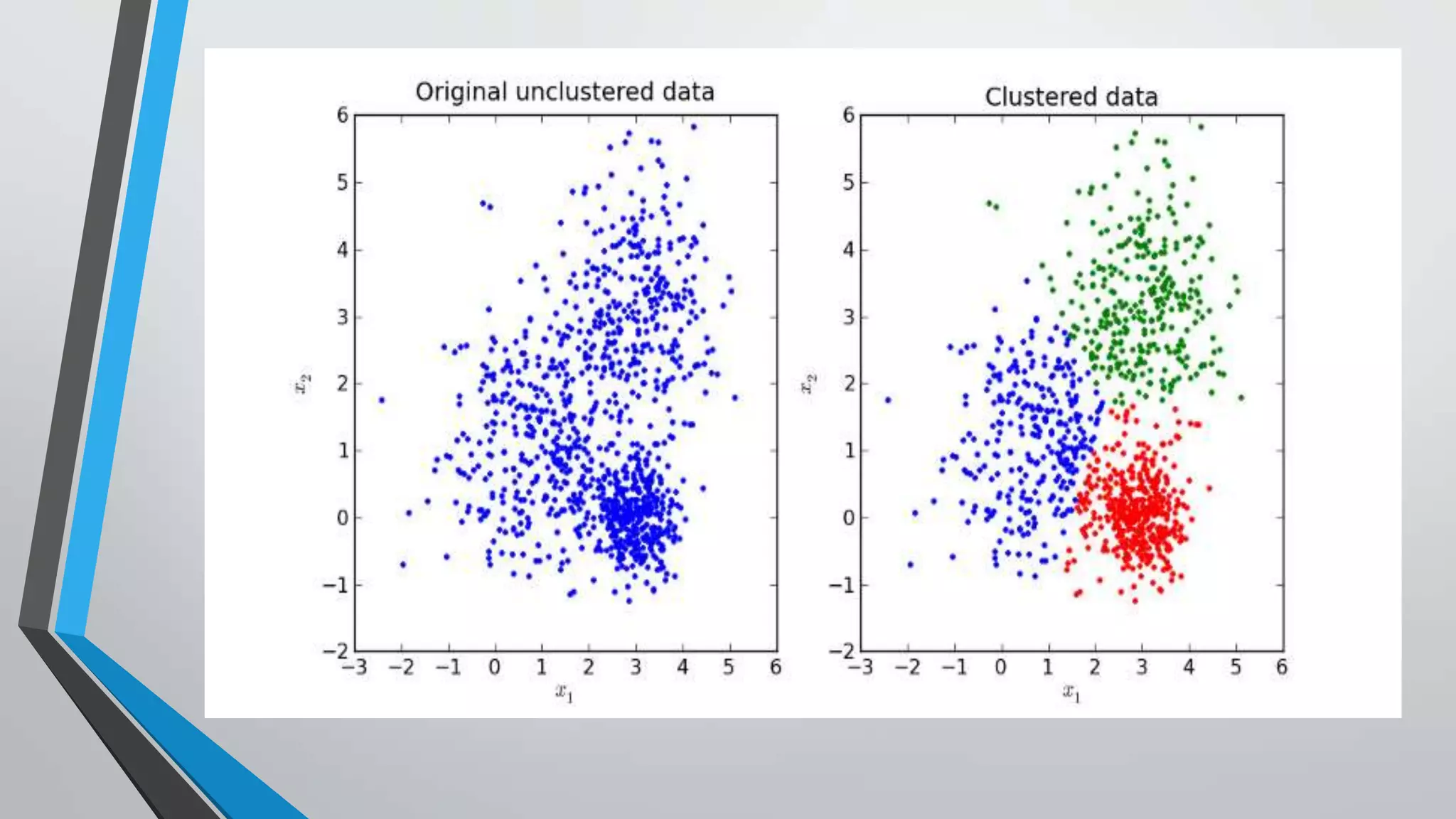
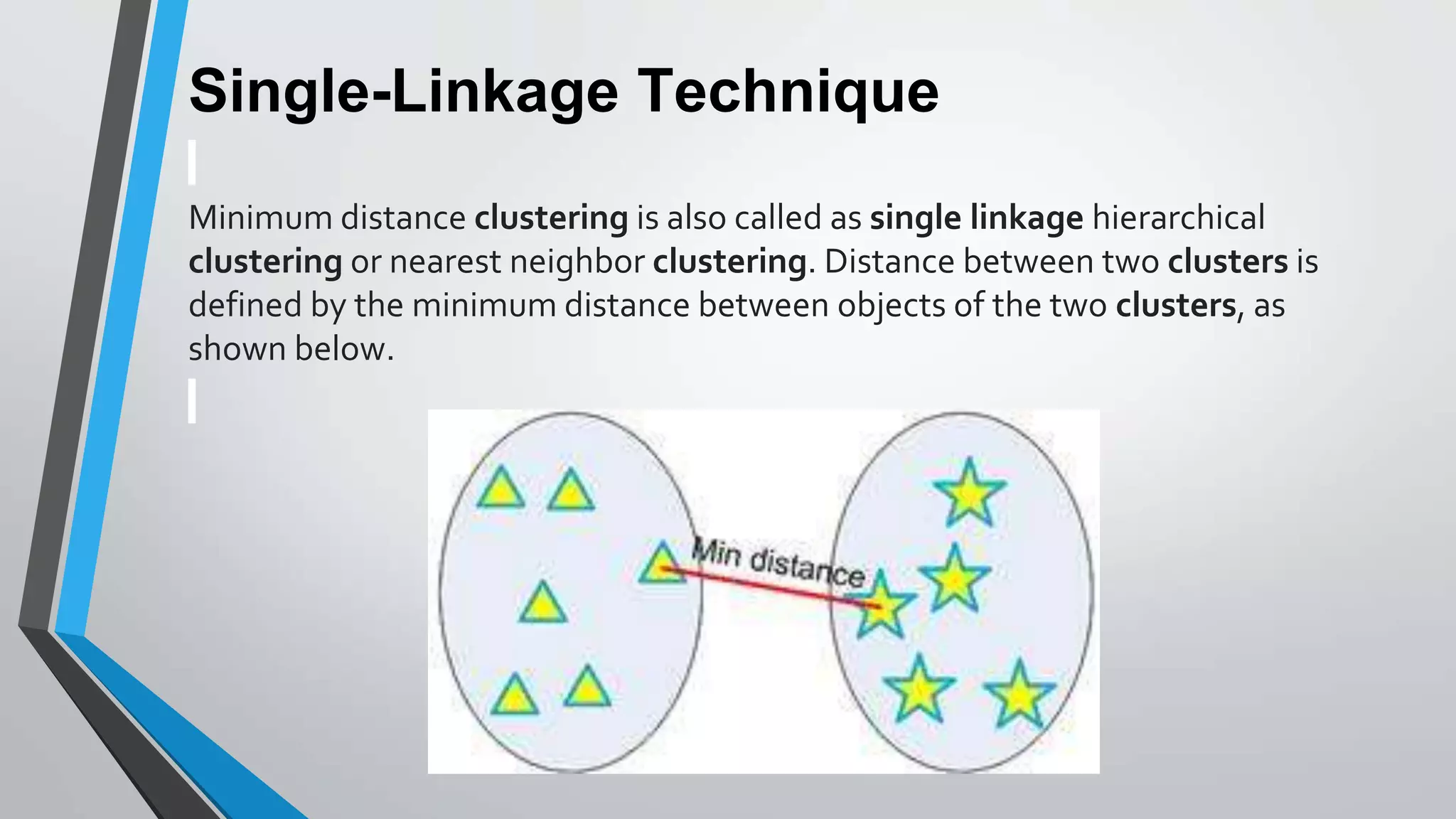
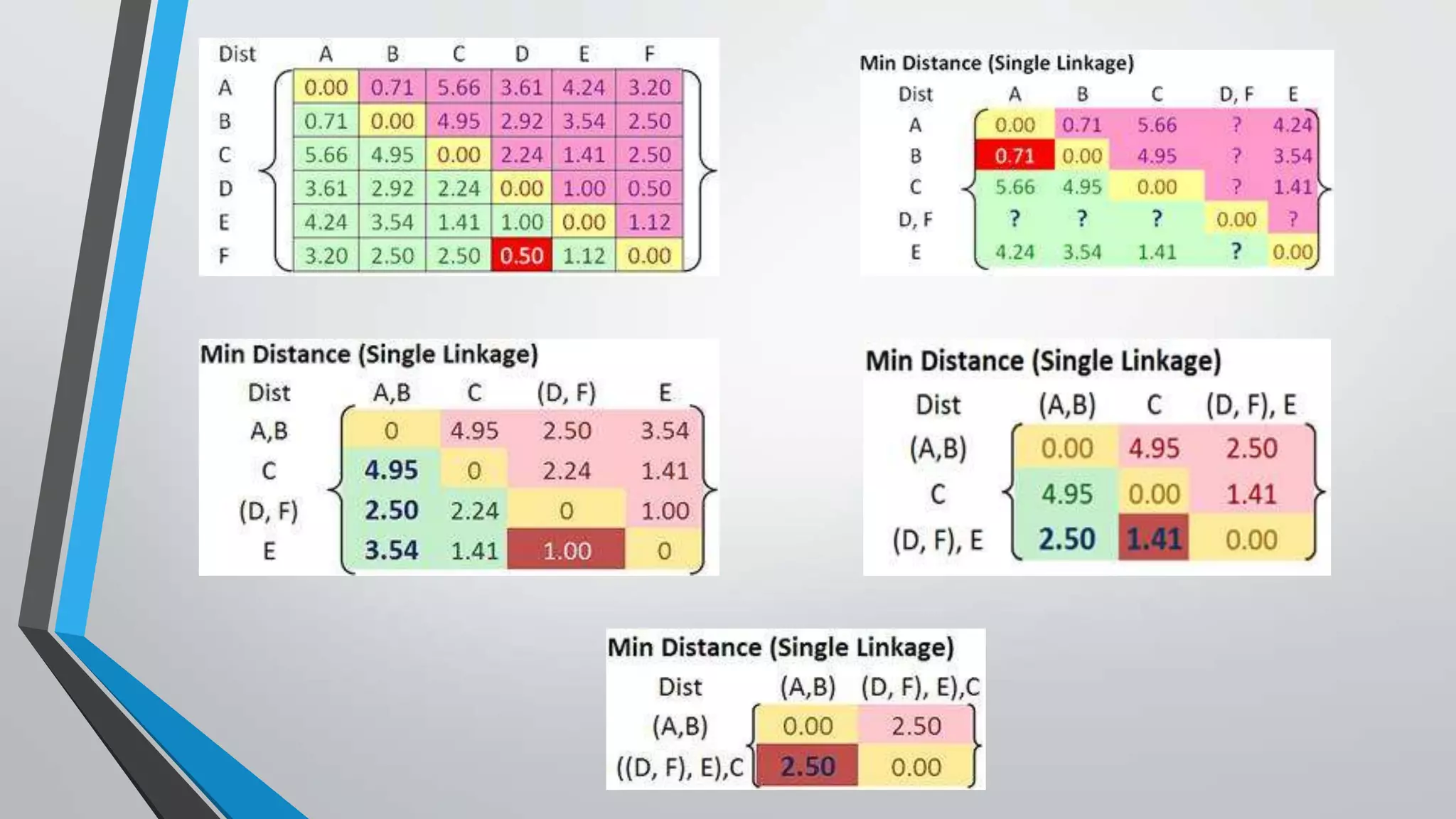
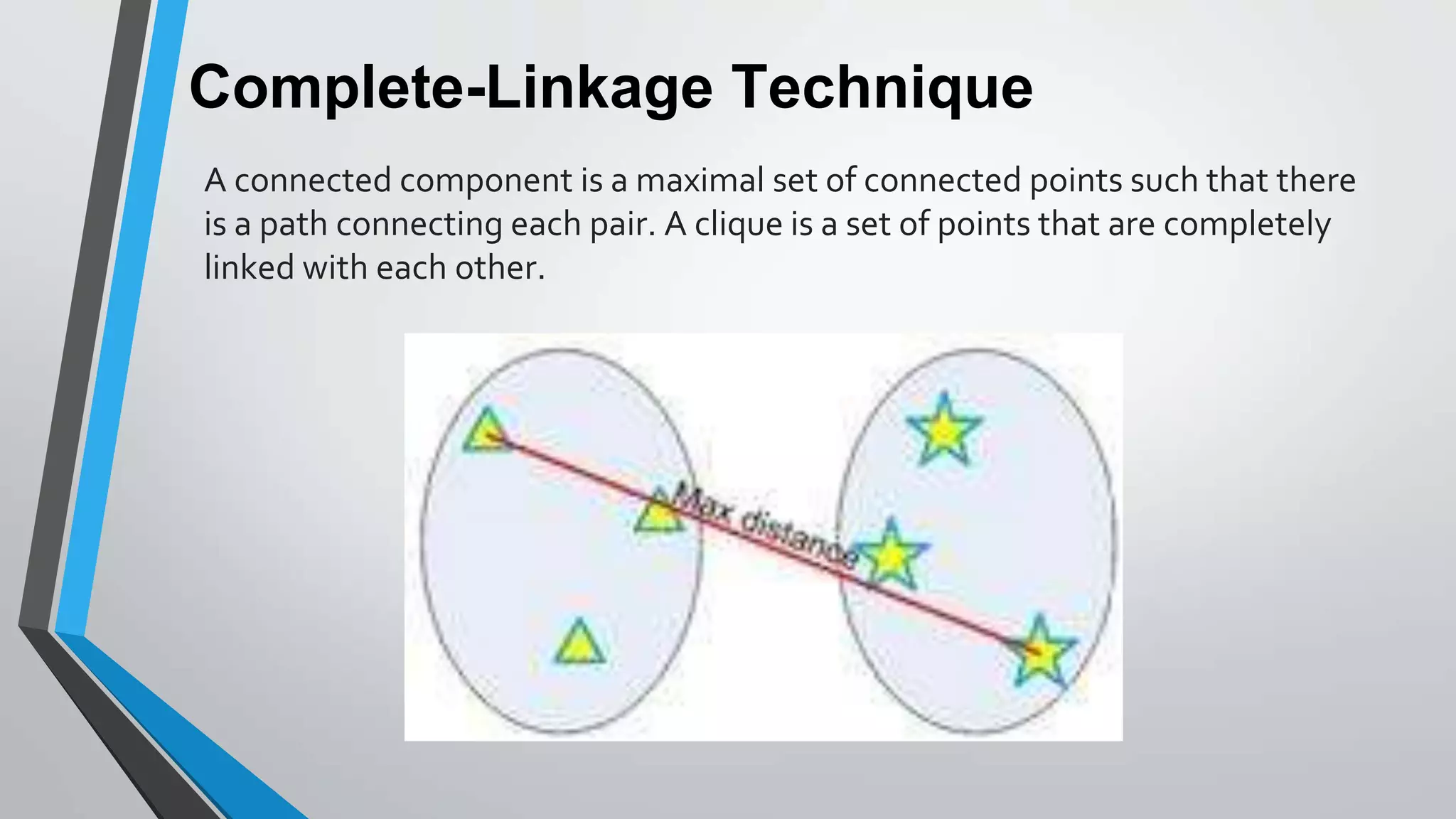
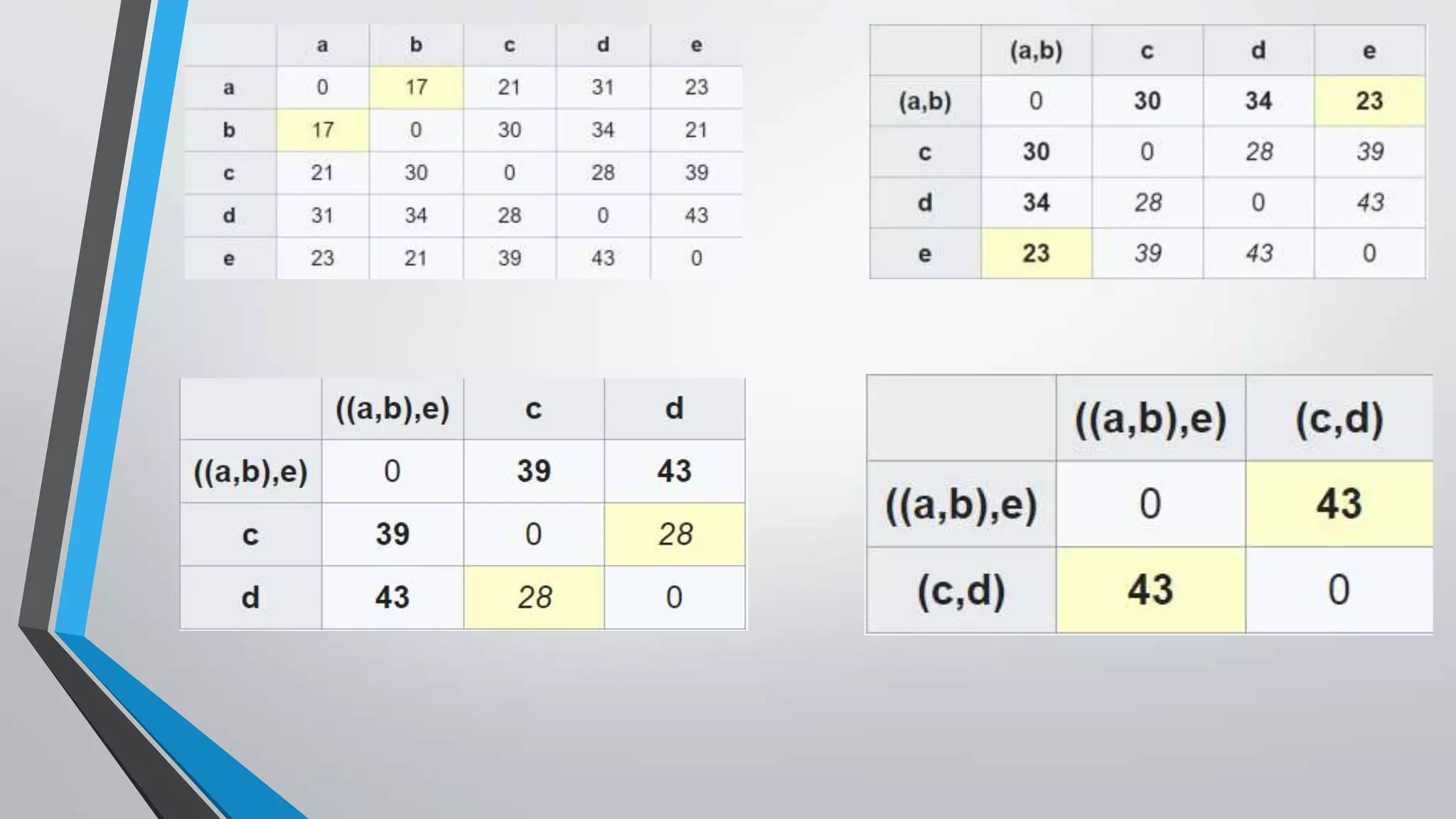
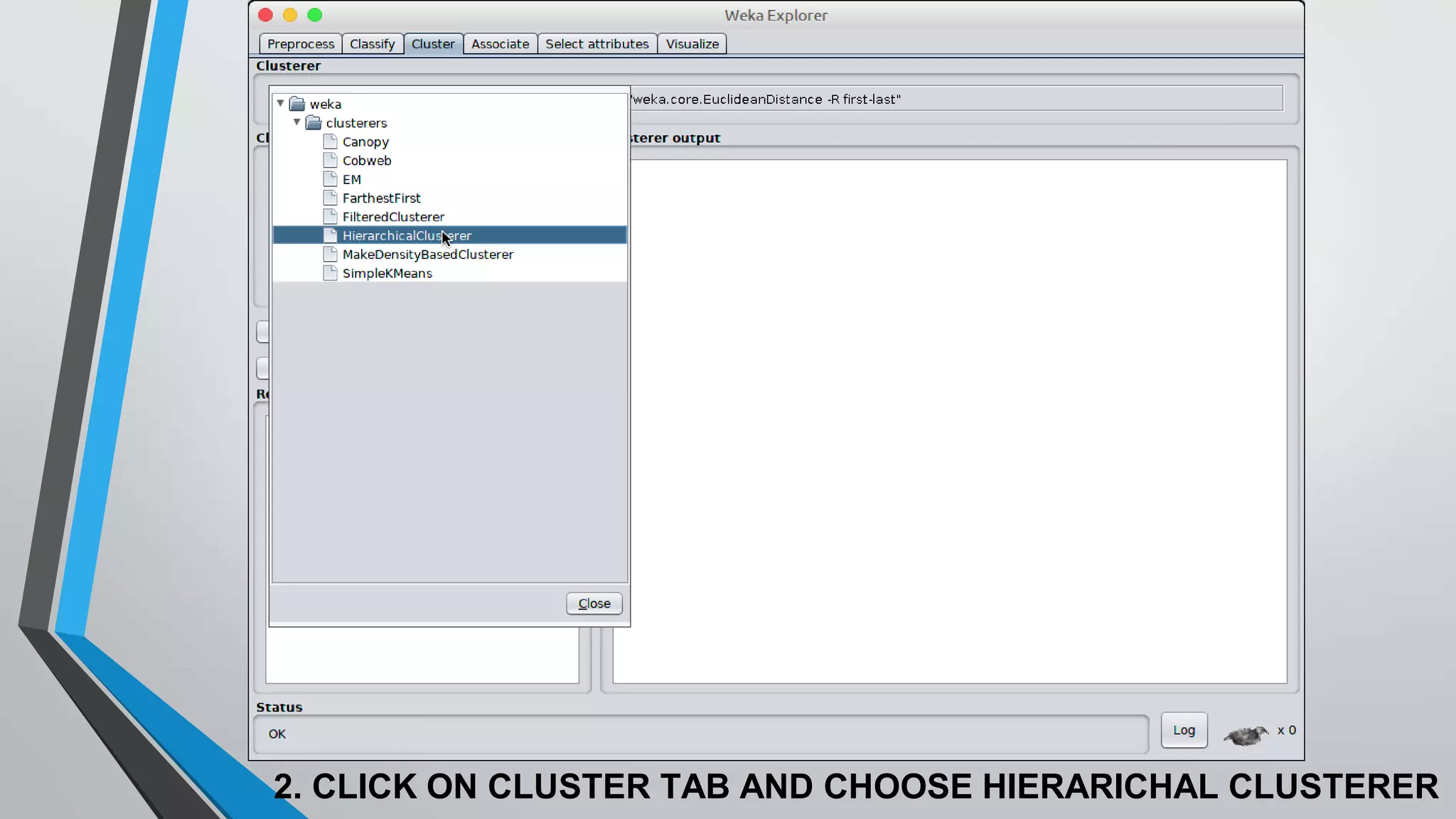
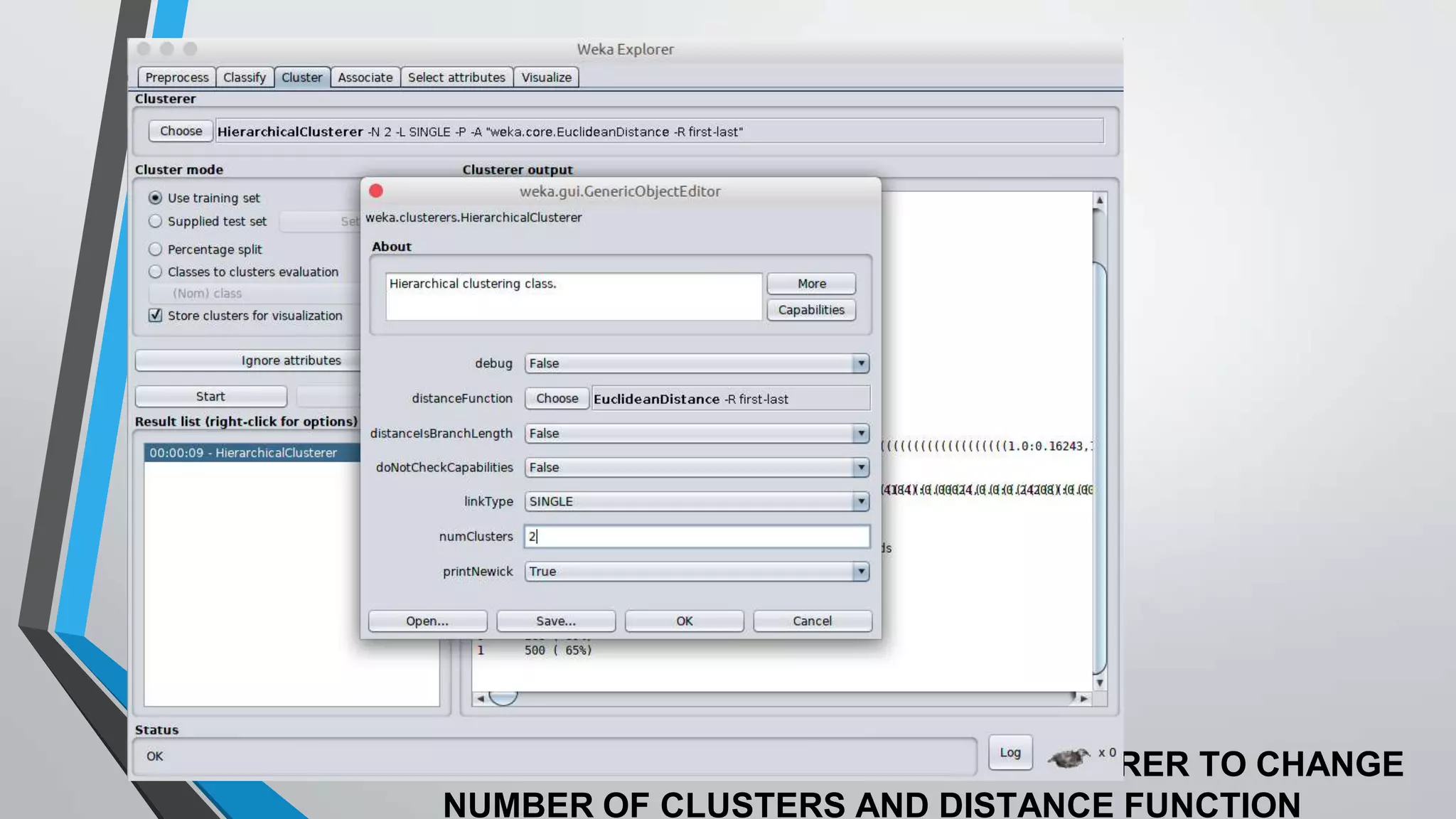
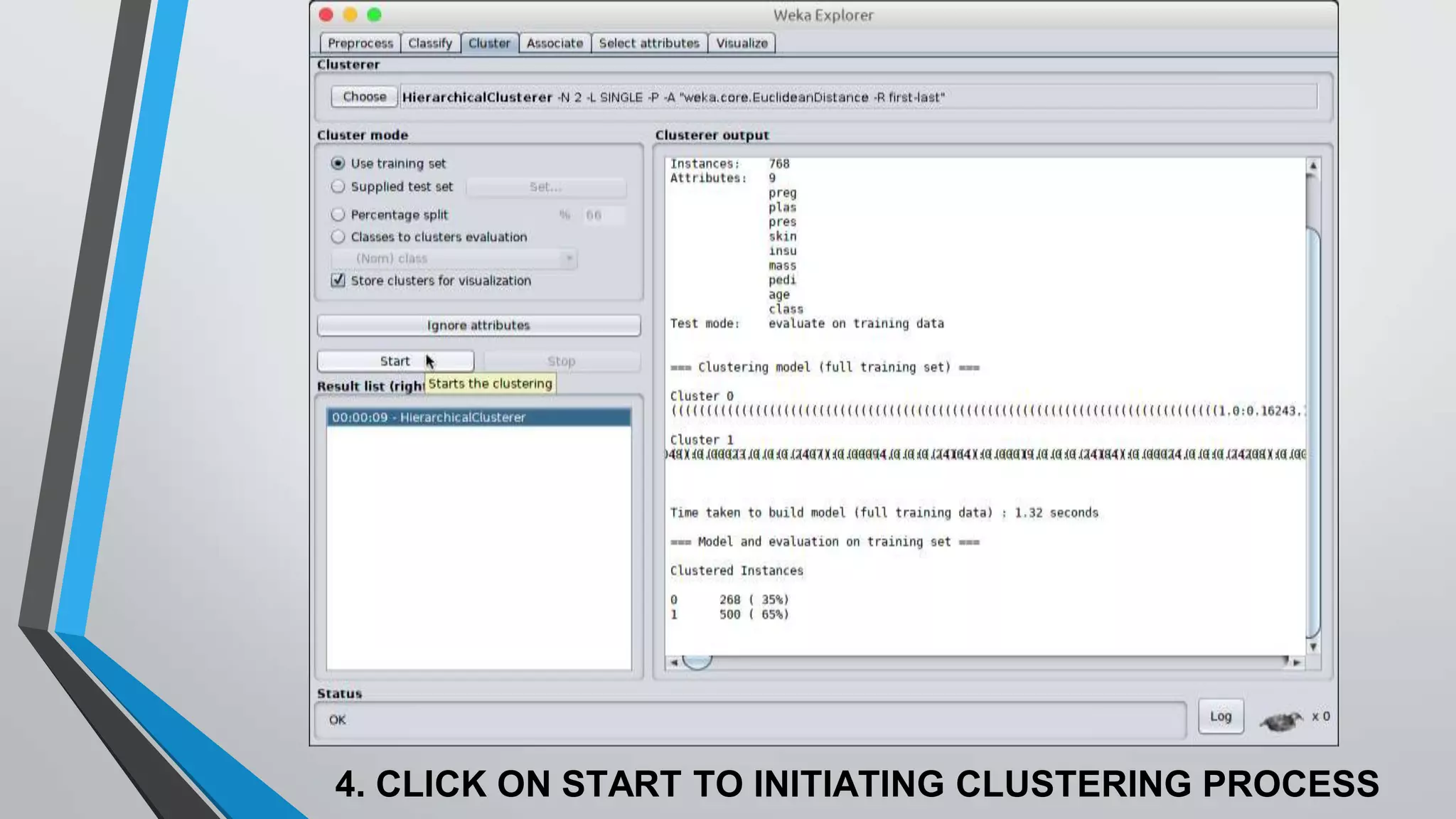
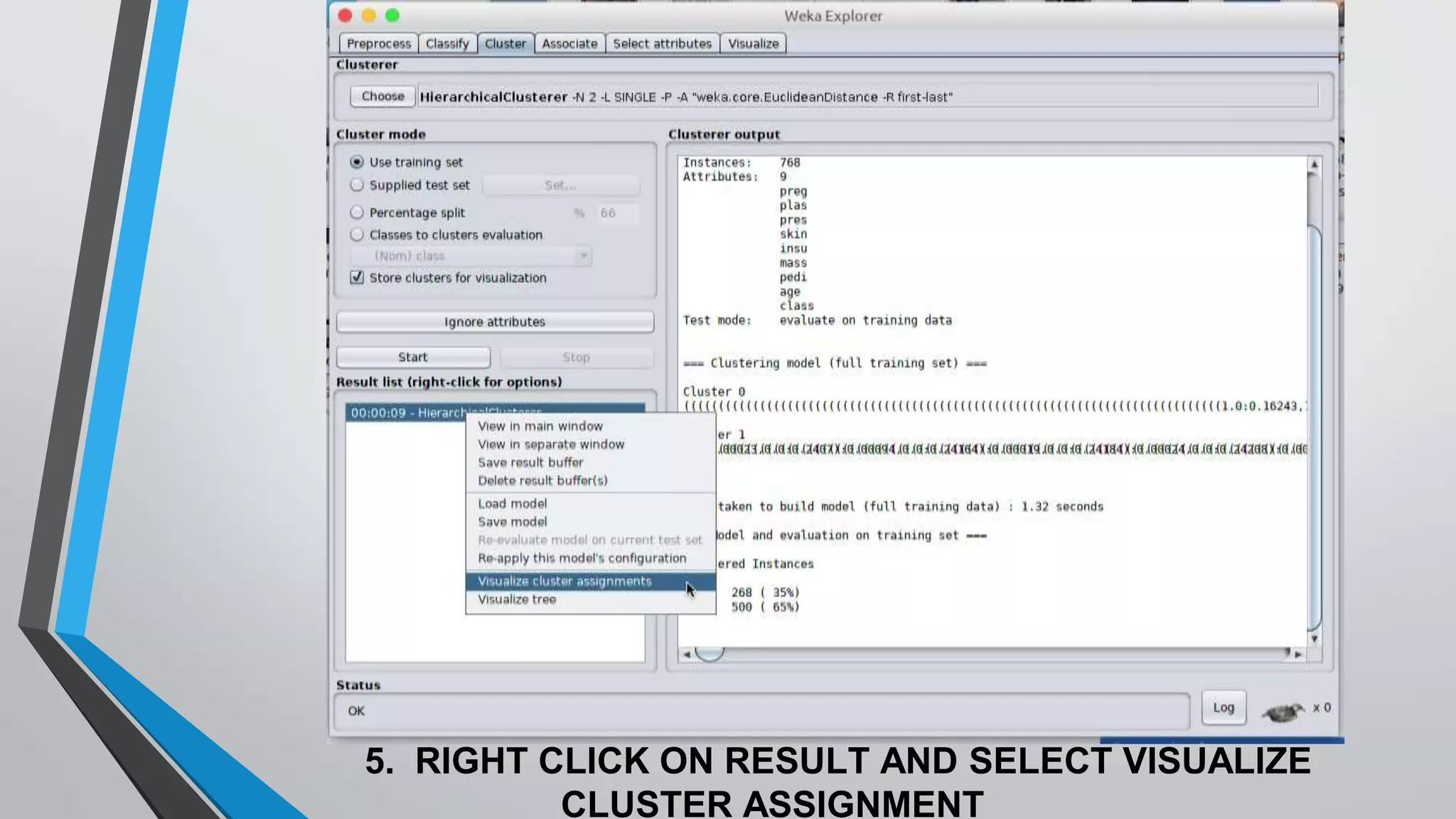
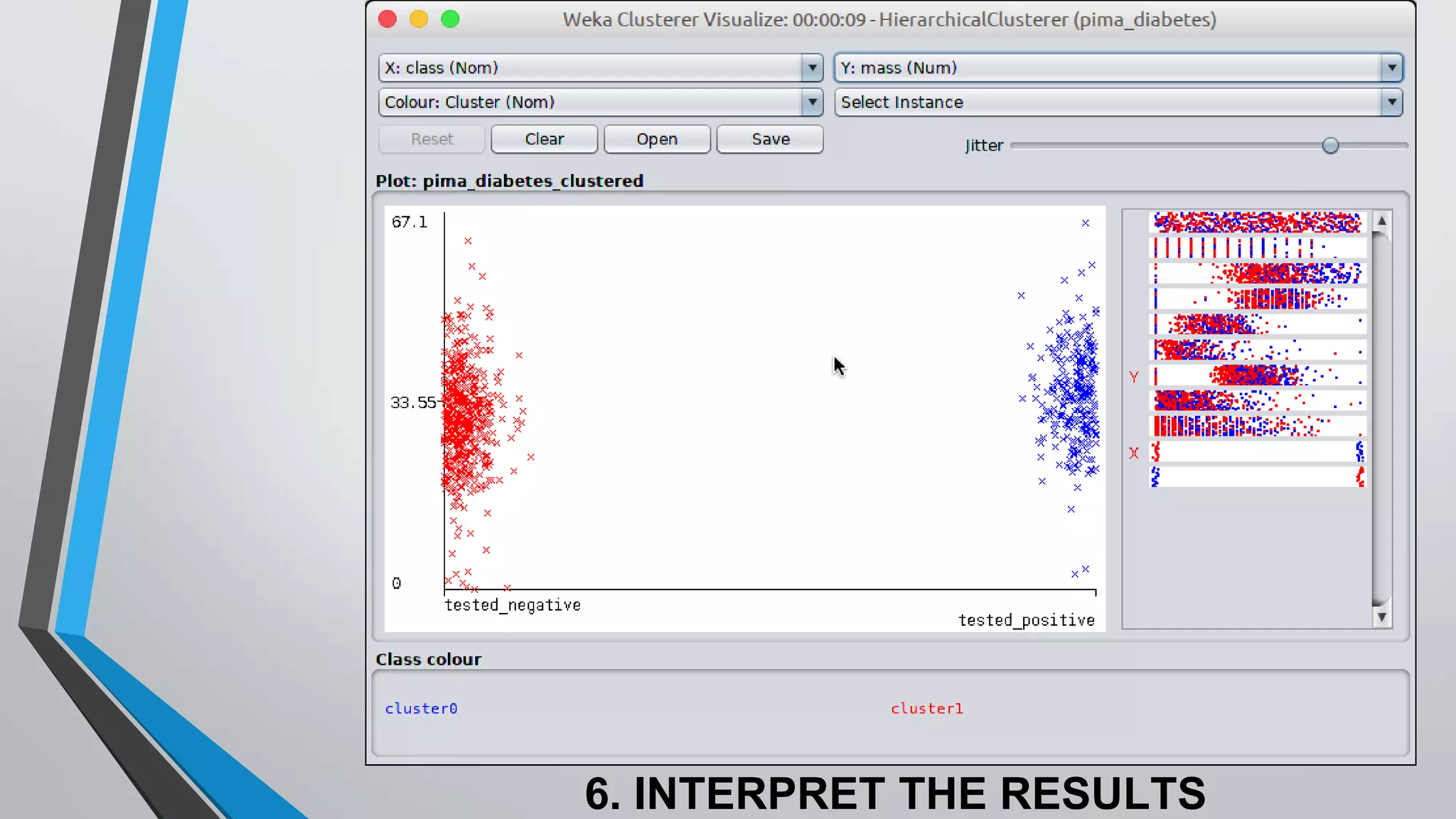
The document presents information on hierarchical clustering techniques. It defines clustering as dividing data into groups such that points within a group are similar to each other and dissimilar to points in other groups. It provides examples of clustering applications in marketing, biology, libraries, insurance, and city planning. It then describes three agglomerative clustering techniques: single-linkage, complete-linkage, and average linkage. Finally, it outlines steps to implement hierarchical clustering in the WEKA tool.