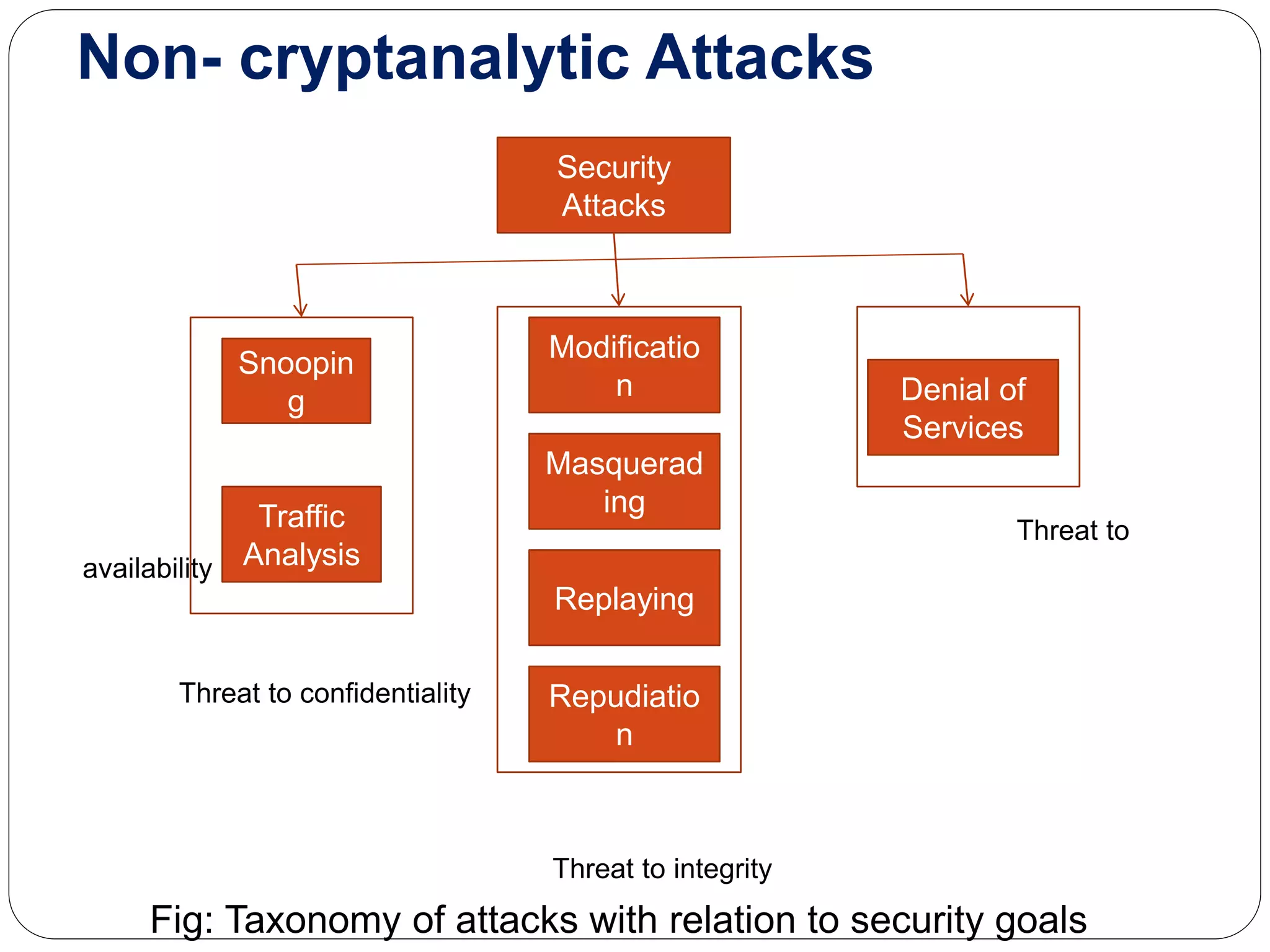
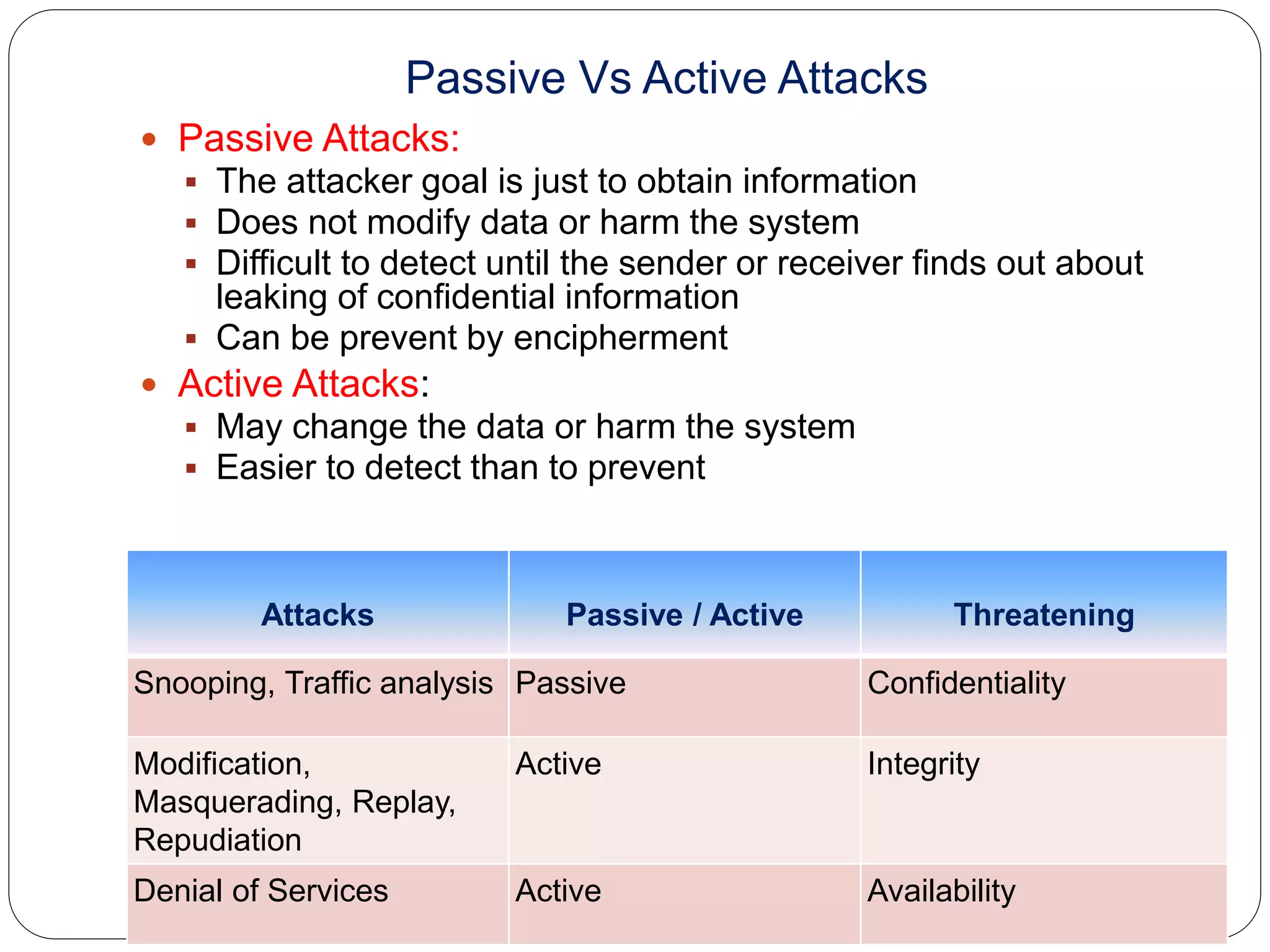
This document discusses information security goals of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It describes two types of cryptographic attacks: cryptanalytic attacks which try to ascertain a secret key through statistical or algebraic techniques, and non-cryptanalytic attacks which threaten the security goals. Non-cryptanalytic attacks include snooping, traffic analysis, modification, denial of services, repudiation, replaying, and masquerading. Attacks can be either passive, where the goal is just obtaining information without modifying data, or active, where the attacker may change data or harm the system. Passive attacks are difficult to detect while active attacks are easier to detect.