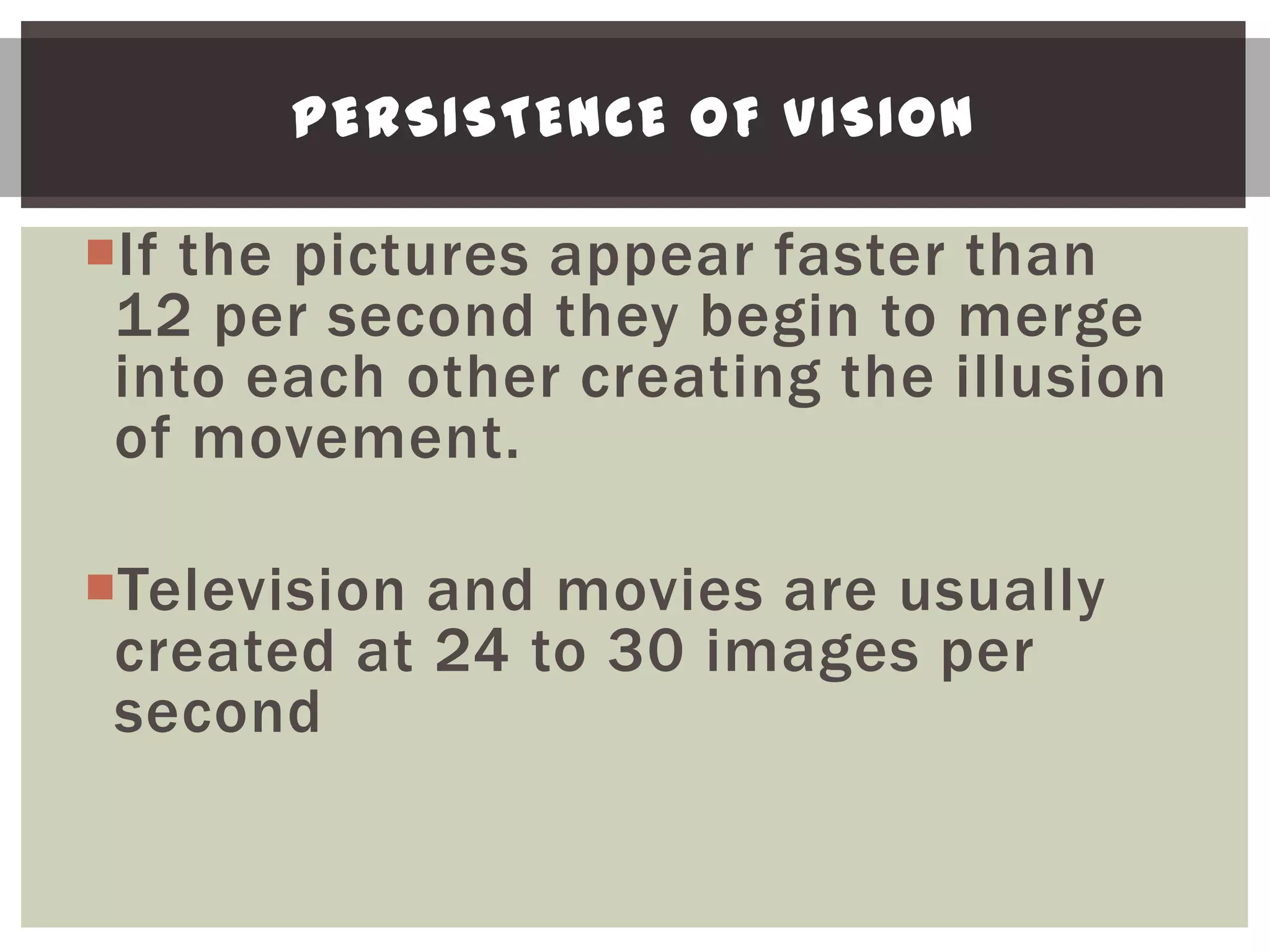
The document provides an overview of animation, explaining its definition as the creation of the illusion of movement through a series of still images, and details the three major types of animation: hand-drawn, stop motion, and computer animation. It discusses the concept of persistence of vision, which is essential for animation to be effective, and highlights the significance of storyboards in filmmaking. Additionally, the document emphasizes the widespread use of animation across various media and its relevance to audiences of all ages.