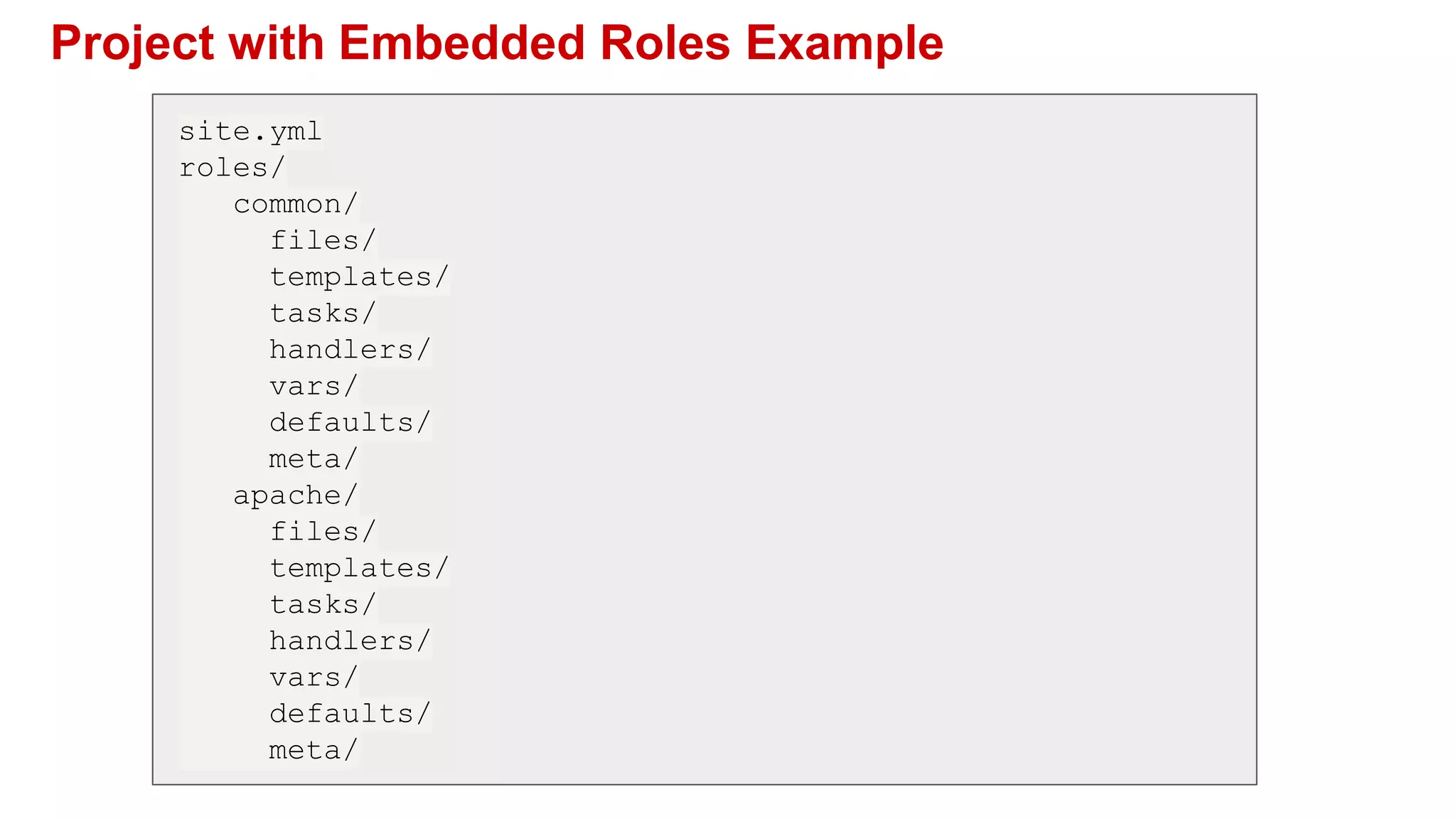
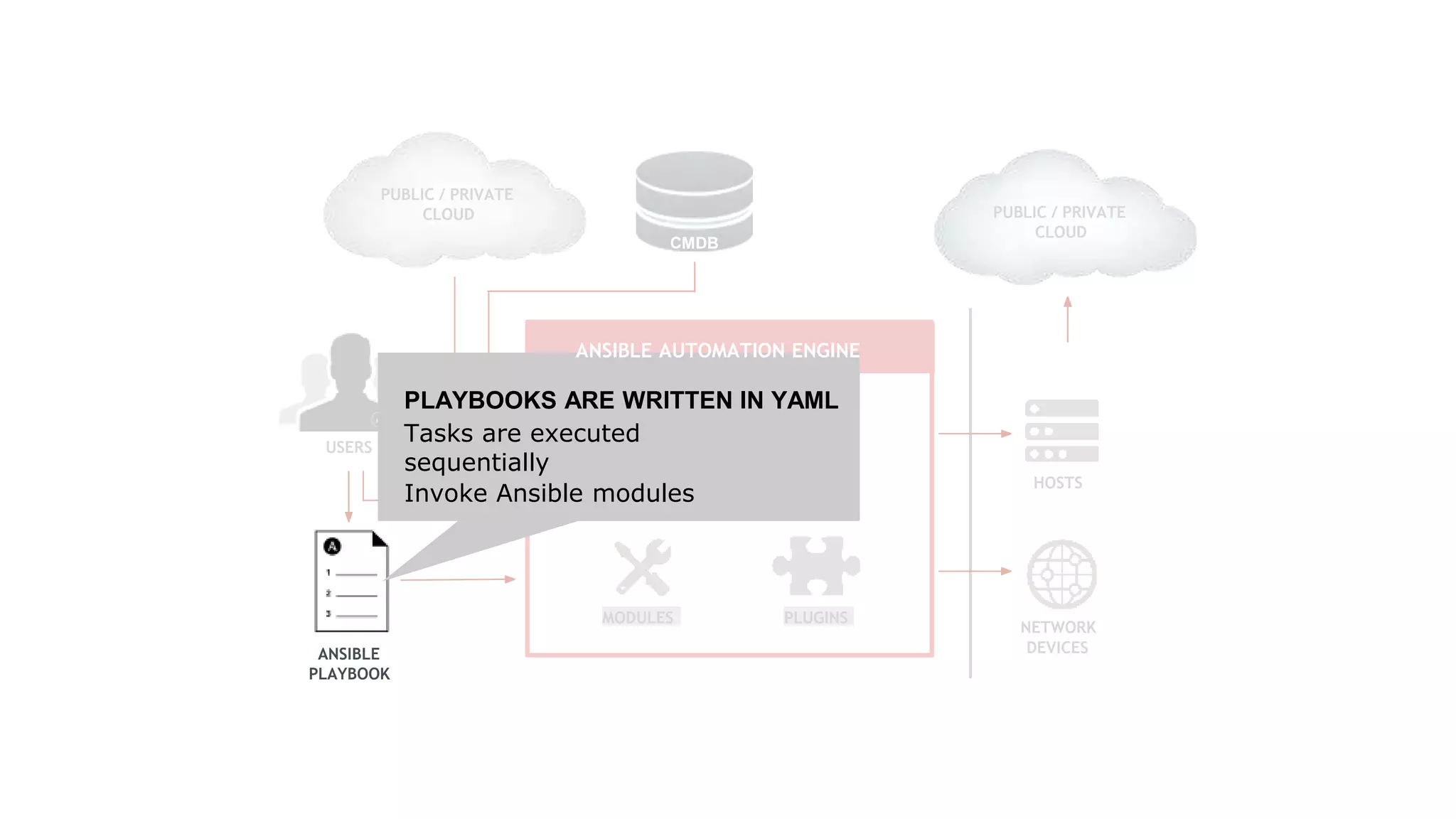
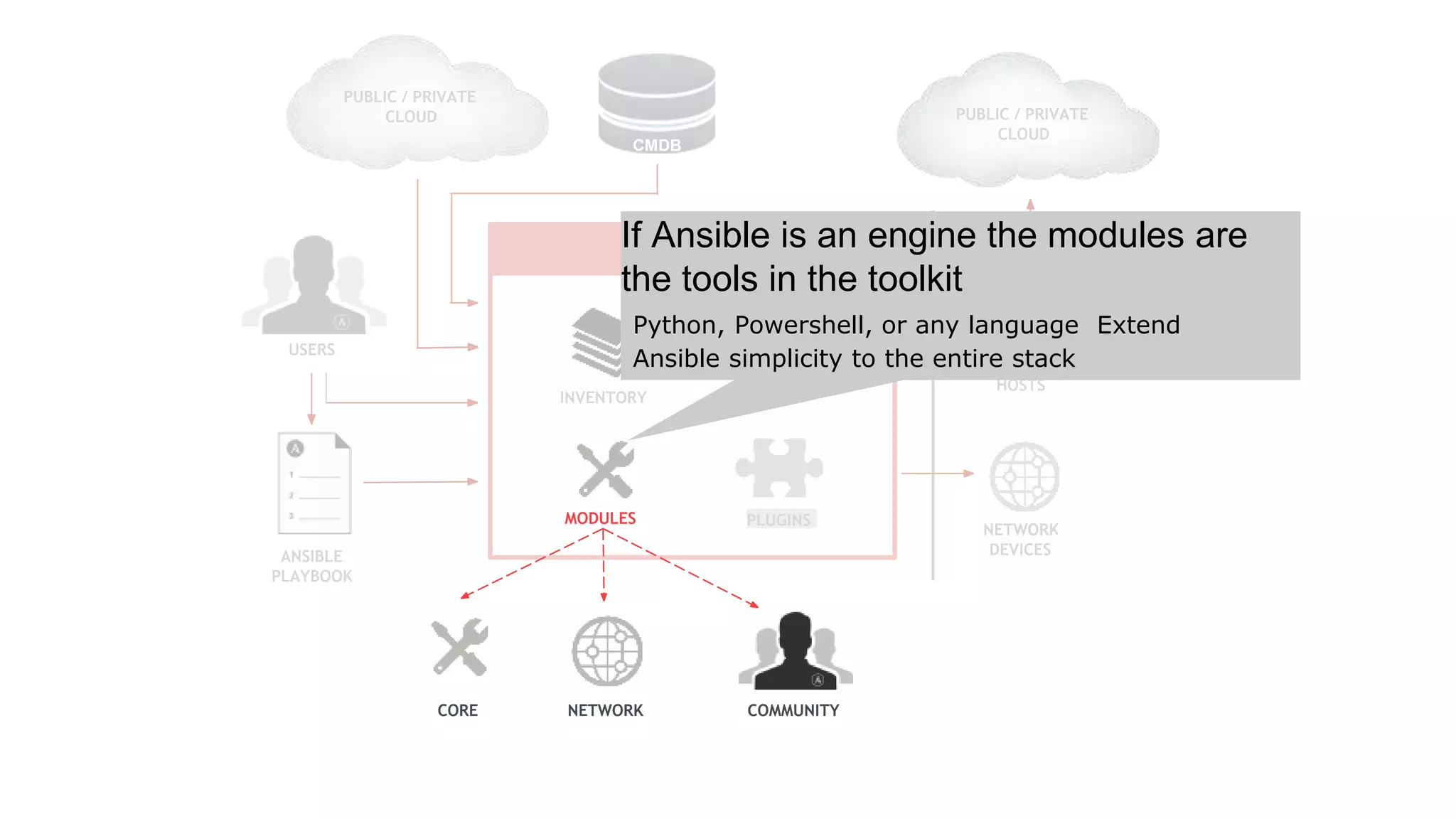
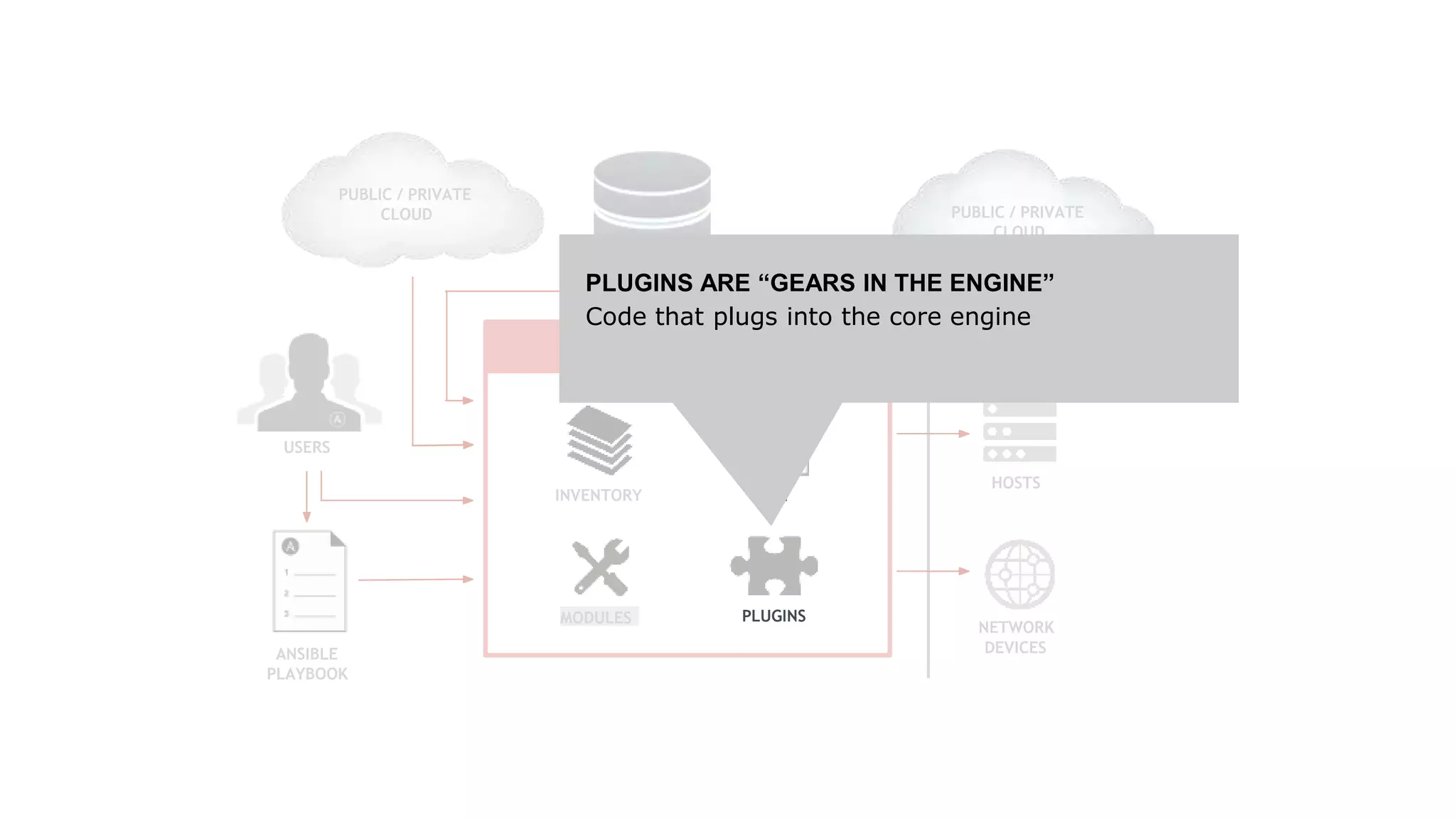
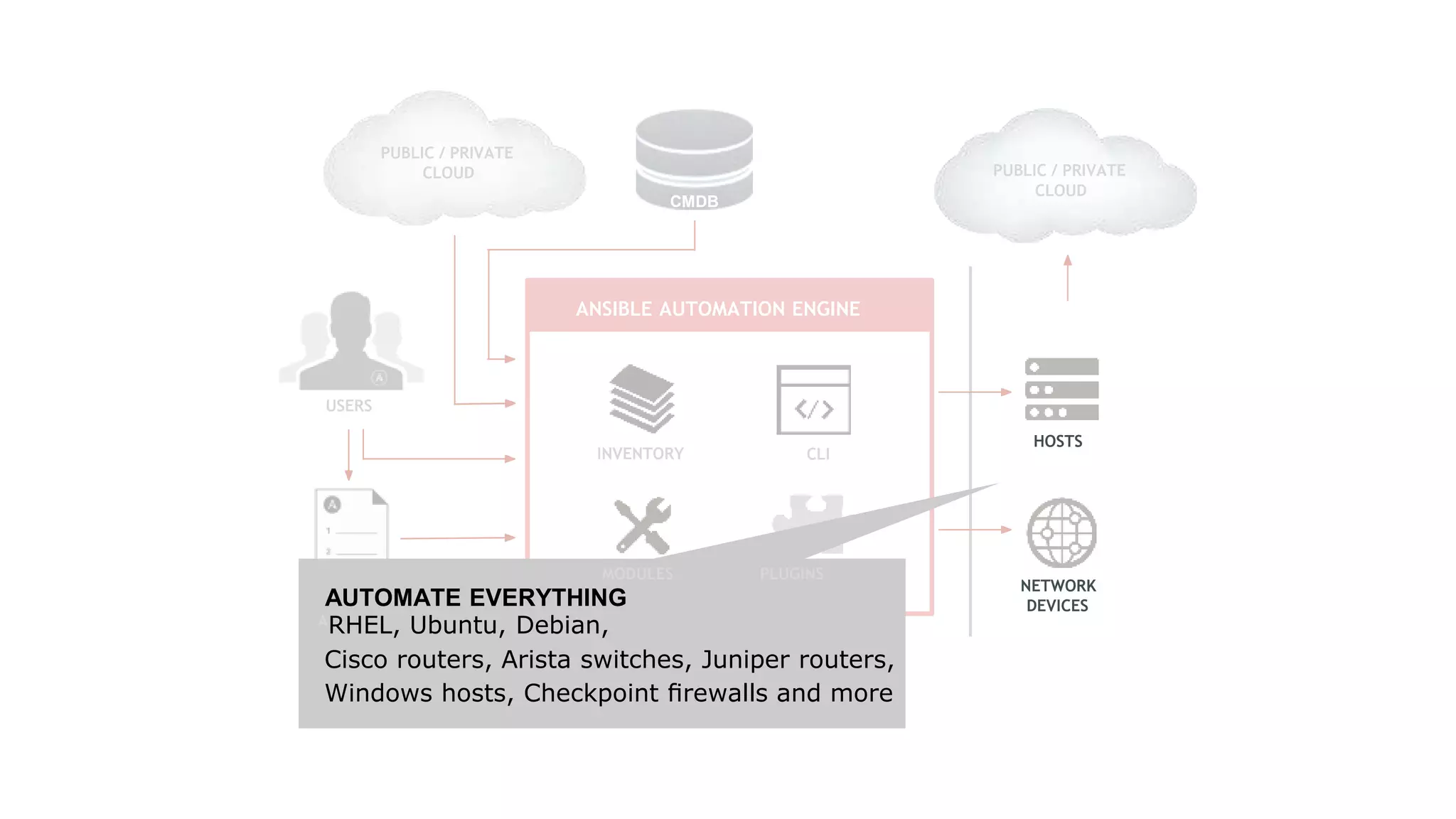
Ansible is a powerful agentless automation platform that simplifies IT application infrastructure management through playbooks written in YAML. It enables orchestration, configuration management, and application deployment across various technologies without requiring special coding skills. With extensive community support, thousands of contributors, and numerous modules, Ansible facilitates efficient and secure automation across diverse environments.





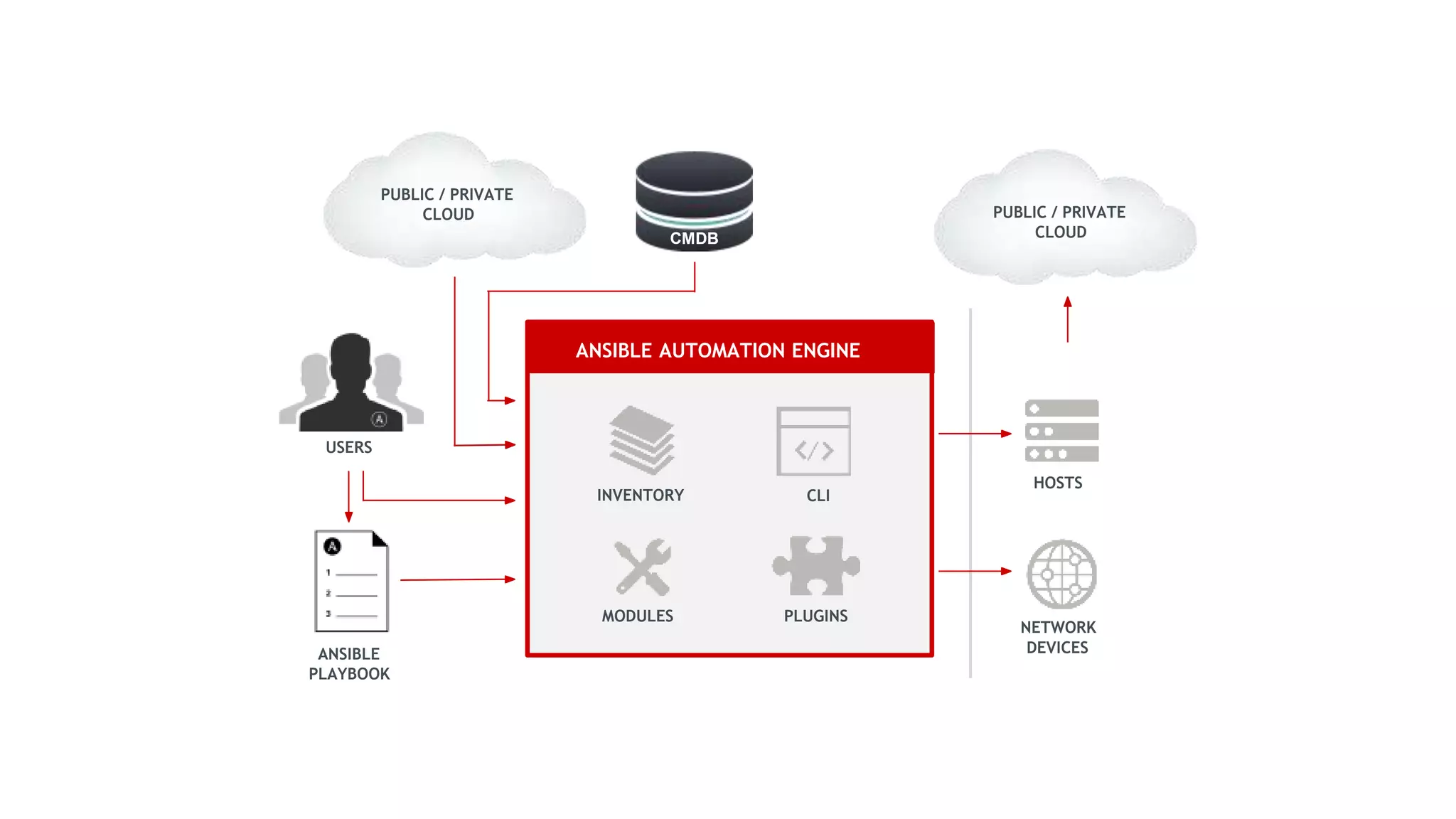
![CMDB
USERS
HOSTS
NETWORK
ANSIBLE
PLAYBOOK
PUBLIC / PRIVATE
CLOUD
PUBLIC / PRIVATE
CLOUD
MODULES PLUGINS
INVENTORY
INVENTORY
[web]
ANSIBLE AUTOMATION
EwNeGbIsNeErver1
.example.com
webserver2.example.com
[db]
dbserver1.example.com
CLI
[switches]
leaf01.internal.com
leaf02.internal.com
[firewalls]
checkpoint01.internDaEVlI.
CcESom
[lb]
f5-01.internal.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-to-ansible-sep7-meetup-190904145303/75/Intro-to-ansible-sep7-meetup-12-2048.jpg)






![Static Inventory Example
[control]
tower ansible_host=10.42.0.2
[web]
node-[1:3] ansible_host=10.42.0.[6:8]
[haproxy]
haproxy ansible_host=10.42.0.100
[all:vars]
ansible_user=vagrant
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=~/.vagrant.d/insecure_private_key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-to-ansible-sep7-meetup-190904145303/75/Intro-to-ansible-sep7-meetup-20-2048.jpg)