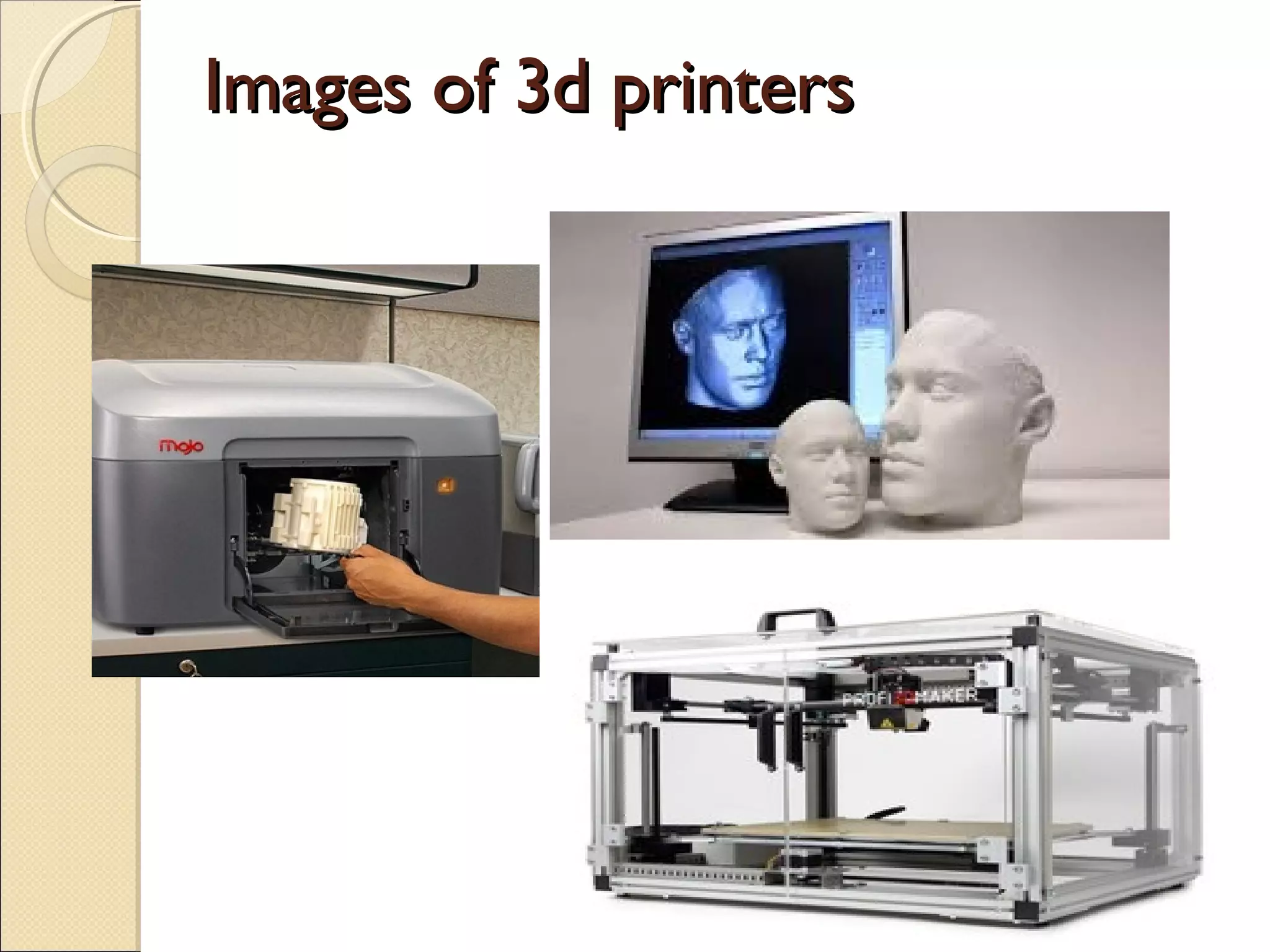
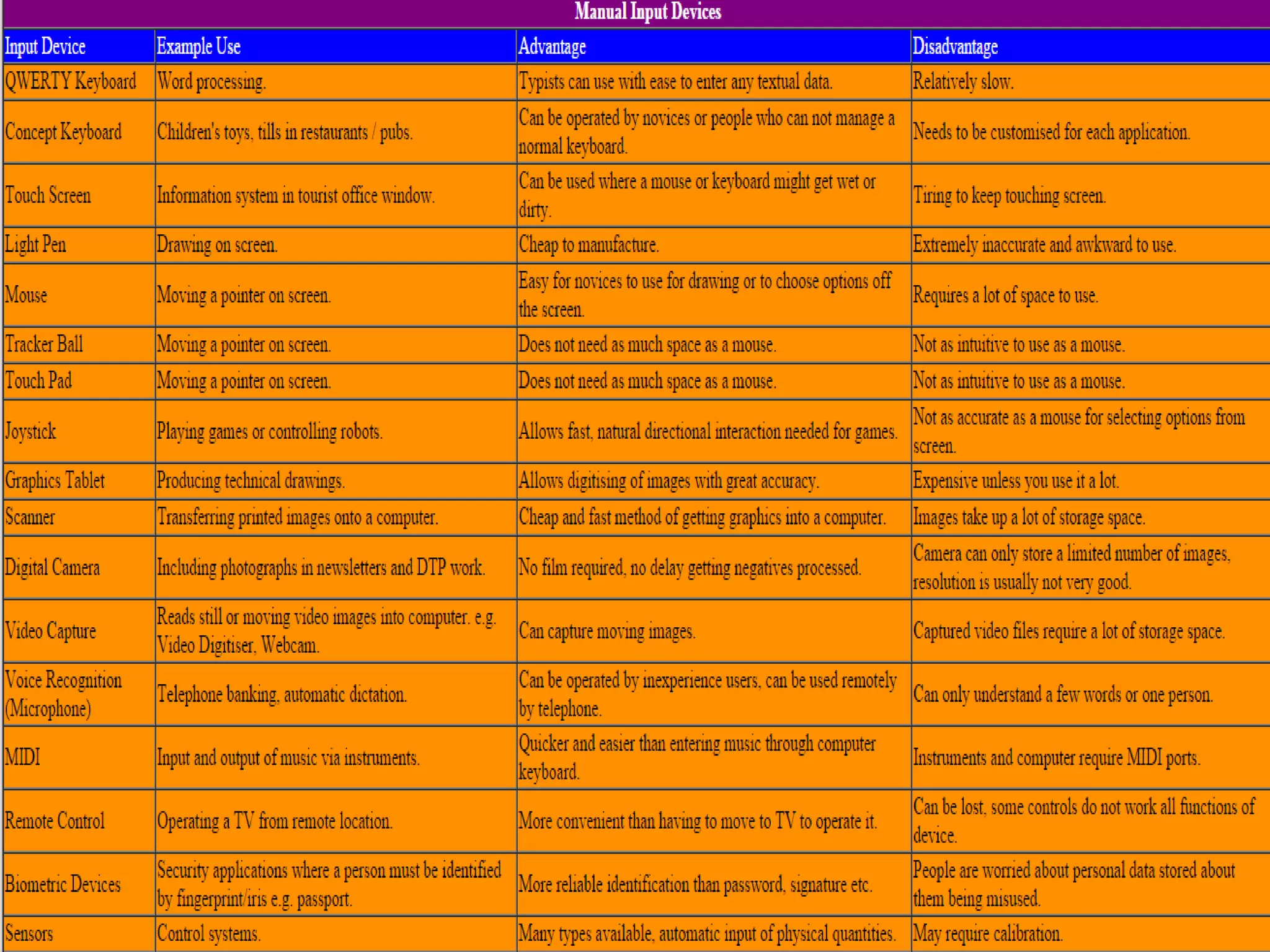
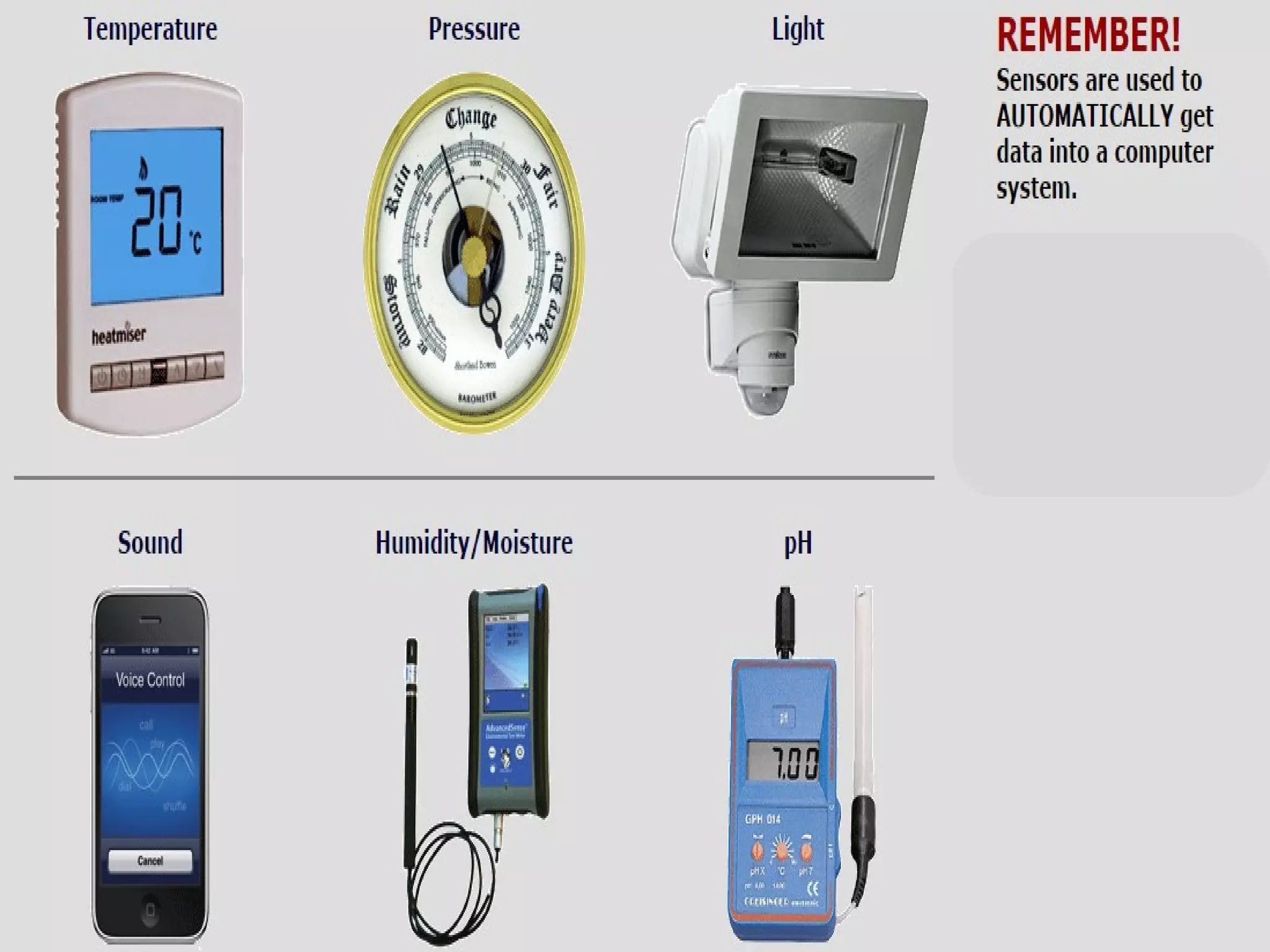
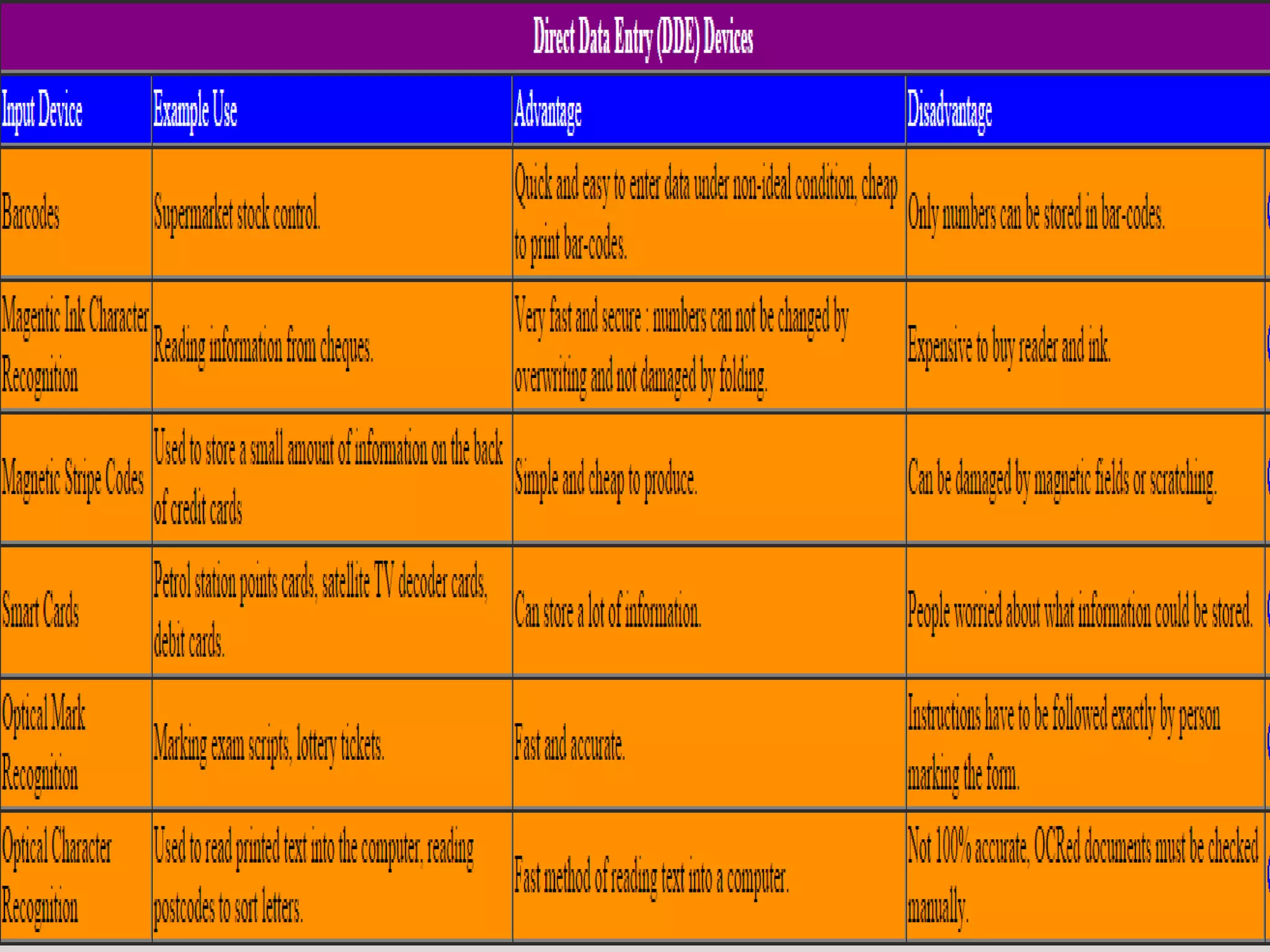
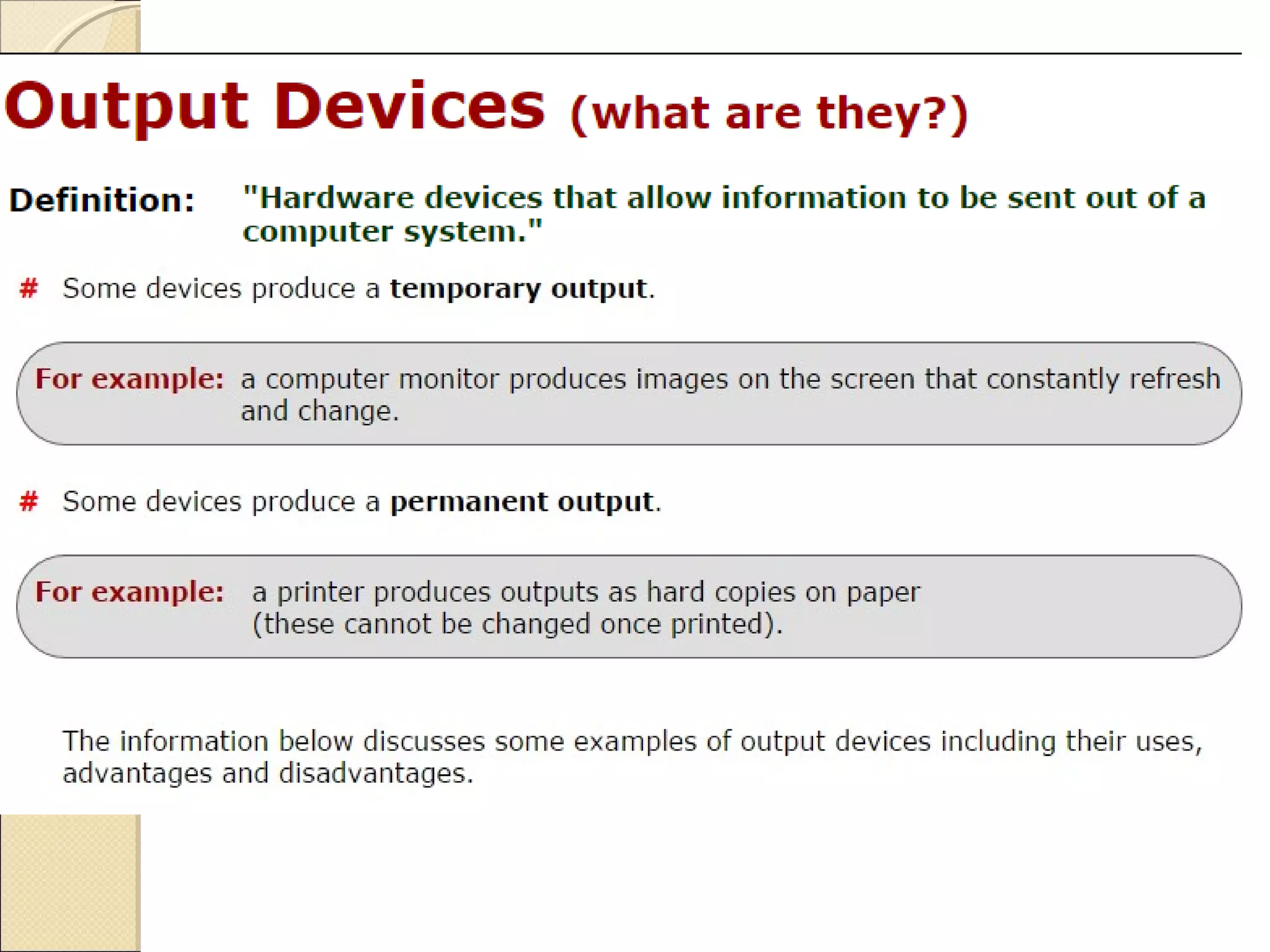
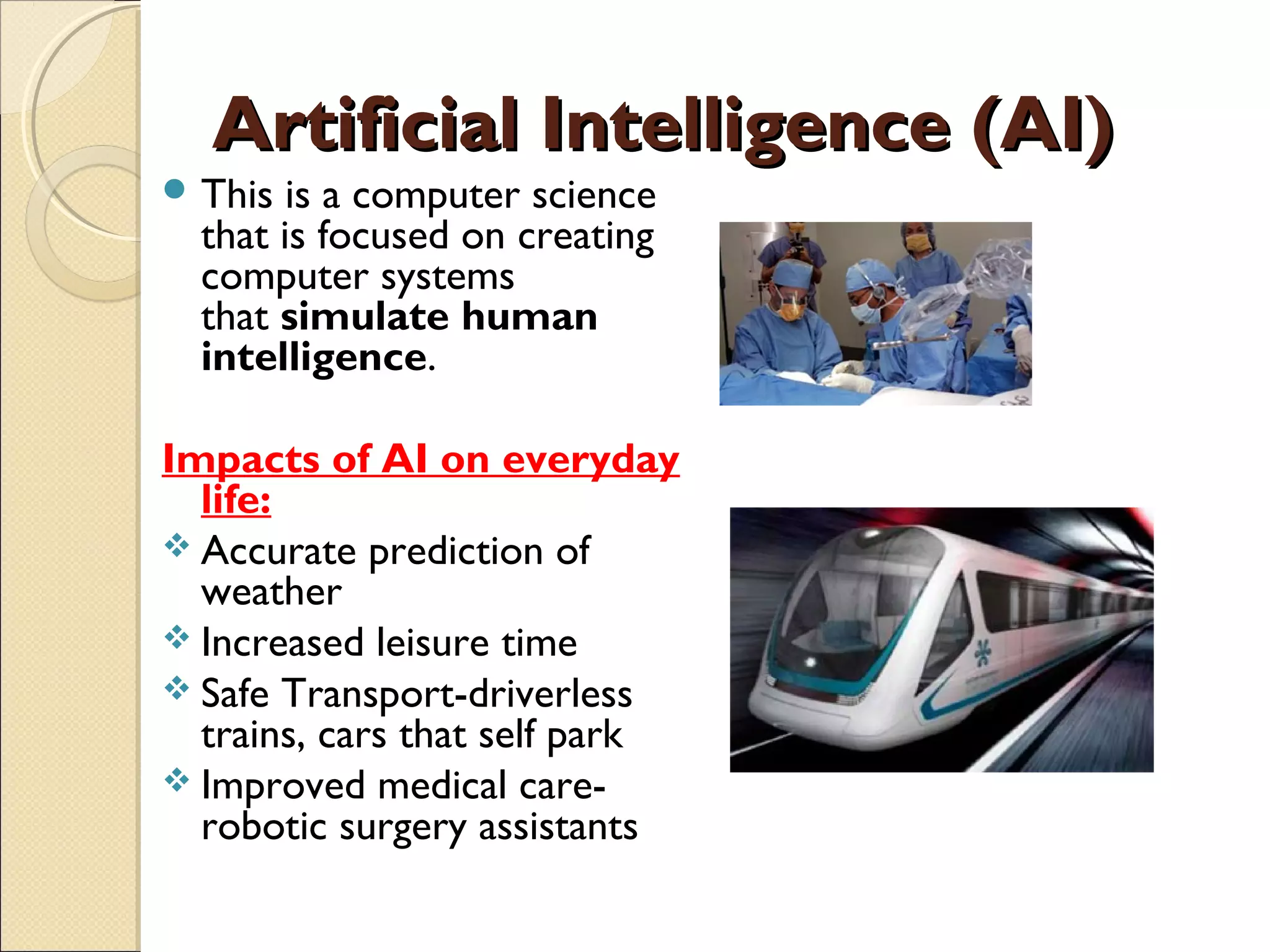
The document discusses various input and output devices as well as new technologies. It describes manual input devices that require human entry of data and direct data entry devices that transfer information automatically. Key criteria for comparing input devices are outlined. Examples of input devices include keyboards, mice, scanners, and cameras. Output devices discussed include printers, monitors, and 3D printers. New technologies summarized include artificial intelligence, biometrics, quantum cryptography, computer assisted translation, virtual reality, and 3D/holographic imaging. Their applications and impacts on everyday life are briefly described.