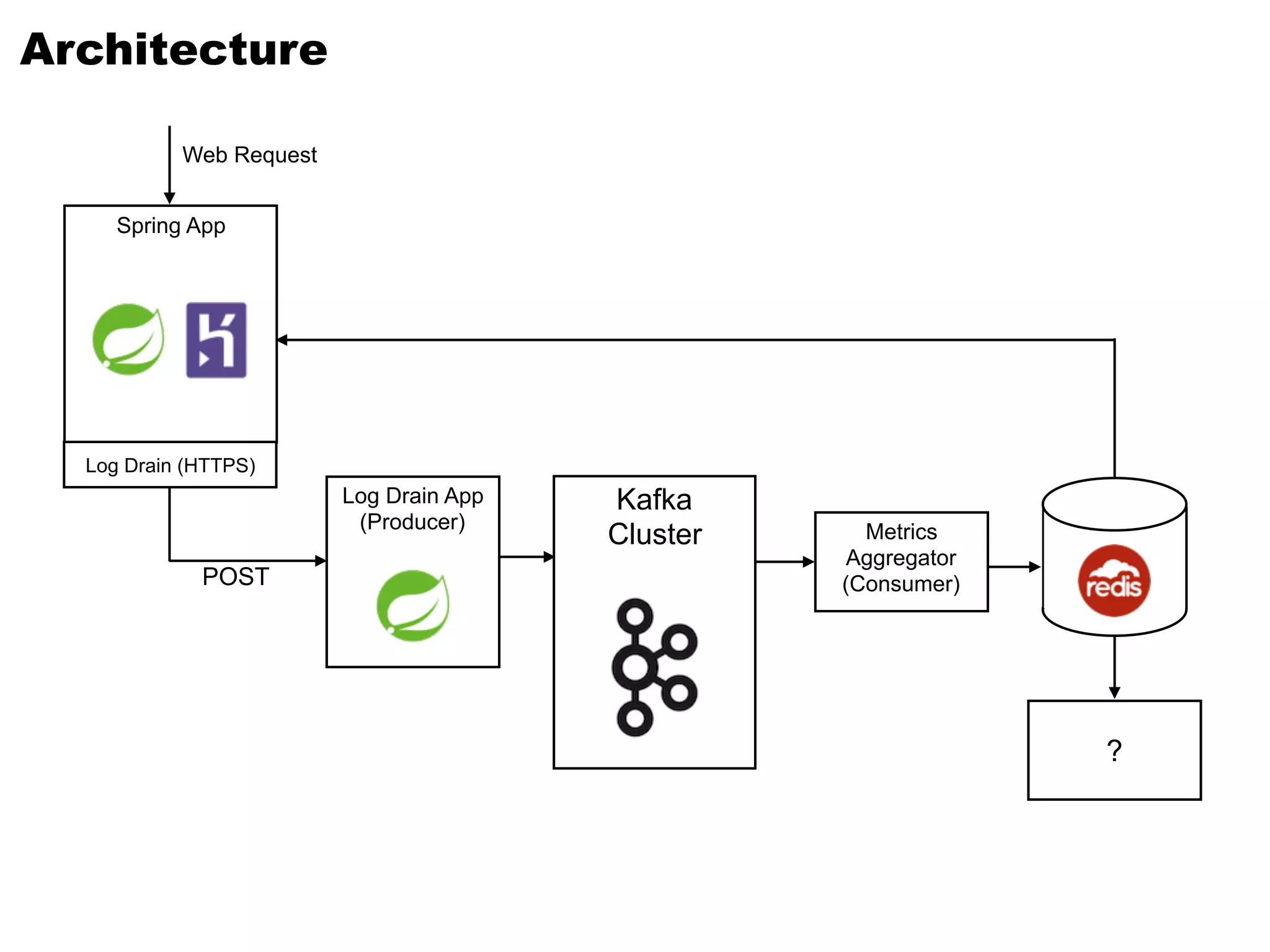
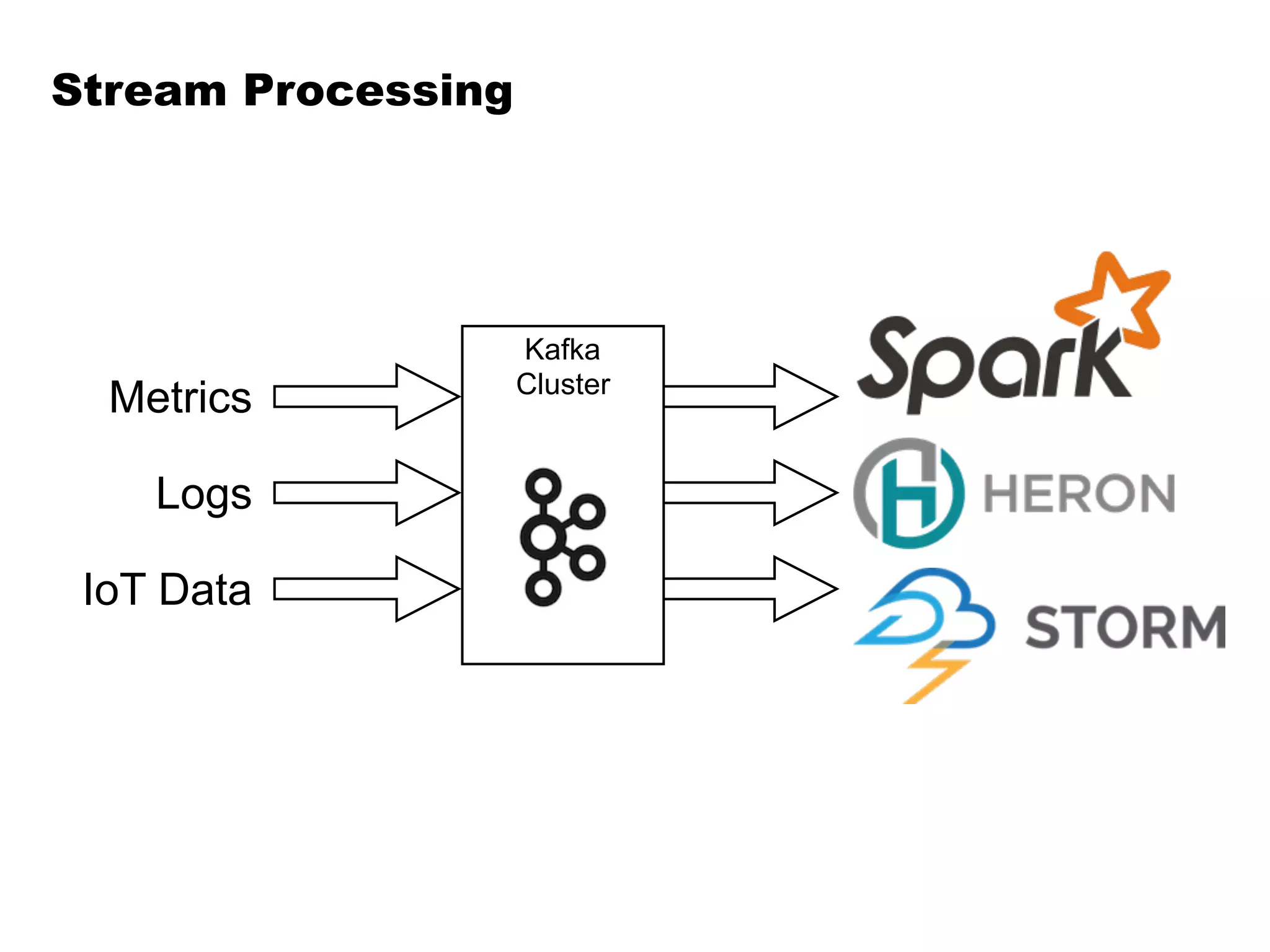
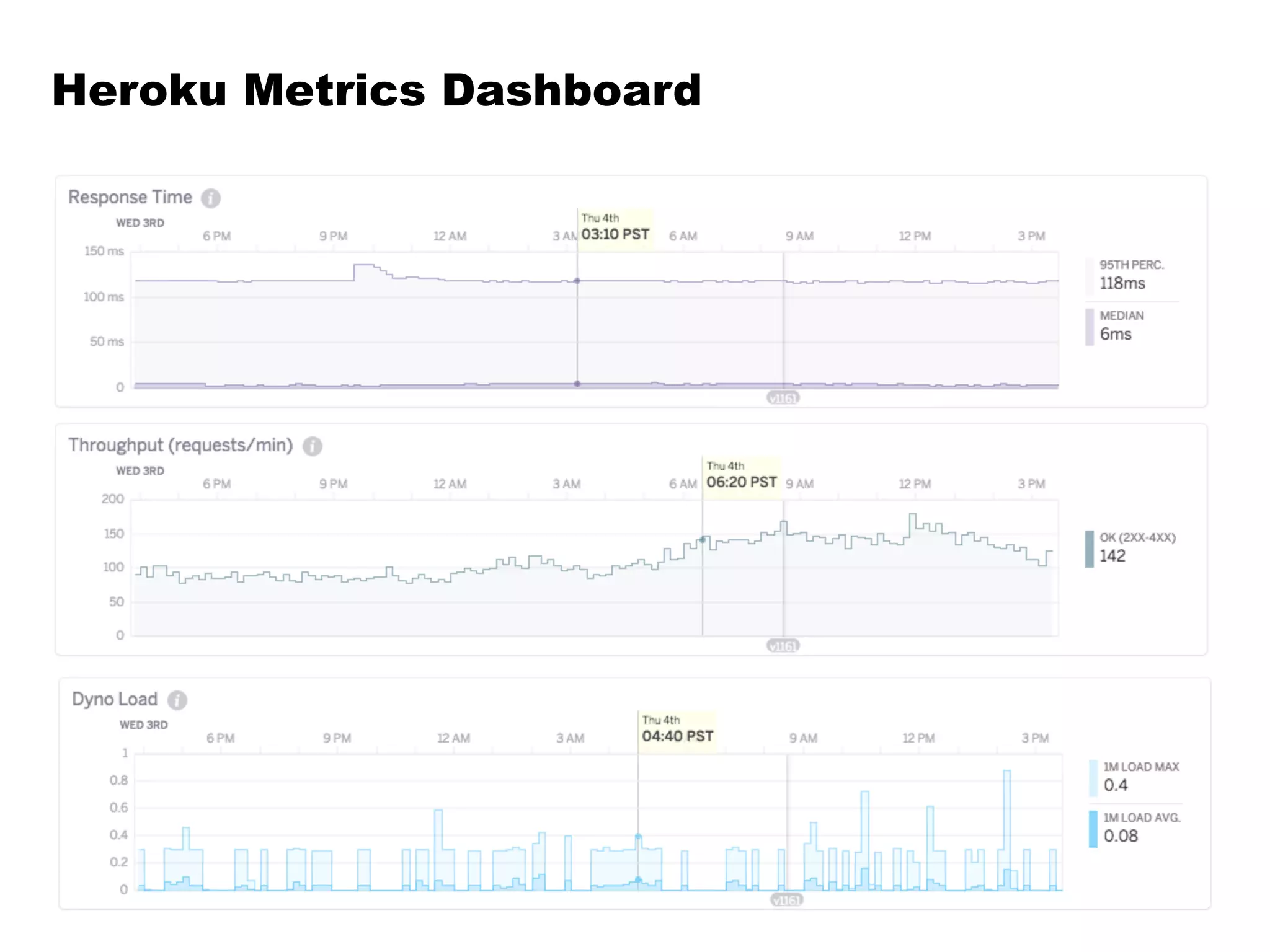
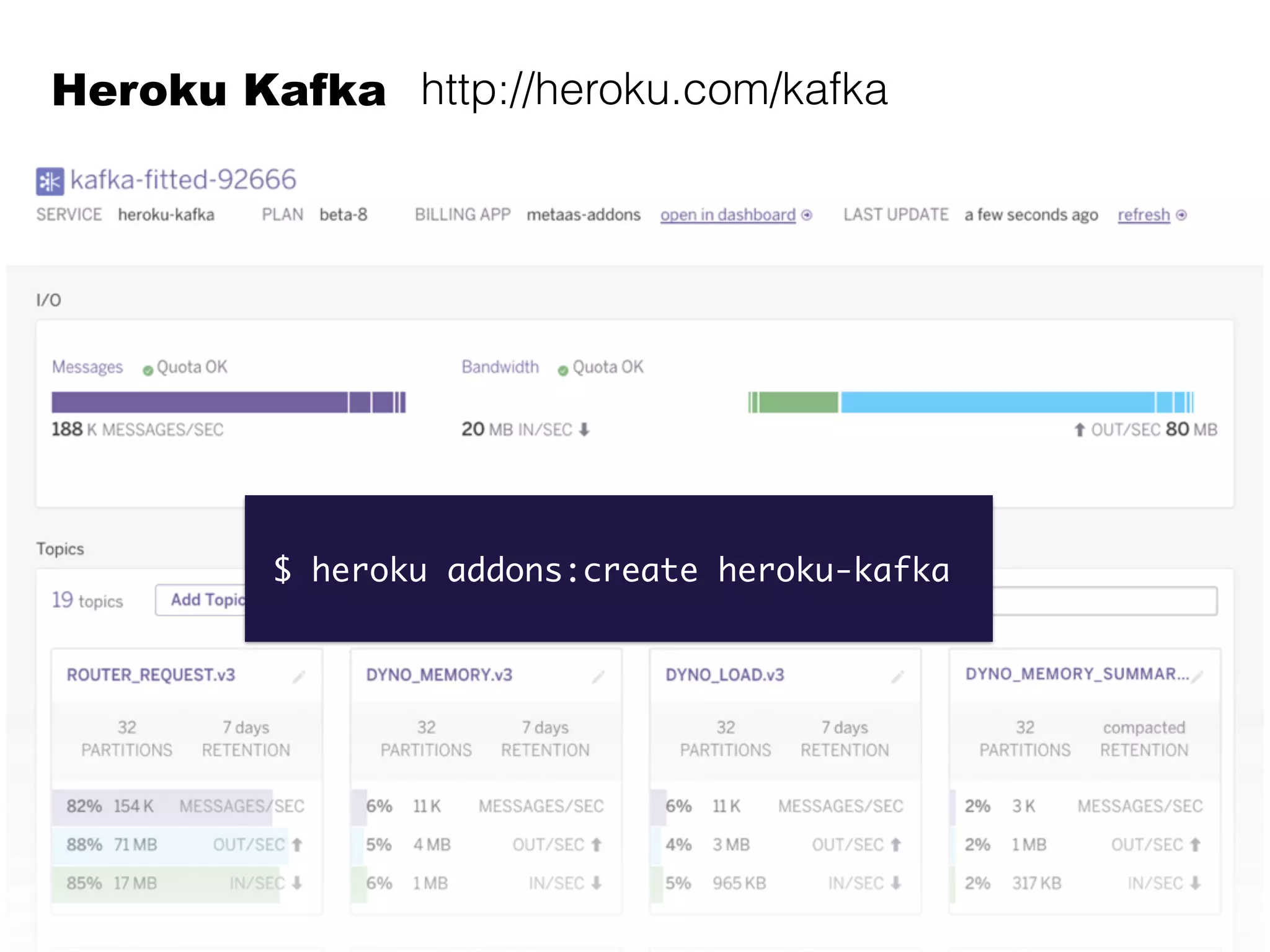
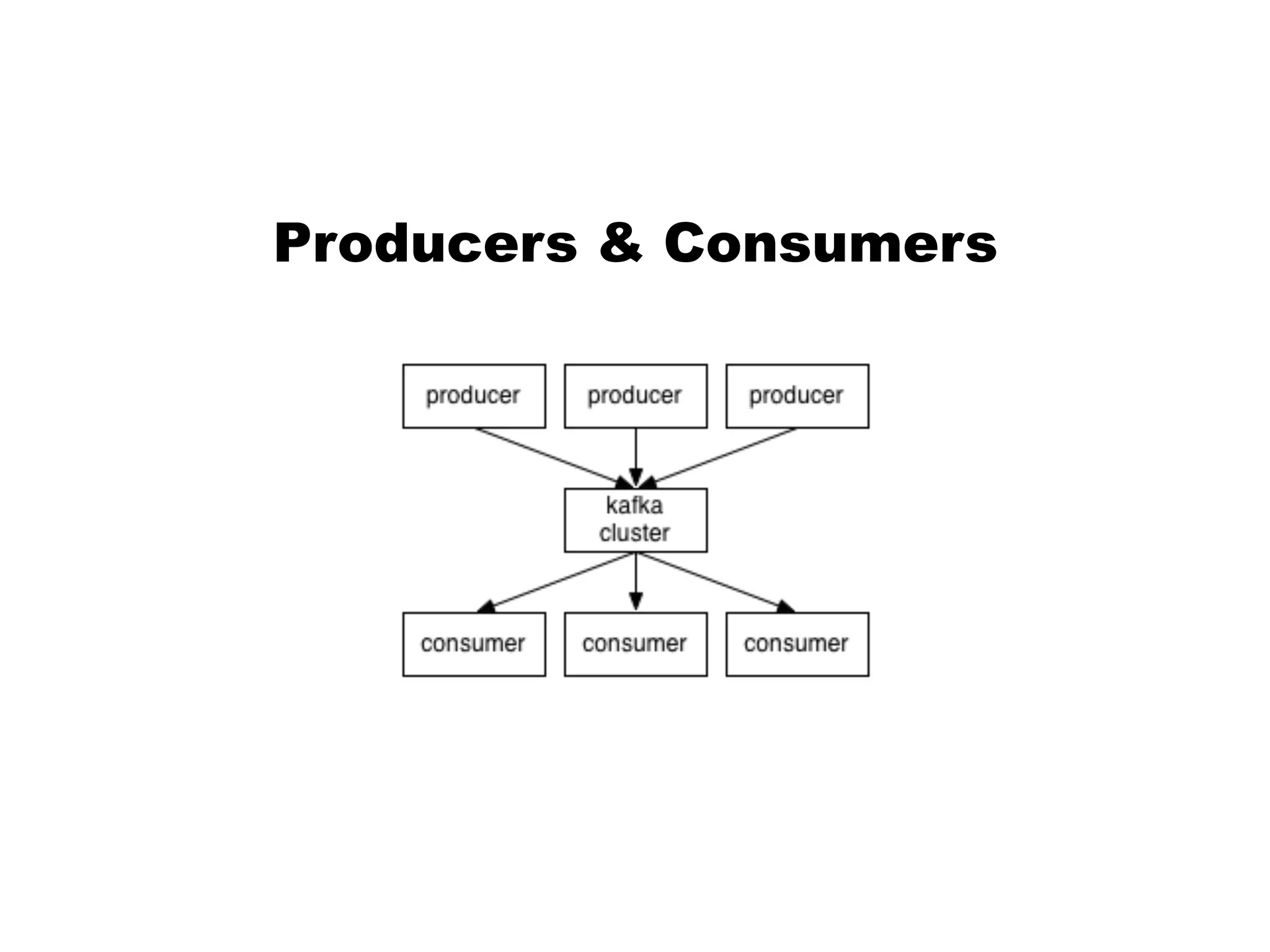
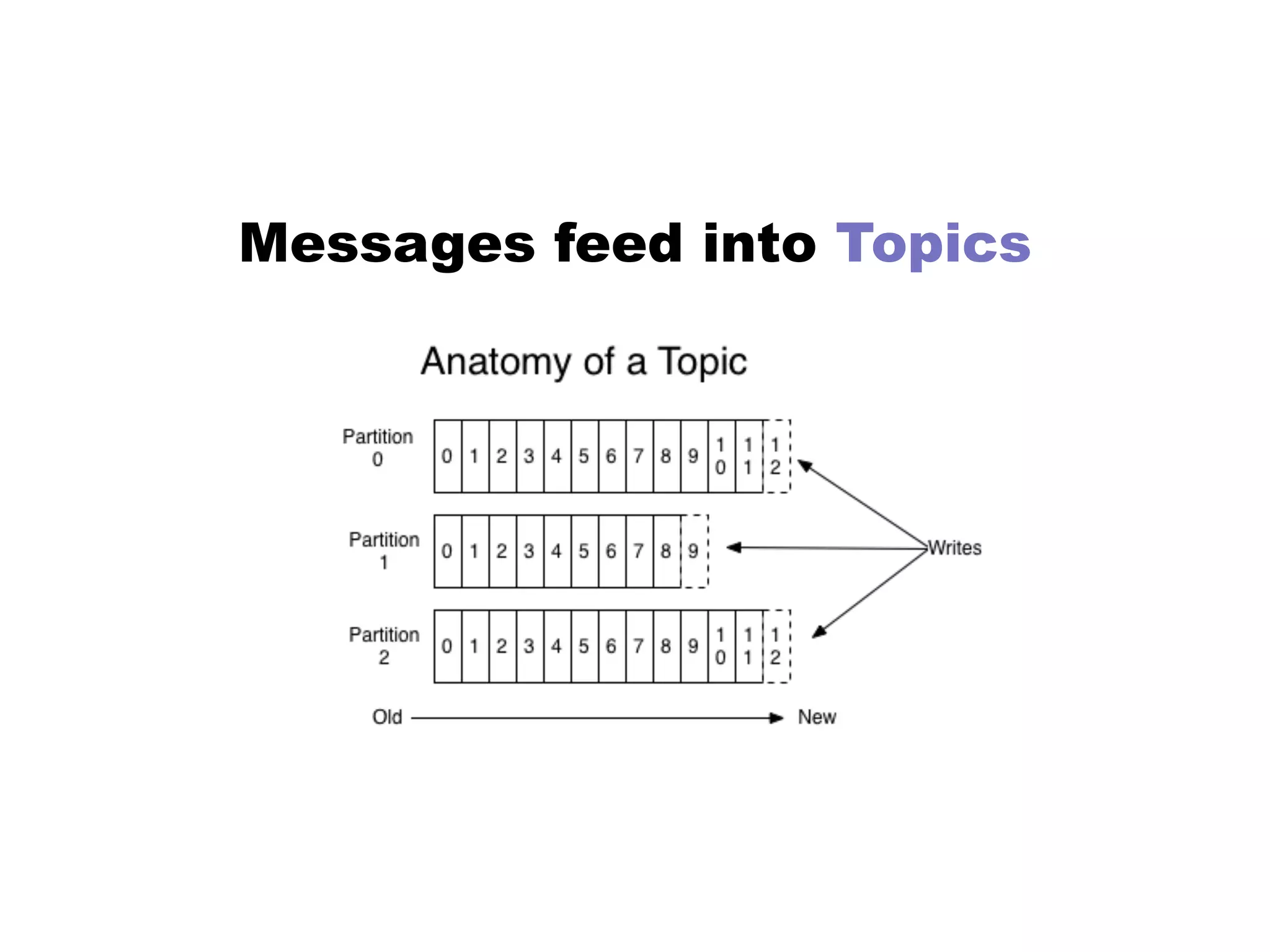
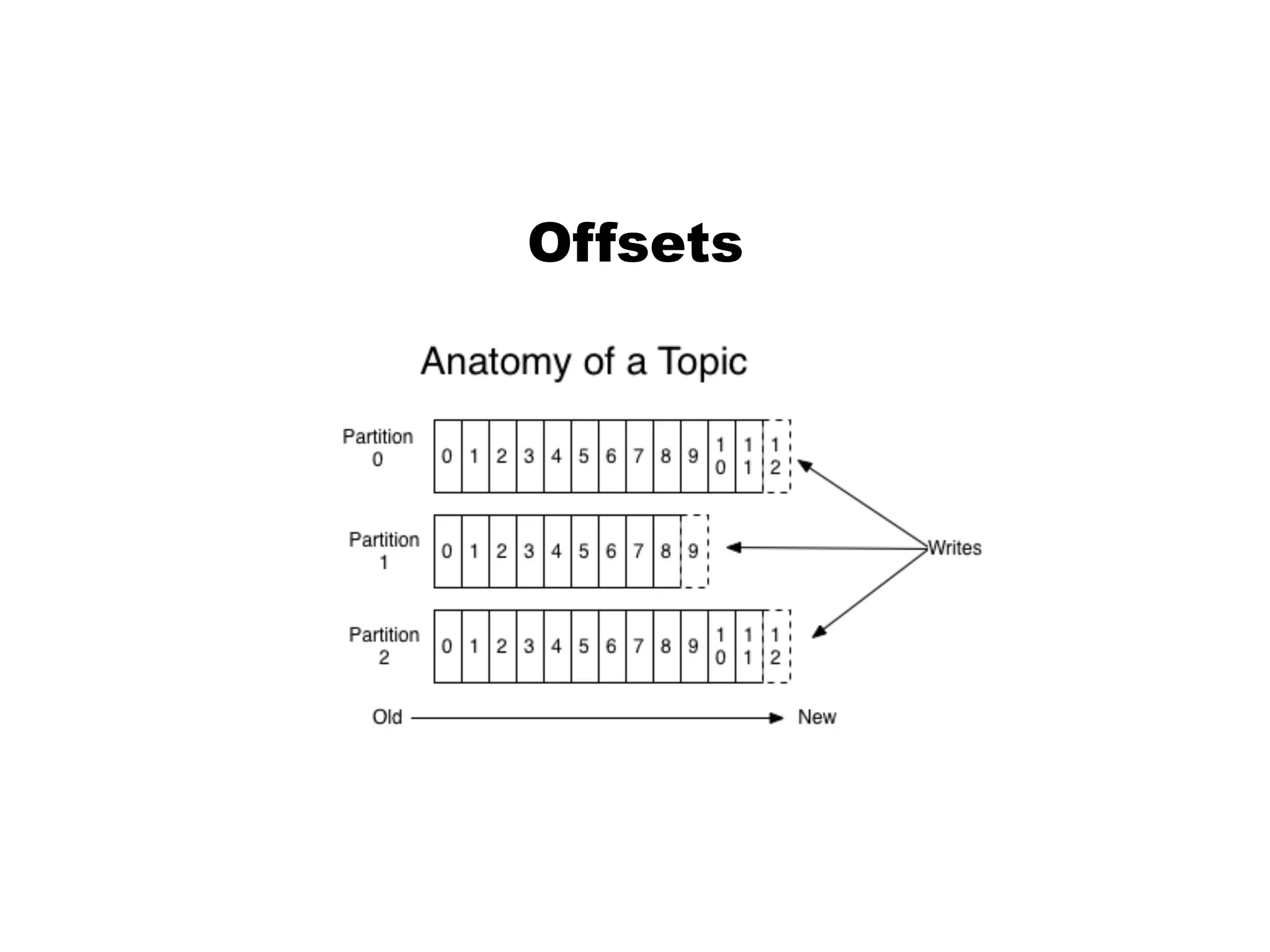
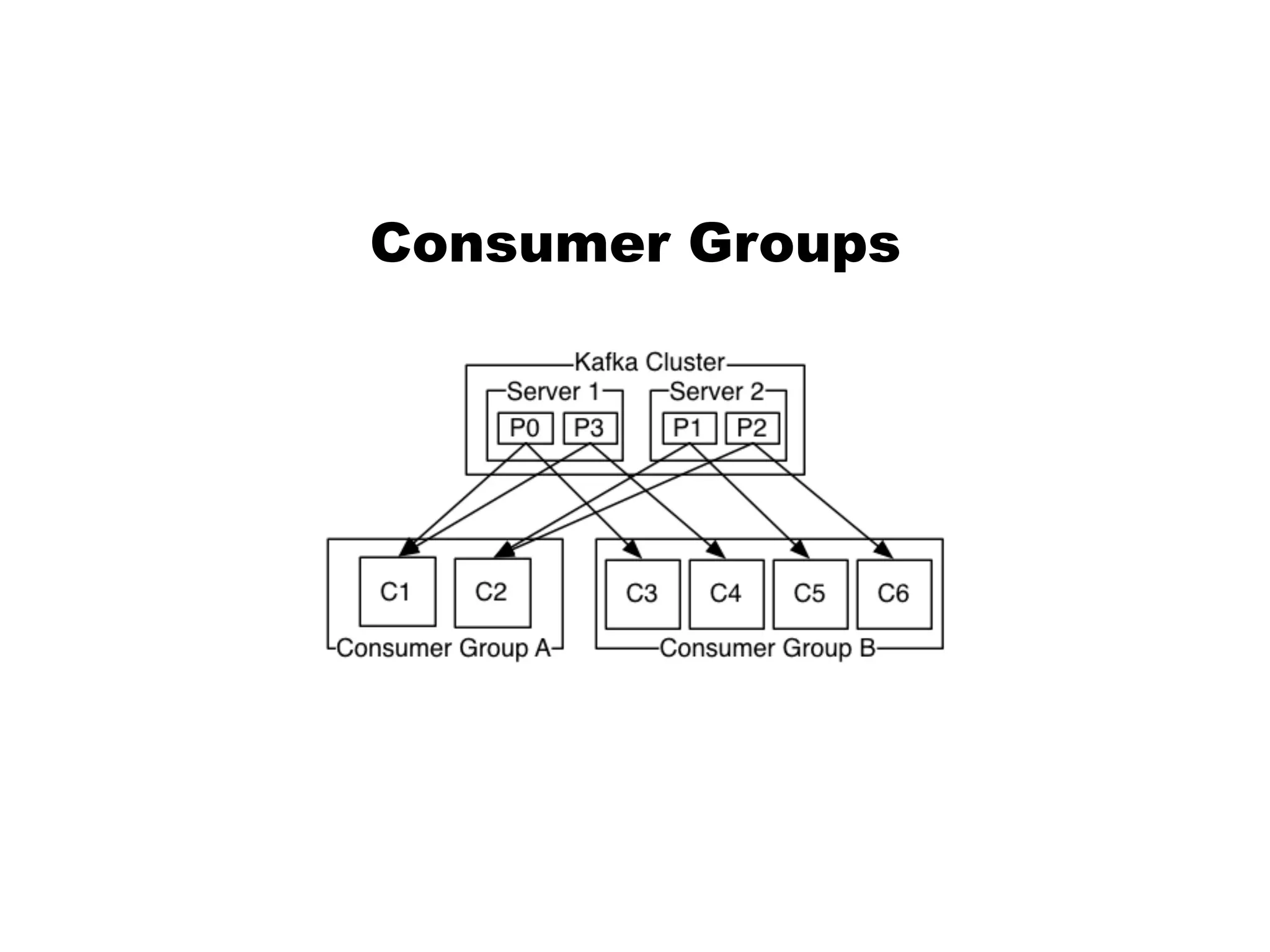
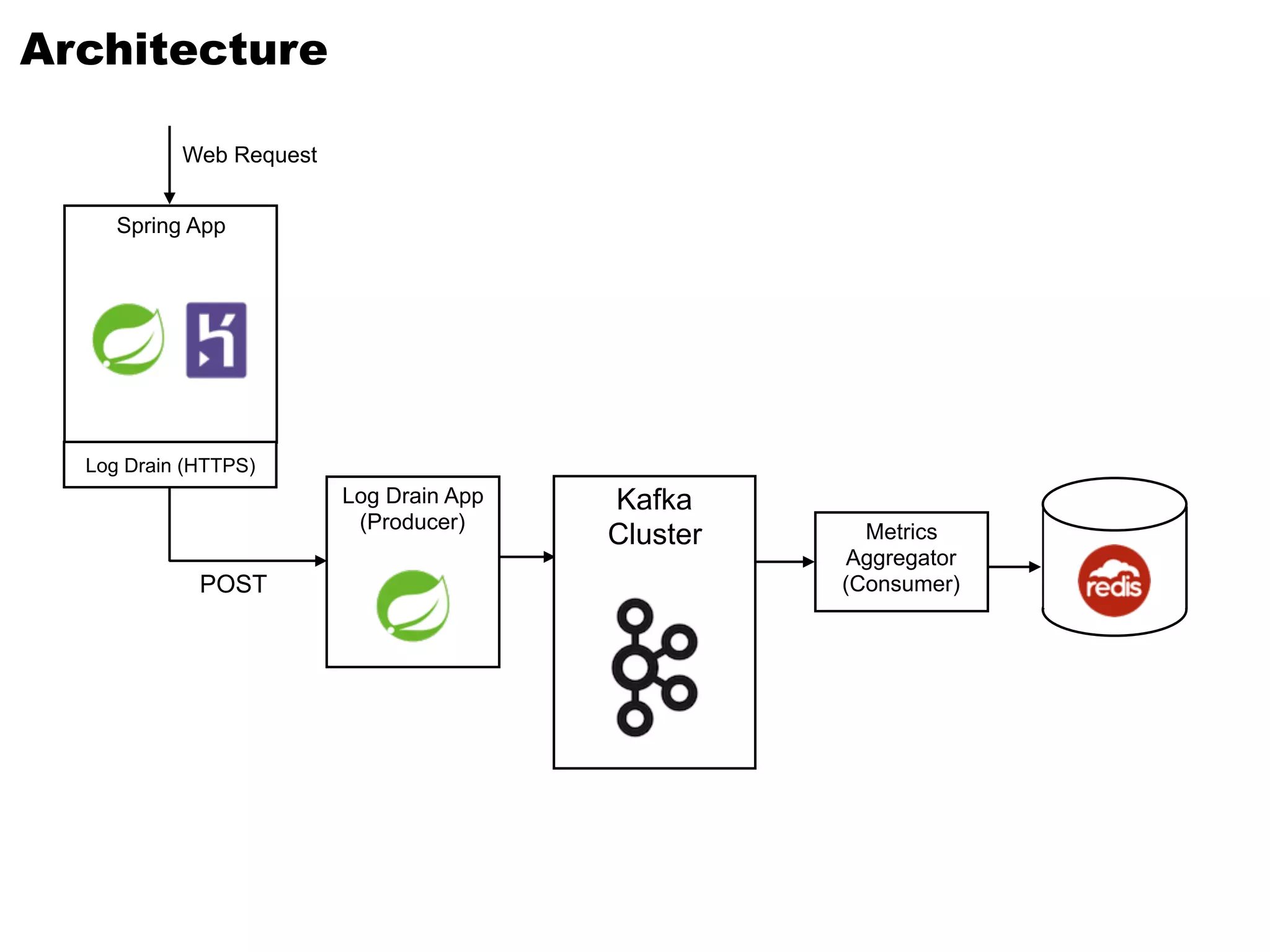
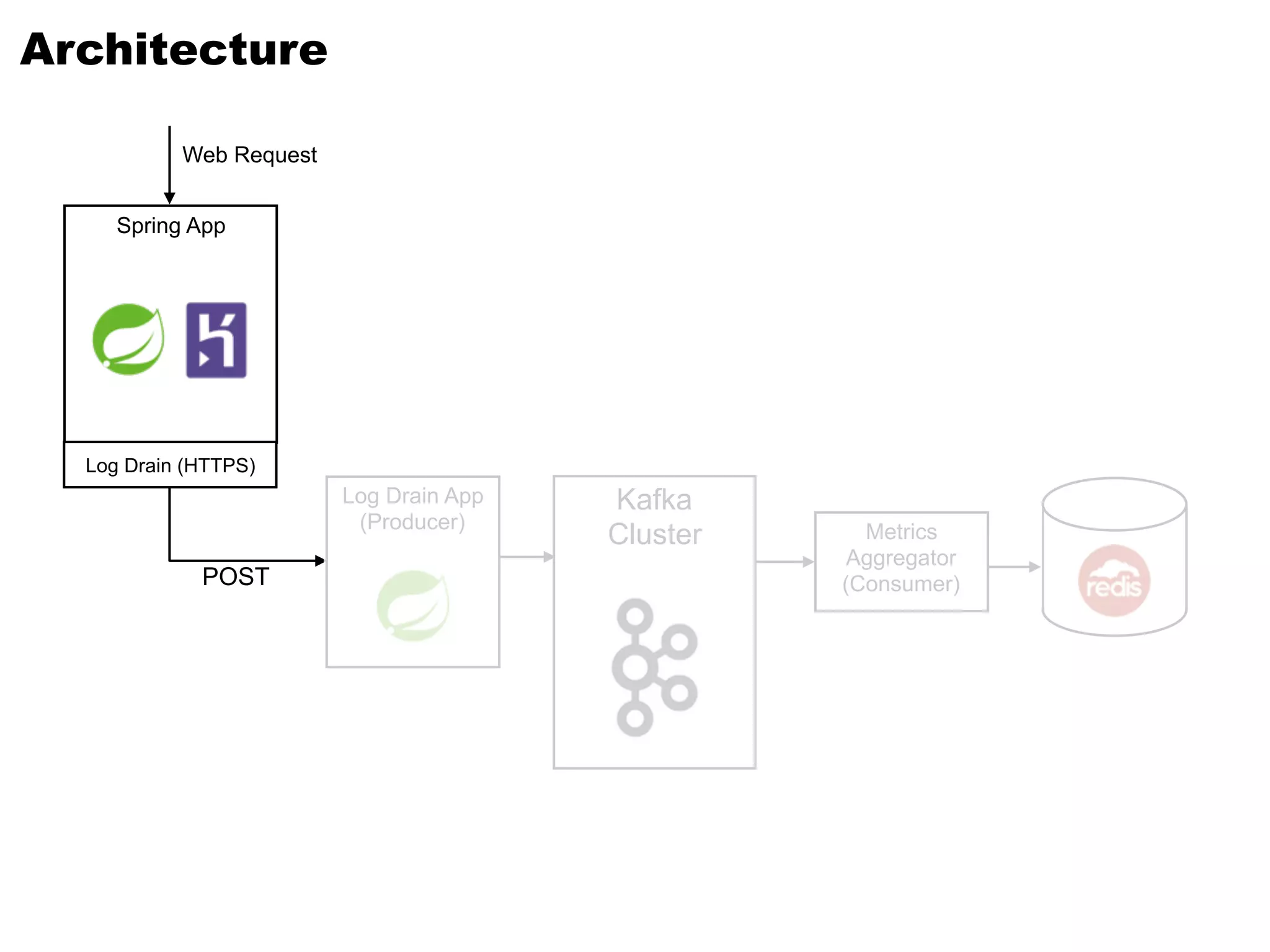
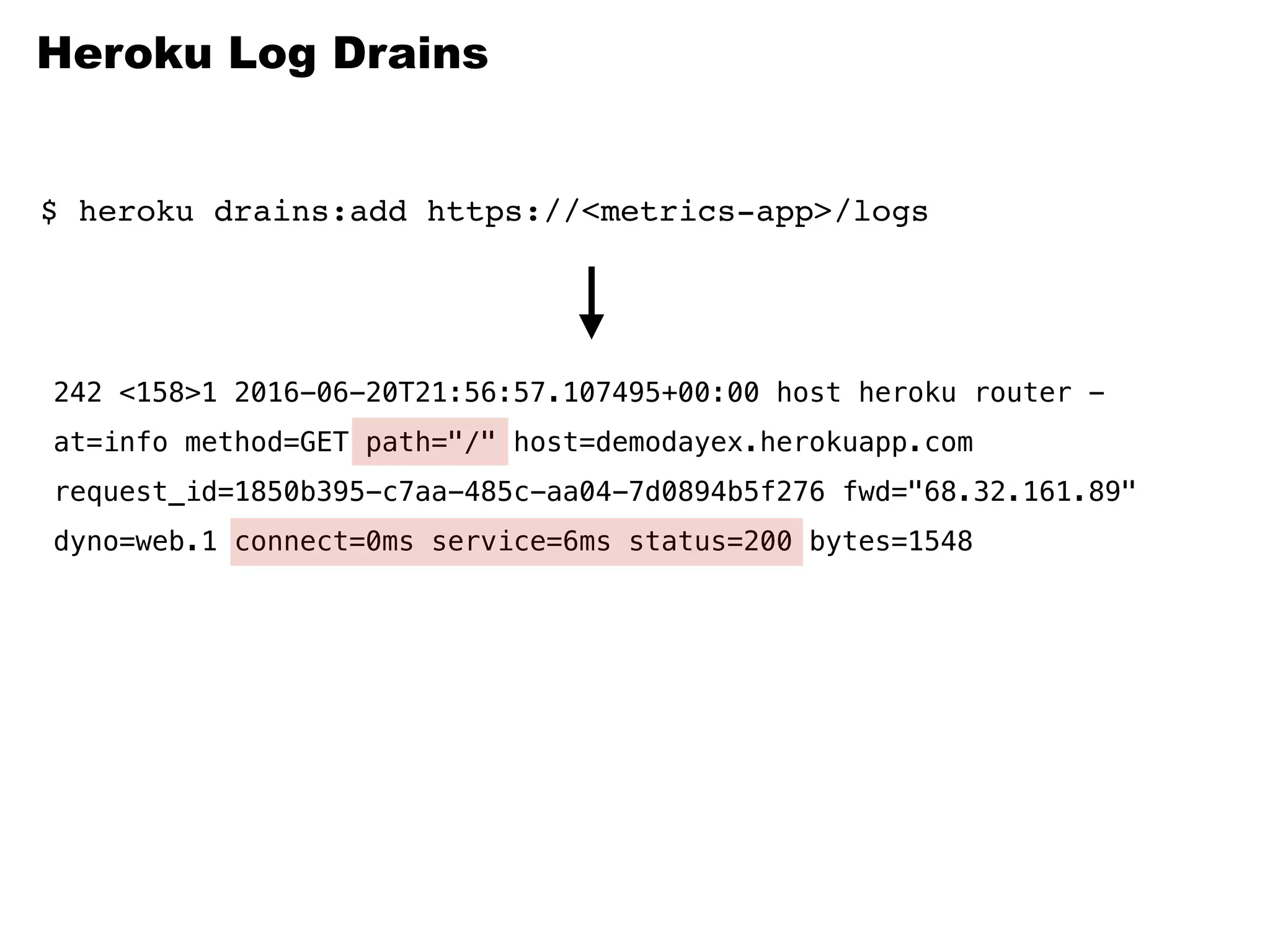
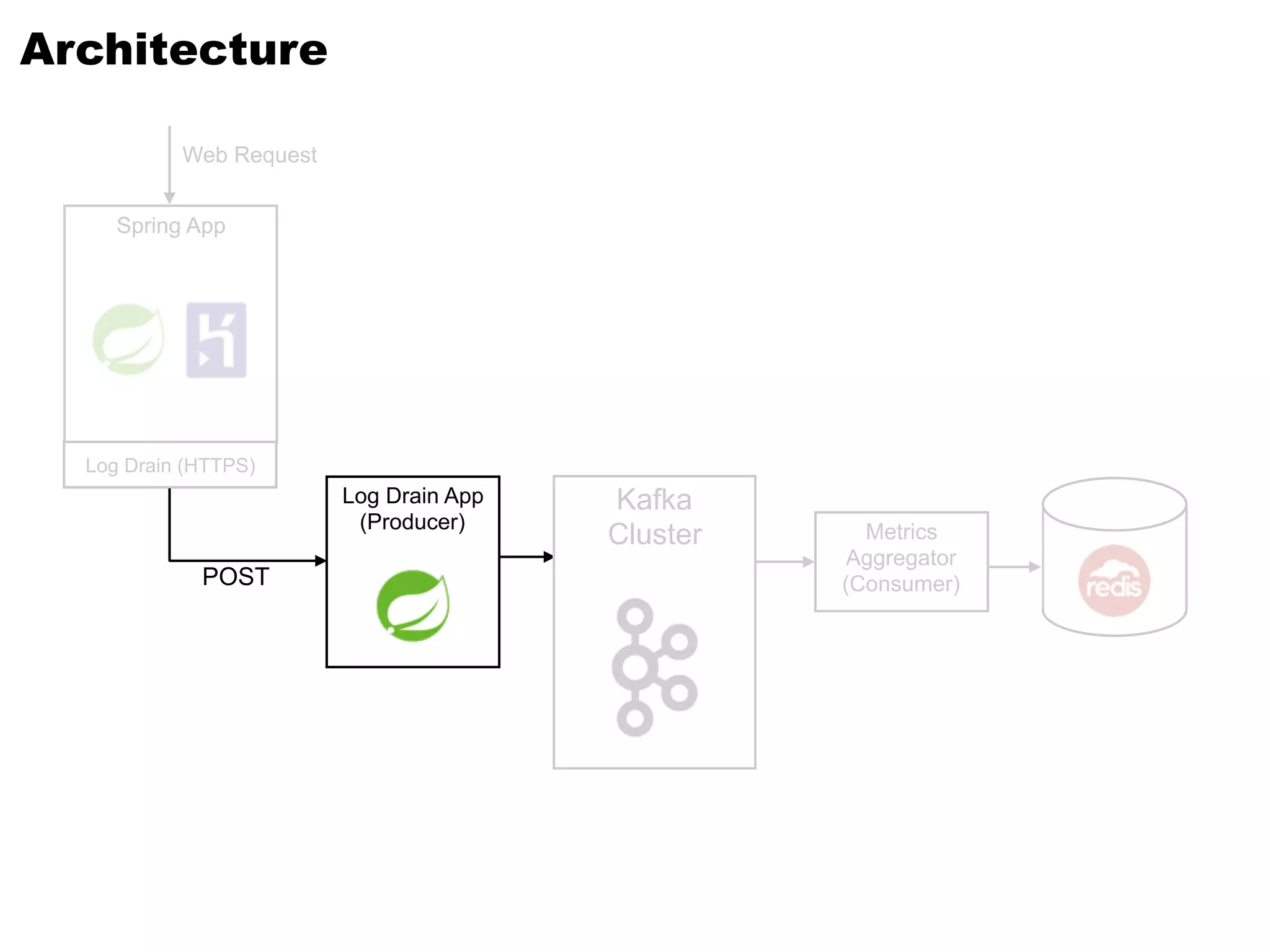
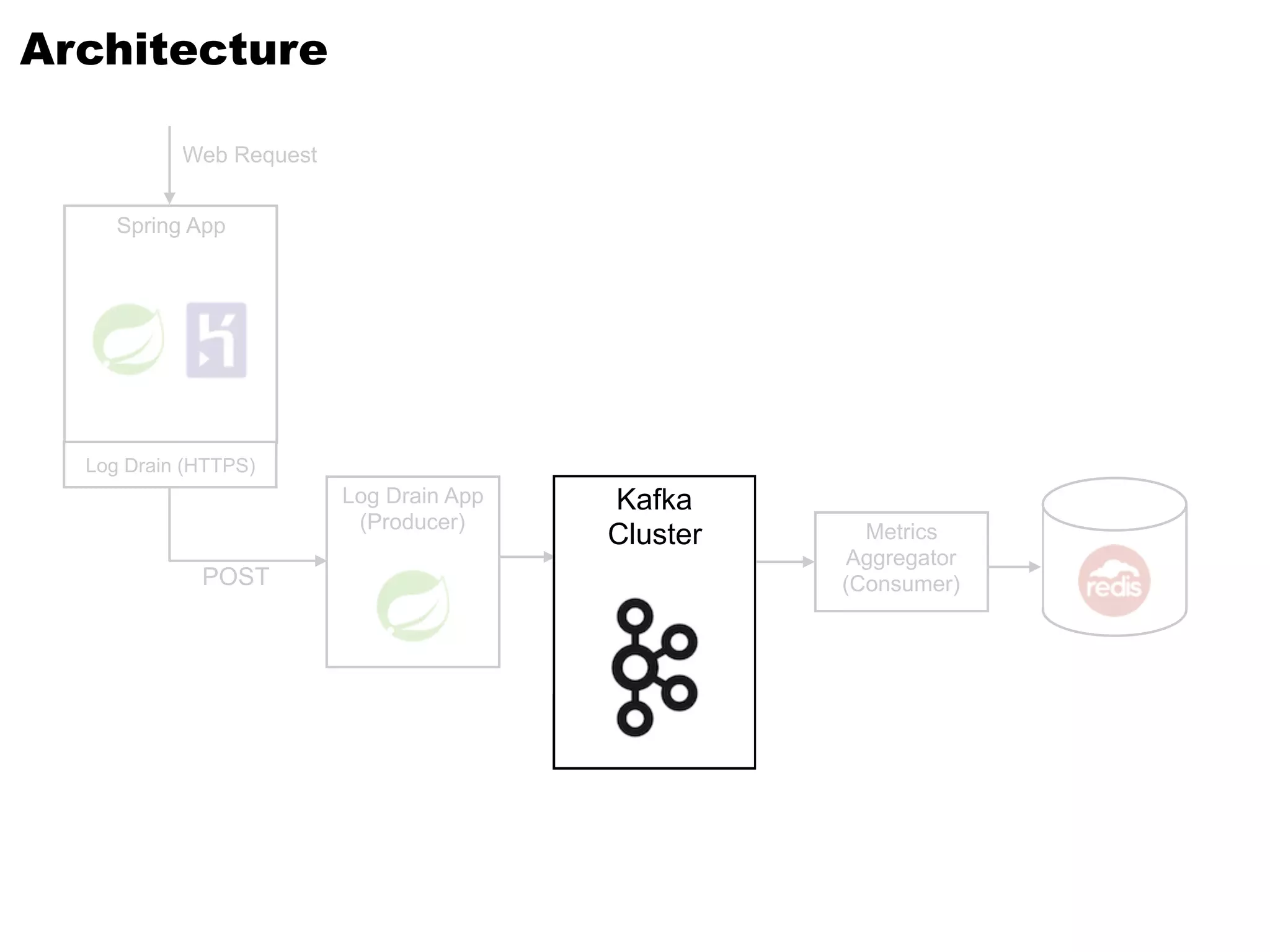
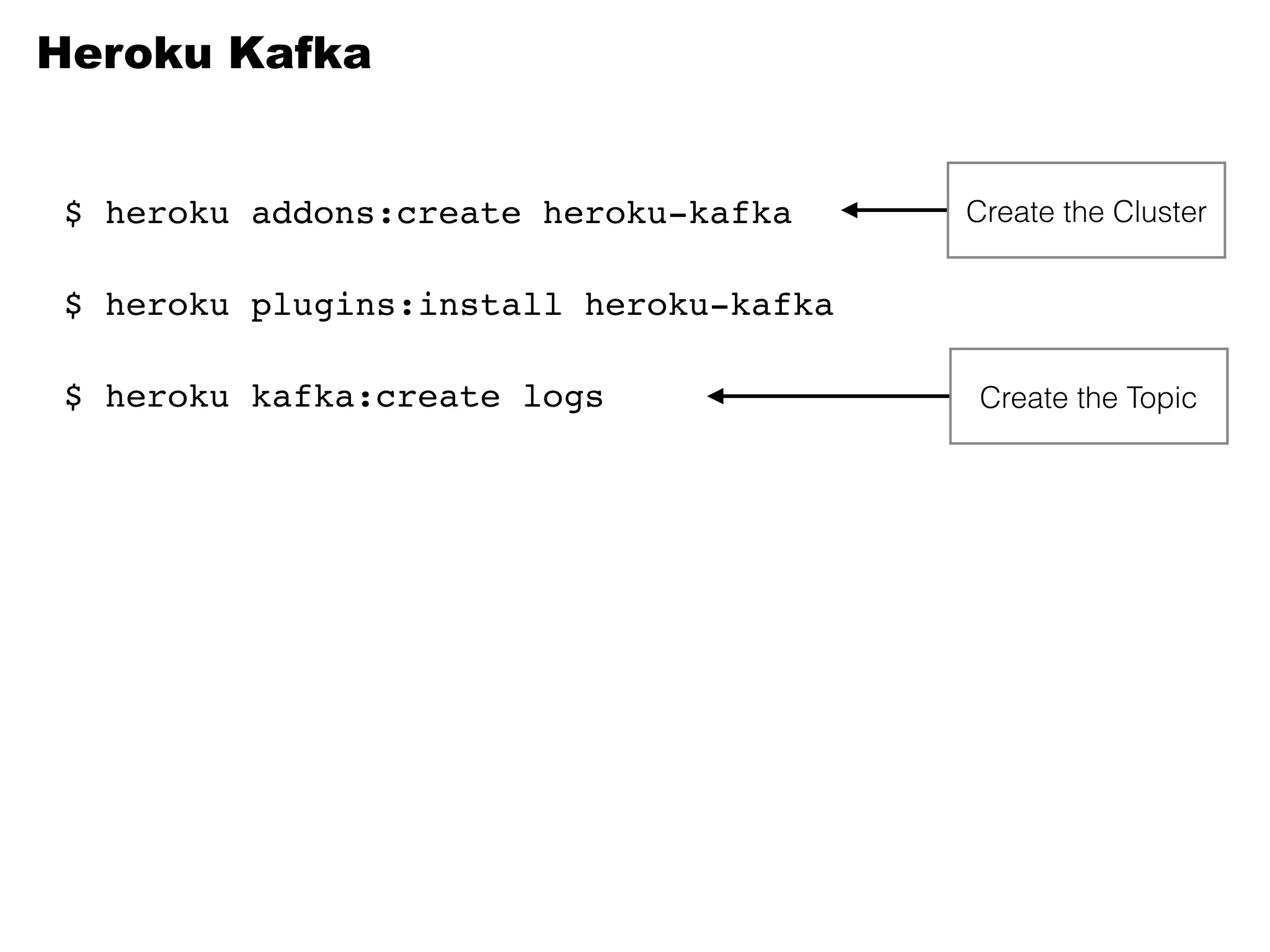
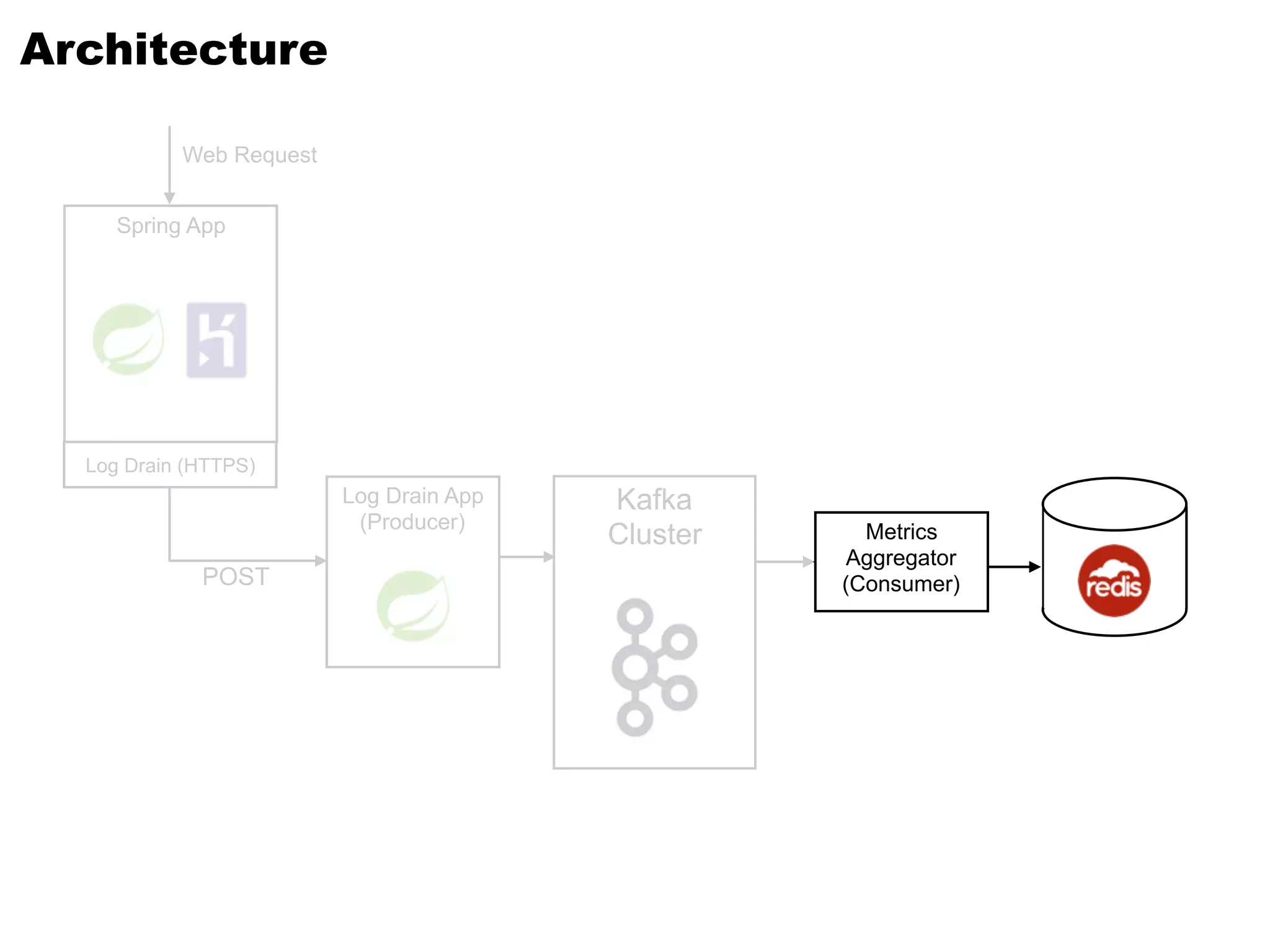
Kafka is a distributed streaming platform that allows for publishing and subscribing to streams of records. It provides functionality for building real-time data pipelines and streaming apps. The document discusses Kafka concepts like producers, consumers, topics, partitions and offsets. It also provides examples of using Kafka with Java and Spring, and describes how Heroku uses Kafka for logging and metrics aggregation.































![@RequestMapping(value = "/logs", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String logs(@RequestBody String body) throws IOException {
// "application/logplex-1" does not conform to RFC5424.
// It leaves out STRUCTURED-DATA but does not replace it with
// a NILVALUE. To workaround this, we inject empty STRUCTURED-DATA.
String[] parts = body.split("router - ");
String log = parts[0] + "router - [] " + (parts.length > 1 ? parts[1] : "");
RFC6587SyslogDeserializer parser = new RFC6587SyslogDeserializer();
InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(log.getBytes());
Map<String, ?> messages = parser.deserialize(is);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(messages);
template.send("logs", json);
return "ok";
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kafka-160919232826/75/I-can-t-believe-it-s-not-a-queue-Kafka-and-Spring-45-2048.jpg)


![public class Metrics {
// ...
public static void main(String[] args) { /* … */ }
public Metrics() throws Exception {
// ...
URI redisUri = new URI(System.getenv("REDIS_URL"));
pool = new JedisPool(redisUri);
}
private void start() {
// ...
running.set(true);
executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executor.submit(this::loop);
stopLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
}
}
Main Consumer Class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kafka-160919232826/75/I-can-t-believe-it-s-not-a-queue-Kafka-and-Spring-51-2048.jpg)