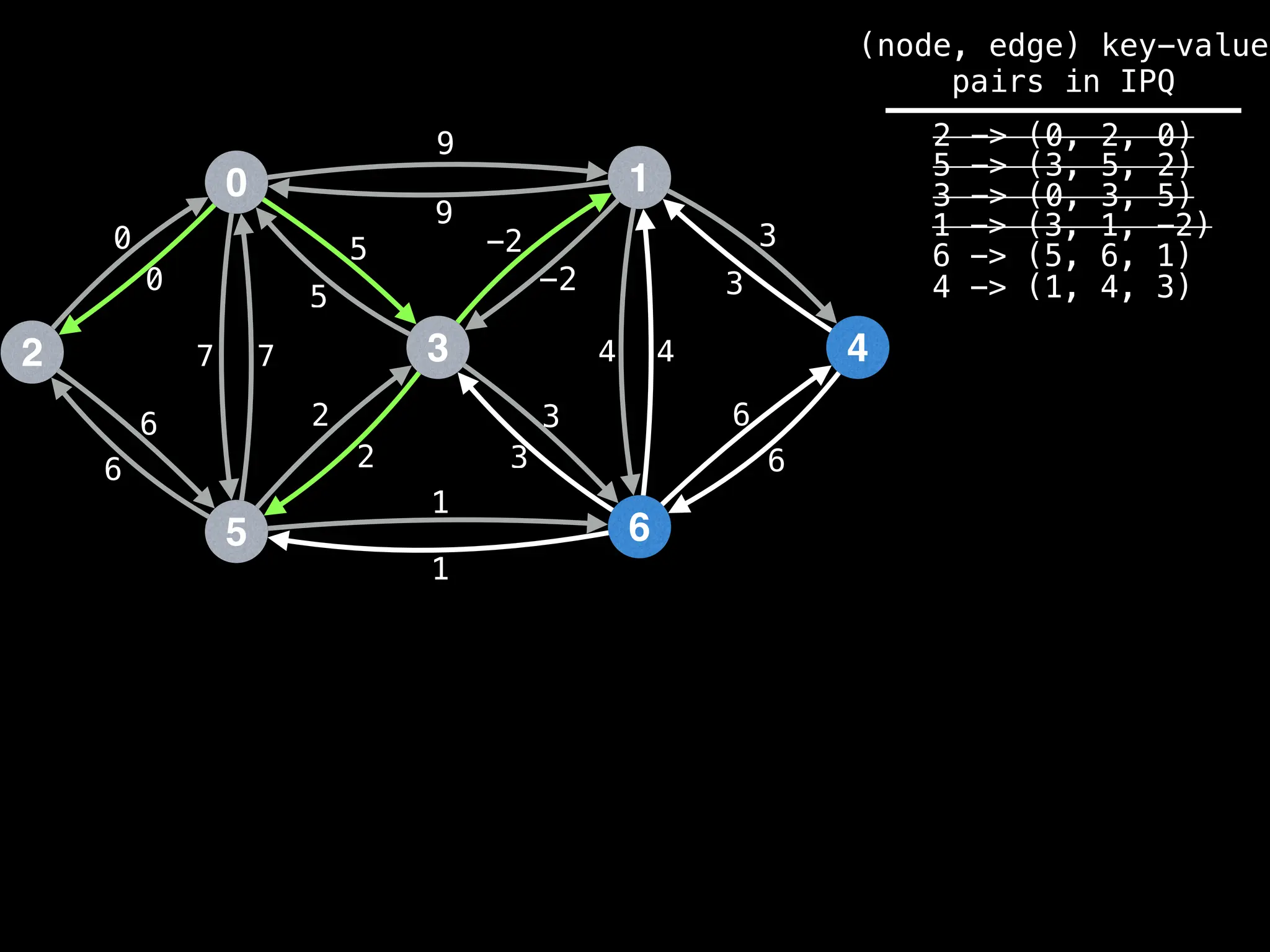
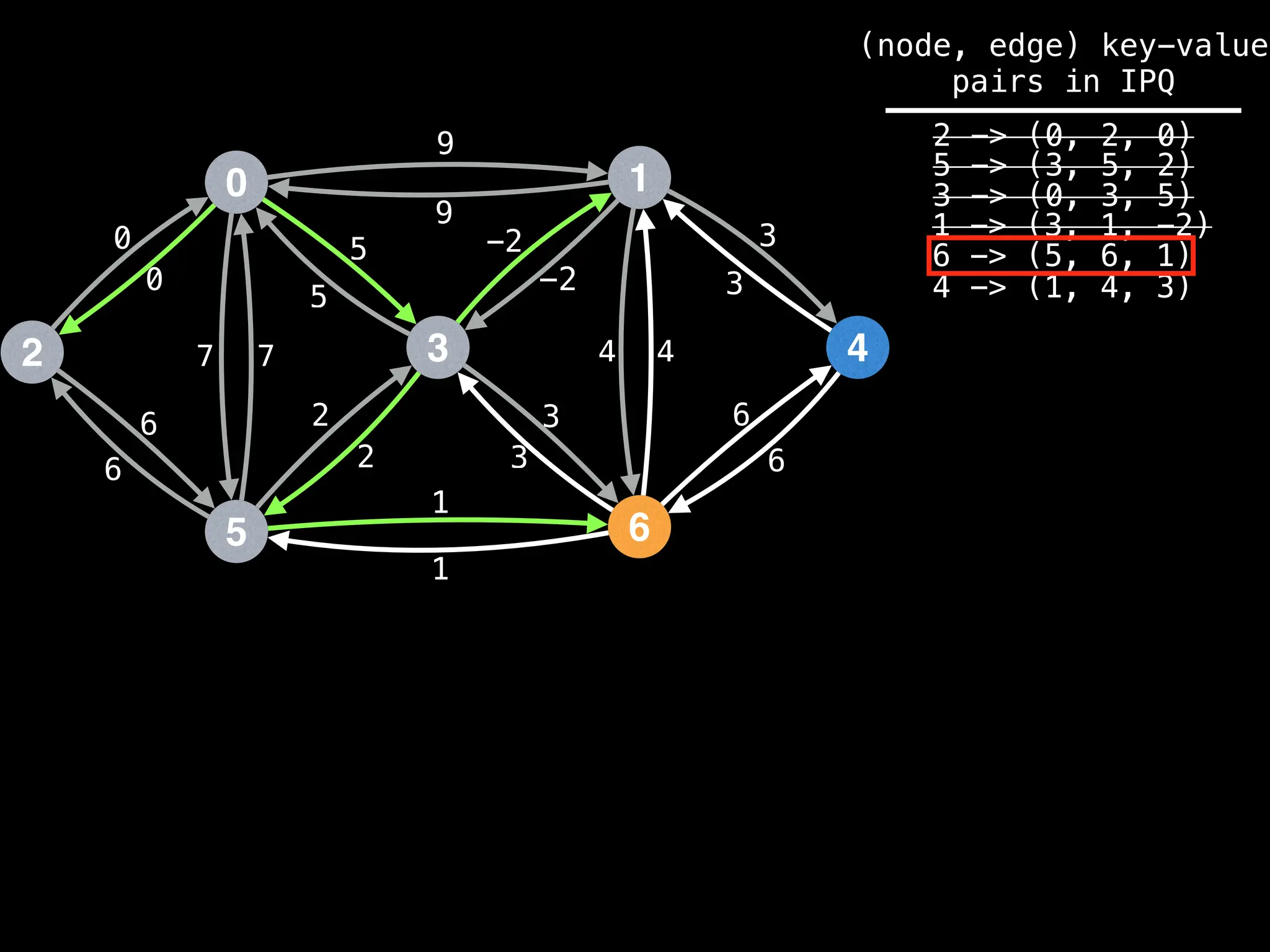
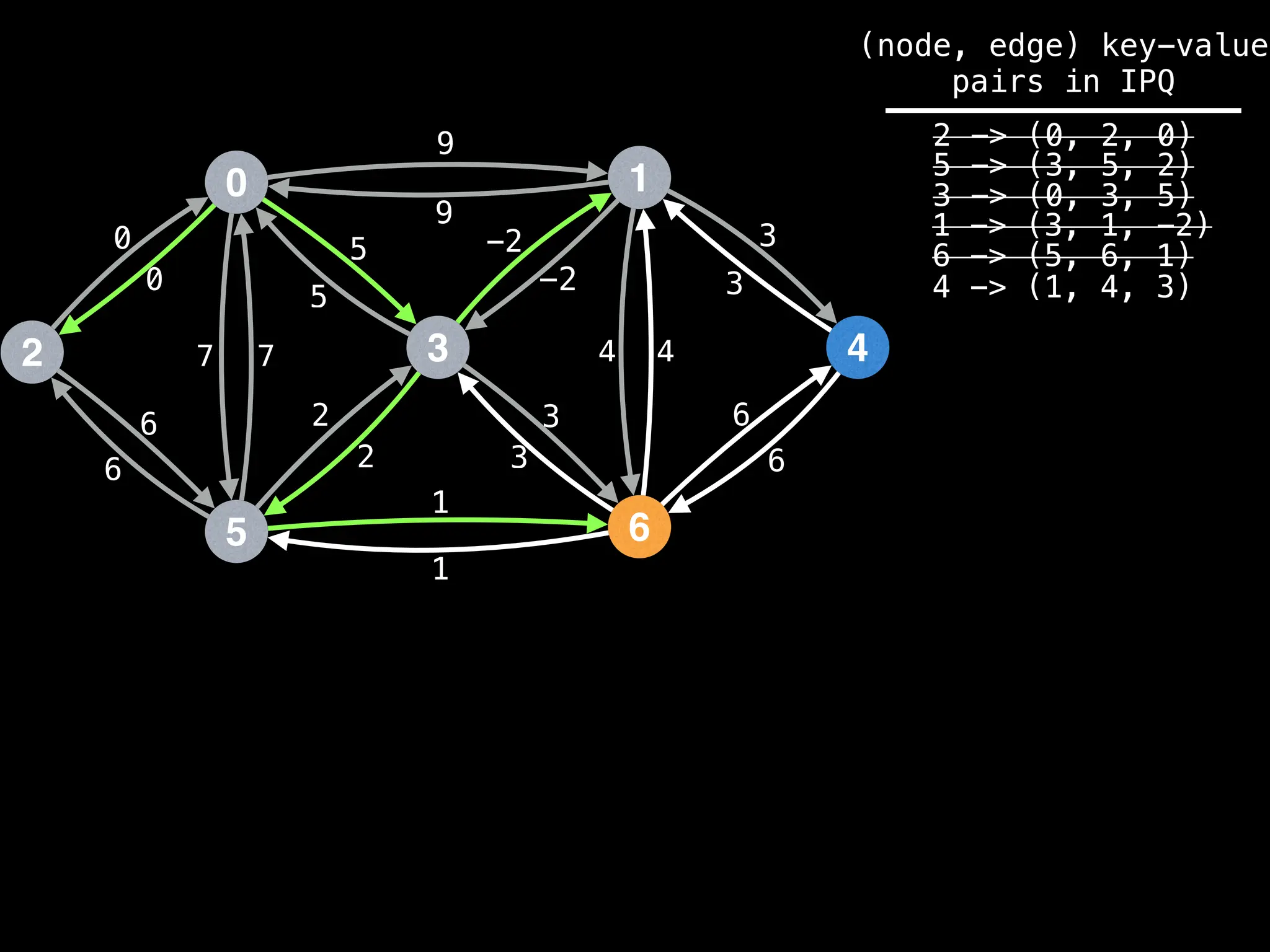
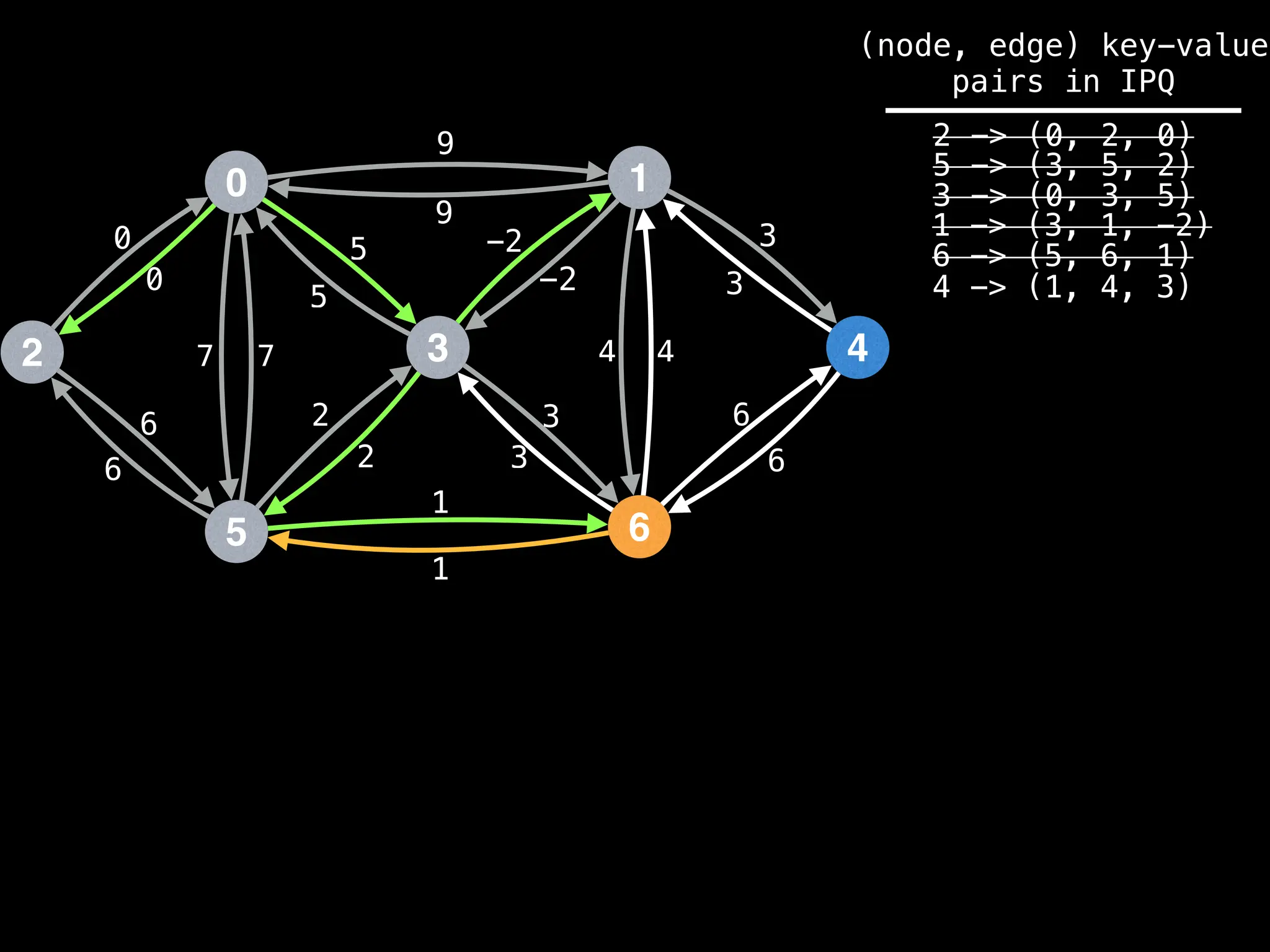
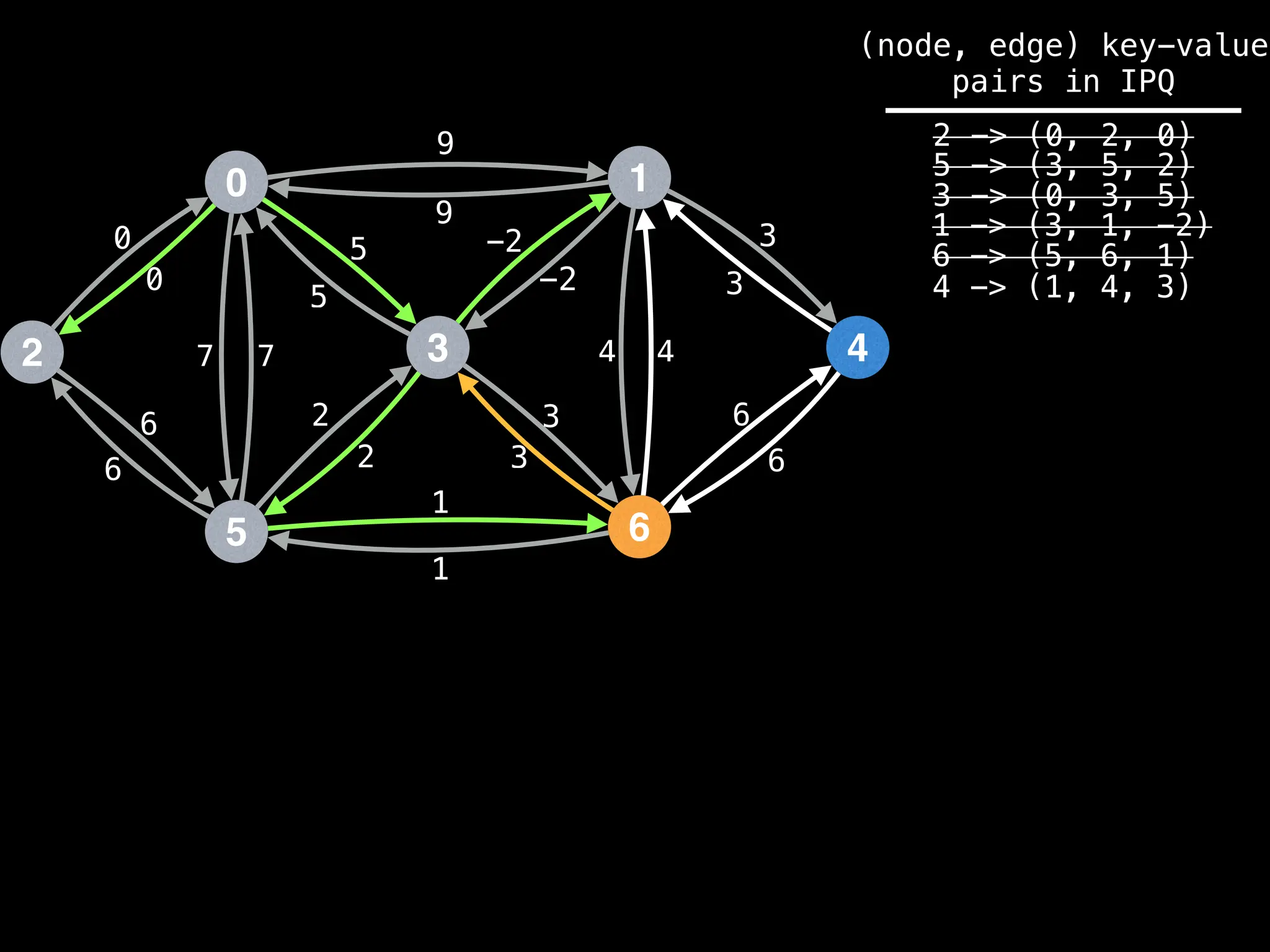
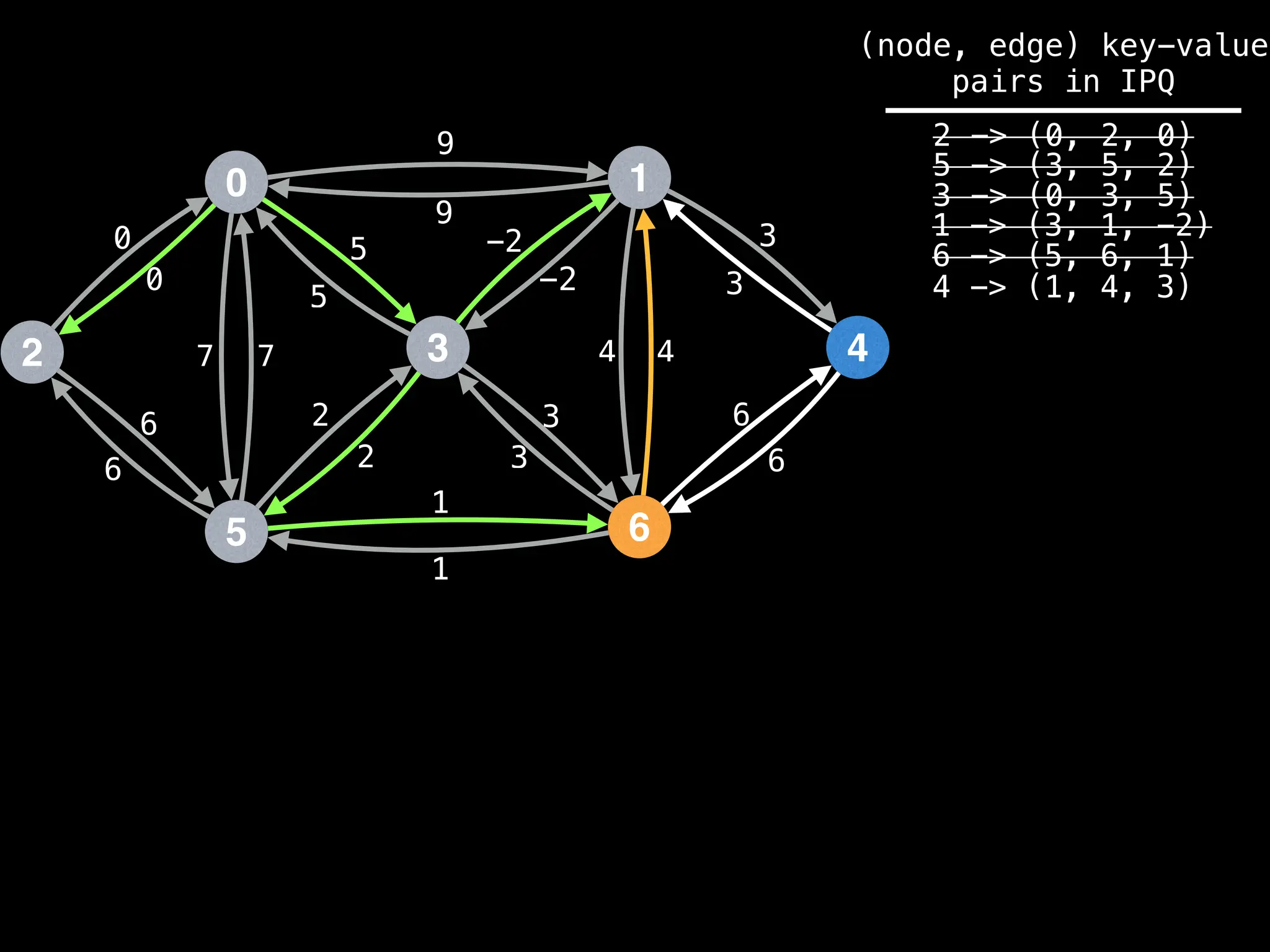
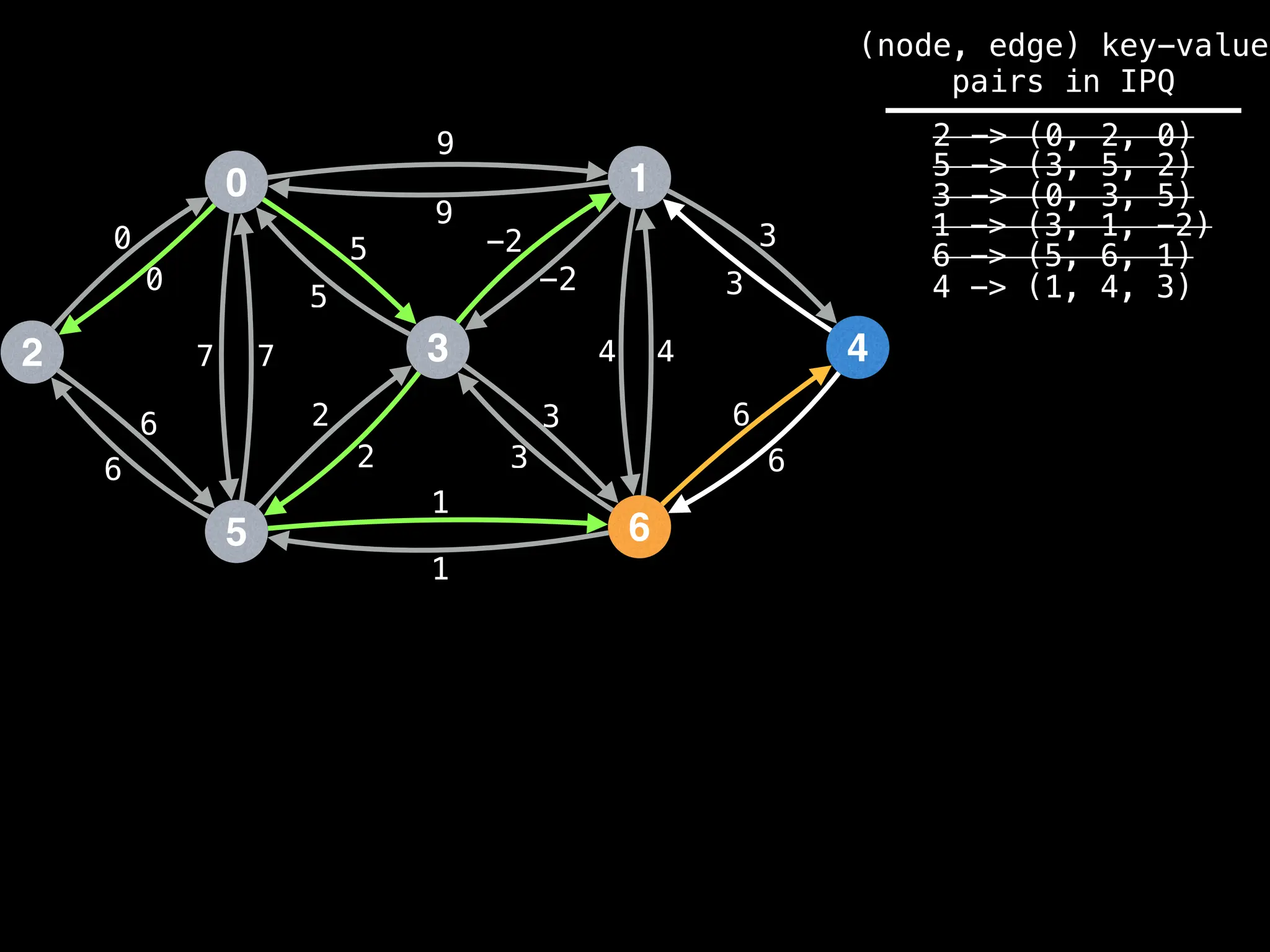
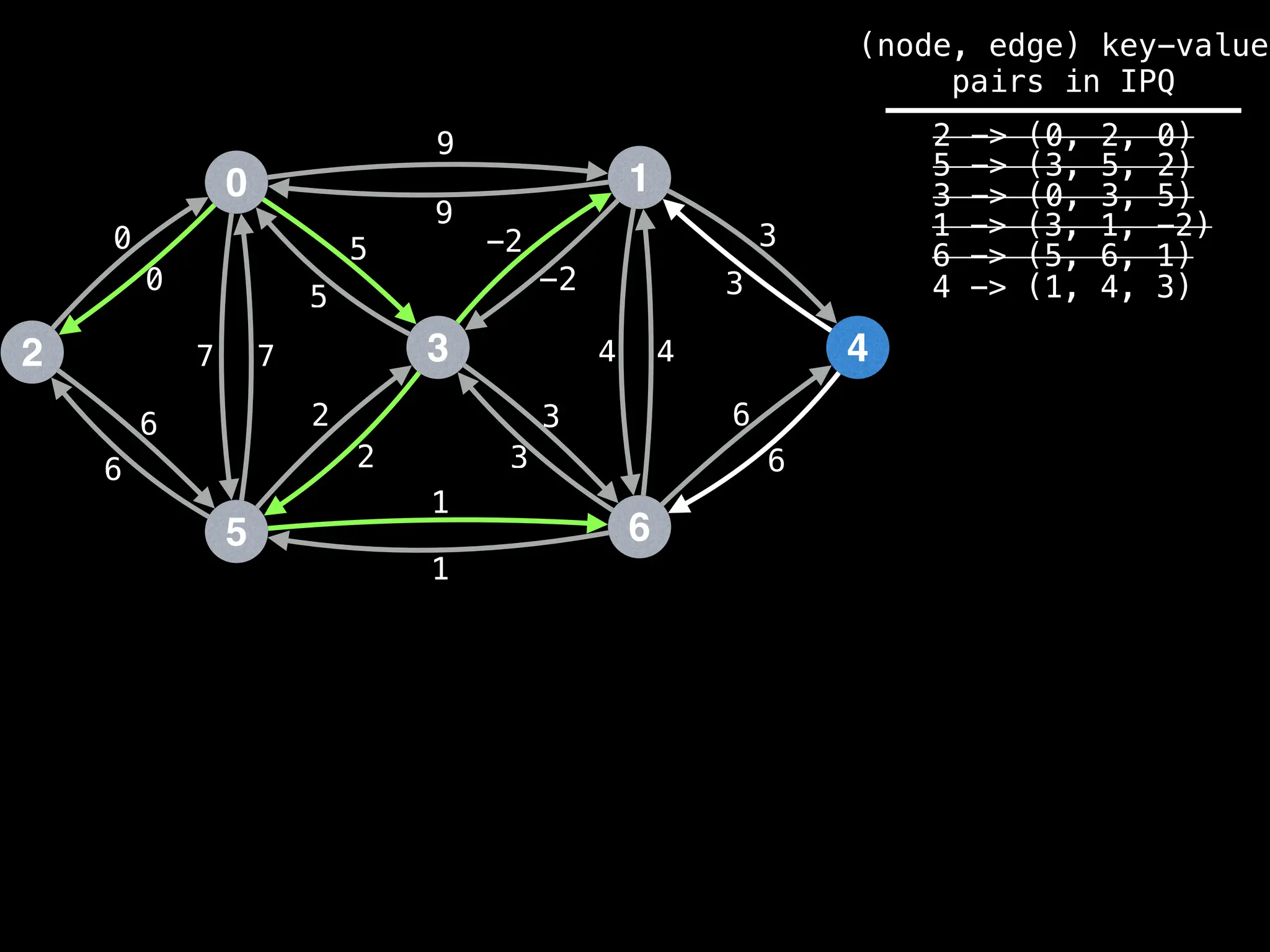
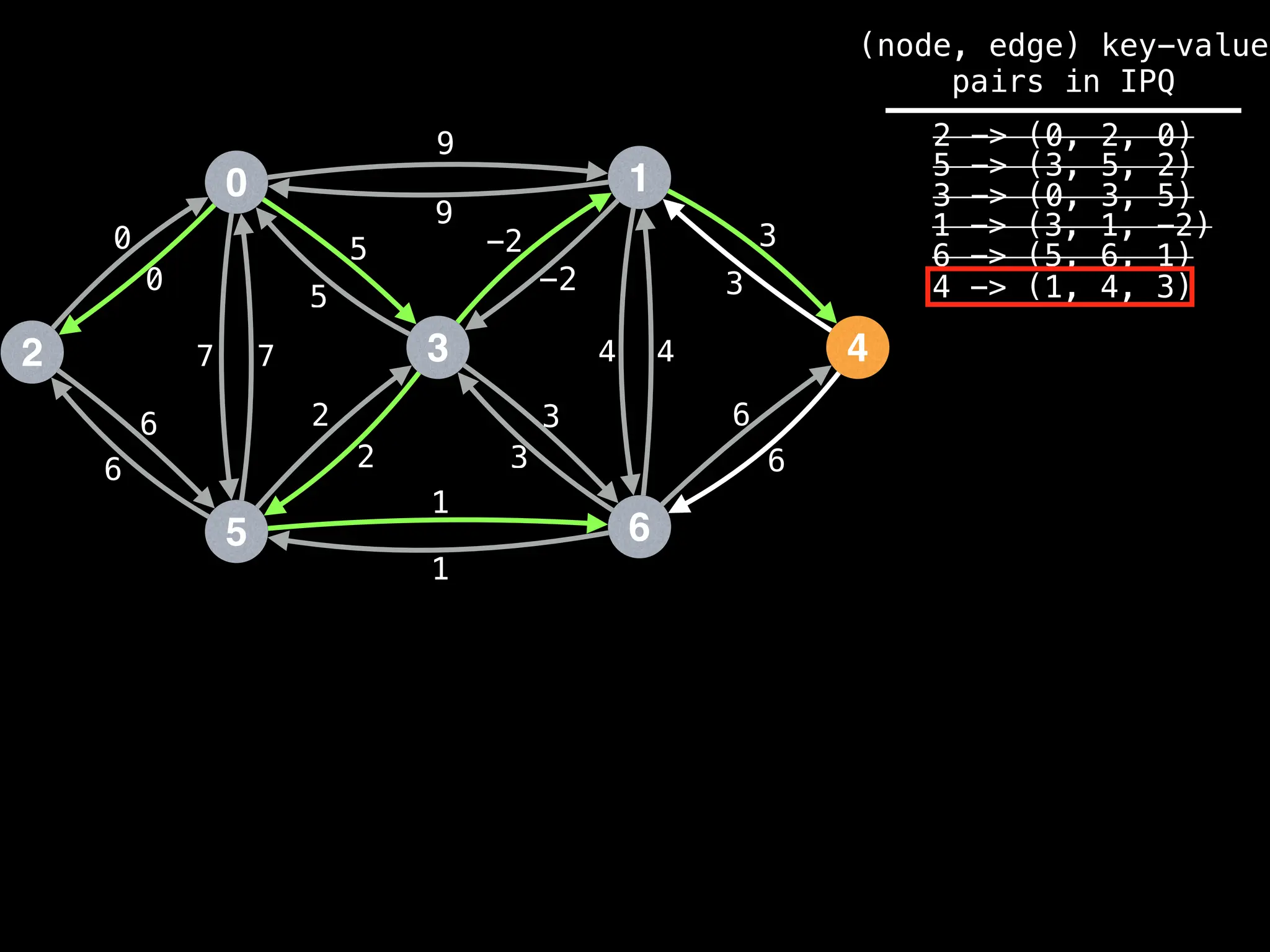
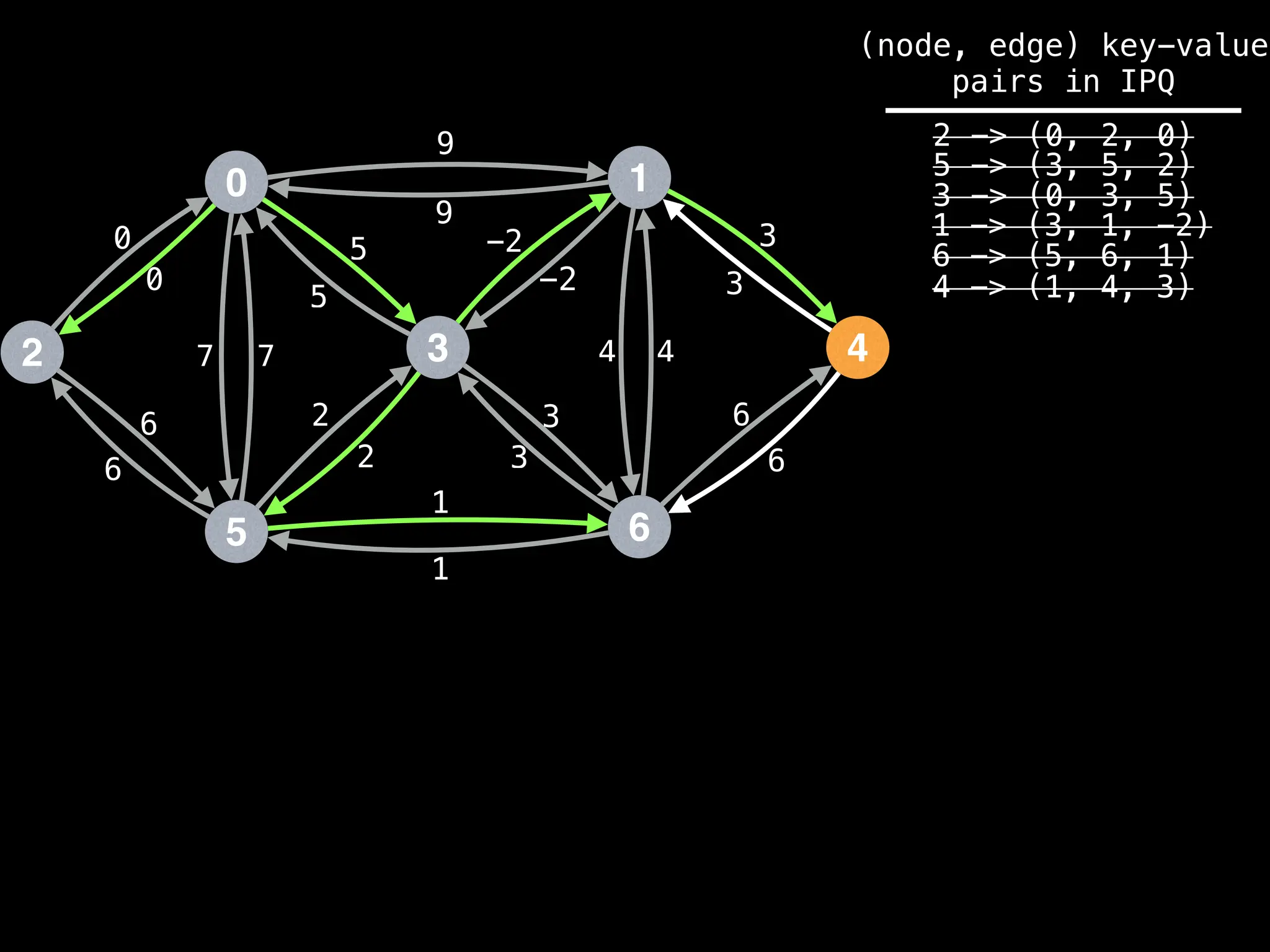
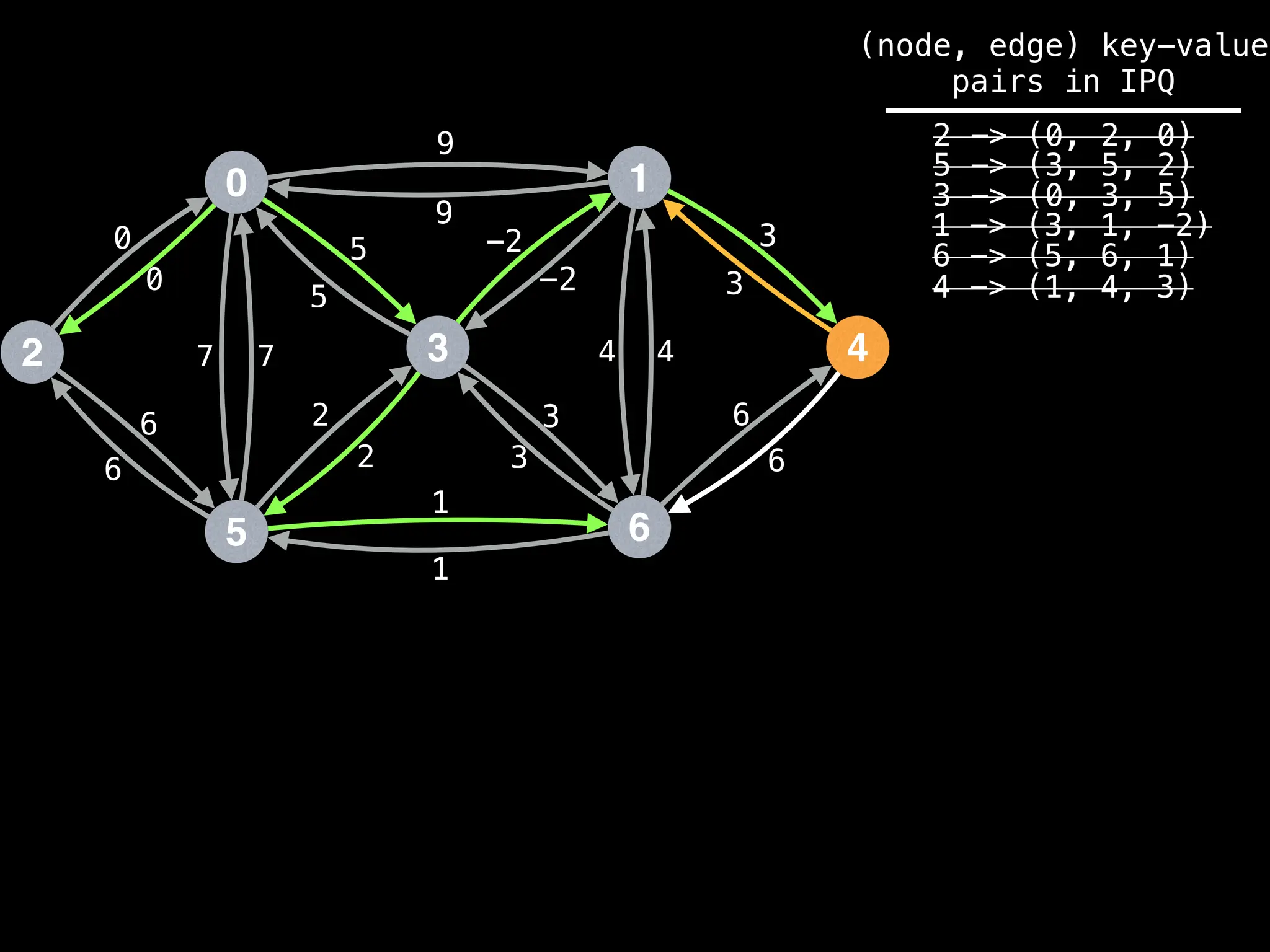
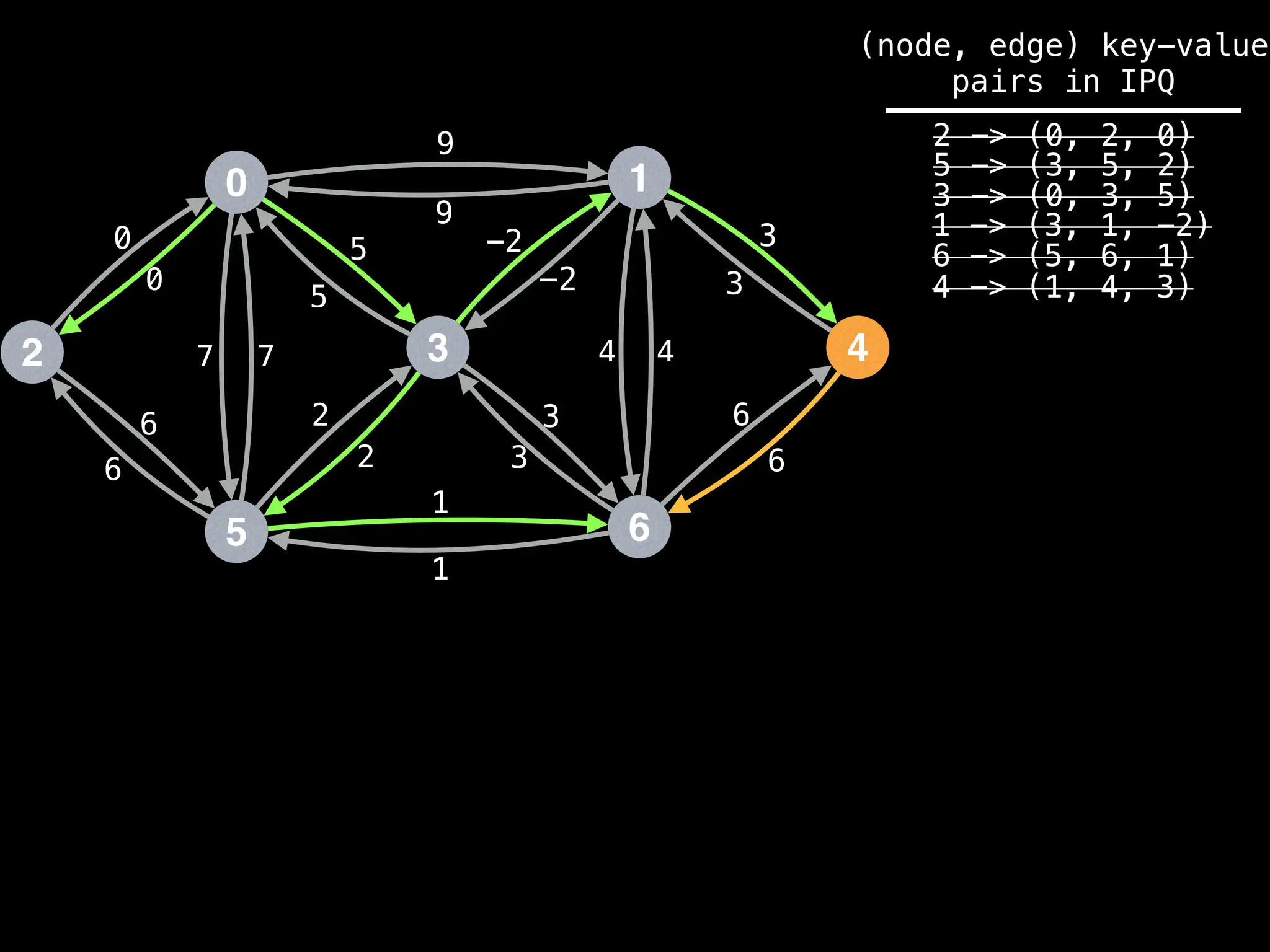
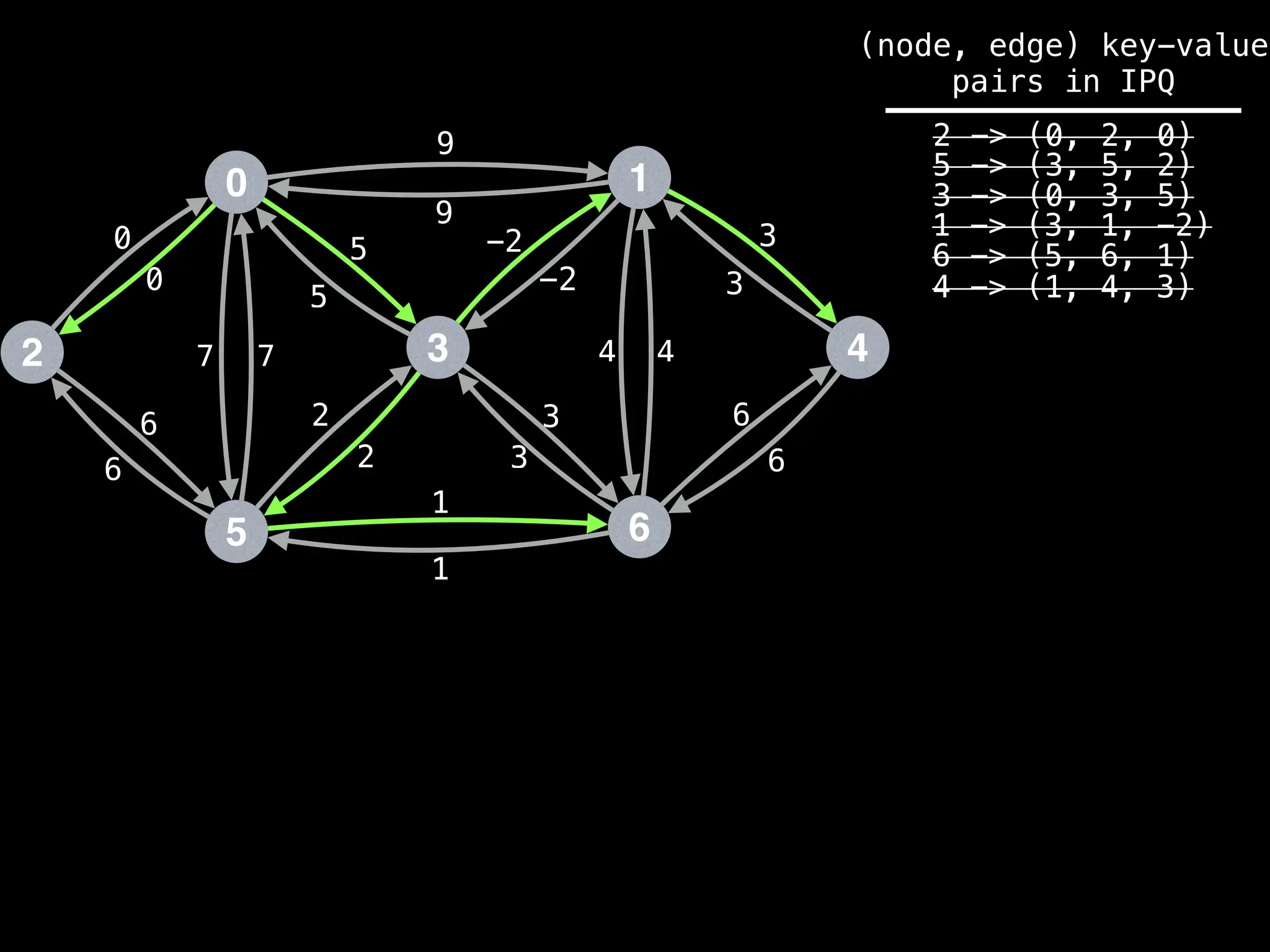
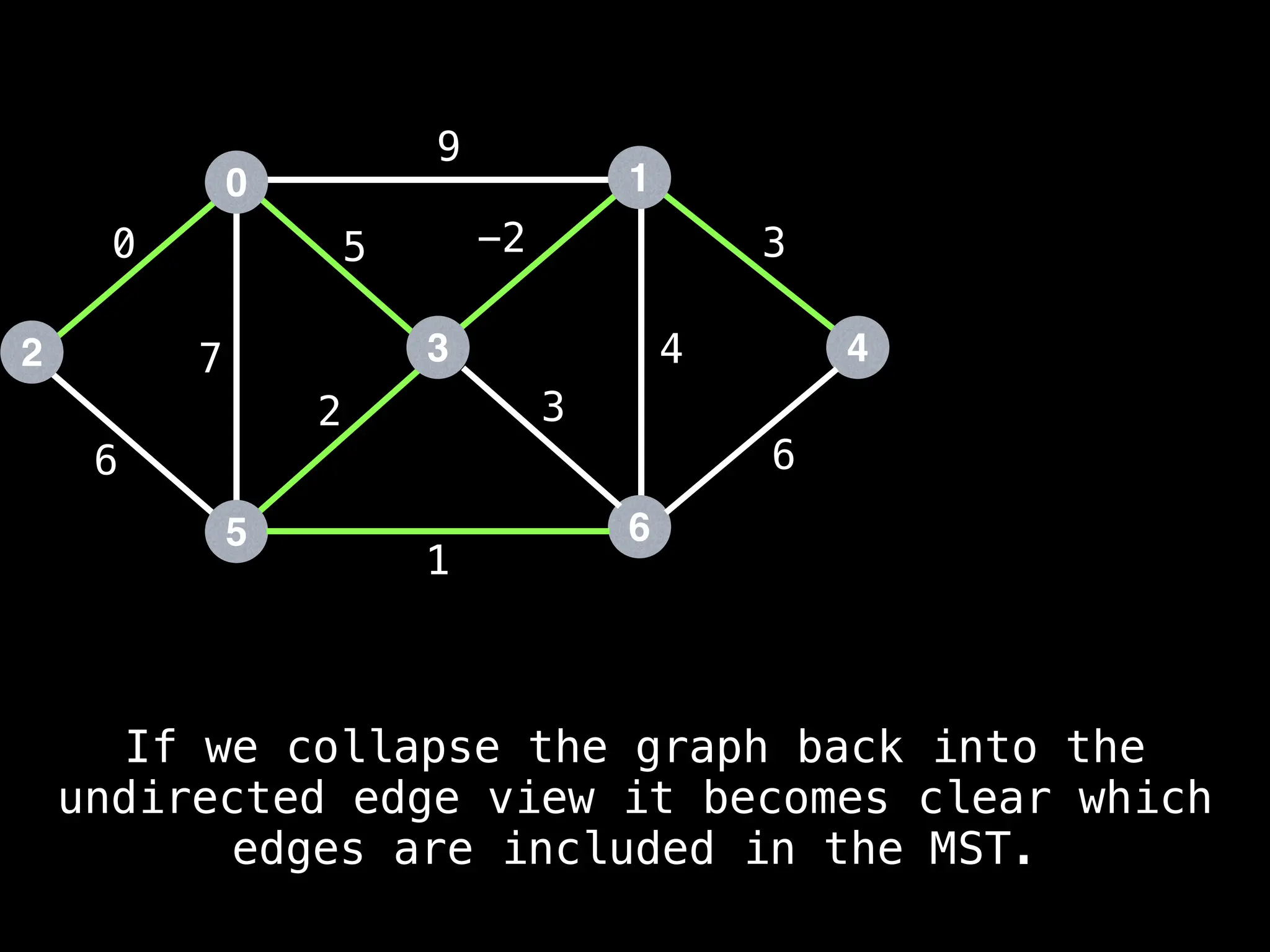
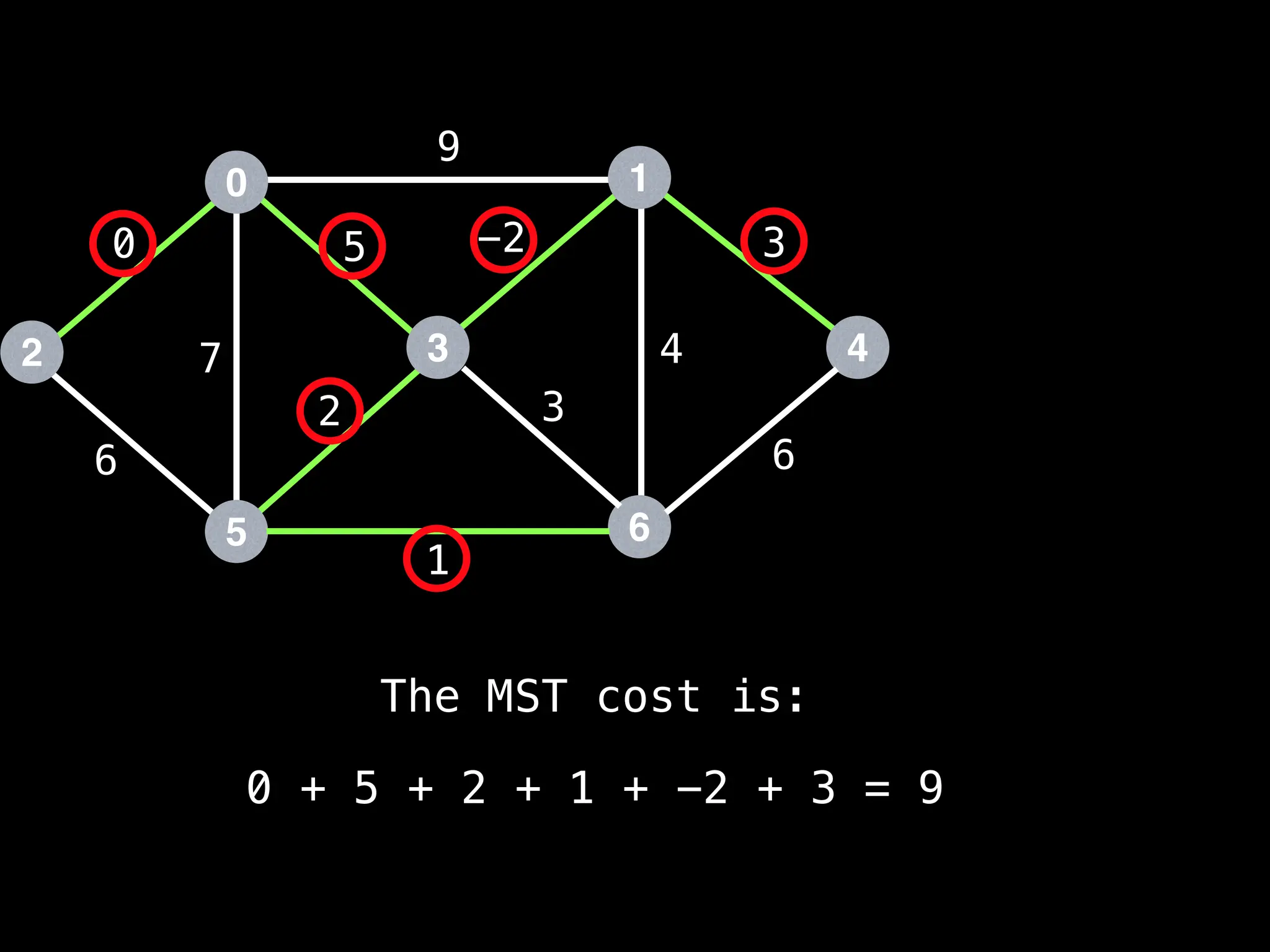
![n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
ipq = … # IPQ data structure; stores (node index, edge object)
# pairs. The edge objects consist of {start node, end
# node, edge cost} tuples. The IPQ sorts (node index,
# edge object) pairs based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n
Eager Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1411-2048.jpg)
![Eager Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
ipq = … # IPQ data structure; stores (node index, edge object)
# pairs. The edge objects consist of {start node, end
# node, edge cost} tuples. The IPQ sorts (node index,
# edge object) pairs based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1412-2048.jpg)
![Eager Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
ipq = … # IPQ data structure; stores (node index, edge object)
# pairs. The edge objects consist of {start node, end
# node, edge cost} tuples. The IPQ sorts (node index,
# edge object) pairs based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1413-2048.jpg)
![Eager Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
ipq = … # IPQ data structure; stores (node index, edge object)
# pairs. The edge objects consist of {start node, end
# node, edge cost} tuples. The IPQ sorts (node index,
# edge object) pairs based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1414-2048.jpg)
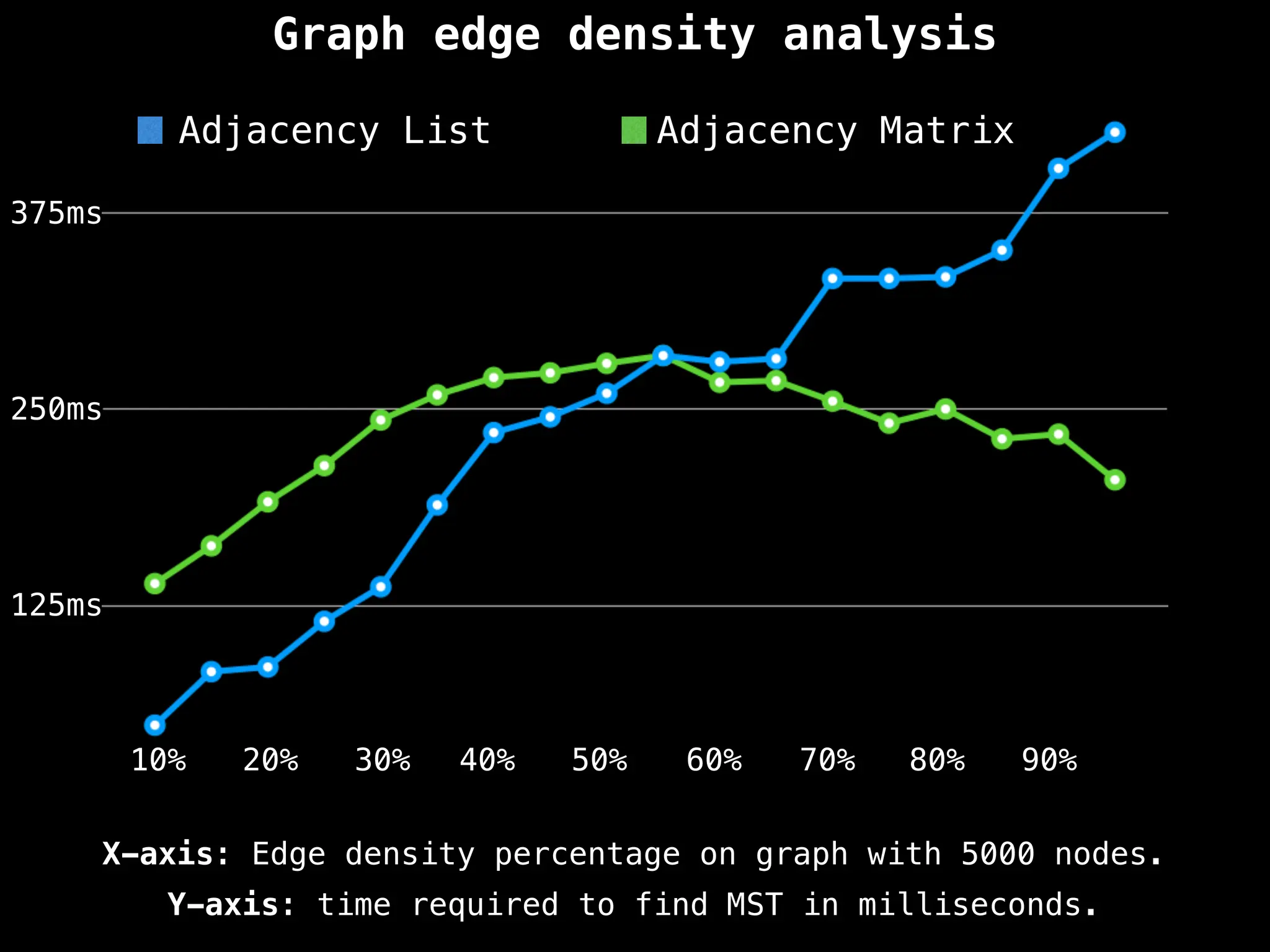
![Eager Prim’s Pseudo Code
Let’s define a few variables we’ll need:
n = … # Number of nodes in the graph.
ipq = … # IPQ data structure; stores (node index, edge object)
# pairs. The edge objects consist of {start node, end
# node, edge cost} tuples. The IPQ sorts (node index,
# edge object) pairs based on min edge cost.
g = … # Graph representing an adjacency list of weighted edges.
# Each undirected edge is represented as two directed
# edges in g. For especially dense graphs, prefer using
# an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list to
# improve performance.
visited = [false, …, false] # visited[i] tracks whether node i
# has been visited; size n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1416-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1417-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1418-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1419-2048.jpg)
![function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)
Helper method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1420-2048.jpg)
![Helper method
function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1421-2048.jpg)
![Helper method
function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1422-2048.jpg)
![Helper method
function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1423-2048.jpg)
![Helper method
function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1424-2048.jpg)
![Helper method
function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1425-2048.jpg)
![function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)
Helper method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1426-2048.jpg)
![function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)
Helper method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1427-2048.jpg)
![Helper method
function relaxEdgesAtNode(currentNodeIndex):
# Mark the current node as visited.
visited[currentNodeIndex] = true
# Get all the edges going outwards from the current node.
edges = g[currentNodeIndex]
for (edge : edges):
destNodeIndex = edge.to
# Skip edges pointing to already visited nodes.
if visited[destNodeIndex]:
continue
if !ipq.contains(destNodeIndex):
# Insert edge for the first time.
ipq.insert(destNodeIndex, edge)
else:
# Try and improve the cheapest edge at destNodeIndex with
# the current edge in the IPQ.
ipq.decreaseKey(destNodeIndex, edge)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1428-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1429-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1430-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1431-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1432-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1433-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1434-2048.jpg)
![# s - the index of the starting node (0 ≤ s < n)
function eagerPrims(s = 0):
m = n - 1 # number of edges in MST
edgeCount, mstCost = 0, 0
mstEdges = [null, …, null] # size m
relaxEdgesAtNode(s)
while (!ipq.isEmpty() and edgeCount != m):
# Extract the next best (node index, edge object)
# pair from the IPQ
destNodeIndex, edge = ipq.dequeue()
mstEdges[edgeCount++] = edge
mstCost += edge.cost
relaxEdgesAtNode(destNodeIndex)
if edgeCount != m:
return (null, null) # No MST exists!
return (mstCost, mstEdges)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryalgorithms-251006133410-4d515a03/75/graph-theory-algorithms-graph-theory-algorithms-1435-2048.jpg)