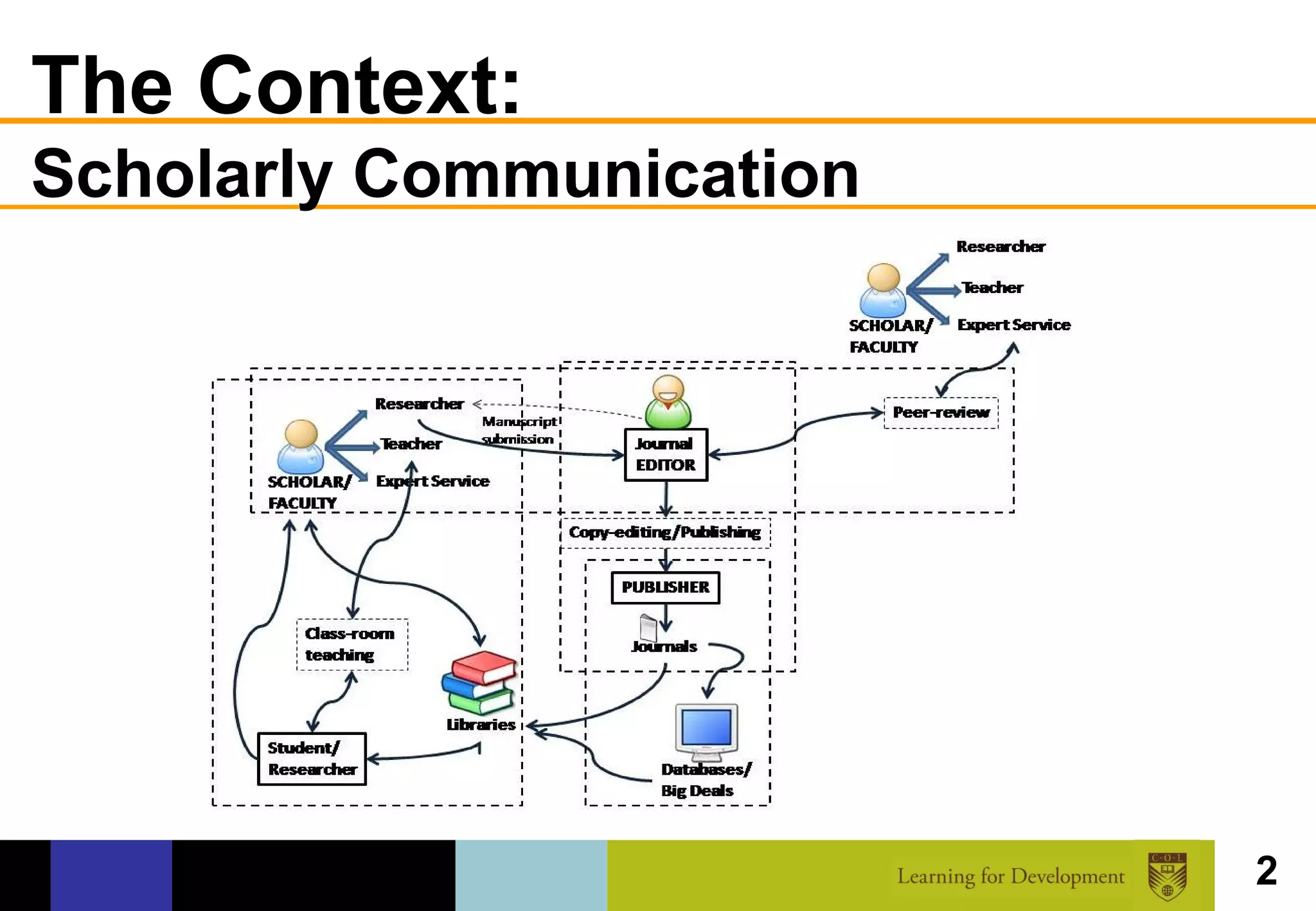
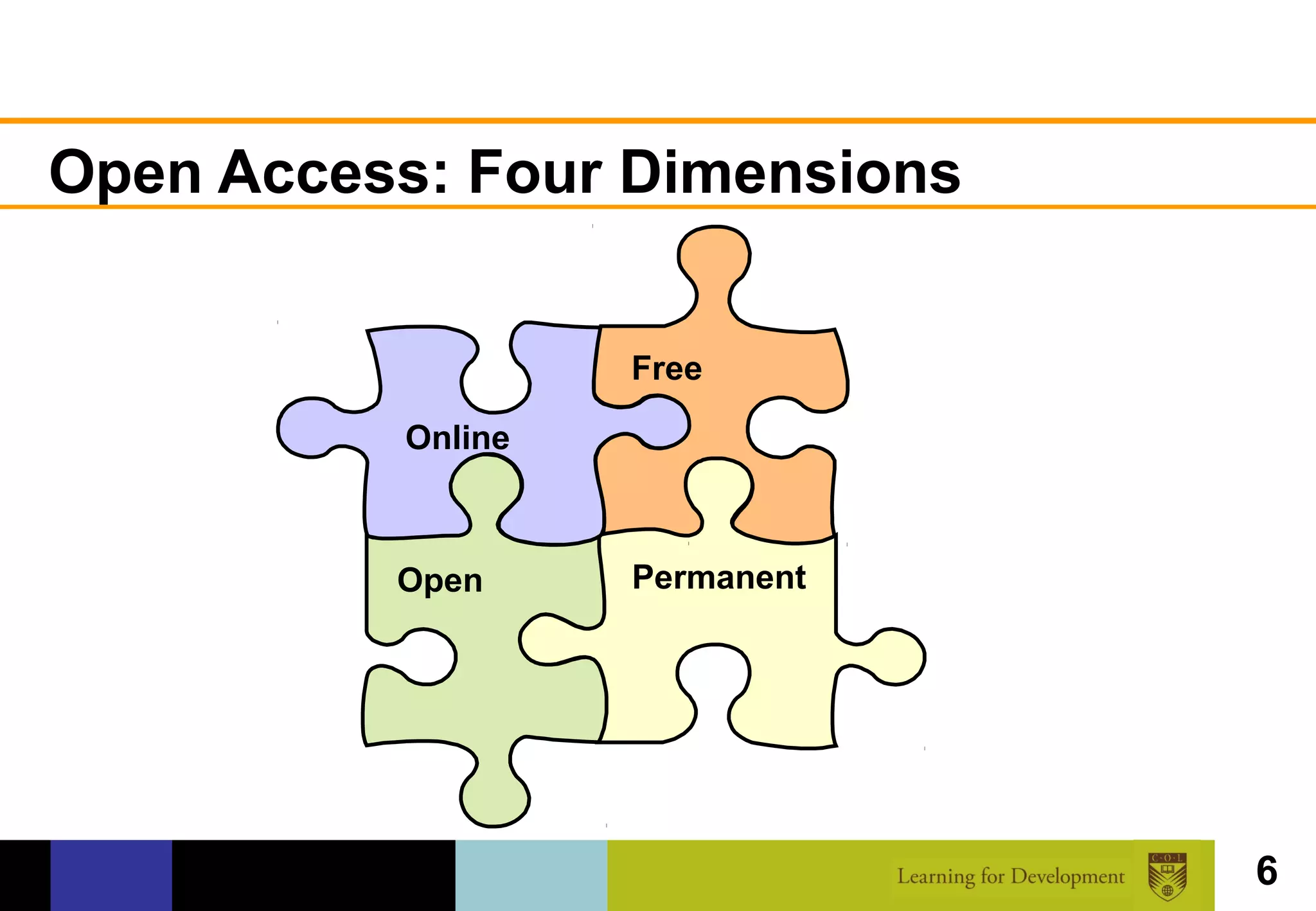
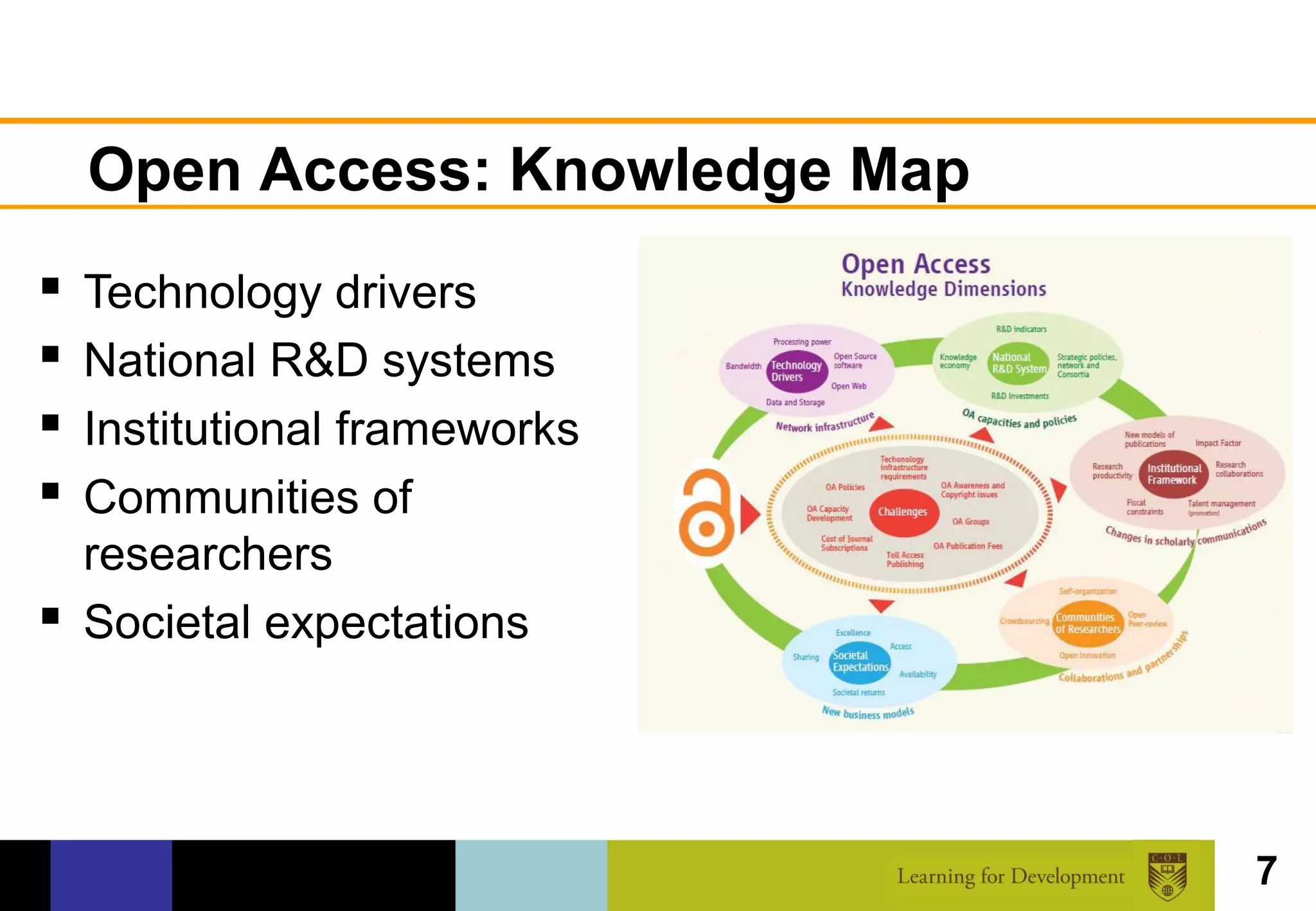
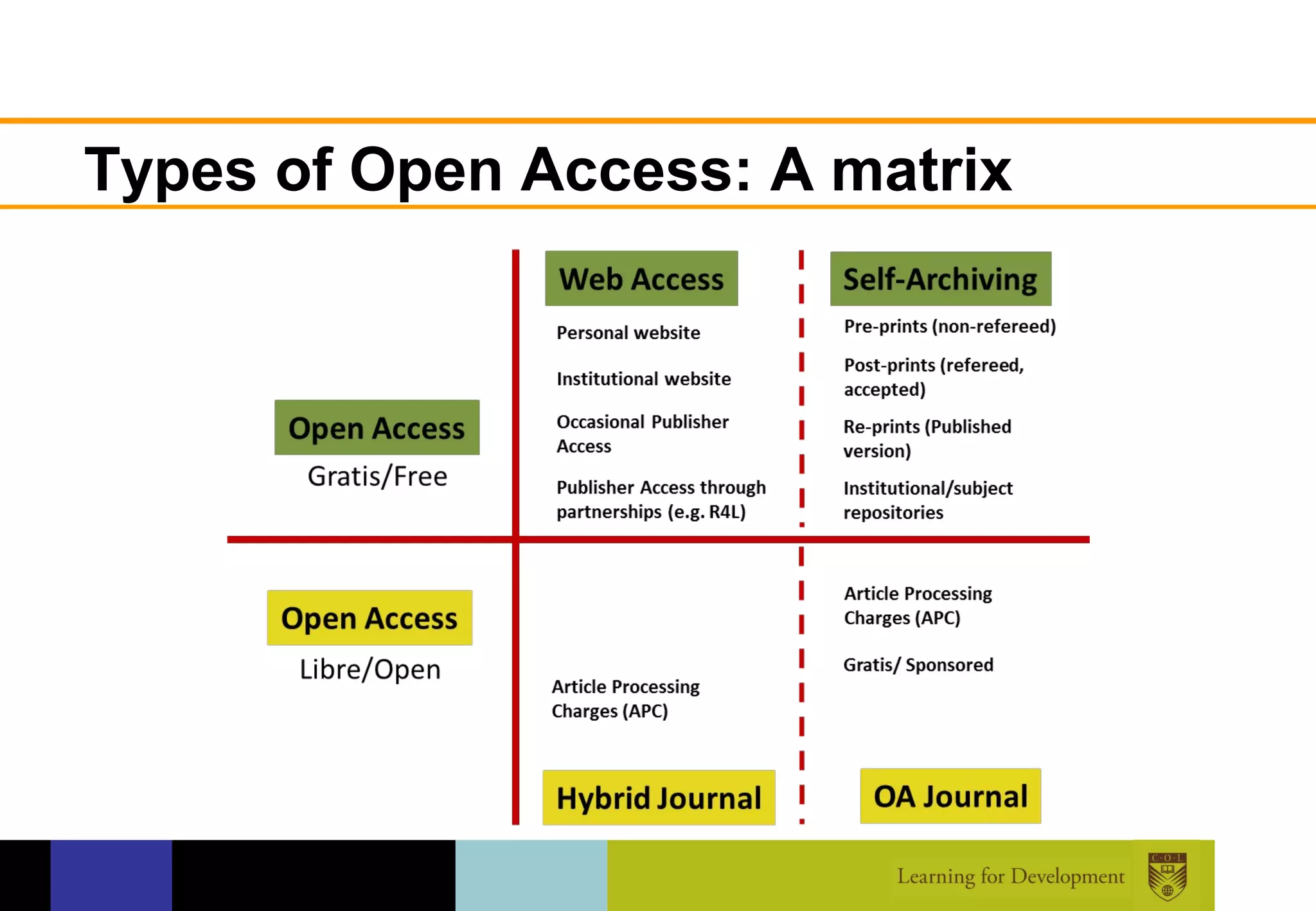
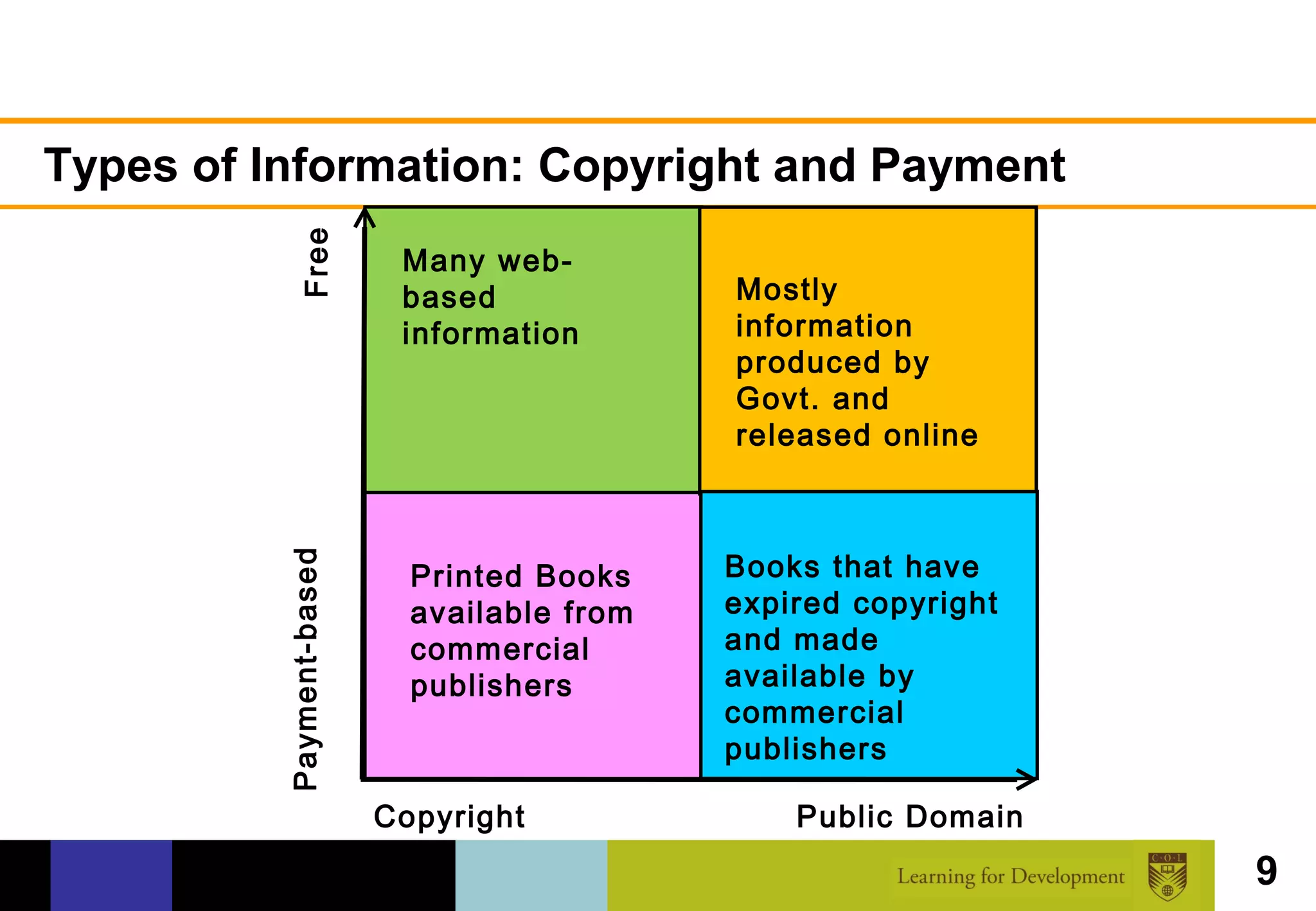
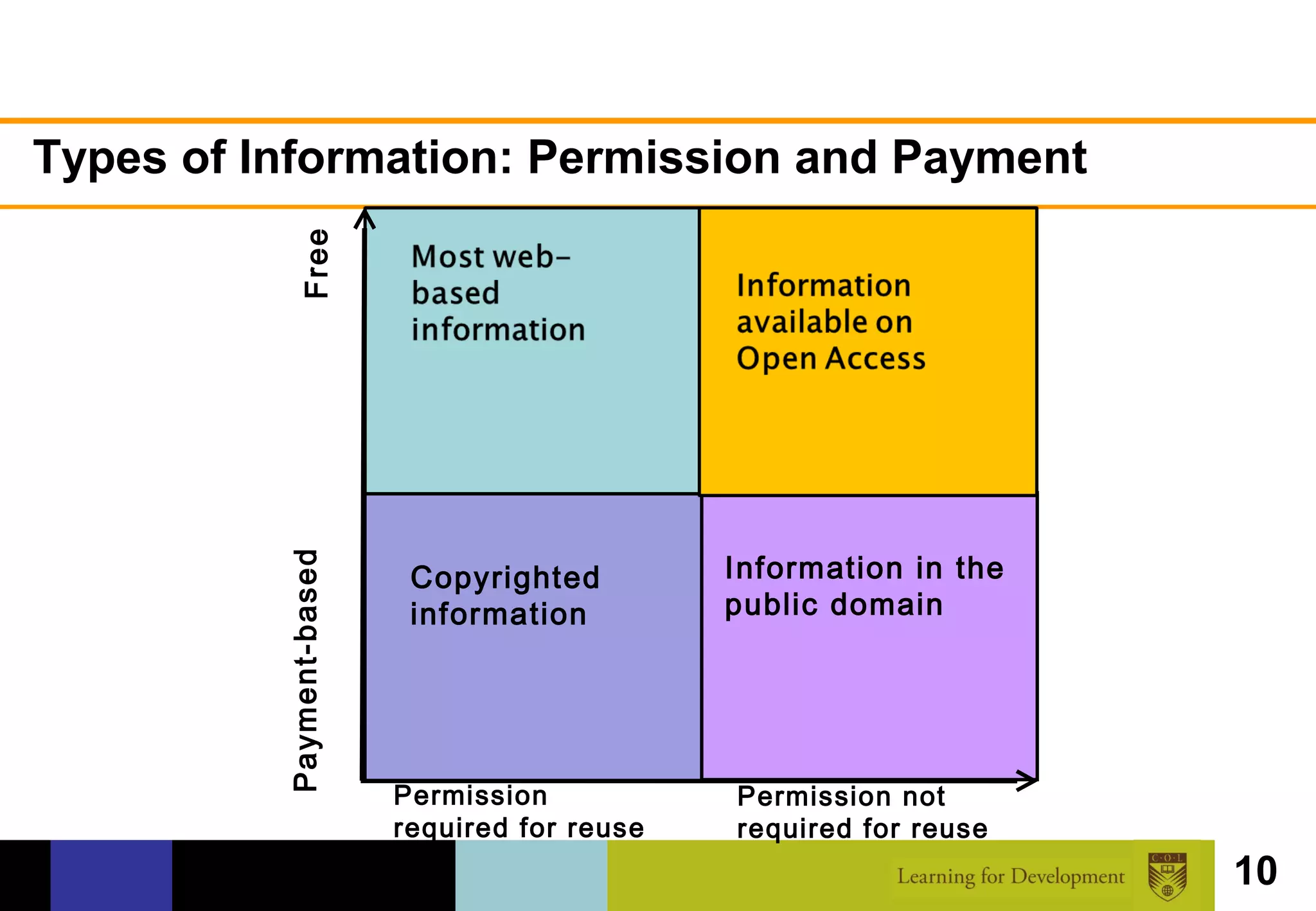
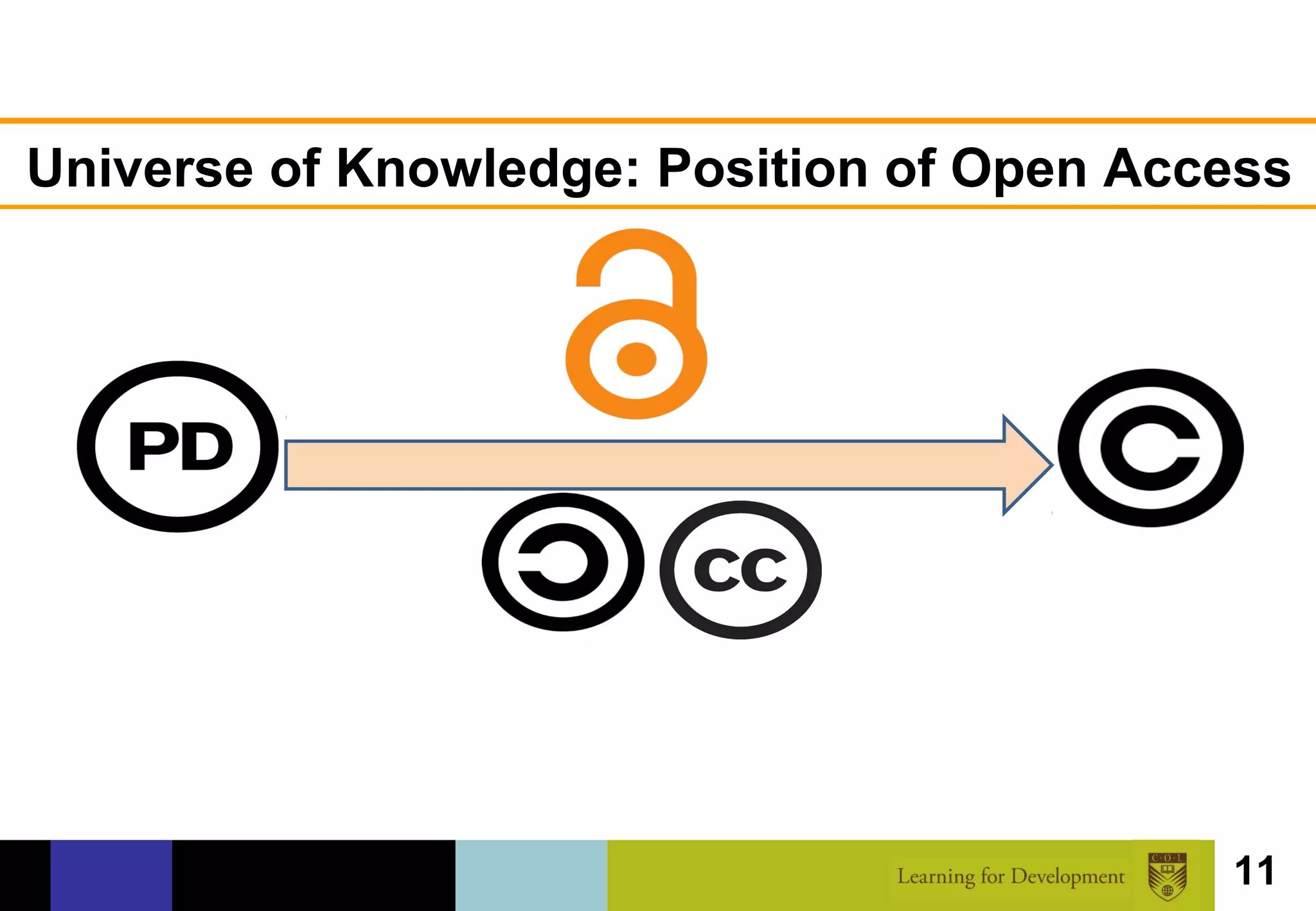
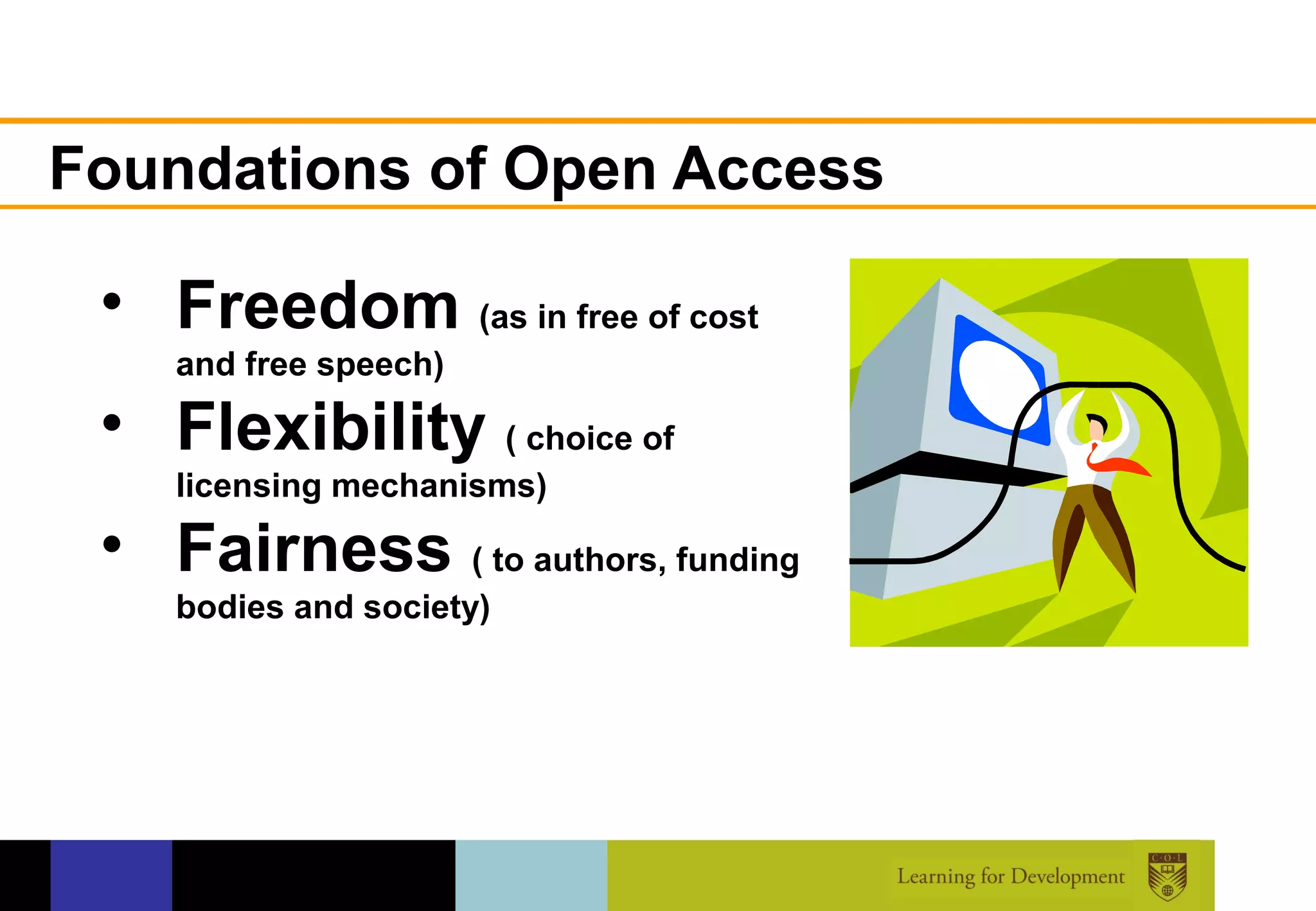
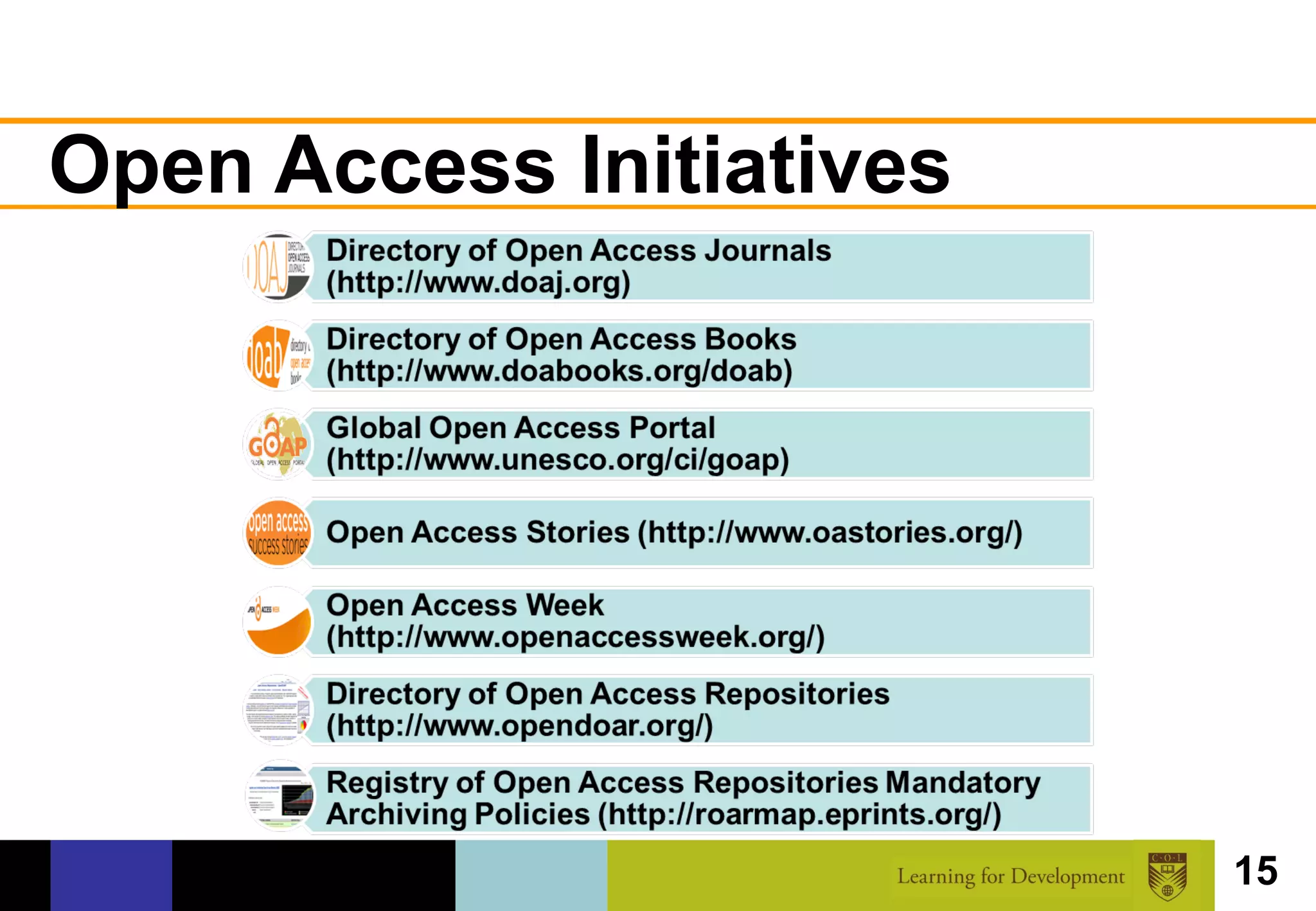
The document discusses the concept of open access within scholarly communication, emphasizing its role in providing free access to peer-reviewed research globally. It outlines the history, types, and foundational principles of open access, while identifying barriers to universal access such as censorship and language. Additionally, it encourages individuals and institutions to support and promote open access initiatives and repositories.