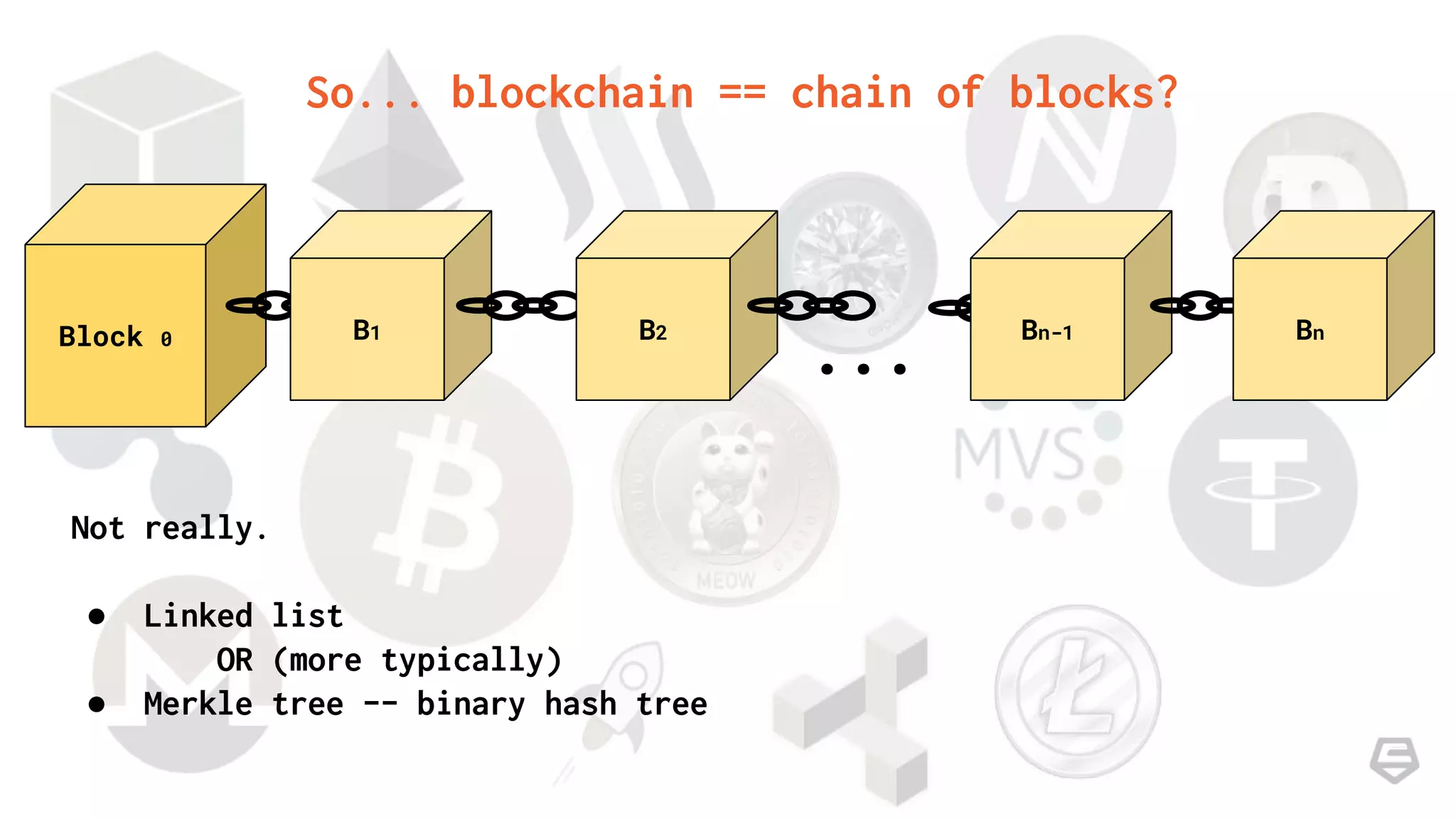
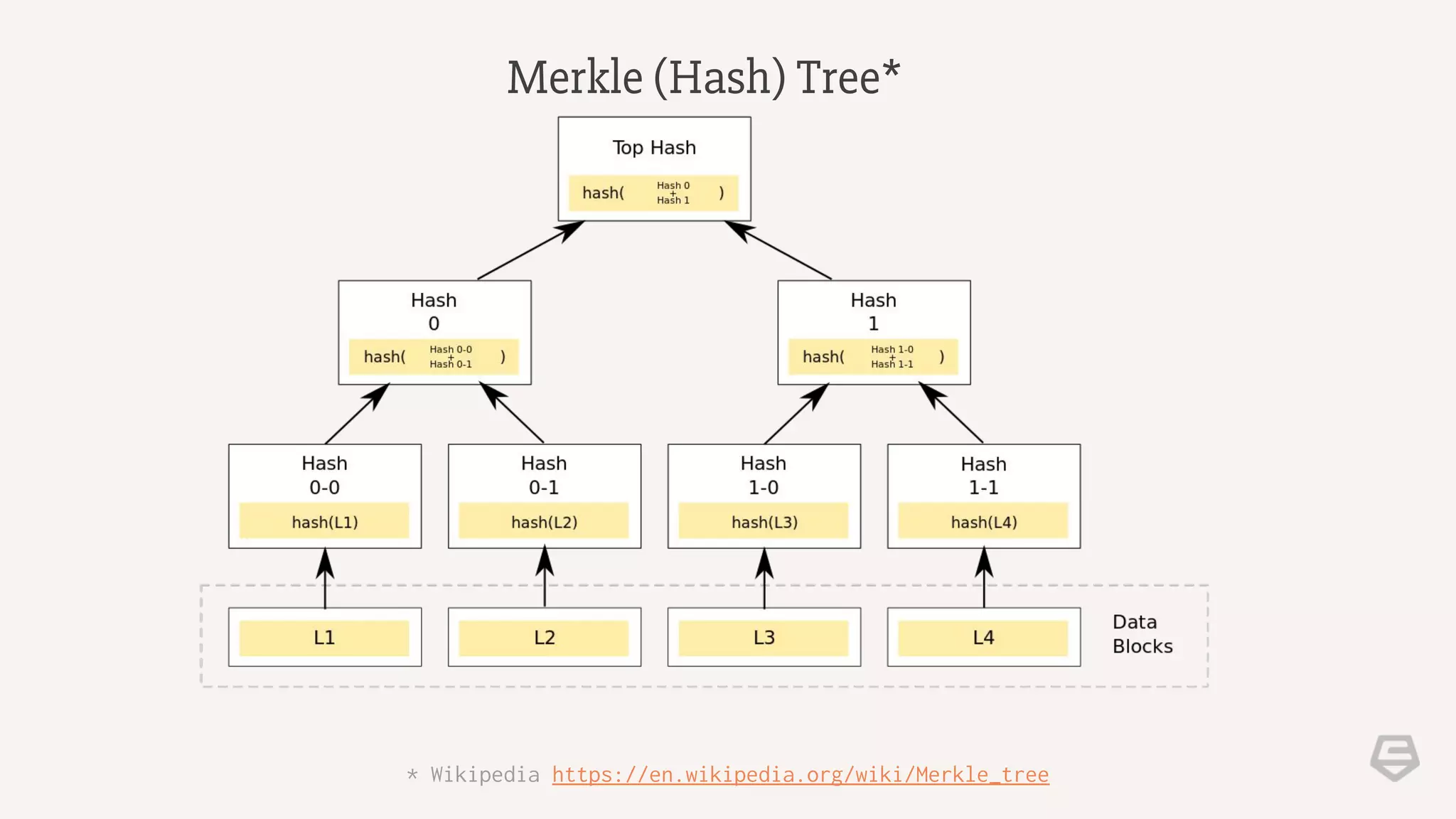
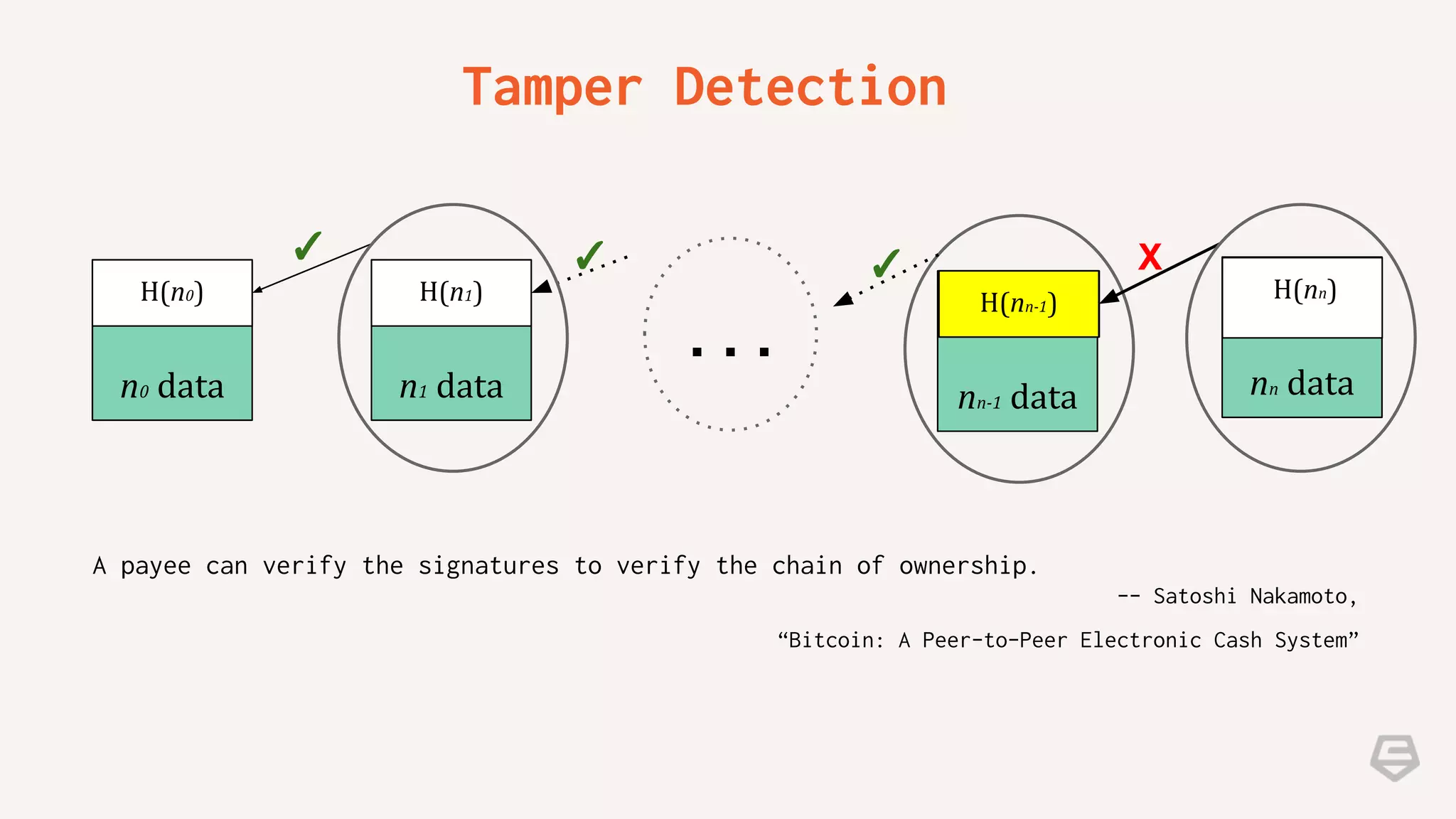
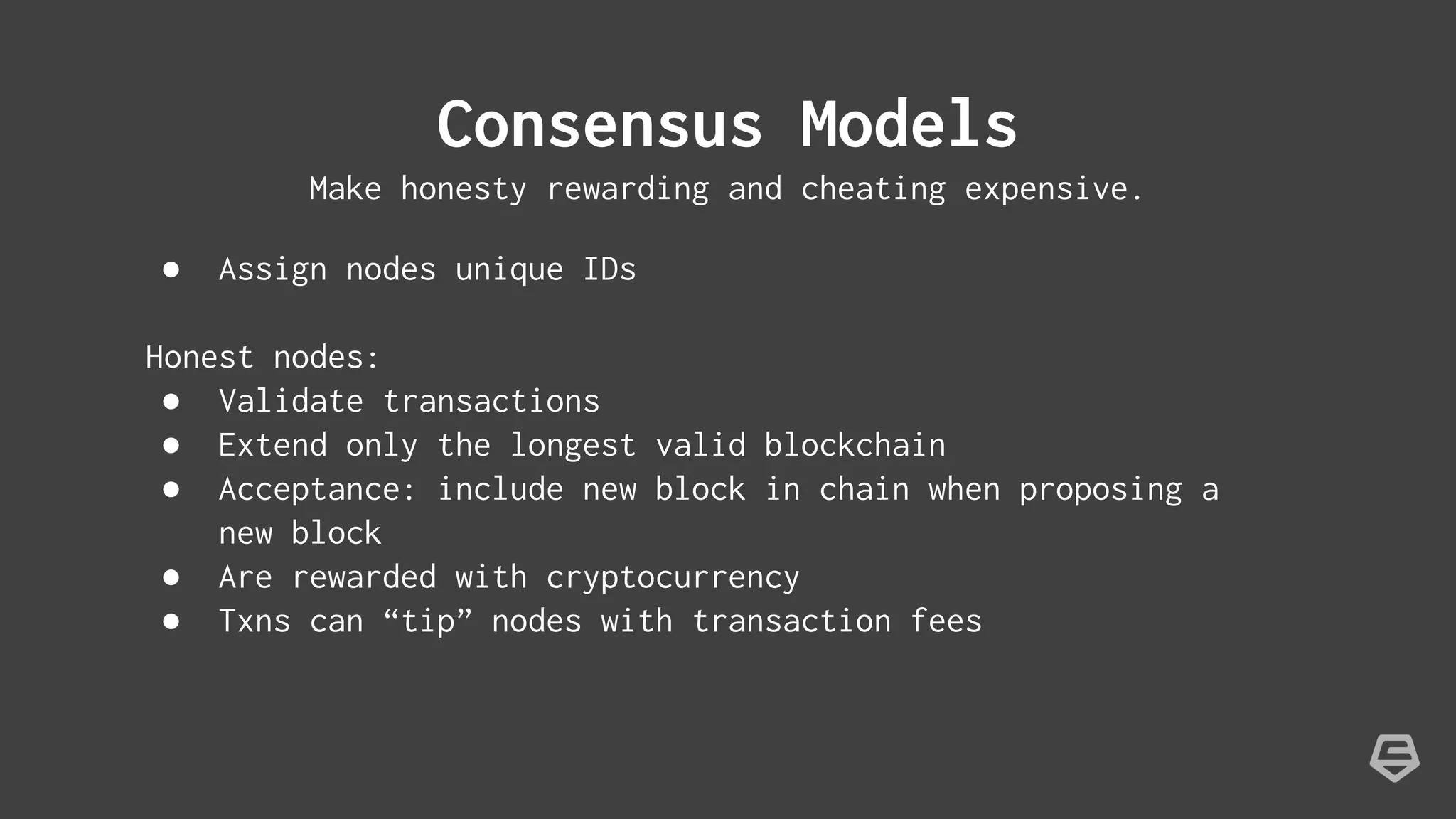
The document provides an introduction to blockchain technology, explaining its core concepts, including transactions, nodes, blocks, and mining. It discusses the significance of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency, exploring its potential applications in various sectors, and highlights the benefits and challenges associated with the technology. Additionally, it touches on potential vulnerabilities and the future implications of blockchain in contexts where trust is essential.














![● What if we made mining do useful work?
○ SETI
○ Protein folding
○ Machine learning
○ Data preservation - Permacoin - storage based
puzzle, distributed storage (Microsoft)
○ Renewables-only mining + use waste heat
○ [ Your great idea here ]
Mining Alternatives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoblockchainslides-180111025459/75/Intro-to-Blockchain-Slides-28-2048.jpg)



![What are some situations where trust is lacking, or eroded?
Could blockchain help here?
● Government corruption
● Health care
● Policing
● Campaign funding
● Behavioral economics
● Lending
● Voting
● [Your Great Idea Here]
The Bright Future](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoblockchainslides-180111025459/75/Intro-to-Blockchain-Slides-32-2048.jpg)






