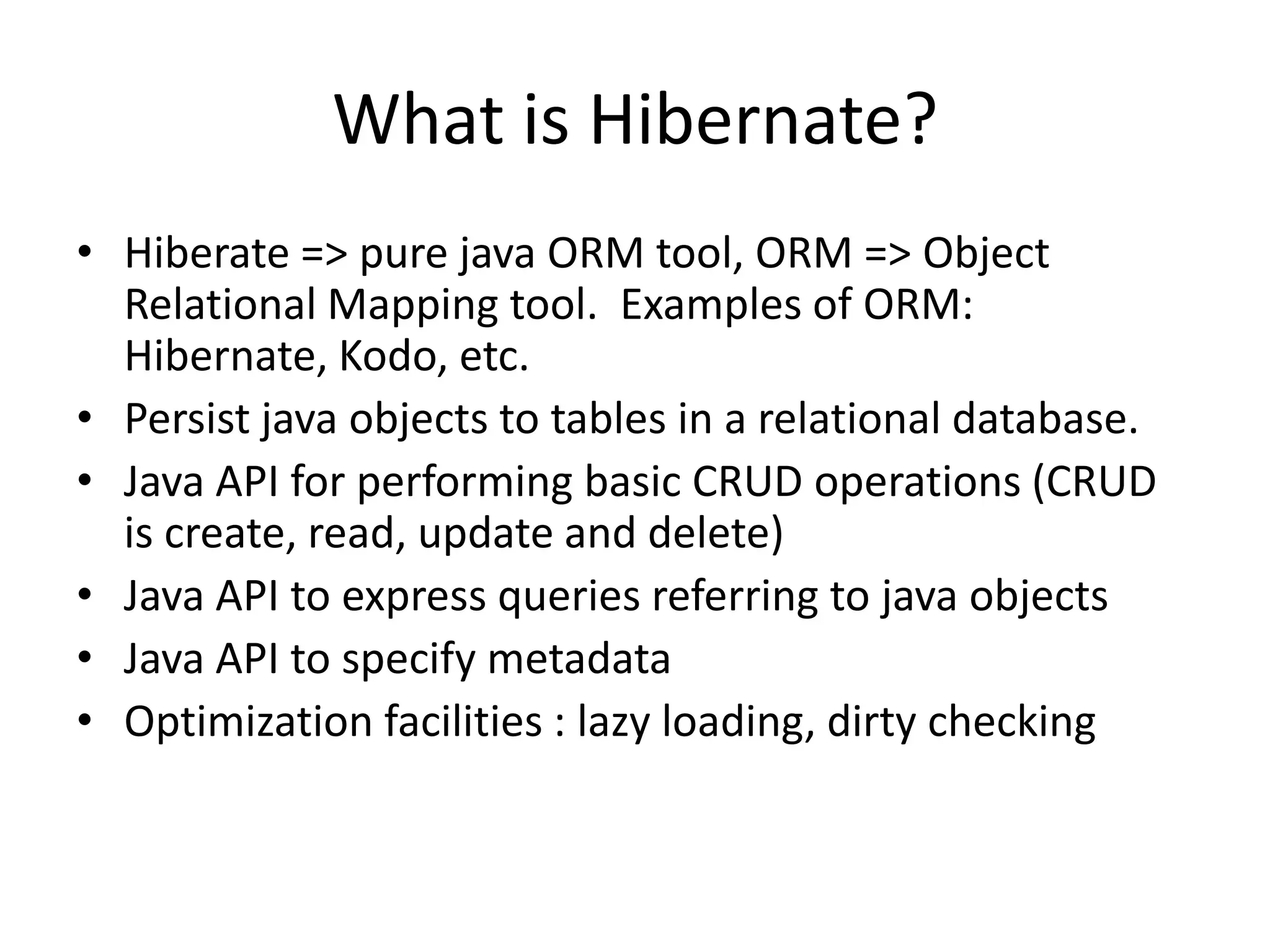
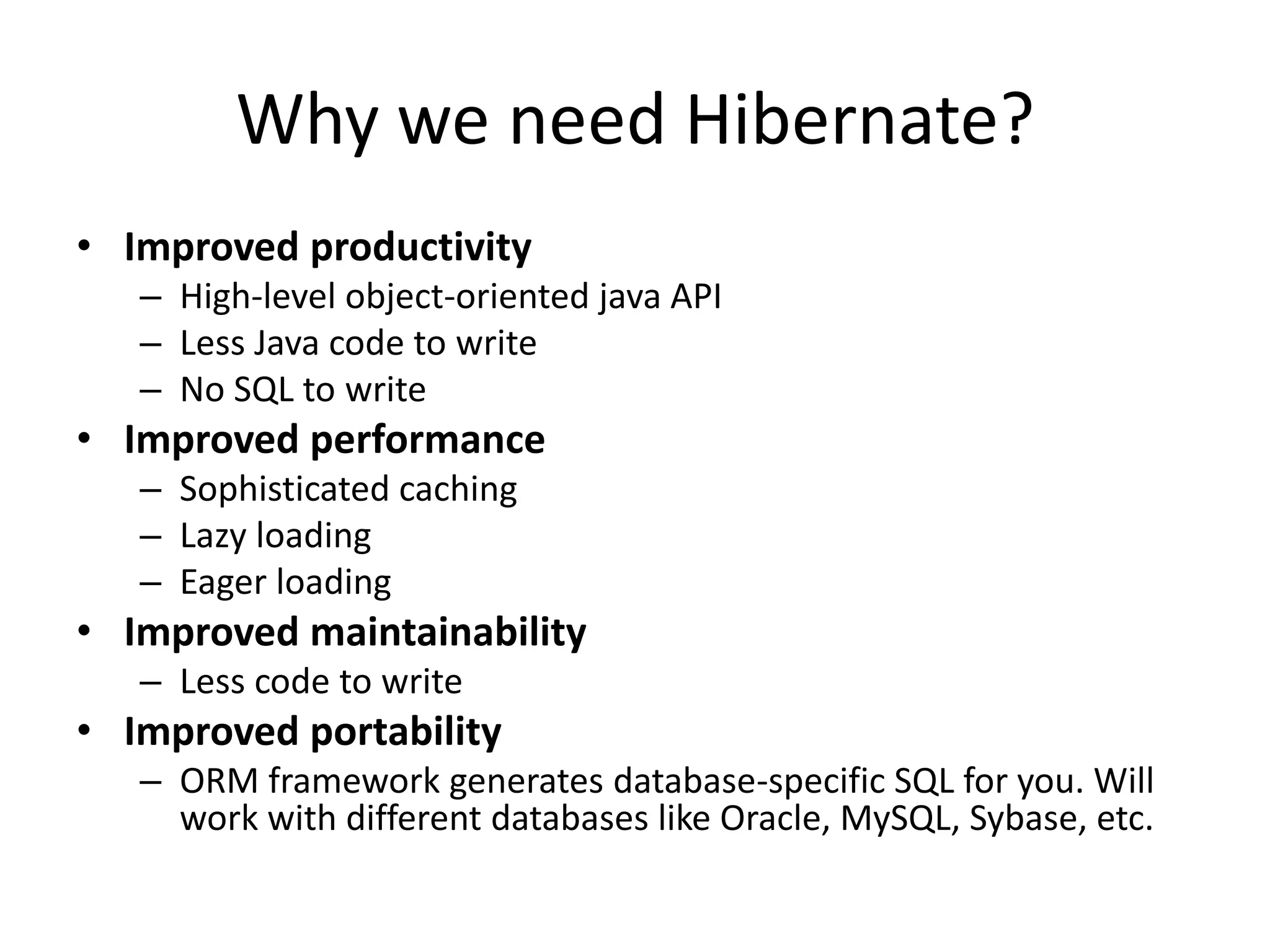
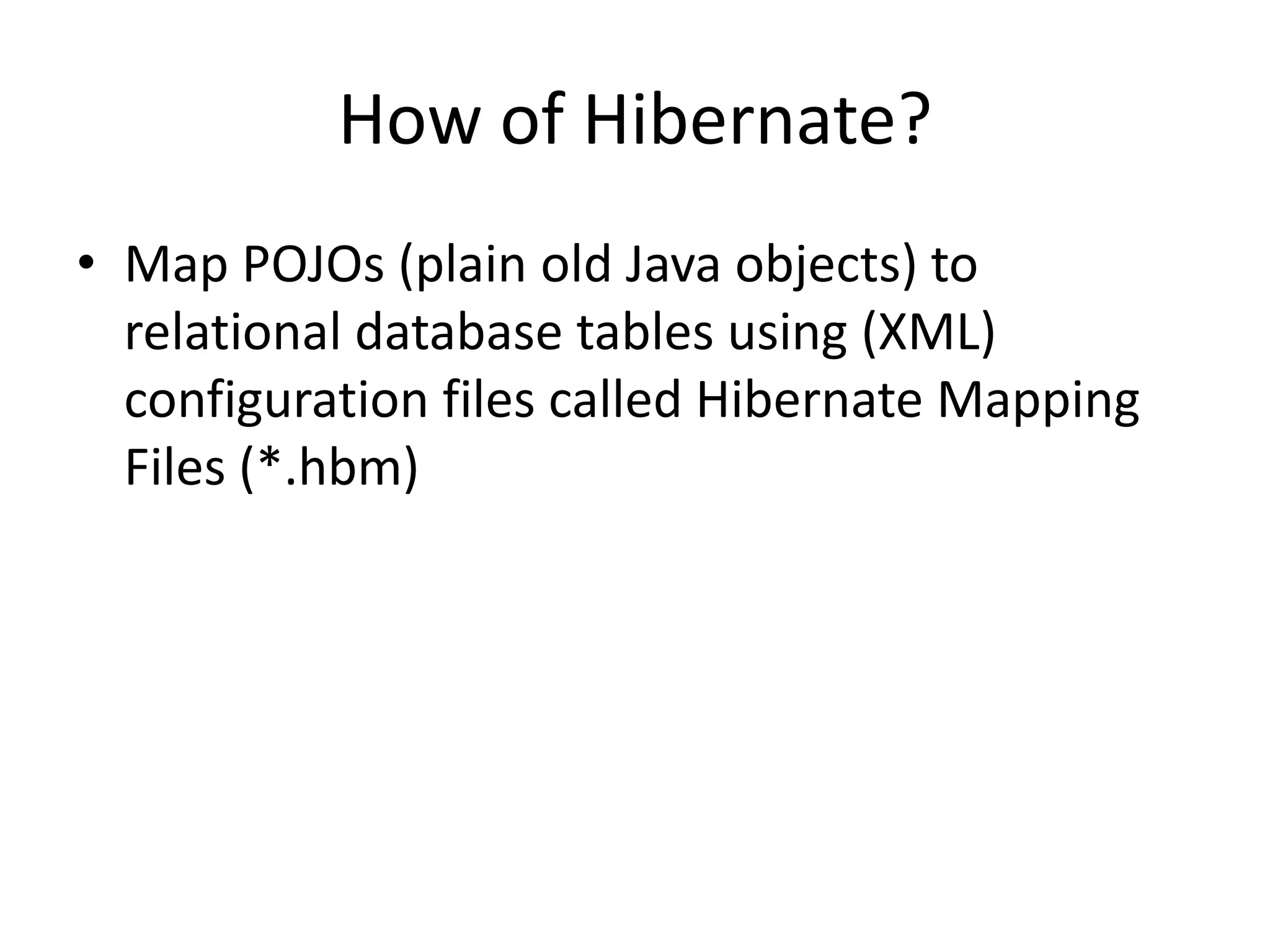
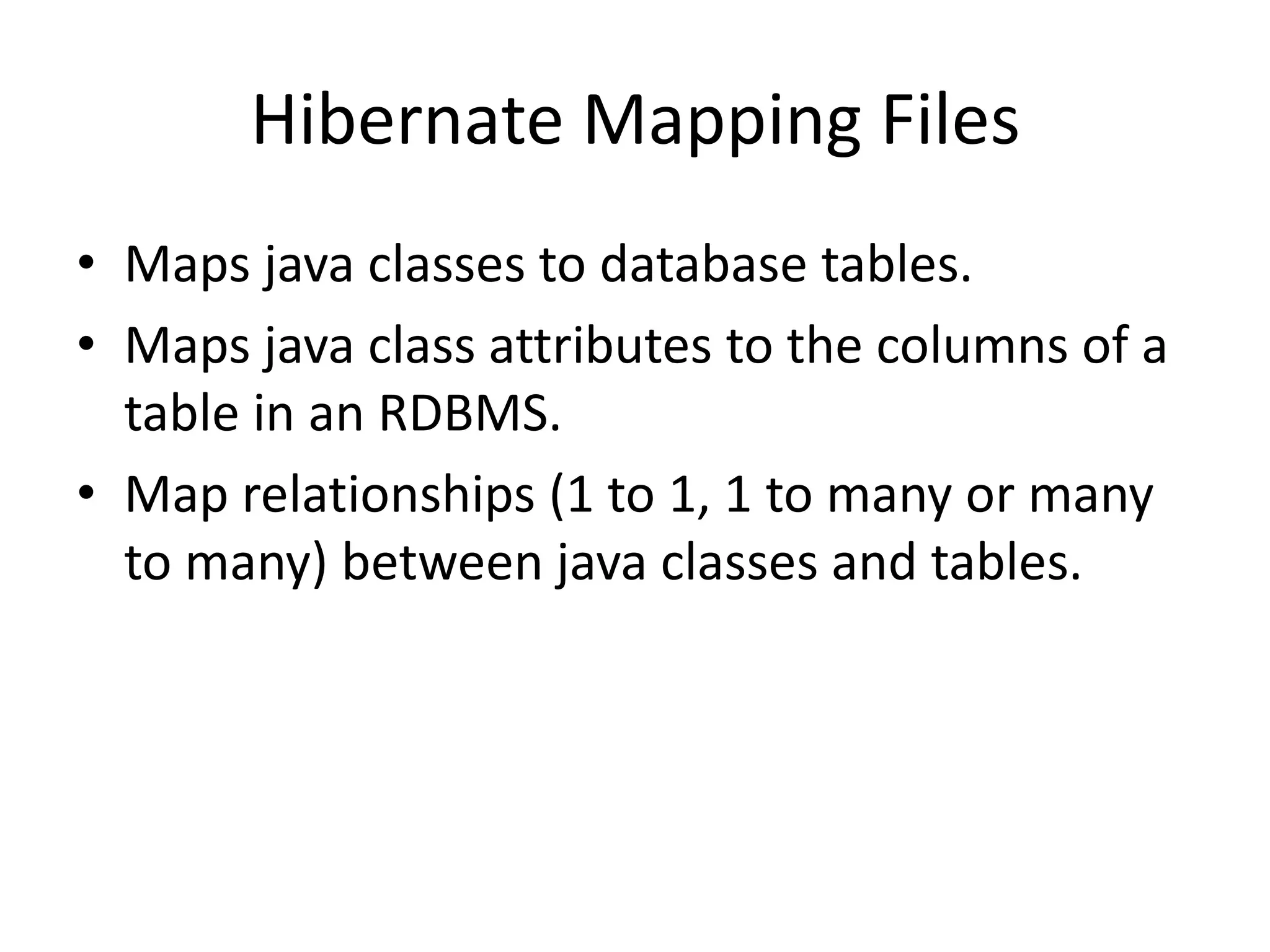
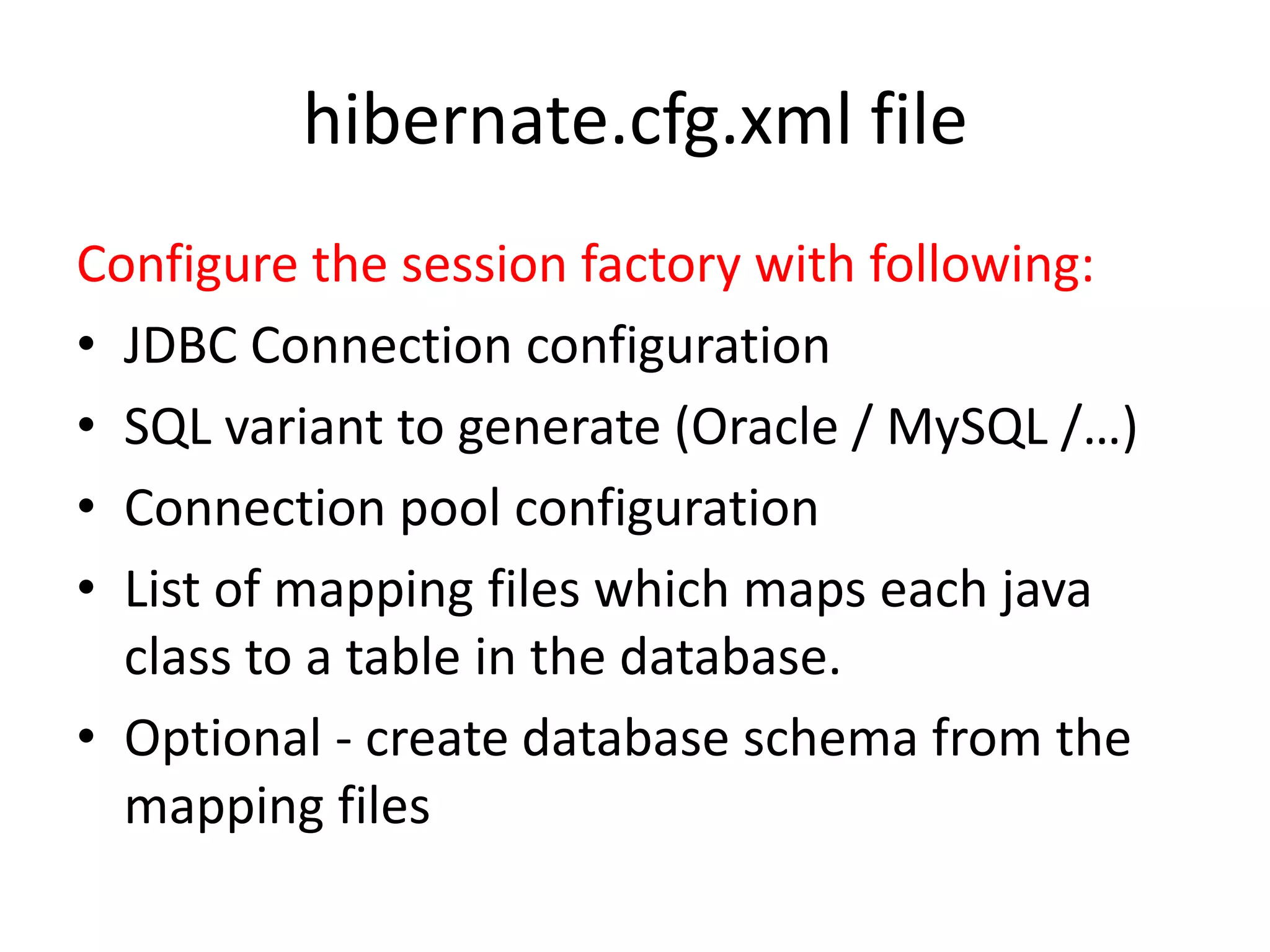
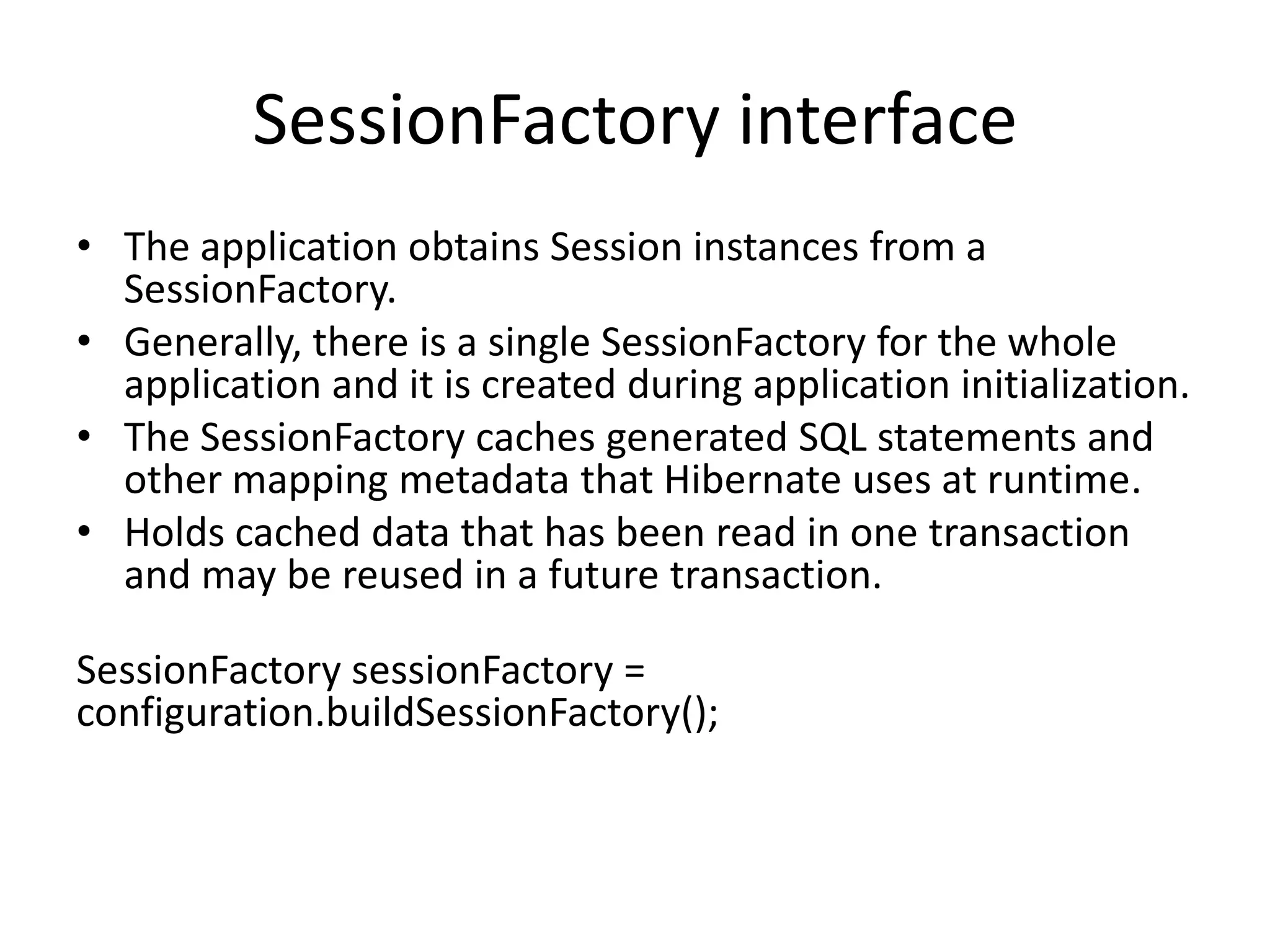
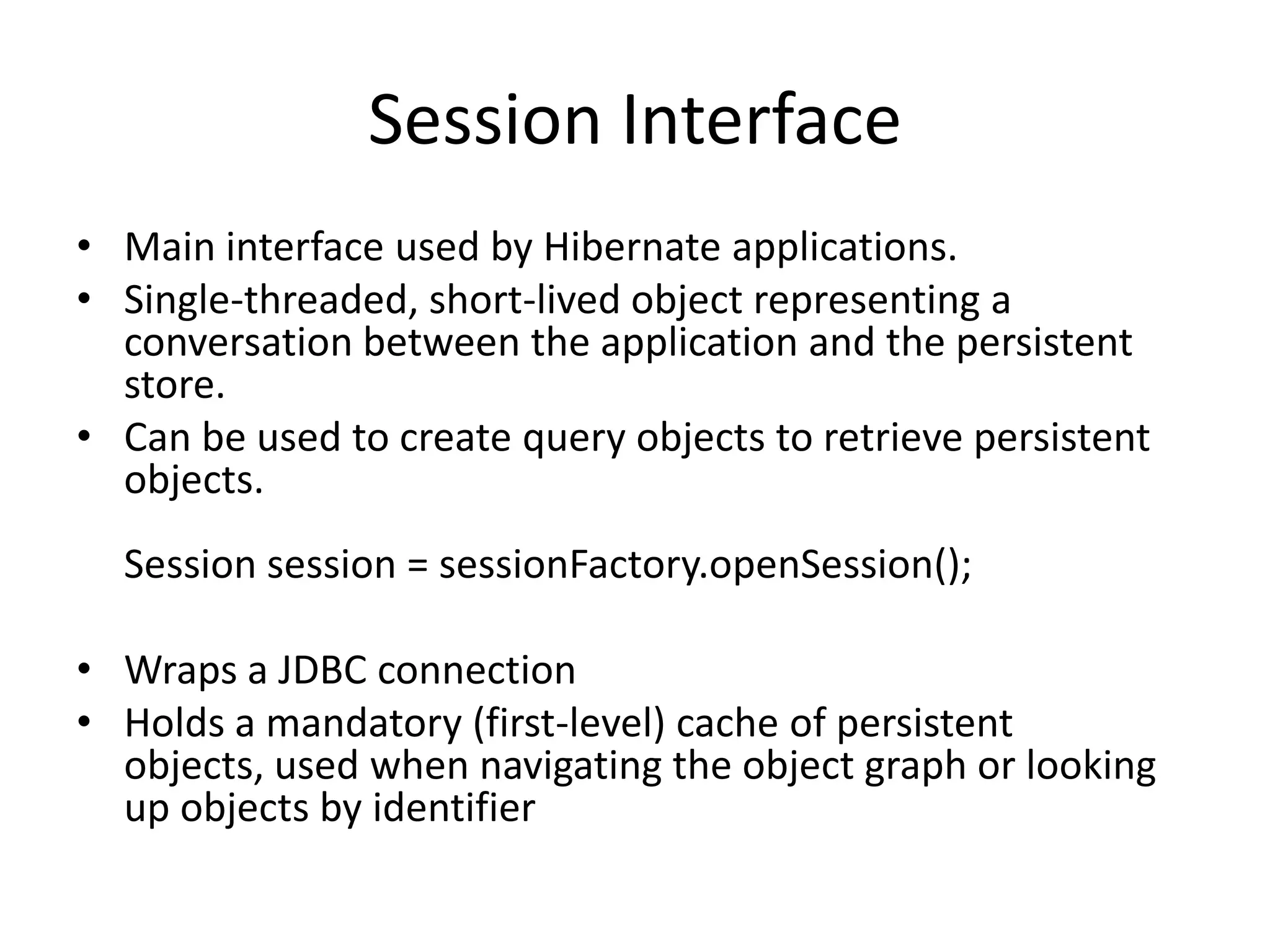
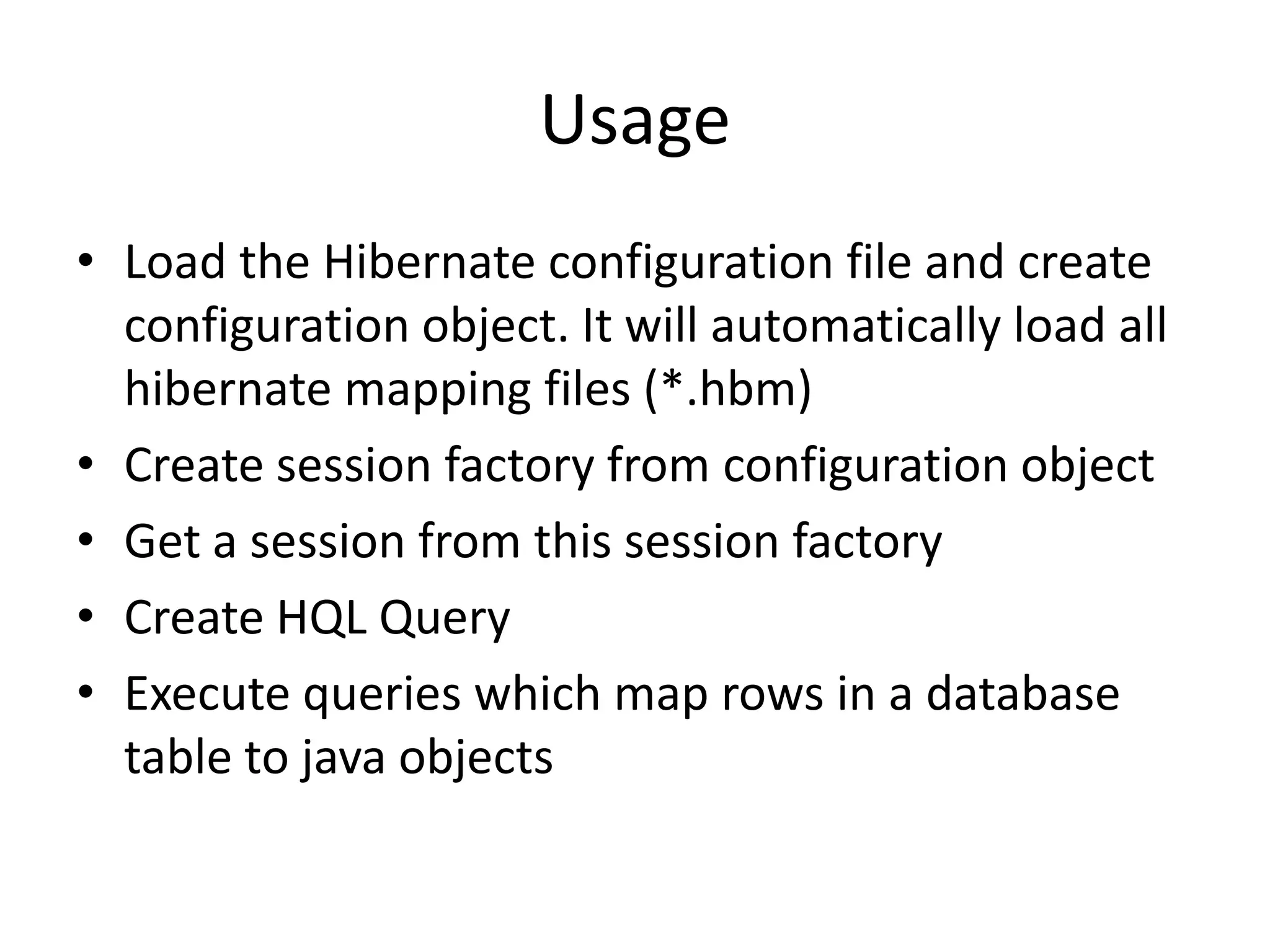
Hibernate is an ORM tool that allows Java objects to be mapped to database tables. It provides a Java API and configuration files to perform CRUD operations on objects and express queries. Hibernate improves productivity by reducing code, improves performance through caching and loading strategies, and improves maintainability and portability. Configuration involves mapping POJOs to tables in XML files and specifying the session factory, which provides session instances to interact with the database. Sessions represent a conversation with the database and allow queries and transactions.