The document provides an overview of intermediate PHP, focusing on arrays, functions, and object-oriented programming. It explains key concepts such as associative and enumerative arrays, array manipulation, sorting functions, user-defined functions, and object properties. Additionally, it touches on class design, type hinting, interfaces, and the use of magic methods.




![<?php
$post = array(
'id' => 1234,
'title' => 'Intermediate PHP',
// …
);
echo $post['title']; // Intermediate PHP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-6-2048.jpg)
![<?php
$post = array(
'id' => 1234,
'title' => 'Intermediate PHP',
// …
);
$post['title'] = 'PHP 201';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-7-2048.jpg)
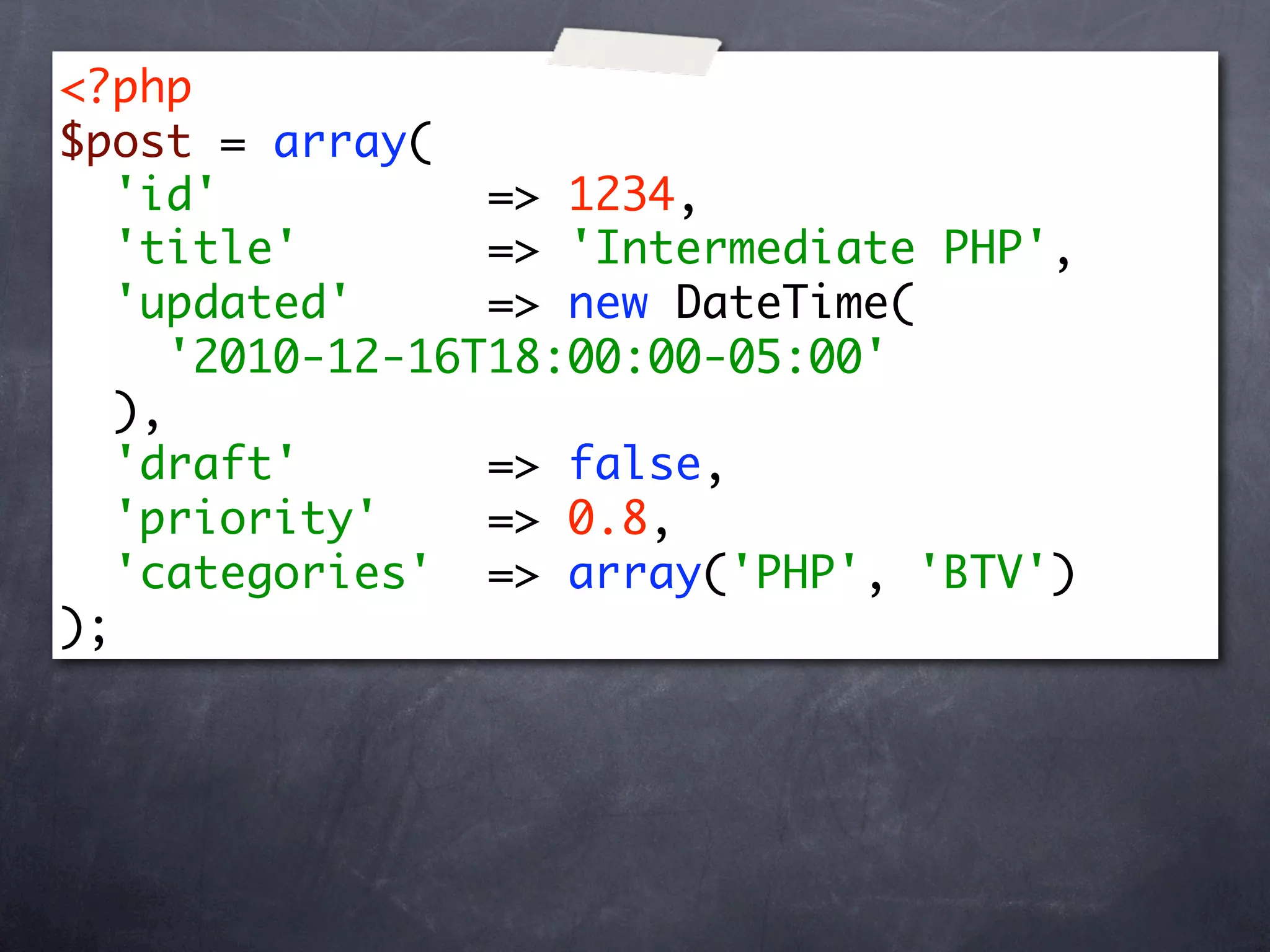
![<?php
$post = array(
'id' => 1234,
'title' => 'Intermediate PHP',
'updated' => new DateTime(
'2010-12-16T18:00:00-05:00'
),
'draft' => false,
'priority' => 0.8,
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
$post['summary'] = 'Arrays, functions, and
objects';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-8-2048.jpg)
![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
$post['categories'][] = 'Programming';
print_r($post['categories']);
/*
Array
(
[0] => PHP
[1] => BTV
[2] => Programming
)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-9-2048.jpg)
![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
$post['categories'][1] = 'Burlington';
print_r($post['categories']);
/*
Array
(
[0] => PHP
[1] => Burlington
)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-10-2048.jpg)

![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
foreach ($post['categories'] as $v) {
echo $v . PHP_EOL;
}
/*
PHP
BTV
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-12-2048.jpg)
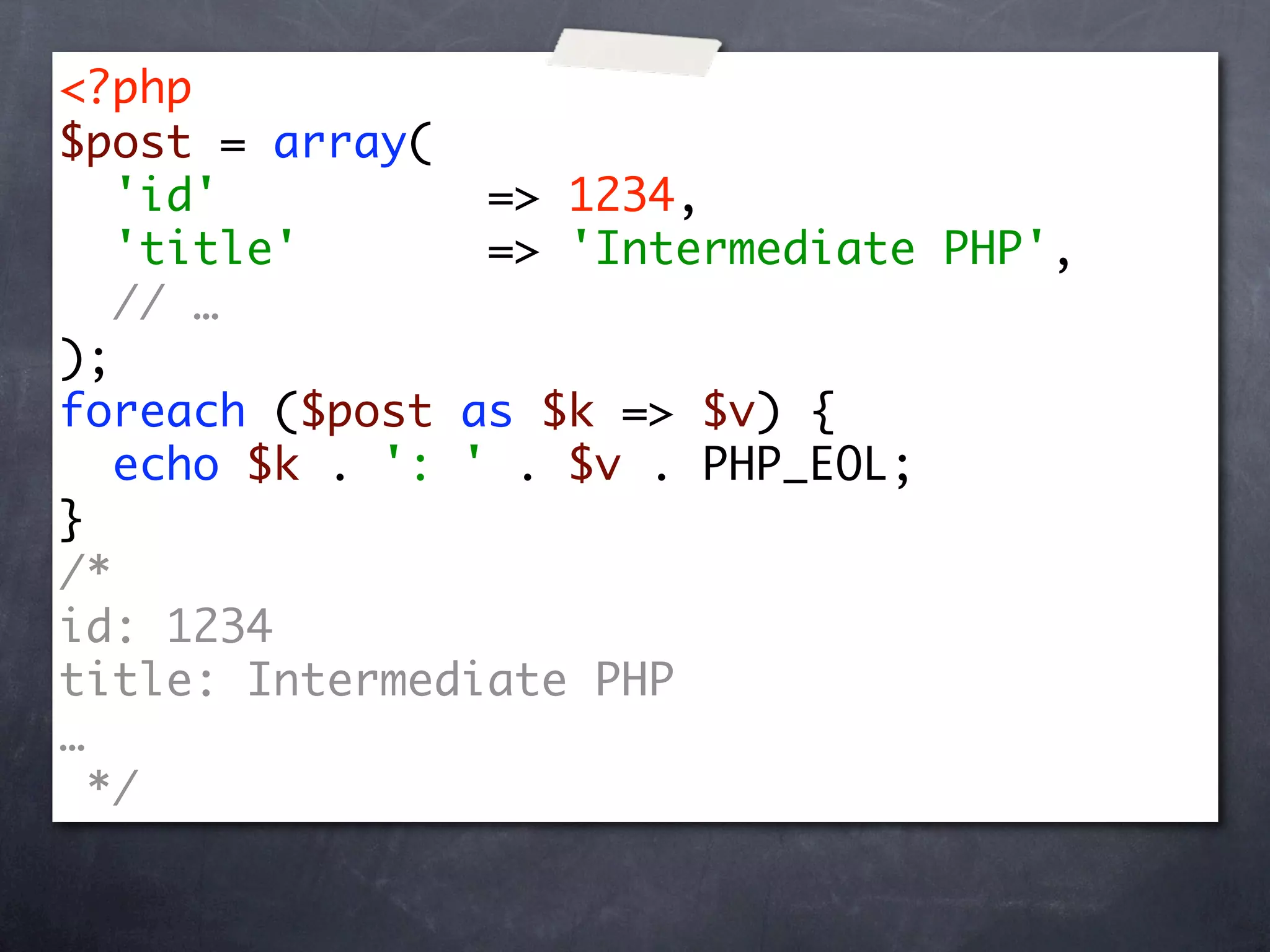
![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
foreach ($post['categories'] as $k => $v) {
echo $k . ': ' . $v . PHP_EOL;
}
/*
0: PHP
1: BTV
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-13-2048.jpg)

![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
echo implode(', ', $post['categories']);
// PHP, BTV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-16-2048.jpg)
![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' =>
explode(', ', 'PHP, BTV')
);
print_r($post['categories']);
/*
Array
(
[0] => PHP
[1] => BTV
)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-17-2048.jpg)

![<?php
$post = array(
'id' => 1234,
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
if (array_key_exists('categories', $post))
{
echo implode(', ', $post['categories']);
} else {
echo 'Uncategorized';
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-19-2048.jpg)
![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
if (in_array('PHP', $post['categories'])) {
echo 'PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor';
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-20-2048.jpg)
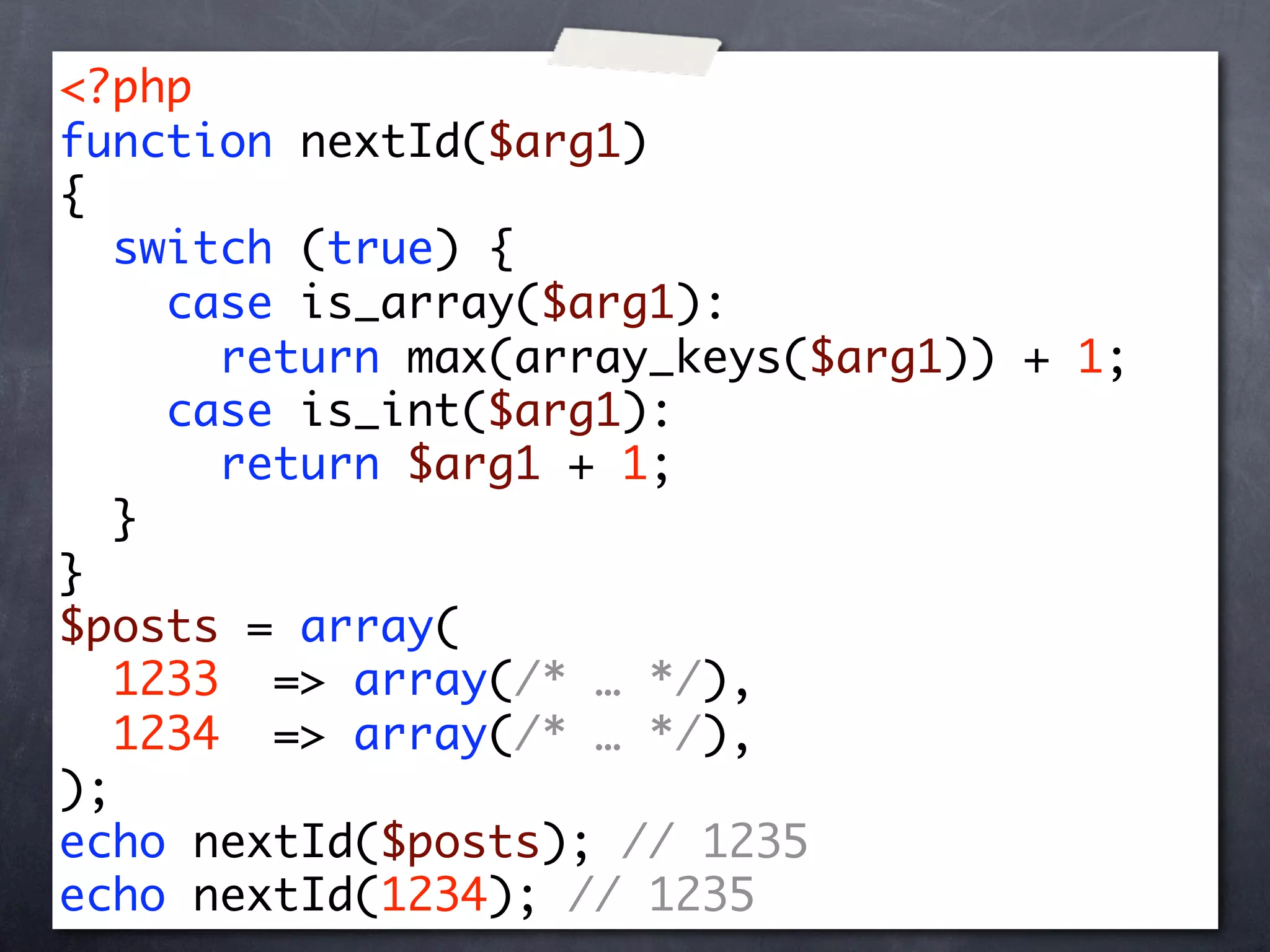
![<?php
$posts = array(
1233 => array(/* … */),
1234 => array(/* … */),
);
print_r(array_keys($posts));
/*
Array
(
[0] => 1233
[1] => 1234
)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-21-2048.jpg)

![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP', 'BTV')
);
sort($post['categories']);
print_r($post['categories']);
/*
Array
(
[0] => BTV
[1] => PHP
)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-23-2048.jpg)




![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('PHP')
);
array_push($post['categories'], 'BTV');
echo array_pop($post['categories']);
// BTV
print_r($post['categories']);
/*
Array
(
[0] => PHP
)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-28-2048.jpg)

![<?php
$post = array(
// …
'categories' => array('BTV')
);
array_unshift($post['categories'], 'PHP');
print_r($post['categories']);
/*
Array
(
[0] => PHP
[1] => BTV
)
*/
echo array_pop($post['categories']);
// BTV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-30-2048.jpg)

![<?php
print_r(get_defined_functions());
/*
Array
(
[internal] => Array
(
[0] => zend_version
[1] => func_num_args
// …
)
[user] => Array
(
)
)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-33-2048.jpg)
![<?php
$functions = get_defined_functions();
echo count($functions['internal']);
// 1857](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intermediate-php-101217100202-phpapp02/75/Intermediate-PHP-34-2048.jpg)