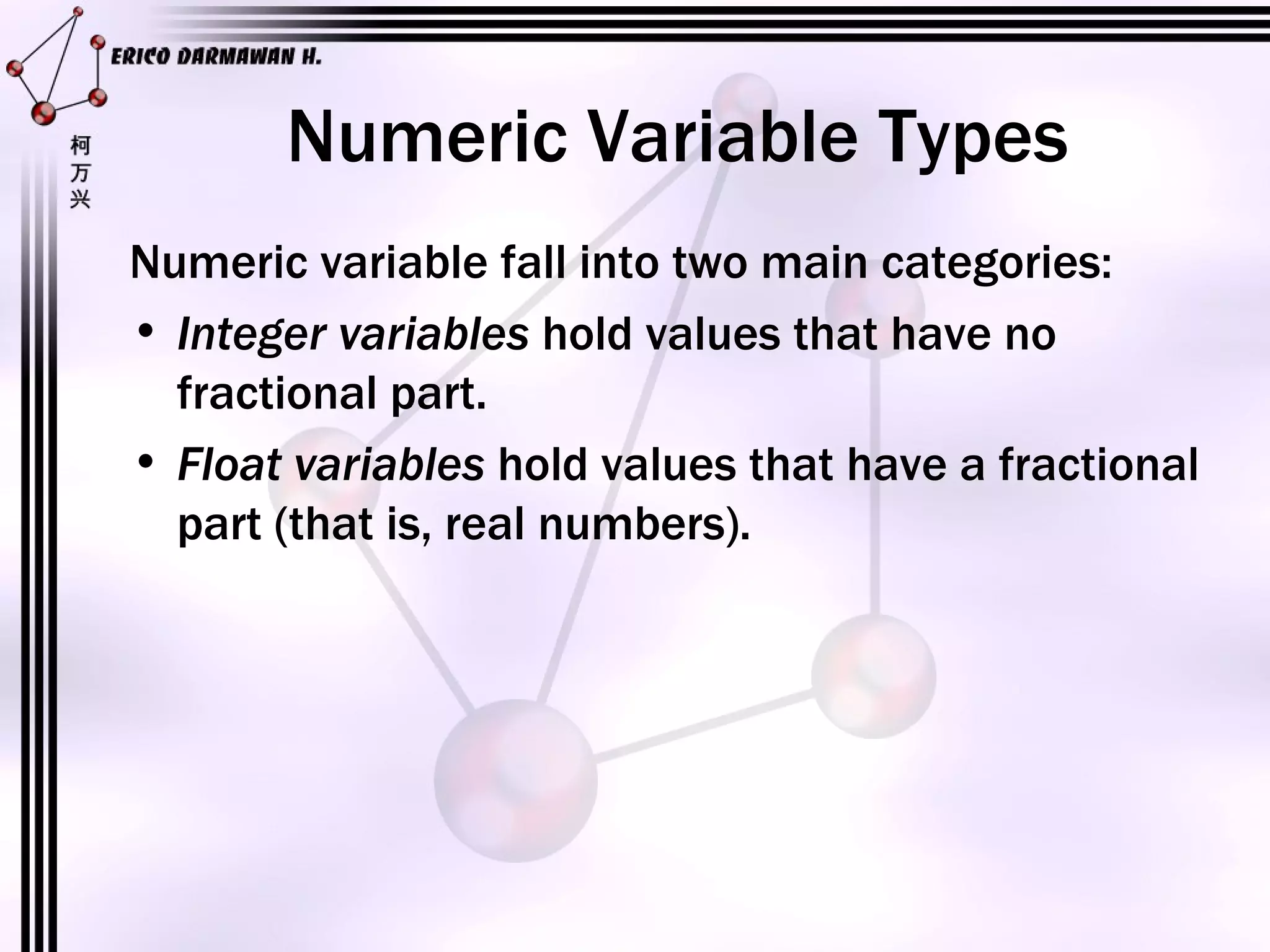
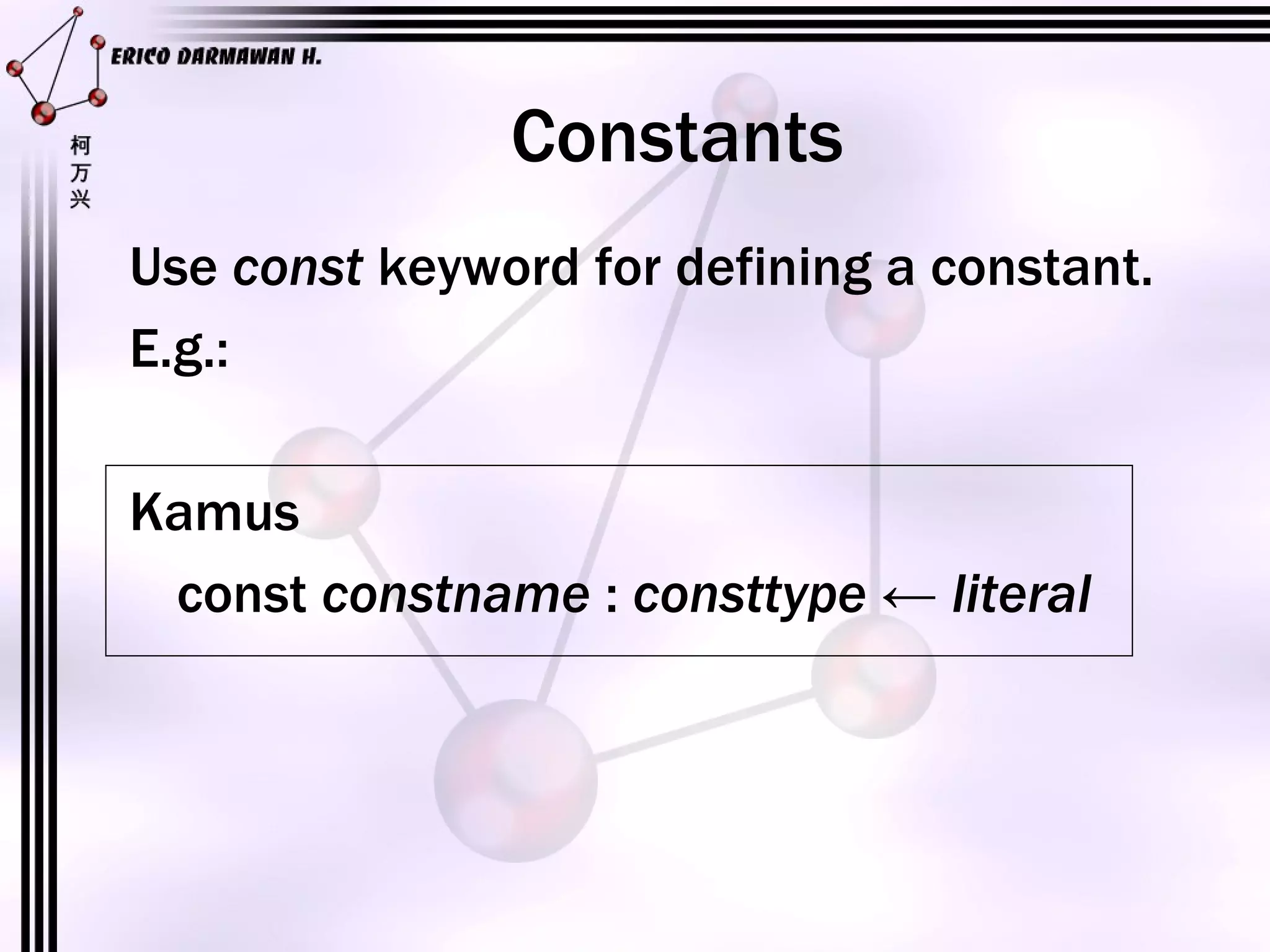
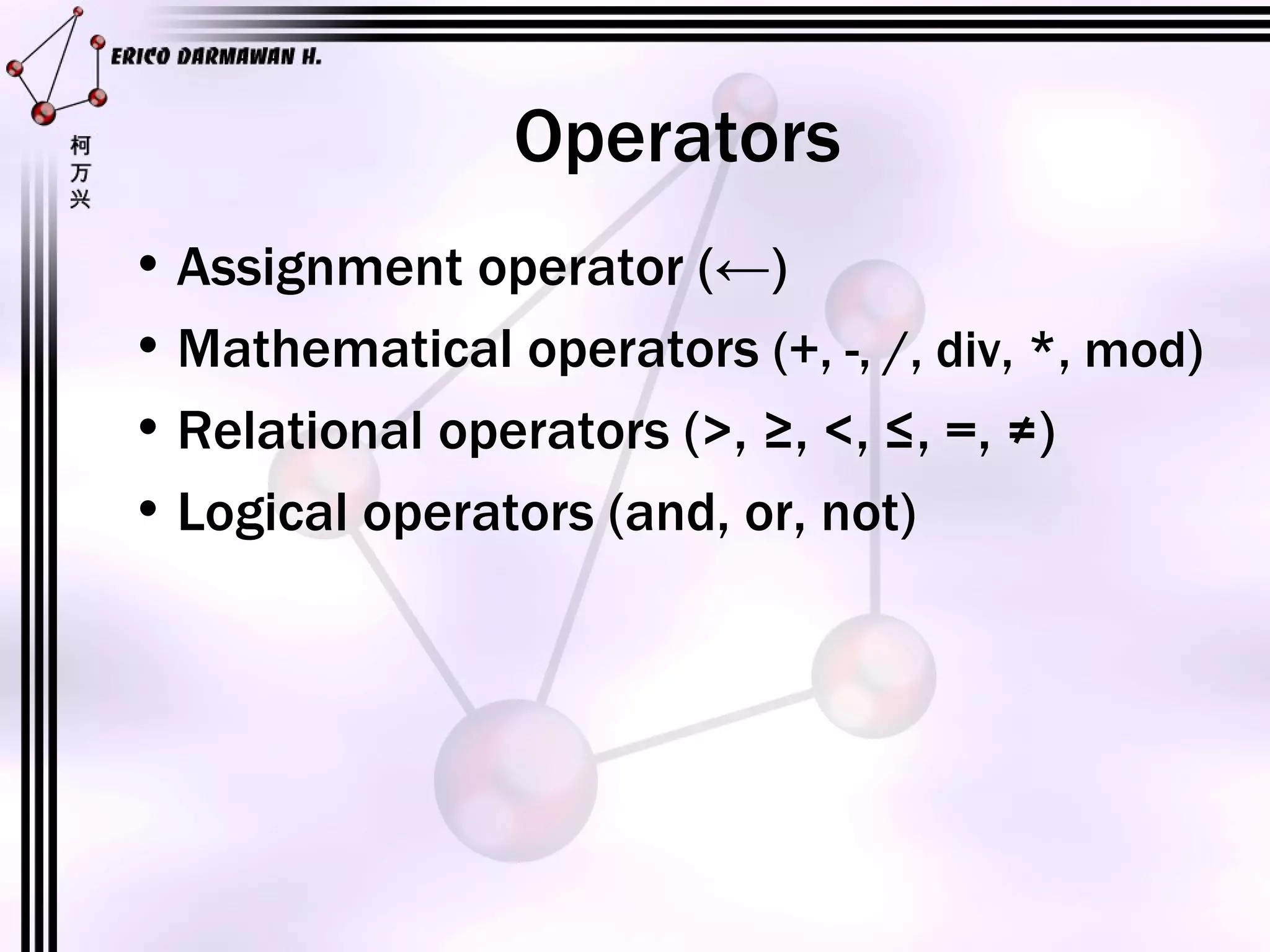
1) The document introduces algorithms and their components such as programs, functions, variables, constants, expressions, and operators.
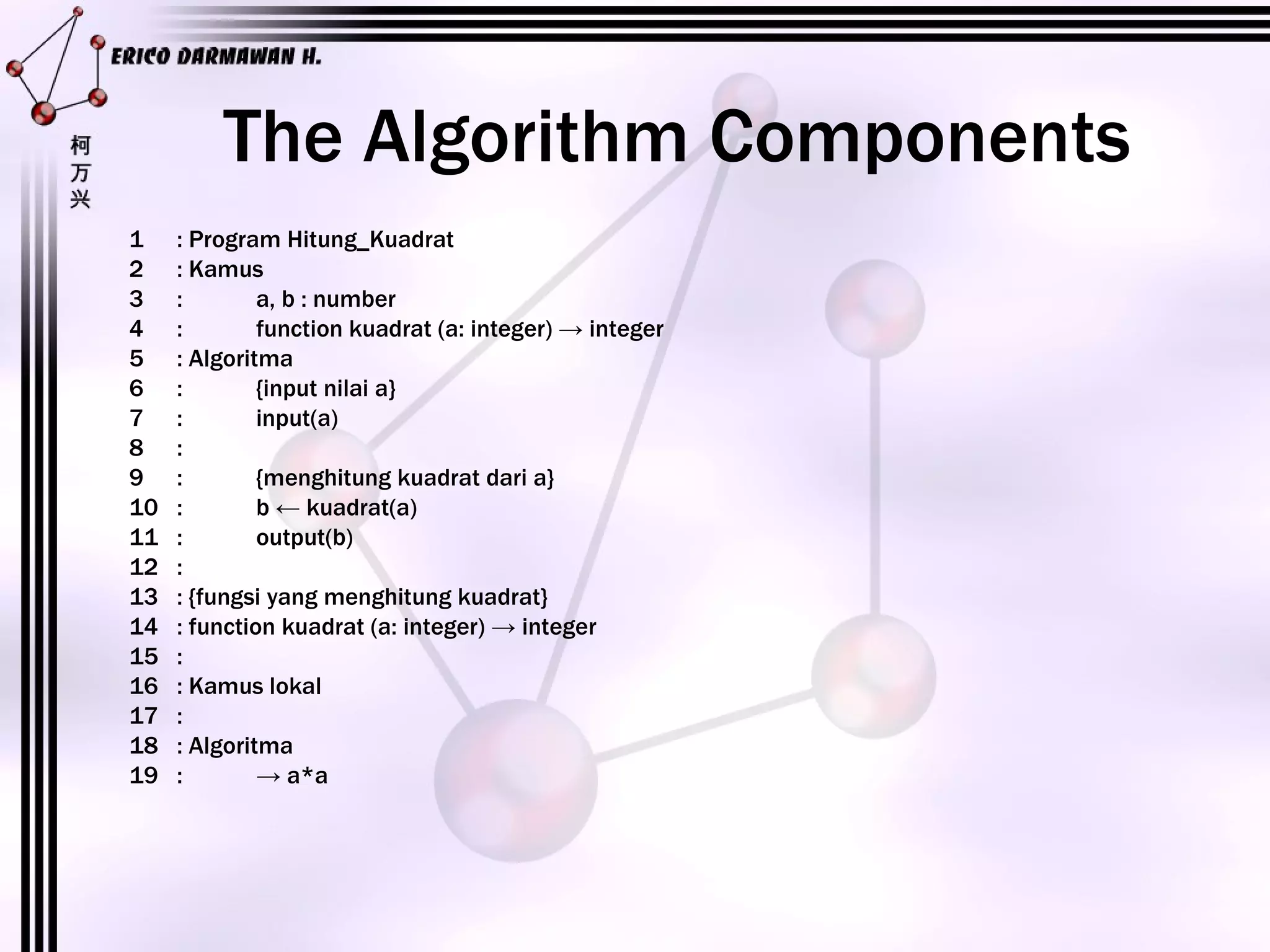
2) An algorithm is defined as a set of steps needed to solve a problem and examples of blackjack and squaring a number are provided.
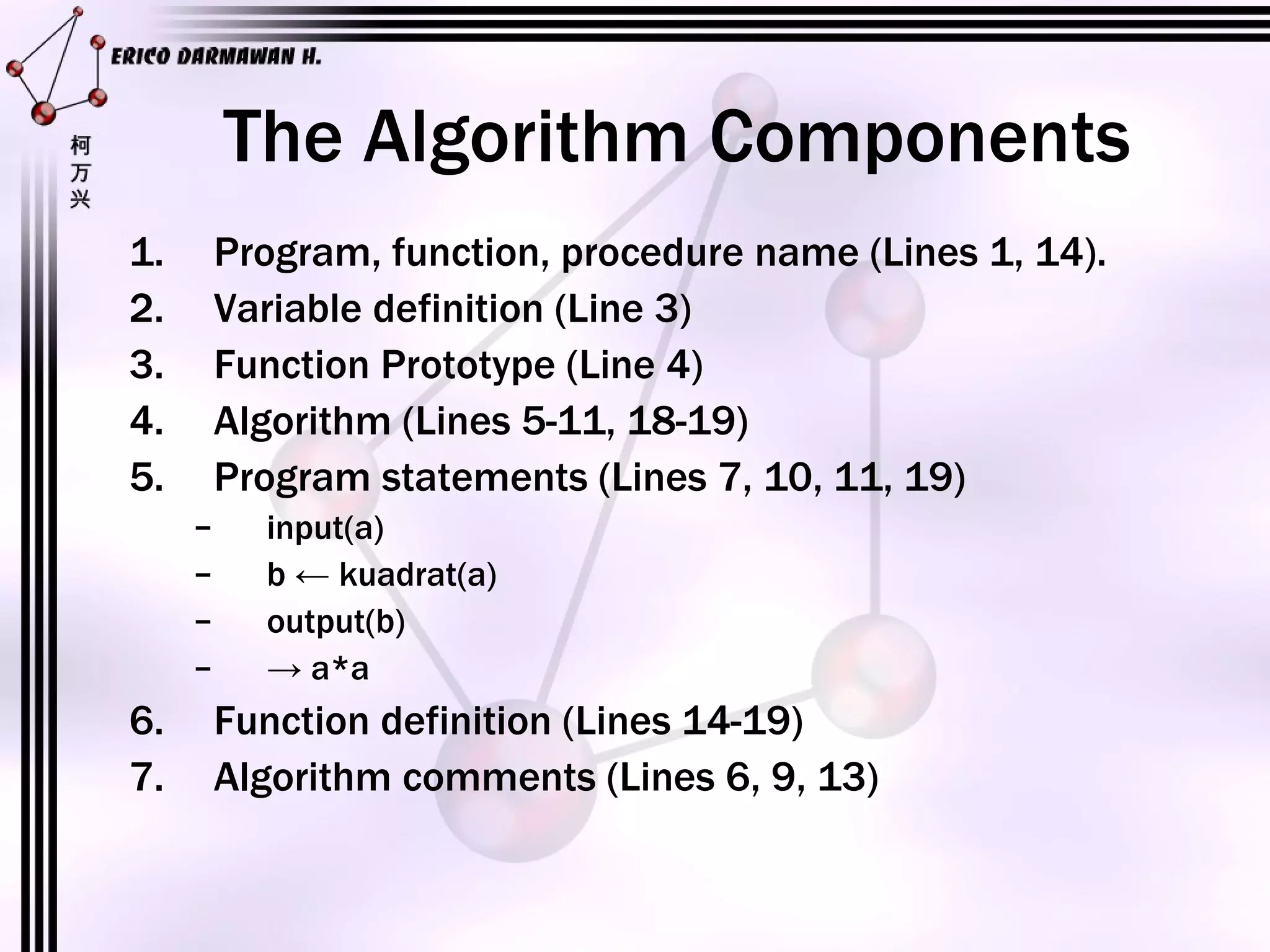
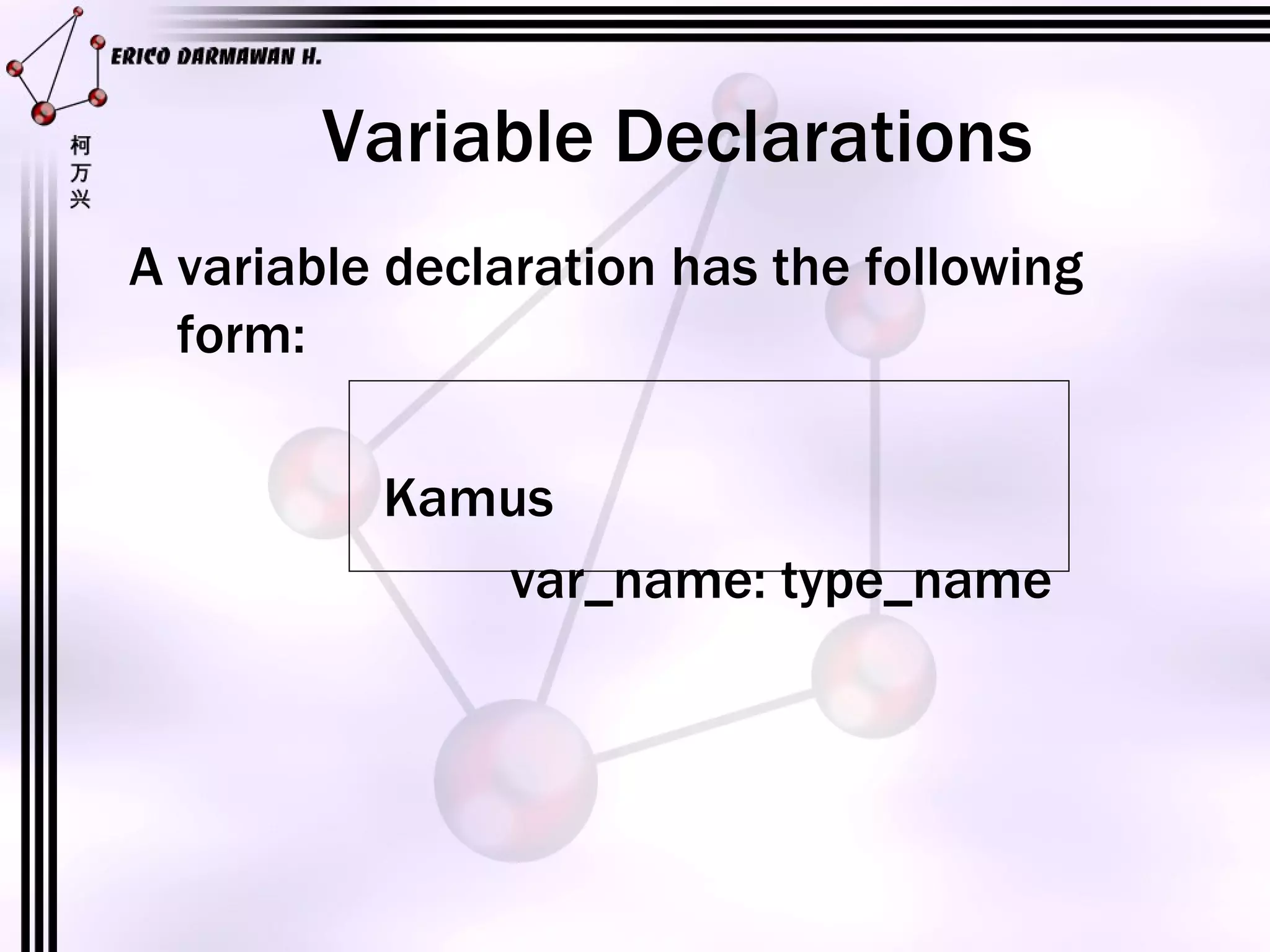
3) The main components of an algorithm are identified as the program name, variable definitions, function prototypes, and the step-by-step algorithm.