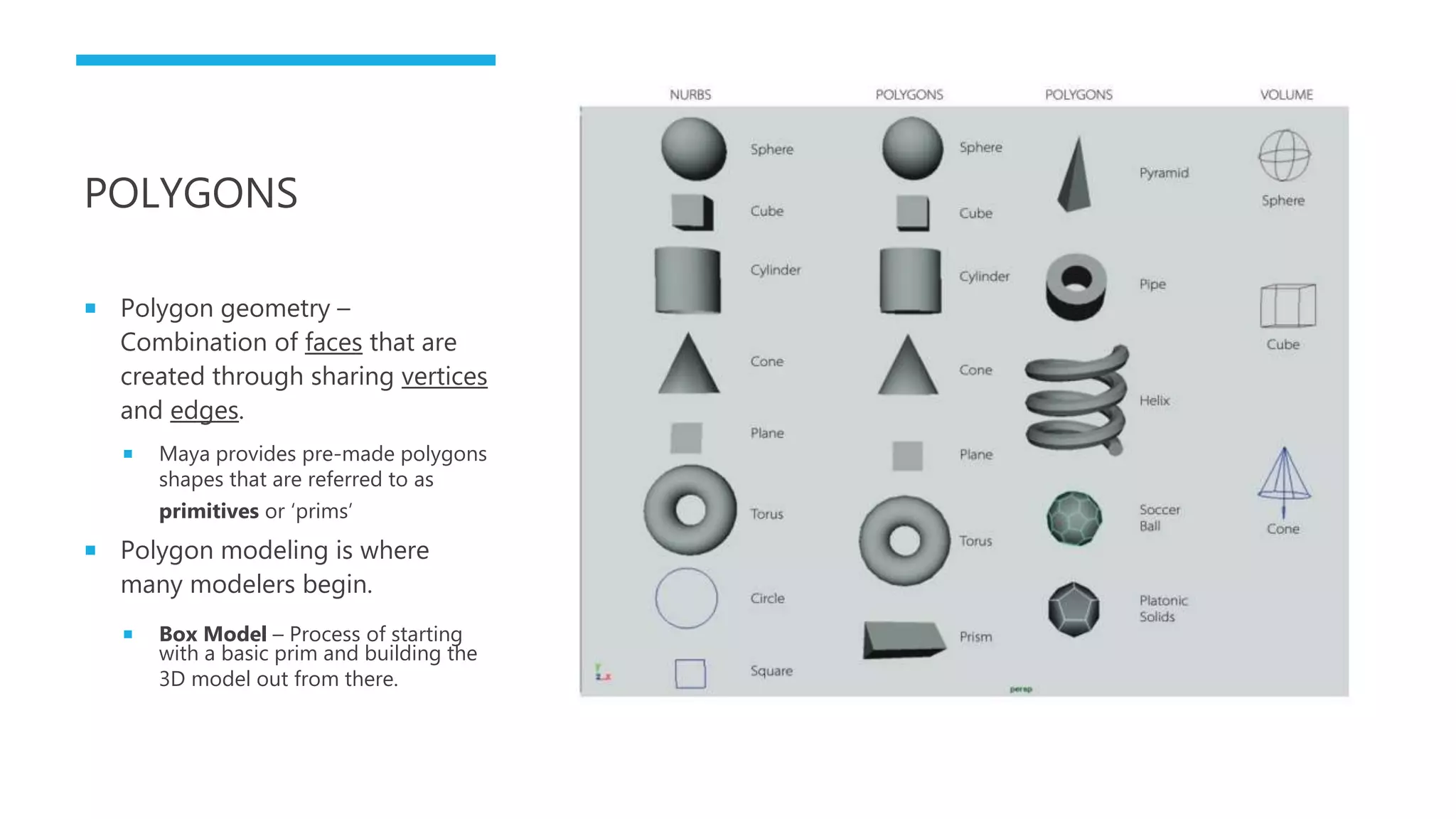
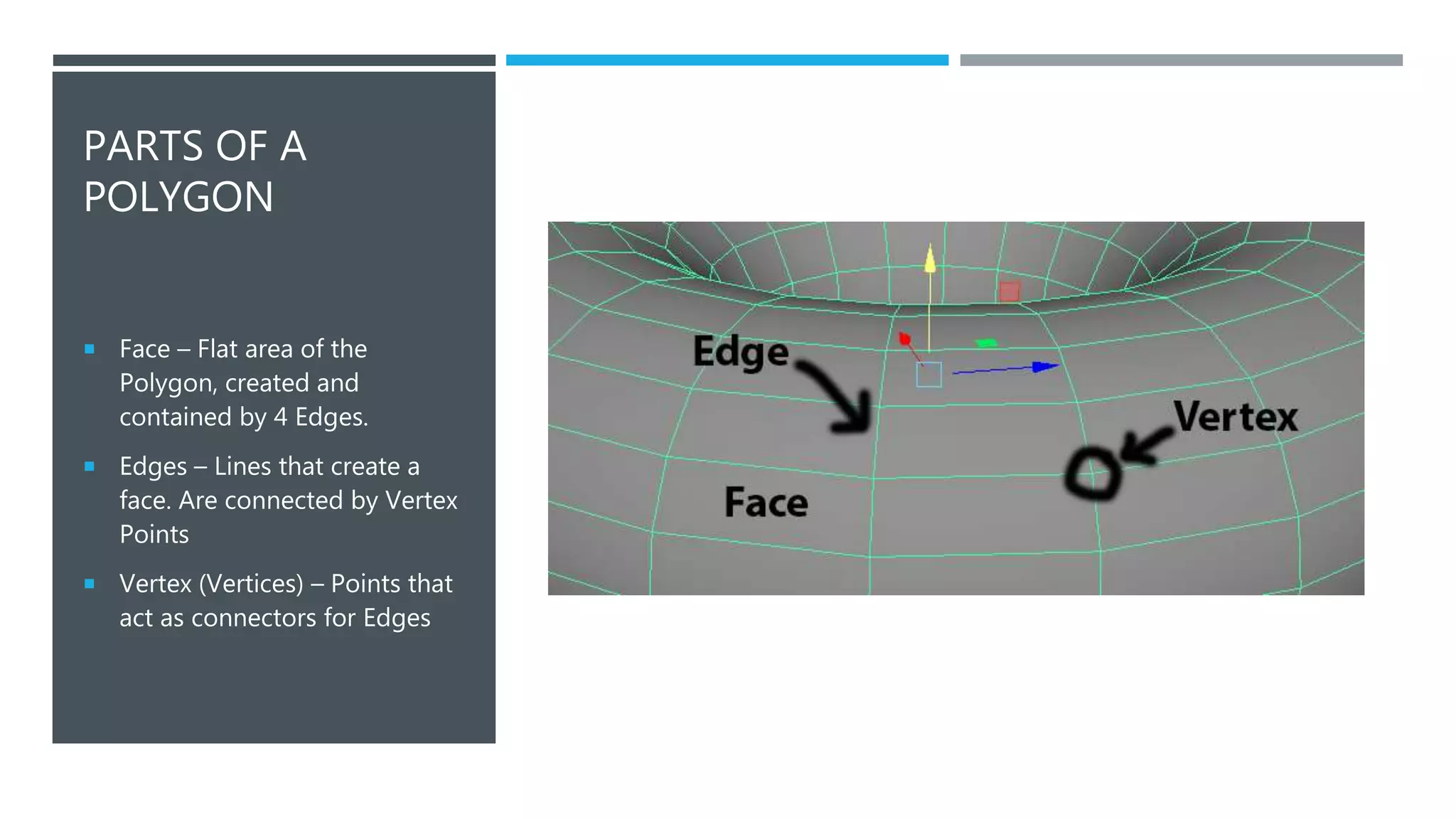
This document provides an introduction to 3D modeling terminology. It defines common terms like CG, CGI, and 3D which refer to computer graphics and three-dimensional modeling. It explains that 3D modeling introduces a Z-axis to provide depth compared to 2D programs. It also describes that 3D models are made of polygon geometry using shapes called primitives, and the basic process of box modeling involves starting with a primitive shape and building out the model. Finally, it lists some common uses of 3D models such as in video games, architecture, and virtual/augmented reality applications.