Download as PDF, PPTX

![Array initialization
The syntax of array initialization is
datatype[] name={item1,item2,...,item n};
OR
name[index position]= item or value;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-2-2048.jpg)
![Accessing array elements
Array elements can be either accessed using
their index value or using the looping statements
Example
System.out.println(a[1]);
or
for(int i =0 ;some condition; i++)
{ System.out.println(a[i]);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-3-2048.jpg)
![Array resizing
Syntax
aname=Arrays.copyOf(aname, new size);
example
int[] a= new int[4];
a= Arrays.copyOf(a, 8);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-4-2048.jpg)
![Two dimensional array
The two dimensional arrays are like a table
The Syntax for declaring a 2-D array is
Dtype [][] name= new Dtype[size][size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-6-2048.jpg)

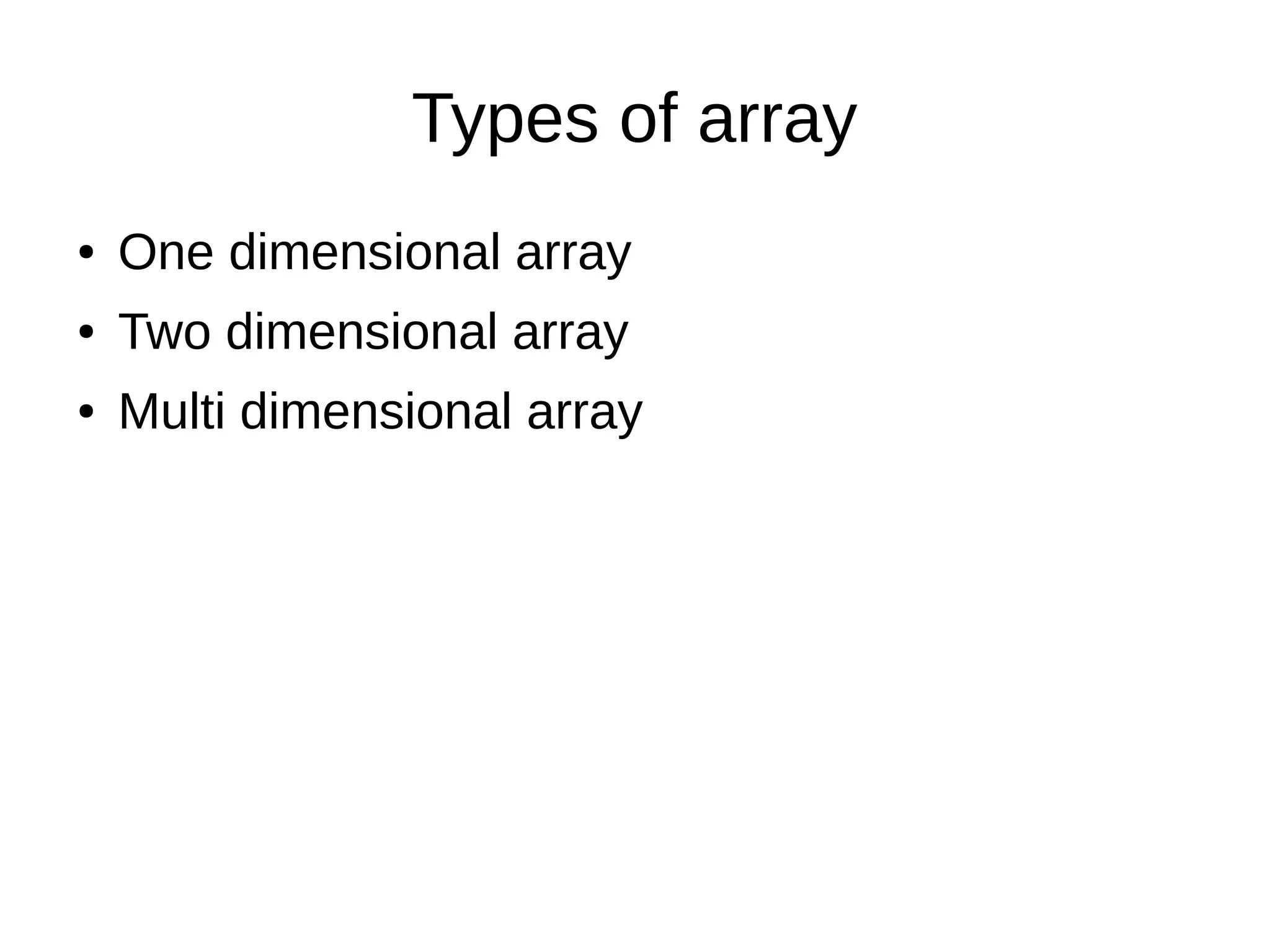
This document discusses arrays in Java, including that an array holds homogeneous data of more than one number, arrays have a fixed length set at creation, and elements can be accessed by index or loop. It also covers initializing arrays, resizing arrays using Arrays.copyOf(), and different types of arrays such as one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and multi-dimensional arrays. Two-dimensional arrays are like tables with rows and columns.

![Array initialization
The syntax of array initialization is
datatype[] name={item1,item2,...,item n};
OR
name[index position]= item or value;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-2-2048.jpg)
![Accessing array elements
Array elements can be either accessed using
their index value or using the looping statements
Example
System.out.println(a[1]);
or
for(int i =0 ;some condition; i++)
{ System.out.println(a[i]);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-3-2048.jpg)
![Array resizing
Syntax
aname=Arrays.copyOf(aname, new size);
example
int[] a= new int[4];
a= Arrays.copyOf(a, 8);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-4-2048.jpg)

![Two dimensional array
The two dimensional arrays are like a table
The Syntax for declaring a 2-D array is
Dtype [][] name= new Dtype[size][size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array-140701220750-phpapp01/75/intorduction-to-Arrays-in-java-6-2048.jpg)